- Skip to content
- Skip to navigation

Why problem-solving is important
As parents, the way you manage problems or disagreements in your relationship affects your child.
By managing problems positively and constructively, you help your child develop well and thrive . When your child sees you behaving and communicating with your partner in this way, your child learns to behave this way too. It can teach your child important skills for life.
When you and your partner find solutions together, you help the whole family have happier, healthier and stronger relationships . And you help to protect your child from the downsides of conflict.
This is because a problem-solving approach can help you and your partner to:
- confront issues, rather than avoid them
- talk and listen respectfully and patiently
- find solutions that you’re both happy with
- break unhelpful habits so problems don’t return
- feel like you’re working as a team.
Ground rules for problem-solving
Before you start problem-solving, it’s a good idea to set ground rules. It’s also important for you and your partner to come up with these rules together.
Here are suggestions for problem-solving ground rules to get you started:
- Either of you can raise a problem for discussion.
- You’ll choose appropriate times and places to raise problems. This might be when your child isn’t around, you’re both calm, there’s enough time to talk and you can both give your full attention.
- Either of you can say ‘no’ if you don’t want to talk about it right then, but you’ll agree to make another time soon to discuss it – no more than 1-2 days after it first comes up.
- If the discussion gets heated, either of you can call for a break to calm down and the other will respect this request.
- You’ll actively listen so you each understand what the other is saying. You’ll also avoid interrupting each other.
- You won’t raise conflict topics in front of other people and your child if you know it’s likely to get heated.
- You’ll keep the conversation respectful at all times, and be aware of your tone, body language and gestures.
- You’ll keep in mind that if one of you has a problem, it’s likely to affect both of you.
Problem-solving: how to do it
Positive problem-solving has 6 basic steps:
- Define the problem.
- Clarify what you each want.
- Brainstorm solutions.
- Evaluate solutions and choose one.
- Try the solution.
- Review the solution.
1. Define the problem
Be clear and specific about the problem:
- Describe what’s happening, how often it’s happening, and who’s involved. For example, ‘In the past 3 weeks, I’ve noticed we’ve argued a lot more than usual’.
- Focus on the issue, not the person. For example, ‘We’re always doing chores or going to children’s sport, and we haven’t been able to relax together. I think it’s affecting our relationship’.
- Acknowledge your part in the problem. For example, ‘I know I started a few of those arguments’.
- Describe the problem with a neutral, non-blaming approach. You could try saying ‘I’ and ‘we’ rather than ‘you’ and phrasing the issue as a question. For example, ‘I’m worried that we haven’t had time for each other lately. Can we talk about how we can spend time together?’
2. Clarify what each of you wants
Be clear about what’s important to each of you. Asking questions can help you clarify things. For example:
- Why do you want/need that?
- Why are you concerned/worried/afraid about that?
- Why don’t you want/need that?
- Why do you think we should avoid that?
Your goal is to have a clear understanding of what you both want. Be patient and focus on listening to each other’s answers.
3. Brainstorm solutions
Write down any and all possible solutions:
- Take turns to suggest ideas.
- Try to get as many ideas as you can, even if some don’t seem relevant. Aim for at least 8-10 ideas.
- Include all ideas. Rejecting ideas can hurt each other’s feelings and stop you from sharing ideas.
- Wait until you’ve got all your ideas down before you talk about them.
4. Evaluate solutions and choose one
Narrow down your brainstorming list to one practical option that can solve your problem:
- Cross off ideas you both agree won’t work.
- If one of you thinks an idea might work, leave it on the list.
- List the advantages and disadvantages for each idea you have left on the list. Look at the advantages first, and try to find something positive about every idea.
- Keep discussions brief so you have enough time to discuss all ideas left on the list.
- Cross off any ideas that clearly have more disadvantages than advantages.
- Rate the remaining options from 1 (not very good) to 10 (very good).
- Choose a solution that you and your partner agree to try. It might not be your preferred solution, but it should be one that you’re comfortable with.
If you can’t find a solution , repeat the brainstorming step and try to come up with different ideas.
If you need new ideas, you could ask trusted friends or family. But first check with your partner if they’re OK with this. Your partner might prefer to keep some of your problems private.
If this still doesn’t work , you could both agree to trying your choice of solution this time and your partner’s choice next time.
5. Try the solution
Commit to the solution by agreeing on the following:
- Who will do what, when and where?
- What will happen if we don’t do the things we’ve agreed on?
- Do we need to keep track of how well our solution is working?
- When will we review how the solution is going?
- How will we know if the solution is working well?
If your solution is related to your child, consider getting them involved in trying the solution, if it’s appropriate.
6. Review the solution
After a set time, look at your solution and talk about how it’s going. You could ask questions like:
- Is the solution working?
- What has worked well? What hasn’t worked?
- What could we do to make things work more smoothly?
If the solution is working, you’ll both notice that the problem is going away. If it isn’t, ask yourselves these questions:
- Was the solution reasonable?
- Did we both give and take?
- Were rules and responsibilities clear to both of us?
- Did we have consequences for breaking the agreement, and were they appropriate?
- Have other issues come up that we need to talk about before our solution will work?
You might find that you need to start the problem-solving process again to find a better solution.
It’s natural to have ups and downs along the way, so set a realistic time frame to try the solution.
And remember to encourage and support each other as you try to solve the problem. For example, ‘I’m glad we’re trying to work on this together’ or ‘It helps when we talk things through. Thanks’.
Your goal is to do things differently and work on compromise. With patience, effort and support for each other, you can find a way to solve your relationship problems.
Getting help with problems in your relationship
If working on problems makes you or your partner very upset or angry, it might help to speak to a relationship counsellor. Relationship counsellors can help you identify what’s causing conflict and come up with practical solutions. You could try the following options:
- Call Relationships Australia in your state or territory on 1300 364 277 .
- Call Family Relationships Online on 1800 050 321 .
- See your GP to talk things through and get a referral to a psychologist or relationship or family counselling service.
- Find a psychologist or counselling service through the Australian Psychology Society , Australian Counselling Association or Psychotherapy and Counselling Federation of Australia .
It’s good if you and your partner can see a counsellor together. But if your partner doesn’t want to go, it’s still worth seeking help by yourself.
Family violence is not OK. If you’re in a relationship that involves family violence, call the National Domestic Family and Sexual Violence Counselling Service on 1800RESPECT (1800 737 732).
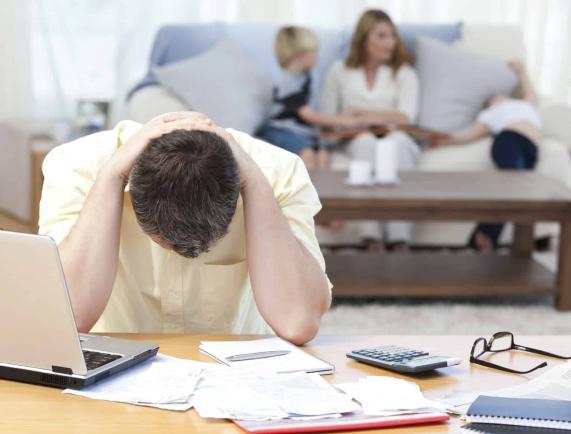

All families deal with relationship difficulties, small or large, at various times throughout the family experience. Family problems come in all shapes and sizes, impacting family dynamics and shaping family relationships. The ways that family members cope with and solve issues provide a framework for family dynamics and set the tone for family life.
How to Solve Family Problems
- Create an Environment of Sharing
- Acknowledge the Problem
- Get to the Deeper Issue
- Focus on the Relationship – Let Go of Anger and Pride
- Get Professional Help
Remember to Take Care of Yourself
Creating a family culture of openness and security, and taking the steps to resolve family issues, can improve relationships and maintain positive family dynamics.
Common Family Problems
Families face a variety of problems, both large and small. Family conflict and relationship problems can include arguments, miscommunication, and misunderstanding. They also can involve deeper issues such as substance abuse, financial instability, mental illness, grief, health problems, and divorce. Sometimes, these issues exist between only two family members, and other times they spread throughout the entire family, creating extended family issues . Some issues, like grief after the loss of a loved one, appear plainly on the surface, while others can be more subtle. Perhaps your child refuses to communicate with you, or your wife doesn’t seem to be a happily married woman .
Family issues often have underlying causes which are not always apparent.. And yet the impact of these root causes can spread throughout the family, creates conflict or emotional strain in several family relationships. Such conflict is especially impactful on a child’s life, creating emotional difficulties that are often carried from their childhood and adolescence into their adult lives and future family relationships.
Create an Environment of Sharing
Families are built on relationships, and relationships are strengthened through healthy communication. An environment of sharing creates the foundation for healthy communication. Family members need to feel safe to share their feelings and discuss their issues and emotions. As a family oriented parent , that means allowing your child to share their point of view without fear of judgment or punishment. Sometimes, a child just needs to feel certain that what they say will be taken seriously. A child who feels safe can talk about difficult or emotional subjects, such as mental health, self-identity, anxiety, or substance abuse. Children who feel safe and respected are much more likely to open up to a parent when struggling with a situation or trying to make a difficult decision. This is also true for other family relationships—not just between parent and child, but between siblings and within the marriage.
Ways to achieve an environment of sharing include:
- Listen. Really listen to the other person before providing advice or counsel. Sometimes, it is better to first ask if advice is welcome. If the answer is no, let it go and follow up later.
- Be willing to share your own feelings. Sometimes things seem obvious to us, but they may not be obvious to your child, spouse, or sibling. Sharing your own feelings without placing blame can bring up new points of view.
- Speak for yourself and avoid blame. When sharing your perspective, present it as just that - your perspective and not the facts.
- Recognize others’ experiences as valid. Telling others how they feel or should feel creates barriers and discourages sharing.
- Be human. Admitting you are wrong, or that you made a mistake, can help others feel more comfortable to admit their own mistakes.
- Model the behavior you want to see. We are all influenced by the people who surround us. Modeling healthy ways to express thoughts and emotions encourages others to do the same.
- Do things together. Families that spend time together engaged in positive activities achieve a sense of closeness that encourages open communication and sharing. Explore shared interests, sports, or service ideas for families . Activities that involve serving others and getting outside are especially fulfilling and often instigate future conversations and closer relationships.
Sharing openly among family members sets the stage for solving family problems and preventing future issues from arising.
Acknowledge the Family Problem
Sometimes family problems stem from something simple like a lack of closeness. Other times the problems involve something much more serious, like abuse. Acknowledging that a problem exists is the first step in doing something to fix the situation. Ignoring issues and pretending everything is fine are common unhealthy coping mechanisms for family members experiencing relationship conflict or emotionally difficult situations.
Lack of acknowledgment can exacerbate issues, fuel negative situations, and culminate in negative or damaging behavior, such as lashing out in anger, aggressive argument, substance abuse, or family violence. Acknowledging a problem as early as possible allows positive action to be taken toward fixing the situation, and may prevent unhealthy coping mechanisms that lead to negative situations.
Sometimes we avoid discussing problems because our past efforts to do so only seemed to make things worse. As a result, we believe that avoiding is better than continuing to fight. In truth, avoiding instead of fighting just leads to other side effects in families. Feeling stuck is often a sign that involving a third party is needed, such as a good marriage and family therapist.
Get to the Deeper Family Issue
After acknowledging that a problem exists, steps can be taken to identify the source of the problem and improve the situation. Most family problems are merely symptoms on the surface of a deeper-rooted cause. Knowing the cause paves the way for greater empathy among family members and illuminates situations that require change. Here are some examples of family problems and their deeper issues:
Conflict between siblings – The majority of families will experience some sibling conflict between children at various times. But if that conflict extends beyond the occasional bickering to consistent emotional arguing or angry or hurtful behavior, then a deeper issue is likely the cause. That deeper issue could involve jealousy or feelings of inadequacy, where one child feels overshadowed by the other. One child could be putting pressure on the other to keep a secret from their parents (such as breaking a rule or lying). The cause could also be external, affecting one child who in turn uses their sibling as a dump truck for unloading their stress, frustration, or anger.
Alcohol abuse or other substance abuse – Family members who abuse alcohol or other substances are often using the activity as an escape mechanism. They could be escaping from a difficult emotional situation, such as grief over the loss of a loved one, financial instability, marriage conflict, or divorce. Or, they could be escaping from physical pain from illness or other health problems. Professional help from a therapist or support group can help to break down the deeper issues that lead people to substance abuse and start them on the road to recovery.
Stress and anxiety in children – These are common effects of a variety of deeper issues. Often, anxiety is triggered by an event or a difficult situation. The stress that stems from it leads to further anxiety, creating a cyclical pattern. The root of the anxiety could be a social issue at school or concern for a friend. It could relate to feeling overwhelmed in school or struggling with an undiagnosed learning disorder. Children often perceive more than they let on and could be reacting to a passing comment from a parent, such as “Our budget is tight this month.” Talking with your child and maintaining trust through open communication encourages children to reveal the source of their anxiety.
Sometimes, identifying the deeper issue and bringing it out in the open is all it takes to resolve a problem. Other times, merely identifying the root cause is just the beginning of the long road to resolution. This important and necessary step will help to develop a plan for resolving issues and encourage understanding within family relationships.
Focus on the Family Relationship – Let Go of Anger and Pride
Anger and pride are the enemies of healthy family relationships. They feed negative emotions, hamper empathy and understanding, and thwart positive and open communication. Holding on to these feelings blocks the path to conflict resolution. Anger and pride are divisive to family relationships and damaging to individual mental health. They are fuel for the cyclical patterns of stress, anxiety, and depression. Despite knowing this, however, letting go of such emotions can be difficult – and sometimes painful. The fear of pain, vulnerability, or failure are often what keeps a person from improving their family relationships and focusing on the importance of family .
One of the best ways to move beyond that fear is to focus on the relationship. Prioritize the goal—a healthier, happier relationship—over the fear of being hurt or the fear of failure. When family problems exist, a person has usually been hurt already, which makes the fear of being hurt again even greater. But while that risk of further hurt is real, the potential for healing and resolution is also real. Focusing on that potential, and letting go of those negative emotions, opens the door to healthier communication, relationship healing, and better mental health.
Get Professional Family Help
Getting professional help is one of the best ways to handle family problems. Some situations, such as those involving abuse, dangerous behavior, or domestic violence, require immediate professional help and formal family assessment . In other situations, such as ongoing disagreements over a certain topic or lack of closeness within a marriage, brief therapy help can provide the catalyst you need to get unstuck and achieve the fulfilling relationship that you each desire.
Many people hold back from seeking professional help because of fears or misunderstandings. Here are some facts about therapy that help to debunk some of these common myths and misconceptions:
Therapy is for everyone - A common misconception about therapy is that it is reserved for people with mental illness, individuals with an emotional disorder, or people who are too weak to handle their own problems. This could not be further from the truth. As humans, we need other humans to work through issues with us. Therapy provides a safe, confidential environment to do just that.
Professional help is available for all types of issues, whether large or small, and in a variety of formats. Family therapy, marriage counseling, support groups, and individual sessions with a therapist are just a few examples. There is also a variety of specialties, including psychology, psychiatry, religious counseling, and much more. At the end of the day, therapy is merely a safe space to work through your family problems with the support of a trained professional.
Therapy is worth your time - Another common misconception is that therapy is a waste of time or money. You could talk to anyone, so why talk to a therapist? Therapists have special expertise gained through extensive professional training. They will not only help you talk about your family issues but will help you to develop strategies for resolving difficult situations. A family therapist can also discuss various types of issues you may be dealing with, and different options for resolution or treatment, such as new scientific approaches to treating a specific issues.
Therapy is safe - One myth about therapy is that there are risks. The risk of being judged (by the therapist or by friends and family) or the risk of being medicated. On the contrary, therapy provides a safe and confidential space to explore all options for healing. Often, professional counseling is all that is needed or desired for family conflict resolution.
Professional help can provide growth and healing for a parent, child, or an entire family, improving family dynamics and emotional health. It can provide mediation and conflict resolution within a marriage, between siblings, or any type of family relationship. Think about the type of support (such as family therapy, religious counseling, or psychiatry) that feels right for your family and seek it out.
It is true that the quality of the professional you work with can make a big difference in the outcome of your therapy. For this reason, it’s often best to seek a referral from a trusted friend or family member. If that feels uncomfortable, consider asking for a referral from your family doctor. If you’ve had a negative experience in the past, consider giving it another try, this time with a trusted referral.
Taking care of yourself and maintaining your mental health is essential when attempting to solve family issues. Maintaining positive, healthy family dynamics starts with a healthy self. Being in a healthy mental space allows you to let go of negative emotions. This, in turn, paves the way for safe and open communication between family members and helps the entire family focus on relationships.
Not only does this place you in the right frame of mind to address family conflict, but it models a healthy example for your children to do the same. It is integral to maintaining a strong family structure that provides a sense of stability and security for children. For a parent, maintaining your mental health can provide you with the strength and perspective needed to maintain the necessary qualities of a good father and mother, such as understanding and empathy.
Taking care of yourself is often easier said than done, especially while feelings of stress, anxiety, or emotional dissatisfaction prevail. Finding a healthy outlet to decompress and let go of stress and other negative emotions can help to maintain a healthy state of mind. Choose a regular time in your schedule just for maintaining you. This could include a daily exercise routine, a therapeutic hobby (such as gardening or journaling), or a weekly therapy session. Taking care of yourself leaves you open to model healthy behavior for your children and to focus on family relationships.
Impact of Family Problems
When not addressed, family problems can have serious impacts on individual family members. Issues such as increased levels of stress and anxiety, emotional difficulties and disorders (such as depression), substance abuse, and addiction, are all likely to surface. Sometimes, these impacts carry on throughout a child’s life. Family problems can especially impact children, who are often capable of perceiving much more than one might think. Children may also perceive a problem, but not be able to fully understand it. Such misunderstandings can lead to greater issues, further affecting family dynamics and individual emotions. Where family issues exist, acknowledge the problem, and take the steps to resolution.
Solving Family Problems
Families experience a wide range of issues, some small and some large. These issues typically involve strain or conflict within family relationships. They can have lasting impacts on individual family members, especially children. Taking steps to address family issues, and seeking resolution among family relationships can ease emotions, promote mental health, and maintain a positive family culture. A family culture quiz by Kinmundo is an easy way for families to evaluate and improve the culture within their family.
A positive family culture requires a structure built on family values that maintains a safe environment for sharing. Open communication in an environment safe from fears of judgment provides a model of stability and security for family members to acknowledge and address important issues with understanding and empathy. Creating such a culture is paramount to solving family issues when they arise.
A family that feels open and safe to share emotions, acknowledge issues, and seek help when needed can maintain positive relationships and mental health. When family members are prepared to resolve family conflict, they can reduce the lasting impacts of difficult situations and fix relationships that may seem broken.
5 Ways to Become a More Family Oriented…

- Contributors
- Advertise With Us
- Privacy Policy
- Unsubscribe From Notifications
- Terms of Service
- Do Not Sell My Data
- Radiant Digital

Family Problems: Unpacking the Dynamics and Finding Solutions

Family problems are something all of us grapple with, whether we’d like to admit it or not. Nobody’s family is perfect and every family faces its own unique set of challenges and hurdles. I’ve learned over time that the key isn’t about completely avoiding these issues, but rather finding effective ways to navigate through them.
Having spent years studying family dynamics, I’ve come to understand that these problems can range from simple disagreements to deep-rooted conflicts extending back generations. It’s important to remember that this doesn’t mean your family is ‘broken’ or ‘dysfunctional’. On the contrary, confronting and working through these issues can often lead to stronger bonds and deeper understanding among family members.
In this article, I’ll delve deeper into some common types of family problems many of us face and offer practical advice on how you can manage them effectively. Remember, it’s not about having a problem-free life, but learning how to deal with those problems when they do arise.
Understanding Family Problems: An Overview
Family problems. We’ve all had them, and let’s be real, they’re never fun. But it’s important to understand that these issues aren’t unique to any one household. In fact, they’re a universal experience.
To put things into perspective, family problems may arise from a multitude of factors. These range from financial difficulties to personal disagreements, health issues or even differing ideologies. It’s like a tricky puzzle that needs careful solving – each family has its own set of pieces with different shapes and sizes.
According to the American Psychological Association (APA), some of the most common family issues include:
- Communication breakdown
- Parental discipline styles
- Substance abuse
- Divorce or separation
- Behavioral problems in children
Here’s an interesting piece of data from APA:
Quite a sobering table, isn’t it? But remember this – understanding is always the first step towards resolution. Afterall, you can’t solve what you don’t understand.
The good news is there are numerous resources available today for families facing such hurdles – professional counseling services, self-help books and online communities are just some examples.
So buckle up! As we delve deeper into this topic over the next few sections, I’m confident we’ll uncover ways to navigate these familial challenges together.
Common Types of Family Problems
Family problems. It’s a phrase we’ve all heard, but what does it actually mean? Well, let’s take a closer dive into the complexities that make up this term.
One common type of family problem is communication breakdown. Often times, members within a family struggle to effectively express their thoughts and feelings to each other. This can result in misunderstandings, conflicts and hurt feelings. A lack of open, honest communication can create tension and lead to further issues down the line.
Next on the list is financial stress. Many families grapple with money-related issues on a regular basis which can lead to significant strain on relationships within the family unit. Financial problems may include job loss, debt accumulation or disagreements about how funds should be managed or spent.
Substance abuse also falls under the umbrella of family problems. When one member suffers from addiction, it inevitably impacts everyone else in the family too – leading to emotional turmoil and instability at home.
Another prevalent type of issue is mental health disorders such as depression or anxiety among family members which often go unnoticed or untreated for long periods of time causing disruption in normal functioning and harmony at home.
Finally there’s divorce or separation – one of the most difficult types of familial disruptions both emotionally and logistically for everyone involved especially children who are caught in between parents’ disputes.
To summarize:
- Communication Breakdown
- Financial Stress
- Substance Abuse
- Mental Health Disorders
- Divorce or Separation
These are just few examples drawn from a vast array of potential challenges families face today. And remember, no two families are alike so what constitutes as ‘problems ‘ will vary greatly depending on individual circumstances and dynamics within each unique household.
Effects of Family Problems on Individual Members
Family problems can take a heavy toll on each member, affecting their psychological well-being, physical health and social interactions. Let’s dive deeper into these effects.
Firstly, on the emotional front, family issues often lead to stress and anxiety. It’s not uncommon for individuals to feel overwhelmed, resulting in sleep problems or mood swings. For children especially, this constant state of tension may lead to behavioral issues at school or home.
The impact isn’t just emotional – it’s physical too. Research has shown that ongoing family strife can manifest as health issues like headaches, high blood pressure or digestive problems. One study found that adults from broken homes were 44% more likely to suffer from a stroke compared with those from stable families.
Socially speaking, these internal struggles can seep into one’s external relationships as well. They may create barriers when forming new relationships or strain existing ones with friends or partners.
Let me share some statistics:
We need to bear in mind though that these figures represent averages and there will always be individual deviations based on personal resilience and available support structures.
In conclusion (without actually saying “in conclusion”), I’ll note how vital it is for families facing difficulties to seek professional help if necessary – therapists and counselors can provide valuable guidance toward resolution and healing.
How to Identify and Address Family Conflicts
Family conflicts can often bubble up without us even realizing it. It’s crucial to be aware of these issues, as addressing them promptly can help maintain a harmonious family environment.
One common indicator of family conflict is consistent disagreement. If you find your family gatherings marred by constant bickering or discord over trivial matters, it’s likely there’s some deeper issue at play. It could be resentment brewing under the surface or unresolved past conflicts making their presence felt.
Another sign could be withdrawal from family activities. When someone in the household begins avoiding spending time with others, it may signal an underlying problem. Whether they’re feeling left out, unheard, or emotionally overwhelmed – such behavior could point towards a potential family conflict.
Now that we’ve identified these signs let’s talk about addressing them:
- Open Communication: Encourage everyone in the house to express their feelings and concerns openly. Make sure they know that it’s okay to disagree sometimes.
- Active Listening: Ensure all parties involved feel heard and understood during discussions about conflicts.
- Seek External Help: If the situation seems too overwhelming for you to handle alone, considering seeking professional guidance from therapists or counselors who specialize in resolving family issues.
Remember, ignoring problems won’t make them disappear magically; instead, it exacerbates them over time. By recognizing and confronting these issues head-on, we have a better chance of fostering peace within our households and strengthening familial bonds.
Strategies for Resolving Family Issues
Family issues, we’ve all got ’em. They’re as common as the cold and can be just as tricky to shake off. But don’t despair! With the right strategies in place, you might find these problems easier to tackle than you’d think.
First off, let’s talk about communication. It’s often at the root of many family conflicts. We’re not mind readers after all, so how else can we understand each other? Regular family meetings can serve as a great platform for everyone to voice their concerns and frustrations in a controlled environment. Remember though, it’s crucial that everyone gets a chance to speak and is treated with respect during these discussions.
Secondly, try practicing empathy. Put yourself in the other person’s shoes for a change. Seeing things from another perspective can lead to some surprising revelations and help defuse tense situations.
Thirdly, consider seeking professional help if needed. There should be no shame or stigma attached to this option. Therapists are trained professionals who can provide valuable insights and advice on handling family disputes.
Lastly but by no means least: patience! Change doesn’t happen overnight and old habits die hard – so give it time !
So there you have it – my top tips for resolving family issues:
- Regular Communication
- Professional Help
Remember these aren’t definitive solutions but rather strategies that could potentially alleviate some of those pesky familial tensions.
Professional Help for Serious Family Problems
Let’s face it, we all have our fair share of family problems. Sometimes they’re small, other times they can be quite serious. But when those problems start to become overwhelming, it’s often best to seek professional help. Psychiatrists, therapists and social workers are trained to handle a wide range of family issues – from marital conflicts to behavioral issues in children.
Family therapy is one such resource that families can tap into. According to the American Association for Marriage and Family Therapy (AAMFT), nearly 90% of clients report an improvement in their emotional health after pursuing therapy. This form of intervention allows every member of the family to voice their thoughts and feelings in a safe environment.
But therapy isn’t the only avenue available for families facing troubles. Support groups also offer a valuable lifeline for individuals grappling with similar issues. These communities provide much-needed comfort, practical advice and reassurance that you’re not alone in your struggles.
For more severe cases where there’s risk involved – such as domestic violence or child abuse – immediate action is crucial. Organizations like the National Domestic Violence Hotline or Child Protective Services are equipped to intervene promptly and ensure safety.
- The National Domestic Violence Hotline : Provides round-the-clock support through phone calls or online chats.
- Child Protective Services (CPS) : An agency dedicated towards ensuring child welfare.
Ultimately, remember this: It’s okay to ask for help when things get tough at home. There are plenty of professionals out there ready and willing to lend a hand. Seeking assistance isn’t a sign of weakness; instead, it shows courage – acknowledging there’s an issue is already half the battle won!
Case Studies: Families Overcoming Difficulties
Let’s dive into some real-life examples of families who’ve faced serious difficulties, and most importantly, how they managed to overcome them. It’s crucial to remember that each family is unique, with their own set of challenges and coping mechanisms.
Meet the Andersons. They’re a middle-aged couple with two kids in high school. Life was sailing smooth until Mr. Anderson lost his job unexpectedly. This sudden loss of income shook their stability and led to significant financial stress within the family unit. But, they didn’t let this setback define them. Instead, they took it as an opportunity for change – Mrs. Anderson returned to work part-time while Mr. Anderson started his own small business.
Next up are the Garcias – a large extended family living under one roof consisting of grandparents, parents, children and grandchildren alike! Their challenge? Communication gaps and generational clashes were tearing at their familial bonds almost daily due to diverse age groups within one household. Their solution? Regular ‘family meetings’ where everyone had an open platform to voice their concerns or issues without judgement or interruption.
Last but not least are the Smiths – a single mother with three young children struggling with time management between work responsibilities and childcare duties after her recent divorce. Her solution? She sought out professional counseling services that helped her develop effective strategies for balancing work-life responsibilities along with nurturing emotional health during this challenging transition period.
These examples serve to remind us that problems within the family unit can be varied and complex, but they’re certainly not insurmountable. It’s all about identifying the issues, being open to seeking help, and most importantly – believing in one’s ability to overcome.
Conclusion: Turning Challenges into Opportunities
The road may be rocky, but let’s not forget that family problems can serve as catalysts for growth and change. I’ve seen it happen time and again. Families, riddled with issues, find a way to turn these challenges into opportunities.
When dealing with family problems, it’s important to remember that every challenge is an opportunity in disguise. For instance:
- A strained relationship can strengthen bonds over time. It might push us out of our comfort zones and force us to communicate more effectively.
- Financial difficulties could lead us to discover new ways of budgeting or even inspire a career shift.
- Disagreements on how to raise children might make us re-evaluate our own values and beliefs.
It’s important not just to focus on the negative aspects of these situations. Instead, see them as chances for personal growth and improved relationships within the family.
Overcoming family problems requires patience, understanding, and resilience. These are traits that we can cultivate during tough times. Once honed, they become invaluable tools in navigating life’s ups and downs.
Remember this: families aren’t perfect because perfection doesn’t exist in any human endeavor. We’re all works-in-progress learning from our experiences – both good and bad! So let’s take those challenges head-on.
- View each challenge as an opportunity for growth.
- Cultivate patience, understanding, and resilience during difficult times.
- Remember that no family is perfect; we’re all learning together!
By adopting this mindset toward any problem you encounter within your family unit you’ll start seeing them less as insurmountable obstacles but rather stepping stones towards better communication skills or stronger relationships between members.
In the end, it’s about changing how we perceive these issues – by turning challenges into opportunities for development – which could ultimately lead to harmonious familial relations down the line!
Related Posts

FamDyn: Uncovering 6 Family Types

Family Loving: Unleashing the Power of Deep Connections at Home

Solving Common Family Problems: Five Essential Steps
Engaging children in the solution of problems..
Posted May 28, 2012
In every family, there will be problems. No matter how positive and empathic we have been, kids will still argue and misbehave, and ask for more than they can have. The demands of our daily lives—and of theirs—will inevitably create conflict and misunderstanding.
Often, there is a recurring problem. The problem may be getting ready for school in the morning or going to sleep at night. Or doing homework, or fighting with siblings. Children may be demanding or disrespectful, or refuse to cooperate when asked. Over time, these common problems of daily living begin to erode the quality of our relationships with our children - and our own pleasure in being parents.
So often, families get stuck. Despite our best intentions, children become stubborn and defensive—and so do we. In today’s post, I will outline five essential principles that we should keep in mind in attempting to solve any challenging problem of family life.
Step 1: Take a Step Back
The first step in solving any recurring problem in the life of a child is to take a step back. Problems of family life are best solved - and perhaps can only be solved—proactively. When we are reacting to our children’s behavior, we will often be reacting badly. Clinicians and parent advisors of all points of view agree on this point.
Children want to solve problems, and they want to do well. Like us, however, they may become frustrated and even feel hopeless that solutions are possible. And, like us, they may just not know what to do.
Look for causes, not just symptoms. You will solve problems more successfully when you have been able to identify the daily experiences in the life of your child that are sources of painful feelings. These may be frustration in learning, or frequent criticism, or bullying , or exclusion.
Then, listen to your child’s grievance. Let him tell you what he believes is unfair in his life. Tell him what is right about what he is saying before you tell him what is wrong. You can say, for example, “I know you feel that we are always on your case about your schoolwork, and maybe we are. But we’re worried and we need to solve this problem.”
Step 2: Place the Problem Before Your Child
Once you have identified a recurrent problematic situation and made some effort to understand its causes, the next step is to place the problem before your child. Say, for example, “We have a problem in the morning, when it’s time to get ready, and I often end up yelling at you,” or “I think we have a shower problem,” or “A lot of times, we have a problem when I tell you that it is time to turn off the television.”
Step 3: Elicit Your Child’s Ideas
It seems almost reflexive for many parents, when faced with a child’s defiance or lack of cooperation, to attempt to solve this problem by imposing a “consequence” for their child’s misbehavior. Although some problems may require this approach, I recommend that you first engage your child in an effort to solve the problem—to elicit her ideas.
In this way, you will often be able to engage her in a search for solutions. She will then be less absorbed in angry and defiant thoughts, less stuck in making demands or continuing the argument. She will begin to think, even if just for that moment, less about getting her way and instead about how to solve a problem, how her needs and the needs of others might be reconciled - an important life lesson, for sure.
Once you have placed the problem before your child and asked for her ideas, give her some time. You can say, for example, “Why don’t you think about it for a while? Let’s talk again later, or tomorrow, and see what your ideas are.” In doing this, you will be teaching yet another important lesson, because this is how most problems in life should be solved.
Step 4: Develop a Plan
In my experience, almost all children respond positively when I tell a family that “I have a plan” to solve a recurrent problem of family life. They may be skeptical, but they listen with interest. Deep down, they want a plan, as much as we do. (I will offer plans for solving specific family problems in future posts.)

Step 5: Express Appreciation and Praise for Increments of Effort and Success
Be sure to offer praise and appreciation for every increment of your child’s effort at compliance and self-control . Your acknowledgment of her effort and progress is a basic principle of successful problem solving.
Psychologists have learned from psychotherapy research that ongoing collaboration is an important element of successful therapy. This is also true in solving problems with our children. We should regularly, proactively, check in with children, and ask, for example, “How do you think we are doing with our morning problem?”
Copyright Ken Barish, Ph.D.
Ken Barish is the author of Pride and Joy: A Guide to Understanding Your Child’s Emotions and Solving Family Problems .

Kenneth Barish, Ph.D. , is a clinical associate professor of Psychology at Weill Medical College, Cornell University.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Support Group
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Family Life
How to Deal With Family Problems
Last Updated: December 14, 2023
This article was co-authored by Tasha Rube, LMSW . Tasha Rube is a Licensed Social Worker based in Kansas City, Kansas. Tasha is affiliated with the Dwight D. Eisenhower VA Medical Center in Leavenworth, Kansas. She received her Masters of Social Work (MSW) from the University of Missouri in 2014. This article has been viewed 360,325 times.
Death, addiction, money troubles, mental illness, separation/divorce, and transitional adjustments all take a toll on the members of a family. During stressful events or when the family’s resources are severely taxed, problems may not be resolved easily. This may lead to hostile disagreements, tension, and resentment. Conflict in the family can affect everyone’s functioning. Handle your family problems by learning effective problem-solving skills.
Developing Healthy Problem-Solving

- Schedule a meeting at a time that is most convenient for everyone. Make everyone aware of the purpose of the meeting and that you want them to arrive with suggestions and solutions at the ready.
- Be mindful that young children may be a hindrance to a family meeting. Huddle them in a separate room if you expect tempers to flair or sensitive information to be discussed.
- Therapists often suggest holding regular family meetings. [1] X Research source This tactic enables family members to bring issues out in the open before resentments develop. Talking with your family regularly can improve communication and the bond that you share.

- Strive to uncover what is important about the current problem. Building a case or bringing up old misdeeds will not assist you in resolving this issue.

- Remember, you are aiming to de-escalate the conflict and work towards a solution. Using “I” statements allows everyone to express themselves while showing respect for others listening. Making an “I” statements allows each person to take ownership of what they are feeling, and suggest a remedy for the problem at the same time.
- Examples of “I” statements include: “I am worried that our family is falling apart. I would like us to work things out.” or “I get scared when Dad drinks a lot because he starts yelling. I wish he could stop drinking”.

- Effective listening allows the other person to feel heard, motivates the other parties to want to listen to you, defuses arguments and strong emotions, and rebuilds the relationship during the conflict.

- Validate your family members by saying something like “I’m really glad you felt comfortable enough to share this with me” or “I appreciate your willingness to work towards a solution”.

Recognizing Communication Roadblocks

- For some people, conflict causes them to become hostile and defensive. This is the “fight” aspect of the physiological “fight or flight” response. These individuals may argue endlessly to remove any responsibility from themselves, or refuse to hear others’ points-of-view.
- Others resort to the “flight” aspect. These individuals may run from conflict at all costs. They may deny there’s a problem or believe there’s nothing they can do to resolve it anyway. Such family members may pretend as if they don’t notice any tension in the household, or downplay its effect on them.

- First work on trying to identify your emotions. Consider what thoughts you’re having, what you feel in your body, and what actions you want to take? For example, maybe you’re thinking “I hate this family.” Your fists are clenched and you want to punch something. Such a strong emotion could be labeled as anger or contempt.
- Next, aim to control and ease these strong emotions so that you can effectively problem-solve. Depending on how you’re feeling participate in a complementary activity to ease your discomfort. For example, if you are sad, you might want to watch a funny movie. If you are angry, it might be helpful to vent to a friend or engage in intense physical activity.

- Using “I” statements are one of the best strategies for minimizing blame and subsequent defensiveness. Say “I fear that your addiction will lead to someone getting hurt” rather than “Addicts are just dangerous people to be around”
Expert Q&A
- Your family consists of some of the most important relationships in your life. Having continuous conflict in this area can drastically affect your life satisfaction. If you cannot resolve family issues, seek professional help. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
Tips from our Readers
- Sometimes, creating distance by leaving is the healthiest thing you can do. Not all family members are inherently trustworthy, beautiful, or helpful, and getting some space can keep a bad problem from getting worse.
- Understand that it is not always your fault. Don't get upset or angry if someone gets on your nerves and you didn't do anything wrong.

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/emotional-fitness/201209/10-tips-holding-family-meeting
- ↑ https://www.focusonthefamily.com/marriage/communication-and-conflict/luve-a-five-step-communication-process-for-conflict-resolution/validation-is-the-third-step-to-conflict-resolution-in-luve
- ↑ https://www.webmd.com/balance/family-therapy-6301
- ↑ https://www.drnadig.com/conflict.htm
About This Article

Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Mar 1, 2018
Did this article help you?

Nov 8, 2019
Steff Irwin
Sep 12, 2016
Ahlam Osman
Jun 6, 2016
Mbasa Mzaca
Nov 17, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Advertisement
Common family issues & how to deal with them, from experts.

No family is perfect, but for people whose family life has never been outright "bad," it can be tricky to spot family issues as they arise. Family problems are much more than abuse or addiction, for example, and include a host of different things that affect every member of a family. Here's how to spot family issues and deal with them, according to experts.
What are family issues?
Family problems or issues include any sort of dynamic, behavior, and/or pattern that disrupts the household or family at large. They can range from smaller, more common challenges like clashing personalities or divvying up household chores, to more intense issues like having a narcissistic parent , abuse, or intergenerational trauma, according to licensed psychotherapist Babita Spinelli, L.P.
The main thing with any family issue is that it creates stress and tension within the family, which in turn negatively affects the members of that family, particularly if there are young children involved.
Types of family issues:
Clashing and/or toxic personalities.
Starting off basic, it's far from uncommon for a family to have clashing personalities. Perhaps siblings don't get along with one another, or one child doesn't get along with one or both parents, psychotherapist Annette Nuñez, Ph.D., LMFT, tells mbg.
This can go a big step further when you're dealing with someone who displays narcissistic tendencies or other toxic traits , Spinelli adds, which introduces a bunch of other issues into the family unit, such as gaslighting or explosive fighting.
Poor communication
Nuñez and Spinelli both note that lack of open and healthy communication is at the root of many more general family problems. As Spinelli explains, if it's really difficult to actually speak to a family member, if there are trust issues , if they dismiss you, or issues get swept under the rug, those are all family issues surrounding communication.
Heavy pressure from parents
Perfectionism within a family can have extremely negative effects on children and their self-worth. As Nuñez notes, when parents shame or dictate how children should feel or be, it can take a toll on their ability to grow as individuals. "Parents do need to have some boundaries but not when it gets to the point where it's emotionally abusive," she explains.
Things like conditional love, or a deep sense of pressure to meet the expectations of your family, indicate some family issues, Spinelli adds. It could even lead to what's known as golden child syndrome .
Different parenting styles
One of the biggest hurdles of parenting as a couple is figuring out how to combine your parenting styles in an effective way. When you can't, it can cause some problems.
"It can cause a lot of tension when parents aren't on the same page with parenting," Nuñez tells mbg. And if you're dealing with extended family, Spinelli adds, having the input of in-laws when it comes to your parenting can also cause some problems.
So many families will deal with challenges surrounding finances, budgeting, and employment. Spinelli says money problems can include one parent making all the money and feeling burdened, not having enough basic funds for what you need, generational issues around poverty or gambling, and so much more. Money touches most areas of our life, and if there are issues here, the effects will be felt within any family.
Managing the household
It might seem juvenile, but chores really matter. If one person is carrying the weight of maintaining the household , that's a lot of responsibility and pressure. Nuñez notes it's important for household labor to be divided up in a fair and age-appropriate way, so one parent doesn't feel taken advantage of, and children begin learning how to take care of themselves.
Unchecked addiction or mental health issues
If a parent (or even a child) is dealing with mental health issues or addiction, that can cause a huge rift within a family unit. It's important for those things to not only be addressed but also talked about in an open and honest way.
As Nuñez explains, "If a parent feels like they're hiding mental illness or any type of substance abuse from a child, kids pick up on that. They pick up on those nonverbal cues of inconsistency, and children do need consistency to have a strong family foundation and feel secure."
Constant arguing
If you grew up thinking constant arguing was normal, according to Spinelli, it's very much not. "Some people don't realize that the constant bickering and arguing is actually an issue—they're just so used to it. They don't realize that when there's yelling or screaming and arguing, that actually creates stress and tension."
It's not uncommon, but yes, divorce certainly does disrupt a family unit and can cause problems when it's swept under the rug. "You'd be surprised how many people haven't processed divorce in the family," Spinelli says, adding, "It really does impact how you see relationships, and models fears around relationships, and often people don't even talk about it in the family."
While it can be hard to avoid, distance within a family can cause a lot of issues around expectations and boundaries, according to Spinelli. For example, as the holidays approach, there are often arguments around who's visiting whom, why someone has decided not to visit that year, and so on, she explains.
Codependency
" Codependency comes in all shapes and sizes," Spinelli tells mbg. While some instances of codependency are mild, the more enmeshment you find within a family, the more the individual members of that family will have a hard time distinguishing their own wants, needs, and desires, she says.
Scheduling conflicts
Nuñez notes that another common family issue is scheduling conflicts. If one or more family members has a busy schedule, it can be hard to connect together and make time for each other. This can look like one parent who works long hours and is rarely home during the day, or issues with scheduling as children get more involved with extracurriculars, she explains.
Intergenerational trauma
Last but not least, intergenerational trauma is a huge, often unaddressed family problem that stems back through generations. According to Spinelli, if past generations experienced things like extreme poverty, racial trauma, sudden death, addiction, mental health issues, and so much more, all of that can be passed down through generations.
"If something has happened in the previous generation, and that family member never dealt with it, that fight-or-flight and what they went through seeps into the other family members," Spinelli says.
How family issues affect us.
There are so many ways all of the aforementioned family issues can affect the members of that family, particularly children in their formative years of life. For example, "Children may start having behavioral issues, which then in return causes parents to get upset and the kids act out more," Nuñez explains. And that's just one more immediate example.
Our childhood experiences play out in adulthood through attachment wounds , as we bring those dysfunctional patterns into our adult relationships, she adds. "Let's say a parent leaves at a developmental age where a child needs a parent, for example. That brings up abandonment issues ," she notes.
Overall, a significant number of unaddressed family issues can make people feel that they don't have true safety in their lives, Spinelli says. "It's going to lead into attachment issues. Maybe they've dealt with abuse, neglect, abandonment, which has created an insecure attachment . They may also become an avoidant because they've never been modeled unconditional love by their primary caregiver," she explains.
Signs of family issues:
- Difficulty with open, honest, and healthy communication
- Frequent fights or bickering
- Frequent yelling and screaming
- Passive-aggressive behavior
- An absent parent or parents (physically and/or emotionally)
- Abuse of any kind (physical, emotional, and/or verbal abuse )
- Codependent behavior and/or enmeshment
- Struggles around finances or employment
- Perfectionism or high standards within the family
- Disagreements on household chores, parenting styles, etc.
- Tension in the household for no clear reason
- Difficulty trusting family members
What to do if you're dealing with family issues:
Identify what the specific issue is..
If you're getting the sense that you're dealing with some family dysfunction, the first thing you'll want to do is get clear on what specifically you're dealing with. Is it controlling parents ? Scheduling conflicts? Lack of communication?
Whatever the issue, Nuñez and Spinelli both note recognizing it is the first step. From there, you can begin processing how you want to bring it up to your family members, which brings us to our next point.
Talk about it.
Nothing gets solved by sweeping it under the rug, and family issues are no exception. Nuñez and Spinelli both say you'll want to address any issues weighing on your mind, even if it's not easy.
"Give yourself permission to say 'Hey, I feel angry or resentful, and I need to talk about this,'" Spinelli says. And as Nuñez notes, you can soften the blow using language that's not directed at them, opting for "I" statements, rather than "you" statements (i.e., "I feel sad when you miss dinner," instead of "You always miss dinner; you're so inconsiderate.")
Nuñez also adds that it's a good idea to pick a low-stress time when you can give each other your undivided attention and energy. (So, probably not around the holidays.)
Consider seeking professional help.
Once you've aired out some of your concerns, it may be necessary to ask for the help of a professional. Whether you opt for individual therapy, couples' therapy , or family therapy is up to you and your family, but any of them can certainly help in understanding how family problems have affected you—and how to deal with them.
"And even if a family doesn't go to therapy, it's important for every person to feel like they have a voice in their family, and to speak up, and to really voice what they need within that unit," Nuñez says.
Set boundaries.
And last but certainly not least, when all else fails, boundaries with family are a necessity in keeping a family dynamic as healthy as possible for everyone. "Really think about the ways you can set boundaries and give yourself permission," Spinelli says.
Whether you opt out of going to every family gathering, keep your distance from family members who make you uncomfortable or angry, or simply tell a family member when their behavior is unacceptable to you, Spinelli says you're completely in your right to do so.
The bottom line.
No family is without a little dysfunction. After all, it was spiritual icon Ram Dass who once said, "'If you think you're enlightened, go spend a week with your family."
But no matter how many problems your family seems to be facing, all it takes is one of you to identify the problems at hand, work through them, and break the chain for future generations.
Enjoy some of our favorite clips from classes
What Is Meditation?
Mindfulness/Spirituality | Light Watkins
Box Breathing
Mindfulness/Spirituality | Gwen Dittmar
What Breathwork Can Address
The 8 limbs of yoga - what is asana.
Yoga | Caley Alyssa
Two Standing Postures to Open Up Tight Hips
How plants can optimize athletic performance.
Nutrition | Rich Roll
What to Eat Before a Workout
How ayurveda helps us navigate modern life.
Nutrition | Sahara Rose
Messages About Love & Relationships
Love & Relationships | Esther Perel
Love Languages

Feeling Disconnected From Your Partner Lately? Do These 3 Things
Tanya Carroll Richardson

A List Of 55 Things To Do With Friends The Next Time You Need Some Inspo
Sarah Regan

I've Used This Suction Toy For 5 Years & Still Orgasm Every Time
Braelyn Wood

These 10-Minute Protein Pancakes Will Start Your Morning On The Right Foot
Valerie Bertinelli

I'm A Longevity Physician & These 3 Things Are Aging Your Skin
Alexandra Engler

6 Best CBD Lotions & Creams For Aches & Joint Comfort
Jamey Powell

Popular Stories

The Importance of Problem Solving and How to Teach it to Kids
Teach your kids to be brilliant problem solvers so they can shine.
We get so lost as parents with all the demands to do more for our children—get better grades, excel at extracurricular activities, have good relationships—that we may be overlooking one of the essential skills they need: problem-solving.
More: A Parent’s Guide to Conscious Discipline
In a Harvard Business Review study about the skills that influence a leader's success, problem-solving ranked third out of 16.
Whether you want your child to get into an Ivy League school, have great relationships, or to be able to take care of the thousands of frustrating tasks that come with adulting, don't miss this significant super-power that helps them succeed.
Our kids face challenges daily when it comes to navigating sibling conflict, a tough math question, or negative peer pressure. Our job as parents or teachers is not to solve everything for them —it is to teach them how to solve things themselves. Using their brains in this way is the crucial ability needed to become confident, smart, and successful individuals.
And the bonus for you is this: instead of giving up or getting frustrated when they encounter a challenge, kids with problem-solving skills manage their emotions, think creatively and learn persistence.
With my children (I have eight), they often pushed back on me for turning the situation back on them to solve, but with some gentle nudging, the application of many tools, and some intriguing conversations, my kids are unbeatable.
Here are some of the best, research-based practices to help your child learn problem-solving so they can build smarter brains and shine in the world:
Don’t have time to read now? Pin it for later:
1. Model Effective Problem-Solving

When you encounter a challenge, think out loud about your mental processes to solve difficulties. Showing your children how you address issues can be done numerous times a day with the tangible and intangible obstacles we all face.
2. Ask for Advice

Ask your kids for advice when you are struggling with something. Your authenticity teaches them that it's common to make mistakes and face challenges.
When you let them know that their ideas are valued, they'll gain the confidence to attempt solving problems on their own.
3. Don't Provide The Answer—Ask More Questions

By not providing a solution, you are helping them to strengthen their mental muscles to come up with their ideas.
At the same time, the task may be too big for them to cognitively understand. Break it down into small steps, and either offer multiple solutions from which they can choose, or ask them leading questions that help them reach the answers themselves.
4. Be Open-Minded

This particular point is critical in building healthy relationships. Reliable partners can hold their values and opinions while also seeing the other's perspective. And then integrate disparate views into a solution.
Teach them to continually ask, "What is left out of my understanding here?"
High-performing teams in business strive for diversity—new points of view and fresh perspectives to allow for more creative solutions. Children need to be able to assess a problem outside of immediate, apparent details, and be open to taking risks to find a better, more innovative approach. Be willing to take on a new perspective.
5. Go Out and Play

It may seem counter-intuitive, but problems get solved during play according to research.
See why independent play is vital for raising empowered children here .
Have you ever banged around an idea in your head with no solution? If so, it's time to get out of your mind and out to play.
Tech companies understand this strategy (I know, I worked at one), by supplying refreshing snacks and ping pong tables and napping pods. And while they have deadlines to meet, they don't micromanage the thinking of their employees.
Offer many activities that will take your child’s mind off of the problem so they can refuel and approach things from a fresh perspective.
Let them see you fail, learn, and try again. Show your child a willingness to make mistakes. When they are solving something, as tricky as it may be, allow your child to struggle, sometimes fail and ultimately learn from experiencing consequences.
Problems are a part of life. They grow us to reach our highest potential. Every problem is there not to make your child miserable, but to lead them closer to their dreams.
Tami Green, America’s most respected life coach, has received magical endorsements by experts from Baylor University and the past president of the American Psychiatric Association. She received her coaching certification from Oprah's enchanting life coach, Dr. Martha Beck. She is a brilliant coach who has helped thousands achieve an exhilarated life through her coaching, classes, and conferences. To see more tips like these, visit her website and join her self-help community here .
About FamilyEducation's Editorial Team

Eight situations that commonly cause family conflict
Writer Leo Tolstoy once observed that “All happy families are alike; each unhappy family is unhappy in its own way.” This may be true in the sense that families are complex units made up of complex individuals, and the ways in which they relate to each other and the circumstances in which they find themselves are unique. One family’s issues may be completely distinct from another’s.
That said, however, there’s a set of broad patterns that tend to cause conflict across many families—whether biological or chosen. To compound the issue, many lack the tools to handle these challenges in a healthy way. Read on for eight of the most common sources of conflict in families, along with steps you can take to try and address or cope with them.

Signs of unhealthy family conflict: Common issues within the family unit
Every family will inevitably face conflict from time to time. However, those that go unresolved or that are dealt with in unhealthy ways can take a toll on members and their relationships with each other. They can lead to chronic stress levels (which can lead to health problems), mental health challenges, and even estrangement, which can make family life difficult.
Some signs of ongoing family conflict that’s not being handled in a healthy way can include:
Passive-aggressive behaviors
Sweeping issues ‘under the rug’
Frequent bickering and/or fighting
Disagreements frequently escalating to yelling/screaming
Frequent periods where some members aren’t speaking to others
A lack of trust between members
Codependent behavior
Abuse of any kind
If you or someone you know is experiencing abuse in any form, you can contact the National Domestic Violence Hotline at 1-800-799-SAFE (7233) for immediate support, advice, and assistance.
8 common causes of family conflict
If you’ve recognized that your family is experiencing conflict, identifying the root cause can be the next step toward managing it. Although many people are already aware of what’s causing the core conflict within their family, it can be helpful to see some of the most common ones listed out—both to provide insight into how multiple issues can overlap and interact, and to take comfort in knowing that you’re not alone in your experience of family problems. See below for some of the most common causes of family stress or discord.
Parental relationship problems
Parents who are constantly fighting—whether they're still together or separated or divorced—can cause tension for all members, especially children. One parent who is in an unhealthy relationship with someone can also be distressing for the other members to observe.
Financial concerns
Many families face serious challenges in meeting the basic needs of all members. Whether it’s because of systemic issues, job loss, inability to work, uncontrolled spending, gambling problems , or another reason, stress and conflict related to money and bills is common.

Health conditions
When one or more family members is experiencing a health challenge—from a chronic physical condition to a mental illness to a disability—it can affect the others. Stress and worry as well as providing care and paying medical bills can sometimes result in tension and other family issues.
Toxic behaviors between family members
Sometimes, stress or dysfunction in a family can be traced primarily to the toxic behaviors of one member. For example, someone who frequently engages in manipulation tactics, dishonesty, scapegoating, or similar behaviors can be extremely difficult or even dangerous to live with. These can be personality traits or signs of certain personality disorders .
Unaddressed trauma related to family issues
In most cases, trauma that has not been effectively and healthily recognized, processed, and healed will cause issues in a person’s life in some way. A family unit that experiences trauma together—such as war, a natural disaster, or the sudden death of a loved one—or vicariously through one member may experience conflict that arises as a result of this unaddressed pain. This can be especially true for various forms of intergenerational trauma .
If you are experiencing trauma, support is available. Please see our Get Help Now page for more resources.
Unhealthy expectations
Family members who feel pressure to conform to unhealthy and/or impossible standards may experience negative effects as a result. For example, a household where each child is expected to perform perfectly in school, never express negative emotions, or never bring up conflict can eventually cause them to disengage or lash out.
Too much or too little time together
Families that have to live in close quarters and spend most or all of their time together are liable to face conflict, as many learned during the COVID-19 lockdown . On the other hand, families that are so busy or live so far apart that they rarely get to spend quality time together could also end up experiencing conflict.
Poor or nonexistent communication
Healthy, honest, frequent communication is widely considered to be the foundation of healthy relationships of all types. Families without it are likely to experience recurrent conflict as issues that arise may not be properly addressed and members may not feel heard.
Addressing family conflict and promoting healthy relationships
After you’ve uncovered the root of the conflict your family is experiencing, the next recommended course of action is usually to engage in open communication about it with your family members. If you’re wondering how to resolve family conflict , setting aside a time when you can calmly and reasonably bring up the issue(s) without being aggressive or accusatory can be effective in some cases. Although you may not be able to solve all the issues with one conversation, it can represent a first step toward collaborating to create a happier, healthier family dynamic together over time.
However, sometimes it’s not feasible or not safe for one person to communicate something that’s been bothering them to others. Some family members may be resistant to even speaking openly about it, much less working toward solutions. Others may engage in extreme reactions that make it difficult to ever get to the root of the problem. In cases like these, therapy could be the next step to consider.
How family therapy can help
Families that are willing to engage in therapy can rely on a family therapist to guide the discussion and the handling of conflict. This type of healthcare professional can equip members with techniques to help with things like communication, problem-solving, and stress management that they can use in the present conflict and in the future. They can also identify and address any mental health challenges that could be affecting any member and, in turn, their family. If you’re interested in locating a family therapist in your area, you can find directories of licensed providers online or ask your physician, friends, or community members for a recommendation.
However, if some or all of your family is unwilling to attend family therapy, you may find it useful to attend individual sessions on your own. While this won’t change the behavior of your family members, it can offer you a safe, nonjudgmental space to express your feelings and get advice on healthy, constructive strategies to try when engaging with them.
If in-person therapy is inaccessible or unaffordable for you, you might consider an online therapy platform like BetterHelp instead where you can get matched with a licensed therapist who you can meet with from home or anywhere else you have an internet connection. Plus, session costs are less than the average in-person visit and comparable to most insurance co-pays. Research suggests that there is likely “no difference in effectiveness” between in-person therapy and online therapy, so you can typically feel confident in whichever format you may choose. See below for reviews of BetterHelp counselors from clients who have faced similar challenges.
Counselor reviews
“Nicole is great! I’ve been seeing her for both couples counseling and individual therapy. She is kind and sympathetic while still being straightforward and practical. She always helps me find ways to overcome obstacles or look at things from another perspective. Also, she has a ton of helpful resources that she has given through the BetterHelp app. It is very convenient and just what I needed to get through a difficult year!”
“Danielle is amazing! She’s helping me grapple with incredibly difficult challenges in one of my most important relationships. She listens well, synthesizes my scattered thoughts & feelings, and offers helpful tools, activities & resources to work on outside of our sessions. Danielle provides honest feedback and creates a safe space. I can feel that she genuinely cares.
Family conflict can be challenging, frustrating, draining, and difficult to face on your own. If you’re looking for support in identifying or handling conflict within your own family, you might consider connecting with a therapist. A family therapist can work with your entire family to build communication and problem-solving skills, while an individual therapist can offer you in particular a safe space to express your emotions and get constructive advice—whether online or in person.
- Improving Family Dynamics And Communication Medically reviewed by Dr. Jerry Crimmins , PsyD, LP
- Family Therapy Methods: Exploring Family Counseling Medically reviewed by Julie Dodson , MA
- Relationships and Relations
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Psychiatry
- v.62(Suppl 2); 2020 Jan
Family Interventions: Basic Principles and Techniques
Mathew varghese.
Department of Psychiatry, National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS), Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Vivek Kirpekar
1 N.K.P. Salve Institute of Medical Sciences, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India
Santosh Loganathan
Introduction.
Mental health professionals in India have always involved families in therapy. However, formal involvement of families occurred about one to two decades after this therapeutic modality was started in the West by Ackerman.[ 1 ] In India, families form an important part of the social fabric and support system, and as a result, they are integral in being part of the treatment and therapeutic process involving an individual with mental illness. Mental illnesses afflict individuals and their families too. When an individual is affected, the stigma of being mentally ill is not restricted to the individual alone, but to family members/caregivers also. This type of stigma is known as “Courtesy Stigma” (Goffman). Families are generally unaware and lack information about mental illnesses and how to deal with them and in turn, may end up maintaining or perpetuating the illness too. Vidyasagar is credited to be the father of Family Therapy in India though he wrote sparingly of his work involving families at the Amritsar Mental Hospital.[ 2 ] This chapter provides salient features of broad principles for providing family interventions for the treating psychiatrist.
TYPES AND GRADES FOR FAMILY INTERVENTIONS
Working with families involves education, counseling, and coping skills with families of different psychiatric disorders. Various interventions exist for different disorders such as depression, psychoses, child, and adolescent related problems and alcohol use disorders. Such families require psychoeducation about the illness in question, and in addition, will require information about how to deal with the index person with the psychiatric illness. Psychoeducation involves giving basic information about the illness, its course, causes, treatment, and prognosis. These basic informative sessions can last from two to six sessions depending on the time available with clients and their families. Simple interventions may include dealing with parent-adolescent conflict at home, where brief counseling to both parties about the expectations of each other and facilitating direct and open communication is required.
Additional family interventions may cover specific aspects such as future plans, job prospects, medication supervision, marriage and pregnancy (in women), behavioral management, improving communication, and so on. These family interventions offering specific information may also last anywhere between 2 and 6 sessions depending on the client's time. For example, explaining the family about the marriage prospects of an individual with a psychiatric illness can be considered a part of psychoeducation too, but specific information about marriage and related concerns require separate handling. At any given time, families may require specific focus and feedback about issues such issues.
Family therapy is a structured form of psychotherapy that seeks to reduce distress and conflict by improving the systems of interactions between family members. It is an ideal counseling method for helping family members adjust to an immediate family member struggling with an addiction, medical issue, or mental health diagnosis. Specifically, family therapists are relational therapists: They are generally more interested in what goes on between the individuals rather than within one or more individuals. Depending on the conflicts at issue and the progress of therapy to date, a therapist may focus on analyzing specific previous instances of conflict, as by reviewing a past incident and suggesting alternative ways family members might have responded to one another during it, or instead proceed directly to addressing the sources of conflict at a more abstract level, as by pointing out patterns of interaction that the family might not have noticed.
Family therapists tend to be more interested in the maintenance and/or solving of problems rather than in trying to identify a single cause. Some families may perceive cause-effect analyses as attempts to allocate blame to one or more individuals, with the effect that for many families, a focus on causation is of little or no clinical utility. It is important to note that a circular way of problem evaluation is used, especially in systemic therapies, as opposed to a linear route. Using this method, families can be helped by finding patterns of behavior, what the causes are, and what can be done to better their situation. Family therapy offers families a way to develop or maintain a healthy and functional family. Patients and families with more difficult and intractable problems such as poor prognosis schizophrenia, conduct and personality disorder, chronic neurotic conditions require family interventions and therapy. The systemic framework approach offers advanced family therapy for such families. This type of advanced therapy requires training that very few centers, such as the Family Psychiatry Center at the National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), Bengaluru, Karnataka, India offer to trainees and residents. These sessions may last anywhere from eight sessions up to 20 or more on occasions [ Table 1 ].
Types and grades of family interventions
Goals of family therapy
Usual goals of family therapy are improving the communication, solving family problems, understanding and handling special family situations, and creating a better functioning home environment. In addition, it also involves:
- Exploring the interactional dynamics of the family and its relationship to psychopathology
- Mobilizing the family's internal strength and functional resources
- Restructuring the maladaptive interactional family styles (including improving communication)
- Strengthening the family's problem-solving behavior.
Reasons for family interventions
The usual reasons for referral are mentioned below. However, it may be possible that sometimes the reasons identified initially may be just a pointer to many other lurking problems within the family that may get discovered eventually during later assessments.
- Marital problems
- Parent–child conflict
- Problems between siblings
- The effects of illness on the family
- Adjustment problems among family members
- Inconsistency parenting skills
- Psychoeducation for family members about an index patient's illness
- Handling expresses emotions.
CHALLENGES FACED BY THE NOVICE THERAPIST
Whether one is a young student, or a seasoned individual therapist, dealing with families can be intimidating at times but also very rewarding if one knows how to deal with them. We have outlined certain challenges that one faces while dealing with families, especially when one is beginning.
Being overeager to help
This can happen with beginner therapists as they are overeager and keen to help and offer suggestions straight away. If the therapist starts dominating the interaction by talking, advising, suggesting, commenting, questioning, and interpreting at the beginning itself, the family falls silent. It is advisable to probe with open-ended questions initially to understand the family.
Poor leadership
It is advisable for the therapist to have control over the sessions. Sometimes, there may be other individuals/family members who maybe authoritative and take control. Especially in crisis situations, when the family fails to function as a unit, the therapist should take control of the session and set certain conditions which in his professional judgment, maximize the chances for success.
Not immersing or engaging/fear or involving
A common problem for the beginning therapist is to become overly involved with the family. However, he may realize this and try to panic and withdraw when he can become distant and cold. Rather, one should gently try to join in with the family earning their true respect and trust before heading to build rapport.
Focusing only on index patient
Many families believe that their problem is because of the index patient, whereas it may seem a tactical error to focus on this person initially. In doing so, it may essentially agree to the family's hypothesis that their problem is arising out of this person. It is preferable, at the outset to inform the family that the problem may lie with the family (especially when referrals are made for family therapies involving multiple members), and not necessarily with any one individual.
Not including all members for sessions
Many therapeutic efforts fail because important family members are not included in the sessions. It is advisable to find out initially who are the key members involved and who should be attending the sessions. Sometimes, involving all members initially and then advising them to return to therapy as and when the need arises is recommended.
Not involving members during sessions
Even though one has involved all members of the family in the sessions, not all of them may be engaged during the sessions. Sometimes, the therapist's own transference may hold back a member of the family in the sessions. Rather, it is recommended that the therapist makes it clear that he/she is open to their presence and interactions, either verbally or nonverbally.
Taking sides with any member of the family
It may be easy to fall into the trap of taking one member's side during sessions leaving the other party doubting the fairness and judgment of the therapist. For example, after meeting one marital partner for a few sessions, the therapist, when entering the couple, discussions may be heavily biased in his views due to his/her prior interaction. Therapists should be aware of this effect and try to be neutral as possible yet take into confidence each member attending the sessions. Therapist's countertransference can easily influence him/her to take sides, especially in families that are overtly blaming from the start, or with one member who may be aggressive in the sessions, or very submissive during the sessions can influence the therapist's sides; and one needs to be aware of this early in the sessions.
Guarded families
Some families put on a guarded façade and refuse to challenge each other in the session. By being neutral and nonjudgmental, sometimes, the therapist can perpetuate this guarded façade put forth by families. Hence, therapists must be able to read this and try to challenge them, listen to microchallenges within the family, must be ready to move in and out from one family member to another, without fixing to one member.
Communicating with the therapist outside sessions
Many families attempt to reduce tension by communicating with therapist outside the session, and beginning therapist are particularly susceptible for such ploys. The family or a member/s may want to meet the therapist outside the sessions by trying to influence the therapist to their views and opinions. Therapists must refrain from such encounters and suggest discussing these issues openly during the sessions. Of course, rarely, there may be sensitive or very personal information that one may want to discuss in person that may be permissible.
Ignoring previous work done by other therapists
It is easy for family therapists to ignore previous therapists. The family therapist's ignorance of the effects of previous therapy can serious hamper the work. By discussing the previous therapist helps the new therapist to understand the problem easily and could save time also.
Getting sucked to the family's affective state/mood
If transference involves the therapist in family structure, the therapist's dependency can overinvolved him in the family's style and tone of interaction. A depressed family causes both: Therapist to relate seriously and sadly. A hostile family may cause the therapist to relate in an attacking manner. The most serious problem can occur when a family is in a state of anxiety, induces the therapist to become anxious and make his/her comments to seem accusatory and blaming. It is very difficult for the beginning therapist to “feel” where the family is affectively, to be empathic, yet to be able to relate at times on a different affective level-to respond according to situations. It is important to be aware of the affective state/mood of the family but slips in and out of that state [ Table 2 ].
Guidelines for conducting interventions with families
FUNCTIONS OF A FAMILY THERAPIST
- The family therapist establishes a useful rapport: Empathy and communication among the family members and between them and himself
- The therapist clarifies conflict by dissolving barriers, confusions, and misunderstandings
- Gradually, the therapist attempts to bring to the family to a mutual and more accurate understanding of what is wrong
- Counteracting inappropriate denials, conflicts
- Lifting hidden intrapersonal conflict to the level of interpersonal interaction.
- The therapist fulfills in part the role of true parent figure, a controller of danger, and a source of emotional support and satisfaction-supplying elements that the family needs but lacks. He introduces more appropriate attitudes, emotions, and images of family relations than the family has ever had
- The therapist works toward penetrating (entering into) and undermining resistances and reducing the intensity of shared currents of conflict, guilt, and fear. He accomplishes these aims mainly using confrontation and interpretation
- The therapist serves as a personal instrument of reality testing for the family.
In carrying out these functions, the family therapist plays a wide range of roles, as:
- An activator
- Interpreter
- Re-integrator
BASIC STEPS FOR FAMILY INTERVENTIONS
The initial phase of therapy, the referral intake.
- Family assessment
- Family formulation and treatment plan
- Formal contract.
Patients and their families are usually referred to as some family problem has been identified. The therapist may be accustomed to the usual one-on-one therapeutic situation involving a patient but may be puzzled in his approach by the presence of many family members and with a lot of information. A few guidelines are similar to the approaches followed while conducting individual therapy. The guidelines for conducting family interventions are given in Table 2 . At the time of the intake, the therapist reviews all the available information in the family from the case file and the referring clinicians. This intake session lasts for 20–30 min and is held with all the available family members. The aim of the intake session is to briefly understand the family's perception of their problem, their motivation and need to undergo family intervention and the therapist assessments of suitability for family therapy. Once this is determined the nature and modality of the therapy is explained to the family and an informal contract is made about modalities and roles of therapist and the family members. The do's and don’ts of the family interventions are laid down to the family at the outset of the process of the interventions.
The family assessment and hypothesis
The assessment of different aspects of family functioning and interactions must typically take about 3–5 sessions with the whole family, each session must last approximately 45 min to an hour. Different therapists may want to take assessments in different ways depending on their style. Mentioned below are a few tasks which are recommended for the therapist to perform. Usually, it is recommended that the naïve therapist starts with a three-generation genogram and then follows-up with the different life cycle stages and family functions as outlined below.
- The three-generation genogram is constructed diagrammatically listing out the index patient's generation and two more related generations, for example, patients and grandparents in an adolescent client or parents and children in a middle-aged client. The ages and composition of the members are recorded, and the transgenerational family patterns and interactions are looked at to understand the family from a longitudinal and epigenetic perspective. The therapist also familiarizes himself with any family dynamics prior to consultation. This gives a broad background to understand the situation the family is dealing with now
- The life cycle of the index family is explored next. The functions of the family and specific roles of different members are delineated in each of the stages of the family life cycle.[ 3 ] The index family is seen from a developmental perspective, and the therapist gets a longitudinal and temporal perspective of the family. Care is taken to see how the family has coped with problems and the process of transition from one stage to another. If children are also part of the family, their discipline and parenting styles are explored (e.g., whether there is inconsistent parenting)
- Problem Solving: Many therapists look at this aspect of the family to see how cohesive or adaptable the family has been. Usually, the family members are asked to describe some stress that the family has faced, i.e., some life events, environmental stressors, or illness in a family member. The therapist then proceeds to get a description of how the family coped with this problem. Here, “circular questions” are employed and therapist focuses on antecedent events. The crisis and the consequent events are examined closely to look for patterns that emerge. The family function (or dysfunction) is heightened when there is a crisis situation and the therapist look at patterns rather than the content described. Thus, the therapist gets an “as if I was there” view of the family. The same inquiry is possible using the technique of enactment[ 4 ]
- The Structural Map: Once the inquiry is over, the therapist draws the structural map, which is a diagrammatic representation of the family system, showing the different subsystems, its boundaries, power structure and relationships between people. Diagrammatic notions used in structural therapy or Bowenian therapy are used to denote relationships (normal, conflictual, or distant) and subsystem boundaries, in different triadic relationships. This can also be done on a timeline to show changes in relationships in different life cycle stages and influences from different life events
- What the client is trying to convey through his/her symptoms?
- What is the role of the family in maintaining these symptoms?
- Why has the family come now?
This circular hypothesis can be confirmed on further inquiry with the family to see how the “dysfunctional equilibrium” is maintained. At this stage, we suggest that a family formulation is generated, hypothesized and analyzed. This leads to a comprehensive systemic formulation involving three generations. This formulation will determine which family members we need to see in a therapy, what interventional techniques we should use and what changes in relationships we should effect. The team will also discuss the minimum, most effective treatment plan which emerges considering the most feasible changes the family can make
- Formal Contract: A brief understanding of the family homeostasis is presented to the family. Sometimes, the full hypothesis may be fed to the family in a noncritical and positive way (“Positive Connotation”), appreciating the way in which the system is functioning the therapist presents the treatment plat to the family and negotiates with the members the plan and action they would like to take up at the present time. The time frame and modality of therapy is contracted with the family, and the therapy is put into force. The frequency and intensity of sessions are determined by the degree of distress felt by the family and the geographical distance from the therapy center, i.e., families may be seen as inpatients at the center if they are in crisis or if they live far away.
The Family Psychiatry Center at The NIMHANS, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India, is one of the centers where formal training in therapy is regularly conducted. An outline of the Family Assessment Proforma[ 5 ] used at this center is given in Figure 1 . Several other structured family assessment instruments are available [ Figure 1 ].

Family assessment proforma (Obtained with permission from the Family Psychiatry Center, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India)
Middle phase of therapy
This phase of therapy forms the major work that is carried out with the family. Depending on the school of therapy, that is used, these sessions may number from a few (strategic) to many sessions lasting many months (psychodynamic). The techniques employed depend on the understanding of the family during the assessment as much as the family – therapist fit. For example, the degree of psychological sophistication of the clients will determine the use of psychodynamic and behavioral techniques. Similarly, a therapist who is comfortable with structural/strategic methods would put these therapies to maximum use. The nature of the disorder and the degree of pathology may also determine the choice of therapy, i.e., behavioral techniques may be used more in chronic psychotic conditions while the more difficult or resistant families may get brief strategic therapies. We will now describe some of the important techniques used with different kinds of problems.
Psychodynamic therapy
This school was one of the first to be described by people like Ackerman and Bowen.[ 1 , 6 ] This method has been made more contextual and briefer by therapists like Boszormenyi-Nasgy and Framo.[ 7 , 8 ] Essentially, the therapist understands the dynamics employed by different members of the family and the interrelationships of these members. These family ego defenses are interpreted to the members and the goal of therapy is to effects emotional insight and working through of new defense patterns. Family transferences may become evident and may need interpretation. Therapy usually lasts from 15 to 30 sessions and this method may be employed in persons who are psychologically sophisticated, and able to understand dynamics and interpretations. Sustained and high motivation is necessary for such a therapy. This method is found useful in couples with marital discord from upper middle-class backgrounds. Time required is a major constraint.
Behavioral methods
Behavioral techniques find use in many types of therapies and conditions. It has been extensively used in chronic psychotic illnesses by workers such as Fallon et al. , (1986) and Anderson et al. [ 9 , 10 ] Psychoeducation and skills training in communication and problem-solving are found very useful among families which do not have very serious dysfunction. Techniques such as modeling or role-plays are useful in improving communication styles and to teach parenting skills with disturbed children. Obviously, motivation for therapy is a major requisite and hence techniques such as contracting, homework assignments are used in couples with marital discord. Behavioral techniques used in sexual dysfunction are also possible when adapted according to clients’ needs.
Structural family therapy
Described by Minuchin; Fishman and Unbarger[ 4 , 11 , 12 ] has become quite popular over the past few years among therapists in India. This is possibly because of many reasons. Our families are available with their manifold subsystems of parents, children, grandparents and structure is easily discerned and changed. In addition, in recent years most clients present with conduct and personality disorders in adolescence and early adulthood. Hence, techniques like unbalancing, boundary-making are quite useful as the common problems involve adolescents who are wielding power with poor marital adjustments between parents. These techniques are useful for many of our clients.
Strategic technique
We have found that these brief techniques can be very powerfully used with families which are difficult and highly resistant to change. We usually employ them when other methods have failed, and we need to take a U-turn in therapy. Techniques employed by the Milan school[ 13 , 14 ] reframing, positive connotation, paradoxical (symptom) prescription have been used effectively. So also have techniques like prescription in brief methods advocated by Erikson, Watzlawick et al. ,[ 15 , 16 ] been useful. Familiarity and competence with these techniques is a must and therapy is usually brief and quickly terminated with prescriptions [ Table 3 ].
Summaries of the different schools of therapies
SES – Socioeconomic status
FAMILY INTERVENTIONS IN SPECIFIC DISORDERS
Techniques to promote family adaptation to illness.
- Heighten awareness of shifting family roles – pragmatic and emotional
- Facilitate major family lifestyle changes
- Increase communication within and outside the family regarding the illness
- Help family to accept what they cannot control, focus energies on what they can
- Find meaning in the illness. Help families move beyond “Why us?”
- Facilitate them grieving inevitable losses–of function, of dreams, of life
- Increase productive collaboration among patients, families, and the health-care team
- Trace prior family experience with the illness through constructing a genogram
- Set individual and family goals related to illness and to nonillness developmental events.
Schizophrenia
Family EE and communication deviance (or lack of clarity and structure in communication) are well-established risk factors for the onset of schizophrenia.
Psychoeducational interventions aim to increase family members’ understanding of the disorder and their ability to manage the positive and negative symptoms of psychosis.
Simple strategies would include reduction of adverse family atmosphere by reducing stress and burden on relatives, reduction of expressions of anger and guilt by the family, helping relatives to anticipate and solve problems, maintenance of reasonable expectations for patient performance, to set appropriate limits whilst maintaining some degree of separation when needed; and changing relatives’ behavior and belief systems.
Programs emphasize family resilience. Address families’ need for education, crisis intervention, skills training, and emotional support.
Bipolar mood disorder
To recognize the early signs and symptoms of bipolar disorder.
Develop strategies for intervening early with new episodes and assure consistency with medication regimens.
Manage moodiness and swings of the patient, anger management, feelings of frustration.
Family conflict and rejection, low family support, ineffective communication, poor expression of affect, abuse, and insecure attachment bonds are primary focus of family therapy associated with depression cognitive-behavioral and interpersonal interventions for depression.
Family-based treatment for anxiety combines family therapy with cognitive-behavioral interventions.
Targets the characteristics of the family environment that support anxiogenic beliefs and avoidant behaviors.
The goal is to disrupt the interactional patterns that reinforce the disorder.
To assist family members in using exposure, reward, relaxation, and response prevention techniques to reduce the patients’ anxieties.
Eating disorders
Target the dysfunctional family processes, namely, enmeshment and overprotectiveness.
To help parents build effective and developmentally appropriate strategies for promoting and monitoring their child's eating behaviors.
Childhood disorders
The primary focus is the development of effective parenting and contingency management strategies that will disrupt the problematic family interactions associated with ADHD and ODD.
Family-based interventions for autism spectrum disorder
Parents taught to use communication and social training tools that are adapted to the needs of their children and apply these techniques to their family interactions at home.
Substance misuse
Enhance the coping ability of family members and reduce the negative consequences of alcohol and drug abuse on concerned relatives; eliminate the family factors that constitute barriers to treatment; use family support to engage and retain the drug and/or alcohol user in therapy; change the characteristics of the family environment that contribute to relapse Al-Anon, AL-teen.
Termination phase
This last phase of therapy is finished in a couple of sessions. The initial goals of therapy are reviewed with the family. The family and the therapist review together the goals which were achieved, and the therapist reminds the family the new patterns/changes which have emerged. The need to continue these new patterns is emphasized. At the same time, the family is cautioned that these new patterns will occur when all members make a concerted effort to see this happen. Family members are reminded that it is easy to fall back to the old patterns of functioning which had produced the unstable equilibrium necessitating consultation.
At termination, the therapist usually negotiates new goals, new tasks or new interactions with the family that they will carry out for the next few months in the follow up period. The family is told that they need to review these new patterns after a couple of months so as to determine how things have gone and how conflicts have been addressed by the family. This way the family has a better chance of sustaining the change created. Sometimes booster sessions are also advised after 6–12 months especially for outstation families who cannot come regularly for follow-ups. These booster sessions will review the progress and negotiate further changes with the family over a couple of sessions. This follow-up period, after therapy is terminated is crucial for working through process and ensures that the client-therapist bond is not severed too quickly. It is easy to deal with the clients’ and therapist’ anxieties if this transition phase is smooth.
SPECIAL SOCIOCULTURAL ISSUES IN THERAPY SPECIFIC TO INDIA
Most Indian families are functionally joint families though they may have a nuclear family structure. Furthermore, unlike the Western world more than two generations readily come for therapy. Hence, it becomes necessary to deal with two to three generations in therapy and also with transgenerational issues. Our families also foster dependency and interdependency rather than autonomy. This issue must also be kept in mind when dealing with parent–child issues. Indians have a varied cultural and religious diversity depending on the region from which the family comes. The therapist has to be familiar with the regional customs, practices, beliefs, and rituals. The Indian family therapist has to also be wary of being too directive in therapy as our families may give the mantle of omnipotence to the therapist and it may be more difficult for us to adopt at one-down or nondirective approach. Hence, while systemic family therapy is eminently possible in India one must keep in mind these sociocultural factors so as to get a good “family-therapist fit.”
Constraint factors in therapy
The economic backwardness of most out families makes therapy feasible and affordable, in terms of time and money spent, only to the middle and upper classes of our society. The poorer families usually drop out of therapy as they have other more pressing priorities. The lack of tertiary social support and welfare or social security makes it less possible to network with other systems. We are also woefully inadequate in terms of trained family therapists to cater to our large population. In our country, distances seem rather daunting and modes of transport and communication are poor for families to readily seek out a therapist. We work with these constraint factors and so the “family-therapy” fit is an important factor for families that are seeking and staying in family therapy. 17
CONCLUSIONS
Over the last few years, a systemic model has evolved for service and for training. The model uses a predominantly systematic framework for understanding families and the techniques for therapy are drawn from different schools namely the structural, strategic, and behavioral psychodynamic therapies.
Appendix: Glossary of terms
The repetitive patterns of interaction that organize the way in which family members relate and interact with each other.
Boundaries are the rules defining who participates in the system and how, i.e., the degree of access outsiders have to the system.
It may comprise of a single person, or several persons joined together by common membership criteria, for example, age, gender, or shared purpose.
When alignments stand in opposition to another part of the system (i.e., when several family members are against another member/s.
The joining together of two or more members. It popularly designates appositive affinity between two units of a system.
Channels of communication are a mechanism that defines “who speaks to whom.” When channels of communication are blocked, needs cannot be fulfilled, problems cannot be solved, and goals cannot be achieved.
Enmeshed families
In which, there is extreme sensitivity among the individual members to each other and their primary subsystem.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
How to Teach Kids Problem-Solving Skills
KidStock / Blend Images / Getty Images
- Steps to Follow
- Allow Consequences
Whether your child can't find their math homework or has forgotten their lunch, good problem-solving skills are the key to helping them manage their life.
A 2010 study published in Behaviour Research and Therapy found that kids who lack problem-solving skills may be at a higher risk of depression and suicidality. Additionally, the researchers found that teaching a child problem-solving skills can improve mental health .
You can begin teaching basic problem-solving skills during preschool and help your child sharpen their skills into high school and beyond.
Why Problem-Solving Skills Matter
Kids face a variety of problems every day, ranging from academic difficulties to problems on the sports field. Yet few of them have a formula for solving those problems.
Kids who lack problem-solving skills may avoid taking action when faced with a problem.
Rather than put their energy into solving the problem, they may invest their time in avoiding the issue. That's why many kids fall behind in school or struggle to maintain friendships .
Other kids who lack problem-solving skills spring into action without recognizing their choices. A child may hit a peer who cuts in front of them in line because they are not sure what else to do.
Or, they may walk out of class when they are being teased because they can't think of any other ways to make it stop. Those impulsive choices may create even bigger problems in the long run.
The 5 Steps of Problem-Solving
Kids who feel overwhelmed or hopeless often won't attempt to address a problem. But when you give them a clear formula for solving problems, they'll feel more confident in their ability to try. Here are the steps to problem-solving:
- Identify the problem . Just stating the problem out loud can make a big difference for kids who are feeling stuck. Help your child state the problem, such as, "You don't have anyone to play with at recess," or "You aren't sure if you should take the advanced math class."
- Develop at least five possible solutions . Brainstorm possible ways to solve the problem. Emphasize that all the solutions don't necessarily need to be good ideas (at least not at this point). Help your child develop solutions if they are struggling to come up with ideas. Even a silly answer or far-fetched idea is a possible solution. The key is to help them see that with a little creativity, they can find many different potential solutions.
- Identify the pros and cons of each solution . Help your child identify potential positive and negative consequences for each potential solution they identified.
- Pick a solution. Once your child has evaluated the possible positive and negative outcomes, encourage them to pick a solution.
- Test it out . Tell them to try a solution and see what happens. If it doesn't work out, they can always try another solution from the list that they developed in step two.
Practice Solving Problems
When problems arise, don’t rush to solve your child’s problems for them. Instead, help them walk through the problem-solving steps. Offer guidance when they need assistance, but encourage them to solve problems on their own. If they are unable to come up with a solution, step in and help them think of some. But don't automatically tell them what to do.
When you encounter behavioral issues, use a problem-solving approach. Sit down together and say, "You've been having difficulty getting your homework done lately. Let's problem-solve this together." You might still need to offer a consequence for misbehavior, but make it clear that you're invested in looking for a solution so they can do better next time.
Use a problem-solving approach to help your child become more independent.
If they forgot to pack their soccer cleats for practice, ask, "What can we do to make sure this doesn't happen again?" Let them try to develop some solutions on their own.
Kids often develop creative solutions. So they might say, "I'll write a note and stick it on my door so I'll remember to pack them before I leave," or "I'll pack my bag the night before and I'll keep a checklist to remind me what needs to go in my bag."
Provide plenty of praise when your child practices their problem-solving skills.
Allow for Natural Consequences
Natural consequences may also teach problem-solving skills. So when it's appropriate, allow your child to face the natural consequences of their action. Just make sure it's safe to do so.
For example, let your teenager spend all of their money during the first 10 minutes you're at an amusement park if that's what they want. Then, let them go for the rest of the day without any spending money.
This can lead to a discussion about problem-solving to help them make a better choice next time. Consider these natural consequences as a teachable moment to help work together on problem-solving.
Becker-Weidman EG, Jacobs RH, Reinecke MA, Silva SG, March JS. Social problem-solving among adolescents treated for depression . Behav Res Ther . 2010;48(1):11-18. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2009.08.006
Pakarinen E, Kiuru N, Lerkkanen M-K, Poikkeus A-M, Ahonen T, Nurmi J-E. Instructional support predicts childrens task avoidance in kindergarten . Early Child Res Q . 2011;26(3):376-386. doi:10.1016/j.ecresq.2010.11.003
Schell A, Albers L, von Kries R, Hillenbrand C, Hennemann T. Preventing behavioral disorders via supporting social and emotional competence at preschool age . Dtsch Arztebl Int . 2015;112(39):647–654. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2015.0647
Cheng SC, She HC, Huang LY. The impact of problem-solving instruction on middle school students’ physical science learning: Interplays of knowledge, reasoning, and problem solving . EJMSTE . 2018;14(3):731-743.
Vlachou A, Stavroussi P. Promoting social inclusion: A structured intervention for enhancing interpersonal problem‐solving skills in children with mild intellectual disabilities . Support Learn . 2016;31(1):27-45. doi:10.1111/1467-9604.12112
Öğülmüş S, Kargı E. The interpersonal cognitive problem solving approach for preschoolers . Turkish J Educ . 2015;4(17347):19-28. doi:10.19128/turje.181093
American Academy of Pediatrics. What's the best way to discipline my child? .
Kashani-Vahid L, Afrooz G, Shokoohi-Yekta M, Kharrazi K, Ghobari B. Can a creative interpersonal problem solving program improve creative thinking in gifted elementary students? . Think Skills Creat . 2017;24:175-185. doi:10.1016/j.tsc.2017.02.011
Shokoohi-Yekta M, Malayeri SA. Effects of advanced parenting training on children's behavioral problems and family problem solving . Procedia Soc Behav Sci . 2015;205:676-680. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.09.106
By Amy Morin, LCSW Amy Morin, LCSW, is the Editor-in-Chief of Verywell Mind. She's also a psychotherapist, an international bestselling author of books on mental strength and host of The Verywell Mind Podcast. She delivered one of the most popular TEDx talks of all time.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is Problem-Solving Therapy?
Arlin Cuncic, MA, is the author of The Anxiety Workbook and founder of the website About Social Anxiety. She has a Master's degree in clinical psychology.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ArlinCuncic_1000-21af8749d2144aa0b0491c29319591c4.jpg)
Daniel B. Block, MD, is an award-winning, board-certified psychiatrist who operates a private practice in Pennsylvania.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/block-8924ca72ff94426d940e8f7e639e3942.jpg)
Verywell / Madelyn Goodnight
Problem-Solving Therapy Techniques
How effective is problem-solving therapy, things to consider, how to get started.
Problem-solving therapy is a brief intervention that provides people with the tools they need to identify and solve problems that arise from big and small life stressors. It aims to improve your overall quality of life and reduce the negative impact of psychological and physical illness.
Problem-solving therapy can be used to treat depression , among other conditions. It can be administered by a doctor or mental health professional and may be combined with other treatment approaches.
At a Glance
Problem-solving therapy is a short-term treatment used to help people who are experiencing depression, stress, PTSD, self-harm, suicidal ideation, and other mental health problems develop the tools they need to deal with challenges. This approach teaches people to identify problems, generate solutions, and implement those solutions. Let's take a closer look at how problem-solving therapy can help people be more resilient and adaptive in the face of stress.
Problem-solving therapy is based on a model that takes into account the importance of real-life problem-solving. In other words, the key to managing the impact of stressful life events is to know how to address issues as they arise. Problem-solving therapy is very practical in its approach and is only concerned with the present, rather than delving into your past.
This form of therapy can take place one-on-one or in a group format and may be offered in person or online via telehealth . Sessions can be anywhere from 30 minutes to two hours long.
Key Components
There are two major components that make up the problem-solving therapy framework:
- Applying a positive problem-solving orientation to your life
- Using problem-solving skills
A positive problem-solving orientation means viewing things in an optimistic light, embracing self-efficacy , and accepting the idea that problems are a normal part of life. Problem-solving skills are behaviors that you can rely on to help you navigate conflict, even during times of stress. This includes skills like:
- Knowing how to identify a problem
- Defining the problem in a helpful way
- Trying to understand the problem more deeply
- Setting goals related to the problem
- Generating alternative, creative solutions to the problem
- Choosing the best course of action
- Implementing the choice you have made
- Evaluating the outcome to determine next steps
Problem-solving therapy is all about training you to become adaptive in your life so that you will start to see problems as challenges to be solved instead of insurmountable obstacles. It also means that you will recognize the action that is required to engage in effective problem-solving techniques.
Planful Problem-Solving
One problem-solving technique, called planful problem-solving, involves following a series of steps to fix issues in a healthy, constructive way:
- Problem definition and formulation : This step involves identifying the real-life problem that needs to be solved and formulating it in a way that allows you to generate potential solutions.
- Generation of alternative solutions : This stage involves coming up with various potential solutions to the problem at hand. The goal in this step is to brainstorm options to creatively address the life stressor in ways that you may not have previously considered.
- Decision-making strategies : This stage involves discussing different strategies for making decisions as well as identifying obstacles that may get in the way of solving the problem at hand.
- Solution implementation and verification : This stage involves implementing a chosen solution and then verifying whether it was effective in addressing the problem.
Other Techniques
Other techniques your therapist may go over include:
- Problem-solving multitasking , which helps you learn to think clearly and solve problems effectively even during times of stress
- Stop, slow down, think, and act (SSTA) , which is meant to encourage you to become more emotionally mindful when faced with conflict
- Healthy thinking and imagery , which teaches you how to embrace more positive self-talk while problem-solving
What Problem-Solving Therapy Can Help With
Problem-solving therapy addresses life stress issues and focuses on helping you find solutions to concrete issues. This approach can be applied to problems associated with various psychological and physiological symptoms.
Mental Health Issues
Problem-solving therapy may help address mental health issues, like:
- Chronic stress due to accumulating minor issues
- Complications associated with traumatic brain injury (TBI)
- Emotional distress
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Problems associated with a chronic disease like cancer, heart disease, or diabetes
- Self-harm and feelings of hopelessness
- Substance use
- Suicidal ideation
Specific Life Challenges
This form of therapy is also helpful for dealing with specific life problems, such as:
- Death of a loved one
- Dissatisfaction at work
- Everyday life stressors
- Family problems
- Financial difficulties
- Relationship conflicts
Your doctor or mental healthcare professional will be able to advise whether problem-solving therapy could be helpful for your particular issue. In general, if you are struggling with specific, concrete problems that you are having trouble finding solutions for, problem-solving therapy could be helpful for you.
Benefits of Problem-Solving Therapy
The skills learned in problem-solving therapy can be helpful for managing all areas of your life. These can include:
- Being able to identify which stressors trigger your negative emotions (e.g., sadness, anger)
- Confidence that you can handle problems that you face
- Having a systematic approach on how to deal with life's problems
- Having a toolbox of strategies to solve the issues you face
- Increased confidence to find creative solutions
- Knowing how to identify which barriers will impede your progress
- Knowing how to manage emotions when they arise
- Reduced avoidance and increased action-taking
- The ability to accept life problems that can't be solved
- The ability to make effective decisions
- The development of patience (realizing that not all problems have a "quick fix")
Problem-solving therapy can help people feel more empowered to deal with the problems they face in their lives. Rather than feeling overwhelmed when stressors begin to take a toll, this therapy introduces new coping skills that can boost self-efficacy and resilience .
Other Types of Therapy
Other similar types of therapy include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and solution-focused brief therapy (SFBT) . While these therapies work to change thinking and behaviors, they work a bit differently. Both CBT and SFBT are less structured than problem-solving therapy and may focus on broader issues. CBT focuses on identifying and changing maladaptive thoughts, and SFBT works to help people look for solutions and build self-efficacy based on strengths.
This form of therapy was initially developed to help people combat stress through effective problem-solving, and it was later adapted to address clinical depression specifically. Today, much of the research on problem-solving therapy deals with its effectiveness in treating depression.
Problem-solving therapy has been shown to help depression in:
- Older adults
- People coping with serious illnesses like cancer
Problem-solving therapy also appears to be effective as a brief treatment for depression, offering benefits in as little as six to eight sessions with a therapist or another healthcare professional. This may make it a good option for someone unable to commit to a lengthier treatment for depression.
Problem-solving therapy is not a good fit for everyone. It may not be effective at addressing issues that don't have clear solutions, like seeking meaning or purpose in life. Problem-solving therapy is also intended to treat specific problems, not general habits or thought patterns .
In general, it's also important to remember that problem-solving therapy is not a primary treatment for mental disorders. If you are living with the symptoms of a serious mental illness such as bipolar disorder or schizophrenia , you may need additional treatment with evidence-based approaches for your particular concern.
Problem-solving therapy is best aimed at someone who has a mental or physical issue that is being treated separately, but who also has life issues that go along with that problem that has yet to be addressed.
For example, it could help if you can't clean your house or pay your bills because of your depression, or if a cancer diagnosis is interfering with your quality of life.
Your doctor may be able to recommend therapists in your area who utilize this approach, or they may offer it themselves as part of their practice. You can also search for a problem-solving therapist with help from the American Psychological Association’s (APA) Society of Clinical Psychology .
If receiving problem-solving therapy from a doctor or mental healthcare professional is not an option for you, you could also consider implementing it as a self-help strategy using a workbook designed to help you learn problem-solving skills on your own.
During your first session, your therapist may spend some time explaining their process and approach. They may ask you to identify the problem you’re currently facing, and they’ll likely discuss your goals for therapy .
Keep In Mind
Problem-solving therapy may be a short-term intervention that's focused on solving a specific issue in your life. If you need further help with something more pervasive, it can also become a longer-term treatment option.
Get Help Now
We've tried, tested, and written unbiased reviews of the best online therapy programs including Talkspace, BetterHelp, and ReGain. Find out which option is the best for you.
Shang P, Cao X, You S, Feng X, Li N, Jia Y. Problem-solving therapy for major depressive disorders in older adults: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials . Aging Clin Exp Res . 2021;33(6):1465-1475. doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01672-3
Cuijpers P, Wit L de, Kleiboer A, Karyotaki E, Ebert DD. Problem-solving therapy for adult depression: An updated meta-analysis . Eur Psychiatry . 2018;48(1):27-37. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2017.11.006
Nezu AM, Nezu CM, D'Zurilla TJ. Problem-Solving Therapy: A Treatment Manual . New York; 2013. doi:10.1891/9780826109415.0001
Owens D, Wright-Hughes A, Graham L, et al. Problem-solving therapy rather than treatment as usual for adults after self-harm: a pragmatic, feasibility, randomised controlled trial (the MIDSHIPS trial) . Pilot Feasibility Stud . 2020;6:119. doi:10.1186/s40814-020-00668-0
Sorsdahl K, Stein DJ, Corrigall J, et al. The efficacy of a blended motivational interviewing and problem solving therapy intervention to reduce substance use among patients presenting for emergency services in South Africa: A randomized controlled trial . Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy . 2015;10(1):46. doi:doi.org/10.1186/s13011-015-0042-1
Margolis SA, Osborne P, Gonzalez JS. Problem solving . In: Gellman MD, ed. Encyclopedia of Behavioral Medicine . Springer International Publishing; 2020:1745-1747. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-39903-0_208
Kirkham JG, Choi N, Seitz DP. Meta-analysis of problem solving therapy for the treatment of major depressive disorder in older adults . Int J Geriatr Psychiatry . 2016;31(5):526-535. doi:10.1002/gps.4358
Garand L, Rinaldo DE, Alberth MM, et al. Effects of problem solving therapy on mental health outcomes in family caregivers of persons with a new diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment or early dementia: A randomized controlled trial . Am J Geriatr Psychiatry . 2014;22(8):771-781. doi:10.1016/j.jagp.2013.07.007
Noyes K, Zapf AL, Depner RM, et al. Problem-solving skills training in adult cancer survivors: Bright IDEAS-AC pilot study . Cancer Treat Res Commun . 2022;31:100552. doi:10.1016/j.ctarc.2022.100552
Albert SM, King J, Anderson S, et al. Depression agency-based collaborative: effect of problem-solving therapy on risk of common mental disorders in older adults with home care needs . The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry . 2019;27(6):619-624. doi:10.1016/j.jagp.2019.01.002
By Arlin Cuncic, MA Arlin Cuncic, MA, is the author of The Anxiety Workbook and founder of the website About Social Anxiety. She has a Master's degree in clinical psychology.

Importance of Problem Solving Skills and How to Nurture them in your Child
We all face problems on a daily basis. You, me—our kids aren’t even exempted. Across all different age groups, there rarely is a day when we don’t experience them.
Teaching our kids to develop resilience can help as they face these challenges. Practical problem solving skills are just as necessary to teach our kids. The methods needed to resolve problems may require other skills such as creativity, critical thinking, emotional intelligence, teamwork, decision making, etc.
Unlike with math problems, life doesn’t just come with one formula or guidebook that’s applicable to solve every little problem we face. Being adaptable to various situations is important. So is nurturing problem solving skills in your child.
Here we’ll take a look at the importance of problem solving skills and some ways to nurture them in your child.
Why do we need problem-solving skills?
One thing that always comes up when we speak of problem-solving skills are the benefits for one’s mental health .
Problems are often complex. This means that problem solving skills aren’t a one-size-fits-all solution to all problems.
Strengthening and nurturing this set of skills helps children cope with challenges as they come. They can face and resolve a wider variety of problems with efficiency and without resulting in a breakdown.
This will help develop your child’s independence, allowing for them to grow into confident, responsible adults.
Another importance of problem-solving skills is its impact on relationships . Whether they be friendships, family, or business relationships, poor problem solving skills may result in relationships breaking apart.
Being able to get to the bottom of a problem and find solutions together, with all the parties involved, helps keep relationships intact and eliminate conflicts as they arise. Being adept at this skill may even help strengthen and deepen relationships.

What steps can you take to nurture your child’s problem-solving skills?
Nurturing problem-solving skills in your child requires more than just focusing on the big picture and laying out steps to resolve problems. It requires that you teach them to find and focus on a problem’s essential components.
This may challenge your child’s critical thinking and creativity, among other things.
Critical Thinking
This refers to the ability of breaking down a complex problem and analyzing its component parts.
The ability to do that will make it easier to come up with logical solutions to almost any problem. Being able to sort through and organize that pile of smaller chunks of information helps them face problems with ease. It also prevents your child from feeling overwhelmed when a huge barrier is laid out in front of them.
Help your child practice critical thinking by asking them questions. Open-ended questions specifically help them think outside the box and analyze the situation.
Teach them to look into possible reasons why something is the way it is. Why is the sky blue? Why are plants green? Encourage them to be curious and ask questions themselves.
Creative thinking is being able to look at different possible reasons and solutions in the context of problem-solving. It’s coming up with ideas and finding new ways of getting around a problem. Or being open to different ways of looking at an object or scenario.
Creative thinking is best nurtured with activities that involve reflection.
Try getting your child’s viewpoint on topics that may have different answers or reasons for taking place. Get them in the habit of brainstorming ideas, doing story-telling activities, and reading books. All of these help broaden a person’s thinking and flex their creative muscles.
Encourage Independence
It’s important to retain your role as an observer, supporter, or facilitator. Step back and let your kids try out their own solutions. Watch what happens while ensuring their safety and well-being.
As an observer, you encourage independence by stepping back and watching how your child resolves the problem in their own way. It may take longer than it would if you jumped in, but leaving them to their own devices can do a lot for nurturing their skills at problem solving.
Support your child by appreciating and acknowledging their efforts. Create a space where they can freely and effectively express their ideas without fear of judgement. Present them with opportunities to play and solve problems on their own. Encourage them to express themselves by brainstorming activities that they might want to do instead of telling them what to do.
These simple steps of overseeing your child can help them become more independent and be resilient enough to tackle problems on their own.
Here at Early Childhood University , we value the importance of enhancing problem solving skills, creativity and critical thinking. Send your little ones to a school that focuses on a child’s holistic development. Give us a call for more information.


Accessibility
“We’re trying to break down barriers”: The role of family support worker
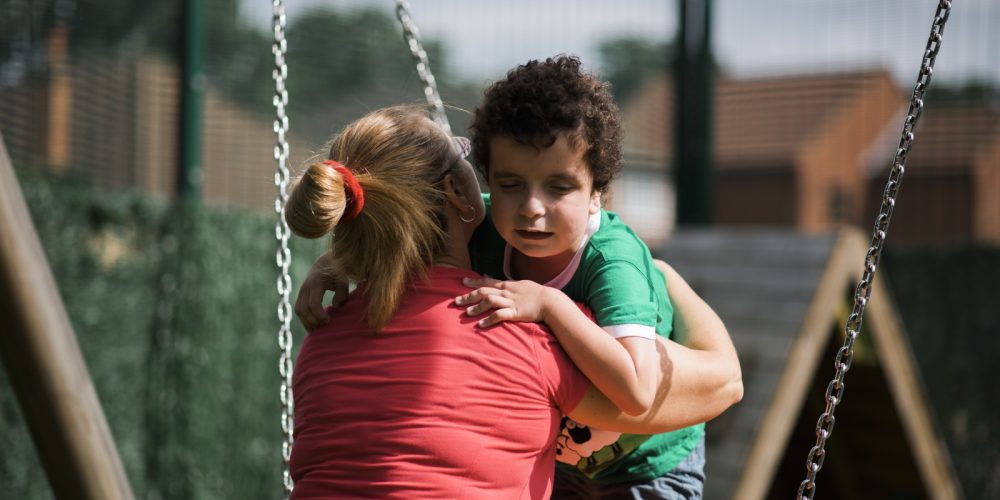

BY: Ciaran Willis
CATEGORY: Blog , News , Press
What is a family support worker?
A family support worker helps families of children with learning disabilities, giving them practical help, advice and emotional support .
Many families of a child with learning disabilities find it hard to get the information they need or are too overwhelmed to find the right support.
For some parents, English is not their first language. Yet they often have stacks of paperwork to read and information to understand.
This is where family support workers come in. Sahara Al-Saad, family worker for Learning Disability Network, London says that for many parents “It’s a bit overwhelming and they need guidance… especially if they’re at the beginning of their Special Educational Needs journey.”
She describes the role as trying to give parents the tools to help themselves – to get the best outcome for their children and the family.
Lucia Balint, who works as a family support worker for Kids Can Achieve in Harrow, says that many parents need emotional, as well as practical support. She says that many people “need direction” about what to do.
Anne Hopewell, who also works in the family support team at Kids Can Achieve, agrees that many parents “do not have the capacity to deal with what’s in front of them.”
The Government does not fund family support workers at KCA or LDN London. Our charities need to raise money for these vital services. If you can, please donate and help us support families in need: Donate to KCA Donate to LDN London
What are some of the main tasks?
- Applying for benefit support
- Providing emotional support for parents
- Advising parents on what support they are entitled to for their child
- Attending appointments with doctors or schools
- Liaising with schools
- Making referrals to food banks
- Translating for parents if English is a second language

What is the process?
The family support team respond to all the people who contact them. Some families are referred by professionals (such as doctors or social workers), while other families find out about family support services on social media or through a parent group and send them a message.
Sahara says that she usually first does an assessment. She speaks to a family to find out more about their situation and what kind of support they need, whether that is about housing problems, schools, or a financial issue.
After that first appointment she will prioritise some issues and solve them. Families often contact the team again if they need more support, Sahara says.
The role can be ad hoc, with families sometimes contacting her again after a year. The job requires you to be flexible and to respond to people’s needs.
Sahara also works with the family support team at Learning Disability Network. Another member of the team, Alexandra, works directly with children and provides therapies. Sahara supports her where necessary with practical assistance, such as translating where possible, and helps the families.
What skills are important to be a family support worker?
Compassion and empathy – to care about and understand the families you support
Determination – to make a difference and get through the (occasional) mountains of paperwork!
An understanding of the schools and benefits systems – to help people understand these
Being a good listener and source of emotional support
Ability to help and empower others – supporting people and giving them the confidence and skills to support their child
Working together – having the people skills to work well with families, other support workers and other organisations
Problem solving
Being assertive and sometimes fearless – trying to understand when to push families to do more for themselves or when to challenge people to help clients
Time management – to manage a busy role, deadlines and appointments

Why should you become a family support worker? “You get parents’ voices heard”
The families team says you get an amazing feeling when you successfully help a family.
Anne says that it’s great to be on the parents’ side, especially when the system can seem like it is against them. “It’s really satisfying – we’re just not another barrier, we’re trying to break down barriers.”
Anne has been to some appointments with parents where the doctors seemed more helpful and responsive to the family because she was there, she says. “You get their voice heard more easily.”
She adds that you also get a great feeling when you see and hear the impact that the work makes: “When parents say they don’t know where they would have been without you.”
Sahara agrees that the role makes a genuine difference.
Sahara says she became a family support worker because she wanted to help end inequality for children with special educational needs.
She says that there’s a lot of “unmet need” and not enough support for parents. A lot of services don’t have the time or resources to help people, she says.
How to become a family support worker?
The team said that the most important thing is your attitude. While there are courses that would be useful to have studied, “the knowledge you can build on the job is more important”, the team said.
Anne and Lucia both have a background in social work. A similar background or knowledge of Psychology and Development Psychology would be useful, but not essential.
It is important however to have good writing, reading and English language skills.
As well, a good understanding of learning disabilities is also important, if you are working for an organisation that supports children with learning disabilities.
If you have a child with a learning disability and need support, please contact [email protected]
Find out more about the work of Kids Can Achieve: https://kidscanachieve.co.uk/
SHARE THIS ARTICLE
Welcome to LDN London – the new name for The Westminster Society
Why Every Educator Needs to Teach Problem-Solving Skills
Strong problem-solving skills will help students be more resilient and will increase their academic and career success .
Want to learn more about how to measure and teach students’ higher-order skills, including problem solving, critical thinking, and written communication?
Problem-solving skills are essential in school, careers, and life.
Problem-solving skills are important for every student to master. They help individuals navigate everyday life and find solutions to complex issues and challenges. These skills are especially valuable in the workplace, where employees are often required to solve problems and make decisions quickly and effectively.
Problem-solving skills are also needed for students’ personal growth and development because they help individuals overcome obstacles and achieve their goals. By developing strong problem-solving skills, students can improve their overall quality of life and become more successful in their personal and professional endeavors.
Problem-Solving Skills Help Students…
develop resilience.
Problem-solving skills are an integral part of resilience and the ability to persevere through challenges and adversity. To effectively work through and solve a problem, students must be able to think critically and creatively. Critical and creative thinking help students approach a problem objectively, analyze its components, and determine different ways to go about finding a solution.
This process in turn helps students build self-efficacy . When students are able to analyze and solve a problem, this increases their confidence, and they begin to realize the power they have to advocate for themselves and make meaningful change.
When students gain confidence in their ability to work through problems and attain their goals, they also begin to build a growth mindset . According to leading resilience researcher, Carol Dweck, “in a growth mindset, people believe that their most basic abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work—brains and talent are just the starting point. This view creates a love of learning and a resilience that is essential for great accomplishment.”
Set and Achieve Goals
Students who possess strong problem-solving skills are better equipped to set and achieve their goals. By learning how to identify problems, think critically, and develop solutions, students can become more self-sufficient and confident in their ability to achieve their goals. Additionally, problem-solving skills are used in virtually all fields, disciplines, and career paths, which makes them important for everyone. Building strong problem-solving skills will help students enhance their academic and career performance and become more competitive as they begin to seek full-time employment after graduation or pursue additional education and training.
Resolve Conflicts
In addition to increased social and emotional skills like self-efficacy and goal-setting, problem-solving skills teach students how to cooperate with others and work through disagreements and conflicts. Problem-solving promotes “thinking outside the box” and approaching a conflict by searching for different solutions. This is a very different (and more effective!) method than a more stagnant approach that focuses on placing blame or getting stuck on elements of a situation that can’t be changed.
While it’s natural to get frustrated or feel stuck when working through a conflict, students with strong problem-solving skills will be able to work through these obstacles, think more rationally, and address the situation with a more solution-oriented approach. These skills will be valuable for students in school, their careers, and throughout their lives.
Achieve Success
We are all faced with problems every day. Problems arise in our personal lives, in school and in our jobs, and in our interactions with others. Employers especially are looking for candidates with strong problem-solving skills. In today’s job market, most jobs require the ability to analyze and effectively resolve complex issues. Students with strong problem-solving skills will stand out from other applicants and will have a more desirable skill set.
In a recent opinion piece published by The Hechinger Report , Virgel Hammonds, Chief Learning Officer at KnowledgeWorks, stated “Our world presents increasingly complex challenges. Education must adapt so that it nurtures problem solvers and critical thinkers.” Yet, the “traditional K–12 education system leaves little room for students to engage in real-world problem-solving scenarios.” This is the reason that a growing number of K–12 school districts and higher education institutions are transforming their instructional approach to personalized and competency-based learning, which encourage students to make decisions, problem solve and think critically as they take ownership of and direct their educational journey.
Problem-Solving Skills Can Be Measured and Taught
Research shows that problem-solving skills can be measured and taught. One effective method is through performance-based assessments which require students to demonstrate or apply their knowledge and higher-order skills to create a response or product or do a task.
What Are Performance-Based Assessments?

With the No Child Left Behind Act (2002), the use of standardized testing became the primary way to measure student learning in the U.S. The legislative requirements of this act shifted the emphasis to standardized testing, and this led to a decline in nontraditional testing methods .
But many educators, policy makers, and parents have concerns with standardized tests. Some of the top issues include that they don’t provide feedback on how students can perform better, they don’t value creativity, they are not representative of diverse populations, and they can be disadvantageous to lower-income students.
While standardized tests are still the norm, U.S. Secretary of Education Miguel Cardona is encouraging states and districts to move away from traditional multiple choice and short response tests and instead use performance-based assessment, competency-based assessments, and other more authentic methods of measuring students abilities and skills rather than rote learning.
Performance-based assessments measure whether students can apply the skills and knowledge learned from a unit of study. Typically, a performance task challenges students to use their higher-order skills to complete a project or process. Tasks can range from an essay to a complex proposal or design.
Preview a Performance-Based Assessment
Want a closer look at how performance-based assessments work? Preview CAE’s K–12 and Higher Education assessments and see how CAE’s tools help students develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and written communication skills.
Performance-Based Assessments Help Students Build and Practice Problem-Solving Skills
In addition to effectively measuring students’ higher-order skills, including their problem-solving skills, performance-based assessments can help students practice and build these skills. Through the assessment process, students are given opportunities to practically apply their knowledge in real-world situations. By demonstrating their understanding of a topic, students are required to put what they’ve learned into practice through activities such as presentations, experiments, and simulations.
This type of problem-solving assessment tool requires students to analyze information and choose how to approach the presented problems. This process enhances their critical thinking skills and creativity, as well as their problem-solving skills. Unlike traditional assessments based on memorization or reciting facts, performance-based assessments focus on the students’ decisions and solutions, and through these tasks students learn to bridge the gap between theory and practice.
Performance-based assessments like CAE’s College and Career Readiness Assessment (CRA+) and Collegiate Learning Assessment (CLA+) provide students with in-depth reports that show them which higher-order skills they are strongest in and which they should continue to develop. This feedback helps students and their teachers plan instruction and supports to deepen their learning and improve their mastery of critical skills.

Explore CAE’s Problem-Solving Assessments
CAE offers performance-based assessments that measure student proficiency in higher-order skills including problem solving, critical thinking, and written communication.
- College and Career Readiness Assessment (CCRA+) for secondary education and
- Collegiate Learning Assessment (CLA+) for higher education.
Our solution also includes instructional materials, practice models, and professional development.
We can help you create a program to build students’ problem-solving skills that includes:
- Measuring students’ problem-solving skills through a performance-based assessment
- Using the problem-solving assessment data to inform instruction and tailor interventions
- Teaching students problem-solving skills and providing practice opportunities in real-life scenarios
- Supporting educators with quality professional development
Get started with our problem-solving assessment tools to measure and build students’ problem-solving skills today! These skills will be invaluable to students now and in the future.

Ready to Get Started?
Learn more about cae’s suite of products and let’s get started measuring and teaching students important higher-order skills like problem solving..

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The first step in solving any recurring problem in the life of a child is to take a step back. Problems of family life are best solved - and perhaps can only be solved—proactively.
Why problem-solving is important. As parents, the way you manage problems or disagreements in your relationship affects your child. By managing problems positively and constructively, you help your child develop well and thrive. When your child sees you behaving and communicating with your partner in this way, your child learns to behave this ...
Get to the Deeper Issue. Focus on the Relationship - Let Go of Anger and Pride. Get Professional Help. Remember to Take Care of Yourself. Creating a family culture of openness and security, and taking the steps to resolve family issues, can improve relationships and maintain positive family dynamics.
Family problems can take a heavy toll on each member, affecting their psychological well-being, physical health and social interactions. Let's dive deeper into these effects. Firstly, on the emotional front, family issues often lead to stress and anxiety. It's not uncommon for individuals to feel overwhelmed, resulting in sleep problems or ...
improving the family's problem-solving abilities; Research from 2019 suggests that family therapy effectively addresses issues with ... Since participation is an important part of family therapy ...
Step 4: Develop a Plan. In my experience, almost all children respond positively when I tell a family that "I have a plan" to solve a recurrent problem of family life. They may be skeptical ...
Talking to your children and promoting open communication and problem solving is just as important as eating well and getting enough exercise and sleep. Create a healthy environment. Your home, workspace, and even social environment can influence your behaviors. Altering your environment can help alleviate stress.
As a parent, I understand the importance of effective family communication and promoting problem-solving in family dynamics.Developing problem-solving skills in families is not only beneficial for resolving conflicts but also essential for the overall growth and well-being of children. By nurturing these skills, parents can equip their children with valuable life skills and create a harmonious ...
Validate your family members by saying something like "I'm really glad you felt comfortable enough to share this with me" or "I appreciate your willingness to work towards a solution". 6. Decide on a solution together. Once everyone has shared their needs, wants, and concerns, then strive for a compromise.
Signs of family issues: Difficulty with open, honest, and healthy communication. Frequent fights or bickering. Frequent yelling and screaming. Passive-aggressive behavior. An absent parent or parents (physically and/or emotionally) Abuse of any kind (physical, emotional, and/or verbal abuse)
Show your child a willingness to make mistakes. When they are solving something, as tricky as it may be, allow your child to struggle, sometimes fail and ultimately learn from experiencing consequences. Problems are a part of life. They grow us to reach our highest potential. Every problem is there not to make your child miserable, but to lead ...
The model conceptualizes problem solving as an important skill that is acquired over time and affected by family experiences. Specifically, adolescents exposed to constructive problem solving experiences in multiple family relationships should learn to resolve problems as they arise, contributing to a sense of mastery.
Families provide an environment that stimulates cognitive skills, such as problem-solving and critical thinking and supports and encourages academic achievements. ... Here are 10 potential reasons why family can be important to you. Family can offer unconditional love. Family gives you strength and support to face difficulties in life.
Families that are willing to engage in therapy can rely on a family therapist to guide the discussion and the handling of conflict. This type of healthcare professional can equip members with techniques to help with things like communication, problem-solving, and stress management that they can use in the present conflict and in the future.
Family meetings can help you, your children, and your co-parent to become closer and to communicate more clearly. By being involved in group decision-making and problem-solving, children see themselves as having responsibility for creating a good home life and they are more likely to feel like an important part of their family.
Family therapists tend to be more interested in the maintenance and/or solving of problems rather than in trying to identify a single cause. Some families may perceive cause-effect analyses as attempts to allocate blame to one or more individuals, with the effect that for many families, a focus on causation is of little or no clinical utility.
Here are the steps to problem-solving: . Identify the problem. Just stating the problem out loud can make a big difference for kids who are feeling stuck. Help your child state the problem, such as, "You don't have anyone to play with at recess," or "You aren't sure if you should take the advanced math class."
Problem-solving therapy is a brief intervention that provides people with the tools they need to identify and solve problems that arise from big and small life stressors. It aims to improve your overall quality of life and reduce the negative impact of psychological and physical illness. Problem-solving therapy can be used to treat depression ...
This will help develop your child's independence, allowing for them to grow into confident, responsible adults. Another importance of problem-solving skills is its impact on relationships. Whether they be friendships, family, or business relationships, poor problem solving skills may result in relationships breaking apart.
Spending time with family helps alleviate that stress. It's an opportunity to talk things out, get feedback, and maybe brainstorm for a solution to the problem that is causing the stress. According to Brandy Drzymkowski, "During the holidays, your closest five people probably shifts to family and friends.
Problem solving is important in child development because confident, capable children usually grow into confident, capable adults. <. If students practice problem solving consistently, they can develop greater situational and social awareness. Additionally, they learn to manage time and develop patience. As students mature, problems they face ...
Sahara agrees that the role makes a genuine difference. Sahara says she became a family support worker because she wanted to help end inequality for children with special educational needs. She says that there's a lot of "unmet need" and not enough support for parents. A lot of services don't have the time or resources to help people ...
Problem-solving skills are important for every student to master. They help individuals navigate everyday life and find solutions to complex issues and challenges. These skills are especially valuable in the workplace, where employees are often required to solve problems and make decisions quickly and effectively.