A Basic Blockchain Technology PPT Presentation You Can Use
Salomon kisters.
This post may contain affiliate links. If you use these links to buy something we may earn a commission. Thanks!

Slide Overview
Slide 1: cover slide.
What is Blockchain technology? What is Bitcoin? How does it work and how can it be used?
Slide 2: The History of Blockchain Part 1
A short history of Bitcoin.
- 2008: The first description of Bitcoin was published in 2008 by an individual or a group under the pseudonym “Satoshi Nakamoto” in a now very famous white paper.
- 2009: The Bitcoin Network goes live and the first Bitcoins are mined.
- 2010: The first cryptocurrency stock exchange for trading Bitcoin is launched.
- 2011: One Bitcoin equals one USD.
Slide 3: The History of Blockchain Part 2
- 2013: One Bitcoin now equals 100 USD.
- 2014: Microsoft starts accepting Bitcoin as payments.
- 2017: One Bitcoin equals 10'000 USD.
Slide 4: Bitcoin is not Blockchain
Bitcoin does not equal Blockchain.
- Bitcoin is a currency and a system that uses a blockchain as underlying datastructure, which can be used for many things, including cryptocurrencies.
- Blockchain is the underlying data structure.
Slide 5: What is a Blockchain?
- A blockchain is a datastructure, which is a growing list of data blocks.
- The data blocks are linked together, such that old blocks cannot be removed or altered.
Slide 6: Bitcoin Ecosystem Part 1
- The Bitcoin ecosystem contains a public network in which anyone, including a malicious participant, can participate without restriction. The amazing breakthrough that came with Bitcoin is that although malicious participants can participate, the system works without a regulator.
Slide 7: Bitcoin Ecosystem Part 2
Slide 8: cutting the middleman, slide 9: building consensus, slide 10: creating witnesses, slide 11: key features.
A public blockchain has some characteristic features:
- Write-only, immutable, transparent data storage.
- Decentralized, no need for intermediaries.
- Consistent state across all participants.
- Resistant against malicious participants.
- Open to everyone.
For converting and preserving blockchain-related documents, consider using the best PPT to PDF converter to ensure the security and accessibility of your information, as demonstrated by our use of a public blockchain for creating secure timestamps.
Slide 12: Challenges
Although Blockchain technology has a strong disruptive power and can change many areas of our daily lives, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed.
- The high energy consumption - Bitcoin uses a lot of energy.
- The scalablity issue - Bitcoin supports far less transactions per second than e.g. VISA.
- It opens up possibilities for money laundering - Some blockchains as Monero are anonymous.
- The question remains as to how far we want to bypass the middleman. Often he can also protect us, e.g. a bank can protact us to the extend that we do not transfer the money to the wrong person.
- How to use blockchain to timestamp and protect documents
Stay informed with the latest insights in Crypto, Blockchain, and Cyber-Security! Subscribe to our newsletter now to receive exclusive updates, expert analyses, and current developments directly to your inbox. Don't miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and stay up-to-date.
Love what you're reading? Subscribe for top stories in Crypto, Blockchain, and Cyber-Security. Stay informed with exclusive updates.
Please note that the Content may have been generated with the Help of AI. The editorial content of OriginStamp AG does not constitute a recommendation for investment or purchase advice. In principle, an investment can also lead to a total loss. Therefore, please seek advice before making an investment decision.
Top Saas-based Blockchain Startups
More and more startups recognize and develop use cases for blockchain beyond cryptocurrencies. Find out about the Top SAAS-based blockchain startups right now.
Top 6 Blockchain Books to Read in 2021 - Dive into Blockchain Technology
Discover the top 6 blockchain books to read in 2021 and delve into blockchain technology to understand its history, use cases, and future potential.
Using Blockchain Technology to Differentiate Your Business - A Competitive Advantage Guide
Learn how to leverage blockchain technology to gain a competitive advantage in your business. Explore examples and benefits of using blockchain for non-functional requirements.
Protect your documents
Your gateway to unforgeable data. Imprint the authenticity of your information with our blockchain timestamp

Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network.
An asset can be tangible (a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding). Virtually anything of value can be tracked and traded on a blockchain network, reducing risk and cutting costs for all involved.
Business runs on information. The faster information is received and the more accurate it is, the better. Blockchain is ideal for delivering that information because it provides immediate, shared, and observable information that is stored on an immutable ledger that only permissioned network members can access. A blockchain network can track orders, payments, accounts, production and much more. And because members share a single view of the truth, you can see all details of a transaction end to end, giving you greater confidence, and new efficiencies and opportunities.
Build a kick-starter blockchain network and start coding with IBM's next-generation blockchain platform.
Register for the guide on sustainability trends
All network participants have access to the distributed ledger and its immutable record of transactions. With this shared ledger, transactions are recorded only once, eliminating the duplication of effort that’s typical of traditional business networks.
No participant can change or tamper with a transaction after it’s been recorded to the shared ledger. If a transaction record includes an error, a new transaction must be added to reverse the error, and both transactions are then visible.
To speed transactions, a set of rules that are called a smart contract is stored on the blockchain and run automatically. A smart contract defines conditions for corporate bond transfers, include terms for travel insurance to be paid and much more.
Those transactions show the movement of an asset that can be tangible (a product) or intangible (intellectual). The data block can record the information of your choice: who, what, when, where, how much. It can even record the condition, such as the temperature of a food shipment.
These blocks form a chain of data as an asset moves from place to place or ownership changes hands. The blocks confirm the exact time and sequence of transactions, and the blocks link securely together to prevent any block from being altered or a block being inserted between two existing blocks.
Each additional block strengthens the verification of the previous block and hence the entire blockchain. Rendering the blockchain tamper-evident, delivering the key strength of immutability. Removing the possibility of tampering by a malicious actor, and builds a ledger of transactions you and other network members can trust.
What needs to change: Operations often waste effort on duplicate record keeping and third-party validations. Record-keeping systems can be vulnerable to fraud and cyberattacks. Limited transparency can slow data verification. And with the arrival of IoT, transaction volumes have exploded. All of this slows business, drains the bottom line, and means that we need a better way. Enter blockchain.
With blockchain, as a member of a members-only network, you can rest assured that you are receiving accurate and timely data. And that your confidential blockchain records are shared only with network members to whom you granted access.
Consensus on data accuracy is required from all network members, and all validated transactions are immutable because they are recorded permanently. No one, not even a system administrator, can delete a transaction.
With a distributed ledger that is shared among members of a network, time-wasting record reconciliations are eliminated. And to speed transactions, a set of rules that are called a smart contract can be stored on the blockchain and run automatically.
Step inside the basics of blockchain technology: how blocks contain data representing anything of value, how they’re chronologically connected in an immutable chain, and the differences between blockchain and cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin.
Learn how the decentralized nature of blockchain sets it apart from traditional record-keeping, the value of a permissioned blockchain for business transactions, and how blockchain promotes new levels of trust and transparency.
The food industry is just one of many being transformed through blockchain technology. Learn how it can trace when, where and how food has been grown, picked, shipped and processed — all while protecting network-participant data.
Blockchain creates trust because it represents a shared record of the truth. Data that everyone can believe in will help power other new technologies that dramatically increase efficiency, transparency and confidence.
A public blockchain is one that anyone can join and participate in, such as Bitcoin. Drawbacks might include the substantial computational power that is required, little or no privacy for transactions, and weak security. These are important considerations for enterprise use cases of blockchain.
A private blockchain network, similar to a public blockchain network, is a decentralized peer-to-peer network. However, one organization governs the network, controlling who is allowed to participate, run a consensus protocol and maintain the shared ledger. Depending on the use case, this can significantly boost trust and confidence between participants. A private blockchain can be run behind a corporate firewall and even be hosted on premises.
Businesses who set up a private blockchain will generally set up a permissioned blockchain network. It is important to note that public blockchain networks can also be permissioned. This places restrictions on who is allowed to participate in the network and in what transactions. Participants need to obtain an invitation or permission to join.
Multiple organizations can share the responsibilities of maintaining a blockchain. These preselected organizations determine who submit transactions or access the data. A consortium blockchain is ideal for business when all participants need to be permissioned and have a shared responsibility for the blockchain.
When building an enterprise blockchain application, it’s important to have a comprehensive security strategy that uses cybersecurity frameworks, assurance services, and best practices to reduce risks against attacks and fraud.
IBM Food Trust is helping Raw Seafoods increase trust across the food supply chain by tracing every catch right from the water — all the way to supermarkets and restaurants.
INBLOCK issues Metacoin cryptocurrency, which is based on Hyperledger Fabric, to help make digital asset transactions faster, more convenient and safer.
The IBM Blockchain Platform can change the way your ecosystem ensures trust, data provenance and efficiency to improve patient care and profitability. Read: Transform healthcare outcomes
Vertrax and Chateau Software launched the first multicloud blockchain solution built on IBM Blockchain Platform to help prevent supply chain disruptions in bulk oil and gas distribution.
The Home Depot is using IBM Blockchain to gain shared and trusted information on shipped and received goods, reducing vendor disputes and accelerating dispute resolution.
Industry leaders are using IBM Blockchain to remove friction, build trust, and unlock new value. Select your segment to see how.
Supply chain Healthcare Government Retail Media and Advertising Oil and gas Telecommunications Manufacturing Insurance Financial services Travel and transportation
Bitcoin is an unregulated, digital currency. Bitcoin uses blockchain technology as its transaction ledger.
This video illustrates the distinction between the two.
The IBM Blockchain Platform is powered by Hyperledger technology. This blockchain solution can help turn any developer into a blockchain developer.
Visit the Hyperledger website for details.
IBM Blockchain Platform Software is optimized to deploy on Red Hat® OpenShift®, Red Hat’s state-of-the-art enterprise Kubernetes platform. This means that you have more flexibility when choosing where to deploy your blockchain network components, whether on-premises, in public clouds, or in hybrid cloud architectures.
For a more detailed look at how a blockchain network operates and how you can use it, read Introduction to distributed ledgers. Learn more from the blockchain tutorial on IBM Developer
Explore the capabilities of the IBM Blockchain Platform, the only fully integrated enterprise-ready blockchain platform that is designed to help you accelerate the development, governance, and operation of a multi-institution business network. Register to download the IBM Blockchain Platform white paper
Get the details on Hyperledger Fabric and discover what’s unique about it, why it matters to business networks and how to start using it. Visit the Hyperledger page on IBM Developer
The quick-start guide for developers explains how to build a kick-starter blockchain network and start coding with the IBM Blockchain Platform Starter Plan. View the quick-start guide for developers
Technical innovators turn to the IBM Blockchain Platform, the leading Hyperledger Fabric platform to build, operate, govern, and grow blockchain solutions across any computing environment through Red Hat® OpenShift®.
As the top-ranked blockchain services provider, IBM Blockchain Services have the expertise to help you build powerful solutions, based on the best technology. More than 1,600 blockchain experts use insights from 100+ live networks to help you build and grow.
Embracing an IBM Blockchain solution is the fastest way to blockchain success. IBM convened networks that make onboarding easy as you join others in transforming the food supply, supply chains, trade finance, financial services, insurance, and media and advertising.
We asked five artists — all new to blockchain — to create art about its key benefits. See what they made, then learn more from IBM clients and business partners in Blockparty, our new webinar series.
Be inspired by how innovators are transforming their businesses using the IBM Blockchain Platform. You can join an existing blockchain network or work with us to create your own.
Learn how our clients are revolutionizing their organizations by using IBM Blockchain to gain tangible business outcomes.
IBM Blockchain solutions use distributed ledger technology and enterprise blockchain to help clients drive operational agility, connectivity and new revenue streams. Move beyond your organization's boundaries with trusted end-to-end data exchange and workflow automation.
What is blockchain?

Blockchain is one of the major tech stories of the past decade. Everyone seems to be talking about it—but beneath the surface chatter there’s not always a clear understanding of what blockchain is or how it works. Despite its reputation for impenetrability, the basic idea behind blockchain is pretty simple. And it has major potential to change industries from the bottom up .
Blockchain is a technology that enables the secure sharing of information. Data, obviously, is stored in a database. Transactions are recorded in an account book called a ledger. A blockchain is a type of distributed database or ledger—one of today’s top tech trends —which means the power to update a blockchain is distributed between the nodes, or participants, of a public or private computer network. This is known as distributed ledger technology, or DLT. Nodes are incentivized with digital tokens or currency to make updates to blockchains.
Get to know and directly engage with senior McKinsey experts on blockchain
Michael Chui is a partner at the McKinsey Global Institute and is based in McKinsey’s Bay Area office, where Marie-Claude Nadeau is a senior partner.
Blockchain allows for the permanent, immutable, and transparent recording of data and transactions. This, in turn, makes it possible to exchange anything that has value, whether that is a physical item or something less tangible.
A blockchain has three central attributes . First, a blockchain database must be cryptographically secure. That means in order to access or add data on the database, you need two cryptographic keys: a public key, which is basically the address in the database, and the private key, which is a personal key that must be authenticated by the network.
Next, a blockchain is a digital log or database of transactions, meaning it happens fully online.
And finally, a blockchain is a database that is shared across a public or private network. One of the most well-known public blockchain networks is the Bitcoin blockchain . Anyone can open a Bitcoin wallet or become a node on the network. Other blockchains may be private networks. These are more applicable to banking and fintech , where people need to know exactly who is participating, who has access to data, and who has a private key to the database. Other types of blockchains include consortium blockchains and hybrid blockchains, both of which combine different aspects of public and private blockchains.
Research from the McKinsey Technology Council suggests that by 2027, up to 10 percent of global GDP could be associated with blockchain-enabled transactions. But in the world of blockchain, what is real and what is just hype? And how can companies use blockchain to increase efficiency and create value? Read on to find out.
Learn more about McKinsey’s Financial Services Practice .
How does blockchain work?
A deeper dive may help in understanding how blockchain and other DLTs work .
When data on a blockchain is accessed or altered, the record is stored in a “block” alongside the records of other transactions. Stored transactions are encrypted via unique, unchangeable hashes, such as those created with the SHA-256 algorithm. New data blocks don’t overwrite old ones; they are appended together so that any changes can be monitored. And since all transactions are encrypted, records are immutable—so any changes to the ledger can be recognized by the network and rejected.
These blocks of encrypted data are permanently “chained” to one another, and transactions are recorded sequentially and indefinitely, creating a perfect audit history that allows visibility into past versions of the blockchain.
When new data is added to the network, the majority of nodes must verify and confirm the legitimacy of the new data based on permissions or economic incentives, also known as consensus mechanisms . When a consensus is reached, a new block is created and attached to the chain. All nodes are then updated to reflect the blockchain ledger.
In a public blockchain network , the first node to credibly prove the legitimacy of a transaction receives an economic incentive. This process is called “mining.”
Here’s a theoretical example to help illustrate how blockchain works. Imagine that someone is looking to buy a concert ticket on the resale market. This person has been scammed before by someone selling a fake ticket, so she decides to try one of the blockchain-enabled decentralized ticket exchange websites that have been created in the past few years. On these sites, every ticket is assigned a unique, immutable, and verifiable identity that is tied to a real person. Before the concertgoer purchases her ticket, the majority of the nodes on the network validate the seller’s credentials, ensuring that the ticket is in fact real. She buys her ticket and enjoys the concert.
What is proof of work and how is it different from proof of stake?
Remember the idea of consensus mechanisms mentioned earlier? There are two ways blockchain nodes arrive at a consensus: through private blockchains, where trusted corporations are the gatekeepers of changes or additions to the blockchain, or through public, mass-market blockchains.
Most public blockchains arrive at consensus by either a proof-of-work or proof-of-stake system . In a proof-of-work system, the first node, or participant, to verify a new data addition or transaction on the digital ledger receives a certain number of tokens as a reward. To complete the verification process, the participant, or “miner,” must solve a cryptographic question. The first miner who solves the puzzle is awarded the tokens.
Originally, people on various blockchains mined as a hobby. But because this process is potentially lucrative , blockchain mining has been industrialized. These proof-of-work blockchain-mining pools have attracted attention for the amount of energy they consume.
In September 2022, Ethereum, an open-source cryptocurrency network, addressed concerns around energy usage by upgrading its software architecture to a proof-of-stake blockchain. Known simply as “the Merge,” this event is seen by cryptophiles as a banner moment in the history of blockchain. With proof-of-stake, investors deposit their crypto coins in a shared pool in exchange for the chance to earn tokens as a reward. In proof-of-stake systems, miners are scored based on the number of native protocol coins they have in their digital wallets and the length of time they have had them. The miner with the most coins at stake has a greater chance to be chosen to validate a transaction and receive a reward.

Introducing McKinsey Explainers : Direct answers to complex questions
How can businesses benefit from blockchain.
Research suggests that blockchain and DLTs could create new opportunities for businesses by decreasing risk and reducing compliance costs, creating more cost-efficient transactions, driving automated and secure contract fulfillment, and increasing network transparency. Let’s break it down further:
- Reduced risk and lower compliance costs . Banks rely on “know your customer” (KYC) processes to bring customers on board and retain them. But many existing KYC processes are outdated and drive costs of as much as $500 million per year, per bank. A new DLT system might require once-per-customer KYC verification, driving efficiency gains, cost reduction, and improved transparency and customer experience.
- Cost-efficient transactions. Digitizing records and issuing them on a universal ledger can help save significant time and costs. In a letter-of-credit deal, for example, two companies opted for a paperless solution and used blockchain to trade nearly $100,000 worth of butter and cheese. By doing so, a process that previously took up to ten days was reduced to less than four hours—from issuing to approving the letter of credit.
- Automated and secure contract fulfillment. Smart contracts are sets of instructions coded into tokens issued on a blockchain that can self-execute under specific conditions. These can enable automated fulfillment of contracts. For example, one retailer wanted to streamline its supply-chain-management efforts, so it began recording all processes and actions, from vendor to customer, and coding them into smart contracts on a blockchain. This effort not only made it easier to trace the provenance of food for safer consumption but also required less human effort and improved the ability to track lost products.
Learn more about McKinsey’s Financial Services Practice .
How are blockchain, cryptocurrency, and decentralized finance connected?
Blockchain enables buyers and sellers to trade cryptocurrencies online without the need for banks or other intermediaries.
All digital assets, including cryptocurrencies, are based on blockchain technology. Decentralized finance (DeFi) is a group of applications in cryptocurrency or blockchain designed to replace current financial intermediaries with smart contract-based services. Like blockchain, DeFi applications are decentralized, meaning that anyone who has access to an application has control over any changes or additions made to it. This means that users potentially have more direct control over their money.
What else can blockchain be used for?
Cryptocurrency is only the tip of the iceberg. Use cases for blockchain are expanding rapidly beyond person-to-person exchanges, especially as blockchain is paired with other emerging technology.
Examples of other blockchain use cases include the following:
- With blockchain, companies can create an indelible audit trail through a sequential and indefinite recording of transactions. This allows for systems that keep static records (of land titles, for example) or dynamic records (such as the exchange of assets).
- Blockchain allows companies to track a transaction down to its current status. This enables companies to determine exactly where the data originated and where it was delivered, which helps to prevent data breaches.
- Blockchain supports smart contracts, which are programs that trigger transactions automatically upon fulfillment of contract criteria.
What are some concerns around the future of blockchain?
While blockchain may be a potential game changer , there are doubts emerging about its true business value . One major concern is that for all the idea-stage use cases, hyperbolic headlines, and billions of dollars of investment, there remain very few practical, scalable use cases of blockchain.
One reason for this is the emergence of competing technologies. In the payments space, for example, blockchain isn’t the only fintech disrupting the value chain—60 percent of the nearly $12 billion invested in US fintechs in 2021 was focused on payments and lending. Given how complicated blockchain solutions can be—and the fact that simple solutions are frequently the best —blockchain may not always be the answer to payment challenges.
Looking ahead, some believe the value of blockchain lies in applications that democratize data, enable collaboration, and solve specific pain points. McKinsey research shows that these specific use cases are where blockchain holds the most potential, rather than those in financial services.
How might blockchain evolve over time?
In the next five years, McKinsey estimates that there will be two primary development horizons for blockchain:
- Growth of blockchain as a service (BaaS). BaaS is a cloud-based service that builds digital products for DLT and blockchain environments without any setup requirements for infrastructure. This is currently being led by Big Tech companies.
- Interoperability across blockchain networks and outside systems. Increased interoperability will mean that disparate blockchain networks and external systems will be able to view, access, and share one another’s data while maintaining integrity. Hardware standardization and scalable consensus algorithms will enable cross-network use cases—such as the Internet of Things on blockchain infrastructure.
These trends will be enabled partly because of increased pressure from regulators and consumers demanding greater supply chain transparency, and partly because of economic uncertainty, as consumers seek out independent, centrally regulated systems. And large corporations launching successful pilots will build confidence for consumers and other organizations.
Potential growth could be inhibited by a few factors: for one, several well-known applications have inherently limited scalability, including energy or infrastructure requirements. Further, uncertainty about regulatory or governance developments could keep consumers shy—for instance, if there is a lack of clarity on who will enforce smart contracts. And, finally, the unresolved threat of cyberattacks remains a fear for potential blockchain users.
What do NFTs have to do with blockchain?
Nonfungible tokens (NFTs) are minted on smart-contract blockchains such as Ethereum or Solana. NFTs represent unique assets that can’t be replicated—that’s the nonfungible part—and can’t be exchanged on a one-to-one basis. These assets include anything from a Picasso painting to a digital lolcat meme. Because NFTs are built on top of blockchains, their unique identities and ownership can be verified through the ledger. With some NFTs, the owner receives a royalty every time the NFT is traded.
The NFT market is extremely volatile : in 2021, one NFT created by the digital artist Mike Winkelmann, also known as Beeple, was sold at Christie’s for $69.3 million. But NFT sales have shrunk dramatically since summer 2022.
How secure is blockchain?
Blockchain has been called a “ truth machine .” While it does eliminate many of the issues that arose in Web 2.0, such as piracy and scamming, it’s not the be-all and end-all for digital security. The technology itself is essentially foolproof, but, ultimately, it is only as noble as the people using it and as good as the data they are adding to it.
A motivated group of hackers could leverage blockchain’s algorithm to their advantage by taking control of more than half of the nodes on the network. With this simple majority, the hackers have consensus and thus the power to verify fraudulent transactions.
In 2022, hackers did exactly that, stealing more than $600 million from the gaming-centered blockchain platform Ronin Network. This challenge, in addition to the obstacles regarding scalability and standardization, will need be addressed. But there is still significant potential for blockchain, both for business and society.
For a more in-depth exploration of these topics, see McKinsey’s “ Blockchain and Digital Assets ” collection. Learn more about McKinsey’s Financial Services Practice —and check out blockchain-related job opportunities if you’re interested in working at McKinsey.
Articles referenced include:
- “ McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2022 ,” August 24, 2022
- “ Forward Thinking on tech and the unpredictability of prediction with Benedict Evans ,” April 6, 2022, Janet Bush and Michael Chui
- “ Seven technologies shaping the future of fintech ,” November 9, 2021, Dick Fong, Feng Han, Louis Liu, John Qu, and Arthur Shek
- “ CBDC and stablecoins: Early coexistence on an uncertain road ,” October 11, 2021, Ian De Bode, Matt Higginson , and Marc Niederkorn
- “ Blockchain and retail banking: Making the connection ,” June 7, 2019, Matt Higginson , Atakan Hilal, and Erman Yugac
- “ Blockchain 2.0: What’s in store for the two ends—semiconductors (suppliers) and industrials (consumers)? ,” January 18, 2019, Gaurav Batra, Rémy Olson, Shilpi Pathak, Nick Santhanam, and Harish Soundararajan
- “ Blockchain’s Occam problem ,” January 4, 2019, Matt Higginson , Marie-Claude Nadeau , and Kausik Rajgopal
- “ Blockchain explained: What it is and isn’t, and why it matters ,” September 28, 2018

Want to know more about blockchain?
Related articles.

Blockchain’s Occam problem

Blockchain beyond the hype: What is the strategic business value?

Blockchain explained: What it is and isn’t, and why it matters
Blockchain .
Blockchain: what it is, how it works, why it matters.

Understanding Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger that stores the record of ownership of digital assets. Any data stored on blockchain is unable to be modified, making the technology a legitimate disruptor for industries like payments, cybersecurity and healthcare.

What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is an immutable digital ledger that enables secure transactions across a peer-to-peer network. It records, stores and verifies data using decentralized techniques to eliminate the need for third parties, like banks or governments. Every transaction is recorded, then stored in a block on the blockchain. Each block is encrypted for protection and chained to the preceding block — hence, “blockchain” — establishing a code-based chronological order. This means that, without consensus of a network, data stored on a blockchain cannot be deleted or modified. These new-age databases act as a single source of truth and, among an interconnected network of computers, facilitate trustless and transparent data exchange.
Apart from moving cryptocurrencies from one wallet to the next, blockchain technology is an emerging technology with wide-ranging application potential, from preventing fraudulent banking and supply-chain bottlenecks to safeguarding medical records.
Why Is Blockchain Important?
Blockchain is a revolutionary technology because it helps reduce security risks, stamp out fraud and bring transparency in a scalable way.
Popularized by its association with cryptocurrency and NFTs , blockchain technology has since evolved to become a management solution for all types of global industries . Today you can find blockchain technology providing transparency for the food supply chain , securing healthcare data , innovating gaming and changing how we handle data and ownership on a large scale.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchains are distributed data-management systems that record every single exchange between their users. These immutable digital documents use several techniques to create a trustless, intermediary-free system.
Let’s start with the blocks. Each block contains stored data, as well as its own unique alphanumeric code, called a hash. These cryptographically generated codes can be thought of as a digital fingerprint. They play a role in linking blocks together, as new blocks are generated from the previous block’s hash code, thus creating a chronological sequence, as well as tamper proofing. Any manipulation to these codes outputs an entirely different string of gibberish, making it easy for participants to spot and reject misfit blocks.
Another key feature to the inner workings of blockchain is decentralization. In lieu of a centralized entity, blockchains distribute control across a peer-to-peer network made up of interconnected computers, or nodes . These nodes are in constant communication with one another, keeping the digital ledger up-to-date. So when a transaction is taking place among two peers, all nodes take part in validating the transaction using consensus mechanisms . These built-in protocols keep all in-network nodes in agreement on a single data set. No blocks can be added to the blockchain until it is verified and has reached consensus. Luckily, this step has been sped up with the advent of smart contracts , which are self-executing programs coded into a blockchain that automate the verification process.
Once a transaction is recorded, it’s considered permanent. Blockchains are one-way operations in that there are no reversible actions. This immutability is part of creating transparency across the network and a trustworthy record of all activities on the blockchain.
Blockchain Decentralization
One of the most important concepts in blockchain technology is decentralization. No one computer or organization can own the chain. Instead, it is a distributed ledger via the nodes connected to the chain. Blockchain nodes can be any kind of electronic device that maintains copies of the chain and keeps the network functioning.
Every node has its own copy of the blockchain and the network must algorithmically approve any newly mined block for the chain to be updated, trusted and verified. Since blockchains are transparent, every action in the ledger can be easily checked and viewed, creating inherent blockchain security. Each participant is given a unique alphanumeric identification number that shows their transactions.
Combining public information with a system of checks-and-balances helps the blockchain maintain integrity and creates trust among users. Essentially, blockchains can be thought of as the scalability of trust via technology.

Benefits of Blockchain
Having a cryptographically secure permanent record comes with perks:
More Security
Cryptography and hashing algorithms ensure that only authorized users are able to unlock information meant for them, and that the data stored on the blockchain cannot be manipulated in any form. Consensus mechanisms, such as proof of work or proof of stake , further enhance security by requiring network participants to agree on the validity of transactions before they are added to the blockchain. Additionally, blockchains operate on a distributed system, where data is stored across multiple nodes rather than one central location — reducing the risk of a single point of failure.
Improved Accuracy
By providing a fully transparent, single-source-of-truth ledger, where transactions are recorded in a chronological and immutable manner, the potential for error or discrepancy drops when compared to centralized databases or manual record-keeping processes. Transactions are objectively authorized by a consensus algorithm and, unless a blockchain is made private, all transactions can be independently verified by users.
Higher Efficiency
Aside from saving paper, blockchain enables reliable cross-team communication, reduces bottlenecks and errors while streamlining overall operations. By eliminating intermediaries and automating verification processes — done via smart contracts — blockchain enjoys reduced transaction costs, timely processing times and optimized data integrity.
Challenges of Blockchain
Although this emerging technology may be tamper proof, it isn’t faultless. Below are some of the biggest obstacles blockchain faces today.
Transaction Limitations
As blockchain networks grow in popularity and usage, they face bottlenecks in processing transactions quickly and cost-effectively. This limitation hampers the widespread adoption of blockchain for mainstream applications, as networks struggle to handle high throughput volumes, leading to congestion and increased transaction fees.
Energy Consumption
The computational power required for certain functions — like Bitcoin ’s proof-of-work consensus mechanism — consumes vast amounts of electricity, raising concerns around environmental impact and high operating costs. Addressing this challenge requires exploring alternative consensus mechanisms, such as proof of stake, which consume significantly less energy while maintaining network security and decentralization.
Scalability Issues
As it is now, every node of a blockchain network stores a copy of the entire data chain and processes every transaction. This requires a certain level of computational power, resulting in slow, congested networks and lagged processing times especially during high-traffic periods. Scalability issues arise due to limitations in block size, block processing times and resource-intensive consensus mechanisms. This is why novel approaches — such as layer 2 scaling solutions, sharding and alternative consensus algorithms — are being developed.
Regulation Concerns
Governments and regulators are still working to make sense of blockchain — more specifically, how certain laws should be updated to properly address decentralization. While some governments are actively spearheading its adoption and others elect to wait-and-see, lingering regulatory and legal concerns hinder blockchain’s market appeal, stalling its technical development.
Blockchain Applications and Use Cases
Blockchain originally started out as a way to safeguard digital records with tamper-proof technology. Since its induction into the mainstream alongside Bitcoin’s debut, the data management protocol has expanded beyond DeFi into its various industries across a wide-range of applications .
For banks, blockchain makes it easier to trade currencies, secure loans and process payments. This tech acts as a single-layer, source-of-truth that’s designed to track every transaction ever made by its users. This immutability protects against fraud in banking, leading to faster settlement times, and provides a built-in monitor for money laundering. Banks also benefit from faster cross-border transactions at reduced costs and high-security data encryption.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing protocols that automate transaction verification. They’re coded into the blockchain and set by predetermined terms. In addition to reducing human error, their function is to facilitate decentralization and create a trustless environment by replacing third-party intermediaries.
Cybersecurity
Deemed a “ new weapon in cybersecurity ,” blockchain’s decentralized, tamper-proof ledger comes with built-in defenses against theft, fraud and unauthorized users via cryptographic coding and consensus mechanisms. Because of this, blockchain has been adopted into cybersecurity arsenals to maintain cryptocurrency, secure bank assets, protect patient health records, fortify IoT devices and even safeguard military and defense data.
Healthcare services primarily use blockchain to securely encrypt patient data stored in their medical records. Particular functions, like smart contracts, automate processes such as insurance claims processing and medication adherence monitoring, which enhances efficiency and reduces administrative overhead. Blockchain also facilitates secure sharing of medical data between healthcare providers, patients and researchers, and is even being recruited by genome-sequencing startups to help crack the genetic code .
In logistics , blockchain acts as a track-and-trace tool that follows the movement of goods through the supply chain. The transparent system offers users real-time visibility of their shipments, from manufacturing to delivery. These insights help compile data, determine faster routes, remove unnecessary middlemen and even defend against cyberattack interference.
Blockchain makes the creation, ownership and trading of NFTs , or non-fungible tokens, possible. The reason why copying these digital assets is not as simple as a quick screen capture is because each NFT is encrypted with blockchain technology, which keeps a live running record of ownership over the piece. Smart contracts govern transactions, assigning and reassigning ownership and delivering royalties to artists as pieces move from wallet to wallet.
Types of Blockchain
As blockchain technology evolves, new variations have surfaced. This section provides a brief introduction to four different models that have developed by demand.
Public Blockchain
Public blockchains are permissionless networks considered to be “fully decentralized.” No one organization or individual controls the distributed ledger, and its users can remain anonymous. As long as a user can provide proof of work, they can participate in the network.
Private Blockchain
Private blockchains are permissioned networks. In the interest of garnering greater control or privacy over a network, private blockchains have a single operator that’s in charge of who can access the network and whether participants can view, verify or create data on the blockchain.
Adding restricted access to an encrypted record-keeping ledger appeals to certain organizations that work with sensitive information, like large enterprises or government agencies.
Consortium Blockchain
Consortium blockchains, also known as federated blockchains, are permissioned networks that are operated by a select group. Multiple users have the power to set the rules, edit or cancel transactions. With shared authority, the blockchain may enjoy a higher rate of efficiency and privacy.
Hybrid Blockchain
Hybrid blockchains combine elements of both public and private networks. They feature selective transparency, which allows blockchain admins to restrict specific parts of the blockchain to certain participant pools while maintaining public visibility over the rest of the thread. This way, organizations are entitled to a certain level of privacy when immutably sharing data independent of a third party.

History of Blockchain
Blockchain’s origin is widely credited to cryptography David Chaum, who first proposed a blockchain-like protocol among a decentralized node network in a 1982 dissertation. Its first traces, however, go all the way back to the 1970s, when computer scientist Ralph Merkle patented Hash trees , also known as Merkle trees, that makes cryptographic linking between blocks of stored data possible.
These theories would come together in 1991, with the launch of the first-ever blockchain product. In an effort to create tamper-proof records in a digital era, scientist Stuart Haber and cryptographer Scott Stornetta developed a computational solution that would time-stamp documents using hash function in a chronological chain of digital certificates. Thanks to the help of mathematician David Bayer, Merkle trees were incorporated into the design the following year, so that data could be consolidated into one block — similar to what we know blockchain’s functionality to be like today.
Then, in 2009, Bitcoin — the world’s first cryptocurrency — debuted. Launched under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto , the peer-to-peer electronic cash system not only established a digital alternative to fiat currency, it also introduced the concept of a public, decentralized blockchain that drops third party intervention. This project was largely responsible for introducing blockchain into our everyday vernacular, and wasn’t rivaled until 2015, with the launch of the Ethereum platform . Its creator, Vitalik Buterin, advances blockchain tech through smart contracts — self-executing programs that automate transaction verification — and decentralized applications, or DApps, that enable developers to partake in Web3 by building their own applications.
And while blockchain is near-synonymous with Web3 and cryptocurrency, the distributed ledger technology has found its way into a number of industries — from easing logistics bottlenecks to providing transparent patient care — in the two decades since its initial real-world application.
Blockchain Timeline
(2008) Satoshi Nakamoto, a pseudonym for a person or group, publishes “ Bitcoin: A Peer to Peer Electronic Cash System .”
(2009) The first successful Bitcoin (BTC) transaction occurs between computer scientist Hal Finney and the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto.
(2010) Florida-based programmer Laszlo Hanycez completes the first ever purchase using Bitcoin — two Papa John’s pizzas.
(2011) 1 BTC = 1 USD, giving the cryptocurrency parity with the US dollar.
(2011) Electronic Frontier Foundation, Wikileaks and other organizations start accepting Bitcoin as donations.
2013) BTC market cap surpasses $1 billion, and Bitcoin reaches $100/BTC.
(2013) Buterin publishes the “ Ethereum Project ” paper, suggesting that blockchain has other possibilities besides Bitcoin (like smart contracts).
(2014) The first-known NFT is minted.
2015 ) Number of merchants accepting BTC exceeds 100,000.
(2015) NASDAQ and San-Francisco blockchain company Chain team up to test the technology for trading shares in private companies.
(2016) Tech giant IBM announces a blockchain strategy for cloud-based business solutions.
(2017) Bitcoin reaches $1,000/BTC.
(2017) Cryptocurrency market cap reaches $150 billion.
(2018) IBM develops a blockchain-based banking platform with large banks like Citi and Barclays signing on.
(2019) China’s President Ji Xinping publicly embraces blockchain as China’s central bank announces it is working on its own cryptocurrency.
(2019) The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) announces the creation of Bakkt, a digital wallet company that includes crypto trading.
(2020 ) BTC almost reaches $30,000 by the end of 2020.
(2020) PayPal announces it will allow users to buy, sell and hold cryptocurrencies.
(2020) The Bahamas becomes the world’s first country to launch its central bank digital currency.
(2021) Bitcoin surpasses $1 trillion in market value.
(2021) Popularity for the implementation of Web3 rises.
(2022) Cryptocurrency loses $2 trillion in market value, due to economic inflation and rising interest rates.
(2022) The U.K. government proposes safeguards for stablecoin holders.
46 Blockchain Companies Paving the Way for the Future
We've rounded up 37 interesting examples of US-based companies using blockchain.

Where to Buy NFTs: 20 Marketplaces and What They Sell
4 lessons from the crypto winter.

5 Companies Hiring Blockchain Developers

How Tech Is Shaping the Future of E-Commerce

What the FTX Trial Means for the Future of Cryptocurrency

Is Generative AI the New Metaverse?
Bitcoin for all: how cash app is redefining the world’s relationship with money.

Here’s How Non-Tech Founders Build High-Tech Startups Without Going Broke

10 Small Business Tech Trends Defining 2023

What Is Bitcoin Cash?

What Is a Rug Pull, Exactly?

Why Tech Needs to Focus on Delivering a Future of Sustainable Abundance
Great companies need great people. that's where we come in..
Browse Course Material
Course info.
- Prof. Gary Gensler
Departments
- Sloan School of Management
As Taught In
- Information Technology
- Algorithms and Data Structures
- Computer Networks
- Cryptography
Learning Resource Types
Blockchain and money, lecture slides.

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
- Cryptocurrency
Blockchain Facts: What Is It, How It Works, and How It Can Be Used
Learn what these digital public ledgers are capable of
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Blockchain?
How does a blockchain work, blockchain decentralization, blockchain transparency, is blockchain secure, bitcoin vs. blockchain, blockchain vs. banks, how are blockchains used, pros and cons of blockchain, benefits of blockchains, drawbacks of blockchains, the bottom line.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A blockchain is a distributed database or ledger shared among a computer network 's nodes. They are best known for their crucial role in cryptocurrency systems for maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions, but they are not limited to cryptocurrency uses. Blockchains can be used to make data in any industry immutable—the term used to describe the inability to be altered.
Because there is no way to change a block, the only trust needed is at the point where a user or program enters data. This aspect reduces the need for trusted third parties, which are usually auditors or other humans that add costs and make mistakes.
Since Bitcoin's introduction in 2009, blockchain uses have exploded via the creation of various cryptocurrencies, decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and smart contracts.
Key Takeaways
- Blockchain is a type of shared database that differs from a typical database in the way it stores information; blockchains store data in blocks linked together via cryptography.
- Different types of information can be stored on a blockchain, but the most common use for transactions has been as a ledger.
- In Bitcoin’s case, blockchain is decentralized so that no single person or group has control—instead, all users collectively retain control.
- Decentralized blockchains are immutable, which means that the data entered is irreversible. For Bitcoin, transactions are permanently recorded and viewable to anyone.
Investopedia / Xiaojie Liu
You might be familiar with spreadsheets or databases. A blockchain is somewhat similar because it is a database where information is entered and stored. But the key difference between a traditional database or spreadsheet and a blockchain is how the data is structured and accessed.
A blockchain consists of programs called scripts that conduct the tasks you usually would in a database: Entering and accessing information and saving and storing it somewhere . A blockchain is distributed, which means multiple copies are saved on many machines, and they must all match for it to be valid.
The blockchain collects transaction information and enters it into a block , like a cell in a spreadsheet containing information. Once it is full, the information is run through an encryption algorithm, which creates a hexadecimal number called the hash.
The hash is then entered into the following block header and encrypted with the other information in the block. This creates a series of blocks that are chained together.
Transaction Process
Transactions follow a specific process, depending on the blockchain they are taking place on. For example, on Bitcoin's blockchain, if you initiate a transaction using your cryptocurrency wallet—the application that provides an interface for the blockchain—it starts a sequence of events.
In Bitcoin, your transaction is sent to a memory pool, where it is stored and queued until a miner or validator picks it up. Once it is entered into a block and the block fills up with transactions, it is closed and encrypted using an encryption algorithm. Then, the mining begins.
The entire network works simultaneously, trying to "solve" the hash. Each one generates a random hash except for the "nonce," short for number used once.
Every miner starts with a nonce of zero, which is appended to their randomly-generated hash. If that number isn't equal to or less than the target hash, a value of one is added to the nonce, and a new block hash is generated. This continues until a miner generates a valid hash, winning the race and receiving the reward.
Generating random hashes until a specific value is found is the "proof-of-work" you hear so much about—it "proves" the miner did the work. The amount of work it takes to validate the hash is why the Bitcoin network consumes so much computational power and energy.
Once a block is closed, a transaction is complete. However, the block is not considered to be confirmed until five other blocks have been validated. Confirmation takes the network about one hour to complete because it averages just under 10 minutes per block (the first block with your transaction and five following blocks multiplied by 10 equals about 60 minutes).
Not all blockchains follow this process. For instance, the Ethereum network randomly chooses one validator from all users with ether staked to validate blocks, which are then confirmed by the network. This is much faster and less energy intensive than Bitcoin's process.
A blockchain allows the data in a database to be spread out among several network nodes—computers or devices running software for the blockchain—at various locations. This not only creates redundancy but maintains the fidelity of the data. For example, if someone tries to alter a record at one instance of the database, the other nodes would prevent it from happening. This way, no single node within the network can alter information held within it.
Because of this distribution—and the encrypted proof that work was done—the information and history (like the transactions in cryptocurrency) are irreversible. Such a record could be a list of transactions (such as with a cryptocurrency), but it also is possible for a blockchain to hold a variety of other information like legal contracts, state identifications, or a company’s inventory.
Because of the decentralized nature of the Bitcoin blockchain, all transactions can be transparently viewed by either having a personal node or using blockchain explorers that allow anyone to see transactions occurring live. Each node has its own copy of the chain that gets updated as fresh blocks are confirmed and added. This means that if you wanted to, you could track a bitcoin wherever it goes.
For example, exchanges have been hacked in the past, resulting in the loss of large amounts of cryptocurrency. While the hackers may have been anonymous—except for their wallet address—the crypto they extracted are easily traceable because the wallet addresses are published on the blockchain.
Of course, the records stored in the Bitcoin blockchain (as well as most others) are encrypted. This means that only the person assigned an address can reveal their identity. As a result, blockchain users can remain anonymous while preserving transparency.
Blockchain technology achieves decentralized security and trust in several ways. To begin with, new blocks are always stored linearly and chronologically. That is, they are always added to the “end” of the blockchain. After a block has been added to the end of the blockchain, previous blocks cannot be changed.
A change in any data changes the hash of the block it was in. Because each block contains the previous block's hash, a change in one would change the following blocks. The network would reject an altered block because the hashes would not match.
Not all blockchains are 100% impenetrable. They are distributed ledgers that use code to create the security level they have become known for. If there are vulnerabilities in the coding, they can be exploited.
For instance, imagine that a hacker runs a node on a blockchain network and wants to alter a blockchain and steal cryptocurrency from everyone else. If they were to change their copy, they would have to convince the other nodes that their copy was the valid one.
They would need to control a majority of the network to do this and insert it at just the right moment. This is known as a 51% attack because you need to control more than 50% of the network to attempt it.
Timing would be everything in this type of attack—by the time the hacker takes any action, the network is likely to have moved past the blocks they were trying to alter. This is because the rate at which these networks hash is exceptionally fast—the Bitcoin network hashed at 348.1 exahashes per second (18 zeros) on April 21, 2023.
Blockchain technology was first outlined in 1991 by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta, two researchers who wanted to implement a system where document timestamps could not be tampered with. But it wasn’t until almost two decades later, with the launch of Bitcoin in January 2009, that blockchain had its first real-world application .
The Bitcoin protocol is built on a blockchain. In a research paper introducing the digital currency, Bitcoin’s pseudonymous creator, Satoshi Nakamoto , referred to it as “a new electronic cash system that’s fully peer-to-peer, with no trusted third party.”
The key thing to understand is that Bitcoin uses blockchain as a means to transparently record a ledger of payments or other transactions between parties.
Blockchain can be used to immutably record any number of data points. This could be in the form of transactions, votes in an election, product inventories, state identifications, deeds to homes, and much more.
Currently, tens of thousands of projects are looking to implement blockchains in various ways to help society other than just recording transactions—for example, as a way to vote securely in democratic elections.
The nature of blockchain’s immutability means that fraudulent voting would become far more difficult. For example, a voting system could work such that each country's citizens would be issued a single cryptocurrency or token.
Each candidate would then be given a specific wallet address, and the voters would send their token or crypto to the address of whichever candidate for whom they wish to vote. The transparent and traceable nature of blockchain would eliminate the need for human vote counting and the ability of bad actors to tamper with physical ballots.
Blockchains have been heralded as a disruptive force in the finance sector, especially with the functions of payments and banking. However, banks and decentralized blockchains are vastly different.
To see how a bank differs from blockchain, let’s compare the banking system to Bitcoin’s blockchain implementation.
As we now know, blocks on Bitcoin’s blockchain store transactional data. Today, more than 23,000 other cryptocurrency systems are running on a blockchain. But it turns out that blockchain is a reliable way of storing data about other types of transactions.
Some companies experimenting with blockchain include Walmart, Pfizer, AIG, Siemens, and Unilever, among others. For example, IBM has created its Food Trust blockchain to trace the journey that food products take to get to their locations.
Why do this? The food industry has seen countless outbreaks of E. coli, salmonella, and listeria; in some cases, hazardous materials were accidentally introduced to foods. In the past, it has taken weeks to find the source of these outbreaks or the cause of sickness from what people are eating.
Using blockchain allows brands to track a food product’s route from its origin, through each stop it makes, to delivery. Not only that, but these companies can also now see everything else it may have come in contact with, allowing the identification of the problem to occur far sooner—potentially saving lives. This is one example of blockchain in practice, but many other forms of blockchain implementation exist.
Banking and Finance
Perhaps no industry stands to benefit from integrating blockchain into its business operations more than banking. Financial institutions only operate during business hours, usually five days a week. That means if you try to deposit a check on Friday at 6 p.m., you will likely have to wait until Monday morning to see that money hit your account.
Even if you make your deposit during business hours, the transaction can still take one to three days to verify due to the sheer volume of transactions that banks need to settle. Blockchain, on the other hand, never sleeps.
By integrating blockchain into banks, consumers might see their transactions processed in minutes or seconds—the time it takes to add a block to the blockchain, regardless of holidays or the time of day or week. With blockchain, banks also have the opportunity to exchange funds between institutions more quickly and securely. Given the size of the sums involved, even the few days the money is in transit can carry significant costs and risks for banks.
The settlement and clearing process for stock traders can take up to three days (or longer if trading internationally), meaning that the money and shares are frozen for that period. Blockchain could drastically reduce that time.
Blockchain forms the bedrock for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. The U.S. dollar is controlled by the Federal Reserve. Under this central authority system, a user’s data and currency are technically at the whim of their bank or government. If a user’s bank is hacked, the client’s private information is at risk.
If the client’s bank collapses or the client lives in a country with an unstable government , the value of their currency may be at risk. In 2008, several failing banks were bailed out—partially using taxpayer money. These are the worries out of which Bitcoin was first conceived and developed.
Blockchain can also give those in countries with unstable currencies or financial infrastructures a more stable currency and financial system. They would have access to more applications and a wider network of individuals and institutions with whom they can do domestic and international business.
By spreading its operations across a network of computers, blockchain allows Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies to operate without the need for a central authority. This not only reduces risk but also the processing and transaction fees.
Using cryptocurrency wallets for savings accounts or as a means of payment is especially profound for those without state identification. Some countries may be war-torn or have governments lacking any real identification infrastructure. Citizens of such countries may not have access to savings or brokerage accounts—and, therefore, no way to safely store wealth.
Healthcare providers can leverage blockchain to store their patients’ medical records securely. When a medical record is generated and signed, it can be written into the blockchain, which provides patients with the proof and confidence that the record cannot be changed. These personal health records could be encoded and stored on the blockchain with a private key so that they are only accessible to specific individuals, thereby ensuring privacy.
Property Records
If you have ever spent time in your local Recorder’s Office, you will know that recording property rights is both burdensome and inefficient. Today, a physical deed must be delivered to a government employee at the local recording office, where it is manually entered into the county’s central database and public index. In the case of a property dispute, claims to the property must be reconciled with the public index.
This process is not just costly and time-consuming, it is also prone to human error, where each inaccuracy makes tracking property ownership less efficient. Blockchain has the potential to eliminate the need for scanning documents and tracking down physical files in a local recording office. If property ownership is stored and verified on the blockchain, owners can trust that their deed is accurate and permanently recorded.
In war-torn countries or areas with little to no government or financial infrastructure and no Recorder’s Office, proving property ownership can be nearly impossible. If a group of people living in such an area can leverage blockchain, then transparent and clear timelines of property ownership could be established.
Smart Contracts
A smart contract is a computer code that can be built into the blockchain to facilitate a contract agreement. Smart contracts operate under a set of conditions to which users agree. When those conditions are met, the terms of the agreement are automatically carried out.
Say, for example, that a potential tenant would like to lease an apartment using a smart contract. The landlord agrees to give the tenant the door code to the apartment as soon as the tenant pays the security deposit. The smart contract would automatically send the door code to the tenant when it was paid. It could also be programmed to change the code if rent wasn't paid or other conditions were met.
Supply Chains
As in the IBM Food Trust example, suppliers can use blockchain to record the origins of materials that they have purchased. This would allow companies to verify the authenticity of not only their products but also common labels such as “Organic,” “Local,” and “Fair Trade.”
As reported by Forbes, the food industry is increasingly adopting the use of blockchain to track the path and safety of food throughout the farm-to-user journey.
As mentioned above, blockchain could facilitate a modern voting system. Voting with blockchain carries the potential to eliminate election fraud and boost voter turnout, as was tested in the November 2018 midterm elections in West Virginia.
Using blockchain in this way would make votes nearly impossible to tamper with. The blockchain protocol would also maintain transparency in the electoral process, reducing the personnel needed to conduct an election and providing officials with nearly instant results. This would eliminate the need for recounts or any real concern that fraud might threaten the election.
For all of its complexity, blockchain’s potential as a decentralized form of record-keeping is almost without limit. From greater user privacy and heightened security to lower processing fees and fewer errors, blockchain technology may very well see applications beyond those outlined above. But there are also some disadvantages.
Improved accuracy by removing human involvement in verification
Cost reductions by eliminating third-party verification
Decentralization makes it harder to tamper with
Transactions are secure, private, and efficient
Transparent technology
Provides a banking alternative and a way to secure personal information for citizens of countries with unstable or underdeveloped governments
Significant technology cost associated with some blockchains
Low transactions per second
History of use in illicit activities, such as on the dark web
Regulation varies by jurisdiction and remains uncertain
Data storage limitations
Accuracy of the Chain
Transactions on the blockchain network are approved by thousands of computers and devices. This removes almost all people from the verification process, resulting in less human error and an accurate record of information. Even if a computer on the network were to make a computational mistake, the error would only be made to one copy of the blockchain and not be accepted by the rest of the network.
Cost Reductions
Typically, consumers pay a bank to verify a transaction or a notary to sign a document. Blockchain eliminates the need for third-party verification—and, with it, their associated costs. For example, business owners incur a small fee when they accept credit card payments because banks and payment-processing companies have to process those transactions. Bitcoin, on the other hand, does not have a central authority and has limited transaction fees.
Decentralization
Blockchain does not store any of its information in a central location. Instead, the blockchain is copied and spread across a network of computers. Whenever a new block is added to the blockchain, every computer on the network updates its blockchain to reflect the change.
By spreading that information across a network, rather than storing it in one central database, blockchain becomes more difficult to tamper with.
Efficient Transactions
Transactions placed through a central authority can take up to a few days to settle. If you attempt to deposit a check on Friday evening, for example, you may not actually see funds in your account until Monday morning. Financial institutions operate during business hours, usually five days a week—but a blockchain works 24 hours a day, seven days a week, and 365 days a year.
On some blockchains, transactions can be completed in minutes and considered secure after just a few. This is particularly useful for cross-border trades, which usually take much longer because of time zone issues and the fact that all parties must confirm payment processing.
Private Transactions
Many blockchain networks operate as public databases, meaning anyone with an internet connection can view a list of the network’s transaction history. Although users can access transaction details, they cannot access identifying information about the users making those transactions. It is a common misperception that blockchain networks like Bitcoin are fully anonymous; they are actually pseudonymous because there is a viewable address that can be associated with a user if the information gets out.
Secure Transactions
Once a transaction is recorded, its authenticity must be verified by the blockchain network. After the transaction is validated, it is added to the blockchain block. Each block on the blockchain contains its unique hash and the unique hash of the block before it. Therefore, the blocks cannot be altered once the network confirms them.
Transparency
Most blockchains are entirely open-source software. This means that everyone can view its code. This gives auditors the ability to review cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin for security. However, it also means there is no real authority on who controls Bitcoin’s code or how it is edited. Because of this, anyone can suggest changes or upgrades to the system. If a majority of the network users agree that the new version of the code with the upgrade is sound and worthwhile, then Bitcoin can be updated.
Banking the Unbanked
Perhaps the most profound facet of blockchain and cryptocurrency is the ability for anyone, regardless of ethnicity, gender, location, or cultural background to use it. According to The World Bank, an estimated 1.3 billion adults do not have bank accounts or any means of storing their money or wealth. Moreover, nearly all of these individuals live in developing countries where the economy is in its infancy and entirely dependent on cash.
These people are often paid in physical cash. They then need to store this physical cash in hidden locations in their homes or other places, incentivizing robbers or violence. While not impossible to steal, crypto makes it more difficult for would-be thieves.
Blockchains of the future are also looking for solutions to not only be a unit of account for wealth storage but also to store medical records, property rights, and a variety of other legal contracts.
Technology Cost
Although blockchain can save users money on transaction fees, the technology is far from free. For example, the Bitcoin network's proof-of-work system to validate transactions consumes vast amounts of computational power. In the real world, the energy consumed by the millions of devices on the Bitcoin network is more than Pakistan consumes annually.
Some solutions to these issues are beginning to arise. For example, bitcoin-mining farms have been set up to use solar power, excess natural gas from fracking sites, or energy from wind farms.
Speed and Data Inefficiency
Bitcoin is a perfect case study for the possible inefficiencies of blockchain. Bitcoin’s PoW system takes about 10 minutes to add a new block to the blockchain. At that rate, it’s estimated that the blockchain network can only manage about three transactions per second (TPS). Although other cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum, perform better than Bitcoin, blockchain still limits them. Legacy brand Visa, for context, can process 65,000 TPS.
Solutions to this issue have been in development for years. There are currently blockchains that boast more than 30,000 TPS. Ethereum's merge between its main net and beacon chain (Sep. 15, 2022) is predicted to allow up to 100,000 TPS after it rolls out a series of upgrades that include sharding—a splitting of the database so that more devices (phones, tablets, and laptops) can run Ethereum. This is expected to increase network participation, reduce congestion, and increase transaction speeds.
The other issue is that each block can only hold so much data. The block size debate has been and continues to be one of the most pressing issues for the scalability of blockchains going forward.
Illegal Activity
While confidentiality on the blockchain network protects users from hacks and preserves privacy, it also allows for illegal trading and activity on the blockchain network. The most cited example of blockchain being used for illicit transactions is probably the Silk Road , an online dark web illegal-drug and money laundering marketplace operating from February 2011 until October 2013, when the FBI shut it down.
The dark web allows users to buy and sell illegal goods without being tracked by using the Tor Browser and make illicit purchases in Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies. This is in stark contrast to U.S. regulations, which require financial service providers to obtain information about their customers when they open an account. They are supposed to verify the identity of each customer and confirm that they do not appear on any list of known or suspected terrorist organizations.
Illicit activity accounted for only 0.24% of all cryptocurrency transactions in 2022.
This system can be seen as both a pro and a con. It gives anyone access to financial accounts, but allows criminals to transact more easily. Many have argued that the good uses of crypto, like banking the unbanked world, outweigh the bad uses of cryptocurrency, especially when most illegal activity is still accomplished through untraceable cash.
Many in the crypto space have expressed concerns about government regulation over cryptocurrencies. While it is getting increasingly difficult and near impossible to end something like Bitcoin as its decentralized network grows, governments could theoretically make it illegal to own cryptocurrencies or participate in their networks.
This concern has grown smaller over time as large companies like PayPal begin to allow customers to use cryptocurrencies on their e-commerce platforms.

What Is a Blockchain in Simple Terms?
Simply put, a blockchain is a shared database or ledger. Pieces of data are stored in data structures known as blocks, and each network node has a replica of the entire database. Security is ensured since the majority will not accept this change if somebody tries to edit or delete an entry in one copy of the ledger.
How Many Blockchains Are There?
The number of live blockchains is growing every day at an ever-increasing pace. As of 2023, there are more than 23,000 active cryptocurrencies based on blockchain, with several hundred more non-cryptocurrency blockchains.
What’s the Difference Between a Private Blockchain and a Public Blockchain?
A public blockchain, also known as an open or permissionless blockchain, is one where anybody can join the network freely and establish a node. Because of their open nature, these blockchains must be secured with cryptography and a consensus system like proof of work (PoW). A private or permissioned blockchain, on the other hand, requires each node to be approved before joining. Because nodes are considered to be trusted, the layers of security do not need to be as robust.
With many practical applications for the technology already being implemented and explored, blockchain is finally making a name for itself in no small part because of Bitcoin and cryptocurrency. As a buzzword on the tongue of every investor in the nation, blockchain stands to make business and government operations more accurate, efficient, secure, and cheap, with fewer middlemen.
As we head into the third decade of blockchain, it’s no longer a question of if legacy companies will catch on to the technology—it’s a question of when. Today, we see a proliferation of NFTs and the tokenization of assets. As a result, the next decades will prove to be a significant period of growth for blockchain.
The comments, opinions, and analyses expressed on Investopedia are for informational purposes online. Read our warranty and liability disclaimer for more info. As of the date this article was written, the author does not own any of the assets discussed here.
Blockchain.com. " Total Hash Rate | Bitcoin ."
Coinbase. " What Is Bitcoin? "
Bitcoin. “ Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System ,” Page 1.
IBM. “ IBM Food Trust .”
Forbes. " 3 Innovative Ways Blockchain Will Build Trust in the Food Industry ."
West Virginia.gov. " Under the Hood: The West Virginia Mobile Voting Pilot ."
The World Bank. " Universal Financial Access 2020 ."
University of Cambridge. " Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index ."
Blockchain.com. " Transaction Rate Per Second | Bitcoin ."
Visa. " Visa Fact Sheet ," Page 1.
Nasdaq. " 6 Top Cryptocurrencies With Smart Contracts ."
Ethereum.org. " Sharding ."
FBI. “ Ross Ulbricht, the Creator and Owner of the Silk Road Website, Found Guilty in Manhattan Federal Court on All Counts .”
Financial Crimes Enforcement Network. " FAQs: Final CIP Rule ," Pages 1, 8.
Chainalysis. " The 2023 Crypto Crime Report ."
CoinMarketCap. " Today's Cryptocurrency Prices by Market Cap ."
- Blockchain Facts: What Is It, How It Works, and How It Can Be Used 1 of 19
- Forget Bitcoin: Blockchain is the Future 2 of 19
- Top 5 Books to Learn About Blockchain 3 of 19
- Blockchain Technology's Three Generations 4 of 19
- Blockchain: One of History's Greatest Inventions? 5 of 19
- How Blockchain is Revolutionizing Content Distribution 6 of 19
- How Blockchain Technology is Changing Real Estate 7 of 19
- 5 Companies Using Blockchain to Change Travel 8 of 19
- Blockchain Is a Game-Changer for Online Advertising 9 of 19
- How Blockchain Is Changing the Energy Industry 10 of 19
- How Health Care Is Moving Toward Blockchain 11 of 19
- How Blockchain Can Help Emerging Economies 12 of 19
- The Blockchain Job Market Is Booming 13 of 19
- Can Blockchain Solve the Global Retirement Crisis? 14 of 19
- How Blockchain Can Protect the Global Economy 15 of 19
- Does Blockchain's Popularity Mean The End Of SWIFT? 16 of 19
- Blockchain Technology Could Revolutionize Traditional Banking 17 of 19
- Banks Claim They're Building Blockchains. They're Not 18 of 19
- What Are the World Bank's Blockchain-Based Bonds? 19 of 19
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/bitcoin-4a77cbed13064596b35f46d2861ab187.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Tutorial Playlist
Blockchain tutorial for beginners.
What is Blockchain Technology? How Does It Work?
What is Blockchain? Features and Use Cases
Why is blockchain important and why does it matter, what is cryptocurrency: types, benefits, history and more, what is blockchain wallet and how does it work, what is ethereum understanding its features and applications.
Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Which One is Better?
Understanding the Fundamentals of Ethereum Mining
What is a smart contract in blockchain, what is dogecoin understanding the crypto-star, dogecoin vs. bitcoin : understanding the world of cryptocurrency.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Dogecoin Mining
A Look Into the Digital Dogecoin Wallet
9 industries that blockchain will disrupt in future, emerging blockchain applications across industries, how to become a blockchain developer a step-by-step guide [updated], the ultimate guide to understand what is nft, the complete guide on solidity programming, the future of shiba inu coin and why invest in it, understanding the fundamentals of ethereum classic, understanding the fundamentals of merkle tree in blockchain, what is cardano: the complete guide of its concepts, what is matic network: exploring the concepts of matic, top 30 blockchain interview questions and answers for 2024, what is tether the ultimate guide, a comprehensive comparison of nft vs. crypto, what is web 3.0 everything you need to know about web 3.0, the complete guide for types of blockchain, what is defi: a new era of digital finance, the complete guide to understand ‘what is ripple’, the complete guide to understand the foundation of what binance is, what is dao: a brief introduction to a new era of technology, a complete guide to understand what stablecoin is, what is blockchain everything you need to know.
Lesson 2 of 33 By Rahul Venugopal

Table of Contents
With close to 3,000 different cryptocurrencies in the market right now, it’s clear that despite their volatile nature, they are here to stay. But did you know almost all cryptocurrencies were born from the same concept?
Nearly all cryptocurrencies are based on blockchain technology. Also referred to as the shared ledger, given its distributed nature, blockchain is considered one of the most secure digital technologies.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a list of records called blocks that store data publicly and in chronological order. The information is encrypted using cryptography to ensure that the privacy of the user is not compromised and data cannot be altered.
Basics to Advanced - Learn It All!
Information on a Blockchain network is not controlled by a centralized authority, unlike modern financial institutions. The participants of the network maintain the data, and they hold the democratic authority to approve any transaction which can happen on a Blockchain network. Therefore, a typical Blockchain network is a public Blockchain.
As long as you have access to the network, you have access to the data within the Blockchain. If you are a participant in the Blockchain network, you will have the same copy of the ledger, which all other participants have. Even if one node or data on one particular participant computer gets corrupted, the other participants will be alerted immediately, and they can rectify it as soon as possible.
To understand the promise of blockchain-enabled cryptocurrencies and their advantages over traditional (fiat) currencies, let’s look at the issues inherent in fiat currency first.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain is a combination of three important technologies - cryptographic keys, a peer-to-peer network, and a digital ledger. The cryptographic keys are of two types - private key and public key. Each individual or node has both of these keys and they are used to create a digital signature.
This digital signature is a unique and secure digital identity reference and the most important aspect of blockchain technology. Every transaction is authorized by the digital signature of the owner.
A deal or transaction is authorized by a mathematical verification in a peer-to-peer network. This peer-to-peer network is a large group of individuals who act as authorities to reach a consensus on transactions, among other things.
All of these transactions are stored in a structure known as the digital ledger. In layman’s terms, the digital ledger works like a spreadsheet containing all the numerous nodes in a network and has the history of all purchases made by each node. The information contained in the digital ledger is highly secure and the digital signature safeguards it from being tampered with. The most interesting part about this ledger is that anyone can see the data, but no one is able to corrupt it.
History of Blockchain
In 1982, David Chaum proposed the first-ever blockchain-like protocol in his dissertation , Computer Systems Established, Maintained, and Trusted by Mutually Suspicious Groups. This concept was further worked on by Stuart Haber and W Scott Stornetta in 1991, where they described the process of a cryptographically secured chain of blocks with timestamps that could not be tampered with.
However, blockchain was first popularized by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. He improved the design using hashcash-like methods to timestamp each block without the need for a central authority or “trusted parties”. These improvements were so innovative and have become the backbone of cryptocurrencies today.
Why Do Transactions Fail?
Imagine two people are making a money transaction. Now, assuming the sender has properly sent the money from his bank, there’s no chance the transaction will fail, right? Actually, there are several things that can go wrong, including:
- Something could have gone wrong at the bank (such as a technical issue)
- The sender’s account could have been hacked
- The transfer limits of the day could have been exceeded
- Debited from one account, never credited on the other side
- Issues with data
However, none of these problems are applicable to cryptocurrencies. First, let’s have a look at what cryptocurrencies are.
What is a Cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency is a form of digital currency that can be used to verify the transfer of assets, control the addition of new units, and secure financial transactions using cryptography.
One of the cryptocurrencies’ most important advantages over normal (fiat) currencies is that they are not controlled by any central authority. Without a central point of failure or a “vault,” the funds cannot be hacked or stolen.
As an analogy, think of the popular Microsoft Excel spreadsheet program. You can make changes to the data on your own that may differ from earlier versions of the spreadsheet that are shared with others. But if you make changes to a Google Sheets document, on the other hand, those changes also show up in every other shared copy. Similarly, the shared and distributed nature of cryptocurrencies keeps everyone on the same page.
Therefore, the transparency and distributed nature of blockchain technology are what make cryptocurrencies (at least those that use the blockchain) secure.
What Are the Types of Cryptocurrencies?
There are several cryptocurrencies available in the market right now. Some of the more popular ones are:
As mentioned earlier, there are close to 3,000 cryptocurrencies in the market—a market that has become nearly saturated with options. Most experts say the vast majority of these options will eventually fail as users begin to coalesce around just a few.
The Bitcoin Story
Bitcoin was introduced in 2009 by someone or a group of people known as Satoshi Nakamoto. It aimed to solve the problem faced by fiat currencies with the help of Blockchain technology. As of 2018, there were more than 1,600 cryptocurrencies that followed the concepts of Bitcoin and Blockchain, including, Ethereum , Litecoin , Dash , and Ripple .
Whenever a sender has made a transaction, he sends Bitcoins to a receiver by submitting the transaction on a public Blockchain network of Bitcoin. The miners around the world do verifications to authenticate users. There are specific participants in the Bitcoin network who are identified as miners, and they verify the authenticity of the sender and the receiver. They also validate whether the sender has enough Bitcoins to send to the receiver and also ensure that the sanity of the underlying Blockchain network to the Bitcoin is not corrupt.
Once the miner has authenticated the transaction and verified all the parameters, the transaction is added to a block, and then that block is made part of the main Blockchain. After this is done, transactions that were associated with the block are executed. Once the transaction is complete, the block is added, and the ledgers across all the nodes are updated, thereby allowing all the participants to have the same copy of the information.
Features of Blockchain
These are the four features of Blockchain which we are going to talk about in detail:
- We have a public distributed ledger, which works using a hashing encryption.
- Every block has a hash value, which is the digital signature of the block.
- All the transactions are approved and verified on the Blockchain network using a proof-of-work consensus algorithm.
- The Blockchain network utilizes the resources of the miners, who are there to validate the transactions for rewards.
Are you interested to learn about Blockchain, Bitcoin, and cryptocurrencies? Check out the Blockchain Certification Training and learn them today.
Public Distributed Ledger
A public distributed ledger is a collection of digital data that is shared, synchronized, and replicated around the world, across multiple sites, countries, and institutions. Now let's consider a blockchain that can be accessed by anyone in the network around the world. If someone tries to alter data in one of the blocks, everyone in the network can see the alteration, because everyone in the network has a copy of the ledger. In this way, data tampering is prevented.
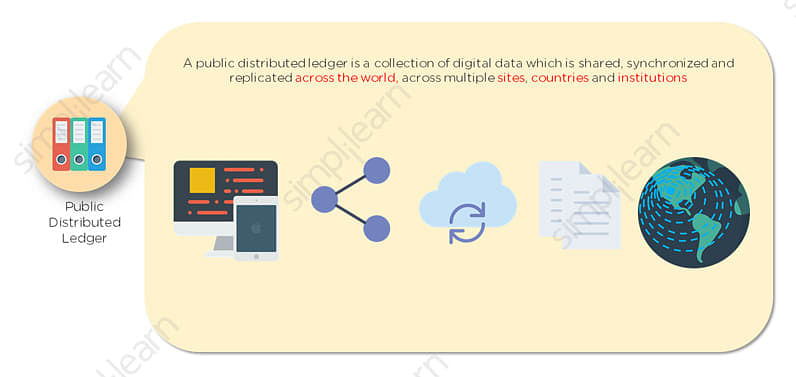
Hash Encryption
Blockchain uses cryptography (see definition of "cryptography" above) to ensure that all the data in the blocks is kept secure from unauthorized access and is not altered. Blockchain uses SHA-256 for encryption. SHA-256 is one of the strongest hash functions available. This cryptographic hash algorithm generates an almost unique 256-bit signature for a text. Blockchain also uses digital signatures to validate users.
Each user has a public and private key. The public key is used to identify the user uniquely, and the private key gives the user access to everything in the account. In the process from the sender's side, the sender's message is passed through a hash function; then, the output is passed through a signature algorithm with the user's private key, then the user's digital signature is obtained. In the transmission, the user's message, digital signature, and public key are transmitted.
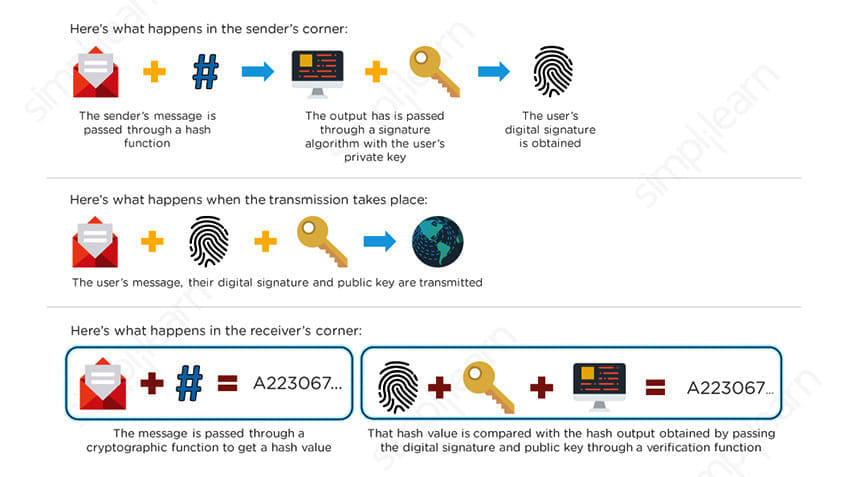
In the process on the receiver's side, the message is passed through a cryptographic function to get a hash value. That hash value is compared with the hash output obtained bypassing the digital signature and public key through a verification function.
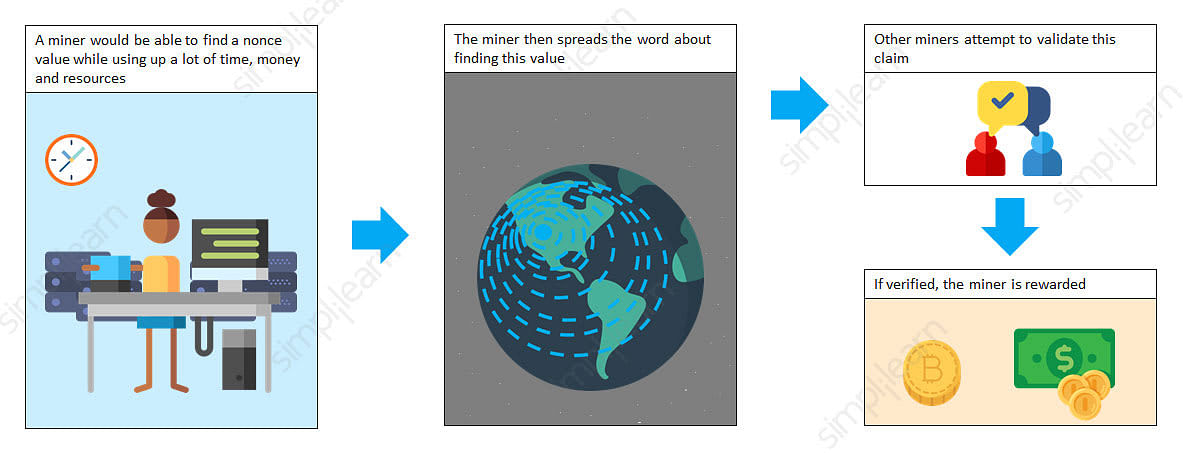
As mentioned, each block in a blockchain uses SHA-256 to encrypt and therefore secure the data. Every block has four fields:
- Previous hash—this field stores the hash of the previous block in the Blockchain
- Transaction details—this field contains information regarding several transactions
- Nonce—this field contains a random value (the nonce value) whose sole purpose is to act as a variate for the hash value
- Hash address—this field contains the unique identification of the block; it is a hex value of 64 characters, both letters, and numbers, obtained by using the SHA-256 algorithm
The first three values (previous hash, transaction details, and nonce) are passed through a hashing function to produce the fourth value, the hash address of that particular block.
Proof of Work
Bitcoin uses a proof-of-work system. What is proof of work? It is a piece of data that's very hard to produce (meaning it takes a lot of time or costs a lot of money) but can be easily verified by others, and it satisfies specific requirements. With bitcoin, proof of work is a competition among miners who want to add a block to the Blockchain—meaning they have to find the nonce value for the block by solving a mathematical puzzle.
Once a miner discovers a nonce value, he or she spreads the word throughout the network, and if other miners validate the claim, the miner is rewarded with 12.5 bitcoins or another form of compensation. Finding a nonce value also adds that block to the Blockchain.
Choosing a nonce value is the primary objective of miners. They have to find a value that is less than the target value. If they find a value greater than the target, then their mining effort is rejected. But if they can successfully generate a hash value using the nonce that is less than the target value, then their effort is accepted. This is where the entire computational power of the miner is used—to generate the hash value.
Finding a nonce value requires a lot of time, money, and resources. When the nonce value is found, the miner spreads the word about finding this value, other miners attempt to validate the claim, and if it's verified, the miner gets the reward. So a miner is rewarded for being the first one to find the nonce, and that adds a block to the Blockchain.
As mentioned, as of today, the reward is 12.5 bitcoins. Every four years, the amount of bitcoin a miner can earn is reduced by half. Mining is the only way new bitcoins can be generated, and it ensures that there's a limit to how many bitcoins can exist in the market.
Mining is the process of a miner being rewarded for finding the appropriate nonce first. Miners get paid in Bitcoins, and a successful verification is the only way the Bitcoins get added to the network. That is the concept of mining, and when a miner has completed the proof of work consensus, he is rewarded.
A miner's fee is 12.5 Bitcoins for adding a block onto the Blockchain; however, the reward reduces by half every four years. When the fourth year approaches, the Bitcoin reward will go down to 6.25 Bitcoins, and miners also get the sum of all the transaction fees for a particular block.
The Walmart Problem
Walmart was facing an issue where people were returning goods citing quality issues. Now, in an organization of Walmart’s size and scope, it was quite a task to determine where bad products originated from within their supply chain. Their supply chain involved the following steps:
To ensure their reputation wasn’t tarnished, they incorporated blockchain into their supply chain. Each event and detail within each step of the supply chain was logged. Now, in the scenario where a product was deemed bad and returned, Walmart would be able to determine where the issue with the product originated from in the supply chain.
Uses of Blockchain
The use of blockchain goes far beyond cryptocurrency and bitcoin . Here are some of the most common uses of blockchain in different industries:
- Anti-money laundering tracking system
- NFT marketplaces
- Original content creation
- Real-time IoT operating systems
- Advertising insights
- Music royalties tracking
- Cross-border payments
- Voting mechanism
- Supply chain and logistics monitoring
Other Fields That Use Blockchain
The financial services industry is an open field that uses blockchain technology extensively, but it's not the only one. Forbes mentions healthcare, crowdfunding, and ride-sharing in its article "Eight Ways Blockchain Will Impact the World Beyond Cryptocurrency." Let's look at a few other fields.
Blockchain technology can be used for things like:
- Tracking luggage, especially with multiple flights in one itinerary and international flights
- Identifying passengers, saving time, and reducing lines and wait times
- Making and accepting payments for services
The rise of digital music has posed problems regarding issues like piracy and artist compensation. Blockchain can:
- Help prevent piracy (illegal sharing) of music files
- Be used to compensate artists for purchased songs and albums
Cyber Security
Even a giant company like Lockheed Martin is using Blockchain in its cybersecurity efforts. Blockchain can:
- Help secure sensitive data, thanks to its cryptography feature
- Eliminate the need for passwords, because users and devices can be authenticated using the public and private keys
Human Resources
Blockchain technology is a natural fit for improving time-consuming and costly HR procedures. For example, it can:
- Eliminate the need to run individual verification checks on potential employees—blockchain transactions can store data regarding identity and employment history
- Track payments and expenses, making things like paying taxes much easier for both employers and employees
Blockchain as a Use Case in Banking
Blockchain finds excellent use in banking. As of now, a user validates his identity to each bank he goes to, over and over. Is there a way we can ease the process with Blockchain? The answer is yes. We can use truffle, ethereum, ganache, and smart contracts, which are part of the Blockchain technology ecosystem, to make it work.
Develop a Bright Future in Blockchain Technology
As you can see, blockchain technology is enabling a whole new class of cryptocurrencies with unparalleled security and ease of use. While not all of the 3,000+ cryptocurrencies being developed are going to last, blockchain technology has a bright future. That’s why getting trained and certified in blockchain technology is a smart choice for your future as well. Simplilearn’s Professional Certificate Program in Blockchain by IIT Kanpur can set you on the right path toward a lucrative career.
Find our Full Stack Java Developer Online Bootcamp in top cities:
About the author.
Rahul Venugopal is a Senior Product Manager with over six years of experience in Digital Marketing, Growth Hacking, and Mobile-App based marketing. He specializes in Online User Behaviour Analysis and Creative and Campaign Optimization.
Recommended Programs
Full Stack Java Developer
Automation Testing Masters Program
Full Stack Web Developer - MERN
*Lifetime access to high-quality, self-paced e-learning content.
Recommended Resources
Blockchain Career Guide: A Comprehensive Playbook To Becoming A Blockchain Developer
Bitcoin Mining Explained
Blockchain Interview Guide
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
- YouTube Thumbnail Downloader
- Image Compressor
- QR Code Generator
- Environment
- Submit An Article
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Introduction to Blockchain
- by Refresh Science
- July 22, 2020 January 6, 2022
Blockchain is a distributed database but its stored devices are not connected with a shared server. In block chain list of records are stored as blocks and they are linked by using cryptography.
Hence we can say that blockchain is a digital record and are used for recording transactions made with crypto currencies such as bitcoins .
If we add a new block it can be linked with the previous block with the help of cryptographic block generated from the previous block. By doing so the block is permanently recorded and it is not broken.
In blockchain previous transactions alteration is very difficult because all subsequent blocks also needs to be altered. We can say that block chain is a purest peer to peer database that is immutable.
Definition of Blockchain
It is an open distributed ledger that record transactions between two persons efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way. Each transaction is secured with a digital signature that proves its authenticity. Every block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a time stamp and transaction information.
Download Blockchain PowerPoint Presentation:
Technology used in blockchain.
Blockchain is a combination of multiple technologies:
Cryptographic Keys:
Cryptographic keys are most important for sending and receiving data. In process a private key and a public address is used. While sending data private key is used to sign it and the end user verify it by using the public key. In block chain we use asymmetric cryptograpgy like ECC.
Network Protocol:
We can choose the network protocol as per our use. To form a peer to peer network two or more electronic devices are linked and resources are shared. A peer is called a node on a network. Peer to peer network is a crucial part of secure blockchain processing.
Distributed Ledger Technology:
A ledger is a collection of shared, replicated and synchronized data. Every data is geographically spread over various computing devices. Any transaction approval and permission in blockchain is handled by distributed networks.
Hashing is converting a data with variable length to a fixed length. It is an one way process. It acts as an verification of a transaction.

Purpose of Blockchain
- Block chain uses online ledger which is very secure.
- There is no third party interference.
- It used distributed ledger which is very transparent.
- It is a digital world offering many new tools and there are many centralized administrators.
- Since there is no third party guarantee cost is very low.
Blockchain in Cryptocurrency
The term blockchain is often used to refer to cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrency is a medium of exchange such as US dollars. It is just an application in the form of e-currency using block chain. It is not governed by any financial institution.
The main difference between blockchain and cryptocurrency is that, cryptocurrency is created and held electronically in forms such as virtual wallet.
It is decentralised and it is not governed by anyone whereas blockchain is an advanced record and it has all information related to cryptocurrency exchanges over a shared system.

Blockchain in cryptocurrency
You might think of Bitcoin and blockchain as two halves of a whole, but in reality, they are very distinct commodities. Olawale Daniel
Blockchain in Insurance
According to a recent survey more than 80% of insurance companies have adopted or planning to implement blockchain technology. The practical application in insurance technology is, with the help of blockchain medical records are encrypted and shared between hospitals and insurers. This helps in cutting duplicated records and lengthy claim processing.
Blockchain also helps in selling and servicing insurance better, faster and cheaper by improving fraud prevention, claim management, health insurance and reinsurance. It also helps to lower the price and provide better experience for customers.
Blockchain Examples
Bitcoins and Cryptocurrency are the widely used blockchain technology.
There are many more examples using blockchain technology. We can say blockchain is revolutionizing in most of the industries.
- Based on blockchain cross gaming video games are developed for example B2Expand.
- Social Engagements such as match pool uses this technique.
- Retail products can be purchased and if there is any malfunction blockchain helps to access information regarding the product.
- Blockpoint simplifies the payment system and allows Mobile wallet, gift card and other point of scale functionality.
- Food industry Network from farmers to groceries is very complex and blockchain makes it easier by tracking down food borne illness challenging.
- Real estates also uses blockchain technology by allowing anyone anywhere in the country to invest in real estate.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain
Advantages:
- Greater Transparency
- Highly secure
- Easily traceable
- High efficiency and speed
- Zero percentage of fraud
- Extremely volatile
Disadvantages:
- More power consumption
- Can be a regulatory problem for financial institutions
Home PowerPoint Templates Blockchain
Blockchain Presentations for PowerPoint and Google Slides
Download our Blockchain Presentations for PowerPoint and Google Slides. In this section, you can find 100% editable slide templates related to Cryptocurrency, Blockchain, Techno Deck, FinTech, and disruptive technology that will help you generate professional presentations quickly and with little effort.

NFT PowerPoint Template

Cryptocurrency Project Proposal PowerPoint Template

Techno Deck PowerPoint Template

FinTech Industry PowerPoint Templates

Cryptocurrency PowerPoint Template
These Blockchain PowerPoint templates were crafted with a color scheme intended to portray Web 3.0 technologies. Navy blue, vibrant fuchsia, and violet hues, although they are fully editable to meet the preferences of our customers.
Our Blockchain PPTs are compatible with PowerPoint and Google Slides and are very easy to modify. Thanks to Blockchain Technology PPT, you will be able to present relevant information about your project and engage your target audience.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the recording of transactions and tracking assets on a network. Thanks to its technology, all participants share access to a single version of the truth, which produces a high level of transparency and trust.
Some fundamental aspects of this technology is that all participants have access to the distributed ledger, where all transactions are recorded only once. This eliminates duplication. In turn, to streamline transactions, a set of pre-established rules, called Smart Contracts, are stored in the blockchain. Thanks to Smart Contracts it is possible to streamline processes and include conditions in certain transactions.
How to present a Blockchain Technology PPT?
The objective of a Blockchain Presentation is to persuade or inform about an established idea or project. Therefore it is important to provide concise and straightforward information, specify the scope, define the purpose of the project and communicate the key activities to be performed. For this, we recommend using pre-made templates compatible with PowerPoint and Google Slides to reduce your work and guide you when creating your presentation.
What are the advantages of using a Blockchain Presentation?
Using a Blockchain PPT helps to organize the information in your presentation in a clear and professional way, guiding you in the creation of your presentation and also when presenting it. Our Blockchain Presentations contain images and graphic resources that help to generate engagement with your audience.
Download Unlimited Content
Our annual unlimited plan let you download unlimited content from slidemodel. save hours of manual work and use awesome slide designs in your next presentation..

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Blockchain powerpoint presentation slides
Use extensively researched Blockchain PowerPoint Presentation Slides to educate your audience about the secure online payment transactions and cryptographic techniques. Show encryption methods and concept of decentralized network that allows the easy transfer of digital values such as currency and data. Bitcoin developers can incorporate this professionally designed content-ready Blockchain PowerPoint presentation templates for their work. This deck covers topics like distributed ledger, working of a distributed ledger, use cases, industrial blockchain benefits, blockchain limitations, and more. Illustrate the idea of transferring funds directly between two parties without any banks or credit card company using blockchain PPT presentation templates. Demonstrate the workings of cryptocurrencies, showcase the process and its benefits with the help of cryptocurrency PPT slides. These templates are completely customizable. You can edit the slides as per your convenience. Change color, text, icon, and font size as per your need. Download now. Engage with disbelievers through our Blockchain Powerpoint Presentation Slides. Explain the grounds for your beliefs.

These PPT Slides are compatible with Google Slides
Compatible With Google Slides

- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
Get Presentation Slides in WideScreen
Get This In WideScreen
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
- Add a user to your subscription for free
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
Do you want to remove this product from your favourites?
PowerPoint presentation slides
PowerPoint presentation slide. It covers total of 19 professionally designed PPT slides. Our PowerPoint experts have included all the necessary layouts, diagrams and templates to meet the needs of the customers. This content ready deck is completely customizable. Edit the color, text and icon as per your requirement. You can also add or delete the content from the presentation as per your need. You can easily download this presentation. They are high resolution PPT templates and are perfectly compatible with Google Slides.

People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
- Diagrams , Shapes , IT , Flat Designs , Visuals and Illustrations , Complete Decks , All Decks , Blockchain Bitcoin , IT , Blockchain
- Cryptocurrency ,
- Distributed Ledger ,
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Blockchain is crucial to corporate operations, especially ways of recording transactions in cryptocurrencies. The technology ensures trust in any financial system and maintains the security of data across computers connected in a person-to-person network.
Blockchain is secure and transparent, even as it does not impact accessibility in any adverse manner.
Primarily used for bitcoin-based transactions, blockchain values trades by enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency in trades. It ensures that data is uncompromised, risk-free from fraud and faults, and is accessible across the network.
Smart contracts is one major application of blockchain, and where considerable progress has been made. Get the template here.
Blockchain, with its emphasis on no intermediary and no particular holder of trust for financial transactions, has emerged as a game-changer for commerce.
At SlideTeam, we have a collection of blockchain PowerPoint Designs that offer an easy and convenient way for corporates to present finance concepts. Using these 100% editable and customizable PPT Layouts, you can communicate messages related to decentralization, smart contracts, and transactions to your audience. Adding blockchain designs to your presentation enables you to highlight aspects of cryptocurrency, distributed ledgers, and more.
Access four pillars of blockchain technology with a click here and use it to better your processes.
Use these presentation visuals to showcase how blockchain revolutionizes financial processes. Additionally, you can deliver a statement about how effective blockchain is for the smooth functioning of modern business.
Let’s explore!
Template 1: Introduction
From corporate clients to underwriting teams and mobile banking to international banks, this slide caters to finance, legal, and commercial services. Whether showcasing treasury department strategies or highlighting the efficiency of outsourced service providers, our PPT design seamlessly integrates third-party services and mortgage providers. This versatile PowerPoint visual is ideal for finance departments, branch sites, and payment service providers. It empowers professionals across job profiles, from financial analysts to branch managers, to effectively communicate and engage their audience.
Template 2: Distributed Ledger
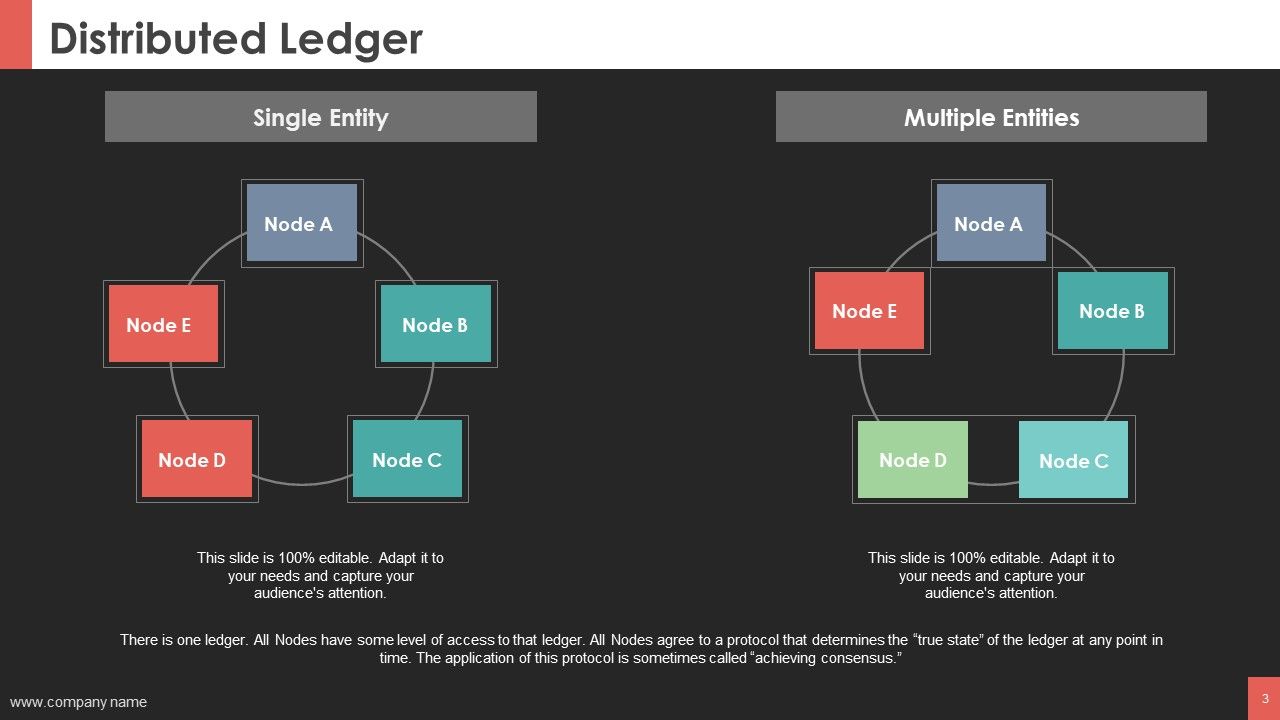
This presentation slide illuminates the crux of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), demonstrating its adaptability across single and multiple-entity agendas. In the single-entity scenario, nodes A, B, C, D, and E congregate to form a robust network, while in the multi-entity setup, nodes A, B, C, D, and E foster alliances among diverse establishments. The PPT layout is ideal for professionals ranging from blockchain developers to compliance officers. It showcases the transformative power of DLT in revolutionizing data management and fostering trust in the digital age.
Template 3: Working of a Distributed Ledger
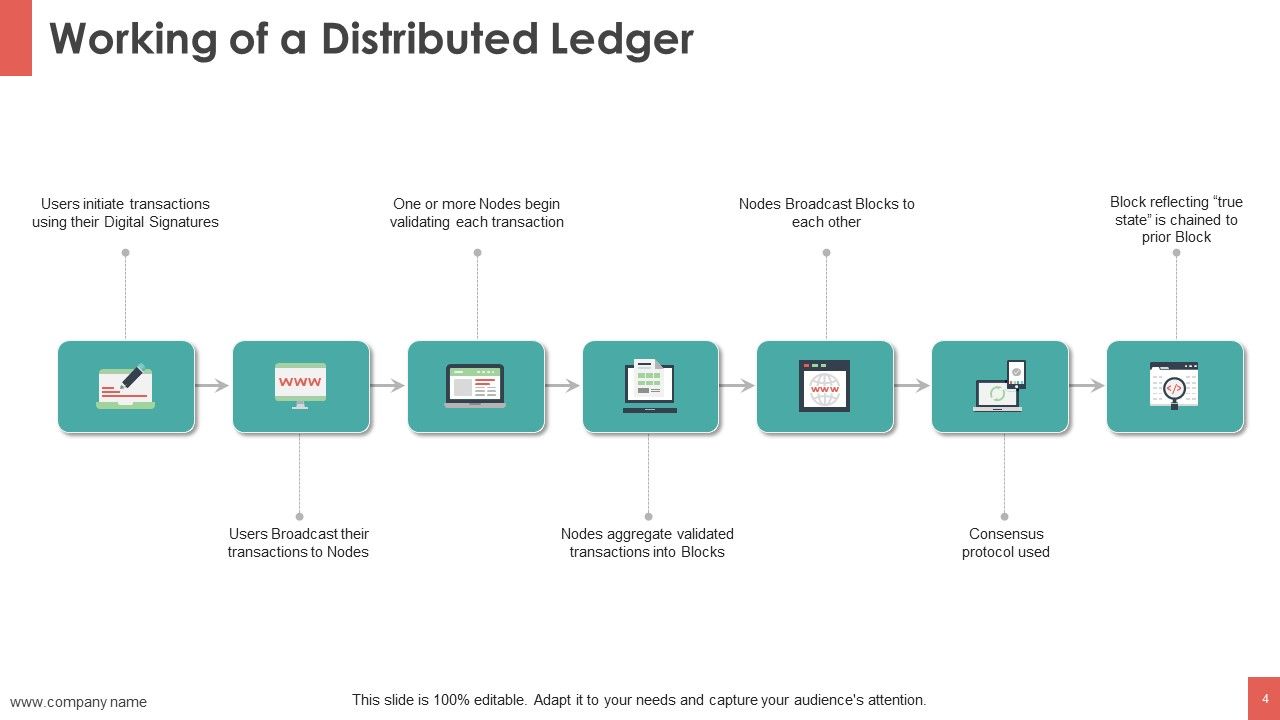
This PPT diagram elucidates the operational dynamics of a DLT, beginning with users initiating transactions via their digital signatures. Subsequently, users broadcast these transactions to nodes, where one or more nodes undertake the validation process. Following validation, nodes aggregate validated transactions into blocks and broadcast them across the network. This comprehensive presentation layout is invaluable for professionals such as blockchain architects, cybersecurity analysts, financial auditors, and software developers.
Template 4: Use of Distributed Ledger
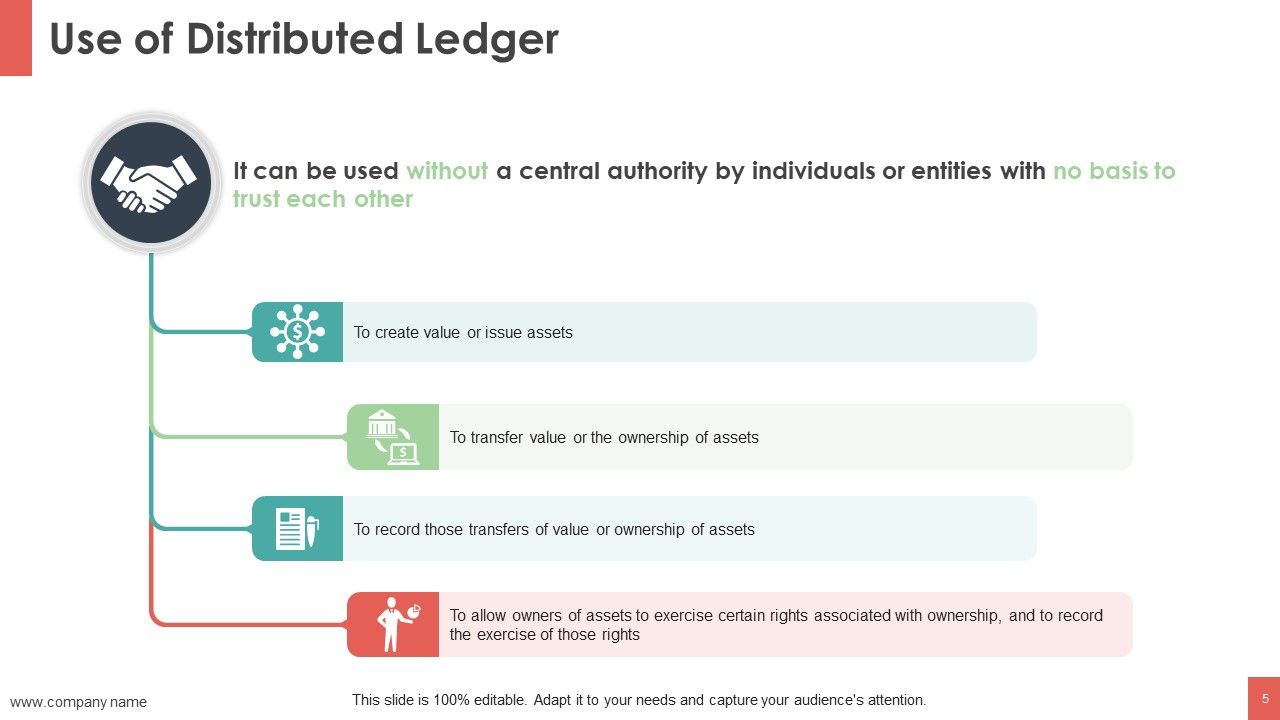
This PowerPoint layout underscores the versatile applications of DLT, which enables the creation, transfer, and recording of asset values and ownership. The slide helps highlight key concepts from issuing assets to facilitating their transfer and recording ownership changes. Furthermore, DLT empowers users to exercise ownership rights efficiently. This PPT diagram adds value to professionals, such as blockchain developers, financial analysts, legal advisors, and compliance officers, offering insights into harnessing DLT's transformative potential in asset management and transactional processes.
Template 5: Smart Contract

This PPT visual effectively illustrates the fundamental concept of smart contracts, where the business rules are embedded within the blockchain and executed with transactions. These contracts are signed and verifiable, with their conditions encoded in a programming language, ensuring transparency and effectiveness. For example, a smart contract might outline the terms for transferring corporate bonds. The slide showcases how intelligent contracts streamline processes and bolster trust across diverse industries.
Template 6: Privacy
This presentation framework highlights the critical significance of privacy within distributed ledger systems. While these ledgers are shared, participants necessitate privacy measures to safeguard sensitive information. It ensures that transactions remain private, with identities not linked to specific transactions or authentication. This PPT layout is indispensable for professionals across domains, including cybersecurity analysts, blockchain developers, compliance officers, and data privacy experts. It offers vital guidance on preserving the confidentiality and integrity of information within decentralized environments, ensuring trust and security across digital transactions.
Template 7: Use cases – Letter of Credit
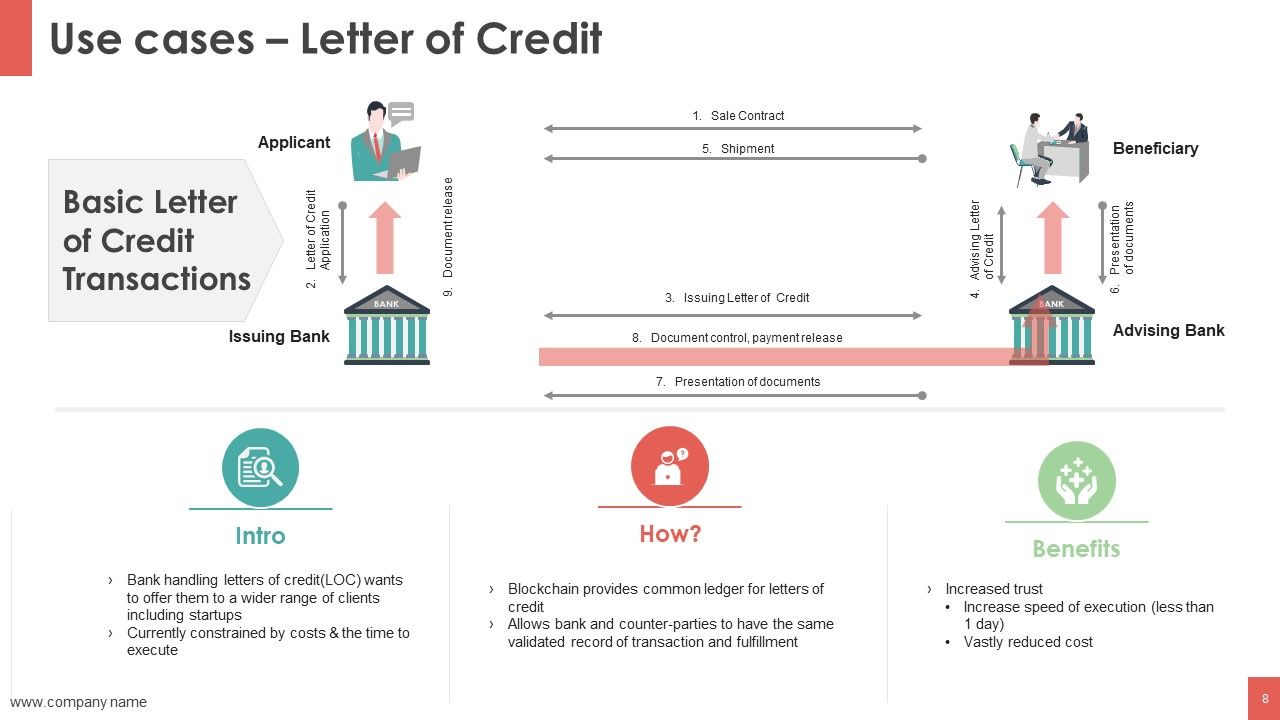
This PowerPoint template showcases the wide-ranging applications of Letters of Credit (LC), an essential tool in international trade. It covers activities from initiating sales contracts and LC applications to issuing and advising LCs. These tasks involve managing shipments, presenting documents, and ensuring document control for payment release. This PPT layout is beneficial for professionals, including trade finance managers, international trade specialists, supply chain managers, and financial analysts. They can leverage this presentation design, as it provides insights into the complex operations of LCs, facilitating seamless transactions and risk mitigation in global commerce.
Template 8: Use Case – Corporate Debt (or Bond)
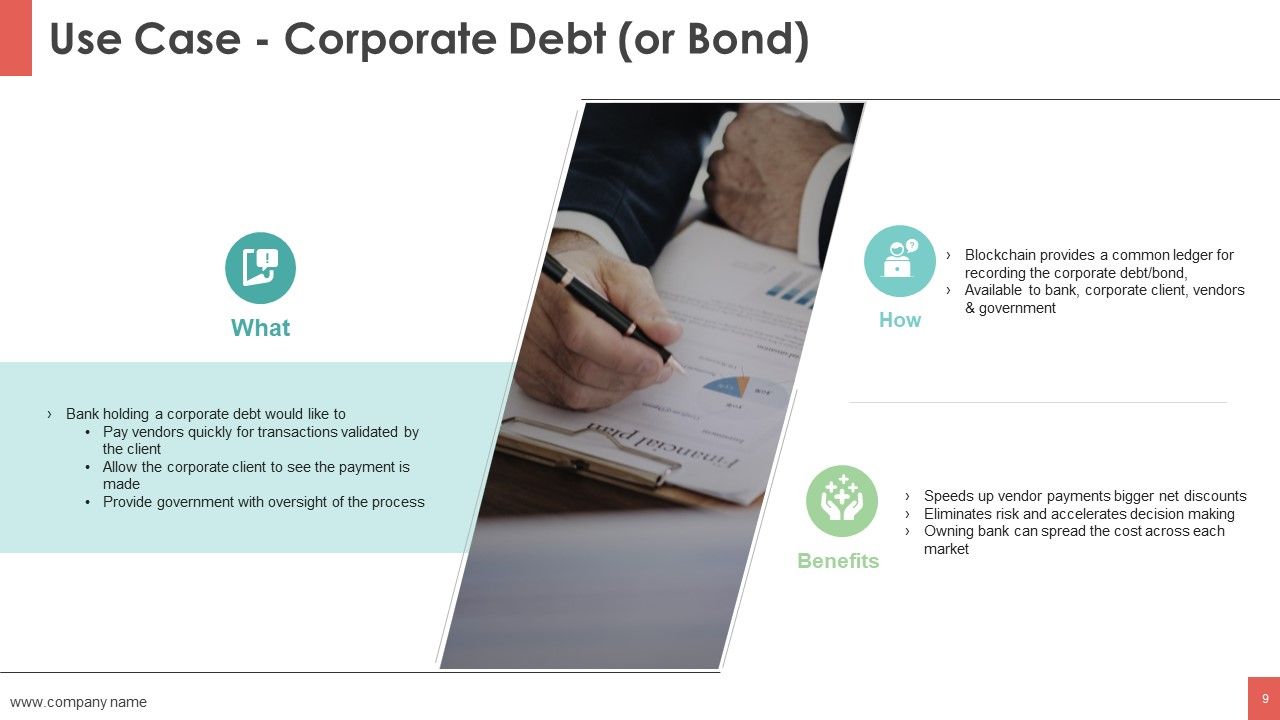
This PowerPoint Design portrays the application of corporate debt or bonds, a significant financial tool in capital markets. It showcases corporate debt, operational workings, and its advantages. Besides this, it helps businesses issue bonds to get investments from investors, obliging them to regular interest payments and repaying the principal amount. The PPT layout depicts the entire process and involves issuing bonds, marketing them to investors, and managing interest payments and redemptions. This presentation slide benefits investment bankers, corporate finance managers, and financial analysts.
Template 9: Industrial Blockchain Benefits
This PowerPoint diagram highlights the advantages of implementing industrial blockchain technology. Industries lower expenses and simplify intricate procedures using blockchain. Additionally, blockchain guarantees reliable recordkeeping, augmenting the integrity and dependability of data. Enhanced accessibility and discoverability of information enhances operational effectiveness. These collaborative, dependable processes enable professionals in diverse roles, such as supply chain managers, logistics coordinators, quality assurance specialists, and IT professionals.
Template 10: Blockchain Limitations
This presentation graphic highlights the limitations of blockchain technology. Blockchain may not be suitable for scenarios requiring high-performance transactions in milliseconds or suit small organizations lacking a business network. It may not directly replace traditional databases or messaging solutions, nor can it always replace transaction processing systems. The PPT diagram helps professionals such as IT architects, technology consultants, project managers, and business analysts effectively use the information to assess the suitability of blockchain for specific use cases and devise alternative solutions where necessary.
Unlocking Future Potential: Blockchain Revolution
Blockchain provides vast potential for corporations across industries. Its capacity to boost transparency, security, and proficiency makes it an excellent resource for driving innovation. It aids businesses in restructuring transactions, mitigating risks, and reducing costs. In this digital age, blockchain allows trades to gain an advantage by unlocking new opportunities and adapting to changing market dynamics. It revolutionizes business operations and helps shape the future of commerce.
Our blockchain presentation designs help you to make your team understand the new dynamics of modern business.
PS Understand how distributed ledgers contribute to better, faster business with a look at this PPT Template on distributed ledgers .
Blockchain powerpoint presentation slides with all 19 slides:
Evoke compassion with our Blockchain Powerpoint Presentation Slides. Develop their feelings for fellow beings.

Ratings and Reviews
by muhammad zia
November 6, 2022
March 18, 2021
by paoo tern
December 24, 2019
by DAVID SNYDER

Entrepreneurship

Berkeley Blockchain Xcelerator June 2022 Updates: CESC Returns, Fairmint Announces Launch & More

The Berkeley Blockchain Xcelerator is an internationally recognized , non-dilutive source of support for startups in the Blockchain ecosystem- formed by a partnership between the Haas School of Business , Blockchain at Berkeley student group, and Berkeley Engineering .- Check out the Xcelerator Homepage .
Berkeley Ecosystem Updates
CESC Returns to UC Berkeley with the Xcelerator Demo Day

Registration Now Open- Paper Submissions due July 28
The Crypto Economics Security Conference (CESC) returns to in-person this fall at UC Berkeley. Past CESC events have attracted over 600 participants.
We invite researchers and practitioners to submit papers, and all to attend.
Paper submissions are due July 28 , registration is now open , and student travel grant applications are now being accepted. Join us!
CESC main conference will include paper presentations & poster sessions. Affiliated events include Blockchain/Web3 career fair and the Berkeley Blockchain Xcelerator Demo Day. Presentations will also be live streamed.
CESC aims to bring together researchers and practitioners to showcase and discuss the most recent developments in blockchain and Web3.
Hosted by Berkeley RDI , a multi-disciplinary campus-wide center, focusing on advancing the science, technology and education of web3, decentralization and empowering of a responsible digital economy, with three core pillars: research, education, and community / entrepreneurship, including the Berkeley Blockchain Xcelerator.
More details at the bottom of this post!
Weekly Xcelerator Interview Spotlight- Aplo (Fall ‘19)
https://medium.com/media/8792fc5b9ac8ac7745a4d6ba5f33f985/href
Xcelerator Team Updates
Fairmint announces launch, raises $7.2M
https://medium.com/media/da08c29dfaebc20e8766d56fec7b1ed1/href
Fairmint empowers every startup to unlock an untapped superpower: their community. Last month, the company announced the public launch of their decentralized community ownership platform . Companies launch Fairmint’s decentralized portal on their website, allowing contributors to receive equity in exchange for time or money they invest.
Using their own technology on their own website, Fairmint has raised $7.2M from more than 300 supporters, including early adopters, partners, customers, angel investors and VCs such as Tim Draper, Boost VC, A Capital and Fabric Ventures. Fairmint is the Web3 layer of the modern startup stack, empowering participation in the ownership economy. Read more about the platform on their launch blog and learn more at Fairmint.com .
Bitgreen files as a DeFi Broker-Dealer, enters Rainforest Collective partnership

Bitgreen filed to launch as a DeFi Broker-Dealer and is entering a partnership with Rainforest Collective- enabling people to donate directly to the communities safeguarding the rainforest .
In Davos, CEO Adam Carver spoke on how blockchains can be a catalyst for a green future! Listen to his comments here .
Alfred Pay integrates with Moneygram for USDC-to-cash payouts

Alfred Pay is one of the early wallet adopters of the MoneyGram x Stellar integration that will allow its users in LATAM to seamlessly cash out their balance for local currency.
The MoneyGram integration aligns directly with Alfred Pay’s mission by merging the traditional remittance system and mobile first/DeFi worlds together. Starting July 2022, Alfred Pay beta users will be able to send cash at 22,000 US MoneyGram locations and cash out at 750 locations across the Dominican Republic. Best of all, this MoneyGram service with be $0 in fees to on/off ramp users onto USDC.
Alfred Pay has also launched the waitlist for its beta. Sign up for early access today and enjoy sending money from US to Dominican Republic with no fees! Strategic local partners have been able to drive up to 8000 individuals to the waitlist and counting. Sign up here .
Vite is listed on Binance, sponsors Consensus 2022

VITE listed on Binance.US this month! VITE/USD and VITE/USDT trading pairs are open, and VITE may be purchased via USD on-ramp. Vite was also a sponsor of Consensus 2022, hosting a booth at the conference and a side event where the team met many industry leaders interested in Vite’s “Zero Gas Layer-1” ecosystem.
Finally- Vite Labs recently launched a Velocity Fund where Vite is seeking to raise $1~2M for a Phase-1 Fund to jumpstart and nurture new projects built on Vite. Read more details on Vite’s recent growth here .
MetaMirror Gallery v2 launches

MetaMirror-built on auth3 Network- has gone live with their Gallery v2, becoming the first NFT marketplace on Oasis Network!
Gallery v2 now allows you to host an auction with $ROSE on any crypto collectible, and sell to specific buyers. It is also equipped with an innovative no-code NFT Launch service called MLaunch- allowing users to both configure their NFT smart contract and set up NFT launch events in a few clicks.
Read more here.
Campground launching public beta

Campground ’s public beta is launching on July 7th! It envisions a world where creators can bootstrap their viral moments, and delivers on this vision by pairing its flexible content creation engine with exceptional creator economics powered by blockchain.
Unlike any NFT marketplace or other blockchain-based creator economy solution, creators can be paid as usual via Campground’s proprietary system, in fiat currency (USD), directly by their followers, without having to invest in or receive payments in cryptocurrency.
Read more here .
Automata Network (2021 Cohort) is listed on Coinbase

Exciting news from Automata Network- a decentralized service protocol that provides middleware-like traceless privacy services for dApps on Ethereum and Polkadot to achieve privacy, high assurance, and frictionless computation – $ATA is now live on Coinbase !
You can log in either through the iOS or Android applications to store or trade the token.
Dtravel launches v2, enabling automated smart contract vacation rental bookings
Dtravel v2 is now live!
Beginning today, property managers and hosts can import their listings to Dtravel v2 via Hostaway and start accepting bookings from guests worldwide. Earlier this year, the team announced an updated direction for Dtravel following extensive host research and market analysis. Using this data, they identified a market opportunity for a novel vacation rental booking model that combines the freedom of direct bookings with the simplicity of online travel agencies (OTAs) — and so Dtravel v2 was born.
After months of building toward this vision and refining the product in consultation with a group of passionate property hosts via our Host Beta Program, Dtravel is proud to have launched the first on-chain travel booking ecosystem powered by smart contracts. Dtravel v2 uses blockchain technology to remove the intermediary, creating a decentralized ecosystem which is ushering in the web3 travel revolution.
Eluv.io (Fall ’19 Cohort) launches WWE Moonsault NFT Project

Eluv.io has partnered with the WWE to bring the WWE fandom to new heights! This launch offers an opportunity for the all wrestling fans to get closer to the action.
With Moonsault, you can claim NFT highlights of your favorite Superstars, legendary matches and iconic moments from WWE history. Learn more about this exciting collaboration here !
Overnight sees 3x TVL growth

Overnight (2022) has crossed a whopping $2.2M in TVL and has achieved this growth amid uncertainty and reluctance around accepting stablecoins.
Overnight continues to grow- and in the midst of uncertain times has managed to provide its users the necessary assurance that they need; being fully collateralised with secure & safe stablecoins — USDC & USDT.
Overnight uses its collateral across a range of diversified stable-to-stable pools (lending & yield-farming) such as Arrakis and Aave to generate 8–12% APY for its users — paid out daily as rebases. This leaves out the question of being on the daily hunt for yields within the DeFi realm as Overnight automatically does this for you.
Apart from being beneficial for yield-seekers, Overnight’s USD+ is also beneficial for protocols as well and its use case extends to Liquidity Provisions as well. With retail actively proclaiming, “Bear,” USD+ offers a way for protocols to achieve a force appreciation of their tokens by having their Liquidity paired relative to it. Positive rebases from USD+ immediately result in both sides of the Liquidity Pool appreciating as the protocol in question has the liquidity paired to a self-appreciating token.
Read more here !
Nil DAO launches new websites, announces new gen-art NFT launchpad on Arbitrum

Nil DAO launches an NFT launchpad on Arbitrum, for dropping any collection in just 2 clicks. At first, the launchpad will be open to creators who apply to become allow-listed. This is for moderation and to maintain a sustainable drop schedule.
Drops mint in ETH and will show up on Arbitrum’s open 2ndary marketplaces. A key marketplace partnership will be announced soon. Check out our fresh new website at https://nil.art/ , and read more about the launchpad here .
AWS Activate offers credit, technical support, and more to developers on using Astar Network (2020 Cohort)

Under this collaboration, projects in our programs are eligible to get up to $100k AWS credit and official technical support from AWS team. The Astar Builders Program was organized to help further the development, growth, and adoption of the Polkadot ecosystem by supporting teams who are building on it.
It allows developers to build applications and infrastructure to meet the blockchain community’s needs, developing and creating apps that can further push the web 3.0 space. As part of the program, Astar ecosystem projects receive technical, networking, fundraising, and marketing support.
OAK Network launches PoS, rewards and grants program, goes to Consensus in Austin

OAK Network , building trustless automation for payments and DeFi, had three key launches and one key partnership announced this month:
- Delegated Proof of Stake for the Turing Network
2. Crowd Loan Rewards and Distribution to the community for the Turing Network crowdloan
3. OAK’s DApp Competition & Grant Program
With over $50K in prizes on the line, we’re looking for developer teams to create DApps that provide transparent user experiences for OAK blockchain. Apply now!
OAK Network partnered with Imbue to bring on-chain notifications to decentralized crowdfunding. Read more here .
OAK Network also participated in Consensus 2022! At Austin, the team recorded two Coindesk Consensus Podcasts and met with countless partners and Dotsama ecosystems members at the OAK Network booth, throughout the conference, and at the events ( source ).
SubQuery Network (2021 Cohort) announces token sale

SubQuery Network recently announced their upcoming token sale will be held in July on TokenSoft . SubQuery enables blockchain developers to index, transform, and query chain data to power their applications.
Already the leading data indexing solution on Polkadot, they have recently integrated with other Layer-1 chains such as Avalanche and Cosmos. The third and final season of their “Frontier” testnet will be public and launching soon. For more information you can visit their website or the SubQuery Foundation website that hosts more information on their launch.
Amplitude launches as Pendulum’s sister project on Kusama

Amplitude’s Kusama crowdloan waitlist is now live and offering 13% bonuses for early sign ups! The trust-minimized Spacewalk bridge connecting Stellar and Polkadot is under development.
Pendulum received a Web3 Foundation grant to further develop the Spacewalk bridge. The Pendulum Grants Program has just launched to provide funding for initiatives building towards the fiat DeFi future.
Additional CESC Information
If you’d like to learn more details about the Crypto Economics Security Conference:
- Visit CESC.io
- Read the most recent CESC announcement
- Sign up for CESC news to receive updates !
Our affiliates and sponsors:

Berkeley Blockchain Xcelerator June 2022 Updates: CESC Returns, Fairmint Announces Launch & More was originally published in Berkeley Blockchain Xcelerator on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Although Blockchain technology has a strong disruptive power and can change many areas of our daily lives, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed. The high energy consumption - Bitcoin uses a lot of energy. The scalablity issue - Bitcoin supports far less transactions per second than e.g. VISA.
This PPT slide covers the major components of blockchain technology. The key elements of a blockchain are a ledger, smart contracts, consensus network, membership, events, systems management, wallet, and systems integration. This PPT template acts as a thorough manual for the presenter, dissecting intricate blockchain elements into easily ...
Excited to learn about the fundamentals of blockchain technology, Checkout presentation on Blockchain Fundamentals - Top Rated for Beginners. Note: If you are creating a blockchain fundamentals pdf, we encourage you to use the slides available here. This will help us reach more audience who wants to know about blockchain fundamentals ...
Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network. An asset can be tangible (a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding). Virtually anything of value can be tracked and traded on a blockchain network ...
Blockchain is a technology that enables the secure sharing of information. Data, obviously, is stored in a database. Transactions are recorded in an account book called a ledger. A blockchain is a type of distributed database or ledger—one of today's top tech trends —which means the power to update a blockchain is distributed between the ...
A. asrithak. Blockchain is a decentralized ledger of all transactions across a peer-to-peer network that allows participants to perform transactions without a central authority. Potential applications include fund transfers, settling trades, voting and more. Blockchain ensures "cash like" coin passing that is unique, immutable and final.
Blockchain is an immutable digital ledger that enables secure transactions across a peer-to-peer network. It records, stores and verifies data using decentralized techniques to eliminate the need for third parties, like banks or governments. Every transaction is recorded, then stored in a block on the blockchain.
Blockchain technology is a software; a protocol for the secure transfer of unique instances of value (e.g. money, property, contracts, and identity credentials) via the internet without requiring a third-party intermediary such as a bank or government. Email over IP, Voice over IP, Money over IP.
It can be used to create value or issue assets. It can be used to transfer value or the ownership of assets. • human being or a Smart Contract can initiate the transfer. It can be used to record those transfers of value or ownership of assets. • records may be very difficult to alter, such that they are sometimes called effectively immutable.
As the world is moving towards adopting blockchain-based solutions, it has become imperative to have sound knowledge about this revolutionary technology. The fundamental knowledge of this technology will help you adapt to the newer trends and even open doors to achieving your professional goals. In order to do so, you must have a clear idea ...
Blockchain is a type of ledger technology that stores and records data. Blockchain is the buzzword that seems to dominate any conversation about the future of technology, from the power of ...
This document provides an introduction to blockchain technology and cryptocurrency. It discusses what blockchain is, how it works using cryptography, peer-to-peer networks, and game theory. It also covers use cases like Bitcoin, altcoins, tokens, ICOs, smart contracts on Ethereum using Solidity, and the Remix IDE.
Template 1: Blockchain Technology PPT Complete Deck. A blockchain complеtе dеck PPT can hеlp by providing an ovеrviеw of thе еntirе blockchain tеchnology, including its componеnts, fеaturеs, and applications. It can also givе an ovеrviеw of blockchain systеms and protocols, and еxplain how thеy work. Additionally, a ...
Blockchain is the technology capable of supporting various applications related to multiple industries like finance, supply chain, manufacturing, etc., but Bitcoin is a currency that relies on Blockchain technology to be secure. Blockchain is an emerging technology with many advantages in an increasingly digital world:
Blockchain Basics and Cryptography (PDF - 1MB) 4 Blockchain Basics and Consensus (PDF - 1.9MB) 5 Blockchain Basics and Transactions, UTXO, and Script Code (PDF - 1.3MB) 6 Lecture by Prof. Gary Gensler: Smart Contracts and DApps (PDF) Guest Lecture by Prof. Lawrence Lessig: Smart Contracts (PDF) 7 Technical Challenges (PDF) 8 Public Policy (PDF ...
Blockchain: A blockchain is a digitized, decentralized, public ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions . Constantly growing as 'completed' blocks (the most recent transactions) are recorded ...
Blockchain is a combination of three important technologies - cryptographic keys, a peer-to-peer network, and a digital ledger. The cryptographic keys are of two types - private key and public key. Each individual or node has both of these keys and they are used to create a digital signature.
Blockchain Technology. Oct 12, 2019 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 46 likes • 80,015 views. Mithileysh Sathiyanarayanan. Basics of Blockchain Technology in various domains. Engineering. 1 of 102. Download now. Blockchain Technology - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Slide 1: This slide introduces Blockchain Technology PPT Presentation.State your Company name and begin. Slide 2: This slide displays Table of Contents of the presentation. Slide 3: The slide brief about what is block chain technology Slide 4: The slide shows what the blockchain is not Slide 5: The slide highlights a brief architecture of Blockchain Architecture Slide 6: The slide displays how ...
Blockchain in Insurance. According to a recent survey more than 80% of insurance companies have adopted or planning to implement blockchain technology. The practical application in insurance technology is, with the help of blockchain medical records are encrypted and shared between hospitals and insurers.
Thanks to Blockchain Technology PPT, you will be able to present relevant information about your project and engage your target audience. What is Blockchain? Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the recording of transactions and tracking assets on a network. Thanks to its technology, all participants share access to a ...
This presentation graphic highlights the limitations of blockchain technology. Blockchain may not be suitable for scenarios requiring high-performance transactions in milliseconds or suit small organizations lacking a business network. It may not directly replace traditional databases or messaging solutions, nor can it always replace ...
In this article, we will be going through our vision and analysis of enterprise blockchains adoption and how we are going to achieve $3 Trillion of added value by 2030 using our blockchain PowerPoint presentation.. 101 Blockchains is a blockchain research and strategic consulting company. We are focused on blockchain technology education and pushing the boundaries of public perception and ...
Presentations will also be live streamed. CESC aims to bring together researchers and practitioners to showcase and discuss the most recent developments in blockchain and Web3. Hosted by Berkeley RDI, ... Dtravel v2 uses blockchain technology to remove the intermediary, creating a decentralized ecosystem which is ushering in the web3 travel ...
Accepted for presentation at the second annual Business for Blockchain Technology conference, the research work offers a groundbreaking, detailed framework for using blockchain technology to ...
Neptune engages in operations across the digital asset ecosystem including Bitcoin mining, proof-of-stake mining, blockchain nodes, decentralized finance (DeFi), and other associated cutting-edge ...
VAP Group is the organizer of Global Blockchain Show and Global AI Show, extraordinary platforms poised to redefine the landscape of blockchain and AI technology respectively, offering dynamic ...
Embracing Digital Economy