Your Modern Business Guide To Data Analysis Methods And Techniques
Table of Contents
1) What Is Data Analysis?
2) Why Is Data Analysis Important?
3) What Is The Data Analysis Process?
4) Types Of Data Analysis Methods
5) Top Data Analysis Techniques To Apply
6) Quality Criteria For Data Analysis
7) Data Analysis Limitations & Barriers
8) Data Analysis Skills
9) Data Analysis In The Big Data Environment
In our data-rich age, understanding how to analyze and extract true meaning from our business’s digital insights is one of the primary drivers of success.
Despite the colossal volume of data we create every day, a mere 0.5% is actually analyzed and used for data discovery , improvement, and intelligence. While that may not seem like much, considering the amount of digital information we have at our fingertips, half a percent still accounts for a vast amount of data.
With so much data and so little time, knowing how to collect, curate, organize, and make sense of all of this potentially business-boosting information can be a minefield – but online data analysis is the solution.
In science, data analysis uses a more complex approach with advanced techniques to explore and experiment with data. On the other hand, in a business context, data is used to make data-driven decisions that will enable the company to improve its overall performance. In this post, we will cover the analysis of data from an organizational point of view while still going through the scientific and statistical foundations that are fundamental to understanding the basics of data analysis.
To put all of that into perspective, we will answer a host of important analytical questions, explore analytical methods and techniques, while demonstrating how to perform analysis in the real world with a 17-step blueprint for success.

What Is Data Analysis?
Data analysis is the process of collecting, modeling, and analyzing data using various statistical and logical methods and techniques. Businesses rely on analytics processes and tools to extract insights that support strategic and operational decision-making.
All these various methods are largely based on two core areas: quantitative and qualitative research.
To explain the key differences between qualitative and quantitative research, here’s a video for your viewing pleasure:
Gaining a better understanding of different techniques and methods in quantitative research as well as qualitative insights will give your analyzing efforts a more clearly defined direction, so it’s worth taking the time to allow this particular knowledge to sink in. Additionally, you will be able to create a comprehensive analytical report that will skyrocket your analysis.
Apart from qualitative and quantitative categories, there are also other types of data that you should be aware of before dividing into complex data analysis processes. These categories include:
- Big data: Refers to massive data sets that need to be analyzed using advanced software to reveal patterns and trends. It is considered to be one of the best analytical assets as it provides larger volumes of data at a faster rate.
- Metadata: Putting it simply, metadata is data that provides insights about other data. It summarizes key information about specific data that makes it easier to find and reuse for later purposes.
- Real time data: As its name suggests, real time data is presented as soon as it is acquired. From an organizational perspective, this is the most valuable data as it can help you make important decisions based on the latest developments. Our guide on real time analytics will tell you more about the topic.
- Machine data: This is more complex data that is generated solely by a machine such as phones, computers, or even websites and embedded systems, without previous human interaction.
Why Is Data Analysis Important?
Before we go into detail about the categories of analysis along with its methods and techniques, you must understand the potential that analyzing data can bring to your organization.
- Informed decision-making : From a management perspective, you can benefit from analyzing your data as it helps you make decisions based on facts and not simple intuition. For instance, you can understand where to invest your capital, detect growth opportunities, predict your income, or tackle uncommon situations before they become problems. Through this, you can extract relevant insights from all areas in your organization, and with the help of dashboard software , present the data in a professional and interactive way to different stakeholders.
- Reduce costs : Another great benefit is to reduce costs. With the help of advanced technologies such as predictive analytics, businesses can spot improvement opportunities, trends, and patterns in their data and plan their strategies accordingly. In time, this will help you save money and resources on implementing the wrong strategies. And not just that, by predicting different scenarios such as sales and demand you can also anticipate production and supply.
- Target customers better : Customers are arguably the most crucial element in any business. By using analytics to get a 360° vision of all aspects related to your customers, you can understand which channels they use to communicate with you, their demographics, interests, habits, purchasing behaviors, and more. In the long run, it will drive success to your marketing strategies, allow you to identify new potential customers, and avoid wasting resources on targeting the wrong people or sending the wrong message. You can also track customer satisfaction by analyzing your client’s reviews or your customer service department’s performance.
What Is The Data Analysis Process?
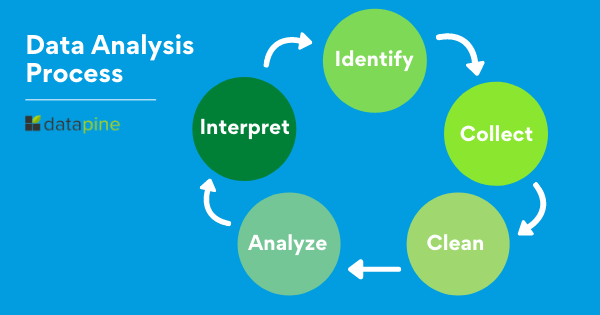
When we talk about analyzing data there is an order to follow in order to extract the needed conclusions. The analysis process consists of 5 key stages. We will cover each of them more in detail later in the post, but to start providing the needed context to understand what is coming next, here is a rundown of the 5 essential steps of data analysis.
- Identify: Before you get your hands dirty with data, you first need to identify why you need it in the first place. The identification is the stage in which you establish the questions you will need to answer. For example, what is the customer's perception of our brand? Or what type of packaging is more engaging to our potential customers? Once the questions are outlined you are ready for the next step.
- Collect: As its name suggests, this is the stage where you start collecting the needed data. Here, you define which sources of data you will use and how you will use them. The collection of data can come in different forms such as internal or external sources, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, and focus groups, among others. An important note here is that the way you collect the data will be different in a quantitative and qualitative scenario.
- Clean: Once you have the necessary data it is time to clean it and leave it ready for analysis. Not all the data you collect will be useful, when collecting big amounts of data in different formats it is very likely that you will find yourself with duplicate or badly formatted data. To avoid this, before you start working with your data you need to make sure to erase any white spaces, duplicate records, or formatting errors. This way you avoid hurting your analysis with bad-quality data.
- Analyze : With the help of various techniques such as statistical analysis, regressions, neural networks, text analysis, and more, you can start analyzing and manipulating your data to extract relevant conclusions. At this stage, you find trends, correlations, variations, and patterns that can help you answer the questions you first thought of in the identify stage. Various technologies in the market assist researchers and average users with the management of their data. Some of them include business intelligence and visualization software, predictive analytics, and data mining, among others.
- Interpret: Last but not least you have one of the most important steps: it is time to interpret your results. This stage is where the researcher comes up with courses of action based on the findings. For example, here you would understand if your clients prefer packaging that is red or green, plastic or paper, etc. Additionally, at this stage, you can also find some limitations and work on them.
Now that you have a basic understanding of the key data analysis steps, let’s look at the top 17 essential methods.
17 Essential Types Of Data Analysis Methods
Before diving into the 17 essential types of methods, it is important that we go over really fast through the main analysis categories. Starting with the category of descriptive up to prescriptive analysis, the complexity and effort of data evaluation increases, but also the added value for the company.
a) Descriptive analysis - What happened.
The descriptive analysis method is the starting point for any analytic reflection, and it aims to answer the question of what happened? It does this by ordering, manipulating, and interpreting raw data from various sources to turn it into valuable insights for your organization.
Performing descriptive analysis is essential, as it enables us to present our insights in a meaningful way. Although it is relevant to mention that this analysis on its own will not allow you to predict future outcomes or tell you the answer to questions like why something happened, it will leave your data organized and ready to conduct further investigations.
b) Exploratory analysis - How to explore data relationships.
As its name suggests, the main aim of the exploratory analysis is to explore. Prior to it, there is still no notion of the relationship between the data and the variables. Once the data is investigated, exploratory analysis helps you to find connections and generate hypotheses and solutions for specific problems. A typical area of application for it is data mining.
c) Diagnostic analysis - Why it happened.
Diagnostic data analytics empowers analysts and executives by helping them gain a firm contextual understanding of why something happened. If you know why something happened as well as how it happened, you will be able to pinpoint the exact ways of tackling the issue or challenge.
Designed to provide direct and actionable answers to specific questions, this is one of the world’s most important methods in research, among its other key organizational functions such as retail analytics , e.g.
c) Predictive analysis - What will happen.
The predictive method allows you to look into the future to answer the question: what will happen? In order to do this, it uses the results of the previously mentioned descriptive, exploratory, and diagnostic analysis, in addition to machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI). Through this, you can uncover future trends, potential problems or inefficiencies, connections, and casualties in your data.
With predictive analysis, you can unfold and develop initiatives that will not only enhance your various operational processes but also help you gain an all-important edge over the competition. If you understand why a trend, pattern, or event happened through data, you will be able to develop an informed projection of how things may unfold in particular areas of the business.
e) Prescriptive analysis - How will it happen.
Another of the most effective types of analysis methods in research. Prescriptive data techniques cross over from predictive analysis in the way that it revolves around using patterns or trends to develop responsive, practical business strategies.
By drilling down into prescriptive analysis, you will play an active role in the data consumption process by taking well-arranged sets of visual data and using it as a powerful fix to emerging issues in a number of key areas, including marketing, sales, customer experience, HR, fulfillment, finance, logistics analytics , and others.
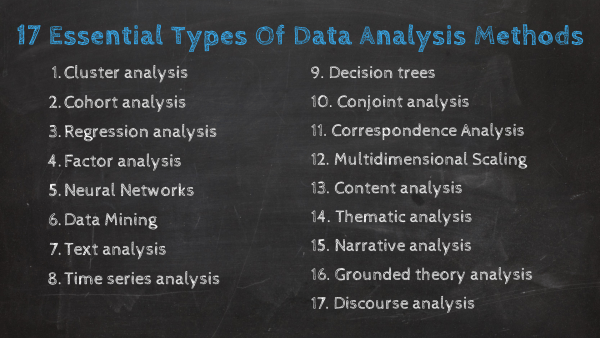
As mentioned at the beginning of the post, data analysis methods can be divided into two big categories: quantitative and qualitative. Each of these categories holds a powerful analytical value that changes depending on the scenario and type of data you are working with. Below, we will discuss 17 methods that are divided into qualitative and quantitative approaches.
Without further ado, here are the 17 essential types of data analysis methods with some use cases in the business world:
A. Quantitative Methods
To put it simply, quantitative analysis refers to all methods that use numerical data or data that can be turned into numbers (e.g. category variables like gender, age, etc.) to extract valuable insights. It is used to extract valuable conclusions about relationships, differences, and test hypotheses. Below we discuss some of the key quantitative methods.
1. Cluster analysis
The action of grouping a set of data elements in a way that said elements are more similar (in a particular sense) to each other than to those in other groups – hence the term ‘cluster.’ Since there is no target variable when clustering, the method is often used to find hidden patterns in the data. The approach is also used to provide additional context to a trend or dataset.
Let's look at it from an organizational perspective. In a perfect world, marketers would be able to analyze each customer separately and give them the best-personalized service, but let's face it, with a large customer base, it is timely impossible to do that. That's where clustering comes in. By grouping customers into clusters based on demographics, purchasing behaviors, monetary value, or any other factor that might be relevant for your company, you will be able to immediately optimize your efforts and give your customers the best experience based on their needs.
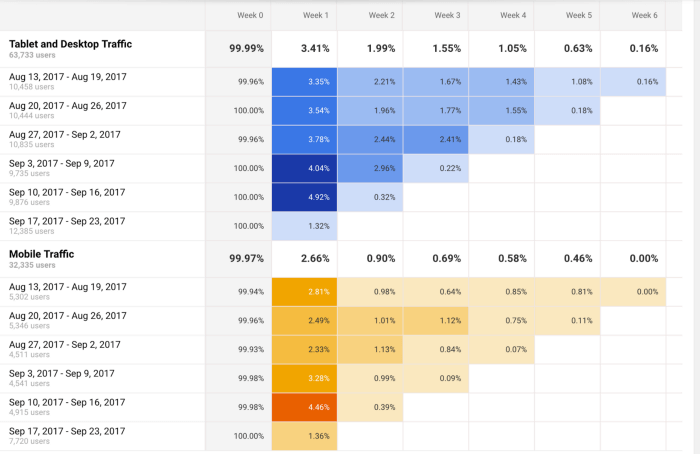
2. Cohort analysis
This type of data analysis approach uses historical data to examine and compare a determined segment of users' behavior, which can then be grouped with others with similar characteristics. By using this methodology, it's possible to gain a wealth of insight into consumer needs or a firm understanding of a broader target group.
Cohort analysis can be really useful for performing analysis in marketing as it will allow you to understand the impact of your campaigns on specific groups of customers. To exemplify, imagine you send an email campaign encouraging customers to sign up for your site. For this, you create two versions of the campaign with different designs, CTAs, and ad content. Later on, you can use cohort analysis to track the performance of the campaign for a longer period of time and understand which type of content is driving your customers to sign up, repurchase, or engage in other ways.
A useful tool to start performing cohort analysis method is Google Analytics. You can learn more about the benefits and limitations of using cohorts in GA in this useful guide . In the bottom image, you see an example of how you visualize a cohort in this tool. The segments (devices traffic) are divided into date cohorts (usage of devices) and then analyzed week by week to extract insights into performance.
3. Regression analysis
Regression uses historical data to understand how a dependent variable's value is affected when one (linear regression) or more independent variables (multiple regression) change or stay the same. By understanding each variable's relationship and how it developed in the past, you can anticipate possible outcomes and make better decisions in the future.
Let's bring it down with an example. Imagine you did a regression analysis of your sales in 2019 and discovered that variables like product quality, store design, customer service, marketing campaigns, and sales channels affected the overall result. Now you want to use regression to analyze which of these variables changed or if any new ones appeared during 2020. For example, you couldn’t sell as much in your physical store due to COVID lockdowns. Therefore, your sales could’ve either dropped in general or increased in your online channels. Through this, you can understand which independent variables affected the overall performance of your dependent variable, annual sales.
If you want to go deeper into this type of analysis, check out this article and learn more about how you can benefit from regression.
4. Neural networks
The neural network forms the basis for the intelligent algorithms of machine learning. It is a form of analytics that attempts, with minimal intervention, to understand how the human brain would generate insights and predict values. Neural networks learn from each and every data transaction, meaning that they evolve and advance over time.
A typical area of application for neural networks is predictive analytics. There are BI reporting tools that have this feature implemented within them, such as the Predictive Analytics Tool from datapine. This tool enables users to quickly and easily generate all kinds of predictions. All you have to do is select the data to be processed based on your KPIs, and the software automatically calculates forecasts based on historical and current data. Thanks to its user-friendly interface, anyone in your organization can manage it; there’s no need to be an advanced scientist.
Here is an example of how you can use the predictive analysis tool from datapine:
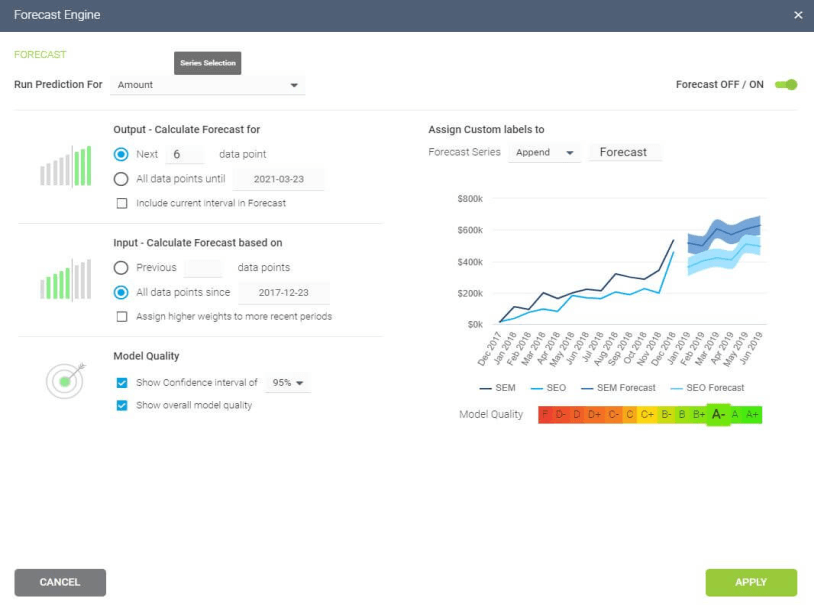
**click to enlarge**
5. Factor analysis
The factor analysis also called “dimension reduction” is a type of data analysis used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors. The aim here is to uncover independent latent variables, an ideal method for streamlining specific segments.
A good way to understand this data analysis method is a customer evaluation of a product. The initial assessment is based on different variables like color, shape, wearability, current trends, materials, comfort, the place where they bought the product, and frequency of usage. Like this, the list can be endless, depending on what you want to track. In this case, factor analysis comes into the picture by summarizing all of these variables into homogenous groups, for example, by grouping the variables color, materials, quality, and trends into a brother latent variable of design.
If you want to start analyzing data using factor analysis we recommend you take a look at this practical guide from UCLA.
6. Data mining
A method of data analysis that is the umbrella term for engineering metrics and insights for additional value, direction, and context. By using exploratory statistical evaluation, data mining aims to identify dependencies, relations, patterns, and trends to generate advanced knowledge. When considering how to analyze data, adopting a data mining mindset is essential to success - as such, it’s an area that is worth exploring in greater detail.
An excellent use case of data mining is datapine intelligent data alerts . With the help of artificial intelligence and machine learning, they provide automated signals based on particular commands or occurrences within a dataset. For example, if you’re monitoring supply chain KPIs , you could set an intelligent alarm to trigger when invalid or low-quality data appears. By doing so, you will be able to drill down deep into the issue and fix it swiftly and effectively.
In the following picture, you can see how the intelligent alarms from datapine work. By setting up ranges on daily orders, sessions, and revenues, the alarms will notify you if the goal was not completed or if it exceeded expectations.
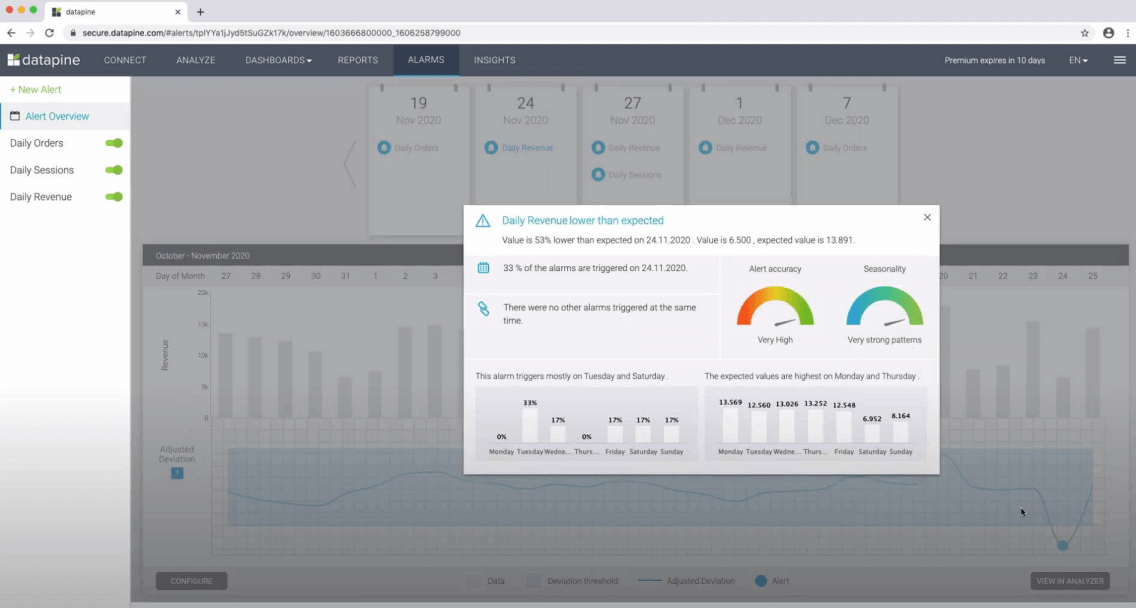
7. Time series analysis
As its name suggests, time series analysis is used to analyze a set of data points collected over a specified period of time. Although analysts use this method to monitor the data points in a specific interval of time rather than just monitoring them intermittently, the time series analysis is not uniquely used for the purpose of collecting data over time. Instead, it allows researchers to understand if variables changed during the duration of the study, how the different variables are dependent, and how did it reach the end result.
In a business context, this method is used to understand the causes of different trends and patterns to extract valuable insights. Another way of using this method is with the help of time series forecasting. Powered by predictive technologies, businesses can analyze various data sets over a period of time and forecast different future events.
A great use case to put time series analysis into perspective is seasonality effects on sales. By using time series forecasting to analyze sales data of a specific product over time, you can understand if sales rise over a specific period of time (e.g. swimwear during summertime, or candy during Halloween). These insights allow you to predict demand and prepare production accordingly.
8. Decision Trees
The decision tree analysis aims to act as a support tool to make smart and strategic decisions. By visually displaying potential outcomes, consequences, and costs in a tree-like model, researchers and company users can easily evaluate all factors involved and choose the best course of action. Decision trees are helpful to analyze quantitative data and they allow for an improved decision-making process by helping you spot improvement opportunities, reduce costs, and enhance operational efficiency and production.
But how does a decision tree actually works? This method works like a flowchart that starts with the main decision that you need to make and branches out based on the different outcomes and consequences of each decision. Each outcome will outline its own consequences, costs, and gains and, at the end of the analysis, you can compare each of them and make the smartest decision.
Businesses can use them to understand which project is more cost-effective and will bring more earnings in the long run. For example, imagine you need to decide if you want to update your software app or build a new app entirely. Here you would compare the total costs, the time needed to be invested, potential revenue, and any other factor that might affect your decision. In the end, you would be able to see which of these two options is more realistic and attainable for your company or research.
9. Conjoint analysis
Last but not least, we have the conjoint analysis. This approach is usually used in surveys to understand how individuals value different attributes of a product or service and it is one of the most effective methods to extract consumer preferences. When it comes to purchasing, some clients might be more price-focused, others more features-focused, and others might have a sustainable focus. Whatever your customer's preferences are, you can find them with conjoint analysis. Through this, companies can define pricing strategies, packaging options, subscription packages, and more.
A great example of conjoint analysis is in marketing and sales. For instance, a cupcake brand might use conjoint analysis and find that its clients prefer gluten-free options and cupcakes with healthier toppings over super sugary ones. Thus, the cupcake brand can turn these insights into advertisements and promotions to increase sales of this particular type of product. And not just that, conjoint analysis can also help businesses segment their customers based on their interests. This allows them to send different messaging that will bring value to each of the segments.
10. Correspondence Analysis
Also known as reciprocal averaging, correspondence analysis is a method used to analyze the relationship between categorical variables presented within a contingency table. A contingency table is a table that displays two (simple correspondence analysis) or more (multiple correspondence analysis) categorical variables across rows and columns that show the distribution of the data, which is usually answers to a survey or questionnaire on a specific topic.
This method starts by calculating an “expected value” which is done by multiplying row and column averages and dividing it by the overall original value of the specific table cell. The “expected value” is then subtracted from the original value resulting in a “residual number” which is what allows you to extract conclusions about relationships and distribution. The results of this analysis are later displayed using a map that represents the relationship between the different values. The closest two values are in the map, the bigger the relationship. Let’s put it into perspective with an example.
Imagine you are carrying out a market research analysis about outdoor clothing brands and how they are perceived by the public. For this analysis, you ask a group of people to match each brand with a certain attribute which can be durability, innovation, quality materials, etc. When calculating the residual numbers, you can see that brand A has a positive residual for innovation but a negative one for durability. This means that brand A is not positioned as a durable brand in the market, something that competitors could take advantage of.
11. Multidimensional Scaling (MDS)
MDS is a method used to observe the similarities or disparities between objects which can be colors, brands, people, geographical coordinates, and more. The objects are plotted using an “MDS map” that positions similar objects together and disparate ones far apart. The (dis) similarities between objects are represented using one or more dimensions that can be observed using a numerical scale. For example, if you want to know how people feel about the COVID-19 vaccine, you can use 1 for “don’t believe in the vaccine at all” and 10 for “firmly believe in the vaccine” and a scale of 2 to 9 for in between responses. When analyzing an MDS map the only thing that matters is the distance between the objects, the orientation of the dimensions is arbitrary and has no meaning at all.
Multidimensional scaling is a valuable technique for market research, especially when it comes to evaluating product or brand positioning. For instance, if a cupcake brand wants to know how they are positioned compared to competitors, it can define 2-3 dimensions such as taste, ingredients, shopping experience, or more, and do a multidimensional scaling analysis to find improvement opportunities as well as areas in which competitors are currently leading.
Another business example is in procurement when deciding on different suppliers. Decision makers can generate an MDS map to see how the different prices, delivery times, technical services, and more of the different suppliers differ and pick the one that suits their needs the best.
A final example proposed by a research paper on "An Improved Study of Multilevel Semantic Network Visualization for Analyzing Sentiment Word of Movie Review Data". Researchers picked a two-dimensional MDS map to display the distances and relationships between different sentiments in movie reviews. They used 36 sentiment words and distributed them based on their emotional distance as we can see in the image below where the words "outraged" and "sweet" are on opposite sides of the map, marking the distance between the two emotions very clearly.
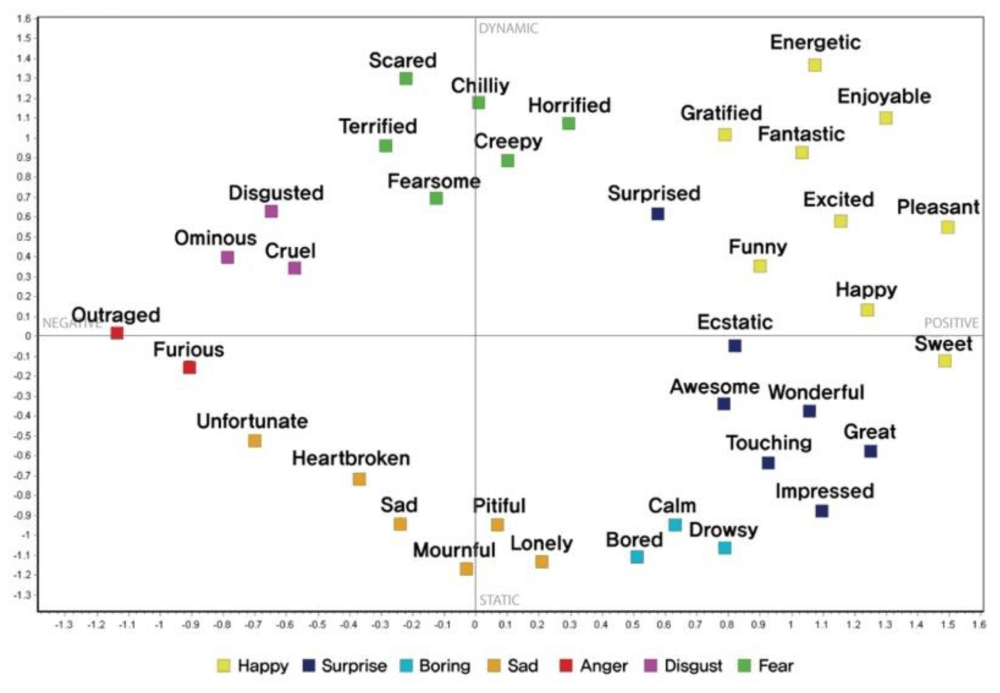
Aside from being a valuable technique to analyze dissimilarities, MDS also serves as a dimension-reduction technique for large dimensional data.
B. Qualitative Methods
Qualitative data analysis methods are defined as the observation of non-numerical data that is gathered and produced using methods of observation such as interviews, focus groups, questionnaires, and more. As opposed to quantitative methods, qualitative data is more subjective and highly valuable in analyzing customer retention and product development.
12. Text analysis
Text analysis, also known in the industry as text mining, works by taking large sets of textual data and arranging them in a way that makes it easier to manage. By working through this cleansing process in stringent detail, you will be able to extract the data that is truly relevant to your organization and use it to develop actionable insights that will propel you forward.
Modern software accelerate the application of text analytics. Thanks to the combination of machine learning and intelligent algorithms, you can perform advanced analytical processes such as sentiment analysis. This technique allows you to understand the intentions and emotions of a text, for example, if it's positive, negative, or neutral, and then give it a score depending on certain factors and categories that are relevant to your brand. Sentiment analysis is often used to monitor brand and product reputation and to understand how successful your customer experience is. To learn more about the topic check out this insightful article .
By analyzing data from various word-based sources, including product reviews, articles, social media communications, and survey responses, you will gain invaluable insights into your audience, as well as their needs, preferences, and pain points. This will allow you to create campaigns, services, and communications that meet your prospects’ needs on a personal level, growing your audience while boosting customer retention. There are various other “sub-methods” that are an extension of text analysis. Each of them serves a more specific purpose and we will look at them in detail next.
13. Content Analysis
This is a straightforward and very popular method that examines the presence and frequency of certain words, concepts, and subjects in different content formats such as text, image, audio, or video. For example, the number of times the name of a celebrity is mentioned on social media or online tabloids. It does this by coding text data that is later categorized and tabulated in a way that can provide valuable insights, making it the perfect mix of quantitative and qualitative analysis.
There are two types of content analysis. The first one is the conceptual analysis which focuses on explicit data, for instance, the number of times a concept or word is mentioned in a piece of content. The second one is relational analysis, which focuses on the relationship between different concepts or words and how they are connected within a specific context.
Content analysis is often used by marketers to measure brand reputation and customer behavior. For example, by analyzing customer reviews. It can also be used to analyze customer interviews and find directions for new product development. It is also important to note, that in order to extract the maximum potential out of this analysis method, it is necessary to have a clearly defined research question.
14. Thematic Analysis
Very similar to content analysis, thematic analysis also helps in identifying and interpreting patterns in qualitative data with the main difference being that the first one can also be applied to quantitative analysis. The thematic method analyzes large pieces of text data such as focus group transcripts or interviews and groups them into themes or categories that come up frequently within the text. It is a great method when trying to figure out peoples view’s and opinions about a certain topic. For example, if you are a brand that cares about sustainability, you can do a survey of your customers to analyze their views and opinions about sustainability and how they apply it to their lives. You can also analyze customer service calls transcripts to find common issues and improve your service.
Thematic analysis is a very subjective technique that relies on the researcher’s judgment. Therefore, to avoid biases, it has 6 steps that include familiarization, coding, generating themes, reviewing themes, defining and naming themes, and writing up. It is also important to note that, because it is a flexible approach, the data can be interpreted in multiple ways and it can be hard to select what data is more important to emphasize.
15. Narrative Analysis
A bit more complex in nature than the two previous ones, narrative analysis is used to explore the meaning behind the stories that people tell and most importantly, how they tell them. By looking into the words that people use to describe a situation you can extract valuable conclusions about their perspective on a specific topic. Common sources for narrative data include autobiographies, family stories, opinion pieces, and testimonials, among others.
From a business perspective, narrative analysis can be useful to analyze customer behaviors and feelings towards a specific product, service, feature, or others. It provides unique and deep insights that can be extremely valuable. However, it has some drawbacks.
The biggest weakness of this method is that the sample sizes are usually very small due to the complexity and time-consuming nature of the collection of narrative data. Plus, the way a subject tells a story will be significantly influenced by his or her specific experiences, making it very hard to replicate in a subsequent study.
16. Discourse Analysis
Discourse analysis is used to understand the meaning behind any type of written, verbal, or symbolic discourse based on its political, social, or cultural context. It mixes the analysis of languages and situations together. This means that the way the content is constructed and the meaning behind it is significantly influenced by the culture and society it takes place in. For example, if you are analyzing political speeches you need to consider different context elements such as the politician's background, the current political context of the country, the audience to which the speech is directed, and so on.
From a business point of view, discourse analysis is a great market research tool. It allows marketers to understand how the norms and ideas of the specific market work and how their customers relate to those ideas. It can be very useful to build a brand mission or develop a unique tone of voice.
17. Grounded Theory Analysis
Traditionally, researchers decide on a method and hypothesis and start to collect the data to prove that hypothesis. The grounded theory is the only method that doesn’t require an initial research question or hypothesis as its value lies in the generation of new theories. With the grounded theory method, you can go into the analysis process with an open mind and explore the data to generate new theories through tests and revisions. In fact, it is not necessary to collect the data and then start to analyze it. Researchers usually start to find valuable insights as they are gathering the data.
All of these elements make grounded theory a very valuable method as theories are fully backed by data instead of initial assumptions. It is a great technique to analyze poorly researched topics or find the causes behind specific company outcomes. For example, product managers and marketers might use the grounded theory to find the causes of high levels of customer churn and look into customer surveys and reviews to develop new theories about the causes.
How To Analyze Data? Top 17 Data Analysis Techniques To Apply

Now that we’ve answered the questions “what is data analysis’”, why is it important, and covered the different data analysis types, it’s time to dig deeper into how to perform your analysis by working through these 17 essential techniques.
1. Collaborate your needs
Before you begin analyzing or drilling down into any techniques, it’s crucial to sit down collaboratively with all key stakeholders within your organization, decide on your primary campaign or strategic goals, and gain a fundamental understanding of the types of insights that will best benefit your progress or provide you with the level of vision you need to evolve your organization.
2. Establish your questions
Once you’ve outlined your core objectives, you should consider which questions will need answering to help you achieve your mission. This is one of the most important techniques as it will shape the very foundations of your success.
To help you ask the right things and ensure your data works for you, you have to ask the right data analysis questions .
3. Data democratization
After giving your data analytics methodology some real direction, and knowing which questions need answering to extract optimum value from the information available to your organization, you should continue with democratization.
Data democratization is an action that aims to connect data from various sources efficiently and quickly so that anyone in your organization can access it at any given moment. You can extract data in text, images, videos, numbers, or any other format. And then perform cross-database analysis to achieve more advanced insights to share with the rest of the company interactively.
Once you have decided on your most valuable sources, you need to take all of this into a structured format to start collecting your insights. For this purpose, datapine offers an easy all-in-one data connectors feature to integrate all your internal and external sources and manage them at your will. Additionally, datapine’s end-to-end solution automatically updates your data, allowing you to save time and focus on performing the right analysis to grow your company.
4. Think of governance
When collecting data in a business or research context you always need to think about security and privacy. With data breaches becoming a topic of concern for businesses, the need to protect your client's or subject’s sensitive information becomes critical.
To ensure that all this is taken care of, you need to think of a data governance strategy. According to Gartner , this concept refers to “ the specification of decision rights and an accountability framework to ensure the appropriate behavior in the valuation, creation, consumption, and control of data and analytics .” In simpler words, data governance is a collection of processes, roles, and policies, that ensure the efficient use of data while still achieving the main company goals. It ensures that clear roles are in place for who can access the information and how they can access it. In time, this not only ensures that sensitive information is protected but also allows for an efficient analysis as a whole.
5. Clean your data
After harvesting from so many sources you will be left with a vast amount of information that can be overwhelming to deal with. At the same time, you can be faced with incorrect data that can be misleading to your analysis. The smartest thing you can do to avoid dealing with this in the future is to clean the data. This is fundamental before visualizing it, as it will ensure that the insights you extract from it are correct.
There are many things that you need to look for in the cleaning process. The most important one is to eliminate any duplicate observations; this usually appears when using multiple internal and external sources of information. You can also add any missing codes, fix empty fields, and eliminate incorrectly formatted data.
Another usual form of cleaning is done with text data. As we mentioned earlier, most companies today analyze customer reviews, social media comments, questionnaires, and several other text inputs. In order for algorithms to detect patterns, text data needs to be revised to avoid invalid characters or any syntax or spelling errors.
Most importantly, the aim of cleaning is to prevent you from arriving at false conclusions that can damage your company in the long run. By using clean data, you will also help BI solutions to interact better with your information and create better reports for your organization.
6. Set your KPIs
Once you’ve set your sources, cleaned your data, and established clear-cut questions you want your insights to answer, you need to set a host of key performance indicators (KPIs) that will help you track, measure, and shape your progress in a number of key areas.
KPIs are critical to both qualitative and quantitative analysis research. This is one of the primary methods of data analysis you certainly shouldn’t overlook.
To help you set the best possible KPIs for your initiatives and activities, here is an example of a relevant logistics KPI : transportation-related costs. If you want to see more go explore our collection of key performance indicator examples .
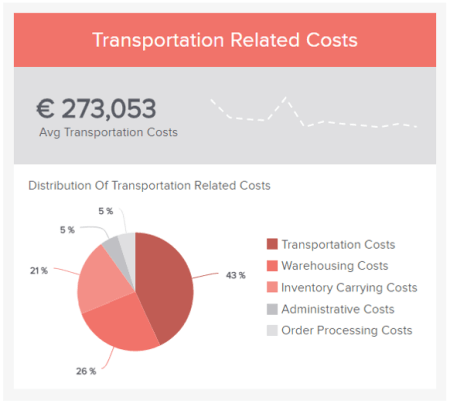
7. Omit useless data
Having bestowed your data analysis tools and techniques with true purpose and defined your mission, you should explore the raw data you’ve collected from all sources and use your KPIs as a reference for chopping out any information you deem to be useless.
Trimming the informational fat is one of the most crucial methods of analysis as it will allow you to focus your analytical efforts and squeeze every drop of value from the remaining ‘lean’ information.
Any stats, facts, figures, or metrics that don’t align with your business goals or fit with your KPI management strategies should be eliminated from the equation.
8. Build a data management roadmap
While, at this point, this particular step is optional (you will have already gained a wealth of insight and formed a fairly sound strategy by now), creating a data governance roadmap will help your data analysis methods and techniques become successful on a more sustainable basis. These roadmaps, if developed properly, are also built so they can be tweaked and scaled over time.
Invest ample time in developing a roadmap that will help you store, manage, and handle your data internally, and you will make your analysis techniques all the more fluid and functional – one of the most powerful types of data analysis methods available today.
9. Integrate technology
There are many ways to analyze data, but one of the most vital aspects of analytical success in a business context is integrating the right decision support software and technology.
Robust analysis platforms will not only allow you to pull critical data from your most valuable sources while working with dynamic KPIs that will offer you actionable insights; it will also present them in a digestible, visual, interactive format from one central, live dashboard . A data methodology you can count on.
By integrating the right technology within your data analysis methodology, you’ll avoid fragmenting your insights, saving you time and effort while allowing you to enjoy the maximum value from your business’s most valuable insights.
For a look at the power of software for the purpose of analysis and to enhance your methods of analyzing, glance over our selection of dashboard examples .
10. Answer your questions
By considering each of the above efforts, working with the right technology, and fostering a cohesive internal culture where everyone buys into the different ways to analyze data as well as the power of digital intelligence, you will swiftly start to answer your most burning business questions. Arguably, the best way to make your data concepts accessible across the organization is through data visualization.
11. Visualize your data
Online data visualization is a powerful tool as it lets you tell a story with your metrics, allowing users across the organization to extract meaningful insights that aid business evolution – and it covers all the different ways to analyze data.
The purpose of analyzing is to make your entire organization more informed and intelligent, and with the right platform or dashboard, this is simpler than you think, as demonstrated by our marketing dashboard .
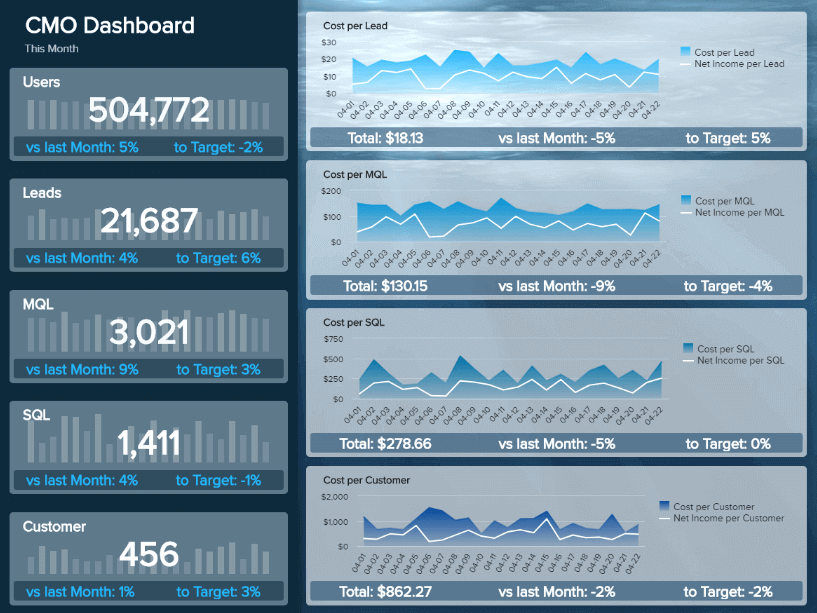
This visual, dynamic, and interactive online dashboard is a data analysis example designed to give Chief Marketing Officers (CMO) an overview of relevant metrics to help them understand if they achieved their monthly goals.
In detail, this example generated with a modern dashboard creator displays interactive charts for monthly revenues, costs, net income, and net income per customer; all of them are compared with the previous month so that you can understand how the data fluctuated. In addition, it shows a detailed summary of the number of users, customers, SQLs, and MQLs per month to visualize the whole picture and extract relevant insights or trends for your marketing reports .
The CMO dashboard is perfect for c-level management as it can help them monitor the strategic outcome of their marketing efforts and make data-driven decisions that can benefit the company exponentially.
12. Be careful with the interpretation
We already dedicated an entire post to data interpretation as it is a fundamental part of the process of data analysis. It gives meaning to the analytical information and aims to drive a concise conclusion from the analysis results. Since most of the time companies are dealing with data from many different sources, the interpretation stage needs to be done carefully and properly in order to avoid misinterpretations.
To help you through the process, here we list three common practices that you need to avoid at all costs when looking at your data:
- Correlation vs. causation: The human brain is formatted to find patterns. This behavior leads to one of the most common mistakes when performing interpretation: confusing correlation with causation. Although these two aspects can exist simultaneously, it is not correct to assume that because two things happened together, one provoked the other. A piece of advice to avoid falling into this mistake is never to trust just intuition, trust the data. If there is no objective evidence of causation, then always stick to correlation.
- Confirmation bias: This phenomenon describes the tendency to select and interpret only the data necessary to prove one hypothesis, often ignoring the elements that might disprove it. Even if it's not done on purpose, confirmation bias can represent a real problem, as excluding relevant information can lead to false conclusions and, therefore, bad business decisions. To avoid it, always try to disprove your hypothesis instead of proving it, share your analysis with other team members, and avoid drawing any conclusions before the entire analytical project is finalized.
- Statistical significance: To put it in short words, statistical significance helps analysts understand if a result is actually accurate or if it happened because of a sampling error or pure chance. The level of statistical significance needed might depend on the sample size and the industry being analyzed. In any case, ignoring the significance of a result when it might influence decision-making can be a huge mistake.
13. Build a narrative
Now, we’re going to look at how you can bring all of these elements together in a way that will benefit your business - starting with a little something called data storytelling.
The human brain responds incredibly well to strong stories or narratives. Once you’ve cleansed, shaped, and visualized your most invaluable data using various BI dashboard tools , you should strive to tell a story - one with a clear-cut beginning, middle, and end.
By doing so, you will make your analytical efforts more accessible, digestible, and universal, empowering more people within your organization to use your discoveries to their actionable advantage.
14. Consider autonomous technology
Autonomous technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), play a significant role in the advancement of understanding how to analyze data more effectively.
Gartner predicts that by the end of this year, 80% of emerging technologies will be developed with AI foundations. This is a testament to the ever-growing power and value of autonomous technologies.
At the moment, these technologies are revolutionizing the analysis industry. Some examples that we mentioned earlier are neural networks, intelligent alarms, and sentiment analysis.
15. Share the load
If you work with the right tools and dashboards, you will be able to present your metrics in a digestible, value-driven format, allowing almost everyone in the organization to connect with and use relevant data to their advantage.
Modern dashboards consolidate data from various sources, providing access to a wealth of insights in one centralized location, no matter if you need to monitor recruitment metrics or generate reports that need to be sent across numerous departments. Moreover, these cutting-edge tools offer access to dashboards from a multitude of devices, meaning that everyone within the business can connect with practical insights remotely - and share the load.
Once everyone is able to work with a data-driven mindset, you will catalyze the success of your business in ways you never thought possible. And when it comes to knowing how to analyze data, this kind of collaborative approach is essential.
16. Data analysis tools
In order to perform high-quality analysis of data, it is fundamental to use tools and software that will ensure the best results. Here we leave you a small summary of four fundamental categories of data analysis tools for your organization.
- Business Intelligence: BI tools allow you to process significant amounts of data from several sources in any format. Through this, you can not only analyze and monitor your data to extract relevant insights but also create interactive reports and dashboards to visualize your KPIs and use them for your company's good. datapine is an amazing online BI software that is focused on delivering powerful online analysis features that are accessible to beginner and advanced users. Like this, it offers a full-service solution that includes cutting-edge analysis of data, KPIs visualization, live dashboards, reporting, and artificial intelligence technologies to predict trends and minimize risk.
- Statistical analysis: These tools are usually designed for scientists, statisticians, market researchers, and mathematicians, as they allow them to perform complex statistical analyses with methods like regression analysis, predictive analysis, and statistical modeling. A good tool to perform this type of analysis is R-Studio as it offers a powerful data modeling and hypothesis testing feature that can cover both academic and general data analysis. This tool is one of the favorite ones in the industry, due to its capability for data cleaning, data reduction, and performing advanced analysis with several statistical methods. Another relevant tool to mention is SPSS from IBM. The software offers advanced statistical analysis for users of all skill levels. Thanks to a vast library of machine learning algorithms, text analysis, and a hypothesis testing approach it can help your company find relevant insights to drive better decisions. SPSS also works as a cloud service that enables you to run it anywhere.
- SQL Consoles: SQL is a programming language often used to handle structured data in relational databases. Tools like these are popular among data scientists as they are extremely effective in unlocking these databases' value. Undoubtedly, one of the most used SQL software in the market is MySQL Workbench . This tool offers several features such as a visual tool for database modeling and monitoring, complete SQL optimization, administration tools, and visual performance dashboards to keep track of KPIs.
- Data Visualization: These tools are used to represent your data through charts, graphs, and maps that allow you to find patterns and trends in the data. datapine's already mentioned BI platform also offers a wealth of powerful online data visualization tools with several benefits. Some of them include: delivering compelling data-driven presentations to share with your entire company, the ability to see your data online with any device wherever you are, an interactive dashboard design feature that enables you to showcase your results in an interactive and understandable way, and to perform online self-service reports that can be used simultaneously with several other people to enhance team productivity.
17. Refine your process constantly
Last is a step that might seem obvious to some people, but it can be easily ignored if you think you are done. Once you have extracted the needed results, you should always take a retrospective look at your project and think about what you can improve. As you saw throughout this long list of techniques, data analysis is a complex process that requires constant refinement. For this reason, you should always go one step further and keep improving.
Quality Criteria For Data Analysis
So far we’ve covered a list of methods and techniques that should help you perform efficient data analysis. But how do you measure the quality and validity of your results? This is done with the help of some science quality criteria. Here we will go into a more theoretical area that is critical to understanding the fundamentals of statistical analysis in science. However, you should also be aware of these steps in a business context, as they will allow you to assess the quality of your results in the correct way. Let’s dig in.
- Internal validity: The results of a survey are internally valid if they measure what they are supposed to measure and thus provide credible results. In other words , internal validity measures the trustworthiness of the results and how they can be affected by factors such as the research design, operational definitions, how the variables are measured, and more. For instance, imagine you are doing an interview to ask people if they brush their teeth two times a day. While most of them will answer yes, you can still notice that their answers correspond to what is socially acceptable, which is to brush your teeth at least twice a day. In this case, you can’t be 100% sure if respondents actually brush their teeth twice a day or if they just say that they do, therefore, the internal validity of this interview is very low.
- External validity: Essentially, external validity refers to the extent to which the results of your research can be applied to a broader context. It basically aims to prove that the findings of a study can be applied in the real world. If the research can be applied to other settings, individuals, and times, then the external validity is high.
- Reliability : If your research is reliable, it means that it can be reproduced. If your measurement were repeated under the same conditions, it would produce similar results. This means that your measuring instrument consistently produces reliable results. For example, imagine a doctor building a symptoms questionnaire to detect a specific disease in a patient. Then, various other doctors use this questionnaire but end up diagnosing the same patient with a different condition. This means the questionnaire is not reliable in detecting the initial disease. Another important note here is that in order for your research to be reliable, it also needs to be objective. If the results of a study are the same, independent of who assesses them or interprets them, the study can be considered reliable. Let’s see the objectivity criteria in more detail now.
- Objectivity: In data science, objectivity means that the researcher needs to stay fully objective when it comes to its analysis. The results of a study need to be affected by objective criteria and not by the beliefs, personality, or values of the researcher. Objectivity needs to be ensured when you are gathering the data, for example, when interviewing individuals, the questions need to be asked in a way that doesn't influence the results. Paired with this, objectivity also needs to be thought of when interpreting the data. If different researchers reach the same conclusions, then the study is objective. For this last point, you can set predefined criteria to interpret the results to ensure all researchers follow the same steps.
The discussed quality criteria cover mostly potential influences in a quantitative context. Analysis in qualitative research has by default additional subjective influences that must be controlled in a different way. Therefore, there are other quality criteria for this kind of research such as credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability. You can see each of them more in detail on this resource .
Data Analysis Limitations & Barriers
Analyzing data is not an easy task. As you’ve seen throughout this post, there are many steps and techniques that you need to apply in order to extract useful information from your research. While a well-performed analysis can bring various benefits to your organization it doesn't come without limitations. In this section, we will discuss some of the main barriers you might encounter when conducting an analysis. Let’s see them more in detail.
- Lack of clear goals: No matter how good your data or analysis might be if you don’t have clear goals or a hypothesis the process might be worthless. While we mentioned some methods that don’t require a predefined hypothesis, it is always better to enter the analytical process with some clear guidelines of what you are expecting to get out of it, especially in a business context in which data is utilized to support important strategic decisions.
- Objectivity: Arguably one of the biggest barriers when it comes to data analysis in research is to stay objective. When trying to prove a hypothesis, researchers might find themselves, intentionally or unintentionally, directing the results toward an outcome that they want. To avoid this, always question your assumptions and avoid confusing facts with opinions. You can also show your findings to a research partner or external person to confirm that your results are objective.
- Data representation: A fundamental part of the analytical procedure is the way you represent your data. You can use various graphs and charts to represent your findings, but not all of them will work for all purposes. Choosing the wrong visual can not only damage your analysis but can mislead your audience, therefore, it is important to understand when to use each type of data depending on your analytical goals. Our complete guide on the types of graphs and charts lists 20 different visuals with examples of when to use them.
- Flawed correlation : Misleading statistics can significantly damage your research. We’ve already pointed out a few interpretation issues previously in the post, but it is an important barrier that we can't avoid addressing here as well. Flawed correlations occur when two variables appear related to each other but they are not. Confusing correlations with causation can lead to a wrong interpretation of results which can lead to building wrong strategies and loss of resources, therefore, it is very important to identify the different interpretation mistakes and avoid them.
- Sample size: A very common barrier to a reliable and efficient analysis process is the sample size. In order for the results to be trustworthy, the sample size should be representative of what you are analyzing. For example, imagine you have a company of 1000 employees and you ask the question “do you like working here?” to 50 employees of which 49 say yes, which means 95%. Now, imagine you ask the same question to the 1000 employees and 950 say yes, which also means 95%. Saying that 95% of employees like working in the company when the sample size was only 50 is not a representative or trustworthy conclusion. The significance of the results is way more accurate when surveying a bigger sample size.
- Privacy concerns: In some cases, data collection can be subjected to privacy regulations. Businesses gather all kinds of information from their customers from purchasing behaviors to addresses and phone numbers. If this falls into the wrong hands due to a breach, it can affect the security and confidentiality of your clients. To avoid this issue, you need to collect only the data that is needed for your research and, if you are using sensitive facts, make it anonymous so customers are protected. The misuse of customer data can severely damage a business's reputation, so it is important to keep an eye on privacy.
- Lack of communication between teams : When it comes to performing data analysis on a business level, it is very likely that each department and team will have different goals and strategies. However, they are all working for the same common goal of helping the business run smoothly and keep growing. When teams are not connected and communicating with each other, it can directly affect the way general strategies are built. To avoid these issues, tools such as data dashboards enable teams to stay connected through data in a visually appealing way.
- Innumeracy : Businesses are working with data more and more every day. While there are many BI tools available to perform effective analysis, data literacy is still a constant barrier. Not all employees know how to apply analysis techniques or extract insights from them. To prevent this from happening, you can implement different training opportunities that will prepare every relevant user to deal with data.
Key Data Analysis Skills
As you've learned throughout this lengthy guide, analyzing data is a complex task that requires a lot of knowledge and skills. That said, thanks to the rise of self-service tools the process is way more accessible and agile than it once was. Regardless, there are still some key skills that are valuable to have when working with data, we list the most important ones below.
- Critical and statistical thinking: To successfully analyze data you need to be creative and think out of the box. Yes, that might sound like a weird statement considering that data is often tight to facts. However, a great level of critical thinking is required to uncover connections, come up with a valuable hypothesis, and extract conclusions that go a step further from the surface. This, of course, needs to be complemented by statistical thinking and an understanding of numbers.
- Data cleaning: Anyone who has ever worked with data before will tell you that the cleaning and preparation process accounts for 80% of a data analyst's work, therefore, the skill is fundamental. But not just that, not cleaning the data adequately can also significantly damage the analysis which can lead to poor decision-making in a business scenario. While there are multiple tools that automate the cleaning process and eliminate the possibility of human error, it is still a valuable skill to dominate.
- Data visualization: Visuals make the information easier to understand and analyze, not only for professional users but especially for non-technical ones. Having the necessary skills to not only choose the right chart type but know when to apply it correctly is key. This also means being able to design visually compelling charts that make the data exploration process more efficient.
- SQL: The Structured Query Language or SQL is a programming language used to communicate with databases. It is fundamental knowledge as it enables you to update, manipulate, and organize data from relational databases which are the most common databases used by companies. It is fairly easy to learn and one of the most valuable skills when it comes to data analysis.
- Communication skills: This is a skill that is especially valuable in a business environment. Being able to clearly communicate analytical outcomes to colleagues is incredibly important, especially when the information you are trying to convey is complex for non-technical people. This applies to in-person communication as well as written format, for example, when generating a dashboard or report. While this might be considered a “soft” skill compared to the other ones we mentioned, it should not be ignored as you most likely will need to share analytical findings with others no matter the context.
Data Analysis In The Big Data Environment
Big data is invaluable to today’s businesses, and by using different methods for data analysis, it’s possible to view your data in a way that can help you turn insight into positive action.
To inspire your efforts and put the importance of big data into context, here are some insights that you should know:
- By 2026 the industry of big data is expected to be worth approximately $273.4 billion.
- 94% of enterprises say that analyzing data is important for their growth and digital transformation.
- Companies that exploit the full potential of their data can increase their operating margins by 60% .
- We already told you the benefits of Artificial Intelligence through this article. This industry's financial impact is expected to grow up to $40 billion by 2025.
Data analysis concepts may come in many forms, but fundamentally, any solid methodology will help to make your business more streamlined, cohesive, insightful, and successful than ever before.
Key Takeaways From Data Analysis
As we reach the end of our data analysis journey, we leave a small summary of the main methods and techniques to perform excellent analysis and grow your business.
17 Essential Types of Data Analysis Methods:
- Cluster analysis
- Cohort analysis
- Regression analysis
- Factor analysis
- Neural Networks
- Data Mining
- Text analysis
- Time series analysis
- Decision trees
- Conjoint analysis
- Correspondence Analysis
- Multidimensional Scaling
- Content analysis
- Thematic analysis
- Narrative analysis
- Grounded theory analysis
- Discourse analysis
Top 17 Data Analysis Techniques:
- Collaborate your needs
- Establish your questions
- Data democratization
- Think of data governance
- Clean your data
- Set your KPIs
- Omit useless data
- Build a data management roadmap
- Integrate technology
- Answer your questions
- Visualize your data
- Interpretation of data
- Consider autonomous technology
- Build a narrative
- Share the load
- Data Analysis tools
- Refine your process constantly
We’ve pondered the data analysis definition and drilled down into the practical applications of data-centric analytics, and one thing is clear: by taking measures to arrange your data and making your metrics work for you, it’s possible to transform raw information into action - the kind of that will push your business to the next level.
Yes, good data analytics techniques result in enhanced business intelligence (BI). To help you understand this notion in more detail, read our exploration of business intelligence reporting .
And, if you’re ready to perform your own analysis, drill down into your facts and figures while interacting with your data on astonishing visuals, you can try our software for a free, 14-day trial .

Data & Finance for Work & Life

Data Analysis: Types, Methods & Techniques (a Complete List)
( Updated Version )
While the term sounds intimidating, “data analysis” is nothing more than making sense of information in a table. It consists of filtering, sorting, grouping, and manipulating data tables with basic algebra and statistics.
In fact, you don’t need experience to understand the basics. You have already worked with data extensively in your life, and “analysis” is nothing more than a fancy word for good sense and basic logic.
Over time, people have intuitively categorized the best logical practices for treating data. These categories are what we call today types , methods , and techniques .
This article provides a comprehensive list of types, methods, and techniques, and explains the difference between them.
For a practical intro to data analysis (including types, methods, & techniques), check out our Intro to Data Analysis eBook for free.
Descriptive, Diagnostic, Predictive, & Prescriptive Analysis
If you Google “types of data analysis,” the first few results will explore descriptive , diagnostic , predictive , and prescriptive analysis. Why? Because these names are easy to understand and are used a lot in “the real world.”
Descriptive analysis is an informational method, diagnostic analysis explains “why” a phenomenon occurs, predictive analysis seeks to forecast the result of an action, and prescriptive analysis identifies solutions to a specific problem.
That said, these are only four branches of a larger analytical tree.
Good data analysts know how to position these four types within other analytical methods and tactics, allowing them to leverage strengths and weaknesses in each to uproot the most valuable insights.
Let’s explore the full analytical tree to understand how to appropriately assess and apply these four traditional types.
Tree diagram of Data Analysis Types, Methods, and Techniques
Here’s a picture to visualize the structure and hierarchy of data analysis types, methods, and techniques.
If it’s too small you can view the picture in a new tab . Open it to follow along!

Note: basic descriptive statistics such as mean , median , and mode , as well as standard deviation , are not shown because most people are already familiar with them. In the diagram, they would fall under the “descriptive” analysis type.
Tree Diagram Explained
The highest-level classification of data analysis is quantitative vs qualitative . Quantitative implies numbers while qualitative implies information other than numbers.
Quantitative data analysis then splits into mathematical analysis and artificial intelligence (AI) analysis . Mathematical types then branch into descriptive , diagnostic , predictive , and prescriptive .
Methods falling under mathematical analysis include clustering , classification , forecasting , and optimization . Qualitative data analysis methods include content analysis , narrative analysis , discourse analysis , framework analysis , and/or grounded theory .
Moreover, mathematical techniques include regression , Nïave Bayes , Simple Exponential Smoothing , cohorts , factors , linear discriminants , and more, whereas techniques falling under the AI type include artificial neural networks , decision trees , evolutionary programming , and fuzzy logic . Techniques under qualitative analysis include text analysis , coding , idea pattern analysis , and word frequency .
It’s a lot to remember! Don’t worry, once you understand the relationship and motive behind all these terms, it’ll be like riding a bike.
We’ll move down the list from top to bottom and I encourage you to open the tree diagram above in a new tab so you can follow along .
But first, let’s just address the elephant in the room: what’s the difference between methods and techniques anyway?
Difference between methods and techniques
Though often used interchangeably, methods ands techniques are not the same. By definition, methods are the process by which techniques are applied, and techniques are the practical application of those methods.
For example, consider driving. Methods include staying in your lane, stopping at a red light, and parking in a spot. Techniques include turning the steering wheel, braking, and pushing the gas pedal.
Data sets: observations and fields
It’s important to understand the basic structure of data tables to comprehend the rest of the article. A data set consists of one far-left column containing observations, then a series of columns containing the fields (aka “traits” or “characteristics”) that describe each observations. For example, imagine we want a data table for fruit. It might look like this:
Now let’s turn to types, methods, and techniques. Each heading below consists of a description, relative importance, the nature of data it explores, and the motivation for using it.
Quantitative Analysis
- It accounts for more than 50% of all data analysis and is by far the most widespread and well-known type of data analysis.
- As you have seen, it holds descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive methods, which in turn hold some of the most important techniques available today, such as clustering and forecasting.
- It can be broken down into mathematical and AI analysis.
- Importance : Very high . Quantitative analysis is a must for anyone interesting in becoming or improving as a data analyst.
- Nature of Data: data treated under quantitative analysis is, quite simply, quantitative. It encompasses all numeric data.
- Motive: to extract insights. (Note: we’re at the top of the pyramid, this gets more insightful as we move down.)
Qualitative Analysis
- It accounts for less than 30% of all data analysis and is common in social sciences .
- It can refer to the simple recognition of qualitative elements, which is not analytic in any way, but most often refers to methods that assign numeric values to non-numeric data for analysis.
- Because of this, some argue that it’s ultimately a quantitative type.
- Importance: Medium. In general, knowing qualitative data analysis is not common or even necessary for corporate roles. However, for researchers working in social sciences, its importance is very high .
- Nature of Data: data treated under qualitative analysis is non-numeric. However, as part of the analysis, analysts turn non-numeric data into numbers, at which point many argue it is no longer qualitative analysis.
- Motive: to extract insights. (This will be more important as we move down the pyramid.)
Mathematical Analysis
- Description: mathematical data analysis is a subtype of qualitative data analysis that designates methods and techniques based on statistics, algebra, and logical reasoning to extract insights. It stands in opposition to artificial intelligence analysis.
- Importance: Very High. The most widespread methods and techniques fall under mathematical analysis. In fact, it’s so common that many people use “quantitative” and “mathematical” analysis interchangeably.
- Nature of Data: numeric. By definition, all data under mathematical analysis are numbers.
- Motive: to extract measurable insights that can be used to act upon.
Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Analysis
- Description: artificial intelligence and machine learning analyses designate techniques based on the titular skills. They are not traditionally mathematical, but they are quantitative since they use numbers. Applications of AI & ML analysis techniques are developing, but they’re not yet mainstream enough to show promise across the field.
- Importance: Medium . As of today (September 2020), you don’t need to be fluent in AI & ML data analysis to be a great analyst. BUT, if it’s a field that interests you, learn it. Many believe that in 10 year’s time its importance will be very high .
- Nature of Data: numeric.
- Motive: to create calculations that build on themselves in order and extract insights without direct input from a human.
Descriptive Analysis
- Description: descriptive analysis is a subtype of mathematical data analysis that uses methods and techniques to provide information about the size, dispersion, groupings, and behavior of data sets. This may sounds complicated, but just think about mean, median, and mode: all three are types of descriptive analysis. They provide information about the data set. We’ll look at specific techniques below.
- Importance: Very high. Descriptive analysis is among the most commonly used data analyses in both corporations and research today.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data under descriptive statistics is sets. A set is simply a collection of numbers that behaves in predictable ways. Data reflects real life, and there are patterns everywhere to be found. Descriptive analysis describes those patterns.
- Motive: the motive behind descriptive analysis is to understand how numbers in a set group together, how far apart they are from each other, and how often they occur. As with most statistical analysis, the more data points there are, the easier it is to describe the set.
Diagnostic Analysis
- Description: diagnostic analysis answers the question “why did it happen?” It is an advanced type of mathematical data analysis that manipulates multiple techniques, but does not own any single one. Analysts engage in diagnostic analysis when they try to explain why.
- Importance: Very high. Diagnostics are probably the most important type of data analysis for people who don’t do analysis because they’re valuable to anyone who’s curious. They’re most common in corporations, as managers often only want to know the “why.”
- Nature of Data : data under diagnostic analysis are data sets. These sets in themselves are not enough under diagnostic analysis. Instead, the analyst must know what’s behind the numbers in order to explain “why.” That’s what makes diagnostics so challenging yet so valuable.
- Motive: the motive behind diagnostics is to diagnose — to understand why.
Predictive Analysis
- Description: predictive analysis uses past data to project future data. It’s very often one of the first kinds of analysis new researchers and corporate analysts use because it is intuitive. It is a subtype of the mathematical type of data analysis, and its three notable techniques are regression, moving average, and exponential smoothing.
- Importance: Very high. Predictive analysis is critical for any data analyst working in a corporate environment. Companies always want to know what the future will hold — especially for their revenue.
- Nature of Data: Because past and future imply time, predictive data always includes an element of time. Whether it’s minutes, hours, days, months, or years, we call this time series data . In fact, this data is so important that I’ll mention it twice so you don’t forget: predictive analysis uses time series data .
- Motive: the motive for investigating time series data with predictive analysis is to predict the future in the most analytical way possible.
Prescriptive Analysis
- Description: prescriptive analysis is a subtype of mathematical analysis that answers the question “what will happen if we do X?” It’s largely underestimated in the data analysis world because it requires diagnostic and descriptive analyses to be done before it even starts. More than simple predictive analysis, prescriptive analysis builds entire data models to show how a simple change could impact the ensemble.
- Importance: High. Prescriptive analysis is most common under the finance function in many companies. Financial analysts use it to build a financial model of the financial statements that show how that data will change given alternative inputs.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data in prescriptive analysis is data sets. These data sets contain patterns that respond differently to various inputs. Data that is useful for prescriptive analysis contains correlations between different variables. It’s through these correlations that we establish patterns and prescribe action on this basis. This analysis cannot be performed on data that exists in a vacuum — it must be viewed on the backdrop of the tangibles behind it.
- Motive: the motive for prescriptive analysis is to establish, with an acceptable degree of certainty, what results we can expect given a certain action. As you might expect, this necessitates that the analyst or researcher be aware of the world behind the data, not just the data itself.
Clustering Method
- Description: the clustering method groups data points together based on their relativeness closeness to further explore and treat them based on these groupings. There are two ways to group clusters: intuitively and statistically (or K-means).
- Importance: Very high. Though most corporate roles group clusters intuitively based on management criteria, a solid understanding of how to group them mathematically is an excellent descriptive and diagnostic approach to allow for prescriptive analysis thereafter.
- Nature of Data : the nature of data useful for clustering is sets with 1 or more data fields. While most people are used to looking at only two dimensions (x and y), clustering becomes more accurate the more fields there are.
- Motive: the motive for clustering is to understand how data sets group and to explore them further based on those groups.
- Here’s an example set:

Classification Method
- Description: the classification method aims to separate and group data points based on common characteristics . This can be done intuitively or statistically.
- Importance: High. While simple on the surface, classification can become quite complex. It’s very valuable in corporate and research environments, but can feel like its not worth the work. A good analyst can execute it quickly to deliver results.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful for classification is data sets. As we will see, it can be used on qualitative data as well as quantitative. This method requires knowledge of the substance behind the data, not just the numbers themselves.
- Motive: the motive for classification is group data not based on mathematical relationships (which would be clustering), but by predetermined outputs. This is why it’s less useful for diagnostic analysis, and more useful for prescriptive analysis.
Forecasting Method
- Description: the forecasting method uses time past series data to forecast the future.
- Importance: Very high. Forecasting falls under predictive analysis and is arguably the most common and most important method in the corporate world. It is less useful in research, which prefers to understand the known rather than speculate about the future.
- Nature of Data: data useful for forecasting is time series data, which, as we’ve noted, always includes a variable of time.
- Motive: the motive for the forecasting method is the same as that of prescriptive analysis: the confidently estimate future values.
Optimization Method
- Description: the optimization method maximized or minimizes values in a set given a set of criteria. It is arguably most common in prescriptive analysis. In mathematical terms, it is maximizing or minimizing a function given certain constraints.
- Importance: Very high. The idea of optimization applies to more analysis types than any other method. In fact, some argue that it is the fundamental driver behind data analysis. You would use it everywhere in research and in a corporation.
- Nature of Data: the nature of optimizable data is a data set of at least two points.
- Motive: the motive behind optimization is to achieve the best result possible given certain conditions.
Content Analysis Method
- Description: content analysis is a method of qualitative analysis that quantifies textual data to track themes across a document. It’s most common in academic fields and in social sciences, where written content is the subject of inquiry.
- Importance: High. In a corporate setting, content analysis as such is less common. If anything Nïave Bayes (a technique we’ll look at below) is the closest corporations come to text. However, it is of the utmost importance for researchers. If you’re a researcher, check out this article on content analysis .
- Nature of Data: data useful for content analysis is textual data.
- Motive: the motive behind content analysis is to understand themes expressed in a large text
Narrative Analysis Method
- Description: narrative analysis is a method of qualitative analysis that quantifies stories to trace themes in them. It’s differs from content analysis because it focuses on stories rather than research documents, and the techniques used are slightly different from those in content analysis (very nuances and outside the scope of this article).
- Importance: Low. Unless you are highly specialized in working with stories, narrative analysis rare.
- Nature of Data: the nature of the data useful for the narrative analysis method is narrative text.
- Motive: the motive for narrative analysis is to uncover hidden patterns in narrative text.
Discourse Analysis Method
- Description: the discourse analysis method falls under qualitative analysis and uses thematic coding to trace patterns in real-life discourse. That said, real-life discourse is oral, so it must first be transcribed into text.
- Importance: Low. Unless you are focused on understand real-world idea sharing in a research setting, this kind of analysis is less common than the others on this list.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful in discourse analysis is first audio files, then transcriptions of those audio files.
- Motive: the motive behind discourse analysis is to trace patterns of real-world discussions. (As a spooky sidenote, have you ever felt like your phone microphone was listening to you and making reading suggestions? If it was, the method was discourse analysis.)
Framework Analysis Method
- Description: the framework analysis method falls under qualitative analysis and uses similar thematic coding techniques to content analysis. However, where content analysis aims to discover themes, framework analysis starts with a framework and only considers elements that fall in its purview.
- Importance: Low. As with the other textual analysis methods, framework analysis is less common in corporate settings. Even in the world of research, only some use it. Strangely, it’s very common for legislative and political research.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful for framework analysis is textual.
- Motive: the motive behind framework analysis is to understand what themes and parts of a text match your search criteria.
Grounded Theory Method
- Description: the grounded theory method falls under qualitative analysis and uses thematic coding to build theories around those themes.
- Importance: Low. Like other qualitative analysis techniques, grounded theory is less common in the corporate world. Even among researchers, you would be hard pressed to find many using it. Though powerful, it’s simply too rare to spend time learning.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful in the grounded theory method is textual.
- Motive: the motive of grounded theory method is to establish a series of theories based on themes uncovered from a text.
Clustering Technique: K-Means
- Description: k-means is a clustering technique in which data points are grouped in clusters that have the closest means. Though not considered AI or ML, it inherently requires the use of supervised learning to reevaluate clusters as data points are added. Clustering techniques can be used in diagnostic, descriptive, & prescriptive data analyses.
- Importance: Very important. If you only take 3 things from this article, k-means clustering should be part of it. It is useful in any situation where n observations have multiple characteristics and we want to put them in groups.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data is at least one characteristic per observation, but the more the merrier.
- Motive: the motive for clustering techniques such as k-means is to group observations together and either understand or react to them.
Regression Technique
- Description: simple and multivariable regressions use either one independent variable or combination of multiple independent variables to calculate a correlation to a single dependent variable using constants. Regressions are almost synonymous with correlation today.
- Importance: Very high. Along with clustering, if you only take 3 things from this article, regression techniques should be part of it. They’re everywhere in corporate and research fields alike.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data used is regressions is data sets with “n” number of observations and as many variables as are reasonable. It’s important, however, to distinguish between time series data and regression data. You cannot use regressions or time series data without accounting for time. The easier way is to use techniques under the forecasting method.
- Motive: The motive behind regression techniques is to understand correlations between independent variable(s) and a dependent one.
Nïave Bayes Technique
- Description: Nïave Bayes is a classification technique that uses simple probability to classify items based previous classifications. In plain English, the formula would be “the chance that thing with trait x belongs to class c depends on (=) the overall chance of trait x belonging to class c, multiplied by the overall chance of class c, divided by the overall chance of getting trait x.” As a formula, it’s P(c|x) = P(x|c) * P(c) / P(x).
- Importance: High. Nïave Bayes is a very common, simplistic classification techniques because it’s effective with large data sets and it can be applied to any instant in which there is a class. Google, for example, might use it to group webpages into groups for certain search engine queries.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data for Nïave Bayes is at least one class and at least two traits in a data set.
- Motive: the motive behind Nïave Bayes is to classify observations based on previous data. It’s thus considered part of predictive analysis.
Cohorts Technique
- Description: cohorts technique is a type of clustering method used in behavioral sciences to separate users by common traits. As with clustering, it can be done intuitively or mathematically, the latter of which would simply be k-means.
- Importance: Very high. With regard to resembles k-means, the cohort technique is more of a high-level counterpart. In fact, most people are familiar with it as a part of Google Analytics. It’s most common in marketing departments in corporations, rather than in research.
- Nature of Data: the nature of cohort data is data sets in which users are the observation and other fields are used as defining traits for each cohort.
- Motive: the motive for cohort analysis techniques is to group similar users and analyze how you retain them and how the churn.
Factor Technique
- Description: the factor analysis technique is a way of grouping many traits into a single factor to expedite analysis. For example, factors can be used as traits for Nïave Bayes classifications instead of more general fields.
- Importance: High. While not commonly employed in corporations, factor analysis is hugely valuable. Good data analysts use it to simplify their projects and communicate them more clearly.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful in factor analysis techniques is data sets with a large number of fields on its observations.
- Motive: the motive for using factor analysis techniques is to reduce the number of fields in order to more quickly analyze and communicate findings.
Linear Discriminants Technique
- Description: linear discriminant analysis techniques are similar to regressions in that they use one or more independent variable to determine a dependent variable; however, the linear discriminant technique falls under a classifier method since it uses traits as independent variables and class as a dependent variable. In this way, it becomes a classifying method AND a predictive method.
- Importance: High. Though the analyst world speaks of and uses linear discriminants less commonly, it’s a highly valuable technique to keep in mind as you progress in data analysis.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful for the linear discriminant technique is data sets with many fields.
- Motive: the motive for using linear discriminants is to classify observations that would be otherwise too complex for simple techniques like Nïave Bayes.
Exponential Smoothing Technique
- Description: exponential smoothing is a technique falling under the forecasting method that uses a smoothing factor on prior data in order to predict future values. It can be linear or adjusted for seasonality. The basic principle behind exponential smoothing is to use a percent weight (value between 0 and 1 called alpha) on more recent values in a series and a smaller percent weight on less recent values. The formula is f(x) = current period value * alpha + previous period value * 1-alpha.
- Importance: High. Most analysts still use the moving average technique (covered next) for forecasting, though it is less efficient than exponential moving, because it’s easy to understand. However, good analysts will have exponential smoothing techniques in their pocket to increase the value of their forecasts.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful for exponential smoothing is time series data . Time series data has time as part of its fields .
- Motive: the motive for exponential smoothing is to forecast future values with a smoothing variable.
Moving Average Technique
- Description: the moving average technique falls under the forecasting method and uses an average of recent values to predict future ones. For example, to predict rainfall in April, you would take the average of rainfall from January to March. It’s simple, yet highly effective.
- Importance: Very high. While I’m personally not a huge fan of moving averages due to their simplistic nature and lack of consideration for seasonality, they’re the most common forecasting technique and therefore very important.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful for moving averages is time series data .
- Motive: the motive for moving averages is to predict future values is a simple, easy-to-communicate way.
Neural Networks Technique
- Description: neural networks are a highly complex artificial intelligence technique that replicate a human’s neural analysis through a series of hyper-rapid computations and comparisons that evolve in real time. This technique is so complex that an analyst must use computer programs to perform it.
- Importance: Medium. While the potential for neural networks is theoretically unlimited, it’s still little understood and therefore uncommon. You do not need to know it by any means in order to be a data analyst.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful for neural networks is data sets of astronomical size, meaning with 100s of 1000s of fields and the same number of row at a minimum .
- Motive: the motive for neural networks is to understand wildly complex phenomenon and data to thereafter act on it.
Decision Tree Technique
- Description: the decision tree technique uses artificial intelligence algorithms to rapidly calculate possible decision pathways and their outcomes on a real-time basis. It’s so complex that computer programs are needed to perform it.
- Importance: Medium. As with neural networks, decision trees with AI are too little understood and are therefore uncommon in corporate and research settings alike.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful for the decision tree technique is hierarchical data sets that show multiple optional fields for each preceding field.
- Motive: the motive for decision tree techniques is to compute the optimal choices to make in order to achieve a desired result.
Evolutionary Programming Technique
- Description: the evolutionary programming technique uses a series of neural networks, sees how well each one fits a desired outcome, and selects only the best to test and retest. It’s called evolutionary because is resembles the process of natural selection by weeding out weaker options.
- Importance: Medium. As with the other AI techniques, evolutionary programming just isn’t well-understood enough to be usable in many cases. It’s complexity also makes it hard to explain in corporate settings and difficult to defend in research settings.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data in evolutionary programming is data sets of neural networks, or data sets of data sets.
- Motive: the motive for using evolutionary programming is similar to decision trees: understanding the best possible option from complex data.
- Video example :
Fuzzy Logic Technique
- Description: fuzzy logic is a type of computing based on “approximate truths” rather than simple truths such as “true” and “false.” It is essentially two tiers of classification. For example, to say whether “Apples are good,” you need to first classify that “Good is x, y, z.” Only then can you say apples are good. Another way to see it helping a computer see truth like humans do: “definitely true, probably true, maybe true, probably false, definitely false.”
- Importance: Medium. Like the other AI techniques, fuzzy logic is uncommon in both research and corporate settings, which means it’s less important in today’s world.
- Nature of Data: the nature of fuzzy logic data is huge data tables that include other huge data tables with a hierarchy including multiple subfields for each preceding field.
- Motive: the motive of fuzzy logic to replicate human truth valuations in a computer is to model human decisions based on past data. The obvious possible application is marketing.
Text Analysis Technique
- Description: text analysis techniques fall under the qualitative data analysis type and use text to extract insights.
- Importance: Medium. Text analysis techniques, like all the qualitative analysis type, are most valuable for researchers.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful in text analysis is words.
- Motive: the motive for text analysis is to trace themes in a text across sets of very long documents, such as books.
Coding Technique
- Description: the coding technique is used in textual analysis to turn ideas into uniform phrases and analyze the number of times and the ways in which those ideas appear. For this reason, some consider it a quantitative technique as well. You can learn more about coding and the other qualitative techniques here .
- Importance: Very high. If you’re a researcher working in social sciences, coding is THE analysis techniques, and for good reason. It’s a great way to add rigor to analysis. That said, it’s less common in corporate settings.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful for coding is long text documents.
- Motive: the motive for coding is to make tracing ideas on paper more than an exercise of the mind by quantifying it and understanding is through descriptive methods.
Idea Pattern Technique
- Description: the idea pattern analysis technique fits into coding as the second step of the process. Once themes and ideas are coded, simple descriptive analysis tests may be run. Some people even cluster the ideas!
- Importance: Very high. If you’re a researcher, idea pattern analysis is as important as the coding itself.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful for idea pattern analysis is already coded themes.
- Motive: the motive for the idea pattern technique is to trace ideas in otherwise unmanageably-large documents.
Word Frequency Technique
- Description: word frequency is a qualitative technique that stands in opposition to coding and uses an inductive approach to locate specific words in a document in order to understand its relevance. Word frequency is essentially the descriptive analysis of qualitative data because it uses stats like mean, median, and mode to gather insights.
- Importance: High. As with the other qualitative approaches, word frequency is very important in social science research, but less so in corporate settings.
- Nature of Data: the nature of data useful for word frequency is long, informative documents.
- Motive: the motive for word frequency is to locate target words to determine the relevance of a document in question.
Types of data analysis in research
Types of data analysis in research methodology include every item discussed in this article. As a list, they are:
- Quantitative
- Qualitative
- Mathematical
- Machine Learning and AI
- Descriptive
- Prescriptive
- Classification
- Forecasting
- Optimization
- Grounded theory
- Artificial Neural Networks
- Decision Trees
- Evolutionary Programming
- Fuzzy Logic
- Text analysis
- Idea Pattern Analysis
- Word Frequency Analysis
- Nïave Bayes
- Exponential smoothing
- Moving average
- Linear discriminant
Types of data analysis in qualitative research
As a list, the types of data analysis in qualitative research are the following methods:
Types of data analysis in quantitative research
As a list, the types of data analysis in quantitative research are:
Data analysis methods
As a list, data analysis methods are:
- Content (qualitative)
- Narrative (qualitative)
- Discourse (qualitative)
- Framework (qualitative)
- Grounded theory (qualitative)
Quantitative data analysis methods
As a list, quantitative data analysis methods are:
Tabular View of Data Analysis Types, Methods, and Techniques
About the author.
Noah is the founder & Editor-in-Chief at AnalystAnswers. He is a transatlantic professional and entrepreneur with 5+ years of corporate finance and data analytics experience, as well as 3+ years in consumer financial products and business software. He started AnalystAnswers to provide aspiring professionals with accessible explanations of otherwise dense finance and data concepts. Noah believes everyone can benefit from an analytical mindset in growing digital world. When he's not busy at work, Noah likes to explore new European cities, exercise, and spend time with friends and family.
File available immediately.

Notice: JavaScript is required for this content.

Data Analysis Techniques in Research – Methods, Tools & Examples

Varun Saharawat is a seasoned professional in the fields of SEO and content writing. With a profound knowledge of the intricate aspects of these disciplines, Varun has established himself as a valuable asset in the world of digital marketing and online content creation.

Data analysis techniques in research are essential because they allow researchers to derive meaningful insights from data sets to support their hypotheses or research objectives.
Data Analysis Techniques in Research : While various groups, institutions, and professionals may have diverse approaches to data analysis, a universal definition captures its essence. Data analysis involves refining, transforming, and interpreting raw data to derive actionable insights that guide informed decision-making for businesses.

A straightforward illustration of data analysis emerges when we make everyday decisions, basing our choices on past experiences or predictions of potential outcomes.
If you want to learn more about this topic and acquire valuable skills that will set you apart in today’s data-driven world, we highly recommend enrolling in the Data Analytics Course by Physics Wallah . And as a special offer for our readers, use the coupon code “READER” to get a discount on this course.
Table of Contents
What is Data Analysis?
Data analysis is the systematic process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and interpreting data with the objective of discovering valuable insights and drawing meaningful conclusions. This process involves several steps:
- Inspecting : Initial examination of data to understand its structure, quality, and completeness.
- Cleaning : Removing errors, inconsistencies, or irrelevant information to ensure accurate analysis.
- Transforming : Converting data into a format suitable for analysis, such as normalization or aggregation.
- Interpreting : Analyzing the transformed data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships.
Types of Data Analysis Techniques in Research
Data analysis techniques in research are categorized into qualitative and quantitative methods, each with its specific approaches and tools. These techniques are instrumental in extracting meaningful insights, patterns, and relationships from data to support informed decision-making, validate hypotheses, and derive actionable recommendations. Below is an in-depth exploration of the various types of data analysis techniques commonly employed in research:
1) Qualitative Analysis:
Definition: Qualitative analysis focuses on understanding non-numerical data, such as opinions, concepts, or experiences, to derive insights into human behavior, attitudes, and perceptions.
- Content Analysis: Examines textual data, such as interview transcripts, articles, or open-ended survey responses, to identify themes, patterns, or trends.
- Narrative Analysis: Analyzes personal stories or narratives to understand individuals’ experiences, emotions, or perspectives.
- Ethnographic Studies: Involves observing and analyzing cultural practices, behaviors, and norms within specific communities or settings.
2) Quantitative Analysis:
Quantitative analysis emphasizes numerical data and employs statistical methods to explore relationships, patterns, and trends. It encompasses several approaches:
Descriptive Analysis:
- Frequency Distribution: Represents the number of occurrences of distinct values within a dataset.
- Central Tendency: Measures such as mean, median, and mode provide insights into the central values of a dataset.
- Dispersion: Techniques like variance and standard deviation indicate the spread or variability of data.
Diagnostic Analysis:
- Regression Analysis: Assesses the relationship between dependent and independent variables, enabling prediction or understanding causality.
- ANOVA (Analysis of Variance): Examines differences between groups to identify significant variations or effects.
Predictive Analysis:
- Time Series Forecasting: Uses historical data points to predict future trends or outcomes.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Techniques like decision trees, random forests, and neural networks predict outcomes based on patterns in data.
Prescriptive Analysis:
- Optimization Models: Utilizes linear programming, integer programming, or other optimization techniques to identify the best solutions or strategies.
- Simulation: Mimics real-world scenarios to evaluate various strategies or decisions and determine optimal outcomes.
Specific Techniques:
- Monte Carlo Simulation: Models probabilistic outcomes to assess risk and uncertainty.
- Factor Analysis: Reduces the dimensionality of data by identifying underlying factors or components.
- Cohort Analysis: Studies specific groups or cohorts over time to understand trends, behaviors, or patterns within these groups.
- Cluster Analysis: Classifies objects or individuals into homogeneous groups or clusters based on similarities or attributes.
- Sentiment Analysis: Uses natural language processing and machine learning techniques to determine sentiment, emotions, or opinions from textual data.
Also Read: AI and Predictive Analytics: Examples, Tools, Uses, Ai Vs Predictive Analytics
Data Analysis Techniques in Research Examples
To provide a clearer understanding of how data analysis techniques are applied in research, let’s consider a hypothetical research study focused on evaluating the impact of online learning platforms on students’ academic performance.
Research Objective:
Determine if students using online learning platforms achieve higher academic performance compared to those relying solely on traditional classroom instruction.
Data Collection:
- Quantitative Data: Academic scores (grades) of students using online platforms and those using traditional classroom methods.
- Qualitative Data: Feedback from students regarding their learning experiences, challenges faced, and preferences.
Data Analysis Techniques Applied:
1) Descriptive Analysis:
- Calculate the mean, median, and mode of academic scores for both groups.
- Create frequency distributions to represent the distribution of grades in each group.
2) Diagnostic Analysis:
- Conduct an Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) to determine if there’s a statistically significant difference in academic scores between the two groups.
- Perform Regression Analysis to assess the relationship between the time spent on online platforms and academic performance.
3) Predictive Analysis:
- Utilize Time Series Forecasting to predict future academic performance trends based on historical data.
- Implement Machine Learning algorithms to develop a predictive model that identifies factors contributing to academic success on online platforms.
4) Prescriptive Analysis:
- Apply Optimization Models to identify the optimal combination of online learning resources (e.g., video lectures, interactive quizzes) that maximize academic performance.
- Use Simulation Techniques to evaluate different scenarios, such as varying student engagement levels with online resources, to determine the most effective strategies for improving learning outcomes.
5) Specific Techniques:
- Conduct Factor Analysis on qualitative feedback to identify common themes or factors influencing students’ perceptions and experiences with online learning.
- Perform Cluster Analysis to segment students based on their engagement levels, preferences, or academic outcomes, enabling targeted interventions or personalized learning strategies.
- Apply Sentiment Analysis on textual feedback to categorize students’ sentiments as positive, negative, or neutral regarding online learning experiences.
By applying a combination of qualitative and quantitative data analysis techniques, this research example aims to provide comprehensive insights into the effectiveness of online learning platforms.
Also Read: Learning Path to Become a Data Analyst in 2024
Data Analysis Techniques in Quantitative Research
Quantitative research involves collecting numerical data to examine relationships, test hypotheses, and make predictions. Various data analysis techniques are employed to interpret and draw conclusions from quantitative data. Here are some key data analysis techniques commonly used in quantitative research:
1) Descriptive Statistics:
- Description: Descriptive statistics are used to summarize and describe the main aspects of a dataset, such as central tendency (mean, median, mode), variability (range, variance, standard deviation), and distribution (skewness, kurtosis).
- Applications: Summarizing data, identifying patterns, and providing initial insights into the dataset.
2) Inferential Statistics:
- Description: Inferential statistics involve making predictions or inferences about a population based on a sample of data. This technique includes hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, t-tests, chi-square tests, analysis of variance (ANOVA), regression analysis, and correlation analysis.
- Applications: Testing hypotheses, making predictions, and generalizing findings from a sample to a larger population.
3) Regression Analysis:
- Description: Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to model and examine the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. Linear regression, multiple regression, logistic regression, and nonlinear regression are common types of regression analysis .
- Applications: Predicting outcomes, identifying relationships between variables, and understanding the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
4) Correlation Analysis:
- Description: Correlation analysis is used to measure and assess the strength and direction of the relationship between two or more variables. The Pearson correlation coefficient, Spearman rank correlation coefficient, and Kendall’s tau are commonly used measures of correlation.
- Applications: Identifying associations between variables and assessing the degree and nature of the relationship.
5) Factor Analysis:
- Description: Factor analysis is a multivariate statistical technique used to identify and analyze underlying relationships or factors among a set of observed variables. It helps in reducing the dimensionality of data and identifying latent variables or constructs.
- Applications: Identifying underlying factors or constructs, simplifying data structures, and understanding the underlying relationships among variables.
6) Time Series Analysis:
- Description: Time series analysis involves analyzing data collected or recorded over a specific period at regular intervals to identify patterns, trends, and seasonality. Techniques such as moving averages, exponential smoothing, autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA), and Fourier analysis are used.
- Applications: Forecasting future trends, analyzing seasonal patterns, and understanding time-dependent relationships in data.
7) ANOVA (Analysis of Variance):
- Description: Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a statistical technique used to analyze and compare the means of two or more groups or treatments to determine if they are statistically different from each other. One-way ANOVA, two-way ANOVA, and MANOVA (Multivariate Analysis of Variance) are common types of ANOVA.
- Applications: Comparing group means, testing hypotheses, and determining the effects of categorical independent variables on a continuous dependent variable.
8) Chi-Square Tests:
- Description: Chi-square tests are non-parametric statistical tests used to assess the association between categorical variables in a contingency table. The Chi-square test of independence, goodness-of-fit test, and test of homogeneity are common chi-square tests.
- Applications: Testing relationships between categorical variables, assessing goodness-of-fit, and evaluating independence.
These quantitative data analysis techniques provide researchers with valuable tools and methods to analyze, interpret, and derive meaningful insights from numerical data. The selection of a specific technique often depends on the research objectives, the nature of the data, and the underlying assumptions of the statistical methods being used.
Also Read: Analysis vs. Analytics: How Are They Different?
Data Analysis Methods
Data analysis methods refer to the techniques and procedures used to analyze, interpret, and draw conclusions from data. These methods are essential for transforming raw data into meaningful insights, facilitating decision-making processes, and driving strategies across various fields. Here are some common data analysis methods:
- Description: Descriptive statistics summarize and organize data to provide a clear and concise overview of the dataset. Measures such as mean, median, mode, range, variance, and standard deviation are commonly used.
- Description: Inferential statistics involve making predictions or inferences about a population based on a sample of data. Techniques such as hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis are used.
3) Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA):
- Description: EDA techniques involve visually exploring and analyzing data to discover patterns, relationships, anomalies, and insights. Methods such as scatter plots, histograms, box plots, and correlation matrices are utilized.
- Applications: Identifying trends, patterns, outliers, and relationships within the dataset.
4) Predictive Analytics:
- Description: Predictive analytics use statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze historical data and make predictions about future events or outcomes. Techniques such as regression analysis, time series forecasting, and machine learning algorithms (e.g., decision trees, random forests, neural networks) are employed.
- Applications: Forecasting future trends, predicting outcomes, and identifying potential risks or opportunities.
5) Prescriptive Analytics:
- Description: Prescriptive analytics involve analyzing data to recommend actions or strategies that optimize specific objectives or outcomes. Optimization techniques, simulation models, and decision-making algorithms are utilized.
- Applications: Recommending optimal strategies, decision-making support, and resource allocation.
6) Qualitative Data Analysis:
- Description: Qualitative data analysis involves analyzing non-numerical data, such as text, images, videos, or audio, to identify themes, patterns, and insights. Methods such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and narrative analysis are used.
- Applications: Understanding human behavior, attitudes, perceptions, and experiences.
7) Big Data Analytics:
- Description: Big data analytics methods are designed to analyze large volumes of structured and unstructured data to extract valuable insights. Technologies such as Hadoop, Spark, and NoSQL databases are used to process and analyze big data.
- Applications: Analyzing large datasets, identifying trends, patterns, and insights from big data sources.
8) Text Analytics:
- Description: Text analytics methods involve analyzing textual data, such as customer reviews, social media posts, emails, and documents, to extract meaningful information and insights. Techniques such as sentiment analysis, text mining, and natural language processing (NLP) are used.
- Applications: Analyzing customer feedback, monitoring brand reputation, and extracting insights from textual data sources.
These data analysis methods are instrumental in transforming data into actionable insights, informing decision-making processes, and driving organizational success across various sectors, including business, healthcare, finance, marketing, and research. The selection of a specific method often depends on the nature of the data, the research objectives, and the analytical requirements of the project or organization.
Also Read: Quantitative Data Analysis: Types, Analysis & Examples
Data Analysis Tools
Data analysis tools are essential instruments that facilitate the process of examining, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data to uncover useful information, make informed decisions, and drive strategies. Here are some prominent data analysis tools widely used across various industries:
1) Microsoft Excel:
- Description: A spreadsheet software that offers basic to advanced data analysis features, including pivot tables, data visualization tools, and statistical functions.
- Applications: Data cleaning, basic statistical analysis, visualization, and reporting.
2) R Programming Language:
- Description: An open-source programming language specifically designed for statistical computing and data visualization.
- Applications: Advanced statistical analysis, data manipulation, visualization, and machine learning.
3) Python (with Libraries like Pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, and Seaborn):
- Description: A versatile programming language with libraries that support data manipulation, analysis, and visualization.
- Applications: Data cleaning, statistical analysis, machine learning, and data visualization.
4) SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences):
- Description: A comprehensive statistical software suite used for data analysis, data mining, and predictive analytics.
- Applications: Descriptive statistics, hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and advanced analytics.
5) SAS (Statistical Analysis System):
- Description: A software suite used for advanced analytics, multivariate analysis, and predictive modeling.
- Applications: Data management, statistical analysis, predictive modeling, and business intelligence.
6) Tableau:
- Description: A data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive and shareable dashboards and reports.
- Applications: Data visualization , business intelligence , and interactive dashboard creation.
7) Power BI:
- Description: A business analytics tool developed by Microsoft that provides interactive visualizations and business intelligence capabilities.
- Applications: Data visualization, business intelligence, reporting, and dashboard creation.
8) SQL (Structured Query Language) Databases (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server):
- Description: Database management systems that support data storage, retrieval, and manipulation using SQL queries.
- Applications: Data retrieval, data cleaning, data transformation, and database management.
9) Apache Spark:
- Description: A fast and general-purpose distributed computing system designed for big data processing and analytics.
- Applications: Big data processing, machine learning, data streaming, and real-time analytics.
10) IBM SPSS Modeler:
- Description: A data mining software application used for building predictive models and conducting advanced analytics.
- Applications: Predictive modeling, data mining, statistical analysis, and decision optimization.
These tools serve various purposes and cater to different data analysis needs, from basic statistical analysis and data visualization to advanced analytics, machine learning, and big data processing. The choice of a specific tool often depends on the nature of the data, the complexity of the analysis, and the specific requirements of the project or organization.
Also Read: How to Analyze Survey Data: Methods & Examples
Importance of Data Analysis in Research
The importance of data analysis in research cannot be overstated; it serves as the backbone of any scientific investigation or study. Here are several key reasons why data analysis is crucial in the research process:
- Data analysis helps ensure that the results obtained are valid and reliable. By systematically examining the data, researchers can identify any inconsistencies or anomalies that may affect the credibility of the findings.
- Effective data analysis provides researchers with the necessary information to make informed decisions. By interpreting the collected data, researchers can draw conclusions, make predictions, or formulate recommendations based on evidence rather than intuition or guesswork.
- Data analysis allows researchers to identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. This can lead to a deeper understanding of the research topic, enabling researchers to uncover insights that may not be immediately apparent.
- In empirical research, data analysis plays a critical role in testing hypotheses. Researchers collect data to either support or refute their hypotheses, and data analysis provides the tools and techniques to evaluate these hypotheses rigorously.
- Transparent and well-executed data analysis enhances the credibility of research findings. By clearly documenting the data analysis methods and procedures, researchers allow others to replicate the study, thereby contributing to the reproducibility of research findings.
- In fields such as business or healthcare, data analysis helps organizations allocate resources more efficiently. By analyzing data on consumer behavior, market trends, or patient outcomes, organizations can make strategic decisions about resource allocation, budgeting, and planning.
- In public policy and social sciences, data analysis is instrumental in developing and evaluating policies and interventions. By analyzing data on social, economic, or environmental factors, policymakers can assess the effectiveness of existing policies and inform the development of new ones.
- Data analysis allows for continuous improvement in research methods and practices. By analyzing past research projects, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes based on data-driven insights, researchers can refine their approaches and enhance the quality of future research endeavors.
However, it is important to remember that mastering these techniques requires practice and continuous learning. That’s why we highly recommend the Data Analytics Course by Physics Wallah . Not only does it cover all the fundamentals of data analysis, but it also provides hands-on experience with various tools such as Excel, Python, and Tableau. Plus, if you use the “ READER ” coupon code at checkout, you can get a special discount on the course.
For Latest Tech Related Information, Join Our Official Free Telegram Group : PW Skills Telegram Group
Data Analysis Techniques in Research FAQs
What are the 5 techniques for data analysis.
The five techniques for data analysis include: Descriptive Analysis Diagnostic Analysis Predictive Analysis Prescriptive Analysis Qualitative Analysis
What are techniques of data analysis in research?
Techniques of data analysis in research encompass both qualitative and quantitative methods. These techniques involve processes like summarizing raw data, investigating causes of events, forecasting future outcomes, offering recommendations based on predictions, and examining non-numerical data to understand concepts or experiences.
What are the 3 methods of data analysis?
The three primary methods of data analysis are: Qualitative Analysis Quantitative Analysis Mixed-Methods Analysis
What are the four types of data analysis techniques?
The four types of data analysis techniques are: Descriptive Analysis Diagnostic Analysis Predictive Analysis Prescriptive Analysis
- Why is Data Analytics Skills Important?

Data analytics skills are important for candidates to stand out from other candidates during a job interview and better their…
- Which Course is Best for Business Analyst? (Business Analysts Online Courses)

Many reputed platforms and institutions offer online certification courses which can help you land job offers in relevant companies. In…
- What is Data Analytics in Database?

Database analytics is a method of interpreting and analyzing data stored inside the database to extract meaningful insights. Read the…

Related Articles
- Finance Data Analysis: What is a Financial Data Analysis?
- What are Data Analysis Tools?
- Best Courses For Data Analytics: Top 10 Courses For Your Career in Trend
- Big Data: What Do You Mean By Big Data?
- Top 20 Big Data Tools Used By Professionals
- 10 Most Popular Big Data Analytics Tools
- Top Best Big Data Analytics Classes 2024


The 7 Most Useful Data Analysis Methods and Techniques

Data analytics is the process of analyzing raw data to draw out meaningful insights. These insights are then used to determine the best course of action.
When is the best time to roll out that marketing campaign? Is the current team structure as effective as it could be? Which customer segments are most likely to purchase your new product?
Ultimately, data analytics is a crucial driver of any successful business strategy. But how do data analysts actually turn raw data into something useful? There are a range of methods and techniques that data analysts use depending on the type of data in question and the kinds of insights they want to uncover.
You can get a hands-on introduction to data analytics in this free short course .
In this post, we’ll explore some of the most useful data analysis techniques. By the end, you’ll have a much clearer idea of how you can transform meaningless data into business intelligence. We’ll cover:
- What is data analysis and why is it important?
- What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data?
- Regression analysis
- Monte Carlo simulation
- Factor analysis
- Cohort analysis
- Cluster analysis
- Time series analysis
- Sentiment analysis
- The data analysis process
- The best tools for data analysis
- Key takeaways
The first six methods listed are used for quantitative data , while the last technique applies to qualitative data. We briefly explain the difference between quantitative and qualitative data in section two, but if you want to skip straight to a particular analysis technique, just use the clickable menu.
1. What is data analysis and why is it important?
Data analysis is, put simply, the process of discovering useful information by evaluating data. This is done through a process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data using analytical and statistical tools, which we will explore in detail further along in this article.
Why is data analysis important? Analyzing data effectively helps organizations make business decisions. Nowadays, data is collected by businesses constantly: through surveys, online tracking, online marketing analytics, collected subscription and registration data (think newsletters), social media monitoring, among other methods.
These data will appear as different structures, including—but not limited to—the following:
The concept of big data —data that is so large, fast, or complex, that it is difficult or impossible to process using traditional methods—gained momentum in the early 2000s. Then, Doug Laney, an industry analyst, articulated what is now known as the mainstream definition of big data as the three Vs: volume, velocity, and variety.
- Volume: As mentioned earlier, organizations are collecting data constantly. In the not-too-distant past it would have been a real issue to store, but nowadays storage is cheap and takes up little space.
- Velocity: Received data needs to be handled in a timely manner. With the growth of the Internet of Things, this can mean these data are coming in constantly, and at an unprecedented speed.
- Variety: The data being collected and stored by organizations comes in many forms, ranging from structured data—that is, more traditional, numerical data—to unstructured data—think emails, videos, audio, and so on. We’ll cover structured and unstructured data a little further on.
This is a form of data that provides information about other data, such as an image. In everyday life you’ll find this by, for example, right-clicking on a file in a folder and selecting “Get Info”, which will show you information such as file size and kind, date of creation, and so on.
Real-time data
This is data that is presented as soon as it is acquired. A good example of this is a stock market ticket, which provides information on the most-active stocks in real time.
Machine data
This is data that is produced wholly by machines, without human instruction. An example of this could be call logs automatically generated by your smartphone.
Quantitative and qualitative data
Quantitative data—otherwise known as structured data— may appear as a “traditional” database—that is, with rows and columns. Qualitative data—otherwise known as unstructured data—are the other types of data that don’t fit into rows and columns, which can include text, images, videos and more. We’ll discuss this further in the next section.
2. What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative data?
How you analyze your data depends on the type of data you’re dealing with— quantitative or qualitative . So what’s the difference?
Quantitative data is anything measurable , comprising specific quantities and numbers. Some examples of quantitative data include sales figures, email click-through rates, number of website visitors, and percentage revenue increase. Quantitative data analysis techniques focus on the statistical, mathematical, or numerical analysis of (usually large) datasets. This includes the manipulation of statistical data using computational techniques and algorithms. Quantitative analysis techniques are often used to explain certain phenomena or to make predictions.
Qualitative data cannot be measured objectively , and is therefore open to more subjective interpretation. Some examples of qualitative data include comments left in response to a survey question, things people have said during interviews, tweets and other social media posts, and the text included in product reviews. With qualitative data analysis, the focus is on making sense of unstructured data (such as written text, or transcripts of spoken conversations). Often, qualitative analysis will organize the data into themes—a process which, fortunately, can be automated.
Data analysts work with both quantitative and qualitative data , so it’s important to be familiar with a variety of analysis methods. Let’s take a look at some of the most useful techniques now.
3. Data analysis techniques
Now we’re familiar with some of the different types of data, let’s focus on the topic at hand: different methods for analyzing data.
a. Regression analysis
Regression analysis is used to estimate the relationship between a set of variables. When conducting any type of regression analysis , you’re looking to see if there’s a correlation between a dependent variable (that’s the variable or outcome you want to measure or predict) and any number of independent variables (factors which may have an impact on the dependent variable). The aim of regression analysis is to estimate how one or more variables might impact the dependent variable, in order to identify trends and patterns. This is especially useful for making predictions and forecasting future trends.
Let’s imagine you work for an ecommerce company and you want to examine the relationship between: (a) how much money is spent on social media marketing, and (b) sales revenue. In this case, sales revenue is your dependent variable—it’s the factor you’re most interested in predicting and boosting. Social media spend is your independent variable; you want to determine whether or not it has an impact on sales and, ultimately, whether it’s worth increasing, decreasing, or keeping the same. Using regression analysis, you’d be able to see if there’s a relationship between the two variables. A positive correlation would imply that the more you spend on social media marketing, the more sales revenue you make. No correlation at all might suggest that social media marketing has no bearing on your sales. Understanding the relationship between these two variables would help you to make informed decisions about the social media budget going forward. However: It’s important to note that, on their own, regressions can only be used to determine whether or not there is a relationship between a set of variables—they don’t tell you anything about cause and effect. So, while a positive correlation between social media spend and sales revenue may suggest that one impacts the other, it’s impossible to draw definitive conclusions based on this analysis alone.
There are many different types of regression analysis, and the model you use depends on the type of data you have for the dependent variable. For example, your dependent variable might be continuous (i.e. something that can be measured on a continuous scale, such as sales revenue in USD), in which case you’d use a different type of regression analysis than if your dependent variable was categorical in nature (i.e. comprising values that can be categorised into a number of distinct groups based on a certain characteristic, such as customer location by continent). You can learn more about different types of dependent variables and how to choose the right regression analysis in this guide .
Regression analysis in action: Investigating the relationship between clothing brand Benetton’s advertising expenditure and sales
b. Monte Carlo simulation
When making decisions or taking certain actions, there are a range of different possible outcomes. If you take the bus, you might get stuck in traffic. If you walk, you might get caught in the rain or bump into your chatty neighbor, potentially delaying your journey. In everyday life, we tend to briefly weigh up the pros and cons before deciding which action to take; however, when the stakes are high, it’s essential to calculate, as thoroughly and accurately as possible, all the potential risks and rewards.
Monte Carlo simulation, otherwise known as the Monte Carlo method, is a computerized technique used to generate models of possible outcomes and their probability distributions. It essentially considers a range of possible outcomes and then calculates how likely it is that each particular outcome will be realized. The Monte Carlo method is used by data analysts to conduct advanced risk analysis, allowing them to better forecast what might happen in the future and make decisions accordingly.
So how does Monte Carlo simulation work, and what can it tell us? To run a Monte Carlo simulation, you’ll start with a mathematical model of your data—such as a spreadsheet. Within your spreadsheet, you’ll have one or several outputs that you’re interested in; profit, for example, or number of sales. You’ll also have a number of inputs; these are variables that may impact your output variable. If you’re looking at profit, relevant inputs might include the number of sales, total marketing spend, and employee salaries. If you knew the exact, definitive values of all your input variables, you’d quite easily be able to calculate what profit you’d be left with at the end. However, when these values are uncertain, a Monte Carlo simulation enables you to calculate all the possible options and their probabilities. What will your profit be if you make 100,000 sales and hire five new employees on a salary of $50,000 each? What is the likelihood of this outcome? What will your profit be if you only make 12,000 sales and hire five new employees? And so on. It does this by replacing all uncertain values with functions which generate random samples from distributions determined by you, and then running a series of calculations and recalculations to produce models of all the possible outcomes and their probability distributions. The Monte Carlo method is one of the most popular techniques for calculating the effect of unpredictable variables on a specific output variable, making it ideal for risk analysis.
Monte Carlo simulation in action: A case study using Monte Carlo simulation for risk analysis
c. Factor analysis
Factor analysis is a technique used to reduce a large number of variables to a smaller number of factors. It works on the basis that multiple separate, observable variables correlate with each other because they are all associated with an underlying construct. This is useful not only because it condenses large datasets into smaller, more manageable samples, but also because it helps to uncover hidden patterns. This allows you to explore concepts that cannot be easily measured or observed—such as wealth, happiness, fitness, or, for a more business-relevant example, customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Let’s imagine you want to get to know your customers better, so you send out a rather long survey comprising one hundred questions. Some of the questions relate to how they feel about your company and product; for example, “Would you recommend us to a friend?” and “How would you rate the overall customer experience?” Other questions ask things like “What is your yearly household income?” and “How much are you willing to spend on skincare each month?”
Once your survey has been sent out and completed by lots of customers, you end up with a large dataset that essentially tells you one hundred different things about each customer (assuming each customer gives one hundred responses). Instead of looking at each of these responses (or variables) individually, you can use factor analysis to group them into factors that belong together—in other words, to relate them to a single underlying construct. In this example, factor analysis works by finding survey items that are strongly correlated. This is known as covariance . So, if there’s a strong positive correlation between household income and how much they’re willing to spend on skincare each month (i.e. as one increases, so does the other), these items may be grouped together. Together with other variables (survey responses), you may find that they can be reduced to a single factor such as “consumer purchasing power”. Likewise, if a customer experience rating of 10/10 correlates strongly with “yes” responses regarding how likely they are to recommend your product to a friend, these items may be reduced to a single factor such as “customer satisfaction”.
In the end, you have a smaller number of factors rather than hundreds of individual variables. These factors are then taken forward for further analysis, allowing you to learn more about your customers (or any other area you’re interested in exploring).
Factor analysis in action: Using factor analysis to explore customer behavior patterns in Tehran
d. Cohort analysis
Cohort analysis is a data analytics technique that groups users based on a shared characteristic , such as the date they signed up for a service or the product they purchased. Once users are grouped into cohorts, analysts can track their behavior over time to identify trends and patterns.
So what does this mean and why is it useful? Let’s break down the above definition further. A cohort is a group of people who share a common characteristic (or action) during a given time period. Students who enrolled at university in 2020 may be referred to as the 2020 cohort. Customers who purchased something from your online store via the app in the month of December may also be considered a cohort.
With cohort analysis, you’re dividing your customers or users into groups and looking at how these groups behave over time. So, rather than looking at a single, isolated snapshot of all your customers at a given moment in time (with each customer at a different point in their journey), you’re examining your customers’ behavior in the context of the customer lifecycle. As a result, you can start to identify patterns of behavior at various points in the customer journey—say, from their first ever visit to your website, through to email newsletter sign-up, to their first purchase, and so on. As such, cohort analysis is dynamic, allowing you to uncover valuable insights about the customer lifecycle.
This is useful because it allows companies to tailor their service to specific customer segments (or cohorts). Let’s imagine you run a 50% discount campaign in order to attract potential new customers to your website. Once you’ve attracted a group of new customers (a cohort), you’ll want to track whether they actually buy anything and, if they do, whether or not (and how frequently) they make a repeat purchase. With these insights, you’ll start to gain a much better understanding of when this particular cohort might benefit from another discount offer or retargeting ads on social media, for example. Ultimately, cohort analysis allows companies to optimize their service offerings (and marketing) to provide a more targeted, personalized experience. You can learn more about how to run cohort analysis using Google Analytics .
Cohort analysis in action: How Ticketmaster used cohort analysis to boost revenue
e. Cluster analysis
Cluster analysis is an exploratory technique that seeks to identify structures within a dataset. The goal of cluster analysis is to sort different data points into groups (or clusters) that are internally homogeneous and externally heterogeneous. This means that data points within a cluster are similar to each other, and dissimilar to data points in another cluster. Clustering is used to gain insight into how data is distributed in a given dataset, or as a preprocessing step for other algorithms.
There are many real-world applications of cluster analysis. In marketing, cluster analysis is commonly used to group a large customer base into distinct segments, allowing for a more targeted approach to advertising and communication. Insurance firms might use cluster analysis to investigate why certain locations are associated with a high number of insurance claims. Another common application is in geology, where experts will use cluster analysis to evaluate which cities are at greatest risk of earthquakes (and thus try to mitigate the risk with protective measures).
It’s important to note that, while cluster analysis may reveal structures within your data, it won’t explain why those structures exist. With that in mind, cluster analysis is a useful starting point for understanding your data and informing further analysis. Clustering algorithms are also used in machine learning—you can learn more about clustering in machine learning in our guide .
Cluster analysis in action: Using cluster analysis for customer segmentation—a telecoms case study example
f. Time series analysis
Time series analysis is a statistical technique used to identify trends and cycles over time. Time series data is a sequence of data points which measure the same variable at different points in time (for example, weekly sales figures or monthly email sign-ups). By looking at time-related trends, analysts are able to forecast how the variable of interest may fluctuate in the future.
When conducting time series analysis, the main patterns you’ll be looking out for in your data are:
- Trends: Stable, linear increases or decreases over an extended time period.
- Seasonality: Predictable fluctuations in the data due to seasonal factors over a short period of time. For example, you might see a peak in swimwear sales in summer around the same time every year.
- Cyclic patterns: Unpredictable cycles where the data fluctuates. Cyclical trends are not due to seasonality, but rather, may occur as a result of economic or industry-related conditions.
As you can imagine, the ability to make informed predictions about the future has immense value for business. Time series analysis and forecasting is used across a variety of industries, most commonly for stock market analysis, economic forecasting, and sales forecasting. There are different types of time series models depending on the data you’re using and the outcomes you want to predict. These models are typically classified into three broad types: the autoregressive (AR) models, the integrated (I) models, and the moving average (MA) models. For an in-depth look at time series analysis, refer to our guide .
Time series analysis in action: Developing a time series model to predict jute yarn demand in Bangladesh
g. Sentiment analysis
When you think of data, your mind probably automatically goes to numbers and spreadsheets.
Many companies overlook the value of qualitative data, but in reality, there are untold insights to be gained from what people (especially customers) write and say about you. So how do you go about analyzing textual data?
One highly useful qualitative technique is sentiment analysis , a technique which belongs to the broader category of text analysis —the (usually automated) process of sorting and understanding textual data.
With sentiment analysis, the goal is to interpret and classify the emotions conveyed within textual data. From a business perspective, this allows you to ascertain how your customers feel about various aspects of your brand, product, or service.
There are several different types of sentiment analysis models, each with a slightly different focus. The three main types include:
Fine-grained sentiment analysis
If you want to focus on opinion polarity (i.e. positive, neutral, or negative) in depth, fine-grained sentiment analysis will allow you to do so.
For example, if you wanted to interpret star ratings given by customers, you might use fine-grained sentiment analysis to categorize the various ratings along a scale ranging from very positive to very negative.
Emotion detection
This model often uses complex machine learning algorithms to pick out various emotions from your textual data.
You might use an emotion detection model to identify words associated with happiness, anger, frustration, and excitement, giving you insight into how your customers feel when writing about you or your product on, say, a product review site.
Aspect-based sentiment analysis
This type of analysis allows you to identify what specific aspects the emotions or opinions relate to, such as a certain product feature or a new ad campaign.
If a customer writes that they “find the new Instagram advert so annoying”, your model should detect not only a negative sentiment, but also the object towards which it’s directed.
In a nutshell, sentiment analysis uses various Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms and systems which are trained to associate certain inputs (for example, certain words) with certain outputs.
For example, the input “annoying” would be recognized and tagged as “negative”. Sentiment analysis is crucial to understanding how your customers feel about you and your products, for identifying areas for improvement, and even for averting PR disasters in real-time!
Sentiment analysis in action: 5 Real-world sentiment analysis case studies
4. The data analysis process
In order to gain meaningful insights from data, data analysts will perform a rigorous step-by-step process. We go over this in detail in our step by step guide to the data analysis process —but, to briefly summarize, the data analysis process generally consists of the following phases:
Defining the question
The first step for any data analyst will be to define the objective of the analysis, sometimes called a ‘problem statement’. Essentially, you’re asking a question with regards to a business problem you’re trying to solve. Once you’ve defined this, you’ll then need to determine which data sources will help you answer this question.
Collecting the data
Now that you’ve defined your objective, the next step will be to set up a strategy for collecting and aggregating the appropriate data. Will you be using quantitative (numeric) or qualitative (descriptive) data? Do these data fit into first-party, second-party, or third-party data?
Learn more: Quantitative vs. Qualitative Data: What’s the Difference?
Cleaning the data
Unfortunately, your collected data isn’t automatically ready for analysis—you’ll have to clean it first. As a data analyst, this phase of the process will take up the most time. During the data cleaning process, you will likely be:
- Removing major errors, duplicates, and outliers
- Removing unwanted data points
- Structuring the data—that is, fixing typos, layout issues, etc.
- Filling in major gaps in data
Analyzing the data
Now that we’ve finished cleaning the data, it’s time to analyze it! Many analysis methods have already been described in this article, and it’s up to you to decide which one will best suit the assigned objective. It may fall under one of the following categories:
- Descriptive analysis , which identifies what has already happened
- Diagnostic analysis , which focuses on understanding why something has happened
- Predictive analysis , which identifies future trends based on historical data
- Prescriptive analysis , which allows you to make recommendations for the future

Visualizing and sharing your findings
We’re almost at the end of the road! Analyses have been made, insights have been gleaned—all that remains to be done is to share this information with others. This is usually done with a data visualization tool, such as Google Charts, or Tableau.
Learn more: 13 of the Most Common Types of Data Visualization
To sum up the process, Will’s explained it all excellently in the following video:
5. The best tools for data analysis
As you can imagine, every phase of the data analysis process requires the data analyst to have a variety of tools under their belt that assist in gaining valuable insights from data. We cover these tools in greater detail in this article , but, in summary, here’s our best-of-the-best list, with links to each product:
The top 9 tools for data analysts
- Microsoft Excel
- Jupyter Notebook
- Apache Spark
- Microsoft Power BI
6. Key takeaways and further reading
As you can see, there are many different data analysis techniques at your disposal. In order to turn your raw data into actionable insights, it’s important to consider what kind of data you have (is it qualitative or quantitative?) as well as the kinds of insights that will be useful within the given context. In this post, we’ve introduced seven of the most useful data analysis techniques—but there are many more out there to be discovered!
So what now? If you haven’t already, we recommend reading the case studies for each analysis technique discussed in this post (you’ll find a link at the end of each section). For a more hands-on introduction to the kinds of methods and techniques that data analysts use, try out this free introductory data analytics short course. In the meantime, you might also want to read the following:
- The Best Online Data Analytics Courses for 2024
- What Is Time Series Data and How Is It Analyzed?
- What is Spatial Analysis?
Qualitative Data Analysis Methods 101:
The “big 6” methods + examples.
By: Kerryn Warren (PhD) | Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (D.Tech) | May 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Qualitative data analysis methods. Wow, that’s a mouthful.
If you’re new to the world of research, qualitative data analysis can look rather intimidating. So much bulky terminology and so many abstract, fluffy concepts. It certainly can be a minefield!
Don’t worry – in this post, we’ll unpack the most popular analysis methods , one at a time, so that you can approach your analysis with confidence and competence – whether that’s for a dissertation, thesis or really any kind of research project.
What (exactly) is qualitative data analysis?
To understand qualitative data analysis, we need to first understand qualitative data – so let’s step back and ask the question, “what exactly is qualitative data?”.
Qualitative data refers to pretty much any data that’s “not numbers” . In other words, it’s not the stuff you measure using a fixed scale or complex equipment, nor do you analyse it using complex statistics or mathematics.
So, if it’s not numbers, what is it?
Words, you guessed? Well… sometimes , yes. Qualitative data can, and often does, take the form of interview transcripts, documents and open-ended survey responses – but it can also involve the interpretation of images and videos. In other words, qualitative isn’t just limited to text-based data.
So, how’s that different from quantitative data, you ask?
Simply put, qualitative research focuses on words, descriptions, concepts or ideas – while quantitative research focuses on numbers and statistics . Qualitative research investigates the “softer side” of things to explore and describe , while quantitative research focuses on the “hard numbers”, to measure differences between variables and the relationships between them. If you’re keen to learn more about the differences between qual and quant, we’ve got a detailed post over here .
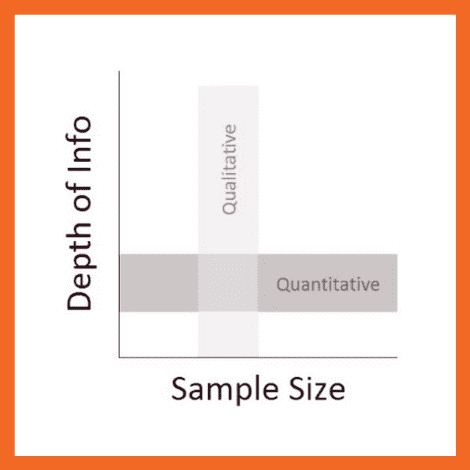
So, qualitative analysis is easier than quantitative, right?
Not quite. In many ways, qualitative data can be challenging and time-consuming to analyse and interpret. At the end of your data collection phase (which itself takes a lot of time), you’ll likely have many pages of text-based data or hours upon hours of audio to work through. You might also have subtle nuances of interactions or discussions that have danced around in your mind, or that you scribbled down in messy field notes. All of this needs to work its way into your analysis.
Making sense of all of this is no small task and you shouldn’t underestimate it. Long story short – qualitative analysis can be a lot of work! Of course, quantitative analysis is no piece of cake either, but it’s important to recognise that qualitative analysis still requires a significant investment in terms of time and effort.
Need a helping hand?
In this post, we’ll explore qualitative data analysis by looking at some of the most common analysis methods we encounter. We’re not going to cover every possible qualitative method and we’re not going to go into heavy detail – we’re just going to give you the big picture. That said, we will of course includes links to loads of extra resources so that you can learn more about whichever analysis method interests you.
Without further delay, let’s get into it.
The “Big 6” Qualitative Analysis Methods
There are many different types of qualitative data analysis, all of which serve different purposes and have unique strengths and weaknesses . We’ll start by outlining the analysis methods and then we’ll dive into the details for each.
The 6 most popular methods (or at least the ones we see at Grad Coach) are:
- Content analysis
- Narrative analysis
- Discourse analysis
- Thematic analysis
- Grounded theory (GT)
- Interpretive phenomenological analysis (IPA)
Let’s take a look at each of them…
QDA Method #1: Qualitative Content Analysis
Content analysis is possibly the most common and straightforward QDA method. At the simplest level, content analysis is used to evaluate patterns within a piece of content (for example, words, phrases or images) or across multiple pieces of content or sources of communication. For example, a collection of newspaper articles or political speeches.
With content analysis, you could, for instance, identify the frequency with which an idea is shared or spoken about – like the number of times a Kardashian is mentioned on Twitter. Or you could identify patterns of deeper underlying interpretations – for instance, by identifying phrases or words in tourist pamphlets that highlight India as an ancient country.
Because content analysis can be used in such a wide variety of ways, it’s important to go into your analysis with a very specific question and goal, or you’ll get lost in the fog. With content analysis, you’ll group large amounts of text into codes , summarise these into categories, and possibly even tabulate the data to calculate the frequency of certain concepts or variables. Because of this, content analysis provides a small splash of quantitative thinking within a qualitative method.
Naturally, while content analysis is widely useful, it’s not without its drawbacks . One of the main issues with content analysis is that it can be very time-consuming , as it requires lots of reading and re-reading of the texts. Also, because of its multidimensional focus on both qualitative and quantitative aspects, it is sometimes accused of losing important nuances in communication.
Content analysis also tends to concentrate on a very specific timeline and doesn’t take into account what happened before or after that timeline. This isn’t necessarily a bad thing though – just something to be aware of. So, keep these factors in mind if you’re considering content analysis. Every analysis method has its limitations , so don’t be put off by these – just be aware of them ! If you’re interested in learning more about content analysis, the video below provides a good starting point.
QDA Method #2: Narrative Analysis
As the name suggests, narrative analysis is all about listening to people telling stories and analysing what that means . Since stories serve a functional purpose of helping us make sense of the world, we can gain insights into the ways that people deal with and make sense of reality by analysing their stories and the ways they’re told.
You could, for example, use narrative analysis to explore whether how something is being said is important. For instance, the narrative of a prisoner trying to justify their crime could provide insight into their view of the world and the justice system. Similarly, analysing the ways entrepreneurs talk about the struggles in their careers or cancer patients telling stories of hope could provide powerful insights into their mindsets and perspectives . Simply put, narrative analysis is about paying attention to the stories that people tell – and more importantly, the way they tell them.
Of course, the narrative approach has its weaknesses , too. Sample sizes are generally quite small due to the time-consuming process of capturing narratives. Because of this, along with the multitude of social and lifestyle factors which can influence a subject, narrative analysis can be quite difficult to reproduce in subsequent research. This means that it’s difficult to test the findings of some of this research.
Similarly, researcher bias can have a strong influence on the results here, so you need to be particularly careful about the potential biases you can bring into your analysis when using this method. Nevertheless, narrative analysis is still a very useful qualitative analysis method – just keep these limitations in mind and be careful not to draw broad conclusions . If you’re keen to learn more about narrative analysis, the video below provides a great introduction to this qualitative analysis method.
QDA Method #3: Discourse Analysis
Discourse is simply a fancy word for written or spoken language or debate . So, discourse analysis is all about analysing language within its social context. In other words, analysing language – such as a conversation, a speech, etc – within the culture and society it takes place. For example, you could analyse how a janitor speaks to a CEO, or how politicians speak about terrorism.
To truly understand these conversations or speeches, the culture and history of those involved in the communication are important factors to consider. For example, a janitor might speak more casually with a CEO in a company that emphasises equality among workers. Similarly, a politician might speak more about terrorism if there was a recent terrorist incident in the country.
So, as you can see, by using discourse analysis, you can identify how culture , history or power dynamics (to name a few) have an effect on the way concepts are spoken about. So, if your research aims and objectives involve understanding culture or power dynamics, discourse analysis can be a powerful method.
Because there are many social influences in terms of how we speak to each other, the potential use of discourse analysis is vast . Of course, this also means it’s important to have a very specific research question (or questions) in mind when analysing your data and looking for patterns and themes, or you might land up going down a winding rabbit hole.
Discourse analysis can also be very time-consuming as you need to sample the data to the point of saturation – in other words, until no new information and insights emerge. But this is, of course, part of what makes discourse analysis such a powerful technique. So, keep these factors in mind when considering this QDA method. Again, if you’re keen to learn more, the video below presents a good starting point.
QDA Method #4: Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis looks at patterns of meaning in a data set – for example, a set of interviews or focus group transcripts. But what exactly does that… mean? Well, a thematic analysis takes bodies of data (which are often quite large) and groups them according to similarities – in other words, themes . These themes help us make sense of the content and derive meaning from it.
Let’s take a look at an example.
With thematic analysis, you could analyse 100 online reviews of a popular sushi restaurant to find out what patrons think about the place. By reviewing the data, you would then identify the themes that crop up repeatedly within the data – for example, “fresh ingredients” or “friendly wait staff”.
So, as you can see, thematic analysis can be pretty useful for finding out about people’s experiences , views, and opinions . Therefore, if your research aims and objectives involve understanding people’s experience or view of something, thematic analysis can be a great choice.
Since thematic analysis is a bit of an exploratory process, it’s not unusual for your research questions to develop , or even change as you progress through the analysis. While this is somewhat natural in exploratory research, it can also be seen as a disadvantage as it means that data needs to be re-reviewed each time a research question is adjusted. In other words, thematic analysis can be quite time-consuming – but for a good reason. So, keep this in mind if you choose to use thematic analysis for your project and budget extra time for unexpected adjustments.

QDA Method #5: Grounded theory (GT)
Grounded theory is a powerful qualitative analysis method where the intention is to create a new theory (or theories) using the data at hand, through a series of “ tests ” and “ revisions ”. Strictly speaking, GT is more a research design type than an analysis method, but we’ve included it here as it’s often referred to as a method.
What’s most important with grounded theory is that you go into the analysis with an open mind and let the data speak for itself – rather than dragging existing hypotheses or theories into your analysis. In other words, your analysis must develop from the ground up (hence the name).
Let’s look at an example of GT in action.
Assume you’re interested in developing a theory about what factors influence students to watch a YouTube video about qualitative analysis. Using Grounded theory , you’d start with this general overarching question about the given population (i.e., graduate students). First, you’d approach a small sample – for example, five graduate students in a department at a university. Ideally, this sample would be reasonably representative of the broader population. You’d interview these students to identify what factors lead them to watch the video.
After analysing the interview data, a general pattern could emerge. For example, you might notice that graduate students are more likely to read a post about qualitative methods if they are just starting on their dissertation journey, or if they have an upcoming test about research methods.
From here, you’ll look for another small sample – for example, five more graduate students in a different department – and see whether this pattern holds true for them. If not, you’ll look for commonalities and adapt your theory accordingly. As this process continues, the theory would develop . As we mentioned earlier, what’s important with grounded theory is that the theory develops from the data – not from some preconceived idea.
So, what are the drawbacks of grounded theory? Well, some argue that there’s a tricky circularity to grounded theory. For it to work, in principle, you should know as little as possible regarding the research question and population, so that you reduce the bias in your interpretation. However, in many circumstances, it’s also thought to be unwise to approach a research question without knowledge of the current literature . In other words, it’s a bit of a “chicken or the egg” situation.
Regardless, grounded theory remains a popular (and powerful) option. Naturally, it’s a very useful method when you’re researching a topic that is completely new or has very little existing research about it, as it allows you to start from scratch and work your way from the ground up .

QDA Method #6: Interpretive Phenomenological Analysis (IPA)
Interpretive. Phenomenological. Analysis. IPA . Try saying that three times fast…
Let’s just stick with IPA, okay?
IPA is designed to help you understand the personal experiences of a subject (for example, a person or group of people) concerning a major life event, an experience or a situation . This event or experience is the “phenomenon” that makes up the “P” in IPA. Such phenomena may range from relatively common events – such as motherhood, or being involved in a car accident – to those which are extremely rare – for example, someone’s personal experience in a refugee camp. So, IPA is a great choice if your research involves analysing people’s personal experiences of something that happened to them.
It’s important to remember that IPA is subject – centred . In other words, it’s focused on the experiencer . This means that, while you’ll likely use a coding system to identify commonalities, it’s important not to lose the depth of experience or meaning by trying to reduce everything to codes. Also, keep in mind that since your sample size will generally be very small with IPA, you often won’t be able to draw broad conclusions about the generalisability of your findings. But that’s okay as long as it aligns with your research aims and objectives.
Another thing to be aware of with IPA is personal bias . While researcher bias can creep into all forms of research, self-awareness is critically important with IPA, as it can have a major impact on the results. For example, a researcher who was a victim of a crime himself could insert his own feelings of frustration and anger into the way he interprets the experience of someone who was kidnapped. So, if you’re going to undertake IPA, you need to be very self-aware or you could muddy the analysis.

How to choose the right analysis method
In light of all of the qualitative analysis methods we’ve covered so far, you’re probably asking yourself the question, “ How do I choose the right one? ”
Much like all the other methodological decisions you’ll need to make, selecting the right qualitative analysis method largely depends on your research aims, objectives and questions . In other words, the best tool for the job depends on what you’re trying to build. For example:
- Perhaps your research aims to analyse the use of words and what they reveal about the intention of the storyteller and the cultural context of the time.
- Perhaps your research aims to develop an understanding of the unique personal experiences of people that have experienced a certain event, or
- Perhaps your research aims to develop insight regarding the influence of a certain culture on its members.
As you can probably see, each of these research aims are distinctly different , and therefore different analysis methods would be suitable for each one. For example, narrative analysis would likely be a good option for the first aim, while grounded theory wouldn’t be as relevant.
It’s also important to remember that each method has its own set of strengths, weaknesses and general limitations. No single analysis method is perfect . So, depending on the nature of your research, it may make sense to adopt more than one method (this is called triangulation ). Keep in mind though that this will of course be quite time-consuming.
As we’ve seen, all of the qualitative analysis methods we’ve discussed make use of coding and theme-generating techniques, but the intent and approach of each analysis method differ quite substantially. So, it’s very important to come into your research with a clear intention before you decide which analysis method (or methods) to use.
Start by reviewing your research aims , objectives and research questions to assess what exactly you’re trying to find out – then select a qualitative analysis method that fits. Never pick a method just because you like it or have experience using it – your analysis method (or methods) must align with your broader research aims and objectives.

Let’s recap on QDA methods…
In this post, we looked at six popular qualitative data analysis methods:
- First, we looked at content analysis , a straightforward method that blends a little bit of quant into a primarily qualitative analysis.
- Then we looked at narrative analysis , which is about analysing how stories are told.
- Next up was discourse analysis – which is about analysing conversations and interactions.
- Then we moved on to thematic analysis – which is about identifying themes and patterns.
- From there, we went south with grounded theory – which is about starting from scratch with a specific question and using the data alone to build a theory in response to that question.
- And finally, we looked at IPA – which is about understanding people’s unique experiences of a phenomenon.
Of course, these aren’t the only options when it comes to qualitative data analysis, but they’re a great starting point if you’re dipping your toes into qualitative research for the first time.
If you’re still feeling a bit confused, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research process to help you develop your best work.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

84 Comments
This has been very helpful. Thank you.
Thank you madam,
Thank you so much for this information
I wonder it so clear for understand and good for me. can I ask additional query?
Very insightful and useful
Good work done with clear explanations. Thank you.
Thanks so much for the write-up, it’s really good.
Thanks madam . It is very important .
thank you very good
This has been very well explained in simple language . It is useful even for a new researcher.
Great to hear that. Good luck with your qualitative data analysis, Pramod!
This is very useful information. And it was very a clear language structured presentation. Thanks a lot.
Thank you so much.
very informative sequential presentation
Precise explanation of method.
Hi, may we use 2 data analysis methods in our qualitative research?
Thanks for your comment. Most commonly, one would use one type of analysis method, but it depends on your research aims and objectives.
You explained it in very simple language, everyone can understand it. Thanks so much.
Thank you very much, this is very helpful. It has been explained in a very simple manner that even a layman understands
Thank nicely explained can I ask is Qualitative content analysis the same as thematic analysis?
Thanks for your comment. No, QCA and thematic are two different types of analysis. This article might help clarify – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/nhs.12048
This is my first time to come across a well explained data analysis. so helpful.
I have thoroughly enjoyed your explanation of the six qualitative analysis methods. This is very helpful. Thank you!
Thank you very much, this is well explained and useful
i need a citation of your book.
Thanks a lot , remarkable indeed, enlighting to the best
Hi Derek, What other theories/methods would you recommend when the data is a whole speech?
Keep writing useful artikel.
It is important concept about QDA and also the way to express is easily understandable, so thanks for all.
Thank you, this is well explained and very useful.
Very helpful .Thanks.
Hi there! Very well explained. Simple but very useful style of writing. Please provide the citation of the text. warm regards
The session was very helpful and insightful. Thank you
This was very helpful and insightful. Easy to read and understand
As a professional academic writer, this has been so informative and educative. Keep up the good work Grad Coach you are unmatched with quality content for sure.
Keep up the good work Grad Coach you are unmatched with quality content for sure.
Its Great and help me the most. A Million Thanks you Dr.
It is a very nice work
Very insightful. Please, which of this approach could be used for a research that one is trying to elicit students’ misconceptions in a particular concept ?
This is Amazing and well explained, thanks
great overview
What do we call a research data analysis method that one use to advise or determining the best accounting tool or techniques that should be adopted in a company.
Informative video, explained in a clear and simple way. Kudos
Waoo! I have chosen method wrong for my data analysis. But I can revise my work according to this guide. Thank you so much for this helpful lecture.
This has been very helpful. It gave me a good view of my research objectives and how to choose the best method. Thematic analysis it is.
Very helpful indeed. Thanku so much for the insight.
This was incredibly helpful.
Very helpful.
very educative
Nicely written especially for novice academic researchers like me! Thank you.
choosing a right method for a paper is always a hard job for a student, this is a useful information, but it would be more useful personally for me, if the author provide me with a little bit more information about the data analysis techniques in type of explanatory research. Can we use qualitative content analysis technique for explanatory research ? or what is the suitable data analysis method for explanatory research in social studies?
that was very helpful for me. because these details are so important to my research. thank you very much
I learnt a lot. Thank you
Relevant and Informative, thanks !
Well-planned and organized, thanks much! 🙂
I have reviewed qualitative data analysis in a simplest way possible. The content will highly be useful for developing my book on qualitative data analysis methods. Cheers!
Clear explanation on qualitative and how about Case study
This was helpful. Thank you
This was really of great assistance, it was just the right information needed. Explanation very clear and follow.
Wow, Thanks for making my life easy
This was helpful thanks .
Very helpful…. clear and written in an easily understandable manner. Thank you.
This was so helpful as it was easy to understand. I’m a new to research thank you so much.
so educative…. but Ijust want to know which method is coding of the qualitative or tallying done?
Thank you for the great content, I have learnt a lot. So helpful
precise and clear presentation with simple language and thank you for that.
very informative content, thank you.
You guys are amazing on YouTube on this platform. Your teachings are great, educative, and informative. kudos!
Brilliant Delivery. You made a complex subject seem so easy. Well done.
Beautifully explained.
Thanks a lot
Is there a video the captures the practical process of coding using automated applications?
Thanks for the comment. We don’t recommend using automated applications for coding, as they are not sufficiently accurate in our experience.
content analysis can be qualitative research?
THANK YOU VERY MUCH.
Thank you very much for such a wonderful content
do you have any material on Data collection
What a powerful explanation of the QDA methods. Thank you.
Great explanation both written and Video. i have been using of it on a day to day working of my thesis project in accounting and finance. Thank you very much for your support.
very helpful, thank you so much
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
Basic statistical tools in research and data analysis
Zulfiqar ali.
Department of Anaesthesiology, Division of Neuroanaesthesiology, Sheri Kashmir Institute of Medical Sciences, Soura, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India
S Bala Bhaskar
1 Department of Anaesthesiology and Critical Care, Vijayanagar Institute of Medical Sciences, Bellary, Karnataka, India
Statistical methods involved in carrying out a study include planning, designing, collecting data, analysing, drawing meaningful interpretation and reporting of the research findings. The statistical analysis gives meaning to the meaningless numbers, thereby breathing life into a lifeless data. The results and inferences are precise only if proper statistical tests are used. This article will try to acquaint the reader with the basic research tools that are utilised while conducting various studies. The article covers a brief outline of the variables, an understanding of quantitative and qualitative variables and the measures of central tendency. An idea of the sample size estimation, power analysis and the statistical errors is given. Finally, there is a summary of parametric and non-parametric tests used for data analysis.
INTRODUCTION
Statistics is a branch of science that deals with the collection, organisation, analysis of data and drawing of inferences from the samples to the whole population.[ 1 ] This requires a proper design of the study, an appropriate selection of the study sample and choice of a suitable statistical test. An adequate knowledge of statistics is necessary for proper designing of an epidemiological study or a clinical trial. Improper statistical methods may result in erroneous conclusions which may lead to unethical practice.[ 2 ]
Variable is a characteristic that varies from one individual member of population to another individual.[ 3 ] Variables such as height and weight are measured by some type of scale, convey quantitative information and are called as quantitative variables. Sex and eye colour give qualitative information and are called as qualitative variables[ 3 ] [ Figure 1 ].

Classification of variables
Quantitative variables
Quantitative or numerical data are subdivided into discrete and continuous measurements. Discrete numerical data are recorded as a whole number such as 0, 1, 2, 3,… (integer), whereas continuous data can assume any value. Observations that can be counted constitute the discrete data and observations that can be measured constitute the continuous data. Examples of discrete data are number of episodes of respiratory arrests or the number of re-intubations in an intensive care unit. Similarly, examples of continuous data are the serial serum glucose levels, partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood and the oesophageal temperature.
A hierarchical scale of increasing precision can be used for observing and recording the data which is based on categorical, ordinal, interval and ratio scales [ Figure 1 ].
Categorical or nominal variables are unordered. The data are merely classified into categories and cannot be arranged in any particular order. If only two categories exist (as in gender male and female), it is called as a dichotomous (or binary) data. The various causes of re-intubation in an intensive care unit due to upper airway obstruction, impaired clearance of secretions, hypoxemia, hypercapnia, pulmonary oedema and neurological impairment are examples of categorical variables.
Ordinal variables have a clear ordering between the variables. However, the ordered data may not have equal intervals. Examples are the American Society of Anesthesiologists status or Richmond agitation-sedation scale.
Interval variables are similar to an ordinal variable, except that the intervals between the values of the interval variable are equally spaced. A good example of an interval scale is the Fahrenheit degree scale used to measure temperature. With the Fahrenheit scale, the difference between 70° and 75° is equal to the difference between 80° and 85°: The units of measurement are equal throughout the full range of the scale.
Ratio scales are similar to interval scales, in that equal differences between scale values have equal quantitative meaning. However, ratio scales also have a true zero point, which gives them an additional property. For example, the system of centimetres is an example of a ratio scale. There is a true zero point and the value of 0 cm means a complete absence of length. The thyromental distance of 6 cm in an adult may be twice that of a child in whom it may be 3 cm.
STATISTICS: DESCRIPTIVE AND INFERENTIAL STATISTICS
Descriptive statistics[ 4 ] try to describe the relationship between variables in a sample or population. Descriptive statistics provide a summary of data in the form of mean, median and mode. Inferential statistics[ 4 ] use a random sample of data taken from a population to describe and make inferences about the whole population. It is valuable when it is not possible to examine each member of an entire population. The examples if descriptive and inferential statistics are illustrated in Table 1 .
Example of descriptive and inferential statistics

Descriptive statistics
The extent to which the observations cluster around a central location is described by the central tendency and the spread towards the extremes is described by the degree of dispersion.
Measures of central tendency
The measures of central tendency are mean, median and mode.[ 6 ] Mean (or the arithmetic average) is the sum of all the scores divided by the number of scores. Mean may be influenced profoundly by the extreme variables. For example, the average stay of organophosphorus poisoning patients in ICU may be influenced by a single patient who stays in ICU for around 5 months because of septicaemia. The extreme values are called outliers. The formula for the mean is

where x = each observation and n = number of observations. Median[ 6 ] is defined as the middle of a distribution in a ranked data (with half of the variables in the sample above and half below the median value) while mode is the most frequently occurring variable in a distribution. Range defines the spread, or variability, of a sample.[ 7 ] It is described by the minimum and maximum values of the variables. If we rank the data and after ranking, group the observations into percentiles, we can get better information of the pattern of spread of the variables. In percentiles, we rank the observations into 100 equal parts. We can then describe 25%, 50%, 75% or any other percentile amount. The median is the 50 th percentile. The interquartile range will be the observations in the middle 50% of the observations about the median (25 th -75 th percentile). Variance[ 7 ] is a measure of how spread out is the distribution. It gives an indication of how close an individual observation clusters about the mean value. The variance of a population is defined by the following formula:

where σ 2 is the population variance, X is the population mean, X i is the i th element from the population and N is the number of elements in the population. The variance of a sample is defined by slightly different formula:

where s 2 is the sample variance, x is the sample mean, x i is the i th element from the sample and n is the number of elements in the sample. The formula for the variance of a population has the value ‘ n ’ as the denominator. The expression ‘ n −1’ is known as the degrees of freedom and is one less than the number of parameters. Each observation is free to vary, except the last one which must be a defined value. The variance is measured in squared units. To make the interpretation of the data simple and to retain the basic unit of observation, the square root of variance is used. The square root of the variance is the standard deviation (SD).[ 8 ] The SD of a population is defined by the following formula:

where σ is the population SD, X is the population mean, X i is the i th element from the population and N is the number of elements in the population. The SD of a sample is defined by slightly different formula:

where s is the sample SD, x is the sample mean, x i is the i th element from the sample and n is the number of elements in the sample. An example for calculation of variation and SD is illustrated in Table 2 .
Example of mean, variance, standard deviation

Normal distribution or Gaussian distribution
Most of the biological variables usually cluster around a central value, with symmetrical positive and negative deviations about this point.[ 1 ] The standard normal distribution curve is a symmetrical bell-shaped. In a normal distribution curve, about 68% of the scores are within 1 SD of the mean. Around 95% of the scores are within 2 SDs of the mean and 99% within 3 SDs of the mean [ Figure 2 ].

Normal distribution curve
Skewed distribution
It is a distribution with an asymmetry of the variables about its mean. In a negatively skewed distribution [ Figure 3 ], the mass of the distribution is concentrated on the right of Figure 1 . In a positively skewed distribution [ Figure 3 ], the mass of the distribution is concentrated on the left of the figure leading to a longer right tail.

Curves showing negatively skewed and positively skewed distribution
Inferential statistics
In inferential statistics, data are analysed from a sample to make inferences in the larger collection of the population. The purpose is to answer or test the hypotheses. A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. Hypothesis tests are thus procedures for making rational decisions about the reality of observed effects.
Probability is the measure of the likelihood that an event will occur. Probability is quantified as a number between 0 and 1 (where 0 indicates impossibility and 1 indicates certainty).
In inferential statistics, the term ‘null hypothesis’ ( H 0 ‘ H-naught ,’ ‘ H-null ’) denotes that there is no relationship (difference) between the population variables in question.[ 9 ]
Alternative hypothesis ( H 1 and H a ) denotes that a statement between the variables is expected to be true.[ 9 ]
The P value (or the calculated probability) is the probability of the event occurring by chance if the null hypothesis is true. The P value is a numerical between 0 and 1 and is interpreted by researchers in deciding whether to reject or retain the null hypothesis [ Table 3 ].
P values with interpretation

If P value is less than the arbitrarily chosen value (known as α or the significance level), the null hypothesis (H0) is rejected [ Table 4 ]. However, if null hypotheses (H0) is incorrectly rejected, this is known as a Type I error.[ 11 ] Further details regarding alpha error, beta error and sample size calculation and factors influencing them are dealt with in another section of this issue by Das S et al .[ 12 ]
Illustration for null hypothesis

PARAMETRIC AND NON-PARAMETRIC TESTS
Numerical data (quantitative variables) that are normally distributed are analysed with parametric tests.[ 13 ]
Two most basic prerequisites for parametric statistical analysis are:
- The assumption of normality which specifies that the means of the sample group are normally distributed
- The assumption of equal variance which specifies that the variances of the samples and of their corresponding population are equal.
However, if the distribution of the sample is skewed towards one side or the distribution is unknown due to the small sample size, non-parametric[ 14 ] statistical techniques are used. Non-parametric tests are used to analyse ordinal and categorical data.
Parametric tests
The parametric tests assume that the data are on a quantitative (numerical) scale, with a normal distribution of the underlying population. The samples have the same variance (homogeneity of variances). The samples are randomly drawn from the population, and the observations within a group are independent of each other. The commonly used parametric tests are the Student's t -test, analysis of variance (ANOVA) and repeated measures ANOVA.
Student's t -test
Student's t -test is used to test the null hypothesis that there is no difference between the means of the two groups. It is used in three circumstances:

where X = sample mean, u = population mean and SE = standard error of mean

where X 1 − X 2 is the difference between the means of the two groups and SE denotes the standard error of the difference.
- To test if the population means estimated by two dependent samples differ significantly (the paired t -test). A usual setting for paired t -test is when measurements are made on the same subjects before and after a treatment.
The formula for paired t -test is:

where d is the mean difference and SE denotes the standard error of this difference.
The group variances can be compared using the F -test. The F -test is the ratio of variances (var l/var 2). If F differs significantly from 1.0, then it is concluded that the group variances differ significantly.
Analysis of variance
The Student's t -test cannot be used for comparison of three or more groups. The purpose of ANOVA is to test if there is any significant difference between the means of two or more groups.
In ANOVA, we study two variances – (a) between-group variability and (b) within-group variability. The within-group variability (error variance) is the variation that cannot be accounted for in the study design. It is based on random differences present in our samples.
However, the between-group (or effect variance) is the result of our treatment. These two estimates of variances are compared using the F-test.
A simplified formula for the F statistic is:

where MS b is the mean squares between the groups and MS w is the mean squares within groups.
Repeated measures analysis of variance
As with ANOVA, repeated measures ANOVA analyses the equality of means of three or more groups. However, a repeated measure ANOVA is used when all variables of a sample are measured under different conditions or at different points in time.
As the variables are measured from a sample at different points of time, the measurement of the dependent variable is repeated. Using a standard ANOVA in this case is not appropriate because it fails to model the correlation between the repeated measures: The data violate the ANOVA assumption of independence. Hence, in the measurement of repeated dependent variables, repeated measures ANOVA should be used.
Non-parametric tests
When the assumptions of normality are not met, and the sample means are not normally, distributed parametric tests can lead to erroneous results. Non-parametric tests (distribution-free test) are used in such situation as they do not require the normality assumption.[ 15 ] Non-parametric tests may fail to detect a significant difference when compared with a parametric test. That is, they usually have less power.
As is done for the parametric tests, the test statistic is compared with known values for the sampling distribution of that statistic and the null hypothesis is accepted or rejected. The types of non-parametric analysis techniques and the corresponding parametric analysis techniques are delineated in Table 5 .
Analogue of parametric and non-parametric tests

Median test for one sample: The sign test and Wilcoxon's signed rank test
The sign test and Wilcoxon's signed rank test are used for median tests of one sample. These tests examine whether one instance of sample data is greater or smaller than the median reference value.
This test examines the hypothesis about the median θ0 of a population. It tests the null hypothesis H0 = θ0. When the observed value (Xi) is greater than the reference value (θ0), it is marked as+. If the observed value is smaller than the reference value, it is marked as − sign. If the observed value is equal to the reference value (θ0), it is eliminated from the sample.
If the null hypothesis is true, there will be an equal number of + signs and − signs.
The sign test ignores the actual values of the data and only uses + or − signs. Therefore, it is useful when it is difficult to measure the values.
Wilcoxon's signed rank test
There is a major limitation of sign test as we lose the quantitative information of the given data and merely use the + or – signs. Wilcoxon's signed rank test not only examines the observed values in comparison with θ0 but also takes into consideration the relative sizes, adding more statistical power to the test. As in the sign test, if there is an observed value that is equal to the reference value θ0, this observed value is eliminated from the sample.
Wilcoxon's rank sum test ranks all data points in order, calculates the rank sum of each sample and compares the difference in the rank sums.
Mann-Whitney test
It is used to test the null hypothesis that two samples have the same median or, alternatively, whether observations in one sample tend to be larger than observations in the other.
Mann–Whitney test compares all data (xi) belonging to the X group and all data (yi) belonging to the Y group and calculates the probability of xi being greater than yi: P (xi > yi). The null hypothesis states that P (xi > yi) = P (xi < yi) =1/2 while the alternative hypothesis states that P (xi > yi) ≠1/2.
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test
The two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test was designed as a generic method to test whether two random samples are drawn from the same distribution. The null hypothesis of the KS test is that both distributions are identical. The statistic of the KS test is a distance between the two empirical distributions, computed as the maximum absolute difference between their cumulative curves.
Kruskal-Wallis test
The Kruskal–Wallis test is a non-parametric test to analyse the variance.[ 14 ] It analyses if there is any difference in the median values of three or more independent samples. The data values are ranked in an increasing order, and the rank sums calculated followed by calculation of the test statistic.
Jonckheere test
In contrast to Kruskal–Wallis test, in Jonckheere test, there is an a priori ordering that gives it a more statistical power than the Kruskal–Wallis test.[ 14 ]
Friedman test
The Friedman test is a non-parametric test for testing the difference between several related samples. The Friedman test is an alternative for repeated measures ANOVAs which is used when the same parameter has been measured under different conditions on the same subjects.[ 13 ]
Tests to analyse the categorical data
Chi-square test, Fischer's exact test and McNemar's test are used to analyse the categorical or nominal variables. The Chi-square test compares the frequencies and tests whether the observed data differ significantly from that of the expected data if there were no differences between groups (i.e., the null hypothesis). It is calculated by the sum of the squared difference between observed ( O ) and the expected ( E ) data (or the deviation, d ) divided by the expected data by the following formula:

A Yates correction factor is used when the sample size is small. Fischer's exact test is used to determine if there are non-random associations between two categorical variables. It does not assume random sampling, and instead of referring a calculated statistic to a sampling distribution, it calculates an exact probability. McNemar's test is used for paired nominal data. It is applied to 2 × 2 table with paired-dependent samples. It is used to determine whether the row and column frequencies are equal (that is, whether there is ‘marginal homogeneity’). The null hypothesis is that the paired proportions are equal. The Mantel-Haenszel Chi-square test is a multivariate test as it analyses multiple grouping variables. It stratifies according to the nominated confounding variables and identifies any that affects the primary outcome variable. If the outcome variable is dichotomous, then logistic regression is used.
SOFTWARES AVAILABLE FOR STATISTICS, SAMPLE SIZE CALCULATION AND POWER ANALYSIS
Numerous statistical software systems are available currently. The commonly used software systems are Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS – manufactured by IBM corporation), Statistical Analysis System ((SAS – developed by SAS Institute North Carolina, United States of America), R (designed by Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman from R core team), Minitab (developed by Minitab Inc), Stata (developed by StataCorp) and the MS Excel (developed by Microsoft).
There are a number of web resources which are related to statistical power analyses. A few are:
- StatPages.net – provides links to a number of online power calculators
- G-Power – provides a downloadable power analysis program that runs under DOS
- Power analysis for ANOVA designs an interactive site that calculates power or sample size needed to attain a given power for one effect in a factorial ANOVA design
- SPSS makes a program called SamplePower. It gives an output of a complete report on the computer screen which can be cut and paste into another document.
It is important that a researcher knows the concepts of the basic statistical methods used for conduct of a research study. This will help to conduct an appropriately well-designed study leading to valid and reliable results. Inappropriate use of statistical techniques may lead to faulty conclusions, inducing errors and undermining the significance of the article. Bad statistics may lead to bad research, and bad research may lead to unethical practice. Hence, an adequate knowledge of statistics and the appropriate use of statistical tests are important. An appropriate knowledge about the basic statistical methods will go a long way in improving the research designs and producing quality medical research which can be utilised for formulating the evidence-based guidelines.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Qualitative Data Analysis: What is it, Methods + Examples

In a world rich with information and narrative, understanding the deeper layers of human experiences requires a unique vision that goes beyond numbers and figures. This is where the power of qualitative data analysis comes to light.
In this blog, we’ll learn about qualitative data analysis, explore its methods, and provide real-life examples showcasing its power in uncovering insights.
What is Qualitative Data Analysis?
Qualitative data analysis is a systematic process of examining non-numerical data to extract meaning, patterns, and insights.
In contrast to quantitative analysis, which focuses on numbers and statistical metrics, the qualitative study focuses on the qualitative aspects of data, such as text, images, audio, and videos. It seeks to understand every aspect of human experiences, perceptions, and behaviors by examining the data’s richness.
Companies frequently conduct this analysis on customer feedback. You can collect qualitative data from reviews, complaints, chat messages, interactions with support centers, customer interviews, case notes, or even social media comments. This kind of data holds the key to understanding customer sentiments and preferences in a way that goes beyond mere numbers.
Importance of Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data analysis plays a crucial role in your research and decision-making process across various disciplines. Let’s explore some key reasons that underline the significance of this analysis:
In-Depth Understanding
It enables you to explore complex and nuanced aspects of a phenomenon, delving into the ‘how’ and ‘why’ questions. This method provides you with a deeper understanding of human behavior, experiences, and contexts that quantitative approaches might not capture fully.
Contextual Insight
You can use this analysis to give context to numerical data. It will help you understand the circumstances and conditions that influence participants’ thoughts, feelings, and actions. This contextual insight becomes essential for generating comprehensive explanations.
Theory Development
You can generate or refine hypotheses via qualitative data analysis. As you analyze the data attentively, you can form hypotheses, concepts, and frameworks that will drive your future research and contribute to theoretical advances.
Participant Perspectives
When performing qualitative research, you can highlight participant voices and opinions. This approach is especially useful for understanding marginalized or underrepresented people, as it allows them to communicate their experiences and points of view.
Exploratory Research
The analysis is frequently used at the exploratory stage of your project. It assists you in identifying important variables, developing research questions, and designing quantitative studies that will follow.
Types of Qualitative Data
When conducting qualitative research, you can use several qualitative data collection methods , and here you will come across many sorts of qualitative data that can provide you with unique insights into your study topic. These data kinds add new views and angles to your understanding and analysis.
Interviews and Focus Groups
Interviews and focus groups will be among your key methods for gathering qualitative data. Interviews are one-on-one talks in which participants can freely share their thoughts, experiences, and opinions.
Focus groups, on the other hand, are discussions in which members interact with one another, resulting in dynamic exchanges of ideas. Both methods provide rich qualitative data and direct access to participant perspectives.
Observations and Field Notes
Observations and field notes are another useful sort of qualitative data. You can immerse yourself in the research environment through direct observation, carefully documenting behaviors, interactions, and contextual factors.
These observations will be recorded in your field notes, providing a complete picture of the environment and the behaviors you’re researching. This data type is especially important for comprehending behavior in their natural setting.
Textual and Visual Data
Textual and visual data include a wide range of resources that can be qualitatively analyzed. Documents, written narratives, and transcripts from various sources, such as interviews or speeches, are examples of textual data.
Photographs, films, and even artwork provide a visual layer to your research. These forms of data allow you to investigate what is spoken and the underlying emotions, details, and symbols expressed by language or pictures.
When to Choose Qualitative Data Analysis over Quantitative Data Analysis
As you begin your research journey, understanding why the analysis of qualitative data is important will guide your approach to understanding complex events. If you analyze qualitative data, it will provide new insights that complement quantitative methodologies, which will give you a broader understanding of your study topic.
It is critical to know when to use qualitative analysis over quantitative procedures. You can prefer qualitative data analysis when:
- Complexity Reigns: When your research questions involve deep human experiences, motivations, or emotions, qualitative research excels at revealing these complexities.
- Exploration is Key: Qualitative analysis is ideal for exploratory research. It will assist you in understanding a new or poorly understood topic before formulating quantitative hypotheses.
- Context Matters: If you want to understand how context affects behaviors or results, qualitative data analysis provides the depth needed to grasp these relationships.
- Unanticipated Findings: When your study provides surprising new viewpoints or ideas, qualitative analysis helps you to delve deeply into these emerging themes.
- Subjective Interpretation is Vital: When it comes to understanding people’s subjective experiences and interpretations, qualitative data analysis is the way to go.
You can make informed decisions regarding the right approach for your research objectives if you understand the importance of qualitative analysis and recognize the situations where it shines.
Qualitative Data Analysis Methods and Examples
Exploring various qualitative data analysis methods will provide you with a wide collection for making sense of your research findings. Once the data has been collected, you can choose from several analysis methods based on your research objectives and the data type you’ve collected.
There are five main methods for analyzing qualitative data. Each method takes a distinct approach to identifying patterns, themes, and insights within your qualitative data. They are:
Method 1: Content Analysis
Content analysis is a methodical technique for analyzing textual or visual data in a structured manner. In this method, you will categorize qualitative data by splitting it into manageable pieces and assigning the manual coding process to these units.
As you go, you’ll notice ongoing codes and designs that will allow you to conclude the content. This method is very beneficial for detecting common ideas, concepts, or themes in your data without losing the context.
Steps to Do Content Analysis
Follow these steps when conducting content analysis:
- Collect and Immerse: Begin by collecting the necessary textual or visual data. Immerse yourself in this data to fully understand its content, context, and complexities.
- Assign Codes and Categories: Assign codes to relevant data sections that systematically represent major ideas or themes. Arrange comparable codes into groups that cover the major themes.
- Analyze and Interpret: Develop a structured framework from the categories and codes. Then, evaluate the data in the context of your research question, investigate relationships between categories, discover patterns, and draw meaning from these connections.
Benefits & Challenges
There are various advantages to using content analysis:
- Structured Approach: It offers a systematic approach to dealing with large data sets and ensures consistency throughout the research.
- Objective Insights: This method promotes objectivity, which helps to reduce potential biases in your study.
- Pattern Discovery: Content analysis can help uncover hidden trends, themes, and patterns that are not always obvious.
- Versatility: You can apply content analysis to various data formats, including text, internet content, images, etc.
However, keep in mind the challenges that arise:
- Subjectivity: Even with the best attempts, a certain bias may remain in coding and interpretation.
- Complexity: Analyzing huge data sets requires time and great attention to detail.
- Contextual Nuances: Content analysis may not capture all of the contextual richness that qualitative data analysis highlights.
Example of Content Analysis
Suppose you’re conducting market research and looking at customer feedback on a product. As you collect relevant data and analyze feedback, you’ll see repeating codes like “price,” “quality,” “customer service,” and “features.” These codes are organized into categories such as “positive reviews,” “negative reviews,” and “suggestions for improvement.”
According to your findings, themes such as “price” and “customer service” stand out and show that pricing and customer service greatly impact customer satisfaction. This example highlights the power of content analysis for obtaining significant insights from large textual data collections.
Method 2: Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis is a well-structured procedure for identifying and analyzing recurring themes in your data. As you become more engaged in the data, you’ll generate codes or short labels representing key concepts. These codes are then organized into themes, providing a consistent framework for organizing and comprehending the substance of the data.
The analysis allows you to organize complex narratives and perspectives into meaningful categories, which will allow you to identify connections and patterns that may not be visible at first.
Steps to Do Thematic Analysis
Follow these steps when conducting a thematic analysis:
- Code and Group: Start by thoroughly examining the data and giving initial codes that identify the segments. To create initial themes, combine relevant codes.
- Code and Group: Begin by engaging yourself in the data, assigning first codes to notable segments. To construct basic themes, group comparable codes together.
- Analyze and Report: Analyze the data within each theme to derive relevant insights. Organize the topics into a consistent structure and explain your findings, along with data extracts that represent each theme.
Thematic analysis has various benefits:
- Structured Exploration: It is a method for identifying patterns and themes in complex qualitative data.
- Comprehensive knowledge: Thematic analysis promotes an in-depth understanding of the complications and meanings of the data.
- Application Flexibility: This method can be customized to various research situations and data kinds.
However, challenges may arise, such as:
- Interpretive Nature: Interpreting qualitative data in thematic analysis is vital, and it is critical to manage researcher bias.
- Time-consuming: The study can be time-consuming, especially with large data sets.
- Subjectivity: The selection of codes and topics might be subjective.
Example of Thematic Analysis
Assume you’re conducting a thematic analysis on job satisfaction interviews. Following your immersion in the data, you assign initial codes such as “work-life balance,” “career growth,” and “colleague relationships.” As you organize these codes, you’ll notice themes develop, such as “Factors Influencing Job Satisfaction” and “Impact on Work Engagement.”
Further investigation reveals the tales and experiences included within these themes and provides insights into how various elements influence job satisfaction. This example demonstrates how thematic analysis can reveal meaningful patterns and insights in qualitative data.
Method 3: Narrative Analysis
The narrative analysis involves the narratives that people share. You’ll investigate the histories in your data, looking at how stories are created and the meanings they express. This method is excellent for learning how people make sense of their experiences through narrative.
Steps to Do Narrative Analysis
The following steps are involved in narrative analysis:
- Gather and Analyze: Start by collecting narratives, such as first-person tales, interviews, or written accounts. Analyze the stories, focusing on the plot, feelings, and characters.
- Find Themes: Look for recurring themes or patterns in various narratives. Think about the similarities and differences between these topics and personal experiences.
- Interpret and Extract Insights: Contextualize the narratives within their larger context. Accept the subjective nature of each narrative and analyze the narrator’s voice and style. Extract insights from the tales by diving into the emotions, motivations, and implications communicated by the stories.
There are various advantages to narrative analysis:
- Deep Exploration: It lets you look deeply into people’s personal experiences and perspectives.
- Human-Centered: This method prioritizes the human perspective, allowing individuals to express themselves.
However, difficulties may arise, such as:
- Interpretive Complexity: Analyzing narratives requires dealing with the complexities of meaning and interpretation.
- Time-consuming: Because of the richness and complexities of tales, working with them can be time-consuming.
Example of Narrative Analysis
Assume you’re conducting narrative analysis on refugee interviews. As you read the stories, you’ll notice common themes of toughness, loss, and hope. The narratives provide insight into the obstacles that refugees face, their strengths, and the dreams that guide them.
The analysis can provide a deeper insight into the refugees’ experiences and the broader social context they navigate by examining the narratives’ emotional subtleties and underlying meanings. This example highlights how narrative analysis can reveal important insights into human stories.
Method 4: Grounded Theory Analysis
Grounded theory analysis is an iterative and systematic approach that allows you to create theories directly from data without being limited by pre-existing hypotheses. With an open mind, you collect data and generate early codes and labels that capture essential ideas or concepts within the data.
As you progress, you refine these codes and increasingly connect them, eventually developing a theory based on the data. Grounded theory analysis is a dynamic process for developing new insights and hypotheses based on details in your data.
Steps to Do Grounded Theory Analysis
Grounded theory analysis requires the following steps:
- Initial Coding: First, immerse yourself in the data, producing initial codes that represent major concepts or patterns.
- Categorize and Connect: Using axial coding, organize the initial codes, which establish relationships and connections between topics.
- Build the Theory: Focus on creating a core category that connects the codes and themes. Regularly refine the theory by comparing and integrating new data, ensuring that it evolves organically from the data.
Grounded theory analysis has various benefits:
- Theory Generation: It provides a one-of-a-kind opportunity to generate hypotheses straight from data and promotes new insights.
- In-depth Understanding: The analysis allows you to deeply analyze the data and reveal complex relationships and patterns.
- Flexible Process: This method is customizable and ongoing, which allows you to enhance your research as you collect additional data.
However, challenges might arise with:
- Time and Resources: Because grounded theory analysis is a continuous process, it requires a large commitment of time and resources.
- Theoretical Development: Creating a grounded theory involves a thorough understanding of qualitative data analysis software and theoretical concepts.
- Interpretation of Complexity: Interpreting and incorporating a newly developed theory into existing literature can be intellectually hard.
Example of Grounded Theory Analysis
Assume you’re performing a grounded theory analysis on workplace collaboration interviews. As you open code the data, you will discover notions such as “communication barriers,” “team dynamics,” and “leadership roles.” Axial coding demonstrates links between these notions, emphasizing the significance of efficient communication in developing collaboration.
You create the core “Integrated Communication Strategies” category through selective coding, which unifies new topics.
This theory-driven category serves as the framework for understanding how numerous aspects contribute to effective team collaboration. This example shows how grounded theory analysis allows you to generate a theory directly from the inherent nature of the data.
Method 5: Discourse Analysis
Discourse analysis focuses on language and communication. You’ll look at how language produces meaning and how it reflects power relations, identities, and cultural influences. This strategy examines what is said and how it is said; the words, phrasing, and larger context of communication.
The analysis is precious when investigating power dynamics, identities, and cultural influences encoded in language. By evaluating the language used in your data, you can identify underlying assumptions, cultural standards, and how individuals negotiate meaning through communication.
Steps to Do Discourse Analysis
Conducting discourse analysis entails the following steps:
- Select Discourse: For analysis, choose language-based data such as texts, speeches, or media content.
- Analyze Language: Immerse yourself in the conversation, examining language choices, metaphors, and underlying assumptions.
- Discover Patterns: Recognize the dialogue’s reoccurring themes, ideologies, and power dynamics. To fully understand the effects of these patterns, put them in their larger context.
There are various advantages of using discourse analysis:
- Understanding Language: It provides an extensive understanding of how language builds meaning and influences perceptions.
- Uncovering Power Dynamics: The analysis reveals how power dynamics appear via language.
- Cultural Insights: This method identifies cultural norms, beliefs, and ideologies stored in communication.
However, the following challenges may arise:
- Complexity of Interpretation: Language analysis involves navigating multiple levels of nuance and interpretation.
- Subjectivity: Interpretation can be subjective, so controlling researcher bias is important.
- Time-Intensive: Discourse analysis can take a lot of time because careful linguistic study is required in this analysis.
Example of Discourse Analysis
Consider doing discourse analysis on media coverage of a political event. You notice repeating linguistic patterns in news articles that depict the event as a conflict between opposing parties. Through deconstruction, you can expose how this framing supports particular ideologies and power relations.
You can illustrate how language choices influence public perceptions and contribute to building the narrative around the event by analyzing the speech within the broader political and social context. This example shows how discourse analysis can reveal hidden power dynamics and cultural influences on communication.
How to do Qualitative Data Analysis with the QuestionPro Research suite?
QuestionPro is a popular survey and research platform that offers tools for collecting and analyzing qualitative and quantitative data. Follow these general steps for conducting qualitative data analysis using the QuestionPro Research Suite:
- Collect Qualitative Data: Set up your survey to capture qualitative responses. It might involve open-ended questions, text boxes, or comment sections where participants can provide detailed responses.
- Export Qualitative Responses: Export the responses once you’ve collected qualitative data through your survey. QuestionPro typically allows you to export survey data in various formats, such as Excel or CSV.
- Prepare Data for Analysis: Review the exported data and clean it if necessary. Remove irrelevant or duplicate entries to ensure your data is ready for analysis.
- Code and Categorize Responses: Segment and label data, letting new patterns emerge naturally, then develop categories through axial coding to structure the analysis.
- Identify Themes: Analyze the coded responses to identify recurring themes, patterns, and insights. Look for similarities and differences in participants’ responses.
- Generate Reports and Visualizations: Utilize the reporting features of QuestionPro to create visualizations, charts, and graphs that help communicate the themes and findings from your qualitative research.
- Interpret and Draw Conclusions: Interpret the themes and patterns you’ve identified in the qualitative data. Consider how these findings answer your research questions or provide insights into your study topic.
- Integrate with Quantitative Data (if applicable): If you’re also conducting quantitative research using QuestionPro, consider integrating your qualitative findings with quantitative results to provide a more comprehensive understanding.
Qualitative data analysis is vital in uncovering various human experiences, views, and stories. If you’re ready to transform your research journey and apply the power of qualitative analysis, now is the moment to do it. Book a demo with QuestionPro today and begin your journey of exploration.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

QuestionPro BI: From Research Data to Actionable Dashboards
Apr 22, 2024

21 Best Customer Advocacy Software for Customers in 2024
Apr 19, 2024

10 Quantitative Data Analysis Software for Every Data Scientist
Apr 18, 2024

11 Best Enterprise Feedback Management Software in 2024
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
COVID-19 vaccination performance of the U.S. states: a hybrid model of DEA and ensemble machine learning methods
- Original Research
- Published: 23 April 2024
Cite this article

- Ozlem Cosgun ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1352-1764 1 ,
- Gamze Ogcu Kaya 2 &
- Cumhur Cosgun 3
Vaccination is seen as the most promising one among the efforts to stop COVID-19 and the U.S. government has given great importance to vaccination. However, which states have performed well in administering COVID-19 vaccines and which have not is an open significant question. Another important question is what makes a state more successful than others when evaluating vaccination performance. To answer both of these questions, we proposed a hybrid method that consists of Data Envelopment Analysis and Ensemble ML Methods. DEA was employed to find the vaccine efficiency of the states using the data aggregated from counties. ML techniques are then applied for the vaccine efficiency prediction and understanding the significance of the variables in the prediction. Our findings revealed that there are considerable differences between U.S. States’ performance and only 16 of the states were efficient in terms of their vaccination performance. Furthermore, Light GBM, Random Forest and XGBoost models provided the best results among the five ensemble machine learning methods that were applied. Therefore, an information fusion-based sensitivity analysis method was used to combine the results of each ML technique and ascertain the relative significance of the factors in the prediction of the efficiency. As the findings for factors affecting vaccination performance, percentage of vaccine doses delivered and COVID-19 deaths were found to be the major influential factors on the prediction of the efficiency and percentage of fully vaccinated people, the number of healthcare employees and human development index followed these variables.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Ardabili, S. F., Mosavi, A., Ghamisi, P., Ferdinand, F., Varkonyi-Koczy, A. R., Reuter, U., Rabczuk, T., & Atkinson, P. M. (2020). COVID-19 outbreak prediction with machine learning. Algorithms , 13 (10), 249.
Article Google Scholar
Basri, A., & Arif, M. (2021). Classification of seizure types using Random Forest Classifier. Advances in Science and Technology Research Journal , 15 (3), 167–178. https://doi.org/10.12913/22998624/140542 .
Batista, A. F. M., Miraglia, J. L., Donato, T. H. R., & Filho, A. D. P. (2021). COVID-19 diagnosis prediction in emergency care patients: A machine learning approach. medRxiv . https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.04.20052092 .
Brigato, L., & Iocchi, L. (2021). On the Effectiveness of Deep Ensembles for Small Data Tasks, International Conference on Learning Representations .
Brownlee, J. (2020). How to Develop a Light Gradient Boosted Machine (LightGBM) Ensemble. Accessed at September 28, 2021. https://machinelearningmastery.com/light-gradient-boosted-machine-lightgbm-ensemble/ .
U.S. Census Bureau (2023). County Population Totals and Components of Change: 2020–2022. https://www.census.gov/data/tables/time-series/demo/popest/2020s-counties-total.html .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2021a). Cases and Deaths in the U.S., https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/cases-updates/us-cases-deaths . Accessed September, 2021.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2021b). Cases and Deaths among Healthcare Personnel, https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#health-care-personnel , Accessed September, 2021.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. (2021c). Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines in Preventing Hospitalization Among Adults Aged ≥ 65 Years — COVID-NET, 13 States, February–April 2021, 70(32);1088–1093, https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7032e3.htm .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021d). COVID-19 risks and vaccine information for older adults .:text=The%20risk%20increases%20for%20people,having%20certain%20underlying%20medical%20conditions. https://www.cdc.gov/aging/covid19/covid19-older-adults.html#:~ .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2023). COVID Data Tracker. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccinations_vacc-total-delivered-total .
Charnes, A., Cooper, W. W., & Rhodes, E. (1978). Measuring the efficiency of decision-making units. European Journal of Operational Research , 429–443.
Chen, Y., Wang, J., Zhu, J., Sherman, H. D., & Chou, S. (2019). How the great recession affects performance: A case of Pennsylvania hospitals using DEA. Annals of Operations Research , 77–99.
Chengsheng, T. U., Huacheng, L. I. U., & Bing, X. U. (2017). AdaBoost typical Algorithm and its application research. MATEC Web of Conferences 139, 00222, https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201713900222 .
Colubri, A., Silver, T., Fradet, T., Retzepi, K., Fry, B., & Sabeti, P. (2016). Transforming clinical data into actionable prognosis models: Machine-learning framework and field-deployable app to predict outcome of Ebola patients. Plos Neglected Tropical Diseases .
Darabi, N., Ebrahimvandi, A., Hosseinichimeh, N., & Triantis, K. (2021). A DEA evaluation of US States’ Healthcare Systems in terms of their birth outcomes. Expert Systems with Applications , 182.
Data Central COVID-19 Vaccine tracker. (nd). https://data.news-leader.com/covid-19-vaccine-tracker/ .
Davis, G. (1989). Sensitivity analysis in neural net solutions. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man Cybern , 19 , 1078–1082.
de Oliveira, B. R. B., da Penha Sobral, A. I. G., Marinho, M. L. M., et al. (2021). Determinants of access to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine: A preliminary approach. Int J Equity Health , 20 , 183. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-021-01520-4 .
Delen, D. (2010). A comparative analysis of machine learning techniques for student retention management. Decision Support Systems , 49 , 498–506.
Delen, D., Kuzey, C., & Uyar, A. (2013). Measuring firm performance using financial ratios: A decision tree approach. Expert Systems with Applications , 40 (10), 3970–3983.
U.S. Department of Commerce U.S. Census Bureau (2020). Resident Population for the 50 States, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico: 2020 . https://www2.census.gov / programs surveys / decennial/ 2020/ data/apportionment/apportionment-2020-Table 02.pdf.
Devi, S. S., Solanki, V. K., & Laskar, R. H. (2020). Recent advances on big data analysis for malaria prediction and various diagnosis methodologies. Handbook of Data Science Approaches for Biomedical Engineering, 153–184.
Food and Drug Administration (2020b). F DA Briefing Document Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine . https://www.fda.gov/media/144246/download .
Food and Drug Administration (2021). FDA issues Emergency Use Authorization for third COVID-19 vaccine . https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-issues-emergency-use-authorization-third-COVID-19 -vaccine.
Food and Drug Administration (2020a). FDA Briefing Document Moderna COVID-19 vaccine . https://www.fda.gov/media/144434/download .
Fuller, C., Biros, D. P., & Delen, D. (2011). An investigation of data and text mining methods for real world deception detection. Expert Systems with Applications , 38 (7), 8392–8398.
Gallant, A. J., Nicholls, L. A. B., Rasmussen, S., Cogan, N., Young, D., & Williams, L. (2021). Changes in attitudes to vaccination as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic: A longitudinal study of older adults in the UK. PloS One , 16 (12), e0261844. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0261844 .
Global Data Lab (2020). Human Development Indices (5.0) https://globaldatalab.org/shdi/shdi/?levels=1%2B4&interpolation=1&extrapolation=0&nearest_real=0
Götz, G., Herold, D., Klotz, P., & Schäfer, J. T. (2021). Efficiency in COVID-19 Vaccination Campaigns—A Comparison across Germany’s Federal States, Vaccines , 9, 788.
Han, S., & Jeong, J. (2020). An weighted CNN Ensemble Model with small amount of data for Bearing Fault diagnosis. Procedia Computer Science , 175 , 88–95.
Hancock, J. T., & Khoshgoftaar, T. M. (2020). CatBoost for big data: An interdisciplinary review. Journal of Big Data , 7 , 94. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-020-00369-8 .
Hu, X., Zhang, H., Mei, H., Xiao, D., Li, Y., & Li, M. (2020). Landslide susceptibility mapping using the Stacking Ensemble Machine Learning Method in Lushui, Southwest China. Applied Sciences , 10 (11), 4016.
Human Development Report (2020). https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/technical-notes-calculating-human-development-indices.pdf .
Jeon, S., Lee, Y. F., & Koumi, K. (2022). COVID-19 vaccination: Sociopolitical and Economic Impact in the United States. Epidemiologia (Basel) , 3 (4), 502–517. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia3040038 PMID: 36416793; PMCID: PMC9680412.
Kaiser Health News (2020). Total Health Care Employment . https://www.kff.org/other/state-indicator/total-health-careemployment/current Timeframe = 0&selectedRows=%7B%22states%22:%7B%22all%22:%7B%7D%7D,22wrapups%22:%7B%22unitedstates%22:%7B%7D%7D%7D&sorodel=%7B%22colId%22:%22Location%22, %22sort%22:%22desc%22%7D.
Kamel, M. A., & Mousa, M. E. S. (2021). Measuring operational efficiency of isolation hospitals during COVID-19 pandemic using data envelopment analysis: A case of Egypt, Benchmarking. An International Journal , 28 (7), 2178–2201.
Google Scholar
Khanday, A. M., Rabani, S., Khan, Q., Rouf, N., & Din, M. M. (2020). Machine learning based approaches for detecting COVID-19 using clinical text data. Int J Inf Technol , 12 (3), 731–739.
Klebanova, T., Poluektova, N., & Rudachenk, O. (2021). Applying of Data Envelopment Analysis to study public administration effectiveness during a pandemic , online: http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2927/paper8.pdf .
Krauss, C., Do, X. A., & Huck, N. (2017). Deep neural networks, gradient-boosted trees, random forests: Statistical arbitrage on the S&P 500. European Journal of Operational Research , 259 , 689–702.
Kumar, R. (2020). AdaBoost and Gradient Boost– Comparitive Study Between 2 Popular Ensemble Model Techniques. https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2020/10/adaboost-and-gradient-boost-comparitive-study-between-2-popular-ensemble-model-techniques/ .
Li, J. P., Haq, A. U., Din, S. U., Khan, J., Khan, A., & Saboor, A. (2020). Heart Disease Identification Method using machine learning classification in E-Healthcare. Ieee Access: Practical Innovations, Open Solutions , 8 , 107562–107582.
Machine Learning Mastery (2021). A Gentle Introduction to XGBoost for Applied Machine Learning . https://machinelearningmastery.com/gentle-introduction-xgboost-applied-machine-learning/ .
Malik, Z. A., & Senjiati, I. H. (2020). Efficiency Service Handling COVID 19 the Institute of Zakat by Method of Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA). Journal of Islamic Business and Economic Review , 3(2).
Mariano, E., Torres, B., Almeida, M., Ferraz, D., Rebelatto, D., & Mello, J. C. S. (2021). Brazilian States in the Context of COVID-19 Pandemic: An Index Proposition using Network Data Envelopment Analysis, I.E.E.E. Latin America Transactions, Vol. 19, No. 6.
Maya Clinic (2022). U.S. COVID-19 vaccine tracker: See your state’s progress, https://www.mayoclinic.org/coronavirus-COVID-19 /vaccine-tracker.
Mendola, M., Tonelli, F., Garletti, F. S., Greco, D., Fiscella, M., Cucchi, I., Costa, M. C., & Carrer, P. (2021). COVID-19 impact and vaccine effectiveness among healthcare workers of a large University Hospital in Lombardy, Italy. Med Lav. 23;112(6):453–464. https://doi.org/10.23749/mdl.v112i6.11983 . PMID: 34939623; PMCID: PMC8759047.
Misra, S., & Li, H. (2020). Noninvasive fracture characterization based on the classification of sonic wave travel times. Machine Learning for Subsurface Characterization , 243–287.
Mo, H., Sun, H., Liu, J., & Wei, S. (2019). Developing window behavior models for residential buildings using XGBoost algorithm. Energy and Buildings , 205 , 109564.
Mohanta, K. K., Sharanappa, D. S., & Aggarwal, A. (2021). Efficiency analysis in the management of COVID-19 pandemic in India based on data envelopment analysis, Current Research in Behavioral Sciences, 2.
Mourad, N., Habib, A. M., & Tharwat, A. (2021). Appraising healthcare systems’ efficiency in facing COVID-19 through data envelopment analysis. Decision Science Letters , 10 (3), 301–310.
Nahra, T. A., Mendez, D., & Alexander, J. A. (2009). Employing super-efficiency analysis as an alternative to DEA: An application in outpatient substance abuse treatment. European Journal of Operational Research , 196 , 3, 1097–1106.
Nepomuceno, T. C. C., Silva, W. M. N., Nepomuceno, K. T. C., & Barros, I. K. F. (2020). A DEA-Based complexity of needs Approach for Hospital beds Evacuation during the COVID-19 outbreak. Hindawi Journal of Healthcare Engineering .
Nistor, C. S., Ștefănescu, C. A., & Crișan, A. (2017). Performance through efficiency in the Public Healthcare System– A DEA Approach in an Emergent Country. Studia Universitatis Babes-Bolyai Oeconomica , 62 (1), 31–49.
Nti, I. K., Adekoya, A. F., & Weyori, B. A. (2020). A comprehensive evaluation of ensemble learning for stock-market prediction. Journal of Big Data 7(20).
Onen, Z., & Sayin, S. (2018). Evaluating Healthcare System Efficiency of OECD Countries: A DEA-Based Study, Operations Research Applications in Health Care Management , pp. 141–158.
Ontario Agency for Health Protection and Promotion (Public Health Ontario). (2021). COVID-19 real-world vaccine effectiveness– what we know so far . Queen’s Printer for Ontario.
Parbat, D. (2020). A Python based Support Vector Regression Model for prediction of Covid19 cases in India. Chaos, Solitons, and Fractals , 138.
Prompetchara, E., Ketloy, C., & Palaga, T. (2020). Immune responses in COVID-19 and potential vaccines: Lessons learned from SARS and MERS epidemic. Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology , 38 (1), 1–9.
Rasolomanana, O. M. (2021). Ensemble Neural Network Using A Small Dataset For The Prediction Of Bankruptcy: Combining Numerical And Textual Data, Hokkaido University Collection of Scholarly and Academic Papers. http://hdl.handle.net/2115/82952 .
Rays, Y. E., & Lemqeddem, H. A. (2021). Data Envelopment Analysis and Malmquist Index Application: Efficiency of Primary Health Care in Morocco and COVID-19. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education , 12 (5), 971–983.
Regulatory Affairs Professionals Society (2020). https://www.raps.org/news-and-articles/news-articles/2020/3/COVID-19-vaccine-tracker .
Rustagi, V., Bajaj, M., Tanvi, Sgnh, P., Aggarwal, R., Alajmi, M. F., Hussain, A., Hassan, I., Gingh, A., & Singh, I. K. (2022). Analyzing the Effect of Vaccination over COVID cases and deaths in Asian Countries using machine learning models. Fron Cell Microbiol . https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.806265 .
Rustam, F., et al. (2020). COVID-19 future forecasting using supervised machine learning models. Ieee Access: Practical Innovations, Open Solutions , 8 , 101489–101499.
Saltelli, A. (2002). Making best use of model evaluations to compute sensitivity indices. Computer Physics Communications , 145 (2), 280–297.
Samantha, A., Matthew, R., Olivia, P., Liz, H., & Cailey, M. (2020). COVID-19 Risks and Impacts Among Health Care Workers by Race/Ethnicity, Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.kff.org/report-section/COVID-19-risks-and-impacts-among-health-care-workers-by-race-ethnicity-issue-brief/ .
Samut, P. K., & Cafrı, R. (2015). Analysis of the efficiency determinants of health systems in OECD countries by DEA and panel tobit. Social indicators research (pp. 1–20). Springer.
Sarwar, M. A., Kamal, N., Hamid, W., & Shah, M. A. (2018). Prediction of Diabetes Using Machine Learning Algorithms in Healthcare, 24th International Conference on Automation and Computing , 1–6.
Soares, P., Rocha, J. V., Moniz, M., Gama, A., Laires, P. A., Pedro, A. R., Dias, S., Leite, A., & Nunes, C. (2021). Factors Associated with COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy. Vaccines , 9 , 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9030300 .
Stats America (2020). USA States in profile . http://www.statsamerica.org/sip/rank_list.aspx?rank_label=pop46&ct=S09
Su, E. C. Y., Hsiao, C. H., Chen, Y. T., & Yu, S. H. (2021). An examination of COVID-19 mitigation efficiency among 23 countries. Healthcare , 9.
Thammasiri, D., Delen, D., Meesad, P., & Kasap, N. (2014). A critical assessment of imbalanced class distribution problem: The case of predicting freshmen student attrition. Expert Systems with Applications , 41 (2), 321–330.
The New York Times (2021a). Covid in the U.S.: Latest Map and Case Count . https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2021/us/covid-cases.html .
The New York Times (2021b). See How Vaccinations Are Going in Your County and State . https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/us/COVID-19-vaccine-doses.html .
The Guardian (2021). West Virginia battles Covid surge after failing to build on early vaccine success. https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2021/sep/15/west-virginia-covid-surge-vaccination .
United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Dynamics (2019). Data Query: Population by age and sex (thousands) . https://population.un.org/wpp/DataQuery/ . Published 2019. Accessed September 27, 2021.
US Cities Demographics (nd). https://public.opendatasoft.com/explore/dataset/us-cities-demographics/table/?refine.state=New+York .
Wu, Z., Zhou, C., Xu, F., & Lou, W. (2020). A CS-AdaBoost-BP model for product quality inspection. Annals of Operations Research . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03798-z .
Yadav, M., Perumal, M., & Srinivas, M. (2020). Analysis on Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Using Machine Learning Methods, Chaos, Solitons and Fractals .
Zhu, Y., Xie, C., Wang, G., & Yan, X. (2017). Comparison of individual, ensemble and integrated ensemble machine learning methods to predict China’s SME credit risk in supply chain finance. Neural Comput & Applic , 28 , 41–50.
County Health Ranking and Roadmaps. (2023). Health Data . https://www.countyhealthrankings.org/health-data
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Information Management and Business Analytics, Montclair State University, 1 Normal Ave, Montclair, NJ, 07043, USA
Ozlem Cosgun
Department of Industrial Engineering, Sampoerna University, Jakarta, 12780, Indonesia
Gamze Ogcu Kaya
Pennsylvania Department of Transportation, Bureau of Construction and Materials, 81 Lab Lane, Harrisburg, PA, 17110-2543, USA
Cumhur Cosgun
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ozlem Cosgun .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cosgun, O., Ogcu Kaya, G. & Cosgun, C. COVID-19 vaccination performance of the U.S. states: a hybrid model of DEA and ensemble machine learning methods. Ann Oper Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-024-06008-2
Download citation
Received : 11 November 2021
Accepted : 16 April 2024
Published : 23 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-024-06008-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Machine learning
- Ensemble methods
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Table of Contents
What is data collection, why do we need data collection, what are the different data collection methods, data collection tools, the importance of ensuring accurate and appropriate data collection, issues related to maintaining the integrity of data collection, what are common challenges in data collection, what are the key steps in the data collection process, data collection considerations and best practices, choose the right data science program, are you interested in a career in data science, what is data collection: methods, types, tools.

The process of gathering and analyzing accurate data from various sources to find answers to research problems, trends and probabilities, etc., to evaluate possible outcomes is Known as Data Collection. Knowledge is power, information is knowledge, and data is information in digitized form, at least as defined in IT. Hence, data is power. But before you can leverage that data into a successful strategy for your organization or business, you need to gather it. That’s your first step.
So, to help you get the process started, we shine a spotlight on data collection. What exactly is it? Believe it or not, it’s more than just doing a Google search! Furthermore, what are the different types of data collection? And what kinds of data collection tools and data collection techniques exist?
If you want to get up to speed about what is data collection process, you’ve come to the right place.
Transform raw data into captivating visuals with Simplilearn's hands-on Data Visualization Courses and captivate your audience. Also, master the art of data management with Simplilearn's comprehensive data management courses - unlock new career opportunities today!
Data collection is the process of collecting and evaluating information or data from multiple sources to find answers to research problems, answer questions, evaluate outcomes, and forecast trends and probabilities. It is an essential phase in all types of research, analysis, and decision-making, including that done in the social sciences, business, and healthcare.
Accurate data collection is necessary to make informed business decisions, ensure quality assurance, and keep research integrity.
During data collection, the researchers must identify the data types, the sources of data, and what methods are being used. We will soon see that there are many different data collection methods . There is heavy reliance on data collection in research, commercial, and government fields.
Before an analyst begins collecting data, they must answer three questions first:
- What’s the goal or purpose of this research?
- What kinds of data are they planning on gathering?
- What methods and procedures will be used to collect, store, and process the information?
Additionally, we can break up data into qualitative and quantitative types. Qualitative data covers descriptions such as color, size, quality, and appearance. Quantitative data, unsurprisingly, deals with numbers, such as statistics, poll numbers, percentages, etc.
Before a judge makes a ruling in a court case or a general creates a plan of attack, they must have as many relevant facts as possible. The best courses of action come from informed decisions, and information and data are synonymous.
The concept of data collection isn’t a new one, as we’ll see later, but the world has changed. There is far more data available today, and it exists in forms that were unheard of a century ago. The data collection process has had to change and grow with the times, keeping pace with technology.
Whether you’re in the world of academia, trying to conduct research, or part of the commercial sector, thinking of how to promote a new product, you need data collection to help you make better choices.
Now that you know what is data collection and why we need it, let's take a look at the different methods of data collection. While the phrase “data collection” may sound all high-tech and digital, it doesn’t necessarily entail things like computers, big data , and the internet. Data collection could mean a telephone survey, a mail-in comment card, or even some guy with a clipboard asking passersby some questions. But let’s see if we can sort the different data collection methods into a semblance of organized categories.
Primary and secondary methods of data collection are two approaches used to gather information for research or analysis purposes. Let's explore each data collection method in detail:
1. Primary Data Collection:
Primary data collection involves the collection of original data directly from the source or through direct interaction with the respondents. This method allows researchers to obtain firsthand information specifically tailored to their research objectives. There are various techniques for primary data collection, including:
a. Surveys and Questionnaires: Researchers design structured questionnaires or surveys to collect data from individuals or groups. These can be conducted through face-to-face interviews, telephone calls, mail, or online platforms.
b. Interviews: Interviews involve direct interaction between the researcher and the respondent. They can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing. Interviews can be structured (with predefined questions), semi-structured (allowing flexibility), or unstructured (more conversational).
c. Observations: Researchers observe and record behaviors, actions, or events in their natural setting. This method is useful for gathering data on human behavior, interactions, or phenomena without direct intervention.
d. Experiments: Experimental studies involve the manipulation of variables to observe their impact on the outcome. Researchers control the conditions and collect data to draw conclusions about cause-and-effect relationships.
e. Focus Groups: Focus groups bring together a small group of individuals who discuss specific topics in a moderated setting. This method helps in understanding opinions, perceptions, and experiences shared by the participants.
2. Secondary Data Collection:
Secondary data collection involves using existing data collected by someone else for a purpose different from the original intent. Researchers analyze and interpret this data to extract relevant information. Secondary data can be obtained from various sources, including:
a. Published Sources: Researchers refer to books, academic journals, magazines, newspapers, government reports, and other published materials that contain relevant data.
b. Online Databases: Numerous online databases provide access to a wide range of secondary data, such as research articles, statistical information, economic data, and social surveys.
c. Government and Institutional Records: Government agencies, research institutions, and organizations often maintain databases or records that can be used for research purposes.
d. Publicly Available Data: Data shared by individuals, organizations, or communities on public platforms, websites, or social media can be accessed and utilized for research.
e. Past Research Studies: Previous research studies and their findings can serve as valuable secondary data sources. Researchers can review and analyze the data to gain insights or build upon existing knowledge.
Now that we’ve explained the various techniques, let’s narrow our focus even further by looking at some specific tools. For example, we mentioned interviews as a technique, but we can further break that down into different interview types (or “tools”).
Word Association
The researcher gives the respondent a set of words and asks them what comes to mind when they hear each word.
Sentence Completion
Researchers use sentence completion to understand what kind of ideas the respondent has. This tool involves giving an incomplete sentence and seeing how the interviewee finishes it.
Role-Playing
Respondents are presented with an imaginary situation and asked how they would act or react if it was real.
In-Person Surveys
The researcher asks questions in person.
Online/Web Surveys
These surveys are easy to accomplish, but some users may be unwilling to answer truthfully, if at all.
Mobile Surveys
These surveys take advantage of the increasing proliferation of mobile technology. Mobile collection surveys rely on mobile devices like tablets or smartphones to conduct surveys via SMS or mobile apps.
Phone Surveys
No researcher can call thousands of people at once, so they need a third party to handle the chore. However, many people have call screening and won’t answer.
Observation
Sometimes, the simplest method is the best. Researchers who make direct observations collect data quickly and easily, with little intrusion or third-party bias. Naturally, it’s only effective in small-scale situations.
Accurate data collecting is crucial to preserving the integrity of research, regardless of the subject of study or preferred method for defining data (quantitative, qualitative). Errors are less likely to occur when the right data gathering tools are used (whether they are brand-new ones, updated versions of them, or already available).
Among the effects of data collection done incorrectly, include the following -
- Erroneous conclusions that squander resources
- Decisions that compromise public policy
- Incapacity to correctly respond to research inquiries
- Bringing harm to participants who are humans or animals
- Deceiving other researchers into pursuing futile research avenues
- The study's inability to be replicated and validated
When these study findings are used to support recommendations for public policy, there is the potential to result in disproportionate harm, even if the degree of influence from flawed data collecting may vary by discipline and the type of investigation.
Let us now look at the various issues that we might face while maintaining the integrity of data collection.
In order to assist the errors detection process in the data gathering process, whether they were done purposefully (deliberate falsifications) or not, maintaining data integrity is the main justification (systematic or random errors).
Quality assurance and quality control are two strategies that help protect data integrity and guarantee the scientific validity of study results.
Each strategy is used at various stages of the research timeline:
- Quality control - tasks that are performed both after and during data collecting
- Quality assurance - events that happen before data gathering starts
Let us explore each of them in more detail now.
Quality Assurance
As data collecting comes before quality assurance, its primary goal is "prevention" (i.e., forestalling problems with data collection). The best way to protect the accuracy of data collection is through prevention. The uniformity of protocol created in the thorough and exhaustive procedures manual for data collecting serves as the best example of this proactive step.
The likelihood of failing to spot issues and mistakes early in the research attempt increases when guides are written poorly. There are several ways to show these shortcomings:
- Failure to determine the precise subjects and methods for retraining or training staff employees in data collecting
- List of goods to be collected, in part
- There isn't a system in place to track modifications to processes that may occur as the investigation continues.
- Instead of detailed, step-by-step instructions on how to deliver tests, there is a vague description of the data gathering tools that will be employed.
- Uncertainty regarding the date, procedure, and identity of the person or people in charge of examining the data
- Incomprehensible guidelines for using, adjusting, and calibrating the data collection equipment.
Now, let us look at how to ensure Quality Control.
Become a Data Scientist With Real-World Experience
Quality Control
Despite the fact that quality control actions (detection/monitoring and intervention) take place both after and during data collection, the specifics should be meticulously detailed in the procedures manual. Establishing monitoring systems requires a specific communication structure, which is a prerequisite. Following the discovery of data collection problems, there should be no ambiguity regarding the information flow between the primary investigators and staff personnel. A poorly designed communication system promotes slack oversight and reduces opportunities for error detection.
Direct staff observation conference calls, during site visits, or frequent or routine assessments of data reports to spot discrepancies, excessive numbers, or invalid codes can all be used as forms of detection or monitoring. Site visits might not be appropriate for all disciplines. Still, without routine auditing of records, whether qualitative or quantitative, it will be challenging for investigators to confirm that data gathering is taking place in accordance with the manual's defined methods. Additionally, quality control determines the appropriate solutions, or "actions," to fix flawed data gathering procedures and reduce recurrences.
Problems with data collection, for instance, that call for immediate action include:
- Fraud or misbehavior
- Systematic mistakes, procedure violations
- Individual data items with errors
- Issues with certain staff members or a site's performance
Researchers are trained to include one or more secondary measures that can be used to verify the quality of information being obtained from the human subject in the social and behavioral sciences where primary data collection entails using human subjects.
For instance, a researcher conducting a survey would be interested in learning more about the prevalence of risky behaviors among young adults as well as the social factors that influence these risky behaviors' propensity for and frequency. Let us now explore the common challenges with regard to data collection.
There are some prevalent challenges faced while collecting data, let us explore a few of them to understand them better and avoid them.
Data Quality Issues
The main threat to the broad and successful application of machine learning is poor data quality. Data quality must be your top priority if you want to make technologies like machine learning work for you. Let's talk about some of the most prevalent data quality problems in this blog article and how to fix them.
Inconsistent Data
When working with various data sources, it's conceivable that the same information will have discrepancies between sources. The differences could be in formats, units, or occasionally spellings. The introduction of inconsistent data might also occur during firm mergers or relocations. Inconsistencies in data have a tendency to accumulate and reduce the value of data if they are not continually resolved. Organizations that have heavily focused on data consistency do so because they only want reliable data to support their analytics.
Data Downtime
Data is the driving force behind the decisions and operations of data-driven businesses. However, there may be brief periods when their data is unreliable or not prepared. Customer complaints and subpar analytical outcomes are only two ways that this data unavailability can have a significant impact on businesses. A data engineer spends about 80% of their time updating, maintaining, and guaranteeing the integrity of the data pipeline. In order to ask the next business question, there is a high marginal cost due to the lengthy operational lead time from data capture to insight.
Schema modifications and migration problems are just two examples of the causes of data downtime. Data pipelines can be difficult due to their size and complexity. Data downtime must be continuously monitored, and it must be reduced through automation.
Ambiguous Data
Even with thorough oversight, some errors can still occur in massive databases or data lakes. For data streaming at a fast speed, the issue becomes more overwhelming. Spelling mistakes can go unnoticed, formatting difficulties can occur, and column heads might be deceptive. This unclear data might cause a number of problems for reporting and analytics.
Become a Data Science Expert & Get Your Dream Job
Duplicate Data
Streaming data, local databases, and cloud data lakes are just a few of the sources of data that modern enterprises must contend with. They might also have application and system silos. These sources are likely to duplicate and overlap each other quite a bit. For instance, duplicate contact information has a substantial impact on customer experience. If certain prospects are ignored while others are engaged repeatedly, marketing campaigns suffer. The likelihood of biased analytical outcomes increases when duplicate data are present. It can also result in ML models with biased training data.
Too Much Data
While we emphasize data-driven analytics and its advantages, a data quality problem with excessive data exists. There is a risk of getting lost in an abundance of data when searching for information pertinent to your analytical efforts. Data scientists, data analysts, and business users devote 80% of their work to finding and organizing the appropriate data. With an increase in data volume, other problems with data quality become more serious, particularly when dealing with streaming data and big files or databases.
Inaccurate Data
For highly regulated businesses like healthcare, data accuracy is crucial. Given the current experience, it is more important than ever to increase the data quality for COVID-19 and later pandemics. Inaccurate information does not provide you with a true picture of the situation and cannot be used to plan the best course of action. Personalized customer experiences and marketing strategies underperform if your customer data is inaccurate.
Data inaccuracies can be attributed to a number of things, including data degradation, human mistake, and data drift. Worldwide data decay occurs at a rate of about 3% per month, which is quite concerning. Data integrity can be compromised while being transferred between different systems, and data quality might deteriorate with time.
Hidden Data
The majority of businesses only utilize a portion of their data, with the remainder sometimes being lost in data silos or discarded in data graveyards. For instance, the customer service team might not receive client data from sales, missing an opportunity to build more precise and comprehensive customer profiles. Missing out on possibilities to develop novel products, enhance services, and streamline procedures is caused by hidden data.
Finding Relevant Data
Finding relevant data is not so easy. There are several factors that we need to consider while trying to find relevant data, which include -
- Relevant Domain
- Relevant demographics
- Relevant Time period and so many more factors that we need to consider while trying to find relevant data.
Data that is not relevant to our study in any of the factors render it obsolete and we cannot effectively proceed with its analysis. This could lead to incomplete research or analysis, re-collecting data again and again, or shutting down the study.
Deciding the Data to Collect
Determining what data to collect is one of the most important factors while collecting data and should be one of the first factors while collecting data. We must choose the subjects the data will cover, the sources we will be used to gather it, and the quantity of information we will require. Our responses to these queries will depend on our aims, or what we expect to achieve utilizing your data. As an illustration, we may choose to gather information on the categories of articles that website visitors between the ages of 20 and 50 most frequently access. We can also decide to compile data on the typical age of all the clients who made a purchase from your business over the previous month.
Not addressing this could lead to double work and collection of irrelevant data or ruining your study as a whole.
Dealing With Big Data
Big data refers to exceedingly massive data sets with more intricate and diversified structures. These traits typically result in increased challenges while storing, analyzing, and using additional methods of extracting results. Big data refers especially to data sets that are quite enormous or intricate that conventional data processing tools are insufficient. The overwhelming amount of data, both unstructured and structured, that a business faces on a daily basis.
The amount of data produced by healthcare applications, the internet, social networking sites social, sensor networks, and many other businesses are rapidly growing as a result of recent technological advancements. Big data refers to the vast volume of data created from numerous sources in a variety of formats at extremely fast rates. Dealing with this kind of data is one of the many challenges of Data Collection and is a crucial step toward collecting effective data.
Low Response and Other Research Issues
Poor design and low response rates were shown to be two issues with data collecting, particularly in health surveys that used questionnaires. This might lead to an insufficient or inadequate supply of data for the study. Creating an incentivized data collection program might be beneficial in this case to get more responses.
Now, let us look at the key steps in the data collection process.
In the Data Collection Process, there are 5 key steps. They are explained briefly below -
1. Decide What Data You Want to Gather
The first thing that we need to do is decide what information we want to gather. We must choose the subjects the data will cover, the sources we will use to gather it, and the quantity of information that we would require. For instance, we may choose to gather information on the categories of products that an average e-commerce website visitor between the ages of 30 and 45 most frequently searches for.
2. Establish a Deadline for Data Collection
The process of creating a strategy for data collection can now begin. We should set a deadline for our data collection at the outset of our planning phase. Some forms of data we might want to continuously collect. We might want to build up a technique for tracking transactional data and website visitor statistics over the long term, for instance. However, we will track the data throughout a certain time frame if we are tracking it for a particular campaign. In these situations, we will have a schedule for when we will begin and finish gathering data.
3. Select a Data Collection Approach
We will select the data collection technique that will serve as the foundation of our data gathering plan at this stage. We must take into account the type of information that we wish to gather, the time period during which we will receive it, and the other factors we decide on to choose the best gathering strategy.
4. Gather Information
Once our plan is complete, we can put our data collection plan into action and begin gathering data. In our DMP, we can store and arrange our data. We need to be careful to follow our plan and keep an eye on how it's doing. Especially if we are collecting data regularly, setting up a timetable for when we will be checking in on how our data gathering is going may be helpful. As circumstances alter and we learn new details, we might need to amend our plan.
5. Examine the Information and Apply Your Findings
It's time to examine our data and arrange our findings after we have gathered all of our information. The analysis stage is essential because it transforms unprocessed data into insightful knowledge that can be applied to better our marketing plans, goods, and business judgments. The analytics tools included in our DMP can be used to assist with this phase. We can put the discoveries to use to enhance our business once we have discovered the patterns and insights in our data.
Let us now look at some data collection considerations and best practices that one might follow.
We must carefully plan before spending time and money traveling to the field to gather data. While saving time and resources, effective data collection strategies can help us collect richer, more accurate, and richer data.
Below, we will be discussing some of the best practices that we can follow for the best results -
1. Take Into Account the Price of Each Extra Data Point
Once we have decided on the data we want to gather, we need to make sure to take the expense of doing so into account. Our surveyors and respondents will incur additional costs for each additional data point or survey question.
2. Plan How to Gather Each Data Piece
There is a dearth of freely accessible data. Sometimes the data is there, but we may not have access to it. For instance, unless we have a compelling cause, we cannot openly view another person's medical information. It could be challenging to measure several types of information.
Consider how time-consuming and difficult it will be to gather each piece of information while deciding what data to acquire.
3. Think About Your Choices for Data Collecting Using Mobile Devices
Mobile-based data collecting can be divided into three categories -
- IVRS (interactive voice response technology) - Will call the respondents and ask them questions that have already been recorded.
- SMS data collection - Will send a text message to the respondent, who can then respond to questions by text on their phone.
- Field surveyors - Can directly enter data into an interactive questionnaire while speaking to each respondent, thanks to smartphone apps.
We need to make sure to select the appropriate tool for our survey and responders because each one has its own disadvantages and advantages.
4. Carefully Consider the Data You Need to Gather
It's all too easy to get information about anything and everything, but it's crucial to only gather the information that we require.
It is helpful to consider these 3 questions:
- What details will be helpful?
- What details are available?
- What specific details do you require?
5. Remember to Consider Identifiers
Identifiers, or details describing the context and source of a survey response, are just as crucial as the information about the subject or program that we are actually researching.
In general, adding more identifiers will enable us to pinpoint our program's successes and failures with greater accuracy, but moderation is the key.
6. Data Collecting Through Mobile Devices is the Way to Go
Although collecting data on paper is still common, modern technology relies heavily on mobile devices. They enable us to gather many various types of data at relatively lower prices and are accurate as well as quick. There aren't many reasons not to pick mobile-based data collecting with the boom of low-cost Android devices that are available nowadays.
The Ultimate Ticket to Top Data Science Job Roles
1. What is data collection with example?
Data collection is the process of collecting and analyzing information on relevant variables in a predetermined, methodical way so that one can respond to specific research questions, test hypotheses, and assess results. Data collection can be either qualitative or quantitative. Example: A company collects customer feedback through online surveys and social media monitoring to improve their products and services.
2. What are the primary data collection methods?
As is well known, gathering primary data is costly and time intensive. The main techniques for gathering data are observation, interviews, questionnaires, schedules, and surveys.
3. What are data collection tools?
The term "data collecting tools" refers to the tools/devices used to gather data, such as a paper questionnaire or a system for computer-assisted interviews. Tools used to gather data include case studies, checklists, interviews, occasionally observation, surveys, and questionnaires.
4. What’s the difference between quantitative and qualitative methods?
While qualitative research focuses on words and meanings, quantitative research deals with figures and statistics. You can systematically measure variables and test hypotheses using quantitative methods. You can delve deeper into ideas and experiences using qualitative methodologies.
5. What are quantitative data collection methods?
While there are numerous other ways to get quantitative information, the methods indicated above—probability sampling, interviews, questionnaire observation, and document review—are the most typical and frequently employed, whether collecting information offline or online.
6. What is mixed methods research?
User research that includes both qualitative and quantitative techniques is known as mixed methods research. For deeper user insights, mixed methods research combines insightful user data with useful statistics.
7. What are the benefits of collecting data?
Collecting data offers several benefits, including:
- Knowledge and Insight
- Evidence-Based Decision Making
- Problem Identification and Solution
- Validation and Evaluation
- Identifying Trends and Predictions
- Support for Research and Development
- Policy Development
- Quality Improvement
- Personalization and Targeting
- Knowledge Sharing and Collaboration
8. What’s the difference between reliability and validity?
Reliability is about consistency and stability, while validity is about accuracy and appropriateness. Reliability focuses on the consistency of results, while validity focuses on whether the results are actually measuring what they are intended to measure. Both reliability and validity are crucial considerations in research to ensure the trustworthiness and meaningfulness of the collected data and measurements.
Are you thinking about pursuing a career in the field of data science? Simplilearn's Data Science courses are designed to provide you with the necessary skills and expertise to excel in this rapidly changing field. Here's a detailed comparison for your reference:
Program Name Data Scientist Master's Program Post Graduate Program In Data Science Post Graduate Program In Data Science Geo All Geos All Geos Not Applicable in US University Simplilearn Purdue Caltech Course Duration 11 Months 11 Months 11 Months Coding Experience Required Basic Basic No Skills You Will Learn 10+ skills including data structure, data manipulation, NumPy, Scikit-Learn, Tableau and more 8+ skills including Exploratory Data Analysis, Descriptive Statistics, Inferential Statistics, and more 8+ skills including Supervised & Unsupervised Learning Deep Learning Data Visualization, and more Additional Benefits Applied Learning via Capstone and 25+ Data Science Projects Purdue Alumni Association Membership Free IIMJobs Pro-Membership of 6 months Resume Building Assistance Upto 14 CEU Credits Caltech CTME Circle Membership Cost $$ $$$$ $$$$ Explore Program Explore Program Explore Program
We live in the Data Age, and if you want a career that fully takes advantage of this, you should consider a career in data science. Simplilearn offers a Caltech Post Graduate Program in Data Science that will train you in everything you need to know to secure the perfect position. This Data Science PG program is ideal for all working professionals, covering job-critical topics like R, Python programming , machine learning algorithms , NLP concepts , and data visualization with Tableau in great detail. This is all provided via our interactive learning model with live sessions by global practitioners, practical labs, and industry projects.
Data Science & Business Analytics Courses Duration and Fees
Data Science & Business Analytics programs typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
Recommended Reads
Data Science Career Guide: A Comprehensive Playbook To Becoming A Data Scientist
Capped Collection in MongoDB
An Ultimate One-Stop Solution Guide to Collections in C# Programming With Examples
Managing Data
Difference Between Collection and Collections in Java
What Are Java Collections and How to Implement Them?
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
Data scientist.
- Add the IBM Advantage to your Learning
- 25 Industry-relevant Projects and Integrated labs
Caltech Data Sciences-Bootcamp
- Exclusive visit to Caltech’s Robotics Lab
Caltech Post Graduate Program in Data Science
- Earn a program completion certificate from Caltech CTME
- Curriculum delivered in live online sessions by industry experts
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Techniques – Methods, Types and Examples
Research Techniques – Methods, Types and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Techniques
Definition:
Research techniques refer to the various methods, processes, and tools used to collect, analyze, and interpret data for the purpose of answering research questions or testing hypotheses.
Methods of Research Techniques
The methods of research techniques refer to the overall approaches or frameworks that guide a research study, including the theoretical perspective, research design, sampling strategy, data collection and analysis techniques, and ethical considerations. Some common methods of research techniques are:
- Quantitative research: This is a research method that focuses on collecting and analyzing numerical data to establish patterns, relationships, and cause-and-effect relationships. Examples of quantitative research techniques are surveys, experiments, and statistical analysis.
- Qualitative research: This is a research method that focuses on collecting and analyzing non-numerical data, such as text, images, and videos, to gain insights into the subjective experiences and perspectives of the participants. Examples of qualitative research techniques are interviews, focus groups, and content analysis.
- Mixed-methods research: This is a research method that combines quantitative and qualitative research techniques to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a research question. Examples of mixed-methods research techniques are surveys with open-ended questions and case studies with statistical analysis.
- Action research: This is a research method that focuses on solving real-world problems by collaborating with stakeholders and using a cyclical process of planning, action, and reflection. Examples of action research techniques are participatory action research and community-based participatory research.
- Experimental research : This is a research method that involves manipulating one or more variables to observe the effect on an outcome, to establish cause-and-effect relationships. Examples of experimental research techniques are randomized controlled trials and quasi-experimental designs.
- Observational research: This is a research method that involves observing and recording behavior or phenomena in natural settings to gain insights into the subject of study. Examples of observational research techniques are naturalistic observation and structured observation.
Types of Research Techniques
There are several types of research techniques used in various fields. Some of the most common ones are:
- Surveys : This is a quantitative research technique that involves collecting data through questionnaires or interviews to gather information from a large group of people.
- Experiments : This is a scientific research technique that involves manipulating one or more variables to observe the effect on an outcome, to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Case studies: This is a qualitative research technique that involves in-depth analysis of a single case, such as an individual, group, or event, to understand the complexities of the case.
- Observational studies : This is a research technique that involves observing and recording behavior or phenomena in natural settings to gain insights into the subject of study.
- Content analysis: This is a research technique used to analyze text or other media content to identify patterns, themes, or meanings.
- Focus groups: This is a research technique that involves gathering a small group of people to discuss a topic or issue and provide feedback on a product or service.
- Meta-analysis: This is a statistical research technique that involves combining data from multiple studies to assess the overall effect of a treatment or intervention.
- Action research: This is a research technique used to solve real-world problems by collaborating with stakeholders and using a cyclical process of planning, action, and reflection.
- Interviews : Interviews are another technique used in research, and they can be conducted in person or over the phone. They are often used to gather in-depth information about an individual’s experiences or opinions. For example, a researcher might conduct interviews with cancer patients to learn more about their experiences with treatment.
Example of Research Techniques
Here’s an example of how research techniques might be used by a student conducting a research project:
Let’s say a high school student is interested in investigating the impact of social media on mental health. They could use a variety of research techniques to gather data and analyze their findings, including:
- Literature review : The student could conduct a literature review to gather existing research studies, articles, and books that discuss the relationship between social media and mental health. This will provide a foundation of knowledge on the topic and help the student identify gaps in the research that they could address.
- Surveys : The student could design and distribute a survey to gather information from a sample of individuals about their social media usage and how it affects their mental health. The survey could include questions about the frequency of social media use, the types of content consumed, and how it makes them feel.
- Interviews : The student could conduct interviews with individuals who have experienced mental health issues and ask them about their social media use, and how it has impacted their mental health. This could provide a more in-depth understanding of how social media affects people on an individual level.
- Data analysis : The student could use statistical software to analyze the data collected from the surveys and interviews. This would allow them to identify patterns and relationships between social media usage and mental health outcomes.
- Report writing : Based on the findings from their research, the student could write a report that summarizes their research methods, findings, and conclusions. They could present their report to their peers or their teacher to share their insights on the topic.
Overall, by using a combination of research techniques, the student can investigate their research question thoroughly and systematically, and make meaningful contributions to the field of social media and mental health research.
Purpose of Research Techniques
The Purposes of Research Techniques are as follows:
- To investigate and gain knowledge about a particular phenomenon or topic
- To generate new ideas and theories
- To test existing theories and hypotheses
- To identify and evaluate potential solutions to problems
- To gather data and evidence to inform decision-making
- To identify trends and patterns in data
- To explore cause-and-effect relationships between variables
- To develop and refine measurement tools and methodologies
- To establish the reliability and validity of research findings
- To communicate research findings to others in a clear and concise manner.
Applications of Research Techniques
Here are some applications of research techniques:
- Scientific research: to explore, investigate and understand natural phenomena, and to generate new knowledge and theories.
- Market research: to collect and analyze data about consumer behavior, preferences, and trends, and to help businesses make informed decisions about product development, pricing, and marketing strategies.
- Medical research : to study diseases and their treatments, and to develop new medicines, therapies, and medical technologies.
- Social research : to explore and understand human behavior, attitudes, and values, and to inform public policy decisions related to education, health care, social welfare, and other areas.
- Educational research : to study teaching and learning processes, and to develop effective teaching methods and instructional materials.
- Environmental research: to investigate the impact of human activities on the environment, and to develop solutions to environmental problems.
- Engineering Research: to design, develop, and improve products, processes, and systems, and to optimize their performance and efficiency.
- Criminal justice research : to study crime patterns, causes, and prevention strategies, and to evaluate the effectiveness of criminal justice policies and programs.
- Psychological research : to investigate human cognition, emotion, and behavior, and to develop interventions to address mental health issues.
- Historical research: to study past events, societies, and cultures, and to develop an understanding of how they shape our present.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
Help | Advanced Search
Astrophysics > Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics
Title: pipeline provenance for analysis, evaluation, trust or reproducibility.
Abstract: Data volumes and rates of research infrastructures will continue to increase in the upcoming years and impact how we interact with their final data products. Little of the processed data can be directly investigated and most of it will be automatically processed with as little user interaction as possible. Capturing all necessary information of such processing ensures reproducibility of the final results and generates trust in the entire process. We present PRAETOR, a software suite that enables automated generation, modelling, and analysis of provenance information of Python pipelines. Furthermore, the evaluation of the pipeline performance, based upon a user defined quality matrix in the provenance, enables the first step of machine learning processes, where such information can be fed into dedicated optimisation procedures.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative analysis tends to be quite flexible and relies on the researcher's judgement, so you have to reflect carefully on your choices and assumptions and be careful to avoid research bias. Quantitative analysis methods. Quantitative analysis uses numbers and statistics to understand frequencies, averages and correlations (in descriptive ...
There are several techniques to analyze the data in qualitative research, but here are some commonly used methods, Content Analysis: It is widely accepted and the most frequently employed technique for data analysis in research methodology. It can be used to analyze the documented information from text, images, and sometimes from the physical ...
KPIs are critical to both qualitative and quantitative analysis research. This is one of the primary methods of data analysis you certainly shouldn't overlook. To help you set the best possible KPIs for your initiatives and activities, here is an example of a relevant logistics KPI: transportation-related costs.
For many researchers unfamiliar with qualitative research, determining how to conduct qualitative analyses is often quite challenging. Part of this challenge is due to the seemingly limitless approaches that a qualitative researcher might leverage, as well as simply learning to think like a qualitative researcher when analyzing data. From framework analysis (Ritchie & Spencer, 1994) to content ...
Description: Quantitative data analysis is a high-level branch of data analysis that designates methods and techniques concerned with numbers instead of words. It accounts for more than 50% of all data analysis and is by far the most widespread and well-known type of data analysis.
The two "branches" of quantitative analysis. As I mentioned, quantitative analysis is powered by statistical analysis methods.There are two main "branches" of statistical methods that are used - descriptive statistics and inferential statistics.In your research, you might only use descriptive statistics, or you might use a mix of both, depending on what you're trying to figure out.
The SAGE Handbook of. Qualitative Data Analysis. Uwe Flick. 00-Flick-Prelims.indd 5 29-Oct-13 2:00:39 PM. Data analysis is the central step in qualitative research. Whatever the data are, it is their analysis that, in a decisive way, forms the outcomes of the research. Sometimes, data collection is limited to recording and docu- menting ...
Data analysis techniques in research are essential because they allow researchers to derive meaningful insights from data sets to support their hypotheses or research objectives.. Data Analysis Techniques in Research: While various groups, institutions, and professionals may have diverse approaches to data analysis, a universal definition captures its essence.
data analysis, the process of systematically collecting, cleaning, transforming, describing, modeling, and interpreting data, generally employing statistical techniques. Data analysis is an important part of both scientific research and business, where demand has grown in recent years for data-driven decision making.Data analysis techniques are used to gain useful insights from datasets, which ...
Data analysis techniques. Now we're familiar with some of the different types of data, let's focus on the topic at hand: different methods for analyzing data. a. Regression analysis. Regression analysis is used to estimate the relationship between a set of variables.
QDA Method #1: Qualitative Content Analysis. Content analysis is possibly the most common and straightforward QDA method. At the simplest level, content analysis is used to evaluate patterns within a piece of content (for example, words, phrases or images) or across multiple pieces of content or sources of communication. For example, a collection of newspaper articles or political speeches.
Data Analysis. Definition: Data analysis refers to the process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, drawing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. It involves applying various statistical and computational techniques to interpret and derive insights from large datasets.
How to conduct qualitative research? Given that qualitative research is characterised by flexibility, openness and responsivity to context, the steps of data collection and analysis are not as separate and consecutive as they tend to be in quantitative research [13, 14].As Fossey puts it: "sampling, data collection, analysis and interpretation are related to each other in a cyclical ...
Thematic analysis is a highly popular technique among qualitative researchers for analyzing qualitative data, which usually comprises thick descriptive data. ... At this pivotal stage, findings from thematic analysis and other research methods are combined into a unified conceptual model with the goal of providing an explanation for the ...
Statistical methods involved in carrying out a study include planning, designing, collecting data, analysing, drawing meaningful interpretation and reporting of the research findings. The statistical analysis gives meaning to the meaningless numbers, thereby breathing life into a lifeless data. The results and inferences are precise only if ...
Method 1: Content Analysis. Content analysis is a methodical technique for analyzing textual or visual data in a structured manner. In this method, you will categorize qualitative data by splitting it into manageable pieces and assigning the manual coding process to these units.
Statistical analysis is the most common quantitative research analysis method. It involves using statistical tools and techniques to analyze the numerical data collected during the research process. Statistical analysis can be used to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses and theories. Regression ...
Step 1: Consider your aims and approach. Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method. Step 4: Choose your data collection methods. Step 5: Plan your data collection procedures. Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies. Other interesting articles.
Qualitative Research. Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus ...
The basic goal of a good public opinion poll is to give everyone in the population, regardless of their wealth, age, education, race, knowledge of politics or experience with it, an equal voice about the issues of the day. We use a technique called "random sampling" to try to accomplish this.
Another important question is what makes a state more successful than others when evaluating vaccination performance. To answer both of these questions, we proposed a hybrid method that consists of Data Envelopment Analysis and Ensemble ML Methods. DEA was employed to find the vaccine efficiency of the states using the data aggregated from ...
Qualitative research methods. Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods.These are some of the most common qualitative methods: Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes. Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations. Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among ...
Data collection is the process of collecting and evaluating information or data from multiple sources to find answers to research problems, answer questions, evaluate outcomes, and forecast trends and probabilities. It is an essential phase in all types of research, analysis, and decision-making, including that done in the social sciences ...
Examples of quantitative research techniques are surveys, experiments, and statistical analysis. Qualitative research: This is a research method that focuses on collecting and analyzing non-numerical data, such as text, images, and videos, to gain insights into the subjective experiences and perspectives of the participants.
Pipeline Provenance for Analysis, Evaluation, Trust or Reproducibility. Michael A. C. Johnson, Hans-Rainer Klöckner, Albina Muzafarova, Kristen Lackeos, David J. Champion, Marta Dembska, Sirko Schindler, Marcus Paradies. Data volumes and rates of research infrastructures will continue to increase in the upcoming years and impact how we ...
This research investigates the behavior and frequency evolution of extreme waves in coastal areas through a combination of physical modeling, spectral analysis, and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques. Laboratory experiments were conducted in a wave flume, deploying various wave spectra, including JONSWAP (γ = 7), JONSWAP (γ = 3.3), and Pierson-Moskowitz, using the dispersive focusing ...