
Best Nursing Research Topics for Students
What is a nursing research paper.
- What They Include
- Choosing a Topic
- Best Nursing Research Topics
- Research Paper Writing Tips

Writing a research paper is a massive task that involves careful organization, critical analysis, and a lot of time. Some nursing students are natural writers, while others struggle to select a nursing research topic, let alone write about it.
If you're a nursing student who dreads writing research papers, this article may help ease your anxiety. We'll cover everything you need to know about writing nursing school research papers and the top topics for nursing research.
Continue reading to make your paper-writing jitters a thing of the past.
Popular Online Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) Programs

GCU's College of Nursing and Health Care Professions has a nearly 35-year tradition of preparing students to fill evolving healthcare roles as highly qualified professionals. GCU offers a full spectrum of nursing degrees, from a pre-licensure BSN degree to a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) program.
Enrollment: Nationwide
- MSN - Family NP
- MSN - Adult Gerontology Acute Care NP
- MSN - Nursing Education
- MSN - Health Informatics
- MSN - Public Health Nursing
- MSN - Health Care Quality & Patient Safety
- MBA & MSN - Nursing Leadership in Health Care Systems
- See more GCU nursing programs

At Purdue Global, discover a faster, more affordable way to earn your Nursing degree. Purdue Global is committed to keeping your tuition costs as low as possible and helping you find the most efficient path to your degree.
Enrollment: Nationwide, but certain programs have state restrictions. Check with Purdue for details.
- Accelerated BSN-to-MSN
- MSN - Adult-Gerontology Acute Care NP
- MSN - Psychiatric Mental Health NP
- MSN - Nurse Educator
- MSN - Executive Leader
- MSN - Nurse Informatics
- MSN/MBA Dual Degree
- See more Purdue nursing programs

Capella’s online RN-to-BSN degree is an accredited program designed for working nurses. Thousands of nurses have completed their BSN program with FlexPath, that allows you to control your pace and set your own deadlines. With FlexPath, you can complete your RN-to-BSN program in 9 months and under $10,000. Fastest 25% of students. Cost varies by pace, transfer credits, other factors. Fees apply.
Enrollment: Nationwide, but certain programs have state restrictions. Check with Capella for details.
- MSN - Adult-Gerontology Primary Care NP
- MSN - Nursing Informatics
- MSN - Care Coordination
- MSN - Nursing Leadership & Admin
- See more Capella nursing programs

WGU's award-winning online programs are created to help you succeed while graduating faster and with less debt. WGU is a CCNE accredited, nonprofit university offering nursing bachelor's and master's degrees.
- BSN-to-MSN - Nursing Education
- RN-to-MSN - Nursing Education
- BSN-to-MSN - Family NP
- BSN-to-MSN - Psychiatric Mental Health NP
- RN-to-MSN - Nursing Leadership & Management
- See more WGU nursing programs

A nursing research paper is a work of academic writing composed by a nurse or nursing student. The paper may present information on a specific topic or answer a question.
During LPN/LVN and RN programs, most papers you write focus on learning to use research databases, evaluate appropriate resources, and format your writing with APA style. You'll then synthesize your research information to answer a question or analyze a topic.
BSN , MSN , Ph.D., and DNP programs also write nursing research papers. Students in these programs may also participate in conducting original research studies.
Writing papers during your academic program improves and develops many skills, including the ability to:
- Select nursing topics for research
- Conduct effective research
- Analyze published academic literature
- Format and cite sources
- Synthesize data
- Organize and articulate findings
About Nursing Research Papers
When do nursing students write research papers.
You may need to write a research paper for any of the nursing courses you take. Research papers help develop critical thinking and communication skills. They allow you to learn how to conduct research and critically review publications.
That said, not every class will require in-depth, 10-20-page papers. The more advanced your degree path, the more you can expect to write and conduct research. If you're in an associate or bachelor's program, you'll probably write a few papers each semester or term.
Do Nursing Students Conduct Original Research?
Most of the time, you won't be designing, conducting, and evaluating new research. Instead, your projects will focus on learning the research process and the scientific method. You'll achieve these objectives by evaluating existing nursing literature and sources and defending a thesis.
However, many nursing faculty members do conduct original research. So, you may get opportunities to participate in, and publish, research articles.
Example Research Project Scenario:
In your maternal child nursing class, the professor assigns the class a research paper regarding developmentally appropriate nursing interventions for the pediatric population. While that may sound specific, you have almost endless opportunities to narrow down the focus of your writing.
You could choose pain intervention measures in toddlers. Conversely, you can research the effects of prolonged hospitalization on adolescents' social-emotional development.
What Does a Nursing Research Paper Include?
Your professor should provide a thorough guideline of the scope of the paper. In general, an undergraduate nursing research paper will consist of:
Introduction : A brief overview of the research question/thesis statement your paper will discuss. You can include why the topic is relevant.
Body : This section presents your research findings and allows you to synthesize the information and data you collected. You'll have a chance to articulate your evaluation and answer your research question. The length of this section depends on your assignment.
Conclusion : A brief review of the information and analysis you presented throughout the body of the paper. This section is a recap of your paper and another chance to reassert your thesis.
The best advice is to follow your instructor's rubric and guidelines. Remember to ask for help whenever needed, and avoid overcomplicating the assignment!
How to Choose a Nursing Research Topic
The sheer volume of prospective nursing research topics can become overwhelming for students. Additionally, you may get the misconception that all the 'good' research ideas are exhausted. However, a personal approach may help you narrow down a research topic and find a unique angle.
Writing your research paper about a topic you value or connect with makes the task easier. Additionally, you should consider the material's breadth. Topics with plenty of existing literature will make developing a research question and thesis smoother.
Finally, feel free to shift gears if necessary, especially if you're still early in the research process. If you start down one path and have trouble finding published information, ask your professor if you can choose another topic.
The Best Research Topics for Nursing Students
You have endless subject choices for nursing research papers. This non-exhaustive list just scratches the surface of some of the best nursing research topics.
1. Clinical Nursing Research Topics
- Analyze the use of telehealth/virtual nursing to reduce inpatient nurse duties.
- Discuss the impact of evidence-based respiratory interventions on patient outcomes in critical care settings.
- Explore the effectiveness of pain management protocols in pediatric patients.
2. Community Health Nursing Research Topics
- Assess the impact of nurse-led diabetes education in Type II Diabetics.
- Analyze the relationship between socioeconomic status and access to healthcare services.
3. Nurse Education Research Topics
- Review the effectiveness of simulation-based learning to improve nursing students' clinical skills.
- Identify methods that best prepare pre-licensure students for clinical practice.
- Investigate factors that influence nurses to pursue advanced degrees.
- Evaluate education methods that enhance cultural competence among nurses.
- Describe the role of mindfulness interventions in reducing stress and burnout among nurses.
4. Mental Health Nursing Research Topics
- Explore patient outcomes related to nurse staffing levels in acute behavioral health settings.
- Assess the effectiveness of mental health education among emergency room nurses .
- Explore de-escalation techniques that result in improved patient outcomes.
- Review the effectiveness of therapeutic communication in improving patient outcomes.
5. Pediatric Nursing Research Topics
- Assess the impact of parental involvement in pediatric asthma treatment adherence.
- Explore challenges related to chronic illness management in pediatric patients.
- Review the role of play therapy and other therapeutic interventions that alleviate anxiety among hospitalized children.
6. The Nursing Profession Research Topics
- Analyze the effects of short staffing on nurse burnout .
- Evaluate factors that facilitate resiliency among nursing professionals.
- Examine predictors of nurse dissatisfaction and burnout.
- Posit how nursing theories influence modern nursing practice.
Tips for Writing a Nursing Research Paper
The best nursing research advice we can provide is to follow your professor's rubric and instructions. However, here are a few study tips for nursing students to make paper writing less painful:
Avoid procrastination: Everyone says it, but few follow this advice. You can significantly lower your stress levels if you avoid procrastinating and start working on your project immediately.
Plan Ahead: Break down the writing process into smaller sections, especially if it seems overwhelming. Give yourself time for each step in the process.
Research: Use your resources and ask for help from the librarian or instructor. The rest should come together quickly once you find high-quality studies to analyze.
Outline: Create an outline to help you organize your thoughts. Then, you can plug in information throughout the research process.
Clear Language: Use plain language as much as possible to get your point across. Jargon is inevitable when writing academic nursing papers, but keep it to a minimum.
Cite Properly: Accurately cite all sources using the appropriate citation style. Nursing research papers will almost always implement APA style. Check out the resources below for some excellent reference management options.
Revise and Edit: Once you finish your first draft, put it away for one to two hours or, preferably, a whole day. Once you've placed some space between you and your paper, read through and edit for clarity, coherence, and grammatical errors. Reading your essay out loud is an excellent way to check for the 'flow' of the paper.
Helpful Nursing Research Writing Resources:
Purdue OWL (Online writing lab) has a robust APA guide covering everything you need about APA style and rules.
Grammarly helps you edit grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Upgrading to a paid plan will get you plagiarism detection, formatting, and engagement suggestions. This tool is excellent to help you simplify complicated sentences.
Mendeley is a free reference management software. It stores, organizes, and cites references. It has a Microsoft plug-in that inserts and correctly formats APA citations.
Don't let nursing research papers scare you away from starting nursing school or furthering your education. Their purpose is to develop skills you'll need to be an effective nurse: critical thinking, communication, and the ability to review published information critically.
Choose a great topic and follow your teacher's instructions; you'll finish that paper in no time.

Joleen Sams is a certified Family Nurse Practitioner based in the Kansas City metro area. During her 10-year RN career, Joleen worked in NICU, inpatient pediatrics, and regulatory compliance. Since graduating with her MSN-FNP in 2019, she has worked in urgent care and nursing administration. Connect with Joleen on LinkedIn or see more of her writing on her website.

Plus, get exclusive access to discounts for nurses, stay informed on the latest nurse news, and learn how to take the next steps in your career.
By clicking “Join Now”, you agree to receive email newsletters and special offers from Nurse.org. We will not sell or distribute your email address to any third party, and you may unsubscribe at any time by using the unsubscribe link, found at the bottom of every email.

PICOT Question Examples for Nursing Research

Are you looking for examples of nursing PICOT questions to inspire your creativity as you research for a perfect nursing topic for your paper? You came to the right place.
We have a comprehensive guide on how to write a good PICO Question for your case study, research paper, white paper, term paper, project, or capstone paper. Therefore, we will not go into the details in this post. A good PICOT question possesses the following qualities:
- A clinical-based question addresses the nursing research areas or topics.
- It is specific, concise, and clear.
- Patient, problem, or population.
- Intervention.
- Comparison.
- Includes medical, clinical, and nursing terms where necessary.
- It is not ambiguous.
For more information, read our comprehensive PICOT Question guide . You can use these questions to inspire your PICOT choice for your evidence-based papers , reports, or nursing research papers.
If you are stuck with assignments and want some help, we offer the best nursing research assignment help online. We have expert nursing writers who can formulate an excellent clinical, research, and PICOT question for you. They can also write dissertations, white papers, theses, reports, and capstones. Do not hesitate to place an order.
List of 180 Plus Best PICOT Questions to Get Inspiration From
Here is a list of nursing PICO questions to inspire you when developing yours. Some PICOT questions might be suitable for BSN and MSN but not DNP. If you are writing a change project for your DNP, try to focus on PICOT questions that align to process changes.
- Among healthy newborn infants in low- and middle-income countries (P), does early skin-to-skin contact of the baby with the mother in the first hour of life (I) compared with drying and wrapping (C) have an impact on neonatal mortality, hypothermia or initiation/exclusivity/ duration of breastfeeding (O)?
- Is it necessary to test blood glucose levels 4 times daily for a patient suffering from Type 1 diabetes?
- Does raising the head of the bed of a mechanically ventilated patient reduce the chances of pneumonia?
- Does music therapy is an effective mode of PACU pain management for patients who are slowly coming out from their anesthesia?
- For all neonates (P), should vitamin K prophylaxis (I) be given for the prevention of vitamin K deficiency bleeding (O)?
- For young infants (0-2 months) with suspected sepsis managed in health facilities (P), should third generation cephalosporin monotherapy (I) replace currently recommended ampicillin-gentamicin combination (C) as first line empiric treatment for preventing death and sequelae (O)?
- In low-birth-weight/pre-term neonates in health facilities (P), is skin-to-skin contact immediately after birth (I) more effective than conventional care (C) in preventing hypothermia (O)?
- In children aged 2–59 months (P), what is the most effective antibiotic therapy (I, C) for severe pneumonia (O)?
- Is skin-to-skin contact of the infant with the mother a more assured way of ensuring neonatal mortality compared to drying and wrapping?
- Are oral contraceptives effective in stopping pregnancy for women above 30 years?
- Is spironolactone a better drug for reducing the blood pressure of teenagers when compared to clonidine?
- What is the usefulness of an LP/spinal tap after the beginning of antivirals for a pediatric population suffering from fever?
- In children aged 2–59 months in developing countries (P), which parenteral antibiotic or combination of antibiotics (I), at what dose and duration, is effective for the treatment of suspected bacterial meningitis in hospital in reducing mortality and sequelae (O)?
- Does the habit of washing hands third-generation workers decrease the events of infections in hospitals?
- Is the intake of zinc pills more effective than Vitamin C for preventing cold during winter for middle-aged women?
- In children with acute severe malnutrition (P), are antibiotics (I) effective in preventing death and sequelae (O)?
- Among, children with lower respiratory tract infection (P), what are the best cut off oxygen saturation levels (D), at different altitudes that will determine hypoxaemia requiring oxygen therapy (O)?
- In infants and children in low-resource settings (P), what is the most appropriate method (D) of detecting hypoxaemia in hospitals (O)?
- In children with shock (P), what is the most appropriate choice of intravenous fluid therapy (I) to prevent death and sequelae (O)?
- In fully conscious children with hypoglycaemia (P) what is the effectiveness of administering sublingual sugar (I)?
- Is using toys as distractions during giving needle vaccinations to toddlers an effective pain response management?
- What is the result of a higher amount of potassium intake among children with low blood pressure?
- Is cup feeding an infant better than feeding through tubes in a NICU setup?
- Does the intervention of flushing the heroin via lines a more effective way of treating patients with CVLs/PICCs?
- Is the use of intravenous fluid intervention a better remedy for infants under fatal conditions?
- Do bedside shift reports help in the overall patient care for nurses?
- Is home visitation a better way of dealing with teen pregnancy when compared to regular school visits in rural areas?
- Is fentanyl more effective than morphine in dealing with the pain of adults over the age of 50 years?
- What are the health outcomes of having a high amount of potassium for adults over the age of 21 years?
- Does the use of continuous feed during emesis a more effective way of intervention when compared to the process of stopping the feed for a short period?
- Does controlling the amount of sublingual sugar help completely conscious children suffering from hypoglycemia?
- Is the lithotomy position an ideal position for giving birth to women in labor?
- Does group therapy help patients with schizophrenia to help their conversational skills?
- What are the probable after-effects, in the form of bruises and other injuries, of heparin injection therapy for COPD patients?
- Would standardized discharge medication education improve home medication adherence in adults age 65 and older compared to-standardized discharge medication education?
- In patients with psychiatric disorders is medication non-compliance a greater risk compared with adults experiencing chronic illness?
- Is the use of beta-blockers for lowering blood pressure for adult men over the age of 70 years effective?
- Nasal swab or nasal aspirate? Which one is more effective for children suffering from seasonal flu?
- What are the effects of adding beta-blockers for lowering blood pressure for adult men over the age of 70 years?
- Does the process of stopping lipids for 4 hours an effective measure of obtaining the desired TG level for patients who are about to receive TPN?
- Is medical intervention a proper way of dealing with childhood obesity among school-going children?
- Can nurse-led presentations of mental health associated with bullying help in combating such tendencies in public schools?
- What are the impacts of managing Prevacid before a pH probe study for pediatric patients with GERD?
- What are the measurable effects of extending ICU stays and antibiotic consumption amongst children with sepsis?
- Does the use of infrared skin thermometers justified when compared to the tympanic thermometers for a pediatric population?
- What are the roles of a pre-surgery cardiac nurse in order to prevent depression among patients awaiting cardiac operation?
- Does the increase in the habit of smoking marijuana among Dutch students increase the chances of depression?
- What is the direct connection between VAP and NGT?
- Is psychological intervention for people suffering from dementia a more effective measure than giving them a placebo?
- Are alarm sensors effective in preventing accidents in hospitals for patients over the age of 65 years?
- Is the sudden change of temperature harmful for patients who are neurologically devastated?
- Is it necessary to test blood glucose levels, 4 times a day, for a patient suffering from Type 1 diabetes?
- Is the use of MDI derive better results, when compared to regular nebulizers, for pediatric patients suffering from asthma?
- What are the effects of IVF bolus in controlling the amount of Magnesium Sulfate for patients who are suffering from asthma?
- Is the process of stopping lipids for 4 hours an effective measure of obtaining the desired TG level for patients who are about to receive TPN?
- What are the standards of vital signs for a pediatric population?
- Is daily blood pressure monitoring help in addressing the triggers of hypertension among males over 65 years?
- Does receiving phone tweets lower blood sugar levels for people suffering from Type 1 diabetes?
- Are males over the age of 30 years who have smoked for more than 1 year exposed to a greater risk of esophageal cancer when compared to the same age group of men who have no history of smoking?
- Does the increase in the use of mosquito nets in Uganda help in the reduction of malaria among the infants?
- Does the increase in the intake of oral contraceptives increase the chances of breast cancer among 20-30 years old women in the UK?
- In postpartum women with postnatal depression (P), does group therapy (I) compared to individual therapy (C) improve maternal-infant bonding (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In patients with chronic pain (P), does mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (I) compared to pharmacotherapy (C) improve quality of life (O) after 12 weeks (T)?
- In patients with type 2 diabetes (P), does continuous glucose monitoring (I) compared to self-monitoring of blood glucose (C) improve glycemic control (O) over a period of three months (T)?
- In patients with chronic kidney disease (P), does a vegetarian diet (I) compared to a regular diet (C) slow the decline in renal function (O) after one year (T)?
- In pediatric patients with acute otitis media (P), does delayed antibiotic prescribing (I) compared to immediate antibiotic prescribing (C) reduce antibiotic use (O) within one week (T)?
- In older adults with dementia (P), does pet therapy (I) compared to no pet therapy (C) decrease agitation (O) after three months (T)?
- In patients with chronic heart failure (P), does telemonitoring of vital signs (I) compared to standard care (C) reduce hospital readmissions (O) within six months (T)?
- In patients with anxiety disorders (P), does exposure therapy (I) compared to cognitive therapy (C) reduce anxiety symptoms (O) after 12 weeks (T)?
- In postpartum women with breastfeeding difficulties (P), does lactation consultation (I) compared to standard care (C) increase breastfeeding rates (O) after four weeks (T)?
- In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (P), does long-acting bronchodilator therapy (I) compared to short-acting bronchodilator therapy (C) improve lung function (O) after three months (T)?
- In patients with major depressive disorder (P), does bright light therapy (I) compared to placebo (C) reduce depressive symptoms (O) after six weeks (T)?
- In patients with diabetes (P), does telemedicine-based diabetes management (I) compared to standard care (C) improve glycemic control (O) over a period of six months (T)?
- In patients with chronic kidney disease (P), does a low-phosphorus diet (I) compared to a regular diet (C) decrease serum phosphate levels (O) after one year (T)?
- In pediatric patients with acute gastroenteritis (P), does probiotic supplementation (I) compared to placebo (C) reduce the duration of diarrhea (O) within 48 hours (T)?
- In patients with chronic pain (P), does acupuncture (I) compared to sham acupuncture (C) reduce pain intensity (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In older adults at risk of falls (P), does a home modification program (I) compared to no intervention (C) reduce the incidence of falls (O) over a period of six months (T)?
- In patients with schizophrenia (P), does cognitive remediation therapy (I) compared to standard therapy (C) improve cognitive function (O) after one year (T)?
- In patients with chronic kidney disease (P), does angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (I) compared to angiotensin receptor blockers (C) slow the progression of renal disease (O) over a period of two years (T)?
- In postoperative patients (P), does chlorhexidine bathing (I) compared to regular bathing (C) reduce the risk of surgical site infections (O) within 30 days (T)?
- In patients with type 2 diabetes (P), does a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet (I) compared to a low-fat diet (C) improve glycemic control (O) over a period of six months (T)?
- In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (P), does pulmonary rehabilitation combined with telemonitoring (I) compared to standard pulmonary rehabilitation (C) improve exercise capacity (O) after three months (T)?
- In patients with heart failure (P), does a nurse-led heart failure clinic (I) compared to usual care (C) improve self-care behaviors (O) after six months (T)?
- In postpartum women with postnatal depression (P), does telephone-based counseling (I) compared to face-to-face counseling (C) reduce depressive symptoms (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In patients with chronic migraine (P), does prophylactic treatment with topiramate (I) compared to amitriptyline (C) reduce the frequency of migraines (O) after three months (T)?
- In pediatric patients with acute otitis media (P), does watchful waiting (I) compared to immediate antibiotic treatment (C) reduce the duration of symptoms (O) within seven days (T)?
- In older adults with dementia (P), does reminiscence therapy (I) compared to usual care (C) improve cognitive function (O) after three months (T)?
- In patients with chronic heart failure (P), does telemonitoring combined with a medication reminder system (I) compared to telemonitoring alone (C) reduce hospital readmissions (O) within six months (T)?
- In patients with asthma (P), does self-management education (I) compared to standard care (C) reduce asthma exacerbations (O) over a period of one year (T)?
- In postoperative patients (P), does the use of wound dressings with antimicrobial properties (I) compared to standard dressings (C) reduce the incidence of surgical site infections (O) within 30 days (T)?
- In patients with chronic kidney disease (P), does mindfulness-based stress reduction (I) compared to usual care (C) improve psychological well-being (O) over a period of three months (T)?
- In adult patients with chronic pain (P), does biofeedback therapy (I) compared to relaxation techniques (C) reduce pain intensity (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In patients with type 2 diabetes (P), does a low-glycemic index diet (I) compared to a high-glycemic-index diet (C) improve glycemic control (O) over a period of six months (T)?
- In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (P), does regular physical activity (I) compared to no physical activity (C) improve health-related quality of life (O) after three months (T)?
- In patients with major depressive disorder (P), does mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (I) compared to antidepressant medication (C) reduce depressive symptoms (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In postpartum women (P), does perineal warm compresses (I) compared to standard perineal care (C) reduce perineal pain (O) after vaginal delivery (T)?
- In patients with chronic kidney disease (P), does a low-protein, low-phosphorus diet (I) compared to a low-protein diet alone (C) slow the progression of renal disease(O) after two years (T)?
- In pediatric patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (P), does mindfulness-based interventions (I) compared to medication alone (C) improve attention and behavior (O) after six months (T)?
- In patients with chronic pain (P), does cognitive-behavioral therapy (I) compared to physical therapy (C) reduce pain interference (O) after 12 weeks (T)?
- In elderly patients with osteoarthritis (P), does aquatic exercise (I) compared to land-based exercise (C) improve joint flexibility and reduce pain (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In patients with multiple sclerosis (P), does high-intensity interval training (I) compared to moderate-intensity continuous training (C) improve physical function (O) after three months (T)?
- In postoperative patients (P), does preoperative carbohydrate loading (I) compared to fasting (C) reduce postoperative insulin resistance (O) within 24 hours (T)?
- In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (P), does home-based tele-rehabilitation (I) compared to center-based rehabilitation (C) improve exercise capacity (O) after six months (T)?
- In patients with rheumatoid arthritis (P), does tai chi (I) compared to pharmacological treatment (C) reduce joint pain and improve physical function (O) after six months (T)?
- In postpartum women with postpartum hemorrhage (P), does early administration of tranexamic acid (I) compared to standard administration (C) reduce blood loss (O) within two hours (T)?
- In patients with hypertension (P), does mindfulness meditation (I) compared to relaxation techniques (C) reduce blood pressure (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In elderly patients with hip fractures (P), does multidisciplinary geriatric care (I) compared to standard care (C) improve functional outcomes (O) after three months (T)?
- In patients with chronic kidney disease (P), does aerobic exercise (I) compared to resistance exercise (C) improve renal function (O) after six months (T)?
- In patients with major depressive disorder (P), does add-on treatment with omega-3 fatty acids (I) compared to placebo (C) reduce depressive symptoms (O) after 12 weeks (T)?
- In postoperative patients (P), does preoperative education using multimedia materials (I) compared to standard education (C) improve patient satisfaction (O) after surgery (T)?
- In patients with type 2 diabetes (P), does a plant-based diet (I) compared to a standard diet (C) improve glycemic control (O) after three months (T)?
- In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (P), does high-flow oxygen therapy (I) compared to standard oxygen therapy (C) improve exercise tolerance (O) after three months (T)?
- In patients with heart failure (P), does nurse-led telephone follow-up (I) compared to standard care (C) reduce hospital readmissions (O) within six months (T)?
- In postpartum women with postnatal depression (P), does online cognitive-behavioral therapy (I) compared to face-to-face therapy (C) reduce depressive symptoms (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In patients with chronic migraine (P), does mindfulness-based stress reduction (I) compared to medication alone (C) reduce the frequency and severity of migraines (O) after three months (T)?
- In older adults with delirium (P), does structured music intervention (I) compared to standard care (C) reduce the duration of delirium episodes (O) during hospitalization (T)?
- In patients with chronic low back pain (P), does yoga (I) compared to physical therapy (C) reduce pain intensity (O) after six weeks (T)?
- In pediatric patients with acute otitis media (P), does watchful waiting with pain management (I) compared to immediate antibiotic treatment (C) reduce the need for antibiotics (O) within one week (T)?
- In patients with schizophrenia (P), does family psychoeducation (I) compared to standard treatment (C) improve medication adherence (O) over a period of six months (T)?
- In patients with chronic kidney disease (P), does a low-phosphorus diet (I) compared to a regular diet (C) slow the progression of renal disease (O) after one year (T)?
- In postoperative patients (P), does wound irrigation with saline solution (I) compared to povidone-iodine solution (C) reduce the incidence of surgical site infections (O) within 30 days (T)?
- In patients with type 1 diabetes (P), does continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (I) compared to multiple daily injections (C) improve glycemic control (O) over a period of six months (T)?
- In postoperative patients (P), does the use of prophylactic antibiotics (I) compared to no antibiotics (C) reduce the incidence of surgical site infections (O) within 30 days (T)?
- In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (P), does smoking cessation counseling (I) compared to no counseling (C) decrease the frequency of exacerbations (O) over a period of six months (T)?
- In patients with diabetes (P), does a multidisciplinary team approach (I) compared to standard care (C) improve self-management behaviors (O) over a period of one year (T)?
- In pregnant women with gestational hypertension (P), does bed rest (I) compared to regular activity (C) reduce the risk of developing preeclampsia (O) before delivery (T)?
- In patients with chronic kidney disease (P), does angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (I) compared to placebo (C) slow the progression of renal disease (O) over a period of two years (T)?
- In older adults with hip fractures (P), does early surgical intervention (I) compared to delayed surgery (C) improve functional outcomes (O) after six months (T)?
- In patients with major depressive disorder (P), does exercise (I) compared to antidepressant medication (C) reduce depressive symptoms (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In children with autism spectrum disorder (P), does applied behavior analysis (I) compared to standard therapy (C) improve social communication skills (O) over a period of one year (T)?
- In postoperative patients (P), does the use of incentive spirometry (I) compared to no spirometry (C) decrease the incidence of postoperative pulmonary complications (O) within seven days (T)?
- In patients with hypertension (P), does a combination of diet modification and exercise (I) compared to medication alone (C) lower blood pressure (O) after six months (T)?
- In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (P), does home oxygen therapy (I) compared to no oxygen therapy (C) improve exercise capacity (O) after threemonths (T)?
- In patients with heart failure (P), does a multidisciplinary heart failure management program (I) compared to standard care (C) reduce hospital readmissions (O) within six months (T)?
- In postpartum women with postnatal depression (P), does mindfulness meditation (I) compared to relaxation techniques (C) reduce depressive symptoms (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In patients with chronic kidney disease (P), does a low-sodium diet (I) compared to a regular diet (C) lower blood pressure (O) after six months (T)?
- In pediatric patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (P), does neurofeedback training (I) compared to medication (C) improve attention and behavior (O) after six months (T)?
- In patients with chronic pain (P), does transcranial direct current stimulation (I) compared to sham stimulation (C) reduce pain intensity (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In older adults with osteoporosis (P), does a structured exercise program (I) compared to no exercise (C) improve bone mineral density (O) after six months (T)?
- In patients with type 2 diabetes (P), does a low-carbohydrate, high-protein diet (I) compared to a standard diet (C) improve glycemic control (O) over a period of six months (T)?
- In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (P), does mindfulness-based stress reduction (I) compared to usual care (C) improve dyspnea symptoms (O) after three months (T)?
- In postpartum women with postnatal depression (P), does online peer support (I) compared to individual therapy (C) reduce depressive symptoms (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In patients with chronic kidney disease (P), does resistance training (I) compared to aerobic training (C) improve muscle strength (O) after six months (T)?
- In pediatric patients with asthma (P), does a written asthma action plan (I) compared to verbal instructions (C) reduce emergency department visits (O) within six months (T)?
- In patients with chronic pain (P), does yoga (I) compared to pharmacological treatment (C) reduce pain interference (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In older adults at risk of falls (P), does a multifactorial falls prevention program (I) compared to no intervention (C) reduce the rate of falls (O) over a period of six months (T)?
- In patients with schizophrenia (P), does cognitive-behavioral therapy (I) compared to medication alone (C) reduce positive symptom severity (O) after six months (T)?
- In postpartum women with breastfeeding difficulties (P), does breast massage (I) compared to no massage (C) improve milk flow (O) after four weeks (T)?
- In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (P), does long-term oxygen therapy (I) compared to short-term oxygen therapy (C) improve survival rates (O) after one year (T)?
- In patients with major depressive disorder (P), does repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (I) compared to sham treatment (C) reduce depressive symptoms (O) after six weeks (T)?
- In patients with diabetes (P), does a digital health app (I) compared to standard care (C) improve medication adherence (O) over a period of six months (T)?
- In patients with chronic kidney disease (P), does a low-potassium diet (I) compared to a regular diet (C) lower serum potassium levels (O) after one year (T)?
- In pediatric patients with acute gastroenteritis (P), does oral rehydration solution (I) compared to intravenous fluid therapy (C) reduce hospital admissions (O) within 48 hours (T)?
- In patients with chronic pain (P), does hypnotherapy (I) compared to no hypnotherapy (C) reduce pain intensity (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- In older adults at risk of falls (P), does a tai chi program (I) compared to no exercise program (C) improve balance and stability (O) after six months (T)?
- In patients with chronic heart failure (P), does a home-based self-care intervention (I) compared to standard care (C) reduce hospital readmissions (O) within six months (T)?
- In patients with anxiety disorders (P), does acceptance and commitment therapy (I) compared to cognitive-behavioral therapy (C) reduce anxiety symptoms (O) after 12 weeks (T)?
- In postpartum women with breastfeeding difficulties (P), does the use of nipple shields (I) compared to no nipple shields (C) improve breastfeeding success (O) after four weeks (T)?
- In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (P), does a comprehensive self-management program (I) compared to usual care (C) improve health-related quality of life (O) after three months (T)?
- In patients with major depressive disorder (P), does internet-based cognitive-behavioral therapy (I) compared to face-to-face therapy (C) reduce depressive symptoms (O) after eight weeks (T)?
- Does the increase in the habit of smoking marijuana among Dutch students increase the likelihood of depression?
- Does the use of pain relief medication during surgery provide more effective pain reduction compared to the same medication given post-surgery?
- Does the increase in the intake of oral contraceptives increase the risk of breast cancer among women aged 20-30 in the UK?
- Does the habit of washing hands among healthcare workers decrease the rate of infections in hospitals?
- Does the use of modern syringes help in reducing needle injuries among healthcare workers in America?
- Does encouraging male work colleagues to talk about sexual harassment decrease the rate of depression in the workplace?
- Does bullying in boarding schools in Scotland increase the likelihood of domestic violence within a 20-year timeframe?
- Does breastfeeding among toddlers in urban United States decrease their chances of obesity as pre-schoolers?
- Does the increase in the intake of antidepressants among urban women aged 30 years and older affect their maternal health?
- Does forming work groups to discuss domestic violence among the rural population of the United States reduce stress and depression among women?
- Does the increased use of mosquito nets in Uganda help in reducing malaria cases among infants?
- Can colon cancer be more effectively detected when colonoscopy is supported by an occult blood test compared to colonoscopy alone?
- Does regular usage of low-dose aspirin effectively reduce the risk of heart attacks and stroke for women above the age of 80 years?
- Is yoga an effective medical therapy for reducing lymphedema in patients recovering from neck cancer?
- Does daily blood pressure monitoring help in addressing the triggers of hypertension among males over 65 years?
- Does a regular 30-minute exercise regimen effectively reduce the risk of heart disease in adults over 65 years?
- Does prolonged exposure to chemotherapy increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases among teenagers suffering from cancer?
- Does breastfeeding among toddlers in the urban United States decrease their chances of obesity as pre-schoolers?
- Are first-time mothers giving birth to premature babies more prone to postpartum depression compared to second or third-time mothers in the same condition?
- For women under the age of 50 years, is a yearly mammogram more effective in preventing breast cancer compared to a mammogram done every 3 years?
- After being diagnosed with blood sugar levels, is a four-times-a-day blood glucose monitoring process more effective in controlling the onset of Type 1 diabetes?
Related: How to write an abstract poster presentation.
You can never go wrong with getting expertly written examples as a source for your inspiration. They factor in all the qualities of a good PICO question, which sets you miles ahead in your research process.
If you need a personalized approach to choosing a good PICOT question and writing a problem and purpose statement, our nursing paper acers can help you.
Nursing research specialists work with nursing students, professional nurses, and medical students to advance their academic and career goals. We offer private, reliable, confidential, and top-quality services.
Struggling with
Related Articles

How to Make SOAP Notes for a Nursing Class Assignment

Writing a Medicine Essay: Guide, Types, Tips, and Topics

How to Write a Policy Analysis Paper : A Nursing/Med Student Guide
NurseMyGrades is being relied upon by thousands of students worldwide to ace their nursing studies. We offer high quality sample papers that help students in their revision as well as helping them remain abreast of what is expected of them.

How to Write a Nursing Research Proposal Topics | Guide & Examples [Updated]
Rachel andel rn, bsn.
- July 24, 2023
- Nursing Writing Guides
Nursing research proposal topics can vary greatly, depending on the type of research you’re looking to conduct.
Whether you are interested in studying public health issues or improving patient care through innovative research methods, something on this list likely appeals to you.
Here’s a guide on writing a nursing research proposal and nursing research proposal topics , DNP research proposal topics, current nursing research proposal topics, and nursing research examples.
Working on a Nursing Research Proposal?
Get original papers written according to your instructions and save time for what matters most.
How to Write a Nursing Research Proposal
A nursing research proposal serves as a blueprint for conducting studies that address important clinical questions, explore innovative interventions, and contribute to the overall body of nursing knowledge.
To create a strong nursing research proposal, there are several key considerations that nursing students must take into account, which include;
- Defining a clear and concise research question addresses an important nursing knowledge gap.
- Selecting an appropriate research design and methodology that aligns with the research question and objectives.
- Ensuring ethical considerations are addressed and appropriate measures are in place to protect the rights and welfare of participants.
- Determining an appropriate sample size and recruitment strategy to ensure adequate statistical power and generalizability of findings.
- Developing a detailed data analysis plan that aligns with the research design and objectives.
- Consider dissemination and knowledge translation strategies to ensure research findings reach the intended audience and positively impact nursing practice.
Key components of a Nursing Research Proposa l
When creating a nursing research proposal, including all the components contributing to a comprehensive and well-structured document is crucial.
Understanding these components will ensure that your proposal is clear and organized and addresses the necessary aspects of your research endeavor.
Problem Statement
- It should provide a clear description of a problem that will be solved.
- It shows the gap between the current situation and the future goal to improve it.
Research Question
- The research question forms the foundation of your nursing research proposal. It is a concise and focused statement that outlines the main objective of your research.
- Your research question should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), enabling you to address a particular problem or gap in the existing literature.
Study Design
- The study design section outlines the methodology and approach you will employ to conduct your research.
- It includes details on the type of study, such as quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods, and explains how data will be collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
- The study design should align with your research question and ensure the validity and reliability of your findings.
Methodology
- The methodology component of your nursing research proposal describes the specific techniques and procedures you will use to gather data.
- This may include surveys, interviews, observations, or systematic reviews.
- Clearly outlining your methodology ensures transparency and allows others to reproduce your study if needed.
Sample Size Determination
- Determining an appropriate sample size is crucial in nursing research to ensure your findings’ statistical power and representativeness.
- This section will explain how you calculated the required sample size based on the research question, study design, and expected effect size.
- It is essential to consider factors such as the population size, confidence level, and desired margin of error.
Ethical Considerations
- Ethical considerations play a vital role in nursing research.
- This component addresses the protection and well-being of participants, safeguarding their privacy and confidentiality, and the potential risks and benefits associated with the study.
- Ethical considerations also involve obtaining informed consent from participants and ensuring compliance with institutional review boards or ethical committees.
Nursing Research Proposal Outline
| Introduction | An overview of the research topic and its significance |
| Literature Review | Summary of existing literature and theoretical frameworks |
| Research Question | A clear formulation of the main research question |
| Study Design | Explanation of the chosen qualitative research methods and their appropriateness |
| Data Collection | Details of how data will be collected, such as interviews or observations |
| Data Analysis | Description of the thematic analysis process and data interpretation |
| Ethical Considerations | Discussion of ethical principles to be followed in the research |
| Limitations | Acknowledgement of potential limitations and how they will be addressed |
| Conclusion | Summary of the study’s potential impact and future directions |
List of Nursing research proposal topics
- Racial and ethnic disparities in nursing care
- The impact of technology on nursing care
- Prevalence and determinants of burnout in nurses
- Quality of life for people with chronic illnesses served by nurses
- Effectiveness of nurse-led interventions for short-term weight loss in adults
- Nursing home adjusted Living Experience Surveys: measuring resident satisfaction and quality of life
- Identification and characterization of health disparities among LGBT elders in long-term care facilities
- Role of nurses in the early detection and management of cancer diagnosis
- Effects of delegation on nurse burnout, patient safety, and coordination of care
- The use of technology in home health care: a study of patient and nurse perspectives11. The impact of nurse staffing on patient safety
- Effectiveness of Nurse-led interventions for promoting healthy physical Activity in hospitalized patients.
- The role of nurses in the development and implementation of evidence-based pain management guidelines
- Effectiveness of patient-centred communication interventions to reduce bed sores in nursing home residents
- Identification and characterization of best practices for providing hospice care
- Nurse-led stress reduction interventions for long-term care staff
- Nurses’ perceptions of work-life balance: a qualitative study
- Development and evaluation of a web-based tool to support caregiver adherence to oral health care guidelines among long-term care residents
- Effects of sleep deprivation on nurses’ cognitive performance, satisfaction with work, and daytime sleepiness
- A study exploring the association between nurse staffing levels and rates of infection in a university hospital setting
- A qualitative study exploring how nurses manage transitions from inpatient to outpatient settings
- The use of social media by nurses in an acute hospital setting
- Nurses’ experiences with burnout: a cross-sectional study
- Nurse preparedness for pandemic influenza: an examination of the role of professional development
- The use of telehealth in long-term care settings: a study of nurses’ experiences
- Nurses’ experiences with chronic pain: a qualitative study
- The impact of the Affordable Care Act on the workforce and nursing
- Nursing care plans for patients with dementia: a systematic review
- Implementation of evidence-based interventions for preventing falls in older adults living in long-term care facilities
- Nurse staffing and quality of patient care: a cross-sectional study
- Use of social media by nurses during preoperative assessment
- Nurses’ perceptions of resident safety in an acute hospital setting: a qualitative study
- The effects of nurse staffing on patient satisfaction and outcomes in an acute hospital setting
- A comparative study investigating the use of videoconferencing among nurses in different specialties
- A qualitative study exploring how nurse educators use technology to engage students in online learning environments
- Examining the effect on patient safety when using electronic health records to order medications on off-hours
- Nurse staffing, work demands, and burnout in neonatal intensive care units 38. Factors that predict nurses’ decision to leave their jobs
- Effects of nurse-led interventions to improve care for veterans with chronic pain
- The use of wearable technology in hospitals: a systematic review
- Review and assessment of technologies used to support nurses during surgery
- Nursing care plans for patients with cancer: a systematic review
- Nurse-led interventions to prevent falls in older adults living in long-term care facilities: a systematic review
- The use of electronic health records to inform clinical decision making: a systematic review
- Implementation of evidence-based interventions to improve patient safety in hospitals
- A qualitative study exploring how nurses use technology in the workplace
- Factors influencing nurse satisfaction with their work and workplace culture
- Identification and assessment of best practices for preoperative patient communication in the surgical setting
- Effectiveness of nurse-led stress reduction interventions on nurses’ burnout
- Nurse staffing, workload, and burnout in intensive care units: a cross-sectional study
- There are many other nursing research proposal topics that can be explored in order to improve patient care .
Some additional potential nursing research proposal topics include:
- Assessing the effectiveness of nurse-led interventions for reducing readmissions among hospitalized patients
- Evaluating the impact of nurse call patterns on patient safety
- Analyzing the influence of nurse staffing levels on patient outcomes
- Determining the best methods for measuring patient satisfaction with nurse care
- Studying the factors influencing nurse decision making
- Investigating the feasibility and effectiveness of using remote patient monitoring technology to improve patient care
DNP Research proposal topics
There are countless nursing research proposal topics that could be explored in a doctoral or post-doctoral program. Below is a list of some DNP Research proposal topics consider:
- Investigating the feasibility and effectiveness of using remote patient monitoring technology to improve patient care
- The effect of sleep deprivation on nurses
- The use of technology in nursing care
- Investigating the relationship between patient satisfaction and nurse retention
- Studying nutrition-related issues in the context of nursing
- Assessing the impact of patient satisfaction on nurse recruitment and retention
- The relationship between patient satisfaction and nurse retention
- Investigating the feasibility of using remote patient monitoring technology in healthcare settings
- Evaluating the impact of patient satisfaction on nurse retention
- Research the best methods for measuring patient satisfaction with nurse care
- Studying the feasibility of using remote patient monitoring technology in healthcare settings
Check out the additional DNP Research proposal topics as suggested by a Nursing Instructor
- Nursing research on dementia care
- Nursing research on neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) management
- Nursing research on palliative care
- Nursing research on wound healing and reconstruction 5. Nursing research on pediatric health nursing
- Nursing research on geriatric care
- Nursing research on pharmacology for nursing
- Nursing research on infection control in the acute care setting
- Nursing research on nutrition for nursing
- The Effect of Health Education on Patient Outcomes
- Development and Evaluation of Nursing Intervention Programs
- Assessment of Patient Satisfaction with Nursing Services
- Advocating for Improved Patient-Nurse Communication
- Assessing the Effectiveness of Interventions to Address Nurses’ Burnout
- Investigating the Relationship between Nurse workload and Patient outcomes7. Evaluating the Impact of Technology on Nursing Care
- Investigating the Relationship between Professionalism and Patient Outcomes
- Studying Nutrition-Related Issues in the Context of Nursing
- Evaluating Patient-Nurse Interactions in the Context of Home Health Services
The list of DNP Research proposal topics above should guide you in creating a Research proposal.
Current Nursing research proposal topics
Nursing research proposal topics can vary greatly, depending on the type of research you’re looking to conduct. Some common topics include:
- The effects of sleep deprivation on nurses
- The effect of patient communication skills on nurses’ outcomes
- How to improve patient safety in nursing care
- How to reduce readmissions among hospitalized patients
- Study the feasibility of using remote patient monitoring technology in healthcare settings
- Evaluate the impact of patient satisfaction on nurse recruitment and retention
- Evaluate the impact of nurse staffing levels on patient outcomes
- Research the feasibility of using remote patient monitoring technology in healthcare settings
- Research the impact of patient satisfaction on nurse recruitment and retention
- Opioid use in the elderly
- Preterm birth and neonatal care
- Mobile health technology in nursing
- Nursing home quality improvement
- The impact of social media on nursing
Nursing research proposal topics can vary greatly, so it’s important to select a topic that is of interest to you and that will help you to improve patient care .
Nursing research proposal writing tips
When preparing your nursing research proposal, it’s important to keep the following tips in mind:
- Be organized
Planning and organizing your data will make your research proposal more concise and easier to read. Start by identifying the specific question you want to answer, and then list all the relevant sources that you consulted in order to reach your conclusions. Use headings and subheadings to help organize your information , and be sure to include detailed citations for all sources used.
- Use effective writing techniques
To produce a well-written research proposal, use effective writing techniques such as strong thesis statements , clear language, and well-organized data. You should also make use of persuasive arguments, vivid descriptions, and concrete examples in order to make your case for the proposed study .
- Include references
In order for your nursing research proposal to be accepted, it must include references from reliable sources that support your findings. Always cite the source where you obtained the data presented in your proposal, as well as any other sourcesthat you used in order to support your arguments.
- Make sure your proposal is properly formatted
Your nursing research proposal should be properly formatted and error-free in order to be accepted for review. Always use the correct style and grammar when writing, and make sure all data is properly referenced. avoid using excessive jargon or acronyms, and try to keep your presentation as concise as possible.
- Submit your proposal well in advance of the deadline
The sooner you submit your proposal, the better chance you have of being accepted for review. Make sure to follow the submission guidelines outlined by the journal you are submitting to, as well as the submission system specific to that journal .
Nursing Research Proposal Examples
- Evidence-Based Practice Project Proposal Research Design Comparison
- Evidence-Based Practice Project Proposal Presentation
- Evidence-Based Practice Project Proposal: Organizational Culture and Readiness
- Project Proposal Identification of Nursing Practice Problem Assignment
- EBP Proposal – Section E: Duck’s Change Curve Model
- Capstone Project Change Proposal Presentation
- Draft Proposal Development 1 Part 2 of Chapter 1
- Evidence-Based Practice Proposal – Complete Proposal – Sample Project
- Evidence-Based Practice Proposal – Evaluation of Process – Solved Essay
- Evidence Based Practice Proposal: Implementation Plan – Solved Essay
- Evidence-Based Proposal – Solved Essay
- Benchmark – Community Teaching Plan: Community Teaching Work Plan Proposal Example – Solved Essay
- Evidence-Based Practice Project Proposal
In this article, we will provide you with some ideas for nursing research proposal topics that can be used in any discipline. Whether you are interested in studying public health issues or improving patient care through innovative research methods, there is likely something on this list that appeals to you. So get started on your Nursing Research Proposal now by placing an order with us.
Nursingstudy.org has the top and most qualified writers to help with any of your assignments. All you need to do is place an order with us

Working On an Assignment With Similar Concepts Or Instructions?
A Page will cost you $12, however, this varies with your deadline.
We have a team of expert nursing writers ready to help with your nursing assignments. They will save you time, and improve your grades.
Whatever your goals are, expect plagiarism-free works, on-time delivery, and 24/7 support from us.
Here is your 15% off to get started. Simply:
- Place your order ( Place Order )
- Click on Enter Promo Code after adding your instructions
- Insert your code – Get20
All the Best,
Have a subject expert Write for You Now
Have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, what you'll learn.
- Nursing Careers
- Nursing Paper Solutions
- Nursing Theories
- Nursing Topics and Ideas
Related Posts
- How to Write a DNP Project Executive Summary: Comprehensive Guide for Nursing Students
- DNP Project Gantt Chart Guide for Nursing Students
- How to Prepare a Stakeholder Management Chart for a DNP Project: Tips and an Example
Important Links
Knowledge base.
Nursingstudy.org helps students cope with college assignments and write papers on various topics. We deal with academic writing, creative writing, and non-word assignments.
All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. All the work should be used per the appropriate policies and applicable laws.
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Phone: +1 628 261 0844
Mail: [email protected]

We Accept:

@2015-2024, Nursingstudy.org
- Dean's Message
- Mission Statement
- Diversity At VUSN
- Our History
- Faculty Fellows & Honors
- Accreditation
- Privacy Policy
- Academic Programs
- Master of Science in Nursing
- Master of Nursing
- Doctor of Nursing Practice
- PhD in Nursing Science
- Post-Master's Certificate
- Postdoctoral Program
- Special (Non-Degree) Students
- Admissions Information
- Admissions Requirements
- MSN Admissions
- MN Admissions
- DNP Admissions
- PhD Admissions
- Post-Master's Certificates
- Postdoctoral Admissions
- Center for Research Development and Scholarship (CRDS)
- Signature Areas
- CRDS Behavorial Labs
- Research Resources
- Faculty Scholarship Program
- Research Faculty
- Preparing For Practice
- Faculty Practice Network
- Credentialing Process
- Faculty Practice History
- Vanderbilt Nurse-Midwifery Faculty Practice
- What is Advanced Practice Nursing?
- Preceptor Resources
- The Vanderbilt Advantage
- Making A Difference
- Informatics
- Global Health
- Organizations
- Veterans/Military
Examples of Research Questions
Phd in nursing science program, examples of broad clinical research questions include:.
- Does the administration of pain medication at time of surgical incision reduce the need for pain medication twenty-four hours after surgery?
- What maternal factors are associated with obesity in toddlers?
- What elements of a peer support intervention prevent suicide in high school females?
- What is the most accurate and comprehensive way to determine men’s experience of physical assault?
- Is yoga as effective as traditional physical therapy in reducing lymphedema in patients who have had head and neck cancer treatment?
- In the third stage of labor, what is the effect of cord cutting within the first three minutes on placenta separation?
- Do teenagers with Type 1 diabetes who receive phone tweet reminders maintain lower blood sugars than those who do not?
- Do the elderly diagnosed with dementia experience pain?
- How can siblings’ risk of depression be predicted after the death of a child?
- How can cachexia be prevented in cancer patients receiving aggressive protocols involving radiation and chemotherapy?
Examples of some general health services research questions are:
- Does the organization of renal transplant nurse coordinators’ responsibilities influence live donor rates?
- What activities of nurse managers are associated with nurse turnover? 30 day readmission rates?
- What effect does the Nurse Faculty Loan program have on the nurse researcher workforce? What effect would a 20% decrease in funds have?
- How do psychiatric hospital unit designs influence the incidence of patients’ aggression?
- What are Native American patient preferences regarding the timing, location and costs for weight management counseling and how will meeting these preferences influence participation?
- What predicts registered nurse retention in the US Army?
- How, if at all, are the timing and location of suicide prevention appointments linked to veterans‘ suicide rates?
- What predicts the sustainability of quality improvement programs in operating rooms?
- Do integrated computerized nursing records across points of care improve patient outcomes?
- How many nurse practitioners will the US need in 2020?
PhD Resources
- REQUEST INFO
- CAREER SERVICES
- PRIVACY POLICY
- VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY
- VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER
DISTINCTIONS

- Practice Test
- Fundamentals of Nursing
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Medical and Surgical Nursing
- Perioperative Nursing
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing
- Maternal & Child Nursing
- Community Health Nursing
- Pathophysiology
- Nursing Research
- Study Guide and Strategies
- Nursing Videos
- Work for Us!
- Privacy Policy

- Nursing Notes
200+ Great Ideas of Nursing Research Topics to Get Started

Running out of topic ideas for your nursing research paper?
Stay on this page to find really cool and helpful lists of interesting research topics for your nursing dissertation or thesis.
What are Some Cool topics to Research?
Whenever students are asked to work on a research paper or present their thesis, the very first concern for them is choosing a unique, interesting, and research-worthy topic that makes their research significant and has enough future scope.
When it comes to finding a unique topic without working on something that’s already been done, most of the nursing and healthcare students struggle. A good research topic should be unique, relevant to current times, and have future scope as well. And you’ll find all three qualities in the topics mentioned below:
1. Primary Healthcare Nursing Research Topics
Primary healthcare refers to essential or basic health care service based on socially acceptable and scientifically sound methods and technology. Since it includes physical, social, emotional, and mental well-being, there are many topics for nursing scholars to explore:
- Strengthening primary healthcare system as the first line of referral system
- Introduction of home health nursing in the community set up
- Primary health care delivery system clinical pathways
- From home visits to home health care: strengthening primary health care delivery system
- Expanding the roles of community health nurses
- Millennial models of health care system
- Strengthening disease surveillance program in the community health set-up
- Home health care of debilitated patients
- Acceptance of evidence-based practice in the primary health care
- Strengthening continuity of care in the community / home health care post hospitalization
- Physical rehabilitation and occupational therapy in the community health care setting
2. Good Research Topics in Healthcare Management
Healthcare management is the management, administration, or oversight of healthcare systems, hospitals, public health systems, and other medical facilities. Since it comprises the overall management of all the work of the hospitals, it opens avenues for a lot of research work. Take, for example, the following:
- Evaluating who is responsible for failure in surgeries?
- Healthcare Contracts Limitations
- Medical Home Service
- Analysing nursing channels that nurses can use for becoming physicians?
- Gender Bias in Nursing Profession
- Starting Private Practice as a Nurse
- Medicare: Pros and Cons
- What are the most appropriate methods for increasing staff retention in a health care setting?
- Nursing Uniform Code Rules
- Role of nurses in enhancing a hospital quality improvement
- Legal Risks with Non-English Patients
- Medical Marijuana: Risk, Benefits, and Management Rules
- Shortage of Men in Healthcare
- Health tracking apps for continuity of care post discharge to home
- Telehealth: the impact of virtual care to urban and rural areas
- Strategic referral system to prevent tertiary hospital congestion
- Clinical pathways for referral system
- Drive-thru pharmacy
- Strenghtening the roles of social works and social workers in the health care team
- Case management approach in the healthcare delivery system
- Defining and application of Expected Length of Stay in patient management
- Impact of case managers in Expected Length of Stay and patient outcomes
- Redefining hospital cultures on bed rest versus mobilization
- Redefining hospital cultures on diet and food services
- Redefining hospital cultures on the assumption of the sick roles
- Strict implementation of Expected Length of Stay to prevent hospital congestion
- Roles of Case manager in the Clinical pathways
- Case Manager as a new nursing role an specialization
- Nurse navigator as a new form of nurse entrepreneurship
- Case management clinical pathway for smooth admission, patient flow and continuity of care after discharge
- Increase nursing specialization
- Internet savvy for healthcare providers
3. Nursing Research Topics about Pain Management
Pain management, in nursing, includes study of all the interventions nurses can make during their hospital hours – mainly to relieve a patient’s pain or ailments through medicinal interventions. Pain is complex, with many treatment options such as therapies, medicines, and also mind-body techniques. Nursing research scholars can research about the following topics:
- Pain management in children suffering from life-limiting illnesses: learning about the best practices
- Headache Treatment Protocol
- A closer look at hemophilia patient’s pain management
- Myofascial Pain Rehabilitation
- Labor and delivery: best practices for pain management
- Using Opioid for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Fetal pain perception: analysis by medical experts
- Innovative Injection Use
- Therapeutic Injections: Cons & Pros
- Cognitive hypnotherapy application: how effective are they in pain management?
- Evaluating the effectiveness of Benson’s relaxation therapy as a pain management practice.
- Post-discharge pain-management strategies: evaluating their effectiveness in a health care setting?
- Phantom Pains Phenomenon
- Pain management in cancer patients: best practices according to expert nurses
- Spinal cord nerve injury related to chronic constipation
- Mobile pain unit
4. Pediatric Nursing Research Topics
In Pediatric nursing, the nursing staff is responsible for medical care of the children and neonates, and adolescents – mainly in a day-clinic or the in-patient setting. Though the main role of child health nursing is administering procedures and medicines to all children as per their prescribed nursing care plans, the research scholars can write papers on the following topics:
- Speech Disorders Therapy
- ADHD Causes & treatment
- Prevalence of misdiagnosis in child health or paediatric ward
- Vaccination & Autism
- Systematic review of range of child health nursing services in UK
- Antibiotic Resistance in Preschool Children
- Mental and Emotional health of children under 10
- Eating Disorders in Children
- Social Media Impact on Teenagers
- Seizures Causes in Infants
- Teething issues in children under 10
- Psychological Aspects of Infant Care
- Use of social media platforms in preparation and prevention of hospital phobia among pediatric groups
- Family engagement in the pediatric care by using hospital information system
- Safety and efficacy of telehealth for pediatric patients
What are the Current issues in Nursing?
Nursing is a high-pressure job. It demands patience, determination, and perseverance. As a high-pressure job, it gets quite challenging and leads to issues from time to time. Some of the examples being staff shortages, long working hours, workplace hazards, personal health, and workplace violence. All of these can be addressed in nursing research papers:
- Analysis of the registered nurse workforce and the relationship to work environments
- Transforming loss: A developing concept for nursing
- Nursing Staff Shortages
- Nursing Practitioners
- Meeting Patient Expectations: A challenge for nurses
- Biggest obstacles nurses face in their education and maintaining career alongside
- Workplace Violence and Hazards Nurses face
- Diversity in Healthcare
- Importance of Community Nursing
- Future of Nursing in the Digital Age
- What measure can a nurse take for helping a person with their eating disorder?
- Clinical Nurse Roles
- How can nurses help in treating patients who already know they don’t have a survival rate?
- Ethics and Homeless People Treatment
- Critical Care Nursing Management
- A nurse’s role in helping and assisting patients with chronic diseases?
- Nursing Theorists Works
- Remote Intensive Care Unit
- Stress Management Practice for Nurses Working in Night Shifts
- Between Career & Professional Service
- Preceptorship and training after distant education program and online learning
- Centralized infectious disease surveillance
- Centralized reporting of chronic diseases
- Patient become more educated: the pros and cons of social media
- Fake news and misinformation on health related issue with the rise of social media platforms
- BPO and call centers for medical procedures booking and admission to decongest emergency room
- Application of BPO in the quality assurance monitoring in documentation
What are Some of the Research Topic Ideas in Surgical Nursing?
- Moral distress among nurses in Surgical units
- Patient’s satisfaction and experience about care provided by nurses in the surgical units
- Organizational effects on patient satisfaction in surgical units
- Medical-Surgical nurses and their perceived leadership abilities as responders in patient deterioration events
- Role of Nurses in Surgical Wards
- Medical-surgical nursing: Critical thinking in client care
- Pain assessment and management in surgical nursing
- Understanding technology in contemporary surgical nursing
- Understanding Medical surgical nursing as an integrated approach
- Standardising fast-track surgical nursing care
- Mobilization team for the fast recovery of post-operative patients
- Use of telehealth for pre-operative preparations and elective surgical admissions to lessen hospital length of stay among surgical patients
- Continuity of care post surgery in the community health care
What have been some of the more important nursing research questions discussed in nursing class?
If you are here to find more important topics for your nursing dissertations, then scroll through this section for topics that are often discussed in nursing classes. Nursing research articles and topics change over time. However, we find these relevant to current times and challenges in healthcare:
1. Research topic ideas for Midwifery Nursing
Nurse-midwife, as a licensed healthcare professional, specialises in child birth and also women’s reproductive health. Apart from attending pregnant women during childbirth, they are responsible for several roles during emergencies, and pre and postnatal care. Hence, opening avenues for research topics such as:
- Role of nurses in improving patient safety during childbirth: Evidence from obstetric trauma
- Evaluate the impact of delayed umbilical cord clamping after child birth
- Maternal & Neonatal Practices in Rural Areas
- Emerging trends in obstetrical and midwifery nursing
- First Antenatal Appointment Analysis
- Limiting interventions during a low-risk labour
- Mental Illness & Post-natal Period
- Analysing the role of prenatal care in pregnant women
- Shift Study Midwives & Length
- Evaluating impact of AIDS and Hepatitis B in the pregnant women
- Self-Instruction Kits & Natal Safety
- Studying advanced trends in obstetrics and gynaecology
- Midwifery Continued Care
- Evaluating pros and cons of labouring in water
- Gestational Weight Gain Challenges
- Vitamin D’s role as a supplement during pregnancy
- Studying clinical reasoning integration into midwifery practice
- Obese Pregnant Women Safety Rules
- A decade after BEmONC and CEmONC
2. Health Promotion Research Topics
Health promotion mainly comes from behavioral social science which draws from the environmental, biological, psychological, medical, and physical sciences for promoting health and preventing diseases. For health promotion, the research topics include the following:
- Healthcare Dangers of Digital Age
- Benefits and Shortages of Telemedicine
- Healthy living and Preventive medicine for Senior Citizens
- Role of School Nurses
- Obstacles for Smoking cessation
- Healthy Eating & Sports
- Causes of Youth Inactivity
- Roles of Parents for Healthy Lifestyle of Children
- Obesity and Mental Stability
- Pharmacist Responsibility
- Social Media and Educational Strategies
- HealthBank as new form of medical insurance inside the hospital organization
- Collaboration of private health insurance company with public and private hospitals
3. Adult Research Topics for Nursing Students
As a nursing scholar, you can also write research papers on adult healthcare, disease prevention, and management. Take, for example, reasons behind anxiety disorders in adults. Find more topics in the list below:
- Nurses’ experiences with urinary catheter insertion: A qualitative focus group study
- Clinical Cardiology Innovations
- CV Imaging Process
- Migraine Case Example
- Bipolar Disorder Non-Chemical Practices
- Mental Health & Psychiatric Care in Adults
- Online nursing education program
- Self care in Nursing
- Home health care for longterm vented patients
- Clinical Instructor, Preceptorship, Educator and Professor as specialized field requiring licensure
- Specialization program in nursing education
4. Geriatric Care Nursing Journal Topics
Nurses working in Geriatric care and management are responsible for coordinating and planning care of the elderly people dealing with mental or physical disabilities. Some of the research work topic ideas for geriatric care include the following:
- Cerebrovascular Disease and Stroke in Elderly people
- Pain in elderly people: Assessment and Management
- Joint Disorders Study in Elderly Population
- Rapid Nutritional assessment in Elderly
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Bladder Cancer Therapy
- Atrial Fibrillation Study
- Critical Care Requirements
- Cardiovascular Risk Reduction
- Geriatrics Ethics
- Restless Legs Syndrome
- Parkinson’s Disease Precautions
- Geriatric care clinical pathways of care: holistic approach
What are the recent nursing research paper topics?
If you’re facing the challenge of choosing a recent nursing research topic, we’ve got your back. Many nurses, including experienced and freshers, are faced with this challenge at some point. But there’s no need to panic. So, without further ado, let’s jump-start the list of most recent research topics for nursing students:
1. Women’s Health Nursing Research Topics
Research topics related to women’s health are always trending, relevant, and have future scope as well. Hence, these topics are still worth exploring and researching:
- Culture affects women’s health
- Substance Abuse and Addiction in Women
- Menopause Challenges
- Infertility Ethical Rules
- Ovarian Cancer and Ovarian Disorder Analysis
- Modern Neonatal Practices
- Pregnancy Prevention Measures
- Sepsis after labour
- Cosmetic Dermatology
- Cystic Fibroids
- Sleep Disorders in Women
- Reproductive Endocrinology
- Women’s Sexual Health Disorders
- HPV and Cervical Cancer
- Vaginal Atrophy Causes
- Sleep disturbances in Women
2. Mental Health Nursing Research Articles Topics
Research papers focusing on mental health are still one of the most read and referred papers. And there’s still more scope for research on topics such as:
- Evaluating the concept of Integrated Mental and Physical Health Care
- Psychiatric Nursing and Mental Health
- Possible skills required for Nurses in Mental health care setting
- Assessing the mental health of nurses
- Depression Causes
- Schizophrenia Diagnostics
- Alcohol Addiction Disorders
- Bipolar Disorder
- Studying the impact of PTSD in the Army Veterans
- Impact of Video Games on Teenage Aggression
- Stress Among Police Officers
- Psychiatric Patient Ethics
- Forbidden Substances: Prevention and Use
- Bioterrorism Medicine
- Physical Traumas & Recovery Methods
- Application of Nursing Case Management in Psychiatry
Nursing leaders have called for research focusing on which of the following topics?
If you’d like to take an expert’s opinion before choosing a topic for your nursing dissertation, this section will be helpful. Our list of best nursing research topics doesn’t end here. We’ve got here more interesting topics that are recommended by nursing leaders and experts. Take a look at some more relevant topics:
- Preterm Labor Dangers
- Labor and Delivery Management Practices
- Saving Mother & Child Challenges
- Abortion Care Ethical Side
- Adolescent Gynecology Education
- Antenatal Care Recommendations
- Hypertensive Disorders Causes
- Newborn Resuscitation Rules
- Caesarean Section Preparation
- Delivery Room Behavior Checklist
- Nurses play vital roles in healthcare. Why are they invisible in the media?
- Increasing nursing research capacity: The roles of nurse scientists within healthcare systems
- Microeconomics and macroeconomics for sources of hospital funds
- Diverting patients and funds to economical services
- Culture vs evidence based practice
- Social media influencer in health education dissemination
- Acceptance of evidence based practice in the hospital
- Impact of socio-cultural nursing to evidence-based practice
- Hindrances in the implementation of evidence-based practice
- Nursing faculty shortage and brain-drain
- Online continuing professional education and development
Academic Writing Service: Work Directly With the Experts
The are list of best nursing research paper topics ends here. However, we still have something helpful for you. Writing a dissertation or a nursing paper is time consuming – needless to mention the mental exertion. That explains why the majority of students prefer seeking research writing help.
Take, for example, apessay.com , a place where you can get in touch with registered experts who have successfully passed their competency examinations to provide academic writing service at an affordable rate. The three USPs include plagiarism free content, complete privacy and security standards to protect your personal info, and money-back guarantee.

What makes apessay.com academic writing service unique is you can work in direct cooperation with your preferred writer and consult them for everything – from choosing a relevant topic to revisions for final submission.
Feel free to get professional help from nursing research paper writing service which will take care of your nursing papers online.
Final Thoughts
Nursing research topics for a dissertation or thesis should not be difficult to find through the ideas suggestion above. Just make sure that you provide a twist (segment or expand the topic, perhaps) and come up with a unique topic for your paper.
During the initial stages of finalising a nursing research topic, you can struggle with a lot of choices or overwhelming information. However, when you start to consider a research topic’s limitations and scope, and outline your topic into a question, you’ll be able to get a better understanding of the topic you can manage in terms of workload.
We hope these nursing research topics mentioned above help you find that unique thesis statement or idea you’re looking for. In case you’re still having a tough time making a choice, leave us a comment or drop a mail, and we will direct you to better resources.
- https://www.journals.elsevier.com/applied-nursing-research/recent-articles
- https://www.syberscribe.com.au/blog/10-emerging-trends-healthcare-technology-2019-beyond/
- https://www.purdueglobal.edu/blog/nursing/top-10-nursing-trends/
- http://ojin.nursingworld.org/
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Evidence-based practice in nursing: beyond the scientific proof of care, nursing research definition: the importance and nurses roles.
It’s was very helpful for me
Disparities in enumeration of staff nurses in developing countries are not researched on.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Privacy Policy

Home » 500+ Nursing Research Topic Ideas
500+ Nursing Research Topic Ideas
Table of Contents

Nursing research plays a crucial role in advancing healthcare and improving patient outcomes. As a field that is constantly evolving, there is a great need for new ideas and innovative approaches to address the challenges faced by nurses in their day-to-day practice. In this article, we will explore some exciting nursing research topic ideas that can help guide the development of new studies and inspire nurses to make meaningful contributions to the field. From exploring the impact of technology on nursing practice to investigating the effectiveness of alternative therapies, there is no shortage of interesting and important topics to explore in the world of nursing research.
Nursing Research Topic Ideas
Nursing Research Topic Ideas are as follows:
- The effectiveness of telemedicine in providing nursing care.
- The relationship between nurse staffing levels and patient outcomes.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on medication adherence in chronic disease management.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing burnout among nurses.
- The influence of cultural competence on patient satisfaction with nursing care.
- The effects of virtual reality simulation training on nursing students’ clinical competencies.
- The impact of nurse practitioner-led care on chronic disease management in primary care.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led discharge planning on patient outcomes.
- The influence of nurse-to-patient ratios on the incidence of hospital-acquired infections.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led health coaching on lifestyle modifications in patients with chronic diseases.
- The effects of interprofessional collaboration on patient outcomes in acute care settings.
- The impact of nurse-led patient education on medication adherence in older adults.
- The relationship between nurse work environment and patient safety outcomes.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led cognitive-behavioral therapy on anxiety and depression in patients with chronic pain.
- The influence of nurse staffing levels on patient satisfaction with nursing care.
- The effects of a nurse-led palliative care program on quality of life for patients with terminal illnesses.
- The impact of nurse-led group therapy on social support and quality of life in patients with chronic illnesses.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led motivational interviewing on smoking cessation in patients with mental health disorders.
- The relationship between nurse staffing levels and patient length of stay in acute care settings.
- The effects of nurse-led behavioral interventions on weight loss and management in patients with obesity.
- The influence of nurse-led interventions on self-care management in patients with heart failure.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led mindfulness-based stress reduction programs on caregiver burden in family caregivers of patients with dementia.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on pain management in patients with sickle cell disease.
- The relationship between nurse staffing levels and patient readmission rates.
- The effects of nurse-led motivational interviewing on medication adherence in patients with hypertension.
- The influence of nurse-led telehealth programs on glycemic control in patients with diabetes.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on patient outcomes in postoperative care.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on patient satisfaction with hospital food services.
- The relationship between nurse staffing levels and patient falls in acute care settings.
- The effects of nurse-led interventions on patient anxiety and stress in the preoperative period.
- The influence of nurse-led interventions on wound healing in patients with chronic ulcers.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on postpartum depression in new mothers.
- The impact of nurse-led transitional care on hospital readmissions in older adults.
- The relationship between nurse work environment and nurse retention.
- The effects of nurse-led music therapy on anxiety and depression in patients with dementia.
- The influence of nurse-led mindfulness-based interventions on sleep quality in patients with insomnia.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on symptom management in patients with cancer.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on patient satisfaction with care coordination.
- The relationship between nurse staffing levels and patient mortality in critical care settings.
- The effects of nurse-led interventions on patient outcomes in end-of-life care.
- The impact of mindfulness meditation on the mental health of nursing students.
- The effect of patient education on the adherence to medication regimens in older adults.
- The role of nurse-led interventions in improving physical activity levels in sedentary individuals.
- The efficacy of telehealth in managing chronic conditions in rural communities.
- The effect of music therapy on anxiety and pain in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
- The impact of cultural competency training on nursing students’ attitudes towards diverse patient populations.
- The effectiveness of peer support interventions in reducing readmission rates among individuals with heart failure.
- The use of virtual reality in nursing education to improve clinical decision-making skills.
- The role of family caregivers in end-of-life care decision making.
- The impact of nurse-led discharge planning on hospital readmission rates.
- The effect of a structured communication tool on interdisciplinary communication and collaboration in acute care settings.
- The role of nurses in promoting vaccination uptake in underserved communities.
- The impact of early mobilization on functional outcomes in critically ill patients.
- The effectiveness of an interdisciplinary team approach in managing chronic pain in older adults.
- The role of nursing in addressing the opioid epidemic.
- The effect of a nurse-led weight management program on obesity-related health outcomes.
- The impact of technology-based interventions on medication adherence in individuals with psychiatric disorders.
- The effectiveness of a nursing-led smoking cessation program in hospitalized patients.
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy sleep habits in children.
- The effect of a nurse-led intervention on caregiver burden in family caregivers of stroke survivors.
- The impact of nurse-led motivational interviewing on lifestyle behavior change in individuals with chronic conditions.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led care transitions in reducing hospital readmissions.
- The role of nursing in promoting advance care planning among older adults.
- The impact of a nurse-led education program on self-care management in individuals with diabetes.
- The effect of nurse-led education on medication adherence in individuals with hypertension.
- The role of nurses in identifying and addressing social determinants of health in underserved populations.
- The impact of a nurse-led exercise program on physical function and quality of life in older adults.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led education on smoking cessation in pregnant women.
- The role of nurses in promoting health literacy among diverse patient populations.
- The effect of a nurse-led fall prevention program on fall-related injuries in older adults.
- The impact of a nurse-led education program on medication safety in hospitalized patients.
- The effectiveness of a nurse-led mindfulness-based stress reduction program in individuals with chronic pain.
- The role of nurses in managing the care of individuals with multiple chronic conditions.
- The effect of nurse-led patient education on the prevention of hospital-acquired infections.
- The impact of nurse-led coaching on self-management in individuals with heart failure.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led care coordination in improving care transitions for individuals with complex medical needs.
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy eating habits in children and adolescents.
- The effect of a nurse-led symptom management program on quality of life in individuals with advanced cancer.
- The impact of a nurse-led program on the self-efficacy of individuals with chronic conditions.
- The role of nurses in promoting sexual health education among adolescents.
- The effect of a nurse-led peer support program on mental health outcomes in individuals with substance use disorders.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing hospital-acquired pressure ulcers.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led education on nutrition and physical activity in pregnant women.
- The role of nurses in addressing health disparities in marginalized communities.
- The effect of nurse-led mindfulness interventions on the mental health of healthcare providers.
- The impact of a nurse-led program on medication adherence and quality of life in individuals with HIV/AIDS.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in reducing healthcare-associated infections in long-term care facilities.
- The role of nurses in promoting palliative care for individuals with advanced dementia.
- The effect of a nurse-led exercise program on cognitive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing falls in hospitalized older adults.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on reducing medication errors in hospitalized patients.
- The role of nurses in promoting sexual and reproductive health among LGBTQ+ individuals.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on improving medication adherence in individuals with mental health conditions.
- The impact of nurse-led coaching on self-care management in individuals with chronic kidney disease.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on improving sleep quality in individuals with chronic pain.
- The role of nurses in promoting oral health in individuals with intellectual disabilities.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on reducing the incidence of hospital-acquired delirium.
- The impact of a nurse-led program on the self-care management of individuals with heart failure.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led education on self-care management in individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy lifestyle behaviors in adolescents with type 1 diabetes.
- The effect of a nurse-led program on the prevention of central line-associated bloodstream infections.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing healthcare costs for individuals with chronic conditions.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on improving the quality of life of individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- The role of nurses in promoting early detection and management of sepsis in hospitalized patients.
- The effect of nurse-led education on promoting breastfeeding among new mothers.
- The impact of a nurse-led program on the management of chronic pain in individuals with sickle cell disease.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on improving medication adherence in individuals with heart failure.
- The role of nurses in promoting health literacy and patient empowerment among individuals with low health literacy.
- The effect of a nurse-led program on the prevention of catheter-associated urinary tract infections.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing readmission rates in individuals with heart failure.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on improving medication adherence in individuals with chronic kidney disease.
- The role of nurses in promoting self-care management among individuals with depression.
- The effect of a nurse-led program on improving the quality of life of individuals with spinal cord injuries.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing medication errors in outpatient settings.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led education on promoting healthy lifestyle behaviors among older adults with chronic conditions.
- The role of nurses in promoting self-management among individuals with schizophrenia.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on improving mental health outcomes in individuals with chronic pain.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing hospital length of stay for individuals with heart failure.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on improving the quality of life of individuals with chronic hepatitis C.
- The role of nurses in promoting pain management strategies for patients with sickle cell disease.
- The effect of a nurse-led education program on improving the quality of life for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and their caregivers.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing healthcare-associated infections in the neonatal intensive care unit.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on improving self-care management and quality of life for patients with chronic kidney disease.
- The role of nurses in promoting patient safety through effective communication strategies.
- The effect of a nurse-led program on reducing readmission rates in patients with congestive heart failure.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on improving end-of-life care for patients with advanced cancer.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led education on improving the nutritional status of patients with diabetes.
- The role of nurses in promoting evidence-based practices for the prevention and treatment of pressure ulcers.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on reducing anxiety and depression in patients with chronic pain.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing medication errors in the emergency department.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led education on promoting tobacco cessation among patients with respiratory diseases.
- The role of nurses in promoting culturally competent care for patients from diverse backgrounds.
- The effect of a nurse-led program on improving sleep quality and quantity for patients with sleep disorders.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on improving self-management and quality of life for patients with heart failure.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on reducing the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill patients.
- The role of nurses in promoting early recognition and management of sepsis in the emergency department.
- The effect of nurse-led education on improving patient satisfaction with pain management.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing healthcare costs for patients with chronic conditions.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led education on promoting adherence to medication regimens among patients with HIV/AIDS.
- The role of nurses in promoting patient-centered care for patients with chronic diseases.
- The effect of a nurse-led program on improving pain management in patients with dementia.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing the incidence of falls in hospitalized patients.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on improving wound healing in patients with chronic wounds.
- The role of nurses in promoting early detection and management of delirium in hospitalized patients.
- The effect of nurse-led education on improving patient outcomes after cardiac surgery.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing healthcare-associated infections in long-term care facilities.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led education on promoting healthy eating behaviors among adolescents with obesity.
- The role of nurses in promoting patient safety through effective hand hygiene practices.
- The effect of a nurse-led program on improving functional status and quality of life for patients with Parkinson’s disease.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing readmission rates in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on improving patient outcomes after hip replacement surgery.
- The role of nurses in promoting effective communication between patients and healthcare providers.
- The effect of nurse-led education on improving medication management in patients with multiple chronic conditions.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing healthcare costs for patients with mental health conditions.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led education on promoting physical activity among patients with cardiovascular diseases.
- The role of nurses in promoting patient-centered care for patients with substance use disorders.
- The effect of a nurse-led program on improving self-care management and quality of life for patients with asthma.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing the incidence of central line-associated bloodstream infections in the intensive care unit.
- The role of nurses in promoting resilience among healthcare providers during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on improving adherence to tuberculosis medication.
- The impact of nurse-led programs on improving end-of-life care in hospice settings.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on reducing the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia.
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy sleep habits in hospitalized children.
- The effect of nurse-led education on improving wound care management in individuals with diabetes.
- The impact of a nurse-led program on improving patient satisfaction in emergency departments.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on reducing medication errors in pediatric settings.
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy aging among older adults living in rural communities.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on improving oral hygiene in individuals with cancer undergoing chemotherapy.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing the incidence of hospital-acquired infections in neonatal intensive care units.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led education on improving pain management in individuals with sickle cell disease.
- The role of nurses in promoting mental health awareness and support in the workplace.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on improving hand hygiene compliance among healthcare providers.
- The impact of a nurse-led program on improving self-management in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions on reducing readmission rates in individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy lifestyle behaviors among individuals with HIV/AIDS.
- The effect of nurse-led education on improving medication adherence in individuals with schizophrenia.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing falls in older adults living in long-term care facilities.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led programs on improving communication and teamwork in healthcare settings.
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy eating habits among adolescents with obesity.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on improving pain management in individuals with cancer.
- The impact of a nurse-led program on improving self-management in individuals with heart failure.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led education on promoting healthy sexuality in individuals with disabilities.
- The role of nurses in promoting mental health among homeless populations.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on improving self-care management in individuals with multiple sclerosis.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing medication errors in geriatric settings.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led programs on improving patient outcomes in acute care settings.
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy coping mechanisms among individuals with chronic pain.
- The effect of nurse-led education on improving wound care management in individuals with venous leg ulcers.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing hospital readmission rates in individuals with chronic kidney disease.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led programs on improving end-of-life care in nursing homes.
- The role of nurses in promoting safe medication administration in pediatric settings.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on improving sleep quality in individuals with depression.
- The impact of nurse-led programs on improving pain management in individuals with fibromyalgia.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led education on improving communication skills among healthcare providers.
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy lifestyle behaviors among individuals with mental health conditions.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on improving self-care management in individuals with chronic heart failure.
- The impact of nurse-led programs on improving patient outcomes in rehabilitation settings.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led education on promoting healthy habits among individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Interesting Nursing Research Topic Ideas
- The impact of nurse-led health education on the management of chronic diseases in low-income communities.
- The effectiveness of using telehealth technology to monitor and manage patients with mental health disorders.
- The role of nursing in promoting ethical and responsible use of AI in healthcare.
- The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health of frontline nurses.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques on reducing burnout among nurses.
- Exploring the experiences of male nurses in a predominantly female profession.
- The impact of nurse-patient communication on patient satisfaction and clinical outcomes.
- The effectiveness of music therapy in reducing anxiety and pain among patients in intensive care units.
- The impact of social media on nursing education and professional development.
- The impact of nurse-to-patient ratios on patient outcomes and nurse satisfaction.
- The use of simulation-based training in nursing education to improve clinical competency.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in reducing hospital readmissions.
- The impact of interprofessional collaboration on patient safety and quality of care.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led smoking cessation interventions in promoting smoking cessation among patients.
- The role of nurses in promoting sexual and reproductive health among adolescent girls.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in improving medication adherence among patients with chronic diseases.
- The impact of cultural competence training on nursing practice and patient outcomes.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in improving sleep quality among shift-working nurses.
- The role of nurses in promoting vaccination uptake among underserved populations.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on improving self-care behaviors among patients with heart failure.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in improving pain management among cancer patients.
- The impact of nurse-led care coordination on improving care transitions for patients with multiple chronic conditions.
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy aging and preventing age-related diseases.
- The effectiveness of peer mentoring programs in promoting professional development among novice nurses.
- The impact of nurse-led palliative care interventions on improving end-of-life care for patients with terminal illnesses.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in reducing falls among elderly patients in long-term care facilities.
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing chronic diseases in the community.
- The impact of nurse-led discharge planning on reducing hospital readmissions and improving patient outcomes.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in improving glycemic control among patients with diabetes.
- The role of nurses in promoting mental health and wellbeing among healthcare professionals.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions in promoting self-management behaviors among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led motivational interviewing in promoting physical activity among sedentary patients.
- The role of nurses in promoting safe medication use and preventing medication errors.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions in improving nutritional status among patients with malnutrition.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in promoting breastfeeding among new mothers.
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy work environments and preventing workplace violence.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions in promoting early detection and management of hypertension.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in improving adherence to antiretroviral therapy among patients with HIV.
- The role of nurses in promoting evidence-based practice and improving patient outcomes.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions in promoting smoking cessation among pregnant women.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in improving sleep quality among patients with obstructive sleep apnea.
- The role of nurses in promoting patient safety and preventing medical errors.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions in improving symptom management among patients with advanced cancer.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in promoting hand hygiene compliance among healthcare workers.
Evidence-Based Practice Nursing Research Topic Ideas
- The effect of nurse-led education on medication adherence in patients with chronic illnesses.
- The use of telehealth to improve patient outcomes in rural communities.
- The impact of music therapy on pain management in postoperative patients.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction in reducing burnout in nursing staff.
- The effect of exercise on the prevention of falls in elderly patients.
- The use of simulation-based training in improving clinical competency in nursing students.
- The effect of nurse-led discharge planning on readmission rates.
- The effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions for agitation in patients with dementia.
- The impact of bedside reporting on patient safety and satisfaction.
- The effect of aromatherapy on anxiety in hospitalized patients.
- The use of standardized protocols to reduce catheter-associated urinary tract infections.
- The effectiveness of peer support in improving diabetes self-management.
- The impact of patient-centered care on outcomes for patients with chronic illnesses.
- The effect of nursing interventions on the prevention of pressure ulcers.
- The use of telemonitoring to improve outcomes in heart failure patients.
- The effect of early mobility programs on outcomes in critically ill patients.
- The effectiveness of team-based care in improving outcomes for patients with complex medical conditions.
- The use of acupressure to manage postoperative nausea and vomiting.
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on the prevention of central line-associated bloodstream infections.
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in reducing symptoms of depression in patients with chronic illnesses.
- The effect of mindfulness-based interventions on pain management in cancer patients.
- The use of telepsychiatry in improving access to mental health care in rural communities.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led smoking cessation interventions.
- The impact of a family-centered care approach on outcomes for critically ill pediatric patients.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on medication adherence in patients with hypertension.
- The use of music therapy to improve sleep in hospitalized patients.
- The effectiveness of patient education in reducing hospital readmissions.
- The impact of nursing interventions on the prevention of falls in hospitalized patients.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on glycemic control in patients with diabetes.
- The use of mindfulness-based interventions to reduce stress in nursing students.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in reducing healthcare-associated infections.
- The impact of a multidisciplinary approach to pain management on outcomes for patients with chronic pain.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on the prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia.
- The use of telehealth to provide palliative care to patients with advanced illnesses.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in reducing the incidence of pressure injuries in long-term care facilities.
- The impact of a nurse-led transitional care program on outcomes for patients with heart failure.
- The effect of a nurse-led sepsis protocol on early recognition and treatment.
- The use of animal-assisted therapy in the management of anxiety and depression in hospitalized patients.
- The effectiveness of a nurse-led motivational interviewing intervention in improving self-care behaviors in patients with chronic illnesses.
- The impact of a nurse-led hand hygiene program on healthcare-associated infections.
- The effect of nurse-led interventions on the prevention of surgical site infections.
- The use of telehealth to provide mental health services to underserved populations.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in improving pain management in elderly patients with dementia.
- The impact of a nurse-led transitional care program on outcomes for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- The effect of a nurse-led program on the prevention of urinary tract infections in long-term care facilities.
Nursing Research Topic Ideas Medical Surgical Nursing
- The Effectiveness of Pre-operative Education on Patient Outcomes in Medical-Surgical Nursing.
- A Comparative Study of the Effect of Manual Turning vs. Mechanical Turning on Pressure Injury Prevention in Hospitalized Patients.
- The Impact of Postoperative Pain Management on the Length of Hospital Stay for Surgical Patients.
- The Role of Nursing Interventions in Reducing the Incidence of Falls in Medical-Surgical Units.
- The Effect of Nursing Shortage on Patient Outcomes in Medical-Surgical Units.
- A Study of Nurse-Patient Communication and its Impact on Patient Satisfaction in Medical-Surgical Units.
- The Efficacy of Non-pharmacological Interventions in Reducing Anxiety and Stress among Medical-Surgical Patients.
- A Comparison of Standardized Nursing Care Plans vs. Individualized Nursing Care Plans in Medical-Surgical Units.
- The Impact of Nurse Staffing Levels on Patient Outcomes in Medical-Surgical Units.
- A Study of Medication Adherence among Medical-Surgical Patients.
- The Effect of Family-Centered Care on Patient Outcomes in Medical-Surgical Units.
- A Study of Wound Care Management in Medical-Surgical Nursing.
- The Impact of Nursing Rounds on Patient Outcomes in Medical-Surgical Units.
- A Comparison of Two Nursing Care Models in Medical-Surgical Units.
- A Study of Pain Management Practices in Medical-Surgical Nursing.
- The Effectiveness of Discharge Planning on Patient Outcomes in Medical-Surgical Nursing.
- A Comparative Study of the Effect of Traditional vs. High-Fidelity Simulation Training on Nursing Competence in Medical-Surgical Units.
- The Impact of Multidisciplinary Rounds on Patient Outcomes in Medical-Surgical Units.
- A Study of Hand Hygiene Practices among Medical-Surgical Nurses.
- The Effect of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Nurses’ Well-being and Job Satisfaction in Medical-Surgical Units.
- A Comparative Study of the Effect of Bedside Shift Reporting vs. Traditional Shift Reporting on Patient Safety in Medical-Surgical Units.
- The Impact of Nursing Education on Pressure Injury Prevention in Medical-Surgical Nursing.
- A Study of Nurse Leadership Styles and their Effect on Patient Outcomes in Medical-Surgical Units.
- The Effect of Teamwork on Patient Safety in Medical-Surgical Units.
- A Comparative Study of the Effect of Electronic Health Records vs. Paper-Based Records on Nursing Documentation in Medical-Surgical Units.
- The Impact of Nursing Knowledge on Medication Safety in Medical-Surgical Nursing.
- A Study of Palliative Care Practices in Medical-Surgical Nursing.
- The Effect of Exercise Interventions on the Rehabilitation of Medical-Surgical Patients.
- A Comparative Study of the Effect of RN-BSN Programs vs. ADN Programs on Nursing Competence in Medical-Surgical Units.
- The Impact of Cultural Competence on Patient Satisfaction in Medical-Surgical Units.
- A Study of Advanced Practice Nursing in Medical-Surgical Units.
- The Effectiveness of Clinical Decision Support Systems on Medication Safety in Medical-Surgical Nursing.
- A Comparative Study of the Effect of Direct vs. Indirect Care on Nursing Workload in Medical-Surgical Units.
- The Impact of Staff Education on Sepsis Management in Medical-Surgical Nursing.
- A Study of Patient Education Practices in Medical-Surgical Nursing.
- The Effect of Nursing Care Models on Patient Safety in Medical-Surgical Units.
- A Comparative Study of the Effect of Nurse-led vs. Physician-led Rounds on Patient Outcomes in Medical-Surgical Units.
- The Impact of Patient Experience on Nurse Job Satisfaction in Medical-Surgical Units.
- A Study of Medication Errors in Medical-Surgical Nursing.
Nursing Research Topics About Community
- The effectiveness of community health worker programs in improving health outcomes among underserved populations
- The role of nurses in promoting community-based health initiatives and prevention programs
- The impact of neighborhood characteristics on health outcomes and health behaviors
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in reducing health disparities in rural communities
- Examining the effects of community-based palliative care programs on end-of-life care
- Investigating the factors influencing healthcare access and utilization among homeless populations
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on vaccination rates in low-income communities
- Assessing the effectiveness of nurse-led telehealth programs in rural and remote communities
- Examining the role of community-based nursing in disaster preparedness and response
- The effects of social determinants of health on maternal and child health outcomes in disadvantaged communities
- Investigating the impact of nurse-led interventions on substance abuse and addiction in community settings
- The effectiveness of community-based health promotion programs in reducing obesity rates
- The impact of cultural competency training on nursing practice in diverse communities
- Examining the effects of community-based nursing on healthcare costs and utilization
- Investigating the effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in improving mental health outcomes in community settings
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy aging and preventing age-related illnesses in community settings
- The effects of community-based interventions on reducing hospital readmissions for chronic conditions
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on access to healthcare for undocumented immigrants
- The effectiveness of school-based nurse-led interventions in promoting adolescent health
- Examining the effects of community-based nursing on reducing emergency department visits for non-emergent conditions
- Investigating the impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing infant mortality rates in disadvantaged communities
- The role of nurses in promoting health equity and reducing health disparities in underserved communities
- The effects of community-based nursing on improving medication adherence and reducing medication errors
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on improving health literacy in disadvantaged communities
- Investigating the effectiveness of community-based nursing in reducing readmissions for heart failure patients
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy aging and preventing age-related illnesses in long-term care settings
- Examining the effects of community-based nursing on reducing healthcare costs for chronic conditions
- Investigating the impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing sexually transmitted infections in high-risk communities
- The effectiveness of community-based nursing in reducing hospital-acquired infections in long-term care facilities
- The role of nurses in promoting mental health and well-being in community settings
- The effects of community-based nursing on reducing healthcare utilization for chronic conditions
- Investigating the impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing healthcare costs for low-income populations
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in improving health outcomes among immigrant populations
- Examining the role of community-based nursing in promoting healthy lifestyle behaviors in high-risk populations
- Investigating the impact of nurse-led interventions on improving health outcomes for LGBTQ+ populations
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in promoting breast cancer screening in disadvantaged communities
- The role of nurses in promoting health equity and reducing health disparities in migrant populations
- The effects of community-based nursing on improving end-of-life care for patients with advanced illness
- Investigating the impact of nurse-led interventions on improving health outcomes for individuals with disabilities in community settings
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in reducing rates of cardiovascular disease in high-risk communities
- Examining the role of community-based nursing in promoting healthy eating behaviors and reducing food insecurity
- Investigating the impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing healthcare costs for chronic pain management in community settings
Nursing Research Topics for BSc Students
- The impact of nursing interventions on patient satisfaction in post-operative care.
- The relationship between nurse staffing levels and patient outcomes in ICU.
- The role of the nurse in promoting patient safety in a pediatric setting.
- The effectiveness of simulation-based training in nursing education.
- The impact of electronic medical records on nursing practice.
- The experiences of nursing students during clinical placements.
- The role of the nurse in managing chronic illness in the elderly.
- The relationship between nursing care and patient outcomes in palliative care.
- The effectiveness of interprofessional collaboration in healthcare teams.
- The impact of nursing leadership styles on job satisfaction and retention.
- The role of the nurse in promoting self-management in patients with chronic conditions.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions for nursing students.
- The relationship between nurse staffing and patient mortality in acute care settings.
- The experiences of nurses working in rural healthcare settings.
- The role of the nurse in promoting health literacy among patients.
- The effectiveness of nursing interventions for reducing hospital readmissions.
- The relationship between nurse burnout and patient safety.
- The experiences of family caregivers of patients with dementia.
- The role of the nurse in managing symptoms in patients with cancer.
- The impact of cultural competence on patient-centered care.
- The relationship between nursing care and patient outcomes in psychiatric settings.
- The experiences of nurses working in home healthcare settings.
- The role of the nurse in promoting healthy lifestyle choices among patients.
- The effectiveness of nursing interventions for reducing healthcare-associated infections.
- The relationship between nurse staffing and patient satisfaction in emergency departments.
- The experiences of nurses working with patients with substance abuse disorders.
- The role of the nurse in promoting medication adherence in patients with chronic conditions.
- The impact of technology on nursing practice and patient outcomes.
- The relationship between nursing education and patient outcomes.
- The experiences of nurses working with patients with developmental disabilities.
- The role of the nurse in promoting patient-centered care in long-term care settings.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led care for patients with chronic conditions.
- The relationship between nurse staffing and patient outcomes in rehabilitation settings.
- The experiences of nurses working in hospice care.
- The role of the nurse in promoting mental health and wellness in patients.
- The impact of nursing interventions on patient outcomes in maternal and child health.
- The relationship between nurse burnout and patient outcomes in critical care settings.
- The experiences of nurses working with patients with eating disorders.
- The role of the nurse in promoting patient safety in surgical settings.
- The effectiveness of nursing interventions for reducing pain in patients with chronic conditions.
- The relationship between nursing care and patient outcomes in primary care settings.
- The experiences of nurses working in disaster response settings.
- The role of the nurse in promoting cultural humility in healthcare.
- The impact of nursing interventions on patient outcomes in infectious disease management.
- The relationship between nurse staffing and patient outcomes in neonatal care.
- The experiences of nurses working with patients with traumatic brain injuries.
- The role of the nurse in promoting end-of-life care and advance care planning.
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions for managing depression in patients with chronic conditions.
- The relationship between nursing care and patient outcomes in geriatric care.
- The experiences of nurses working in correctional healthcare settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

500+ Quantitative Research Titles and Topics

500+ Sports Research Topics

500+ Educational Research Topics

300+ Chemistry Research Topics

500+ Astronomy Research Topics

1000+ Sociology Research Topics

- Joyner Library
- Laupus Health Sciences Library
- Music Library
- Digital Collections
- Special Collections
- North Carolina Collection
- Teaching Resources
- The ScholarShip Institutional Repository
- Country Doctor Museum
Evidence-Based Practice for Nursing: Asking the Clinical Question
- What is Evidence-Based Practice?
- Asking the Clinical Question
- Finding Evidence
- Evaluating the Evidence
- Articles, Books & Web Resources on EBN
Identifying the Problem
Clinical questions arise from various cues, problems, and/or observations from patient care, nursing practice, or broader changes in healthcare knowledge and delivery. The most important step in Evidence-Based Nursing (EBN) is to correctly identify a problem through patient assessment or practice assessment, processes that require reflection by the nurse on clinical practice, in conjunction with a knowledge of the patient's present circumstances. The ability to identify the problem is the foundation for evidence-based nursing ; if a nurse fails to identify a problem correctly, then all the evidence she/he locates and the resulting decision-making will be irrelevant (Haddock, 2005).
The information below describes how to frame the question once the patient or practice assessment and the resulting problem identification have occurred.
Background vs. Foreground
An early step in framing the clinical question is to determine the type of question: background or foreground . The type of question helps to determine the resource to access to answer the question.
- A question root (who, what, when, etc.) with a verb
- A disorder, treatment, test, or other aspect of healthcare
- e.g. What causes migraines? How often do women over 40 need a mammogram?
- Books are generally better resources for answering background questions.
- Patient/population characteristics, problem
- Interventions or Exposures
- Articles are typically more specific and current, making them better suited for foreground questions.
Types of Questions
Clinical questions
Clinical questions typically fall into one of four main categories:
- Etiology (or harm/risk factors) : What causes the problem?
- Diagnosis: Does this patient have this problem?
- Therapy: What is the best treatment for this problem?
- Prognosis: What will the outcome of the problem be?
* Knowing the type of clinical question is important later in the EBN process--once the nurse goes to look for studies that will answer his/her question.
Nursing Practice Questions:
In nursing, many other questions about practice will also arise, with some of the questions resulting from the nursing principle of working with rather than on the patient. These questions can be quantitative or qualitative in nature. Examples include:
- What other, validated instruments for measuring this condition or phenomenon (e.g. pain) exist and how do they compare to the one we currently use?
- Should a nurse deliver patient education on the patient's disease/condition near the beginning or the end of an appointment or consultation?
- How do caregivers of patients with [x] cope with the burden of care and how can nurses assess the level of caregiver burden and/or support the caregivers?
- << Previous: What is Evidence-Based Practice?
- Next: Finding Evidence >>
- Last Updated: Jan 12, 2024 10:03 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ecu.edu/ebn
List of 350 Brilliant Nursing Research Topics to Investigate in 2024

Nursing education is challenging. Writing hundreds of tedious nursing research pieces is the most frustrating part. But we know how to help you! Discover 350 exciting nursing research topics and learn how to choose the best one.
- Primary Care Topics
- Public Health Topics
- Emergency Nursing Topics
- Midwifery Topics
- Neonatal Nursing Topics
- Pediatric Research Topics
- Nutrition Topics
- Mental Health Topics
- Healthcare Management Topics
- Medical Ethics Topics
- Nursing Leadership Topics
- Qualitative and Quantitative Research
- How to Choose a Nursing Topic
Process of Nursing Research
350 interesting nursing research topics.
Nursing research topics for college students can cover various areas of this field. Below you will find a list of 350 exciting ideas, which we have divided into different areas of activity. No matter what nursing research is in your sphere of interest. We’ve got you covered! You can also check research essay samples on the same topic for more inspiration.
Primary Care Research Topics
Primary care is the leading clinical service that sustains the health of an entire nation. The study of this topic is mandatory for the stable development of the healthcare system. Here are primary nursing research titles examples:
- What healthcare problems can be in primary care?
- The role of private health care providers in primary care.
- Peculiarities of vaccination in rural areas.
- Basic methods for assessing the quality of primary care .
- The role of modern technology in primary care .
- Basic techniques of evaluating the patient’s health .
- Private sector activities in primary care .
- The necessity to provide childcare services.
- Primary care and chronic pain problem .
- Vaccination programs : pros and cons.
- The role of social workers in primary care.
- Responsibility of the pharmacist for public health.
- Effective methods of asthma prevention.
- Advantages and disadvantages of home nursing care.
- How can primary care system help fight depression?
- Vaccination of the elderly: challenges and potential benefits.
- Principles of preventive medicine: primary care for the elderly.
- Migraine diagnosis and treatment methods.
- Innovative methods in cardiology .
- Major causes of anxiety disorders in adults.
- The problem of obesity treatment in primary care .
- Effective ways of taking anamnesis.
- Methods for diagnosing stroke in the elderly.
- Basic precautions for Parkinson’s disease .
- Basic requirements for intensive care .
- Connection of primary care and information technology training .
- Sleep disorders in women.
- Standard protocol for the treatment of headache in adults.
- Basic guidelines for primary care for disaster victims.
- The role of government agencies in primary care.
Based on previous papers, you can try to come up with your nursing research topics, for example, on infection control.

Research Topics in Public Health
The public health area has a strong connection with government issues. However, it is doctors who study the basis of all problems. So, let’s check out these special nursing research paper topics!
- The role of governmental organizations in the public health system .
- Effectiveness of government programs to prevent drug addiction .
- What role do parents play in promoting children’s health?
- Features of the school nurses’ work.
- The importance of proper nutrition and exercise .
- Telemedicine : advantages and disadvantages.
- The role of government in providing nursing education.
- The importance of long-term care facilities to the healthcare system .
- Discovering public health’s primary functions .
- Promoting healthy lifestyle in old age.
- Sedentary change programs for adolescents.
- Educational strategies for healthcare organizations in social media.
- Ways to educate young people about a positive body image .
- Formation of public behavior in the problem of cancer prevention.
- Occupational health and safety for workers in hazardous professions.
- Connection of modern technologies and public health system .
- Government AIDS awareness programs.
- State programs to increase awareness of heart disease .
- Government programs aimed at maintaining a healthy work environment .
- Health promotion methods.
- Companies against alcohol: examples from history.
- Public health policies: sugary drink tax .
- Raising awareness of the importance of vaccines .
- How is lung cancer related to air condition?
- Promotion of activity among children with disabilities .
- Disease eradication as a leading public health policy target .
- Government mental health awareness programs.
- Improving individual health as a way to counter epidemics .
- Ways of transmission of infectious diseases .
- Educating children about the importance of sports .
Public health is an excellent topic choice for a nursing dissertation. Try it!
Emergency Nursing Research Topics
New studies are essential for new practical approaches for nurses in emergencies. Try to discover new methods with these critical care nursing research topics!
- What role can stress play in emergency nursing?
- How to deal with anaphylactic shock?
- Effective methods of providing emergency care .
- Features of decision-making by a nurse in critical situations.
- Analysis of the effectiveness of emergency assistance in case of accidents.
- Analysis of the extreme degrees of pain in a patient.
- Diagnosing problems in ER.
- Emergency training methods.
- How to increase chances to save a drowning person?
- Models for reducing violence in emergency departments.
- The problem of rural residents’ access to ambulance services.
- Can family stay close to the patient during resuscitation?
- What effect do tasers have on the development of heart disease ?
- Diagnosing sepsis in emergencies.
- Effective methods of dealing with the effects of using pepper sprays.
- Screening for alcohol and drug addiction in adolescents.
- The role of ambulance crews in the fight against human trafficking .
- Identification and assistance to victims of violence.
- How to deal with unwanted patient behavior?
- Pediatric trauma and shock.
- Psychiatric screening in first aid cars.
- Ways to develop tolerance in first-aid workers.
- Effective ER worker behavior models.
- The role of private clinics in providing emergency services.
- The role of nurses in the ambulance crew.
- Common causes of death in ER patients.
- Correct gender policy towards ER staff.
- How to organize a working emergency care system?
- How to help relatives survive the death of a patient?
- Techniques for teaching nurses to diagnose and respond to life threats quickly.
These nursing research topics for critical care would be an excellent choice for your papers!
Midwifery Research Topics
Midwifery is one of the more challenging medical areas. We picked 30 of the best nursing research topics on pregnancy and prenatal care to help you improve your knowledge! Take a look:
- How can midwifery recognize domestic violence?
- Excess weight problems during pregnancy .
- How to analyze the effectiveness of childbirth ?
- Disease prevention during pregnancy.
- Effective methods of newborn resuscitation.
- Features of adolescent education in gynecology.
- Prenatal nursing care.
- Precautions for preterm labor.
- Rules of conduct for staff in the delivery room.
- Basic rules for saving mother and child.
- Preparing staff and the patient for a caesarean section.
- Preventing depression during pregnancy.
- Features and importance of family planning .
- Childbirth in water: advantages and disadvantages.
- Features of caring for pregnant women with breast cancer .
- The influence of the autonomic nervous system on the course of pregnancy.
- Methods for predicting preeclampsia.
- Diseases of the cervix associated with human papillomavirus .
- Frequency and possible complications of pregnancy and cervical disease.
- Treatment tactics of pregnancy complications in women with disorders of the upper urinary tract.
- Identifying asymptomatic pregnancy complications.
- The use of modern technologies in the treatment of fetal diseases.
- Features of the reproductive system after termination of pregnancy.
- Reasons for using iodine supplementation during pregnancy.
- Prevention of complications after operations on the pelvic organs .
- Impact of epilepsy on reproductive health .
- Features of reproductive behavior in students and ways to correct it.
- The effect of oral contraceptives on the contents of immune complexes in the blood.
- Operative delivery and influence on the child.
- Psychological assistance to patients with infertility .
Remember some of these nursing research topics on midwifery. Profs love them!
Neonatal Nursing Research Topics
Neonatal studies are one of the most innovative medical spheres. Check out this brilliant list of research topics for nursing students in the neonatal area. They will help you better understand the neonatal care importance.
- The importance of hand hygiene in neonatal units .
- Features of neonatal practice in rural areas.
- The leading causes of child mortality .
- How neonatal care has evolved in recent decades.
- Hygiene of newborns and skincare for babies.
- Postpartum infant care basics.
- Principles of breastfeeding infants.
- Predicting feeding problems and treatments.
- The leading causes of seizures in newborns and methods of treatment.
- Eating disorder in infants.
- Methods for predicting diseases in newborn children.
- Effective medical practices for babies.
- Nursing ethics for newborn care.
- Features of modern neonatal practices.
- Features of the development of the pulmonary tract of newborns.
- Studies of the lungs of a newborn: functions and structural features.
- Influence of inflammatory processes on the infant’s brain.
- The role of biomarkers in the diagnosis of traumatic brain injury in infants.
- The importance of neonatal health services.
- Basic strategies for modeling neonatal education.
- Monitoring the quality of neonatal services.
- Influence of neonatal care on the further treatment of a newborn.
- Impact of maternal obesity on infant development.
- Causes of abnormal neurological development in children.
- Use of hormones to regulate fetal lung development.
- Diagnosis of diaphragmatic hernia in infants.
- Potential lung disease in premature babies.
- Using nitric oxide to treat premature babies.
- Parental drug use and effects on fetal neurological development.
- Use of biomarkers for neonatal sepsis.
A nursing dissertation on neonatal issues is always a wise choice!
Pediatric Nursing Research Topics
Studies in pediatrics are aimed to help students discover children’s health issues to solve. Innovative approaches are mandatory to fight modern challenges. Check out these research topics for nursing students; they’ll help you become more informed:
- The importance of self-care nursing in pediatrics.
- Features of the treatment of children with autism .
- Childhood obesity problem.
- Features of vaccination of minors.
- Therapy for speech disorders .
- Causes of diabetes in young people.
- Music therapy and phlebotomy.
- Suboptimal diabetes: causes and methods of intervention.
- Causes of increased fatigue in adolescents.
- HIV prevention in adolescence.

- Preventing unwanted teenage pregnancies .
- Features of the use of painkillers in children.
- Methods for analyzing adolescent behavior.
- Features of the work of the pediatric department in schools.
- The importance of health promotion in pediatrics .
- Ways to connect with your child.
- Pediatric care basics.
- How can a healthcare professional deal with adolescent aggression ?
- Reducing the risk in children receiving oxygen therapy .
- The role of molecular markers in the diagnosis of childhood leukemia .
- Psychological help for children with cancer .
- Assessment of language models in children with autism.
- The use of stem cells in the treatment of childhood diseases.
- How do environmental problems affect the development of a child’s body?
- Implications of passive smoker syndrome for children.
- Possible complications of measles in children .
- Methods for diagnosing asthma in children .
- Common causes of Tourette’s syndrome in children.
- How does anorexia affect cognitive function in children?
- Diagnosis of ear infections in childhood.
We guess this ultimate list of research topics in pediatric nursing will be helpful for you!
Nutrition Research Topics for College Students
The eating habits of modern people can be harmful to the body. Therefore, doctors are seriously studying the current problems in this area. Here you can find tons of excellent nursing research topics on nutrition and its possible issues.
- What are referral reasons for the dietary assessment?
- Nutrition assistance for the elderly.
- Effects of stress on childhood metabolism .
- Prevention of obesity in adolescents.
- Linking diet to behavioral changes.
- How social media influences teen food choices .
- Patient nutrition problem in healthcare policy .
- Predicting and assessing diabetes .
- The problem of dietary intervention in the elderly.
- Promoting healthy eating as a way to fight obesity.
- Nursing promotion of healthy homemade food.
- Effects of good nutrition on fetal development .
- How does nutrition affect a child’s development ?
- Root causes of weight gain : a clinical study.
- Common diseases caused by poor nutrition .
- Nutrition screening for the elderly.
- The nutritional problem of children with autism .
- The importance of proper nutrition during pregnancy .
- Baby food: preventing eating disorders.
- Diet as a cause of dementia development in adults.
- Osteoporosis: the role of diet in disease prevention.
- The role of diet in healthy aging.
- What is the relationship between cancer and diet ?
- Nursing role in the safety of nutrition.
- The main benefits of a healthy diet : advice to patients.
- The role of parents in maintaining healthy eating habits in children.
- The relationship between healthy eating and cognitive development .
- Modern trends in youth nutrition.
- The nurse’s role in maintaining quality nutrition for pregnant women .
- Innovative nursing nutritional care.
Now let’s move to the next section – research topics in mental health!
Mental Health Nursing Research Topics
Mental health problems are more relevant now than ever. According to the National Alliance on Mental Illness , nearly 20% of the US adult population suffers from mental health problems. That’s why psychiatry research topics capture the interest of college students.
- The importance of nursing in mental health safety .
- Features of mental disorder in alcohol dependence .
- How does police work affect mental health?
- The connection between video games and the development of teenage aggression.
- How is schizophrenia diagnosed?

- Main theories in mental health studies .
- Features of bipolar mental disorder .
- Causes and prevention of drug addiction .
- Mental health problems of athletes after physical injuries .
- Conditions for the use of psychotherapy .
- Reasons and methods for tackling health imbalances.
- The influence of phone usage on mental health .
- Brain stimulation techniques.
- Diversity of sexual orientation psychology features.
- Methods for dealing with physical violence.
- The effectiveness of traditional methods of treating mental illness .
- Features of mental support for the patient’s relatives.
- The role of nurses in the management of geriatric patients with mental disorders.
- Combating burnout in the practice of healthcare professionals.
- The problem of war veterans’ mental health .
- The phenomenon of occupational deformation as a type of mental disorder.
- Chest pain as a symptom of mental health problems in adults.
- The relationship between increased risk of cancer and depression.
- Basic treatments for dementia .
- Nursing refugee mental health help .
- The practice of mirror therapy in rehabilitation.
- Methods to help victims of violence.
- Helping patients after a stroke .
- The use of antipsychotics : benefits and harms.
- How belly massage helps fight residual stomach volume.
We believe you’re going to find one of the best psychiatric nursing research topics!
Healthcare Management Research Topics
The effective functioning of the health care system is impossible without competent leadership. Therefore, nursing research study topics on healthcare management are as important as the others!
- The importance of financial management for the healthcare industry .
- Assessment of the economic component of primary health care .
- How does bias affect healthcare funding?
- How to properly organize health care at home?
- The Importance of a Unified Nursing Code.
- How risk management affects healthcare projects?
- Gender policy in health management .
- Features of the initial stages of private medical practice.
- The importance of the apology law.
- Features of selling medical marijuana .
- Features of healthcare contracts.
- The problem of human resources in the healthcare industry .
- The problem of the shortage of men in healthcare.
- Medicare: how to get benefits.
- How to improve the minimum level of nursing training ?
- Modern trends in the healthcare management area .
- Staff uniform rules.
- Legal risks of medical personnel .
- Gender bias in nursing.
- Features of the organization of the first aid service in private sector.
- Risk management in healthcare.
- The connection of healthcare and conflict management .
- Ways to solve staffing problems in healthcare.
- Ensuring the personnel safety from infectious diseases .
- Strategies to improve the emotional health of employees.
- What is the danger of not having enough nursing staff for patients?
- Personnel policy in public medical institutions.
- International nursing training.
- Basic principles of management in healthcare facilities.
- Possible ways to get a nursing promotion.
These nursing research titles on healthcare management will impress your professors!
Medical Ethics Research Paper Topics
Controversial issues in the field of medical ethics are felt more and more acutely every year. That is why they need to be solved, and research topics related to nursing ethics present a good opportunity for highlighting them:
- The role of ethical values in the nursing decision-making process .
- Particular ethics of data collection in primary care.
- The ethical dilemma of abortion.
- Moral choice in opioid addiction .
- Features of ethics in helping the homeless .
- Ethics of care for patients with mental disorders .
- Phantom pain phenomenon.
- Features of cultural perception in the work of nurses.
- How can religious beliefs affect medical ethics?
- The role of relatives in the treatment of geriatric patients .
- Ethics of the need to increase sales in medicine.
- The problem of sexualizing the image of a nurse.
- The importance of solving moral dilemmas in nursing .
- Assisting female patients by male nurses .
- What are the main medical ethics principles?
- Ethics of care for geriatric patients.
- The problem of compulsory vaccination : solutions.
- The dilemma of artificial feeding of patients.
- Ethics of nursing in preventive medicine.
- The importance of a hospital work ethic.
- The U.S. standard of ethics for nursing .
- The dilemma of medical ethics .
- The difference in medical ethics in Asian countries and European countries.
- How can medical ethics conflict with religious beliefs?
- Assisting suicide as a dilemma in medical ethics.
- The ethical problem of marijuana usage for medical purposes .
- The impact of cultural patterns on medical ethics .
- Child maltreatment : a medical ethics dilemma.
- Implementation of international medical ethics standards for healthcare development.
- Methods for monitoring compliance with medical ethics.
Nursing ethics research questions have a tendency to be the most interesting ones!
Nursing Leadership Paper Topics
The principle of developing leadership among nurses is vital for improving the performance of any clinic. This list consists of 30 nursing research topics about leadership in healthcare field:
- What role does leadership play in nursing?
- Which skills are necessary for effective nursing leadership performance?
- The nurse’s role in providing quality health care .
- Why is it important for nurses to attend medical conferences?
- Features of the classification of nurses.
- What is a retention strategy for experienced nurses?
- How does nursing leadership development affect patient outcomes?
- The problem of obtaining a diploma for a nurse.
- Nursing leadership : key challenges and opportunities.
- Ethical issues in nursing leadership .
- Protecting staff interests in nursing management .
- Analyzing college students’ nursing leadership experience .
- Effective nursing leadership styles .
- Ways to develop nursing leadership in private healthcare facilities.
- Nursing manual: Betty Newman theory.
- The importance of intuitiveness in the workplace.
- The importance of conflict resolution in the nursing leadership sphere .
- Patient advocacy opportunities for the lead nurse.
- Nursing manual: theory of intellectual capital.
- Effective models of professional practice in nursing.
- Professional opportunities for nursing graduates in nursing leadership .
- What are modern approaches in nursing leadership?
- Transformational leadership model for nursing.
- Fundamental theories for effective nursing leadership .
- Methods for applying leadership theories to nursing .
- What is the need for effective nursing leadership ?
- Methods for monitoring the effectiveness of nursing leadership .
- Principles of delegation of authority in nursing leadership practice.
- The importance of nursing leadership in strategic hospital planning.
- Nursing leadership as a method to retain experienced staff.
Evidence-based nursing topics on leadership can become a great start to your career!

Easy Topics for Nursing Qualitative and Quantitative Research
The division into qualitative and quantitative research can be confusing. But don’t worry, we’ll help you figure it out! Each type of nursing research topic and other materials may depend on dry numbers or subjective opinions. Keep reading for more detailed information and examples of quantitative and qualitative research topics in nursing!
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Nursing Research
Empirical research methods can be divided into two broad categories: quantitative and qualitative. As their name suggests, each view relies on specific types of data. Therefore, your nursing paper topics can also reveal either qualitative or quantitative aspects of the problem. Let’s take a quick look at the main differences between these two methods.
The quantitative method relies entirely on numbers and statistics. Your task is to find patterns and come to a conclusion by analyzing a large amount of data. This type of nursing research is as structured and objective as possible. These are the quantitative method characteristics:
- Sources of information are polls, reviews, records, documents.
- The deductive methodology involved.
- As objective as possible.
- The main content is numbers and data.
- Validity depends on the selected analysis tools.
The qualitative method , on the contrary, is a reflection of the author’s thoughts and conclusions. It depends entirely on the depth of understanding of the problem and the existing materials on the nursing thesis topics. The task of the researcher is to analyze previous works and create their theory through reflection. Check the qualitative method characteristics:
- Sources of information: focus groups, document reviews, interviews.
- The inductive process is involved.
- The subjective opinion of the author is allowed.
- The main content is text and reflections.
- Validity depends on the skill of the author.
You can check lists of topics for nursing research ideas in these spheres below!
Qualitative Nursing Research Topics
Qualitative analysis is a complex but critical aspect of medical practice. Nursing qualitative research topics are designed for students to develop skills of analyzing challenging issues and make proper conclusions:
- The role of technology in improving the quality of nursing care .
- Empowering nurses to prescribe: advantages and disadvantages.
- The problem of equality between doctors and nurses .
- Nursing stereotypes.
- Issues of accreditation of medical schools.
- The problem of systemic racism in the healthcare system.
- How nursing has changed in the 20th and 21st centuries.
- The importance of nursing staff in primary care .
- Priority of cancer in adults.
- Advantages and disadvantages of qualitative research in nursing .
These qualitative nursing research topics can help you improve your analytical skills significantly!
Quantitative Nursing Research Topics
Quantitative type of scientific work is all about statistics, percentages, and numbers. Prepare yourself to analyze tons of information with these nursing quantitative research topics:
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of primary patient care.
- The leading causes of heart disease .
- Analysis of the efficacy of telemedicine .
- The problem of an overabundance of information noise in the modern world.
- Evaluation of methods of assistance in suicide attempts.
- Statistical analysis of the benefits of diets .
- Causes of mental illness in women.
- Using unconventional methods to treat diabetes .
- Benefits of probiotics for treating diarrhea .
- Methods for assessing pain in critically ill patients.
For a successful paper, it’s importnt to pick a good research topics for nursing students based on quantitative evidence.
How to choose a Nursing Research Topic?
Choosing a quality nursing research topic idea can be a daunting task. This is mainly because the variety of possible options is simply too large. But don’t worry, here are some simple tips to help you choose the theme that’s right for you!
📜 Remove large-scale topics . You should not waste your energy on massive topics. Instead, choose narrow evidence-based ideas that allow you to focus on one issue. 📜 Use personal experience . One cannot be informed in all aspects of medicine. So when you write about a topic you have no experience with, you risk getting bogged down in hours of tedious research. Try to remember what problems you faced yourself. This way, you will already have a basic knowledge of the topic. 📜 Review literature . A large amount of ready-made research a topic will be an excellent help in writing about it. Try to do a systematic nursing topics review to find more examples. This does not mean that you should copy the work of another medic. On the contrary, it will be a good opportunity for you to highlight additional information. Therefore, before choosing from easy nursing research topics, look at how much information is already in the public domain.
What is the process of nursing research? Oh, that’s a tricky question. Let’s look at the main stages you need to go through!
✨ Define the research problem . To solve a problem, you first need to find it. That is why the first thing you should do is choose a nursing research question. If you have any experience with the topic, that will be a big plus! ✨ Develop hypothesis . Now, you need to think and create your theory. It can be of any form. The main thing is to make a connection between the data pieces and find a pattern. Of course, the hypothesis must be consistent with the current nursing research topics. ✨ Literature review . Before you start writing, it’s important to tighten your knowledge of the central thesis of the topic you’ve selected. Try reading other people’s research, finding the statistics you want, and just surfing the internet. ✨ Prepare an outline . It is essential to formulate a plan for your work before you start working on it. The more detailed you describe each paragraph of your article, the less time you will need to write it. Quality work begins with a quality plan! ✨ Conduct research . Now you start the longest and most important part of the whole nursing project. You should delve deeper into the problem and find the information you need. Everything that you write should help you prove your hypothesis in one way or another. ✨ Make a conclusion and develop further recommendations . After you have processed all the material, it is time to write a conclusion. Here, you must indicate whether you have succeeded in proving the hypothesis and recommend the application for your scientific work.
Congratulations, you did it! Writing a good paper is not that difficult. It all depends on a well-chosen research topic in the nursing field; luckily, you have a list of 350 topics to look through in this article! You can find more nursing research ideas on our website!
❓ What Is Translational Research in Nursing?
Translational research is a kind of scientific work, and its task is to transform theory into new practical approaches. In other words, discoveries made in laboratories become the basis for creating a new actionable framework in nursing.
❓ What Is an Example of a Clinical Question?
The clinical question is an integral part of your scientific work. It can relate to categories such as the cause of the problem, the manifestation of the disease in the patient, possible solutions, and potential results. A well-formulated clinical question helps you write a quality article.
❓ How to Determine Level of Evidence in Nursing Research?
Several criteria determine the level of evidence in nursing research. These include quality of design, validity, and applicability of results to patient care. Therefore, you should constantly monitor the reliability of your sources and the correctness of your conclusions.
❓ What Are Some Controversial Issues in Nursing?
In modern nursing, there are some controversial issues, mainly of an ethical nature. Such problems include the issue of vaccination of people who are against it, artificial nutrition, opioid addiction, and others. There is a lively discussion about how to act correctly in some instances and what factors the decision may depend on.
📎 References:
- Evidence-Based Practice: PICO. Duke University .
- Asking the clinical question. Penn State University
- Evidence-Based Practice Toolkit. Darrell W. Krueger Library
- Top 5 Ethical Issues in Nursing. American Mobile
- Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methods.
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research – What Is the difference? Imotions
- The Seven Steps of the Research Process. Teacherph
- Research Paper Writing Guide. Grammarly
- Choosing a research topic. Florida Gulf Coast University
- Nursing Process. NCBI
- Sample Research Topics. CFAES
- Selecting a Research Topic: Overview. MIT Libraries
- Three Important Nursing Subjects Students Should Know. Distant learning systems
- Evidence-Based Practice Tutorial: Asking Clinical Questions. University of Maryland
- Top 5 Ethical Issues in Nursing. Avant Healthcare
- Ethical Issues in Nursing: Explanations & Solutions. Duquesne University
- Clinical & Translational Research. UNC
- Writing a Thesis for Nursing School | Nursejournal.org
- A practical approach to the process of writing a dissertation. Nursing Times
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter X
- Share to LinkedIn
You might also like
Memorable human trafficking essay: topics & outline [2024], credible sources 101: how to evaluate them + 60 reliable websites for students, 265 powerful research proposal topics to consider [+ writing tips].

Ask a Librarian
How can I help you today?
A live human is ready to help.

Find & Cite | Research Help | Collections | Services | About
- Cook Library
- Research Guides
- Formulating a Research Question
- Information Literacy in Nursing
- Cultural Competency in Nursing
- Databases and Apps
- Books and Journals
- Clinical Skills
- Nursing Research Videos
Before You Start Searching
Clinical and epidemiological question frameworks.
- Basic Literature Searching
- Advanced Literature Searching
- Searching for Evidence with ABCDE
- Citation Management
- Citing Sources: APA and Other Styles
Step One: Start to formulate a research question or topic.
Aiming for clarity at the beginning of the project can help you get started right. It can be helpful to use one of the question frameworks detailed below.
Step Two: Do some background searching on the topic.
Taking a look in relevant resources to see what's already been written about your topic will help you understand how you can best contribute to the body of literature. It will also help you grasp the terminology around the topic, so that you'll be more prepared to do an effective literature search.

Step Three: Narrow down the question or topic if needed.
You may find that your original topic is too broad. After you have taken the time to evaluate what's already been written about your topic, you'll have a better understanding of what you're interested in.
Step Four: Meet with your librarian.
Step five: create a search for your topic in an appropriate database..
Try one of these tried and true clinical or quantitative research question frameworks. Not sure where to start? PICO is the most common clinical question framework. and PEO works well for public health and epidemiology.
- Condition, Context, Population
- Aromataris, E., & Munn, Z. (2017). Joanna Briggs Institute reviewer's manual. The Joanna Briggs Institute. Available from JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis .
- Population, Exposure of Interest, Outcome or Response
- Population or Problem, Intervention or Exposure, Comparison or Control, Outcome
- Heneghan, C., & Badenoch, D. (2002). Evidence-based medicine toolkit. London: BMJ Books. https://www.worldcat.org/title/evidence-based-medicine-toolkit/oclc/62307845
- Population or Problem, Intervention or Exposure, Comparison or Control, Outcome, Study Type
- Methley, A. M., Campbell, S., Chew-Graham, C., McNally, R., & Cheraghi-Sohi, S. (2014). PICO, PICOS and SPIDER: a comparison study of specificity and sensitivity in three search tools for qualitative systematic reviews. BMC health services research, 14, 579. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-014-0579-0 .
- Population or Problem, Intervention or Exposure, Comparison or Control, Outcome, Time
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: A key to evidence-based decisions. ACP Journal Club, 123(3), A12-A12. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7582737/
- Population, Index Test, Reference Test, Diagnosis of Interest
- << Previous: Datasets
- Next: Searching for Evidence >>
- Last Updated: Jun 24, 2024 2:18 PM
- URL: https://towson.libguides.com/NURS
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
- MEDICAL ASSISSTANT
- Abdominal Key
- Anesthesia Key
- Basicmedical Key
- Otolaryngology & Ophthalmology
- Musculoskeletal Key
- Obstetric, Gynecology and Pediatric
- Oncology & Hematology
- Plastic Surgery & Dermatology
- Clinical Dentistry
- Radiology Key
- Thoracic Key
- Veterinary Medicine
- Gold Membership
Research Problem and Purpose
Chapter 5 Research Problem and Purpose http://evolve.elsevier.com/Grove/practice/ We are constantly asking questions to better understand ourselves and the world around us. This human ability to wonder and ask creative questions about behaviors, experiences, and situations in the world provides a basis for identifying research topics and problems. Identifying a problem is the initial step, and one of the most significant, in conducting quantitative, qualitative, outcomes, and intervention research. The research purpose evolves from the problem and directs the subsequent steps of the research process. Research topics are concepts, phenomena of interest, or broad problem areas that researchers can focus on to enhance evidence-based nursing. Research topics contain numerous potential research problems, and each problem provides the basis for developing many purposes. Thus, the identification of a relevant research topic and a challenging, significant problem can facilitate the development of numerous study purposes to direct a lifetime program of research. However, the abundance of research topics and potential problems frequently is not apparent to nurses struggling to identify their first study problem. This chapter differentiates a research problem from a purpose, identifies sources for research problems, and provides a background for formulating a problem and purpose for study. The criteria for determining the feasibility of a proposed study problem and purpose are described. The chapter concludes with examples of research topics, problems, and purposes from current quantitative, qualitative, outcomes, and intervention studies. What Is a Research Problem and Purpose? A research problem is an area of concern where there is a gap in the knowledge base needed for nursing practice. Research is conducted to generate knowledge that addresses the practice concern, with the ultimate goal of providing evidence-based health care. A research problem can be identified by asking questions such as the following: What is wrong or is of concern in this clinical situation? What knowledge is needed to improve this situation? Will a particular intervention work in this clinical situation? What is known about this intervention’s effectiveness? Would another intervention be more effective in producing the desired outcomes? By questioning and reviewing the literature, researchers begin to recognize a specific area of concern and the knowledge gap that surrounds it. The knowledge gap, or what is not known about this clinical problem, determines the complexity and number of studies needed to generate essential knowledge for nursing practice ( Craig & Smyth, 2012 ; Creswell, 2009 ). In addition to the area of concern, the research problem identifies a population and sometimes a setting for the study. A research problem includes significance, background, and a problem statement. The significance of a problem indicates the importance of the problem to patients and families, nursing, healthcare system, and society. The background for a research problem briefly identifies what we know about the problem area. The problem statement identifies the specific gap in the knowledge needed for practice. A research problem from the study by Grady, Entin, Entin, and Brunye (2011) is presented as an example. This study was conducted to examine the effectiveness of educational messages or information on the knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors of people with diabetes. “Diabetes prevalence has reached epidemic proportions in this country. The health and economic consequences for Americans with this disease are overwhelming and expected to grow as our population continues to age. Approximately 23.6 million people in the United States have diabetes and, despite the disease being underreported as a cause of death, diabetes was listed as the seventh leading cause of death in the United States in 2006 ( Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2008a ). The direct medical costs of diabetes care and complications of $116 billion, together with indirect costs of $58 billion related to disability and reduced productivity, resulted in an estimated economic cost of diabetes totaling $174 billion in 2007 ( American Diabetes Association, 2009 ).… Complications contribute to a risk of death among individuals with diabetes that is about 2 times higher than that of individuals without diabetes ( Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2008a ). Amputations and foot ulcerations are the most common consequences of diabetic neuropathy and the major causes of morbidity and disability in people with diabetes. Approximately 2% to 3% of individuals with diabetes develop one or more foot ulcers each year, and an estimated 15% will develop a foot ulcer during their lifetime ( Singh, Armstrong, & Lipsky, 2005 ) [ problem significance ].… As the cornerstone of diabetes treatment and an integral part of a self-management regime, education of patients with diabetes takes place in both inpatient and outpatient venues.… Patient education takes time in the continuum of care that an already overworked staff is challenged to provide.… The research cited in the reviews of Boren et al. (2006) and Jackson et al. (2006) provides evidence that delivery of healthcare information can be accomplished effectively without involving diabetes educators or nurses and offers support for the use of information-technology-based education as an alternative way to provide information and guidance to persons with diabetes [ problem background ]. However, regardless of whether the information is presented in person or via technology, a relevant and still-open question is how to present the information so as to foster positive attitudinal and behavioral change and maximize the long-term effectiveness of health management education [ problem statement ].” ( Grady et al., 2011 , pp. 22-23) In this example, the research problem identifies an area of concern (incidence, costs, and complications of diabetes) for a particular population (persons with diabetes) in selected settings (inpatient and outpatient venues). Grady and colleagues (2011) clearly identified the significance of the problem, which is extensive and relevant to patients, families, nursing, healthcare system, and society. The problem background focuses on key research conducted to examine the effectiveness of health education on the management of diabetes. The last sentence in this example is the problem statement, which identifies the gap in the knowledge needed for practice. In this study, there is limited research on how to present diabetic education to maximize its effectiveness on attitudinal and behavioral change in people with this chronic illness. The research problem in this example includes concepts or research topics such as diabetes prevalence, economic consequences, complications of diabetes, consequences of diabetic neuropathy, health management education, self-management, and attitudinal and behavioral changes. Health management education is an abstract concept, and a variety of nursing actions or interventions could be implemented to determine their effectiveness in promoting long-term attitudinal and behavioral changes in persons with diabetes. Thus, each problem may generate many research purposes. The knowledge gap regarding how to present information to foster positive attitudinal and behavioral changes in persons with diabetes provides clear direction for formulating the research purpose. The research purpose is a clear, concise statement of the specific focus or aim of the study that is generated on the basis of the research problem. The purpose usually indicates the type of study (quantitative, qualitative, outcomes, or intervention) to be conducted and often includes the variables, population, and setting for the study. The goals of quantitative research include identifying and describing variables, examining relationships among variables, and determining the effectiveness of interventions in managing clinical problems ( Creswell, 2009 ; Shadish, Cook, & Campbell, 2002 ). The goals of qualitative research include exploring a phenomenon, such as depression as it is experienced by pregnant women; developing theories to describe and manage clinical situations; examining the health practices of certain cultures; describing health-related issues, events, and situations; and determining the historical evolution of the profession ( Marshall & Rossman, 2011 ; Munhall, 2012 ). The focus of outcomes research is to identify, describe, and improve the outcomes or end results of patient care ( Doran, 2011 ). Intervention research focuses on investigating the effectiveness of nursing interventions in achieving the desired outcomes in natural settings ( Forbes, 2009 ). Regardless of the type of research, every study needs a clearly expressed purpose statement to guide it. Grady et al. (2011) clearly identified their study purpose following their research problem statement of the gap in the knowledge base. Thus, the purpose of their study was to “examine the impact of information framing in an educational program about proper foot care and its importance for preventing diabetic complications on long-term changes in foot care knowledge, attitudes, and behavior” ( Grady et al., 2011 , p. 23). This research purpose indicates that these investigators conducted a quantitative quasi-experimental study to determine the effectiveness of an independent variable or intervention (information framing educational program about diabetic foot care and prevention of complications) on the dependent or outcome variables (foot care knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors). The researchers also identified two hypotheses to direct their study, which included the four variables identified (see Chapter 8 for a discussion of hypotheses). The study findings indicated that the gain-framed messages focused on the benefits of taking action were significantly more effective in promoting positive behavioral changes in people with diabetes than the loss-framed messages focused on the costs of not taking action. A gain-framed message might be stated as follows: “Achieving normal blood sugar increases your feelings of health and well being and promotes control of your illness.” A loss-framed message might be worded as follows: “Poorly controlled blood sugars can lead to complications of neuropathy, foot lesions, and amputation.” Grady et al. (2011) also found that changes in knowledge affected changes in attitudes and that attitudes were direct predictors of long-term behavior management of diabetes. The findings from this study and other research provide evidence of the effectiveness of information messages in sustaining health promoting behavior by people with diabetes. Sources of Research Problems Research problems are developed from many sources, but you need to be curious, astute, and imaginative to identify problems from the sources. The sources for research problems included in this text are (1) clinical practice, (2) researcher and peer interactions, (3) literature review, (4) theories, and (5) research priorities identified by funding agencies and specialty groups. Researchers often use more than one source to identify and refine their research problem. Clinical Practice The practice of nursing must be based on knowledge or evidence generated through research. Thus, clinical practice is an extremely important source for research problems. Problems can evolve from clinical observations. For example, while watching the behavior of a patient and family in crisis, you may wonder how you as a nurse might intervene to improve the family’s coping skills. A review of patient records, treatment plans, and procedure manuals might reveal concerns or raise questions about practice that could be the basis for research problems. For example, you may wonder: What nursing intervention will open the lines of communication with a patient who has had a stroke? What is the impact of home visits on the level of function, readjustment to the home environment, and rehospitalization pattern of a child with a severe chronic illness? What is the most effective treatment for acute and chronic pain? What is the best pharmacological agent or agents for treating hypertension in elderly, diabetic patients—angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), diuretic, beta blocker, calcium channel blocker, or alpha antagonist, or a combination of these drugs? What are the most effective pharmacological and nonpharmacological treatments for a patient with a serious and persistent mental illness? What are the needs of stroke survivors from their perspective? What are the cultural factors that promote better birth outcomes in Hispanic women? These clinical questions could direct you in identifying a significant research problem and purpose. Extensive patient data, such as diagnoses, treatments, and outcomes, are now computerized. Analyzing this information might generate research problems that are significant to a clinic, community, or national healthcare system. For example, you may ask: Why has adolescent obesity increased so rapidly in the past 10 years, and what treatments will be effective in managing this problem? What pharmacological and nonpharmacological treatments have been most effective in treating common acute illnesses such as otitis media, sinusitis, and bronchitis in your practice or nationwide? What are the outcomes (patient health status and costs) for treating such chronic illnesses as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia in your practice? Review of agency patient data often reveals patterns and trends in a clinical setting and helps nurses and students to identify patient care problems. Because health care is constantly changing in response to consumer needs and trends in society, the focus of current research varies according to these needs and trends. For example, research evidence is needed to improve practice outcomes for infants and new mothers, the elderly and residents in nursing homes, and persons from vulnerable and culturally diverse populations. Healthcare agencies would benefit from studies of varied healthcare delivery models. Society would benefit from interventions recognized to promote health and prevent illness. In summary, clinically focused research is essential if nurses are to develop the knowledge needed for evidence-based practice (EBP) ( Brown, 2009 ; Melnyk & Fineout-Overholt, 2011 ). Researcher and Peer Interactions Interactions with researchers and peers offer valuable opportunities for generating research problems. Experienced researchers serve as mentors and help novice researchers to identify research topics and formulate problems. Nursing educators assist students in selecting research problems for theses and dissertations. When possible, students conduct studies in the same area of research as the faculty. Faculty members can share their expertise regarding their research program, and the combined work of the faculty and students can build a knowledge base for a specific area of practice. This type of relationship could also be developed between an expert researcher and a nurse clinician. Because nursing research is critical for designation as a Magnet facility by the American Nurses Credentialing Center © (ANCC, 2012) , hospitals and healthcare systems employ nurse researchers for the purpose of guiding studies conducted by staff nurses. Building an EBP for nursing requires collaboration between nurse researchers and clinicians as well as with researchers from other health-related disciplines. Interdisciplinary research teams have the expertise to increase the quality and quantity of studies conducted. Being a part of a research team is an excellent way to expand your understanding of the research process. Beveridge (1950) identified several reasons for discussing research ideas with others. Ideas are clarified and new ideas are generated when two or more people pool their thoughts. Interactions with others enable researchers to uncover errors in reasoning or information. These interactions are also a source of support in discouraging or difficult times. In addition, another person can provide a refreshing or unique viewpoint, which helps avoid conditioned thinking, or following an established habit of thought. A workplace that encourages interaction can stimulate nurses to identify research problems. Nursing conferences and professional meetings also provide excellent opportunities for nurses to discuss their ideas and brainstorm to identify potential research problems. The Internet has greatly extended the ability of researchers and clinicians around the world to share ideas and propose potential problems for research. Most colleges or schools of nursing have websites that identify faculty research interests and provide mechanisms for contacting individuals who are conducting research in your area of interest. Thus, interactions with others are essential to broaden your perspective and knowledge base and to support you in identifying significant research problems and purposes. Literature Review Reviewing research journals, such as Advances in Nursing Science, Applied Nursing Research, Clinical Nursing Research, Evidence-Based Nursing, International Journal of Psychiatric Nursing Research, Journal of Nursing Scholarship, Journal of Advanced Nursing, Journal of Research in Nursing, Nursing Research, Nursing Science Quarterly, Research in Nursing & Health, Scholarly Inquiry for Nursing Practice: An International Journal, Southern Online Journal of Nursing Research, and Western Journal of Nursing Research , as well as theses and dissertations will acquaint novice researchers with studies conducted in an area of interest. The nursing specialty journals, such as American Journal of Maternal Child Nursing, Archives of Psychiatric Nursing, Dimensions of Critical Care, Heart & Lung, Infant Behavior and Development, Journal of Pediatric Nursing , and Oncology Nursing Forum, also place a high priority on publishing research findings. Reviewing research articles enables you to identify an area of interest and determine what is known and not known in this area. The gaps in the knowledge base provide direction for future research. (See Chapter 6 for the process of reviewing the literature.) At the completion of a research project, an investigator often makes recommendations for further study. These recommendations provide opportunities for others to build on a researcher’s work and strengthen the knowledge in a selected area. For example, the Grady et al. (2011 , p. 27) study, introduced earlier in this chapter, provided recommendations for further research to examine “the longer term eventualities of gain- and loss-framed messages on preventative behaviors.” They also recommended examining how long the gain-framed message might last and when it would be “necessary to provide another message presentation to bolster effective self-care behavior” (p. 27). These researchers also encouraged others to validate their findings through replication studies that varied the content and delivery format of educational messages provided persons with diabetes. Replication of Studies Reviewing the literature is a way to identify a study to replicate. Replication involves reproducing or repeating a study to determine whether similar findings will be obtained ( Fahs, Morgan, & Kalman, 2003 ). Replication is essential for knowledge development because it (1) establishes the credibility of the findings, (2) extends the generalizability of the findings over a range of instances and contexts, (3) reduces the number of type I and type II errors, (4) corrects the limitations in studies’ methodologies, (5) supports theory development, and (6) lessens the acceptance of erroneous results. Some researchers replicate studies because they agree with the findings and wonder whether the findings will hold up in different settings with different subjects over time. Others want to challenge the findings or interpretations of prior investigators. Some researchers develop research programs focused on expanding the knowledge needed for practice in an area. This program of research often includes replication studies that strengthen the evidence for practice. Four different types of replications are important in generating sound scientific knowledge for nursing: (1) exact, (2) approximate, (3) concurrent, and (4) systematic extension ( Haller & Reynolds, 1986 ). An exact (or identical) replication involves duplicating the initial researcher’s study to confirm the original findings. All conditions of the original study must be maintained; thus, “there must be the same observer, the same subjects, the same procedure, the same measures, the same locale, and the same time” ( Haller & Reynolds, 1986 , p. 250). Exact replications might be thought of as ideal to confirm original study findings, but these are frequently not attainable. In addition, one would not want to replicate the errors in an original study, such as small sample size, weak design, or poor-quality measurement methods. When conducting an approximate (or operational) replication , the subsequent researcher repeats the original study under similar conditions, following the methods as closely as possible. The intent is to determine whether the findings from the original study hold up despite minor changes in the research conditions. If the findings generated through replication are consistent with the findings of the original study, then the knowledge is considered more credible and has a greater probability of accurately reflecting the real world. If the replication fails to support the original findings, the designs and methods of both studies should be examined for limitations and weaknesses, and further research must be conducted. Conflicting findings might also generate additional theoretical insights and provide new directions for research. For a concurrent (or internal) replication , the researcher collects data for the original study and the replication study simultaneously thereby checking the reliability of the original study findings. The confirmation, through replication of the original study findings, is part of the original study’s design. For example, your research team might collect data simultaneously at two different hospitals to compare and contrast the findings. Consistency in the findings increases the credibility of the study and the likelihood that others will be able to generalize the findings. Some expert researchers obtain funding to conduct multiple concurrent replications, in which a number of individuals conduct repetitions of a single study, but with different samples in different settings. Clinical trials that examine the effectiveness of the pharmacological management of chronic illnesses, such as diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, are examples of concurrent replication studies. As each study is completed, the findings are compiled in a report that specifies the series of replications that were conducted to generate these findings. Some outcome studies involve concurrent replication to determine whether the outcomes vary for different healthcare providers and healthcare settings across the United States ( Brink & Wood, 1979 ; Brown, 2009 ; Doran, 2011 ). A systematic (or constructive) replication is done under distinctly new conditions. The researchers conducting the replication do not follow the design or methods of the original researchers; rather, the second investigative team identifies a similar problem but formulates new methods to verify the first researchers’ findings ( Haller & Reynolds, 1986 ). The aim of this type of replication is to extend the findings of the original study and test the limits of the generalizability of such findings. Intervention research might use this type of replication to examine the effectiveness of various interventions devised to address a practice problem. Nurse researchers need to actively replicate studies to develop strong research evidence for practice. However, the number of nursing studies replicated continues to be limited. The replications of studies might be limited because (1) some view replication as less scholarly or less important than original research, (2) the discipline of nursing lacks adequate resources and funding for conducting replication studies, and (3) editors of journals publish fewer replication studies than original studies ( Fahs et al., 2003 ). However, the lack of replication studies severely limits the generation of sound research findings needed for EBP in nursing. Thus, replicating a study should be respected as a legitimate scholarly activity for both expert and novice researchers. Funding from both private and federal sources is needed to support the conduct of replication studies, with a commitment from journal editors to publish these studies. Replication provides an excellent learning opportunity for the novice researcher to conduct a significant study, validate findings from previous research, and generate new research evidence about different populations and settings. Students studying for a master’s of science in nursing degree could be encouraged to replicate studies for their theses, possibly to replicate faculty studies. Expert researchers, with programs of research, implement replication studies to generate sound evidence for use in practice. When publishing a replication study, researchers need to designate the type of replication conducted and the contribution the study made to the existing body of knowledge. Theory Theories are an important source for generating research problems because they set forth ideas about events and situations in the real world that require testing ( Chinn & Kramer, 2008 ). In examining a theory, you may note that it includes a number of propositions and that each proposition is a statement of the relationship of two or more concepts. A research problem and purpose could be formulated to explore or describe a concept or to test a proposition from a theory. Middle range theories are the ones most commonly used as frameworks for quantitative studies and are tested as part of the research process ( Smith & Liehr, 2008 ). In qualitative research, the purpose of the study might be to generate a theory or framework to describe a unique event or situation ( Marshall & Rossman, 2011 ; Munhall, 2012 ). Some researchers combine ideas from different theories to develop maps or models for testing through research. The map serves as the framework for the study and includes key concepts and relationships from the theories that the researchers want to study. Frenn, Malin, and Bansal (2003 , p. 38) conducted a quasi-experimental study to examine the effectiveness of a “4-session Health Promotion/Transtheoretical Model-guided intervention in reducing percentage of fat in the diet and increasing physical activity among low- to middle-income culturally diverse middle school students.” The intervention was based on the “components of two behaviorally based research models that have been well tested among adults—Health Promotion Model ( Pender, 1996 ) and Transtheoretical Model ( Prochaska, Norcross, Fowler, Follick, & Abrams, 1992 )—but have not been tested regarding low-fat diet with middle school-aged children” ( Frenn et al., 2003 , p. 36). They developed a model of the study framework (see Figure 5-1 ) and described the concepts and propositions from the model that guided the development of different aspects of their study. Figure 5-1 The health promotion stage of change model: A synthesis of health promotion and transtheoretical models guiding low-fat diet intervention for students in an urban middle school. “A combined Health Promotion/Transtheoretical Model guided the intervention designed for this study [see Figure 5-1 ]. The first individual characteristic examined in this study was temptation (low self-efficacy), defined as the inability to overcome barriers in sustaining a low-fat diet … and an intervention helping adolescents develop behavioral control may enhance self-efficacy and improve health habits. The second characteristic common to both the Health Promotion and Transtheoretical Models was benefits/barriers. In a study of fifth- through seventh- grade children, Baranowski and Simons-Morton (1990) found the most common barriers to reducing saturated fat in the diet were (a) giving up preferred foods, (b) meals outside the home that contained fat, (c) not knowing what foods were low in fat, and (d) not wanting to take the time to read labels. The last individual characteristic used in this study was access to low-fat foods. This concept from the Health Promotion Model is important in a middle school-aged population, as they are, to some extent, dependent on others for the types of food available.” ( Frenn et al., 2003 , pp. 37-38) Frenn et al. (2003) used the Pender (1996) Health Promotion Model and the Transtheoretical Model ( Prochaska et al., 1992 ), which are middle range theories, to develop the following research questions to guide their study: “(a) Do demographic variables, access to low-fat foods, perceived self-efficacy, benefits/barriers, and stages of change predict percentage of fat reported in the diet by middle school-aged children? (b) Does the application of a Health Promotion/Transtheoretical Model intervention in 4 classroom sessions significantly improve adoption of a diet lower in fat and duration of physical activity as compared with a control group of students not engaged with the program?” ( Frenn et al., 2003 , p. 39) The findings from a study either support or do not support the relationships identified in the model. The study by Frenn et al. (2003) added support to the Health Promotion/Transtheoretical Model with their findings that the classroom intervention decreased dietary fat and increased physical activity for middle school–age adolescents. Further research is needed to determine whether classroom interventions over time reduce body mass index, body weight, and the percentage of body fat of overweight and obese adolescents. As a graduate student, you could use this model as a framework and test some of the relationships in your clinical setting. Research Priorities Since 1975, expert researchers, specialty groups, professional organizations, and funding agencies have identified nursing research priorities. The research priorities for clinical practice were initially identified in a study by Lindeman (1975) . Those original research priorities included nursing interventions related to stress, care of the aged, pain management, and patient education. Developing evidence-based nursing interventions in these areas continues to be a priority. Many professional nursing organizations use websites to communicate their current research priorities. For example, the American Association of Critical-Care Nurses (AACN) determined initial research priorities for this specialty in the early 1980s ( Lewandowski & Kositsky, 1983 ) and revised these priorities on the basis of patients’ needs and the changes in health care. The current AACN (2011) research priorities are identified on this organization’s website as (1) effective and appropriate use of technology to achieve optimal patient assessment, management, or outcomes, (2) creation of a healing, humane environment, (3) processes and systems that foster the optimal contribution of critical care nurses, (4) effective approaches to symptom management, and (5) prevention and management of complications. AACN (2011) has also identified future research needs under the following topics: medication management, hemodynamic monitoring, creating healing environments, palliative care and end-of-life issues, mechanical ventilation, monitoring of neuroscience patients, and noninvasive monitoring. If your specialty is critical care, this list of research needs might help you identify a priority problem and purpose for study. The American Organization of Nurse Executives (AONE, 2012) provides a discussion of their education and research priorities online at http://www.aone.org/education/index.shtml/ . For 2011-2012, AONE identified more than 25 research priorities in four strategic areas: (1) design of future patient care delivery systems, (2) healthful practice environments, (3) leadership, and (4) the positioning of nurse leaders as valued healthcare executives and managers. To promote the design of future patient care delivery systems, AONE encourages research focused on new technology, patient safety, and the work environment that allows strategies for improvement crucial to the success of the delivery system. In the area of healthful practice environments, AONE encourages research focused on practice environments that attract and retain nurses and that promote professional growth and continuous learning, including mentoring of staff nurses and nursing leaders. In the area of leadership, AONE encourages research focused on evidence-based leadership capacity, measurement of patient care quality outcomes, and technology to complement patient care. To promote the positioning of nurse leaders as valued healthcare executives and managers, AONE encourages research focused on patient safety and quality, disaster preparedness, and workforce shortages. AONE recognizes the importance of supporting education and research initiatives to create a healthy work environment, a quality healthcare system, and strong nurse executives. You can search online for the research priorities of other nursing organizations to help you identify priority problems for study. A significant funding agency for nursing research is the National Institute of Nursing Research (NINR). A major initiative of the NINR is the development of a national nursing research agenda that involves identifying nursing research priorities, outlining a plan for implementing priority studies, and obtaining resources to support these priority projects. The NINR has an annual budget of more than $90 million, with approximately 74% of the budget used for extramural research project grants, 7% for predoctoral and postdoctoral training, 6% for research management and support, 5% for the centers program in specialized areas, 5% for other research including career development, 2% for the intramural program, and 1% for contracts and other expenses (see NINR at http://www.ninr.nih.gov/ ). The NINR (2011) developed four strategies for building the science of nursing: “(1) integrating biological and behavior science for better health; (2) adopting, adapting, and generating new technologies for better health care; (3) improving methods for future scientific discoveries; and (4) developing scientists for today and tomorrow.” The areas of research emphasis include: (1) promoting health and preventing disease, (2) improving quality of life, (3) eliminating health disparities, and (4) setting directions for end-of-life research ( NINR, 2011 ). Specific research priorities were identified for each of these four areas of research emphasis and were included in the NINR Strategic Plan. These research priorities provide important information for nurses seeking funding from the NINR. Details about the NINR mission, strategic plan, and areas of funding are available on its website at http://www.ninr.nih.gov/AboutNINR/NINRMissionandStrategicPlan/ . Another federal agency that is funding healthcare research is the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). The purpose of the AHRQ is to enhance the quality, appropriateness, and effectiveness of healthcare services, and access to such services, by establishing a broad base of scientific research and promoting improvements in clinical practice and in the organization, financing, and delivery of healthcare services. Some of the current AHRQ funding priorities are research focused on prevention; health information technology; patient safety; long-term care; pharmaceutical outcomes; system capacity and emergency preparedness; and the cost, organization, and socioeconomics of health care. For a complete list of funding opportunities and grant announcements, see the AHRQ website at http://www.ahrq.gov/ . The World Health Organization (WHO) is encouraging the identification of priorities for a common nursing research agenda among countries. A quality healthcare delivery system and improved patient and family health have become global goals. By 2020, the world’s population is expected to increase by 94%, with the elderly population growing by almost 240%. Seven of every 10 deaths are expected to be caused by noncommunicable diseases, such as chronic conditions (heart disease, cancer, and depression) and injuries (unintentional and intentional). The priority areas for research identified by WHO are to (1) improve the health of the world’s most marginalized populations, (2) study new diseases that threaten public health around the world, (3) conduct comparative analyses of supply and demand of the health workforce of different countries, (4) analyze the feasibility, effectiveness, and quality of education and practice of nurses, (5) conduct research on healthcare delivery modes, and (6) examine the outcomes for healthcare agencies, providers, and patients around the world ( WHO, 2012 ). A discussion of WHO’s mission, objectives, and research policies can be found online at http://www.who.int/rpc/en . The Healthy People 2020 website identifies and prioritizes health topics and objectives for all age groups over the next decade ( U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2012 ). These health topics and objectives direct future research in the areas of health promotion, illness prevention, illness management, and rehabilitation and can be accessed online at http://www.healthypeople.gov/2020/topicsobjectives2020/default.aspx/ . In summary, funding organizations, professional organizations, and governmental healthcare organizations, both national and international, are sources for identifying priority research problems and offer opportunities for obtaining funding for future research.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Related posts:
- Ethics in Research
- Objectives, Questions, Hypotheses, and Study Variables
- Using Statistics to Examine Relationships
- Selecting a Quantitative Research Design
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Comments are closed for this page.

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals
You are here
- Volume 21, Issue 1
- Nursing issues
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Helen Noble 1 ,
- Allison Shorten 2
- 1 School of Nursing and Midwifery, Queens University Belfast , Belfast , UK
- 2 Department of Family, Community and Health Sciences , University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Nursing , Birmingham , Alabama , USA
- Correspondence to Dr Helen Noble, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Queens University Belfast, Belfast BT9 7BL, UK; helen.noble{at}qub.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2017-102850
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
EBN perspectives bring together key issues from the commentaries in one of our nursing topic themes.
Introduction
This article is part of Evidence Based Nursing ( EBN ) Perspective series. In this series, published commentaries related to a specific nursing theme are collated and highlights are discussed. The topic for this edition is ‘nursing issues’, covering 21 commentaries published from October 2016 over a 12-month period. A summary of works is organised into key themes, research methods are identified and important implications for practice and future research are explored.
Evidence-Based Nursing commentaries on nursing issues (October 2016–October 2017)
Theme 1: professional issues—nursing workforce/workplace.
Staffing and nurse-perceived quality of care (http://ebn.bmj.com/content/20/1/19).
Greater nurse autonomy associated with lower mortality and failure to rescue rates (http://ebn.bmj.com/content/20/2/56).
Health, psychosocial and workplace characteristics may identify nurses and midwives at risk of high absenteeism (http://ebn.bmj.com/content/20/3/83).
Good peer relationships can attenuate the negative effect of horizontal violence on job satisfaction (http://ebn.bmj.com/content/19/3/91).
Simple variations to traditional models of care can dramatically improve emergency department performance (http://ebn.bmj.com/content/20/3/87).
Emergency department nurses report high workload and management pressure to meet 4-hour treatment targets (http://ebn.bmj.com/content/19/3/90).
Information gaps in medication communication during clinical handover calls for a different approach (http://ebn.bmj.com/content/19/4/125).
Nurses require confidence, knowledge and communication skills for referrals to doctors (http://ebn.bmj.com/content/20/3/84).
Reporting of professional misconduct is influenced by nurses’ level of education and managerial experience (http://ebn.bmj.com/content/20/3/89).
Mindfulness training can reduce depression and anxiety among nurses (http://ebn.bmj.com/content/20/2/57).
Theme 2: Evidence-based nursing care—patient care/therapies
Earplugs could be an effective sleep hygiene strategy to reduce delirium …
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
Nursing Doctoral Programs: DNP & PhD
- Where to Start?
- Find Articles/Databases
- Reference Resources
- Evidence Summaries & Clinical Guidelines
- Drug Information
- Health Data & Statistics
- Patient/Consumer Facing Materials
- Images and Streaming Video
- Grey Literature
- Mobile Apps & "Point of Care" Tools
- Test Instruments This link opens in a new window
- Framing Research Questions
- Selecting Databases
- Building the Search
- Expanding a Search
- Filtering / Narrowing the Search
- Cited Reference Searching
- Saving Searches
- Alerting Services
- Finding Full Text
- What are Literature Reviews?
- Conducting & Reporting Systematic Reviews
- Finding Systematic Reviews
- Tutorials & Tools for Literature Reviews
- Locating Qualitative Research This link opens in a new window
- Critical Appraisal Resources
- Citing Sources
- Writing/Publishing
- Data Management This link opens in a new window
- Deposit in the Institutional Repository
Defining the Question: Foreground & Background Questions
In order to most appropriately choose an information resource and craft a search strategy, it is necessary to consider what kind of question you are asking: a specific, narrow "foreground" question, or a broader background question that will help give context to your research?
Foreground Questions
A "foreground" question in health research is one that is relatively specific, and is usually best addressed by locating primary research evidence.
Using a structured question framework can help you clearly define the concepts or variables that make up the specific research question.
Across most frameworks, you’ll often be considering:
- a who (who was studied - a population or sample)
- a what (what was done or examined - an intervention, an exposure, a policy, a program, a phenomenon)
- a how ([how] did the [what] affect the [who] - an outcome, an effect).
PICO is the most common framework for developing a clinical research question, but multiple question frameworks exist.
PICO (Problem/Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome)
Appropriate for : clinical questions, often addressing the effect of an intervention/therapy/treatment
Example : For adolescents with type II diabetes (P) does the use of telehealth consultations (I) compared to in-person consultations (C) improve blood sugar control (O)?
| Element | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| opulation / problem | Who is the group of people being studied? | adolescents with T2D |
| ntervention | What is the intervention being investigated? (independent variable) | telehealth consultations |
| omparison | To what is the intervention being compared? | in person consultations |
| utcome | What are the desired outcomes of the intervention? (dependent variable) | blood sugar control |
Framing Different Types of Clinical Questions with PICO
Different types of clinical questions are suited to different syntaxes and phrasings, but all will clearly define the PICO elements. The definitions and frames below may be helpful for organizing your question:
Intervention/Therapy
Questions addressing how a clinical issue, illness, or disability is treated.
"In__________________(P), how does__________________(I) compared to_________________(C) affect______________(O)?"
Questions that address the causes or origin of disease, the factors which produce or predispose toward a certain disease or disorder.
"Are_________________(P), who have_________________(I) compared with those without_________________(C) at_________________risk for/of_________________(O) over_________________(T)?"
Questions addressing the act or process of identifying or determining the nature and cause of a disease or injury through evaluation.
In_________________(P) are/is_________________(I) compared with_________________(C) more accurate in diagnosing_________________(O)?
Prognosis/Prediction:
Questions addressing the prediction of the course of a disease.
In_________________(P), how does_________________(I) compared to_________________ (C) influence_________________(O)?
Questions addressing how one experiences a phenomenon or why we need to approach practice differently.
"How do_________________(P) with_________________(I) perceive_________________(O)?"
Adapted from: Melnyk, B. M., & Fineout-Overholt, E. (2011). Evidence-based practice in nursing & healthcare: A guide to best practice. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Beyond PICO: Other Types of Question Frameworks
PICO is a useful framework for clinical research questions, but may not be appropriate for all kinds of reviews. Also consider:
PEO (Population, Exposure, Outcome)
Appropriate for : describing association between particular exposures/risk factors and outcomes
Example : How do preparation programs (E) influence the development of teaching competence (O) among novice nurse educators (P)?
| Element | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| opulation | Who is the group of people being studied? | novice nurse educators |
| xposure | What is the population being exposed to (independent variable)? | preparation programs |
| utcome | What is the outcome that may be affected by the exposure (dependent variable)? | teaching competence |
SPIDER (Sample, Phenomenon of Interest, Design, Evaluation, Research Type)
Appropriate for : questions of experience or perspectives (questions that may be addressed by qualitative or mixed methods research)
Example : What are the experiences and perspectives (E) of undergraduate nursing students (S) in clinical placements within prison healthcare settings (PI)?
| Element | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ample | Who is the group of people being studied? | undergraduate nursing students |
| henomenon of nterest | What are the reasons for behavior and decisions? | clinical placements in prison healthcare settings |
| esign | How has the research been collected (e.g., interview, survey)? | interview and surveys |
| valuation | What is the outcome being impacted? | attitudes, experiences and reflections on learning |
| esearch type | What type of research? | qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods |
SPICE (Setting, Perspective, Intervention/phenomenon of Interest, Comparison, Evaluation)
Appropriate for : evaluating the outcomes of a service, project, or intervention
Example : What are the impacts and best practices for workplace (S) transition support programs (I) for the retention (E) of newly-hired, new graduate nurses (P)?
| Element | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| etting | What is the context for the question? (Where?) | nursing workplaces (healthcare settings) |
| erspective | For whom is this intervention/program/service designed (users, potential users, stakeholders)? | new graduate nurses |
| ntervention/Interest/Exposure | What action is taken for the users, potential users, or stakeholders? | long term transition support programs (residency/mentorship) |
| omparison | What are the alternative interventions? | no or limited transition support / orientation |
| valuation | What is the results of the intervention or service/how is success measured? | retention of newly hired nurses |
PCC (Problem/population, Concept, Context)
Appropriate for : broader (scoping) questions
Example : How do nursing schools (Context) teach, measure, and maintain nursing students ' (P) technological literacy (Concept))throughout their educational programs?
| Element | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| What are the important characteristics of the participants, or the problem of focus? | nursing students | |
| oncept | What is the core concept being examined by the review? | technological literacy |
| ontext | What is the context for the question? (Could include geographic location, or details about the setting of interest)? | nursing schools |
Background Questions
To craft a strong and reasonable foreground research question, it is important to have a firm understanding of the concepts of interest. As such, it is often necessary to ask background questions, which ask for more general, foundational knowledge about a disorder, disease, patient population, policy issue, etc.
For example, consider the PICO question outlined above:
"For adolescents with type II diabetes does the use of telehealth consultations compared to in-person consultations improve blood sugar control ?
To best make sense of the literature that might address this PICO question, you would also need a deep understanding of background questions like:
- What are the unique barriers or challenges related to blood sugar management in adolescents with TII diabetes?
- What are the measures of effective blood sugar control?
- What kinds of interventions would fall under the umbrella of 'telehealth'?
- What are the qualitative differences in patient experience in telehealth versus in-person interactions with healthcare providers?
- << Previous: Tutorials/Help
- Next: Selecting Databases >>
- Last Updated: Jun 26, 2024 3:00 PM
- URL: https://guides.nyu.edu/doctoralnursing
150 Qualitative and Quantitative Nursing Research Topics for Students

Do not be lazy to spend some time researching and brainstorming. You can either lookup for the popular nursing research topics on social media networks or news or ask a professional writer online to take care of your assignment. What you should not do for sure is refuse to complete any of your course projects. You need every single task to be done if you wish to earn the highest score by the end of a semester.
In this article, we will share 150 excellent nursing research topics with you. Choose one of them or come up with your own idea based on our tips, and you’ll succeed for sure!
Table of Contents
Selecting the Top Ideas for Your Essays in Healthcare & Medicine
Would you like to learn how to write a research paper topic for nursing students? We will share some tips before offering lists of ideas.
Start with the preliminary research. You can get inspired on various websites offering ideas for students as well as academic help. Gather with your classmates and brainstorm by putting down different themes that you can cover. You should take your interests into consideration, but still, remember that ideas must relate to your lessons recently covered in class. You have to highlight keywords and main phrases to use in your text.
Before deciding on one of the numerous nursing school research topics, you should consult your tutor. Make sure that he or she approves the idea. Start writing only after that.
50 Popular Nursing Research Topics
Are you here to find the most popular research topics? They change with each new year as the innovations and technologies move on. We have collected the top discussed themes in healthcare for you.
- Problems Encountered by the Spouses of the Patients with Dyslexia
- Ethics in Geriatrics
- Checklist for the Delivery Room Behavior
- Parkinson Disease: Causes and Development
- Exercises Used to Improve Mental Health
- Effective Tips for Antenatal Treatment
- Syndrome of the Restless Legs: How to Treat It
- Behavior Assessment in Pediatric Primary Care
- Why Can Mother’s Health Be under the Threat During the Child Birth?
- Recommendations for Creating Strong Nursing Communities
- Alzheimer’s Disease and Proper Treatment
- Pre-Term Labor Threats
- Music Therapy and Lactation
- Influence of Ageism on Mental Health
- Newborn Resuscitation Practices
- Effective Therapy for Bladder Cancer
- Approaches to Improving Emotional Health of Nurses
- Skin-to-skin Contact by mothers and Its Consequences
- Does a Nurse Have a Right to Prescribe Drugs?
- Research on Atrial Fibrillation
- Pros & Cons of Water Birth
- Prevention Measures for Those Who Have to Contact Infectious Diseases
- Stroke Disease and Ways to Cure It
- The Role of Governmental Policies on the Hiring of Healthcare Professionals
- Demands for the Critical Care
- Joint Issue Research in Elderly Population
- Why Should Nurses and Healthcare Workers Cooperate?
- The Role of Good Leadership Skills in Nursing Profession
- How to Minimize the Threat of Cardiovascular Problems
- What Should a Nurse Do When an Elderly Refuses to Eat?
- Main Reasons for the Depression to Occur
- Methods Used to Detect an Abused Elderly Patient
- Treatment and Prevention of Acne and Other Skin Problems
- Consequences of the So-Called “Cold Therapy”
- End-of-Life Care Interventions That Work
- Risk factors for Osteoporosis in Female Population
- Alcohol Addiction and How to Get Rid of It
- Emerging Ethical Problems in Pain Management
- Psychiatric Patient Ethics
- How to Teach Female Population about Menopause Management
- Reasons for Aged Patients to Use Alcohol in Nursing Homes
- Family Engagement in Primary Healthcare
- Do the Race and Gender of a Patient Play a Role in Pain Management?
- PTSD in the Veterans of the United States Army
- How to Prepare a Nurse for Primary Healthcare
- The Correlation between Teen Aggression and Video Games
- Outcomes of Abdominal Massage in Critically Sick Population
- Developing an Effective Weight Loss Program: Case Study
- Comparing and Contrasting Public Health Nursing Models in Various Regions
- Mirror Therapy for Stroke Patients Who Are Partially Paralyzed
50 Interesting Nursing Research Topics
Do you wish to impress the target audience? Are you looking for the most interesting nursing research topics? It is important to consider time and recently covered themes. People tend to consider a topic an interesting one only if it is relevant. We have prepared the list of curious ideas for your project.
- Reasons for Hypertensive Diseases
- Self-Care Management and Sickle Cell Grown-Up Patients
- Schizophrenia Symptoms, Treatment, and Diagnostics
- Acute Coronary Syndrome Care
- Getting Ready with Caesarean Section
- What Are Some of the Cold and Cough Medicines?
- Why Do Patients Suffer from Anxiety Disorders?
- Use of the Forbidden Substances in Medicine
- How to Make Wise and Safe Medical Decisions
- CV Imaging Procedure
- Complementary vs. Alternative Therapy
- Can Some Types of Grains Prevent Cardiovascular Diseases?
- Restrictions of Medical Contracts
- How to Cope with High Levels of Stress
- Legal Threats with Non-English Patients
- The Basics of Palliative Care
- Clinical Cardiology Innovations
- How to Reduce Body Temperature in Household Conditions
- What Causes Type II Diabetes?
- Ways to Control Blood Pressure at Home
- Dental/Oral Health in the US
- Is There a Gender Bias in Nursing Profession?
- Gyno Education for the Young Girls
- Bipolar Disorder and Its Main Symptoms
- Methods Used to Recover after Physical Traumas
- The Principles of Sports Medicine
- The Gap between Female and Male Healthcare Professionals
- Increasing the Efficiency of Asthma Management in Educational Establishments
- Different Roles of Clinical Nurses
- Case Study: Successful Treatment of Migraine
- In-depth Analysis of the Ovarian Disorder
- Distant Intensive Treatment Until Questions
- Proper Treatment of Sleep Disorders
- How to Overcome Stressful Situations during Night Shifts
- Effective Methods to Prevent Breast Cancer
- Future of Healthcare & Medicine (Based on Modern Innovations)
- Approaches to Treating Insomnia
- Reproductive Endocrinology
- Diversity in the Field of Medicine
- Issues Associated with Menopause
- Causes and Effects of the Vaginal Atrophy
- Is Child’s Health Insurance a Right or a Privilege?
- Best Practices for Nursing Practitioners
- What Does the Phenomenon of Phantom Pains Stand for?
- Ethical Aspects of Infertility
- Protocol for Headache Treatment
- Moral Aspects of Euthanasia
- Treatment of Homeless People
- Why Should Healthcare System Be Made Free Everywhere in the World?
- Pain Restrictions Evaluation
50 Good Nursing Research Topics
Here is one more list of the nursing topics for research paper. We hope that at least one of these ideas will inspire you or give a clue.
- Advantages of Pet Therapy in Kids with the Autism Disorder
- Contemporary Approaches to Vaccinating Teenagers
- eHealth: The Effectiveness of Telecare and eCare
- Burn-Out in the Nursing Profession: Effective Ways to Handle Stress
- Healing of Bone Injuries
- Providing Spiritual Care: Does It Make Sense?
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Opioid Usage
- Symptoms in ER That Cannot Be Explained by Medicine
- Contemporary Neonatal Practices
- Disorders with the Sexual Heath of an Average Woman
- Typical Causes of Headache
- Top Measures Used to Prevent Pregnancy
- Strategies Used by Government to Finance Healthcare System
- The Possible Consequences of Abortion for Women
- Evaluation of Childbirth Efficacy
- Quality Evaluation Techniques in Healthcare & Medicine
- Maternal Practices in Urban Areas
- Childcare Services Integration in Primary Medicine
- Rules for Pregnant Women Who Suffer from Obesity
- Mental Causes of Anorexia Nervosa
- Self-Instruction Kits
- Post-Natal Period Recommendations
- Midwifery Continuous Treatment & Care
- Case Study: Analyzing Positive Birth Experience
- Issues Related to the Gestational Weight Gain
- The Importance of Healthy Nutrition and Hydration
- What Are the Obligations of Every Nurse in Any Situation?
- Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of ADHD
- Management of Disease and Prevention Methods
- The Importance of Kid and Teen Vaccination
- Termination of Pregnancy: Risks for Female Health
- Obligations of Every Pharmacist
- How to Prevent Child Obesity
- How to Stick to the Safe Sex Culture
- What Are the Main Symptoms of Autism?
- Ethics of the Healthcare Sales Promotion Campaigns
- Pros and Cons of Telemedicine
- Ethics in Pediatric Care
- Therapies Used to Treat Speech Disorders
- Medical Uniform Code Principles
- Psychological Sides of Infant Treatment
- Reasons for Seizures to Happen in Young Adolescents
- Healthcare Home Service and Self-Medicine
- How to Deal with Various Types of Eating Disorders
- Treatment of Patients in Prison
- Patient Security and Human Factors
- Bad Habits and Illnesses Impacted by Social Media and Pop Culture
- Apology Legislation and Regulations
- Antibiotic Resistance in Small Kids
- Nursing Marijuana Management & Control
You should also know that there are qualitative and quantitative nursing research topics. If you decide to base your study on numbers and figures, you should think about the second category. In quantitative research papers, writers must provide statistical data and interpret it to defend a thesis statement or find a solution to the existing problem.
Keep in mind that you can always count on the help of our professional essay writers. They will come up with the good nursing research topics and even compose the whole paper for you if you want.

15% OFF Your first order!
Aviable for the first 1000 subscribers, hurry up!
You might also like:

Why You Should Read a Data Gathering Procedure Example

What Is Culture and What Are Some Popular Culture Essay Topics?
Money-back guarantee
24/7 support hotline
Safe & secure online payment
45 Research Problem Examples & Inspiration

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
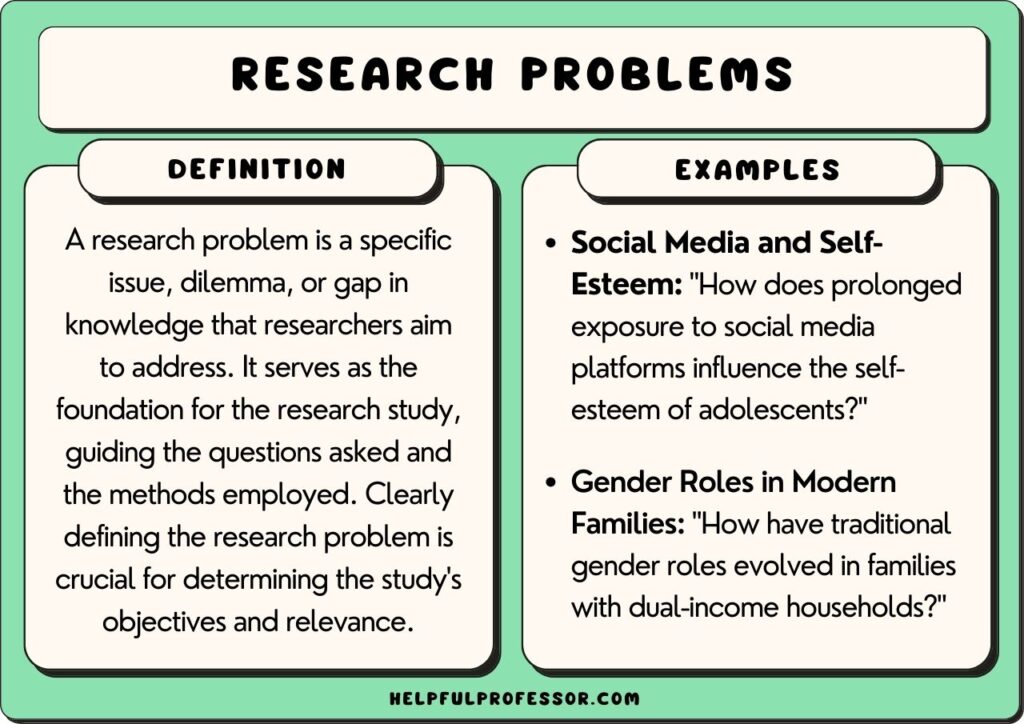
A research problem is an issue of concern that is the catalyst for your research. It demonstrates why the research problem needs to take place in the first place.
Generally, you will write your research problem as a clear, concise, and focused statement that identifies an issue or gap in current knowledge that requires investigation.
The problem will likely also guide the direction and purpose of a study. Depending on the problem, you will identify a suitable methodology that will help address the problem and bring solutions to light.
Research Problem Examples
In the following examples, I’ll present some problems worth addressing, and some suggested theoretical frameworks and research methodologies that might fit with the study. Note, however, that these aren’t the only ways to approach the problems. Keep an open mind and consult with your dissertation supervisor!

Psychology Problems
1. Social Media and Self-Esteem: “How does prolonged exposure to social media platforms influence the self-esteem of adolescents?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Comparison Theory
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking adolescents’ social media usage and self-esteem measures over time, combined with qualitative interviews.
2. Sleep and Cognitive Performance: “How does sleep quality and duration impact cognitive performance in adults?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Psychology
- Methodology : Experimental design with controlled sleep conditions, followed by cognitive tests. Participant sleep patterns can also be monitored using actigraphy.
3. Childhood Trauma and Adult Relationships: “How does unresolved childhood trauma influence attachment styles and relationship dynamics in adulthood?
- Theoretical Framework : Attachment Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of attachment styles with qualitative in-depth interviews exploring past trauma and current relationship dynamics.
4. Mindfulness and Stress Reduction: “How effective is mindfulness meditation in reducing perceived stress and physiological markers of stress in working professionals?”
- Theoretical Framework : Humanist Psychology
- Methodology : Randomized controlled trial comparing a group practicing mindfulness meditation to a control group, measuring both self-reported stress and physiological markers (e.g., cortisol levels).
5. Implicit Bias and Decision Making: “To what extent do implicit biases influence decision-making processes in hiring practices?
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Dissonance Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design using Implicit Association Tests (IAT) to measure implicit biases, followed by simulated hiring tasks to observe decision-making behaviors.
6. Emotional Regulation and Academic Performance: “How does the ability to regulate emotions impact academic performance in college students?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Theory of Emotion
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys measuring emotional regulation strategies, combined with academic performance metrics (e.g., GPA).
7. Nature Exposure and Mental Well-being: “Does regular exposure to natural environments improve mental well-being and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression?”
- Theoretical Framework : Biophilia Hypothesis
- Methodology : Longitudinal study comparing mental health measures of individuals with regular nature exposure to those without, possibly using ecological momentary assessment for real-time data collection.
8. Video Games and Cognitive Skills: “How do action video games influence cognitive skills such as attention, spatial reasoning, and problem-solving?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Load Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design with pre- and post-tests, comparing cognitive skills of participants before and after a period of action video game play.
9. Parenting Styles and Child Resilience: “How do different parenting styles influence the development of resilience in children facing adversities?”
- Theoretical Framework : Baumrind’s Parenting Styles Inventory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of resilience and parenting styles with qualitative interviews exploring children’s experiences and perceptions.
10. Memory and Aging: “How does the aging process impact episodic memory , and what strategies can mitigate age-related memory decline?
- Theoretical Framework : Information Processing Theory
- Methodology : Cross-sectional study comparing episodic memory performance across different age groups, combined with interventions like memory training or mnemonic strategies to assess potential improvements.
Education Problems
11. Equity and Access : “How do socioeconomic factors influence students’ access to quality education, and what interventions can bridge the gap?
- Theoretical Framework : Critical Pedagogy
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative data on student outcomes with qualitative interviews and focus groups with students, parents, and educators.
12. Digital Divide : How does the lack of access to technology and the internet affect remote learning outcomes, and how can this divide be addressed?
- Theoretical Framework : Social Construction of Technology Theory
- Methodology : Survey research to gather data on access to technology, followed by case studies in selected areas.
13. Teacher Efficacy : “What factors contribute to teacher self-efficacy, and how does it impact student achievement?”
- Theoretical Framework : Bandura’s Self-Efficacy Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys to measure teacher self-efficacy, combined with qualitative interviews to explore factors affecting it.
14. Curriculum Relevance : “How can curricula be made more relevant to diverse student populations, incorporating cultural and local contexts?”
- Theoretical Framework : Sociocultural Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of curricula, combined with focus groups with students and teachers.
15. Special Education : “What are the most effective instructional strategies for students with specific learning disabilities?
- Theoretical Framework : Social Learning Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing different instructional strategies, with pre- and post-tests to measure student achievement.
16. Dropout Rates : “What factors contribute to high school dropout rates, and what interventions can help retain students?”
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking students over time, combined with interviews with dropouts.
17. Bilingual Education : “How does bilingual education impact cognitive development and academic achievement?
- Methodology : Comparative study of students in bilingual vs. monolingual programs, using standardized tests and qualitative interviews.
18. Classroom Management: “What reward strategies are most effective in managing diverse classrooms and promoting a positive learning environment?
- Theoretical Framework : Behaviorism (e.g., Skinner’s Operant Conditioning)
- Methodology : Observational research in classrooms , combined with teacher interviews.
19. Standardized Testing : “How do standardized tests affect student motivation, learning, and curriculum design?”
- Theoretical Framework : Critical Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative analysis of test scores and student outcomes, combined with qualitative interviews with educators and students.
20. STEM Education : “What methods can be employed to increase interest and proficiency in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields among underrepresented student groups?”
- Theoretical Framework : Constructivist Learning Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing different instructional methods, with pre- and post-tests.
21. Social-Emotional Learning : “How can social-emotional learning be effectively integrated into the curriculum, and what are its impacts on student well-being and academic outcomes?”
- Theoretical Framework : Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of student well-being with qualitative interviews.
22. Parental Involvement : “How does parental involvement influence student achievement, and what strategies can schools use to increase it?”
- Theoretical Framework : Reggio Emilia’s Model (Community Engagement Focus)
- Methodology : Survey research with parents and teachers, combined with case studies in selected schools.
23. Early Childhood Education : “What are the long-term impacts of quality early childhood education on academic and life outcomes?”
- Theoretical Framework : Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development
- Methodology : Longitudinal study comparing students with and without early childhood education, combined with observational research.
24. Teacher Training and Professional Development : “How can teacher training programs be improved to address the evolving needs of the 21st-century classroom?”
- Theoretical Framework : Adult Learning Theory (Andragogy)
- Methodology : Pre- and post-assessments of teacher competencies, combined with focus groups.
25. Educational Technology : “How can technology be effectively integrated into the classroom to enhance learning, and what are the potential drawbacks or challenges?”
- Theoretical Framework : Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK)
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing classrooms with and without specific technologies, combined with teacher and student interviews.
Sociology Problems
26. Urbanization and Social Ties: “How does rapid urbanization impact the strength and nature of social ties in communities?”
- Theoretical Framework : Structural Functionalism
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative surveys on social ties with qualitative interviews in urbanizing areas.
27. Gender Roles in Modern Families: “How have traditional gender roles evolved in families with dual-income households?”
- Theoretical Framework : Gender Schema Theory
- Methodology : Qualitative interviews with dual-income families, combined with historical data analysis.
28. Social Media and Collective Behavior: “How does social media influence collective behaviors and the formation of social movements?”
- Theoretical Framework : Emergent Norm Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of social media platforms, combined with quantitative surveys on participation in social movements.
29. Education and Social Mobility: “To what extent does access to quality education influence social mobility in socioeconomically diverse settings?”
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking educational access and subsequent socioeconomic status, combined with qualitative interviews.
30. Religion and Social Cohesion: “How do religious beliefs and practices contribute to social cohesion in multicultural societies?”
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys on religious beliefs and perceptions of social cohesion, combined with ethnographic studies.
31. Consumer Culture and Identity Formation: “How does consumer culture influence individual identity formation and personal values?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Identity Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining content analysis of advertising with qualitative interviews on identity and values.
32. Migration and Cultural Assimilation: “How do migrants negotiate cultural assimilation and preservation of their original cultural identities in their host countries?”
- Theoretical Framework : Post-Structuralism
- Methodology : Qualitative interviews with migrants, combined with observational studies in multicultural communities.
33. Social Networks and Mental Health: “How do social networks, both online and offline, impact mental health and well-being?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Network Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys assessing social network characteristics and mental health metrics, combined with qualitative interviews.
34. Crime, Deviance, and Social Control: “How do societal norms and values shape definitions of crime and deviance, and how are these definitions enforced?”
- Theoretical Framework : Labeling Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of legal documents and media, combined with ethnographic studies in diverse communities.
35. Technology and Social Interaction: “How has the proliferation of digital technology influenced face-to-face social interactions and community building?”
- Theoretical Framework : Technological Determinism
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative surveys on technology use with qualitative observations of social interactions in various settings.
Nursing Problems
36. Patient Communication and Recovery: “How does effective nurse-patient communication influence patient recovery rates and overall satisfaction with care?”
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys assessing patient satisfaction and recovery metrics, combined with observational studies on nurse-patient interactions.
37. Stress Management in Nursing: “What are the primary sources of occupational stress for nurses, and how can they be effectively managed to prevent burnout?”
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of stress and burnout with qualitative interviews exploring personal experiences and coping mechanisms.
38. Hand Hygiene Compliance: “How effective are different interventions in improving hand hygiene compliance among nursing staff, and what are the barriers to consistent hand hygiene?”
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing hand hygiene rates before and after specific interventions, combined with focus groups to understand barriers.
39. Nurse-Patient Ratios and Patient Outcomes: “How do nurse-patient ratios impact patient outcomes, including recovery rates, complications, and hospital readmissions?”
- Methodology : Quantitative study analyzing patient outcomes in relation to staffing levels, possibly using retrospective chart reviews.
40. Continuing Education and Clinical Competence: “How does regular continuing education influence clinical competence and confidence among nurses?”
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking nurses’ clinical skills and confidence over time as they engage in continuing education, combined with patient outcome measures to assess potential impacts on care quality.
Communication Studies Problems
41. Media Representation and Public Perception: “How does media representation of minority groups influence public perceptions and biases?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cultivation Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of media representations combined with quantitative surveys assessing public perceptions and attitudes.
42. Digital Communication and Relationship Building: “How has the rise of digital communication platforms impacted the way individuals build and maintain personal relationships?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Penetration Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative surveys on digital communication habits with qualitative interviews exploring personal relationship dynamics.
43. Crisis Communication Effectiveness: “What strategies are most effective in managing public relations during organizational crises, and how do they influence public trust?”
- Theoretical Framework : Situational Crisis Communication Theory (SCCT)
- Methodology : Case study analysis of past organizational crises, assessing communication strategies used and subsequent public trust metrics.
44. Nonverbal Cues in Virtual Communication: “How do nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions and gestures, influence message interpretation in virtual communication platforms?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Semiotics
- Methodology : Experimental design using video conferencing tools, analyzing participants’ interpretations of messages with varying nonverbal cues.
45. Influence of Social Media on Political Engagement: “How does exposure to political content on social media platforms influence individuals’ political engagement and activism?”
- Theoretical Framework : Uses and Gratifications Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys assessing social media habits and political engagement levels, combined with content analysis of political posts on popular platforms.
Before you Go: Tips and Tricks for Writing a Research Problem
This is an incredibly stressful time for research students. The research problem is going to lock you into a specific line of inquiry for the rest of your studies.
So, here’s what I tend to suggest to my students:
- Start with something you find intellectually stimulating – Too many students choose projects because they think it hasn’t been studies or they’ve found a research gap. Don’t over-estimate the importance of finding a research gap. There are gaps in every line of inquiry. For now, just find a topic you think you can really sink your teeth into and will enjoy learning about.
- Take 5 ideas to your supervisor – Approach your research supervisor, professor, lecturer, TA, our course leader with 5 research problem ideas and run each by them. The supervisor will have valuable insights that you didn’t consider that will help you narrow-down and refine your problem even more.
- Trust your supervisor – The supervisor-student relationship is often very strained and stressful. While of course this is your project, your supervisor knows the internal politics and conventions of academic research. The depth of knowledge about how to navigate academia and get you out the other end with your degree is invaluable. Don’t underestimate their advice.
I’ve got a full article on all my tips and tricks for doing research projects right here – I recommend reading it:
- 9 Tips on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 19 Top Cognitive Psychology Theories (Explained)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 119 Bloom’s Taxonomy Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ All 6 Levels of Understanding (on Bloom’s Taxonomy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Self-Actualization Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy)
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Warning: The NCBI web site requires JavaScript to function. more...
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on a Study of National Needs for Biomedical and Behavioral Research Personnel. Personnel Needs and Training for Biomedical and Behavioral Research: The 1983 Report. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1983.

Personnel Needs and Training for Biomedical and Behavioral Research: The 1983 Report.
- Hardcopy Version at National Academies Press
6. Nursing Research
Problems encountered in the practice of nursing are widely varied, important to the health care system, and deserving of a national research effort. Research on these problems, which cover issues ranging from methods to alleviate anxiety and pain to improving the prospects for high-risk infants, is conducted mainly by nurses with doctoral degrees in biomedical and behavioral fields. There were about 2,500 such individuals in 1980 but only 7 percent reported research as a major activity. The numbers are increasing, but a solid core of well-trained investigators has not yet been developed to address all nursing research issues.
- INTRODUCTION
The goal of nursing research is to facilitate the development of clinical nursing interventions which will improve health outcomes and contribute to the optimal delivery of care. To this end, according to the American Nurses' Association, nursing research “develops knowledge about health and the promotion of health over the full life span, care of persons with health problems and disabilities, and nursing actions to enhance the ability of individuals to respond effectively to actual or potential health problems. So defined, nursing research “complement[s] biomedical research, which is primarily concerned with causes and treatments of disease.” 1
- EXAMPLES OF NURSING RESEARCH
The scope of nursing research is very broad, including, for example:
- studies to reduce the complications of hospitalization and surgery (such as respiratory or circulatory problems) and factors that negatively influence recovery
- studies to improve the prospects for high risk infants and their parents (on prematurity, stress-induced complications in childbirth, child abuse, and developmental disabilities, for instance)
- studies of methods to alleviate anxiety, stress, and pain associated with illness or disability
- studies to facilitate the utilization of new technological developments in patient care (such as those concerned with nasogastric tube feeding of hospital patients and techniques for recovery and maintenance of eating and grasping abilities following stroke), (Jacox and Walike, 1975, pp. 2–5).
The Division of Nursing of the Bureau of Health Professions, Health Resources and Services Administration (DHHS) classifies nursing research into six categories: “fundamental,” nursing practice, nursing profession, delivery of nursing services, nursing education, and utilization. Although research in all these categories is likely to have an impact on health outcomes or improved patient care, those with the most direct impact are fundamental and nursing practice research, which jointly accounted for the bulk of all funded studies as of the end of FY 1981 (HRSA, 1983).
The distinction between fundamental and nursing practice research is important and is regarded both by the Division of Nursing and by the nursing profession generally as central to an understanding of the nature and scope of nursing research. Fundamental research is research which addresses or focuses on the biological and/or behavioral functioning of human beings, their environments, and their social systems. It constitutes the science base from which nursing or other clinical practice theories can be developed and tested. The findings and theories developed through fundamental research constitute the pool of knowledge and theories which health practitioners and researchers of various types, including nurses, can draw upon to develop clinical intervention strategies and/or to test the effectiveness and efficiency of different practice methods (Bloch, 1981, p. 87). Examples of fundamental biological and/or behavioral research deemed relevant to the field of nursing and funded by the Division of Nursing include studies on the responses of children to pain, the perceptions of the elderly as concerns their physical functioning and health care needs, the effects of radiotherapy on cancer patients, and the effects of caffeine on pregnancy outcomes.
Nursing practice research, on the other hand, specifically addresses issues related to the practice of nursing as a profession— with nursing interventions, procedures, techniques, and/or methods of patient care being the focus of inquiry. Research designs used in practice research are typically experimental, explicitly postulating and testing the linkages between one or more nursing interventions, procedures, or processes and patient outcomes in controlled experiments. The processes, procedures, techniques, or interventions which are “tested” may be technical, physical, verbal, cognitive, psychosocial, and/or interpersonal. Practice research funded by the Division of Nursing has included studies on endotracheal aspiration of critically ill patients, nurse attention to psychological distress among medical-surgical patients, the effect of nurse empathy on patients, the stress of radiation treatment for cancer patients, and the effectiveness of prenatal care provided to Navajo women, among many others.
While nursing research ultimately aims at improving patient care for persons with existing health impairments and reducing or preventing health-related problems for others, some nursing research explicitly addresses, or has implications for, the relative costs of different types of interventions, procedures, settings, and providers of care—that is, for cost-effective patient care. Fagin ( Am. J. Nursing , Dec. 1982), for example, reviews a number of studies conducted over the past 10 years which demonstrate that innovations in nursing practice and alternative methods of service delivery, treatment, and care can provide equivalent or superior patient outcomes at cost savings over more traditional or usual methods. Reducing hospital length of stay, preventing rehospitalization, reducing the number of outpatient visits, and reducing absenteeism have been among the cost savings demonstrated by some of these studies. Long- or short-term nursing intervention with mothers having a history of child abuse, for example, was found to result in a lower rate of child rehospitalization due to parental abuse or neglect; the addition of a nurse practitioner to a small industrial company's health service was found to reduce employee time lost from work; and patient education programs and educational counseling of patients with a variety of surgical or medical problems have been found to reduce hospital length of stay, hospital readmission rates, the number of outpatient visits, and so forth, compared to control groups not receiving such nursing interventions.
Home care as an alternative to hospitalization was the focus of a number of the studies Fagin reviewed, and all indicated potential or actual savings of home care over hospitalization. For example, training patients to administer intravenous antibiotics at home reduced hospitalization time and treatment expense. Likewise, the mean cost of home care for children dying of cancer with care coordinated by nurses and provided by parents (and physicians serving as consultants) was 18 times less expensive than that provided in a hospital setting for similar children.
- FUTURE NURSING RESEARCH AGENDA
The Commission on Nursing Research of the American Nurses' Association suggests an agenda for the 1980s that would give priority to research that will generate knowledge “to guide practice” in the following broad areas:
- promoting health and well-being, as well as competency for personal care and personal health, among all age groups (including identification of the determinants of wellness and health functioning in individuals and families)
- decreasing the negative impact of health problems on coping abilities, productivity, and life satisfaction of individuals and families
- designing and developing cost-effective health care systems in meeting the nursing needs of the population
- ensuring that the nursing care needs of “vulnerable groups” (including but not limited to racial and ethnic minorities and underserved populations, such as the elderly, the mentally ill, and the poor) are met ( Nursing Research , 1980).
- THE SUPPLY OF RESEARCH PERSONNEL AND DEMAND FOR NURSES WITH DOCTORATES
Nursing research is conducted by investigators trained in numerous disciplines, including general medicine, various medical specialties, various branches of biomedical research, and the behavioral sciences. This diffusion of investigators makes it hard to accurately estimate the number of investigators performing nursing research. However, most nursing research funded by the Division of Nursing, HRSA, is being conducted by nurses, of whom the vast majority have doctorates in nursing or other disciplines. 2 This report therefore focuses on the supply of nurses with doctorates.
The evolution of nursing from a nonacademic discipline relying on apprentice-type training to a recognized profession with its own academic credentials and body of research has been slow, and is still progressing. Until the early 1970s the majority of new Registered Nurses (RNs) were trained in hospital-based nursing schools that conferred diplomas and prepared students for Registered Nurse licensure. By 1981 that mode of preparation had fallen to less than 20 percent. Almost half of newly licensed RNs in 1981 were prepared in associate degree programs (usually in community colleges) and one-third were prepared in baccalaureate programs in 4-year colleges and universities (IOM, 1983, p. 55). Although diploma prepared RNs are declining both as a proportion of new RNs and in absolute numbers, in 1980 they still represented half the supply of employed RNs. Nurses trained in associate degree programs represented 20 percent and RNs with baccalaureate or higher degrees represented 29 percent (IOM, 1983, p. 77). This last group, numbering 364,400 nurses, is the actual and potential pool of nurse researchers since graduates of diploma and associate degree programs are not eligible for advanced degrees unless they upgrade their educational level 3 .
Number of Nurses with Doctorate Degrees
The most comprehensive and most recent study of nurses with doctoral degrees was conducted by the American Nurses' Association (1981). The study estimated that approximately 2,500 (0.15 percent of 1.66 million licensed RNs) held doctoral degrees in 1980. 4 However, although the number is still relatively small, it is increasing rapidly. Between 1963 and 1969 only about 30 nurses earned doctorates each year (ANA, 1981, p. 14). Today that figure is closer to 150 (NLN, 1981, Tables 72 and 73).
There has also been a radical change in the education of nurses with doctorates. The ANA study identified 17 different doctoral degrees obtained by nurses. Up to 1965 the most frequently earned degree was the Ed.D., which was succeeded by the Ph.D. in the 1970s. The professional nursing degree (DNS) was first awarded in the 1960s and has become increasingly represented in new doctoral degrees (ANA, 1981, p. 30). The increase in nursing doctoral degrees has been paralleled by an increase in the number of doctoral programs in nursing education departments—22 in 1981–82 compared to 2 in 1959–60 (NLN, 1983).
Time Spent in Research
However, not all nurses with doctorates are engaged in research activities. Table 6.1 shows that 75 percent of nurses with doctorates are employed in schools of nursing (largely those that offer baccalaureate and higher degrees). Not surprisingly, the amount of time spent in research varies according to the type and place of employment, but overall fewer than 7 percent of the nurses surveyed reported research as a major function (ANA, 1981, p. 44). Table 6.1 also shows that the nurses employed in nursing schools spend, on average, less time on research than nurses in some other settings—for example, other health professional schools. Since most nurses with doctorates work in schools of nursing, this is of concern to those attempting to generate increased nursing research.
Average Percent of Time Spent in Research by Work Setting and Percent of Nurses with Doctorates, 1980.
In 1970, an evaluation of a program designed to encourage faculty research noted that deans and directors of programs found it difficult to free faculty for research, and questioned how much could be expected from faculty in terms of a combined teaching and research load (Abdellah, 1970).
A comment of this sort indicates that research activity may have been regarded as a secondary activity for faculty in nursing schools. In the intervening decade, however, there has been a radical change. More recent data suggest that the expansion of nursing education has increased the demand for doctorally prepared faculty. A survey of 58 graduate nursing programs in 40 states found a need for 1,080 faculty with doctorates in the next 5 years. The survey found that the greatest need was for faculty with preparation that emphasized research and nursing theory development (McElmurry, et al. , 1982, pp. 5–10).
The Institute of Medicine in 1983 estimated that 5,800 nurses with doctorates would be working by the end of 1990–3,000 with doctorates from nursing programs and 2,800 with doctorates in other fields (IOM, 1983, p. 144). This represents an increase of 2,800 nurses with doctorates from the 1980 estimate of 3,000—probably just enough to fill the demand in the 40 states mentioned earlier, but far less than the 1990 projection of need for 14,000 doctorally prepared nurses made by the Health Resources and Services Administration, Division of Nursing (IOM, 1983, p. 145). The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services based its projections of the need for doctorally prepared nurses on the judgment-of-need criteria developed by the Western Interstate Commission on Higher Education. A national panel of expert consultants was convened to establish criteria for staffing patterns and the educational preparation of RNs to meet service needs in different health care settings (hospitals, nursing homes, home care, etc.) and in units within those settings (E.R., newborn units, etc.). If this estimate of demand is even approximately accurate, nurses with doctorates should have no problem finding employment for the next decade at least.
The Infrastructure for Research
A simple enumeration of the number of people qualified to conduct research and the amount of time spent in that activity does not encompass all the important variables that affect the amount of research being conducted. One of these is research funding, which will be discussed later. Another, which is a prerequisite for research, can be described as the infrastructure—the elements that need to be in place before a research area can become established and grow. For nursing research some of the infrastructure is still in the process of development. In 1977 this Committee noted that “even today there are less than 2,000 registered nurses who have completed doctoral education, scarely more than an average of one doctorally trained nurse for each school of nursing in the United States” (NRC, 1975–81, 1977 Report, p. 156). By 1980 only 7 percent of full-time nurse-faculty held doctoral degrees (NLN, 1982, p. 94). This compares unfavorably with other disciplines. Well over 50 percent of the faculty of 20 schools of public health held doctorates and more than 90 percent of faculty held doctorates in schools offering doctoral and other degrees in departments of psychology, physical sciences, biological sciences, mathematical and social sciences, and engineering (IOM, 1983, p. 136).
The relative scarcity of doctorally prepared faculty in nursing schools is likely to have several effects. First, nurses with new doctorates can find ready employment in schools of nursing and are less likely to pursue pure research careers where funding is hard to obtain. Second, as mentioned earlier, nursing school faculty with doctorates are likely to be heavily engaged in teaching and administration at the expense of research, and third, nurses being educated by faculty who do not have the research degree and are not primarily engaged in research do not have role models who might lead them to research careers. Finally, as this Committee noted in 1981, the rapid growth of doctoral training programs (which the data suggest has outstripped the growth in supply of doctorally prepared faculty) has resulted in programs of less than optimal quality (NRC, 1981). 5 In short, nursing research still lacks the solid core of research trained and oriented teachers that are vital to any area of research .
Funds for Nursing Research
The Division of Nursing, HRSA, provided about $5 million annually in funds targeted to nursing research. In 1982 this dropped to close to $3.5 million. The Institute of Medicine in its 1983 study said that this “is not a level of visibility and scientific prestige to encourage scientifically oriented RNs to pursue careers devoted to research…(IOM, 1983, p. 19).” The same report notes that “A substantial share of the health care dollar is expended on direct nursing care…” and that “Despite the fact that nurses represent the largest single group of professionals in the providing of health services to the people of this country, there is a remarkable dearth of research in nursing practice” (IOM, 1983, pp. 216–217). In a stronger statement the study says that “Research in nursing has been handicapped by inadequate levels of support” and contrasts the $5 million annually for nursing research with $1.7 billion for biomedical research between 1976 and 1981, and with dental research which receives five times as much as nursing research (IOM, 1983, p. 137). The study committee suggests that “an increase on the order of $5 million per year for research could have a substantial impact in stimulating growth of capacity for research on nursing-related matters” (IOM, 1983, p. 22).
Other federal money is available for nursing research through the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute of Mental Health, the National Center for Health Services Research, the National Science Foundation, and other agencies. How much these agencies spend for nursing research is not clear. The National Institutes of Health in 1982 made awards worth roughly $2.8 million for projects that were defined as having nursing as a primary component. However, many of these were for training or curriculum development rather than research into nursing practice, and in many cases the abstracts of projects indicated only tangential nursing interest (National Institutes of Health, 1983).
Other sources of funds include the American Nurses' Foundation, which makes small (up to $2,100) awards. The number depends on available funds—23 in 1983, 12 in 1982.
Training Grants and Fellowships
If an adequate supply of qualified individuals to educate researchers and conduct research is an essential component of the infrastructure for research, training grants are a mechanism that can help the development of that infrastructure.
The Division of Nursing, HRSA, currently administers two programs that support graduate nurse training. The largest is for Advanced Training of Professional Nurses. This program awards grants to graduate schools of nursing and schools of public health which allocate the funds to full-time graduate students. Funding for this program totaled $7 million in 1965, and increased to $13 million in 1974. Until 1977 awards were made to undergraduate as well as graduate students. Since 1977 eligibility has been confined to graduate students. In 1983 funding dropped to $9.5 million. Those funds supported approximately 3,500 students in 137 schools, with each student receiving an average of $2,715 (Buchanan, 1983).
The second program—the National Research Service Awards (NRSA)— offers pre- and postdoctoral fellowships to students in nursing and relevant disciplines and institutional grants to schools to support full-time training in research. This program has been funded at about $1 million annually for the past 5 years (see Appendix Table D2 ). A few additional training awards in nursing research are made by the NIH. The Division of Nursing expects to make 38–45 new awards in FY 1983 (Wood, 1983). Only three institutional awards have been made since 1977 and all were phased out in 1981.
Since 1977 this Committee has developed recommendations concerning the number of students to be supported under the NRSA authority in the area of nursing research, the distribution between pre- and postdoctoral students, and the distribution between schools of nursing and other schools and basic science and non-science departments. The general view has been that federal support for nursing research training should emphasize the improvement of programs of demonstrated capability rather than the further proliferation of nursing doctoral programs. The Committee has also recommended that the emphasis of the fellowship programs should be on predoctoral support to increase the pool of research personnel, and provide research faculty to staff the proliferating doctoral nursing programs. In 1977 the Committee recommended that 29 percent of fellowships be awarded to students in graduate schools of nursing in 1979 and should rise to 57 percent by 1981. It was anticipated that schools of nursing would substantially increase their ability to provide research training. In the same report the Committee recommended that the proportion of fellowships in non-science departments fall from 29 percent to zero between 1979 and 1981.
Although the data are not available to show whether the recommendations concerning the training sites of students have been implemented, Table 6.2 shows the Committee's recommendations compared to actual awards where the data are available. Two points are clear from the table. First, funding has not allowed the NRSA fellowship program to reach the recommended levels of support. Second, the proportion of postdoctoral awards has remained well within the limits recommended by the Committee.
Actual and Recommended NRSA Training Awards in Nursing Research, FY 1979–81.
Table 6.2 shows the Committee's recommendations compared to actual awards and demonstrates that for each year funding has failed to allow the programs to reach the recommended levels of support—by substantial shortfalls. For example, in 1979 total awards were only 56 percent of the recommendations. In the following two years that proportion fell to 49 percent. In each year the shortfall in traineeships was greater than in fellowships, with traineeships reaching only 26 percent of the recommended number in 1979, compared to 65 percent for fellowships. In 1981 the gap was even wider with trainees attaining only 17 percent of the recommended level and fellowships achieving 66 percent.
The Institute of Medicine in its study of nursing education reviewed the programs of federal support and recommended an expansion of support of fellowships, loans, and programs at the graduate level “to assist in increasing the rate of growth in the numbers of nurses with masters and doctoral degrees in nursing and relevant disciplines” (IOM, 1983, p. 9). (It should be noted that two members of the committee made a statement of exception to the words “and relevant disciplines.” They argued that nurses should have advanced education in their own discipline—nursing—for a number of reasons including preparation for leadership in nursing and to develop competencies unique to nursing.)
In view of the continued high demand for doctorally prepared nurses and the relative immaturity of the emerging field of nursing research, we agree with the general conclusions of the IOM study. There is a need to continue to promote expertise in nursing research, and financial support for graduate students is a proven mechanism for doing so. As stated in Chapter 1 , the Committee reiterates its past recommendations for research training programs in nursing research under the NRSA Act and extends them through 1987.
Statements of the American Nurses' Association, 1981, as quoted in IOM, 1983.
An informal review of principal investigators awarded research grants by the Division of Nursing in HRSA revealed that through the 1960s nurses with masters degrees were awarded grants. Since the early 1970s most principal investigators of funded projects have doctorates.
It should be noted that a significant number of nurses advance through the educational system. Thirty-five percent of nurses with baccalaureates and half of the nurses with graduate degrees initially prepared for RN licensure in associate degree or diploma programs.
Health Resources and Services Administration estimated the number of nurses with doctorates to be 4,100 in 1980 (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 1982, Table 3). Although this is substantially higher than the ANA estimates it still represents only 0.25 percent of licensed RNs.
Under the Nurse Training Act (P.L. 94–63) some special funding is available to institutions with graduate nursing programs. About 90 programs receive support each year, 10 percent of them being doctoral programs. Appropriations for this Advanced Nursing Training program were at the $12 million level for 3 years, falling to $9.6 million in FY 1982.
- Cite this Page Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on a Study of National Needs for Biomedical and Behavioral Research Personnel. Personnel Needs and Training for Biomedical and Behavioral Research: The 1983 Report. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1983. 6., Nursing Research.
In this Page
Other titles in this collection.
- The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health
Recent Activity
- Nursing Research - Personnel Needs and Training for Biomedical and Behavioral Re... Nursing Research - Personnel Needs and Training for Biomedical and Behavioral Research
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper?

What is a problem statement in research, and why is it crucial? A research problem statement is a clear and precise declaration that identifies the issue or challenge your study aims to tackle. It needs to be understandable to both experts and non-experts alike. You can ensure your statement is effective by basing it on established knowledge and avoiding unsupported claims. This way, you can create a solid foundation for your research.
Okay, we answered what is a problem statement, but why is grounding your statement in a literature review important? A thorough review of existing studies not only provides context but also connects your research to the broader scientific community. This approach helps ensure that your problem statement is both relevant and meaningful, guiding your empirical investigation with a strong, evidence-based foundation.
To effectively write a research problem statement, follow these steps:
- Begin by pinpointing the broad field or subject area that captures your interest.
- Narrow down this general area to a particular issue or challenge that needs attention.
- Provide context by explaining why the problem is important and what gap in current knowledge it addresses.
- Articulate the problem in a clear, succinct manner, ensuring that the language is accessible to your target audience.
- Write in an unbiased and neutral tone, steering clear of subjective language and personal opinions.
Homework Made Simple!
Stop wrestling with your assignments and let our experts simplify it for you!
How to Write a Problem Statement in Specific Situations
Now, let our online essay writer service address how to write a problem statement for a research paper tailored to different research contexts.
Academic Research
In academic research, a problem statement is written after conducting a preliminary literature review. This initial review helps you identify gaps in current knowledge and frame your problem within the context of existing studies. The problem statement should then clearly articulate the specific issue you intend to investigate, its significance, and how your research will contribute to the field.
- Preliminary Literature Review : Identify gaps or inconsistencies in existing research.
- Define the Problem : State the issue clearly, based on the literature review.
- Significance : Explain why the problem matters and what new insights your research will provide.
Business and Management
In business and management contexts, problem statements often address practical issues that impact organizational performance or strategy. These statements are usually formulated after identifying a specific challenge or inefficiency within the company.
- Identify a Challenge : Pinpoint a specific problem affecting the organization.
- Gather Data : Collect relevant data to understand the problem's scope and impact.
- State the Problem : Clearly describe the issue, focusing on its business implications.
- Propose Objectives : Outline the goals of your research or proposed solutions.
Social and Policy Research
For social and policy research, problem statements focus on societal issues or policy gaps. These statements should highlight the broader implications of the problem and the potential impact of the research findings on policy or society.
- Identify a Social Issue : Choose a relevant social or policy issue that needs investigation.
- Contextualize : Provide background information to frame the issue within a larger societal context.
- Define the Problem : Clearly state the issue and its implications for society or policy.
- Significance : Explain how addressing the problem can lead to social or policy improvements.
What is Included in a Problem Statement
.webp)
A comprehensive problem statement does more than just identify a gap in understanding or a lack of essential data. It also explains the importance of addressing this gap. Here are key components to include:
| 🕵️♂️Identification of the Gap | Clearly articulate the specific gap in knowledge or data that your research will address. |
| 💡Significance of the Gap | Explain why this gap matters. How will filling this gap contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your field? |
| 📚Contribution to Knowledge | Discuss how your research will enhance or expand current understanding. Why is your research important? |
| 🔍Multiple Solutions | Acknowledge that there may be multiple solutions to the problem. Emphasize the need for further research to explore these potential solutions. |
| 🎯Research Objectives | Once you have identified the problem and the necessity for a solution or further study, outline how you plan to collect and present the needed data. |
Step 1. Contextualize the Problem
To effectively understand how to write a problem statement for a research paper, you should first contextualize the problem and start by offering background information that sets the stage for your research. This involves presenting the broader area of study and then narrowing it down to the specific issue you will address. By doing so, you help your audience understand the environment in which the problem exists.
Example: If your research focuses on the impact of financial literacy programs on small business owners' ability to secure loans, begin with an overview of the importance of financial literacy in business. Discuss how small businesses contribute to the economy and summarize previous studies on financial literacy's general effects on business success. This context helps to frame your specific research question within the larger discourse.
Detailed Steps:
- Introduce the General Area : Begin with a broad discussion of the field.
- Highlight Key Issues : Identify major themes or problems in the field.
- Narrow Down : Focus on the specific issue your research will address.
Step 2. Establish the Study's Significance
After setting the context, it's crucial to explain why your research is significant. This involves articulating the importance of the problem statement and how your research will contribute to the field. Here, you answer questions like: Why does this problem matter? Who will benefit from the findings?
Example: Continuing with the financial literacy example, explain why understanding its impact on small business owners' ability to secure loans is crucial. Highlight the potential consequences of poor financial literacy, such as higher loan rejection rates, increased financial instability, and business failures. Emphasize how your research could inform policymakers, financial institutions, and educational program designers, leading to more effective financial literacy programs and better support for small businesses.
- Highlight the Gap : Clearly state what is missing in current research.
- Discuss Implications : Explain the broader impact of addressing this gap.
- Identify Beneficiaries : Point out who will benefit from your research findings.
Step 3. Set Your Objectives
Your statement should conclude with clear research aims and objectives. This section outlines what you intend to achieve and the steps you will take to address the problem. Be specific about your research goals and the methods you will use to accomplish them.
Example: For the financial literacy and loan acquisition study, your aims might include evaluating the current financial literacy levels among small business owners, examining the correlation between financial literacy and loan approval rates, and assessing the effectiveness of existing financial literacy programs. Your objectives could be to conduct surveys of small business owners, analyze loan application data, and develop recommendations for improving financial literacy programs based on your findings.
- State Your Aims : Clearly articulate the primary goals of your research.
- Outline Your Objectives : Break down the aims into specific, actionable objectives.
- Describe Your Methods : Briefly mention the research methods you will use to achieve these objectives.
Problem Statement Example
Here, we prepared two research problem statement examples that can serve as unique templates for developing your own statement.
Characteristics of a Research Problem Statement
According to Kerlinger, a good problem statement asks what relationship exists between two or more variables. When learning how to write a problem statement, make sure it has the following characteristics:
.webp)
| 🎯Focus on a Single Issue | Concentrate on one problem at a time to keep the research focused and avoid confusion. For example, study how changes in tax policies affect investments in small businesses, rather than looking at broader economic issues. |
| 🚫No Blaming | Present the problem objectively without pointing fingers. For instance, say, "There is a decrease in water quality in our local river," instead of blaming local industries for polluting the river. |
| 🤔Avoid Specific Solutions | Identify the problem without suggesting specific fixes. For example, instead of recommending "Raising the minimum wage," discuss how income inequality is growing among low-wage workers, leaving room for different solutions to be considered. |
| 🔍Defined by Behaviors and Conditions | Describe the problem in terms of observable actions or measurable situations. For example, "High school dropout rates in our district have risen by 20% in the past five years," highlights a specific issue impacting the community. |
| 📏Specific and Measurable | Clearly define the problem using precise terms that allow for measurement and evaluation. For instance, stating, "Customer satisfaction scores have dropped by 15% in the last quarter," provides a measurable metric to assess the problem. |
| 📣Reflects Community Concerns | Incorporate feedback from community surveys or consultations into the problem statement. For example, stating, "Residents are worried about the lack of affordable housing options," reflects local priorities and concerns. |
Writing a clear problem statement helps you pinpoint the exact issue, explain why it matters, and set specific goals. Whether you're looking into social issues or business problems, a well-defined statement directs your study toward valuable insights and solutions. If you ever need expert research proposal help , remember that together, we can transform your ideas into impactful studies that drive positive change!
Scratching Your Head Over Problem Statements?
Don't overcomplicate it - let our experts show you how it's done right!
What is a Problem Statement in Research?
How to write a problem statement, how do you structure a good problem statement.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- Rupam. (n.d.). Research Problem and its Characteristics . https://www.tpscollegepatna.org/admin-panel/image/content/Research%20Problem%20and%20its%20Characteristics.pdf
- Characteristics of a Quality Problem Statement . (n.d.). https://static1.squarespace.com/static/57e9e21f2e69cf4b7cee5ba0/t/5935d3e003596eebfc6b0463/1496699873373/Characteristics+of+a+Quality+Problem+Statement+%281%29.pdf
.webp)
- Open access
- Published: 25 June 2024
Skill development practice-related challenges, and associated factors among nursing students
- Bizuayehu Atinafu Ataro 1 ,
- Almaz Addisie 2 ,
- Temesgen Geta Hardido 1 ,
- Getachew Nigussie Bolado 1 ,
- Dawit Simeon Bilate 1 ,
- Yakob Lencha Leka 3 &
- Beskut Bezabih 1
BMC Nursing volume 23 , Article number: 429 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Nurse students reportedly face lots of challenges during skill development practice in health institutions. However, the prevalence of challenges and factors associated aren’t well understood yet.
The objective of the study was to identify the challenges experienced by nursing students in health institutions during skill development practice.
A cross-sectional study was employed on the participants selected using a simple random sampling technique. The data was cleaned using Epi-data and exported to SPSS for analysis. Logistic regression analysis and correlation analysis were carried out to identify the associated factors.
The participants are more challenged by instructor factors (43.6%) and facility factors (40%). The prevalence of the challenge was 16.9%. Substance use and learning institutions are found to be independent predictors. A negative correlation was identified between the total challenge score and the overall competency score.
The determined nursing students’ challenges are strong enough to affect the quality of education; therefore, it is essential to plan and improve the students’ integrated supportive supervision.
Peer Review reports
Nursing education contains theoretical and practical aspects. A large portion of nursing education is undertaken at health institutions. Clinical skill development institutions play an essential role in achieving professional competence, as nursing is a practical-based discipline. The clinical practice environment can determine nursing students’ choice or rejection of a nursing field as a profession. The teaching and learning process conducted at a clinical exercise facility is affected by lots of factors even though it paves the way for nursing students to gain mental, psychological, and psychomotor skills that are necessary for patient care [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ].
The clinical learning environment includes the clinical setting, clinical staff, patients, and tutors. Challenges around the clinical environment affect the quality of nursing education and influence the achievement of learning outcomes; hence, there should be a plan to select the best clinical learning environment, which is difficult to achieve in developing nations [ 1 , 2 ].
An internship site is a potential source of anxiety, disappointment, and disgust; therefore, the link between the instructors, staff nurses, and patients is very essential to form the student’s clinical training, to cope, and to reduce the real shock [ 1 ]. As the students are required to equip themselves with the expected skills such as independence, critical thinking, communication, time management, responsibility, accountability, and clinical judgment via clinical practice, the quality of the practicum setting is vital and fine to realize the demanded product by averting the upcoming institutional shock [ 3 ]. A standardized clinical practice institution has a positive effect on the student’s professional growth, whereas a suboptimal clinical practice environment could retard their professional development process [ 10 , 11 ].
The academic experience developed by poor clinical instruction exposes the students to performance alteration in the clinical area, which in turn negatively affects their skill development at health institutions [ 11 ]. Identifying challenges encountered by nursing students during clinical practice could help the stakeholders solve the identified problems, which contributes to professional endurance [ 2 ]. Whereas reluctance to recognize the challenges could bump the teaching and learning process productivity at a health facility [ 12 ].
The students’ ineffective contact with the clinical learning environment reportedly resulted in a significant surge in the academic failure rate. The outnumbered nursing students are forced to leave their profession as a result of the many challenges experienced during skill development practice [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 ].
The nursing students’ inadequate skills lead to anxiety in real work. In significant numbers of the highest institutions, fresh graduates have plenty of theoretical knowledge, but they aren’t competent enough in the skill aspect. To boost the quality of health system function with adequate numbers of skilled, interested, and reinforced nurses who show good work ethics at all times, the possible constraints around skill development sites should be identified and solved [ 11 , 14 ].
The clinical area where nurses acquire clinical skills in sub-Saharan Africa is challenged by individual factors (student and nurse tutor factors), socioeconomic factors, and the hospital environment [ 16 , 17 , 18 ]. A study done in Ghana showed that nursing students failed to apply theory to practice because of the absence of a strong supportive supervision system in clinical settings [ 6 ].
Some students have an unfavorable attitude toward clinical practice, and the majority of them reported that a late approach to clinical practice makes them not adequately prepared for clinical practice; therefore, more supportive and relevant interventions should be implemented based on the identified challenges to help the students achieve a higher level of skill development. Furthermore, determining the challenges being bumped during professional skill development could help to work on the gap, advance training, and boost the quality of clinical practice [ 15 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 ]. Therefore, the current study was carried out to identify the challenges in health institutions faced by nursing students.
Study objectives
To determine the challenges experienced by nursing students during skill development practice in health institutions.
To identify the factors associated with challenges faced by nursing students during skill development practice in health institutions.
Materials and methods
Research design and setting.
A cross-sectional study was carried out at the highest institutions of Addis Ababa City, which is the capital city of Ethiopia and the headquarters of the African Union. The study was conducted from February 15 to April 30, 2022.
Participants and sample size calculation
All third- and fourth-year undergraduate nursing students with over one year of clinical practice experience from both public and private higher institutions who are available during a study period were considered as a study population and included in the study.
The sample size was determined by a single population proportion formula. A simple random sampling technique was used for the selection of study subjects. N was 373, and P was 25.2% from previous research [ 21 ]. Based on this formula n = 290. As the study population was less than 10,000 finite populations, a correction formula was applied to get \(163\) , and after adding a 5% non-responsive rate, the final sample size required for this study was 172 subjects.
The final sample size was allocated to the selected institutions by proportion [ 22 ] (Fig. 1 ).

Sampling procedure
Dependent variable
Challenges faced during skill development practice.
Independent variables
Socio-demographic characteristics - age, sex, ethnic group, marital status, religion, and others.
Possible factors affecting clinical setting practice - individual student nurse factors, staff nurses factors, instructor factors, management factors, facilities/clinical education factors, and clinical practice competence-related factors.
Operational definitions
Challenge: score ranges from 40 to 200.
More challenged or higher challenge score- a median score of 120 and above.
The rest were categorized as having minimal or low challenge.
With one item it was 3, and with 40 items it was 120.
Data collection and tool
The data was collected by trained data collectors. The data was collected by an English-version tool adapted from a related study and amended after the pilot test based on the prevailing context of nursing schools in Ethiopia to make it fit the study population [ 21 , 23 ]. After the pilot test, the content validity was tested, the tool had good construct validity, and Cronbach’s alpha was 0.831. The entailed changes to the tool include: ambiguity and interpretation-related issues were identified and resolved; errors were identified and fixed; the response rate was identified; discrepancies were detected and managed; and the appropriateness of the allotted time was determined and revised. The instrument had three sections. Section one: sociodemographic variables include age, sex, institution name, marital status, and others. Section two: a closed-ended item that assesses a challenge in a clinical setting. Section three: six closed-ended items for competency assessment. A tool had a 5-point Likert scale to represent the challenges in a clinical setting for a topic scored on a 5-point scale.
Data analysis
Epidata and Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) software version 26 were used for this study to clean and analyze the data, respectively. Logistic regression analysis and correlation analysis were carried out to identify the associated factors, and significance was declared at a p-value of < 0.05.
Socio-demographic characteristics of the study participants
A total of 172 nursing students participated in the study, with a response rate of 100%. Of the 172 study participants, 123 (71.5%) were female, and 133 (77.3%) of them were in the age group of 18–25 years. 108 (62.8%) were Orthodox religious followers, and 69 (40.1%) were from St. Mary Health Science College (Table 1 ).
Prevalence of challenge
Concerning the management domain, more challenges are reported on the resource or equipment aspect. Furthermore, 12.2% of the participants reported failure in communication between students and tutors. 11% of the participants reported insufficient preparation skills before the internship, and 51.2% of the participants indicated that they were challenged by resource or equipment limitations. Participants were most challenged by instructor factors (43.6%). 9.3% of the participants mentioned that they feel discriminated against when not allowed to participate in patient rounding with students of medicine and reported the presence of discrimination between them and other health science students.
The prevalence of challenges among nursing students was found to be 16.9% (Fig. 2 ).

Prevalence of Challenges among the participants
Factors associated with the challenge of nursing students
Religion, residence, entrance year, learning institution, and substance use were found to have an association with challenges in the bivariate analysis. However, after controlling for the effect of confounding factors in multivariable analysis, substance use and learning institutions were found to have a significant association.
A statistically significant negative moderate correlation was identified between the total challenge score and the overall competency score. This implies that as the students’ challenge score increases, their competency score decreases. This finding is supported by bivariate logistic regression: for each additional score in the total challenge score, the odds that the nursing students will have a good competency decrease by about 3% (Table 2 ).
The prevalence of challenges among nursing students was found to be 16.9%, which is lower than a study conducted in the Amhara region, northern Ethiopia (25.2%), and the University of Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia (48.7%) [ 16 , 24 ]. The possible reason for the variation is the difference in the characteristics of the study participants. Some studies included only public learning institutions, while others included only private institutions, whereas this study included both public and private higher education institutions.
The odds of having a challenge for study participants who were substance users were 8.25 times higher than those who were not substance users. The possible justification for this association might be that substance users are less likely to comply with the standards of the teaching and learning process, which might have the potential to develop a negative attitude toward those who teach them, such as instructors and nurse staff.
The percent odds of facing challenges for those who were learning in Public Education Institution B were 90% lower than those learning in Private Education Institution A. Similarly, the percent odds of having a challenge for the participants from Private Education Institution B were 97% less than those of the participants from Private Education Institution A. This implies that these two learning institutions, namely Public Education Institution B and Private Education Institution B, are using a relatively good practical education system for their students. In a study done in Iran, Benha Public Hospital had the highest mean score of challenge (65.3%) among private hospitals [ 17 ].
For action to take place in practical areas to resolve problems, Wambui et al.’s study [ 13 ] revealed that proper treatment and communication with students an important items for nursing teachers to be role models for students. That remark agrees with the findings of this study as 12.2% of the students in this study lack proper communication with their instructors.
9.3% of the participants mentioned that they feel discriminated against when not allowed participation in patient rounding with students of medicine and reported the presence of discrimination between them and other health science students; the finding was consistent with a study done in Iran [ 17 ]. The students’ lack of skill as a result of inadequate preparation before arriving at the clinical environment creates problems for them and nursing teachers ( 25 – 26 ), those findings are supported by this study’s finding as about 11% of the participants didn’t have sufficient preparation before the internship. Concerning the management domain, 51.2% of the study participants indicated that they are challenged by resource or equipment limitations. This showed that the participants of this study were more challenged than the participants of a study conducted in Northwest Ethiopia (22.9% of the participants were outspoken about the shortage of equipment that affected their skill development accomplishment) [ 24 ].
Generally, the participants are more challenged by instructor factors (43.6%) which corroborates the findings of other studies [ 27 ]. Hence, nurse instructors should undertake strong supportive supervision and should have effective communication with their students.
Limitations of the study
The study was undertaken via an institutional-based comparative cross-sectional study design using a self-administered English version of a questionnaire adapted from a related study, and amended after the pretest; hence the study didn’t address the issue of casual relationships. Therefore, the authors recommend that researchers consider a longitudinal study and a mixed approach while thinking about conducting further studies on related titles.
The prevalence of challenges nursing students face in their practical education was found to be reasonable. There was a moderately negative correlation between the students’ challenge score and their competency score, which indicates the negative effect of the student’s challenge on their competency level. Therefore, statistically significant factors should be considered in the effort made to reduce the students’ challenge level and improve the quality of practical education.
The instructors and clinical facilitators are better able to assist the students in linking theory with practice successfully, as a higher percentage of the student nurses are being challenged by instructor-related factors. Working on the reduction of substance use among the students is demanded to reduce the challenge resulting from substance use and to improve the competency of the students as well.
Generally, the results of this study could have a significant contribution to nursing practice and the development of nursing skills as it has identified major challenges encountered by nursing students during skill development practice at health institutions. So that the stakeholders and the responsible bodies can work on the identified major challenges and associated factors to improve the quality of education, particularly in the practicum domain.
Data availability
All information and materials described in the research will be freely available to any researchers wishing to use them for non-commercial purposes without breaching participant confidentiality. The datasets used during the current study is not publicly available in order to maintain data security but is available from corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Addis Ababa University
Bachelor of Science
Clinical learning environment
Ethiopian Birr
Focus Group Discussion
Gregorian Calendar
Health Workers
Interquartile Range
Institutional Review Board
Operation Room
Ibrahim A, Aly A. Clinical judgment among nursing interns. Clin Nurs Stud. 2018;6(3). https://doi.org/10.5430/cns.v6n3p19 .
Kim H, Suh EEJA. The effects of an interactive nursing skills mobile application on nursing students’ knowledge, self-efficacy, and skills performance: A randomized controlled trial. 2018;12(1):17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anr.2018.01.001 .
Adjei CA, Sarpong C, Attafuah PA, Amertil NP, Akosah YA. We’ll check vital signs only till we finish the school: experiences of student nurses regarding intra-semester clinical placement in Ghana. BMC Nurs. 2018;17(1):23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-018-0292-0 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Farzi S, Shahriari M. Farzi SJJoe, promotion h. Exploring the challenges of clinical education in nursing and strategies to improve it: A qualitative study. 2018;7. https://doi.org/10.4103%2Fjehp.jehp_169_17
Eyikara E, Baykara ZGJWJETCI. The importance of Simulation. Nurs Educ. 2017;9(1):2–7. https://doi.org/10.18844/wjet.v9i1.543 .
Article Google Scholar
Bussard ME, Jessee MA, El-Banna MM, Cantrell MA, Alrimawi I, Marchi NM, Gonzalez LI, Rischer K, Coy ML, Poledna M, Lavoie P. Current practices for assessing clinical judgment in nursing students and new graduates: a scoping review. Nurse Educ Today. 2023 Dec;21:106078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2023.106078 .
Immonen K, Oikarainen A, Tomietto M, Kääriäinen M, Tuomikoski A-M, Kaučič BM et al. Assessment of nursing students’ competence in clinical practice: A systematic review of reviews. 2019;100:103414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2019.103414 .
Alharbi AR, Alhosis KF. The challenges and difficulties of the nursing interns during their clinical internship in Qassim Region, Saudi Arabia. Saudi J Health Sci. 2019;8(1):6. https://doi.org/10.4103/sjhs.sjhs_143_18 .
Adib-Hajbaghery M, Sharifi NJN. Effect of simulation training on the development of nurses and nursing students’ critical thinking: A systematic literature review. 2017;50:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2016.12.011 .
MacLean S, Kelly M, Geddes F, Della PJN. Use of simulated patients to develop communication skills in nursing education: an integrative review. 2017;48:90–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2016.09.018 .
Gouifrane R, Lajane H, Benmokhtar S, Dehbi F, Radid MJTONJ. Investigating learning challenges from the perspective of nursing students and educators at a university in Casablanca. Morocco. 2020;14(1). https://doi.org/10.2174/1874434602014010109 .
Drateru KCJTAU. Uganda. Challenges Experienced by Student Nurses During Skill Acquisition at The Clinical Area. Nur Primary Care. 2019;3(3):1–4. 2021. https://doi.org/10.33425/2639-9474.1104 .
Wambui WM, Githui SN. Nurse Interns’ Satisfaction With The Clinical Learning Environment: A Cross-Sectional Study. 2019. URL: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/360021595 .
Turner K, Sitanon T, Charoensuk S, von Bormann S, Sawaengdee KJJTRTAN. Nurse competencies and associated factors in the context of nursing education institutions in Thailand. 2019;20:93–URL101: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344464308 .
Gemuhay HM, Kalolo A, Mirisho R, Chipwaza B, Nyangena EJNR. Practice. Factors affecting performance in clinical practice among preservice diploma nursing students in Northern Tanzania. 2019;2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3453085 . eCollection 2019.
Getie A, Tsige Y, Birhanie E, Tlaye KG, Demis AJB. Clinical practice competencies and associated factors among graduating nursing students attending universities in Northern Ethiopia: institution-based cross-sectional study. 2021;11(4):e044119. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-044119 .
Safan SM, Ebrahim RMR. Problems and obstacles facing nursing interns and its relation to their performance at clinical setting: a comparative study. Am J Nurs. 2018;7(6):304–DOI. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajns.20180706.24 .
Hailu M, Welday M, Haftu A, Tadesse D, Weldeamanel T, Amsalu B, Guta A, Kassie N, Sema A, Mohammed A, Abdurashid N. Clinical practice competence and its associated factors among midwifery and nursing students at dire dawa health sciences colleges, East Ethiopia, 2020. Advances in Medical Education and Practice. 2021 Dec 30:1539–47. https://doi.org/10.2147/AMEP.S347080 .
Okamoto R, Koide K, Maura Y, Tanaka MJOJN. Realities of reflective practice skill among public health nurses in Japan and related learning and lifestyle factors. 2017;7(5):513–23. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojn.2017.75040 .
Lundell Rudberg S, Westerbotn M, Sormunen T, Scheja M, Lachmann HJB. Undergraduate nursing students’ experiences of becoming a professional nurse: a longitudinal study. 2022;21(1):219. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-022-01002-0 .
Zenani NE. Challenges experienced by second and third-year nursing students when integrating theory into practice in a selected clinical setting in the Western Cape Province. 2017.
Behnam M, Kamran A, Savadpoor MT, Nasiri K, Khaki M, Ghassemi N, et al. The compatibility of the new undergraduate nursing curriculum with occupational needs from the viewpoint of the faculty members of some north and north-west Universities of Medical Sciences of Iran. Future Med Educ J. 2018;8(4):39–45. https://doi.org/10.22038/fmej.2018.34659.1225 .
Lee H, Shimotakahara R, Fukada A, Shinbashi S, Ogata SJH. Impact of differences in clinical training methods on generic skills development of nursing students: a text mining analysis study. 2019;5(3). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01285 .
Aragaw Y, Sinishaw W, Daba W, Mekie M. Attitude of nursing and midwifery students towards clinical practice and its associated factors in Northwest Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. BMC Res Notes. 2019;12(1):205. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-019-4230-3 .
Kamphinda S, Chilemba EB. Clinical supervision and support: perspectives of undergraduate nursing students on their clinical learning environment in Malawi. Curationis. 2019;42(1). https://doi.org/10.4102/curationis.v42i1.1812 .
Jothishanmugam A, MOHAMMED A, HAMID HIAA, ALI MAAJIJoHSviHiijipiav. Perception of nursing students about the nursing profession. 2019;30864. URL: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348650666 .
Bennett LLJAJ, The Gap Between Nursing Education and Clinical Skills. 2017;28 (4). URL:https://www.proquest.com/docview/2039834640?sourcetype=Scholarly%20Journal .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors express their heartfelt gratitude to God, first and foremost, for lending a helping hand in the successful completion of this research. Last but not least, the authors thank the management and staff of the health institution that participated in this study for their contributions.
Funding for this study was not provided by any institution or agency
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Wolaita Sodo University, Wolaita Sodo, Ethiopia
Bizuayehu Atinafu Ataro, Temesgen Geta Hardido, Getachew Nigussie Bolado, Dawit Simeon Bilate & Beskut Bezabih
Addis Ababa University, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Almaz Addisie
Dawro Tarcha Teaching Hospital, Dawro Tercha, Ethiopia
Yakob Lencha Leka
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
B.A.A., and A.A. were the principal investigators and leading authors of the study, prepared the manuscript, trained field researchers for data collection, and wrote the draft and reviews of the manuscript. T.G.H., G.N.B., D.S.B., Y.L.L., and B.B. participated in the data analysis, interpretation, conceptualization of the paper (report), manuscript preparation, review of the manuscript for publication, and other necessary document preparation for publication. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Bizuayehu Atinafu Ataro .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical approval was obtained from the Addis Ababa University Institutional Review Board on February 11, 2022, and the data was collected from February 15 to April 30, 2022. Written, informed consent was obtained from the subjects before study initiation. The study was conducted after permission from concerned management bodies was obtained. All the necessary measures have been taken to secure the rights, autonomy, and confidentiality of the study subjects according to the Helsinki Declaration.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Ataro, B.A., Addisie, A., Hardido, T.G. et al. Skill development practice-related challenges, and associated factors among nursing students. BMC Nurs 23 , 429 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-02115-4
Download citation
Received : 04 March 2024
Accepted : 19 June 2024
Published : 25 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-02115-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Skill development practice
- Associated factors
- Nursing student
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Research Problem
Ai generator.

A research problem is a specific issue or gap in knowledge that a researcher aims to address through systematic investigation. It forms the foundation of a study, guiding the research question, research design , and potential outcomes. Identifying a clear research problem is crucial as it often emerges from existing literature, theoretical frameworks, and practical considerations. In a student case study , the research question and hypothesis stem from the identified research problem.
What is a Research Problem?
A research problem is a specific issue, difficulty, contradiction, or gap in knowledge that a researcher aims to address through systematic investigation. It forms the basis of a study, guiding the research question, research design, and the formulation of a hypothesis.
Examples of Research Problem
- Impact of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health : Investigating how social media usage affects the mental health and well-being of teenagers.
- Climate Change and Agricultural Productivity : Examining the effects of climate change on crop yields and farming practices.
- Online Learning and Student Engagement : Assessing the effectiveness of online learning platforms in maintaining student engagement and academic performance.
- Healthcare Access in Rural Areas : Exploring the barriers to healthcare access in rural communities and potential solutions.
- Workplace Diversity and Employee Performance : Analyzing how workplace diversity influences team dynamics and employee productivity.
- Renewable Energy Adoption : Studying the factors that influence the adoption of renewable energy sources in urban versus rural areas.
- AI in Healthcare Diagnostics : Evaluating the accuracy and reliability of artificial intelligence in medical diagnostics.
- Gender Disparities in STEM Education : Investigating the causes and consequences of gender disparities in STEM education and careers.
- Urbanization and Housing Affordability : Exploring the impact of rapid urbanization on housing affordability and availability in major cities.
- Public Transportation Efficiency : Assessing the efficiency and effectiveness of public transportation systems in reducing urban traffic congestion.
Research Problem Examples for Students
- The Impact of Homework on Academic Achievement in High School Students
- The Relationship Between Sleep Patterns and Academic Performance in College Students
- The Effects of Extracurricular Activities on Social Skills Development
- Influence of Parental Involvement on Students’ Attitudes Toward Learning
- The Role of Technology in Enhancing Classroom Learning
- Factors Contributing to Student Anxiety During Exams
- The Effectiveness of Peer Tutoring in Improving Reading Skills
- Challenges Faced by International Students in Adapting to New Educational Systems
- Impact of Nutrition on Concentration and Academic Performance
- The Role of Socioeconomic Status in Access to Higher Education Opportunities
Research Problems Examples in Education
- Effect of Class Size on Student Learning Outcomes
- Impact of Technology Integration in Classroom Instruction
- Influence of Teacher Professional Development on Student Achievement
- Challenges in Implementing Inclusive Education for Students with Disabilities
- Effectiveness of Bilingual Education Programs on Language Proficiency
- Role of Parental Involvement in Enhancing Academic Performance
- Impact of School Leadership on Teacher Retention and Job Satisfaction
- Assessment of Remote Learning Efficacy During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Barriers to STEM Education Participation Among Female Students
- Effect of Socioeconomic Status on Access to Quality Education
Research Problems Examples in Business
- Impact of Employee Engagement on Productivity and Retention
- Effectiveness of Social Media Marketing Strategies on Consumer Behavior
- Challenges in Implementing Sustainable Business Practices
- Influence of Leadership Styles on Organizational Performance
- Role of Corporate Culture in Driving Innovation
- Impact of Remote Work on Team Collaboration and Communication
- Strategies for Managing Supply Chain Disruptions
- Effect of Customer Feedback on Product Development
- Challenges in Expanding into International Markets
- Influence of Brand Loyalty on Customer Retention
Basic Research Problem Examples
- Effect of Sleep on Cognitive Function
- Impact of Exercise on Mental Health
- Influence of Diet on Academic Performance
- Role of Social Support in Stress Management
- Impact of Screen Time on Children’s Behavior
- Effects of Pollution on Public Health
- Influence of Music on Mood and Productivity
- Role of Genetics in Disease Susceptibility
- Impact of Advertising on Consumer Choices
- Effects of Climate Change on Local Wildlife
Research Problem in Research Methodology
A research problem in research methodology refers to an issue or gap in the process of conducting research that requires a solution. Examples include:
- Validity and Reliability of Measurement Tools : Ensuring that instruments used for data collection consistently produce accurate results.
- Selection of Appropriate Sampling Techniques : Determining the best sampling method to ensure the sample represents the population accurately.
- Bias in Data Collection and Analysis : Identifying and minimizing biases that can affect the validity of research findings.
- Ethical Considerations in Research : Addressing ethical issues related to participant consent, confidentiality, and data protection.
- Generalizability of Research Findings : Ensuring that research results are applicable to broader populations beyond the study sample.
- Mixed Methods Research Design : Effectively integrating qualitative and quantitative approaches in a single study.
- Data Interpretation and Reporting : Developing accurate and unbiased interpretations and reports of research findings.
- Longitudinal Study Challenges : Managing the complexities of conducting studies over extended periods.
- Control of Extraneous Variables : Identifying and controlling variables that can affect the dependent variable outside the study’s primary focus.
- Developing Theoretical Frameworks : Constructing robust frameworks that guide the research process and support hypothesis development.
Characteristics of a Research Problem
- Clarity : The research problem should be clearly defined, unambiguous, and understandable to all stakeholders.
- Specificity : It should be specific and narrow enough to be addressed comprehensively within the scope of the research.
- Relevance : The problem should be significant and relevant to the field of study, contributing to the advancement of knowledge or practice.
- Feasibility : It should be practical and manageable, considering the resources, time, and capabilities available to the researcher.
- Novelty : The research problem should address an original question or gap in the existing literature, providing new insights or perspectives.
- Researchability : The problem should be researchable using scientific methods, including data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Ethical Considerations : The research problem should be ethically sound, ensuring no harm to participants or the environment.
- Alignment with Objectives : The problem should align with the research objectives and goals, guiding the direction and purpose of the study.
- Measurability : It should be possible to measure and evaluate the outcomes related to the problem using appropriate metrics and methodologies.
- Contextualization : The problem should be placed within a broader context, considering theoretical frameworks, existing literature, and practical applications.
Types of Research Problems
- Aim: To describe the characteristics of a specific phenomenon or population.
- Example: “What are the key features of successful online education programs?”
- Aim: To compare two or more groups, variables, or phenomena.
- Example: “How does employee satisfaction differ between remote and on-site workers?”
- Aim: To determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables.
- Example: “What is the impact of leadership style on employee productivity?”
- Aim: To examine the relationship between two or more variables.
- Example: “What is the relationship between social media usage and self-esteem among teenagers?”
- Aim: To explore a new or under-researched area where little information is available.
- Example: “What are the emerging trends in consumer behavior post-pandemic?”
- Aim: To solve a specific, practical problem faced by an organization or society.
- Example: “How can small businesses improve their cybersecurity measures?”
- Aim: To expand existing theories or develop new theoretical frameworks.
- Example: “How can existing theories of motivation be integrated to better understand employee behavior?”
- Aim: To evaluate the effects of policies or suggest improvements.
- Example: “What are the effects of the new minimum wage laws on small businesses?”
- Aim: To investigate ethical issues within a field or practice.
- Example: “What are the ethical implications of AI in decision-making processes?”
- Aim: To address issues that span multiple disciplines or fields of study.
- Example: “How can principles of environmental science and economics be combined to develop sustainable business practices?”
How to Define a Research Problem
Defining a research problem involves several key steps that help in identifying and articulating a specific issue that needs investigation. Here’s a structured approach:
- Choose a general area of interest or field relevant to your expertise or curiosity. This can be broad initially and will be narrowed down through the next steps.
- Review existing research to understand what has already been studied. This helps in identifying gaps, inconsistencies, or areas that need further exploration.
- Based on your literature review, refine your broad topic to a more specific issue or aspect that has not been adequately addressed.
- Ensure the problem is significant and relevant to the field. It should address a real-world issue or theoretical gap that contributes to advancing knowledge or solving practical problems.
- Clearly articulate the problem in a concise and precise manner. This statement should explain what the problem is, why it is important, and how it impacts the field.
- Develop specific research questions that your study will answer. These questions should be directly related to your problem statement and guide the direction of your research.
- Establish clear research objectives that outline what you aim to achieve. Formulate hypotheses if applicable, which are testable predictions related to your research questions.
- Consider the resources, time, and scope of your study. Ensure that the research problem you have defined is feasible to investigate within the constraints you have.
- Discuss your defined research problem with peers, mentors, or experts in the field. Feedback can help refine and improve your problem statement.
Importance of Research Problem
The research problem is crucial as it forms the foundation of any research study, guiding the direction and focus of the investigation. It helps in:
- Defining Objectives : Clarifies the purpose and objectives of the research, ensuring the study remains focused and relevant.
- Guiding Research Design : Determines the methodology and approach, including data collection and analysis techniques.
- Identifying Significance : Highlights the importance and relevance of the study, demonstrating its potential impact on the field.
- Focusing Efforts : Helps researchers concentrate their efforts on addressing specific issues, leading to more precise and meaningful results.
- Resource Allocation : Assists in the efficient allocation of resources, including time, funding, and manpower, by prioritizing critical aspects of the research.
FAQ’s
Why is defining a research problem important.
Defining a research problem is crucial because it guides the research process, helps focus on specific objectives, and determines the direction of the study.
How do you identify a research problem?
Identify a research problem by reviewing existing literature, considering real-world issues, discussing with experts, and reflecting on personal experiences and observations.
What is the difference between a research problem and a research question?
A research problem identifies the issue to be addressed, while a research question is a specific query the research aims to answer.
Can a research problem change during the study?
Yes, a research problem can evolve as new data and insights emerge, requiring refinement or redefinition to better align with findings.
How do you formulate a research problem?
Formulate a research problem by clearly stating the issue, outlining its significance, and specifying the context and scope of the problem.
What is the role of literature review in identifying a research problem?
A literature review helps identify gaps, inconsistencies, and unresolved issues in existing research, which can guide the formulation of a research problem.
How does a research problem impact the research design?
The research problem shapes the research design by determining the methodology, data collection techniques, and analysis strategies needed to address the issue.
What are common sources of research problems?
Common sources include academic literature, practical experiences, societal issues, technological advancements, and gaps identified in previous research.
How specific should a research problem be?
A research problem should be specific enough to guide focused research but broad enough to allow comprehensive investigation and meaningful results.
How do research objectives relate to the research problem?
Research objectives are specific goals derived from the research problem, detailing what the study aims to achieve and how it plans to address the problem.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Clinical Nursing Research Topics. Analyze the use of telehealth/virtual nursing to reduce inpatient nurse duties. Discuss the impact of evidence-based respiratory interventions on patient outcomes in critical care settings. Explore the effectiveness of pain management protocols in pediatric patients. 2.
A good PICOT question possesses the following qualities: A clinical-based question addresses the nursing research areas or topics. It is specific, concise, and clear. Patient, problem, or population. Intervention. Comparison. Outcome. Includes medical, clinical, and nursing terms where necessary. It is not ambiguous.
Think of these examples as jumping-off points to fuel your own curiosity: 50+ useful PICO questions for nursing research. P (Population) I (Intervention) C (Comparison) O (Outcome) T (Timeframe) General Nursing. Adult ICU patients with sepsis. Early goal-directed therapy protocol. Standard care. Mortality rates, long-term outcomes. 6 months ...
Current Nursing research proposal topics. Nursing research proposal topics can vary greatly, depending on the type of research you're looking to conduct. Some common topics include: The effects of sleep deprivation on nurses. The use of technology in nursing care. The effect of patient communication skills on nurses' outcomes.
Examples of some general health services research questions are: Does the organization of renal transplant nurse coordinators' responsibilities influence live donor rates? What activities of nurse managers are associated with nurse turnover? 30 day readmission rates? What effect does the Nurse Faculty Loan program have on the nurse researcher ...
2. Mental Health Nursing Research Articles Topics. Research papers focusing on mental health are still one of the most read and referred papers. And there's still more scope for research on topics such as: Evaluating the concept of Integrated Mental and Physical Health Care. Psychiatric Nursing and Mental Health.
Research is a systematic process of validating, refining, and generating knowledge. It is used by members of the healthcare team, such as nurses, to answer questions that come up when caring for clients. A research problem is a specific area of knowledge that needs further investigation and it is sometimes phrased as a question.
Nursing research plays a crucial role in advancing healthcare and improving patient outcomes. As a field that is constantly evolving, there is a great need for new ideas and innovative approaches to address the challenges faced by nurses in their day-to-day practice. In this article, we will explore some exciting nursing research topic ideas ...
If you're interested in specializing in pediatric nursing, you may focus your research on a topic within childhood nursing. Here are some examples of research topics: Antibiotics impact on childhood immunities. Effects of childhood exposure to environmental pollutants. Effects of second-hand smoke inhalation in early life.
INTRODUCTION. Research is a way of thinking: examining critically the. various aspects of your day-to-day work; understanding and formulating guiding principles that. govern a procedure; and developing and, testing new. theories that contribute to the advancement of your. practice and profession (Odunze, 2019).
The most important step in Evidence-Based Nursing (EBN) is to correctly identify a problem through patient assessment or practice assessment, processes that require reflection by the nurse on clinical practice, in conjunction with a knowledge of the patient's present circumstances.
research. The nursing literature can also be a valuable source for research-able problems, particularly for the novice researcher (Burns & Grove, 2007; Norwood, 2010; Polit & Beck, 2010). For example, the researcher might identify a topic of interest and then review the nursing research literature to determine which kinds of studies
Updated: May 2nd, 2024. Nursing education is challenging. Writing hundreds of tedious nursing research pieces is the most frustrating part. But we know how to help you! Discover 350 exciting nursing research topics and learn how to choose the best one. 1 hour! We'll write a 100% customized paper this fast.
Step Five: Create a search for your topic in an appropriate database. After meeting with your librarian, you should have a good idea of what terms you might use and where you can search for your topic. Do a couple of searches to find the best results and mark the papers you want to keep by grabbing the permalink, citation, or by emailing it to ...
The research purpose evolves from the problem and directs the subsequent steps of the research process. Research topics are concepts, phenomena of interest, or broad problem areas that researchers can focus on to enhance evidence-based nursing. Research topics contain numerous potential research problems, and each problem provides the basis for ...
A summary of works is organised into key themes, research methods are identified and important implications for practice and future research are explored. The 21 commentaries are grouped into three themes (box): professional issues— which include nursing workforce and workplace issues; evidence-based nursing care — specifically related to ...
Conclusion. The influencing factors of clinical nurses' problem-solving dilemma are diverse. Hospital managers and nursing educators should pay attention to the problem-solving of clinical nurses, carry out a series of training and counselling of nurses by using the method of situational simulation, optimize the nursing management mode, learn to use new media technology to improve the ...
A "foreground" question in health research is one that is relatively specific, and is usually best addressed by locating primary research evidence. Using a structured question framework can help you clearly define the concepts or variables that make up the specific research question. Across most frameworks, you'll often be considering:
Objectives. • The purpose of research is to answer questions, whether they come from curiosity or a practical need. • Research Problem statements are statements of the difference between what is known and what needs to be known about the topic and addressed by the research process. • The discrepancy, whether it is a small crack or a large ...
50 Good Nursing Research Topics. Here is one more list of the nursing topics for research paper. We hope that at least one of these ideas will inspire you or give a clue. Advantages of Pet Therapy in Kids with the Autism Disorder. Contemporary Approaches to Vaccinating Teenagers.
45 Research Problem Examples & Inspiration. A research problem is an issue of concern that is the catalyst for your research. It demonstrates why the research problem needs to take place in the first place. Generally, you will write your research problem as a clear, concise, and focused statement that identifies an issue or gap in current ...
Example: Problem statements focused on patient experiences, preferences, and outcomes foster a patient-centered approach to nursing research, ensuring that studies are relevant, meaningful, and impactful for those receiving care.
Problems encountered in the practice of nursing are widely varied, important to the health care system, and deserving of a national research effort. Research on these problems, which cover issues ranging from methods to alleviate anxiety and pain to improving the prospects for high-risk infants, is conducted mainly by nurses with doctoral degrees in biomedical and behavioral fields. There were ...
Here, we prepared two research problem statement examples that can serve as unique templates for developing your own statement. The Stakeholder Problem Statement. ... is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach ...
Background Nurse students reportedly face lots of challenges during skill development practice in health institutions. However, the prevalence of challenges and factors associated aren't well understood yet. Objective The objective of the study was to identify the challenges experienced by nursing students in health institutions during skill development practice. Method A cross-sectional ...
A research problem is a specific issue or gap in knowledge that a researcher aims to address through systematic investigation. It forms the foundation of a study, guiding the research question, research design, and potential outcomes.Identifying a clear research problem is crucial as it often emerges from existing literature, theoretical frameworks, and practical considerations.
Here's another example of randomization problems — with public data. Upworthy Research Archive. Nathan Matias, Kevin Munger, Marianne Aubin Le Quere, and Charles Ebersole worked with Upworthy to curate and release a data set of over 15,000 experiments, with a total of over 150,000 treatments. Each of these experiments modifies the headline ...