
- Master Your Homework
- Do My Homework

Research Paper vs. Research Article: What’s the Difference?
Research papers and research articles are two different forms of academic writing, with distinct characteristics. Although they share some similarities in terms of format and purpose, there are important distinctions between the two types that should be understood by students who wish to write either form effectively. This article will explain the differences between a research paper and a research article, outlining their unique features and applications. Furthermore, it will offer guidance on how best to approach each type when crafting an effective piece for scholarly consumption.
I. Introduction to Research Paper vs. Research Article
Ii. defining a research paper and a research article, iii. comparative analysis of structure, content, and writing styles between the two types of scholarly documents, iv. pros & cons of conducting either a formal or an informal study, v. concluding remarks: how to choose between the different approaches when completing academic assignments, vi. limitations in comparing these texts as distinct forms of scholarly outputs, vii. future directions for understanding similarities & differences across all kinds of academic writings.
Research Paper vs. Research Article
The academic world is full of a variety of different writing styles, each with its own unique purpose and goals. Two particularly important forms are the research paper and the research article. Each has their own distinct features that make them uniquely suited to certain tasks within academia – let’s take a closer look at what sets them apart from one another!
A research paper , as you might expect, presents in-depth analysis on an issue or topic using evidence gathered through primary sources such as field work, laboratory experiments, surveys, interviews etc., whereas a research article , typically published in scholarly journals or online publications like websites & blogs addresses specific findings derived from secondary sources like books or other papers related to said subject matter. The former requires more effort & dedication from the author due to it being time consuming & involving careful structuring along with rigorous citation format adherence; while the latter focuses mainly on providing succinct yet comprehensive overviews regarding topics which have already been extensively discussed by experts in depth previously elsewhere – taking into account present day developments/breakthroughs if necessary before finally offering opinionated conclusions pertaining to said subjects.
Exploring the Characteristics of a Research Paper and Article
- Research paper:
- Research article:
A research paper is an extended form of writing that presents and supports an argument on a particular topic. It provides evidence for the opinion or idea in the form of facts, data, analysis, opinions from authorities in specific fields etc. The objective is to make original claims based on careful evaluation of information available on a given subject. It requires significant effort as one needs to be able to distill complex topics into concisely articulated points that are supported by solid evidence.
On the other hand, a research article is usually written for publication either online or printed through journals or magazines. These articles have been peer-reviewed which means they follow certain academic standards established within their discipline while presenting factual conclusions related to ongoing debates and arguments raised by preceding works. They generally provide new insight into existing knowledge rather than build upon it using more primary sources such as surveys and experiments conducted independently by authors themselves.
Comparison of Structure, Content and Writing Styles between Research Papers and Articles For the purpose of scholarly communication, both research papers and articles play a vital role. Though there is no hard-and-fast rule that distinguishes them from each other in terms of structure or content, they usually differ significantly in their style. In comparison to research papers, articles typically have a much smaller length requirement. They can range anywhere from 1 page to as many as 30 pages depending on the journal guidelines – making them more accessible for readers who are seeking concise summaries with quick insights into topics. On the contrary, research papers tend to be longer documents that delve deeper into an issue by providing extensive background information; detailed analysis; arguments bolstered by sources such as peer-reviewed journals or interviews; conclusion sections tying up any loose ends etc.
- Research Papers: Longer documents which provide extensive coverage about an issue.
- Articles: Short pieces covering high level overviews without going too deep.
When it comes down to writing styles used for these two types of documents – Authors generally follow formal academic language while creating research paper whereas article writers tend to use more casual tones in order to appeal wider audience groups. Additionally authors will often adopt conversational elements like anecdotes when crafting articles so that readers can get better understanding about specific points being discussed within context.
Formal vs. Informal Study: A Critical Analysis The choice between conducting a formal or informal study may be difficult for researchers due to the advantages and drawbacks of each approach. Depending on their research topic, scientists must carefully weigh up the pros and cons before deciding which course of action is most suitable for them.
A formal study , as conducted in many research papers and articles, often requires more time-consuming effort from researchers than an informal one because it involves using specific methodologies such as surveys, interviews, experiments etc., gathering quantitative data that needs to be statistically analyzed by employing reliable statistical methods. On the other hand, a formal investigation allows researchers to obtain objective information from well-defined populations about predetermined variables through systematic procedures that can yield precise results with larger external validity – making it possible to make generalizations beyond those studied in this particular case.
Conversely, an informal study , also known as participant observation or field work requires less structured approaches where collecting qualitative data is usually achieved via conversations with informants instead of strict instrumentations; thus allowing greater interaction between researcher and subjects resulting in increased understanding of contextually situated phenomena within its natural setting rather than artificially created ones used in laboratories’ studies – leading to deeper insights into complex social processes . Also noteworthy is its lower financial cost when compared against highly expensive equipment needed for undertaking large scale scientific investigations.. However despite yielding valuable first person accounts which might not have been obtained elsewhere , such observations are sometimes criticized due challenges related accuracy given reliance on subjective interpretations while generating evidence without significant use of control variables .
Selecting the Optimal Approach for Academic Assignments When it comes to completing academic assignments, there are various approaches one can take. In order to ensure success and optimal results, it is important that students consider all of their options carefully before making a choice.
Research papers often require extensive research and careful consideration when selecting an approach. Using primary sources such as books or peer-reviewed articles may be more reliable in comparison to secondary sources such as websites or blogs which are usually less credible due to lack of credibility checks by professionals within the field. Additionally, data analysis can help strengthen arguments while also adding clarity to any work produced during the course of completion; however, understanding how best utilize this analytical tool effectively requires additional practice and experience on behalf of the student undertaking it. For research articles, detailed knowledge about particular topics may lead towards better outcomes but general familiarity with content areas is sufficient enough for success here too. The key lies in being able identify appropriate methods quickly through use critical thinking skills coupled with clear objectives pertaining specifically each assignment itself at hand prior its execution – this way mistakes are avoided thus delivering quality results each time..
Comparative Analyses of Scholarly Outputs
- Scholarly output, such as research papers and articles, are subject to scrutiny when attempting to make comparisons.
- Due to the differences between these two types of outputs, it can be difficult or impossible to achieve a true comparison.
Comparing scholarly outputs is not always possible due to their distinct forms. Research papers typically have more depth than an article on the same topic which may mean that even though both documents might discuss similar topics in some aspects they will differ greatly in others. Furthermore, the format of each type of document contributes further complexities; for example, a research paper is often much longer and requires extensive background information before any conclusions can be drawn while articles tend towards presenting results with little room left for interpretation. The style used by authors also adds difficulty; many times research papers include complex jargon necessary for understanding specific points whereas an article strives for simplicity so its target audience can comprehend all material without excessive effort. These limitations prevent proper analysis from being done since one piece could provide certain details while another provides only bits related thereto leading readers into confusion if attempting to compare them directly despite intentions otherwise. It then becomes clear that academic pieces should instead remain separate entities rather than compared against each other since doing so would lead only too frustration given current constraints therein found.
Exploring the Similarities and Differences Between Academic Writings
As our understanding of academic writings continues to evolve, so too must our appreciation for both their similarities and differences. From research papers to research articles, it is important to consider how each one contributes unique insight into a given topic or issue.
The research paper and research article may look similar on the surface, but upon closer inspection one can see significant differences in their format, purpose, and audience. The key distinctions between these two forms of written work are scope of content covered, type of analysis used to draw conclusions or develop knowledge from data or evidence presented, and intended readership. Ultimately, understanding the essential characteristics that distinguish a research paper from a research article is beneficial for anyone who produces such texts as it will help them craft an effective product that aligns with its desired purposes.
Understanding Scientific Journals and Articles: How to approach reading journal articles
by Anthony Carpi, Ph.D., Anne E. Egger, Ph.D., Natalie H. Kuldell
Listen to this reading
Did you know that scientific literature goes all the way back to 600 BCE? Although scientific articles have changed some – for example, Isaac Newton wrote about the fun he had with prisms in a 1672 scientific article – the basics remain the same. This ensures that published research becomes part of the archive of scientific knowledge upon which other scientists can build.
Scientists make their research available to the community by publishing it in scientific journals.
In scientific papers, scientists explain the research that they are building on, their research methods, data and data analysis techniques, and their interpretation of the data.
Understanding how to read scientific papers is a critical skill for scientists and students of science.
We've all read the headlines at the supermarket checkout line: "Aliens Abduct New Jersey School Teacher" or "Quadruplets Born to 99-Year-Old Woman: Exclusive Photos Inside." Journals like the National Enquirer sell copies by publishing sensational headlines, and most readers believe only a fraction of what is printed. A person more interested in news than gossip could buy a publication like Time, Newsweek or Discover . These magazines publish information on current news and events, including recent scientific advances. These are not original reports of scientific research , however. In fact, most of these stories include phrases like, "A group of scientists recently published their findings on..." So where do scientists publish their findings?
Scientists publish their original research in scientific journals, which are fundamentally different from news magazines. The articles in scientific journals are not written by journalists – they are written by scientists. Scientific articles are not sensational stories intended to entertain the reader with an amazing discovery, nor are they news stories intended to summarize recent scientific events, nor even records of every successful and unsuccessful research venture. Instead, scientists write articles to describe their findings to the community in a transparent manner.
- Scientific journals vs. popular media
Within a scientific article, scientists present their research questions, the methods by which the question was approached, and the results they achieved using those methods. In addition, they present their analysis of the data and describe some of the interpretations and implications of their work. Because these articles report new work for the first time, they are called primary literature . In contrast, articles or news stories that review or report on scientific research already published elsewhere are referred to as secondary .
The articles in scientific journals are different from news articles in another way – they must undergo a process called peer review , in which other scientists (the professional peers of the authors) evaluate the quality and merit of research before recommending whether or not it should be published (see our Peer Review module). This is a much lengthier and more rigorous process than the editing and fact-checking that goes on at news organizations. The reason for this thorough evaluation by peers is that a scientific article is more than a snapshot of what is going on at a certain time in a scientist's research. Instead, it is a part of what is collectively called the scientific literature, a global archive of scientific knowledge. When published, each article expands the library of scientific literature available to all scientists and contributes to the overall knowledge base of the discipline of science.
Comprehension Checkpoint
- Scientific journals: Degrees of specialization

Figure 1: Nature : An example of a scientific journal.
There are thousands of scientific journals that publish research articles. These journals are diverse and can be distinguished according to their field of specialization. Among the most broadly targeted and competitive are journals like Cell , the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), Nature , and Science that all publish a wide variety of research articles (see Figure 1 for an example). Cell focuses on all areas of biology, NEJM on medicine, and both Science and Nature publish articles in all areas of science. Scientists submit manuscripts for publication in these journals when they feel their work deserves the broadest possible audience.
Just below these journals in terms of their reach are the top-tier disciplinary journals like Analytical Chemistry, Applied Geochemistry, Neuron, Journal of Geophysical Research , and many others. These journals tend to publish broad-based research focused on specific disciplines, such as chemistry, geology, neurology, nuclear physics, etc.
Next in line are highly specialized journals, such as the American Journal of Potato Research, Grass and Forage Science, the Journal of Shellfish Research, Neuropeptides, Paleolimnology , and many more. While the research published in various journals does not differ in terms of the quality or the rigor of the science described, it does differ in its degree of specialization: These journals tend to be more specialized, and thus appeal to a more limited audience.
All of these journals play a critical role in the advancement of science and dissemination of information (see our Utilizing the Scientific Literature module for more information). However, to understand how science is disseminated through these journals, you must first understand how the articles themselves are formatted and what information they contain. While some details about format vary between journals and even between articles in the same journal, there are broad characteristics that all scientific journal articles share.
- The standard format of journal articles
In June of 2005, the journal Science published a research report on a sighting of the ivory-billed woodpecker, a bird long considered extinct in North America (Fitzpatrick et al., 2005). The work was of such significance and broad interest that it was displayed prominently on the cover (Figure 2) and highlighted by an editorial at the front of the journal (Kennedy, 2005). The authors were aware that their findings were likely to be controversial, and they worked especially hard to make their writing clear. Although the article has no headings within the text, it can easily be divided into sections:

Figure 2: A picture of the cover of Science from June 3, 2005.
Title and authors: The title of a scientific article should concisely and accurately summarize the research . Here, the title used is "Ivory-billed Woodpecker ( Campephilus principalis ) Persists in North America." While it is meant to capture attention, journals avoid using misleading or overly sensational titles (you can imagine that a tabloid might use the headline "Long-dead Giant Bird Attacks Canoeists!"). The names of all scientific contributors are listed as authors immediately after the title. You may be used to seeing one or maybe two authors for a book or newspaper article, but this article has seventeen authors! It's unlikely that all seventeen of those authors sat down in a room and wrote the manuscript together. Instead, the authorship reflects the distribution of the workload and responsibility for the research, in addition to the writing. By convention, the scientist who performed most of the work described in the article is listed first, and it is likely that the first author did most of the writing. Other authors had different contributions; for example, Gene Sparling is the person who originally spotted the bird in Arkansas and was subsequently contacted by the scientists at the Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology. In some cases, but not in the woodpecker article, the last author listed is the senior researcher on the project, or the scientist from whose lab the project originated. Increasingly, journals are requesting that authors detail their exact contributions to the research and writing associated with a particular study.
Abstract: The abstract is the first part of the article that appears right after the listing of authors in an article. In it, the authors briefly describe the research question, the general methods , and the major findings and implications of the work. Providing a summary like this at the beginning of an article serves two purposes: First, it gives readers a way to decide whether the article in question discusses research that interests them, and second, it is entered into literature databases as a means of providing more information to people doing scientific literature searches. For both purposes, it is important to have a short version of the full story. In this case, all of the critical information about the timing of the study, the type of data collected, and the potential interpretations of the findings is captured in four straightforward sentences as seen below:
The ivory-billed woodpecker ( Campephilus principalis ), long suspected to be extinct, has been rediscovered in the Big Woods region of eastern Arkansas. Visual encounters during 2004 and 2005, and analysis of a video clip from April 2004, confirm the existence of at least one male. Acoustic signatures consistent with Campephilus display drums also have been heard from the region. Extensive efforts to find birds away from the primary encounter site remain unsuccessful, but potential habitat for a thinly distributed source population is vast (over 220,000 hectares).
Introduction: The central research question and important background information are presented in the introduction. Because science is a process that builds on previous findings, relevant and established scientific knowledge is cited in this section and then listed in the References section at the end of the article. In many articles, a heading is used to set this and subsequent sections apart, but in the woodpecker article the introduction consists of the first three paragraphs, in which the history of the decline of the woodpecker and previous studies are cited. The introduction is intended to lead the reader to understand the authors' hypothesis and means of testing it. In addition, the introduction provides an opportunity for the authors to show that they are aware of the work that scientists have done before them and how their results fit in, explicitly building on existing knowledge.
Materials and methods: In this section, the authors describe the research methods they used (see The Practice of Science module for more information on these methods). All procedures, equipment, measurement parameters , etc. are described in detail sufficient for another researcher to evaluate and/or reproduce the research. In addition, authors explain the sources of error and procedures employed to reduce and measure the uncertainty in their data (see our Uncertainty, Error, and Confidence module). The detail given here allows other scientists to evaluate the quality of the data collected. This section varies dramatically depending on the type of research done. In an experimental study, the experimental set-up and procedure would be described in detail, including the variables , controls , and treatment . The woodpecker study used a descriptive research approach, and the materials and methods section is quite short, including the means by which the bird was initially spotted (on a kayaking trip) and later photographed and videotaped.
Results: The data collected during the research are presented in this section, both in written form and using tables, graphs, and figures (see our Using Graphs and Visual Data module). In addition, all statistical and data analysis techniques used are presented (see our Statistics in Science module). Importantly, the data should be presented separately from any interpretation by the authors. This separation of data from interpretation serves two purposes: First, it gives other scientists the opportunity to evaluate the quality of the actual data, and second, it allows others to develop their own interpretations of the findings based on their background knowledge and experience. In the woodpecker article, the data consist largely of photographs and videos (see Figure 3 for an example). The authors include both the raw data (the photograph) and their analysis (the measurement of the tree trunk and inferred length of the bird perched on the trunk). The sketch of the bird on the right-hand side of the photograph is also a form of analysis, in which the authors have simplified the photograph to highlight the features of interest. Keeping the raw data (in the form of a photograph) facilitated reanalysis by other scientists: In early 2006, a team of researchers led by the American ornithologist David Sibley reanalyzed the photograph in Figure 3 and came to the conclusion that the bird was not an ivory-billed woodpecker after all (Sibley et al, 2006).
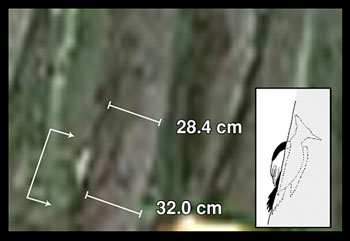
Figure 3: An example of the data presented in the Ivory-billed woodpecker article (Fitzpatrick et al ., 2005, Figure 1).
Discussion and conclusions: In this section, authors present their interpretation of the data , often including a model or idea they feel best explains their results. They also present the strengths and significance of their work. Naturally, this is the most subjective section of a scientific research article as it presents interpretation as opposed to strictly methods and data, but it is not speculation by the authors. Instead, this is where the authors combine their experience, background knowledge, and creativity to explain the data and use the data as evidence in their interpretation (see our Data Analysis and Interpretation module). Often, the discussion section includes several possible explanations or interpretations of the data; the authors may then describe why they support one particular interpretation over the others. This is not just a process of hedging their bets – this how scientists say to their peers that they have done their homework and that there is more than one possible explanation. In the woodpecker article, for example, the authors go to great lengths to describe why they believe the bird they saw is an ivory-billed woodpecker rather than a variant of the more common pileated woodpecker, knowing that this is a likely potential rebuttal to their initial findings. A final component of the conclusions involves placing the current work back into a larger context by discussing the implications of the work. The authors of the woodpecker article do so by discussing the nature of the woodpecker habitat and how it might be better preserved.
In many articles, the results and discussion sections are combined, but regardless, the data are initially presented without interpretation .
References: Scientific progress requires building on existing knowledge, and previous findings are recognized by directly citing them in any new work. The citations are collected in one list, commonly called "References," although the precise format for each journal varies considerably. The reference list may seem like something you don't actually read, but in fact it can provide a wealth of information about whether the authors are citing the most recent work in their field or whether they are biased in their citations towards certain institutions or authors. In addition, the reference section provides readers of the article with more information about the particular research topic discussed. The reference list for the woodpecker article includes a wide variety of sources that includes books, other journal articles, and personal accounts of bird sightings.
Supporting material: Increasingly, journals make supporting material that does not fit into the article itself – like extensive data tables, detailed descriptions of methods , figures, and animations – available online. In this case, the video footage shot by the authors is available online, along with several other resources.
- Reading the primary literature
The format of a scientific article may seem overly structured compared to many other things you read, but it serves a purpose by providing an archive of scientific research in the primary literature that we can build on. Though isolated examples of that archive go as far back as 600 BCE (see the Babylonian tablets in our Description in Scientific Research module), the first consistently published scientific journal was the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London , edited by Henry Oldenburg for the Royal Society beginning in 1666 (see our Scientific Institutions and Societies module). These early scientific writings include all of the components listed above, but the writing style is surprisingly different than a modern journal article. For example, Isaac Newton opened his 1672 article "New Theory About Light and Colours" with the following:
I shall without further ceremony acquaint you, that in the beginning of the Year 1666...I procured me a Triangular glass-Prisme, to try therewith the celebrated Phenomena of Colours . And in order thereto having darkened my chamber, and made a small hole in my window-shuts, to let in a convenient quantity of the Suns light, I placed my Prisme at his entrance, that it might be thereby refracted to the opposite wall. It was at first a very pleasing divertissement, to view the vivid and intense colours produced thereby; but after a while applying my self to consider them more circumspectly, I became surprised to see them in an oblong form; which, according to the received laws of Refraction, I expected should have been circular . (Newton, 1672)

Figure 4: Isaac Newton described the rainbow produced by a prism as a "pleasing divertissement."
Newton describes his materials and methods in the first few sentences ("... a small hole in my window-shuts"), describes his results ("an oblong form"), refers to the work that has come before him ("the received laws of Refraction"), and highlights how his results differ from his expectations. Today, however, Newton 's statement that the "colours" produced were a "very pleasing divertissement" would be out of place in a scientific article (Figure 4). Much more typically, modern scientific articles are written in an objective tone, typically without statements of personal opinion to avoid any appearance of bias in the interpretation of their results. Unfortunately, this tone often results in overuse of the passive voice, with statements like "a Triangular glass-Prisme was procured" instead of the wording Newton chose: "I procured me a Triangular glass-Prisme." The removal of the first person entirely from the articles reinforces the misconception that science is impersonal, boring, and void of creativity, lacking the enjoyment and surprise described by Newton. The tone can sometimes be misleading if the study involves many authors, making it unclear who did what work. The best scientific writers are able to both present their work in an objective tone and make their own contributions clear.
The scholarly vocabulary in scientific articles can be another obstacle to reading the primary literature. Materials and Methods sections often are highly technical in nature and can be confusing if you are not intimately familiar with the type of research being conducted. There is a reason for all of this vocabulary, however: An explicit, technical description of materials and methods provides a means for other scientists to evaluate the quality of the data presented and can often provide insight to scientists on how to replicate or extend the research described.
The tone and specialized vocabulary of the modern scientific article can make it hard to read, but understanding the purpose and requirements for each section can help you decipher the primary literature. Learning to read scientific articles is a skill, and like any other skill, it requires practice and experience to master. It is not, however, an impossible task.
Strange as it seems, the most efficient way to tackle a new article may be through a piecemeal approach, reading some but not all the sections and not necessarily in their order of appearance. For example, the abstract of an article will summarize its key points, but this section can often be dense and difficult to understand. Sometimes the end of the article may be a better place to start reading. In many cases, authors present a model that fits their data in this last section of the article. The discussion section may emphasize some themes or ideas that tie the story together, giving the reader some foundation for reading the article from the beginning. Even experienced scientists read articles this way – skimming the figures first, perhaps, or reading the discussion and then going back to the results. Often, it takes a scientist multiple readings to truly understand the authors' work and incorporate it into their personal knowledge base in order to build on that knowledge.
- Building knowledge and facilitating discussion
The process of science does not stop with the publication of the results of research in a scientific article. In fact, in some ways, publication is just the beginning. Scientific journals also provide a means for other scientists to respond to the work they publish; like many newspapers and magazines, most scientific journals publish letters from their readers.
Unlike the common "Letters to the Editor" of a newspaper, however, the letters in scientific journals are usually critical responses to the authors of a research study in which alternative interpretations are outlined. When such a letter is received by a journal editor, it is typically given to the original authors so that they can respond, and both the letter and response are published together. Nine months after the original publication of the woodpecker article, Science published a letter (called a "Comment") from David Sibley and three of his colleagues, who reinterpreted the Fitzpatrick team's data and concluded that the bird in question was a more common pileated woodpecker, not an ivory-billed woodpecker (Sibley et al., 2006). The team from the Cornell lab wrote a response supporting their initial conclusions, and Sibley's team followed that up with a response of their own in 2007 (Fitzpatrick et al., 2006; Sibley at al., 2007). As expected, the research has generated significant scientific controversy and, in addition, has captured the attention of the public, spreading the story of the controversy into the popular media.
For more information about this story see The Case of the Ivory-Billed Woodpecker module.
Table of Contents
Activate glossary term highlighting to easily identify key terms within the module. Once highlighted, you can click on these terms to view their definitions.
Activate NGSS annotations to easily identify NGSS standards within the module. Once highlighted, you can click on them to view these standards.
- Hirsh Health Sciences
- Webster Veterinary
Guide to Scholarly Articles
- What is a Scholarly Article?
- Scholarly vs. Popular vs. Trade Articles
Types of Scholarly Articles
Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-methods articles, why does this matter.
- Anatomy of Scholarly Articles
- Tips for Reading Scholarly Articles
Scholarly articles come in many different formats each with their own function in the scholarly conversation. The following are a few of the major types of scholarly articles you are likely to encounter as you become a part of the conversation. Identifying the different types of scholarly articles and knowing their function will help you become a better researcher.
Original/Empirical Studies
- Note: Empirical studies can be subdivided into qualitative studies, quantitative studies, or mixed methods studies. See below for more information
- Usefulness for research: Empirical studies are useful because they provide current original research on a topic which may contain a hypothesis or interpretation to advance or to disprove.
Literature Reviews
- Distinguishing characteristic: Literature reviews survey and analyze a clearly delaminated body of scholarly literature.
- Usefulness for research: Literature reviews are useful as a way to quickly get up to date on a particular topic of research.
Theoretical Articles
- Distinguishing characteristic: Theoretical articles draw on existing scholarship to improve upon or offer a new theoretical perspective on a given topic.
- Usefulness for research: Theoretical articles are useful because they provide a theoretical framework you can apply to your own research.
Methodological Articles
- Distinguishing characteristic: Methodological articles draw on existing scholarship to improve or offer new methodologies for exploring a given topic.
- Usefulness for research: Methodological articles are useful because they provide a methodologies you can apply to your own research.
Case Studies
- Distinguishing characteristic: Case studies focus on individual examples or instances of a phenomenon to illustrate a research problem or a a solution to a research problem.
- Usefulness for research: Case studies are useful because they provide information about a research problem or data for analysis.
Book Reviews
- Distinguishing characteristic: Book reviews provide summaries and evaluations of individual books.
- Usefulness for research: Book reviews are useful because they provide summaries and evaluations of individual books relevant to your research.
Adapted from the Publication manual of the American Psychological Association : the official guide to APA style. (Sixth edition.). (2013). American Psychological Association.
Qualitative articles ask "why" questions where as quantitative articles ask "how many/how much?" questions. These approaches are are not mutually exclusive. In fact, many articles combine the two in a mixed-methods approach.
We can think of these different kinds of scholarly articles as different tools designed for different tasks. What research task do you need to accomplish? Do you need to get up to date on a give topic? Find a literature review. Do you need to find a hypothesis to test or to extend? Find an empirical study. Do you need to explore methodologies? Find a methodological article.
- << Previous: Scholarly vs. Popular vs. Trade Articles
- Next: Anatomy of Scholarly Articles >>
- Last Updated: Aug 23, 2023 8:53 AM
- URL: https://researchguides.library.tufts.edu/scholarly-articles
- SpringerLink shop
Types of journal articles
It is helpful to familiarise yourself with the different types of articles published by journals. Although it may appear there are a large number of types of articles published due to the wide variety of names they are published under, most articles published are one of the following types; Original Research, Review Articles, Short reports or Letters, Case Studies, Methodologies.
Original Research:
This is the most common type of journal manuscript used to publish full reports of data from research. It may be called an Original Article, Research Article, Research, or just Article, depending on the journal. The Original Research format is suitable for many different fields and different types of studies. It includes full Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion sections.
Short reports or Letters:
These papers communicate brief reports of data from original research that editors believe will be interesting to many researchers, and that will likely stimulate further research in the field. As they are relatively short the format is useful for scientists with results that are time sensitive (for example, those in highly competitive or quickly-changing disciplines). This format often has strict length limits, so some experimental details may not be published until the authors write a full Original Research manuscript. These papers are also sometimes called Brief communications .
Review Articles:
Review Articles provide a comprehensive summary of research on a certain topic, and a perspective on the state of the field and where it is heading. They are often written by leaders in a particular discipline after invitation from the editors of a journal. Reviews are often widely read (for example, by researchers looking for a full introduction to a field) and highly cited. Reviews commonly cite approximately 100 primary research articles.
TIP: If you would like to write a Review but have not been invited by a journal, be sure to check the journal website as some journals to not consider unsolicited Reviews. If the website does not mention whether Reviews are commissioned it is wise to send a pre-submission enquiry letter to the journal editor to propose your Review manuscript before you spend time writing it.
Case Studies:
These articles report specific instances of interesting phenomena. A goal of Case Studies is to make other researchers aware of the possibility that a specific phenomenon might occur. This type of study is often used in medicine to report the occurrence of previously unknown or emerging pathologies.
Methodologies or Methods
These articles present a new experimental method, test or procedure. The method described may either be completely new, or may offer a better version of an existing method. The article should describe a demonstrable advance on what is currently available.
Back │ Next
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
Basics of scientific and technical writing
- Career Central
- Published: 01 March 2021
- Volume 46 , pages 284–286, ( 2021 )
Cite this article

- Morteza Monavarian 1 , 2
5723 Accesses
2 Citations
6 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction to scientific/technical writing
Scientific/technical writing is an essential part of research. The outcome of a research activity should be shared with others in the form of scientific paper publications; some ideas require a patent to reserve the implementation rights; and almost any research activity requires a funding source, for which a grant proposal is necessary. Therefore, it is crucial to know the differences among writing papers, patents, and grant proposals and how to prepare them in a research environment ( Figure 1 ).

Three major types of scientific/technical writing covered in the three-part series.
The publication of papers is a standard way to share knowledge and transfer methods in scientific communities, thus a pivotal part of any research activity, especially in an academic environment. In industry, where financial profit is a key factor, patents are possibly more favorable.
Types of paper publications
There are different types of paper publications, depending on the content, audience, purpose, length, and scope: original research, review articles, invited articles, conference proceedings, comments/errata, and press releases ( Figure 2 ).
Original research articles may be published in journals or conference proceedings (or preprints in arXiv) and target specific audiences within a field of research. Journal research papers require peer review that typically involves an editor and two reviewers. For conference proceedings, there is usually no direct peer-review process, but the work has to be presented in the corresponding conference to be eligible for publication.
In contrast to original research articles, which are written on special topics within a field of research, review articles normally cover an overview of research and tend to be longer. Review articles do not necessarily reflect on novel data or ideas and could be similar to a book chapter. However, unlike review articles, book chapters or books are usually written when the target field of research is fully established. In a review paper, figures are typically not original and reprinted from other publications, for which a copyright permission from the original publishing journal is required.
Invited articles are written in response to an invitation by a journal editor or a conference organizer in a specific field of research or for a special issue. An invited article could be a review article or original research. Invited articles are normally written by peers or researchers with significant contributions to a field of research.
Other items published include comments or errata. The purpose of a comment on a published article is to bring points of criticism to the attention of the readers as well as the authors of the original article. The comments can be published in the same journal as the original paper. Errata correct mistakes in an article after publication.
Finally, press releases target a more general audience and normally report on a review/overview of recently published research. The author of the press release is not the same as that of the original article. Unlike peer-reviewed research articles, press release articles are usually not citable.
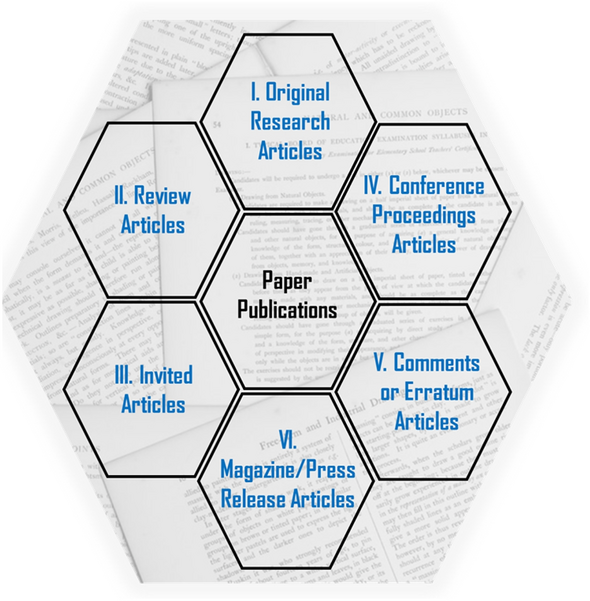
Six major types of paper publications.
Writing structures and styles
Different articles have different structures. A research article typically consists of a title, author list and affiliations, abstract, main body, conclusions, acknowledgments, and references.
A good title should be concise, to the point, and free of abbreviations. Author lists and affiliations include whoever has intellectually contributed to the paper (identifying at least one corresponding author and email address), with the order approved by all of the co-authors. A good abstract should give a full, but short, overview of the work with both qualitative and quantitative data summaries. An abstract should be self-contained, meaning it should not require a referral to a reference or figure. Abstracts are usually written in the present tense and have an active voice.
Unlike letters with no sections within the main body, the main body of research articles normally contains several sections (e.g., introduction, methods and approach, results, and discussions). The introduction should contain a deep literature review of the field as the basis for motivating the current work. The last paragraph of the introduction usually summarizes what to expect from the article. The following sections will demonstrate study methods, results, and discussions/interpretations of the results, including plots, tables, and figures.
Conclusions summarize the findings of the paper and may point out any future directions. The acknowledgment lists all funding support and gratitude toward anyone who helped with the work, not including those listed as co-authors. The reference section lists all references in a format described in the journal submission guidelines. Using reference management software (such as Zotero, Mendeley, BibTex) makes organizing the references less cumbersome. A good scholarly research article should have citations for almost any claims made within the main body, to ensure proper connections to the prior research in the field.
Unlike patents, papers require a deep scientific background and should be straight to the point. While patents include all aspects of the idea, papers typically have space limitations, so should therefore be concise. The data in research articles should speak for itself. The language of a research paper should be clear and simple and not include metaphors or slang.
Where to submit
The submission target depends on several factors: (1) scope of the journal, (2) length of the paper (letters versus regular length articles), (3) access (regular versus open access), and (4) impact factor (IF). The scope of the journal is probably the first thing to consider; you cannot publish a biological paper in a humanity journal. Regarding length, a letter is much shorter and usually does not have section headings. It depends on the discipline, but sometimes letters are more favorable because of the shorter publication time, preparation simplicity, and more readability (takes less time to read, which may also improve the visibility of the paper). In terms of access, you may pay publication charges to receive open access, or some journals charge publication fees upon acceptance. Open access papers could potentially get more visibility than normal publications.
IF is a specific journal parameter indicating the average number of citations per published article over a certain period of time. Paying serious attention to IF could oppose the mission of science itself, as it could mean that you judge a paper only by where it is being published and not by its intrinsic values (also called high IF syndrome).
Submission, peer-review, and decisions
Your article will enter the peer-review process upon submission. If done properly, the peer-review process not only avoids false or inconsistent data from being published (and helps science in this regard), but also improves your paper and removes any potential errors/issues or vague discussion. During submission, some journals may ask you to include/exclude reviewers. If there are researchers who may have a direct conflict with your work, you may list them as excluded reviewers. You may also suggest to include reviewers who have relevant experience.
Serving as a reviewer may help you with your own writing, as it assists in developing critical thinking. However, for the sake of science, try peer-reviewing for lesser-known journals (the high-impact journals already have many reviewers). Decisions on your article could be (1) reject: cannot be accepted to this journal; (2) referral to other journals; submit to another journal; (3) accept: accepted as is; (4) major revisions: not accepted, but could be accepted upon significant improvement (upon approval from reviewers); and (5) minor revision: accept but needs slight revisions (no need to go through a peer review again).
Copyrights and archiving
Most journals obtain copyrights from the authors before submission via a copyright transfer form. Hence, re-publishing the same data and plots in another journal is often forbidden. Also, the language of a paper should have a significant difference from an already published paper to avoid plagiarism. In the case where some content (e.g., figure or table) needs to be re-published in another paper (e.g., for review articles or thesis/dissertations), one can request a copyright permission from the original publishing journal. Also, archiving of one’s published papers in personal profile websites (e.g., Researchgate or LinkedIn) is usually forbidden, unless the paper is published as open access.
Final tips for paper publication
Read, read, read! There is probably no better way of improving writing skills than reading other articles and books.
Make illustrative and self-contained figures that can stand on their own.
Know your audience when selecting a journal. Find out which journals are normally targeted by people in your research community.
Protect yourself from high impact factor (IF) syndrome. Journals with a high IF may have very subjective decision criteria. It is sometimes more important to have your paper published than to spend a couple of years waiting for publication in a high-impact journal.
Serve as a reviewer. Get a sense of how a peer-review process feels in order to establish critical thinking. Before submitting your article, self-review.
Look forward to a constructive peer review. It definitely improves your paper (always good to have a view from different perspective).
Enjoy your publications!
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Materials Department, University of California Santa Barbara, Santa Barbara, CA, USA
Morteza Monavarian
Solid State Lighting & Energy Electronics Center, University of California Santa Barbara, Santa Barbara, CA, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Additional information
This article is the first in a three-part series in MRS Bulletin that will focus on writing papers, patents, and proposals.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Monavarian, M. Basics of scientific and technical writing. MRS Bulletin 46 , 284–286 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43577-021-00070-y
Download citation
Published : 01 March 2021
Issue Date : March 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1557/s43577-021-00070-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Scientific and Scholarly Writing
- Literature Searches
- Tracking and Citing References
Parts of a Scientific & Scholarly Paper
Introduction.
- Writing Effectively
- Where to Publish?
- Capstone Resources
Different sections are needed in different types of scientific papers (lab reports, literature reviews, systematic reviews, methods papers, research papers, etc.). Projects that overlap with the social sciences or humanities may have different requirements. Generally, however, you'll need to include:
INTRODUCTION (Background)
METHODS SECTION (Materials and Methods)
What is a title
Titles have two functions: to identify the main topic or the message of the paper and to attract readers.
The title will be read by many people. Only a few will read the entire paper, therefore all words in the title should be chosen with care. Too short a title is not helpful to the potential reader. Too long a title can sometimes be even less meaningful. Remember a title is not an abstract. Neither is a title a sentence.
What makes a good title?
A good title is accurate, complete, and specific. Imagine searching for your paper in PubMed. What words would you use?
- Use the fewest possible words that describe the contents of the paper.
- Avoid waste words like "Studies on", or "Investigations on".
- Use specific terms rather than general.
- Use the same key terms in the title as the paper.
- Watch your word order and syntax.
The abstract is a miniature version of your paper. It should present the main story and a few essential details of the paper for readers who only look at the abstract and should serve as a clear preview for readers who read your whole paper. They are usually short (250 words or less).
The goal is to communicate:
- What was done?
- Why was it done?
- How was it done?
- What was found?
A good abstract is specific and selective. Try summarizing each of the sections of your paper in a sentence two. Do the abstract last, so you know exactly what you want to write.
- Use 1 or more well developed paragraphs.
- Use introduction/body/conclusion structure.
- Present purpose, results, conclusions and recommendations in that order.
- Make it understandable to a wide audience.
- << Previous: Tracking and Citing References
- Next: Writing Effectively >>
- Last Updated: Apr 17, 2024 3:27 PM
- URL: https://libraryguides.umassmed.edu/scientific-writing

- Richard G. Trefry Library
Q. What's the difference between a research article (or research study) and a review article?

- Course-Specific
- Textbooks & Course Materials
- Tutoring & Classroom Help
- Writing & Citing
- 44 Articles & Journals
- 3 Artificial Intelligence
- 11 Capstone/Thesis/Dissertation Research
- 37 Databases
- 56 Information Literacy
- 9 Interlibrary Loan
- 9 Need help getting started?
- 22 Technical Help
Answered By: Priscilla Coulter Last Updated: Jul 29, 2022 Views: 232091
A research paper is a primary source ...that is, it reports the methods and results of an original study performed by the authors . The kind of study may vary (it could have been an experiment, survey, interview, etc.), but in all cases, raw data have been collected and analyzed by the authors , and conclusions drawn from the results of that analysis.
Research papers follow a particular format. Look for:
- A brief introduction will often include a review of the existing literature on the topic studied, and explain the rationale of the author's study. This is important because it demonstrates that the authors are aware of existing studies, and are planning to contribute to this existing body of research in a meaningful way (that is, they're not just doing what others have already done).
- A methods section, where authors describe how they collected and analyzed data. Statistical analyses are included. This section is quite detailed, as it's important that other researchers be able to verify and/or replicate these methods.
- A results section describes the outcomes of the data analysis. Charts and graphs illustrating the results are typically included.
- In the discussion , authors will explain their interpretation of their results and theorize on their importance to existing and future research.
- References or works cited are always included. These are the articles and books that the authors drew upon to plan their study and to support their discussion.
You can use the library's article databases to search for research articles:
- A research article will nearly always be published in a peer-reviewed journal; click here for instructions on limiting your searches to peer-reviewed articles.
- If you have a particular type of study in mind, you can include keywords to describe it in your search . For instance, if you would like to see studies that used surveys to collect data, you can add "survey" to your topic in the database's search box. See this example search in our EBSCO databases: " bullying and survey ".
- Several of our databases have special limiting options that allow you to select specific methodologies. See, for instance, the " Methodology " box in ProQuest's PsycARTICLES Advanced Search (scroll down a bit to see it). It includes options like "Empirical Study" and "Qualitative Study", among many others.
A review article is a secondary source ...it is written about other articles, and does not report original research of its own. Review articles are very important, as they draw upon the articles that they review to suggest new research directions, to strengthen support for existing theories and/or identify patterns among exising research studies. For student researchers, review articles provide a great overview of the existing literature on a topic. If you find a literature review that fits your topic, take a look at its references/works cited list for leads on other relevant articles and books!
You can use the library's article databases to find literature reviews as well! Click here for tips.
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 7 No 0
Related Topics
- Articles & Journals
- Information Literacy
Need personalized help? Librarians are available 365 days/nights per year! See our schedule.

Learn more about how librarians can help you succeed.
- Follow us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
- Criminal Justice
- Environment
- Politics & Government
- Race & Gender
Expert Commentary
White papers, working papers, preprints, journal articles: What’s the difference?
In this updated piece, we explain the most common types of research papers journalists will encounter, noting their strengths and weaknesses.

Republish this article

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License .
by Denise-Marie Ordway, The Journalist's Resource February 25, 2022
This <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org/media/working-papers-research-articles/">article</a> first appeared on <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org">The Journalist's Resource</a> and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.<img src="https://journalistsresource.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/cropped-jr-favicon-150x150.png" style="width:1em;height:1em;margin-left:10px;">
This tip sheet, originally published in May 2018, has been updated to include preprint research, a type of research featured often in news coverage of the coronavirus pandemic.
Journalists rely most often on four types of research in their work. White papers, working papers, preprints and peer-reviewed journal articles.
How are they different? And which is best?
Below, we explain each, pointing out its strengths and weaknesses. As always, we urge journalists to use care in selecting any research to ground their coverage and fact-check claims.
Peer-reviewed article
Peer-reviewed research — the kind that appears in academic journals and that we highlight here at The Journalist’s Resource — has undergone a detailed critique by scholars with expertise in the field. While peer-reviewed research is generally the most reliable, journalists should keep in mind that publication in a prestigious journal is no guarantee of quality and that no single university or research organization always does the best research on a given topic.
It is safe to assume, however, that articles published in top-tier journals have been reviewed and given a stamp of approval by a number of accomplished scholars. For journalists who are uncertain, we’ve put together a list of 13 questions to ask to gauge the quality of a research article.
Keep in mind that not everything that appears in a scholarly journal has been peer reviewed. Journals publish various types of content, including book reviews, editorials, letters to the editor and, sometimes, even poetry.
Working paper
This broad category describes research papers that have not been peer reviewed or published in a journal. Working papers can be in various stages of completion. One might be ready for publication in a prestigious journal while another requires significant editing and other changes that could actually alter its main findings. Sometimes, working paper findings are so preliminary, authors will advise against citing their work .
Even so, working papers are a great way for journalists to gain access to new research quickly. The peer-review and publication process can take months to a year or longer, which means that by the time studies get published, their findings are sometimes not as useful or the data are old.
In choosing working papers, journalists should communicate with scholars about the progress of their research and how confident they are in their findings. It’s a good idea to seek corroboration from peer-reviewed research and to ask other researchers for help assessing a study.
A preprint is similar to a working paper in that it has not been vetted through a formal peer-review process. However, preprints tend to be more complete . Also, preprints submitted to public servers such as the Social Science Research Network and the health sciences server medRxiv get a cursory screening before they’re published online for public view.
Preprints, like academic journal articles, are assigned a Digital Object Identifier , or DOI, and become a permanent part of the scientific record.
White paper
A white paper is a report, often compiled by government agencies, businesses and nonprofit organizations, that outlines an issue and often explores possible solutions to a problem. For example, in November 2021, the federal Office of Community Oriented Policing Services released a white paper looking at factors that help or hinder law enforcement recruitment of Black Americans. Earlier in the year, the Advanced Technology Academic Research Center published a white paper on the American Rescue Plan ‘s widespread implications for government agencies.
In the business world, white papers also are used for marketing purposes — to describe a new product or approach, for instance, or diagnose a problem.
While a white paper can help journalists get up to speed quickly on an issue, it’s important to note some white papers advocate a specific position or policy change. Some rely on incomplete research or research that has not been peer reviewed.
Looking for more guidance on writing about research? Check out our tip sheets on covering biomedical research preprints amid the coronavirus and what journalists should know about peer review .
The Journalist’s Resource would like to thank Matthew Baum , the Marvin Kalb professor of global communications and professor of public policy at Harvard Kennedy School, for his help preparing this tip sheet.
About The Author
Denise-Marie Ordway
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
Difference between Research Papers and Technical Articles for Journal Publication
- Difference between Paper and Article for Scientific Writings
- Difference between Vertical search and Horizontal search
- Difference between Software Inspection and Technical Review
- Difference between Research Paper and Review Paper
- Difference between Data Science and Operations Research
- Difference between <article> tag and <section> tag
- Difference between Qualitative research and Quantitative research
- Difference between Fundamental and Technical Analysis
- Difference between Information System and Information Technology
- Difference Between Article and Essay
- Difference between Project Report and Research Report
- Difference between Functional Testing and Implementational Testing Approach
- Difference between Project Engineer and Mechanical Engineer
- Difference between Elasticsearch and Solr
- Difference between semantic and non-semantic elements
- Differences between Interface and Integration Testing
- Technical Product Manager vs Product Manager | Difference Between
- Difference Between Journal and Ledger
- What Is The Difference Between NATA And JEE Paper 2?
Research Papers: Research Papers are write-ups which record the result/report examinations tired specific zone. For the most part, they take an up to this point obscure issue in a given field, propose an arrangement for it and assess the status of the arrangement in comparison with other modern solutions. In this way, in a sense, they move the wilderness of information within the field. Based on the nature and reason of the movement carried out, and the way the write-up is composed. Technical Articles: A technical article is an editorial for a magazine or an internet benefit that’s about a specialized point, and regularly the article drills down into a few low-level of detail. May be computers, maybe material science or chemistry or any other science. It can be around math. It can be approximately pharmaceutical or wellbeing or diet. It can be around the material science of cooking. There are truly thousands of potential points of specialized articles. Below is a table of differences between Research Papers and Technical Articles:
.Difference-table { border-collapse: collapse; width: 100%; } .Difference-table td { text-color: black !important; border: 1px solid #5fb962; text-align: left !important; padding: 8px; } .Difference-table th { border: 1px solid #5fb962; padding: 8px; } .Difference-table tr>th{ background-color: #c6ebd9; vertical-align: middle; } .Difference-table tr:nth-child(odd) { background-color: #ffffff; }
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Difference Between
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Different brain structures in females lead to more severe cognitive deficits after concussion than males
Axons in brains of female mammals may be more vulnerable to damage, penn medicine research finds.
Important brain structures that are key for signaling in the brain are narrower and less dense in females, and more likely to be damaged by brain injuries, such as concussion. Long-term cognitive deficits occur when the signals between brain structures weaken due to the injury. The structural differences in male and female brains might explain why females are more prone to concussions and experience longer recovery from the injury than their male counterparts, according to a preclinical study led by the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, published this week in Acta Neuropathologica .
Each year, approximately 50 million individuals worldwide suffer a concussion, also referred to as mild traumatic brain injury (TBI). However, there is nothing "mild" about this condition for the more than 15 percent of individuals who suffer persisting cognitive dysfunction, which includes difficulty concentrating, learning and remembering new information, and making decisions.
Although males make up the majority of emergency department visits for concussion, this has been primarily attributed to their greater exposure to activities with a risk of head impacts compared to females. In contrast, it has recently been observed that female athletes have a higher rate of concussion and appear to have worse outcomes than their male counterparts participating in the same sport.
"Clinicians have observed for a long time that females suffer from concussion at higher rates than males in the same sports, and that they take longer to recover cognitive function, but couldn't explain the underlying mechanisms of this phenomenon," said senior author Douglas Smith, MD, a professor of Neurosurgery and director of Penn's Center for Brain Injury and Repair. "The variances in brain structures of females and males not only illuminate why this disparity exists, but also exposes biomarkers, such as axon protein fragments, that can be measured in the blood to determine injury severity, monitor recovery, and eventually help identify and develop treatments that help patients repair these damaged structures and restore cognitive function."
If neurons are telephones that send messages between brain cells, axons are the lines that connect them, allowing communication across the brain. These axons form bundles that make up white matter in the brain and play a large role in learning and communication between different brain regions. Axons are delicate structures and are vulnerable to damage from concussion.
Communication between axons in the brain is powered by sodium channels that serve as the brain's electric grid. When axons are damaged, these sodium channels are also impaired, which causes loss of signaling in the brain. The loss of signaling causes the cognitive impairment experienced by individuals after concussion.
In this study, researchers used large animal models of concussion to identify differences in brains of males and females after a concussion. They found that females had a higher population of smaller axons, which researchers demonstrated are more vulnerable to injury. They also reported that in these models, females had greater loss of sodium channels after concussion.
"The differences in brain structure not only tell us a lot about how brain injury affects males and females differently but could offer insights in other brain conditions that impact axons, like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease," said Smith. "If female brains are more vulnerable to damage from concussion, they might also be more vulnerable to neurodegeneration, and it's worth further research to understand how sex influences the structure and functions of the brain."
This research was funded by the National Institutes of Health (R01NS092398, R01NS038104, R01NS094003, U54NS115322, K08NS110929, K23NS123340), the Department of Defense (HT94252311039, W81XWH-21-1-0590, HT9425-23-1-0981), and the Alzheimer's Association (AARFD-23-1144656).
- Brain Tumor
- Accident and Trauma
- Nervous System
- Psychology Research
- Brain Injury
- Intelligence
- Disorders and Syndromes
- Gender Difference
- Brain damage
- Traumatic brain injury
- Cerebral contusion
- Head injury
- Social cognition
- Psycholinguistics
Story Source:
Materials provided by University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Hailong Song, Alexandra Tomasevich, Andrew Paolini, Kevin D. Browne, Kathryn L. Wofford, Brian Kelley, Eashwar Kantemneni, Justin Kennedy, Yue Qiu, Andrea L. C. Schneider, Jean-Pierre Dolle, D. Kacy Cullen, Douglas H. Smith. Sex differences in the extent of acute axonal pathologies after experimental concussion . Acta Neuropathologica , 2024; 147 (1) DOI: 10.1007/s00401-024-02735-9
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- High-Efficiency Photonic Integrated Circuit
- Life Expectancy May Increase by 5 Years by 2050
- Toward a Successful Vaccine for HIV
- Highly Efficient Thermoelectric Materials
- Toward Human Brain Gene Therapy
- Whale Families Learn Each Other's Vocal Style
- AI Can Answer Complex Physics Questions
- Otters Use Tools to Survive a Changing World
- Monogamy in Mice: Newly Evolved Type of Cell
- Sustainable Electronics, Doped With Air
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.

Cultural Relativity and Acceptance of Embryonic Stem Cell Research
Article sidebar.

Main Article Content
There is a debate about the ethical implications of using human embryos in stem cell research, which can be influenced by cultural, moral, and social values. This paper argues for an adaptable framework to accommodate diverse cultural and religious perspectives. By using an adaptive ethics model, research protections can reflect various populations and foster growth in stem cell research possibilities.
INTRODUCTION
Stem cell research combines biology, medicine, and technology, promising to alter health care and the understanding of human development. Yet, ethical contention exists because of individuals’ perceptions of using human embryos based on their various cultural, moral, and social values. While these disagreements concerning policy, use, and general acceptance have prompted the development of an international ethics policy, such a uniform approach can overlook the nuanced ethical landscapes between cultures. With diverse viewpoints in public health, a single global policy, especially one reflecting Western ethics or the ethics prevalent in high-income countries, is impractical. This paper argues for a culturally sensitive, adaptable framework for the use of embryonic stem cells. Stem cell policy should accommodate varying ethical viewpoints and promote an effective global dialogue. With an extension of an ethics model that can adapt to various cultures, we recommend localized guidelines that reflect the moral views of the people those guidelines serve.
Stem cells, characterized by their unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, enable the repair or replacement of damaged tissues. Two primary types of stem cells are somatic stem cells (adult stem cells) and embryonic stem cells. Adult stem cells exist in developed tissues and maintain the body’s repair processes. [1] Embryonic stem cells (ESC) are remarkably pluripotent or versatile, making them valuable in research. [2] However, the use of ESCs has sparked ethics debates. Considering the potential of embryonic stem cells, research guidelines are essential. The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) provides international stem cell research guidelines. They call for “public conversations touching on the scientific significance as well as the societal and ethical issues raised by ESC research.” [3] The ISSCR also publishes updates about culturing human embryos 14 days post fertilization, suggesting local policies and regulations should continue to evolve as ESC research develops. [4] Like the ISSCR, which calls for local law and policy to adapt to developing stem cell research given cultural acceptance, this paper highlights the importance of local social factors such as religion and culture.
I. Global Cultural Perspective of Embryonic Stem Cells
Views on ESCs vary throughout the world. Some countries readily embrace stem cell research and therapies, while others have stricter regulations due to ethical concerns surrounding embryonic stem cells and when an embryo becomes entitled to moral consideration. The philosophical issue of when the “someone” begins to be a human after fertilization, in the morally relevant sense, [5] impacts when an embryo becomes not just worthy of protection but morally entitled to it. The process of creating embryonic stem cell lines involves the destruction of the embryos for research. [6] Consequently, global engagement in ESC research depends on social-cultural acceptability.
a. US and Rights-Based Cultures
In the United States, attitudes toward stem cell therapies are diverse. The ethics and social approaches, which value individualism, [7] trigger debates regarding the destruction of human embryos, creating a complex regulatory environment. For example, the 1996 Dickey-Wicker Amendment prohibited federal funding for the creation of embryos for research and the destruction of embryos for “more than allowed for research on fetuses in utero.” [8] Following suit, in 2001, the Bush Administration heavily restricted stem cell lines for research. However, the Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005 was proposed to help develop ESC research but was ultimately vetoed. [9] Under the Obama administration, in 2009, an executive order lifted restrictions allowing for more development in this field. [10] The flux of research capacity and funding parallels the different cultural perceptions of human dignity of the embryo and how it is socially presented within the country’s research culture. [11]
b. Ubuntu and Collective Cultures
African bioethics differs from Western individualism because of the different traditions and values. African traditions, as described by individuals from South Africa and supported by some studies in other African countries, including Ghana and Kenya, follow the African moral philosophies of Ubuntu or Botho and Ukama , which “advocates for a form of wholeness that comes through one’s relationship and connectedness with other people in the society,” [12] making autonomy a socially collective concept. In this context, for the community to act autonomously, individuals would come together to decide what is best for the collective. Thus, stem cell research would require examining the value of the research to society as a whole and the use of the embryos as a collective societal resource. If society views the source as part of the collective whole, and opposes using stem cells, compromising the cultural values to pursue research may cause social detachment and stunt research growth. [13] Based on local culture and moral philosophy, the permissibility of stem cell research depends on how embryo, stem cell, and cell line therapies relate to the community as a whole . Ubuntu is the expression of humanness, with the person’s identity drawn from the “’I am because we are’” value. [14] The decision in a collectivistic culture becomes one born of cultural context, and individual decisions give deference to others in the society.
Consent differs in cultures where thought and moral philosophy are based on a collective paradigm. So, applying Western bioethical concepts is unrealistic. For one, Africa is a diverse continent with many countries with different belief systems, access to health care, and reliance on traditional or Western medicines. Where traditional medicine is the primary treatment, the “’restrictive focus on biomedically-related bioethics’” [is] problematic in African contexts because it neglects bioethical issues raised by traditional systems.” [15] No single approach applies in all areas or contexts. Rather than evaluating the permissibility of ESC research according to Western concepts such as the four principles approach, different ethics approaches should prevail.
Another consideration is the socio-economic standing of countries. In parts of South Africa, researchers have not focused heavily on contributing to the stem cell discourse, either because it is not considered health care or a health science priority or because resources are unavailable. [16] Each country’s priorities differ given different social, political, and economic factors. In South Africa, for instance, areas such as maternal mortality, non-communicable diseases, telemedicine, and the strength of health systems need improvement and require more focus. [17] Stem cell research could benefit the population, but it also could divert resources from basic medical care. Researchers in South Africa adhere to the National Health Act and Medicines Control Act in South Africa and international guidelines; however, the Act is not strictly enforced, and there is no clear legislation for research conduct or ethical guidelines. [18]
Some parts of Africa condemn stem cell research. For example, 98.2 percent of the Tunisian population is Muslim. [19] Tunisia does not permit stem cell research because of moral conflict with a Fatwa. Religion heavily saturates the regulation and direction of research. [20] Stem cell use became permissible for reproductive purposes only recently, with tight restrictions preventing cells from being used in any research other than procedures concerning ART/IVF. Their use is conditioned on consent, and available only to married couples. [21] The community's receptiveness to stem cell research depends on including communitarian African ethics.
c. Asia
Some Asian countries also have a collective model of ethics and decision making. [22] In China, the ethics model promotes a sincere respect for life or human dignity, [23] based on protective medicine. This model, influenced by Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), [24] recognizes Qi as the vital energy delivered via the meridians of the body; it connects illness to body systems, the body’s entire constitution, and the universe for a holistic bond of nature, health, and quality of life. [25] Following a protective ethics model, and traditional customs of wholeness, investment in stem cell research is heavily desired for its applications in regenerative therapies, disease modeling, and protective medicines. In a survey of medical students and healthcare practitioners, 30.8 percent considered stem cell research morally unacceptable while 63.5 percent accepted medical research using human embryonic stem cells. Of these individuals, 89.9 percent supported increased funding for stem cell research. [26] The scientific community might not reflect the overall population. From 1997 to 2019, China spent a total of $576 million (USD) on stem cell research at 8,050 stem cell programs, increased published presence from 0.6 percent to 14.01 percent of total global stem cell publications as of 2014, and made significant strides in cell-based therapies for various medical conditions. [27] However, while China has made substantial investments in stem cell research and achieved notable progress in clinical applications, concerns linger regarding ethical oversight and transparency. [28] For example, the China Biosecurity Law, promoted by the National Health Commission and China Hospital Association, attempted to mitigate risks by introducing an institutional review board (IRB) in the regulatory bodies. 5800 IRBs registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry since 2021. [29] However, issues still need to be addressed in implementing effective IRB review and approval procedures.
The substantial government funding and focus on scientific advancement have sometimes overshadowed considerations of regional cultures, ethnic minorities, and individual perspectives, particularly evident during the one-child policy era. As government policy adapts to promote public stability, such as the change from the one-child to the two-child policy, [30] research ethics should also adapt to ensure respect for the values of its represented peoples.
Japan is also relatively supportive of stem cell research and therapies. Japan has a more transparent regulatory framework, allowing for faster approval of regenerative medicine products, which has led to several advanced clinical trials and therapies. [31] South Korea is also actively engaged in stem cell research and has a history of breakthroughs in cloning and embryonic stem cells. [32] However, the field is controversial, and there are issues of scientific integrity. For example, the Korean FDA fast-tracked products for approval, [33] and in another instance, the oocyte source was unclear and possibly violated ethical standards. [34] Trust is important in research, as it builds collaborative foundations between colleagues, trial participant comfort, open-mindedness for complicated and sensitive discussions, and supports regulatory procedures for stakeholders. There is a need to respect the culture’s interest, engagement, and for research and clinical trials to be transparent and have ethical oversight to promote global research discourse and trust.
d. Middle East
Countries in the Middle East have varying degrees of acceptance of or restrictions to policies related to using embryonic stem cells due to cultural and religious influences. Saudi Arabia has made significant contributions to stem cell research, and conducts research based on international guidelines for ethical conduct and under strict adherence to guidelines in accordance with Islamic principles. Specifically, the Saudi government and people require ESC research to adhere to Sharia law. In addition to umbilical and placental stem cells, [35] Saudi Arabia permits the use of embryonic stem cells as long as they come from miscarriages, therapeutic abortions permissible by Sharia law, or are left over from in vitro fertilization and donated to research. [36] Laws and ethical guidelines for stem cell research allow the development of research institutions such as the King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, which has a cord blood bank and a stem cell registry with nearly 10,000 donors. [37] Such volume and acceptance are due to the ethical ‘permissibility’ of the donor sources, which do not conflict with religious pillars. However, some researchers err on the side of caution, choosing not to use embryos or fetal tissue as they feel it is unethical to do so. [38]
Jordan has a positive research ethics culture. [39] However, there is a significant issue of lack of trust in researchers, with 45.23 percent (38.66 percent agreeing and 6.57 percent strongly agreeing) of Jordanians holding a low level of trust in researchers, compared to 81.34 percent of Jordanians agreeing that they feel safe to participate in a research trial. [40] Safety testifies to the feeling of confidence that adequate measures are in place to protect participants from harm, whereas trust in researchers could represent the confidence in researchers to act in the participants’ best interests, adhere to ethical guidelines, provide accurate information, and respect participants’ rights and dignity. One method to improve trust would be to address communication issues relevant to ESC. Legislation surrounding stem cell research has adopted specific language, especially concerning clarification “between ‘stem cells’ and ‘embryonic stem cells’” in translation. [41] Furthermore, legislation “mandates the creation of a national committee… laying out specific regulations for stem-cell banking in accordance with international standards.” [42] This broad regulation opens the door for future global engagement and maintains transparency. However, these regulations may also constrain the influence of research direction, pace, and accessibility of research outcomes.
e. Europe
In the European Union (EU), ethics is also principle-based, but the principles of autonomy, dignity, integrity, and vulnerability are interconnected. [43] As such, the opportunity for cohesion and concessions between individuals’ thoughts and ideals allows for a more adaptable ethics model due to the flexible principles that relate to the human experience The EU has put forth a framework in its Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being allowing member states to take different approaches. Each European state applies these principles to its specific conventions, leading to or reflecting different acceptance levels of stem cell research. [44]
For example, in Germany, Lebenzusammenhang , or the coherence of life, references integrity in the unity of human culture. Namely, the personal sphere “should not be subject to external intervention.” [45] Stem cell interventions could affect this concept of bodily completeness, leading to heavy restrictions. Under the Grundgesetz, human dignity and the right to life with physical integrity are paramount. [46] The Embryo Protection Act of 1991 made producing cell lines illegal. Cell lines can be imported if approved by the Central Ethics Commission for Stem Cell Research only if they were derived before May 2007. [47] Stem cell research respects the integrity of life for the embryo with heavy specifications and intense oversight. This is vastly different in Finland, where the regulatory bodies find research more permissible in IVF excess, but only up to 14 days after fertilization. [48] Spain’s approach differs still, with a comprehensive regulatory framework. [49] Thus, research regulation can be culture-specific due to variations in applied principles. Diverse cultures call for various approaches to ethical permissibility. [50] Only an adaptive-deliberative model can address the cultural constructions of self and achieve positive, culturally sensitive stem cell research practices. [51]
II. Religious Perspectives on ESC
Embryonic stem cell sources are the main consideration within religious contexts. While individuals may not regard their own religious texts as authoritative or factual, religion can shape their foundations or perspectives.
The Qur'an states:
“And indeed We created man from a quintessence of clay. Then We placed within him a small quantity of nutfa (sperm to fertilize) in a safe place. Then We have fashioned the nutfa into an ‘alaqa (clinging clot or cell cluster), then We developed the ‘alaqa into mudgha (a lump of flesh), and We made mudgha into bones, and clothed the bones with flesh, then We brought it into being as a new creation. So Blessed is Allah, the Best of Creators.” [52]
Many scholars of Islam estimate the time of soul installment, marked by the angel breathing in the soul to bring the individual into creation, as 120 days from conception. [53] Personhood begins at this point, and the value of life would prohibit research or experimentation that could harm the individual. If the fetus is more than 120 days old, the time ensoulment is interpreted to occur according to Islamic law, abortion is no longer permissible. [54] There are a few opposing opinions about early embryos in Islamic traditions. According to some Islamic theologians, there is no ensoulment of the early embryo, which is the source of stem cells for ESC research. [55]
In Buddhism, the stance on stem cell research is not settled. The main tenets, the prohibition against harming or destroying others (ahimsa) and the pursuit of knowledge (prajña) and compassion (karuna), leave Buddhist scholars and communities divided. [56] Some scholars argue stem cell research is in accordance with the Buddhist tenet of seeking knowledge and ending human suffering. Others feel it violates the principle of not harming others. Finding the balance between these two points relies on the karmic burden of Buddhist morality. In trying to prevent ahimsa towards the embryo, Buddhist scholars suggest that to comply with Buddhist tenets, research cannot be done as the embryo has personhood at the moment of conception and would reincarnate immediately, harming the individual's ability to build their karmic burden. [57] On the other hand, the Bodhisattvas, those considered to be on the path to enlightenment or Nirvana, have given organs and flesh to others to help alleviate grieving and to benefit all. [58] Acceptance varies on applied beliefs and interpretations.
Catholicism does not support embryonic stem cell research, as it entails creation or destruction of human embryos. This destruction conflicts with the belief in the sanctity of life. For example, in the Old Testament, Genesis describes humanity as being created in God’s image and multiplying on the Earth, referencing the sacred rights to human conception and the purpose of development and life. In the Ten Commandments, the tenet that one should not kill has numerous interpretations where killing could mean murder or shedding of the sanctity of life, demonstrating the high value of human personhood. In other books, the theological conception of when life begins is interpreted as in utero, [59] highlighting the inviolability of life and its formation in vivo to make a religious point for accepting such research as relatively limited, if at all. [60] The Vatican has released ethical directives to help apply a theological basis to modern-day conflicts. The Magisterium of the Church states that “unless there is a moral certainty of not causing harm,” experimentation on fetuses, fertilized cells, stem cells, or embryos constitutes a crime. [61] Such procedures would not respect the human person who exists at these stages, according to Catholicism. Damages to the embryo are considered gravely immoral and illicit. [62] Although the Catholic Church officially opposes abortion, surveys demonstrate that many Catholic people hold pro-choice views, whether due to the context of conception, stage of pregnancy, threat to the mother’s life, or for other reasons, demonstrating that practicing members can also accept some but not all tenets. [63]
Some major Jewish denominations, such as the Reform, Conservative, and Reconstructionist movements, are open to supporting ESC use or research as long as it is for saving a life. [64] Within Judaism, the Talmud, or study, gives personhood to the child at birth and emphasizes that life does not begin at conception: [65]
“If she is found pregnant, until the fortieth day it is mere fluid,” [66]
Whereas most religions prioritize the status of human embryos, the Halakah (Jewish religious law) states that to save one life, most other religious laws can be ignored because it is in pursuit of preservation. [67] Stem cell research is accepted due to application of these religious laws.
We recognize that all religions contain subsets and sects. The variety of environmental and cultural differences within religious groups requires further analysis to respect the flexibility of religious thoughts and practices. We make no presumptions that all cultures require notions of autonomy or morality as under the common morality theory , which asserts a set of universal moral norms that all individuals share provides moral reasoning and guides ethical decisions. [68] We only wish to show that the interaction with morality varies between cultures and countries.
III. A Flexible Ethical Approach
The plurality of different moral approaches described above demonstrates that there can be no universally acceptable uniform law for ESC on a global scale. Instead of developing one standard, flexible ethical applications must be continued. We recommend local guidelines that incorporate important cultural and ethical priorities.
While the Declaration of Helsinki is more relevant to people in clinical trials receiving ESC products, in keeping with the tradition of protections for research subjects, consent of the donor is an ethical requirement for ESC donation in many jurisdictions including the US, Canada, and Europe. [69] The Declaration of Helsinki provides a reference point for regulatory standards and could potentially be used as a universal baseline for obtaining consent prior to gamete or embryo donation.
For instance, in Columbia University’s egg donor program for stem cell research, donors followed standard screening protocols and “underwent counseling sessions that included information as to the purpose of oocyte donation for research, what the oocytes would be used for, the risks and benefits of donation, and process of oocyte stimulation” to ensure transparency for consent. [70] The program helped advance stem cell research and provided clear and safe research methods with paid participants. Though paid participation or covering costs of incidental expenses may not be socially acceptable in every culture or context, [71] and creating embryos for ESC research is illegal in many jurisdictions, Columbia’s program was effective because of the clear and honest communications with donors, IRBs, and related stakeholders. This example demonstrates that cultural acceptance of scientific research and of the idea that an egg or embryo does not have personhood is likely behind societal acceptance of donating eggs for ESC research. As noted, many countries do not permit the creation of embryos for research.
Proper communication and education regarding the process and purpose of stem cell research may bolster comprehension and garner more acceptance. “Given the sensitive subject material, a complete consent process can support voluntary participation through trust, understanding, and ethical norms from the cultures and morals participants value. This can be hard for researchers entering countries of different socioeconomic stability, with different languages and different societal values. [72]
An adequate moral foundation in medical ethics is derived from the cultural and religious basis that informs knowledge and actions. [73] Understanding local cultural and religious values and their impact on research could help researchers develop humility and promote inclusion.
IV. Concerns
Some may argue that if researchers all adhere to one ethics standard, protection will be satisfied across all borders, and the global public will trust researchers. However, defining what needs to be protected and how to define such research standards is very specific to the people to which standards are applied. We suggest that applying one uniform guide cannot accurately protect each individual because we all possess our own perceptions and interpretations of social values. [74] Therefore, the issue of not adjusting to the moral pluralism between peoples in applying one standard of ethics can be resolved by building out ethics models that can be adapted to different cultures and religions.
Other concerns include medical tourism, which may promote health inequities. [75] Some countries may develop and approve products derived from ESC research before others, compromising research ethics or drug approval processes. There are also concerns about the sale of unauthorized stem cell treatments, for example, those without FDA approval in the United States. Countries with robust research infrastructures may be tempted to attract medical tourists, and some customers will have false hopes based on aggressive publicity of unproven treatments. [76]
For example, in China, stem cell clinics can market to foreign clients who are not protected under the regulatory regimes. Companies employ a marketing strategy of “ethically friendly” therapies. Specifically, in the case of Beike, China’s leading stem cell tourism company and sprouting network, ethical oversight of administrators or health bureaus at one site has “the unintended consequence of shifting questionable activities to another node in Beike's diffuse network.” [77] In contrast, Jordan is aware of stem cell research’s potential abuse and its own status as a “health-care hub.” Jordan’s expanded regulations include preserving the interests of individuals in clinical trials and banning private companies from ESC research to preserve transparency and the integrity of research practices. [78]
The social priorities of the community are also a concern. The ISSCR explicitly states that guidelines “should be periodically revised to accommodate scientific advances, new challenges, and evolving social priorities.” [79] The adaptable ethics model extends this consideration further by addressing whether research is warranted given the varying degrees of socioeconomic conditions, political stability, and healthcare accessibilities and limitations. An ethical approach would require discussion about resource allocation and appropriate distribution of funds. [80]
While some religions emphasize the sanctity of life from conception, which may lead to public opposition to ESC research, others encourage ESC research due to its potential for healing and alleviating human pain. Many countries have special regulations that balance local views on embryonic personhood, the benefits of research as individual or societal goods, and the protection of human research subjects. To foster understanding and constructive dialogue, global policy frameworks should prioritize the protection of universal human rights, transparency, and informed consent. In addition to these foundational global policies, we recommend tailoring local guidelines to reflect the diverse cultural and religious perspectives of the populations they govern. Ethics models should be adapted to local populations to effectively establish research protections, growth, and possibilities of stem cell research.
For example, in countries with strong beliefs in the moral sanctity of embryos or heavy religious restrictions, an adaptive model can allow for discussion instead of immediate rejection. In countries with limited individual rights and voice in science policy, an adaptive model ensures cultural, moral, and religious views are taken into consideration, thereby building social inclusion. While this ethical consideration by the government may not give a complete voice to every individual, it will help balance policies and maintain the diverse perspectives of those it affects. Embracing an adaptive ethics model of ESC research promotes open-minded dialogue and respect for the importance of human belief and tradition. By actively engaging with cultural and religious values, researchers can better handle disagreements and promote ethical research practices that benefit each society.
This brief exploration of the religious and cultural differences that impact ESC research reveals the nuances of relative ethics and highlights a need for local policymakers to apply a more intense adaptive model.
[1] Poliwoda, S., Noor, N., Downs, E., Schaaf, A., Cantwell, A., Ganti, L., Kaye, A. D., Mosel, L. I., Carroll, C. B., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2022). Stem cells: a comprehensive review of origins and emerging clinical roles in medical practice. Orthopedic reviews , 14 (3), 37498. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.37498
[2] Poliwoda, S., Noor, N., Downs, E., Schaaf, A., Cantwell, A., Ganti, L., Kaye, A. D., Mosel, L. I., Carroll, C. B., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2022). Stem cells: a comprehensive review of origins and emerging clinical roles in medical practice. Orthopedic reviews , 14 (3), 37498. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.37498
[3] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2023). Laboratory-based human embryonic stem cell research, embryo research, and related research activities . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/blog-post-title-one-ed2td-6fcdk ; Kimmelman, J., Hyun, I., Benvenisty, N. et al. Policy: Global standards for stem-cell research. Nature 533 , 311–313 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/533311a
[4] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2023). Laboratory-based human embryonic stem cell research, embryo research, and related research activities . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/blog-post-title-one-ed2td-6fcdk
[5] Concerning the moral philosophies of stem cell research, our paper does not posit a personal moral stance nor delve into the “when” of human life begins. To read further about the philosophical debate, consider the following sources:
Sandel M. J. (2004). Embryo ethics--the moral logic of stem-cell research. The New England journal of medicine , 351 (3), 207–209. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp048145 ; George, R. P., & Lee, P. (2020, September 26). Acorns and Embryos . The New Atlantis. https://www.thenewatlantis.com/publications/acorns-and-embryos ; Sagan, A., & Singer, P. (2007). The moral status of stem cells. Metaphilosophy , 38 (2/3), 264–284. http://www.jstor.org/stable/24439776 ; McHugh P. R. (2004). Zygote and "clonote"--the ethical use of embryonic stem cells. The New England journal of medicine , 351 (3), 209–211. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp048147 ; Kurjak, A., & Tripalo, A. (2004). The facts and doubts about beginning of the human life and personality. Bosnian journal of basic medical sciences , 4 (1), 5–14. https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2004.3453
[6] Vazin, T., & Freed, W. J. (2010). Human embryonic stem cells: derivation, culture, and differentiation: a review. Restorative neurology and neuroscience , 28 (4), 589–603. https://doi.org/10.3233/RNN-2010-0543
[7] Socially, at its core, the Western approach to ethics is widely principle-based, autonomy being one of the key factors to ensure a fundamental respect for persons within research. For information regarding autonomy in research, see: Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, & National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research (1978). The Belmont Report. Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research.; For a more in-depth review of autonomy within the US, see: Beauchamp, T. L., & Childress, J. F. (1994). Principles of Biomedical Ethics . Oxford University Press.
[8] Sherley v. Sebelius , 644 F.3d 388 (D.C. Cir. 2011), citing 45 C.F.R. 46.204(b) and [42 U.S.C. § 289g(b)]. https://www.cadc.uscourts.gov/internet/opinions.nsf/6c690438a9b43dd685257a64004ebf99/$file/11-5241-1391178.pdf
[9] Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005, H. R. 810, 109 th Cong. (2001). https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/109/hr810/text ; Bush, G. W. (2006, July 19). Message to the House of Representatives . National Archives and Records Administration. https://georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov/news/releases/2006/07/20060719-5.html
[10] National Archives and Records Administration. (2009, March 9). Executive order 13505 -- removing barriers to responsible scientific research involving human stem cells . National Archives and Records Administration. https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/removing-barriers-responsible-scientific-research-involving-human-stem-cells
[11] Hurlbut, W. B. (2006). Science, Religion, and the Politics of Stem Cells. Social Research , 73 (3), 819–834. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40971854
[12] Akpa-Inyang, Francis & Chima, Sylvester. (2021). South African traditional values and beliefs regarding informed consent and limitations of the principle of respect for autonomy in African communities: a cross-cultural qualitative study. BMC Medical Ethics . 22. 10.1186/s12910-021-00678-4.
[13] Source for further reading: Tangwa G. B. (2007). Moral status of embryonic stem cells: perspective of an African villager. Bioethics , 21(8), 449–457. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8519.2007.00582.x , see also Mnisi, F. M. (2020). An African analysis based on ethics of Ubuntu - are human embryonic stem cell patents morally justifiable? African Insight , 49 (4).
[14] Jecker, N. S., & Atuire, C. (2021). Bioethics in Africa: A contextually enlightened analysis of three cases. Developing World Bioethics , 22 (2), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12324
[15] Jecker, N. S., & Atuire, C. (2021). Bioethics in Africa: A contextually enlightened analysis of three cases. Developing World Bioethics, 22(2), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12324
[16] Jackson, C.S., Pepper, M.S. Opportunities and barriers to establishing a cell therapy programme in South Africa. Stem Cell Res Ther 4 , 54 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt204 ; Pew Research Center. (2014, May 1). Public health a major priority in African nations . Pew Research Center’s Global Attitudes Project. https://www.pewresearch.org/global/2014/05/01/public-health-a-major-priority-in-african-nations/
[17] Department of Health Republic of South Africa. (2021). Health Research Priorities (revised) for South Africa 2021-2024 . National Health Research Strategy. https://www.health.gov.za/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/National-Health-Research-Priorities-2021-2024.pdf
[18] Oosthuizen, H. (2013). Legal and Ethical Issues in Stem Cell Research in South Africa. In: Beran, R. (eds) Legal and Forensic Medicine. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32338-6_80 , see also: Gaobotse G (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[19] United States Bureau of Citizenship and Immigration Services. (1998). Tunisia: Information on the status of Christian conversions in Tunisia . UNHCR Web Archive. https://webarchive.archive.unhcr.org/20230522142618/https://www.refworld.org/docid/3df0be9a2.html
[20] Gaobotse, G. (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[21] Kooli, C. Review of assisted reproduction techniques, laws, and regulations in Muslim countries. Middle East Fertil Soc J 24 , 8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43043-019-0011-0 ; Gaobotse, G. (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[22] Pang M. C. (1999). Protective truthfulness: the Chinese way of safeguarding patients in informed treatment decisions. Journal of medical ethics , 25(3), 247–253. https://doi.org/10.1136/jme.25.3.247
[23] Wang, L., Wang, F., & Zhang, W. (2021). Bioethics in China’s biosecurity law: Forms, effects, and unsettled issues. Journal of law and the biosciences , 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsab019 https://academic.oup.com/jlb/article/8/1/lsab019/6299199
[24] Wang, Y., Xue, Y., & Guo, H. D. (2022). Intervention effects of traditional Chinese medicine on stem cell therapy of myocardial infarction. Frontiers in pharmacology , 13 , 1013740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1013740
[25] Li, X.-T., & Zhao, J. (2012). Chapter 4: An Approach to the Nature of Qi in TCM- Qi and Bioenergy. In Recent Advances in Theories and Practice of Chinese Medicine (p. 79). InTech.
[26] Luo, D., Xu, Z., Wang, Z., & Ran, W. (2021). China's Stem Cell Research and Knowledge Levels of Medical Practitioners and Students. Stem cells international , 2021 , 6667743. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6667743
[27] Luo, D., Xu, Z., Wang, Z., & Ran, W. (2021). China's Stem Cell Research and Knowledge Levels of Medical Practitioners and Students. Stem cells international , 2021 , 6667743. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6667743
[28] Zhang, J. Y. (2017). Lost in translation? accountability and governance of Clinical Stem Cell Research in China. Regenerative Medicine , 12 (6), 647–656. https://doi.org/10.2217/rme-2017-0035
[29] Wang, L., Wang, F., & Zhang, W. (2021). Bioethics in China’s biosecurity law: Forms, effects, and unsettled issues. Journal of law and the biosciences , 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsab019 https://academic.oup.com/jlb/article/8/1/lsab019/6299199
[30] Chen, H., Wei, T., Wang, H. et al. Association of China’s two-child policy with changes in number of births and birth defects rate, 2008–2017. BMC Public Health 22 , 434 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-12839-0
[31] Azuma, K. Regulatory Landscape of Regenerative Medicine in Japan. Curr Stem Cell Rep 1 , 118–128 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40778-015-0012-6
[32] Harris, R. (2005, May 19). Researchers Report Advance in Stem Cell Production . NPR. https://www.npr.org/2005/05/19/4658967/researchers-report-advance-in-stem-cell-production
[33] Park, S. (2012). South Korea steps up stem-cell work. Nature . https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2012.10565
[34] Resnik, D. B., Shamoo, A. E., & Krimsky, S. (2006). Fraudulent human embryonic stem cell research in South Korea: lessons learned. Accountability in research , 13 (1), 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/08989620600634193 .
[35] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics, 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
[36] Association for the Advancement of Blood and Biotherapies. https://www.aabb.org/regulatory-and-advocacy/regulatory-affairs/regulatory-for-cellular-therapies/international-competent-authorities/saudi-arabia
[37] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: Interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics , 21 (1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
[38] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: Interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics , 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
Culturally, autonomy practices follow a relational autonomy approach based on a paternalistic deontological health care model. The adherence to strict international research policies and religious pillars within the regulatory environment is a great foundation for research ethics. However, there is a need to develop locally targeted ethics approaches for research (as called for in Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics, 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6), this decision-making approach may help advise a research decision model. For more on the clinical cultural autonomy approaches, see: Alabdullah, Y. Y., Alzaid, E., Alsaad, S., Alamri, T., Alolayan, S. W., Bah, S., & Aljoudi, A. S. (2022). Autonomy and paternalism in Shared decision‐making in a Saudi Arabian tertiary hospital: A cross‐sectional study. Developing World Bioethics , 23 (3), 260–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12355 ; Bukhari, A. A. (2017). Universal Principles of Bioethics and Patient Rights in Saudi Arabia (Doctoral dissertation, Duquesne University). https://dsc.duq.edu/etd/124; Ladha, S., Nakshawani, S. A., Alzaidy, A., & Tarab, B. (2023, October 26). Islam and Bioethics: What We All Need to Know . Columbia University School of Professional Studies. https://sps.columbia.edu/events/islam-and-bioethics-what-we-all-need-know
[39] Ababneh, M. A., Al-Azzam, S. I., Alzoubi, K., Rababa’h, A., & Al Demour, S. (2021). Understanding and attitudes of the Jordanian public about clinical research ethics. Research Ethics , 17 (2), 228-241. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016120966779
[40] Ababneh, M. A., Al-Azzam, S. I., Alzoubi, K., Rababa’h, A., & Al Demour, S. (2021). Understanding and attitudes of the Jordanian public about clinical research ethics. Research Ethics , 17 (2), 228-241. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016120966779
[41] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[42] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[43] The EU’s definition of autonomy relates to the capacity for creating ideas, moral insight, decisions, and actions without constraint, personal responsibility, and informed consent. However, the EU views autonomy as not completely able to protect individuals and depends on other principles, such as dignity, which “expresses the intrinsic worth and fundamental equality of all human beings.” Rendtorff, J.D., Kemp, P. (2019). Four Ethical Principles in European Bioethics and Biolaw: Autonomy, Dignity, Integrity and Vulnerability. In: Valdés, E., Lecaros, J. (eds) Biolaw and Policy in the Twenty-First Century. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 78. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05903-3_3
[44] Council of Europe. Convention for the protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being with regard to the Application of Biology and Medicine: Convention on Human Rights and Biomedicine (ETS No. 164) https://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/full-list?module=treaty-detail&treatynum=164 (forbidding the creation of embryos for research purposes only, and suggests embryos in vitro have protections.); Also see Drabiak-Syed B. K. (2013). New President, New Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research Policy: Comparative International Perspectives and Embryonic Stem Cell Research Laws in France. Biotechnology Law Report , 32 (6), 349–356. https://doi.org/10.1089/blr.2013.9865
[45] Rendtorff, J.D., Kemp, P. (2019). Four Ethical Principles in European Bioethics and Biolaw: Autonomy, Dignity, Integrity and Vulnerability. In: Valdés, E., Lecaros, J. (eds) Biolaw and Policy in the Twenty-First Century. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 78. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05903-3_3
[46] Tomuschat, C., Currie, D. P., Kommers, D. P., & Kerr, R. (Trans.). (1949, May 23). Basic law for the Federal Republic of Germany. https://www.btg-bestellservice.de/pdf/80201000.pdf
[47] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Germany . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-germany
[48] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Finland . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-finland
[49] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Spain . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-spain
[50] Some sources to consider regarding ethics models or regulatory oversights of other cultures not covered:
Kara MA. Applicability of the principle of respect for autonomy: the perspective of Turkey. J Med Ethics. 2007 Nov;33(11):627-30. doi: 10.1136/jme.2006.017400. PMID: 17971462; PMCID: PMC2598110.
Ugarte, O. N., & Acioly, M. A. (2014). The principle of autonomy in Brazil: one needs to discuss it ... Revista do Colegio Brasileiro de Cirurgioes , 41 (5), 374–377. https://doi.org/10.1590/0100-69912014005013
Bharadwaj, A., & Glasner, P. E. (2012). Local cells, global science: The rise of embryonic stem cell research in India . Routledge.
For further research on specific European countries regarding ethical and regulatory framework, we recommend this database: Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Europe . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-europe
[51] Klitzman, R. (2006). Complications of culture in obtaining informed consent. The American Journal of Bioethics, 6(1), 20–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15265160500394671 see also: Ekmekci, P. E., & Arda, B. (2017). Interculturalism and Informed Consent: Respecting Cultural Differences without Breaching Human Rights. Cultura (Iasi, Romania) , 14 (2), 159–172.; For why trust is important in research, see also: Gray, B., Hilder, J., Macdonald, L., Tester, R., Dowell, A., & Stubbe, M. (2017). Are research ethics guidelines culturally competent? Research Ethics , 13 (1), 23-41. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016116650235
[52] The Qur'an (M. Khattab, Trans.). (1965). Al-Mu’minun, 23: 12-14. https://quran.com/23
[53] Lenfest, Y. (2017, December 8). Islam and the beginning of human life . Bill of Health. https://blog.petrieflom.law.harvard.edu/2017/12/08/islam-and-the-beginning-of-human-life/
[54] Aksoy, S. (2005). Making regulations and drawing up legislation in Islamic countries under conditions of uncertainty, with special reference to embryonic stem cell research. Journal of Medical Ethics , 31: 399-403.; see also: Mahmoud, Azza. "Islamic Bioethics: National Regulations and Guidelines of Human Stem Cell Research in the Muslim World." Master's thesis, Chapman University, 2022. https://doi.org/10.36837/ chapman.000386
[55] Rashid, R. (2022). When does Ensoulment occur in the Human Foetus. Journal of the British Islamic Medical Association , 12 (4). ISSN 2634 8071. https://www.jbima.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/2-Ethics-3_-Ensoulment_Rafaqat.pdf.
[56] Sivaraman, M. & Noor, S. (2017). Ethics of embryonic stem cell research according to Buddhist, Hindu, Catholic, and Islamic religions: perspective from Malaysia. Asian Biomedicine,8(1) 43-52. https://doi.org/10.5372/1905-7415.0801.260
[57] Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[58] Lecso, P. A. (1991). The Bodhisattva Ideal and Organ Transplantation. Journal of Religion and Health , 30 (1), 35–41. http://www.jstor.org/stable/27510629 ; Bodhisattva, S. (n.d.). The Key of Becoming a Bodhisattva . A Guide to the Bodhisattva Way of Life. http://www.buddhism.org/Sutras/2/BodhisattvaWay.htm
[59] There is no explicit religious reference to when life begins or how to conduct research that interacts with the concept of life. However, these are relevant verses pertaining to how the fetus is viewed. (( King James Bible . (1999). Oxford University Press. (original work published 1769))
Jerimiah 1: 5 “Before I formed thee in the belly I knew thee; and before thou camest forth out of the womb I sanctified thee…”
In prophet Jerimiah’s insight, God set him apart as a person known before childbirth, a theme carried within the Psalm of David.
Psalm 139: 13-14 “…Thou hast covered me in my mother's womb. I will praise thee; for I am fearfully and wonderfully made…”
These verses demonstrate David’s respect for God as an entity that would know of all man’s thoughts and doings even before birth.
[60] It should be noted that abortion is not supported as well.
[61] The Vatican. (1987, February 22). Instruction on Respect for Human Life in Its Origin and on the Dignity of Procreation Replies to Certain Questions of the Day . Congregation For the Doctrine of the Faith. https://www.vatican.va/roman_curia/congregations/cfaith/documents/rc_con_cfaith_doc_19870222_respect-for-human-life_en.html
[62] The Vatican. (2000, August 25). Declaration On the Production and the Scientific and Therapeutic Use of Human Embryonic Stem Cells . Pontifical Academy for Life. https://www.vatican.va/roman_curia/pontifical_academies/acdlife/documents/rc_pa_acdlife_doc_20000824_cellule-staminali_en.html ; Ohara, N. (2003). Ethical Consideration of Experimentation Using Living Human Embryos: The Catholic Church’s Position on Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research and Human Cloning. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology . Retrieved from https://article.imrpress.com/journal/CEOG/30/2-3/pii/2003018/77-81.pdf.
[63] Smith, G. A. (2022, May 23). Like Americans overall, Catholics vary in their abortion views, with regular mass attenders most opposed . Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2022/05/23/like-americans-overall-catholics-vary-in-their-abortion-views-with-regular-mass-attenders-most-opposed/
[64] Rosner, F., & Reichman, E. (2002). Embryonic stem cell research in Jewish law. Journal of halacha and contemporary society , (43), 49–68.; Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[65] Schenker J. G. (2008). The beginning of human life: status of embryo. Perspectives in Halakha (Jewish Religious Law). Journal of assisted reproduction and genetics , 25 (6), 271–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-008-9221-6
[66] Ruttenberg, D. (2020, May 5). The Torah of Abortion Justice (annotated source sheet) . Sefaria. https://www.sefaria.org/sheets/234926.7?lang=bi&with=all&lang2=en
[67] Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[68] Gert, B. (2007). Common morality: Deciding what to do . Oxford Univ. Press.
[69] World Medical Association (2013). World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA , 310(20), 2191–2194. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.281053 Declaration of Helsinki – WMA – The World Medical Association .; see also: National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research. (1979). The Belmont report: Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research . U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.hhs.gov/ohrp/regulations-and-policy/belmont-report/read-the-belmont-report/index.html
[70] Zakarin Safier, L., Gumer, A., Kline, M., Egli, D., & Sauer, M. V. (2018). Compensating human subjects providing oocytes for stem cell research: 9-year experience and outcomes. Journal of assisted reproduction and genetics , 35 (7), 1219–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-018-1171-z https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6063839/ see also: Riordan, N. H., & Paz Rodríguez, J. (2021). Addressing concerns regarding associated costs, transparency, and integrity of research in recent stem cell trial. Stem Cells Translational Medicine , 10 (12), 1715–1716. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.21-0234
[71] Klitzman, R., & Sauer, M. V. (2009). Payment of egg donors in stem cell research in the USA. Reproductive biomedicine online , 18 (5), 603–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1472-6483(10)60002-8
[72] Krosin, M. T., Klitzman, R., Levin, B., Cheng, J., & Ranney, M. L. (2006). Problems in comprehension of informed consent in rural and peri-urban Mali, West Africa. Clinical trials (London, England) , 3 (3), 306–313. https://doi.org/10.1191/1740774506cn150oa
[73] Veatch, Robert M. Hippocratic, Religious, and Secular Medical Ethics: The Points of Conflict . Georgetown University Press, 2012.
[74] Msoroka, M. S., & Amundsen, D. (2018). One size fits not quite all: Universal research ethics with diversity. Research Ethics , 14 (3), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016117739939
[75] Pirzada, N. (2022). The Expansion of Turkey’s Medical Tourism Industry. Voices in Bioethics , 8 . https://doi.org/10.52214/vib.v8i.9894
[76] Stem Cell Tourism: False Hope for Real Money . Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI). (2023). https://hsci.harvard.edu/stem-cell-tourism , See also: Bissassar, M. (2017). Transnational Stem Cell Tourism: An ethical analysis. Voices in Bioethics , 3 . https://doi.org/10.7916/vib.v3i.6027
[77] Song, P. (2011) The proliferation of stem cell therapies in post-Mao China: problematizing ethical regulation, New Genetics and Society , 30:2, 141-153, DOI: 10.1080/14636778.2011.574375
[78] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[79] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2024). Standards in stem cell research . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/5-standards-in-stem-cell-research
[80] Benjamin, R. (2013). People’s science bodies and rights on the Stem Cell Frontier . Stanford University Press.
Mifrah Hayath
SM Candidate Harvard Medical School, MS Biotechnology Johns Hopkins University
Olivia Bowers
MS Bioethics Columbia University (Disclosure: affiliated with Voices in Bioethics)
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
Early iterations of the AI applications we interact with most today were built on traditional machine learning models. These models rely on learning algorithms that are developed and maintained by data scientists. In other words, traditional machine learning models need human intervention to process new information and perform any new task that falls outside their initial training.
For example, Apple made Siri a feature of its iOS in 2011. This early version of Siri was trained to understand a set of highly specific statements and requests. Human intervention was required to expand Siri’s knowledge base and functionality.
However, AI capabilities have been evolving steadily since the breakthrough development of artificial neural networks in 2012, which allow machines to engage in reinforcement learning and simulate how the human brain processes information.
Unlike basic machine learning models, deep learning models allow AI applications to learn how to perform new tasks that need human intelligence, engage in new behaviors and make decisions without human intervention. As a result, deep learning has enabled task automation, content generation, predictive maintenance and other capabilities across industries .
Due to deep learning and other advancements, the field of AI remains in a constant and fast-paced state of flux. Our collective understanding of realized AI and theoretical AI continues to shift, meaning AI categories and AI terminology may differ (and overlap) from one source to the next. However, the types of AI can be largely understood by examining two encompassing categories: AI capabilities and AI functionalities.
1. Artificial Narrow AI
Artificial Narrow Intelligence, also known as Weak AI (what we refer to as Narrow AI), is the only type of AI that exists today. Any other form of AI is theoretical. It can be trained to perform a single or narrow task, often far faster and better than a human mind can.
However, it can’t perform outside of its defined task. Instead, it targets a single subset of cognitive abilities and advances in that spectrum. Siri, Amazon’s Alexa and IBM Watson are examples of Narrow AI. Even OpenAI’s ChatGPT is considered a form of Narrow AI because it’s limited to the single task of text-based chat.
2. General AI
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), also known as Strong AI , is today nothing more than a theoretical concept. AGI can use previous learnings and skills to accomplish new tasks in a different context without the need for human beings to train the underlying models. This ability allows AGI to learn and perform any intellectual task that a human being can.
3. Super AI
Super AI is commonly referred to as artificial superintelligence and, like AGI, is strictly theoretical. If ever realized, Super AI would think, reason, learn, make judgements and possess cognitive abilities that surpass those of human beings.
The applications possessing Super AI capabilities will have evolved beyond the point of understanding human sentiments and experiences to feel emotions, have needs and possess beliefs and desires of their own.
Underneath Narrow AI, one of the three types based on capabilities, there are two functional AI categories:
1. Reactive Machine AI
Reactive machines are AI systems with no memory and are designed to perform a very specific task. Since they can’t recollect previous outcomes or decisions, they only work with presently available data. Reactive AI stems from statistical math and can analyze vast amounts of data to produce a seemingly intelligent output.
Examples of Reactive Machine AI
- IBM Deep Blue: IBM’s chess-playing supercomputer AI beat chess grandmaster Garry Kasparov in the late 1990s by analyzing the pieces on the board and predicting the probable outcomes of each move.
- The Netflix Recommendation Engine: Netflix’s viewing recommendations are powered by models that process data sets collected from viewing history to provide customers with content they’re most likely to enjoy.
2. Limited Memory AI
Unlike Reactive Machine AI, this form of AI can recall past events and outcomes and monitor specific objects or situations over time. Limited Memory AI can use past- and present-moment data to decide on a course of action most likely to help achieve a desired outcome.
However, while Limited Memory AI can use past data for a specific amount of time, it can’t retain that data in a library of past experiences to use over a long-term period. As it’s trained on more data over time, Limited Memory AI can improve in performance.
Examples of Limited Memory AI
- Generative AI: Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT, Bard and DeepAI rely on limited memory AI capabilities to predict the next word, phrase or visual element within the content it’s generating.
- Virtual assistants and chatbots: Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant, Cortana and IBM Watson Assistant combine natural language processing (NLP) and Limited Memory AI to understand questions and requests, take appropriate actions and compose responses.
- Self-driving cars: Autonomous vehicles use Limited Memory AI to understand the world around them in real-time and make informed decisions on when to apply speed, brake, make a turn, etc.
3. Theory of Mind AI
Theory of Mind AI is a functional class of AI that falls underneath the General AI. Though an unrealized form of AI today, AI with Theory of Mind functionality would understand the thoughts and emotions of other entities. This understanding can affect how the AI interacts with those around them. In theory, this would allow the AI to simulate human-like relationships.
Because Theory of Mind AI could infer human motives and reasoning, it would personalize its interactions with individuals based on their unique emotional needs and intentions. Theory of Mind AI would also be able to understand and contextualize artwork and essays, which today’s generative AI tools are unable to do.
Emotion AI is a theory of mind AI currently in development. AI researchers hope it will have the ability to analyze voices, images and other kinds of data to recognize, simulate, monitor and respond appropriately to humans on an emotional level. To date, Emotion AI is unable to understand and respond to human feelings.
4. Self-Aware AI
Self-Aware AI is a kind of functional AI class for applications that would possess super AI capabilities. Like theory of mind AI, Self-Aware AI is strictly theoretical. If ever achieved, it would have the ability to understand its own internal conditions and traits along with human emotions and thoughts. It would also have its own set of emotions, needs and beliefs.
Emotion AI is a Theory of Mind AI currently in development. Researchers hope it will have the ability to analyze voices, images and other kinds of data to recognize, simulate, monitor and respond appropriately to humans on an emotional level. To date, Emotion AI is unable to understand and respond to human feelings.
Computer vision
Narrow AI applications with computer vision can be trained to interpret and analyze the visual world. This allows intelligent machines to identify and classify objects within images and video footage.
Applications of computer vision include:
- Image recognition and classification
- Object detection
- Object tracking
- Facial recognition
- Content-based image retrieval
Computer vision is critical for use cases that involve AI machines interacting and traversing the physical world around them. Examples include self-driving cars and machines navigating warehouses and other environments.
Robots in industrial settings can use Narrow AI to perform routine, repetitive tasks that involve materials handling, assembly and quality inspections. In healthcare, robots equipped with Narrow AI can assist surgeons in monitoring vitals and detecting potential issues during procedures.
Agricultural machines can engage in autonomous pruning, moving, thinning, seeding and spraying. And smart home devices such as the iRobot Roomba can navigate a home’s interior using computer vision and use data stored in memory to understand its progress.
Expert systems
Expert systems equipped with Narrow AI capabilities can be trained on a corpus to emulate the human decision-making process and apply expertise to solve complex problems. These systems can evaluate vast amounts of data to uncover trends and patterns to make decisions. They can also help businesses predict future events and understand why past events occurred.
IBM has pioneered AI from the very beginning, contributing breakthrough after breakthrough to the field. IBM most recently released a big upgrade to its cloud-based, generative AI platform known as watsonx. IBM watsonx.ai brings together new generative AI capabilities, powered by foundation models and traditional machine learning into a powerful studio spanning the entire AI lifecycle. With watsonx.ai, data scientists can build, train and deploy machine learning models in a single collaborative studio environment.
Get email updates about AI advancements, strategies, how-tos, expert perspectives and more.
Explore watsonx.ai today
Get our newsletters and topic updates that deliver the latest thought leadership and insights on emerging trends.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research paper: Research article: A research paper is an extended form of writing that presents and supports an argument on a particular topic. It provides evidence for the opinion or idea in the form of facts, data, analysis, opinions from authorities in specific fields etc. The objective is to make original claims based on careful evaluation ...
There is no definitive distinction between papers and articles that can be applied to all scientific disciplines. Usage varies between disciplines. and within disciplines it can vary depending on context. Both the examples quoted refer to 'writings' that are surveys (in other areas often termed reviews) — one in the field of a social science (economics) and the other in a numerical ...
This makes review articles distinctly different from scientific research papers. While the primary aim of the latter is to develop new arguments by reporting original research, the former is focused on summarising and synthesising previous ideas, studies, and arguments, without adding new experimental contributions. ... What is the difference ...
The standard format of journal articles. In June of 2005, the journal Science published a research report on a sighting of the ivory-billed woodpecker, a bird long considered extinct in North America (Fitzpatrick et al., 2005). The work was of such significance and broad interest that it was displayed prominently on the cover (Figure 2) and highlighted by an editorial at the front of the ...
Theoretical Articles. Distinguishing characteristic: Theoretical articles draw on existing scholarship to improve upon or offer a new theoretical perspective on a given topic. Usefulness for research: Theoretical articles are useful because they provide a theoretical framework you can apply to your own research.
Original Research: This is the most common type of journal manuscript used to publish full reports of data from research. It may be called an Original Article, Research Article, Research, or just Article, depending on the journal. The Original Research format is suitable for many different fields and different types of studies.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
A good scholarly research article should have citations for almost any claims made within the main body, to ensure proper connections to the prior research in the field. Unlike patents, papers require a deep scientific background and should be straight to the point. While patents include all aspects of the idea, papers typically have space ...
Finally, scientific research involves interpreting and trying to make sense of those data — going beyond the data themselves to draw conclusions about the underlying phenomenon being studied. Driving the whole research endeavor are one or more research problems or questions that the researcher is trying to address and potentially solve.
6. A research paper is a paper containing original research. That is, if you do some work to add (or try to add) new knowledge to a field of study, and then present the details of your approach and findings in a paper, that paper can be called a research paper. Not all academic papers contain original research; other kinds of academic papers ...
Different sections are needed in different types of scientific papers (lab reports, literature reviews, systematic reviews, methods papers, research papers, etc.). Projects that overlap with the social sciences or humanities may have different requirements. Generally, however, you'll need to include: TITLE. ABSTRACT. INTRODUCTION (Background)
A research paper is a primary source...that is, it reports the methods and results of an original study performed by the authors. The kind of study may vary (it could have been an experiment, survey, interview, etc.), but in all cases, raw data have been collected and analyzed by the authors, and conclusions drawn from the results of that analysis. ...
A paper is for the most part unpublished. Article is nearly continuously a chunk of composing that's published in a journal. Paper as the title suggest one has got to come out with a subject Objective that's researchable, targets which are specific, measurable, attainable, practical, and time-bound. An article is anything thing of intrigued ...
Preprints, like academic journal articles, are assigned a Digital Object Identifier, or DOI, and become a permanent part of the scientific record. White paper. A white paper is a report, often compiled by government agencies, businesses and nonprofit organizations, that outlines an issue and often explores possible solutions to a problem.
4- A research article examines a potential or existing concept and discusses its effects. A thesis may be provided in a research paper, although it will not be as detailed. 5- Both differs in terms of formatting and length. A Longer in length whereas research article might be 15 pages long, but it's not always the case.
Often "paper" has no limit. Typically the shorter the length limit, the more prestigious it is and the tougher the acceptance criteria. The subject matter covered by the journal is the same for all categories. Some journals also have a "review" category which includes papers which are not original research. Often a review is by invitation only.
Dec 11, 2017. There are different types of scholarly literature. Some of these require researchers to conduct an original study, whereas others can be based on previously published research. Understanding each of these types and also how they differ from one another can be rather confusing for researchers, especially early career researchers.
The research paper will be based on the analysis and interpretation of this data. A review article or review paper is based on other published articles. It does not report original research. Review articles generally summarize the existing literature on a topic in an attempt to explain the current state of understanding on the topic.
Research Papers. Technical Articles. Research paper carries more weight on the basic issues. Technical article puts more accentuation on the technique angle, not necessary announcing on the discoveries. A research paper won't warrant as broad of a reference list. A technical article, a peruser can anticipate to discover an broad book index.
DOI: 10.11648/j.ijaaa.20241002.12 Corpus ID: 269562689; The Concept of Difference in Architecture: Transpositions Between Insides and Outsides @article{Pantelidou2024TheCO, title={The Concept of Difference in Architecture: Transpositions Between Insides and Outsides}, author={Charikleia Pantelidou}, journal={International Journal of Architecture, Arts and Applications}, year={2024}, url={https ...
Difference #1: The Author. Commercial white papers are written by a company's in-house staff or by a freelance writer under contract. The writer meets with the marketing staff to discuss the information to be presented, to determine an angle, and set parameters on facts and messaging. The author may have a background in the topic or product ...
DOI: 10.37118/ijdr.26851.06.2023 Corpus ID: 259509393; Relationship between gender differences and impulse buying behaviour: a case of college-going students in kolkata @article{2023RelationshipBG, title={Relationship between gender differences and impulse buying behaviour: a case of college-going students in kolkata}, author={}, journal={International Journal of Development Research}, year ...
Long-term cognitive deficits occur when the signals between brain structures weaken due to the injury. The structural differences in male and female brains might explain why females are more prone ...
Flame retardants (FRs) are added to vehicles to meet flammability standards, such as US Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard FMVSS 302. However, an understanding of which FRs are being used, sources in the vehicle, and implications for human exposure is lacking. US participants (n = 101) owning a vehicle of model year 2015 or newer hung a silicone passive sampler on their rearview mirror for ...
Voices in Bioethics is currently seeking submissions on philosophical and practical topics, both current and timeless. Papers addressing access to healthcare, the bioethical implications of recent Supreme Court rulings, environmental ethics, data privacy, cybersecurity, law and bioethics, economics and bioethics, reproductive ethics, research ethics, and pediatric bioethics are sought.
Theory of Mind AI would also be able to understand and contextualize artwork and essays, which today's generative AI tools are unable to do. Emotion AI is a theory of mind AI currently in development. AI researchers hope it will have the ability to analyze voices, images and other kinds of data to recognize, simulate, monitor and respond ...