- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources

How to Write a Good Research Question (w/ Examples)
What is a Research Question?
A research question is the main question that your study sought or is seeking to answer. A clear research question guides your research paper or thesis and states exactly what you want to find out, giving your work a focus and objective. Learning how to write a hypothesis or research question is the start to composing any thesis, dissertation, or research paper. It is also one of the most important sections of a research proposal .
A good research question not only clarifies the writing in your study; it provides your readers with a clear focus and facilitates their understanding of your research topic, as well as outlining your study’s objectives. Before drafting the paper and receiving research paper editing (and usually before performing your study), you should write a concise statement of what this study intends to accomplish or reveal.
Research Question Writing Tips
Listed below are the important characteristics of a good research question:
A good research question should:
- Be clear and provide specific information so readers can easily understand the purpose.
- Be focused in its scope and narrow enough to be addressed in the space allowed by your paper
- Be relevant and concise and express your main ideas in as few words as possible, like a hypothesis.
- Be precise and complex enough that it does not simply answer a closed “yes or no” question, but requires an analysis of arguments and literature prior to its being considered acceptable.
- Be arguable or testable so that answers to the research question are open to scrutiny and specific questions and counterarguments.
Some of these characteristics might be difficult to understand in the form of a list. Let’s go into more detail about what a research question must do and look at some examples of research questions.
The research question should be specific and focused
Research questions that are too broad are not suitable to be addressed in a single study. One reason for this can be if there are many factors or variables to consider. In addition, a sample data set that is too large or an experimental timeline that is too long may suggest that the research question is not focused enough.
A specific research question means that the collective data and observations come together to either confirm or deny the chosen hypothesis in a clear manner. If a research question is too vague, then the data might end up creating an alternate research problem or hypothesis that you haven’t addressed in your Introduction section .
The research question should be based on the literature
An effective research question should be answerable and verifiable based on prior research because an effective scientific study must be placed in the context of a wider academic consensus. This means that conspiracy or fringe theories are not good research paper topics.
Instead, a good research question must extend, examine, and verify the context of your research field. It should fit naturally within the literature and be searchable by other research authors.
References to the literature can be in different citation styles and must be properly formatted according to the guidelines set forth by the publishing journal, university, or academic institution. This includes in-text citations as well as the Reference section .
The research question should be realistic in time, scope, and budget
There are two main constraints to the research process: timeframe and budget.
A proper research question will include study or experimental procedures that can be executed within a feasible time frame, typically by a graduate doctoral or master’s student or lab technician. Research that requires future technology, expensive resources, or follow-up procedures is problematic.
A researcher’s budget is also a major constraint to performing timely research. Research at many large universities or institutions is publicly funded and is thus accountable to funding restrictions.
The research question should be in-depth
Research papers, dissertations and theses , and academic journal articles are usually dozens if not hundreds of pages in length.
A good research question or thesis statement must be sufficiently complex to warrant such a length, as it must stand up to the scrutiny of peer review and be reproducible by other scientists and researchers.
Research Question Types
Qualitative and quantitative research are the two major types of research, and it is essential to develop research questions for each type of study.
Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research questions are specific. A typical research question involves the population to be studied, dependent and independent variables, and the research design.
In addition, quantitative research questions connect the research question and the research design. In addition, it is not possible to answer these questions definitively with a “yes” or “no” response. For example, scientific fields such as biology, physics, and chemistry often deal with “states,” in which different quantities, amounts, or velocities drastically alter the relevance of the research.
As a consequence, quantitative research questions do not contain qualitative, categorical, or ordinal qualifiers such as “is,” “are,” “does,” or “does not.”
Categories of quantitative research questions
Qualitative research questions.
In quantitative research, research questions have the potential to relate to broad research areas as well as more specific areas of study. Qualitative research questions are less directional, more flexible, and adaptable compared with their quantitative counterparts. Thus, studies based on these questions tend to focus on “discovering,” “explaining,” “elucidating,” and “exploring.”
Categories of qualitative research questions
Quantitative and qualitative research question examples.

Good and Bad Research Question Examples
Below are some good (and not-so-good) examples of research questions that researchers can use to guide them in crafting their own research questions.
Research Question Example 1
The first research question is too vague in both its independent and dependent variables. There is no specific information on what “exposure” means. Does this refer to comments, likes, engagement, or just how much time is spent on the social media platform?
Second, there is no useful information on what exactly “affected” means. Does the subject’s behavior change in some measurable way? Or does this term refer to another factor such as the user’s emotions?
Research Question Example 2
In this research question, the first example is too simple and not sufficiently complex, making it difficult to assess whether the study answered the question. The author could really only answer this question with a simple “yes” or “no.” Further, the presence of data would not help answer this question more deeply, which is a sure sign of a poorly constructed research topic.
The second research question is specific, complex, and empirically verifiable. One can measure program effectiveness based on metrics such as attendance or grades. Further, “bullying” is made into an empirical, quantitative measurement in the form of recorded disciplinary actions.
Steps for Writing a Research Question
Good research questions are relevant, focused, and meaningful. It can be difficult to come up with a good research question, but there are a few steps you can follow to make it a bit easier.
1. Start with an interesting and relevant topic
Choose a research topic that is interesting but also relevant and aligned with your own country’s culture or your university’s capabilities. Popular academic topics include healthcare and medical-related research. However, if you are attending an engineering school or humanities program, you should obviously choose a research question that pertains to your specific study and major.
Below is an embedded graph of the most popular research fields of study based on publication output according to region. As you can see, healthcare and the basic sciences receive the most funding and earn the highest number of publications.
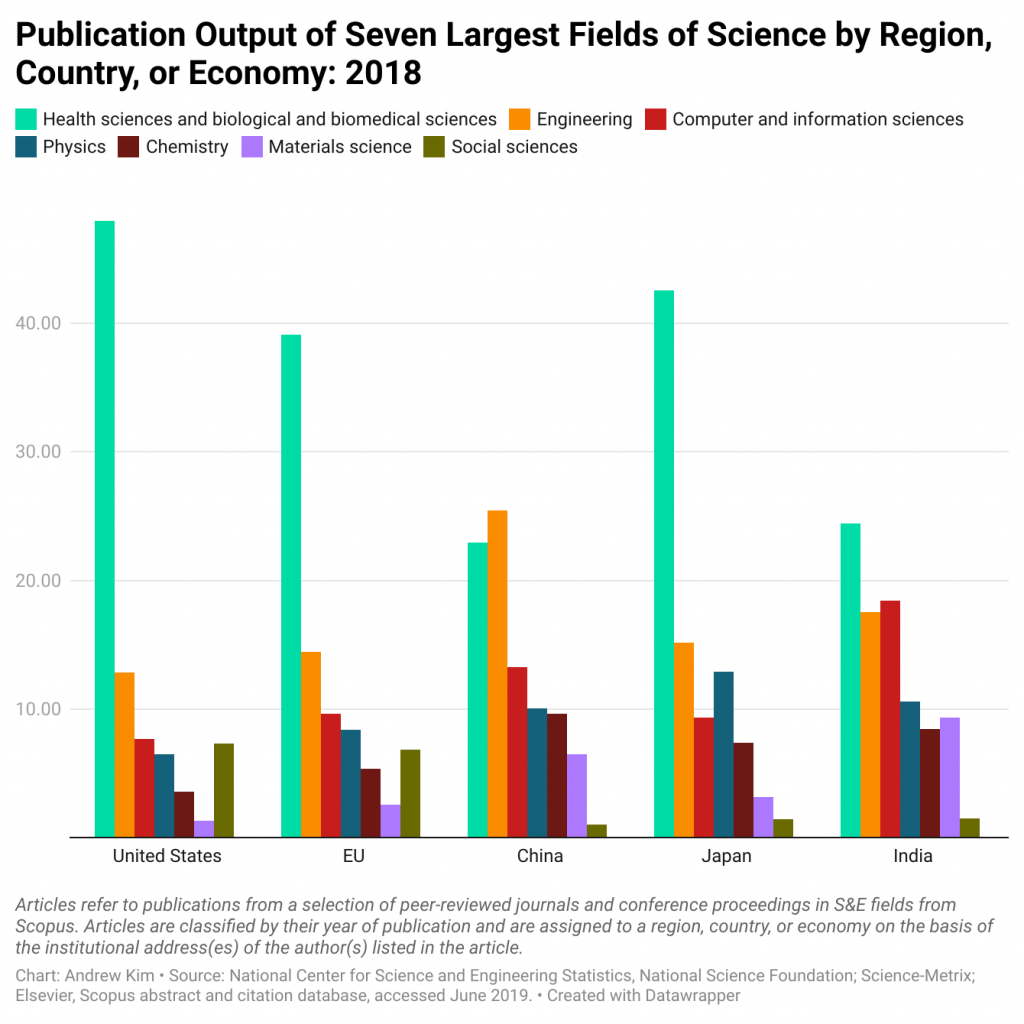
2. Do preliminary research
You can begin doing preliminary research once you have chosen a research topic. Two objectives should be accomplished during this first phase of research. First, you should undertake a preliminary review of related literature to discover issues that scholars and peers are currently discussing. With this method, you show that you are informed about the latest developments in the field.
Secondly, identify knowledge gaps or limitations in your topic by conducting a preliminary literature review . It is possible to later use these gaps to focus your research question after a certain amount of fine-tuning.
3. Narrow your research to determine specific research questions
You can focus on a more specific area of study once you have a good handle on the topic you want to explore. Focusing on recent literature or knowledge gaps is one good option.
By identifying study limitations in the literature and overlooked areas of study, an author can carve out a good research question. The same is true for choosing research questions that extend or complement existing literature.
4. Evaluate your research question
Make sure you evaluate the research question by asking the following questions:
Is my research question clear?
The resulting data and observations that your study produces should be clear. For quantitative studies, data must be empirical and measurable. For qualitative, the observations should be clearly delineable across categories.
Is my research question focused and specific?
A strong research question should be specific enough that your methodology or testing procedure produces an objective result, not one left to subjective interpretation. Open-ended research questions or those relating to general topics can create ambiguous connections between the results and the aims of the study.
Is my research question sufficiently complex?
The result of your research should be consequential and substantial (and fall sufficiently within the context of your field) to warrant an academic study. Simply reinforcing or supporting a scientific consensus is superfluous and will likely not be well received by most journal editors.

Editing Your Research Question
Your research question should be fully formulated well before you begin drafting your research paper. However, you can receive English paper editing and proofreading services at any point in the drafting process. Language editors with expertise in your academic field can assist you with the content and language in your Introduction section or other manuscript sections. And if you need further assistance or information regarding paper compositions, in the meantime, check out our academic resources , which provide dozens of articles and videos on a variety of academic writing and publication topics.
Libraries & Cultural Resources
Research guides, guide to research and writing for the academic study of religion.
- Topic Pyramids
- Research Assignment Parameters
- Thesis statement
- Identifying Interests
- Controversy
- Availability of Sources
- Preliminary Research
- Developing Your Question and Thesis
- Research Question and Thesis Statement Examples
- Periodicals
- Primary Sources
- Reference Works - Encyclopedias, Dictionaries, Biographies etc
- Journal Articles
- Primary Sources This link opens in a new window
- Web Search Engines
- Web Directories
- Invisible Web
- Does the Library hold the article I need?
- Locating resources unavailable at U of C Library
- Content of Databases
- Standardized Terminology
- Review Quiz Databases
- Keyword Searching
- Search Limits
- Phrase Searching
- Truncations and Wildcards
- Boolean Operators
- Proximity Operators
- Natural Language Searching
- Searching Basics Quiz
- Search Overview
- Selecting Records
- Combing Searchers
- General Criteria
- Quoting in text
- in Text Citations
- List of References
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Staying Organized
- Links to Writing Help
- Sources Used in Creating this Workbook
Research Question and Thesis
If you have followed all the previous steps, you should be very close to developing a good question if you haven’t already. Here are a few examples of good and bad questions to help you distinguish an effective research question from an ineffective one.
Example #1: Why has religious fundamentalism arisen in North America?
Example #2: what is the relationship between theology and religious studies.
This is a good start, but it is much too general.
What does Donald Wiebe say about theology and religious studies?
This is more specific but you still need to bring the controversy to the forefront. As it stands, it invites a mere summary of Donald Wiebe's position.
Good research questions on this topic might be :
- Are there any conceptual problems with Wiebe's distinction between theology and religious studies?
- Does Wiebe's position on the distinction between theology and religious studies represent a radical departure from previous understandings of the relationship between the two?
- Does Wiebe's agenda to eliminate theology from Religious Studies have any unforeseen or undesirable practical implications?
All three of these questions have a narrower focus and can be answered in a variety of ways. Answering any of these questions will generate a thesis statement. Remember, the answer that you give to a research question is your thesis statement.
For further examples of good research questions, see Research Strategies by Badke .
The Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement directly answers your research question, and takes a stand (rather than announces the subject) that others might dispute. In other words, it is provocative and contestable. A strong thesis clearly asserts your position or conclusion and avoids vague language (e.g. “It seems…). Your thesis should be obvious, easy to find, and clearly stated in the opening paragraph of your paper. The rest of your paper is devoted to substantiating your thesis by offering evidence in support of your claim. Remember, that it is perfectly acceptable to change your thesis if the evidence leads you to an alternative conclusion.
For examples of strong thesis statements, look for abstracts and articles from peer-reviewed journals and books, and attempt to find the thesis in each of these sources. The author(s) of these sources typically state their conclusions in several different ways.
Examples of thesis statements are italicized in the abstracts provided below.
“S tating the problem under discussion as "Islam and Science" is false because this formulation implies that there is such a thing as a reified and ahistorical and hence immutable "Islam" that is responsible for advancing or impeding scientific activity, both past and present. In fact, Islam, like all other religions, is the specific ideology of a particular, historically determined society (i.e., Islam in Baghdad in the 830s, in Damascus in 1300, in Cairo around 1000, etc.) and has itself no historical agency; what that particular society accomplishes in the way of science wholly depends on who is using that ideology (if it is being used) and to what ends. The analysis of scientific activity in Islamic societies, therefore, can proceed only from the investigation of the social and political factors at play in each particular case. Injecting the notion of “Islam” into these discussions merely obfuscates the issue and confuses students, distracting them from historical analysis and political action.” Source: Gutas, Dimitri. 2003. “Islam and Science: A False Statement of the Problem.” Islam & Science 1, no.2: 215-20.
“In this response article, some of the most challenging aspects of Islam and science discourse are discussed. Responding to the specific issues of the relationship between Islam and science and the normative Islamic tradition, the article explores the claims of a secular view that there is no such thing as essential Islam and that there is no relationship between Islam and the scientific tradition that arose in the Islamic civilization. This view is refuted on the basis of historical, logical and internal evidence .” Source: Iqbal, Muzaffar. 2003. “Islam and Science: Responding to a False Approach.” Islam & Science , 1, no. 2: 221-34.
“This rejoinder is a further contribution to the debate begun by M. Iqbal and D. Gutas on the differing perspectives and methodological assumptions of faith-based and secular approaches to the study of the history of science in religious cultures. While the arguments presented are to some degree ad hominem, they do aim to highlight certain logical inconsistencies in the conceptualization of the role of religion in the study of science and in the revisionist portrayal of as a causal agent that functions independently of its adherents .” Source : Reisman, David C. 2004. “An Unfortunate Response: Iqbal on Gutas.” Islam & Science 2, no.1: 63-73.
- << Previous: Developing Your Question and Thesis
- Next: Selecting Sources >>
- Last Updated: Jun 9, 2022 2:27 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ucalgary.ca/research-and-writing-religion
Libraries & Cultural Resources
- 403.220.8895
Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
The “Golden Thread” Explained Simply (+ Examples)
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022
The research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Master of Fine Arts
Writing a research question.
- Searching Library Databases
- Finding Journal Articles
- Search Tips
- Literature Reviews
- Assessing Resources
- Citing Sources
- Theses and Dissertations
- Thesis Submission Process
There are many ways to get research help. Visit the research help desk, book an appointment with your liaison librarian, or ask us questions through email our AskAway. See the Research Help page for details.
- Contact the Library
- Make a suggestion We want to hear from ECU students, staff and faculty! Is there a book you would like to see in the collection that we don't already have? Do you have any other suggestions for the library in general? Let us know.
Research Question
The following is from the ECUAD Writing Center Handout: Writing a Research Question.
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, complex and arguable question that will lay the groundwork for a thesis by offering a focus for your exploration of a topic that interests you. Although a strong research question is a good place to start your thesis, you should be prepared for it to change as you carry out primary and secondary research.
What are the steps to writing a research question?
The following steps are merely a guideline for the very beginning of the process of writing a research question. You might not follow them in exact order and you might return to or move between them at different points in your research process.
- Choose a general topic that interests you. Start broadly, then narrow as you begin the research process. General topics might include broad issues such as “literacy” or “body image.”
- Do some preliminary research on your general topic. Consult periodicals and journals on your topic to see what has been explored in depth and what holes might remain.
- Start asking questions. Taking into consideration the above, start asking yourself “how” and “why” questions about your general topic. For example, “Why is there a correlation between poverty and childhood illiteracy?” or “How can public health officials respond to body image issues in young women?”
- Evaluate your question. At several stages in your research process, you will want to come back to “test” your research question to make sure it still meets your research objectives. Use the ideas below about what makes a good research question to evaluate your question.
What makes a good research question?
None of these are absolute rules (except, perhaps, the first and the last), but rather goals to reach toward through the process of writing and revising your research question.
- Interesting: choose something that excites you enough to keep you going through the researching, designing and writing process.
- Clear : avoid vague words. Too vague: Why are social networking sites harmful? This question may be a good place to start but it is too vague to effectively guide a thesis project to its conclusion. It does not specify which social networking sites or state what harm (physical? emotional? financial?) is being caused to whom. Moreover, this question takes as a given that this “harm” exists. Clear: How are online users experiencing or addressing privacy issues on social networking sites such as Facebook and Twitter? With this question, you are able to clearly understand all the variables at play. It not only specifies the sites (Facebook and Twitter), but also the type of harm (privacy issues) and who is harmed (online users).
- Focused : A good research question narrows the focus of the research to a manageable level for the project at hand. Too Broad: How do we fight illiteracy? This question certainly addresses a real issue but it will yield too many answers for you to be able to effectively deal with in a single thesis. Again, it is a good place to start but far too broad to carry on very far. Focused: How can an internet-based design tool be designed to increase interest in reading amongst primary school boys in Canada? This question is still complex, but it offers a much more manageable task.
- Complex : A research question should never yield a simple yes or no answer. Rather, it should open up possibilities for primary and secondary research and complex discussions. Too simple: How many women in Canada between the ages of 18 and 34 are obese? This question can be answered with a simple statistic. Complex: How might childhood education tools be designed to help prevent obesity within Canadian women?
- Arguable: Your research question should offer up an opportunity for you to take an arguable position—that is, one that others may disagree with and that can be supported by evidence. Raises a problem: This is particularly important in design research and is a consideration you will return to again and again throughout the research process. Before you start investigating a designed outcome (which is what most design research centres around), you need first to identify a real-world problem that your outcome can address or question. Concise: The final version of your research question will be quite concise, with no unnecessary qualifiers. But this need not be a major consideration early in your research process.
- Writing a research question Handout on writing a research question created by the ECU Writing Centre
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Searching Library Databases >>
- Last Updated: Feb 15, 2024 7:26 PM
- URL: https://guides.ecuad.ca/mfa
Think of yourself as a member of a jury, listening to a lawyer who is presenting an opening argument. You'll want to know very soon whether the lawyer believes the accused to be guilty or not guilty, and how the lawyer plans to convince you. Readers of academic essays are like jury members: before they have read too far, they want to know what the essay argues as well as how the writer plans to make the argument. After reading your thesis statement, the reader should think, "This essay is going to try to convince me of something. I'm not convinced yet, but I'm interested to see how I might be."
An effective thesis cannot be answered with a simple "yes" or "no." A thesis is not a topic; nor is it a fact; nor is it an opinion. "Reasons for the fall of communism" is a topic. "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" is a fact known by educated people. "The fall of communism is the best thing that ever happened in Europe" is an opinion. (Superlatives like "the best" almost always lead to trouble. It's impossible to weigh every "thing" that ever happened in Europe. And what about the fall of Hitler? Couldn't that be "the best thing"?)
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay.
Steps in Constructing a Thesis
First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication. Does the author contradict himself or herself? Is a point made and later reversed? What are the deeper implications of the author's argument? Figuring out the why to one or more of these questions, or to related questions, will put you on the path to developing a working thesis. (Without the why, you probably have only come up with an observation—that there are, for instance, many different metaphors in such-and-such a poem—which is not a thesis.)
Once you have a working thesis, write it down. There is nothing as frustrating as hitting on a great idea for a thesis, then forgetting it when you lose concentration. And by writing down your thesis you will be forced to think of it clearly, logically, and concisely. You probably will not be able to write out a final-draft version of your thesis the first time you try, but you'll get yourself on the right track by writing down what you have.
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction. Although this is not required in all academic essays, it is a good rule of thumb.
Anticipate the counterarguments. Once you have a working thesis, you should think about what might be said against it. This will help you to refine your thesis, and it will also make you think of the arguments that you'll need to refute later on in your essay. (Every argument has a counterargument. If yours doesn't, then it's not an argument—it may be a fact, or an opinion, but it is not an argument.)
This statement is on its way to being a thesis. However, it is too easy to imagine possible counterarguments. For example, a political observer might believe that Dukakis lost because he suffered from a "soft-on-crime" image. If you complicate your thesis by anticipating the counterargument, you'll strengthen your argument, as shown in the sentence below.
Some Caveats and Some Examples
A thesis is never a question. Readers of academic essays expect to have questions discussed, explored, or even answered. A question ("Why did communism collapse in Eastern Europe?") is not an argument, and without an argument, a thesis is dead in the water.
A thesis is never a list. "For political, economic, social and cultural reasons, communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" does a good job of "telegraphing" the reader what to expect in the essay—a section about political reasons, a section about economic reasons, a section about social reasons, and a section about cultural reasons. However, political, economic, social and cultural reasons are pretty much the only possible reasons why communism could collapse. This sentence lacks tension and doesn't advance an argument. Everyone knows that politics, economics, and culture are important.
A thesis should never be vague, combative or confrontational. An ineffective thesis would be, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because communism is evil." This is hard to argue (evil from whose perspective? what does evil mean?) and it is likely to mark you as moralistic and judgmental rather than rational and thorough. It also may spark a defensive reaction from readers sympathetic to communism. If readers strongly disagree with you right off the bat, they may stop reading.
An effective thesis has a definable, arguable claim. "While cultural forces contributed to the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe, the disintegration of economies played the key role in driving its decline" is an effective thesis sentence that "telegraphs," so that the reader expects the essay to have a section about cultural forces and another about the disintegration of economies. This thesis makes a definite, arguable claim: that the disintegration of economies played a more important role than cultural forces in defeating communism in Eastern Europe. The reader would react to this statement by thinking, "Perhaps what the author says is true, but I am not convinced. I want to read further to see how the author argues this claim."
A thesis should be as clear and specific as possible. Avoid overused, general terms and abstractions. For example, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because of the ruling elite's inability to address the economic concerns of the people" is more powerful than "Communism collapsed due to societal discontent."
Copyright 1999, Maxine Rodburg and The Tutors of the Writing Center at Harvard University
How to Write a Master's Thesis: A Guide to Planning Your Thesis, Pursuing It, and Avoiding Pitfalls
#scribendiinc
Part 1: Initial Considerations
Who needs to write a master’s thesis.
Thesis writing is one of the more daunting challenges of higher education. That being said, not all master's students have to write a thesis. For example, fields that place a stronger emphasis on applied knowledge, such as nursing, business, and education, tend to have projects and exams to test students on the skills and abilities associated with those fields. Conversely, in disciplines that require in-depth research or highly polished creative abilities, students are usually expected to prove their understanding and independence with a thesis.
What's Your Goal?
Do you want to write a thesis? The process is a long one, often spanning years. It's best to know exactly what you want before you begin. Many people are motivated by career goals. For example, hiring managers may see a master's degree as proof that the candidate is an expert within their field and can lead, motivate, and demonstrate initiative for themselves and others. Others dream of earning their doctorate, and they see a master's degree as a stepping stone toward their Ph.D .

No matter what your desired goal is, you should have one before you start your thesis. With your goal in mind, your work will have a purpose, which will allow you to measure your progress more easily.
Major Types of Theses
Once you've carefully researched or even enrolled in a master's program—a feat that involves its own planning and resources —you should know if you are expected to produce a quantitative (which occurs in many math and science programs), qualitative (which occurs in many humanities programs), or creative (which occurs in many creative writing, music, or fine arts programs) thesis.
Time and Energy Considerations
Advanced degrees are notoriously time and energy consuming. If you have a job, thesis writing will become your second job. If you have a family, they will need to know that your thesis will take a great deal of your attention, energy, and focus.

Your studies should not consume you, but they also should not take a back seat to everything else. You will be expected to attend classes, conduct research, source relevant literature, and schedule meetings with various people as you pursue your master's, so it's important to let those you care about know what's going on.
As a general note, most master's programs expect students to finish within a two-year period but are willing to grant extra time if requested, especially if that time is needed to deal with unexpected life events (more on those later).
Part 2: Form an Initial Thesis Question, and Find a Supervisor
When to begin forming your initial thesis question.
Some fields, such as history, may require you to have already formed your thesis question and to have used it to create a statement of intent (outlining the nature of your research) prior to applying to a master’s program. Others may require this information only after you've been accepted. Most of the time, you will be expected to come up with your topic yourself. However, in some disciplines, your supervisor may assign a general research topic to you.
Overall, requirements vary immensely from program to program, so it's best to confirm the exact requirements of your specific program.
What to Say to Your Supervisor
You will have a supervisor during your master's studies. Have you identified who that person will be? If yes, have you introduced yourself via email or phone and obtained information on the processes and procedures that are in place for your master's program? Once you've established contact, request an in-person meeting with him or her, and take a page of questions along with you. Your questions might include:
- Is there a research subject you can recommend in my field?
- I would like to pursue [target research subject] for my thesis. Can you help me narrow my focus?
- Can you give me an example of a properly formatted thesis proposal for my program?
Don't Be Afraid to Ask for Help (to a Degree)
Procedures and expectations vary from program to program, and your supervisor is there to help remove doubt and provide encouragement so you can follow the right path when you embark on writing your thesis. Since your supervisor has almost certainly worked with other graduate students (and was one at some point), take advantage of their experience, and ask questions to put your mind at ease about how to write a master’s thesis.
That being said, do not rely too heavily on your supervisor. As a graduate student, you are also expected to be able to work independently. Proving your independent initiative and capacity is part of what will earn you your master's degree.
Part 3: Revise Your Thesis
Read everything you can get your hands on.
Whether you have a question or need to create one, your next step is simple and applies to all kinds of theses: read.

Seek Out Knowledge or Research Gaps
Read everything you can that relates to the question or the field you are studying. The only way you will be able to determine where you can go is to see where everyone else has been. After you have read some published material, you will start to spot gaps in current research or notice things that could be developed further with an alternative approach. Things that are known but not understood or understood but not explained clearly or consistently are great potential thesis subjects. Addressing something already known from a new perspective or with a different style could also be a potentially valuable project. Whichever way you choose to do it, keep in mind that your project should make a valuable contribution to your field.

Talk with Experts in Your Field (and Don't Be Afraid to Revise Your Thesis)
To help narrow down your thesis topic, talk to your supervisor. Your supervisor will have an idea of what is current in your field and what can be left alone because others are already working on it. Additionally, the school you are attending will have programs and faculty with particular areas of interest within your chosen field.
On a similar note, don't be surprised if your thesis question changes as you study. Other students and researchers are out there, and as they publish, what you are working on can change. You might also discover that your question is too vague, not substantial enough, or even no longer relevant. Do not lose heart! Take what you know and adjust the question to address these concerns as they arise. The freedom to adapt is part of the power you hold as a graduate student.
Part 4: Select a Proposal Committee
What proposal committees are and why they're useful.
When you have a solid question or set of questions, draft a proposal.

You'll need an original stance and a clear justification for asking, and answering, your thesis question. To ensure this, a committee will review your thesis proposal. Thankfully, that committee will consist of people assigned by your supervisor or department head or handpicked by you. These people will be experts who understand your field of study and will do everything in their power to ensure that you are pursuing something worthwhile. And yes, it is okay to put your supervisor on your committee. Some programs even require that your supervisor be on your committee.
Just remember that the committee will expect you to schedule meetings with them, present your proposal, respond to any questions they might have for you, and ultimately present your findings and thesis when all the work is done. Choose those who are willing to support you, give constructive feedback, and help address issues with your proposal. And don't forget to give your proposal a good, thorough edit and proofread before you present it.
How to Prepare for Committee Meetings
Be ready for committee meetings with synopses of your material for committee members, answers for expected questions, and a calm attitude. To prepare for those meetings, sit in on proposal and thesis defenses so you can watch how other graduate students handle them and see what your committee might ask of you. You can even hold rehearsals with friends and fellow students acting as your committee to help you build confidence for your presentation.

Part 5: Write Your Thesis
What to do once your proposal is approved.
After you have written your thesis proposal and received feedback from your committee, the fun part starts: doing the work. This is where you will take your proposal and carry it out. If you drafted a qualitative or quantitative proposal, your experimentation or will begin here. If you wrote a creative proposal, you will now start working on your material. Your proposal should be strong enough to give you direction when you perform your experiments, conduct interviews, or craft your work. Take note that you will have to check in with your supervisor from time to time to give progress updates.

Thesis Writing: It's Important to Pace Yourself and Take Breaks
Do not expect the work to go quickly. You will need to pace yourself and make sure you record your progress meticulously. You can always discard information you don't need, but you cannot go back and grab a crucial fact that you can't quite remember. When in doubt, write it down. When drawing from a source, always create a citation for the information to save your future self time and stress. In the same sense, you may also find journaling to be a helpful process.
Additionally, take breaks and allow yourself to step away from your thesis, even if you're having fun (and especially if you're not). Ideally, your proposal should have milestones in it— points where you can stop and assess what you've already completed and what's left to do. When you reach a milestone, celebrate. Take a day off and relax. Better yet, give yourself a week's vacation! The rest will help you regain your focus and ensure that you function at your best.
How to Become More Comfortable with Presenting Your Work
Once you start reaching your milestones, you should be able to start sharing what you have. Just about everyone in a graduate program has experience giving a presentation at the front of the class, attending a seminar, or watching an interview. If you haven't (or even if you have), look for conferences and clubs that will give you the opportunity to learn about presenting your work and become comfortable with the idea of public speaking. The more you practice talking about what you are studying, the more comfortable you'll be with the information, which will make your committee defenses and other official meetings easier.
Published authors can be called upon to present at conferences, and if your thesis is strong, you may receive an email or a phone call asking if you would share your findings onstage.
Presenting at conferences is also a great way to boost your CV and network within your field. Make presenting part of your education, and it will become something you look forward to instead of fear.
What to Do If Your Relationship with Your Supervisor Sours
A small aside: If it isn't already obvious, you will be communicating extensively with others as you pursue your thesis. That also means that others will need to communicate with you, and if you've been noticing things getting quiet, you will need to be the one to speak up. Your supervisor should speak to you at least once a term and preferably once a week in the more active parts of your research and writing. If you give written work to your supervisor, you should have feedback within three weeks.
If your supervisor does not provide feedback, frequently misses appointments, or is consistently discouraging of your work, contact your graduate program advisor and ask for a new supervisor. The relationship with your supervisor is crucial to your success, especially if she or he is on your committee, and while your supervisor does not have to be friendly, there should at least be professional respect between you.
What to Do If a Crisis Strikes
If something happens in your life that disrupts everything (e.g., emotional strain, the birth of a child, or the death of a family member), ask for help. You are a human being, and personal lives can and do change without warning. Do not wait until you are falling apart before asking for help, either. Learn what resources exist for crises before you have one, so you can head off trauma before it hits. That being said, if you get blindsided, don't refuse help. Seek it out, and take the time you need to recover. Your degree is supposed to help you become a stronger and smarter person, not break you.
Part 6: Polish and Defend Your Master's Thesis
How to write a master’s thesis: the final stages.
After your work is done and everything is written down, you will have to give your thesis a good, thorough polishing. This is where you will have to organize the information, draft it into a paper format with an abstract, and abbreviate things to help meet your word-count limit. This is also where your final editing and proofreading passes will occur, after which you will face your final hurdle: presenting your thesis defense to your committee. If they approve your thesis, then congratulations! You are now a master of your chosen field.
Conclusion and Parting Thoughts
Remember that you do not (and should not) have to learn how to write a master’s thesis on your own. Thesis writing is collaborative, as is practically any kind of research.

While you will be expected to develop your thesis using your own initiative, pursue it with your own ambition, and complete it with your own abilities, you will also be expected to use all available resources to do so. The purpose of a master's thesis is to help you develop your own independent abilities, ensuring that you can drive your own career forward without constantly looking to others to provide direction. Leaders get master's degrees. That's why many business professionals in leadership roles have graduate degree initials after their last names. If you already have the skills necessary to motivate yourself, lead others, and drive change, you may only need your master's as an acknowledgement of your abilities. If you do not, but you apply yourself carefully and thoroughly to the pursuit of your thesis, you should come away from your studies with those skills in place.
A final thought regarding collaboration: all theses have a section for acknowledgements. Be sure to say thank you to those who helped you become a master. One day, someone might be doing the same for you.
Image source: Falkenpost/Pixabay.com
We’re Masters at Master’s Theses! Make Yours Shine.
Let our expert academic editors perfect your writing, or get a free sample, about the author.

A Scribendi in-house editor, Anthony is happily putting his BA in English from Western University to good use with thoughtful feedback and incisive editing. An avid reader and gamer, he can be found during his off hours enjoying narrative-driven games and obscure and amusing texts, as well as cooking for his family.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation

Selecting a Thesis Committee

Thesis/Dissertation Writing Series: How to Write a Literature Review
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).


Writing your thesis and conducting a literature review
- Writing your thesis
- Your literature review
Defining a research question
- Choosing where to search
- Search strings
- Limiters and filters
- Developing inclusion/exclusion criteria
- Managing your search results
- Screening, evaluating and recording
- Snowballing and grey literature
- Further information and resources
You will either be provided with a research topic by your supervisor or have an idea of a research topic that you would like to investigate. Make sure that you chose a topic that interests you as you will be spending a lot of time on the topic. A good starting place is to run a scoping or exploratory search to give you:
- An overview of the key issues of the topic;
- Discover how much research exists and if there is enough of a gap to conduct a review;
- Provide the content for developing aims and objectives;
- Identify any authors or subject terms.
Depending on what you find you may need to amend your research topic.
Once you have decided on your topic you will need to determine your research question. Your question should be clear and focussed, but also answerable and searchable. A well formulated research question, one that is clear, focussed and answerable, will help to structure your research process, determine the scope of your research, and focus your searches to help guide the selection of papers.
To help you define and develop your research question you can use frameworks such as PEO or PICO. Other frameworks are available.
Using frameworks: PEO or PICO
Two frameworks that are commonly used at Cranfield University are PEO (which tends to be used for qualitative research) and PICO (which tends to be used for quantitative research):
P opulation and/or problem = The subject of your enquiry e.g., an industry, organisation, community, or individuals
E xposure = Use for a specific intervention, phenomenon etc.
O utcomes or themes = What are the effects of the exposure on the population/problem? Are there any improvements?
P opulation and/or problem = The subject of your enquiry e.g. an industry, organisation, community, or individuals
I ntervention or Exposure = What is the main intervention or issue to be considered?
C omparison = What can you compare the intervention or issue to? (note: not all questions will need to include a comparison)
O utcomes or themes = What are your outcomes? What do you hope to be the result of the intervention?
This stage will also help you to identify your inclusion and exclusion criteria, the parameters for what you want to find in your search and when you would exclude a paper from your study. You will need to stick to this criterion throughout to avoid bias later.
Finally write a protocol to explain the steps that you will intake in your review, the rationale, hypothesis, and methodology. Refer to the PRISMA checklist for guidance.
- << Previous: Your literature review
- Next: Choosing where to search >>
- Last Updated: Feb 21, 2024 2:01 PM
- URL: https://library.cranfield.ac.uk/writing-your-thesis
Dissertations & projects: Research questions
- Research questions
- The process of reviewing
- Project management
- Literature-based projects
Jump to content on these pages:
“The central question that you ask or hypothesis you frame drives your research: it defines your purpose.” Bryan Greetham, How to Write Your Undergraduate Dissertation
This page gives some help and guidance in developing a realistic research question. It also considers the role of sub-questions and how these can influence your methodological choices.
Choosing your research topic
You may have been provided with a list of potential topics or even specific questions to choose from. It is more common for you to have to come up with your own ideas and then refine them with the help of your tutor. This is a crucial decision as you will be immersing yourself in it for a long time.
Some students struggle to find a topic that is sufficiently significant and yet researchable within the limitations of an undergraduate project. You may feel overwhelmed by the freedom to choose your own topic but you could get ideas by considering the following:
Choose a topic that you find interesting . This may seem obvious but a lot of students go for what they think will be easy over what they think will be interesting - and regret it when they realise nothing is particularly easy and they are bored by the work. Think back over your lectures or talks from visiting speakers - was there anything you really enjoyed? Was there anything that left you with questions?
Choose something distinct . Whilst at undergraduate level you do not have to find something completely unique, if you find something a bit different you have more opportunity to come to some interesting conclusions. Have you some unique experiences that you can bring: personal biography, placements, study abroad etc?
Don't make your topic too wide . If your topic is too wide, it will be harder to develop research questions that you can actually answer in the context of a small research project.
Don't make your work too narrow . If your topic is too narrow, you will not be able to expand on the ideas sufficiently and make useful conclusions. You may also struggle to find enough literature to support it.
Scope out the field before deciding your topic . This is especially important if you have a few different options and are not sure which to pick. Spend a little time researching each one to get a feel for the amount of literature that exists and any particular avenues that could be worth exploring.
Think about your future . Some topics may fit better than others with your future plans, be they for further study or employment. Becoming more expert in something that you may have to be interviewed about is never a bad thing!
Once you have an idea (or even a few), speak to your tutor. They will advise on whether it is the right sort of topic for a dissertation or independent study. They have a lot of experience and will know if it is too much to take on, has enough material to build on etc.
Developing a research question or hypothesis
Research question vs hypothesis.
First, it may be useful to explain the difference between a research question and a hypothesis. A research question is simply a question that your research will address and hopefully answer (or give an explanation of why you couldn't answer it). A hypothesis is a statement that suggests how you expect something to function or behave (and which you would test to see if it actually happens or not).
Research question examples
- How significant is league table position when students choose their university?
- What impact can a diagnosis of depression have on physical health?
Note that these are open questions - i.e. they cannot be answered with a simple 'yes' or 'no'. This is the best form of question.
Hypotheses examples
- Students primarily choose their university based on league table position.
- A diagnosis of depression can impact physical health.
Note that these are things that you can test to see if they are true or false. This makes them more definite then research questions - but you can still answer them more fully than 'no they don't' or 'yes it does'. For example, in the above examples you would look to see how relevant other factors were when choosing universities and in what ways physical health may be impacted.
For more examples of the same topic formulated as hypotheses, research questions and paper titles see those given at the bottom of this document from Oakland University: Formulation of Research Hypothesis
Which do you need?
Generally, research questions are more common in the humanities, social sciences and business, whereas hypotheses are more common in the sciences. This is not a hard rule though, talk things through with your supervisor to see which they are expecting or which they think fits best with your topic.
What makes a good research question or hypothesis?
Unless you are undertaking a systematic review as your research method, you will develop your research question as a result of reviewing the literature on your broader topic. After all, it is only by seeing what research has already been done (or not) that you can justify the need for your question or your approach to answering it. At the end of that process, you should be able to come up with a question or hypothesis that is:
- Clear (easily understandable)
- Focused (specific not vague or huge)
- Answerable (the data is available and analysable in the time frame)
- Relevant (to your area of study)
- Significant (it is worth answering)
You can try a few out, using a table like this (yours would all be in the same discipline):
A similar, though different table is available from the University of California: What makes a good research topic? The completed table has some supervisor comments which may also be helpful.
Ultimately, your final research question will be mutually agreed between yourself and your supervisor - but you should always bring your own ideas to the conversation.
The role of sub-questions
Your main research question will probably still be too big to answer easily. This is where sub-questions come in. They are specific, narrower questions that you can answer directly from your data.
So, looking at the question " How much do online users know and care about how their self-images can be used by Apple, Google, Microsoft and Facebook? " from the table above, the sub-questions could be:
- What rights do the terms and conditions of signing up for Apple, Google, Microsoft and Facebook accounts give those companies regarding the use of self-images?
- What proportion of users read the terms and conditions when creating accounts with these companies?
- How aware are users of the rights they are giving away regarding their self-images when creating accounts with these companies?
- How comfortable are users with giving away these rights?

Together, the answers to your sub-questions should enable you to answer the overarching research question.
How do you answer your sub-questions?
Depending on the type of dissertation/project your are undertaking, some (or all) the questions may be answered with information collected from the literature and some (or none) may be answered by analysing data directly collected as part of your primary empirical research .
In the above example, the first question would be answered by documentary analysis of the relevant terms and conditions, the second by a mixture of reviewing the literature and analysing survey responses from participants and the last two also by analysing survey responses. Different projects will require different approaches.

Some sub-questions could be answered by reviewing the literature and others from empirical study.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Searching >>
- Last Updated: Feb 28, 2024 10:39 AM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/dissertations
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.

List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

Cybersecurity in Higher Education: Safeguarding Students and Faculty Data

How To Write An Argumentative Essay

Beyond Google Scholar: Why SciSpace is the best alternative
The top 10 thesis defense questions (+ how to prepare strong answers)
Crafting a thesis is significant, but defending it often feels like the ultimate test. While nerve-wracking, proper preparation can make it manageable. Prepare for your thesis defense with insights on the top questions you can expect, including strategies for answering convincingly.
Mastering the thesis defense: cultivate a success mindset
Question 1: why did you choose this particular topic for your research, question 2: how does your research contribute to the existing body of knowledge, question 3: what are the key findings of your research, question 4: can you defend your research methodology, question 5: how did you analyze the data and what challenges did you encounter, question 6: what theoretical frameworks or references underpin your research, question 7: how did you address ethical considerations in your research, question 8: in what ways does your research contribute to the field, question 9: how did you ensure your research was free from bias, question 10: where can future research go from here.
Nurturing a success mindset for your defense is pivotal. This means adopting a mental outlook geared towards achieving favorable outcomes during your thesis defense. To truly excel in this pivotal academic moment, it’s imperative to cultivate both confidence and composure.
Confidence enables you to present your research with conviction, while composure allows you to navigate any challenges with grace and clarity.
Remember, you know your thesis best, so trust in your expertise.
In essence, a success mindset encompasses the belief in your abilities, coupled with the ability to remain calm and focused under pressure.
Stay composed and focused, relying on your thorough preparation. If you encounter a question you can’t answer, gracefully guide the conversation back to familiar topics.
Use strategic responses when needed. For example, if a question goes beyond your thesis scope, acknowledge its relevance but steer back to your focused areas. Similarly, if you’re unfamiliar with a theory or literature, admit it but offer related insights or perspectives.
By embracing these principles and staying confident and adaptable, you’ll navigate your thesis defense with ease.
This question delves into the origins of your academic journey, aiming to understand not just what you studied, but the underlying motivations and processes that drove your exploration. It’s not merely about the superficial aspects of your research, but rather about the deeper intellectual curiosity that ignited your quest.
To effectively respond, take the opportunity to elaborate on the intricacies of your journey. Begin by unpacking the specific interests or questions that sparked your intellectual curiosity in the subject matter. What events, experiences, or influences led you to delve into this particular area of study? Providing an anecdote or example that vividly illustrates the genesis of your scholarly pursuit can be helpful.
Moreover, discuss the gaps you identified in the existing literature that motivated you to contribute to your field. What deficiencies or unanswered questions did you observe? How did these gaps inspire you to embark on your research journey with the aim of filling these voids? By articulating the specific shortcomings in the current body of knowledge, you demonstrate a nuanced understanding of your research area and underscore the significance of your work.
Additionally, highlight any personal or academic experiences that played a pivotal role in steering you towards your chosen topic. Whether it was a transformative educational experience, a profound personal interest, or a meaningful encounter, these experiences can offer valuable insights into the origins of your scholarly pursuits.
In summary, when articulating your narrative, consider the following key points:
- Unpack the specific interests or questions that sparked your intellectual curiosity.
- Discuss the gaps in the existing literature that motivated your research.
- Highlight any personal or academic experiences that influenced your choice of topic.
This question delves into the vital role your research plays within the existing body of knowledge, urging you to articulate its significance and impact. It’s not merely about the subject matter you’ve studied, but also about the unique contributions and advancements your research brings to your field. To effectively respond, delve into the intricacies of your work and its implications for the broader academic landscape.
Begin by emphasizing the novelties and breakthroughs your research introduces. Highlight specific aspects of your study that represent advancements in understanding or methodologies. Whether it’s a novel approach to a longstanding problem, the discovery of new phenomena, or the development of innovative methodologies, these contributions underscore the significance of your research within the academic community.
Next, describe how your work engages with or challenges current conversations in your field. Discuss the existing paradigms or theories your research builds upon or critiques. Articulate how your findings contribute to ongoing debates or reshape prevailing understandings. By positioning your research within the broader context of scholarly discourse, you showcase its relevance and impact on the evolving landscape of your field.
Illuminate how your findings could influence future research trajectories. Explore potential avenues for further inquiry that emerge from your research findings. Consider how your work opens up new questions or areas of exploration for future researchers. By identifying these potential research directions, you demonstrate the forward-looking nature of your work and its potential to shape the future trajectory of your field.
In summary, when addressing how your research contributes to the existing body of knowledge, consider the following key points:
- Emphasize the novelties and breakthroughs your research introduces.
- Describe the conversations in your field that your work engages with or challenges.
- Illuminate how your findings could influence future research trajectories.
Addressing the question of your research’s key findings demands skill, as it necessitates succinctly summarizing your work while conveying its significance. To effectively respond, distill your findings into digestible takeaways that encapsulate the essence of your research. Identify the central discoveries or outcomes of your study, ensuring clarity and conciseness in your presentation.
Furthermore, relate these findings to the broader implications they hold for your field. Articulate how your research contributes to advancing knowledge or addressing pressing issues within your academic discipline. Consider the potential impact of your findings on theory, practice, or policy, highlighting their relevance and significance within the larger scholarly community.
Additionally, be prepared to elucidate the nuances and complexities involved in your results. While providing a concise summary of your findings is essential, it’s equally important to acknowledge the intricacies and limitations of your research. Discuss any methodological considerations, unexpected outcomes, or areas for further investigation, demonstrating a nuanced understanding of your work.
In summary, when addressing the key findings of your research, consider the following key points:
- Distill your findings into digestible takeaways.
- Relate the outcomes to the broader implications they hold for your field.
- Be prepared to shed light on the nuances and complexities involved in your results.
Defending your research methodology entails a comprehensive understanding of its rationale, alignment with research objectives, and acknowledgment of potential limitations. It’s not merely about explaining the methods employed but also justifying why they were chosen over alternative approaches. To effectively respond, delve into the intricacies of your methodology and its implications for the study.
Begin by elucidating the reasons for selecting the chosen methodology over alternatives. Discuss the specific advantages or suitability of the selected approach in addressing the research questions or objectives. Consider factors such as feasibility, appropriateness for the research context, and compatibility with the theoretical framework guiding your study.
Furthermore, explain how your chosen methods align with your research objectives. Articulate how the selected methodology enables you to achieve the intended outcomes and contribute to answering the research questions. Discuss how each methodological choice supports the overall research design and furthers the overarching goals of the study.
Be prepared to discuss the limitations inherent in your chosen methodology and how you mitigated them. Acknowledge any constraints or shortcomings associated with the selected approach, such as potential biases, sample size limitations, or data collection challenges. Demonstrate your awareness of these limitations and discuss the strategies implemented to address or minimize their impact on the validity and reliability of your findings.
In summary, when defending your research methodology, consider the following key points:
- Justify the methodology with reasons for selecting it over alternatives.
- Explain the methods’ alignment with your research objectives.
- Be ready to discuss the limitations and how you mitigated them.
Addressing the intricacies of data analysis involves not only outlining the techniques employed but also navigating the challenges encountered and evaluating the reliability and validity of the interpretations drawn. When responding to inquiries about data analysis, it’s essential to provide a comprehensive understanding of the methodologies employed, the obstacles faced, and the strategies utilized to ensure the accuracy and credibility of the findings.
Begin by outlining the techniques used for data analysis. Describe the specific methods, tools, and software employed to process and interpret the data collected. Whether it involved quantitative statistical analysis, qualitative coding techniques, or a combination of both, provide insights into the analytical framework guiding your study. Additionally, discuss the rationale behind the chosen analytical approach and how it aligns with the research objectives and questions.
Next, share the hurdles faced during the data analysis process and how you overcame them. Reflect on any challenges encountered, such as data cleaning issues, missing data, or unexpected patterns in the dataset. Discuss the steps taken to address these challenges, whether through iterative refinement of analytical techniques, consultation with peers or supervisors, or adaptation of the research design. Highlighting your ability to navigate obstacles demonstrates resilience and resourcefulness in overcoming methodological challenges.
Furthermore, discuss the reliability and validity of your data interpretation. Evaluate the rigor and credibility of your analytical process, considering factors such as data integrity, consistency, and relevance to the research objectives. Discuss any measures taken to ensure the trustworthiness of the findings, such as inter-coder reliability checks, triangulation of data sources, or member checking with participants. By critically examining the reliability and validity of your data interpretation, you provide insights into the robustness of your analytical approach and the credibility of the conclusions drawn.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about data analysis, consider the following key points:
- Outline the techniques used for data analysis.
- Share the hurdles faced during the process and how you overcame them.
- Discuss the reliability and validity of your data interpretation.
Exploring the theoretical underpinnings of your research involves delving into the foundational frameworks and seminal works that informed your study’s conceptual framework and analytical approach. When responding to inquiries about theoretical frameworks , it’s essential to provide a comprehensive understanding of the theories and references that shaped your research, elucidate their influence on your hypothesis and analysis, and reflect on the potential contributions or revisions your study may offer to existing theoretical foundations.
Begin by naming the key theories and seminal works that guided your research. Identify the theoretical frameworks that provided the conceptual scaffolding for your study, as well as the seminal works that shaped your understanding of the research area. Discuss how these theories and references informed your research design, methodology, and analytical approach, providing a theoretical lens through which to interpret your findings.
Elucidate on how these frameworks shaped your hypothesis and analysis. Describe how the theoretical perspectives and insights gleaned from seminal works informed the development of your research questions, hypotheses, and analytical framework. Discuss the ways in which these theoretical frameworks guided your data collection and interpretation, influencing the selection of variables, measures, and analytical techniques employed in your study.
Reflect on how your research may contribute to or revise these theoretical foundations. Consider the implications of your findings for advancing existing theoretical frameworks or revising established paradigms within your field. Discuss how your research extends or challenges current theoretical perspectives, offering new insights, conceptual refinements, or empirical evidence that may enrich or reshape prevailing theories. By critically examining the relationship between your research and existing theoretical frameworks, you provide insights into the broader theoretical implications and contributions of your study.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about theoretical frameworks, consider the following key points:
- Name the key theories and seminal works that guided your research.
- Elucidate on how these frameworks shaped your hypothesis and analysis.
- Reflect on how your research may contribute to or revise these theoretical foundations.
When addressing ethical considerations in your research, it’s essential to demonstrate a commitment to upholding ethical standards and protecting the rights and well-being of participants. Responding to inquiries about ethical protocols involves explaining the steps taken to ensure ethical conduct throughout the research process, describing the consent process and data protection measures implemented, and mentioning any institutional review board (IRB) approvals obtained.
Begin by explaining the ethical protocols you followed. Detail the ethical guidelines, codes of conduct, or regulatory frameworks that informed your research design and conduct. Discuss how these guidelines influenced decisions regarding participant recruitment, data collection methods, confidentiality protocols, and data storage procedures, emphasizing your adherence to ethical principles throughout the research process.
Describe the consent process, if applicable, and how you protected participants’ data. Provide insights into how informed consent was obtained from participants, including the procedures used to inform participants about the research purpose, risks, benefits, and their rights. Discuss any measures taken to safeguard participants’ privacy and confidentiality, such as anonymizing data, securing data storage, and limiting access to sensitive information, ensuring the protection of participants’ identities and personal information.
Mention any institutional ethics review board approvals you obtained. Highlight any formal ethical review processes or approvals obtained from relevant regulatory bodies, such as IRBs or ethics committees. Discuss how the research protocol was reviewed for compliance with ethical guidelines and standards, including considerations of participant welfare, informed consent procedures, and data protection measures. By acknowledging the oversight and approval of institutional review bodies, you demonstrate your commitment to ethical integrity and accountability in conducting research involving human subjects.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about ethical considerations in your research, consider the following key points:
- Explain the ethical protocols you followed.
- Describe the consent process and data protection measures implemented.
- Mention any institutional ethics review board approvals obtained.
When discussing the contributions of your research to the field, it’s essential to highlight the novel insights and potential impact your thesis offers. Responding to inquiries about your research’s significance involves detailing the unique perspectives and fresh understanding it brings to the academic discourse, as well as considering its implications for future research or practice and arguing its relevance within the broader academic community.
Begin by detailing the novel insights your thesis provides. Articulate the key findings, discoveries, or perspectives that distinguish your research from existing literature and contribute to advancing knowledge within your field. Discuss how your study fills gaps in current understanding, challenges established assumptions, or offers innovative approaches to addressing pressing issues, highlighting its potential to generate new avenues of inquiry and broaden the scope of scholarly discourse.
Discuss how your findings might influence future research or practice. Consider the implications of your research for shaping future scholarship, informing policy decisions, or guiding professional practice within relevant domains. Reflect on the potential practical applications, theoretical advancements, or methodological innovations stemming from your findings, highlighting their significance for advancing the field and addressing real-world challenges.
Be prepared to argue the relevance of your research within the broader academic community. Articulate the broader significance of your study within the context of current debates, trends, or priorities within your discipline. Discuss how your research aligns with existing scholarly agendas, contributes to interdisciplinary dialogue, or addresses pressing societal concerns, underscoring its relevance and potential impact on shaping the direction of future research and practice.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about the contributions of your research to the field, consider the following key points:
- Detail the novel insights your thesis provides.
- Discuss how your findings might influence future research or practice.
- Be prepared to argue the relevance of your research within the broader academic community.
When ensuring the integrity of your research and minimizing bias, it’s crucial to maintain objectivity and rigor throughout the study. Responding to inquiries about bias involves discussing the steps taken to uphold objectivity, describing any blind or double-blind procedures employed, and acknowledging and mitigating any unavoidable biases that may have arisen during the research process.
Begin by discussing the steps taken to maintain objectivity and rigor. Detail the strategies implemented to minimize the influence of personal biases, preconceptions, or external factors on the research outcomes. This may include adhering to a predetermined research protocol, using standardized procedures for data collection and analysis, and engaging in peer review or validation processes to ensure the reliability and validity of the findings.
Describe any blind or double-blind procedures employed in the study. Explain how blinding techniques were used to prevent bias in data collection, analysis, or interpretation. This may involve withholding certain information from researchers or participants to minimize the potential for conscious or unconscious bias to influence the results. Discuss how these procedures were implemented and their impact on enhancing the credibility and impartiality of the research outcomes.
Acknowledge any unavoidable biases that may have emerged during the research process and discuss how they were mitigated. Reflect on the inherent limitations or sources of bias in the study design, data collection methods, or participant selection criteria. Discuss the steps taken to minimize the impact of these biases, such as conducting sensitivity analyses, controlling for confounding variables, or triangulating data sources to corroborate findings.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about bias in your research, consider the following key points:
- Discuss steps taken to maintain objectivity and rigor.
- Describe any blind or double-blind procedures employed.
- Acknowledge any unavoidable biases and discuss how they were mitigated.
When considering the potential trajectory of your research topic, it’s essential to identify areas where further investigation could yield valuable insights, discuss unexplored questions that emerged from your research, and reflect on the limitations of your study as starting points for future research endeavors. Responding to inquiries about the future direction of research involves suggesting fruitful areas for further investigation, highlighting unresolved questions, and leveraging the limitations of your study as opportunities for future exploration.
Begin by suggesting areas where further investigation could be fruitful. Identify specific gaps, ambiguities, or unanswered questions within the existing literature that warrant additional inquiry. Consider emerging trends, advancements in technology or methodology, or pressing societal issues that may inform potential research directions. Propose research topics or hypotheses that build upon the findings of your study and extend the boundaries of current knowledge within your field.
Discuss unexplored questions that arose from your research. Reflect on any unexpected findings, anomalies, or areas of ambiguity that emerged during the course of your study. Consider how these unanswered questions or unresolved issues could serve as catalysts for future research endeavors, prompting further investigation into related phenomena, alternative explanations, or novel research methodologies.
Reflect on the limitations of your study as starting points for future research. Acknowledge any constraints, biases, or methodological shortcomings that may have influenced the outcomes or interpretations of your study. Discuss how these limitations provide opportunities for future research to refine methodologies, address confounding variables, or explore alternative theoretical frameworks. Consider how addressing these limitations could enhance the validity, reliability, and generalizability of future research findings within your field.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about the potential trajectory of your research topic, consider the following key points:
- Suggest areas where further investigation could be fruitful.
- Discuss unexplored questions that arose from your research.
- Reflect on the limitations of your study as starting points for future research.
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox!
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
How to harness theoretical and conceptual frameworks for groundbreaking research
25 short graduation quotes: inspiration in four words or less, related articles.

How to write a literature review introduction (+ examples)

Sample emails to your thesis supervisor

75 linking words for academic writing (+examples)

How to write a fantastic thesis introduction (+15 examples)

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Research Questions – How to-Guide | Definition & Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Definition: Research Question
The research question states the aim of a paper in form of a question. The purpose of writing the paper is to provide an answer to the research questions No article/paper can cover all aspects of a broad topic.
You must select a more specific aspect that has the potential to yield significant results as part of the topic and then find a connection to your Thesis Statement .
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 What is a Research Question?
- 4 Dos and Don’ts
- 5 Finding the right words
- 6 Sample research questions
- 7 Research question vs. title
- 8 The research question: Where it belongs
- 9 In summary
- 10 References
What is a Research Question?
The research question lies at the heart of every piece of academic writing . The research question determines the sources to be quoted, how to structure the argument, and what a paper aims at.
The research question narrows down the topic and makes sure that the paper has a common thread. Moreover, the research question gives the reader a clear idea of what to expect from the paper.
You cannot start writing without having a research question in mind. It is easiest to think of a research question as a Wh-question . Finding an answer to the research question you formulate is your personal contribution. You must state your research question right at the beginning, as part of the introduction.
Also useful: What is plagiarism?
How do you write a research question?
- Choose an interesting research topic . Something you’re interested in.
- Conduct some exploratory research.
- Begin formulating questions around areas of your topic that you think need more research.
- Conduct further research and narrow in on a few of your preliminary research questions.
- Pick your final research question and refine it.
What makes a good research question?
It’s important that your research question is focused on one single research topic , or a few interdependent topics. If your research question is too vague, then you will find it difficult to stay on topic whilst writing. It’s a good idea to focus on an unresolved problem- a problem that you never found a solution/many solutions for in your research. Your goal will be to resolve this problem in your paper.
How is the research question different from the hypothesis?
The hypothesis states your educated prediction regarding what you will find during your research. A hypothesis is used mostly in experimental or correlational research. It is your preliminary answer to your research question.
On the other hand, your research question states the aim of your paper and it is connected to your thesis statement . Throughout your paper, the hypothesis will be supported or contradicted with the collection and analysis of data.
What are the types of research questions?
There are many different types of research questions. However, the most common types are:
- Descriptive questions
- Relationship-based questions (explanation)
- criticism/improvement-based questions
Already refined your research question? Then you’re ready to begin writing your research proposal . It’s a long process, but stick with it and your paper will be done before you know it!
How do I write a research question for a thesis?
The process for writing a research question for a bachelor’s thesis or a master’s thesis stays the same. You begin with your inital research before narrowing in further on a few specific topics. The only difference is that your thesis will be significantly larger than a mid-semester paper so you will need more time to conduct some very intensive research before you begin writing.
The aim of a research question
“The research question is also the question why you should delight the world with another pile of printed paper” (cf. Winter 2004: 28).
A bachelor’s or master’s thesis is not something you write just for the sake of writing something. The aim is to create new scientific knowledge or to test and newly interpret existing theories. To achieve this aim, a thorough literature research is necessary to find an under-researched topic having new aspects you can focus on – a gap in scientific literature, so to speak.
To be even more precise: you can pose a very specific research question that nobody has asked before.
Esselborn-Krumbiegel says it is essential to understand what is required of every academic piece of writing, namely finding an answer to an open question (cf. 2002: 60). First, you have to find a topic and then formulate a research question derived from said topic . The topic as such will only be dealt with in terms of your specific research question (cf. Franck & Stary 2009: 167).
General example for creating a research question
The following diagram depicts how to proceed from a broad topic to a precise research question.
Concrete example using the topic of media violence
The following example shows how to derive a detailed research question from the topic “Media Violence”:
Example: How the topic, problem, research question, and aim of the paper are interrelated
Examples: deriving a research question from a topic.
Dos and Don’ts
Take your time when formulating your research question – it will definitely pay off! Be careful not to pose a research question that is ambiguous. People might wonder if you actually know what you want to work on and which research question you are setting out to answer (cf. Kornmeier 2013: 71).
The following list details Dos and Don’ts of writing a good research question to make sure you know what to include and what to avoid when formulating your research question (cf. Karmasin & Ribing 2014: 24; Samac, Prenner & Schwetz 2009: 47).
Examples of good and bad research questions
The Center for Innovation in Research and Teaching (CIRT) suggests how to transform a bad research question into a good research questions using the following examples:
(cf. CIRT, n.d., https://cirt.gcu.edu/research/developmentresources/tutorials/question . Last accessed 19 th Feb 2019)
Finding the right words
The easiest way to formulate a research question is to turn your whole bachelor’s thesis into one question . This will help to define the aim of your bachelor’s thesis (cf. Samac, Prenner & Schwetz 2009: 46). You can make choices concerning the literature, the structure and the content, as well as the study design, only if you have a very clear idea of what you want to write about (cf. Kornmeier 2013: 56).
The research question can also be formulated as an interrogative sentence, e.g. “The question this paper sets out to answer is…” or “This paper deals with the following question:…” (cf. Kruse 2010: 80). A question mark signals to the reader that there is an unresolved problem and your work offers a solution.
A good research question is precise and narrow . Andermann, Drees & Grätz say it is a cardinal error if an author thinks that everything that s/he has read about a topic must go into the paper. In a figurative sense, starting with Adam and Eve and the original sin, as well as trying to reinvent the wheel, are major mistakes for prospective scientists (cf. 2006: 33).
Sample research questions
In addition to developing the main research question, you have to be clear about the connection of your sub-research questions. Moreover, you have to figure out what type of research question you want to deal with. Otherwise, you run the risk of including everything you find out about a term or a statement during your literature research even if the latter play only a minor role in your research question (cf. Bänsch & Alewell 2013: 3-4).
Research question vs. title
(cf. Kruse 2007: 128)
The research question: Where it belongs
The research question determines the contents and the methods used in your bachelor’s and master’s thesis. Therefore, the research question must be introduced at the very beginning of your work. Moreover, the sole purpose of your paper is to answer the research question, so it is essential that the reader understands your research question. So you need to know: How to write an introduction
In your introduction, you should briefly introduce the topic and its relevance. Right after this, you have to pose your research question and highlight how it is part of a larger topic (cf. Oertner, St. John, & Thelen 2014: 31). You can split the research question into sub research questions, which should reflect in the structure of your paper. This means you are answering a bigger research question successively (cf. Karmasin & Ribing 2014: 24; Esselborn-Krumbiegel 2002: 64).
After all, longer papers like a master’s thesis do not consist of one big chapter only. Rather, several chapters building on each other are needed to adequately answer the research question (state of research, methods, empirical data collection, data analysis, etc.). Don’t forget to answer the research question in your thesis statement .
- The research question is central to every bachelor’s and master’s thesis. It determines the content, the structure, and the aim of an academic paper — i.e., finding an answer to the research question.
- The research question is closely related to the topic and the title of the paper. You will never be able to deal with all aspects of a topic. The research question is the narrowed down version that shows which particular aspect you want to focus on in your thesis/paper.
- The research question is best phrased as a Wh-question and must address a problem/an aspect that is new (no other paper has dealt with this issue/looked at this issue from the same angle).
- It is not your task to reinvent the wheel. The research question narrows down the topic and, thus, excludes aspects that are not essential to the research question.
- Answering your research question is your personal contribution to science and represents newly generated knowledge.
- The research question is part of the introduction , right after a brief introduction of the topic.
- There are different types of research questions: descriptive, explanatory, creative, critical/evaluative, and utopic.
- It is important to ensure that a research question is never vague or biased. It pays off to take enough time to formulate a research question properly. Moreover, a research question must be researchable and relevant for the field of study.
Andermann, Ulrich, Martin Drees & Frank Götz. 2006. Wie verfasst man wissenschaftliche Arbeiten? 3 rd Ed. Mannheim: Dudenverlag.
Bänsch, Axel & Dorothea Alewell. 2013. Wissenschaftliches Arbeiten . 11 th Ed. Munich: Oldenbourg Verlag.
CIRT. “Writing a Good Research Question”, in: CIRT. https://cirt.gcu.edu/research/developmentresources/tutorials/question . Last accessed 26 th Mar 2019.
Esselborn-Krumbiegel, Helga. 2002. Von der Idee zum Text – Eine Anleitung zum wissenschaftlichen Schreiben . Paderborn: Ferdinand Schöningh.
Flinn, Chad. “What makes a good research question”, in: Chad Flinn. https://malat-webspace.royalroads.ca/rru0054/what-makes-a-good-research-question/ . Last accessed 26 th Mar 2019.
Franck, Norbert & Joachim Stary. 2009. Die Technik des wissenschaftlichen Arbeitens . 15 th Ed. Paderborn: Ferdinand Schöningh.
Karmasin, Matthias & Rainer Ribing. 2014. Die Gestaltung wissenschaftlicher Arbeiten. 8 th Ed. Vienna: Facultas.
Kruse, Otto. 2007. Keine Angst vor dem leeren Blatt – Ohne Schreibblockaden durchs Studium . 12 th Ed. Frankfurt: Campus.
Kruse, Otto. 2010. Lesen und Schreiben – Der richtige Umgang mit Texten im Studium. Konstanz: UVK Verlagsgesellschaft.
Kornmeier, Martin. 2013. Wissenschaftlich schreiben leicht gemacht – für Bachelor, Master und Dissertation . 6 th Ed. Bern: Haupt.
Lamar Memorial Library. “Creating a Research Question”, in: Lamar Memorial Library. https://library.maryvillecollege.edu/c.php?g=616334&p=4320157 . Last accessed 26 th Mar 2019.
Lewis A. Jackson Library. “Forming a Research Question”, in: Lewis A. Jackson Library. http://indwes.libguides.com/c.php?g=71141&p=458447 . Last accessed 26 th Mar 2019.
Oertner, Monika, Illona St. John & Gabriele Thelen. 2014. Wissenschaftlich Schreiben – Ein Praxisbuch für Schreibtrainer und Studierende . Paderborn: Wilhelm Fink.
Rossig, Wolfram E. & Joachim Prätsch. 2005. Wissenschaftliche Arbeiten . 5 th Ed. Weyhe: PRINT-TEC.
Samac, Klaus, Monika Prenner & Herbert Schwetz. 2009. Die Bachelorarbeit an Universität und Fachhochschule . Vienna: Facultas.
Winter, Wolfgang. 2005. Wissenschaftliche Arbeiten schreiben . 2 nd Ed. Frankfurt: Redline Wirtschaft.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process . It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to your field.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
In the final product, you can also provide a chapter outline for your readers. This is a short paragraph at the end of your introduction to inform readers about the organizational structure of your thesis or dissertation. This chapter outline is also known as a reading guide or summary outline.
Table of contents
How to outline your thesis or dissertation, dissertation and thesis outline templates, chapter outline example, sample sentences for your chapter outline, sample verbs for variation in your chapter outline, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis and dissertation outlines.
While there are some inter-institutional differences, many outlines proceed in a fairly similar fashion.
- Working Title
- “Elevator pitch” of your work (often written last).
- Introduce your area of study, sharing details about your research question, problem statement , and hypotheses . Situate your research within an existing paradigm or conceptual or theoretical framework .
- Subdivide as you see fit into main topics and sub-topics.
- Describe your research methods (e.g., your scope , population , and data collection ).
- Present your research findings and share about your data analysis methods.
- Answer the research question in a concise way.
- Interpret your findings, discuss potential limitations of your own research and speculate about future implications or related opportunities.
For a more detailed overview of chapters and other elements, be sure to check out our article on the structure of a dissertation or download our template .
To help you get started, we’ve created a full thesis or dissertation template in Word or Google Docs format. It’s easy adapt it to your own requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template

It can be easy to fall into a pattern of overusing the same words or sentence constructions, which can make your work monotonous and repetitive for your readers. Consider utilizing some of the alternative constructions presented below.
Example 1: Passive construction
The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise.
Example 2: IS-AV construction
You can also present your information using the “IS-AV” (inanimate subject with an active verb ) construction.
A chapter is an inanimate object, so it is not capable of taking an action itself (e.g., presenting or discussing). However, the meaning of the sentence is still easily understandable, so the IS-AV construction can be a good way to add variety to your text.
Example 3: The “I” construction
Another option is to use the “I” construction, which is often recommended by style manuals (e.g., APA Style and Chicago style ). However, depending on your field of study, this construction is not always considered professional or academic. Ask your supervisor if you’re not sure.
Example 4: Mix-and-match
To truly make the most of these options, consider mixing and matching the passive voice , IS-AV construction , and “I” construction .This can help the flow of your argument and improve the readability of your text.
As you draft the chapter outline, you may also find yourself frequently repeating the same words, such as “discuss,” “present,” “prove,” or “show.” Consider branching out to add richness and nuance to your writing. Here are some examples of synonyms you can use.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
The title page of your thesis or dissertation goes first, before all other content or lists that you may choose to include.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/dissertation-thesis-outline/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation table of contents in word | instructions & examples, figure and table lists | word instructions, template & examples, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

- [email protected]
- Shapiro Library
- SNHU Library Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ: What is a thesis statement and how do I write one?
- 7 Academic Integrity & Plagiarism
- 60 Academic Support, Writing Help, & Presentation Help
- 27 Access/Remote Access
- 7 Accessibility
- 9 Building/Facilities
- 7 Career/Job Information
- 26 Catalog/Print Books
- 26 Circulation
- 128 Citing Sources
- 14 Copyright
- 310 Databases
- 24 Directions/Location
- 18 Faculty Resources/Needs
- 7 Hours/Contacts
- 2 Innovation Lab & Makerspace/3D Printing
- 25 Interlibrary Loan
- 43 IT/Computer/Printing Support
- 3 Library Instruction
- 37 Library Technology Help
- 6 Multimedia
- 17 Online Programs
- 19 Periodicals
- 25 Policies
- 8 RefWorks/Citation Managers
- 4 Research Guides (LibGuides)
- 217 Research Help
- 23 University Services
Last Updated: Apr 01, 2024 Views: 12
What is a thesis statement.
A thesis statement is a sentence that states the main idea of your paper. It is not just a statement of fact, but a statement of position. What argument are you making about your topic? Your thesis should answer that question.
How long should my thesis statement be?
Thesis statements are often just one sentence. Keep thesis statements concise, without extra words or information. If you are having trouble keeping your thesis statement to one sentence, consider the following:
- Is your thesis is specific enough?
- Does your thesis directly supports your paper?
- Does your thesis accurately describes your purpose or argue your claim?
Can I see some example thesis statements?
The following websites have examples of thesis statements:
- Thesis Statements This link opens in a new window (UNC)
- Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements This link opens in a new window (OWL at Purdue)
- Writing an Effective Thesis Statement This link opens in a new window (Indiana River State College)
These web resources may be helpful if you are looking for examples. However, be sure to evaluate any sources you use! The Shapiro Library cannot vouch for the accuracy of information provided on external websites.
Where can I find more information?
Video tutorials.
- The Persuasive Thesis: How to Write an Argument This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Research and Citation Playlist This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Planning a Paper series: Drafting a Thesis Statement This link opens in a new window ( Infobase Learning Cloud - SNHU Login Required)
More Information
- Build a Critical Analysis Thesis This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Build a Compare & Contrast Thesis This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Build a History Thesis This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Build a Persuasive Thesis This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
Further Help
This information is intended to be a guideline, not expert advice. Please speak to your instructor about the appropriate way to craft thesis statements for your class assignments and projects.
Campus Students
To access Academic Support, visit your Brightspace course and select “Tutoring and Mentoring” from the Academic Support pulldown menu.
Online Students
To access help with citations and more, visit the Academic Support via modules in Brightspace:
- Academic Support Overview: Getting Help with your Schoolwork This link opens in a new window
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 0 No 0
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) are a self-serve option for users to search and find answers to their questions.
Use the search box above to type your question to search for an answer or browse existing FAQs by group, topic, etc.
Tell Me More
Link to Question Form
More assistance.
Submit a Question
Related FAQs
BC.EDU LINKS
- Boston College
- Campus Life
- Jesuit, Catholic
- Academic Calendar
- BC Magazine
- Directories
- Offices, Services, Resources
- Agora Portal
- Maps & Directions
- Undergraduate
Honors Program - Senior Thesis
- Foreign Study
- The B.A./M.A. Program in History
- Degree Audit Errors
- Scholar of the College Projects
The Honors Program is open to all majors with a GPA of 3.5 in History, and centers around an original piece of research and writing undertaken with the guidance of a thesis advisor. The six-credit program involves a seminar, one-on-one consultations with the advisor, and a 50-60 page thesis.
- Who is eligible?
- Who should consider doing an honors thesis?
What is the timeline?
- What does the thesis entail?
- What can I do with a thesis?
Eligible seniors have the opportunity to write a 12-credit thesis (counting as four upper-division electives) as a Scholar of the College. The Scholar of the College program follows the same timeline, but the thesis requirements are more extensive and the thesis involves a more ambitious project.
If you are hoping to go to graduate school in the humanities, you should seriously consider writing a thesis because it will give you a sense of the kind of work that will be expected at that level.
But you need not have graduate school in mind to write a thesis. If you want to bring all of your undergraduate training to bear on a single, challenging project the honors program is for you. The thesis experience, picking a topic, researching it and producing an original piece of writing will challenge you in ways you have not yet been challenged. It is also incredibly rewarding. Working with other seniors and one-on-one with award winning faculty is a once in a lifetime experience. Such an accomplishment is the culmination of a liberal arts education and will set you up for a lifetime of achievement.
Junior Year
Senior Year
What does the thesis look like at the end of the process?
The thesis itself should be about 50-60 pages long and generally includes multiple chapters. It should be bound in a clear plastic binder that will both hold the pages securely and permit the title page to be read without opening it. Plastic binders are available at most stationary stores. You can also get it bound more formally at the campus printer. See here for more details .
Thesis Binding Details
The thesis alone is an impressive accomplishment but you can also take advantage of further publishing opportunities. There are two different kinds of publishing opportunity. The first and easiest is to deposit it with the Boston College eScholarship repository. The second involves an application and editing process to an undergraduate journal. This process is more involved than asimply placing your thesis in a repository, but it is more prestigious and has the potential to reach more readers.
Online eScholarship Repository
Boston College eScholarship@BC is the institutional repository of Boston College, managed by the Boston College University Libraries. The aim of eScholarship@BC is to showcase and preserve Boston College's scholarly output in digital form and to make it freely accessible globally. The repository supports the social justice mission of the University and promotes the goals of the University Libraries by providing access to scholarly resources wherever they are needed.
Please note: Undergraduates have the right to restrict access to their theses in the following ways:
- Access to undergraduate honors theses will be determined by the student depositor(s) and may be limited to the Boston College campus.
- Embargo periods may be applied based on publisher policies or at the request of copyright holder, restricting access to item(s) for a given time.
- Items may include individual statements regarding rights permissions and conditions, which will be included with the public record display.
Undergraduate Journals
Oracle: the history journal of boston college .
Oracle: The History Journal of Boston College is Boston College's primary venue for undergraduate historical scholarship. Founded in 2019, Oracle serves as a resource for current and prospective students of history, whether at Boston College or otherwise. Sponsored by the Boston College Department of History, Oracle is guided by the belief that the study of history is important to more fully understanding the complexities of our modern, globalized world. Whether you are an author, researcher, librarian, or otherwise interested reader, we hope that the scholarship featured by Oracle is an informative and engaging source for further study.
Columbia Undergraduate Journal of History
The Columbia Undergraduate Journal of History the United States' leading undergraduate social science research journal. We publish papers from all social science disciplines, including political science, economics, sociology, history, psychology, linguistics, law, anthropology, criminology, cultural and area studies, development studies, and demography.
Elements was founded in September 2004 by a group of twenty undergraduate students. The journal published its first issue in May of 2005, featuring research articles written by Boston College undergraduates along with shorter special features. The goal of the publication is to become a forum for the exchange of original ideas within and across disciplines at the university. Staff members read and evaluate all submitted manuscripts and select the best articles on the basis of quality of scholarship as well as readability. Faculty members are occasionally consulted to assist staff members in the evaluation process.
Ezra's Archives
Ezra's Archives is a publication put forth annually by the Cornell Historical Society. This journal, launched in the Spring of 2011, showcases stellar examples of undergraduate research in the field of history. In the Fall of 2011, Ezra's Archives expanded to accept submissions from undergraduates at other universities. If you are interested in applying for a position on the editorial board, submitting a paper, or learning more about the journal, please email cornellhistoricalsociety@gmail.com .
History Matters, Appalachian State University
This undergraduate History Matters history journal is published annually on a website by the History Department at Appalachian State University. The journal is edited by undergraduates with the help of a faculty board. All submissions and editing must be completed while authors are still undergraduates.
Journal of Undergraduate International Studies, University of Wisconsin The Journal of Undergraduate International Studies at the University of Wisconsin-Madison invites unpublished reflections on a wide range of academic and creative disciplines from contributors worldwide. Submitting authors should be within one semester of graduation. Topics include, but are not limited to, international conflict and resolution environmental issues, economics, development and trade, global security and international health.
The Yale Historical Review
The Yale Historical Review provides undergraduates an opportunity to have their exceptional work highlighted and encourages the diffusion of original historical ideas on campus by providing a forum for outstanding undergraduate history papers covering any historical topic. Students may submit history papers they've written over the course of their college careers.
Report, United States Military Academy
Report is a historical review that publishes the work of undergraduate students. They are expanding to include submissions from students at other colleges and universities. They encourage submissions from all undergraduates interested in historical research. Report is published both electronically and in booklet form during the spring and fall semesters. Please do not submit works already submitted to of published by other academic journals, and refer to the Chicago Manual of Style for citation guidelines and footnote form. Please include an email address and phone number with submissions. Contact the editors at Report.USMA@gmail.com with any questions.
Questions about the honors program or Senior Thesis?

Prof. Michael Glass
michael.glass@bc.edu
If you have additional questions, please contact Prof. Michael Glass, director of the honors program.
Contact Prof. Glass
History Department Stokes Hall South, 3rd Floor
617-552-3781
College of Agricultural, Consumer & Environmental Sciences
Illinois Extension
- Beef Cattle
- Community Planning
- Environment
- Houseplants
- Local Government Education
- Rainfall Management
- Fruit Trees
- Vegetable Gardening
- Newsletters
- Online Courses
- Publications
- Summer Resources
- Contact Staff
- Find an Office
- Social Media
- Administration and Educator Teams
- Geographic Organizational Leadership
- Communications and Information Technology
- Planning, Reporting, and Evaluation
- Volunteer and Career Development
- Energy Education Council
- Illini Science Policy Program
- Illinois Indiana Sea Grant
- Master Gardeners
- Master Naturalists
- Plant Clinic
- Research and Education Centers
- Home and Community Education
- 2024 Extension Collaboration Grants
- Economic and Functional Impact
- Agriculture and AgriBusiness Impact
- Community and Economic Development Impact
- Family and Consumer Sciences Impact
- Integrated Health Disparities Impact
- Natural Resources, Environment, and Energy Impact
- SNAP-Education Impact
- Extension Funded Research Projects
- FYI Internal Communications
- Strategic Planning
- Extension Councils
- Professional Associations
Master Naturalists put research into action around the state and in your backyard

What is a Master Naturalist?
We get that question a lot at University of Illinois Extension. Master Naturalists are many things: Advocates, volunteers, teachers, and environmental stewards.
Around the state and in your backyard, these trained volunteers connect their communities with the natural world by contributing to scientific research, leading educational programs, and putting their unique skills and talents to use through conservation and restoration projects.
Last year, more than 880 Master Naturalists put in nearly 70,500 hours removing invasive species, monitoring the health of waterways, raising and releasing monarch butterflies, teaching youth about the environment, and investing in the future of our natural areas.
- 886 Master Naturalists volunteered in Illinois
- 148 people took the training and became Master Naturalists
- 73,035 hours were volunteered.
The Illinois Extension Master Naturalist program leverages the expertise of university scientists and environmental partners to train adult volunteers to be environmental advocates. Our goal is to empower nature enthusiasts and help them put research into action wherever they live.

What does being a Master Naturalist look like?
Below are a few examples of the projects Master Naturalists are involved in. Explore more about how we’re putting knowledge to work in the 2023 Impact Report.
Read the 2023 Impact Report
Discovery of remnant prairie leads to educational outreach and conservation
In 2018, three Master Naturalists from Carroll, Lee, and Whiteside counties were exploring natural areas at the Lake Carroll Association community when they stumbled upon remnant prairie patches. Now, the association has more than 35 acres of native areas, a one-acre demonstration prairie, a pollinator garden, a new wetland filtering water before it enters the lake, expanded hiking trails, and so much more.
A walk in the woods transforms fourth graders’ relationship with nature
Kids ‘n Nature Adventure is a unique immersive afterschool and summer program partnership between the Illinois Extension Will County Master Naturalists, Joliet District 86 Grade Schools, and the Joliet Park District. The program gives 200 fourth-grade students from six underserved schools a chance to experience the natural world. The program began in 2005 and more than 2,000 youth have participated.
Repurposed feed and seed bags support pollinator project
Bird seed and pet food bags need to be sturdy, so they are often made from woven polypropylene plastic. This also makes them difficult to recycle, so like many other single-use plastics, they often end up in landfills. Master Naturalist Mona Maas has saved more than 300 bags from this fate by turning them into hand-sewn totes. These rugged recycled totes also have the added bonus of being a fundraiser to support a local pollinator garden.
Interested in becoming a Master Naturalist?
Learn how you can be a positive force for change by becoming an Illinois Extension Master Naturalist .
About the Blog
Naturalist News is a blog by University of Illinois Extension Master Naturalist staff and volunteers who bring you stories highlighting the individuals, places, wildlife and plants that make this state amazing. Join us each week to learn something new, be inspired and become connected to your own community by recognizing the amazing ways we are all intertwined.
Sign up for the Naturalist News email
About the Author
Emily Steele is a marketing communications manager on the Illinois Extension communications team and supports projects for natural resources, environment, and energy staff statewide including the Master Naturalist program, weather and climate, forestry, invasives, and nutrient loss reduction. She has a M.S. in Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences from University of Illinois and a B.A. in Journalism from Eastern Illinois University.
Naturalist News
Related content.

IOE - Faculty of Education and Society
- Departments and centres
- Innovation and enterprise
- Teacher Education College

IOE alumni named winners of the 2024 BERA Master’s Dissertation and Doctoral Thesis awards
27 March 2024
Dr Emily Macleod (PhD) and Kate Fox (Education and International Development MA) have won the British Educational Research Association (BERA) Doctoral and Master’s Thesis prizes respectively.

The awards are given in recognition of academic excellence and research rigour within the field of educational research.
Emily Macleod won for her thesis, “The status and safety of teaching: A longitudinal study of why some young people in England become teachers, and why others do not.” She investigated young people’s motivations behind pursuing – or not pursuing – the profession amidst the context of national and international teacher shortages.
She completed her PhD at IOE’s Department of Education, Practice and Society in 2023, and was a co-host on IOE’s podcast series Research for the Real World . She continues on as an honorary postdoctoral fellow. She also worked on the ASPIRES research project studying young people's science and career aspirations, before which she was a secondary school teacher.
Kate Fox won for her MA dissertation entitled “Building bridges or barriers? A study of home, community, and school literacy practices in rural Tanzania.”
Her dissertation centres the experiences of parents from rural communities within the Tanzanian education system – and the diverse ways families and communities contribute to young children’s literacy learning.
Kate completed her Master’s degree at IOE in 2023. She is now a Research Officer with the IOE Research Development team, and a Research Assistant working on two multi-institutional projects: Climate-U and Equitable research cultures . Her career in education spans 20 years as a teacher, headteacher and teacher trainer in Tanzania and the UK.
Related links
- Read more: BERA announces 2024 Master’s Dissertation and Doctoral Thesis winners
- Emily on ‘Why do people aspire to become teachers?’ RFTRW: S19E03
- More about Kate Fox
- More about Dr Emily Macleod
- Research for the Real World podcast
- ASPIRES project
Centre for Education and International Development
Emily Macleod (left) and Kate Fox (right).
Related News
Related events, related case studies, related research projects, press and media enquiries.
UCL Media Relations +44 (0)7747 565 056
- Request info
- Majors & Degrees
- Prospective Students
- Current Undergraduate Students
- Current Graduate Students
- Online Students
- Alumni and Friends
- Faculty and Staff
USM Honors College Students Present Thesis Research at Marketing Conference
Tue, 03/26/2024 - 09:14am | By: Van Arnold

University of Southern Mississippi (USM) Honors College students Haeden Overby and Patrick Tyson presented their thesis research during the 2024 Association of Marketing Theory and Practice Conference (AMTP) held earlier this month in Hilton Head, S.C.
Overby, a hospitality and tourism management major, and Tyson, an anthropology, sociology, and Spanish major, presented individual research papers, as well as a collaborative project, at the international and interdisciplinary academic marketing conference which brings together academic theory and real-world marketing practices.
This year’s conference saw more than 100 submissions. Of the 33 student paper submissions across undergraduate, Master's, and Ph.D. levels, Overby’s thesis paper – “Service robots’ effect on branding and consumers' intentions through online reviews” - won the James E. Randall Best Student Paper Award.
“Haeden and Patrick are exceptional students in my class. Their passion for research and dedication to their thesis projects have impressed me,” said Dr. Wei Wang, Associate Professor, Hospitality and Tourism Management Program Coordinator who served as both students’ thesis advisor. “Moreover, their active involvement and leadership roles on campus exemplify their commitment to excellence beyond academics,”
Tyson presented a research paper titled, “Uncertainty avoidance moderation over film-motivated tourists' views on destination image, place attachment, and intentions.”
Collaboratively, they presented a paper titled, “Cookies and calamari: Squid Game’s “Dalgona” and cutting shapes from its impact on Korean product purchase and travel intentions.”
“My advisors, Dr. Wei Wang and Dr. Banu Bas, have been incredibly patient teaching me about the research process, and I would not have been able to succeed without their support,” said Overby. “Dr. Randall is retiring from the AMTP conference this year, and the award was named after him for the first time. I am pleased to be the first recipient of the award under his name and am incredibly thankful I had the chance to meet him when I was presented the award.”
Added Overby, “This accomplishment has become great motivation to continue my research in marketing and to cross the finish line of submitting my thesis. I am glad to bring home a new award for Southern Miss Business!"
More information about the conference can be found here .
To learn more about USM’s College of Business and Economic Development, call 601.266.4659.
Categories: Business and Economic Development Honors College
Recent News Articles
University forum to feature award-winning fiction writer john green april 9, usm student awards day highlights scholarship, leadership, service, usm center for stem education distributes solar eclipse kits to 120 schools.
Nevada Today
2024 three-minute thesis competition finalists announced, graduate students will compete in the final event on april 11.

2023 3MT winners from left to right: Keely Rodriguez, Kendra Isable, Candi Block, Isabel Penaloza, Fatema Azmee, Yu Rong and Justice Best.
The buzz is back with the Graduate School’s annual Three-Minute Thesis (3MT) Competition this spring! Earlier this month, 42 graduate students rocked the stage in front of a live audience all vying for a chance to advance to the final round and win cash prizes.
A panel of esteemed University faculty and postdocs had the challenging task of judging this year’s preliminary event, evaluating students’ presentation skills and research content. If you are unfamiliar with 3MT, it is an annual spectacle where master’s and doctoral students are tasked with condensing their research into a lightning-fast, three-minute presentation with only a single slide. It is an adrenaline-fueled sprint through the world of academia!
Since 2015, the Graduate School has hosted this event, showcasing the power, beauty and brilliance of graduate education at the University. In addition, recent winners of this competition have gone on to compete, and place, in regional 3MT competitions putting the University on the map as a hotbed of intellectual prowess.
We are thrilled to announce this year’s 16 finalists (see below) and cannot wait for the final showdown. The 3MT final round of competition is set to take place on Thursday, April 11, at 7 p.m. in the Wells Fargo Auditorium at the Mathewson-IGT Knowledge Center. Students, family, faculty and community members are invited to join us and witness firsthand the awe-inspiring brilliance of our scholars. For those who cannot attend in person, the event will be live-streamed via Zoom so please register here on Formstack to receive the information.
Congratulations to the 2024 3MT finalists! Good luck on April 11.
(The finalists below are listed alphabetically by last name.)
Master’s Category:
- M.A. Criminal Justice
- "What do our phones teach us about incarceration? A social media content analysis"
- M.S. Ecology, Evolution and Conservation Biology
- “Sustaining the beating heart of Cambodia: Fisheries management in southeast Asia's largest lake”
- “Zeroing in on gun violence”
- M.S. Biochemistry
- “May the pericytes be with you: Transport engineers you never knew existed!”
- M.S. Chemistry
- “Chemically recyclable dithioacetal polymers”
- M.A. History
- “Pushed to the limit: How the 1998 China floods revolutionized the relationship between China and the natural world”
- M.S. Teaching History (M.A.T.H.)
- “Dust in the wind dude: The Owens Valley everywhere except, in the Owens Valley”
- “Winterfat restoration in a changing climate”
Doctoral Category:
- Ph.D. History
- “Creating the Enemy: The origins of the inter-American Cold War in the 1940s”
- Ph.D. Biomedical Engineering
- “Electrifying the fight-or-flight response: Nanosecond electric pulses for neuromodulation “
- Ph.D. Education - Literacy Studies
- “P re-service teachers experiences teaching K-8 Multilingual Students' (MLS) writing”
- Ph.D. Clinical Psychology
- “Identifying predictors of racial trauma to inform treatment development “
- Ph.D. Cell and Molecular Biology
- “Lighting the way: Tools to prepare for future pandemics”
- Ph.D. Education - Equity, Diversity and Language
- “Bridging the gaps: Evaluating the intervention programs to overcome academic disparities”
- Ph.D. Civil and Environmental Engineering
- “Accelerating bridge construction connections behavior during near fault motions”
- Ph.D. Political Science
- “Tough sell: Rising powers, domestic legitimation and costly international initiatives”
Research & Innovation
Senators Rosen, Cortez Masto worked with University President Brian Sandoval to secure more than $4 million for research programs at the University of Nevada, Reno
The funding will support research initiatives across the state

Start-up company Atlas Magnetics ‘graduates’ from University, moves to larger facility
Expecting to make $30M+ of revenue in 2025, modern electronics company sees big growth within two years with equipment, space, other resources supported through NCAR

University of Nevada, Reno and Arizona State University awarded grant to study future of biosecurity
Mitigating risks associated with pandemic pathogen, high-risk biological agents focus of nearly $870,000 NIH-funded project

Civil and Environmental Engineering shows its potential to industry partners at Infrastructure Forum
Research centers and labs showcased at March 18 event

Editor's Picks

A look at careers of substance and impact

NASA astronaut Eileen Collins shares stories at Women in Space event

Neurodiversity Alliance to hold panel and lunch social March 21 during Neurodiversity Celebration Week
KIDS University offers summer camps to keep kids engaged and learning
Registration now open for more than 20 camps to be held on campus June and July

University of Nevada, Reno Beta Alpha Psi shines at BAP Mid-Year Meeting 2024
A recap of success in innovation

Mackay Muckers take gold in International Collegiate Mining Competition
Ten students traveled to Montana to show off their traditional mining skills

An interview with 2024 Reno City Artist Chris Lanier
University of Nevada, Reno at Lake Tahoe artist and faculty reflects on upcoming art shows and his appreciation of smaller moments in life

TEDxReno: Spreading ideas, inspiring action, and building community
The independently organized event is on April 6 in Lawlor Events Center and offers $25 tickets for students

Leading the charge in organ donation awareness with UNR Med's SODA chapter
UNR Med student helps fellow future doctors by promoting organ donation education, debunking myths and advocating for empathy

Mark your calendar: College of Education & Human Development Career Fair
The Career Fair will be held on Tuesday, April 2, and will host employers ready to connect with University students

Sagebrushers season 3 ep. 1: College of Business Dean Gregory Mosier
College of Business prepares for the future of business education, enhanced business partnerships and the new building on the south end of campus


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Be Robust. A research question that is robust has the capacity to generate complex results. Your question should have the capacity to produce multiple insights about various aspects of the theoretical construct you are exploring. It should not be a question to which the answer is "yes" or "no" because such an answer is not a complex result.
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
It can be difficult to come up with a good research question, but there are a few steps you can follow to make it a bit easier. 1. Start with an interesting and relevant topic. Choose a research topic that is interesting but also relevant and aligned with your own country's culture or your university's capabilities.
Research questions must be aligned with other aspects of the thesis, dissertation, or project study proposal, such as the problem statement, research design, and analysis strategy. To summarize: Idea >Reviewing literature > Identifying the gap in theory or practice >Problem and Purpose Statements >Research question
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Research Question Examples 🧑🏻🏫. 25+ Practical Examples & Ideas To Help You Get Started. By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | October 2023. A well-crafted research question (or set of questions) sets the stage for a robust study and meaningful insights. But, if you're new to research, it's not always clear what exactly constitutes a good ...
Your thesis statement directly answers your research question, and takes a stand (rather than announces the subject) that others might dispute. In other words, it is provocative and contestable. A strong thesis clearly asserts your position or conclusion and avoids vague language (e.g. "It seems…).
The research aims, objectives and research questions (collectively called the "golden thread") are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you're crafting a research proposal, dissertation or thesis.We receive questions almost every day about this "holy trinity" of research and there's certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we've crafted this post to help ...
The objective of this guide is to show you what a master's thesis written in the monograph form involves. If you are writing an article-based thesis, please see the guide written for article-based ... regard as best suited to explore the relevant the thesis research question. Chapter 5: Discussion The discussion of the findings can be included ...
Research questions should not be answerable with a simple "yes" or "no" or by easily-found facts. They should, instead, require both research and analysis on the part of the writer. They often begin with "How" or "Why.". Begin your research. After you've come up with a question, think about the possible paths your research ...
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, complex and arguable question that will lay the groundwork for a thesis by offering a focus for your exploration of a topic that interests you. Although a strong research question is a good place to start your thesis, you should be prepared for it to change as you carry out primary and secondary ...
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
1. Start with a broad topic. A broad topic provides writers with plenty of avenues to explore in their search for a viable research question. Techniques to help you develop a topic into subtopics and potential research questions include brainstorming and concept mapping.
Part 2: Form an Initial Thesis Question, and Find a Supervisor When to Begin Forming Your Initial Thesis Question. Some fields, such as history, may require you to have already formed your thesis question and to have used it to create a statement of intent (outlining the nature of your research) prior to applying to a master's program. Others ...
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, project, or thesis. It pinpoints exactly what you want to find out and gives your work a ...
A well formulated research question, one that is clear, focussed and answerable, will help to structure your research process, determine the scope of your research, and focus your searches to help guide the selection of papers. To help you define and develop your research question you can use frameworks such as PEO or PICO.
First, it may be useful to explain the difference between a research question and a hypothesis. A research question is simply a question that your research will address and hopefully answer (or give an explanation of why you couldn't answer it). A hypothesis is a statement that suggests how you expect something to function or behave (and which ...
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It's typically submitted at the end of your master's degree or as a capstone of your bachelor's degree. However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners.
Crafting a thesis is significant, but defending it often feels like the ultimate test. While nerve-wracking, proper preparation can make it manageable. Prepare for your thesis defense with insights on the top questions you can expect, including strategies for answering convincingly. Contents Mastering the thesis defense: cultivate a success mindsetQuestion 1: Why did you choose
A Masters dissertation will be longer than the undergraduate equivalent - usually it'll be somewhere between 15,000 and 20,000 words, but this can vary widely between courses, institutions and countries. To answer your overall research question comprehensively, you'll be expected to identify and examine specific areas of your topic.
The research question is central to every bachelor's and master's thesis. It determines the content, the structure, and the aim of an academic paper — i.e., finding an answer to the research question. The research question is closely related to the topic and the title of the paper. You will never be able to deal with all aspects of a topic.
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
What is a thesis statement? A thesis statement is a sentence that states the main idea of your paper. It is not just a statement of fact, but a statement of position. What argument are you making about your topic? Your thesis should answer that question. How long should my thesis statement be? Thesis statements are often just one sentence.
The Honors Program is open to all majors with a GPA of 3.5 in History, and centers around an original piece of research and writing undertaken with the guidance of a thesis advisor. The six-credit program involves a seminar, one-on-one consultations with the advisor, and a 50-60 page thesis.
What is a Master Naturalist? We get that question a lot at University of Illinois Extension. Master Naturalists are many things: Advocates, volunteers, teachers, and environmental stewards. Around the state and in your backyard, these trained volunteers connect their communities with the natural world by contributing to scientific research, leading educational programs, and putting their ...
Kate completed her Master's degree at IOE in 2023. She is now a Research Officer with the IOE Research Development team, and a Research Assistant working on two multi-institutional projects: Climate-U and Equitable research cultures. Her career in education spans 20 years as a teacher, headteacher and teacher trainer in Tanzania and the UK.
Of the 33 student paper submissions across undergraduate, Master's, and Ph.D. levels, Overby's thesis paper - "Service robots' effect on branding and consumers' intentions through online reviews" - won the James E. Randall Best Student Paper Award. ... USM Honors College Students Present Thesis Research at Marketing Conference ...
Graduate students will compete in the final event on April 11. Research & Innovation | April 02, 2024. Loren Pietsch. 2023 3MT winners from left to right: Keely Rodriguez, Kendra Isable, Candi Block, Isabel Penaloza, Fatema Azmee, Yu Rong and Justice Best. The buzz is back with the Graduate School's annual Three-Minute Thesis (3MT ...