

Free Online Plagiarism Checker
Possible plagiarism detected!
If you submit this paper, your institution may take disciplinary measures against you. The content requires editing and modification of parts. We know how to make it unique.
This is weighted average of all matches in your text. For example, if half of your paper is 100% plagiarized, your score would be 50%
Well done, your text is unique!
Need an essay written but don't have the time?
With PapersOwl you’ll get it professionally researched, written and received right on time!
Make it unique with
Increase your SEO performance with
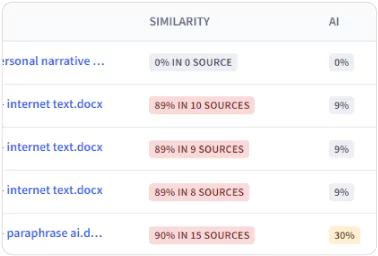
Text matches these sources
Verifying your text. It’ll take approximately 10 seconds
Get a 100% accurate report from an advanced AI-powered writing assistant. Our plagiarism checker works with all common file formats.
- Deep Search
- Check in real time
- Data Safety
How to avoid plagiarism?
Proper citation style.
Avoid plagiarism by always listing the source and formatting it correctly when you are note-taking. Take care of the proper formatting and citation style when using content from outside sources.
Write on your own
Avoid borrowing and overusing large pieces of the content from outside sources, especially from Wikipedia. Write your own thoughts and use sources only to support your opinion (remember to cite it though!).
Rewriting Service
PapersOwl expert can rewrite up to 75% of your content, edit and proofread your paper to make it plagiarism free and ready to use.
Editing Service
PapersOwl expert can edit up to 50% of your content, proofread and polish your paper to make it plagiarism free and ready to use.
Writing Service
PapersOwl expert can rewrite your paper from scratch according to instructions and guidelines and make it plagiarism free and ready to use.
Suits your similarity index. Consider using it!
Plagiarism Checker Review
Get speed and uniqueness when you use the free Papersowl plagiarism checker that accepts an unlimited word count compared to other platforms.
Online Plagiarism Checker For Students
Writing an academic paper can be challenging when you’re not sure if it’s original enough to pass a plagiarism check. Of course, students take information from various sites before writing their own text. Sometimes, it just so happens that certain parts are very similar to your resources, making your professor think that you’ve just copied work from somewhere. That’s why it’s crucial for any modern college or university student to ensure that their work has 100% original content to maintain academic integrity.
Luckily, a free plagiarism checker online can solve this issue quickly and easily. Many professional writing services use a plagiarism checker for research paper. However, students sometimes forget that they should too. But with so many options that pop up when you ask Google to “check my paper for plagiarism”, how do you choose the right one for detection? We’ve got the solution in the form of PapersOwl’s free plagiarism checker tool! Our simple tool makes it convenient to check any writing task without having to spend a dime. It works quickly and highly accurately, ensuring that you get the top grade you deserve. So, if you want to check plagiarism online before turning your task in, head over to our website and get started!
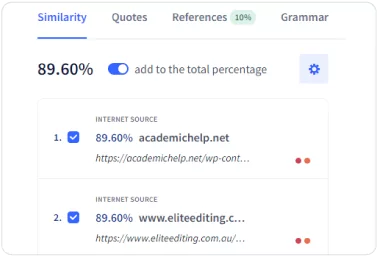
Accurate Check for Plagiarism with Percentage
Many students wishing to produce original content aren’t quite sure how to get an exact percentage of plagiarised text in their work. This percentage is important since many universities have a certain limit of non-unique words you can have in your essay for it to be considered okay. If your plagiarism search doesn’t give you the exact percentage, you can’t be sure if your assignment will go through or not.
When using a free plagiarism tool, it’s essential to have this data provided to you. Only when you have it can you decide which parts to change and which ones to chuck out to achieve your desired results. Plagiarized content is a big issue in modern educational institutions, so getting reliable and trustworthy results is vital. This is the most essential requirement when you check plagiarism.
PapersOwl’s plagiarism detection tool gives you all the information you need to fix plagiarized content. Whether you’ve fallen victim to accidental plagiarism or have tried to make your life easier by copying some text from different sources, you’ll get an accurate percentage with our plagiarism checker online. If you’re wondering how to check paper for plagiarism, it’s nothing complicated at all! Simply visit our site, paste your whole essay into the relevant text box or upload the text file, click on Check For Plagiarism, and you’ll get accurate plagiarism results in a matter of seconds. You’ll see the problematic parts with plagiarism detected highlighted, with links to where similar content exists. Our service with plagiarism detector will also give you the option to check my paper for plagiarism and then to hire a professional writer to fix your task quickly if you’re busy with other things!
The Fastest Plagiarism Checker Online
Gaining insight into duplicate content only works if you get your results quickly. There are so many free plagiarism software online that promise to do the job for you. However, a lot of them are clunky, slow, and inaccurate. How can you produce original work without similarity detection you can trust?
PapersOwl stands out in this regard because it will detect plagiarism in seconds. This is a plagiarism scanner that’s able to perform a Swift Check to give you a uniqueness check right there and then. It also conducts a Deep Search, going through millions of sources on the internet to check for plagiarism. A document of about 1500 words takes only about 10 seconds to get processed! You get a clear plagiarism score of how much text is plagiarized and how much is original. All the sources that your essay matches are listed based on how much similarity there is in your academic writing. And on top of that, you get a handy Make It Unique button that’ll take you to an order page where you can ask our expert writers to rewrite your work and make it 100% unique.
All of this is done almost instantly, allowing students to continue working on their assignments without missing a beat. Not every plagiarism detection software works this quickly, making ours the best one you’ll ever use.
Plagiarism Checker Helps Boost Your Grade
A lot of students make the mistake of considering their papers automatically free from plagiarism. After all, they’ve written it themselves, so how could it be problematic? What they don’t realize is that it’s very easy to borrow some information mistakenly. Turning such a paper in can cause multiple problems, as your professor might think you haven’t done the work at all.
That is why you should always use a plagiarism scanner to test for plagiarized content in your college papers. Our online plagiarism checker for students is designed for this exact purpose. A simple, free plagiarism check could help you check plagiarism, fix any mistakes you see, and submit high-quality text that no one will question.
Our plagiarism detector has a lot going for it. It makes plagiarism detection easier than ever before. Unlike copying and pasting each passage individually into Google, simply upload the whole file into our plagiarism checker free for students, and you don’t have to do anything else. All the matches are highlighted so you know what to change.
The plagiarism test will give you a uniqueness percentage too. This will help you figure out where you stand and how much time you need to adjust anything if required. So, using our copyright checker online free to check your writing is essential. This way, you’ll submit the task only when you’re sure it meets the level of uniqueness required by your school. As a result, your grades will drastically improve when you check for plagiarism.
Benefits of Free Plagiarism Checker for Students
Our professional online plagiarism checker work offers too many benefits to ignore. With our plagiarism detector, you can enjoy highly accurate results as a comprehensive report. The plagiarism checker for students is designed to help you achieve 100% uniqueness without hassle. Here are the key advantages you can enjoy when you check plagiarism free with our plagiarism detection tool:
It’s completely free! We know you are on a tight budget and should be able to check your paper for plagiarism without worrying about payments, so we’ve made the best similarity checker free for all!
Our software detects plagiarism swiftly. It’ll show you detailed results in as little as 10 seconds so you can continue working immediately.
The report from our plagiarism tool gives you access to all the links from where it has detected similarities in your work. You can head to the relevant sites and see which information you must rewrite to improve your results.
Our best free plagiarism checker doesn’t require any skills and presents its services in a simple-to-use interface that anyone can use.
The plagiarism test allows you to get professional help with your work if you’re short on time. Simply ask one of our writers to rewrite the problematic parts of your text and enjoy top grades.
With PapersOwl plagiarism detector, there’s no need to search the internet for an accurate tool. We have many satisfied students worldwide who can vouch for our plagiarism-checking services. Give our online plagiarism checker free tries as often as you want and see how easy it is to produce original essays without spending a penny!
Free Tools for Writing
PapersOwl is a well-known provider of all types of academic papers.
- Research paper
- Dissertation
and many more
- Stuck with a lot of homework assignments?
- Worried about making your work 100% plagiarism free?
- Looking for a writing help with affordable price?
How Does Plagiarism Checker Work?
- If you already have a completed text, all you need is just to copy-paste the whole thing in the special box of the chosen plagiarism tool or website, choose suitable settings (if any), then press “check for plagiarism”. It is quite simple and takes just a few moments.
- Once you have pressed “check for plagiarism”, the system will analyze your text and compare it with different sources to find similarities. As a rule, the duration depends on the text’s length. A standard free online plagiarism checker with percentage can give you the result within five minutes or less.
- When the system finishes the work you will be transmitted to the reporting page – it contains the comprehensive report on your work, a percentage of its uniqueness, and a list of sources on which similarities were detected. Often, such tools also highlight the overlaps that were found.
As you can see, it is simple. However, for the best and reliable result you have to be careful. There are tons of programs and online tools that can be used but keep in mind that many of them work differently and not all are good for you. To be confident in the truthfulness of the received result, you need to select the best plagiarism checker because only a professional and high-quality software can detect all similarities and give you a reasoned assessment.
Polish your paper and get rid of plagiarism!
We’ll change up to 75% of your paper, edit and proofread it.
- Reliable Editors
- Any Field of Study
- Fair Prices
Free Plagiarism Checker is rated 4.7 /5 based on 738 user reviews.
Want your voice to count in? Send us your review with all the details.
Advantages Of Plagiarism Checker By PapersOwl
Why choose us? Our service offers a professional online plagiarism checker with report that will provide you with a comprehensive report to make you confident in the 100% uniqueness of your paper. Our free plagiarism checker for students guarantees the best check and here are the key advantages of using our tool that prove this:
You don’t need to pay anything to check your paper for plagiarism because we know the value of original and unique works.
One of the main benefits of our antiplagiat checker online is that it works so fast that you will not even have enough time to make yourself a cup of coffee while it analyzes your text, and it is safe!
We use the latest and the best algorithms and software in order to provide you with an advanced check and help you receive the high-quality papers.
It is simple in use and won’t take much time!
Many students have already confirmed that our free tool is a great and convenient feature that helped them detect and fix errors that could lead to a failure. With us, you will no longer need to look for a different scanner!
Leaving already?
Get 10% off your first order!
* you'll see the discount on checkout page
OUR WRITERS
You can choose the writers after viewing information about them. Just select the writer whose experience is closest to your subject.

Completed orders: 918
Understanding Plagiarism and its Dangers in Academics
- Paper Type: Essay (Any Type)
- Subject: English
Completed orders: 865
Should the government raise the federal minimum wage?
- Subject: Law

Completed orders: 1109
Obesity in America
Plagiarism Checker FAQ
Can i check my essay for plagiarism free online, can i use papersowl plagiarism checker as a student for free, can i check my research paper for plagiarism for free, will the papersowl plagiarism report be the same as at my university, what are the consequences of plagiarism, why wait place an order right now.
Simply fill out the form, click the button, and have no worries!
Free plagiarism checker by EasyBib
Check for plagiarism, grammar errors, and more.
- Expert Check
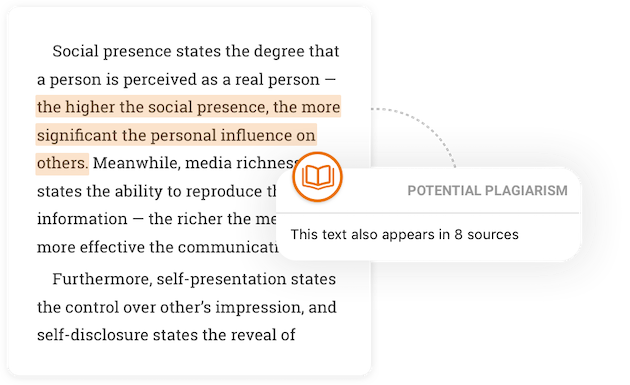
Check for accidental plagiarism
Avoid unintentional plagiarism. Check your work against billions of sources to ensure complete originality.

Find and fix grammar errors
Turn in your best work. Our smart proofreader catches even the smallest writing mistakes so you don't have to.

Get expert writing help
Improve the quality of your paper. Receive feedback on your main idea, writing mechanics, structure, conclusion, and more.
What students are saying about us

"Caught comma errors that I actually struggle with even after proofreading myself."
- Natasha J.

"I find the suggestions to be extremely helpful especially as they can instantly take you to that section in your paper for you to fix any and all issues related to the grammar or spelling error(s)."
- Catherine R.

Check for unintentional plagiarism
Easily check your paper for missing citations and accidental plagiarism with the EasyBib plagiarism checker. The EasyBib plagiarism checker:
- Scans your paper against billions of sources.
- Identifies text that may be flagged for plagiarism.
- Provides you with a plagiarism score.
You can submit your paper at any hour of the day and quickly receive a plagiarism report.
What is the EasyBib plagiarism checker?
Most basic plagiarism checkers review your work and calculate a percentage, meaning how much of your writing is indicative of original work. But, the EasyBib plagiarism checker goes way beyond a simple percentage. Any text that could be categorized as potential plagiarism is highlighted, allowing you time to review each warning and determine how to adjust it or how to cite it correctly.
You’ll even see the sources against which your writing is compared and the actual word for word breakdown. If you determine that a warning is unnecessary, you can waive the plagiarism check suggestion.
Plagiarism is unethical because it doesn’t credit those who created the original work; it violates intellectual property and serves to benefit the perpetrator. It is a severe enough academic offense, that many faculty members use their own plagiarism checking tool for their students’ work. With the EasyBib Plagiarism checker, you can stay one step ahead of your professors and catch citation mistakes and accidental plagiarism before you submit your work for grading.

Why use a plagiarism checker?
Imagine – it’s finals week and the final research paper of the semester is due in two days. You, being quite familiar with this high-stakes situation, hit the books, and pull together a ten-page, last-minute masterpiece using articles and materials from dozens of different sources.
However, in those late, coffee-fueled hours, are you fully confident that you correctly cited all the different sources you used? Are you sure you didn’t accidentally forget any? Are you confident that your teacher’s plagiarism tool will give your paper a 0% plagiarism score?
That’s where the EasyBib plagiarism checker comes in to save the day. One quick check can help you address all the above questions and put your mind at ease.
What exactly is plagiarism?
Plagiarism has a number of possible definitions; it involves more than just copying someone else’s work. Improper citing, patchworking, and paraphrasing could all lead to plagiarism in one of your college assignments. Below are some common examples of accidental plagiarism that commonly occur.
Quoting or paraphrasing without citations
Not including in-text citations is another common type of accidental plagiarism. Quoting is taking verbatim text from a source. Paraphrasing is when you’re using another source to take the same idea but put it in your own words. In both cases, it’s important to always cite where those ideas are coming from. The EasyBib plagiarism checker can help alert you to when you need to accurately cite the sources you used.
Patchwork plagiarism
When writing a paper, you’re often sifting through multiple sources and tabs from different search engines. It’s easy to accidentally string together pieces of sentences and phrases into your own paragraphs. You may change a few words here and there, but it’s similar to the original text. Even though it’s accidental, it is still considered plagiarism. It’s important to clearly state when you’re using someone else’s words and work.
Improper citations
Depending on the class, professor, subject, or teacher, there are multiple correct citation styles and preferences. Some examples of common style guides that are followed for citations include MLA, APA, and Chicago style. When citing resources, it’s important to cite them accurately. Incorrect citations could make it impossible for a reader to track down a source and it’s considered plagiarism. There are EasyBib citation tools to help you do this.
Don’t fall victim to plagiarism pitfalls. Most of the time, you don’t even mean to commit plagiarism; rather, you’ve read so many sources from different search engines that it gets difficult to determine an original thought or well-stated fact versus someone else’s work. Or worse, you assume a statement is common knowledge, when in fact, it should be attributed to another author.
When in doubt, cite your source!
Time for a quick plagiarism quiz!
Which of the following requires a citation?
- A chart or graph from another source
- A paraphrase of an original source
- Several sources’ ideas summarized into your own paragraph
- A direct quote
- All of the above
If you guessed option E than you’d be correct. Correct punctuation and citation of another individual’s ideas, quotes, and graphics are a pillar of good academic writing.
What if you copy your own previous writing?
Resubmitting your own original work for another class’s assignment is a form of self-plagiarism, so don’t cut corners in your writing. Draft an original piece for each class or ask your professor if you can incorporate your previous research.
What features are available with the EasyBib plagiarism checker?
Along with providing warnings and sources for possible plagiarism, the EasyBib plagiarism checker works alongside the other EasyBib tools, including a grammar checker and a spell checker . You’ll receive personalized feedback on your thesis and writing structure too!
The plagiarism checker compares your writing sample with billions of available sources online so that it detects plagiarism at every level. You’ll be notified of which phrases are too similar to current research and literature, prompting a possible rewrite or additional citation. You’ll also get feedback on your paper’s inconsistencies, such as changes in text, formatting, or style. These small details could suggest possible plagiarism within your assignment.
And speaking of citations, there are also EasyBib citation tools available. They help you quickly build your bibliography and avoid accidental plagiarism. Make sure you know which citation format your professor prefers!
Great! How do I start?
Simply copy and paste or upload your essay into the checker at the top of this page. You’ll receive the first five grammar suggestions for free! To try the plagiarism checker for free, start your EasyBib Plus three-day free trial.* If you love the product and decide to opt for premium services, you’ll have access to unlimited writing suggestions and personalized feedback.
The EasyBib plagiarism checker is conveniently available 24 hours a day and seven days a week. You can cancel anytime. Check your paper for free today!.
*See Terms and Conditions
Visit www.easybib.com for more information on helpful EasyBib writing and citing tools.
For informational guides and on writing and citing, visit the EasyBib guides homepage .
Plagiarism Checker by Quetext
Free plagiarism checker: how it works, enter text into plagiarism detection tool.
We make it simple. Just copy and paste all content from your document into our plagiarism checker and hit the ‘Check Plagiarism’ button to get started.
Evaluate text for plagiarism
Our plagiarism detection tool uses DeepSearch™ Technology to identify any content throughout your document that might be plagiarized. We identify plagiarized content by running the text through three steps:
- 1.) Contextual Analysis
- 2.) Fuzzy Matching
- 3.) Conditional Scoring
Accurate plagiarism results
After evaluating the text against billions of internet sources, you will be provided with a plagiarism score showing the percentage of text that is an exact or near-match to existing text online.
Resolve plagiarism risk and use citations
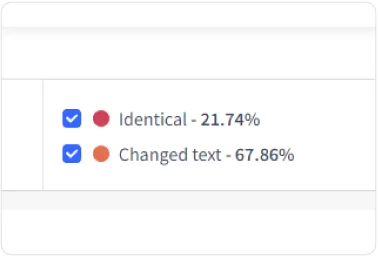
Our ColorGrade™ feedback feature highlights exact matches vs. near-exact or “fuzzy” matches with corresponding colors. From there, you can resolve plagiarism issues by deleting or altering the at-risk copy. Or, you can use our handy “Cite Source” feature to generate citations in MLA, APA, and Chicago formats and insert the citations directly into your document.
Plagiarism Checker Benefits
Whether producing original content or verifying that of others, there’s a lot to gain from using a plagiarism checker. Accurate, automatic detection of duplicate content facilitates the copy-checking process for teachers, students, content writers, and more. Results showing the exact percentage of plagiarized content allows users to see exactly how much text has been copied and where they need to re-word.
For Teachers
Before homework can be graded for quality, it must first be confirmed as original. Our easy-to-use tool arms teachers with a simple, effective way to verify and grade students’ work. Educators at all levels can benefit from ensuring academic integrity through a comprehensive plagiarism check. From K-12, all the way through higher education, teachers are faced with the task of verifying the originality of the work of dozens, if not hundreds, of students each year. Automating this process frees teachers up to focus on the quality of work, rather than be bogged down by its originality.
For Students
While the prevalence of academic plagiarism is on the rise, much of it is arguably unintentional. A simple, yet accurate and comprehensive, plagiarism checker offers students peace of mind when submitting written content for grading. It is much easier to do a quick check for potential plagiarism before submission rather than convince a teacher after the fact that your academic integrity is not in question. And Quetext even takes checking for plagiarism a step further, helping students identify and cite the source itself with our built-in citation generator.
For Copywriters
Plagiarism risk is not restricted to academia. Anyone tasked with writing for an individual or business has an ethical and legal responsibility to produce original content. On top of that, content writers are often tasked with producing content on topics outside of their wheelhouse, leaving them reliant on the work of others for their research. Our plagiarism checker gives content writers a quick and easy method to prevent copyright infringement. Checking even lengthy pieces of writing takes only a few minutes, keeping companies’ public content in check and writers’ integrity intact.
Types of Plagiarism
It’s important to understand that plagiarism expands far beyond just copying someone else’s work word-for-word. There are several different types of plagiarism that should be avoided.
Self-Plagiarism
Many believe that, as long as they produced the work at some point in the past, they can include it in future pieces. However, even if you were the original author, that original work must be cited in order to not be flagged as plagiarism. Treat your past self as a totally separate author; be sure to include all relevant citations and quotations, the same as you would for any other source.
Patchwork Plagiarism
Patchwork plagiarism is the act of piecing together a "patchwork" of existing content to form something new. Assembling unoriginal content in this manner often involves some paraphrasing, with only slight changes. This type of plagiarism can be tricky and can certainly occur unintentionally, especially in academia. Since academic writing is largely based on the research of others, a well-meaning student can inadvertently end up plagiarizing.
Mosaic Plagiarism
Mosaic plagiarism is synonymous with patchwork plagiarism. It describes the process of loosely rearranging or restating another's work without issuing proper credit. It can occur accidentally or intentionally. For authors, mosaic plagiarism endangers their academic integrity or reputation as a writer. For those checking content originality, such as teachers, mosaic plagiarism can easily appear to be original content, which can make mosaic plagiarism especially difficult to detect manually.
Accidental Plagiarism
Plagiarism doesn’t have to be intentional to still be considered plagiarism — even in early academia, where students are just learning how to properly cite others’ work. While there may be no ill intent from the student, most schools have policies explicitly treating accidental plagiarism the same as intentional plagiarism. Students are expected to know how to properly issue credit to other authors. Similarly, content writers risk damage to their reputation if they produce plagiarized content, regardless of intent.
Plagiarism Checker FAQ
What is plagiarism.
Plagiarism is representing someone else’s work as your own. In educational contexts, there are differing definitions of plagiarism depending on the institution. Plagiarism is considered a violation of academic integrity and a breach of journalistic ethics.
What percentage of a paper can be plagiarized (or copied) and still be considered unique?
Generally speaking, similar or exact copies of another source should be kept under 15% for the total text of the article/paper/essay. As a best practice, citations should be used whenever using another source word-for-word.
What’s the difference between deliberate and accidental plagiarism?
Deliberate plagiarism is purposely copying works from books, articles, webpages, or someone else’s paper and representing it as your original work. Alternatively, accidental plagiarism occurs in a few different ways:
- Incorrectly citing another person’s works
- Failing to paraphrase another person’s works - even when citing it correctly
- Reusing your own previous papers and inadvertently representing it as a new idea
What are the consequences of plagiarism?
The consequences for plagiarizing another person’s works vary. But broadly speaking, the types of consequences can be grouped by person and profession.
Plagiarism consequences for students
Maintaining academic integrity is a top priority for every educational institution. As already mentioned, ignorance of how to properly cite sources is not an excuse for plagiarism. It is the student’s responsibility to ensure they are submitting work that has not been plagiarized.
Failure to do so can result in disciplinary action, including an automatic failed grade, removal from a class, or expulsion from a school or university. Students who are allowed to continue at their institution following an act of plagiarism may encounter mistrust and additional scrutiny from teachers and instructors.
Plagiarism consequences for copywriters
Copywriters stake their reputation (and by extension, that of their client or company) on their writing. All copywriters must produce completely original content for their clients.
The consequences for plagiarism here are clear: Copywriters who plagiarize the content of others will quickly find it difficult to obtain paying assignments. Similar to academic situations, it is the copywriter’s own responsibility to ensure that their content is 100% original.
Research Paper Plagiarism Checker AcademicHelp
Secure the uniqueness of your scholarly work.
Advanced Scholarly Database Access
Contextual Analysis Technology
Source Integration Guidance
Bolster your research integrity.

Remember Me
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
Trusted Online Plagiarism Checker For Students and Academics

How to Use the Paperpal Plagiarism Checker to Write Responsibly
Check your paper for similarity
Review report for actionable items
Write in your own voice
Cite any overlooked sources
Maintain Academic Integrity with the Best Plagiarism Check Tool
Achieve writing excellence with our secure, reliable plagiarism checker

Paperpal Offers More Than An Online Plagiarism Checker

Paperpal Prime provides comprehensive language correction, paraphrasing, and generative AI writing capabilities to transform your academic writing.
Online Paraphrasing Tool
Use Rewrite to paraphrase content and add variety, achieve an academic tone, and reduce length to achieve clear, concise, impactful academic writing.
Free Grammar Checker
Benefit from in-depth grammar checks that quickly identify and correct spelling, punctuation, and complex language and grammar errors in minutes.
Generative AI Assistant
Access our suite of secure generative AI features designed to help you overcome writer’s block and deliver high-quality, original content, every time.
Frequently Asked Questions: Paperpal’s Plagiarism Checker
How can i access paperpal’s plagiarism check, how many pages or words can i check per month, will my unused quota transfer to the next month, what software is being used to detect similarity, what database is my writing checked against, how do i interpret the similarity score, why did i get a high similarity score after polishing language with paperpal using copilot’s ai-generated text, can paperpal ensure that my content is not flagged by plagiarism or ai detection tools, my paper is completely original. why is my similarity score so high, what types of documents can i upload, are my documents stored and added to turnitin’s database, understand plagiarism and ethical writing.
Want to master the basics of plagiarism and learn how to use AI tools responsibly? Check out these curated articles on plagiarism and ethical academic writing guidelines!

Self-plagiarism in research: What it is and how to avoid it
Self-plagiarism in research should be strictly avoided. Yet, it’s quite common to find early career researchers, and sometimes even experienced scholars...

The Do’s & Don’ts of Using Generative AI Tools Ethically in Academia
Generative AI has ushered in a new era of possibilities, redefining the way we create content, analyze data...

Addressing Your Queries on AI Ethics, Plagiarism, and AI Detection
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) tools into the academic writing process has sparked numerous debates...

Top 5 ethical considerations in research
While research is based on the pillars of innovation, trust, and transparency, it also requires scientists and academics...
Get Paperpal
Regional Websites
Connect with us
Shape the future
We are always looking for inspiration, feedback, and ideas. With your help we can make Paperpal even more amazing together!


How to Avoid Plagiarism in Research Papers (Part 1)
Writing a research paper poses challenges in gathering literature and providing evidence for making your paper stronger. Drawing upon previously established ideas and values and adding pertinent information in your paper are necessary steps, but these need to be done with caution without falling into the trap of plagiarism . In order to understand how to avoid plagiarism , it is important to know the different types of plagiarism that exist.
What is Plagiarism in Research?
Plagiarism is the unethical practice of using words or ideas (either planned or accidental) of another author/researcher or your own previous works without proper acknowledgment. Considered as a serious academic and intellectual offense, plagiarism can result in highly negative consequences such as paper retractions and loss of author credibility and reputation. It is currently a grave problem in academic publishing and a major reason for paper retractions .
It is thus imperative for researchers to increase their understanding about plagiarism. In some cultures, academic traditions and nuances may not insist on authentication by citing the source of words or ideas. However, this form of validation is a prerequisite in the global academic code of conduct. Non-native English speakers face a higher challenge of communicating their technical content in English as well as complying with ethical rules. The digital age too affects plagiarism. Researchers have easy access to material and data on the internet which makes it easy to copy and paste information.
Related: Conducting literature survey and wish to learn more about scientific misconduct? Check out this resourceful infographic today!
How Can You Avoid Plagiarism in a Research Paper?
Guard yourself against plagiarism, however accidental it may be. Here are some guidelines to avoid plagiarism.
1. Paraphrase your content
- Do not copy–paste the text verbatim from the reference paper. Instead, restate the idea in your own words.
- Understand the idea(s) of the reference source well in order to paraphrase correctly.
- Examples on good paraphrasing can be found here ( https://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/QPA_paraphrase.html )
2. Use Quotations
Use quotes to indicate that the text has been taken from another paper. The quotes should be exactly the way they appear in the paper you take them from.
3. Cite your Sources – Identify what does and does not need to be cited
- The best way to avoid the misconduct of plagiarism is by self-checking your documents using plagiarism checker tools.
- Any words or ideas that are not your own but taken from another paper need to be cited .
- Cite Your Own Material—If you are using content from your previous paper, you must cite yourself. Using material you have published before without citation is called self-plagiarism .
- The scientific evidence you gathered after performing your tests should not be cited.
- Facts or common knowledge need not be cited. If unsure, include a reference.
4. Maintain records of the sources you refer to
- Maintain records of the sources you refer to. Use citation software like EndNote or Reference Manager to manage the citations used for the paper
- Use multiple references for the background information/literature survey. For example, rather than referencing a review, the individual papers should be referred to and cited.
5. Use plagiarism checkers
You can use various plagiarism detection tools such as iThenticate or HelioBLAST (formerly eTBLAST) to see how much of your paper is plagiarised .
Tip: While it is perfectly fine to survey previously published work, it is not alright to paraphrase the same with extensive similarity. Most of the plagiarism occurs in the literature review section of any document (manuscript, thesis, etc.). Therefore, if you read the original work carefully, try to understand the context, take good notes, and then express it to your target audience in your own language (without forgetting to cite the original source), then you will never be accused with plagiarism (at least for the literature review section).
Caution: The above statement is valid only for the literature review section of your document. You should NEVER EVER use someone else’s original results and pass them off as yours!
What strategies do you adopt to maintain content originality? What advice would you share with your peers? Please feel free to comment in the section below.
If you would like to know more about patchwriting, quoting, paraphrasing and more, read the next article in this series!
Nice!! This article gives ideas to avoid plagiarism in a research paper and it is important in a research paper.
the article is very useful to me as a starter in research…thanks a lot!
it’s educative. what a wonderful article to me, it serves as a road map to avoid plagiarism in paper writing. thanks, keep your good works on.
I think this is very important topic before I can proceed with my M.A
it is easy to follow and understand
Nice!! These articles provide clear instructions on how to avoid plagiarism in research papers along with helpful tips.
Amazing and knowledgeable notes on plagiarism
Very helpful and educative, I have easily understood everything. Thank you so much.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
- Language & Grammar
- Reporting Research
Best Plagiarism Checker Tool for Researchers — Top 4 to choose from!
While common writing issues like language enhancement, punctuation errors, grammatical errors, etc. can be dealt…

How to Use Synonyms Effectively in a Sentence? — A way to avoid plagiarism!
Do you remember those school days when memorizing synonyms and antonyms played a major role…

- Manuscripts & Grants
Reliable and Affordable Plagiarism Detector for Students in 2022
Did you know? Our senior has received a rejection from a reputed journal! The journal…

- Publishing Research
- Submitting Manuscripts
3 Effective Tips to Make the Most Out of Your iThenticate Similarity Report
This guest post is drafted by an expert from iThenticate, a plagiarism checker trusted by the world’s…

How Can Researchers Avoid Plagiarism While Ensuring the Originality of Their Manuscript?
How Can Researchers Avoid Plagiarism While Ensuring the Originality of Their…
Is Your Reputation Safe? How to Ensure You’re Passing a Spotless Manuscript to Your…
Should the Academic Community Trust Plagiarism Detectors?

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
- Utility Menu
fa3d988da6f218669ec27d6b6019a0cd
A publication of the harvard college writing program.
Harvard Guide to Using Sources
- The Honor Code
How to Avoid Plagiarism
It's not enough to know why plagiarism is taken so seriously in the academic world or to know how to recognize it. You also need to know how to avoid it. The simplest cases of plagiarism to avoid are the intentional ones: If you copy a paper from a classmate, buy a paper from the Internet, copy whole passages from a book, article, or Web site without citing the author, you are plagiarizing. Here's the best advice you'll ever receive about avoiding intentional plagiarism: If you're tempted to borrow someone else's ideas or plagiarize in any way because you're pressed for time, nervous about how you're doing in a class, or confused about the assignment, don't do it . The problems you think you're solving by plagiarizing are really minor compared to the problems you will create for yourself by plagiarizing. In every case, the consequences of plagiarism are much more serious than the consequences of turning in a paper late or turning in a paper you're not satisfied to have written.
"...the consequences of plagiarism are much more serious than the consequences of turning in a paper late..."
The consequences of accidental plagiarism are equally daunting and should be avoided at all costs. Whether or not you intended to plagiarize, you will still be held responsible. As a member of an intellectual community you are expected to respect the ideas of others in the same way that you would respect any other property that didn't belong to you, and this is true whether you plagiarize on purpose or by accident. The best way to make sure you don't plagiarize due to confusion or carelessness is to 1) understand what you're doing when you write a paper and 2) follow a method that is systematic and careful as you do your research . In other words, if you have a clear sense of what question you're trying to answer and what knowledge you're building on, and if you keep careful, clear notes along the way, it's much easier to use sources effectively and responsibly and, most of all, to write a successful paper. If you have questions about plagiarism at any point in your research or writing process, ask. It's always better to ask questions than it is to wait for an instructor to respond to work that you have turned in for a grade. Once you have turned in your final work, you will be held responsible for misuse of sources.
With these principles in mind, here are some guidelines for conducting research responsibly:
Keep track of your sources; print electronic sources
While it's easy enough to keep a stack of books or journal articles on your desk where you can easily refer back to them, it's just as important to keep track of electronic sources. When you save a PDF of a journal article, make sure you put it into a folder on your computer where you'll be able to find it. When you consult a Web site, log the Web address in a separate document from the paper you're writing so that you'll be able to return to the Web site and cite it correctly. You should also print the relevant pages from any Web sites you use, making sure you note the complete URL and the date on which you printed the material. Because electronic sources aren't stable and Web pages can be deleted without notice, beware of directing your readers to sources that might have disappeared. Check when the Web site you're using was last updated and update the URLs as you work and once again right before you submit your essay. If an electronic source disappears before you submit your work, you will need to decide whether or not to keep the source in your paper. If you have printed the source and can turn it in with your paper, you should do so. If you have not printed the source, you should consult your instructor about whether or not to use that source in your paper.
The library has several helpful resources for managing your sources, including RefWorks .
Keep sources in correct context
Whenever you consult a source, you should make sure you understand the context, both of the ideas within a source and of the source itself. You should also be careful to consider the context in which a source was written. For example, a book of essays published by an organization with a political bias might not present an issue with adequate complexity for your project.
The question of context can be more complicated when you're working with Internet sources than with print sources because you may see one Web page as separate from an entire Web site and use or interpret that page without fully understanding or representing its context. For example, a definition of "communism" taken from a Web site with a particular political agenda might provide one interpretation of the meaning of the word—but if you neglect to mention the context for that definition you might use it as though it's unbiased when it isn't. Likewise, some Internet searches will take you to a URL that's just one Web page within a larger Web site; be sure to investigate and take notes on the context of the information you're citing.
Research can often turn out to be more time-consuming that you anticipate. Budget enough time to search for sources, to take notes, and to think about how to use the sources in your essay. Moments of carelessness are more common when you leave your essay until the last minute and are tired or stressed. Honest mistakes can lead to charges of plagiarism just as dishonesty can; be careful when note-taking and when incorporating ideas and language from electronic sources so you always know what language and ideas are yours and what belongs to a source.
Don't cut and paste: File and label your sources
Never cut and paste information from an electronic source straight into your own essay, and never type verbatim sentences from a print source straight into your essay. Instead, open a separate document on your computer for each source so you can file research information carefully. When you type or cut and paste into that document, make sure to include the full citation information for the print source or the full URL and the date you copied the page(s). For Web sources, make sure to cite the page from which you're taking information, which may not necessarily be the home page of the site you're using. Use logical and precise names for the files you create, and add citation information and dates. This allows you to retrieve the files easily, deters you from accidentally deleting files, and helps you keep a log of the order in which your research was conducted. It's a good idea to add a note to each file that describes how you might use the information in that file. Remember: you're entering a conversation with your sources, and accurate file names and notes can help you understand and engage that conversation. And, of course, always remember to back up your files.
Keep your own writing and your sources separate
Work with either the printed copy of your source(s) or (in the case of online sources), the copy you pasted into a separate document—not the online version—as you draft your essay. This precaution not only decreases the risk of plagiarism but also enables you to annotate your sources in various ways that will help you understand and use them most effectively in your essay.
Keep your notes and your draft separate
Be careful to keep your research notes separate from your actual draft at all stages of your writing process. This will ensure that you don't cut language from a source and paste it into your paper without proper attribution. If you work from your notes, you're more likely to keep track of the boundaries between your own ideas and those in a source.
Paraphrase carefully in your notes; acknowledge your sources explicitly when paraphrasing
When you want to paraphrase material, it's a good idea first to paste the actual quotation into your notes (not directly into your draft) and then to paraphrase it (still in your notes). Putting the information in your own words will help you make sure that you've thought about what the source is saying and that you have a good reason for using it in your paper. Remember to use some form of notation in your notes to indicate what you've paraphrased and mention the author's name within the material you paraphrase. You should also include all citation information in your notes.
When you decide to use paraphrased material in your essay, make sure that you avoid gradually rewording the paraphrased material from draft to draft until you lose sight of the fact that it's still a paraphrase. Also, avoid excessive paraphrasing in which your essay simply strings together a series of paraphrases. When the ideas taken from your sources start to blend in deceptively with your own thinking, you will have a more difficult time maintaining the boundaries between your ideas and those drawn from sources. Finally, whenever you paraphrase, make sure you indicate, at each logical progression, that the ideas are taken from an authored source.
Avoid reading a classmate's paper for inspiration
If you're in a course that requires peer review or workshops of student drafts, you are going to read your classmates' work and discuss it. This is a productive way of exchanging ideas and getting feedback on your work. If you find, in the course of this work, that you wish to use someone else's idea at some point in your paper (you should never use someone else's idea as your thesis, but there may be times when a classmate's idea would work as a counterargument or other point in your paper), you must credit that person the same way you would credit any other source. On the other hand, if you find yourself reading someone else's paper because you're stuck on an assignment and don't know how to proceed, you may end up creating a problem for yourself because you might unconsciously copy that person's ideas. When you're stuck, make an appointment with your instructor or go to the Writing Center for advice on how to develop your own ideas.
Don't save your citations for later
Never paraphrase or quote from a source without immediately adding a citation. You should add citations in your notes, in your response papers, in your drafts, and in your revisions. Without them, it's too easy to lose track of where you got a quotation or an idea and to end up inadvertently taking credit for material that's not your own.
Quote your sources properly
Always use quotation marks for directly quoted material, even for short phrases and key terms.
Keep a source trail
As you write and revise your essay, make sure that you keep track of your sources in your notes and in each successive draft of your essay. You should begin this process early, even before you start writing your draft. Even after you've handed in your essay, keep all of your research notes and drafts. You ought to be able to reconstruct the path you took from your sources to your notes and from your notes to your drafts and revision. These careful records and clear boundaries between your writing and your sources will help you avoid plagiarism. And if you are called upon to explain your process to your instructor, you'll be able to retrace the path you took when thinking, researching, and writing, from the essay you submitted back through your drafts and to your sources.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- NATURE INDEX
- 01 May 2024
Plagiarism in peer-review reports could be the ‘tip of the iceberg’
- Jackson Ryan 0
Jackson Ryan is a freelance science journalist in Sydney, Australia.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Time pressures and a lack of confidence could be prompting reviewers to plagiarize text in their reports. Credit: Thomas Reimer/Zoonar via Alamy
Mikołaj Piniewski is a researcher to whom PhD students and collaborators turn when they need to revise or refine a manuscript. The hydrologist, at the Warsaw University of Life Sciences, has a keen eye for problems in text — a skill that came in handy last year when he encountered some suspicious writing in peer-review reports of his own paper.
Last May, when Piniewski was reading the peer-review feedback that he and his co-authors had received for a manuscript they’d submitted to an environmental-science journal, alarm bells started ringing in his head. Comments by two of the three reviewers were vague and lacked substance, so Piniewski decided to run a Google search, looking at specific phrases and quotes the reviewers had used.
To his surprise, he found the comments were identical to those that were already available on the Internet, in multiple open-access review reports from publishers such as MDPI and PLOS. “I was speechless,” says Piniewski. The revelation caused him to go back to another manuscript that he had submitted a few months earlier, and dig out the peer-review reports he received for that. He found more plagiarized text. After e-mailing several collaborators, he assembled a team to dig deeper.

Meet this super-spotter of duplicated images in science papers
The team published the results of its investigation in Scientometrics in February 1 , examining dozens of cases of apparent plagiarism in peer-review reports, identifying the use of identical phrases across reports prepared for 19 journals. The team discovered exact quotes duplicated across 50 publications, saying that the findings are just “the tip of the iceberg” when it comes to misconduct in the peer-review system.
Dorothy Bishop, a former neuroscientist at the University of Oxford, UK, who has turned her attention to investigating research misconduct, was “favourably impressed” by the team’s analysis. “I felt the way they approached it was quite useful and might be a guide for other people trying to pin this stuff down,” she says.
Peer review under review
Piniewski and his colleagues conducted three analyses. First, they uploaded five peer-review reports from the two manuscripts that his laboratory had submitted to a rudimentary online plagiarism-detection tool . The reports had 44–100% similarity to previously published online content. Links were provided to the sources in which duplications were found.
The researchers drilled down further. They broke one of the suspicious peer-review reports down to fragments of one to three sentences each and searched for them on Google. In seconds, the search engine returned a number of hits: the exact phrases appeared in 22 open peer-review reports, published between 2021 and 2023.
The final analysis provided the most worrying results. They took a single quote — 43 words long and featuring multiple language errors, including incorrect capitalization — and pasted it into Google. The search revealed that the quote, or variants of it, had been used in 50 peer-review reports.
Predominantly, these reports were from journals published by MDPI, PLOS and Elsevier, and the team found that the amount of duplication increased year-on-year between 2021 and 2023. Whether this is because of an increase in the number of open-access peer-review reports during this time or an indication of a growing problem is unclear — but Piniewski thinks that it could be a little bit of both.
Why would a peer reviewer use plagiarized text in their report? The team says that some might be attempting to save time , whereas others could be motivated by a lack of confidence in their writing ability, for example, if they aren’t fluent in English.
The team notes that there are instances that might not represent misconduct. “A tolerable rephrasing of your own words from a different review? I think that’s fine,” says Piniewski. “But I imagine that most of these cases we found are actually something else.”
The source of the problem
Duplication and manipulation of peer-review reports is not a new phenomenon. “I think it’s now increasingly recognized that the manipulation of the peer-review process, which was recognized around 2010, was probably an indication of paper mills operating at that point,” says Jennifer Byrne, director of biobanking at New South Wales Health in Sydney, Australia, who also studies research integrity in scientific literature.
Paper mills — organizations that churn out fake research papers and sell authorships to turn a profit — have been known to tamper with reviews to push manuscripts through to publication, says Byrne.

The fight against fake-paper factories that churn out sham science
However, when Bishop looked at Piniewski’s case, she could not find any overt evidence of paper-mill activity. Rather, she suspects that journal editors might be involved in cases of peer-review-report duplication and suggests studying the track records of those who’ve allowed inadequate or plagiarized reports to proliferate.
Piniewski’s team is also concerned about the rise of duplications as generative artificial intelligence (AI) becomes easier to access . Although his team didn’t look for signs of AI use, its ability to quickly ingest and rephrase large swathes of text is seen as an emerging issue.
A preprint posted in March 2 showed evidence of researchers using AI chatbots to assist with peer review, identifying specific adjectives that could be hallmarks of AI-written text in peer-review reports .
Bishop isn’t as concerned as Piniewski about AI-generated reports, saying that it’s easy to distinguish between AI-generated text and legitimate reviewer commentary. “The beautiful thing about peer review,” she says, is that it is “one thing you couldn’t do a credible job with AI”.
Preventing plagiarism
Publishers seem to be taking action. Bethany Baker, a media-relations manager at PLOS, who is based in Cambridge, UK, told Nature Index that the PLOS Publication Ethics team “is investigating the concerns raised in the Scientometrics article about potential plagiarism in peer reviews”.

How big is science’s fake-paper problem?
An Elsevier representative told Nature Index that the publisher “can confirm that this matter has been brought to our attention and we are conducting an investigation”.
In a statement, the MDPI Research Integrity and Publication Ethics Team said that it has been made aware of potential misconduct by reviewers in its journals and is “actively addressing and investigating this issue”. It did not confirm whether this was related to the Scientometrics article.
One proposed solution to the problem is ensuring that all submitted reviews are checked using plagiarism-detection software. In 2022, exploratory work by Adam Day, a data scientist at Sage Publications, based in Thousand Oaks, California, identified duplicated text in peer-review reports that might be suggestive of paper-mill activity. Day offered a similar solution of using anti-plagiarism software , such as Turnitin.
Piniewski expects the problem to get worse in the coming years, but he hasn’t received any unusual peer-review reports since those that originally sparked his research. Still, he says that he’s now even more vigilant. “If something unusual occurs, I will spot it.”
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-01312-0
Piniewski, M., Jarić, I., Koutsoyiannis, D. & Kundzewicz, Z. W. Scientometrics https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-024-04960-1 (2024).
Article Google Scholar
Liang, W. et al. Preprint at arXiv https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2403.07183 (2024).
Download references
Related Articles

- Peer review
- Research management

Algorithm ranks peer reviewers by reputation — but critics warn of bias
Nature Index 25 APR 24

Researchers want a ‘nutrition label’ for academic-paper facts
Nature Index 17 APR 24

Rwanda 30 years on: understanding the horror of genocide
Editorial 09 APR 24

Structure peer review to make it more robust
World View 16 APR 24

Is ChatGPT corrupting peer review? Telltale words hint at AI use
News 10 APR 24

Mount Etna’s spectacular smoke rings and more — April’s best science images
News 03 MAY 24

How reliable is this research? Tool flags papers discussed on PubPeer
News 29 APR 24
Seeking Global Talents, the International School of Medicine, Zhejiang University
Welcome to apply for all levels of professors based at the International School of Medicine, Zhejiang University.
Yiwu, Zhejiang, China
International School of Medicine, Zhejiang University
Assistant, Associate, or Full Professor
Athens, Georgia
University of Georgia
Associate Professor - Synthetic Biology
Position Summary We seek an Associate Professor in the department of Synthetic Biology (jcvi.org/research/synthetic-biology). We invite applicatio...
Rockville, Maryland
J. Craig Venter Institute
Associate or Senior Editor (microbial genetics, evolution, and epidemiology) Nature Communications
Job Title: Associate or Senior Editor (microbial genetics, evolution, and epidemiology), Nature Communications Locations: London, New York, Philade...
New York (US)
Springer Nature Ltd
Postdoctoral Research Fellow
Two postdoctoral positions offered at HMS to study the role hypothalamic leptin resistance in control of neuron activity
Boston, Massachusetts (US)
Boston Children’s Hospital-Ozcan Lab
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Effectiveness of intervention programs in reducing plagiarism by university students: a systematic review provisionally accepted.

- 1 National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
Plagiarism in universities is a problem with potential academic, social, ethical, and legal implications. Systematic review research on academic integrity programs, including plagiarism, has been conducted, but few studies have assessed plagiarism. Therefore, this review synthesizes knowledge on the effect of educational interventions designed to prevent or reduce plagiarism by university students. Method: A systematic review was performed using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) criteria to analyze experimental or quasiexperimental studies aimed at reducing plagiarism through objective assessments. The search strategy was implemented in Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus, PsycArticles, ProQuest, ERIC, Redalyc, SciELO, and Tesiunam. Results: Six interventions were evaluated, and 1,631 undergraduate students were included pursuing different majors from different universities. The intervention and assessment strategies varied considerably between studies, 5 of which reported a lower plagiarism frequency in the intervention group than in the control group. Conclusions: The results suggest that interventions with practical elements, such as plagiarism detection, paraphrasing, citation skills, in addition to using software to identify similarities, may reduce plagiarism. However, few studies include an objective evaluation, so more research is needed.
Keywords: plagiarism, university students, Academic dishonesty, academic integrity, CHEATING
Received: 19 Dec 2023; Accepted: 29 Apr 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Miranda-Rodríguez, Sánchez-Nieto and Ruiz-Rodríguez. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Dr. Rubén Andrés Miranda-Rodríguez, National Autonomous University of Mexico, México City, Mexico
People also looked at

Yale professor accuses Columbia prez Shafik of plagiarism, ‘intellectual theft’ in resurfaced 1994 research paper
E mbattled Columbia University president Nemat “Minouche” Shafik screwed a former underling out of credit on a research paper published 30 years ago, a Yale University professor claims.
Ahmed Mushfiq Mobarak posted the bombshell allegations in a blistering thread on X early Friday, juxtaposing images of a 1992 report Shafik co-authored for World Bank with researcher Sushenjit Bandyopadhyay, along with a journal published in Oxford Economic Papers two years later in which Bandyopadhyay’s name was removed.
Mobarak, an economics and management professor at Yale, told The Post the findings and research cited in both papers are pretty much equal.
“It got rewritten, but fundamentally it’s the same paper,” he alleged.
“We can’t get in the room and [learn] what sentences did he write and what sentences she wrote, but what we do know is his contribution was sufficient to warrant co-authorship [in 1992],” he added. “What is not common is for someone to be a co-author and then suddenly their name is taken off.”
Instead, Bandyopadhyay is only “thanked” in an acknowledgement section in the back of the 1994 published journal — which screams of “power asymmetry” considering Shafik was then Bandyopadhyay’s boss, alleged Mobarak.
Bandyopadhyay declined comment when asked whether he felt slighted.
However, Mobarak, also a former World Bank consultant and University of Maryland graduate, said he spoke to Bandyopadhyay about the issue and that Bandyopadhyay believes he should have been credited as a co-author in the second paper. The professor conceded Bandyopadhyay never said anything “negative” about the Columbia president.
“This [1994] paper is lifted almost entirely from a 1992 report coauthored with consultant not credited in the publication,” wrote Mobarak on X. “This is wholesale intellectual theft, not subtle plagiarism.”
At the time both papers were written, Shafik was a vice president for World Bank and Bandyopadhyay, a consultant who also attended the University of Maryland.
Mobarak’s allegations echo plagiarism accusations leveled against former Harvard University president Claudine Gay, who eventually resigned in disgrace in January .
Columbia University spokesperson Ben Chang shot down the Yale professor’s claims, saying “this is an absurd attempt at running a well-known playbook, and it has no credibility.”

ChatGPT in higher education - a synthesis of the literature and a future research agenda
- Open access
- Published: 02 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Pritpal Singh Bhullar 1 ,
- Mahesh Joshi 2 &
- Ritesh Chugh ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0061-7206 3
11 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
ChatGPT has emerged as a significant subject of research and exploration, casting a critical spotlight on teaching and learning practices in the higher education domain. This study examines the most influential articles, leading journals, and productive countries concerning citations and publications related to ChatGPT in higher education, while also shedding light on emerging thematic and geographic clusters within research on ChatGPT’s role and challenges in teaching and learning at higher education institutions. Forty-seven research papers from the Scopus database were shortlisted for bibliometric analysis. The findings indicate that the use of ChatGPT in higher education, particularly issues of academic integrity and research, has been studied extensively by scholars in the United States, who have produced the largest volume of publications, alongside the highest number of citations. This study uncovers four distinct thematic clusters (academic integrity, learning environment, student engagement, and scholarly research) and highlights the predominant areas of focus in research related to ChatGPT in higher education, including student examinations, academic integrity, student learning, and field-specific research, through a country-based bibliographic analysis. Plagiarism is a significant concern in the use of ChatGPT, which may reduce students’ ability to produce imaginative, inventive, and original material. This study offers valuable insights into the current state of ChatGPT in higher education literature, providing essential guidance for scholars, researchers, and policymakers.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
ChatGPT, or Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer, is a popular generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) chatbot developed by OpenAI, employing natural language processing to deliver interactive human-like conversational experiences (Jeon et al., 2023 ; Angelis et al., 2023 ). ChatGPT utilises a pre-trained language learning model, derived from an extensive big-data corpus, to predict outcomes based on a given prompt (Crawford et al., 2023 ; Geerling et al., 2023 ; Li et al., 2023 ). Since its inception, ChatGPT has attracted widespread attention and popularity and has the potential to disrupt the education sector (Rana, 2023 ). According to a research survey of adults conducted by the Pew Research Centre, approximately 60% of adults in the United States and 78% of adults in Asia possess knowledge of ChatGPT; furthermore, men are more familiar with ChatGPT than women (Vogels, 2023 ). The study also found that among ethnic groups globally, individuals of Asian descent have the highest level of familiarity with AI-based large language models (LLMs).
People have found value in using ChatGPT for a wide range of purposes, including generating creative content, answering questions, providing explanations, offering suggestions, and even having casual conversations (Crawford et al., 2023 ; Throp, 2023 ; Wu et al., 2023 ). Furthermore, ChatGPT is an effective digital assistant for facilitating a thorough understanding of diverse and intricate subjects using simple and accessible language. Given these features, ChatGPT has the potential to bring about a paradigm shift in traditional methods of delivering instruction and revolutionise the future of education (Tlili et al., 2023 ). ChatGPT stands out as a promising tool for open education, enhancing the independence and autonomy of autodidactic learners through personalised support, guidance, and feedback, potentially fostering increased motivation and engagement (Firat, 2023 ). Its capabilities encompass facilitating complex learning, asynchronous communication, feedback provision, and cognitive offloading (Memarian & Doleck, 2023 ).
However, the rapid expansion of ChatGPT has also aroused apprehensions in the academic world, particularly after reports surfaced that the New York Department of Education had unexpectedly imposed a ban on access to the tool due to concerns about academic integrity violations (Sun et al., 2023 ; Neumann et al., 2023 ; Crawford et al., 2023 ). Students who use ChatGPT to produce superior written assignments may have an unfair advantage over peers who lack access (Farrokhnia et al., 2023 ; Cotton et al., 2023 ). Ethical concerns about the deployment of LLMs include the potential for bias, effects on employment, misuse and unethical deployment, and loss of integrity. However, there has been little research on the potential dangers that a sophisticated chatbot such as ChatGPT poses in the realm of higher education, particularly through the lens of a systematic literature review and bibliometric techniques.
In this light, this paper explores the literature on the application of ChatGPT in higher education institutions and the obstacles encountered in various disciplines from the perspectives of both faculty and students. The paper aims to analyse the current state of the field by addressing the following overarching research questions using bibliographic coupling, co-occurrence analysis, citation analysis, and co-authorship analysis:
What are the most influential articles in terms of citations in research related to ChatGPT in education?
What are the top journals and countries in terms of publication productivity related to the implications of ChatGPT in higher education institutions?
What are the emerging thematic clusters in research on the role and challenges of ChatGPT in teaching and learning in higher education institutions?
What are the geographic clusters in research on the role and challenges of ChatGPT in teaching and learning in higher education institutions?
2 Methodology
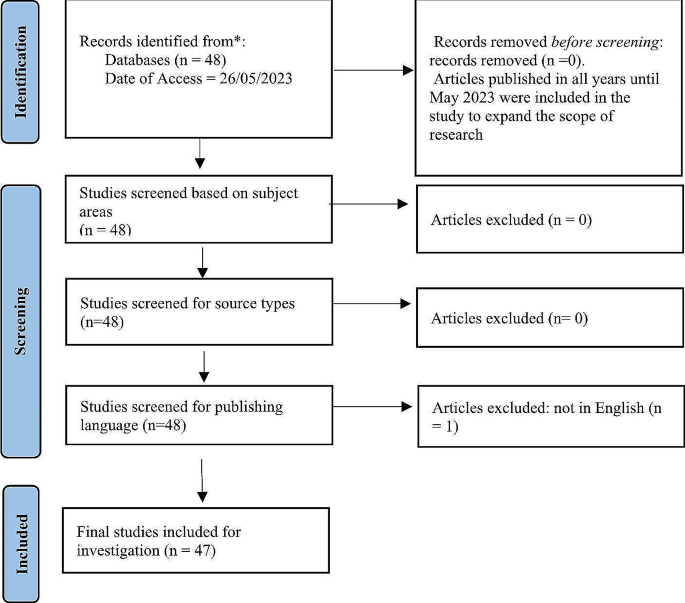
In conducting this study, publications on the impact of ChatGPT on various aspects of higher education institutions were systematically identified through an extensive search using Elsevier’s Scopus database, a comprehensive repository hosting over 20,000 globally ranked, peer-reviewed journals (Mishra et al., 2017 ; Palomo et al., 2017 ; Vijaya & Mathur, 2023 ). Scopus is a widely used database for bibliometric analyses and is considered one of the “largest curated databases covering scientific journals” (pg. 5116) in different subject areas (Singh et al., 2021 ). Widely acclaimed for its comprehensive coverage, Scopus has been extensively employed in bibliometric analyses across diverse disciplines, as evidenced by studies in capital structure theories, business research, entrepreneurial orientation and blockchain security (Bajaj et al., 2020 ; Donthu et al., 2020 ; Gupta et al., 2021 ; Patrício & Ferreira, 2020 ). Notably, despite the “extremely high” correlation between the Web of Science and Scopus databases, Scopus’s status as a superior and versatile data source for literature extraction is reinforced by its broader coverage of subject areas and categories compared to the narrower journal scope of Web of Science, facilitating scholars in locating literature most pertinent to the review area (Archambault et al., 2009 ; Paul et al., 2021 ). To ensure a systematic literature review, we adhered to the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis (PRISMA) guidelines (Page et al., 2021 ) for the search, identification, selection, reading, and data extraction from the articles retrieved through the Scopus database (Fig. 1 ). Reliance on a single database is acceptable within the PRISMA framework (Moher et al., 2009 ).
Employing Boolean-assisted search queries, we aimed to capture a comprehensive range of topics related to ChatGPT’s impact on higher education institutions. Specific search queries were carefully selected to ensure a broad yet relevant search scope and included the following:
“ChatGPT and Teaching learning in universities” OR “Effect of ChatGPT in higher education institution” OR “ChatGPT and student assessment in higher education” OR “ChatGPT and academic integrity” OR “ChatGPT and teaching pedagogy in higher education institution” OR “ChatGPT and cheating student course assignment” OR “ChatGPT and teaching in higher education” OR “Implications of ChatGPT in higher education institutions” OR “ChatGPT and evaluation criteria in higher education institution” OR “ChatGPT in universities” OR “ChatGPT and student learnings. ”
The study includes papers published and included in the Scopus database on or before May 26, 2023 on the theme of ChatGPT and higher education. This timeframe was chosen to encompass the most recent and relevant literature available up to the point of data retrieval. Papers identified through the search queries underwent inclusion or exclusion based on predetermined criteria. Specifically, only papers published in journals were considered for this study, as these undergo a peer-review process and are subject to stringent selection criteria set by the journals, ensuring their quality and reliability. Papers in conference proceedings were excluded from the start of the search. Only papers written in English were included to maintain consistency and clarity, whereas others were excluded. Of the 48 research papers that were initially identified, 47 were ultimately selected for the bibliometric analysis, which was conducted using VOSviewer, a bibliometric analysis tool.
PRISMA Flowchart
From the identified pool of 47 articles, the analysis uncovered a nuanced distribution of research methodologies. Specifically, 11 studies were grounded in quantitative research methodologies, underscoring a quantitative focus within the literature. In contrast, a substantial majority of 31 articles embraced a qualitative framework, showcasing a diverse spectrum that included pure qualitative research, editorials, letters to the editor, and opinion pieces. Furthermore, the review brought to light four literature reviews, signifying a synthesis of existing knowledge, and identified one study that strategically employed a mixed-methods approach, blending both qualitative and quantitative research techniques.
To address the research questions, the selected publications underwent analysis using various bibliometric techniques. For the first and second research questions, citation analysis was employed. For the third and fourth research questions, bibliographic analysis was performed in VOSviewer software to generate clusters.
3 Findings and discussion
3.1 publication trend.
Information from the Scopus database indicates that academics began focusing on investigating various aspects of ChatGPT’s potential in higher education in 2022, as they published their findings in 2023. All academic articles in reputable publications in the Scopus database were published in 2023.
3.2 Citation analysis
Table 1 presents the top ten articles according to the number of citations. The number of articles increased significantly in 2023, consistent with the emerging nature and growing relevance of the topic. Exploring the ramifications of ChatGPT in higher education is a recent focal point for scholars, with numerous aspects warranting deeper investigation. The limited citation count, as anticipated, underscores that publications from 2023 are in the early stages of gaining visibility and recognition within the academic community.
The article by Thorp ( 2023 ), entitled “ChatGPT is fun, but not an author”, has received the highest number of citations (79). Thorp stresses the risks associated with implementing ChatGPT in the classroom. Although ChatGPT is an innovative AI tool, significant barriers remain to its implementation in the field of education. According to Thorp, using ChatGPT in academic writing is still inefficient. Thorp also expresses concerns about the rising prevalence of ChatGPT in the fabrication of scientific publications. The second most-cited work, “How Does ChatGPT Perform on the United States Medical Licensing Examination?” by Gilson and colleagues, has received 27 citations. Gilson et al. ( 2023 ) evaluated the accuracy, speed and clarity of ChatGPT’s responses to questions on the United States Medical Licensing Examination’s Step 1 and Step 2 tests. The text responses generated by ChatGPT were evaluated using three qualitative metrics: the logical justification of the chosen answer, the inclusion of information relevant to the question, and the inclusion of information extraneous to the question. The model attained a level of proficiency comparable to that of a third-year medical student. The study demonstrates the potential utility of ChatGPT as an interactive educational resource in the field of medicine to facilitate the acquisition of knowledge and skills. Third is Kasneci et al.’s article “ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education”, with 13 citations. This paper examines the benefits and drawbacks of using language models in the classroom from the perspectives of both teachers and students. The authors find that these comprehensive language models can serve as a supplement rather than a replacement for classroom instruction. Each of the remaining top-ten articles mentioned the impact of ChatGPT on academic integrity in education and had received fewer than ten citations at the time of analysis.
Table 2 presents the top 10 journals in terms of the number of citations of publications related to the topic of ChatGPT in higher education. The journal Science , which published “ChatGPT is fun, but not an author,” was deemed most influential because it received the highest number of citations (79). JMIR Medical Education has published two articles that have been cited by 30 other research articles on the same topic. Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practise has published the most articles: three. Innovations in Education and Teaching International has published two articles on this topic, which together have been cited by six articles.
As shown in Table 3 , the majority of research articles pertaining to ChatGPT and higher education have originated from countries in Asia. Six of the top 10 countries for publishing articles on this topic are located in the Asian continent. However, the most influential studies in terms of citations have been produced by the United States, Germany, Australia, and the United Kingdom. Combined, these countries have received a total of 63 citations, with individual counts of 36, 17, 7, and 7, respectively. These four countries have 90% of the total citations of the top 10 most productive countries in the field of research on higher education perspectives on ChatGPT.
3.3 Bibliographic coupling
3.3.1 thematic clusters.
Four thematic clusters (TCs) were identified from the included research articles, as shown in Table 4 . VOSviewer was used to perform clustering based on bibliographic coupling. This method identifies relations between documents by examining publications that cite the same sources (Boyack & Klavans, 2010 ). VOSviewer clusters articles with a common knowledge base, assigning each publication to exactly one cluster. To implement this clustering technique, we assessed the co-occurrence of bibliographic references among articles within our dataset. Co-occurrence was determined by identifying shared references between articles, indicating a thematic connection (Boyack & Klavans, 2010 ). Articles sharing common references were considered to co-occur, enabling us to quantify the extent of thematic relationships based on the frequency of shared references. We identified and categorised thematic clusters within our dataset through the combined approach of VOSviewer clustering and co-occurrence analysis. This method typically results in a distribution of clusters, with a limited number of larger clusters and a more substantial number of smaller clusters.
The clusters were derived through an analysis of subordinate articles extracted from the Scopus database. VOSviewer systematically organised similar articles into distinct clusters based on the shared patterns of bibliographic references (Van Eck & Waltman, 2010 ). To ensure methodological transparency and robustness, we established clear criteria and parameters for clustering. Specifically, keywords with a minimum frequency ( n = 5) were included in the analysis, and co-occurrence was calculated based on a pairwise comparison method. This systematic approach ensured the meaningful representation of thematic relationships within the dataset, guided by insights from previous literature (Jarneving, 2007 ). Using cluster analysis techniques, the articles were organised into cohesive groups characterised by the degree of thematic homogeneity guided by the nature of the research findings. This approach ensured a robust representation of the underlying thematic structure (Jarneving, 2007 ).
Furthermore, to mitigate the risk of subjective bias in thematic categorisation, a counter-coding approach was employed. A second researcher independently categorised thematic clusters identified by VOSviewer to assess inter-rater agreement. The level of agreement between the two researchers was assessed using Cohen’s kappa coefficient, ensuring the reliability and validity of the thematic classification process. The resulting kappa coefficient (0.69) indicated substantial agreement, suggesting a high level of agreement beyond what would be expected by chance alone (Gisev et al., 2013 ). Furthermore, the nomenclature assigned to each cluster was finalised based on the predominant research theme emerging from the analysis, providing a concise and informative label for each group.
TC1: ChatGPT and Academic Integrity: Cotton et al. ( 2023 ) describe ChatGPT as a double-edged sword that potentially threatens academic integrity. AI essay writing systems are programmed to churn out essays based on specific guidelines or prompts, and it can be difficult to distinguish between human and machine-generated writing. Thus, students could potentially use these systems to cheat by submitting essays that are not their original work (Dehouche, 2021 ). Kasneci et al. ( 2023 ) argue that effective pedagogical practices must be developed in order to implement large language models in classrooms. These skills include not only a deep understanding of the technology but also an appreciation of its constraints and the vulnerability of complex systems in general. In addition, educational institutions need to develop a clearly articulated plan for the successful integration and optimal use of big language models in educational contexts and teaching curricula. In addition, students need to be taught how to verify information through a teaching strategy emphasising critical thinking effectively. Possible bias in the generated output, the need for continuous human supervision, and the likelihood of unforeseen effects are just a few of the challenges that come with the employment of AI systems. Continuous monitoring and transparency are necessary to ensure academic integrity while using ChatGPT. Lim et al. ( 2023 ) report that ChatGPT poses academic integrity challenges for the faculty of higher education institutions, who must verify whether academic work (assignments, research reports, etc.) submitted by students is derived from the fresh perspective of data analysis or plagiarised and recycled (copying and pasting original work) by ChatGPT. ChatGPT may threaten student learning and classroom engagement if students have access to information and course assignments without assessing their integrity. Perkins ( 2023 ) also expresses concerns regarding academic integrity in the use of ChatGPT. Students are utilising ChatGPT to complete their course assignments without attribution rather than producing original work. Higher education institutions must establish clear boundaries regarding academic integrity and plagiarism in light of the growing utilisation of AI tools in academic and research settings. In addition, the challenges posed by AI essay writing systems like ChatGPT necessitate a multifaceted approach to safeguard academic integrity. Educational institutions should invest in comprehensive educational programs that not only teach students the ethical use of technology but also incorporate rigorous assessments of critical thinking skills. Additionally, integrating AI literacy into the curriculum, with a focus on understanding the limitations and potential biases of big language models, can empower students to discern between human and machine-generated content.
TC2: ChatGPT and Learning Environment: According to Crawford et al. ( 2023 ), increased stress levels and peer pressure among university students have created a favourable environment for the use of AI tools. ChatGPT provides enhanced educational opportunities for college-level students. It can help students identify areas they may have overlooked, offer guidance on additional reading materials, and enhance existing peer and teacher connections. In addition, ChatGPT can propose alternative methods of evaluating students beyond conventional assignments. Crawford et al. ( 2023 ) recommend providing practical assignments incorporating ChatGPT as a supplementary tool to reduce plagiarism. Su ( 2023 ) documents that ChatGPT can provide students with a personalised learning experience based on their specific needs. In addition, the ChatGPT platform can be used to create a virtual coaching system that offers prompt feedback to educators during their classroom evaluations. This approach fosters critical thinking and supports early childhood educators in refining their teaching methodologies to optimise interactive learning outcomes for students. Tang ( 2023b ) proposes that bolstering research integrity can be achieved by imposing restrictions on the utilisation of NLP-generated content in research papers. Additionally, the author advocates for transparency from researchers, emphasising the importance of explicitly stating the proportion of NLP-generated content incorporated in their papers. This recommendation prompts a critical examination of the role of AI-generated content in scholarly work, emphasising the importance of nurturing independent research and writing skills for both students and researchers.
TC3: ChatGPT and Student Engagement: Lee ( 2023 ) examines the ability of ChatGPT to provide an interactive learning experience and boost student engagement beyond textbook pedagogy. Iskender ( 2023 ) explains that ChatGPT provides a mechanism for students to generate and investigate diverse concepts expeditiously, thereby helping them engage in imaginative and evaluative thinking on specific subject matter. This approach has the potential to optimise time management for students and allow them to concentrate on more advanced cognitive activities. AI tools such as ChatGPT can potentially enhance the personalisation of learning materials by providing visual aids and summaries that can aid the learning process and significantly improve students’ competencies. Hence, leveraging ChatGPT in education can revolutionise learning by facilitating interactive experiences, nurturing imaginative thinking, and optimising time management for students.
TC4: ChatGPT and Scholarly Research: Ivanov and Soliman ( 2023 ) and Yan ( 2023 ) focus on the practical applications and implications of LLMs like ChatGPT in educational settings and scholarly research within the context of language learning, writing, and tourism. Yan’s investigation into ChatGPT’s application in second-language writing examines its effectiveness in addressing specific writing tasks at the undergraduate level. The findings underscore the nuanced balance between the strengths of ChatGPT and the inherent limitations in handling demanding academic writing tasks. Nevertheless, ChatGPT is also labelled as an ‘all-in-one’ solution for scholarly research and writing (Yan, 2023 ). In parallel, Ivanov and Soliman ( 2023 ) highlight that ChatGPT can assist scholars in the field of tourism research by composing preliminary literature reviews, substantiating their chosen methodologies, and creating visual aids such as tables and charts. Furthermore, the researchers outline that ChatGPT could provide valuable methodological ideas and insights by helping researchers generate questions and corresponding scales for inclusion in questionnaires. Hence, ChatGPT has the potential to become a valuable ally as a facilitator in academic writing processes and has the potential to transform the research workflow.
3.3.2 Geographic clusters
The results of the country-based bibliographic analysis are summarised in Table 5 . The present study utilised the prevailing research theme in the existing literature as a framework for categorising the countries into four distinct clusters on the basis of the number of documents published from different countries.
Cluster 1: Implications of ChatGPT for Student Examinations and Education : Cluster 1 is composed of five countries: Germany, Ireland, South Korea, Taiwan, and the United States. Researchers in these countries have emphasised the potential role of ChatGPT in higher education within the context of AI language models. Eleven research articles related to this theme were published by researchers based in the United States, the most in this cluster. The top three articles in Table 1 are from the United States. The study entitled “Opportunities and Challenges of Large Language Models for Education,” was authored by German researchers (Kasneci et al., 2023 ) and has been widely cited in the academic community (13 citations). The remaining studies were conducted by researchers from South Korea and Taiwan and focused on the impact of ChatGPT on the education sector and its associated opportunities and challenges. This cluster demonstrates that students could benefit greatly from using ChatGPT in performing various academic tasks, such as reviewing and revising their work, verifying the accuracy of homework answers, and improving the quality of their essays. It has also aided postgraduates whose first language is not English improve their writing, as ChatGPT can be instructed to rewrite a paragraph in a scholarly tone from scratch. The outcomes have demonstrated significant efficacy, thereby alleviating the cognitive load associated with translation for these students, enabling them to concentrate on the substance of their writing rather than the intricacies of composing in an unfamiliar language. To harness the potential benefits, future research could focus on developing targeted training programs for students and educators that emphasise the effective utilisation of ChatGPT to enhance not only academic tasks but also language proficiency for non-native English speakers, addressing both cognitive load and language intricacies.
Cluster 2: ChatGPT and Academic Integrity : Cluster 2 comprises research studies conducted by authors from Japan, Bangladesh, Hong Kong, Nigeria, Pakistan, UAE, the UK, Vietnam and the Netherlands. The most influential study in this cluster, “Unlocking the power of ChatGPT: A framework for applying Generative AI in education”, was authored by researchers from Hong Kong (Su & Yang, 2023 ). They document that ChatGPT can be used to respond to student inquiries, reducing the time and effort required of educators and allowing them to focus their resources on other activities, such as scholarly investigations. Farrokhnia et al. ( 2023 ) and Yeadon et al. ( 2023 ) state that ChatGPT can write scientific abstracts with fabricated data and essays that can evade detection by reviewers. According to Liebrenz et al. ( 2023 ), ChatGPT tends to produce erroneous and incoherent responses, thereby raising the potential for disseminating inaccurate information in scholarly literature. The higher-order cognitive abilities of ChatGPT are relatively low, especially in areas related to creativity, critical thinking, reasoning, and problem-solving. ChatGPT could reduce students’ motivation to explore topics independently, draw their own conclusions, and solve problems independently (Kasneci et al., 2023 ). Ibrahim et al. ( 2023 ) find that ChatGPT can engage students in their academic pursuits. ChatGPT can enhance the writing abilities of non-native English speakers to allow them to concentrate on higher-order cognitive processes. This technological development allows faculty members to allocate more attention to conceptualisation and writing rather than focusing on the mechanics of grammar and spelling. However, there is a debate among intellectuals regarding the implications of AI for content creation, with some asserting that it detracts from innovative content development. The possibility that ChatGPT threatens academic honesty by facilitating essay plagiarism is being acknowledged. In addition, in the absence of appropriate citations, this textual content may violate copyright regulations. Cotton et al. ( 2023 ) express concerns about the potential impact of ChatGPT on academic integrity and plagiarism. Their work corroborates Dehouche’s ( 2021 ) assertion that students may use ChatGPT to engage in academic dishonesty by submitting essays that are not their original work. According to Cotton et al. ( 2023 ), ChatGPT users have a competitive advantage over non-users and can achieve higher grades on their coursework assignments by utilising the AI-based language tool. They classify ChatGPT as a versatile instrument with the potential to pose a threat to academic integrity, noting that AI essay writing systems are specifically programmed to generate content based on specific parameters or prompts, thereby challenging the discernment between human-authored and machine-generated content. Distinguishing between the academic work produced by students and the content of ChatGPT when evaluating assignments is a significant challenge for faculty. It is recommended that academic staff continually monitor student assignments for academic misconduct infractions, coupled with transparent communication about the potential risks associated with AI-generated content.
Cluster 3: ChatGPT and Students’ Learning : Cluster 3 comprises Malaysia, China and Australia. This cluster mainly includes studies of the role of AI-based models in student learning. Researchers from Australia (Crawford et al., 2023 ; Lim et al., 2023 ; Lawrie, 2023 ; Li et al., 2023 ; Seth et al., 2023 ; Cingillioglu, 2023 ; Skavronskaya, 2023 ; and Johinke, 2023 ) have contributed the most (8 studies) to this cluster and put their weight behind the role of AI and student learning in various disciplines. One of the most influential papers, “Generative AI and the future of education: Ragnarök or reformation? A paradoxical perspective from management educators”, was authored by researchers from both Australia and Malaysia (Lim et al., 2023 ) and reflected on the role of AI in classroom learning and teaching. Rather than banning AI tools, the authors advocate for the productive use of these tools in classrooms to facilitate more engaging student learning. Another Australian study titled, “Leadership is needed for ethical ChatGPT: Character, assessment, and learning using artificial intelligence (AI)” (Crawford et al., 2023 ) highlights AI as an alternative path of learning for students. ChatGPT can promptly evaluate students’ assignments and help them identify areas of weakness. Educators have the option to provide innovative assessments to their students instead of adhering solely to conventional assessments. ChatGPT can augment pedagogical approaches, evaluation structures, and the comprehensive educational milieu by reinforcing the trilateral association among instructors, learners, and technology. The implementation of ChatGPT can provide students with a personalised and interactive learning and research experience facilitated by virtual tutors and customised recommendations. In light of the research in this cluster, the integration of ChatGPT into education should inspire a paradigm shift towards a more dynamic and personalised learning environment. Institutions can explore strategic partnerships with AI researchers to develop context-specific applications of ChatGPT that cater to diverse educational needs, promoting a symbiotic relationship between human instructors, students, and technology for an enriched learning experience.
Cluster 4: ChatGPT and Field-specific Research : This cluster includes research by authors in Asian and European countries (India, Oman, Bulgaria and New Zealand) that has emphasised the potential role of ChatGPT in the medical and tourism industries. Authors from India explored the role of ChatGPT in the medical field (Seetharaman, 2023 ; Subramani et al., 2023 ). Seetharaman ( 2023 ) reports that ChatGPT offers supplementary language assistance to students who are not proficient in English, enabling them to enhance their language proficiency and effectively communicate in English, the principal language of instruction in medical establishments. The ChatGPT platform has the potential to serve as a tool for medical students to replicate patient interactions in a simulated environment, such as accurately obtaining medical histories and documenting symptoms. According to Subramani et al. ( 2023 ), ChatGPT is a highly efficient and user-friendly AI technology that can aid healthcare professionals in various aspects, such as diagnosis, critical decision-making, and devising appropriate treatment plans. ChatGPT has demonstrated impressive performance on medical exams, indicating its potential as a valuable resource for enhancing medical education and assessment (Subramani et al., 2023 ) and can support interdisciplinarity in tourism research (Nautiyal et al., 2023 ). Ivanov and Soliman ( 2023 ) note the potential of ChatGPT to serve as a digital instructor to provide students with enhanced and effective learning experiences and outcomes. Digital instructors can impart knowledge in diverse languages and thus can be used to educate individuals of varying nationalities and backgrounds in the field of tourism. Furthermore, LLM-based chatbots, including ChatGPT, can assess written assignments and provide direction on linguistic proficiency, syntax, and composition, ultimately enhancing students’ scholarly writing proficiency. In exploring the intersection of ChatGPT with medical education, institutions can pioneer innovative approaches by using the platform to create immersive, simulated patient interactions that go beyond language assistance, allowing medical students to practice nuanced skills such as medical history gathering and symptom documentation. Simultaneously, leveraging ChatGPT as a versatile digital instructor offers a unique opportunity to provide cross-cultural and multilingual education, contributing to a more inclusive and globally competent workforce within the tourism industry.
3.4 Challenges of ChatGPT in higher education
In addition to some previously mentioned challenges, such as the potential for plagiarism, the investigation also identified other key challenges in implementing ChatGPT within the context of higher education’s teaching and learning environment. Wu and Yu ( 2023 ) found that the benefits of AI-based ChatGPT are more in higher education as compared to primary and secondary education. The study also reported that the novelty effects of AI chatbots may enhance learning outcomes in brief interventions, but their efficacy diminishes in longer interventions.
First, the implementation of ChatGPT within the educational context engenders learning impediments. In the absence of adequate monitoring and regulation, the technology could lead to human unintelligence and unlearning, but teachers will become more adaptive and create authentic assessments to enhance student learning (Alafnan et al., 2023 ; Lawrie, 2023 ). Second, the technology could be used in a manner that violates students’ privacy. If the model is not adequately secured, it could surreptitiously gather confidential data from students without their explicit awareness or authorisation (Kanseci, 2023). Third, the technology could facilitate discrimination against particular students. If the model is not trained on a dataset that accurately represents the entire student population, it has the potential to create disparities in educational access (Cingillioglu, 2023 ; Lin et al., 2023 ). Fourth, according to Ivanov and Soloman (2023), ChatGPT lacks access to real-time data. Therefore, its responses may be inconsequential, inaccurate, or outdated. The information provided in response to a specific query may also be insufficient. Gao et al. (2022) highlight the need for further investigation of the precision and scholarly authenticity of ChatGPT. Fifth, it may be difficult for ChatGPT to comprehend the context and subtleties of complex academic subjects and answer complex questions (Adetayo, 2023 ; Eysenbach, 2023 ; Neumann et al., 2023 ). The system can misinterpret inquiries, offer inadequate or inaccurate responses, or struggle to comprehend the fundamental purpose behind questions (Clark, 2023 ). In particular, ChatGPT may not have the requisite expertise in highly specialised or advanced subjects such as advanced mathematics or specific sciences. Hence, it may not deliver precise and accurate answers (Neumann et al., 2023 ; Fergus et al., 2023 ). Karaali ( 2023 ) claimed that the primary emphasis in the field of AI is currently directed towards the enhancement of advanced cognitive abilities and mental processes associated with quantitative literacy and quantitative reasoning. However, it is important to acknowledge that fundamental skills such as writing, critical thinking, and numeracy continue to serve as essential foundational components among students. Although AI is making significant progress in fundamental domains, it appears that students are experiencing a decline in performance in the context of fundamental skills. Consequently, NLP-based adaptive learner support and education require further investigation (Bauer et al., 2023 ).
In addressing the challenges of ChatGPT in education, educators need to adapt and develop authentic assessments that mitigate the risk of human unlearning, ensuring that technology enhances, rather than hinders, student learning experiences. Simultaneously, recognising the limitations of ChatGPT in comprehending the nuances of highly specialised subjects underscores the importance of balancing advancements in AI’s cognitive abilities with continued emphasis on fundamental skills like critical thinking, writing, and numeracy, urging a reevaluation of priorities in AI-driven educational research towards comprehensive learner support.
4 Conclusion, implications and agenda for future research
This study identified the most influential articles and top journals and countries in terms of citations and publication productivity related to ChatGPT in higher education, as well as highlighted emerging thematic clusters and geographic clusters in research on the role and challenges of ChatGPT in teaching and learning in higher education institutions. Articles on the topic of ChatGPT in higher education published up to May 2023 were identified by searching the Scopus database. Given the emergent nature of ChatGPT starting in late 2022, all the included articles were published in 2023. Thus, this specific research domain remains relatively unexplored. The findings of this analysis reveal that the United States is the most productive country in terms of research on the role of ChatGPT in higher education, especially relating to academic integrity and research. US researchers also emerged as the most influential in terms of number of citations in the literature. Our findings corroborate those of previous research (Crompton & Burke, 2023 ). However, 60% of the articles in our shortlisted literature emanated from Asian countries.
Four thematic clusters (academic integrity, student engagement, learning environment and research) were identified. Furthermore, the country-based bibliographic analysis revealed that research has focused on student examinations, academic integrity, student learning and field-specific research in medical and tourism education (Nautiyal et al., 2023 ; Subramani et al., 2023 ). Plagiarism is recognised as a major challenge that hinders students’ creativity, innovativeness and originality when using ChatGPT in their academic pursuits. To mitigate the potential drawbacks of using ChatGPT in educational and research settings, proactive measures should be taken to educate students and researchers alike on the nature of plagiarism, its negative impacts and academic integrity (Shoufan, 2023 ; Teixeira, 2023 ) Educators may ask students to provide a written acknowledgement of the authenticity of their assignments and their non-reliance on ChatGPT. Such an acknowledgement would discourage students from utilising ChatGPT in their academic and research endeavours and establish accountability for their academic pursuits. In addition, educators should develop authentic assessments that are ChatGPT-proof.
ChatGPT lacks emotional intelligence and empathy, both of which are crucial in effectively addressing the emotional and psychological dimensions of the learning process (Farrokhnia et al., 2023 ; Neumann et al., 2023 ). Higher education institutions may encounter challenges in using ChatGPT to deliver suitable assistance, comprehension, or direction to students needing emotional or mental health support. The significance of human interaction in learning cannot be overstated. Achieving a balance between using AI and the advantages of human guidance and mentorship is a persistent challenge that requires attention (Neumann et al., 2023 ; Rahman et al., 2023 ). Strzelecki ( 2023 ) observed in his research that behavioural intention and personal innovativeness are the two major determinants behind the adoption of ChatGPT among students.
4.1 Implications
The findings of the present study have numerous important implications. This study provides insight into the current state of ChatGPT in higher education and thus can serve as valuable guidance for academics, practitioners, and policymakers. The study’s findings contribute to the literature by providing new insights into the role of ChatGPT and strategies for mitigating its negative aspects and emphasising its positive attributes.
First, the implementation of AI in education can improve academic performance and student motivation, particularly by facilitating personalised learning. Educational institutions should monitor and regulate students’ use of such technologies proactively. Higher education institutions also ought to prioritise the training of their educators in effectively utilising AI technologies, including ChatGPT. Concurrently, it is imperative for these institutions to equip students with comprehensive academic integrity training, shedding light on the appropriate and inappropriate applications of AI tools like ChatGPT. This includes creating awareness about the potential consequences of utilising these technologies for dishonest practices. Furthermore, educational establishments need to urgently revisit and refine their academic integrity policies to address the evolving landscape shaped by the integration of artificial intelligence tools in various academic facets. This proactive approach will foster a learning environment that embraces technological advancements and upholds the principles of honesty and responsible use. Institutional regulations on accountability and transparency should guide the frameworks that govern the use of AI in the campus environment (Pechenkina, 2023 ; Sun & Hoelscher, 2023 ; Dencik & Sanchez-Monedero, 2022 ).
Second, faculty members must proactively replace traditional coursework with modern alternatives that foster elevated levels of critical thinking among students, as suggested by Zhai ( 2022 ). Educators and learners can augment the academic material produced by ChatGPT with their own insights and information obtained from credible scholarly resources (Emenike & Emenike, 2023 ).
Third, ChatGPT should not be considered a threat to the education sector but a supplementary tool for human instruction that can enhance teaching and learning. It is imperative to acknowledge that the vital role of human educators cannot be replaced (Karaali, 2023 ) Moreover, ChatGPT can potentially enhance the accessibility and inclusivity of higher education. Alternative formats, linguistic support, and individualised explanations can help students who are studying English as a second language, are not native English speakers, or have other unique learning needs. Furthermore, Alnaqbi and Fouda ( 2023 ) highlight the implications of AI in evaluating the teaching style of faculty in higher education by collecting the feedback of students through social media and ChatGPT.
Fourth, the faculty in higher education institutions could address ethical concerns by providing students with explicit and comprehensive guidelines about the prescribed structure of academic assignments (Cotton et al., 2023 ; Gardner & Giordano, 2023 ). This practice can facilitate the production of more cohesive assignments. In addition, teachers can use rubrics to assess assignments and blend automated and manual assessment methodologies to evaluate students’ comprehension of the subject matter (Cotton et al., 2023 ; Shoufan, 2023 ).
In summary, using ChatGPT is recommended for enhancing creativity, refining writing proficiency, and improving research abilities. Nonetheless, it is crucial to emphasise that ChatGPT should not be employed as a substitute for critical thinking and producing original work. While it serves as a valuable tool for augmentation, upholding the integrity of independent thought and authentic content creation in academic endeavours is essential.
4.2 Limitations
The present study acknowledges several limitations. Firstly, the reliance on Scopus as the primary data source for bibliometric analysis may have limitations in capturing the full landscape of relevant literature. Future research may consider incorporating additional databases like Web of Science to ensure a comprehensive assessment. Secondly, due to the English language restriction in the review, potentially relevant studies may have been omitted. Future research could enhance inclusivity by extending its scope to encompass papers written in languages other than English. Thirdly, the current study exclusively focused on journal articles. Expanding the scope to include diverse sources, such as conference proceedings or book chapters, could offer a more comprehensive overview.
Additionally, as a rapidly evolving field, literature published after our inclusion dates need capturing, and future studies should consider adjusting their inclusion criteria to accommodate the dynamic nature of the subject matter. Lastly, the specificity of the bibliometric data search, centred around terms like ChatGPT, AI, higher education, and academic integrity, may have excluded certain relevant articles. Future studies should consider employing more generalised search parameters to encompass synonyms associated with these terms.
4.3 Future scope
The findings of the study suggest new avenues for future research. The effectiveness of evaluation criteria for assessments incorporating ChatGPT-generated text needs to be investigated. Specifically, the appropriate level of ChatGPT-produced text that students may use in academic tasks or assessments has not been established. Research on the ethical implications of using AI tools such as ChatGPT in higher education is also needed. Issues pertaining to data confidentiality, bias, and transparency in algorithms used for decision-making remain to be addressed. Feasible approaches for mitigating the excessive reliance of scholars and learners on ChatGPT or similar AI models are needed. Researchers could also explore the implementation of verification processes that go beyond traditional plagiarism detection methods, accounting for the unique challenges posed by AI systems. Future research in this domain could focus on establishing guidelines and best practices for the integration of AI tools like ChatGPT in academic settings, ensuring a balance between technological innovation and the preservation of academic rigour. Finally, the literature on ChatGPT in higher education has largely focused on the medical and tourism sectors. Future researchers must explore applications of ChatGPT in other disciplines.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Adetayo, A. J. (2023). ChatGPT and librarians for reference consultations. Internet Reference Services Quarterly , 27 (3), 131–147.
Article Google Scholar
AlAfnan, M. A., Dishari, S., Jovic, M., & Lomidze, K. (2023). ChatGPT as an educational tool: Opportunities, challenges, and recommendations for communication, business writing, and composition courses. Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Technology , 3 (2), 60–68. https://doi.org/10.37965/jait.2023.0184 .
Alnaqbi, N. M., & Fouda, W. (2023). Exploring the role of ChatGPT and social media in enhancing student evaluation of teaching style in higher education using Neutrosophic sets. International Journal of Neutrosophic Science , 20 (4), 181–190.
Angelis, L. D., Baglivo, F., Arzilli, G., Privitera, G. P., Ferragina, P., Tozzi, A. E., & Rizzo, C. (2023). ChatGPT and the rise of large language models: The new AI-driven infodemic threat in public health. Frontiers in Public Health , 11 , 1–8.
Archambault, E., Campbell, D., Gingras, Y., & Larivière, V. (2009). Comparing bibliometric statistics obtained from the web of Science and Scopus. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology , 60 (7), 1320–1326.
Bajaj, Y., Kashiramka, S., & Singh, S. (2020). Application of capital structure theories: A systematic review. Journal of Advances in Management Research , 18 (2), 173–199. https://doi.org/10.1108/JAMR-01-2020-001 .
Bauer, E., Greisel, M., Kuznetsov, I., Berndt, M., Kollar, I., Dresel, M., Fischer, M. R., & Fischer, F. (2023). Using natural language processing to support peer-feedback in the age of artificial intelligence: A cross-disciplinary framework and a research agenda. British Journal of Educational Technology , 54 (5), 1222–1245.
Boyack, K. W., & Klavans, R. (2010). Co-citation analysis, bibliographic coupling, and direct citation: Which citation approach represents the research front most accurately? Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology , 61 (12), 2389–2404.
Cingillioglu, I. (2023). Detecting AI-generated essays: The ChatGPT challenge. International Journal of Information and Learning Technology , 40 (3), 259–268. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJILT-03-2023-0043 .
Clark, T. M. (2023). Investigating the Use of an Artificial Intelligence Chatbot with General Chemistry exam questions. Journal of Chemical Education , 100 (5), 1905–1916.
Cotton, D. R. E., Cotton, P. A., & Shipway, J. R. (2023). Chatting and cheating: Ensuring academic integrity in the era of ChatGPT. Innovations in Education and Teaching International , 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2190148 .
Crawford, J., Cowling, M., & Allen, K. (2023). Leadership is needed for ethical ChatGPT: Character, assessment, and learning using artificial intelligence (AI). Journal of University Teaching & Learning Practice , 20 (3), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.3.02 .
Crompton, H., & Burke, D. (2023). Artificial intelligence and higher education: The state of the field. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education , 20 , 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-023-00392-8 .
Dehouche, N. (2021). Plagiarism in the age of massive generative pre-trained transformers (GPT-3). Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics , 2 , 17–23. https://doi.org/10.3354/esep00195 .
Dencik, L., & Sanchez-Monedero, J. (2022). Data justice. Internet Policy Review , 11 (1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.14763/2022.1.1615 .
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., & Pattnaik, D. (2020). Forty-five years of Journal of Business Research : A bibliometric analysis. Journal of Business Research , 109 , 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.10.039 .
Emenike, M., & Emenike, B. (2023). Was this title generated by ChatGPT? Considerations for artificial intelligence text-generation software programs for chemists and chemistry educators. Journal of Chemical Education , 100 (4), 1413–1418. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00063 .
Eysenbach, G. (2023). The role of ChatGPT, generative language models, and artificial intelligence in medical education: A conversation with ChatGPT and a call for papers. JMIR Medical Education , 6 (9), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.2196/46885 .
Farrokhnia, M., Banihashem, K. S., Noroozi, O., & Wals, A. (2023). A SWOT analysis of ChatGPT: Implications for educational practice and research. Innovations in Education and Teaching International , 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2195846 .
Fergus, S., Botha, M., & Ostovar, M. (2023). Evaluating academic answers generated using ChatGPT. Journal of Chemical Education , 100 (4), 1672–1675. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00087 .
Firat, M. (2023). How chat GPT can transform autodidactic experiences and open education. Department of Distance Education, Open Education Faculty , Anadolu University, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/9ge8m .
Gardner, D. E., & Giordano, A. E. (2023). The challenges and value of undergraduate oral exams in the physical chemistry classrooms: A useful tool in the assessment toolbox. Journal of Chemical Education , 100 (5), 1705–1709.
Geerling, W., Mateer, G. D., Wooten, J., & Damodaran, N. (2023). ChatGPT has aced the test of understanding in college economics: Now what? The American Economist , 68 (2), 233–245.
Gilson, A., Safranek, C. W., Huang, T., Socrates, V., Chi, L., Taylor, R. A., & Chartash, D. (2023). How does ChatGPT perform on the United States medical licensing examination? The implications of large language models for medical education and knowledge assessment. JMIR Medical Education , 9 , 1–9. https://doi.org/10.2196/45312 .
Gisev, N., Bell, J. S., & Chen, T. F. (2013). Interrater agreement and interrater reliability: Key concepts, approaches, and applications. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy , 9 (3), 330–338.
Gupta, R., Pandey, R., & Sebastian, V. J. (2021). International entrepreneurial orientation (IEO): A bibliometric overview of scholarly research. Journal of Business Research , 125 , 74–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.12.00 .
Ibrahim, H., Asim, R., & Zaffar, F. (2023). Rethinking homework in the age of artificial intelligence. Intelligent Systems , 38 (2), 24–27.
Google Scholar
Iskender, A. (2023). Holy or Unholy? Interview with Open AI’s ChatGPT. European Journal of Tourism Research , 34 , 3414. https://doi.org/10.54055/ejtr.v34i.3169 .
Ivanov, S., & Soliman, M. (2023). Game of algorithms: ChatGPT implications for the future of tourism education and research. Journal of Tourism Futures , 9 (2), 214–221.
Jarneving, B. (2007). Bibliographic coupling and its application to research-front and other core documents. Journal of Informetrics , 1 (4), 287–307.
Jeon, J., Lee, S., & Cho, S. (2023). A systematic review of research on speech-recognition chatbots for language learning: Implications for future directions in the era of large language models. Interactive Learning Environment , 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2023.2204343 .
Johinke, R., Cummings, R., & Di Lauro, F. (2023). Reclaiming the technology of higher education for teaching digital writing in a post-pandemic world. Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practice , 20 (2), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.02.01 .
Karaali, G. (2023). Artificial Intelligence, Basic skills, and quantitative literacy. Numeracy , 16 (1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.5038/1936-4660.16.1.1438 .
Kasneci, E., Seßler, K., Küchemann, S., Bannert, M., Dementieva, D., Fischer, F., & Kasneci, G. (2023). ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learning and Individual Differences , 103 (2023), 102274–102271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2023.102274 .
Lawrie, G. (2023). Establishing a delicate balance in the relationship between artificial intelligence and authenticate assessment in student learning. Chemistry Education Research and Practice , 24 (2), 392–393.
Lee, H. (2023). The rise of ChatGPT: Exploring its potential in medical education. Anatomical Science Education , 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.2270 .
Li, Y., Sha, L., Yan, L., Lin, J., Raković, M., Galbraith, K., Lyons, K., Gašević, D., & Chen, G. (2023). Can large language models write reflectively. Computer and Education: Artificial Intelligence , 4 (2023), 100140–100141.
Liebrenz, M., Schleifer, R., Buadze, A., Bhugra, D., & Smith, A. (2023). Generating scholarly content with ChatGPT: Ethical challenges for medical publishing. Lancet Digital Health , 5 (3), e105–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(23)00019-5 .
Lim, W. M., Gunasekara, A., Pallant, J. L., Pallant, J. I., & Pechenkina, E. (2023). Generative AI and the future of education: Ragnarök or reformation? A paradoxical perspective from management educators. The International Journal of Management Education , 21 (2), 1–13.
Lin, C. C., Huang, A. Y. Q., Stephen, J. H., & Yang (2023). A review of AI-Driven conversational chatbots implementation methodologies and challenges (1999–2022). Sustainability , 15 (5), 4012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054012 .
Memarian, B., & Doleck, T. (2023). ChatGPT in education: Methods, potentials and limitations. Computers in Human Behavior: Artificial Humans , 100022 , 1–11.
Mishra, D., Gunasekaran, A., Papadopoulos, T., & Hazen, B. (2017). Green supply chain performance measures: A review and bibliometric analysis. Sustainable Production and Consumption , 10 , 85–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2017.01.003
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., & The PRISMA Group. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Annals of Internal Medicine , 151 (4), 264–269.
Nautiyal, R., Albrecht, J. N., & Nautiyal, A. (2023). ChatGPT and tourism academia. Annals of Tourism Research , 99 , 1–3.
Neumann, M., Rauschenberger, M., & Schon, E-M. (2023). 2023 IEEE/ACM 5th International Workshop on Software Engineering Education for the Next Generation (SEENG), Melbourne, Australia, 2023, pp. 29–32, https://doi.org/10.1109/SEENG59157.2023.00010 .
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., … & Moher, D. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ , 372 (71), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Palomo, J., Figueroa-Domecq, C., & Laguna, P. (2017). Women, peace and security state-of-art: A bibliometric analysis in social sciences based on SCOPUS database. Scientometrics , 113 (1), 123–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2484-x .
Patrício, L. D., & Ferreira, J. J. (2020). Blockchain security research: Theorizing through bibliographic-coupling analysis. Journal of Advances in Management Research , 18 (1), 1–35. https://doi.org/10.1108/JAMR-04-2020-0051 .
Paul, J., Lim, W. M., O’Cass, A., Hao, A. W., & Bresciani, S. (2021). Scientific procedures and rationales for systematic literature reviews (SPAR-4-SLR). International Journal of Consumer Studies . https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12695 .
Pechenkina, K. (2023). Artificial intelligence for good? Challenges and possibilities of AI in higher education from a data justice perspective. In L. Czerniewicz, & C. Cronin (Eds.), Higher education for good: Teaching and learning futures (#HE4Good) . Open Book.
Perkins, M. (2023). Academic integrity considerations of AI large Language models in the post-pandemic era: ChatGPT and beyond. Journal of University Teaching & Learning Practice , 20 (2), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.02.07 .
Rahman, M., Mostafizer, & Yutaka Watanobe. (2023). ChatGPT for Education and Research: Opportunities, threats, and strategies. Applied Sciences , 13 (9), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095783 .
Rana, S. (2023). AI and GPT for Management scholars and practitioners: Guidelines and implications. FIIB Business Review , 12 (1), 7–9.
Seetharaman, R. (2023). Revolutionising medical education: Can ChatGPT boost subjective learning and expression? Journal of Medical System , 47 (61), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-023-01957-w .
Seth, I., Bulloch, G., & Lee, C. H. A. (2023). Redefining academic integrity, authorship, and innovation: The impact of ChatGPT on surgical research. Annals of Surgical Oncology , 30 , 5284–5285. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-023-13642-w .
Shoufan, A. (2023). Exploring students’ perceptions of ChatGPT: Thematic analysis and follow-up survey. IEEE Access , 11, 38805–38818, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3268224 .
Singh, V. K., Singh, P., Karmakar, M., Leta, J., & Mayr, P. (2021). The journal coverage of web of Science, Scopus and dimensions: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics , 126 , 5113–5142.
Skavronskaya, L., Hadinejad, A., & Cotterell, D. (2023). Reversing the threat of artificial intelligence to opportunity: A discussion of ChatGPT in tourism education. Journal of Teaching in Travel & Tourism , 23 , 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/15313220.2023.2196658 .
Strzelecki, A. (2023). To use or not to use ChatGPT in higher education? A study of students’ acceptance and use of technology. Interactive Learning Environments , 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2023.2209881 .
Su, J., & Yang, W. (2023). Unlocking the power of ChatGPT: A framework for applying generative AI in education. ECNU Review of Education , 6 (3), 355–366.
Subramani, M., Jallel, I., & Mohan, S. K. (2023). Evaluating the performance of ChatGPT in medical physiology university examination of phase I MBBS. Advances in Physical Education , 47 , 270–271.
Sun, G. H., & Hoelscher, S. H. (2023). The ChatGPT Storm and what Faculty can do. Nurse Educator , 48 , 119–124.
Tang, G. (2023a). Academic journals cannot simply require authors to declare that they used ChatGPT. Irish Journal of Medical Science , 192 (6), 3195–3196.
Tang, G. (2023b). Letter to editor: Academic journals should clarify the proportion of NLP-generated content in papers. Accountability in Research , 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1080/08989621.2023.2180359 .
Teixeira da Silva, J. A. (2023). How are authors’ contributions verified in the ICMJE model? Plant Cell Reports , 42 , 1529–1153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-023-03022-9 .
Thorp, H. H. (2023). ChatGPT is fun, but not an author. Science , 379 (6630), 313–313.
Tlili, A., Shehata, B., Adarkwah, M., Bozkurt, A., Hickey, D. T., Huang, R., & Agyemang, B. (2023). What if the devil is my guardian angel: ChatGPT as a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart Learning Environments , 10 (15), 1–24.
Van Eck, N., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics , 84 (2), 523–538.
Vijaya, V., & Mathur, H. P. (2023). A decade of donation-based crowdfunding: A bibliometric analysis using the SCOPUS Database. Purushartha , 15 (2), 32–51.
Vogels, E. A. (2023). A majority of Americans have heard of ChatGPT, but few have tried it themselves, https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2023/05/24/a-majority-of-americans-have-heard-of-chatgpt-but-few-have-tried-it-themselves/ .
Wu, R., & Yu, Z. (2023). Do AI Chatbots improve students learning outcome? Evidence from a meta analysis. British Journal of Educational Technology . https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.13334 .
Wu, T. Y., He, S. Z., Liu, J. P., Sun, S. Q., Liu, K., Han, Q. L., & Tang, Y. (2023). A brief overview of ChatGPT: The history, status quo and potential future development. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica , 10 (5), 1122–1136. https://doi.org/10.1109/JAS.2023.123618 .
Yan, D. (2023). Impact of ChatGPT on learners in a L2 writing practicum: An exploratory investigation. Education and Information Technologies , 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11742-4 .
Yeadon, W., Inyang, O-O., Mizouri, A., Peach, A., & Testrow, C. P. (May 2023). The death of the short-term physics essay in the coming AI revolution. Physics Education , 58 , 1–13.
Zhai, X. (2022). ChatGPT user experience: Implications for education. SSRN , 4312418 , 1–18.
Download references
Open Access funding enabled and organized by CAUL and its Member Institutions
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University Business School, Maharaja Ranjit Singh Punjab Technical University, Punjab, India
Pritpal Singh Bhullar
Department of Financial Planning and Tax, School of Accounting, Information Systems and Supply Chain, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia
Mahesh Joshi
School of Engineering and Technology, CML‑NET & CREATE Research Centres, Central Queensland University, Queensland, Australia
Ritesh Chugh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ritesh Chugh .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
No Conflict of Interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Bhullar, P.S., Joshi, M. & Chugh, R. ChatGPT in higher education - a synthesis of the literature and a future research agenda. Educ Inf Technol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12723-x
Download citation
Received : 04 October 2023
Accepted : 16 April 2024
Published : 02 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12723-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Artificial Intelligence
- Generative AI
- Higher education
- Academic integrity
- Systematic review
- Bibliometric analysis
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Check your Paper and get a Report with Plagiarism Percentage. Free Usage ⌛Quick Results ☝️ High Quality. Services ... Many professional writing services use a plagiarism checker for research paper. However, students sometimes forget that they should too. But with so many options that pop up when you ask Google to "check my paper for ...
Our plagiarism checker, AI Detector, Citation Generator, proofreading services, paraphrasing tool, grammar checker, summarize, and free Knowledge Base content are designed to help students produce quality academic papers. We make every effort to prevent our software from being used for fraudulent or manipulative purposes.
Easily check your paper for missing citations and accidental plagiarism with the EasyBib plagiarism checker. The EasyBib plagiarism checker: Scans your paper against billions of sources. Identifies text that may be flagged for plagiarism. Provides you with a plagiarism score. You can submit your paper at any hour of the day and quickly receive ...
Self plagiarism: "Publication of one's own data that have already been published is not acceptable since it distorts scientific record." 1 Self-plagiarized publications do not contribute to scientific work; they just increase the number of papers published without justification in scientific research. 8 The authors get benefit in the form of increased number of published papers. 8 Self ...
Creative thinking and plagiarism. Plagiarism is often revealed in works of novice non-Anglophone authors who are exposed to a conservative educational environment that encourages copying and memorizing and rejects creative thinking [12, 13].The gaps in training on research methodology, ethical writing, and acceptable editing support are also viewed as barriers to targeting influential journals ...
Plagiarism can be detected by your professor or readers if the tone, formatting, or style of your text is different in different parts of your paper, or if they're familiar with the plagiarized source.. Many universities also use plagiarism detection software like Turnitin's, which compares your text to a large database of other sources, flagging any similarities that come up.
5. Mosaic or Patchwork Plagiarism. One of the more mischievous ways to abstain from writing original work is mosaic plagiarism. Patchwork or mosaic plagiarism occurs when an author stitches together a research paper by lending pieces from multiple sources and weaving them as their creation.
To avoid plagiarism, you need to correctly incorporate these sources into your text. You can avoid plagiarism by: Keeping track of the sources you consult in your research. Paraphrasing or quoting from your sources (by using a paraphrasing tool and adding your own ideas) Crediting the original author in an in-text citation and in your reference ...
Plagiarism Checker Benefits. Whether producing original content or verifying that of others, there's a lot to gain from using a plagiarism checker. Accurate, automatic detection of duplicate content facilitates the copy-checking process for teachers, students, content writers, and more. Results showing the exact percentage of plagiarized ...
AcademicHelp's Research Paper Plagiarism Checker is more than simply a tool; it's also a scholarly excellence companion. This specialized scanner is intended to suit the specific requirements of researchers, instructors, and students engaged in advanced learning. By ensuring that your research articles are unique and have integrity, you may ...
Using the plagiarism and AI checker is easy. You paste your paper text or upload your writing and set the tool to check for plagiarism or AI produced text. Our AI already knows to eliminate commonly grouped together words or phrases to avoid highlighting these common terms as plagiarism. It then highlights material you submitted that is ...
Run your academic papers through our plagiarism check to identify similarity or overlooked citations. Step 2. Review report for actionable items. ... Self-plagiarism in research: What it is and how to avoid it. Self-plagiarism in research should be strictly avoided. Yet, it's quite common to find early career researchers, and sometimes even ...
There are ways to avoid plagiarism, and should just be followed simple steps when writing a paper. There are several ways to avoid plagiarism ( 1, 6 ): Paraphrasing - When information is found that is great for research, it is read and written with own words. Quote - Very efficient way to avoid plagiarism.
Free Online Plagiarism Checker. Paste the text of your paper or essay into the editor below (or upload a file) and select the "Get Report" button to immediately check your paper for plagiarism. Upload File. By uploading, your document will be auto-corrected by our grammar checker and will be shared on our. Student Brands websites.
An intellectual pr oduct of one's own. It is no accident that plagiarism is discussed in relation to research, although it is also clearly. relevant in r elation to music, literature, art, and ...
Research methodology. The plagiarism tools in this research are tested using 4 test documents, ranging from unedited to heavily edited.. Each test document consisted of plagiarized sections from 140 sources like Wikipedia articles, news articles, open-access journal articles, websites, theses and dissertations, and PDFs.. This setup allowed us to analyze:
Plagiarism is a well-known and growing issue in the academic world. It is estimated to make up a substantial part of the total number of serious deviations from good research practice (Titus et al. 2008; Vitse and Poland 2012).For some journals it is indeed a serious problem, with up to a third of the published papers containing plagiarism (Zhang 2010; Baždaric et al. 2012; Butler 2010).
Guard yourself against plagiarism, however accidental it may be. Here are some guidelines to avoid plagiarism. 1. Paraphrase your content. Do not copy-paste the text verbatim from the reference paper. Instead, restate the idea in your own words. Understand the idea (s) of the reference source well in order to paraphrase correctly.
How to Avoid Plagiarism. It's not enough to know why plagiarism is taken so seriously in the academic world or to know how to recognize it. You also need to know how to avoid it. The simplest cases of plagiarism to avoid are the intentional ones: If you copy a paper from a classmate, buy a paper from the Internet, copy whole passages from a ...
(A tip "In the case of plagiarism detected there is a great option (button) to make it unique with the BEST Paraphrasing tool."). In case no matches are found, a message will display "100% Unique" So, if you ever need to do a quick plagiarism check or are looking for free plagiarism software online, DupliChecker.com is the place for it! Besides, we would love to get suggestions and ...
Committee on publication ethics definition. In 1999, the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) defined plagiarism as, "plagiarism ranges from the unreferenced use of others' published and unpublished ideas, including research grant applications to submission under "new" authorship of a complete paper, sometimes in a different language.
Paper mills — organizations that churn out fake research papers and sell authorships to turn a profit — have been known to tamper with reviews ... Preventing plagiarism . Publishers seem to be ...
Plagiarism in universities is a problem with potential academic, social, ethical, and legal implications. Systematic review research on academic integrity programs, including plagiarism, has been conducted, but few studies have assessed plagiarism. Therefore, this review synthesizes knowledge on the effect of educational interventions designed to prevent or reduce plagiarism by university ...
Embattled Columbia University president Nemat "Minouche" Shafik screwed a former underling out of credit on a research paper published 30 years ago, a Yale University professor claims. Ahmed ...
Certainly, database search for papers tagged for plagiarism is limited to indexed journals only, which keeps non-indexed journals (both low-quality and deceptive journals) out of focus.5,21 Moreover, journal coverage may vary from one database to the other as reported in a recent paper on research dissemination in South Asia.22 Therefore, both ...
ChatGPT has emerged as a significant subject of research and exploration, casting a critical spotlight on teaching and learning practices in the higher education domain. This study examines the most influential articles, leading journals, and productive countries concerning citations and publications related to ChatGPT in higher education, while also shedding light on emerging thematic and ...