Essay on Operations Management
Operations management is the process of managing the production of goods and services. Thus operations is a broad term that encompasses both hard-goods manufacturing management and service management.
Traditionally, the term ‘production’ brings to mind smokestacks, assembly lines and machine shops. However, the functional field of production and operations management (P/OM) refers to the broader idea of the producing activities of all kinds of organisations — manufacturing or service, public or private, large or small, profit or non-profit.
Operations management refers to the set of managerial activities that organisations engage in to create their products and services.
These activities were earlier called “production management”. In those days, “production” seemed to focus too narrowly on manufacturing. When managers began to expand their view of production to include services and other intangible products, the term “production and operations management” evolved. So “operations management” is rapidly becoming the generally accepted phrase.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Operations and Conversion Processes:
Operations, as a conversion process, can be visualised as consisting of the elements shown as solid lines in Fig. 22.1. Let us examine the inputs, conversion processes, outputs and feedback and control cycle depicted in the figure from an operations perspective.
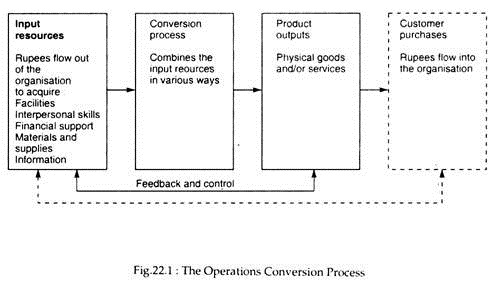
Product Outputs:
The primary driving force of operations management is the desired end- product(s). Operations managers and operative employees must have a clear and precise definition of the product(s), including the key product attributes, the important quality characteristics, and quality standards for each attribute.
They also need to know how many of each product are needed and at what times to meet customer demand. In other words, operations employees need a clear picture of what they are trying to accomplish in their day-to-day activities.
Conversion Process:
Conversion processes may involve any of several different types of technologies, and technologies vary widely. Petroleum processing in a refinery operation utilises a continuous-process technology; automobile manufacturers employ primarily a mass-production technology; an aircraft manufacturer uses unit or small-batch technology.
Operations relies on receiving resources from other parts of the organisation and from the external environment of business. Operations cannot occur for very long without continuous supply of inputs. Some of these resources are more or less permanent, such as buildings and land devoted to production, whereas others are transient resources that are consumed fully on a day-to-day basis, such as raw materials and office supplies.
Feedback and Control:
Operations management systems are directed toward achieving goals. Once operations goals are established, controls help the system conform to standards of efficiency and effectiveness. Managers obtain information for evaluating system performance by monitoring various stages of the conversion process, the inputs and the product outputs.
The control system must provide timely information so that appropriate actions can be taken. Deviations from control standards are a prime basis for changing the inputs, the conversion process, or even the product or service design.
Operations as a Management Challenge:
The problems they face revolve around the acquisition and utilisation of resources for conversion. Some familiar operations activities and roles include purchasing, production forecasting, work flow and process analysis, job design, inventory control, production scheduling, quality control supervision, and manufacturing management.
These activities and roles seek to achieve balance and consistency among the three elements: inputs, the conversion process and outputs. These elements, in turn, must be in balance with and consistent with the other functions of the overall organisation. Therefore, each organisation has different expectations of its operations function, and the operations function in one organisation has different capabilities from that in another.
A set of product output specification that cannot be achieved in one conversion process may perhaps be easily met in another. The capability of the process, then, must match the output goals. A mismatch requires managers to decide whether to change the goals, product or conversion process. Similarly, input resources must be consistent with and supportive of the conversion process and its product output goals.
The proper outputs flowing from the conversion process indicate that the operations function is effective. Such success is usually not an accident, or at least sustained success is not. To maintain successful operations the production system must extend well beyond the operations activities.
In Fig. 22.1, for example, the dashed lines show the completion of the monetary resource cycle, emphasising that consumed outputs create the monetary resources that sustain operations and all other activities of the organisation.
In other words, products must be sold. Because the available monetary resources are limited, managers try to allocate them in a rational manner among all the organisation’s activities, including the operations function, by developing plans.
Related Articles:
- 2 Activities Performed by Operations Management
- Operations Design (With Diagram)| Management
- 7 Most Important Features of Management
- Production System: Concept and Models | Industries | Production Management

We use cookies
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
How to Write the Conclusion for a Report on Operations Management
by Gwendolen Akard
Published on 26 Sep 2017
Operations management is a broad area of business management that involves labor relations, statistics, manufacturing control, and policy creation, among other things. The conclusion for a report on operations management should be fairly in-depth and free of fluff, but at the same time goal oriented.
Reiterate the main theme of the report. What was the problem or issue discussed in the report? What factors were talked about? Touch briefly upon each of these things as an introductory part of the conclusion.
Evaluate whether the issue was solved, if there was one. What was changed? What still needs to be improved upon?
Talk about future goals. Which are the most important? Reducing production time, improving employee training, controlling costs, etc. are examples of operations management goals that might be considered.
Briefly discuss strategies to achieve any goals. What is the number one thing that needs to be achieved for business to more forward?
Avoid fluff. The point of a report on operations management is to evaluate the systems in place, not to act as a feel-good essay. That being said, it is good to end on a positive, goal-oriented note.
Don’t include statistics in the conclusion. Stay away from fluff at all costs. Summarize, clarify, and create goals.

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
118 Operations Management Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Operations management is a crucial aspect of any organization, as it involves overseeing the production of goods and services efficiently and effectively. As a student studying operations management, you may be required to write essays on various topics related to this field. To help you brainstorm ideas for your next essay, here are 118 operations management essay topic ideas and examples:
- The role of operations management in achieving organizational goals
- The importance of quality management in operations
- Lean manufacturing principles and their impact on operations
- Just-in-time inventory management and its benefits
- Total quality management and its implementation in organizations
- The relationship between operations management and supply chain management
- The impact of technology on operations management
- The concept of value stream mapping in operations
- Operations management strategies for reducing waste
- The role of forecasting in operations management
- The benefits of implementing Six Sigma in operations
- The impact of globalization on operations management
- The use of data analytics in operations management
- The role of operations managers in decision-making
- The challenges of managing operations in a service industry
- The importance of capacity planning in operations management
- The impact of inventory management on customer satisfaction
- The role of operations management in sustainability
- The benefits of implementing a just-in-time production system
- The impact of e-commerce on operations management
- The concept of supply chain integration in operations management
- The role of operations management in disaster recovery planning
- The impact of outsourcing on operations management
- The importance of process mapping in operations management
- The benefits of implementing a quality management system
- The challenges of managing operations in a global supply chain
- The role of operations management in reducing costs
- The impact of inventory control on operations efficiency
- The concept of process improvement in operations management
- The benefits of implementing a lean production system
- The challenges of managing operations in a fast-paced environment
- The impact of technology on supply chain management
- The role of operations management in customer relationship management
- The benefits of implementing a continuous improvement program
- The challenges of managing operations in a regulated industry
- The impact of automation on operations management
- The role of operations management in new product development
- The benefits of implementing a just-in-time delivery system
- The challenges of managing operations in a competitive market
- The impact of logistics on operations management
- The role of operations management in risk management
- The benefits of implementing a total quality management system
- The challenges of managing operations in a complex environment
- The impact of inventory optimization on operations efficiency
- The role of operations management in supply chain visibility
- The benefits of implementing a demand forecasting system
- The challenges of managing operations in a volatile market
- The impact of digital transformation on operations management
- The role of operations management in sustainability initiatives
- The benefits of implementing a lean manufacturing system
- The challenges of managing operations in a rapidly changing industry
- The impact of supply chain disruptions on operations management
- The role of operations management in supplier relationship management
- The benefits of implementing a continuous improvement culture
- The challenges of managing operations in a global economy
- The impact of demand variability on operations efficiency
- The role of operations management in product lifecycle management
- The benefits of implementing a just-in-time manufacturing system
- The challenges of managing operations in a highly regulated industry
- The impact of technology on inventory management
- The role of operations management in supply chain risk management
- The benefits of implementing a quality control system
- The challenges of managing operations in a complex supply chain
- The impact of process automation on operations efficiency
- The role of operations management in demand planning
- The benefits of implementing a lean supply chain
- The challenges of managing operations in a dynamic market
- The impact of supply chain collaboration on operations management
- The role of operations management in product design
- The benefits of implementing a demand planning system
- The challenges of managing operations in a fast-paced industry
- The impact of technology on supply chain visibility
- The role of operations management in supply chain optimization
- The benefits of implementing a lean distribution system
- The challenges of managing operations in a highly competitive market
- The impact of demand forecasting on operations efficiency
- The role of operations management in supplier performance management
- The benefits of implementing a quality assurance system
- The impact of process improvement on operations efficiency
- The role of operations management in inventory optimization
- The benefits of implementing a just-in-time inventory system
- The challenges of managing operations in a volatile environment
- The impact of technology on demand forecasting
- The role of operations management in supply chain resilience
- The benefits of implementing a continuous improvement process
- The challenges of managing operations in a rapidly changing market
- The impact of supply chain disruptions on operations efficiency
- The role of operations management in supplier risk management
- The benefits of implementing a quality management program
- The challenges of managing operations in a complex industry
- The impact of process automation on supply chain management
- The role of operations management in demand variability
- The benefits of implementing a lean production process
- The challenges of managing operations in a regulated market
- The impact of technology on inventory control
- The role of operations management in supply chain agility
- The benefits of implementing a just-in-time manufacturing process
- The impact of demand planning on operations efficiency
- The role of operations management in supplier collaboration
- The challenges of managing operations in a dynamic supply chain
- The impact of process optimization on operations efficiency
- The role of operations management in inventory management
- The benefits of implementing a lean supply chain system
- The challenges of managing operations in a fast-paced market
- The impact of technology on supply chain optimization
- The role of operations management in demand forecasting
- The challenges of managing operations in a competitive industry
- The impact of supply chain collaboration on operations efficiency
- The role of operations management in product development
- The benefits of implementing a demand planning process
- The role of operations management in supplier performance
- The benefits of implementing a quality assurance program
In conclusion, operations management is a diverse and complex field that requires careful planning and execution to ensure the efficient production of goods and services. By choosing one of the above topics for your next essay, you will be able to delve deeper into the various aspects of operations management and gain a better understanding of how it impacts organizations. Good luck with your essay writing!
Want to research companies faster?
Instantly access industry insights
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Leverage powerful AI research capabilities
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2024 Pitchgrade
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Operations Management, Essay Example
Pages: 1
Words: 263
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Operations managers are in charge of managing activities that contribute to the production of goods and/or services. Being an Operations Manager in Wal-Mart, my direct responsibilities consist of managing the operations procedure (planning, organizing, implementing, improving) and operations approach. My indirect responsibilities involve cooperating and communicating with executives whose roles and decisions influence operations (personnel, finance, and marketing).
Planning and forecasting relates to the future impact of today’s resolution and is the primary function of management, including Operations Management. In order for a manager to plan and forecast, he/she has to clearly understand and appreciate the organization’s vision and mission in the contemporary world of fierce competition. Motivational support of the entire business combined with the culture and values set by the top management should supply an Operations Manager with planning tips and assist with satisfying the customers. Planning is essential for getting a clear picture of organizational objectives and calculating the possible outcomes of important or minor decisions. Planning helps to build a visible framework for effective decision making process. Moreover, planning reduces the possibility of a crisis and saves valuable resources.
In order for me to generate forecasts and plans while working for Wal-Mart, I would carefully study the areas of my responsibility: Asset Management, Human Resource Management, and Cost Management. Planning to create workshops for employees, hire new professional workers and managers, checking the equipment and forecasting the product shortages, preparing for the acquisition of cheaper or more expensive resources is what this job calls for.
Galloway, L. (1998) Principles of Operations Management , ITP.
Lewis, J. (2005). Project Planning, Scheduling, and Control . McGraw Hill.
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Occupational Safety and Health Administration Assignment, Research Paper Example
Ethnic Humor, Essay Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Business Operations Management
What I Learned in Operations Management: Insights and Perspectives
Table of contents, introduction, strategic importance of operations, efficiency vs. effectiveness, process design and improvement, supply chain dynamics, capacity planning and resource allocation, managing quality and customer satisfaction, decision-making in uncertainty, technology and innovation, collaboration and communication.
*minimum deadline
Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below

- Leadership Development
- Service Marketing
- Competition
Related Essays
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
- The Open University
- Accessibility hub
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University
My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning
About this free course
Become an ou student, download this course, share this free course.

Start this free course now. Just create an account and sign in. Enrol and complete the course for a free statement of participation or digital badge if available.
Congratulations! You have now reached the end of this free course, Introduction to operations management . This course has introduced the operations management function to you. After studying this course, you should now feel that you can:
- define the roles and responsibilities of operations managers and the challenges they face, with them usually controlling most of an organisation’s assets, and being responsible for the design, planning and improvement of their processes
- understand the input–process–output framework, and extensions of it, and apply it to a wide range of operations
- examine the types of transformation processes occurring within operations, converting input resources to value-added outputs
- understand that well-designed and well-run operations can impact on the long-term competitiveness of an organisation, and badly run operations expose the organisation to many risks – sometimes relatively simple errors in management can lead to very costly failures that go beyond simple rework or waste
- analyse the content of an operations strategy
- know that if you manage any type of resource, you can consider yourself to be an operations manager as you will be responsible for some kind of process.
This OpenLearn course is an adapted extract from the Open University course B207 Shaping business opportunities [ Tip: hold Ctrl and click a link to open it in a new tab. ( Hide tip ) ] .
- WRITING CENTER
- CUSTOMER AREA
- Client Reviews
- Our Writers
- Sample Papers
- Study Resources
Get Your Grades Improved by Our Professional Writers - We are Trusted by Thousands of Students!
Global compose inc. constantly employs professional homework writing help writers from usa, uk, ca and au. the writers are highly trained professionals, comprising of 500+ masters and ph.d level writers available 24/7. we assist clients who either have difficulty completing their assignments, sick or in need family time. to get started, submit your instructions., calculate your order price.
Use Discount Code: FIRST5 at Checkout FIRST5 -->
PRICE BEFORE DISCOUNT: $15.00
- Essay Writing Examples
Sample Essay on Operations Management
Get Homework Help on this topic - Check the Quality of Writing from this Sample
If you are looking for assignment help on this topic or similar topic, click on order now button to submit your details. once we have your order details, your assignment will be assigned to one of our best writers, who will then proceed to write your paper and deliver it within your specified deadline. thank you for choosing us today.
Introduction
A contemporary organization strives to excel in lean production, customer-centric provision, flexible manufacturing, and large customization among others. The capability to attain these qualities aids organizations sustain their operations. Operation management is about transforming ideas into products and planning as well as controlling all structures and the systems that generate services and goods. Customers need products that can meet their needs and ensure they get value for money. Such products are supposed to be affordable, dependable, exclusive, and standardized. Effective operations management has the capability of adding value to its venture by increasing productivity, cost minimization, and development of quality products. Operations management ought to know the kind of customers they deal with in order to prioritize their needs. The purpose of this study is to analyze and discuss the importance of operations management industries.
Importance of Operations Management to Industry
All the business organizations place emphasis on how to flourish and survive in future. How an organization is able to manage its resources is what determines how it related to its external environment and the ability it has to meet the needs of stakeholders. Operations management is crucial in an industry since it helps in administration of industry resources. It is a vital part of the industry’s strategy. Operations management is of great importance since it exercises an approach that is systematic to the production of goods. For example, a manufacturer of an electrical bulb processes raw material though use of productive resources, however, the results are bulbs of different ratings (Mahadevan 4). As such, operation management offers an approach that is systematic in transformation of raw materials into quality products and generation of revenue.
Operations management is important in reduction of production costs. Whenever an industry produces a variety of products in large scale and uses the latest technology, the costs of production decline as a result of economies of scale.
MTR Foods is one of the fastest-growing companies in India dealing with food processing with a market turnover of US$ 20million (Mahadevan 3). The growth is the result of technological ability and the quality of its products. MTR deals in production of various products familiar to both domestic and the foreign customers. Most of these are ready-to-eat products that attract a large number of customers. Additionally, the manufacturing facility of MTR Foods is located at environs of Bangalore, where labor is guaranteed to be cheap.
Efficient operations management thus is fundamental in helping the industry improve its revenue earnings. This is achieved through production of quality products and increase in customer satisfaction. Operations must be flexible to adapt to changes required by customers. Industrial products are tangible and once made, it is difficult to change the products. As such, quality management is an aspect that is crucial in an industry. Perception of products plays a crucial role in the mind of customers regarding the quality of the company’s products.
The amount an industry invests in production of goods can easily be reduced through operations management. Operations management aims at reduction of costs and acquiring higher revenues through controlling and cautious operations. A lean manufacturing strategy is what helped Toyota Company eradicate unnecessary resources that were not adding value to its products. Operations management inspires innovations in utilization of industry resources and identification of non-value added resources. Technological changes have permitted industries to streamline processes, as well as improve on supply chain collaboration.
Majority of multinational corporations have enjoyed success in the global arena as a result of efficient operation managements. Toyota Company has achieved remarkable success for years as a result of its aggressive marketing and production of what customers in western countries want (Brown, Bessant and Lammings 31). Affordability, design, reliability and durability make customers across the globe refer Toyota cars to others from western nations. Spare parts are readily available as well making maintenance of Japanese automobiles easier. Toyota Company has been capable of value chain creation in its products as a result of its efficient operations management.
Operations management creates basis of innovation by establishing a foundation for knowledge and operations in the industry. Success of the iPod, Apple’s product was the result of its sleek design, which had the capability to hold a lot when compared to other devices of a similar size with the iPod yet they could not contain as many songs (Boyer and Verma 10). This benefit, together with marketing perspective, gave iPod benefit in unlimited market and pricing. Apple Company as well gained the foundation by helping the company introduce more versions, as such, gaining competitive edge in the industry.
In operations management, the constraints theory is equally fundamental since it helps the operations manager recognize imperceptible constraints that might hinder the industry from attaining its preferred goals. As such, operations management services on such constraints though it strategies on how they can be minimized. Constraints can either be external or internal. The operations manager needs to be in a position to always recognize issues offering many constraints to a firm and handling them first.
Any industry that has long-term goals uses its forecasting techniques to establish probable future operations. Operations management therefore is accountable for preparation regarding the industry’s future. Forecasting helps operations managers to formulate ideal plans and get rid of uncertainty in future. The need for balancing supply with demand is what necessitates the industry to forecast the market. For example, Toyota needs to exercise time series in order to forecast the trend in demand of SUVs as well as what will take place in a span of 3 years’ time. This will help in making an investment that can meet that demand. Additionally, it gives the operations manager enough time to carry out research as well as employ innovative techniques in the manufacture process.
Industrial products are fundamentally classified into two categories: necessities and luxuries. Necessities refers to products perceived as extremely essential while luxuries are products individuals can live without. Making products perceived as necessities and delivering them into the market is critical, since customers continue to purchase the items though there might be a shortage. Operations management therefore ensues necessities are available in the market always, at the right price and to the right customers. Luxury products necessitate operations management to be innovative, as such products keep losing fashion once they flood the market.
Every industry endeavors to distribute its products to a target market. This only happens when the industry is able to acquire raw materials, place them into processing plant and then, pack them as finished products. Production of goods in industries involves the transformation of inputs into finished products. The operations management has the responsibility to maintain a supply chain via high levels of shared working procedures and norms so as to increase operational fit between the industries (Brown, Bessant & Lamming 104). When H-P entered the PC market, it served as a manufacturer. Later, it opted to make a shift from manufacturing to assembling. The shift prompted the company to become rigorous in supply relations through its entire supply chain. Additionally, H-P merged with Compaq, its competitor in 2001 so as to consolidate its supply chain, leading to its success (107). Operations management is vital in placing an industry into a strategic position so it can sustain its competitiveness. Operations managers as well research on the products of the company and make a decision on what it should offer customers without disrupting the operations of the company. Samsung Electronics, in order to save its display business from being unprofitable in the future, made the decision to incorporate the flat-panel display venture to its semiconductor business (Ramstad and Lee). The aim of the merger was to hide the dwindling unit in the robust performing chip operation and also offer competition to other products by Samsung.
In economic terms, industries use operations management for purposes of analyzing explicit aspects of processing to the point where they can add value as well as place competitive cost. The industry, equally has to earn profits in order to satisfy shareholders. Transformation of the raw materials into finished products involves the addition of value, reflected in the course of pricing. Operations management takes into consideration all processes that are part of transformation, which includes innovation, research, packing, transport, mixing and packaging. For example, wheat is transported to a factory using trucks. It is ground into flour, mixed into dough then baked into bread inside the factory. Slices of bread are packed and packaged, to be distributed to customers. Operations management takes part in fixing a price in the value chain. Prices as well are set to a point where the customers can afford the products as well as compete with other firms.
Most industries face an increased demand for pertinent activities aimed at conservation of the environment. Customers, legislators and advocacy groups push industries to implement environmental conservation strategies, covering pollution, management of waste, re-manufacturing and recycling. The practice is one aligned to quality management, integrated in the process of transformation. A firm that is able to take into consideration environmental issues in order to create value for its products, as such, raisin expectation of shareholders. Environmental responsibility is a fundamental aspect of operations management. Firms train their employees on issues of the environment while embracing environmental technology so as to improve production. Operations management therefore benefits environmental management via cost reduction and customer satisfaction.
It is very important for an industry to conform to legal standards in the course of its operations. Conforming to such standards helps the industry to operate and safeguard its facility as well as minimize legal liability. Operations management helps keep in check changes that might occur in standards in order to advise the industry on the changes that need to be implemented. To ensure production efficiency, operations management needs to allow standard activities to begin early in the course of the processing life cycle so as to meet legal codes.
Operations management as well covers people. Ergonomics involves study of workers in an industry with the purpose of minimizing stress and reducing injuries while working. The ergonomics process is established by risk reduction strategies and the approach means all factors contributing to workers injury or illness need to be addressed and identified promptly (Smith 49). Ergonomics is necessary for purpose of checking the performance of a business. Several ergonomics risk factors can be easily recognized and the operations manager offers a solution to work through the team. Toyota Company plant in Georgetown, Ky., US experienced a change in design of its models which resulted to ergonomic inefficiencies and risks, especially with rear spoiler installation (52). The operations management of the company commissioned an external consulting firm to carry out an assessment of ergonomics risk. The consulting firm recommended that the company should design hand tools which could be used to harness wire installation. The tools that were newly designed allowed the mechanics to work on the trunk from outside eliminating waste motions and ergonomic risk while saving time.
Is Operations Management Rated sane to finance, Human Resources, R&D or Marketing?
Operations management achievements are related closely to human resources, finances, marketing and development as well as research. Operations managements works to reduce the costs of a firm and offers competition to other firms. As such, operating managers need to check on the finances of the firm in order to attain these goals. They make decision of the number of employees needed to carry out packaging and processing. Depending on an industry, operations management is important in the management of human resources and materials to attain the desired objectives.
Operations management undertakes research and development (R&D) in order to establish whether the products of the firm meet changing demands of customers and sustain the firm in the market. The operations manager is also fully responsible for determination of how much will be spent on research and marketing. An industry should not manufacture products if it does not understand its target market. Hence, it must plan on how it can reach its customers and increase sales.
Sample Essay on Operations Management: Conclusion
Operation management is essential, as it assists in the management of an organizations resources. It offers the key to achieve competitive advantage for an industry by offering quality, affordable and reliable products in the market. Customers as well look forward for products incorporating technology and offering value for money. Operations management is mandated with making sure the production costs are kept low and that the expectations of shareholders are met. Industries manufacture different kinds of products in accordance to their target customers. The industry strives to make adjustments to meet the needs of customers through research and innovations. A successful firm needs to invest on environmental conservation activities, as customers are attracted to products that meet high environmental standards. Operations management needs to invest in product design as well to attract more customers so they can buy the firm’s products.
Sample Essay on Operations Management: References
Was this Sample Essay on Operations Management useful? Would you like to get further assistance with your assignment? Contact us today; We are a leading academic research company, with a range of specialized services . From General Essays to Ph.D. Thesis, we guarantee your holistic help. Our prices are affordable and competitive. What is more, we have a collection of sample papers in every field just for you. Place your ORDER NOW ! You may want to consider checking our Essay Writing Services , Research Paper , Thesis Writing Services , Coursework Help , among others.
Boyer, Kenneth K, and Rohit Verma. Operations & Supply Chain Management for the 21st Century. Mason, Ohio: South-Western/Cengage Learning, 2010. Print.
Brown, Steve, J R. Bessant, and Richard Lamming. Strategic Operations Management. , 2013. Print.
Mahadevan, B. Operations Management: Theory and Practice. Upper Saddle River: Pearson, 2010. Print.
Ramstad, Evan and Jung-Al Lee. Samsung Combines Component Operations. The Wall Street Journal, July 2, 2011. Web. 6 March 2014. online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304584004576418732760372012
Smith, Scott. “Elements of Effective Ergonomics.” Industrial Engineer: IE 35.2 (2003): 49-52. Business Source Complete. Web. 6 Mar. 2014.
Do you have an Assignment on a Similar or Related Topic? We can Help You Right Now! Click on the Order Now button...
Are you looking for homework writing help on this topic? This question was posted by one of our client seeking homework help. If you are therefore looking for an assignment to submit, then click on ORDER NOW button or contact us today. Our Professional Writers will be glad to write your paper from scratch, and delivered within your deadline. Perfect choice for your excellent grades! www.globalcompose.com.
We ensure that assignment instructions are followed, the paper is written from scratch. If you are not satisfied by our service, you can either request for refund or unlimited revisions for your order at absolutely no extra pay. Once the writer has completed your paper, the editors check your paper for any grammar/formatting/plagiarism mistakes, then the final paper is sent to your email.
Writing Features
Affordable Writing Services
Experienced Writing Team
24/7 Team of Writers
Professional E ssay Writers
Quality Measures
Trained Support Team
Non-Plagiarized Papers
Well Researched Papers
Free Writing Resources
Privacy | Confidentiality
We do not share your personal information with any company or person. we have also ensured that the ordering process is secure; you can check the security feature in the browser. for confidentiality purposes, all papers are sent to your personal email. if you have any questions, contact us any time via email, live chat or our phone number., our clients testimonials, a team of +500 masters and ph.d level homework writing help writers available 24/7 cannot get it wrong. the following are customer reviews about the quality of our services..
“Thanks for offering your professional assistance on this one. Topic was confusing but writer worked it out”
Added 24 Minutes Ago
“Thanks, I like the literature review, it is discussed in depth. Have looked at the results section and it is conclusive as I expected. Thank you”
Added 12 Hours Ago
“I like the discussion on the case study. Thank you. Am satisfied and wanted to request that same writer will handle my future assignments”
Added 30 Minutes Ago
“I was paranoid about online writing services, but on this one, the results are evident that you are much better. Will order more papers”

Added 3 Minutes Ago
“I think the paper is alright. If I can book the writer for the soon upcoming assignment, it will be great. Thanks”
Added 6 Minutes Ago
Why choose our homework writing help, we try to work as diligent as we can to help you meet your homework’s deadline. our support staff is always online 24/7 to help clarify any issues or concerns you have regarding our services. talk to us today to find out how our writers may be of help to you., customized papers, we consider your instructions and specifications in order to tailor the paper to suit your expectations., only professional writers, all our writers have a masters or ph.d and are well trained to handle assignments in various disciplines at different education levels., fast and reliable, our writers are capable of handling any assignment with short deadline and deliver without any delay, thus saving you time and energy, round the clock support, our customer support is always ready to offer real time assistance of day and night, through email, live-chat and phone., cost effective prices, we save you money with our affordable prices and huge discounts on all assignments., 100% original papers, all our papers are thoroughly researched and written from scratch. be sure of completely non-plagiarized papers., our ordering process, to get started with our homework writing help, simply click on the order now button. its easy, secure and takes less than 2 minutes to complete. the following steps illustrates the entire process., fill the order form: include all instructions and files for your assignment., submit your payment via card or paypal so that your order can be processed., a writer works on your paper and submits to editors upon completion., the completed paper is examined by our editors, then sent to your email, want to learn from experts check the writing tips below.
Final Paper Assignments
- Thesis Writing Help
- Dissertation Chapters
- Writing Research Papers
- Project Writing
- Term Paper Writing
- Speech Writing
Weekly Assignments
- Essay Writing
- Coursework Writing
- Assignment Writing Help
- Homework Writing Help
- Book Review Writing
- Movie Review Writing
Creative Assignments
- Power Points Preparation
- Analyzing Case Studies
- Creative Writing Papers
- Critical Thinking Writing
- Annotated Bibliography
- Capstone Project Writing
Admission Papers
- Writing Scholarship Essay
- Writing Admission Essays
- Writing Application Essays
- Writing Entrance Essays
- Personal Statement Essays
- Reaction Paper Writing
Samples of our Writing Illustrated Below
We have compiled a list of samples written by our writers for your review. you can use these samples to write your paper. you must however cite the source properly. if you are looking for a non-plagiarised paper, click on the order button. our professionals will work on your order. are you looking for writing tips check the list on this page. we are glad that we could help..
- Discussion Essay Homework
- Dissertation/Thesis Writing
- Book Review Paper
- Business Plan Homework
- Capstone Project Paper
- Creative Writing Homework
- Critical Thinking Homework
- Application Essay Homework
- Case Study Homework
- Literature Review Homework
- Personal Reflection Homework
- Reflection Essay Homework
- Research Proposal Homework
- Annotated bibliography Paper
- Article Review Homework
- Research Paper Homework
- Movie Review Sample
- Term Paper Sample
- Admission Essay Homework
- Argumentative Essay Paper
- Response Essay Homework
A List of Related Papers On This Category is Provided Below
- Sample Essay Paper on Self-leadership
- Essay Sample Paper on Globalization
- Sample Essay Assignment on St. Patrick’s Day
- Sample Essay on Wine Industry Research Paper
- Sample Essay on Beloved Essay
- Sample Essay Writing Paper on The Network Design Project
- Sample Essay on Laissez-faire Leadership Style
- Sample Essay on Penticton in Okanagan Valley
- Argumentative Essay on Cell Phones
- Sample Al Capone Essay
- Essay Sample on Fashion and Inner Self
- Sample Essay Writing Paper on Blood Donation process
- Essay Sample on Globalization
- Sample Essay On Criminal Justice System
- Sample Essay Writing Paper on Kanye West MTV Award Interview 2002
- Essay on Business Ethics
- Essay Sample on Interactive and Digital Marketing
- Sample Essay Writing Paper on Single Story
- Research Paper on Crowd Management Plan
Get your Homework Written by our Top-Notch Writers Now
Operations and Supply Chain Management Report
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Literature review, difference between scm and om, operation strategy of toyota, sustainable competitive advantage, lean and agile.
The aim of the paper is to understand supply chain management (SCM) and operations management (OM) as strategies to gain sustainable competitive advantage. A brief review of the two is conducted ton SCM and OM literature.
Then, two case studies –
- supply chain strategy of Wal-Mart and
- operations strategy of Toyota are presented in the paper.
The last part presents a theoretical understanding, with examples, and shows how supply chain and operations strategies can become competitive advantage for companies. The paper also presents the difference between SCM and OM.
Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management is the sequence in which different stages of a process, to fulfill customer need of a product, is satisfied. Metzner, DeWitt, Keebler, Min, Nix, Smith and Zacharia defined supply chain as “a set of three or more entities (organizations or individuals) directly involved in the upstream and downstream flows of products, services, finances, and/or information from a source to a customer.”
The supply chain process is divided into five stages: supplier, manufacturer, distributor, retailer, and customer. In essence, the process of placing an order by the customer and the various stages that occur to deliver that product is exhibited in the supply chain.
This helps in streamlining the process of supply of the product from manufacturing to the customer and enhances distribution performance. Chopra and Meindl showed two basic types of supply chain based on the way processes are formed – cycle view and push/pull view.
The cycle view of the supply chain points out that the five different stages of the supply chain operate in a cyclical manner.
The push/pull view the supply chain with the pull process execution of the supply chain is initiated with the customer order while in case of the push process it is initiated in anticipation of the customer order .
The main advantage of an integrated system where the supply and the demand side are integrated to form a seamless process helps in monitoring and planning the operational process.
This is mutually beneficial for all the stakeholders as the risks and benefits are mutually shared. It enhances coordination among the supply chain members and increases transparency of the distribution process.
A proper supply chain management helps businesses to gain competitive advantage. Competitive advantages are the needs of the customers, relative to its competitors, that an organization aims to provide through its product and/or service offerings.
Organizations can gain strategic fit between their SCM strategy and competitive strategy by three methods –
- understanding their SCM risks and their customers,
- ascertaining the SCM competencies,
- realizing strategic fit.
Power conducted a literature review to understand the SCM practices from a strategic viewpoint. The study demonstrated that it is important to undertake a holistic view of the participation and interaction of the participants of the supply chain.
Operations Management
Operations management is the process of designing and planning the products, processes, and supply chain. It entails undertaking proper planning to acquire, design, and plan resources to carry out a function.
Operations management (OM) is “a set of activities that create value in form goods and services by transforming inputs into outputs” . Leseure pointed out that operations management is essential for the performance of an organization.
Traditionally, the internal performance of an organization’s operations ahs been designed under cost, quality, delivery, speed, and flexibility. The literature on OM is replete with the debate over the importance of operations as a strategy to gain sustainable competitive advantage for a firm.
Bettley, Mayle and Tantoush points out that many researchers (like Michael Porter) have pointed out that an operations strategy is not enough to attain sustainable competitive advantage as operations can be emulated.
Researchers and practitioners have put stress on resource-based approach and they believe only a few “good” companies can sustain competitive advantage using operations strategy . Hayes and Upton emphasizes that the role of operations is much larger than just formulation of strategy.
Further, it helps the companies to position their product. The main question asked by customers while purchasing a product is ‘why should I buy it’.
Operations strategy helps the companies formulate a position for the product based on which the company streamlines the whole of its functioning. Thus, a positioning strategy helps the company identify how it would like to be differentiated in its chosen market from its competitors.
Therefore, by positioning the product better than the competitors and in accordance to the needs of the consumers a company can gain competitive advantage in a market.
Another method of gaining competitive advantage for a company is by executing the existing strategies better than their competitors implement.
For instance, shifting the place of production to a low-cost location may be a good decision in the short-run but to make it a sustainable advantage companies have to be very efficient to continue the strategy sustainable for long-term.
For instance, as a retaliation to Wal-Mart’s strategy to computerize its product procurement and inventory control system, Kmart failed to realize that sampling emulating the act will solve its problems. Soon Kmart realized that their employees were not trained to operate the systems.
Often SCM and OM are confused and used interchangeably.
However, both are completely different. SCM is the process of sharing resource information and planning logistic right from the point of procurement of raw material, to manufacturing, and then distributing it, until the product reaches the consumers.
On the other hand, OM is the process of planning and managing the resources required for the production and delivery of the product to the consumers.
In a way, SCM is a subset of OM for the latter is concerned with the production process apart from the delivery and distribution. More importantly, the difference between the two can be further delineated as follows:
- SCM aims to reduce inefficiencies in the complete chain of processes from supply of raw material to delivery to the customer. On the other hand, OM has a broader range of activities in monitoring and planning the wider set of operations regarding the manufacturing of the product.
- SCM deals with monitoring the raw material required for the production and ensuring that the right material is being delivered for production. OM deal with all that is necessary for the actual production process.
- SCM is based on activities irrespective of the nature of the business while OM is concerned with the business the operations are being conducted.
- More broadly, SCM is mostly concerned with the activities that occur outside the organization’s premises such as shipping, warehouses, distribution, while OM is concerned with the activities occurring inside the premises.
Though both are different, both are essential in maintaining a sustainable business strategy. Overall, it can be pointed out that SCM is a part of the OM. SCM looks into the operational logistics while OM looks into the overall picture of the manufacturing of the product.
Supply Chain Strategy of Wal-Mart
Wal-Mart has used supply chain strategy to gain competitive advantage for long time.
The following case study of Wal-Mart’s supply chain will demonstrate that a successful supply chain can reduce cost of product considerably and enable companies to provide product at highly competitive pricing. Wal-Mart is the world’s largest retailer with highest sales per square foot.
Wal-Mart’s success from a regional discount retailer to an international discount retailer has been mostly due to their efficient supply chain management.
Wal-Mart has assumed a successful leadership position in the global retail market mostly due to efficient management of its supply chain.
The supply chain strategy of Wal-Mart is based on four factors: vendor management, distribution channel management, technology, and integration all the processes.
Wal-Mart’s strategy has been to procure their products at lowest possible cost. Figure 1 below shows the supply chain strategy of Wal-Mart. Wal-Mart sources its products from different vendors worldwide and procures the products at cheapest possible cost.
This helps them to sell their products at the lowest possible prices. These products are then sent to the different warehouses at different places, and since then all the products are sent to the retail outlets according to the demand of each retail store.
Wal-Mart follows a push, supply chain strategy wherein the products are first sourced based on an anticipated demand from the customers. In case of Wal-Mart the main issue is sources the large quantity demand and at different places. Further,
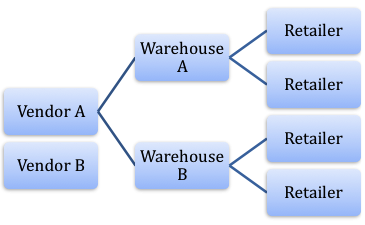
Procurement
The first section to consider in Wal-Mart’s supply chain is their suppliers or vendors. For instance, Wal-Mart had problems with P&G as a supplier initially; for the latter’s organizational processes were too complex for Wal-Mart’s efficiency oriented culture.
In order to overcome this problem, Wal-Mart invited its partners to jointly develop vendor management, inventory management, and category management . Wal-Mart bypasses intermediaries to directly procure the products from the manufacturers to minimize cost.
Recently Wal-Mart has also invested heavily in making its supply chain environmentally compatible by choosing more environmentally conscious vendors and supply chain partners .
Distribution
Wal-Mart has its warehouses and distribution centers at different locations of the US and other countries where it operates.
The warehouses have a large inventory of the goods sold in the Wal-Mart outlets and each retail store is replenished with the stock of goods with efficient product demand forecasting system.
The company uses advanced technology such as RFID, hand held computer systems, and bar code, which makes keeping large inventory in the warehouses economical . In 2007, 80 percent of the products of Wal-Mart were distributed through 121 company owned distribution centers.
Only the suppliers for electronic and prescription drug products supplied directly to the stores.
The inventory management system used by all employees accessible through their hand held computers allowed them to access a particular product exactly to its location on a particular shelf increased efficiency considerably.
A company owned logistics systems with over 3500 trucks and 75000 employees in the logistics department, who helped the company to replenish its stores twice daily.
Further to reduce the time of logistics and make its supply chain more efficient Wal-Mart uses a technique called “Cross Docking” that allows the company to procure the product directly from the manufacturer and directly delivering it to the customer, almost eliminating the time and cost involved for distribution from warehouses.
Inventory Management
Due to large number of stores and huge scale of operation, Wal-Mart ensures that it uses proper inventory management system to ensure continuous flow of products.Further, it also has to regulate the inventory cost.
For this, since 1980s, Wal-Mart has used satellite communication systems that allowed the company managers to closely monitor the operations within each store and analyze the amount of product that has to be replenished at the end of daily operations.
Further, the company takes precautionary measure to reduce unproductive inventory by use of advanced technology such as RFID and bar code. It also allows the stores to manage the stock allowing small packages and well-timed price mark down.
The operations management system developed in Japanese, especially that in Toyota has been named as the Toyota Production System (TPS). The lean management system developed by the Japanese manufacturer demonstrates the current state of operations management.
The main point that one must understand before undertaking a study of the TPS is that the company did not consciously adopt it, instead it grew naturally through its operations over five decades.
The operation strategy of Toyota is based on a strong interaction of the operations management as the core strategy and other disciplinary interfaces . TPS can be descried through four rules according to Spear and Bowen (1999) –
- All work conducted by the company must be defined in terms of “content, sequence, timing, and outcome” .
- All customer-supplier relation must be direct and consent to accept or reject the order must be defined in a simple yes-no process.
- The way a product is produced and delivered must be simple and direct.
- Employees at the lowest level of the organizational hierarchy make all improvements in the products.
These four rules greatly simplify the operational process and make it extremely flexible. The TPS method ahs been summarized in five steps –
- long term vision,
- continuous improvement (Kaizen),
- going back to the source to find out the facts (Genchi Genbutsu),
TPS is based on two key concepts that Toyota follows – just-in-time (JIT) and stoppage of production in case defects are identified (Jidoka).
JIT emphasizes on the continuity of production with maximum supply of inventory and raw material for continuous, uninterrupted flow of production. Further, the TPS system also aims at elimination of any excess waste such as overproduction or inventory.
Toyota aims for change in the operational strategy and a flexible strategy over a longer period rather than short run cost effectiveness. The total quality management (TQM) strategy employed at Toyota enables it to integrate its manufacturing operations with other disciplines (see figure 2).
The Toyota production line is designed specifically to ensure that once implemented, the plan does not change until the process is specifically redesigned. Therefore, in case of installation of a seat in a car, if plastic bolts are required for fixing the seat, the employee orders it from the specific handler.
The supplier makes request for the bolts with his own suppliers and sends to the designated person.
According to the Toyota operations strategy, the bolts will not be delivered to the next available person or machine but to that specific person, and if he is not available, there exists some problem with the production line and it is redesigned .
The operation strategy in Toyota is not based on one specific aspect but encumbers all the management disciplines to make it a complete process. Thus, Spear points out that it is impossible to understand how TPS works until one immerses oneself in the practical process of the operations .
The competitive strategy of a company defines how a company aims to satisfy its customer needs through its products and services . Competitive advantage, therefore, is a means of building competencies in a particular business. Building barriers to prevent imitation of the strategy can help companies achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
Research shows that companies who stress on supply chain strategy as a primary strategy have a high level of sustainable competitive advantage and organizational performance .
The companies that use SCM as their core competency usually operate based on the following aspects: supply chain integration, information sharing, cross-functional communication, and supplier involvement.
Efficient supply chain management is based on demand forecasting, strategic planning, and apposite inventory supervision . For instance, consider the case of the adoption of RFID in supply chain of Wal-Mart. Emulating Wal-Mart, Kmart too adopted RFID for managing its supply chain.
However, the new technology created complexities for Kmart, as the people using the technology were not adept to use it.
Further, Wal-Mart’s supply chain strategy has given the company many other sustainable competitive advantages such as low cost procurement, optimal inventory, and better in-house brands.
The methods that a company must employ to make their supply chain strategy competitive are –
- A company must remember to collaborate with their supply chain partners rather than competing with them. The success of each stakeholder of the supply chain will have a positive impact on the supply chain’s success.
- A company must integrate all the process together and preventing compartmentalization of functions. In case of certain companies, employees loose focus and start identifying themselves with the function rather than with their company. Therefore, integration of the culture of togetherness is important to gain competitive advantage.
- A company has to keep the supply chain as simple as possible to gain competitive advantage out of it. For instance, incorporation of ERP to the supply chain may be helpful to simplify the processes, however, one may be enamored by the technology and add up non-essential tasks to the supply chain making it complex.
- When a problem occurs it is important to look into the issue rather than treating the symptom leading to the problem.
- A company must create constant vigilance to track cost drivers in the existing supply chain.
Organizations can achieve sustainable competitive advantage through adopting proper operations strategy. We exemplify the case of Toyota to understand the issue.
Toyota’s operation management is unique and it is difficult to understand, as it is believed, because it was not imposed on the company but evolved through decades of operation. Emulation of such a strategy is difficult for it does not work on a set formula.
Therefore, in order to achieve sustained competitive advantage out of operational strategy a company must allow it to develop through its organizational culture and integrate it within its system rather than imposing it from outside.
The main criterion of an agile supply chain is the emphasis on time as a competitive advantage. In terms of competitive advantage, it is important for a company to choose between agility and lean (see figure 3).
Figure 3: Agile and Lean supply chain.
| High | Agile | Agility required when demand is unpredictable and high degree of variety in product is required | |
| Variety | Lean | Lean is appropriate for high volume low variety industry | |
| Low | Variability | High |
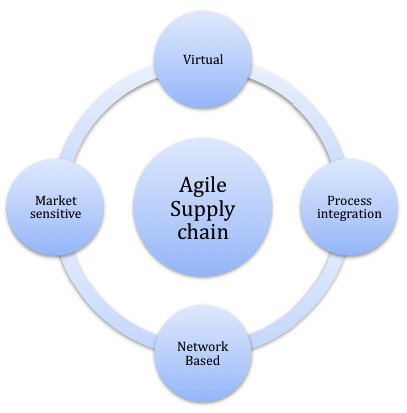
Agile supply chain is one which has the four characteristics described in figure 4. An agile supply chain must be market sensitive, implying it can understand the changes in market demand. Such supply chains rely on demand forecast, rather than actual demand .
Use of information technology helps the company to create a virtual supply chain that reduces inventory and increases use of information.
Process integration is essential, as it enhances coordination between buyers and sellers. Further, all the partners of the supply chain are closely linked within the network.
A lean supply chain is one that emphasizes on doing more with less . It is often used to show lean manufacturing, which incorporates just in time approach to manufacturing. One such example is the manufacturing process of Toyota.
SCM and OM strategy have assumed great importance for businesses today. However, the adoption of either or both the strategies is business specific.
For instance, in case of an organization like Wal-Mart an agile supply chain strategy is more conducive as it provides it the agility and flexibility to adapt to the ever-changing demand of the market.
On the other hand, for a manufacturing based company like Toyota with few product offerings but large investment requirement a lean production system is more appropriate.
Either of these strategies can be turned into sustainable competitive advantages by building barrier against competitors emulating the strategy.
Bettley, A, Mayle, D & Tantoush, T 2005, ‘Introduction to Theme 1: Operations as a Strategy’, in Operations Management: a Strategic Approach , Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA.
Byrnes, J 2003, Supply Chain management in a Wal-Mart World . Web.
Chopra, S & Meindl, P 2007, Supply chain management: strategy, planning, and operations , 3rd edn, Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
Christopher, M 2000, ‘The Agile Supply Chain : Competing in Volatile Markets ‘, Industrial Marketing Management , vol 29, no. 1, pp. 37-44.
Hayes, RH & Upton, DM 2005, ‘Operations-based Strategy’, in Operations Management: a Strategic Approach , Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA.
Heizer, J, Render, B & Rajshekhar, J 2009, Operations Management , Pearson Education, New York.
Leseure, M 2010, Key Concepts in Operations Management , Sage, Thousand Oaks, California.
Li, S, Ragu-Nathan, B, Ragu-Nathan, TS & Rao, SS 2006, ‘The impact of supply chainmanagement practices on competitive advantage and organizational performance ‘, Omega – International Journal of Management Science , vol 34, pp. 107–124.
Mentzer, JT, DeWitt, W, Keebler, JS, Min, S, Nix, NW, Smith, CD & Zacharia, ZG 2001, ‘Defining Supply Chain Management’, JOurnal of Business Logistics , vol 22, no. 2, pp. 1-25.
Plambeck, E & Denend, L 2011, ‘ The Greening of Wal-Mart’s Supply Chain ‘, Supply Chain Management Review , vol September/October, pp. 16-23. Web.
Power, D 2005, ‘Supply chain management implementation and integration: a literature review’, Supply Chain Management: an International Journal , vol 10, no. 4, pp. 252-263.
Spear, SJ 2004, ‘Learning to lead at Toyota’, Harvard Business Review , vol 82, no. 5, pp. 78-91.
Spear, S & Bowen, HK 1999, ‘Decoding the DNA of the Toyota production system’, Harvard Business Review , vol 77, pp. 96-108.
Toyota 2012, Toyota Global Vision and Strategy . Web.
Voss, CA 1995, ‘Operations management – from Taylor to Toyota – and Beyond? ‘, British Journal of Management , vol 6, no. Special, pp. 17-29.
- Efficiency of Supply chain Management
- Supply Chain Risk Management: Increasing Resilience to Internal and External Threats
- An Introduction to the Supply Chain Management
- Operations Management and Supply Chains
- The Book "Agile: The Insights You Need"
- Operations and Supply Chain Strategies of Wal-Mart and Toyota
- Information Technology in Logistics Management
- Reverse Logistics at the Planning
- Supply Chain Management Techniques
- Walmart’s Supply Chain
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, July 9). Operations and Supply Chain Management. https://ivypanda.com/essays/operations-and-supply-chain-management/
"Operations and Supply Chain Management." IvyPanda , 9 July 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/operations-and-supply-chain-management/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Operations and Supply Chain Management'. 9 July.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Operations and Supply Chain Management." July 9, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/operations-and-supply-chain-management/.
1. IvyPanda . "Operations and Supply Chain Management." July 9, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/operations-and-supply-chain-management/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Operations and Supply Chain Management." July 9, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/operations-and-supply-chain-management/.
- Inventory Management
How RFID enhances inventory and warehouse management | Benefits and implementation
Ever wished your inventory could talk? With RFID, it can. This cutting-edge tech is transforming how businesses track and manage their stock, making those inventory headaches a thing of the past.
Let's face it: traditional inventory methods are a pain. Manual counts, misplaced items, inaccurate stock levels—sound familiar? RFID tackles these problems head-on, turning your warehouse from a guessing game into a well-oiled machine.
This guide will dive into the world of RFID. It'll break down how it works, why it matters, and how it can give your business a serious edge. Whether you're running a massive distribution centre or a small stockroom, RFID might just be the game-changer you've been looking for.
What is RFID?
RFID, or radio frequency identification, is a cutting-edge tracking technology. It works by attaching small electronic tags to items and using specialized readers to identify and monitor them.
Here's how it works:
RFID tags hold product information electronically.
Readers use radio waves to detect and read these tags.
Tags can be scanned quickly, even without a direct line of sight.
Initially created for general object tracking, RFID has become a game-changer in inventory and warehouse management. It’s a step up from traditional barcodes, offering real-time data on stock levels and locations. This technology makes inventory processes smoother, cuts down on manual work, and improves accuracy.
How RFID works
RFID systems consist of four main components:
Tags: These are small devices attached to items for tracking. They come in two types:
Passive tags - Activated by the scanner's signal.
Active tags - Battery-powered for longer-range communication.
Readers: These devices interact with the tags to collect data. They come in various forms:
Stationary units for fixed locations.
Handheld devices for mobile use.
Antennas: These components facilitate communication between readers and tags.
Software: This translates the collected data into useful information for inventory management systems.
RFID systems operate on different frequencies, each suited for specific applications. This versatility allows for efficient inventory tracking and management without manual counting. RFID systems make it a more efficient inventory management technology compared to traditional barcode scanning with its real-time visibility, reduced labor, better security, and longer read range. This helps businesses improve their supply chain operations by providing automated data collection, real-time inventory visibility, and reduced labor costs.
Implementing RFID in inventory and warehouse management
Planning and preparation .
First things first: Take a look at how you're handling inventory right now. Where are the bottlenecks? What's causing headaches for your team? This isn't just busy work; it's about finding the sweet spots where RFID can really shine. Create a planning sheet. Having clear targets helps you design an RFID system that actually does what you need it to do.
Choosing the right RFID technology
Picking the best RFID solution for your warehouse isn't just important—it's critical. Think of it as choosing the right tool for a complex job. Get it right, and you'll wonder how you ever managed without it.
Here's what to keep in mind:
What are you tracking? Different materials play nice (or not so nice) with RFID signals. Metal items, for instance, might need special tags.
What's your warehouse like? Is it hot and humid, or cold and dry? Believe it or not, this matters for RFID performance.
How far do you need to read tags? Across the aisle or across the warehouse? This affects your choice of technology.
Remember, the goal isn't to get the fanciest tech. It's about finding the RFID solution that'll make your warehouse run like clockwork.
Installation and training
Proper setup matters .
Implementing RFID effectively requires careful planning and execution. Here's what a successful installation involves:
Site surveys: Assess your warehouse for optimal RFID placement.
Hardware setup: Position readers and antennas strategically.
Software integration: Connect RFID to your existing systems.
Be prepared to tackle common challenges, such as signal interference and tag positioning. If not addressed, these issues can impact performance.
Consider DHL's approach: They conducted extensive testing and staff training before full deployment. This strategy led to a smooth transition with minimal operational disruptions.
Empowering your team
For RFID to reach its full potential, your staff needs proper training. An effective program should:
Educate employees on the benefits and usage of RFID.
Address concerns about new technology.
Ensure staff comfort with the system through hands-on practice.
Remember, investing time in proper setup and thorough training pays off in smoother operations and better results from your RFID system.
Benefits of RFID
Real-time tracking and visibility .
RFID technology turns your inventory into a living, breathing system. By tagging items with smart labels, businesses gain an instant, up-to-the-minute view of their stock and where everything is located.
Since RFID tags are attached to products or cases or contain unique identifiers and product information when a tagged item passes by, the reader instantly captures its data. There is no manual scanning, and no line-of-sight is needed.
This data flows straight into your inventory management system, updating stock levels and locations in real-time. This level of visibility lets you spot trends, prevent stockouts, and make smarter decisions on the fly.
Improving accuracy and productivity
RFID technology creates a digital fingerprint for each item, drastically reducing human errors that often plague manual systems. Think of it as giving your inventory a voice—each product can now effectively communicate its presence and location.
This digital approach transforms tedious tasks into efficient processes. With more accurate data and freed-up staff time, businesses can make better-informed decisions, respond quicker to market changes, and ultimately drive higher profits. RFID automates these time-consuming activities, freeing up your team to focus on more valuable tasks like customer service and sales strategies.
Advanced stock management and security
RFID turns inventory from a static list into a dynamic asset. In large fulfilment centres, RFID doesn't just track items; it ensures critical stock stays at the right levels. RFID tags on products constantly feed data to readers throughout your warehouse. Your inventory system uses this info to spot trends and predict needs.
For sensitive industries and products, like pharmaceuticals, RFID is a game-changer. It provides real-time tracking and authentication. Every tagged item has a unique digital fingerprint. This means you can trace a product's journey from factory to shelf, ensuring it's the real deal and hasn't been tampered with. It's like having a security guard for every single item.
RFID optimizes fulfilment and secures critical supplies. This tech gives businesses a strategic edge, turning inventory management into a powerful tool for success.
Streamlining logistics and supply chain
RFID is the backbone of a seamless supply chain. It's like giving your entire logistics network a shared brain, making sure everything moves in perfect synchronization.
In production lines, these tags make sure the right parts arrive at the right time. Imagine a car assembly line where every component "checks in" as it arrives. No more hunting for missing parts or dealing with unexpected shortages. RFID keeps things running smoothly, cutting downtime and boosting efficiency.
When a product leaves your warehouse, RFID readers log its departure. As it moves through distribution centres and onto delivery trucks, the system tracks its progress in real time. This means you can spot and solve issues before they snowball into major problems.
With RFID, supply chains become more agile and responsive. It's not just about tracking items; it's about predicting needs, solving problems, and keeping your business one step ahead.
Elevating customer service and omnichannel strategies
RFID is changing the retail game. Remember the last time you couldn't find your size? Or when you saw something online but couldn't find it in-store? RFID is tackling these headaches head-on.
RFID tags on products act like tiny, smart price tags. They communicate with readers throughout the store, giving real-time updates on what's in stock and where it's located. This means when a customer asks for a specific item, staff can find it in seconds, not minutes. No more disappearing into the stockroom, hoping it's there somewhere.
RFID bridges the gap between online and in-store inventories. See an item online? RFID can tell you if it's available at your local store for immediate pickup. This seamless integration means fewer disappointed customers and more sales.
RFID makes shopping smoother and smarter, and it is all about making your life easier. With RFID, every customer gets VIP treatment, and every sale is an opportunity to impress.
Conclusion
From boosting inventory accuracy to streamlining supply chains and enhancing customer experiences, RFID is transforming how businesses operate, from the warehouse floor to the retail storefront.
Sure, implementing RFID requires some upfront investment and planning. Still, for companies willing to take the leap, the benefits are clear: increased efficiency, reduced costs, and the ability to stay competitive in an increasingly digital marketplace.
So, is it time for your business to join the RFID revolution? Only you can answer that.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked
Optimize stock control with Zoho Inventory

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Conclusion. The aim of this course has been to give you an introductory overview of operations management. Operations is one of the central functions of all organisations The first learning outcome was that you should be able to 'define "operations" and "operations management"'.I took the view in this session that operations embraces all the activities required to create and ...
Operations management deals with the procedures that ensure that a firm delivers the desired product and service to the client. Get a custom essay on Operations Management: Theory and Practice. It considers the concepts of quality, efficiency, and responsiveness to customers (Mahadevan, 2010). These concepts relate to the methodologies of ...
Other activities are purchase inventory control, quality control, storage, logistics and evaluation of processes. The main purpose of operational management is to ensure that these business processes and activities are carried out efficiently and effectively. Operation management is therefore concerned with the internal processes of a business.
Essay On Operations Management. Operations management (OM) is that phase of an organization where inputs are put into operations to acquire required output (services) without compromising on quality. In other words operations management is also described as combining and transforming various resources in the operations sub-system into value ...
KFC Operations Management: Delivering Finger-Lickin' Good Efficiency. 3. 10 Critical Decisions of Operations Management. 4. The Impact of External Factors on Operations Management. 5. Optimizing Operations: Maximizing Output, Minimizing Waste. 6. Operations Management in the Global Economy: Trends and Best Practices. 7.
Essay on Operations Management. Operations management is the process of managing the production of goods and services. Thus operations is a broad term that encompasses both hard-goods manufacturing management and service management. Traditionally, the term 'production' brings to mind smokestacks, assembly lines and machine shops.
The point of a report on operations management is to evaluate the systems in place, not to act as a feel-good essay. That being said, it is good to end on a positive, goal-oriented note. Don't include statistics in the conclusion. Stay away from fluff at all costs. Summarize, clarify, and create goals. Operations management is a broad area of ...
Operations management (OM) encompasses the design, implementation, and control of the processes that transform inputs into outputs within an organization. Its role in business success is undeniable. 2. Efficient Use of Resources. OM optimizes the allocation of resources, including labor, capital, and materials, to minimize costs and maximize ...
Operation management (OM) includes organizational processes such as technology (information and engineering), accounting, finance, and human resources. Procurement and inbound logistic as well as warehousing and outbound logistics are examples of macro operations of operation management. Other operations include customer service, marketing, and ...
In conclusion, operations management is a diverse and complex field that requires careful planning and execution to ensure the efficient production of goods and services. By choosing one of the above topics for your next essay, you will be able to delve deeper into the various aspects of operations management and gain a better understanding of ...
Operations managers are in charge of managing activities that contribute to the production of goods and/or services. Being an Operations Manager in Wal-Mart, my direct responsibilities consist of managing the operations procedure (planning, organizing, implementing, improving) and operations approach. My indirect responsibilities involve ...
Operations management emphasizes the importance of designing products and services with quality in mind, implementing quality control processes, and actively seeking feedback to drive continuous improvement. Decision-Making in Uncertainty. Operations management taught me the art of decision-making in uncertain and dynamic environments.
Essentially, operations management is concerned with the overall management of effective processes. Operations is also fundamentally concerned with the transformation of inputs to outputs as reflected in Figure 1 below. Figure 1: Transformation Process. Inputs can include physical raw materials, equipment, staff, or information.
Operations management is an important area in managing a firm. It can be defined as the area of management related to design and operation of business processes in production of goods or services. In a nutshell, it is the transformation of resources into product and/or services as depicted in figure 1. The competitive advantage of a firm is ...
Operations management essay example for your inspiration. ️ 2530 words. Read and download unique samples from our free paper database. ... Conclusion. The success of any business depends on the strategies that are taken by the business. Good strategies that can lead to good results are based on proper analysis of the operating environment.
This course has introduced the operations management function to you. After studying this course, you should now feel that you can: know that if you manage any type of resource, you can consider yourself to be an operations manager as you will be responsible for some kind of process. This OpenLearn course is an adapted extract from the Open ...
Operation management main function is produce the goods and providing best services to their clients. While operations management has a strong long-term strategic role to play In organisations, it has an equally strong short-term, daily operational role as Well. A large part of operations management deals with the planning, organising ...
Decent Essays. 466 Words. 2 Pages. Open Document. Operations Management. Operations management focuses on managing the processes of producing and distributing products and services. Operations activities often include product creation, development, production and distribution. It deals with all operations within the organization.
Operations management is an interdisciplinary activity that relies on various other activities within a firm. Just-in-Time is an effective concept that can be used to improve operations management efficiency if applied properly. Just-in-Time concept can only be successful if it is supported by all the stakeholders, especially the employees ...
Operations management is defined as "the design and management of products, processes, services and supply chains. It considers the acquisition, development, and utilization of resources that firms need to deliver the goods and services their clients want" (What is operations management, 2012, MIT Sloan).
Operation Management Essay. Introduction The management of resources which produces and delivers products and services is operation management. The part of an organization that is responsible for this activity is the operation function. And the people responsible for managing some or all of the resources which makes up the operations function ...
Sample Essay on Operations Management. MTR Foods is one of the fastest-growing companies in India dealing with food processing with a market turnover of US$ 20million (Mahadevan 3). The growth is the result of technological ability and the quality of its products. MTR deals in production of various products familiar to both domestic and the ...
Operations management is the process of designing and planning the products, processes, and supply chain. It entails undertaking proper planning to acquire, design, and plan resources to carry out a function. Remember! This is just a sample.
This helps businesses improve their supply chain operations by providing automated data collection, real-time inventory visibility, and reduced labor costs. Implementing RFID in inventory and warehouse management Planning and preparation . First things first: Take a look at how you're handling inventory right now. Where are the bottlenecks?