

20 Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloning Humans
Numerous science fiction movies have examined the idea of cloning humans. Some of them take an approach that suggests it’s a way to save the world, like in The Fifth Element, when Leeloo is a clone of what must be combined with four other elements to save the world. In The Island, two clones escape from a research facility after learning that their fate is to be surrogates and organ suppliers.
Even a campy comedy like Twins shows us that there are dangers to consider when cloning humans. You might be able to take cells from a guy like Arnold Schwarzenegger, but scientists might end up with a result closer to Danny DeVito.
The advantages and disadvantages of cloning humans often look at the concept from a spiritual or ethical standpoint. We must also examine the scientific risks that occur when undertaking this procedure. It is also notable to point out that several countries have formally banned this practice, and many more have passed laws that prohibit human reproductive cloning.
List of the Advantages of Cloning Humans
1. Cloning humans could help us find new ways to recover from trauma. Interventional orthopedics is a non-surgical possibility that uses a patient’s cells to help fix an injury that occurs during a traumatic event. Strains or sprains to ligaments typically heal in 6 weeks or less with rest. When a tear happens then the primary treatment option is to apply a tissue graft – especially with ACL injuries. Doctors place the new ligament at a steeper angle to support the healing process.
The current method increases a patient’s risk of cartilage damage and osteoarthritis later in life. Through the practices of human cloning, the cells could begin to repair themselves. This science imagines an opportunity for a speedier recovery because doctors can duplicate the exact cells that the body requires.
2. It could help couples resolve problems with fertility. Couples who are unable to conceive naturally could create children through human cloning to have an authentic genetic relative. Infertility could become a problem of the past because physicians could take the hereditary portrait of each parent, introduce it into an embryo outside of the body, and conceivably grow the fetus in a laboratory setting.
This method could help countries like Japan who are struggling with low birth rates. The Japanese culture could see a reduction of up to 40 million people by the year 2060 without the introduction of cloning measures.
3. Cloning humans could lead to new advances in medical science. The human cloning process could help to generate new advances in medical science. The possibility of sharing genetic material could help to prevent or cure diseases that may harm that person’s life by creating a duplicated individual. It could also create a new line of research that is equal to what we see now with embryonic stem cell therapies.
4. Cloning humans would allow us to explore the potential benefits of modifying genes. Nazi Germany took the approach of euthanasia and forced sterilization as a way to improve their genetic profile. Scientists could look at gene modification without causing harm to others because of the science of cloning.
Human cloning requires a precise form of genetic engineering. Using our current technologies, we would implement enzymes from bacteria to locate genes within our DNA to create the necessary modifications for duplication. This technology has been in place since 2015, which means it is not something from which we are entirely unfamiliar.
5. Cloning humans could reduce the impact of diseases in ways that vaccinations cannot. Human cloning could help us to begin curing genetic diseases such as cystic fibrosis or thalassemia. Genetic modification could also help us deal with complicated maladies such as heart disease or schizophrenia. This scientific process could help us to discover new ways to combat the natural aging process, including possible opportunities to stop it.
Babies would no longer need to go through a genetic lottery before birth to know what their human potentiality would be during their lifetime. Human cloning could even begin to reduce the overall cost of disease treatments around the world.
6. Cloning humans could help us correct today’s conditions for tomorrow’s generation. Human cloning processes would help the medical community discover and correct the reasons for many of today’s physical and mental conditions. About 1 in 10 children in the United States and Europe currently take a medication like Adderall to help with attention-deficit disorders. Their poor self-control decisions can lead to educational deficits that can impact them throughout their lives. It creates a natural inequality that can set their children back because they are not in the same socioeconomic groups as “normal” people.
7. Cloning humans would help us to eliminate defective chromosomes and genetic profiles. If a person has an extra chromosome or one is missing, then that condition is called “aneuploidy.” There is an increased risk of a genetic disorder when women have children later in life. Several different conditions can result from this outcome, such as Patau and Edwards syndrome, where there is an extra chromosome on the 13 or 18. Most children born with Trisomy 13 or 18 die within the first year of life, and severe congenital disabilities may result in a stillbirth.
Human cloning would provide us with technologies that could prevent these outcomes from occurring. It could also help when something like Turner syndrome appears, which happens when a damaged or missing X chromosome affects girls.
8. Cloning humans would allow us to create stem cells ethically. Many of today’s stem cell lines were created over 20 years ago for research purposes. Although there is no degradation in the quality of the work, more scientists could look for breakthroughs if there were more strands available. Human cloning would allow us to replicate the existing cells into multiple lines without the need to impact the potentiality of life. Cloning is a way to create genetically identical cells that could help to create better health outcomes for people, especially if they suffer from a rare genetic disease.
9. Cloning humans could make people more resilient to disease. Human cloning processes could help to replicate a natural resistance to illnesses, ailments, and conditions when discovered in the general population. There have been a select group of people who have a natural resistance to specific diseases for as long as diseases have impacted humanity. When the CCR5 gene mutates, it creates a natural resistance to HIV.
Researchers have found a group of women in West Africa had a natural immunity to the Ebola virus despite repetitive exposures to it. Cloning humans allows us to take advantage of these natural immunities to create a new level of resiliency against the diseases that affect us each year.
10. Cloning humans could help us to be ready for global warming. Evolutionary processes allow us to begin adapting to the changing circumstances on our planet, including global warming issues. Future generations could benefit from human cloning because it would speed up the developmental cycles as natural selection attempts to give humanity more strength. We could take the genetic profile from the most resilient people, apply it to new births, and build a civilization that is ready for the potential challenges ahead.
11. Cloning humans would allow our best and brightest to continue impacting the world. Imagine a world where the smartest, most influential people in every category of research could continue working because of human cloning. What would we know if Albert Einstein were still alive today? How would our civilization change if Leonardo da Vinci could work with modern tools instead of what was available in his time?
Art, science, literature, manufacturing, and every other industry could see massive gains in innovation if human cloning were allowed. It wouldn’t allow for immortality, but this process could help us to guarantee more outcomes instead of relying on chance.
12. Cloning humans could lead us toward organ development or regeneration. About 10,000 people on any given day in the United States are waiting on a list to receive a critical organ. Many of them will stay in that position for several months. The waiting time can even be years in some situations. Through the processes of human cloning, we could learn how to duplicate organ tissues from existing resources to help provide more positive outcomes in this area. Instead of waiting for a random donation, doctors could proceed with cells taken from each patient.
List of the Disadvantages of Cloning Humans
1. Cloning humans might always be an imperfect science. When we look at the success rate of animal cloning, a successful embryo gets created about 1% of the time in the best of circumstances. Scientists have tried to bring back species from extinction using harvested cells without much success, with most offspring dying minutes after they are born – if they even reach that stage in the first place. Dolly the Sheep might be a success story, but this disadvantage is the reason why several governments around the world have made it illegal to try this approach with human cells.
2. Cloning humans would be a technology initially priced only for the wealthy. Human cloning would create more classism in our societies instead of equality, especially in the early days of this technology’s release. Our socio-economic divides would still be in place because those with money could afford more characteristics, add-ons, or processes for their clones than those who are fighting to put groceries on their table. Even if everyone could afford to make clones one day to support their families, the people who could adopt this tech early would still have significant advantages over those who did not.
3. Cloning humans might create a rapidly aging population. The information that cells obtain as they age gets designated within their material structures. When a child begins to grow, they create genetic data that their genome keeps. We know that cloning is possible, but what we do not understand yet is how the information contained in our DNA would change through this process.
If age imprinting happens on a genetic level, then providing embryos with mature cells could create concerns with unanticipated aging. This process could lead to new genetic syndromes and an increase in the risk of premature death.
4. Cloning humans could alter our perceptions of individuality. Cloning humans would create at least two individuals with the same genetic profile. Each person would have their brains and bodies so that they would be like any other person with a genome profile. Each person would develop uniquely based on their circumstances, but there would also be concerns with individuality due to the physical similarities involved.
The people who do not embrace the idea of cloning humans could start to treat those who do differently. This outcome would end up creating a world that’s potentially similar to what the movie Gattaca portrayed.
5. Cloning humans would reduce the diversity of our genetic makeup. When there are only a handful of unique genetic specimens remaining in a species, then this creates a “bottleneck” where their survival is greatly endangered. We need diversity within our genome to reduce the risk of disorders forming due to our close relationships with one another. The health needs of people in the Ashkenazi Jewish population is evidence of this potential disadvantage.
Several conditions are more likely to occur when humans stay within the same genetic profile. Spinal muscular atrophy, Tay-Sachs disease, cystic fibrosis, and other long-term conditions can arise at a risk rate of 10% when a genetic bottleneck occurs in humans.
6. Cloning humans would lead to the exploitation of women. The only way that we can begin to clone humans is to have enough viable embryos available for scientists to use. IVF centers have over 400,000 of them in storage in the United States, but the need would be much higher than this. Scientists would need to produce enough cloned fetuses to create a sufficient quantity of viable stem cell lines. Women would receive medication injections that would help them to ovulate rapidly. Then there would be a requirement to undergo an invasive procedure to extract eggs to begin the embryo-making process.
Even under today’s best practices circumstances, up to 5% of women experience hyperstimulation when they begin IVF treatments. It is a side effect that leads to ongoing abdominal pain, reproductive health concerns, and infertility in rare cases.
7. Cloning humans would turn people into potential commodities. Even individuals who support the advancement of stem cell and embryonic research are against the idea of creating embryos specifically for research purposes. The danger we have when looking at the science of cloning humans is that society might try to produce medical outcomes for others.
Activated cells are still part of the human experience. Therapeutic human cloning might contribute to medical information that we can use in the future, but the costs may be too high to notice any benefits happening from this approach.
8. Cloning humans would change how we approach grief and unexpected loss. We live in a world where about 15,000 children under the age of 5 die every day. This figure has dropped dramatically since the 1990s when it topped 34,000, but it is still way too high. One child under 15 dies at an average of every five seconds, and the rate is 60 times higher in the highest mortality countries compared to those with the lowest rates. The idea of cloning humans would change how these parents approach grief because science could provide them with an exact duplicate.
It wouldn’t be the same child, but the new offspring would look and possibly act in the same way. If the parents give this clone the same name, it might feel like that initial loss never happened. This approach to life could eventually devalue it to the point where we shrug apathetically if something terrible happens. You can just go make a replacement.
Cloning humans often creates a “Sixth Day” debate about ethics. Many of our creation stories suggest that a deity produced two humans to begin populating our planet. This scientific process would change that process so that natural reproduction wouldn’t be the only way to have children. Anyone could potentially copy themselves with some cell collection and a laboratory setting that can grow a fetus.
When we examine the advantages and disadvantages of cloning humans, we’re asking ourselves the deeper theological questions that may not have answers. Would each copy have a soul? Does consciousness transfer into the new body?
Does a human clone age faster than offspring that are produced from more natural methods?
These are questions we might not need to answer just yet, but the science of cloning is advancing. We may need to address these critical points soon.
Sciencing_Icons_Science SCIENCE
Sciencing_icons_biology biology, sciencing_icons_cells cells, sciencing_icons_molecular molecular, sciencing_icons_microorganisms microorganisms, sciencing_icons_genetics genetics, sciencing_icons_human body human body, sciencing_icons_ecology ecology, sciencing_icons_chemistry chemistry, sciencing_icons_atomic & molecular structure atomic & molecular structure, sciencing_icons_bonds bonds, sciencing_icons_reactions reactions, sciencing_icons_stoichiometry stoichiometry, sciencing_icons_solutions solutions, sciencing_icons_acids & bases acids & bases, sciencing_icons_thermodynamics thermodynamics, sciencing_icons_organic chemistry organic chemistry, sciencing_icons_physics physics, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-physics fundamentals, sciencing_icons_electronics electronics, sciencing_icons_waves waves, sciencing_icons_energy energy, sciencing_icons_fluid fluid, sciencing_icons_astronomy astronomy, sciencing_icons_geology geology, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-geology fundamentals, sciencing_icons_minerals & rocks minerals & rocks, sciencing_icons_earth scructure earth structure, sciencing_icons_fossils fossils, sciencing_icons_natural disasters natural disasters, sciencing_icons_nature nature, sciencing_icons_ecosystems ecosystems, sciencing_icons_environment environment, sciencing_icons_insects insects, sciencing_icons_plants & mushrooms plants & mushrooms, sciencing_icons_animals animals, sciencing_icons_math math, sciencing_icons_arithmetic arithmetic, sciencing_icons_addition & subtraction addition & subtraction, sciencing_icons_multiplication & division multiplication & division, sciencing_icons_decimals decimals, sciencing_icons_fractions fractions, sciencing_icons_conversions conversions, sciencing_icons_algebra algebra, sciencing_icons_working with units working with units, sciencing_icons_equations & expressions equations & expressions, sciencing_icons_ratios & proportions ratios & proportions, sciencing_icons_inequalities inequalities, sciencing_icons_exponents & logarithms exponents & logarithms, sciencing_icons_factorization factorization, sciencing_icons_functions functions, sciencing_icons_linear equations linear equations, sciencing_icons_graphs graphs, sciencing_icons_quadratics quadratics, sciencing_icons_polynomials polynomials, sciencing_icons_geometry geometry, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-geometry fundamentals, sciencing_icons_cartesian cartesian, sciencing_icons_circles circles, sciencing_icons_solids solids, sciencing_icons_trigonometry trigonometry, sciencing_icons_probability-statistics probability & statistics, sciencing_icons_mean-median-mode mean/median/mode, sciencing_icons_independent-dependent variables independent/dependent variables, sciencing_icons_deviation deviation, sciencing_icons_correlation correlation, sciencing_icons_sampling sampling, sciencing_icons_distributions distributions, sciencing_icons_probability probability, sciencing_icons_calculus calculus, sciencing_icons_differentiation-integration differentiation/integration, sciencing_icons_application application, sciencing_icons_projects projects, sciencing_icons_news news.
- Share Tweet Email Print
- Home ⋅
- Science ⋅
- Biology ⋅
- Molecular Genetics (Biology): An Overview
The Pros & Cons of Cloning

Advantages & Disadvantages of Cloning
As far as anyone really knows, scientists have yet to clone a human being, and there are no federal laws against it in the United State. However, seven states prohibit it altogether, and 10 states only allow it for biomedical research. While more than 30 countries formally ban cloning for reproductive purposes, China, England, Israel, Singapore and Sweden do allow cloning for research, but disallow reproductive cloning.
Cloning Definition
The definition of a clone as explained by Encyclopaedia Britannica is a cell or living thing, an organism, that is "genetically identical to the original cell or organism" from which it comes. The word itself comes from the ancient Greek word "klon," which means twig. Single-cell organisms like some yeasts and bacteria naturally reproduce clones of parent cells via budding or binary fission. Individual body cells within plants and animals are clones that occur during a cell-reproduction process called mitosis.
Cloned Animals
In 2017, scientists in Shanghai succeeded in cloning two genetically identical long-tailed macaques, small brown and black monkeys with body lengths of 16 to 28 inches. The last successful cloning of a primate was in 1998, but scientists have also cloned about 20 different types of animals including dogs, pigs, frogs, mice, cows and rabbits since the first cloned animal in 1996.
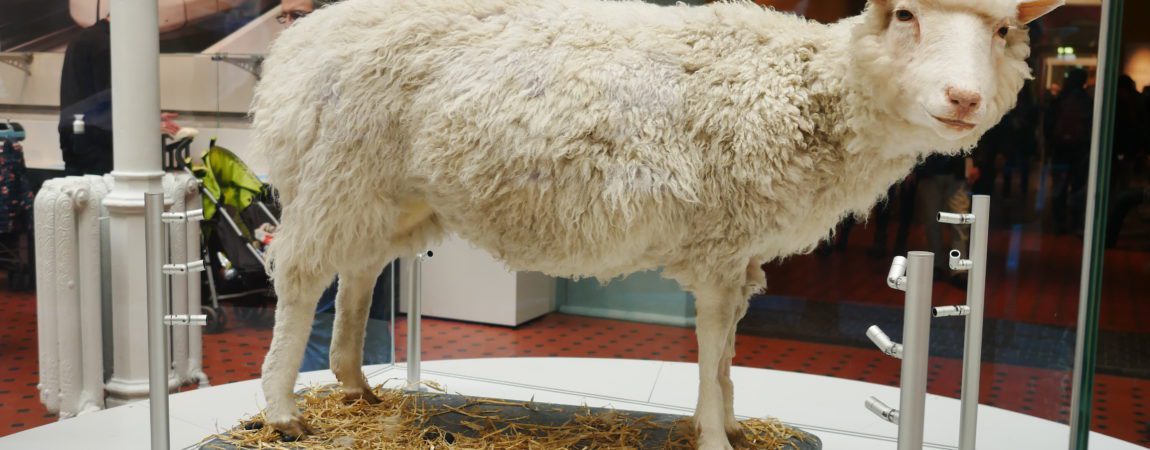
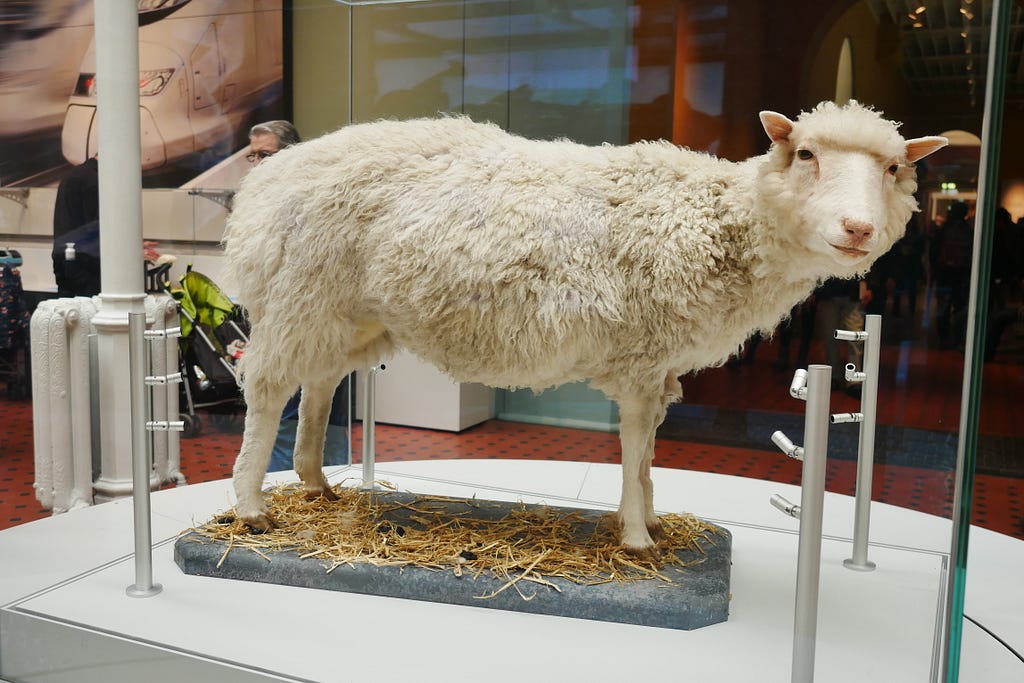
The First Cloned Animal: Dolly the Sheep
The first successful animal cloning occurred over 22 years ago, after a Scottish Blackface sheep surrogate mother gave birth to Dolly on July 5, 1996, at the Roslin Institute, part of the University of Edinburgh. Cloned from a six-year-old Dorset sheep, scientists analyzed her DNA at her first birthday and discovered that the telomeres at the end of her DNA strands (think eraser on a pencil head) were shorter that they should be for her age. As animals and humans age, these telomeres become shorter. The average age for sheep runs between six to 12 years. Dolly died when she was six, and though she had shortened telomeres, she lived an average life and produced multiple offspring through natural methods, but she also developed diseases in her later years.
Human Cloning Pros and Cons
The pros or advantages of human cloning include:
- Infertility: Infertile people or same-sex couples could have children made from cloned cells.
- Organ replacement: A clone, like in the movie, "The Island," could be a source for transplant organs or tissue. (There are ethical issues that arise from this, however.)
- Genetic research: Cell cloning could assist scientists in gene editing and research.
- Selective human traits: After editing or removing bad genes, cloning could lead engineered humans for specific traits.
- Human development: Cloning could enhance and advance human development.
The cons or disadvantages of human cloning raise moral, ethical and safety issues:
- Reproductive cloning: The negatives of human cloning including the making of designer babies.
- Human cloning: Could be a violation of the clone's individual human rights.
- Embryonic cloning: Cellular degradation occurs when too many clones are made from embryos.
- Unique identities: Cloning raises the question of a moral or human right to an exclusive identity.
- Societal impacts: Human cloning could produce psychological distress for the clone and society.
Effects of Cloning
While the purpose of cloning is to create an exact replica – if scientists cloned a human that appears identical to the original – it raises the questions as to whether the cloned human is an individual separate from the original and is due the same rights as any other human. Human cloning research and techniques could subject the clone to unacceptable risks such as a shortened life, bad health or other unknown problems. In the end, legalizing cloning on a wide-scale basis could lead to a disrespect for human life and the individual worth of a person, which might ultimately diminish all humans in the end.
Related Articles
Who invented cloning & when, gene editing is not about making designer babies, what makes dna fingerprinting unique, pros & cons of cloning plants & animals, pros and cons of recombinant dna technology, ethics research paper topics, a list of five characteristics of chromosomes, the importance of studying human dna genetics, how to write a notation of a karyotype, when is a mutation in a dna molecule passed to offspring, difference between recombinant dna & genetic engineering, how do i compare frankenstein & cloning, what are the differences between pcr and cloning, the production of recombinant human growth hormones..., what is embryo cloning, four major types of chromosomes, the differences in fraternal & paternal twins, recombinant dna technology for vaccine development, how are genes on sex chromosomes inherited.
- CNN: Monkey See, Monkey 2: Scientists Clone Monkeys Using Technique That Created Dolly the Sheep
- Encyclopaedia Britannica: Macaque
- The University of Edinburgh: The Life of Dolly
- North Carolina State Extension: Sheep Facts
- Georgetown University: Cloning Human Beings
- Johns Hopkins University: Ask an Expert: How Close Are We to Cloning Humans?
- The New Atlantis: Appendix: State Laws on Human Cloning
- Encyclopaedia Britannica: Clone
About the Author
As a journalist and editor for several years, Laurie Brenner has covered many topics in her writings, but science is one of her first loves. Her stint as Manager of the California State Mining and Mineral Museum in California's gold country served to deepen her interest in science which she now fulfills by writing for online science websites. Brenner is also a published sci-fi author. She graduated from San Diego's Coleman College in 1972.
Find Your Next Great Science Fair Project! GO
We Have More Great Sciencing Articles!
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- Search this website
Fung Institute for Engineering Leadership

Op-ed: The dangers of cloning
May 11, 2020 by Berkeley Master of Engineering
Satomi Angelika Murayama, MEng ’20 (ME)

“Sometime, somewhere, someone will generate a cloned human being.” — Ronald Green for Scientific American, 1999
Background on cloning
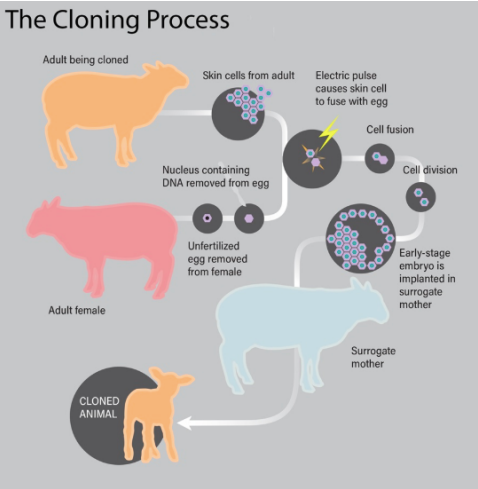
The low success rate of cloning and its medical complications
A mismatch of the public’s expectations with reality.
“We need to realize that cloning would produce a baby, not an adult.”
The ethical and moral concerns that surround cloning humans
“Cloning humans could lead to serious violations of human rights as well as human dignity, and it is up to authorities, laws and institutions to make sure to protect cloned individuals from being exploited.”
Concluding remarks
About the author:.
- “Eugenics — HISTORY.” October 28, 2019. Accessed November 1, 2019.
- Green, Ronald M. “I, Clone — Scientific American.” September 3, 1999. Accessed November 1, 2019.
- Savulescu, Julian. 1999. “Should we clone human beings? Cloning as a source of tissue for transplantation”. Journal of Medical Ethics. 25:87–95.
- “Therapeutic Cloning | Definition of Therapeutic Cloning at Dictionary.Com.” n.d. Accessed November 4, 2019.
- Weintraub, Karen. “20 Years after Dolly the Sheep Led the Way — Where Is Cloning Now? -Scientific American.” July 5, 2016. Accessed November 1, 2019.
- Weintraub, Karen. “Cloning’s Long Legacy — And Why It’ll Never Be Used on Humans|DiscoverMagazine.Com.” April 29, 2019. Accessed November 1, 2019.
- Weldon, Dave. “Why Human Cloning Must Be Banned Now | The Center for Bioethics & Human Dignity.” March 31, 2002. Accessed November 1, 2019.
- “What Is the Difference between Reproductive and Therapeutic Cloning? | NYSTEM.” n.d. Accessed November 1, 2019.
Mudd Hall 1798 Scenic Avenue Berkeley, CA 94709
(510) 642-0633 [email protected]
- Job Opportunities
Copyright © 2024 Accessibility • Nondiscrimination • Privacy • Sitemap
Prospective MEng Students
Sign up for our mailing list to receive program news and updates including information sessions, class visits and opportunities to connect with an admissions advisor.
Whether or Not Human Cloning Should Be Allowed Essay
Introduction, disadvantages of cloning humans, benefits of cloning, my recommendation, reference list.
Cloning can be defined as the process of producing an embryo which has similar genes to its parents and implanting it to a surrogate mother. A number of organizations have also given slightly different definitions for cloning. One such definition is that cloning is the preservation of cells in cultures to produce tissues, organs and even embryos (Head, 2010, p. 1).
It is a method of reproduction that is viewed as a prospective haven for people with reproduction problems. Cloning has attracted substantial ethics-related questions since its discovery. The first clone was a lamb named Dolly and since its birth, the possibilities and speculations of human cloning has attracted a lot of ethical questions concerning the same.
Up to date, the acceptability of human cloning is depended on personal opinion and its applicability is largely based on theory (Head, 2010, p. 1). This is despite the fact that cloning of cells to form tissues has been widely used in therapeutic procedures to treat people in hospital. Let us have a look at the benefits and the disadvantages of cloning.
Human cloning has more disadvantages than its benefits. Firstly, it is true that cloning is not in accordance with the Christian faith. Thus Christians, who make the world’s most popular religion, will feel as if they are playing God if they get involved in cloning activities. Among the weightiest arguments against cloning is the fact that the cloning of embryos makes them vulnerable and therefore the resultant child may develop serious problems for the rest of his/her life.
However, scientists argue that cloning may be developed to be more safe that the normal delivery as more advancements are made. Another disadvantage associated with human cloning is the fact that while cloning a human being, a number of embryos may be killed during testing (Farnsworth, 2000, p. 1). This is, arguably, killing of a human being and thus it taints the ethics behind the practice of human cloning.
There is also the issue about the expectations that people are bound to have on their clones. The original person will have very high expectations on the clone and this could lead to considerable pressure on the clone and disappointments on the part of the original person. This can be explained by the fact that with the identity that identical twins have and their differences in personality, nothing better is expected from clones.
Another worry is that since clones will be known to be copies of people, they may be discriminated against and thus their lives would be difficult. However baseless this claim appears to be, it has a point and its applicability would depend on how human clones would look. If they will be such that a person can identify a clone just by looking at him/her, then the argument is justified.
As mentioned above the technology of cloning is still inferior. During the development of the first clone, Dolly, more than 250 eggs were used and only one survived. It is thus apparent that application of this technology would have major drawbacks in terms of taking chances on life. It is possible that during testing, a number of embryos would be formed before the desirable embryo is formed.
This means that these embryos may be frozen for future use (Head, 2010, p. 1) or even destroyed, if their standards are unacceptable. This may be taken as the treating of a human being as an animal and it could attract considerable action by human rights activists. Besides the possible protests by human rights activists, the cloning process may prove to be haunting to the doctors in case they realize that they have been terminating lives by experimentation.
Cloning is associated with a number of benefits that make pro-cloning activists believe strongly in their convictions. For instance, cloning of human cells has been constructively applied in therapeutic cloning to which is used largely during organ transplant mts. It is used to ensure that the donated organ fits the patient and saves the patient from taking lots o drugs normally meant to suppress immunity.
However, most of these benefits are beaten by logic and a closer examination reveals the fact that we should not encourage cloning of human beings. One of the benefits of cloning is the fact that it is able to provide children to people with fertility problems.
However, it will be more reasonable to adopt homeless kids and offer them a home instead of undergoing the risky cloning procedure. Another benefit of cloning that is frequently cited by pro-cloning activists is the fact that people with genetic illnesses who do not wish to pass their sicknesses to their kids have an option with cloning. However, it is arguable that such people will do better with adoption of the numerous homeless children in orphanages.
It has been widely argued that adoption of cloning as a legal medical exercise would lead to creation of people with perfected characteristics since the genes that are used are often chosen and it is logical that a person wishing to get a child will go for a donor with good characteristics. This is both a good thing and a bad thing. This is because such people will not have a lot of heath and other problems but it will lead to a set-up that could bring problems.
These problems will most probably be experienced in social life. Among the evidently controversial benefits of cloning is the idea of body replacements which is so far theoretical. It suggests that a person having a given problem can be reconstructed to live as another person who does not have the problems he/she has. This is among the suggestions associated with cloning that has made people question the ethical appropriateness of cloning (McKay, 2010, p. 1).
As evidenced in the discussion above, my opinion about the cloning controversy is that, in as much as cloning is a highly admirable technological advancement, it is wrong to pursue human cloning. This statement is made with reference to the cloning of cells to form an embryo.
It is wrong to try to pursue ways of making life other than the way that God created us to use. It is no wonder that the process of cloning cells to form embryos is associated with a myriad of problems. Even for people who do not believe that God exists, should be discouraged by the killing of tens or hundreds of embryos in the lab during the testing period.
Additionally, the uncertainties that face human clones in terms of health, similarity to the original person and the like should also discourage people from taking such kinds of people (Farnsworth, 2000, p. 1). It is clear that anyone supporting embryo-forming cloning has not given the subject a keener thought since so many possible problems that could come with child-formation cloning can easily be acquired.
Despite the fact that cell-physiology is a complex process and it is normally cheaper to engage in tissue growth cloning. This kind of cloning is simpler and it has better objectives. This is because most clone-generated tissues are used by doctors to save lives in hospitals by helping them to treat major health complications (McKay, 2010, p. 1).
Humans have repeatedly got themselves into problems after doing things just because they could do them. We should thus be very careful before we start using any discovery in a bid to benefit from it. It is specifically necessary for a re-examination of the intricacies of cloning in order to make informed decisions on whether to legalize it or not.
Cloning should be studied deeply to establish the dangers it poses to a child it bears. At the same time, we should ensure that we fully understand the ethical issues posed by cloning before we claim to be pro-cloning. It is only in the case of commendable technological advancement that embryonic cloning should be allowed.
This is because some measures will have been put in place to ensure that we do not get disappointed after paying for cloning services. It can be clearly seen that the disadvantages of cloning outweigh its benefits and thus cloning should be discouraged at all cost.
Farnsworth, J. (2000). To clone or not to clone: The Ethical Question . Web.
Head, T. (2010). Should human cloning be banned? Web.
McKay, C. (2010). Should the cloning of human beings be prohibited? Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 23). Whether or Not Human Cloning Should Be Allowed. https://ivypanda.com/essays/whether-or-not-human-cloning-should-be-allowed/
"Whether or Not Human Cloning Should Be Allowed." IvyPanda , 23 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/whether-or-not-human-cloning-should-be-allowed/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Whether or Not Human Cloning Should Be Allowed'. 23 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Whether or Not Human Cloning Should Be Allowed." February 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/whether-or-not-human-cloning-should-be-allowed/.
1. IvyPanda . "Whether or Not Human Cloning Should Be Allowed." February 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/whether-or-not-human-cloning-should-be-allowed/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Whether or Not Human Cloning Should Be Allowed." February 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/whether-or-not-human-cloning-should-be-allowed/.
- The Human Cloning Debates
- Ethics of Cloning
- Cloning Humans as a Controversial Question
- Cloning in Terms of Society and Theology
- Human and Animal Production Cloning Concepts
- Molecular, Cell and Organism Cloning Techniques
- The Cloning Controversy
- Kazuo Ishiguro’s “Never Let Me Go” and Major Ethical Dilemmas Raised
- No to Cloning for Medical Research
- The Case of Human Cloning at Kyunghee University
- Hunger’s Nature and Factors That Influence It: Biological Concept
- The effect of glucosamine supplementation on people
- Strawberries History
- Stem Cell Research Implementation
- Cognitive Growth Stages: Piaget & Freud
- Search Menu
- Advance Articles
- Clinical Case Studies
- Journal Club
- Clinical Chemistry Podcasts
- Clinical Trainee Council
- Special Issues
- Clinical Chemistry Guide to Scientific Writing
- Clinical Chemistry Guide to Manuscript Review
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Call for Papers
- Why Publish?
- About Clinical Chemistry
- Editorial Board
- Advertising & Corporate Services
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Article Contents
- < Previous
The Cloning Debates and Progress in Biotechnology
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Paul L Wolf, George Liggins, Dan Mercola, The Cloning Debates and Progress in Biotechnology, Clinical Chemistry , Volume 43, Issue 11, 1 November 1997, Pages 2019–2020, https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/43.11.2019
- Permissions Icon Permissions
The perception by humans of what is doable is itself a great determiner of future events. Thus, the successful sheep cloning experiment leading to “Dolly” by Ian Wilmut and associates at Roslin Institute, Midlothian, UK, compels us to look in the mirror and consider the issue of human cloning. Should it occur, and if not, how should that opposing mandate be managed? If human cloning should have an acceptable role, what is that role and how should it be monitored and supervised?
In the February 27, 1997, issue of Nature , Ian Wilmut et al. reported that they cloned a sheep (which they named “Dolly”) by transferring the nuclear DNA from an adult sheep udder cell into an egg whose DNA had been removed ( 1 ). Their cloning experiments have led to widespread debate on the potential application of this remarkable technique to the cloning of humans. Following the Scottish researchers’ startling report, President Clinton declared his opposition to using this technique to clone humans. He moved swiftly to order that federal funds not be used for such an experiment and asked an independent panel of experts, the National Bioethics Advisory Commission (NBAC), chaired by Princeton University President Harold Shapiro, to report to the White House with recommendations for a national policy on human cloning. According to recommendations by the NBAC, human cloning is likely to become a crime in the US in the near future. The Commission’s main recommendation is to enact federal legislation to prohibit any attempts, whether in a research or a clinical setting, to create a human through somatic cell nuclear transfer cloning.
The concept of genetic manipulation is not new and has been a general practice for more than a century, through practices ranging from selective cross-pollination in plants to artificial insemination in domestic farm animals.
Wilmut and his colleagues made 277 attempts before they succeeded with Dolly. Previously, investigators had reported successful cloning in frogs, mice, and cattle ( 2 )( 3 )( 4 )( 5 ), and 1 week after Wilmut’s report, Don Wolf and colleagues at the Oregon Regional Primate Research Center reported their cloning of two rhesus monkeys by utilizing embryonic cells. The achievement of Wilmut’s team shocked nucleic acid experts, who thought it would be an impossible feat. They believed that the DNA of adult cells could not perform similarly to the DNA formed when a spermatozoa’s genes mingle with those of an ovum.
On July 25, 1997, the Roslin team also reported the production of lambs that contained human genes ( 6 ). Utilizing techniques similar to those they had used in Dolly, they inserted a human gene into the nuclei of sheep cells. These cells were next inserted into the ova of sheep from which the DNA had been removed. The resulting lambs contained the human gene in every cell. In this new procedure the DNA had been inserted into skin fibroblast cells, which are specialized cells, unlike previous procedures in which DNA was introduced into a fertilized ovum. The new lamb has been named “Polly” because she is a Poll Dorset sheep. The goal of this new genetically engineered lamb is for these lambs to produce human proteins necessary for the treatment of human genetic diseases, such as factor VIII for hemophiliacs, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) substance for patients with cystic fibrosis, tissue plasminogen activator to induce lysis of acute coronary and cerebral artery thrombi, and human growth factor.
Charles Darwin was frightened when he concluded that humans were not specifically separated from all other animals. Not until 20 years after his discovery did he have the courage to publish his findings, which changed the way humans view life on earth. Wilmut’s amazing investigations have also created worldwide fear, misunderstanding, and ethical shock waves. Politicians and a few scientists are proposing legislation to outlaw human cloning ( 7 ). Although the accomplishment of cloning clearly could provide many benefits to medicine and to conservation of endangered species of animals, politicians and a few scientists fear that the cloning procedure will be abused.
The advantages of cloning are numerous. The ability to clone dairy cattle may have a larger impact on the dairy industry than artificial insemination. Cloning might be utilized to produce multiple copies of animals that are especially good at producing meat, milk, or wool. The average cow makes 13 000 pounds (5800 kg) of milk a year. Cloning of cows that are superproducers of milk might result in cows producing 40 000 pounds (18 000 kg) of milk a year.
Wilmut’s recent success in cloning “Polly” represents his main interest in cloning ( 8 ). He believes in cloning animals able to produce proteins that are or may prove to be useful in medicine. Cloned female animals could produce large amounts of various important proteins in their milk, resulting in female animals that serve as living drug factories. Investigators might be able to clone animals affected with human diseases, e.g., cystic fibrosis, and investigate new therapies for the human diseases expressed by these animals.
Another possibility of cloning could be to change the proteins on the cell surface of heart, liver, kidney, or lung, i.e., to produce organs resembling human organs and enhancing the supply of organs for human transplantation. The altered donor organs, e.g., from pigs, would be less subject to rejection by the human recipient. The application of cloning in the propagation of endangered species and conservation of gene pools has been proposed as another important use of the cloning technique ( 9 )( 10 ).
The opponents of cloning have especially focused on banning the cloning of humans ( 11 ). The UK, Australia, Spain, Germany, and Denmark have implemented laws barring human cloning. Opponents of human cloning have cited potential ethical and legal implications. They emphasize that individuals are more than a sum of their genes. A clone of an individual might have a different environment and thus might be a different person psychologically and have a different “soul.” Cloning of a human is replication and not procreation.
Morally questionable uses of genetic material transfer and cloning obviously exist. For example, infertility experts might be especially interested in the cloning technique to produce identical twins, triplets, or quadruplets. Parents of a child who has a terminal illness might wish to have a clone of the child to replace the dying child. The old stigma, eugenics, also raises its ugly head if infertile couples wish to use the nuclear transfer techniques to ensure that their “hard-earned” offspring will possess excellent genes. Moral perspectives will differ tremendously in these cases. Judgments about the appropriateness of such uses are outside the realm of science.
Opponents of animal cloning are concerned that cloning will negate genetic diversity of livestock. This also applies to human cloning, which could negate genetic diversity of humans. Cloning creates, by definition, a second class of human, a human with a determined genotype called into existence, however benevolently, at the behest of another. The insulation of selection-of-mate is lost, and the second class is created. Few contrasts could be so clear. Selection-of-mate is so imprecise that, at present, would-be parents have to accept a complete new genome for the sake of including or excluding one or a few traits; cloning, in contrast, is the precise determination of all genes. If we acknowledge that the creation of a second class of humans is unethical, then we preempt any argument that some motivations for human cloning may be acceptable.
The opponents of cloning also fear that biotechnically cloned foods might increase the risk of humans acquiring some malignancies or infections such as “mad cow disease,” a prion spongiform dementia encephalopathy (human Jakob–Creutzfeldt disease).
The technological advances associated with manipulation of genetic materials now permit us to envision replacement of defective genes with “good” genes. Although current progress is not sufficient to make this practical today for human diseases, any efforts to stop such research as a result of cloning hysteria would preclude the development of true cures for many hereditary human diseases. Unreasonable restrictions on the use of human tissues in gene transfer research will have the inevitable consequences of delaying, if not preventing, the development of strategies to combat defective genes.
Wise legislation will enable humankind to realize the benefits of gene transfer technologies without risking the horrors that could arise from misuse of these technologies. Our hope is that such wise legislation is what will be enacted. In our view, the controversy surrounding human cloning must not lead to prohibitions that would prevent advances similar to those described here.
Wilmut I, Schnieke AE, McWhire J, Kind AJ, Campbell KHS. Viable offspring derived from fetal and adult mammalian cells. Nature 1997 ; 385 : 810 -813.
Pennisi E, Williams N. Will Dolly send in the clones?. Science 1997 ; 275 : 1415 -1416.
Gurdon JB, Laskey RA, Reeves OR. The developmental capacity of nuclei transplanted from keratinized skin cells of adult frogs. J Embryol Exp Morphol 1975 ; 34 : 93 -112.
Prather RS. Nuclei transplantation in the bovine embryo. Assessment of donor nuclei and recipient oocyte. Biol Reprod 1987 ; 37 : 859 -866.
Kwon OY, Kono T. Production of identical sextuplet mice by transferring metaphase nuclei from 4-cell embryos. J Reprod Fert Abst Ser 1996 ; 17 : 30 .
Kolata G. Lab yields lamb with human gene. NY Times 1997;166:July 25;A12..
Specter M, Kolta G. After decades of missteps, how cloning succeeded. NY Times 1997;166:March 3;B6–8..
Ibrahim YM. Ian Wilmut. NY Times 1997;166:February 24;B8..
Ryder OA, Benirschke K. The potential use of “cloning” in the conservation effort. Zoo Biol 1997 ; 16 : 295 -300.
Cohen J. Can cloning help save beleaguered species?. Science 1997 ; 276 : 1329 -1330.
Williams N. Cloning sparks calls for new laws. Science 1997;275:141-5..
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to Your Librarian
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1530-8561
- Print ISSN 0009-9147
- Copyright © 2024 Association for Diagnostics & Laboratory Medicine
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- World J Plast Surg
- v.5(3); 2016 Sep
Cloning: A Review on Bioethics, Legal, Jurisprudence and Regenerative Issues in Iran
Seyedeh leila nabavizadeh.
1 Legal Office, Vice Chancellor of Management Development Resource Planning, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran;
Davood Mehrabani
2 Stem Cell and Transgenic Technology Research Center, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran;
Zabihallah Vahedi
3 College of Law, School of Art, Shahed University, Tehran, Iran
Farzad Manafi
4 Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
In recent years, the cloning technology has remarkably developed in Iran, but unfortunately, the required legal framework has not been created to support and protect such developments yet. This legal gap may lead to abuse of scientific researches to obtain illegal benefits and to undermine the intellectual property rights of scientists and researchers. Thus to prevent such consequences, the attempts should be made to create an appropriate legal-ethical system and an approved comprehensive law. In this review we concluded that the right method is guiding and controlling the cloning technology and banning the technique is not always fruitful. Of course, it should be taken into accounts that all are possible if the religion orders human cloning in the view of jurisprudence and is considered as permission. In other words, although the religious order on human cloning can be an absolute permission based on the strong principle of permission, it is not unlikely that in the future, corruption is proved to be real for them, Jurists rule it as secondary sanctity and even as primary one. If it is proved, the phenomenon is considered as example of required affairs based on creation of ethical, social and medical disorders, religious and ethical rulings cannot be as permission for it, and it seems that it is a point that only one case can be a response to it and it needs nothing but time.
INTRODUCTION
The word “cloning” is referred as “making an identical copy” which has a Greek origin of “Asexual replication of an organism”. Cloning has been used in various fields of biology while the DNA molecule of cells with genetically identical structure is known as a clone. Honey bees propagate by cloning as the queen bee mates once during her life and the eggs propagate in the queen up to thousands of eggs that are further hatched into bees. 1 Although Joshua Lederberg advocated cloning and genetic engineering as a subject of speculation in 20th century, scientists and several authorities started to take the prospect seriously in the mid-1960s. 2 James D. Watson was the person who publicized the potential and the perils of cloning in 1971. 3 With the cloning of a sheep by somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) called Dolly, the idea of cloning of human has become a hot debate subject. 4 Advanced Cell Technology in November 1998 by using SCNT created the first hybrid human clone. A nucleus was taken from a man’s leg cell and was introduced into a cow’s egg while its nucleus was removed. The hybrid cell was cultured, and developed into an embryo and after 12 days, the embryo was destroyed. 5
In 2004 and 2005, pluripotent, embryonic stem cells were successfully harvested from a cloned human blastocyst using SCNT and eleven different patent-specific stem cell lines were created as the first breakthrough in cloning of human. 6 In January 2008, the first five mature human embryos using SCNT were created while each embryo was created by taking a nucleus from a skin cell and inserting it into a human egg from which the nucleus was removed. The embryos could be developed only to the blastocyst stage, and were destroyed later. The “holy grail” that was useful for therapeutic or reproductive cloning was used to generate embryonic stem cell lines. 7 - 9
In 2011, the New York Stem Cell Foundation could generate embyronic stem cell lines, resulting in triploid cells, which were not useful for cloning. 10 - 12 In 2013, embryonic stem cells were created using SCNT. Four embryonic stem cell lines were derived human fetal somatic cells using oocytes from the same donor, ensuring that all mitochondrial DNA inherited was similar. 10 Advanced Cell Technology reported replication of Mitalipov’s results and showed the effectiveness by cloning adult cells using SCNT. 4 , 13 So cloning has attracted attention of physicians, medicolegal specialists, and other scientific circles as it has opened a new window to the human with its therapeutic advantages but with some concerns too. 14
The UNESCO declaration on human genome, the human rights of 1997 and the European Convention on Human Rights and Biomedicine (Strasburg) proposed concerns with this scientific phenomenon and the experimentation on human. 15 After the emerge of human cloning, the legislature passed laws regarding requirements, structures, resources and the evolving capacities of civil rights and the future legal researches, resulting in irreparable consequences; especially, for concerns about human rights and criminal law in the third millennium. 16
In recent years, the cloning technology has remarkably developed Iran, but unfortunately, the required legal framework has not been created to support and protect such developments yet. This legal gap may lead to abuse of scientific researches to obtain illegal benefits and to undermine the intellectual property rights of scientists and researchers. Thus to prevent such consequences, the attempts should be made to create an appropriate legal-ethical system and an approved comprehensive law. 14
Law and ethics are basic and fundamental concepts in this area and according to 4 th principle of constitution law stating that all laws should be in the framework of Islamic regulations and as there is not any specific law related to human cloning in the country, we should refer to accredited judicial decree or ethics. On the other hand, based on principle 177, constitution law, it is an unchangeable principle and it has been constant after all reviews. Although in bioethical and jurisdictional point of view, the status of reproductive and therapeutic cloning is analyzable, and sanction is the legal status of the matter to be required and of great importance. 17
Therefore, legislators should take actions toward criminalization of the issue with respect to principle of legality of crime and punishment. One of the primary and certain principle of criminal law is the principle of legality of crimes and punishments; that is, briefly: first, no action is a crime unless it is already known and attributed as a crime by the legislator; second, no punishment is possible to be ruled unless it is already passed to be executed for the crime by the legislator. 17 The major objective of this review is the legal analysis of the subject. However, the related bioethical and jurisprudential aspects will be discussed.
APPLICATIONS OF CLONING
Work on cloning techniques has advanced our knowledge on developmental biology , especially early human development. Basic understanding on signal transduction together with genetic manipulation within the early human embryo has the potential to respond to many developmental diseases and defects requiring aesthetic and regenerative medicine to enter the field. 18 Cells created by SCNT are beneficial in research of the causes of diseases, and as model systems for drug discovery 19 , 20 Cells produced with SCNT could eventually be used in cell transplantation, 21 or for creation of organs in transplantation, called regenerative medicine . Stem cell therapy is cell transplantation in treatment or prevention of a disease or condition. 22 Bone marrow transplantation is a widely used form of stem cell therapy. 23 The potential use of stem cell therapy in treatment of several diseases is underway. 24 , 25 Regenerative medicine would allow autologous transplantation of stem cells, and removes the risk of organ transplant rejection by the recipient. 26 For instance, in liver diseases, a new liver may be grown using the same genetic material and transplanted to remove the damaged liver. 27 Human pluripotent stem cells have been promised as a reliable source to generate human neurons, with the potential for regenerative medicine in brain and neural damages. 28
HISTORY OF CLONING
Cloning is the outcome of the hard works on use of genetic engineering in animal breeding, treatment of hereditary diseases in human and replicating organisms. 16 In 1901, transfer of nucleus of a salamander embryonic cell to a enucleated cell was successfully undertaken. During 1940-1950, scientists could clone embryos in mammals. In 1956, Spemann’s hypothesis was proved and in 1962, mature frog was produced by transferring nucleus of intestinal cells of tadpoles into the eggs while their nucleus were removed. 29
Sheep cloning from embryonic cells was performed in 1984. In 1994, bovine cloning was conducted from embryonic cells of another cow. In 1996, first cloned animal called Dolly was produced in Scotland using mature cells of mammary glands of a mature sheep. The importance of Dolly was for its production from differentiated cells of mammary glands while the previous cloned animals were produced from embryonic cells. The birth of Dolly led to undermining the impossibility of simulation by differentiated and specific cells. In the late 2000, scientists cloned 8 species of mammals. In 2003, the first cloned mule was produced by the American scientist. In 2005, the first cloning of a dog called Snoopy was carried out. In 2006, the Iranian scientists succeeded to clone a few sheep among the Middle East countries. 29
Bonyana was the first cloned calf in Iran. The birth of this calf was the outcome of a series of researches from 2003 to produce various livestock by IVF. Cloning and genetic engineering lead to the birth of Royana, the cloned sheep and Hanna, the cloned goat. 30 Tamina was the second cloned calf in Iran and it was cloned from the cell origin similar to Bonyana, the first cloned calf. This calf was born with the weight of 70 kg by Caesarian operation in Foka Animal Breeding Complex affiliated to Social Security Organization after the 280-day pregnancy period but after a few hours died due to an acute brucellosis, while Tamina also showed the signs and symptoms of some anatomic disorders at birth. 30
HUMAN CLONING
Reproductive Cloning
Reproductive cloning is the process where the asexual cells are transferred to an egg while its DNA has been removed and after the development of an embryo, it is placed into the recipient uterus. This process can result in production of a human while the cloned individual would totally be identical to the genetic donor. 15
Therapeutic Cloning
The therapeutic cloning also known as embryonic cloning is actually used to produce human embryos for research purposes. The objective of this type of cloning is not the production of a cloned human but the culture of cells is used in human researches and for treatment purposes in regenerative medicine. These cells are very important for biomechanics researchers because they can be used to produce any types of cells of human body. These cells are extracted from embryo after 4 days of cell division. The process of extraction ruins the embryo and this issue creates a lot of ethical concerns. The researchers hope to replace the cloned cells for the cells destroyed by diseases such as Alzheimer’s, cancer, etc. 31
Advantages of Cloning
The cloning technology may have positive and negative effects with advantages as well as disadvantages and even can be with fatal effects. The most important advantages of cloning can be (i) Replicating and propagating plants and animals, (ii) Recreating and replicating extinct or going to extinct animals, (iii) Propagating genes and saving newborns from hereditary diseases, (iv) Helping to discover treatment methods of infertility, (v) Dividing the developed embryo into several cloned embryos so that in case of probable incidents happening to one of them, the other clone can replace it, (vi) Using it to reproduce the ambulated limbs and replicating them to culture and replace the destroyed organs such as liver, heart. One of the advantages can be that the cloned limbs have full genetic adaptation with the recipient individual who is the donor of the stem cells, (vii) Helping to control population regarding shortages of male or female sex due to incidents such as war and earthquake, and (viii) Helping to reduce sorrows and pains of people suffering from the death and absence of their loved ones by cloning them. 32
Disadvantages of Cloning
Because this technology is new and its outcome is not public and common yet, the damages and losses are sometimes resulted as internal damages by nature of the operation and the process of cloning. Sometimes, there are external damages imposed on the cloned society or individual after the cloning operation. Internal damages may be (i) The cloned living organism may encounter genetic problems and complications in long term, (ii) The more the cloned people are in the society, the more their extinction probability will be; because there are about one million four hundred thousand nucleotides in the body of every human and this remarkable variety is the origin of human generation survival; while the decrease in the genetic variety of individuals in a society, which is the result of cloning– highly increase the probability of their death by a special virus or a pathogen, (iii) 99% of attempts to clone human may result in creation of monsters, (iv) Biological disorders such as cancer, (iv) Premature aging: Dolly, the sheep, aged soon after cloning and the cloned baby will age at birth; because if the genetic donor is fifty-year-old, the new born will be a fifty-year-old one, thus, it will be suffering from premature aging like Dolly. 32
External damages can be (i) Belief damages, (ii) Human moral damages, (iii) Cloning propounds a way to stop family establishment and perseverance against the related difficulties and it leads to satisfying sexual instinct and contenting oneself with cloning to have a child, (iv) Cloning is against divine nature. The nature of human and other living things is based on marriage tradition and the Holy Quran frequently emphasized on the creation of human based on the marriage tradition, but cloning is independent of either one of the couples. Besides, marriage has advantages and useful effects such as comfort, friendship, kindness and love in addition to reproduction and propagation of generation and such emotions ruins in cloning. 32
(v) Cloning can result into harmful side effects for the individual like other unnatural methods in medicine. The use of powder milk for breast milk, Caesarian operation for natural delivery, etc. has brought a lot of problems for the individuals and they are not recommended unless required. Cloning will have the same side effects and problems and because there is not a necessity for its operation, and bearing such health and social damages are not scientifically justifiable. A healthy body can affect mental health as proper nutrition does on physical health too. Therefore, regarding children nutrition, it can indirectly be useful to improve mental and spiritual health. It is very important to consider breast feeding for children because breast milk has lots of antibodies and it is easily digested by the newborn increasing the chance of her or his survival. In the verse 233 of Baqarah, Holy Quran, it is stated: mothers should feed their children two years. 32
(vi) Development of cloning and existence of the cloned people in the society can lead to complications arising from the failure to recognize and distinguish; such as failure to recognize students, distinguish criminal from innocent, or recognize wife and husband among similar people and it is obvious that such complications result in anarchy and legal difficulties, and (vii) Cloning human with exceptional physical strength or intelligence and benefiting from them in aggression and oppression of others can be another harmful effect that can provide the background for modern slavery and exploitation of human. 32
Bioethical Issues in Cloning
Bioethics as one of the new branches of “applied normative ethics” is a new field of research which reviews and analyzes challenges caused by using innovations and technologies in bioscience and biomedicine, and also regulates the does and does not in this area in the interdisciplinary space systematically. 33 Considering bioethics in cloning, it refers to different ethical issues especially from religious and secular points of views even human therapeutic and reproductive cloning are not presented commercially, but animals are currently cloned and the technique is used in livestock production. In therapeutic cloning, generate tissue generation takes place to treat patients who cannot obtain transplants, 34 resulting to avoidance of the need for immunosuppressive drugs, 35 and to stave off aging effects. 36 In reproductive cloning, parents who cannot procreate are advised to have access to the cloning technology. 35
The protest against therapeutic cloning is just on the use of embyronic stem cells, which is related to the abortion debate. 35 Regarding reproductive cloning, there are concerns that cloning is not yet highly developed to confirm the safety of the technology, and could be prone to abuse and concerns about how cloned individuals could integrate with the society. 37 - 40 In 2015, about 70 countries declared banning of human cloning. 41
Principles on Elimination of Damages in Cloning
The first principle states that nobody has the right to damage others and has no moral justification. Elimination of damage; especially, next to the principle of equality and non-discrimination will have more importance regarding ethical and human right interpretations. Considering human cloning, it is believed that the only type of cloning that may eliminate these harmful effects can be therapeutic cloning. In other words, the principle of elimination of harm states that the researches on cloning should not harm other humans and or cloned individual. Although cloning may have advantages to human generation such as prevention from genetic disorders and diseases, it may also result in reproduction of humans with specific capabilities and cause the abuse of the cloned individuals by others and its producers as tools. In this way, the cloned individual may suffer from unwanted harms while he basically plays no roles in accepting or refusing the harms. 42
Principles of Usefulness of Cloning
This principle is considered as the second fundamental principle in the bioethics and it is stated that the hidden assignments in this principle prevent imposing harms and losses on others and it is close to conservative views of legal documents and moves toward promotion of goodness; but therapeutic cloning is not opposed in this area. In fact, it can be said that this principle is along with principle of elimination of harm. In other words, the researches should not harm the cloned individual and other people but work on his and other’s favor. Of course, the answer to what advantages the cloning can have for the cloned individual is not clear because the human existence differs from doubtful identity and relative is not considered as special advantage for the individual. If the difference is due to a specific capability, it seems that the specific capability is reproduced more for the benefits of others than the cloned individual himself. 42
Human End-in-Itself in Cloning
Based on this principle which is stated as the third principle, all humans end in themselves and they have a dignity as a human. Thus, we are not authorized to disregard individuals to the level of devices and even animals to satisfy our research objectives in the area of biotechnology. 14 Based on Kant’s formula of end-in-itself, any actions that cause to use humanity as a mere means not as end-in-itself, are forbidden and immoral. There are various interpretations of humanity end-in-itself: not to do anything about a human without his knowledge; respect his freedom, will and independency; help his happiness; and respect others’ humanity. Thus, based on Kant’s formula of end-in-itself, any cloning operations which disrespect the humanity of humans as a mere means for other purposes are forbidden. 29
Therefore, the cloning is forbidden to reproduce and replicate a large group of the cloned humans for the purposes of war or in peace time, such as: hard and overwhelming works, reproduction of useful humans for the society such as the genius of science, politics, and military, and to reproduce children of desired genotypes, and to replace newly-dead spouse, children or relative. In such cloning, humanity of the reproduced humans is not the purpose, but the developing of the society and the meeting of demands of other humans. It seems that the cloning to reproduce a child for infertile couple and the therapeutic cloning (providing that the beginning of humanity and human dignity is not considered from the time of fertilization and conception) to reproduce transplanted organs, is authorized because humanity is not a mere means. 29
In therapeutic cloning, because the current technology is used for welfare, treatment and generally, for serving human and humanity, it is human who is the purpose and it does not conflict with Kant’s formula of humanity fundamentals; (Of course, if we do not consider the embryo as a human), because we solve the problem of some of humans and use some others as a mere means (because all humans do not need this technology). It can be stated that all humans are not used as a mere means, but it should be taken into accounts that Kant’s purpose of not dealing with human as a mere means is quantitative and qualitative. He emphasized on the fact that humanity is not quantitative and should not be acted as a tool. In addition, he forbid the use of human as a tool even by the person himself. 43
The respect to human dignity is in a manner that it is highly considered in the international rules and declarations; for example, in the introduction and some of the articles of International Declaration on Human Genetic Data, 2003, observing the human dignity is a must and also the first article of International Declaration on the Human Genome and Human Rights, 11 November 1997, the human genome is considered as part of human heritage and it declares that human genome is the principle of fundamental unity of all members of the human family and the need for recognition of their inherent dignity and distinction and the article 11 of the declaration knows the human reproductive cloning in contrary to human dignity. 44
Principles of Reciprocity in Cloning
Generally, this principle states that “Act others as you desire to be acted”. Kant’s formula of the universal law regards the same notion. In fact, the formula of human end-in-itself together with this principle can improve normative system of Kant’s ethics. The principle corroborates ban of experiments on human cloning supposing that the clone is considered as human, but it is not believed that other types of cloning is in contrary with this principle. Of course, it is noteworthy that the principle encounters a basic challenge in the area of cloning; because basically, the possibility of reciprocity between the cloned individual and the researcher who reproduces it, is negated; that is, they both are not on equal terms providing reciprocity for both, but the cloned individual unintentionally becomes the objective of the research and the outcome is his different presence in the world of existence. 42
Violating the Principle of Informed Consent in Cloning
One of the main principles of bioethics is the principle of consent. The individual’s consent is one of the issues of cloning operation. The issue considers the consent of the cloned product; that is, whether the cloned individual is satisfied with the cloning operation and permits the unnatural creation method? Obviously, the answer to the question is unknown because the clone does not exist at the time of cloning operation and he cannot state anything on the matter and after birth, the operation is completed and finished. Perhaps, some say that in the natural process, the newborn does not play any role in his birth and creation. In reply, it should be asked how the issues related to the many physical damages and hidden and unknown mental risks in the method of abnormal birth of the cloned child compared with the method of natural birth can be justified? 45
Therefore, pursuant to ethical principles and potential risks of cloning operations, further contemplations are needed on the technology and it should be avoided at least until its hidden aspects are clearly revealed. In regard to consent of the cloned child, the consent and permission of the donor of oocyte, the pregnant mother and even the donor of the somatic cell are also considered and it is an issue which can be harassed and abused. 45
With a review on the mentioned principles, we conclude that the researches on reproductive cloning should include the following six features: (i) Be advantageous to society and impossible for any other methods, (ii) Previously operated on animals, (iii) Operated in a manner that all types of unnecessary physical and mental pains are prevented, (iv) If death or deficiency of the clone is probable, the operation is prevented, (v) Actions taken to protect the individual against damages, deficiency or death, and (vi) The experiments should be stopped if the responsible researcher believes at any phase of the research, continuation of the researches may result in damage, deficiency or death of the tested individual. 42
Bioethical Analysis of Therapeutic Cloning
The subject is more complicated about the therapeutic cloning. By using this technology, it is possible to obtain tissues immunologically compatible with the recipient and it is considered as a definitive treatment for diseases such as Huntington’s, Parkinson’s, Multiple Sclerosis, Myocardial Infarction, etc. Millions of patients around the world benefit from such researches but on the other hand, making such researches requires reproduction and then destruction of the developing embryo. Is it possible to reproduce a human embryo for one’s purpose, but it should be remembered that such embryos are the initial point of life of all human being. It is not right to cut the string of life of the cell collection at the beginning of life for the purpose of medical research. 46
Anyway, assessing the advantages and disadvantages of this technology is complicating and difficult because on one hand, it is a promise of the great probable advantage to the humanity and on the other hand, it causes several moral doubts and concerns at the level of society. What adds more complications to this subject is that: first, it is not certain that scientists achieve what they claim. Second, there might be other alternatives with the same advantages and without the mentioned ethical issues. Such alternatives have already been proposed such as using adult stem cells. The most concerns made by the opposition about litigation of therapeutic cloning are on two axes. 46
The first issue is the destruction of the initial embryos which is considered as disrespect of the newly-reproduced human and the initial point of human life. Second, there is the fear that if the reproductive cloning is banned and the therapeutic cloning becomes free, whereas the initial procedures and techniques of both of the methods are similar, the freedom is abused in this regard and the embryos are developed for the purpose of human cloning. This concern is so serious that the American government strongly criticized to United Nations in a declaration on putting therapeutic cloning out of control and knew it a way to operate reproductive cloning. 46
Because the research institutes which clone the human embryo are able to use it for any purpose; for example, transferring the human embryo to a hired uterus and reproducing it to a human fetus. In spite of all respect for the new life in the frame of human embryo, supporters of therapeutic cloning believe that human dignity and legal status of the six-day embryo is never equal to a mature human and therefore, the moral problems arising from damage of the embryo are fewer than what the opponents claim. They consider an average value for human embryos and believe that using the human embryo at the first stage of development is not objected if cloning is operated in the precise legal framework. 46
Some others believe that embryo is a string of cells and it is worth as much as other cells in a body; thus, doing researches on ancestral cell and therapeutic cloning are the same as other cellular and molecular biology researches and they do not have any types of moral problems. On the other hand, it is noteworthy that the purpose of reproduction of embryos is not “their destruction” but it is to serve life of humans and progress of medical science. To prevent from long-term culture of embryo and future abuse from it, the experiments will be done on embryos of less than 14-day-old. At this stage, organs are not differentiated yet. Supporters agree with the laws which put therapeutic cloning operation in the certain framework and by controlling the process of cloning operation prevent from any abuse and violation from the related regulations. They believe that the benefits of therapeutic cloning are so many that the technology cannot be ignored due to ethical problems. 46
Jurisprudential Analysis of Reproductive and Therapeutic Cloning
This subject is important because reproductive and therapeutic cloning is considered a new technology and is different and various related aspects should be recognized and studied and put into the legal content. 17
JURISPRUDENTIAL ANALYSIS OF REPRODUCTIVE CLONING
Jurisprudence of Sunni Scholars
They discussed cloning with reasons such as interfering in God’s will, corruption on earth, changing tradition, variety, creation and breaking Muslims’ believes, and they expressed their comments by issuing Fatwa, resolutions and declaration. In idea of the religious intellects consider the sanctity of the matter to be so obvious that the opportunity for criticism and discussion of the followers in this area is closed. Some of Sunni scholars exceptionally authorize it in some cases such as treatment of infertility, providing that the technology is guaranteed to be harmless. To keep sanctity of human cloning, some declare the doubtful speech that the cloning process changes the creation process by God and it is an act of evil and forbidden. This challenge is stated by some of the Sunni scholars. They refer to some of the verses and cited comments to emphasize on sanctity of changing creation. Accordingly, change of creation is the temptation of Devil and Devil also tempts to corruption, prostitution and sins; thus, changes in creation is prohibited. 47
Shia Jurists
Generally, the views of Shia scholars on human cloning can be classified in four categories of (i)
The total permit for human cloning: Some of jurists and scholars allow the cloning due to lack of specific documents and clear evidence on the sanctity of cloning and according to the principle of permissibility. For example, Ayatollah Sistani and Ayatollah Fazel Lankarani considered human cloning not to be problematic if is limited to reconstruction of tissue damages. Also, Ayatollah Moosavi Ardabili believes that there is no strict reason for sanctity of human cloning and this operation is permissible if is limited to reconstruction of tissue damages. 17
(ii) Limited permission on human cloning: Based on available documents and according to the first principle in this case, some authorities have allowed human cloning but they believe that if it is widely operated, it would be problematic; such as, recognizing the cloned individuals from one another, therefore, they give authorization by case and they do not allow it at large scale. According to reports by Professor Hassan Javaheri, there is no problem on cloning happening in nature, but it is not legal to be undertaken at large scale. (iii) Secondary sanctity of human cloning: Some of the Shia Jurists believe that human cloning is not a problem in nature based on their arguments, but operating it in laboratories may lead to inevitable corruption such as intervention in natural system. 17
Therefore, to prevent from such corruption, the human cloning is considered as the secondary prohibition. Ayatollahs Seyed Kazem Haery, Sheikh Javad Tabrizi, Seyed Sadegh Shirazi, Yoosef Sanei and Naser Makarem Shirazi supported this statement. Ayatollah Makarem Shirazi responded to an exception in this issue: “Based on religious rules, it is not naturally forbidden but with respect to its probable side effects that may lead to disorders in the human society and they are obvious for experts, its operation will would be problematic. 17
Ayatollah Yoosef Sanei also stated that normalizing and legalizing the cloning in a manner that it is considered the same as having children by marriage, is absolutely not compatible with Islamic regulations and jurisprudence and it results in corruptions which must necessarily be avoided legally, socially, ethically and developmentally. He has declared that the prevention and punishment of its perpetrators and attempters is a must and a rational and religious assumption for all humans especially, legal and executive authorities and propagators. However, he allowed human cloning in rare cases and necessities when it is beneficial for human health and also the use of its scientific aspects; such as the cloning of organs for treatment purpose. 17
(iv) Ultimate prohibition of human cloning: The owners of this attitude basically prohibit human cloning as a sanction action and consider it as the ultimately illegitimate. According to changes in creation and based on the principle of non-possession of body for human and therefore, the danger and necessity of permissibility in this regard showed the ultimate prohibition of human cloning. Despite the four categories and disagreements, most of the jurists banned human cloning. In other words, although according to the principle of presumption of innocence, initially, most of the Islamic intellects ruled on its natural permissibility and those who agreed and prescribed the cloning mentioned some of the applications and functions of this technology.
But ultimately, a large number of the Muslim jurists considered it as the secondary prohibition despite its primary and natural permissibility. Considering the consequences of such abuse, potential and actual corruptions and due to the necessity of life protection and respect to human dignity and the reputation of “the principle of no harm”, they emphasized on the necessity of prohibition of prescribing the process until clearance of all aspects of the issue and safety against probable risks and enough assurance in this regard. 17
Jurisprudential Analysis of Therapeutic Cloning
The significance of jurisprudential analysis of therapeutic cloning is due to the unique features of the technique which play a crucial and exclusive role in treatment of incurable and deadly diseases. Despite such a wonderful role, whose aspects reveal development of scientific researches everyday, it is required that the jurisprudence has comment on the mentioned problem, the problem which is referred as the loss of ethical dignity and human right on the embryo. When embryo is developed, three actions can be undertaken including, (i) To allow to be destroyed, (ii) To place it in uterus where it develops into a human similar to the donor of the cell in terms of growth, and (iii) T use it to obtain stem cells. 48
The operation is the third stage of therapeutic cloning which is described later. It should be known that which one of the three stages of therapeutic cloning is permitted and which is not? Naturally, if only one of the stages is considered prohibited, it is not possible to give fatwa of permission for therapeutic cloning which includes all the stages. The permission of therapeutic cloning is subject to permissibility of all the stages. Now to review the three stages: The first stage is the use of the cell from human body which is automatically not objected. If there is a problem, it is in the next stages which are not related to this stage. 48
In the second stage, the cell is processed and developed for the next stage when the cell is at 6 or 7-day of age. In this process, three actions should be done: (i) Enucleation of cell, (ii) Placing it into the enucleated oocyte, and (iii) Simulating the oocyte by chemical or electrical current to start cell division. This type of manipulation in this stage is not prohibitive itself. The only problem is that it might be banned as the point of prohibition. Of course, this initial point is the time when we know that if the operation begins and due to loss of control, the opportunity of abuse in the situation is available and the development of human embryo becomes inevitable. 48
If human cloning, either as primary or secondary, is a prohibited operation, the operation as the starting point of prohibition will be prevented. But, the third stage is the extraction of the hidden cell mass in the embryo for culturing and obtaining stem cells. This problem caused a serious disagreement in Christianity and Islam in this stage. The problem is the extraction of cell mass which results in disappearing and killing of the fetus and its potential to become a human. To rule out therapeutic cloning, it should be reviewed in three aspects of (i) To review the judgment as “fetal homicide”, (ii) To review the judgment as “sanctity for destruction of the embryo regarding the development in the murder case in the view of the judge and not regarding the customary murder”, and (iii) To review the judgment as “a mere prohibition of embryo destruction”, not prohibited regarding the murder. 48
Naturally, there is a difference between the three categories. The category of sanctity for murder is more severe than the sanctity for the second and third categories. In the third one, the most important rule can be performed easier and more; that is, based on this theory, it can be said that although embryo destruction is banned, whenever a human is suffering from a severe illness and sometimes leading to death, with respect to the more importance of the human life, the embryo is allowed to be destroyed to obtain the stem cell to treat the patient. 48
Legal Analysis of Reproductive and Therapeutic Cloning in Iran
As cloning is not still very common and is in the stage of development and has not been tested after birth, the countries with cloning technology do not have a complete and codified law for it. Human cloning may legally cause problems, including the reproduced individual that will be completely similar to the genetic donor, even his fingerprints, and it is exclusive for everybody and considered as the major factor to arrest the offender. So the genetic owner can commit a crime and escape from law, and allocate his action to the cloned individual or vice versa. Thus, the rights and freedom of both of them will be withdrawn. 31
In addition, the real culprit will not be identified and the rights of the accused person will be ignored. The cloned human does not have a father (because it is not from the male sperm) and a mother (because it is not by composition of gamete) and a sister and a brother and a relative, and it is grown in the uterus which is not of his mother but the surrogate mother. In brief, he is an individual with no relativity. If a virgin woman has a child by cloning of her sexual cell, is her pregnancy legitimate or not? And is the born baby her clone or sister or daughter? Who does the cloned individual inherits? If somebody kills the cloned individual, what are the rules for compensation or retribution? And who is responsible for alimony and custodianship of the cloned individual? There are some other legal problems too. 31 It should be taken into accounts that any anti-science law cause the scientists and researchers to emigrate to other territories and societies with less strict laws. One of the tens of reasons for brain drain is lack of right and proper laws to protect scientists and intellects. 49
At the time of writing the review, it is unlikely that individuals or centers in the country, process the idea of the human cloning and perhaps, they have made arrangements and taken into action in this field. This idea and the probability of its occurrence have revealed the lawful Iranian responsibility more than before and showed the necessity of taking immediate action to fill this legal gap. 17 On the other hand, now when the researches in the field of cloning have started, it is not possible to revert to or ban or ignore them instead, the right action is to direct the researches on cloning and pass the required rules of law for this field. 42
It seems that the prospects of every country about therapeutic cloning are dependent on the worth of human embryo in the legal system. The truth is that even in the countries where abortion is considered as the criminal act and punishable, and exceptionally, the mother’s life is in danger or the fetus is malformed or even the embryo is a result of adultery rape, abortion is predicted. Undoubtedly, therapeutic cloning which is the final solution for the treatment and health of human leads to the destruction of embryo and cannot be placed among any of the aforementioned exceptions because the cloned embryo is merely destroyed for other’s health and not its existence endangers other’s life. Certainly, in the countries where the value of embryonic and fetal is not considered equal to life or even health of the human and due to different reasons, abortion is not legally banned, the therapeutic cloning encounter less challenges. 15
To clarify the criminal liabilities of physicians and law of human cases in genetic experiments and new therapeutic methods such as cloning, the Iranian criminal laws should be studied. Unfortunately, the law of Iran has not changed along with developments and progresses in medical sciences, and Iran is one of the countries where law has not passed about cloning. The only available regulations in our country codified by consultative committees are affiliated to the research institutes include two documents and despite that they are called by laws, the executive bylaws of ethical principles in researches of medical sciences and ethical guides of researches on gametes and embryos, they lack legal standards and sanction and as their titles suggest, they should be called ethics doctrine. Thus, only those cases of Islamic penal code approved in 2013 and law on method of donating embryos to infertile couples approved in 2003 are to be responsive to new challenges. 17
Therefore, if an individual or individuals engage in human cloning, in terms of the legal fundamentals and legal principles, it is not legally possible to prosecute them because with respect to constitution law principle of “legality of offenses and penalties”, it is not possible to consider an act as a crime without a legal element and no punishment is considered for it and the action or leaving of the action can be considered as a crime that a law is passed for it and the action and leaving of the action is considered as a crime by the law and the related punishment is determined. 45
Some might argue that based on principle 167 constitution law states that the judge is bound to endeavor to find the ruling on every case in the law and if not found, according to Islamic sources or fatwa, would issue the ruling. They cannot refuse handling of the case and issuing the ruling under the pretext of silence or deficiency or brevity or conflict of laws. The rule of law can be derived if required, a legal action can be taken into account. In reply to such cases, it should be said that on one hand, the principle mostly includes the civil cases and if its content is accepted in criminal issues, case issues not phenomenon to this extent, would be with effective outcome. The prospects of scholars and views of Islamic jurists and different fatwas and often conflicting responses with uncertainty in dealing with various issues of this technology, are additional reasons to the inadequacy of the response. 45
Although mostly after the emergence of the phenomena and the related challenges, legislators take actions to pass and approve laws with respect to requirements and structure and sources and development capacities of civil rights and future legal researches, if the time gap lengthens between the phenomena and provision of the necessary related law, it causes corruption and irreparable consequences; especially, on the critical and vital issues which have created great concerns about human rights and criminal laws for the human of the third millennium. 17
If person or persons practice human cloning, what legal acts are there to deal with them? Are there any rules considered in the related laws to take legal actions against the operators and users of the technology? If yes, to what extent are they expressive and comprehensive and if not, what should be done against the practice and the perpetrators? If any person or persons practice human cloning, what legal actions are there against them? Some of the practical policies which should be done include public education, description of probable risks and disadvantages of human cloning and placing religious and ethical scholars next to researchers of cloning. 17
Therefore, we can conclude that the right method is guiding and controlling the cloning technology and banning the technique is not always fruitful. Of course, it should be taken into accounts that all are possible if the religion orders human cloning in the view of jurisprudence and is considered as permission. In other words, although the religious order on human cloning can be an absolute permission based on the strong principle of permission, it is not unlikely that in the future, corruption is proved to be real for them, Jurists rule it as secondary sanctity and even as primary one. If it is proved, the phenomenon is considered as example of required affairs based on creation of ethical, social and medical disorders. Religious and ethical rulings cannot be permission for it, and it seems that it is a point that only one case can be a response to it and it needs nothing but time.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Human Cloning: Biology, Ethics, and Social Implications
Affiliations.
- 1 MAGI'S LAB, Rovereto (TN), Italy.
- 2 Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Perugia, Perugia, Italy.
- 3 MAGI EUREGIO, Bolzano, Italy.
- 4 MAGISNAT, Peachtree Corners (GA), USA.
- 5 School of Food Science and Environmental Health, Technological University of Dublin, Dublin, Ireland.
- 6 Department of Psychology and Neuroscience, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Ca-nada.
- 7 Department of Ophthalmology, Center for Ocular Regenerative Therapy, School of Medicine, University of California at Davis, Sacramento, CA, USA.
- 8 Centre for Bioethics, Department of Philosophy and Applied Philosophy, University of St. Cyril and Methodius, Trnava, Slovakia.
- 9 Department of Biotechnology Engineering, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel.
- 10 nstitute of Ophthalmology, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli-IRCCS, Rome, Italy.
- 11 MAGI BALKANS, Tirana, Albania.
- 12 Department of Biotechnology, University of SS. Cyril and Methodius, Trnava, Slovakia.
- 13 International Centre for Applied Research and Sustainable Technology, Bratislava, Slovakia.
- 14 UOC Neurology and Stroke Unit, ASST Lecco, Merate, Italy.
- 15 Center for Preclincal Research and General and Liver Transplant Surgery Unit, Fondazione IRCCS Ca' Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Milan, Italy.
- 16 Department of Pathophysiology and Transplantation, Università degli Studi di Milano, Milan, Italy.
- 17 Department of Biomedical, Surgical and Dental Sciences, Università degli Studi di Milano, Milan, Italy.
- 18 UOC Maxillo-Facial Surgery and Dentistry, Fondazione IRCCS Ca Granda, Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Milan, Italy.
- 19 Department of Medical Genetics, Faculty of Medicine, Near East University, Nicosia, Cyprus.
- 20 Department of Medical Genetics, Erciyes University Medical Faculty, Kayseri, Turkey.
- 21 Vascular Diagnostics and Rehabilitation Service, Marino Hospital, ASL Roma 6, Marino, Italy.
- 22 San Francisco Veterans Affairs Health Care System, University of California, San Francisco, CA, USA.
- 23 Univ. Grenoble Alpes, CNRS, Grenoble INP, TIMC-IMAG, SyNaBi, Grenoble, France.
- 24 Department of Biotechnology, University of Tirana, Tirana, Albania.
- 25 Total Lipedema Care, Beverly Hills, California, and Tucson, Arizona, USA.
- 26 Federation of the Jewish Communities of Slovakia.
- 27 Department of Psychological Health and Territorial Sciences, School of Medicine and Health Sciences, "G. d'Annunzio" University of Chieti-Pescara, Chieti, Italy.
- 28 Unit of Molecular Genetics, Center for Advanced Studies and Technology (CAST), "G. d'Annunzio" University of Chieti-Pescara, Chieti, Italy.
- 29 Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology, University College London, London, UK.
- PMID: 37994769
- DOI: 10.7417/CT.2023.2492
This scholarly article delves into the multifaceted domains of human cloning, encompassing its biological underpinnings, ethical dimensions, and broader societal implications. The exposition commences with a succinct historical and contextual overview of human cloning, segueing into an in-depth exploration of its biological intri-cacies. Central to this biological scrutiny is a comprehensive analysis of somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) and its assorted iterations. The accomplishments and discoveries in cloning technology, such as successful animal cloning operations and advances in the efficiency and viability of cloned embryos, are reviewed. Future improvements, such as reprogramming procedures and gene editing technology, are also discussed. The discourse extends to ethical quandaries intrinsic to human cloning, entailing an extensive contemplation of values such as human dignity, autonomy, and safety. Furthermore, the ramifications of human cloning on a societal plane are subjected to scrutiny, with a dedicated emphasis on ramifications encompassing personal identity, kinship connections, and the fundamental notion of maternity. Culminating the analysis is a reiteration of the imperative to develop and govern human cloning technology judiciously and conscientiously. Finally, it discusses several ethical and practical issues, such as safety concerns, the possibility of exploitation, and the erosion of human dignity, and emphasizes the significance of carefully considering these issues.
Keywords: Human cloning; biology; dignity; ethical considerations; safety; social implications.
Publication types
- Cloning, Organism*
- Nuclear Transfer Techniques*
- Self Concept
- Introduction to Genomics
- Educational Resources
- Policy Issues in Genomics
- The Human Genome Project
- Funding Opportunities
- Funded Programs & Projects
- Division and Program Directors
- Scientific Program Analysts
- Contact by Research Area
- News & Events
- Research Areas
- Research investigators
- Research Projects
- Clinical Research
- Data Tools & Resources
- Genomics & Medicine
- Family Health History
- For Patients & Families
- For Health Professionals
- Jobs at NHGRI
- Training at NHGRI
- Funding for Research Training
- Professional Development Programs
- NHGRI Culture
- Social Media
- Broadcast Media
- Image Gallery
- Press Resources
- Organization
- NHGRI Director
- Mission & Vision
- Policies & Guidance
- Institute Advisors
- Strategic Vision
- Leadership Initiatives
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Partner with NHGRI
- Staff Search
Cloning Fact Sheet
The term cloning describes a number of different processes that can be used to produce genetically identical copies of a biological entity. The copied material, which has the same genetic makeup as the original, is referred to as a clone. Researchers have cloned a wide range of biological materials, including genes, cells, tissues and even entire organisms, such as a sheep.
Do clones ever occur naturally?
Yes. In nature, some plants and single-celled organisms, such as bacteria , produce genetically identical offspring through a process called asexual reproduction. In asexual reproduction, a new individual is generated from a copy of a single cell from the parent organism.
Natural clones, also known as identical twins, occur in humans and other mammals. These twins are produced when a fertilized egg splits, creating two or more embryos that carry almost identical DNA . Identical twins have nearly the same genetic makeup as each other, but they are genetically different from either parent.
What are the types of artificial cloning?
There are three different types of artificial cloning: gene cloning, reproductive cloning and therapeutic cloning.
Gene cloning produces copies of genes or segments of DNA. Reproductive cloning produces copies of whole animals. Therapeutic cloning produces embryonic stem cells for experiments aimed at creating tissues to replace injured or diseased tissues.
Gene cloning, also known as DNA cloning, is a very different process from reproductive and therapeutic cloning. Reproductive and therapeutic cloning share many of the same techniques, but are done for different purposes.
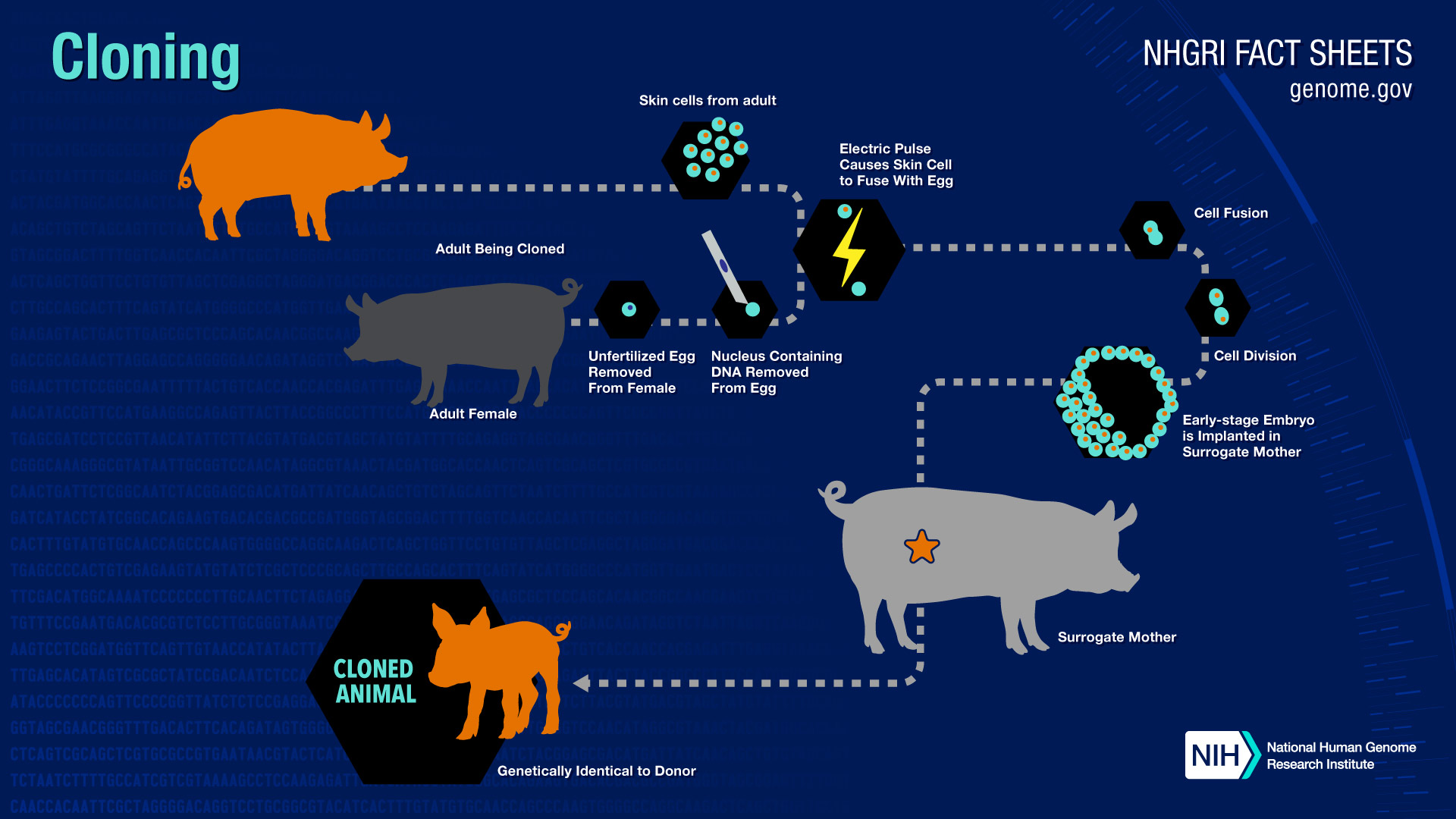
What sort of cloning research is going on at NHGRI?
Gene cloning is the most common type of cloning done by researchers at NHGRI. NHGRI researchers have not cloned any mammals and NHGRI does not clone humans.
How are genes cloned?
Researchers routinely use cloning techniques to make copies of genes that they wish to study. The procedure consists of inserting a gene from one organism, often referred to as "foreign DNA," into the genetic material of a carrier called a vector. Examples of vectors include bacteria, yeast cells, viruses or plasmids, which are small DNA circles carried by bacteria. After the gene is inserted, the vector is placed in laboratory conditions that prompt it to multiply, resulting in the gene being copied many times over.
How are animals cloned?
In reproductive cloning, researchers remove a mature somatic cell , such as a skin cell, from an animal that they wish to copy. They then transfer the DNA of the donor animal's somatic cell into an egg cell, or oocyte, that has had its own DNA-containing nucleus removed.
Researchers can add the DNA from the somatic cell to the empty egg in two different ways. In the first method, they remove the DNA-containing nucleus of the somatic cell with a needle and inject it into the empty egg. In the second approach, they use an electrical current to fuse the entire somatic cell with the empty egg.
In both processes, the egg is allowed to develop into an early-stage embryo in the test-tube and then is implanted into the womb of an adult female animal.
Ultimately, the adult female gives birth to an animal that has the same genetic make up as the animal that donated the somatic cell. This young animal is referred to as a clone. Reproductive cloning may require the use of a surrogate mother to allow development of the cloned embryo, as was the case for the most famous cloned organism, Dolly the sheep.
What animals have been cloned?
Over the last 50 years, scientists have conducted cloning experiments in a wide range of animals using a variety of techniques. In 1979, researchers produced the first genetically identical mice by splitting mouse embryos in the test tube and then implanting the resulting embryos into the wombs of adult female mice. Shortly after that, researchers produced the first genetically identical cows, sheep and chickens by transferring the nucleus of a cell taken from an early embryo into an egg that had been emptied of its nucleus.
It was not until 1996, however, that researchers succeeded in cloning the first mammal from a mature (somatic) cell taken from an adult animal. After 276 attempts, Scottish researchers finally produced Dolly, the lamb from the udder cell of a 6-year-old sheep. Two years later, researchers in Japan cloned eight calves from a single cow, but only four survived.
Besides cattle and sheep, other mammals that have been cloned from somatic cells include: cat, deer, dog, horse, mule, ox, rabbit and rat. In addition, a rhesus monkey has been cloned by embryo splitting.
Have humans been cloned?
Despite several highly publicized claims, human cloning still appears to be fiction. There currently is no solid scientific evidence that anyone has cloned human embryos.
In 1998, scientists in South Korea claimed to have successfully cloned a human embryo, but said the experiment was interrupted very early when the clone was just a group of four cells. In 2002, Clonaid, part of a religious group that believes humans were created by extraterrestrials, held a news conference to announce the birth of what it claimed to be the first cloned human, a girl named Eve. However, despite repeated requests by the research community and the news media, Clonaid never provided any evidence to confirm the existence of this clone or the other 12 human clones it purportedly created.
In 2004, a group led by Woo-Suk Hwang of Seoul National University in South Korea published a paper in the journal Science in which it claimed to have created a cloned human embryo in a test tube. However, an independent scientific committee later found no proof to support the claim and, in January 2006, Science announced that Hwang's paper had been retracted.
From a technical perspective, cloning humans and other primates is more difficult than in other mammals. One reason is that two proteins essential to cell division, known as spindle proteins, are located very close to the chromosomes in primate eggs. Consequently, removal of the egg's nucleus to make room for the donor nucleus also removes the spindle proteins, interfering with cell division. In other mammals, such as cats, rabbits and mice, the two spindle proteins are spread throughout the egg. So, removal of the egg's nucleus does not result in loss of spindle proteins. In addition, some dyes and the ultraviolet light used to remove the egg's nucleus can damage the primate cell and prevent it from growing.
Do cloned animals always look identical?
No. Clones do not always look identical. Although clones share the same genetic material, the environment also plays a big role in how an organism turns out.
For example, the first cat to be cloned, named Cc, is a female calico cat that looks very different from her mother. The explanation for the difference is that the color and pattern of the coats of cats cannot be attributed exclusively to genes. A biological phenomenon involving inactivation of the X chromosome (See sex chromosome ) in every cell of the female cat (which has two X chromosomes) determines which coat color genes are switched off and which are switched on. The distribution of X inactivation, which seems to occur randomly, determines the appearance of the cat's coat.
What are the potential applications of cloned animals?
Reproductive cloning may enable researchers to make copies of animals with the potential benefits for the fields of medicine and agriculture.
For instance, the same Scottish researchers who cloned Dolly have cloned other sheep that have been genetically modified to produce milk that contains a human protein essential for blood clotting. The hope is that someday this protein can be purified from the milk and given to humans whose blood does not clot properly. Another possible use of cloned animals is for testing new drugs and treatment strategies. The great advantage of using cloned animals for drug testing is that they are all genetically identical, which means their responses to the drugs should be uniform rather than variable as seen in animals with different genetic make-ups.
After consulting with many independent scientists and experts in cloning, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) decided in January 2008 that meat and milk from cloned animals, such as cattle, pigs and goats, are as safe as those from non-cloned animals. The FDA action means that researchers are now free to using cloning methods to make copies of animals with desirable agricultural traits, such as high milk production or lean meat. However, because cloning is still very expensive, it will likely take many years until food products from cloned animals actually appear in supermarkets.
Another application is to create clones to build populations of endangered, or possibly even extinct, species of animals. In 2001, researchers produced the first clone of an endangered species: a type of Asian ox known as a guar. Sadly, the baby guar, which had developed inside a surrogate cow mother, died just a few days after its birth. In 2003, another endangered type of ox, called the Banteg, was successfully cloned. Soon after, three African wildcats were cloned using frozen embryos as a source of DNA. Although some experts think cloning can save many species that would otherwise disappear, others argue that cloning produces a population of genetically identical individuals that lack the genetic variability necessary for species survival.
Some people also have expressed interest in having their deceased pets cloned in the hope of getting a similar animal to replace the dead one. But as shown by Cc the cloned cat, a clone may not turn out exactly like the original pet whose DNA was used to make the clone.
What are the potential drawbacks of cloning animals?
Reproductive cloning is a very inefficient technique and most cloned animal embryos cannot develop into healthy individuals. For instance, Dolly was the only clone to be born live out of a total of 277 cloned embryos. This very low efficiency, combined with safety concerns, presents a serious obstacle to the application of reproductive cloning.
Researchers have observed some adverse health effects in sheep and other mammals that have been cloned. These include an increase in birth size and a variety of defects in vital organs, such as the liver, brain and heart. Other consequences include premature aging and problems with the immune system. Another potential problem centers on the relative age of the cloned cell's chromosomes. As cells go through their normal rounds of division, the tips of the chromosomes, called telomeres, shrink. Over time, the telomeres become so short that the cell can no longer divide and, consequently, the cell dies. This is part of the natural aging process that seems to happen in all cell types. As a consequence, clones created from a cell taken from an adult might have chromosomes that are already shorter than normal, which may condemn the clones' cells to a shorter life span. Indeed, Dolly, who was cloned from the cell of a 6-year-old sheep, had chromosomes that were shorter than those of other sheep her age. Dolly died when she was six years old, about half the average sheep's 12-year lifespan.
What is therapeutic cloning?
Therapeutic cloning involves creating a cloned embryo for the sole purpose of producing embryonic stem cells with the same DNA as the donor cell. These stem cells can be used in experiments aimed at understanding disease and developing new treatments for disease. To date, there is no evidence that human embryos have been produced for therapeutic cloning.
The richest source of embryonic stem cells is tissue formed during the first five days after the egg has started to divide. At this stage of development, called the blastocyst, the embryo consists of a cluster of about 100 cells that can become any cell type. Stem cells are harvested from cloned embryos at this stage of development, resulting in destruction of the embryo while it is still in the test tube.
What are the potential applications of therapeutic cloning?
Researchers hope to use embryonic stem cells, which have the unique ability to generate virtually all types of cells in an organism, to grow healthy tissues in the laboratory that can be used replace injured or diseased tissues. In addition, it may be possible to learn more about the molecular causes of disease by studying embryonic stem cell lines from cloned embryos derived from the cells of animals or humans with different diseases. Finally, differentiated tissues derived from ES cells are excellent tools to test new therapeutic drugs.
What are the potential drawbacks of therapeutic cloning?
Many researchers think it is worthwhile to explore the use of embryonic stem cells as a path for treating human diseases. However, some experts are concerned about the striking similarities between stem cells and cancer cells. Both cell types have the ability to proliferate indefinitely and some studies show that after 60 cycles of cell division, stem cells can accumulate mutations that could lead to cancer. Therefore, the relationship between stem cells and cancer cells needs to be more clearly understood if stem cells are to be used to treat human disease.
What are some of the ethical issues related to cloning?
Gene cloning is a carefully regulated technique that is largely accepted today and used routinely in many labs worldwide. However, both reproductive and therapeutic cloning raise important ethical issues, especially as related to the potential use of these techniques in humans.
Reproductive cloning would present the potential of creating a human that is genetically identical to another person who has previously existed or who still exists. This may conflict with long-standing religious and societal values about human dignity, possibly infringing upon principles of individual freedom, identity and autonomy. However, some argue that reproductive cloning could help sterile couples fulfill their dream of parenthood. Others see human cloning as a way to avoid passing on a deleterious gene that runs in the family without having to undergo embryo screening or embryo selection.
Therapeutic cloning, while offering the potential for treating humans suffering from disease or injury, would require the destruction of human embryos in the test tube. Consequently, opponents argue that using this technique to collect embryonic stem cells is wrong, regardless of whether such cells are used to benefit sick or injured people.
Last updated: August 15, 2020

11 Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloning
Cloning is a process that creates new life by copying the cell data of a living host. The cell data is gathered from the host and then implanted into an embryo, which undergoes a normal development cycle. Once born, the individual is a physical copy of the living host that had the cell data collected from it.
The first cloned animal from an adult somatic cell was Dolly the Sheep, a process which was successfully completed in the 1990s. The idea of cloning, however, dates to the 19th century. In 1885, Hans Dreisch became the first person to successfully perform a cloning experiment with a sea urchin.
There are certain advantages and disadvantages of cloning that must be fully evaluated to determine the value of this scientific process. Here are the key points to discuss.
What Are the Advantages of Cloning?
1. Cloning doesn’t need to involve making a whole new person. Imagine if a person has a failing liver. What if the cells of the liver could be cloned so that a new liver could be created and then transplanted? It would be an easy way to solve the organ scarcity issue that currently exists. The process of cloning could also be used to repair or grow new cells to replace damaged or missing ones, which could treat illnesses and genetic disorders.
2. It removes the barrier of infertility. Because cloning uses adult somatic cells, it is a process that allows anyone to have a child that is biologically their own. Even if that person has a reproductive system which does not support fertility, doctors could take the somatic cells and implant them into an embryo, creating new life. This technology would give everyone the chance to become a parent, even if they were not sexually active.
3. It could extend human life capabilities. In the developed world, the average lifespan is approaching 85 years for top nations. Even in the United States, the average lifespan is upward of 70 years for men and women. Not only could cloning help to extend life to even longer lengths, it could be a way to bring the rest of the world up to the current standards as well. In Sierra Leone, for example, the average lifespan for an adult male is just 49.3 years of age.
4. Biological children could be born to same-gender couples. Instead of using sperm or egg banks to create an embryo that could be brought to term, cloning would allow same-gender couples to have a child that was biologically their own. For women, a direct implantation of adult somatic cells wouldn’t even require a male donor at all except for the initial fertilization process to create the embryo. For men, the same would be true regarding the egg requiring fertilization.
5. It could restore balance to families. One of the greatest tragedies that occurs in life is the death of a child. In the United States, 7 out of every 1,000 children under the age of 5. According to information published by CNN, firearms kill nearly 1,300 children in the US every year. Sometimes this happens because of disease or illness. There are also accidents and unpredictable events that can take the life of a child. Cloning offers a process where parents could effectively balance their grief by creating another child. Although the new life would be different, it would also be similar, and that could temper some of the grief that is experienced.
What Are the Disadvantages of Cloning?
1. The results on society would be unpredictable. The most common argument against cloning involve the unknowns that would happen to society. If parents would be able to “manufacture” children to specific genetic profiles, then there is the possibility that genetic variation could decrease. This would result in humanity becoming more susceptible to disease and deformity, requiring more genetic selection, because we would eventually be inbreeding with ourselves.
2. The rich would get richer and the poor would disappear. A society where genetic selection is possible would place a higher emphasis on the socioeconomic means of each person or household. Those who could afford cloning would essentially create their own class, while those who could not afford the process would likely be shunned or disregarded by the rest of society.
3. It is an unpredictable and certain process. Cloning is far from a perfected science. Many of the disadvantages involve the “what ifs” of this science, but there are some facts to think about too. When Dolly was successfully cloned, only 9 eggs out of 300 were successfully implanted with adult somatic cells to create a pregnancy. Out of those 9 eggs, only one was successfully delivered to term. Although advances have been made since Dolly in the field of cloning, the science still has a long way to go.
4. There are unforeseen consequences that we cannot predict. Every advancement in science has some positives, but equal and opposite negatives. The bigger a success, then the bigger a problem there will be to manage. Manipulating human genes will have unpredictable and unforeseen consequences that could change how we live. It could endanger humanity as a species. At the very least, people who are cloned may find themselves dealing with severe health problems at some point in their life.
5. Cloned people could be treated like cattle. If a clone is an exact replica of the host, then embryos could be implanted with the sole purpose of helping with the health of the host instead of treating the clone with equal rights as a human being. Embryonic stem cells might be harvested from a clone. Clones might be used as automatic organ donors. They might be placed into forced labor. The levels of abuse that could occur with this type of technology are immense.
6. Children would still be in abusive situations. According to Michael Petit, President of the Every Child Matters Education Fund, more than 2,000 children, on average, are killed in their own homes by aa family member. Child abuse death rates in the US are 3 times higher than what they are in Canada and 11 times higher than what Italy experiences. The ability to have more children through cloning would only expand these rates unless core changes to family structures could be encouraged. The US already sees an average of 4 children die every day because of abuse and neglect.
The advantages and disadvantages of cloning show us that if this science can be managed ethically, there are still societal implications that must be taken into account. There are unknowns that we cannot plan for. There are potential health benefits, but there are also potential health risks.
How do you feel about the advantages and disadvantages of cloning?
Disadvantages Of Human Cloning
What Is Cloning? Clones are organisms that have identical DNA structures to the parent organism, making them exact genetic copes, it describes a process of creating exact copies of biological entities. Clones can be generated either naturally or in laboratory conditions. Examples would be identical twins in nature and Dolly the sheep is an example of artificial cloning . Many items have been cloned such as cells, genes, tissues and organs. Types of Cloning: There are 2 common ways in which cloning can take place. Reproductive Cloning and Therapeutic Cloning. Reproductive Cloning: Reproductive cloning is where the whole genetic code, this excludes the mitochondrial DNA , of a single somatic cell is reproduced. Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT) is one of the most commonly used cloning techniques. In this technique an unfertilized egg cell is. A somatic cell is taken from an organism that is to be cloned. The nucleus is removed from the somatic cell and inserted into the prepared egg. The new egg is exposed to an electrical pulse stimulate cell division, by doing this the development of an embryo begins. Several days later, the dividing embryo is inserted into the womb of a surrogate mother to carry the devolving foetus to term. The result is a clone – an organism that is genetically the same as the individual from which the somatic cell was taken. The first clone of a mammal was done in 1996 by Keith Campbell of the Roslin Institute in Scotland. The birth of the world’s
Hypnopedia In Aldous Huxley's Brave New World
This piece of evidence tells about three people who donated skin cells, and had them genetically copied, which is one form of cloning just like the way they did in Brave New World” “In a first, Mitalipov and his privately funded team report that these cloned embryos were grown past an eight-cell size (where earlier attempts had stopped) into a full-blown early embryo, containing hundreds of embryonic stem cells. Embryonic cells taken from these cloned embryos were grown into six colonies of cells, the first successfully grown cloned human embryonic stem cells.” This is an example of a process very similar to the Bovkanovsky’s Process and
Pros And Cons Of Therapeutic Cloning
In recent years, there has been and still is much debate over stem cell cloning and its applications. The topics of embryonic stem cells and human cloning are very large and very controversial issues that have many facets to them, and these also tend to be the issues that overshadow the smaller, less heated topics of therapeutic cloning and animal reproductive cloning. Both therapeutic cloning with its hypothetical use in medicine and animal reproductive cloning with its potential to revive extinct species are gallant undertakings, yet both sides also have their share of fallacies and drawbacks. Therapeutic cloning, or somatic cell nuclear transfer, is in essence the process of substituting the nucleus of an egg for that of the genetic material of the organism being cloned.
Year 10 Science Assessment Task: Research
Year 10 Science Assessment Task - Research What is biotechnology? Biotechnology is the use of bimolecular and cellular processes in order to develop new technology and products that will provide assistance towards improving lives and the general health of our planet, Earth. The biological processes of microorganisms have been in use for more than 6,000 years in order to make useful day-to-day products, for example food products, such as bread and cheese and as well as the preserving of dairy products. Why I believe that it is important to understand Biotechnology more?
Playing God Analysis
Animal cloning has been the subject of various scientific experiments for years but only gained little attention until the birth of the very first cloned mammal in 1996, a sheep named Dolly. Since then, scientists have began to clone other animals like cows and mice. The recent success in cloning animals has sparked fierce debates among politicians, scientists, and the general public about the use, morality and ethnicity of cloning animals, plants and possibly
Rough Draft For Frankenstein
"Human Cloning." Biotechnology: In Context, edited by Brenda Wilmoth Lerner and K. Lee Lerner, Gale, 2012. In Context Series. Gale In Context: Science, link.gale.com/apps/doc/TTGGVK544240346/SCIC?u=pocono_moun_shs&sid=bookmark-SCIC&xid=73822afb.
Eugene C. Newman's Argument Against Human Cloning
Cloning is an idea that is often portrayed in science fiction as a way to essentially duplicate another living being. It has been making an appearance in the real world as something that could be useful in the medical and scientific fields as a way to bring back animals or to save peoples’ lives. Due to how unique cloning is, it was portrayed in famous parts of the media such as Jurassic Park. Although cloning does sound promising, it does possess a darker side to it, which does raise both moral and ethical issues. There are articles that do discuss cloning in which they either list the benefits of it or tell us about what moral and ethical issues that do come out of cloning.
Therapeutic Cloning Pros And Cons
Therapeutic cloning, also interchangeable with somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), is a procedure that helps cure ailments in science. To begin the process, the haploid nucleus, that contains the genetic makeup, is separated from the fertilized egg. Somatic cells are then obtained from embryonic tissue and injected into the fertilized egg. If done so correctly, a cleavage is formed and cells divide due to mitotic division. In result, this forms a blastocyst where new stem cells are cultivated for further growth.
Animal Cloning Pros And Cons
Most veterinarians disagree with cloning. From a veterinarian 's perspective, cloning is a way of creating an animal that is predisposed to a surplus of health issues. From organ issues to premature death, the likelihood of creating an animal that does not
Frankenstein Pros And Cons Of Cloning
Scientists have cloned various animals to attempt to reproduce an exact replica of the original animal. One major reason why cloning animals is an ongoing issue is that it causes suffering for animals. It is said that “animal surrogates were manifesting adverse outcomes, and cloned animals were having diseases and even high mortality rates. One of these negative results is the large offspring syndrome (LOS), where clones are large at birth since they came
Cloning In Mary Shelley's Frankenstein
Animal cloning, a subsection of reproductive cloning, occurs by
Essay On The Pros And Cons Of Animal Cloning
Cloning at the gene level is acceptable and is done extensively in research areas. However, therapeutic cloning and reproductive cloning raises skepticism and debate both in the general society and the scientific community. Among the argument raised is the possibility of cloning human beings; whether the individuals derived are seen as a complete human with the whole set of human rights attached to them. Body >>> Scientific Advantage <<< 2 PAR Fiester (2005) states that most of the animal cloning projects are driven by the goal of meeting human needs such as treatment of diseases, food production, and entertainment. However, there are animal cloning projects aimed at conserving endangered or
Cloning Persuasive Speech
Cloning might seem like new technology. However, it is nothing new! Many of you must have heard of Dolly the sheep once in your life. Dolly is the very first mammal to be cloned; it was cloned from an adult sheep’s somatic cell. Just like Dolly, many other animal species such as dogs, cats, horses, pigs, rabbits, frogs, wolves, goats, monkeys, and fish, have been cloned and reproduced.
Pros And Cons Of Regenerative Medicine
Wanted embryos were valuable for their parents. Respect for the moral value regarding the feelings of the parents. Individual’s cells were duplicated it was another issue concern on cloning embryonic stem cell. This was a therapeutic cloning and begins using same procedure as reproductive cloning. If the cell in the therapy usage embryonic there were impediment of possible negation, having cell from different
Argumentative Essay: The Ethics Of Human Cloning
Most people in our society, no matter what level of education that they may have, have heard of the cloning, specifically the cloning of Dolly the lamb, and have some notions regarding the idea of cloning humans. "The successes in animal cloning suggest to some that the technology has matured sufficiently to justify its application to human cloning" (Jaenisch et al.). However, not every agrees that human cloning is a something that should be put into practice (Hoskins). There generally seem to be two basic divisions on this issue: those who find it inappropriate and unethical, and those who find it a reasonable and necessary step in the progression of scientific research (Lustig).
Is Human Cloning Is Wrong Essay
To make a clone, the nucleus from the egg cell of the mother is removed and replaced with the nucleus from the cell of the organism to be cloned. An electric shock triggers the cells to divide by mitosis and an embryo is formed.
More about Disadvantages Of Human Cloning
Related topics.

Disadvantages Of Human Cloning
The term Human cloning refers to artificial human reproduction, which Is the reproduction of human cells and tissue, or replication of a human thus making a copy of that human. Two commonly discussed types of theoretical human cloning are therapeutic cloning and reproductive cloning. To summarize the therapeutic cloning is the process where nuclear transplantation of a patient’s own cells makes an oocyte from which Immune-compatible cells (especially stem cells) can elicit transplants(Farina, A, 2014). Moreover, These cells are stimulated to divide and grow in a petri dish rather in the uterus. However, therapeutic cloning would involve cloning cells from a human for use in medicine and transplants, and is an active area of research, but is not in medical practice anywhere in the world, as of April 2017. Two common methods of therapeutic cloning that are being researched are somatic (relating to the body, moreover as distinct from the mind)-cell nuclear transfer and, more recently, pluripotent (capable of giving rise to several different cell types) stem cell induction. Finally, the second type of cloning is reproductive cloning and involves making an entire cloned human, instead of just specific cells or tissues. Human cloning will one day be possible as a new tool called CRISPR- is already being used to edit the genomes (the haploid set of chromosomes in a gamete or microorganism, or in each cell of a multicellular organism) of insects and animals. Essentially a very sharp
The Pros And Cons Of Cloning
There have been recent studies on animals where the scientist cloned the animals. Cloning is something many people are split on. Some say it is bad some say it is good. I think cloning is a bad thing. Cloning can be a bad thing in many ways. I will be covering some of those ways in this paper.
Pros And Cons Of Cloning
Recently the world has turned its attention to a new development in science, cloning. Cloning is defined as “the process of producing a clone” (Dictionary.com). This has become a big deal because the endless ways we can bring back extinct creatures. Such as, the extinct wooly mammoth, the Tasmanian tiger, and Quagga. With the endless ability to bring back animal from the past with DNA there comes a problem. With human DNA made available so easily science has come to the idea and process of making designer babies. A designer baby is a baby whose genetic makeup has been selected in order to eradicate a particular defect, or to ensure that a particular gene is present. A family gene might be a bad disease which a baby might get when born. Before this, cloning a baby was science fiction idea to people. It was never imagined or even thought possible, but now it is not. Scientist have already started to create ways to clone babies. With this comes the problem of how far should scientist go? This could be both a blessing and a curse.
Cons Of Human Cloning
The topic of cloning has brought much debate in science and also in society. Many
The Dangers Of Human Cloning
There is plainly a huge measure of moral and good stresses as for human cloning. Human life is acknowledged to be important and blessed. Cloning certainly is now and again successful the principal gone through, which infers that human creating leaves will fail miserably. Most would concur that cloning is like murder or manslaughter in any occasion. For the people who don't assume that life is holy, it is basically tissue being disposed of. Cloning is hostile. The most vital piece of a man is their soul, soul or psyche and cloning does not enable one to accomplish this, it rather enables one to endeavor to accomplish some hereditary standard. There is no hobby for cloning, it is inhumane to the point that there are people on this planet with to a great degree cruel desires and human cloning would take into account military utilize. For instance, a country that could clone people could make a massive outfitted power that could attempt to expect control distinctive countries and provoke boundless wars of emotionless men. Individuals should be made through an exhibition of love and not a show of science. One that is cloned can never again be seen as a man, as your identity isn't generally essentially yours; you are giving it to someone else. Another case for instance, if mental oppressor seats had the ability to clone then the world would be an extensively all the more startling spot reliably in fear of being ambushed at any dark time. This, and in addition human cloning could
The recovery period after large scale injuries could be shortened. The effects are analyzed in an article that states, “True healing could occur thanks to the cloning of their own cells to help the recovery process” (“Pros and Cons” 5). Basically, the process of cloning healthy cells could be used as an aid in replenishing damage of unhealthy cells. This process, if it were to be actualized, could help recovery progress in anything from pulled muscles to the paralysis of an entire limb. In theory, the same research can be applied in other areas. If this technology is paired with stem cell research, it could result in a method of repairing physical damage. An article that focused on advances in biotechnology stated that “Another use of cloned stem cells could be the growth of replacement tissues in the laboratory” (LaPensee 15). Necrosis, apoptosis, and lymphocyte diapedesis all cause tissue damage or death. These tissues could be replaced by cloned cells of healthy tissues. This shortens recovery periods and leads to healthier tissue growth.
There are many arguments against cloning. Leon R. Kass bases his argument on repugnance in his article The Wisdom of Repugnance. He is a well-known physician, educator and scientist. Kass perceives cloning as offensive, grotesque revolting, repulsive and wrong. To establish his argument he states, “Most people recoil from the prospect of mass production or human being, with large clones of look-alikes, compromised in their individuality.”1 His rationale is cloning is unnatural, because it is asexual and requires only one parent. Kass believes that cloning turns natural procreation into a manufactured process, which is not natural or moral. In his essay he also points out that cloning will also change the way we see ourselves through our
The Benefits Of Human Cloning : Pros And Cons
For starters, cloning has said to solve the continuous problem of infertility by inserting a clone embryo into the woman’s body. This guarantees infertile couples a child, as opposed to wasting time and money on other painful and emotional procedures that don’t offer this guarantee. The next benefit offers an immense amount of growth in regenerative medicine and assists those with physical disabilities by producing clones of themselves. Why clone themselves if they have a disability? Scientists can use cells from the embryo to customize the regeneration of the new organ, tissue, or body part. As far as cloning an organ goes, this benefits the millions of people who acquired a disease with no cure. For example, diseases such as Alzheimer’s,
Cloning is a number of processes that are used to create genetically identical copies of an organism. Researchers have cloned a number of biological materials, such as genes, cells, tissues and whole organisms, including sheep 's and horses. Cloning can happen naturally in identical twins, but it can also be done in a lab. ("Cloning Fact Sheet").
Cons Of Animal Cloning
According to Kathleen R. Brooks and Jayson L. Lusk (2011) Animal cloning is a process in which scientists can copy the genetic or inherited traits of an animal.
The Pros And Cons Of Human Cloning
When examining how human cloning can increase reproductive freedom, we must first look at what a clone is by definition. “Clone” in its verb tense means to make an identical copy of or in biochemistry, to replicate a fragment of DNA placed in an organism so that there is enough to analyze or use in protein production. This process can be performed for many different uses such as being used to grow in labs, embryotic treatments, genetic screening, anti-aging processes, and reproduction. It is important to note that “human cloning” of embryos will not produce an exact copy of an individual. Rather, it will replicate the same genotype to create a different individual human. ***As a reliable background, in this paper, I will be consistently referencing two main scientific articles. The first is from John Harris, a professor in the Institute of Medicine, Law, and Bioethics at the University of Manchester. His article “Goodbye Dolly” focuses on the nature and practicality of cloning. The other research article is by Alix Magney, a lecturer at the several universities who focuses on bioethics and medical health professionals, and highlights the investigations of the negative impacts of human cloning.
Why Cloning Is Bad
The idea of cloning is useless because it has way more negatives impacts rather than positive. Having someone who is an identical copy of you, made with the same DNA, yet still so far from the Clone. Advances in science like cloning are bad because Cloning transfers everything including diseases and/or abnormalities. Cloning is dangerous because the results are unknown. Something different that is never expected can happen each time. The main reason that Cloning is bad, is because the life of a Clone will be much different and way more tough.
Cloning: Is It Ethical? Essay
Science today is developing at warp speed. We have the capability to do many things, which include the cloning of actual humans! First you may ask what a clone is? A clone is a group of cells or organisms, which are genetically identical, and have all been produced from the same original cell. There are three main types of cloning, two of which aim to produce live cloned offspring and one, which simply aims to produce stem cells and then human organs. These three are: reproductive cloning, embryo cloning and therapeutic cloning. The goal of therapeutic cloning is to produce a healthy copy of a sick person's tissue or organ for transplant, and the goal of both reproductive cloning and embryo cloning is to
Is it right to transplant someone else’s organ into another body who’s in need of one, is it wrong to clone other organisms to gain certain genes to benefit humans for survival. This has been a controversial topic for a long time now. People are arguing if it’s wrong or right to transplants other people organs from the earlier scientific development. Now there is a new issue about cloning, whether it is right or wrong to make a copy of an organism.
The Effects Of Cloning On Human Life
Cloning. The very word instills feelings of excitement, hope, possibilities and a montage of futuristic images of test tubes and beakers and DNA ladders spinning through space. But the word also conjures anxiety, fear and internal struggle over right and wrong, good vs. evil, science vs. religion. The cloning of vital organs or cells to cure diseases could potentially save the lives of millions of people around the world. Throughout the past, experiments have shown the benefits that cloning can give the people of the world. It could give people who cannot reproduce because of infertility a chance to give birth to their own children. If cloning is used
The Human Of Human Cloning
Human cloning is the creation of a genetically identical copy of a human. However, this term not only refers to the entire artificial human, but also the reproduction of human cells and tissues. There are two types of theoretical human cloning: reproductive cloning which would involve making an entire cloned human and the other, therapeutic cloning, which would involve cloning cells from a human for use in medicine and transplants by somatic-cell nuclear transfer or pluripotent stem cell induction.
Related Topics
- Developmental biology
- Somatic cell nuclear transfer
- IELTS Scores
- Life Skills Test
- Find a Test Centre
- Alternatives to IELTS
- General Training
- Academic Word List
- Topic Vocabulary
- Collocation
- Phrasal Verbs
- Writing eBooks
- Reading eBook
- All eBooks & Courses
- Sample Essays
- Human Cloning Essay
IELTS Human Cloning Essay
This is a model answer for a human cloning essay.
If you look at the task, the wording is slightly different from the common 'do you agree or disagree' essay.
However, it is essentially asking the same thing.
As people live longer and longer, the idea of cloning human beings in order to provide spare parts is becoming a reality. The idea horrifies most people, yet it is no longer mere science fiction.
To what extent do you agree with such a procedure?
Have you any reservations?
Understanding the Question and Task

You are asked if you agree with human cloning to use their body parts (in other words, what are the benefits), and what reservations (concerns) you have (in other words, what are the disadvantages).
So the best way to answer this human cloning essay is probably to look at both sides of the issue as has been done in the model answer.
As always, you must read the question carefully to make sure you answer it fully and do not go off topic.
You are specifically being asked to discuss the issue of creating human clones to then use their body parts. If you write about other issues to do with human cloning, you may go off topic.
Model Human Cloning Essay
You should spend about 40 minutes on this task.
Write about the following topic:
Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own experience or knowledge.
Write at least 250 words.
Model Answer for Human Cloning Essay
The cloning of animals has been occurring for a number of years now, and this has now opened up the possibility of cloning humans too. Although there are clear benefits to humankind of cloning to provide spare body parts, I believe it raises a number of worrying ethical issues.
Due to breakthroughs in medical science and improved diets, people are living much longer than in the past. This, though, has brought with it problems. As people age, their organs can fail so they need replacing. If humans were cloned, their organs could then be used to replace those of sick people. It is currently the case that there are often not enough organ donors around to fulfil this need, so cloning humans would overcome the issue as there would then be a ready supply.
However, for good reasons, many people view this as a worrying development. Firstly, there are religious arguments against it. It would involve creating other human beings and then eventually killing them in order to use their organs, which it could be argued is murder. This is obviously a sin according to religious texts. Also, dilemmas would arise over what rights these people have, as surely they would be humans just like the rest of us. Furthermore, if we have the ability to clone humans, it has to be questioned where this cloning will end. Is it then acceptable for people to start cloning relatives or family members who have died?
To conclude, I do not agree with this procedure due to the ethical issues and dilemmas it would create. Cloning animals has been a positive development, but this is where it should end.
(276 words)
The essay is well-organized, with a clear introducion which introduces the topic:
- The cloning of animals has been occurring for a number of years now, and this has now opened up the possibility of cloning humans too.
And it has a thesis statement that makes it clear exactly how the human cloning essay will be structured and what the candidate's opinion is:
- Although there are clear benefits to humankind of cloning to provide spare body parts, I believe it raises a number of worrying ethical issues.
The first body paragraph discusses the advantages of cloning humans, and then the second body paragraph looks at the problems associated with this. The change of direction to look at the other side is clearly marked with a transition word ("however") and a topic sentence:
- However, for good reasons, many people view this as a worrying development.
Other transition words are used effectively to guide the reader through the ideas in the human cloning essay: Firstly,.. Also,... Furthermore,...
The candidate demonstrates that they can use a mix of complex structures. For example:
- Due to breakthroughs in medical science and improved diets, people are living much longer than in the past.
- It would involve creating another human and then eventually killing it in order to use its organs, which it could be argued is murder.
- ...if we have the ability to clone humans, it has to be questioned where this cloning will end.
<<< Back
Next >>>
More Agree / Disagree Essays:

Sample IELTS Writing: Is spending on the Arts a waste of money?
Sample IELTS Writing: A common topic in IELTS is whether you think it is a good idea for government money to be spent on the arts. i.e. the visual arts, literary and the performing arts, or whether it should be spent elsewhere, usually on other public services.

Free University Education Essay: Should it be paid for or free?
Free university education Model IELTS essay. Learn how to write high-scoring IELTS essays. The issue of free university education is an essay topic that comes up in the IELTS test. This essay therefore provides you with some of the key arguments about this topic.

Extinction of Animals Essay: Should we prevent this from happening?
In this extinction of animals essay for IELTS you have to decide whether you think humans should do what they can to prevent the extinction of animal species.

Employing Older People Essay: Is the modern workplace suitable?
Employing Older People Essay. Examine model essays for IELTS Task 2 to improve your score. This essay tackles the issue of whether it it better for employers to hire younger staff rather than those who are older.

Multinational Organisations and Culture Essay
Multinational Organisations and Culture Essay: Improve you score for IELTS Essay writing by studying model essays. This Essay is about the extent to which working for a multinational organisation help you to understand other cultures.

Airline Tax Essay: Would taxing air travel reduce pollution?
Airline Tax Essay for IELTS. Practice an agree and disagree essay on the topic of taxing airlines to reduce low-cost air traffic. You are asked to decide if you agree or disagree with taxing airlines in order to reduce the problems caused.

Ban Smoking in Public Places Essay: Should the government ban it?
Ban smoking in public places essay: The sample answer shows you how you can present the opposing argument first, that is not your opinion, and then present your opinion in the following paragraph.

Dying Languages Essay: Is a world with fewer languages a good thing?
Dying languages essays have appeared in IELTS on several occasions, an issue related to the spread of globalisation. Check out a sample question and model answer.

IELTS Vegetarianism Essay: Should we all be vegetarian to be healthy?
Vegetarianism Essay for IELTS: In this vegetarianism essay, the candidate disagrees with the statement, and is thus arguing that everyone does not need to be a vegetarian.

Paying Taxes Essay: Should people keep all the money they earn?
Paying Taxes Essay: Read model essays to help you improve your IELTS Writing Score for Task 2. In this essay you have to decide whether you agree or disagree with the opinion that everyone should be able to keep their money rather than paying money to the government.

Internet vs Newspaper Essay: Which will be the best source of news?
A recent topic to write about in the IELTS exam was an Internet vs Newspaper Essay. The question was: Although more and more people read news on the internet, newspapers will remain the most important source of news. To what extent do you agree or disagree?

Essay for IELTS: Are some advertising methods unethical?
This is an agree / disagree type question. Your options are: 1. Agree 100% 2. Disagree 100% 3. Partly agree. In the answer below, the writer agrees 100% with the opinion. There is an analysis of the answer.

IELTS Sample Essay: Is alternative medicine ineffective & dangerous?
IELTS sample essay about alternative and conventional medicine - this shows you how to present a well-balanced argument. When you are asked whether you agree (or disagree), you can look at both sides of the argument if you want.
IELTS Internet Essay: Is the internet damaging social interaction?
Internet Essay for IELTS on the topic of the Internet and social interaction. Included is a model answer. The IELTS test usually focuses on topical issues. You have to discuss if you think that the Internet is damaging social interaction.

Return of Historical Objects and Artefacts Essay
This essay discusses the topic of returning historical objects and artefacts to their country of origin. It's an agree/disagree type IELTS question.

Role of Schools Essay: How should schools help children develop?
This role of schools essay for IELTS is an agree disagree type essay where you have to discuss how schools should help children to develop.
Technology Development Essay: Are earlier developments the best?
This technology development essay shows you a complex IELTS essay question that is easily misunderstood. There are tips on how to approach IELTS essay questions

Scientific Research Essay: Who should be responsible for its funding?
Scientific research essay model answer for Task 2 of the test. For this essay, you need to discuss whether the funding and controlling of scientific research should be the responsibility of the government or private organizations.

Examinations Essay: Formal Examinations or Continual Assessment?
Examinations Essay: This IELTS model essay deals with the issue of whether it is better to have formal examinations to assess student’s performance or continual assessment during term time such as course work and projects.

Truthfulness in Relationships Essay: How important is it?
This truthfulness in relationships essay for IELTS is an agree / disagree type essay. You need to decide if it's the most important factor.
Any comments or questions about this page or about IELTS? Post them here. Your email will not be published or shared.
Before you go...
Check out the ielts buddy band 7+ ebooks & courses.

Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
Band 7+ eBooks
"I think these eBooks are FANTASTIC!!! I know that's not academic language, but it's the truth!"
Linda, from Italy, Scored Band 7.5

IELTS Modules:
Other resources:.
- All Lessons
- Band Score Calculator
- Writing Feedback
- Speaking Feedback
- Teacher Resources
- Free Downloads
- Recent Essay Exam Questions
- Books for IELTS Prep
- Useful Links

Recent Articles
Decreasing House Sizes Essay
Apr 06, 24 10:22 AM

Latest IELTS Writing Topics - Recent Exam Questions
Apr 04, 24 02:36 AM

IELTS Essay: English as a Global Language
Apr 03, 24 03:49 PM
Important pages
IELTS Writing IELTS Speaking IELTS Listening IELTS Reading All Lessons Vocabulary Academic Task 1 Academic Task 2 Practice Tests
Connect with us
Copyright © 2022- IELTSbuddy All Rights Reserved
IELTS is a registered trademark of University of Cambridge, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia. This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia.

The Disadvantages of Human Cloning Essay
Carl Traeger Middle School 3000 W. 20th Avenue Oshkosh, WI 54904 Senator Ron Johnson 386 Russell Senate Office Building Washington, DC 20510 Dear Senator Johnson, As we all know human cloning has been thought about for years now. The thought of cloning sounds exciting and a big advancement in medical technology, which it is, but what you may not know, are all of the risks that come with human cloning. Cloning is a very controversial topic to many people. One of the first issues that come to the minds of people is the low success rate. As of right now the success rate of cloning is under 10%. In addition, no human has ever been cloned before and that scares people about the process. ( learn.genetics.utah.edu) Even though there is a very low success rate there still is a 10% chance that it will work, but let’s look at all of the drawbacks that even come with the first step in being successfully cloned. If you are looking into cloning an adult, you have to keep in mind that the clone will start out as an infant. Secondly, even though it will be a clone physically, you have to remember that it will not be the same emotionally or intellectually. (buzzle.com) Even if there is a successful clone there could be social problems that occur due to adaptation to their respective environment. The final fact that has caught the eyes of many people is that even if the clone is successful, it has been proven that there are many disorders that lead to early death. (learn.genetics.utah.edu) Show More
Related Documents: The Disadvantages of Human Cloning Essay
What is the future of humans if we utilise all aspects of available biotechnology essay.
Humans are on a constant quest in the search for perfection and advancement in all areas of life through progressive scientific knowledge. From such a stance, the future of humans appears boundless with all the potential possibilities biotechnology provides, but such developments will cause ethical, social and biological implications. Biotechnology, at its simplest is technology based on biology – it employs the use of cellular and bimolecular processes to develop products and technologies. The…
Words 1646 - Pages 7

Cloning SCIENCE Essay
she died when she was 6 on valentines day 2003. • She had 6 lambs (Bonnie, twins Sally and Rosie, and triplets Lucy, Darcy and cotton) Cloning Dolly the sheep Gregor Mendel • How Gregor Mendel's pea plants help us under stand genetics. The following are the advantages of cloning animals: 1. The creation of identical copies of animals – through cloning, it is possible to create genetically identical animals for organ or tissue transplantation; and the creation of identical copies of only the…
Words 390 - Pages 2
The Pros And Cons Of Reproductive Cloning
Reproductive cloning is the process of genetically duplicating an existing living organism, however all experiments were done on animals. More than 18 mammals have been cloned, however there has been no experimentation with human cloning. The first animal that was cloned was Dolly the Sheep in 1996. More recent experiments followed for example, Dewey the Deer. In 2003, the Texas A&M University College of Veterinary Medicine cloned the first white-tailed deer known as Dewey. He was cloned from…
Words 389 - Pages 2
human cloning Essay
What is the purpose of trying to clone humans? Well, no one really knows. But it is against many people’s religious and ethical views. I am against human cloning. While people are in constant pursuit of ways to improve and advance the quality of human life, some activities in the field of genetics face analysis from many support groups because they are seen as violating fundamental and ethical principles. Human cloning is one area of genetic engineering that has started intense debates. Below are…
Words 914 - Pages 4
Essay on Recent Discoveries in Medicine
people face. Their research has resulted in antidepressant medication, genetic cloning, heart pacemakers and also laser surgery. However, there are some advantages and disadvantages for each procedure of medicine. Each patient is different and would react differently to treatment depending on their medical history. In order to make any decisions about treatment, doctors must inform patients of the advantages and disadvantages of any treatment that may be considered. If you’re suffering from depression…
Words 803 - Pages 4
Biology Revision Essays
Give a disadvantage for GE The inserted genes may have unexpected harmful effects, for example if the organism's genes mutated, it could become dangerous and unpredictable. What are the stages of GE? (3/4) The gene responsible for producing the desirable characteristic is selected, then cut from the DNA using enzymes, and isolated. The gene is inserted into the DNA of another organism, which then replicates, so there are multiple genetically modified organisms. What are the stages of cloning Dolly…
Words 521 - Pages 3

Cloning: Species and genetically Identical Copy Essay
Cloning means making an exact genetically identical copy of an organism. It's basically just another term for asexual reproduction. Cloning can also be done artifically by humans. Benefits of cloning The study of animal clones could lead to greater understanding of the development of the embryo, and of ageing and age related disorders Cloning could be used to help preserve endangered species. Concernes It's possible that cloned animals might not be as healthy as normal ones, e.g Dolly the sheep…
Words 373 - Pages 2
The Dark Side of Cloning Essay
Taylor Gordon Ms. Windsor HHS4M May 1, 2013 “The Dark side of Cloning” Cloning has been one of the most controversial and debatable topics for some time now, regarding its legality. Genetic engineering is very advanced technology but, ask yourself this question, is it really ethical and worth it? Human cloning is unethical and poses many threats to society that will lead to trouble as if there isn’t enough already out there. Also it is highly inefficient, very expensive which comes out of the…
Words 1910 - Pages 8
Argumentative Essay On Human Cloning
Cloning Synthesis Essay The American Heritage Dictionary's defines individualism as the “belief in the primary importance of the individual and in the virtues of self-reliance and personal independence.” With this in mind, individualism is a concept promised to all humans by the United States Constitution as well as being the foundation that the document and the nation were built upon. However, with constant scientific threats of cloning humans, these rights and liberties that have been promised…
Words 1978 - Pages 8
Steve Denton Essays
Problems Created and Solutions Found in Human Genetic Engineering When the topic of cloning, stem cell research, or gene manipulation arises, most people hold a strong opinion about the ethics of such practices. Those opinions tend to be informed by the person’s beliefs about what human life is and what it should be. Questions such as, “Is it ethical to ‘play God’ and control the development of human beings that would otherwise be determined by chance or inherited traits?” often elicit an immediate…
Words 1207 - Pages 5
The advantages and disadvantages of cloning humans as well as the ethical and social problems involved in it!
Pre-university paper, 2002, 14 pages, grade: 2+(b), sabine reinhold (author), 1. introduction.
I think nobody can afford to ignore the progress that is made in science today. Scientific research gives us knowledge about things that nobody ever thought about just a few years ago, for example the cloning of humans.
In this essay I want to focus on this topic with special regard to the advantages and disadvantages and the social and ethical problems. I will start with a definition of cloning. The next part of the essay will be about the beginning of life followed by a listing of arguments about advantages and disadvantages of human cloning. Furthermore my essay will involve a look on cloning and sciene fiction and finish with the economic reasons for cloning humans. My motivation to do the essay about this topic is not only that it is crucial for everybody to think about cloning but in my mind it is also very interesting and exciting to learn more about it. It is a scientific possibility that has become reality. Maybe cloning and genetic engineering will someday even affect my life or that of my children. I hope that I will be able to learn enough about cloning by writing this essay so that I can make up my mind on how I feel about this topic.
1 The word cloning originated from the greek and means sprout or branch.
Cloning is an asexual kind of reproduction. In order to understand the technique we first have to know how sexual reproduction basically works.Every human body cell has a set of 46 chromosomes 2 and every gamete, which is the man’s sperm cell and the woman’s egg cell, has 23 chromosomes. The gametes have only half of the chromosomes a body cell has because during sexual reproduction the egg cell and the sperm cell come together and create a new life which then has a complete set of chromosomes (46) in every body cell again, 23 from the mother and 23 from the father. If gametes would have complete chromosome sets, too, the number of chromosomes in the body cells of the following generations would continue to grow.
Cloning works kind of similar but since the goal is to create something which is genetically identical to one model the fertilization process has to take place with the chromosomes ( the hereditary material) of only one person or thing. This can only be done by scientists in the laboratory (asexual). It works like this: One body cell from the model is taken and the core of the cell is removed (the core contains the whole hereditary material which is on 46 chromosomes). The core of this body cell is then implanted into an “empty” egg cell (empty because the core from the egg cell with the hereditary material on 23 chromosomes has to be removed as well). The fertilized egg cell then contains 46 chromosomes like it contains after sexual fertilization but with the difference that these 46 chromosomes are from one person and not from two, the man and the woman. What happens with this fertilized egg cell next depends on what kind of cloning is to be practised, either therapeutic cloning or reproductive cloning.
2.1 Therapeutic cloning
If therapeutic cloning is practised, the fertilized egg cell is harvested. When the cell has itself a few times divided, the valueable embryonic stem cells can be taken from the developing embryo, hereby the embryo is killed. These embryonic stem cells are so valueable because they can only be won from umbilical cord or from embryos and they are crucial for scientific research. The purpose of therapeutic cloning is to clone things such as organs and tissue for patients in need (see advantages and disadvantages of human cloning).
2.2 Reproductive cloning
If reproductive cloning is practised the fertilized egg cell is implanted into the womans womb where it is able to develop to full maturity like a “normal” sexually fertilized egg cell. Therefore reproductive cloning has the purpose of actually producing a human that is genetically identical to somebody else.
3. When does life begin?
3 There are several opinions regarding this question but the only one that is biologically demonstrable is that life begins with the fertilization of the egg cell. The reason to support this argument is that with fertilization the genetic identity of the new life is already determined completely since the mother’s and the father’s genes 4 are fused together. From this point on the embryo steadily develops and during this process the genetic identity doesn’t change any more. You could say that the genetic identity is like an instruction for the creation of the embryo, it just takes nine months till this instruction is realized. From fertilization on the embryo develops as a human and not to a human.
Some other opinions to the question where life begins are the following:
1) Life begins with birth because before birth the embryo isn’t able to stay alive on it’s own. It needs the mothers body to survive and to develop to full maturity. 2) Life begins when a human has the consciousness to live. Supporting this argument one has to believe that some mentally sick people and coma patients are not living either since they probably don’t have the consciousness to live. 3) Life begins after the first fourteen days,the first three months, etc. It is easily explainable why people favor this argument. Many have problems to define a bunch of cells ( that’s all a human is in the very beginning) as living. After some time ( for example three months) has passed one can at least recognize the shape of an embryo. Argument one has at least a reasoning but the others a hardly acceptable from the biological point of view as there is no proof for them.
The reason why it is important to define the beginning of life is that with its beginning every human has basic human rights that are unimpeachable.These rights are granted to every human without regard of attributes like age, race, sex, state of health or anything else and involve the right of human dignity and the right to live. With cloning we would hurt these human rights, if one believes that life begins with fertilization. When a scientist takes stem cells from an embryo for therapeutic cloning and kills the embryo afterwards it is a violation of the right to live. Furthermore the scientist didn’t respect the human dignity of the embryo because he uses it like a rat for his experiments and then “throws it away”. Some people still defend therapeutic cloning by saying that this kind of cloning is a very valuable technique for scientists in order to learn more about certain diseases but that doesn’t change the crucial point that human dignity is hurt and that’s a violation against the law, at least in industrialized countries where these human rights belong to the law.
Before we can make up our mind on how we feel about cloning we defenetly have to ask us where we see the beginnig of life and we have to know the different advantages and disadvantages of cloning that I will discuss on the following pages.
4. Advantages and disadvantages of human cloning
Although this part of my essay has the title “advantages and disadvantages of human cloning” you will see that I didn’t clearly define every single fact as an advantage or disadvantage. Instead of doing this I wrote down all my knowledge about this fact and left it up to the reader to decide whether he sees it as an advantage or disadvantage. I think this is something that everyone has a different opinion about. I can hardly give one definition and claim this to be right.
4.1 The reversion of the aging process
5 We can reverse our own aging process by using cloning. It works like this: Each cloned body cell is a brand new cell. It is the exact copy from an existing cell but is has the advantage that it is not as old as the model 6 . If a person would copy/ clone his 7 body cells and have these cells inplanted into the body when he is older, this person could renew his body. Someday this technique could allow humans to live to any age they want.
On one hand “this would eleminate fear of old age an death” 8 but on the other hand realising the dream to live forever brings a lot of new problems. We already have the problem that there are too many old people and not enough young people to pay for their pension. This problem would get even bigger. Also old people may be physical healthy but we have no medicine or technique to renew their mind. For some people with mental illness this artificially prolonged life might not be worth living.
4.2 The production of organs
Many people need organ donors but there are often not enough available and the risk that the body rejects the new organ is high. Many patients with an implanted organ need to take a lot of medicine with side effects each day for the rest of their lives to make sure that their body accepts the organ. These side effects lower their life quality.
It is possible to harvest embryonic stem cells and therefore it would be possible to grow organs or tissues, too. Everybody could clone his own organs. The clone shares identical genes to the model and hereby “the chances of rejection are nullified” 9 . It is even possible to grow skin for burn victims by using the victims own skin cells and cloning them. Up to today it is a big problem to help a burn victim. At present the only solution is to take skin from a “less important“ part of the body and put it where it is needed ( e.g. when a persons face is all burned he could use skin from the leg to cover the burned parts ).
4.3 The chance to have children for infertile couples
Cloning could help infertile couples if they want to have children. At the moment those couples have a harsh time. They have to “go through physically and emotionally painful procedures” 10 which are not only expensive and take a lot of time but which are also “estimated to be less than 10 % succsessful” 11 . Current infertility treatments don’t seem to improve soon because “being infertile is not considered a ‘real medical problem’ “ 12 in people’s attitudes.
The solution is called “in vitro fertilization”: One single egg cell has to be taken from the woman’s ovary and put into a dish where it is fertilized with a sperm cell of the man. The fertilized egg cell is than placed into the woman’s womb. It’s guaranteed that this technique is successful.
Seen from the couples point of view using cloning in order to have children is a brilliant idea but what about the ethical views? Cloning children will probably lead to the designer baby since the fertilized egg cell ( which is to be an embryo soon ) could also be enhanced with extra genes for special traits such as musical or athletic talent.
Furthermore the egg cell could be tested for special heriditary diseases. If they don’t excist, the egg cell can be implanted into the woman’s womb, otherwise it will be annihilated. This technique is called pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (pgd).
Maybe the parents want only a boy or a girl. Then, using a procedure called sexing, scientists separate the sperm cells and choose the sex of the planned child.
There are several critical points that have to be considered when talking about those embryo selecting techniques 13 :
1) Choosing one child over another is immoral. By doing this industrialized countries are no better than Third World countries who favor boy babies and often kill girl babies soon after birth. The only difference would be that we “kill“ the egg and not the born baby. At this point we have to get back to the question “where does life begin?“ If it begins, in your opinion, with fertilization, it would make no difference. 2) It is wrong to mess with the natural order. Some people believe that there is a “predetermined goal for the evolution of humankind” 14 . 3) The medicine is misused. Its purpose in the general sense is to heal. 4)Embryo selection will put a lot of pressure on couples who want to have children. First of all if they don’t test their embryo for certain heriditary diseases for example and their child gets sick later, people may reproach them that they could have prevented this. As a consequence every couple is forced to test their baby, even if they don’t want to. Furthermore insurance companies or state regulations could make the condition to only provide health coverage to children who were embryonically screened for the absence of certain diseases.
4.4 The improvement of reconstructive and cosmetic surgery
15 Reconstructive and cosmetic surgery could be improved with the help of cloning. Up to today cosmetic surgery can be risky because the used materials are foreign to the body. Silicone breast implants may cause immune disease, for example. Doctors would have the ability to manufacture bone, fat and connective tissue that matches the patient’s tissues exactly. Every person could change his appearance riskless.
4.5 The curing of diseases that are still uncurable
Cloning can be used to cure currently uncurable diseases. Diseases such as cancer are a “major killer throughout the world” 16 .We may be able to cure cancer if we learn how “cells differentiate into specific kind of tissue and how cancerous cells loose their differentiation” 17 . We could learn about this and then we may be able to develop an effective gene therapy to help sick people. Another example of a currently uncurable disease is Tay-Sachs disease. We could manufacture the enzyme hexoseaminidase A which is calling for the disease when it is absent. Tay-Sachs disease causes an unpreventable death by the age of five 18 .
Using cloning to inquire after such diseases can save many lives.
On the other side we would destroy the natural evolution process (see “The threat to genetic diversity and evolution”).
4.6 The replacement of dead people
Before discussing this topic a big misunderstanding has to be pointed out. Cloning can only produce genetically identical humans but it can’t ensure that the personal beliefs or goals will be similar to the model, too. This means for example that even if somebody would have a baby whose embryo was enhanced with genes for musical talent it isn’t guaranteed that this baby will someday become a famous pianist. The child may have musical talent but what he makes out of these talents, if he uses them or not, is up to the child. If it is not interested in taking piano lessons for example the talent will stay undiscovered. The problem is the same when somebody would try to replace a loved one. Unrealistic expectations on how the character will be might lead to frustration. Of course the outward appearance of the clone will be exactly the same but the personality will be probably different and that’s the critical point here. The clone can never really be a substitute for another person.
Also we have to ask us if it is justifiable from the ethical side. Cloning people to replace others is somewhat similar to have another baby just to create a perfect donor for the already existing sibling that is sick. How would you feel if your parents someday tell you that you were only born for your brother or sister and that you wouldn’t be here now if your sibling wouldn’t have needed your help or wouldn’t have died?
4.7 The threat to genetic diversity and evolution
Clones are genetically like brothers and sisters. Therefore genetic diversity is more and more destroyed by cloning and diseases can easier be spread under equal people. That’s the reason why nobody is allowed to have a sexual relationship with a family member. Humans already destroyed the natural evolution process by inventing all kinds of medecine. In consequence, even if that sounds cruel, people who were chosen to die by nature are still living because we can heal them or at least enable them to live with their illness by using unnatural chemicals (what most of the medecine is). With cloning we would also create people that wouldn’t have been created by nature. That is something revolutional but the question is if humans are allowed to play god and control the evolution process.
4.8 The chance for lesbians to have children
Like all ethical questions the question if being homosexual is considered “normal” or not is one that everybody has own answers and opinions to. It wouldn’t bring us any further to argue about it here. If you accept it or not, technically it is possible to create a baby with the hereditary material from two mothers. They would both have to donate an egg cell. The hereditary material in both egg cells is then separated from the egg cells.Now the egg cell from one mother is fertilized with the hereditary material from the other mother. The fertilized egg cell could then be implanted into either one of the mothers. Of course their baby will later look exactly like the mother who donated the hereditary material.
By the way: that’s how Dolly the sheep was cloned, too, only that the sheep had three mothers. One donated the egg cell, the other donated the hereditary material. The fertilized egg cell was then implanted into the third mother who carried the sheep out. By using cloning for this purpose, Lesbian couples have the possibility to create a family like all other couples, too, but this will probably evoque a lot of protest in society among those who don’t feel that they should have these rights because they don’t accept homosexuality.
4.9 A society that is broken into two classes
If someday many people have been cloned there will consequently envolve two classes of humans: the gene-enhanced and those who were “created” naturally. Of course the gene- enhanced will have a lot of advantages in life since they were given special talents. It is logical that those gene-enhanced people will be the rich ones because only rich parents have the possibility to afford the techniques to enhance their baby with special genes. These rich gene-enhanced people can probably get better jobs than the others because of their special talents so they will get even richer. Rich people often have a lot of authority. If one continues to think this through the rich gene-enhanced people could someday be the most powerful ones and rule over the others.
Also people with hereditary diseases are likely to be excluded from society and to become outsiders because their parents could not afford to test their baby for those diseases before it was born.
5. Cloning and science fiction
19 Now, after you are informed about the cloning of humans in general and it’s advantages and disadvantages (the realistic possibilities that human cloning brings with it), I want to show the unrealistic expectations of cloned humans as well.
We often find these unrealistic expectations in books from science fiction authors and in science fiction movies.These fantasy products tell us horror stories about armies of clones that want to kill humans or the creation of a second Hitler. I want tu use these two examples to demonstrate how unrealistic such horror stories are.
First of all these armies of clones are often described as armies of robots without feelings that are programmed to kill others by their creator and this is not possible. As I already wrote earlier in this essay clones are not much different from other humans except thet they were created by asexual reproduction thus having feelings like “normal” humans, too. The second question is: why would a person create such an army of clones if he would at least have to wait fifteen to twenty years till he could use this army for his interests? Clones can’t grow and develop faster than other humans.
A third problem is that this person would need several women that carrie each clone out and women that are willing to do that may be hard to find.
The idea that a second Hitler could be created is another unrealistic science fiction phantasy. I already mentioned earlier in this essay that one could enhance a person with extra genes for special traits but the clones own will and his surroundings contribute to his character and beliefs as well. Hitler could get so powerful because of the german history. He used the bad situation of Germany and convinced people that he would improve it. A clone of Hitler probably wouldn’t have the possibility to do the same thing at present, the circumstances are not given.
The most important aspect one has to keep in mind when he isn’t sure if something he heard is really possible or just a fictional story is that clones are normal people of flesh and blood, no robots or machines that have no feelings and can be programmed to do certain things. Even if it would be possible to create clones for a certain purpose it probably wouldn’t be allowed since all humans, which involves clones as well of course, have basic human rights and cannot be anyones property.
6. Economic reasons for cloning
20 As you can imagine there probably will be people who try to profit from cloning. I found out some possibilities that people could use. I want to point out that the first two of those are rather unrealistic as they are a violation against human rights and they are hard to realize.
6.1 Information retention
A cloning firm could buy DNA from a top ability worker and produce the clone of this person in another part of the world.When the clone has grown up the cloning firm tells him that he is the clone of a top ability worker but not who is his model. Of course the clone is eager to know who the model is and is probably willing to pay a lot of money to get this information.
6.2 Extract rents from clones via education
Top ability people have greater returns to higher education and top schools get high rents from the top ability people who visit their school. If some top schools would get together and invest in the cloning of top individuals they would make their own future students and get a lot of rent from them later.
6.3 Patents for certain techniques
If a big firm would develop a technique to produce organs for transplantation, for example, and then have this patented it could make a lot of money because all the people who want to use this technique, in this example this would be people who are in need of an organ, would charge this firm.
7. Conclusion
I want to start by pointing out that the thing I learnt best while writing this essay is that this topic is very extensive. You can’t really discuss every detail in a little essay like this one. I hope I managed to give an objective overall view. In my opinion you can’t think either just negative or just positive about cloning. Many things that cloning makes possible have their advantages as well as disadvantages to them. Lets take for example the reversion of the aging process: Many people would like to “live forever”. On the other hand, this will evoque the pension problem (see “advantages and disadvantages of human cloning”).
To my mind the scientific progress today goes really fast and that’s a big problem. We have the possibility to do these big things that nobody has ever done before like cloning but we also have the responsibility for what we do. The question humankind asks today is not “Do we have the possibilty to do it?” but “Do we have the right to do it? Are we ready to stand up for the consequences of our deeds?” Technically it is already possible for a long time to clone humans. Many scientists are eager to try all of the techniques out that they know about but the problem is that the government doesn’t allow them to do it yet. Especially the german government is very strict.
I think that we should allow only therapeutic cloning since this could really help people. But we should have strict regulations. The production of organs and tissue by using therapeutic cloning, for example, should, in my opinion, only be practised when there is absolutely no donor organ for the patient who needs it and he would have to die without the organ. To my mind it would be murder if we know how to manufacture an organ but the patient still has to die because we didn’t use our knowledge. I think it is also justifiable to help infertile couples with cloning but without using embryo selecting techniques.
I reject reproductive cloning though. In my judgement it has no sense to create an identical twin of somebody, especially because the character of the clone is probably different than the character of the model anyways. The special thing about humankind is that everybody is different, why should we want to destroy this multiplicity?
Last but not least I want to say that those parts of my essay which are titled “Advantages and disadvantages of human cloning” and “Economic reasons for cloning” are just speculations. They are not unrealistic but it is important to realize that it hasn’t happened yet. Who knows what the future brings.…
1) Mc Kinnell, Robert Gilmore, Cloning - Leben aus der Retorte, Karlsruhe 1981
2) Silver, Lee M., Remaking Eden, New York 1997
3) Saint - Paul, Gilles, The Economics of Human Cloning, in: IZA Discussion Paper No. 231, pages 3 and 4
4) http://www.humancloning.org/benefits.htm
5) http://www.humancloning.org/publish/posts/142.html
6) http://www.solidaritaet.com/neuesol/2000/35/col1.htm
7) http://cloning.ch/cloning/doku/doku_ewig.html
Hiermit erkläre ich, dass ich die vorliegende Arbeit selbstständig und ohne fremde Hilfe verfasst und keine anderen als die im Literaturverzeichnis angegebenen Hilfsmittel verwendet habe.
Insbesondere versichere ich, dass ich alle wörtlichen und sinngemäßen Übernahmen aus anderen Werken als solche kenntlich gemacht habe.
1 I got this knowledge from my biology class.
2 Chromosomes carry the hereditary material.
3 Compare http://www.solidaritaet.com/neuesol/2000/35/col1.htm and http://cloning.ch/cloning/doku/doku_ewig.html
4 Genes are little units on the chromosomes that carry the hereditary information.
5 Compare http://www.humancloning.org/publish/posts/142.html
6 The model is the person or thing that donates the hereditary material in order to clone it.
7 I decided to use only the male grammatical forms like “he”, “his”, because the essay is easier to read this way, of course the women are meant as well when I talk about “persons”.
8 http://www.humancloning.org/publish/posts/142.html
9 http://www.humancloning.org/publish/posts/142.html
10 http://www.humancloning.org/bebefits.htm
11 http://www.humancloning.org/publish/posts/142.html
12 http://www.humancloning.org/publish/posts/142.html
13 compare point 1), 2) and 3) to “Remaking Eden”, pages 255-257
14 ”Remaking Eden”, page 256
15 compare http://www.humancloning.org/publish/posts/142.html
16 http://www.humancloning.org/publish/posts/142.html
17 http://www.humancloning.org/publish/posts/142.html
18 compare “Remaking Eden“, page 251
19 compare “Cloning-Leben aus der Retorte“, pages 94-98
20 compare “Extract rents from clones via education” and “Information retention” to “The Economics of Human Cloning“, pages 3 and 4.
Ms. Awesome work :)
jbj. xcellent
Thanks Alot :D. Hi Thankyou For Your Advice On Cloning Up There, It Has Really Helped Me On My Coursework At School I Was Stuck Then I Found Your Website To Help Me And I Got A B+ For It Thanks Again X
Facharbeit. Verdammt gute Facharbeit- Respekt

Similar texts

Advantages & Disadvantages of activity based costing with reference to ec...

Technology Delivery Robot. Potential Benefits, Security Concern, Social Probl...

Ethical, Social and Environmental Standards and Practices of Microsoft

Eliminating Drug Addiction: The Ways of Solving the Social Problem in Early S...

Constructing the Social Problem: Causes of Drug Addiction in Early Soviet Med...

Income Inequality in the European Union and its relation to health and social...

Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Social Networks in Business

Group Decision Making in Schools: Advantages and Disadvantages

Gausemeier’s Scenario Management Process. Reflection on the Advantages and Di...

The Advantages and Disadvantages of the British Monarchy in 21st Century Grea...

The Future of Education. Advantages and Disadvantages of Online Education

Informal Second Language Acquisition Through Entertainment Mediums. Advantage...

The Advantages and Disadvantages of E-Recruitment

Advantages and Disadvantages of Arbitration

Advantages and Disadvantages of the Lean Production Process

Assessment Centre for Recruiting. Its Advantages and Disadvantages

The Advantages and Disadvantages of Constructing Free-Trade Zones as an Indus...

E-learning as a Tool of Contemporary Learning. A Brief Overview of Advantages...

Workplace Spirituality. The Ethical and Social Responsibility Implications
Upload papers
Your term paper / thesis:
- Publication as eBook and book - High royalties for the sales - Completely free - with ISBN - It only takes five minutes - Every paper finds readers
Publish now - it's free

- Free Essays
- Citation Generator

Disadvantages of Human Cloning Essay Example
You May Also Find These Documents Helpful
The pros and cons of therapeutic cloning.
“Equipped with his five senses, man explores the universe around him and calls the adventure Science,” According to Edwin Powell Hubble. Science has been expanding and more advanced with today's technology. Scientific advancements are also making good and bad effects and not everyone agrees with all of them. Cloning is one of the scientific advancements that is expanding and it happens for many different reasons and it has many different effects on society.…
Human Cloning Pros And Cons
As revealed earlier, cloning humans has a high failure rate, because there are many barriers put in by nature to prevent an “unnatural” event from occurring. These barriers can happen anytime during the cloning process. For example, the enucleated egg might not be compatible with the donor nucleus, the newly transferred nucleus may not grow and develop properly, the step where the embryo is implanted into the surrogate could fail, or the pregnancy may fail. Even if the pregnancy succeeds, there is no guarantee that the clone will act like a clone unless the right genes are activated. In a transferred human cloning, the scientist has to re-program the nucleus and force it to pretend as if it belongs in an early embryonic stage. If the nucleus is not programmed properly or completely, the embryo will more than likely become abnormal or die. Now, if the embryo manages to pass all of the post-zygotic barriers, “there is a possibility that the [fully developed] cloned individual might carry certain abnormalities…” causing them to live a shorter life span than expected (Wickman). There are also other concerns, besides health-related, such moral issues. The ability to clone individuals could lead to an out-of-control situation created by someone who wants to create an army of genetic replicas by abusing the new…
Pros And Cons Of Artificial Cloning
There are some positives to cloning but only therapeutic cloning when it is used to replicate cells. Therapeutic cloning produces embryonic stem cells for creating tissues to replace injured or diseased tissues(3). This can be used to cure people not harm them. Artificial cloning can be good for the studies and discoveries that have been made but otherwise the animals that die are not helping anyone.…
Human Cloning Pros And Cons Essay
Human Cloning is the creation of a genetically identical copy of an existing, or previously existing, human being or growing cloned tissue from that individual (Cloning Fact Sheet). Scientists remove the nucleus, which contains the genetic material, from an egg. The genetic material from an adult somatic cell is removed and placed in the egg. It now has a complete set of genes. The egg is placed in a petri dish to allow it to develop into an embryo, which is placed into a surrogate mother to continue to grow and develop into a baby (Genetic Science Learning Center). This technique is called nuclear transfer or nuclear transplantation because they transfer the nucleus from one cell to another (Kilner). Therapeutic cloning is a technique of human…
Pros And Cons Of Human Cloning
Let's just say if a clone survives birth and it’s childhood and had Large Offspring Syndrome, If all of the conditions like cardiomyopathy diabetes, high rates of heart and lung damage, kidney failure brain abnormalities etc. The animal in labor and the clone is give birth in a filthy Barn house. In that scenario the clone animal that is giving birth, percentage of life is one in million. Another reason that cloning should not be in society is the lack of diversity. “Cloning involves a process of creating identical genes. As such, there would be a lack of diversity in animalkind. Scientists believe this lack of diversity will lower the different animal race’s ability to adapt. Plus, there would be a lack of diversity in the world leading to everyone looking the same.…
Pros And Cons Of Cloning
cloning. There can be over population. It can pass on infections, egg with a new transferred nucleus can't…
Human Cloning from a Christian Perspective
The safe bet would be to limit cloning to certain medical and food enrichment areas. But, as the cloning genie departs its box, the drive to clone humans and animals quickens. Like stated, we still have wars, we still have criminals on the streets, and we still have problems with our economy. In other…
A Birth to Save a Life
1. I think that it is morally wrong for a child to be created for "parts". Donor children are often referred to as "savior siblings", "spare part sisters", or "bred to order brothers". These names create the assumptin that the children are created merely for instrumental reasons, or to serve as a donor for the sick sibling, and not for their own sake. Same goes for clones, as soon as a clone (or any other human being) has achieved personhood, it deserves the same respect as any other being with those dispositional capacity. The ethical principle of equality demands no less.…
Cloning In Australia Essay
The negative points of cloning greatly outweigh the positive. This is proved by the fact that cloning is currently illegal in Australia, so other people must feel the same way.…
Therapeutic Cloning
The third argument against therapeutic cloning is that it is not safe. There is a possibility of transferring diseases and other malformations to human. Dolly the sheep was the first animal that was ever clone, Dolly die at a young age. Scientist discovered that the problem of the premature death of Dolly was due…
Sociological Impacts of Cloning
The concept of reproductive cloning has many opponents. Opposition comes from governments, religious organizations, citizen advocacy groups and many private individuals. Almost everyone has an opinion regarding cloning. Entire nations have banned reproductive cloning because of the potential for widespread abuse by unscrupulous parties. Many people feel that cloned individuals could be at risk for abuse even through forced servitude. Conceivably, this could even take the form of cloned individuals being trained as ruthless killing machines. Another aspect of reproductive cloning that is equally frightening to some may be the genetic alteration of babies that could cause an imbalance in the natural process. Cloning and all of its research are widely controversial. Many, if not all, social systems are affected. Controversy even surrounds determining what is and what is not…
Analytical Brief Cloning
Cloning is difficult and results are not guaranteed. If scientists make a mistake in the early stages of the cloning process, the clone will no longer be identical. The clone that was created to help in the medical field, for example, will no longer be used for the scientific research. In addition, clones are more likely than their original to develop problems, such as infections, tumors, and other disorders. Typically, clones do not live as long as other creatures produced naturally, so it is as if scientists spent years and thousands of dollars for something that would not last long on Earth. They do not age as other creatures, and scientists have not been able to gather enough data to determine the life of a clone. Sometimes, clones mysteriously die, just as Australia’s first cloned sheep. One day, it “appeared healthy and energetic,” (Cloning Fact Sheet) but it died that very day. There were no signs of illnesses or any other problems, and the reason for death was never…
Three Reasons Why Cloning Should Not Be Allowed
There are people who believe that cloning should be allowed. One of the reasons is that parents can have control in their reproductive lives. Children should be valued by who they are, and parents don’t have the right to choose the physical characteristics or even take away the identities of their children. As a result, cloned children will see themselves as an object but not as a person. Another reason is the possibility of cloning organs to save lives. This argument I see it very insufficient because cloned organs can have some defects and cause some damage in a person’s body and organism if the procedure is not well done. Furthermore most scientists agree that research cloning for medical research is not needed as a source of embryonic stem cells these can be obtained from embryos generated by in vitro fertilization.…
In this article "Cons of Cloning" by Andrea Castro, the point is made that there are many positive things about cloning; but there are also many bad things that could happen if men were to fool around with cloning. The main thing that was pointed out to be the negative part of cloning is that people would lose their individuality. Soon cloning the same people over and over and over and over again would create many problems. There would be less variety of people, or if there were more people than the world would be hard pressed to support the bigger population. The world would have to go find new space, there would be a need for more jobs, more food, more…
Should Cloning of Animals and Humans Be Legal
On the other hand, there are bad points about cloning. The success rates of cloning are very low. Cloning has a 70% failure rate of being mutated. Another bad point is that it will reduce variety in people. So if the environment changes, the clones wouldn’t be able to adapt to the environment.…

Power of Human Academic Assistance vs. AI
R apid advancements in technology have simplified almost every aspect of our lives. From how we work to how we communicate, machines play an increasingly crucial role.
Writing, too, especially in the realm of academia, has been touched by the hands of Artificial Intelligence (AI), and we’re observing a flip of the proverbial pen between humans and bots in real time.
So, when it comes to writing a well-done essay, crafting poetry, or even storytelling, an inevitable question arises: who does it better?
As AI and humans engage in a literary battle, let’s explore their prowess and ponder which of the two reigns supreme concerning academic assistance.
Advantages of Human-Academic Assistance
You can benefit much more from human writers, If you’re a college student, go online and purchase essays for cheap while maintaining high levels of quality and reliability.
Here are some additional benefits that you’ll get when you buy an essay from a human writer:
Creativity and originality
Originality and creativity are two distinct characteristics that are specific to human writers that distinguish their work. These qualities entail:
Voice and tone
A human writer has a distinct personality, tone, and style that shine through their work. When writing your academic paper, you must present your ideas in a way that demonstrates your uniqueness, uses humor and conveys your emotions by showing how you feel about the topic.
Human writers are the only ones capable of achieving that personal touch. It is crucial in writing, as it helps establish a personal connection with your professor and adds authenticity to your work.
Unique ideas
Buying your essays from human writers is a good idea because they can generate innovative and fresh ideas that AI may not. They will infuse the essay with unique observations, insights, and perspectives, making it stand out from the generic content generated by AI, thus earning you high grades.
Emotional intelligence
Human writers have emotional intelligence and can create papers that resonate deeply with your target audience or professor.
Contextual adaptation
Human writers can adapt their work to various purposes, contexts, and audiences. They do this by adjusting their style, language, and tone accordingly. In this way, they can make the academic paper more effective and relatable in conveying varying messages to different groups of people.
Understanding of human nuances
Human beings have the ability to empathize with, comprehend, and perceive cultural contexts, emotions, and the subtle intricacies associated with human communication. Let's breakdown this concept further:
Cultural awareness
Human writers possess cultural knowledge and awareness that shape their understanding of norms, customs, and communication styles across diverse communities.
This understanding allows them to tailor their research and writing to an academic setting and produce content that doesn’t inadvertently cause offense to other students or readers.
Reliability and empathy
Human writers have an innate ability to convey and experience empathy. Such an emotional connection allows the writer to create relatable and engaging work that resonates with other academics at a deeper level.
Adaptability to contexts
Human writers are better skilled at adapting their tone and style to suit the intended medium, audience, and purpose. They can use different writing styles, like informative, persuasive, conversational, or formal, to provide specific instructions that will effectively assist you with any assignment you have.
Limits of Human-Academic Assistance
Despite its many benefits, human assistance in academia has a couple of disadvantages compared to AI, especially with hardware advances that have made AI writing more accessible. They include:
Limited processing capacity
Compared to AI, human writers have limitations like:
- Time constraints where they need to rest and take breaks
- Memory limitations (the inability to retain extensive amounts of data or attain perfect recall);
- Multitasking challenges mean that humans are slower
- Analytical limitations make it hard for human writers to analyze complex data sets accurately and fast
- Humans are also prone to making errors like grammatical mistakes and typos, which take time to edit and proofread.
Subject to human biases
Human writers have biases, either consciously or unconsciously, which can influence how they interpret your instructions or the way they present findings. Such biases can affect the objectivity, clarity, and accuracy of their writing, making them less reliable than AI assistance.
Time demanding
It takes human writers a significant amount of time to develop well-thought-out arguments and ideas. Gathering information, fact-checking, and looking for reliable sources is also time-consuming, especially when writing in specialized fields.
Sticking to a balance between efficiency and quality requires time, and so does perfectionism, which is a characteristic of human writing.
Advantages of AI-Academic Assistance
Speed and efficiency.
If you need speedy assistance with your academic work, then AI is the right tool for you. It boasts rapid processing that lets it generate content in a matter of seconds or minutes, unlike much slower humans.
AI does instantaneous analysis, saving you effort and time by eliminating manual analysis. It also performs automated tasks like formatting, grammar checks, and proofreading, which will free you up to focus on the more creative parts of your assignment.
Lack of human biases
AI is unaffected by prejudices, opinions, or personal beliefs, meaning that it can generate unbiased content and offer balanced perspectives on various tasks. This means that your work will reflect inclusivity and fairness, making it suitable for a wide audience.
Ability to process massive volumes of data
AI can process vast amounts of data, something humans simply cannot do. With algorithms and computing power, AI can go through a lot of data and make sense of it. This makes it possible for AI to draw connections and generate insights from data that will enrich your work in a way that human assistance cannot match.
Disadvantages of AI-Academic Assistance
AI is very powerful, but it has certain limitations when using it for academic work. Such limitations include the following:
Inability to understand cultural nuances
AI is severely limited in accurately interpreting and comprehending human emotions and the cultural variations that influence any piece of writing, including academic work.
AI lacks emotional intelligence and cannot empathize with humans, meaning that the work it generates doesn’t capture the sentiment and essence that would make it remarkable. It cannot incorporate irony, sarcasm, and humor, which are all powerful and important for engagement.
Additionally, because AI cannot fully understand historical contexts, societal norms, and cultural backgrounds, it may generate content with inaccuracies or misinterpretations.
Lack of originality and creativity
AI cannot generate truly unique or creative content. AI lacks the imaginative capacity needed to think outside the box and come up with an entirely new thing.
AI also has the potential to spread fake news and misinformation obtained from its training data that may reinforce harmful narratives or perpetuate inaccuracies. This will undermine your school work’s reliability and credibility, which may lead to poor grades.
Finding the Compromise
We’ve established that both AI and humans have unique abilities. Let’s now talk about how you can use these two powerful resources for the best possible academic assistance:
- You can use AI for research, ideas, and suggestions while you provide creativity, critical thinking skills, and unique perspectives. This will result in high-quality and well-rounded essays.
- You can also use AI as a tool to enhance your writing’s efficiency and accuracy, making it polished and error-free.
In the current age of technology, the debate between human and AI assistance in academics is a hot topic. While both have distinct merits and demerits, it’s difficult to determine which is superior.
However, if you want to play it safe, you can always order essay paper online. All in all, when making such a decision, you can base it on the purpose of the writing.
If your assignment requires efficiency and speed, seek AI assistance, and when a personal connection, authenticity, and depth are required, go for human-academic assistance.
1. YEC. (2023, May 30). 14 Benefits And Drawbacks Of Using AI Tools To Write Business Content. Forbes. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/theyec/2023/05/30/14-benefits-and-drawbacks-of-using-ai-tools-to-write-business-content/
2. Neuroscience News. (n.d.). Human-AI Writing: A Guide to a New Form of Communication. Neuroscience News. Retrieved from https://neurosciencenews.com/ai-human-writing-chatgpt-23892/
3. Dooley, Roger. (2023, December 4). Humans Prefer AI-Generated Content. Forbes. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/rogerdooley/2023/12/04/humans-prefer-ai-generated-content/
4. Dooley, Roger. (2023, December 4). Humans Prefer AI-Generated Content [PDF]. Forbes. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/rogerdooley/2023/12/04/humans-prefer-ai-generated-content/
5. Wartman, K. L., & Krebs, P. (2020). Can Academics Tell Difference Between AI-generated and Human-authored Content? Times Higher Education. Retrieved from https://www.timeshighereducation.com/campus/can-academics-tell-difference-between-aigenerated-and-humanauthored-content
6. Wartman, K. L., & Krebs, P. (2020). Can Academics Tell Difference Between AI-generated and Human-authored Content? [PDF]. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10328544/


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Human cloning more typically refers to "reproductive cloning," the use of somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) to obtain eggs that could develop into adult individuals. Human cloning has occasionally been suggested as a way to improve the genetic endowment of mankind, by cloning individuals of great achievement, for example, in sports ...
7. Cloning humans would help us to eliminate defective chromosomes and genetic profiles. If a person has an extra chromosome or one is missing, then that condition is called "aneuploidy." There is an increased risk of a genetic disorder when women have children later in life.
The cons or disadvantages of human cloning raise moral, ethical and safety issues: Reproductive cloning: The negatives of human cloning including the making of designer babies. Human cloning: Could be a violation of the clone's individual human rights. Embryonic cloning: Cellular degradation occurs when too many clones are made from embryos.
The Ethical Implications of Human Cloning. and on embryos created for research (whether natural or cloned) are morally on a par.This conclusion can be accepted by people who hold very different views about the moral status of the embryo. If cloning for stem cell research violates the respect the embryo is due,then so does stem cell research on ...
This op-ed is part of a series from E295: Communications for Engineering Leaders. In this course, Master of Engineering students were challenged to communicate a topic they found interesting to a broad audience of technical and non-technical readers. Dolly the sheep's taxidermied remains. Dolly was the first mammal cloned from an adult ...
Disadvantages of cloning humans. Human cloning has more disadvantages than its benefits. Firstly, it is true that cloning is not in accordance with the Christian faith. Thus Christians, who make the world's most popular religion, will feel as if they are playing God if they get involved in cloning activities.
Human cloning would enable the duplication of individuals of great talent, genius, character, or other exemplary qualities. The first four reasons for human cloning considered above looked to benefits to specific individuals, usually parents, from being able to reproduce by means of human cloning.
The Cloning Debates and Progress in Biotechnology. The perception by humans of what is doable is itself a great determiner of future events. Thus, the successful sheep cloning experiment leading to "Dolly" by Ian Wilmut and associates at Roslin Institute, Midlothian, UK, compels us to look in the mirror and consider the issue of human cloning.
Cloning is the outcome of the hard works on use of genetic engineering in animal breeding, treatment of hereditary diseases in human and replicating organisms. 16 In 1901, transfer of nucleus of a salamander embryonic cell to a enucleated cell was successfully undertaken. During 1940-1950, scientists could clone embryos in mammals.
Abstract. This scholarly article delves into the multifaceted domains of human cloning, encompassing its biological underpinnings, ethical dimensions, and broader societal implications. The exposition commences with a succinct historical and contextual overview of human cloning, segueing into an in-depth exploration of its biological intri-cacies.
Cloning Fact Sheet. The term cloning describes a number of different processes that can be used to produce genetically identical copies of a biological entity. The copied material, which has the same genetic makeup as the original, is referred to as a clone. Researchers have cloned a wide range of biological materials, including genes, cells ...
Cloning is ubiquitous in nature. The most straightforward reason why someone may want to reproduce through cloning is to have a genetically related child. Cloning would enable parents to have a ...
Disadvantages Of Human Cloning. Good Essays. 1267 Words. 6 Pages. Open Document. injecting them in other parts of the body would be one done to blind patient from Baltimore. In February of 2016, Vanna Belton had her own adult stem cells injected into her retina, and it resulted in her regaining her vision (Crew 1).
Disadvantages of Human Cloning. Nowadays, Clone is a word that is heard throughout the world, especially the United States. Scientists have discovered a way to bring back extinct animals. Many people dream to extend a life time for their loves one and to be able to express their hidden feelings in their mind after their loved one has ...
3. It could extend human life capabilities. In the developed world, the average lifespan is approaching 85 years for top nations. Even in the United States, the average lifespan is upward of 70 years for men and women. Not only could cloning help to extend life to even longer lengths, it could be a way to bring the rest of the world up to the ...
Results: The advantages and drawbacks of cloning was defined according to scientific and legal perspectives. None of the different views investigated in this study accept human cloning, because of ...
The Disadvantages Of Human Cloning. The advantage of human cloning is defective genes could eliminated. "The average person carries 8 defective genes inside them." (Smith, n.d.). Nowadays, defective illness may not be the killer of human but they could be in our future life. As humans continually reproduce, damage to their DNA line increases.
Cloning is the process of creating identical DNA. Human Cloning is a very controversial topic and many people have their own opinions on it. Human cloning can lead to the curing of many diseases and helping people via the use of stem cells. Human cloning can also help stop illegal activity and benefit many people along the way.
The term Human cloning refers to artificial human reproduction, which Is the reproduction of human cells and tissue, or replication of a human thus making a copy of that human. Two commonly discussed types of theoretical human cloning are therapeutic cloning and reproductive cloning. To summarize the therapeutic cloning is the process where ...
This is a model answer for a human cloning essay. If you look at the task, the wording is slightly different from the common 'do you agree or disagree' essay. However, it is essentially asking the same thing. As people live longer and longer, the idea of cloning human beings in order to provide spare parts is becoming a reality.
Cloning is a very controversial topic to many people. One of the first issues that come to the minds of people is the low success rate. As of right now the success rate of cloning is under 10%. In addition, no human has ever been cloned before and that scares people about the process. ( learn.genetics.utah.edu) Even though there is a very low ...
The next part of the essay will be about the beginning of life followed by a listing of arguments about advantages and disadvantages of human cloning. Furthermore my essay will involve a look on cloning and sciene fiction and finish with the economic reasons for cloning humans. My motivation to do the essay about this topic is not only that it ...
Human Cloning is the creation of a genetically identical copy of an existing, or previously existing, human being or growing cloned tissue from that individual (Cloning Fact Sheet). Scientists remove the nucleus, which contains the genetic material, from an egg. The genetic material from an adult somatic cell is removed and placed in the egg.
Human writers have emotional intelligence and can create papers that resonate deeply with your target audience or professor. Contextual adaptation Human writers can adapt their work to various ...