- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →

Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Why Learn Accounting? 6 Benefits

- 02 Oct 2015
Financial accounting has been called the universal language of business, so it makes sense that all business professionals should be fluent.
While you might think non-accountants don't need to study financial accounting, an understanding of key accounting concepts, like the accounting equation and financial statements, can be helpful for all professionals.
Here are six reasons why any professional can benefit from understanding financial accounting.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Accounting and Why Is It Important?
Accounting refers to the process of reporting and communicating financial information about an individual or organization.
In simpler terms, accounting is how a business records its financial information. Accountants, or anyone else tasked with accounting activities, are concerned with capturing a snapshot of an organization’s financial health at a specific point in time.
Some common accounting activities include:
- Recording transactions
- Collecting financial information
- Compiling financial records, reports, and statements
- Preparing tax returns
- Ensuring an organization’s taxes are paid and its financial records comply with the law
There’s a common misconception that only finance and accounting professionals need to be familiar with accounting concepts, but financial accounting is a critical business skill for all professionals.
Whether you’re an entrepreneur who needs to prepare financial records for your company, a business professional trying to better understand and contribute to your organization’s financial decision-making process, or someone who wants to make sense of your own finances, studying basic accounting can provide many benefits.
6 Benefits of Studying Accounting
1. you’ll be able to manage your own finances more effectively.
Be honest: Can you explain where all your money goes after your paycheck gets deposited? With some accounting knowledge under your belt, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of what goes on with your personal finances and learn important skills , such as how to effectively track expenses and work within a budget.
To learn more about how finance and accounting impact your daily life, watch the video below featuring Harvard Business School Professor V.G. Narayanan, who teaches the online course Financial Accounting :
2. You’ll Gain An Understanding of Current Events
There’s no shortage of scandal in the accounting world. You may have heard stories of illicit manipulation of financial documents for personal gain, or seemingly small accounting mistakes with disastrous consequences.
With a basic understanding of accounting, you can understand what these companies have done wrong and why it matters. You’ll also learn how current events related to finance and accounting might impact your organization and industry.
3. You’ll Be Able to Make More Meaningful Contributions at Work
Picture this: You’re in a staff meeting and the chief financial officer (CFO) wants to discuss the past quarter’s financials. If you’ve had an introduction to accounting, you’ll not only be able to understand what the CFO is talking about, but also chime in with your own financial insight and opinions.
With accounting knowledge under your belt, you’ll also be able to determine the financial health of your organization on your own. With this information, you can glean meaningful insights and bring suggestions for improvement to upper management. Ultimately, understanding your company’s finances will help you be more effective in your role.
4. You’ll Be Primed for Entrepreneurial Success
If you own a business or are considering entrepreneurship, you need to understand basic accounting principles to be successful.
Managing costs, cash flow, invoices, vendors, and payroll are all critical components of running a company. Some important accounting skills for entrepreneurs include preparing financial statements, determining how profitable your business is, forecasting future sales, and communicating financial information to stakeholders and investors.
As a business owner, studying accounting can put you one step closer to reaching your entrepreneurial goals.
5. You’ll Have Career Advancement Opportunities
Even if you're not an accountant by trade, accounting skills can help you advance your career. You’ll become more effective in your current role and a more attractive candidate for advanced roles.
Learning financial accounting also presents a pathway for you to transition into a finance or accounting role. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics , employment in financial occupations is expected to grow five percent by 2029, which is faster than the average rate for all occupations. By studying accounting, you’ll develop the skills needed to qualify for such roles.
6. You’ll Improve Your Decision-Making Capabilities
Organizations utilize financial statements like balance sheets and income statements to make data-driven decisions regarding investment opportunities, budgets , and resource allocation.
By learning accounting, you’ll be able to analyze financial statements to help inform business decisions and facilitate communication between your organization and its stakeholders. Not only will accounting skills make you a better decision-maker at work, but you’ll also learn to make more evidence-based decisions in your personal life.

Learning Financial Accounting
No matter your current role, learning about financial accounting can be highly beneficial. You’ll be able to understand your personal and organizational finances, make more data-driven decisions, and advance your career.
Do you want to develop or hone your financial accounting skills? Explore our eight-week online Financial Accounting course and other finance and accounting courses to discover how managers, analysts, and entrepreneurs leverage accounting to drive strategic decision-making.
This post was updated on September 17, 2021. It was originally published on October 2, 2015.
Accounting in Business Essay
Accounting is referred to as “the language of business”. It is an art of recording, classifying and summarizing information about a business entity in relation to economic resources that are used in finding out the causes of success and failure in business. Due to its relevance in business it has been developed into two models; Management accounting, which deals with reporting financial information to the business stakeholders inside the organization to enhance taking managing and operating decisions; and financial accounting which provides useful information to potential and would-be stakeholders in the organization.
This has affected accounting as it has enabled easier provision of information to different groups of people through assortment of data to be handed to the financial accounting and management accounting (Sterling & Bentz, 54).
Accounting provides a body of rules and legislations that directs reporting of financial information referred to as “Generally Accepted Accounting Standards”. These accounting guidelines are adopted by many organizations and provide a standardized platform for businesses to present their financial information to the interested parties.
Jurisprudence application affects accounts and finance in accordance to the culture, religion, race and political background of the region. This is so as the laws govern the type of financial system regarding to spending, saving, investing, giving, property ownership and business marketing (Smith, Keith & Stephens, 78).
It is assumed in business, that a company cannot manage what it cannot measure. This is where an accounting system comes in handy. Without an accounting system a company cannot ascertain whether it is operating profitably or at a loss; it cannot budget cash flows in a given period; and also it cannot manage customer’s turnover or flow of inventory.
Accounting helps businesses to report accurately business transactions. In an accounting system, axiomatisation is used to show how propositions can fit in a deductive and logical system as they not only exist, but there are methods of creating them. This is through checking all measures and risk available and frequency of the object for easier description.
Accounting tends to facilitate intuitive thinking rather than of rational understanding as it is created with its purpose. This is so as accounting work is elusive, impetus, refractive at classification as they can be acknowledged in more than one way and has different interpretations. Accounting does not regulate as it is has no limits which govern it. This is so as it has no rules and regulations as what to account for or not to due to its diversity in the market of business (Power, 23).
Application of physics fundamentals has enabled development of current accounting technology, for example, accounting softwares and cloud computing. Most companies and institutions are implementing cloud accounting over the use of spreadsheets in accounting. This offers an easier method of maintaining financial records and also offers real time access to information (Kirkland & Howard, 89).
However the accounting field has been faced with numerous problems and challenges in attaining its objectives. Accounting has allowed fraudulent behaviors to go on at the expense of the involved parties. In current times a lot of accounting scandals have been witnessed as a result of loopholes in the accounting systems. More recently was the Madoff scandal which fleeced investors billions of dollars due to failure of legislations within the profession to address issues. Other scandals include Sunbeam, Qwest, Worldcom and Arthur Andersen frauds.
Accounting as a profession has been faced by the problem of malpractice by the accountants and lack of proper legislations to guide the professions. Accounting has primitives only on ungrounded standards as the techniques are not founded as it is extensive and thus requires wide research work.
Accounting is a complex subject and involves expertise and necessary infrastructure to maintain an effective accounting system. Many small and medium businesses do not maintain a proper accounting record due to the rigorous process and also it is expensive to acquire the necessary personnel and infrastructure (Ketz, 203; Yamey, 154).
Works Cited
Ketz, Edward. Accounting Ethics: Crisis in accounting ethics . New York: Routledge Publishers, 2006. Print.
Kirkland, Keith & Howard, Stuart. Simple and practical accounting with computers: a guide to the benefits of computerised accounts . London: Kogan Page, 1998. Print.
Sterling, Robert & Bentz, William. “Accounting in Perspective: Contributions to Accounting Thought by Other Disciplines ”. The Accounting Review , Vol. 46, No. 4. 1971. Print.
Power, Michael. Accounting and science: natural inquiry and commercial reason . London: Cambridge University Press, 1996. Print.
Smith, Jack, Keith, Robert & Stephens, William. Accounting principles . Sabine: McGraw-Hill, 1983 Yamey, Basil. Art & accounting . New York: Yale University Press, 1989. Print.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, November 1). Accounting in Business. https://ivypanda.com/essays/accounting-in-business/
"Accounting in Business." IvyPanda , 1 Nov. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/accounting-in-business/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Accounting in Business'. 1 November.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Accounting in Business." November 1, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/accounting-in-business/.
1. IvyPanda . "Accounting in Business." November 1, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/accounting-in-business/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Accounting in Business." November 1, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/accounting-in-business/.
- Accounting and Financial Management and Scandals
- Nortel Accounting Scandal Comprehensive Study
- Scandals in Corporate Accounting Systems at the Hospital
- The Toshiba Accounting Scandal of 2015
- The Toshiba Accounting Scandal
- Satyam Scandal, Its Detection and Aftermath
- The Corporate Accounting Scandals in China
- Tesco Accounting Scandal: Risk Management
- Enron: News, Trials and History of the Scandal
- The Aftermath of the Enron Scandal
- Who is a Leader?
- Quality Management for Organizational Excellence
- Team Leader: Exploiting New Opportunities
- Amazon Company Analysis
- The Pfizer Company Business Model

What is Accounting and Why it Matters For Your Business
Reviewed by
March 4, 2022
This article is Tax Professional approved
When you start a business, you’ve suddenly got all kinds of new responsibilities. One of the most important? Business accounting.
But what exactly is accounting? What value does it provide your business? And how much time is it going to require?
The good news is that with the right people, tools, and resources, accounting doesn’t have to be a black hole for your time.
I am the text that will be copied.
In this post, we’ll cover the basics of accounting, from budgets to other accounting functions. But if you want to jump straight to the how-to, you can download our free guide to small business accounting .
A simple definition of accounting
Accounting is how your business records, organizes, and understands its financial information.
You can think of accounting as a big machine that you put raw financial information into—records of all your business transactions, taxes, projections, etc.—that then tells you a story about the financial state of your business.
Accounting is how you get a clear picture of your financial position. It tells you whether or not you’re making a profit, what your cash flow is, what the current value of your company’s assets and liabilities is, and which parts of your business are actually making money.
Accounting vs. bookkeeping
Accounting and bookkeeping are both part of the same process: keeping your financial records in order. However, bookkeeping is more concerned with recording everyday financial transactions and operations, while accounting puts that financial data to good use through analysis, strategy, and tax planning.
The accounting cycle
Accounting begins with recording transactions. Business transactions—any activity or event that involves your business’s money—need to be put into your company’s general ledger . Recording business transactions this way is part of bookkeeping.
Bookkeeping is the first step of what accountants call the “ accounting cycle ”: a process designed to take in transaction data and spit out accurate and consistent financial reports.
The accounting cycle has six major steps:
- Analyze and record transactions. Collect any invoices, bank or credit statements, and receipts from business transactions.
- Post journal entries to the ledger. It’s time to take those documents and start making journal entries for your transactions. Journal entries include three components of a transaction: when it happened, what it was for, and how much it was. Some businesses use single-entry accounting where only the expense or revenue is entered. But more common is double-entry accounting, which records each transaction in two accounts: where money is coming from and where it’s going.
- Prepare an unadjusted trial balance. At the end of a reporting period, list all of your business’s accounts and figure out their balances.
- Prepare adjusting entries at the end of the period. When you need to update entries you’ve already made, you prepare adjusting entries. For example, if a client is late on paying an invoice and you offer a 5% discount to help them pay, you would enter the discount as an adjusting entry, as opposed to changing the entry you’ve already made.
- Prepare an adjusted trial balance . After entering in adjusting entries, you’re left with an adjusted trial balance. This information is now ready to be turned into financial statements.
- Prepare financial statements. Finally, all the information you’ve collected is converted into your financial statements. This final step includes summarizing all your financial information into succinct reports for easy review.
Accounting software takes your accounting information and automates most of these rules and processes, so we’re going to skip over the gritty details of the accounting cycle and talk about the end product: financial statements.
Suggested reading: A Beginner’s Guide to The Accounting Cycle
Financial statements
Financial statements are reports that summarize how your business is doing financially.
There are three main types of financial statements: the balance sheet , income statement , and cash flow statement . Together, they tell you where your business’s money is and how it got there.
Let’s say you’re a self-employed surfing instructor who bills clients for surfing lessons. Financial statements can tell you what your most profitable months are, how much money you’ve spent on supplies, and what the total value of your business is.
Accounting software can help you generate financial statements easily, or you can have a bookkeeper do it for you.
Suggested reading: The ROI of Hiring a Bookkeeper
Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP)
Every company is different, but in order to make accurate financial comparisons between companies, we need a common language to describe each of them. That’s what generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) are: a series of standards and procedures that accountants at all companies must adhere to when preparing financial statements.
A non-governmental body called the Financial Accounting Standards Board sets the GAAP. While there are no laws enforcing these standards, most lenders and business partners in the United States will require that you adhere to GAAP. If you’re in Canada, you’ll use a different system called International Financial Reporting Standards, or IFRS .
Cash vs. Accrual
You can do your business accounting on a cash or accrual basis. The difference between the two comes down to timing.
Cash basis is the most basic accounting. On a cash basis, you only record transactions when money changes hands. If you receive an invoice on the 10th but don’t pay it until the 15th, the transaction is recorded on the 15th.
With accrual basis, you record transactions twice: when they occur and when they’re paid. For the invoice above, you record the expense on the 10th and the payment on the 15th as two separate transactions.
The method you use depends on what you need from your business finances. Cash basis is simpler and easier to stay on top of, while accrual offers greater insights for more detail-oriented business owners.
Most small businesses have more basic accounting needs, which means cash basis is often the right fit.
Suggested reading: Cash Basis Accounting vs. Accrual Accounting
The different types of accounting
Financial accounting.
Every year, your company will generate financial statements that people outside of your company—people like investors, lenders, government agencies, auditors, potential buyers, etc.—can use to learn more about your business’s financial health and profitability.
Preparing the company’s annual financial statements this way is called financial accounting. If you’re looking to hire a financial accountant, start with looking into how much an accountant costs .
Managerial accounting
Managerial accounting (or management accounting) is similar to financial accounting, with two important exceptions:
- The statements produced by managerial accounting are for internal use only.
- They’re generated much more frequently—often on a quarterly or monthly basis.
If your business ever grows to the point where you need to hire an accountant full-time, most of their time will be taken up by managerial accounting. You’ll be paying them to produce reports that provide regular updates on the company’s financial health and help you interpret those reports.
This is somewhat similar to the work a financial analyst might do, although a financial analyst will also look at past and current trends in the larger economy, not just your business, to inform their recommendations.
Tax accounting
Tax accounting is designed to make sure that you don’t pay more income tax than you are legally required to by the IRS. An example of this is when your accountant provides you with recommendations for how to get the most out of your tax return.
Tax accounting is regulated by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), and the IRS legally requires that your tax accounting adhere to the Internal Revenue Code (IRC).
Cost accounting
Whenever you’re trying to figure out how to increase your margin or deciding if raising prices is a good idea, you’re doing cost accounting.
Cost accounting involves analyzing all of the costs associated with producing an output (whether it be a physical product or service) in order to make better decisions about pricing, spending, and inventory.
Cost accounting is often a prerequisite of managerial accounting because managers use cost accounting reports to make better business decisions. It also feeds into financial accounting since costing data is often required when compiling a balance sheet.
Credit accounting
Credit accounting involves analyzing all of a company’s unpaid bills and liabilities to make sure that a company’s cash isn’t constantly tied up in paying for them.
Credit accounting can be one of the most difficult kinds of accounting to do well, in part because it’s a difficult subject to be critical about. Talking about debts can be a sensitive, but necessary, conversation.
Why accounting matters for your small business
Accounting helps you plan for growth.
Every great journey begins with a roadmap. When you’re planning your company’s growth, it’s essential to set goals. What should your profits look like one year from now? How about in five years?
Keeping up with your accounting helps you stay on top of your business finances. That information is essential to assess how quickly your business is developing and guide future decision making. Without accurate reporting, you won’t have the full financial picture.
Has your cost of goods sold increased? Are margins thinner? Are your growth goals reasonable? Without financial statements, you won’t have an objective answer.
Accounting is essential for securing a loan
Up-to-date financial statements are essential if you want to fund your small business with a loan.
For instance, suppose you want to apply for a Small Business Association (SBA) loan through one of the big banks. You’ll need to provide, on average, three years of financial statements, plus a one-year cash flow projection . It’s virtually impossible to deliver any of these if you don’t have an accounting system in place.
Suggested reading: What to Prepare When Applying for a Business Loan
You need accounting to attract investors or sell your business
You may not be planning to court investors or sell your business right now, but it’s a good idea to leave your options open. And the best way to do that is to put a proper accounting system in place now.
Potential investors, stakeholders, or buyers will expect accounting records vetted by a CPA (Certified Public Accountant) that prove your business is profitable and on track for growth.
Accounting helps you get paid
When a customer owes you money, it appears as Accounts Receivable (AR) on your balance sheet , which is generated automatically by your accounting software or manually by you or your accountant.
The balance sheet tells you how much of your AR you’ve already pocketed during the month and how much is still outstanding.
By referring to your balance sheet, you can track how effectively you’re collecting payment. Then you can put in place processes—like harder payment deadlines or better follow-up with clients—to make sure you get your hands on the money you’ve earned when you need it.
Accounting helps you stay on top of your debts
If your business owes debts to a variety of sources, like credit cards, loans, and accounts payable, you’ll have to jump into multiple accounts to check what you’re left owing.
The balance sheet shows everything you owe in one place. It also shows all your bank account balances so you can reference both at the same time. It’s the perfect report to review to make sure you have the cash available to tend to your debts and plan future payments.
Accounting keeps you out of jail (or at least saves you from fines)
As your business grows, it can be difficult to keep track of all your tax information reporting obligations. What’s more, if there are mistakes in your financial reports, you run the risk of misreporting your income. Either mistake could land you in hot water with the IRS and other regulators.
Solid accounting gives you complete, accurate financial records , which reduces your risk of breaking tax laws and the chance of an audit . And, when you have an accountant filing your taxes for you, you can be sure they’ll be done accurately and on time.
Accounting helps you pay the right amount of taxes (and not a dollar more)
If you don’t pay your tax bill in full, the IRS will fine you . But they won’t give you a gold star for paying too much.
You can tell you’re paying too much in taxes if your business consistently receives large tax refunds.
Remember: a tax refund isn’t free cash from the IRS. It’s money you’ve overpaid the government that you could’ve used to invest in your business instead.
Refunds are often the result of miscalculated quarterly estimated tax payments . To calculate quarterly estimated tax payments accurately, you need to predict your income. It’s almost impossible to do so without reliable financial records produced through accurate accounting.
Suggested reading: The Top 19 Self-Employment Tax Deductions
What an accountant does
An accountant does more than just year-end tax preparation. A skilled CPA will save you time by communicating your company’s financial state to you in clear language, while anticipating your financial needs.
Accounting professionals like CPAs or tax advisors can also provide you with knowledge and insight that are simply inaccessible to non-accountants. These experts can offer guidance on tax deductions you didn’t know you qualified for, tax rules you didn’t know you were breaking, and best practices picked up while working for other companies in your industry.
If those are tips your business can benefit from right now, it might be time to hire an accountant .
Suggested reading: How to Find an Accountant
Accounting solutions
Small business accounting software has made big advancements as more people take the entrepreneurial path.
The self-service software you use is now almost equal to the accounting software used in firms all over the world. There are now a wide array of options available—which one is best for you depends on your business’s accounting needs.
Freshbooks offers integrated invoicing that makes it simple to manage your accounts receivable and your accounting in one place. Automated bank reconciliation will import all transactions from your business bank accounts, but you will have to review and categorize each one. Their time-tracking functionality also makes it easy for freelancers who bill by the hour. Freshbooks is a good fit for someone generating a lot of invoices with a low number of transactions.
Intuit makes both Quickbooks and a payroll processor, and allows you to bundle both for one monthly cost. The payroll service automates payroll taxes, checks, and all year-end forms, but the accounting platform is mostly manual. While the tool is powerful and can help a skilled user navigate multiple aspects of running a business, it takes a good amount of know-how to get the most out of it.
If you prefer a completely hands-off approach to bookkeeping and accounting, Bench might be right for you. Connect your business bank accounts to have transactions automatically imported, categorized, and reviewed by your personal bookkeeper.
Communication is quick and reliable—the Bench platform allows you to send messages straight to your bookkeeper or set up a call to go over any financial questions that might come up. Our premium package even includes tax filing, which makes all accounting tasks completely automated. Learn more about how Bench can help .
Related Posts

Fixed Costs: Everything You Need to Know
Understanding fixed costs can help you become more profitable (and make better business decisions).

How to Do Accounting for a Small Business: Your Quick-Start Guide
Learn how to handle your small business accounting and get the financial information you need to run your business successfully.
How to Pay Off Your Business Debt, Fast
Buried in small business debt? Follow this plan to dig yourself out.
Join over 140,000 fellow entrepreneurs who receive expert advice for their small business finances
Get a regular dose of educational guides and resources curated from the experts at Bench to help you confidently make the right decisions to grow your business. No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.


The Role of Accounting in Business and Why It’s Important
- February 19, 2019

The term accounting is very common, especially during tax season.
But before we dive into the importance of accounting in business, let’s cover the basics – what is accounting?
Accounting refers to the systematic and detailed recording of financial transactions of a business. There are many types, from accounting for small businesses, government, forensic, and management accounting, to accounting for corporations.
Why Is Accounting Important?
Accounting plays a vital role in running a business because it helps you track income and expenditures, ensure statutory compliance, and provide investors, management, and government with quantitative financial information which can be used in making business decisions.
There are three key financial statements generated by your records.
- The income statement provides you with information about the profit and loss
- The balance sheet gives you a clear picture on the financial position of your business on a particular date.
- The cash flow statement is a bridge between the income statement and balance sheet and reports the cash generated and spent during a specific period of time.
It is critical you keep your financial records clean and up to date if you want to keep your business afloat. Here are just a few of the reasons why it is important for your business, big or small!
It Helps in Evaluating the Performance of Business
Your financial records reflect the results of operations as well as the financial position of your small business or corporation. In other words, they help you understand what’s going on with your business financially. Not only will clean and up to date records help you keep track of expenses, gross margin, and possible debt, but it will help you compare your current data with the previous accounting records and allocate your budget appropriately.
It Ensures Statutory Compliance
Laws and regulations vary from state to state, but proper accounting systems and processes will help you ensure statutory compliance when it comes to your business.
The accounting function will ensure that liabilities such as sales tax, VAT, income tax, and pension funds, to name a few, are appropriately addressed.
It Helps to Create Budget and Future Projections
Budgeting and future projections can make or break a business, and your financial records will play a crucial role when it comes to it.
Business trends and projections are based on historical financial data to keep your operations profitable. This financial data is most appropriate when provided by well-structured accounting processes.
It Helps in Filing Financial Statements
Businesses are required to file their financial statements with the Registrar of Companies. Listed entities are required to file them with stock exchanges, as well as for direct and indirect tax filing purposes. Needless to say, accounting plays a critical role in all these scenarios.
Work with PDR CPAs
If you are interested in a prosperous future from a personal and/or business standpoint, reach out to our team of dedicated specialists. When considering accounting, audits, tax or business consulting, one call can make all the difference. Click here to get started – we look forward to working with you!
- Topics: accounting , business planning
Schedule a Consultation
Newsletter sign-up.
Sign up for industry accounting and tax tips below
Interested in our services?
At PDR CPAs, we leverage our 50 years of industry expertise to help you keep your finances strong and your business moving forward.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.4: Explain Why Accounting Is Important to Business Stakeholders
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 2746

The number of decisions we make in a single day is staggering. For example, think about what you had for breakfast this morning. What pieces of information factored into that decision? A short list might include the foods that were available in your home, the amount of time you had to prepare and eat the food, and what sounded good to eat this morning. Let’s say you do not have much food in your home right now because you are overdue on a trip to the grocery store. Deciding to grab something at a local restaurant involves an entirely new set of choices. Can you think of some of the factors that might influence the decision to grab a meal at a local restaurant?
Daily Decisions
Many academic studies have been conducted on the topic of consumer behavior and decision-making. It is a fascinating topic of study that attempts to learn what type of advertising works best, the best place to locate a business, and many other business-related activities.
One such study, conducted by researchers at Cornell University, concluded that people make more than 200 food-related decisions per day. 2
This is astonishing considering the number of decisions found in this particular study related only to decisions involving food. Imagine how many day-to-day decisions involve other issues that are important to us, such as what to wear and how to get from point A to point B. For this exercise, provide and discuss some of the food-related decisions that you recently made.
In consideration of food-related decisions, there are many options you can consider. For example, what types, in terms of ethnic groups or styles, do you prefer? Do you want a dining experience or just something inexpensive and quick? Do you have allergy-related food issues? These are just a few of the myriad potential decisions you might make.
It is no different when it comes to financial decisions. Decision makers rely on unbiased, relevant, and timely financial information in order to make sound decisions. In this context, the term stakeholder refers to a person or group who relies on financial information to make decisions, since they often have an interest in the economic viability of an organization or business. Stakeholders may be stockholders, creditors, governmental and regulatory agencies, customers, management and other employees, and various other parties and entities.
Stockholders
A stockholder is an owner of stock in a business. Owners are called stockholders because in exchange for cash, they are given an ownership interest in the business, called stock. Stock is sometimes referred to as “shares.” Historically, stockholders received paper certificates reflecting the number of stocks owned in the business. Now, many stock transactions are recorded electronically. Introduction to Financial Statements discusses stock in more detail. Corporation Accounting offers a more extensive exploration of the types of stock as well as the accounting related to stock transactions.
Recall that organizations can be classified as for-profit, governmental, or not-for-profit entities. Stockholders are associated with for-profit businesses. While governmental and not-for-profit entities have constituents, there is no direct ownership associated with these entities.
For-profit businesses are organized into three categories: manufacturing, retail (or merchandising), and service. Another way to categorize for-profit businesses is based on the availability of the company stock (see Table 1.1 ). A publicly traded company is one whose stock is traded (bought and sold) on an organized stock exchange such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or the National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotation (NASDAQ) system. Most large, recognizable companies are publicly traded, meaning the stock is available for sale on these exchanges. A privately held company , in contrast, is one whose stock is not available to the general public. Privately held companies, while accounting for the largest number of businesses and employment in the United States, are often smaller (based on value) than publicly traded companies. Whereas financial information and company stock of publicly traded companies are available to those inside and outside of the organization, financial information and company stock of privately held companies are often limited exclusively to employees at a certain level within the organization as a part of compensation and incentive packages or selectively to individuals or groups (such as banks or other lenders) outside the organization.
Publicly Held versus Privately Held Companies
Whether the stock is owned by a publicly traded or privately held company, owners use financial information to make decisions. Owners use the financial information to assess the financial performance of the business and make decisions such as whether or not to purchase additional stock, sell existing stock, or maintain the current level of stock ownership.
Other decisions stockholders make may be influenced by the type of company. For example, stockholders of privately held companies often are also employees of the company, and the decisions they make may be related to day-to-day activities as well as longer-term strategic decisions. Owners of publicly traded companies, on the other hand, will usually only focus on strategic issues such as the company leadership, purchases of other businesses, and executive compensation arrangements. In essence, stockholders predominantly focus on profitability, expected increase in stock value, and corporate stability.
Creditors and Lenders
In order to provide goods and services to their customers, businesses make purchases from other businesses. These purchases come in the form of materials used to make finished goods or resell, office equipment such as copiers and telephones, utility services such as heating and cooling, and many other products and services that are vital to run the business efficiently and effectively.
It is rare that payment is required at the time of the purchase or when the service is provided. Instead, businesses usually extend “credit” to other businesses. Selling and purchasing on credit, which is explored further in Merchandising Transactions and Accounting for Receivables , means the payment is expected after a certain period of time following receipt of the goods or provision of the service. The term creditor refers to a business that grants extended payment terms to other businesses. The time frame for extended credit to other businesses for purchases of goods and services is usually very short, typically thirty-day to forty-five-day periods are common.
When businesses need to borrow larger amounts of money and/or for longer periods of time, they will often borrow money from a lender , a bank or other institution that has the primary purpose of lending money with a specified repayment period and stated interest rate. If you or your family own a home, you may already be familiar with lending institutions. The time frame for borrowing from lenders is typically measured in years rather than days, as was the case with creditors. While lending arrangements vary, typically the borrower is required to make periodic, scheduled payments with the full amount being repaid by a certain date. In addition, since the borrowing is for a long period of time, lending institutions require the borrower to pay a fee (called interest) for the use of borrowing. These concepts and the related accounting practices are covered in Long-Term Liabilities . Table 1.2 Summarizes the differences between creditors and lenders.
Creditor versus Lender
Both creditors and lenders use financial information to make decisions. The ultimate decision that both creditors and lenders have to make is whether or not the funds will be repaid by the borrower. The reason this is important is because lending money involves risk. The type of risk creditors and lenders assess is repayment risk—the risk the funds will not be repaid. As a rule, the longer the money is borrowed, the higher the risk involved.
Recall that accounting information is historical in nature. While historical performance is no guarantee of future performance (repayment of borrowed funds, in this case), an established pattern of financial performance using historical accounting information does help creditors and lenders to assess the likelihood the funds will be repaid, which, in turn, helps them to determine how much money to lend, how long to lend the money for, and how much interest (in the case of lenders) to charge the borrower.
Sources of Funding
Besides borrowing, there are other options for businesses to obtain or raise additional funding (also often labeled as capital). It is important for the business student to understand that businesses generally have three ways to raise capital: profitable operations is the first option; selling ownership—stock—which is also called equity financing, is the second option; and borrowing from lenders (called debt financing) is the final option.
In Introduction to Financial Statements , you’ll learn more about the business concept called “profit.” You are already aware of the concept of profit. In short, profit means the inflows of resources are greater than the outflow of resources, or stated in more business-like terms, the revenues that the company generates are larger or greater than the expenses. For example, if a retailer buys a printer for $150 and sells it for $320, then from the sale it would have revenue of $320 and expenses of $150, for a profit of $170. (Actually, the process is a little more complicated because there would typically be other expenses for the operation of the store. However, to keep the example simple, those were not included. You’ll learn more about this later in the course.)
Developing and maintaining profitable operations (selling goods and services) typically provides businesses with resources to use for future projects such as hiring additional workers, maintaining equipment, or expanding a warehouse. While profitable operations are valuable to businesses, companies often want to engage in projects that are very expensive and/or are time sensitive. Businesses, then, have other options to raise funds quickly, such as selling stock and borrowing from lenders, as previously discussed.
An advantage of selling stock to raise capital is that the business is not committed to a specific payback schedule. A disadvantage of issuing new stock is that the administrative costs (legal and compliance) are high, which makes it an expensive way to raise capital.
There are two advantages to raising money by borrowing from lenders. One advantage is that the process, relative to profitable operations and selling ownership, is quicker. As you’ve learned, lenders (and creditors) review financial information provided by the business in order to make assessments on whether or not to lend money to the business, how much money to lend, and the acceptable length of time to lend. A second, and related, advantage of raising capital through borrowing is that it is fairly inexpensive. A disadvantage of borrowing money from lenders is the repayment commitments. Because lenders require the funds to be repaid within a specific time frame, the risk to the business (and, in turn, to the lender) increases.
These topics are covered extensively in the area of study called corporate finance. While finance and accounting are similar in many aspects, in practicality finance and accounting are separate disciplines that frequently work in coordination in a business setting. Students may be interested to learn more about the educational and career options in the field of corporate finance. Because there are many similarities in the study of finance and accounting, many college students double major in a combination of finance, accounting, economics, and information systems.
CONCEPTS IN PRACTICE
What is profit? In accounting, there is general consensus on the definition of profit. A typical definition of profit is, in effect, when inflows of cash or other resources are greater than outflows of resources.
Ken Blanchard provides another way to define profit. Blanchard is the author of The One Minute Manager , a popular leadership book published in 1982. He is often quoted as saying, “profit is the applause you get for taking care of your customers and creating a motivating environment for your people [employees].” Blanchard’s definition recognizes the multidimensional aspect of profit, which requires successful businesses to focus on their customers, employees, and the community.
Check out this short video of Blanchard’s definition of profit for more information. What are alternative approaches to defining profit?
Governmental and Regulatory Agencies
Publicly traded companies are required to file financial and other informational reports with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) , a federal regulatory agency that regulates corporations with shares listed and traded on security exchanges through required periodic filings Figure 1.6 . The SEC accomplishes this in two primary ways: issuing regulations and providing oversight of financial markets. The goal of these actions is to help ensure that businesses provide investors with access to transparent and unbiased financial information.
As an example of its responsibility to issue regulations, you learn in Introduction to Financial Statements that the SEC is responsible for establishing guidelines for the accounting profession. These are called accounting standards or generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Although the SEC also had the responsibility of issuing standards for the auditing profession, they relinquished this responsibility to the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
In addition, you will learn in Describe the Varied Career Paths Open to Individuals with an Accounting Education that auditors are accountants charged with providing reasonable assurance to users that financial statements are prepared according to accounting standards. This oversight is administered through the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB), which was established in 2002.
The SEC also has responsibility for regulating firms that issue and trade (buy and sell) securities—stocks, bonds, and other investment instruments.
Enforcement by the SEC takes many forms. According to the SEC website, “Each year the SEC brings hundreds of civil enforcement actions against individuals and companies for violation of the securities laws. Typical infractions include insider trading, accounting fraud, and providing false or misleading information about securities and the companies that issue them.” 3 Financial information is a valuable tool that is part of the investigatory and enforcement activities of the SEC.

Financial Professionals and Fraud
You may have heard the name Bernard “Bernie” Madoff. Madoff ( Figure 1.7 ) was the founder of an investment firm, Bernard L. Madoff Investment Securities . The original mission of the firm was to provide financial advice and investment services to clients. This is a valuable service to many people because of the complexity of financial investments and retirement planning. Many people rely on financial professionals, like Bernie Madoff, to help them create wealth and be in a position to retire comfortably. Unfortunately, Madoff took advantage of the trust of his investors and was ultimately convicted of stealing (embezzling) over $50 billion (a low amount by some estimates). Madoff’s embezzlement remains one of the biggest financial frauds in US history.
The fraud scheme was initially uncovered by a financial analyst named Harry Markopolos. Markopolos became suspicious because Madoff’s firm purported to achieve for its investors abnormally high rates of return for an extended period of time. After analyzing the investment returns, Markopolos reported the suspicious activity to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), which has enforcement responsibility for firms providing investment services. While Madoff was initially able to stay a few steps ahead of the SEC, he was charged in 2009 and will spend the rest of his life in prison.
There are many resources to explore the Madoff scandal. You might be interested in reading the book, No One Would Listen: A True Financial Thriller , written by Harry Markopolos. A movie and a TV series have also been made about the Madoff scandal.
In addition to governmental and regulatory agencies at the federal level, many state and local agencies use financial information to accomplish the mission of protecting the public interest. The primary goals are to ensure the financial information is prepared according to the relevant rules or practices as well as to ensure funds are being used in an efficient and transparent manner. For example, local school district administrators should ensure that financial information is available to the residents and is presented in an unbiased manner. The residents want to know their tax dollars are not being wasted. Likewise, the school district administrators want to demonstrate they are using the funding in an efficient and effective manner. This helps ensure a good relationship with the community that fosters trust and support for the school system.
Depending on the perspective, the term customers can have different meanings. Consider for a moment a retail store that sells electronics. That business has customers that purchase its electronics. These customers are considered the end users of the product. The customers, knowingly or unknowingly, have a stake in the financial performance of the business. The customers benefit when the business is financially successful. Profitable businesses will continue to sell the products the customers want, maintain and improve the business facilities, provide employment for community members, and undertake many other activities that contribute to a vibrant and thriving community.
Businesses are also customers. In the example of the electronics store, the business purchases its products from other businesses, including the manufacturers of the electronics. Just as end-user customers have a vested interest in the financial success of the business, business customers also benefit from suppliers that have financial success. A supplier that is financially successful will help ensure the electronics will continue to be available to purchase and resell to the end-use customer, investments in emerging technologies will be made, and improvements in delivery and customer service will result. This, in turn, helps the retail electronics store remain cost competitive while being able to offer its customers a wide variety of products.
Managers and Other Employees
Employees have a strong interest in the financial performance of the organizations for which they work. At the most basic level, employees want to know their jobs will be secure so they can continue to be paid for their work. In addition, employees increase their value to the organization through their years of service, improving knowledge and skills, and accepting positions of increased responsibility. An organization that is financially successful is able to reward employees for that commitment to the organization through bonuses and increased pay.
In addition to promotional and compensation considerations, managers and others in the organization have the responsibility to make day-to-day and long-term (strategic) decisions for the organization. Understanding financial information is vital to making good organizational decisions.
Not all decisions, however, are based on strictly financial information. Recall that managers and other decision makers often use nonfinancial, or managerial, information. These decisions take into account other relevant factors that may not have an immediate and direct link to the financial reports. It is important to understand that sound organizational decisions are often (and should be) based on both financial and nonfinancial information.
In addition to exploring managerial accounting concepts, you will also learn some of the common techniques that are used to analyze the financial reports of businesses. Appendix A further explores these techniques and how stakeholders can use these techniques for making financial decisions.
IFRS CONNECTION
Introduction to international financial reporting standards (ifrs).
In the past fifty years, rapid advances in communications and technology have led the economy to become more global with companies buying, selling, and providing services to customers all over the world. This increase in globalization creates a greater need for users of financial information to be able to compare and evaluate global companies. Investors, creditors, and management may encounter a need to assess a company that operates outside of the United States.
For many years, the ability to compare financial statements and financial ratios of a company headquartered in the United States with a similar company headquartered in another country, such as Japan, was challenging, and only those educated in the accounting rules of both countries could easily handle the comparison. Discussions about creating a common set of international accounting standards that would apply to all publicly traded companies have been occurring since the 1950s and post–World War II economic growth, but only minimal progress was made. In 2002, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) began working more closely together to create a common set of accounting rules. Since 2002, the two organizations have released many accounting standards that are identical or similar, and they continue to work toward unifying or aligning standards, thus improving financial statement comparability between countries.
Why create a common set of international standards? As previously mentioned, the global nature of business has increased the need for comparability across companies in different countries. Investors in the United States may want to choose between investing in a US-based company or one based in France. A US company may desire to buy out a company located in Brazil. A Mexican-based company may desire to borrow money from a bank in London. These types of activities require knowledge of financial statements. Prior to the creation of IFRS, most countries had their own form of generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). This made it difficult for an investor in the United States to analyze or understand the financials of a France-based company or for a bank in London to know all of the nuances of financial statements from a Mexican company. Another reason common international rules are important is the need for similar reporting for similar business models. For example, Nestlé and the Hershey Company are in different countries yet have similar business models; the same applies to Daimler and Ford Motor Company . In these and other instances, despite the similar business models, for many years these companies reported their results differently because they were governed by different GAAP— Nestlé by French GAAP, Daimler by German GAAP, and both the Hershey Company and Ford Motor Company by US GAAP. Wouldn’t it make sense that these companies should report the results of their operations in a similar manner since their business models are similar? The globalization of the economy and the need for similar reporting across business models are just two of the reasons why the push for unified standards took a leap forward in the early twenty-first century.
Today, more than 120 countries have adopted all or most of IFRS or permit the use of IFRS for financial reporting. The United States, however, has not adopted IFRS as an acceptable method of GAAP for financial statement preparation and presentation purposes but has worked closely with the IASB. Thus, many US standards are very comparable to the international standards. Interestingly, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) allows foreign companies that are traded on US exchanges to present their statements under IFRS rules without restating to US GAAP. This occurred in 2009 and was an important move by the SEC to show solidarity toward creating financial statement comparability across countries.
Throughout this text, “IFRS Connection” feature boxes will discuss the important similarities and most significant differences between reporting using US GAAP as created by FASB and IFRS as created by IASB. For now, know that it is important for anyone in business, not just accountants, to be aware of some of the primary similarities and differences between IFRS and US GAAP, because these differences can impact analysis and decision-making.
- 2 B. Wansink and J. Sobal. “Mindless Eating: The 200 Daily Food Decisions We Overlook.” 2007. Environment & Behavior , 39[1], 106–123.
- 3 U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. “What We Do.” June 10, 2013. https://www.sec.gov/Article/whatwedo.html
Why It Matters
Chapter outline.
Liam is excited to be graduating from his MBA program and looks forward to having more time to pursue his business venture. During one of his courses, Liam came up with the business idea of creating trendy workout attire. For his class project, he started silk-screening vintage album cover designs onto tanks, tees, and yoga pants. He tested the market by selling his wares on campus and was surprised how quickly and how often he sold out. In fact, sales were high enough that he decided to go into business for himself. One of his first decisions involved whether he should continue to pay someone else to silk-screen his designs or do his own silk-screening. To do his own silk-screening, he would need to invest in a silk-screening machine.
Liam will need to analyze the purchase of a silk-screening machine to determine the impact on his business in the short term as well as the long term, including the accounting implications related to the expense of this machine. Liam knows that over time, the value of the machine will decrease, but he also knows that an asset is supposed to be recorded on the books at its historical cost. He also wonders what costs are considered part of this asset. Additionally, Liam has learned about the matching principle (expense recognition) but needs to learn how that relates to a machine that is purchased in one year and used for many years to help generate revenue. Liam has a lot of information to consider before making this decision.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-financial-accounting/pages/1-why-it-matters
- Authors: Mitchell Franklin, Patty Graybeal, Dixon Cooper
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Accounting, Volume 1: Financial Accounting
- Publication date: Apr 11, 2019
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-financial-accounting/pages/1-why-it-matters
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-financial-accounting/pages/11-why-it-matters
© Dec 13, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Our team is here to help you choose the right program for your life and your goals.
- How to Apply
- Transfer Credits
- Prospective Students & Parents
- Military Admissions
Master’s title
- Master of Science in Cybersecurity
Bachelor's title
- Accelerated Cyber and Information Security Technology
- Cloud Computing
- Cyber and Information Security Technology
- Cybersecurity
- Data Analytics
- Digital Forensics Technology
- Mobile Development
- Software Development
- Web Design and Development
Associate’s title
- Systems Engineering Master's - Mechatronics
- Electronic Systems Engineering Technology
- Electronics Engineering Technology
- Mechanical Engineering Technology
- Mechatronics (ESET)
- Mechatronics
- Computer-Aided Drafting and Design
- Family Nurse Practitioner (MSN)
- Nursing Education (MSN)
- Bachelor of Science in Nursing (Accelerated BSN)
- Bachelor to BSN Nursing Program (BS to BSN)
- Bachelor of Science in Nursing (RN to BSN)
- Associates Degree in Nursing (ADN)
Diploma title
- Practical Nursing (PN)
- Master's in Healthcare Administration
- Healthcare Administration
- Dental Assistant
- Medical Assisting
- Paramedic (EMT)
- Radiologic Sciences
- Diagnostic Medical Sonography
- Physical Therapist Assistant
- Radiography
- Surgical Technology
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- Business Analytics
- Business Management
- Hospitality Management
- IT Management
- Operations, Logistics, and Supply Chain Management
- Management Master's - Human Resources Management
- Management Master's - Organizational Leadership
- Human Resources Management
- Project Management
- Crime and Intelligence Analysis
- Criminal Justice
- Digital Forensics
- Homeland Security
- Food Service Management
- Baking and Pastry Arts
- Culinary Arts
- Culinary Nutrition
- Electronic Engineering Technology
- RN to BSN Program
- Master of Business Administration
- Virginia Beach
- Newport News
- Northern Virginia
- Orlando Lake Mary
- San Antonio
About ECPI University
Founded in 1966, ECPI University promotes a student-centered learning environment as well as personal and professional development through education.
- Why Choose ECPI
- Mission & Values
- Message from the President
- Accreditation
- Academic Calendar
- Course Catalog
- Career Services
- Bachelor's
- Associate’s
Find the right degree program for you.
- Health Science
- By Degree Level
- Master's
- Associate's & Diplomas
- By Location
- Information Technology
- Engineering Technology
- Explore All Technology Programs
- Explore Our Nursing Programs
- Health Sciences
- Advanced Clinical
- Explore Our Health Science Programs
- General Business Management
- Master of Human Resources Management
- Master of Organizational Leadership
- Explore Our Business Programs
- Explore Our Criminal Justice Programs
- Explore Our Culinary Arts Programs
- North Carolina
- South Carolina
Tuition and Financial Assistance
At ECPI University, an affordable education is within reach. Financial assistance options are available to help you invest in your future.
- How to Pay for College
- Tuition & Fees
- Scholarships
- VA & Military Benefits
- Employer Partnership Program

Why is Accounting Important in Everyday Life?
Accounting is an often overlooked career, and yet it is a skill that’s used regularly in daily life. While it’s true that accounting is most typically viewed as an essential part of the business world , you’re most likely performing some type of accounting task in the “real world” as well. Here are just a few ways you may be using accounting and don’t even know it.
Reconciliation: Making Sure All Your Charges are Correct
Most people like to know how much money they currently have, which means they check it on a regular basis to verify charges. Think about it: when is the last time you logged into your bank account? What were you there for?
Chances are you were checking the balance and looking to see that all the charges were correct. In the accounting world, this is known as reconciliation. Accountants use two sets of records to ensure that the money balances at the end of a recording period. You are reconciling by using receipts or check registers to make sure that everything that cleared your bank account matches what you have for your spending.
Budgeting and Managing Your Spending
What happens if you spend more money than you have? The answer isn’t pleasant to think about. When you overspend , you are left with a zero or negative balance, and often you incur additional banking fees that put you further in the hole. To prevent this from happening, people usually use a budget.

You create a budget by looking at your income and your expenses and make sure that at the end of your pay period you have enough to cover everything. If the numbers don’t line up—in other words, if you spend more than you make—that’s when you budget and work to manage your spending. You do this by cutting down expenses in some areas (such as dining out or entertainment) so you “make ends meet” each month, and hopefully have something left for savings.
An accountant is doing the same thing for an individual, business or organization, but usually with a different goal in mind: to make a profit. They look at cash flows, expenses, inventory, and more. The goal is to have a positive balance at the end of each cycle or period.
Planning for the Future
In economically unstable times, it’s common for people to assess the future. The desire is to have enough so you can stop working, pay for your child’s college tuition, have money for a vacation, a home, or a car. You’re planning ahead financially, and the ultimate goal is a healthy financial future.
Accountants also are consistently working to maintain and expand the financial health of businesses. They do it several ways—just like you do. Investments, savings goals, analyzing, debt control and profitability are just a few key concepts in financial planning. Every time you sit down and think about how you’ll have the money to do important things you are using accounting skills.
Getting Better Grades
School is another place many people use accounting skills. The minute you receive grades you assess where you are. If you don’t like the current standings, you assess what grades you’ll need for the rest of the quarter or semester to end up with the overall grade you want. You also know that those grades affect your future, so you may take action based on the assessment. Accountants also do this—analyze weak spots and look for ways to improve the numbers.
Are you interested in the field of accounting? If you want to be a part of the difference accounting makes in everyone’s lives and earn your Bachelor of Science in Business Administration with a concentration in Accounting , consider ECPI University for your education. With accelerated classes and a year-round schedule you could earn your bachelor’s in as little as 2.5 years. For more information, speak with a friendly admissions counselor today .
It could be the Best Decision You Ever Make !

DISCLAIMER – ECPI University makes no claim, warranty, or guarantee as to actual employability or earning potential to current, past or future students or graduates of any educational program we offer. The ECPI University website is published for informational purposes only. Every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of information contained on the ECPI.edu domain; however, no warranty of accuracy is made. No contractual rights, either expressed or implied, are created by its content.
For more information about ECPI University or any of our programs click here: http://www.ecpi.edu/ or http://ow.ly/Ca1ya .
View the discussion thread.

Where Thought Leaders go for Growth

What is the importance of accounting in business?
Table of contents, what is accounting, better management of the business, real-time decision-making, good planning for the future, a good start of your business, what is the purpose of accounting, benefit for business owners, benefit for business partners, benefit for the company's creditors, general accounting, cost accounting, key takeaway.
Accounting is important to businesses for a variety of reasons. The sustainability and development of a business are conditioned by the generation of profits . However, only the accounts can provide the necessary indicators to know if the turnover achieved covers all expenses.
While the basic principle seems simple, but finding a profitable source is very difficult. You have to adopt good management to be successful, and this also requires a good accounting management system within the company.
So what is the role of accounting in this success? In this article, you will learn about what accounting is, the importance of accounting , its purpose and its benefit in business, also the different types of accounting.
Let’s get right into it now!
Accounting is a fairly general concept. It designates the entire process of receiving accounting items, their classification, their recording, the calculation of the various balances and accounting results, up to the establishment of standard accounting documents.
It is a practical discipline that forms the basis of all management tools. Accounting is a tool that makes it possible to identify, analyze and communicate information relating to the business of an organization as well as to its assets.
Accounting data is expressed in the form of figures, sometimes in quantities but more often in the form of monetary value . All records must be precisely dated.
What is the importance of accounting?
Accounting information provides reliable figures and indicators on the financial situation of the business, which forms an authentic basis for decision-making.
Bookkeeping is not just about knowing what is on debit and credit, assets and liabilities, but it is necessary for strategizing and making critical decisions for the business.
As for the evolution of turnover , it allows us to get an idea of the changes that have marked the sector. Through accounting, decision-makers can get an accurate picture of the company's finances and spot problem areas, which may hinder the development and expansion of the structure.
Decision-makers often prefer to have visibility into the impact of purchases or recruitments made. Real-time bookkeeping makes it easier to budget and track cash flow to bypass potential difficulties on time. This is one of the crucial advantages of having up-to-date accounting data.
To have regularly updated accounts, it is important to call on a modern fiduciary with an online platform, available anytime and anywhere, in order to access accounting information when needed.
Keeping the accounts on a regular basis and keeping them up to date allows better planning for the future. For example, accounting provides indicators on the seasonality of the business, which helps to better manage inventories and the budget allocated to investments in order to ensure the competitiveness and viability of the business in the market.
Well-kept bookkeeping allows you to know your resources and cost centers, as well as the best way to manage them.
In the majority of cases, failures observed during the creation of companies, mismanagement of finances is the main factor of this failure. This is especially the case for entrepreneurs who take charge of their own accounts and who unfortunately do not have all the knowledge and skills required to maintain and manage them.
Hence, they need to call on a fiduciary who has the skills, but also the tools and experience required. Such a choice allows the manager to devote more time to the other managerial aspects of his business and to take more care of the development and growth of his business.
By soliciting a fiduciary, the latter becomes a reliable partner, on whom we can count to preserve the financial health of the structure. Good bookkeeping makes it possible to guarantee the efficiency of the management of the business by having reliable and accurate data.
The general accounts of a business make it possible to record the value of the operations carried out by a business and also to identify the details of what it owns and what it owes .
It makes it possible to list chronologically the movements of money inflows/outflows that the company records, that is to say, to list the sales made and all the resources, the expenses paid, and all the charges; what makes it possible to deduce the operating account and then the net profit for the year (positive or negative) is the profit and loss account.
Another document, drawn up annually, gives a statement of the business's financial balance, detailing what it owns and what it owes, which is the balance sheet . Finally, there is a set of supporting documents that provide details on these recorded transactions.
What is the benefit of accounting for your business?
The accounting report informs the head of the business and the shareholders about the financial situation (all assets and debts) of the business.
It also allows him to know the result (profit or loss) generated during a given period by his business. It is therefore a decision-making solution that makes it possible to determine which activities generate profit and which generate a loss.
Company employees seek to justify an increase in their income. The accounts will let them know the terms of the income distribution , more precisely, the added value generated by the activity of the business.
Reading and analyzing accounting documents will help company stakeholders and investors estimate the chances of improving or deteriorating results in the future using certain methods and to know the future value of the securities.
The company's main creditors (suppliers, bankers) will be able to ensure the quality of their debt . Accounting authorizes you to take stock of the exact situation of the business and its repayment capacity. Bankers will thus be able to determine the acceptable level of credit based on this repayment capacity.
It is for the managers of the business a solution and a source of information essential to good management. All important management decisions (investment decision, financing, profit distribution) are primarily based on the analysis of accounting information.
Types of accounting
There are two main categories of accounting for companies:
- General accounting (intended mainly for external actors)
- Cost accounting (mainly intended for internal analysis)
General accounting is based on the double-entry technique , it aims to chronologically record all the operations carried out by the business. It is an information source for business partners such as customers, suppliers, bankers, insurance companies, tax authorities, etc.
Cost accounting is essentially maintained by medium and large companies, which use it as a strategic management solution. Thus, it is intended more for project managers and executives than for accountants.
Cost accounting or management accounting is non-compulsory accounting , intended primarily for business leaders to enable them to make the right decisions. It is an accounting based on the analysis of charges and costs, it aims at the analysis and determination of the costs and the analytical results of the products and services that the company sells.
Accounting is a scary word. Still, it's not that bad. In practice, this requires regularity and a little rigor. Necessary to meet the company's legal obligations, it also authorizes its performance to be assessed: a decisive tool from all points of view.
And if you now want to know more about the accounting terms related to your business, consult our dedicated article.
Work Smarter : the Appvizer newsletter
New trends and tips to be more efficient at work, in your mailbox.
Best tools for you
Software vendors
Work smarter by appvizer.
Be Stress Free and Tax Ready 🙌 70% Off for 4 Months. BUY NOW & SAVE
70% Off for 4 Months Buy Now & Save
Wow clients with professional invoices that take seconds to create
Quick and easy online, recurring, and invoice-free payment options
Automated, to accurately track time and easily log billable hours
Reports and tools to track money in and out, so you know where you stand
Easily log expenses and receipts to ensure your books are always tax-time ready
Tax time and business health reports keep you informed and tax-time ready
Automatically track your mileage and never miss a mileage deduction again
Time-saving all-in-one bookkeeping that your business can count on
Track project status and collaborate with clients and team members
Organized and professional, helping you stand out and win new clients
Set clear expectations with clients and organize your plans for each project
Client management made easy, with client info all in one place
Pay your employees and keep accurate books with Payroll software integrations
- Team Management
FreshBooks integrates with over 100 partners to help you simplify your workflows
Send invoices, track time, manage payments, and more…from anywhere.
- Freelancers
- Self-Employed Professionals
- Businesses With Employees
- Businesses With Contractors
- Marketing & Agencies
- Construction & Trades
- IT & Technology
- Business & Prof. Services
- Accounting Partner Program
- Collaborative Accounting™
- Accountant Hub
- Reports Library
- FreshBooks vs QuickBooks
- FreshBooks vs HoneyBook
- FreshBooks vs Harvest
- FreshBooks vs Wave
- FreshBooks vs Xero
- Free Invoice Generator
- Invoice Templates
- Accounting Templates
- Business Name Generator
- Estimate Templates
- Help Center
- Business Loan Calculator
- Mark Up Calculator
Call Toll Free: 1.866.303.6061
1-888-674-3175
- All Articles
- Productivity
- Project Management
- Bookkeeping
Resources for Your Growing Business
Accounting and finance: why is it important to your business.

The key to your business lies within the accounting, finance and understanding of the numbers of your company.
Accounting and finance refer to the recording and analyzing of business activities . Understanding where your incoming and outcoming cashflow will help you make better decisions moving forward to avoid failure.
This article will cover: What Is the Purpose of Accounting and Finances in Business? Why Is Accounting so Important to a Business? What Is the Role of Accounting in Business?
NOTE: FreshBooks Support team members are not certified income tax or accounting professionals and cannot provide advice in these areas, outside of supporting questions about FreshBooks. If you need income tax advice please contact an accountant in your area.

What Is the Purpose of Accounting and Finance in Business?
Accounting and finance management is so important when navigating your business.
If you don’t know where your money is going and coming from, there is a very good chance you could lose control of your business. When businesses manage their income and expenses there is a stronger potential for growth. Plus, there’s better access to strategies that can help companies survive unexpected financial downturns.
Here’s how accounting and finances impact your business management.
1) Keep Financial Records
Accounting is essentially a record of a company’s financial activities.
A company’s ledger is where accountants and small business owners can track the income and expenses of a business’ daily operations. An accurate record of a company’s finances can help a business manage their financial future and understand the cash flow .
2) Avoid Legal Problems
Keeping an accurate financial record helps follow important business laws. Overlooking a minor detail could have major implications on your tax management.
Financial managers need to understand what expenses to deduct, how much taxes to pay and when to pay those taxes. Poor financial recording could lead to your company being audited and could land you in unnecessary legal trouble.
Additionally, an oversight in finances improvements to your facility could mean that you’re not following the regulation of safety laws.
3) Make a Budget
Using your financial records and understanding your cash flow can help you create a budget and budget is what keeps your business on track. A budget gives you a current view of your financial standing and helps you navigate your business towards future growth and development.
When creating a budget net income, expenses, goals and anticipating unexpected adjustments must be considered. Staying on top of these numbers is essential to managing your business, so it is important to continually keep checking in on your initial plan and adjust as you go. Good accounting sets up a blueprint for the management of your business and offers a solid foundation for stability and success.
4) Analyzing Performance
Successful business owners are always checking in to see how their business is doing.
A company can assess their financial position by looking at their historical and current records of liabilities and assets and other financial records. A business owner can use this information to gauge how the company is doing.
These records are an opportunity to learn from past mistakes and make more informed decisions about planning for a more lucrative future. Knowing your current financial standing can also help you identify new areas of growth that help you achieve your bottom line.
5) External Communication
The communication of financial information is important when dealing with external parties.
Clear accounting and finance management can be useful when getting a loan from a bank or attracting potential investors .
Good financial management makes it easier for you to provide financial statements to external stakeholders. External users will assess these reports to decide how to proceed with their involvement with your business.
6) Internal Communication
Financial reporting can also help business owners communicate information to internal stakeholders.
This information might be relevant to employees who are interested in profit-sharing and stock-based compensation. This records also allow owners to communicate the strengths and weakness of their business with their teams.
Allowing your team to know your financial standing can tie with a bonus structure that can be used as a productivity incentive.
7) Developing Strategy
Good accounting and finance management inevitably leads to a good strategy. Once you’ve developed a budget and thoroughly analyzed your data, it should be easier to have a better understanding to develop a strategy to achieve your bottom line.
After reviewing your financial records, you will be more empowered to make informed financial decisions on everything from staffing to supply management. Your budget is your map to your strategy and strategy is your key to profitability.

Why Is Accounting so Important to a Business?
Accounting is an important function of a small business and often is referred to as the “Language of Business”.
The financial recording, summarizing, analyzing and recording of financial transactions help owners, managers and investors evaluate a company’s financial health. Knowing this information helps inform more strategic business decisions.
What Is the Role of Accounting in Business?
Accounting is essential to keep track of a business’ activities.
Allocating the business costs to goods or services, creating a budget for business functions and preparing financial reporting for business decisions are all aspects of accounting. Reports can be tailored to inform specific financial management strategies for individual sectors of your business.
RELATED ARTICLES

Save Time Billing and Get Paid 2x Faster With FreshBooks
Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
Get more great content in your Inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive communications from FreshBooks and acknowledge and agree to FreshBook’s Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time by contacting us at [email protected].
👋 Welcome to FreshBooks
To see our product designed specifically for your country, please visit the United States site.
Essay on Accounting: Meaning, Functions, Importance, Principles and Limitations
Essay on Accounting :- 1. Introduction to Accounting 2. Meaning of Accounting 3. Functions 4. Importance 5. Systems 6. Principles 7. Concepts 8. Accounting Conventions 9. Limitations.
- Essay on the Limitations of Accounting
Essay # 1. Introduction to Accounting:
Several thousand years ago when human beings first developed the need to accumulate information about economic resources such as land, livestock and other personal property, accounting got originated. It emerged as an information system formulated for accountability in the exchange of goods and services.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
With the invention of money there was an ease in the manner in which commodities and services were exchanged. Money became a unit of measurement. Throughout history accounting profession has continued to grow in response to the ‘financial information needs’ of individuals and societies.
Accounting is a function of economic and social development. It is the language of business. It records business transactions on a monetary basis in a set of books in a scientific manner. Cash plays a vital role in all types of business activities. One party pays it and the other party receives it. Even in non-cash transactions, cash has to be paid or received in future. Accounting provides information in a classified and a summarized form as financial statements.
It comprises Trading Account, Profit and Loss Account, and Balance Sheet. Account is that aspect of accountability that accounts for the purpose for which cash is paid or received. Trading Account and Profit and Loss Account are prepared to ascertain the profits earned or losses incurred for a particular period. The balance sheet shows the financial position of a business as at a particular point of time.
Accountants are the practitioners of accountancy. They are information specialists who collect, process and report economic information about specific financial events for business and non-business activities. Today, we observe several million individuals engaged in professional accounting activities and several billions dependent on such information. Thus, accounting has a wide scope in the spectrum of economic and social development of any country, be it developed, developing or backward.
ADVERTISEMENTS: (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); Accounting 2. Meaning of Accounting:
Accounting is considered as ‘the language of business’. It is the language employed to communicate financial information of the business to various parties interested in such information. When an event is to be reported (say in English, Hindi, Kannada), certain rules are followed diligently so that what is communicated is understood by the readers appropriately.
Similarly, in accounting also the events of the business are to be communicated to the users by following certain set of rules diligently, so that the firm does not run into the risk of being misunderstood. Accounting language has two important components – (1) symbols in the form of ‘Debit and Credit’ and (2) grammatical rules in the form of generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
Accounting stems from ‘book-keeping’ the science and art of correctly recording in books of account all those business transactions that result in the transfer of money or money’s worth. Accounting relates to the work of maintaining various books of accounts, say, journal proper, subsidiary books, ledger, etc., which are generally done by junior employees as and when the transactions take place.
For this reason these books are called Books of Original Entry. Though the original records are maintained in a systematic way, they cannot by themselves provide information for judgement (decision) unless they are analysed and interpreted. Therefore, accounting comes into the picture.
Examining the cited definitions, we can infer that book-keeping is concerned with recording aspect. On the other hand, being comprehensive in nature, accounting includes book-keeping and spreads its tentacles to the analysis and interpretation of the data recorded. In fact, accounting designs proper system for recording the transactions.
The modern system of accounting is based on ‘double-entry principle’. Being scientific in character, double-entry principle of accounting has definite objectives to fulfill. It prescribes the process through which the objectives can be achieved. Accounting is a macro system.
In its micro system it includes several branches in the form of Financial Accounting, Cost and Management Accounting and others such as Government Accounting, HR Accounting, Inflation Accounting, Environmental Accounting, Farm Accounting, etc.
ADVERTISEMENTS: (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); Accounting 3. Functions of Accounting:
Functions of accounting may be broadly classified into four categories:
1. Historical Function:
The primary function of accounting is historical in nature, i.e., to maintain a correct record. It includes recording, classifying, summarizing, analysing and interpreting the recorded data of an enterprise (an accounting unit). The major objective of this function is to report at regular intervals to owners/shareholders, management and other interested parties in a desired form and format through financial statements.
2. Managerial Function:
The major purpose of this function is to maximize operational efficiency. In this form it helps in planning future activities, controlling day-to-day operations by comparing actual results with predetermined standards. In short, accounting helps in decision making.
3. Legal Function:
From the viewpoint of accountability, accounting should satisfy the legal requirements of Accounting Standards Board (ASB) as well as the government. For example, audit is compulsory for ensuring compliance of standards.
4. Communicating Function:
Accounting, as a language of business, should be in a position to communicate the information to the users of information say, owners/shareholders, management, creditors, employees, consumers, investors, government, etc.
Accounting 4. Importance of Accounting and its Users:
The importance of accounting is unique as it is useful not only to the internal users but also to the external users (direct and indirect users). The importance of accounting can be understood in the popular use of this systematic information by the interested parties (i.e., the data processed in the form and format meaningful to the user). This systematic information is used by interested persons for decision making.
However, there is no unanimity in different countries as to who these interested parties are. For example, Accounting Standards Board (ASB) of USA in its Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts (SFAC) No.1 states that ‘Present and potential investors, creditors and others are the users’. The Corporate Report (1975) London lists all types of users who need accounting information. The Stamp Report (1980) Canada states that because of broader accountability concept in Canada, the range of users is also broader.
However, the International Accounting Standards Committee (IASC) lists investors, employees, lenders, suppliers and other trade creditors, customers, government and their agencies, public and management as users in its framework (1989). Taking into consideration the above list of users, categorization is made as users of information having direct interest and users of information having indirect interest.
1. Users having Direct Interest:
The users having direct interest in accounting information are considered to be owners and potential owners/management, shareholders and potential shareholders, creditors and potential creditors, suppliers and potential suppliers, employees and consumers, government and tax authorities.
They are briefly discussed in the following list:
(a) The owners/shareholders provide funds to an enterprise in the form of capital. Hence, they are interested in accounting information to know whether the business is conducted on sound lines, whether the capital is used properly, whether it is in a position to provide best of the returns on their investment and whether the business is run on legal and ethical norms.
The income statement and the statement of affairs prepared from time to time should be in accordance with the accounting standards so that comparability and decision making become easier.
(b) The management is interested in financial accounting to determine whether the business is profitable, whether the position is sound and whether it has competitive advantage. Financial accounting, being the eyes and ears of management, facilitates decision making in relation to expansion, diversification, etc., and framing of suitable policies for future.
(c) The creditors are interested in the financial soundness of a business. They may be suppliers of goods on credit, lenders of money, bankers and others who would support the enterprise by providing credit facilities. Their main interest is security for credit, apart from income. They carefully scrutinize the income statement and position statement from time to time in addition to watching the business operations closely from outside by means of disciplined enquiry.
(d) The investors/prospective investors (apart from shareholders) are interested to know how far their investment is safe or is going to be safe. They examine carefully the statements of income and position to assess the soundness of the business. Altogether they are interested in the safety of their investment along with returns.
(e) The consumers are interested to get the goods at a fair price (comparatively reduced price). They are much interested to know the control mechanism adopted by the enterprise so that cost reduction is made possible.
(f) The employees are interested in accounting of the enterprise so as to assess the profitability which would be the basic factor for determining higher wages, bonus, better working conditions, etc. The sound financial position of the enterprise encourages them to contribute their best to the firm.
(g) The government (central, state and local bodies) is interested in accounting of the enterprise to know the earnings based on which taxes could be collected to formulate revenue. Further, for compiling ‘national income’ accounting prepared on the basis of accountability becomes essential.
(i) The general public is interested in the accounting of a firm from the point of view of the firm’s social responsibility. In addition, it may comprise prospective lenders, investors, consumers who would closely watch the financial progress of the enterprise.
(j) The researchers are equally interested in accounting of an enterprise. They utilize the data for their research purposes to interprete and suggest new ways of maintaining accounts based on standard measurement, usefulness and decision making.
Thus, the importance of accounting is recognized by its users and with the fact that accountability cannot be established without accounting.
2. Users having Indirect Interest:
The users having indirect interest in accounting information are considered to be financial analysts, stock exchanges, lawyers, regulatory authorities, registration authorities, financial press and reporting agencies, trade associations and labour unions. These users are generally agencies which help/protect such persons or potential persons having a direct interest in them.
Table 6.1 provides decision usefulness of accounting information.
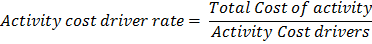
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Career Choice — Why I Want to Be an Accountant
Why I Want to Be an Accountant
- Categories: Career Choice Dream Career
About this sample

Words: 693 |
Published: Sep 7, 2023
Words: 693 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1155 words
2 pages / 790 words
5 pages / 2352 words
3 pages / 1434 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Career Choice
Choosing a career path is a profound decision that reflects one's values, aspirations, and beliefs. In this essay, I will share the reasons why I want to be a pharmacist, and how they align with my core values and beliefs. [...]
Choosing a career path is a significant and deeply personal decision. For me, the path of becoming a Surgical Technologist, often referred to as a Surgical Tech, is not just a career choice; it's a calling. In this essay, I will [...]
I want to become an accountant not only for its promising career prospects but also due to my passion for numbers, analytical thinking, and the essential role accountants play in the financial success of businesses and [...]
Why I want to be a dermatologist is a question that holds personal significance and professional aspirations for me. This essay aims to delve into the motivations behind my desire to pursue a career in dermatology, exploring the [...]
Right from my childhood I am fascinated towards technology whichever communicates each other. Being a kid, I loved playing with the telephone lines in my home and unwittingly listen to my cousin” discussions with the help of [...]
IT Professional Portfolio is an organised collection of relevant artefacts and documents that showcase the individual's qualifications, education, training, skills & experience in Information Technology in line with the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

COMMENTS
What Is Accounting and Why Is It Important? Accounting refers to the process of reporting and communicating financial information about an individual or organization.. In simpler terms, accounting is how a business records its financial information. Accountants, or anyone else tasked with accounting activities, are concerned with capturing a snapshot of an organization's financial health at ...
The Importance of Accounting. Mrs. Townlian Accounting January 19 Accounting is planning, analyzing, and interpreting financial information. Or less commonly known as the art of recording, classifying, summarizing, in a remarkable way, in terms of money, transactions, and events usually of financial classification ("Users Of Accounting").
Importance of Accounting. 1. Keeps a record of business transactions. Accounting is important as it keeps a systematic record of the organization's financial information. Up-to-date records help users compare current financial information to historical data. With full, consistent, and accurate records, it enables users to assess the ...
Financial accounting is an important part of every business, corporation, and other organizations that operate with various sums of money. This system helps people count their profits, calculate their regular expenses, and operate their financial means properly. The following paper will explain what financial accounting is and what role does it ...
Accounting in Business Essay. Accounting is referred to as "the language of business". It is an art of recording, classifying and summarizing information about a business entity in relation to economic resources that are used in finding out the causes of success and failure in business. Due to its relevance in business it has been developed ...
Why It Matters; 1.1 Explain the Importance of Accounting and Distinguish between Financial and Managerial Accounting; 1.2 Identify Users of Accounting Information and How They Apply Information; 1.3 Describe Typical Accounting Activities and the Role Accountants Play in Identifying, Recording, and Reporting Financial Activities; 1.4 Explain Why Accounting Is Important to Business Stakeholders
Accounting helps you stay on top of your debts. If your business owes debts to a variety of sources, like credit cards, loans, and accounts payable, you'll have to jump into multiple accounts to check what you're left owing. The balance sheet shows everything you owe in one place.
Accounting plays a vital role in running a business because it helps you track income and expenditures, ensure statutory compliance, and provide investors, management, and government with quantitative financial information which can be used in making business decisions. There are three key financial statements generated by your records.
The reason this is important is because lending money involves risk. The type of risk creditors and lenders assess is repayment risk—the risk the funds will not be repaid. As a rule, the longer the money is borrowed, the higher the risk involved. Recall that accounting information is historical in nature.
Why It Matters; 1.1 Explain the Importance of Accounting and Distinguish between Financial and Managerial Accounting; 1.2 Identify Users of Accounting Information and How They Apply Information; 1.3 Describe Typical Accounting Activities and the Role Accountants Play in Identifying, Recording, and Reporting Financial Activities; 1.4 Explain Why Accounting Is Important to Business Stakeholders
Accounting can also minimize losses and prevent fraudulent activities. Keeping better records: Accounting is also important because it helps a business keep accurate financial records, which can help safeguard the business against actions by the IRS, FINRA, SEC and other regulators and provide historical data to plan for the company's future.
One of the many roles of accounting is to assess business performance. With the account reports, you can reflect the financial state of your business. Once you comprehend it, you can arrange your ...
The importance of accounting in our daily life shows up everywhere, from tracking our spending to shopping for groceries to paying bills. Chances are, you've used some basic accounting principles already today. In this article, you'll learn about the importance of accounting and see how some of its core elements can be applied in your daily ...
Accountants also are consistently working to maintain and expand the financial health of businesses. They do it several ways—just like you do. Investments, savings goals, analyzing, debt control and profitability are just a few key concepts in financial planning. Every time you sit down and think about how you'll have the money to do ...
March 27, 2023. Accounting is important for small business owners as it helps the owners, managers, investors and other stakeholders in the business evaluate the financial performance of the business. Accounting provides vital information regarding cost and earnings, profit and loss, liabilities and assets for decision making, planning and ...
Accounting is a tool that makes it possible to identify, analyze and communicate information relating to the business of an organization as well as to its assets. Accounting datais expressed in the form of figures, sometimes in quantities but more often in the form of monetary value. All records must be precisely dated.
Punctuation is important; it gives meaning to words, phrases, and sentences. Punctuation creates clarity and adds polish to any writing. Common punctuation errors include apostrophe placement and semicolon use. Papers often have a host of issues with the comma: comma splices, missing commas, and unnecessary commas.
March 27, 2023. The key to your business lies within the accounting, finance and understanding of the numbers of your company. Accounting and finance refer to the recording and analyzing of business activities. Understanding where your incoming and outcoming cashflow will help you make better decisions moving forward to avoid failure.
Accounting is a function of economic and social development. It is the language of business. It records business transactions on a monetary basis in a set of books in a scientific manner. Cash plays a vital role in all types of business activities. One party pays it and the other party receives it.
The most important aspect of any business venture is a simple understanding of the prevailing concepts that could curtail the smooth operations of the business as a going concern. Accounting concepts and principles play a pivotal role in the affairs of a business. There must be a mechanism to understand all the debits and credits of a given ...
Published: Sep 7, 2023. Why I want to be an accountant is a question that reflects the aspirations and motivations of many individuals drawn to the world of finance and numbers. This essay delves into the reasons behind the desire to become an accountant, exploring the multifaceted nature of the profession and the personal and societal ...
Here are seven reasons why you should consider a bachelor's or master's in accounting — and the many jobs for accounting majors that will become available to you once you've earned your degree: 1. You can choose from a variety of careers in the accounting world. Professionals with accounting degrees work in a wide array of roles, from ...