- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons

Difference Between Essay and Report

On the other hand, an essay can be understood as a piece of writing, on a specific topic or subject, which expresses the author’s own ideas and knowledge about the subject.
The basic difference between essay and report is that while an essay is argumentative and idea-based, reports are informative and fact-based. Now, let us move further to understand some more points of differences.
Content: Essay Vs Report
Comparison chart, definition of essay.
An essay can be understood as a comprehensive literary composition, written in a narrative style and presents a particular topic, supports an argument and highlights the writer’s view or ideology. An essay is used to check a person’s outlook and understanding on specific matters and also his/her ability to describe and argue in a way which convinces the reader or informs him/her about a specific topic.
One can make use of learned materials, along with his/her own research, to write an essay effectively. It includes both narrative and subjective thoughts. Further, an essay supports a single idea at a time, for which several components need to be covered in it so as to appear logical and chronological.
It can be a learned argument, observation of day to day life, literary criticism, political manifestos, recollections, and reflections of the writer. It starts with a question and attempts to answer or give suggestions to the problem, on the basis of the existing theories or the writer’s personal opinion and assessment.
While writing an essay, it must be kept in mind that the approach used by the writer should be positive, even if the topic of argument is negative.
Definition of Report
The report implies a well structured factual document which is created and presented after conducting an independent enquiry, research or investigation on a specific subject. It serves as a basis for problem-solving and decision making.
Reports are prepared for a definite purpose and contain relevant information in a proper format, for a particular audience. It is used to identify, observe and analyse the issues, events, findings, that occurred practically, i.e. in real life.
A report is designed with the aim of informing the reader about the event, situation or issue, in a very simple and objective manner, while enabling them to get the desired information quickly and easily. It provides recommendations for future actions. Information collected from research, or from carrying out a project work is presented in a clear and concise manner, under a set of headings and subheadings, that helps the reader to get the desired information quickly and easily.
Characteristics of an Ideal Report
- It must be clear and concise.
- It is written in easy language which the readers can understand easily.
- It has to be appropriate and accurate.
- It should be well drafted and organised, with specific sections, headings and sub-headings.
A report summary can be provided orally, however detailed reports are usually in the form of written documents. It contains – Title Page, Acknowledgement, Authorization Letter, Table of Contents, Executive Summary, Introduction, Discussion, Results, Conclusion, Recommendations and References.
Moreover, Cover letter, Copyright notice, Bibliography, Glossary and Appendices may also form part of a report.
Key Differences Between Essay and Report
The difference Between report and essay is discussed here in detail:
- An essay is a brief literary composition, which is used to describe, present, argue, and analyse the idea or topic. Conversely, a report is a formal and concise document consisting of findings from the practical research. It aims at investigating and exploring the problem under study.
- An essay is written on the basis of subjective analysis of theories and past research, by other people and own ideas, on the concerned subject. As against, a report is objective and factual, which is based on past research, as well as present data and findings.
- An essay talks about general facts and events along with the writer’s personal ideas and views, on the topic in a non-fictional manner. On the contrary, a report contains information which the reader can use to identify the facts or support in decision making or solving issues if any.
- When it comes to sections, a report usually contains different sections, with catchy headings which may attract the attention of the audience. As against, an essay does not have any section, its flow is continuous. However, it is divided into cohesive paragraphs.
- A report uses tables, charts, graphs, diagrams, statistics and many more for a clear and better presentation of the information. But, in the case of essays, they are not used.
- The conclusion in an essay is based on the writer’s personal opinion and views on the topic itself which must be optimistic, and it does not provide any recommendations for future actions. On the other hand, a report gives an independent conclusion, but it may contain the opinion of the experts or previous researchers and recommendations are included, about how the research can be improved and extended.
In a nutshell, Essays are descriptive, subjective and evaluative, whereas, a report is descriptive, objective and analytical. Essays are mainly used in an academic context, whereas reports are preferred in the field of research.
The report is used to present the researched information in a written format, to the audience. Conversely, essays are used to identify what the writer knows about the topic and how well the writer understand the question.
You Might Also Like:

Anna H. Smith says
November 26, 2020 at 3:22 pm
Thank you for explaining this so eloquently. Excellent post, I will keep this handy and refer to it often from now on, the information is so clear and so insightful, thanks for giving a clear difference. It’s a very educative article.!
Presley Dube says
November 20, 2021 at 3:43 pm
very useful to me thank you.
Leonard says
August 8, 2022 at 2:52 pm
Thanks for sharing such nice information about this topic.
Ignatius Phiri says
March 20, 2023 at 10:39 pm
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Essay vs Research Paper: Key Disparities
Table of contents
- 1.1 What Is an Essay?
- 1.2 What Is a Research Paper?
- 2.1 Purpose and Objective
- 2.2 Structure and Organization
- 2.3 Length and Depth
- 2.4 Sources and Evidence
- 2.5 Voice and Style
- 2.6 Audience and Presentation
- 3 Essay vs Research Paper: 10 Points of Difference
- 4 What Is the Difference Between Research Paper and Different Types of Papers
- 5 Let’s Sum Up
Every student needs to write some academic papers for the university. However, even young people with experience can't determine the difference between an essay and a research paper. Although these two areas of academic writing have many similarities, the requirements are still significantly different.
- In this article, you will get a clear definition of an essay and research paper.
- We will outline the key differences between these two types of academic writing.
- You will learn more about the organization, structure, essay and research paper requirements.
- Finally, you will be able to tell the difference between a research paper and an essay.
To get to the heart of the matter of these two academic assignments, we should start by getting an essay vs research paper definition.
Definition and Overview
What is an essay.
An essay is a short piece of work, the purpose of which is to present individual thoughts regarding a chosen topic. Often, essays do not pretend to be scientific but require a defined structure. The basic requirements for an essay suggest writing a five-paragraph piece that contains an introduction, a body, and a conclusion.
What makes your essay unique is your creativity and the novelty of your ideas. To easily structure your thoughts and present them clearly to the reader, you should devote time to drafting an essay . Before you start writing your essay, brainstorm the freshest ideas. Thus, even though all your classmates will use the same five-paragraph structure as you, your ideas will impress the teacher. Experiment with meaning, not form.
What Is a Research Paper?
The difference between an essay and a research paper revolves around the academic approaches. Research work is the depth of study of a selected scientific topic, which should bring scientific novelty by drawing conclusions based on existing research and experiments conducted. For students, it’s not enough to state the facts or express their point of view regarding the topic. Your task is to comprehensively study the subject of research, familiarize yourself with existing opinions, and outline the direction of the upcoming study.
Your teacher will expect you to demonstrate analytical skills, the ability to select reliable sources, and a broad theoretical base on your research topic. Research papers require creativity, erudition, and orientation in the topic.
Key Differences Between Essay and Research Paper
The central difference is the goal of these academic assignments. The essay aims to express an individual point of view and find a creative, fresh approach to an existing topic. A good research paper seeks to introduce scientific novelty by examining existing data and conducting new experiments to analyze the information obtained.
Purpose and Objective
The first and main difference between an essay and a research paper is the purpose of writing . An essay as an academic task has the goal of developing students' creative thinking. It also teaches us a structured presentation of thoughts regarding a certain topic. The student is required to have a non-standard approach, fresh thoughts, and reasoned conclusions on the given topic.
The purpose of the research work is to study a scientific topic in detail. This academic assignment is aimed at assessing the student’s analytical abilities and competence to determine cause-and-effect relationships, filter sources, and formulate logical conclusions. Such work requires theoretical knowledge, preliminary study of existing scientific works, and the ability to formulate goals and research methods.
Moreover, a student is supposed to show the capacity to draw comprehensive conclusions based on available data and information obtained during independent research. This task may seem complicated to students, so they opt for resorting to the help of PapersOwl writing service to save time.
Structure and Organization
To start with, the basic structure of any college essay involves a text consisting of five paragraphs, divided into three main factions: introduction, body part, and conclusion. When students lack time to compose a nicely structured academic essay, they can always pay to write a research paper and have their tasks done by a professional. The introduction presents the topic, sets the main direction for further text, and also works as a bait to motivate the reader to study further work. The introduction is followed by three body paragraphs. Each of the three body paragraphs presents a separate idea.
The last paragraph of any essay is a conclusion. In this paragraph, the college or university student must resume the arguments and ideas presented in the text, summarizing them into the main message of the essay. Often, the idea that you present in your conclusions will be most memorable to the reader.
Consequently, let’s overview the structure of a research paper. Compared to the structure of an essay, the organization of a research paper is much more ornate. This type of work requires a title page and abstract that go before the main body of text. On the title page, the student describes his topic of work, as well as gives contact details. An abstract is a short description of the main ideas and research methods of your work. The research work itself consists of an introduction, background, main part, and conclusions. Also, at the very end, they often add acknowledgments and a list of references, which must be formatted following the required international format.
Length and Depth
The length and depth of analysis between these two academic assignments also differ significantly. As for the essay, it is often a short prose piece whose length does not exceed 1000 words. You are faced with the task of fitting a large array of ideas into a small amount of text. The essay format itself rarely requires rigorous and thorough research of the topic, but you should work on creativity and the presence of a message in your essay. Most academic papers fall in the 300 to 600-word range.
On the other hand, a research paper is a scientific project that includes many theoretical aspects that require analysis and clarification. Thus, the volume is significantly bigger. Basic research paper lengths range from 4,000 to 6,000 words. In this case, you will no doubt have to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the selected sources, formulate a research vector, and spend time conducting your experiments, or ask PapersOwl to do a research paper for you . A research paper is a scientific project that includes many theoretical aspects that require analysis and clarification.
Sources and Evidence
The presence of theoretical sources and references is not a mandatory requirement for an essay. You can state your own thoughts on a given topic without resorting to the help of existing sources. Present your ideas on the topic, giving arguments that seem logical to you. If you do decide to base your paper on existing works, you must be sure to indicate where the information was taken from. And yet, the teacher needs to see your own thoughts rather than a dry listing of existing ideas.
Unlike an essay, a quality research paper must include primary and secondary sources, as well as a specific citation format. Surely, you are not the first person to study this scientific topic. In order not to repeat existing thoughts, you need to conduct a search to form a reliable basis for your study. If you skip this step, you risk basing your paper on misleading scientific findings.
Voice and Style
The very specificity of the essay as an academic paper is the subjective presentation of information. A large percentage of your essay should consist of your perspective and vision of the chosen topic. For this reason, essays often use a less formal and more subjective tone. However, you can still use a large amount of colloquial vocabulary, completely disregarding the norms of formal style. Students often have trouble figuring out the right style for their university assignments. In such cases, a reasonable solution is to seek help from a specialist. When you buy custom-written essays from PapersOwl, you’ll always get a perfectly balanced academic paper.
On the other hand, a research paper is a serious scientific work. The student must maintain a formal tone while complying with all structural requirements. Also, in investigative work, there is little room for subjectivity and a personal approach since an objective style is required. At the same time, do not oversaturate your research work with formalism and standard clichés.
Audience and Presentation
The essay format can be used both in the educational process and in an independent literary style. Therefore, the audience for such a written assignment can be wide and varied. When you’re writing an essay, make sure it’s understandable in academia and for a wide audience.
Research work, on the contrary, is aimed at a range of professionals in the chosen field. Written in scientific language, the goal of this work is to attract the attention of scientists and students of certain majors. Your scientific work should be rich in theory and related terms.
Essay vs Research Paper: 10 Points of Difference
As you may have noticed, research papers and essays have many differences, both global and specific. These two types of academic assignments differ in the purpose of writing, have different structures and formats, and are aimed at testing different skills. And yet, every day, students face difficulties in understanding the basic requirements, which leads to incorrect execution of the task. To summarize the main differences, let's look at the table below.

What Is the Difference Between Research Paper and Different Types of Papers
There are many types of papers, each focusing on different topics, serving different purposes, and requiring a specific structure. Those are different types of essays that share a common ground but differ in the way they present information and arguments.
Analytical paper. The purpose of such an essay is an in-depth analysis of the chosen topic, studying different approaches and points of view, and formulating one’s own conclusions based on the information studied and scientific evidence.
Argumentative paper. This type of essay takes as a basis an ambiguous topic; the author must take a certain position and provide a number of arguments.
Informative paper. It has an informative purpose — a presentation of information to the reader, preceded by careful analysis and selection of data.
Persuasive paper . The purpose of this paper is to present convincing arguments, using chosen writing techniques, confirming the author’s position regarding the selected scientific topic.
To get a high grade, you need to understand the requirements of academic requirements. No matter how informatively rich your work is, if it does not meet the requirements, it cannot be highly appreciated. Each type of academic assignment has its own clearly defined, unique format. It’s necessary to know the difference between a research paper vs argumentative essay so as not to get confused while completing a college assignment. So before you start writing an assignment, make sure you understand the type of academic writing required of you.
Let’s Sum Up
Research papers and essays are aimed at testing various skills of the student, following different structures, and having several requirements. An essay is a more creative writing task, which involves showing originality and expressing a personal opinion on a certain topic. At the same time, a research paper is a type of scientific writing that adheres to a strict structure and uses a formal tone. Understanding the main differences will make your writing process easier, saving you time researching the requirements. Remember that knowing the essence of the assignment is a key factor in writing a decent paper.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
- How it works
What is the Difference Between Essays and Reports?
Published by Alaxendra Bets at August 19th, 2021 , Revised On August 23, 2023
What is the difference between essays and reports? Report writing is a specialised skill that your academic tutor would like you to develop.
Whether you are writing a report in university or business, report writing skills are equally important to get your message across to the readers effectively.
Generally, your academic tutor decides what form of writing you must undertake and will provide the layout requirements in the assignment brief.
However, as you move towards university-level study, you will have the freedom of choice to decide what form of writing you must undertake to address the problem question .
This means that you will need a critical evaluation of what form of writing will be the most appropriate for you, considering a given academic assignment’s requirements.
Whether you are a student or a professional, it is important to understand the key differences between an essay and a report to work out why you should prefer one form of writing over the other.
This article lists the most notable differences between a report and an essay, so whenever you are unsure about which form of writing is the most suitable, you will know exactly what decision is right or wrong.
Difference Between Essays and Reports – Purpose
Purpose of a report.
Typically you will be asked to write a report if you must present an analysis of practical research results. All reports start with the topic background, research aim, and objectives to provide details of what your work will examine.
You may also include a hypothesis in your report if you are testing a proposition with your research. Depending on your topic’s nature and the report writing guidelines laid out by your tutor, you may also have to include a separate section for future recommendations in your report.
Purpose of an Essay
On the other hand, Essays find answers to a question using the researcher’s own critical evaluation of the existing theories. An essay does not directly include any practical research because it only uses the existing literature material.
Difference Between Essays and Reports – Content
The report starts with introducing the topic and lists the aim and objectives your practical research will address.
It quickly moves to report chronological actions such as gathering data and presenting findings from primary research activities and laboratory experiments before the writer finally provides an assessment of the results in the conclusion and recommendations for future sections.
The content of an essay depends on the essay question you need to answer. Whether your essay must be evaluative, argumentative , narrative , discursive, or descriptive will be determined by the nature of your essay question.
However, in general, all essays involve a synthesis of knowledge obtained from existing literature on the given question and the writer’s personal arguments and opinions based on the evidence collected during research.
Whether you have been asked to write an essay or a report, ResearchProspect writers can help you achieve the highest academic grade. We have a large team of academic writers who can meet every bit of your requirements regardless of your academic level and the academic subject.
Difference Between Essays and Reports – Formatting
A report and an essay format are similar as both include an introduction , main body , and conclusion sections. Reports include methodology and analysis in the main body and have a fixed structure.
It is recommended to check your school’s formatting guidelines if you are unsure how to format your report. Further, you can get our professional report writing service that will help you achieve your desired grades.
If you are writing an essay, the essay question’s critical evaluation will determine the structure you must follow in your essay.
Stuck on a report writing assignment? We can help!
Our report writing service Features:
- Expert UK Writers
- Plagiarism-free
- Timely Delivery
- Thorough Research
- Rigorous Quality Control

Difference Between Essays and Reports in a Table
Despite describing these differences, it may not be easy to distinguish between an essay and a report. For example , in some academic disciplines, essays are structured like reports, with headings separating the different parts of an essay. The best practice regarding the style and format suitable to your academic discipline would be to consult your academic tutor.
Learn More About Our Essay Services Order Now
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you differentiate between an essay or a report.
An essay is a concise piece of writing that presents an argument, opinion, or analysis with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. A report is a structured document that conveys information, often including data, findings, and recommendations, typically with headings, sections, and sometimes visual aids.
You May Also Like
Not sure about how to organize an essay? This article is designed to provide a brief yet compact view to master the skill of organization of essay.
Here are some tips on writing the main body paragraphs of an essay to help you correctly plan and organize the most critical part of your academic essay.
No sure what are the types of persuasive essay? This article presents the similarities and differences between the most common types of persuasive essays.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

Reports and essays: key differences

Know what to expect
Explore the main differences between reports and essays and how to write for your assignments
You'll complete assignments with different requirements throughout your degree, so it's important to understand what you need to do for each of them. Here we explore the key differences between reports and essays.
This page describes general features of academic reports and essays. Depending on your subject you may use all of these features, a selection of them, or you may have additional requirements.
There is no single right way to write a report or essay, but they are different assignments. At a glance:
- Reports depend heavily on your subject and the type of report.
- Essays usually have specific content and a planned structure with a focus on sense and flow. You subject might need different types of information in your introduction – some disciplines include a short background and context here, while others begin their discussion, discuss their resources or briefly signpost the topic.
Differences between reports and essays
This table compares reports and essays and provides an outline of the standard structure for each. Your assignment will also depend on your discipline, the purpose of your work, and your audience – so you should check what you need to do in your course and module handbooks, instructions from your lecturer, and your subject conventions.
Table adapted from Cottrell, 2003, p. 209.
The structure of reports
Most reports use an IMRaD structure: Introduction, Methods, Results and Discussion.
Below are some common sections that also appear in reports. Some sections include alternative headings.
1. Table of contents
Your contents shows the number of each report section, its title, page number and any sub-sections. Sub-section numbers and details start under the section title, not the margin or the number.
2. Abstract or Executive summary
This brief summary of the report is usually the last thing you write.
3. Introduction
Your introduction describes the purpose of the report, explains why it necessary or useful, and sets out its precise aims and objectives.
4. Literature review
This describes current research and thinking about the problem or research question, and is often incorporated into the introduction.
5. Methods or Methodology
This describes and justifies the methods or processes used to collect your data.
6. Results or Findings
This section presents the results (or processed data) from the research and may consist of mainly tables, charts and or diagrams.
7. Discussion, or Analysis, or Interpretation
This section analyses the results and evaluates the research carried out.
8. Conclusion
The conclusion summarises the report and usually revisits the aims and objectives.
9. Recommendations
In this section the writer uses the results and conclusions from the report to make practical suggestions about a problem or issue. This may not be required.
10. Appendices
You can include raw data or materials that your report refers to in the appendix, if you need to. The data is often presented as charts, diagrams and tables. Each item should be numbered : for example, write Table 1 and its title; Table 2 and its title, and so on as needed.
Structure of essays
Introduction.
Your essay introduction contextualises and gives background information about the topic or questions being discussed, and sets out what the essay is going to cover.
Your essay body is divided into paragraphs. These paragraphs help make a continuous, flowing text.
The conclusion summarises the main points made in the essay. Avoid introducing new information in your conclusion.
Bibliography or Reference list
This is a list of the resources you've used in your essay. This is usually presented alphabetically by authors’ surname.
Reference for the Table of Distinctions above:
Cottrell, S. (2003). The Study Skills Handbook (2nd ed.). Basingstoke: Palgrave.
Download our report and essay differences revision sheet
Download this page as a PDF for your report and essay revision notes.

Key features of academic reports

Basic essay structure

Writing clear sentences
Find an undergraduate or postgraduate degree course that suits you at Portsmouth.

Guidance and support
Find out about the guidance and support you'll get if you need a helping hand with academic life – or life in general – when you study with us at Portsmouth.

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
Published on September 4, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays.
Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and descriptive essays are about exercising creativity and writing in an interesting way. At university level, argumentative essays are the most common type.
In high school and college, you will also often have to write textual analysis essays, which test your skills in close reading and interpretation.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Argumentative essays, expository essays, narrative essays, descriptive essays, textual analysis essays, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about types of essays.
An argumentative essay presents an extended, evidence-based argument. It requires a strong thesis statement —a clearly defined stance on your topic. Your aim is to convince the reader of your thesis using evidence (such as quotations ) and analysis.
Argumentative essays test your ability to research and present your own position on a topic. This is the most common type of essay at college level—most papers you write will involve some kind of argumentation.
The essay is divided into an introduction, body, and conclusion:
- The introduction provides your topic and thesis statement
- The body presents your evidence and arguments
- The conclusion summarizes your argument and emphasizes its importance
The example below is a paragraph from the body of an argumentative essay about the effects of the internet on education. Mouse over it to learn more.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An expository essay provides a clear, focused explanation of a topic. It doesn’t require an original argument, just a balanced and well-organized view of the topic.
Expository essays test your familiarity with a topic and your ability to organize and convey information. They are commonly assigned at high school or in exam questions at college level.
The introduction of an expository essay states your topic and provides some general background, the body presents the details, and the conclusion summarizes the information presented.
A typical body paragraph from an expository essay about the invention of the printing press is shown below. Mouse over it to learn more.
The invention of the printing press in 1440 changed this situation dramatically. Johannes Gutenberg, who had worked as a goldsmith, used his knowledge of metals in the design of the press. He made his type from an alloy of lead, tin, and antimony, whose durability allowed for the reliable production of high-quality books. This new technology allowed texts to be reproduced and disseminated on a much larger scale than was previously possible. The Gutenberg Bible appeared in the 1450s, and a large number of printing presses sprang up across the continent in the following decades. Gutenberg’s invention rapidly transformed cultural production in Europe; among other things, it would lead to the Protestant Reformation.
A narrative essay is one that tells a story. This is usually a story about a personal experience you had, but it may also be an imaginative exploration of something you have not experienced.
Narrative essays test your ability to build up a narrative in an engaging, well-structured way. They are much more personal and creative than other kinds of academic writing . Writing a personal statement for an application requires the same skills as a narrative essay.
A narrative essay isn’t strictly divided into introduction, body, and conclusion, but it should still begin by setting up the narrative and finish by expressing the point of the story—what you learned from your experience, or why it made an impression on you.
Mouse over the example below, a short narrative essay responding to the prompt “Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself,” to explore its structure.
Since elementary school, I have always favored subjects like science and math over the humanities. My instinct was always to think of these subjects as more solid and serious than classes like English. If there was no right answer, I thought, why bother? But recently I had an experience that taught me my academic interests are more flexible than I had thought: I took my first philosophy class.
Before I entered the classroom, I was skeptical. I waited outside with the other students and wondered what exactly philosophy would involve—I really had no idea. I imagined something pretty abstract: long, stilted conversations pondering the meaning of life. But what I got was something quite different.
A young man in jeans, Mr. Jones—“but you can call me Rob”—was far from the white-haired, buttoned-up old man I had half-expected. And rather than pulling us into pedantic arguments about obscure philosophical points, Rob engaged us on our level. To talk free will, we looked at our own choices. To talk ethics, we looked at dilemmas we had faced ourselves. By the end of class, I’d discovered that questions with no right answer can turn out to be the most interesting ones.
The experience has taught me to look at things a little more “philosophically”—and not just because it was a philosophy class! I learned that if I let go of my preconceptions, I can actually get a lot out of subjects I was previously dismissive of. The class taught me—in more ways than one—to look at things with an open mind.
A descriptive essay provides a detailed sensory description of something. Like narrative essays, they allow you to be more creative than most academic writing, but they are more tightly focused than narrative essays. You might describe a specific place or object, rather than telling a whole story.
Descriptive essays test your ability to use language creatively, making striking word choices to convey a memorable picture of what you’re describing.
A descriptive essay can be quite loosely structured, though it should usually begin by introducing the object of your description and end by drawing an overall picture of it. The important thing is to use careful word choices and figurative language to create an original description of your object.
Mouse over the example below, a response to the prompt “Describe a place you love to spend time in,” to learn more about descriptive essays.
On Sunday afternoons I like to spend my time in the garden behind my house. The garden is narrow but long, a corridor of green extending from the back of the house, and I sit on a lawn chair at the far end to read and relax. I am in my small peaceful paradise: the shade of the tree, the feel of the grass on my feet, the gentle activity of the fish in the pond beside me.
My cat crosses the garden nimbly and leaps onto the fence to survey it from above. From his perch he can watch over his little kingdom and keep an eye on the neighbours. He does this until the barking of next door’s dog scares him from his post and he bolts for the cat flap to govern from the safety of the kitchen.
With that, I am left alone with the fish, whose whole world is the pond by my feet. The fish explore the pond every day as if for the first time, prodding and inspecting every stone. I sometimes feel the same about sitting here in the garden; I know the place better than anyone, but whenever I return I still feel compelled to pay attention to all its details and novelties—a new bird perched in the tree, the growth of the grass, and the movement of the insects it shelters…
Sitting out in the garden, I feel serene. I feel at home. And yet I always feel there is more to discover. The bounds of my garden may be small, but there is a whole world contained within it, and it is one I will never get tired of inhabiting.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Though every essay type tests your writing skills, some essays also test your ability to read carefully and critically. In a textual analysis essay, you don’t just present information on a topic, but closely analyze a text to explain how it achieves certain effects.
Rhetorical analysis
A rhetorical analysis looks at a persuasive text (e.g. a speech, an essay, a political cartoon) in terms of the rhetorical devices it uses, and evaluates their effectiveness.
The goal is not to state whether you agree with the author’s argument but to look at how they have constructed it.
The introduction of a rhetorical analysis presents the text, some background information, and your thesis statement; the body comprises the analysis itself; and the conclusion wraps up your analysis of the text, emphasizing its relevance to broader concerns.
The example below is from a rhetorical analysis of Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech . Mouse over it to learn more.
King’s speech is infused with prophetic language throughout. Even before the famous “dream” part of the speech, King’s language consistently strikes a prophetic tone. He refers to the Lincoln Memorial as a “hallowed spot” and speaks of rising “from the dark and desolate valley of segregation” to “make justice a reality for all of God’s children.” The assumption of this prophetic voice constitutes the text’s strongest ethical appeal; after linking himself with political figures like Lincoln and the Founding Fathers, King’s ethos adopts a distinctly religious tone, recalling Biblical prophets and preachers of change from across history. This adds significant force to his words; standing before an audience of hundreds of thousands, he states not just what the future should be, but what it will be: “The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.” This warning is almost apocalyptic in tone, though it concludes with the positive image of the “bright day of justice.” The power of King’s rhetoric thus stems not only from the pathos of his vision of a brighter future, but from the ethos of the prophetic voice he adopts in expressing this vision.
Literary analysis
A literary analysis essay presents a close reading of a work of literature—e.g. a poem or novel—to explore the choices made by the author and how they help to convey the text’s theme. It is not simply a book report or a review, but an in-depth interpretation of the text.
Literary analysis looks at things like setting, characters, themes, and figurative language. The goal is to closely analyze what the author conveys and how.
The introduction of a literary analysis essay presents the text and background, and provides your thesis statement; the body consists of close readings of the text with quotations and analysis in support of your argument; and the conclusion emphasizes what your approach tells us about the text.
Mouse over the example below, the introduction to a literary analysis essay on Frankenstein , to learn more.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
At high school and in composition classes at university, you’ll often be told to write a specific type of essay , but you might also just be given prompts.
Look for keywords in these prompts that suggest a certain approach: The word “explain” suggests you should write an expository essay , while the word “describe” implies a descriptive essay . An argumentative essay might be prompted with the word “assess” or “argue.”
The vast majority of essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Almost all academic writing involves building up an argument, though other types of essay might be assigned in composition classes.
Essays can present arguments about all kinds of different topics. For example:
- In a literary analysis essay, you might make an argument for a specific interpretation of a text
- In a history essay, you might present an argument for the importance of a particular event
- In a politics essay, you might argue for the validity of a certain political theory
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-types/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, how to write an expository essay, how to write an essay outline | guidelines & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- RMIT Australia
- RMIT Europe
- RMIT Vietnam
- RMIT Global
- RMIT Online
- Alumni & Giving

- What will I do?
- What will I need?
- Who will help me?
- About the institution
- New to university?
- Studying efficiently
- Time management
- Mind mapping
- Note-taking
- Reading skills
- Argument analysis
- Preparing for assessment
- Critical thinking and argument analysis
- Online learning skills
- Starting my first assignment
- Researching your assignment
- What is referencing?
- Understanding citations
- When referencing isn't needed
- Paraphrasing
- Summarising
- Synthesising
- Integrating ideas with reporting words
- Referencing with Easy Cite
- Getting help with referencing
- Acting with academic integrity
- Artificial intelligence tools
- Understanding your audience
- Writing for coursework
- Literature review
- Academic style
- Writing for the workplace
- Spelling tips
- Writing paragraphs
- Writing sentences
- Academic word lists
- Annotated bibliographies
- Artist statement
- Case studies
- Creating effective poster presentations
- Essays, Reports, Reflective Writing
- Law assessments
- Oral presentations
- Reflective writing
- Art and design
- Critical thinking
- Maths and statistics
- Sustainability
- Educators' guide
- Learning Lab content in context
- Latest updates
- Students Alumni & Giving Staff Library
Learning Lab
Getting started at uni, study skills, referencing.
- When referencing isn't needed
- Integrating ideas
Writing and assessments
- Critical reading
- Poster presentations
- Postgraduate report writing
Subject areas
For educators.
- Educators' guide
- Reports vs essays
Students are sometimes unclear about different genres of assessment tasks.
Students often ask the question "What is the difference between a report and an essay?" This short video explains what a report is in academic writing, how it is used in different situations, and the structure of a report including executive summary, introduction, findings and conclusion.
What is a report?
A report is a piece of writing that tells you about some experience, event, or situation. This could include just doing research on some topic, a practical experiment, some issue that has arisen in a company/organisation, or a system, or even a piece of equipment, maybe.
Reports are often problem-based, but not always. It describes what you have found out, and it goes deeper - it explains and analyses what you have found out. Reports are very structured and there is an expected format. They always have sections and headings.
Have a look at this report outline:
“The aim of this report was to investigate Unilab staff attitudes to the use of mobile phones in staff and team meetings. A staff survey and policies on mobile phone use from a number of similar companies were analysed. There was significant support for a clear company policy on mobile phone use, including their banning in certain situations. The results of this research reflected the findings from similar studies. The report concluded that personal mobile phones should not be turned on during all staff meeting times.”
Most reports have executive summaries. In some disciplines, we call it an “abstract”. They are not the same as the introduction. An executive summary summarises the whole report. That means that there will be a sentence or two representing each section of the report. You always write it after you have completed the full report. Have a look at how the writer summarises each main section in one sentence (refer to executive summary above). As you can see, it’s got a very definite structure drawn from the larger report. It is very different to the introduction which just talks about the broad context, the purpose of the report, and what is going to be covered in the following sections. It gives the reader an idea of what is ahead – it does not give the overview like the executive summary.
The other important sections are the Findings and Discussion. This is where you would describe and then analyse your findings. Your findings will be reporting what you have discovered during your research, or your experiment, or an observation you have made. In the discussion section, you must delve deeper: you have to analyse and make sense of these findings and not just state what they are.
Finally, in the conclusion, you summarise your findings or use your findings or to come out with a more unified understanding or outcome. In some disciplines like business, you might be asked to give solutions or recommendations to overcome a problem that you have noticed. Recommendations might have their own section or be included in the conclusion, too.
For more information about reports, try the tutorials. Thanks for watching!
The table below shows the main differences between reports and essays.
- Provides objective information: Can be constructed collaboratively.
- Highly structured into sections identified using headings.
- Sections can be read in isolation of the most of the text: the reader can dip in and out.
- Objective report and analysis of facts.
- Grounded in practice but often links to theory.
- For a specific audience.
- Includes tables, graphs and diagrams.
- Dot points used for conciseness.
- Presents a particular writer's claim or argument.
- Structured by paragraphing with key points identified in topic sentences.
- Paragraphs are read in the context of the whole: the reader starts at the beginning and reads the entire text.
- Subjective argument or interpretation.
- Grounded in theory but sometimes linked to practice.
- For a generalised audience.
- Meaning is conveyed through text.
- Meaning constructed through sentences.
- Purpose of reports and sources to use
- Overall structure of a report
- Sample report structures
Still can't find what you need?
The RMIT University Library provides study support , one-on-one consultations and peer mentoring to RMIT students.
- Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Twitter (opens in a new window)
- Instagram (opens in a new window)
- Linkedin (opens in a new window)
- YouTube (opens in a new window)
- Weibo (opens in a new window)
- Copyright © 2024 RMIT University |
- Accessibility |
- Learning Lab feedback |
- Complaints |
- ABN 49 781 030 034 |
- CRICOS provider number: 00122A |
- RTO Code: 3046 |
- Open Universities Australia
Join thousands of product people at Insight Out Conf on April 11. Register free.
Insights hub solutions
Analyze data
Uncover deep customer insights with fast, powerful features, store insights, curate and manage insights in one searchable platform, scale research, unlock the potential of customer insights at enterprise scale.
Featured reads

Inspiration
Three things to look forward to at Insight Out
Tips and tricks
Make magic with your customer data in Dovetail

Four ways Dovetail helps Product Managers master continuous product discovery
Events and videos
© Dovetail Research Pty. Ltd.
Research report guide: Definition, types, and tips
Last updated
5 March 2024
Reviewed by
From successful product launches or software releases to planning major business decisions, research reports serve many vital functions. They can summarize evidence and deliver insights and recommendations to save companies time and resources. They can reveal the most value-adding actions a company should take.
However, poorly constructed reports can have the opposite effect! Taking the time to learn established research-reporting rules and approaches will equip you with in-demand skills. You’ll be able to capture and communicate information applicable to numerous situations and industries, adding another string to your resume bow.
- What are research reports?
A research report is a collection of contextual data, gathered through organized research, that provides new insights into a particular challenge (which, for this article, is business-related). Research reports are a time-tested method for distilling large amounts of data into a narrow band of focus.
Their effectiveness often hinges on whether the report provides:
Strong, well-researched evidence
Comprehensive analysis
Well-considered conclusions and recommendations
Though the topic possibilities are endless, an effective research report keeps a laser-like focus on the specific questions or objectives the researcher believes are key to achieving success. Many research reports begin as research proposals, which usually include the need for a report to capture the findings of the study and recommend a course of action.
A description of the research method used, e.g., qualitative, quantitative, or other
Statistical analysis
Causal (or explanatory) research (i.e., research identifying relationships between two variables)
Inductive research, also known as ‘theory-building’
Deductive research, such as that used to test theories
Action research, where the research is actively used to drive change
- Importance of a research report
Research reports can unify and direct a company's focus toward the most appropriate strategic action. Of course, spending resources on a report takes up some of the company's human and financial resources. Choosing when a report is called for is a matter of judgment and experience.
Some development models used heavily in the engineering world, such as Waterfall development, are notorious for over-relying on research reports. With Waterfall development, there is a linear progression through each step of a project, and each stage is precisely documented and reported on before moving to the next.
The pace of the business world is faster than the speed at which your authors can produce and disseminate reports. So how do companies strike the right balance between creating and acting on research reports?
The answer lies, again, in the report's defined objectives. By paring down your most pressing interests and those of your stakeholders, your research and reporting skills will be the lenses that keep your company's priorities in constant focus.
Honing your company's primary objectives can save significant amounts of time and align research and reporting efforts with ever-greater precision.
Some examples of well-designed research objectives are:
Proving whether or not a product or service meets customer expectations
Demonstrating the value of a service, product, or business process to your stakeholders and investors
Improving business decision-making when faced with a lack of time or other constraints
Clarifying the relationship between a critical cause and effect for problematic business processes
Prioritizing the development of a backlog of products or product features
Comparing business or production strategies
Evaluating past decisions and predicting future outcomes
- Features of a research report
Research reports generally require a research design phase, where the report author(s) determine the most important elements the report must contain.
Just as there are various kinds of research, there are many types of reports.
Here are the standard elements of almost any research-reporting format:
Report summary. A broad but comprehensive overview of what readers will learn in the full report. Summaries are usually no more than one or two paragraphs and address all key elements of the report. Think of the key takeaways your primary stakeholders will want to know if they don’t have time to read the full document.
Introduction. Include a brief background of the topic, the type of research, and the research sample. Consider the primary goal of the report, who is most affected, and how far along the company is in meeting its objectives.
Methods. A description of how the researcher carried out data collection, analysis, and final interpretations of the data. Include the reasons for choosing a particular method. The methods section should strike a balance between clearly presenting the approach taken to gather data and discussing how it is designed to achieve the report's objectives.
Data analysis. This section contains interpretations that lead readers through the results relevant to the report's thesis. If there were unexpected results, include here a discussion on why that might be. Charts, calculations, statistics, and other supporting information also belong here (or, if lengthy, as an appendix). This should be the most detailed section of the research report, with references for further study. Present the information in a logical order, whether chronologically or in order of importance to the report's objectives.
Conclusion. This should be written with sound reasoning, often containing useful recommendations. The conclusion must be backed by a continuous thread of logic throughout the report.
- How to write a research paper
With a clear outline and robust pool of research, a research paper can start to write itself, but what's a good way to start a research report?
Research report examples are often the quickest way to gain inspiration for your report. Look for the types of research reports most relevant to your industry and consider which makes the most sense for your data and goals.
The research report outline will help you organize the elements of your report. One of the most time-tested report outlines is the IMRaD structure:
Introduction
...and Discussion
Pay close attention to the most well-established research reporting format in your industry, and consider your tone and language from your audience's perspective. Learn the key terms inside and out; incorrect jargon could easily harm the perceived authority of your research paper.
Along with a foundation in high-quality research and razor-sharp analysis, the most effective research reports will also demonstrate well-developed:
Internal logic
Narrative flow
Conclusions and recommendations
Readability, striking a balance between simple phrasing and technical insight
How to gather research data for your report
The validity of research data is critical. Because the research phase usually occurs well before the writing phase, you normally have plenty of time to vet your data.
However, research reports could involve ongoing research, where report authors (sometimes the researchers themselves) write portions of the report alongside ongoing research.
One such research-report example would be an R&D department that knows its primary stakeholders are eager to learn about a lengthy work in progress and any potentially important outcomes.
However you choose to manage the research and reporting, your data must meet robust quality standards before you can rely on it. Vet any research with the following questions in mind:
Does it use statistically valid analysis methods?
Do the researchers clearly explain their research, analysis, and sampling methods?
Did the researchers provide any caveats or advice on how to interpret their data?
Have you gathered the data yourself or were you in close contact with those who did?
Is the source biased?
Usually, flawed research methods become more apparent the further you get through a research report.
It's perfectly natural for good research to raise new questions, but the reader should have no uncertainty about what the data represents. There should be no doubt about matters such as:
Whether the sampling or analysis methods were based on sound and consistent logic
What the research samples are and where they came from
The accuracy of any statistical functions or equations
Validation of testing and measuring processes
When does a report require design validation?
A robust design validation process is often a gold standard in highly technical research reports. Design validation ensures the objects of a study are measured accurately, which lends more weight to your report and makes it valuable to more specialized industries.
Product development and engineering projects are the most common research-report examples that typically involve a design validation process. Depending on the scope and complexity of your research, you might face additional steps to validate your data and research procedures.
If you’re including design validation in the report (or report proposal), explain and justify your data-collection processes. Good design validation builds greater trust in a research report and lends more weight to its conclusions.
Choosing the right analysis method
Just as the quality of your report depends on properly validated research, a useful conclusion requires the most contextually relevant analysis method. This means comparing different statistical methods and choosing the one that makes the most sense for your research.
Most broadly, research analysis comes down to quantitative or qualitative methods (respectively: measurable by a number vs subjectively qualified values). There are also mixed research methods, which bridge the need for merging hard data with qualified assessments and still reach a cohesive set of conclusions.
Some of the most common analysis methods in research reports include:
Significance testing (aka hypothesis analysis), which compares test and control groups to determine how likely the data was the result of random chance.
Regression analysis , to establish relationships between variables, control for extraneous variables , and support correlation analysis.
Correlation analysis (aka bivariate testing), a method to identify and determine the strength of linear relationships between variables. It’s effective for detecting patterns from complex data, but care must be exercised to not confuse correlation with causation.
With any analysis method, it's important to justify which method you chose in the report. You should also provide estimates of the statistical accuracy (e.g., the p-value or confidence level of quantifiable data) of any data analysis.
This requires a commitment to the report's primary aim. For instance, this may be achieving a certain level of customer satisfaction by analyzing the cause and effect of changes to how service is delivered. Even better, use statistical analysis to calculate which change is most positively correlated with improved levels of customer satisfaction.
- Tips for writing research reports
There's endless good advice for writing effective research reports, and it almost all depends on the subjective aims of the people behind the report. Due to the wide variety of research reports, the best tips will be unique to each author's purpose.
Consider the following research report tips in any order, and take note of the ones most relevant to you:
No matter how in depth or detailed your report might be, provide a well-considered, succinct summary. At the very least, give your readers a quick and effective way to get up to speed.
Pare down your target audience (e.g., other researchers, employees, laypersons, etc.), and adjust your voice for their background knowledge and interest levels
For all but the most open-ended research, clarify your objectives, both for yourself and within the report.
Leverage your team members’ talents to fill in any knowledge gaps you might have. Your team is only as good as the sum of its parts.
Justify why your research proposal’s topic will endure long enough to derive value from the finished report.
Consolidate all research and analysis functions onto a single user-friendly platform. There's no reason to settle for less than developer-grade tools suitable for non-developers.
What's the format of a research report?
The research-reporting format is how the report is structured—a framework the authors use to organize their data, conclusions, arguments, and recommendations. The format heavily determines how the report's outline develops, because the format dictates the overall structure and order of information (based on the report's goals and research objectives).
What's the purpose of a research-report outline?
A good report outline gives form and substance to the report's objectives, presenting the results in a readable, engaging way. For any research-report format, the outline should create momentum along a chain of logic that builds up to a conclusion or interpretation.
What's the difference between a research essay and a research report?
There are several key differences between research reports and essays:
Research report:
Ordered into separate sections
More commercial in nature
Often includes infographics
Heavily descriptive
More self-referential
Usually provides recommendations
Research essay
Does not rely on research report formatting
More academically minded
Normally text-only
Less detailed
Omits discussion of methods
Usually non-prescriptive
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 17 February 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 19 November 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

- Master Your Homework
- Do My Homework
The Difference Between a Research Paper and an Essay
This article will explore the key differences between a research paper and an essay. The main distinction lies in their purpose: a research paper is intended to add knowledge to existing literature, while an essay generally aims to present a viewpoint on the subject being discussed. Additionally, different approaches are used when constructing each type of writing; for example, essays focus heavily on personal opinion whereas research papers use data collected from sources such as interviews or experiments. Finally, we’ll discuss how these two forms of writing differ in terms of structure and language usage. By exploring these distinctions more closely, readers will gain insight into which form best suits their needs depending upon their goals and context.
I. Introduction
- II. Definition of a Research Paper
III. Definition of an Essay
Iv. differences in structure and formatting, v. differences in content and purpose.
- VI. Considerations for Completing the Assignment Successfully
VII. Conclusion
Learning the Difference In academia, it is essential for students to understand that there are different types of writing. Research papers and essays both have their place in higher education, yet they serve very distinct purposes. When tasked with any type of assignment, students must ask themselves what kind of paper will best answer the question or achieve the goal set out by their professor.
Essays provide a greater opportunity for creativity as well as expression than research papers do. They require careful planning and organization to establish an argument which can be easily followed through evidence provided within the text body itself – no external resources needed! Essays also tend to focus more on personal opinions rather than facts derived from outside sources making them ideal when working on literary analysis topics like Hamlet’s soliloquies or interpreting MacBeth’s inner monologues.
On contrast, research papers consist primarily of synthesizing information found externally (in books, databases etc.) while using your own critical thinking skillset to draw meaningful conclusions about thematic elements throughout those works. Unlike essay-writing assignments where you can use some creative license when crafting arguments/theories; this type requires meticulous citation work due its reliance on referencing previously established material from other scholars – failure adhere strictly here would result in accusations plagiarism being levied against one’s academic integrity!
An essay is a written work which gives the author’s own argument on an individual subject. It can range from formal to informal, and its primary purpose is to express the opinion of the writer. The structure of an essay usually consists of introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
When discussing essays it is important not to confuse them with research papers or other forms of academic writing. While there are similarities between both styles they do have some key differences in terms of style and content.
- Research Papers: are typically much longer than essays as they go into great detail about their topic; while generally having one main focus for exploration.
- Essays: are shorter pieces that explore multiple topics at once rather than going deep into one specific area.
In general, essays tend to be more creative in nature whereas research papers are seen as dryer documents based around facts collected through rigorous study and analysis. Essays also often require personal opinions which can make them more thought provoking; this does not occur within research paper writing due to their lack creativity or biased interpretation allowed by the researcher themselves.
There are several differences between a research paper and an essay in terms of structure and formatting. The first main difference lies in the length: research papers tend to be longer than essays, which generally range from 500-800 words while research papers can exceed 5,000 words. Furthermore, the format of a research paper follows specific guidelines that must be adhered to for successful completion; for example they often include sections such as abstracts, introductions, methods/materials used, results/findings and discussions. On the other hand essays require minimal structuring with only introduction body paragraphs and conclusion.
- A Research Paper has a more detailed outline compared to an essay.
When attempting to distinguish between a research paper and an essay, it is useful to consider their content and purpose. While both can be written on the same topic, they have important differences in terms of structure, emphasis and intent.
- Research Papers: Research papers are typically longer than essays; this allows for more in-depth investigation into a subject matter. They require extensive analysis of reliable sources related to the chosen field or topic. These pieces should include appropriate facts from these sources as evidence for the writer’s opinions or theories.
- Essays: Essays tend to be shorter than research papers due to their more focused scope of argumentation or discussion. The goal here is usually either persuasive or explanatory with less weight given towards factual data gathering as compared with research papers since the information already exists within scholarly materials.
Having discussed the differences between a research paper and an essay, it can be concluded that each has its own distinct purpose. While both are useful for assessing knowledge within a field of study, they serve different ends.
- The focus is on gathering information from existing sources to analyze or evaluate findings in order to draw conclusions about a topic.
In conclusion, the difference between a research paper and an essay lies in their scope of discussion. While essays focus on drawing conclusions based off arguments, research papers look for evidence to back up said conclusions. Both are important components in constructing academic discourse, though with distinct focuses that should be kept in mind when writing either form. In short, understanding the fundamental differences between these two forms will help any student or researcher navigate this exciting landscape of knowledge production with greater ease and clarity than ever before!

Difference Between Research Paper and Essay
October 23, 2023

Description: Comparison of research papers vs. essays, along with the explanation of the differences and similarities between the two types of academic papers. A short guide to understanding essay writing and research writing with definitions of the terms “essay” and “research paper”.
How Does Research Paper Differ From Essay?
Students often have to deal with two different types of academic writing assignments: an essay and a research paper. Writing essays and research papers can be difficult and confusing due to the many similarities they have. To avoid confusion when writing either of these, it’s important to learn their differences. Understanding the differences between an essay and a research paper is also a great way to improve your academic writing skills. This article aims to help you understand the key differences between essay and research paper writing assignments when you come across them. We’ll study their features, look for relevant academic terminology, and learn what differentiates them. To get to the bottom of the difference between these two academic assignments, we should first define essay vs research paper.
What is an Essay?
An essay is a short piece of writing that aims to express personal views on a particular topic. It should have at least three pieces of evidence to back up the argument. Essays are typically shorter in length and less complex than research writing. At the same time, essay writing has its own specifics, so using expert proofreading services is a good idea if you aren’t confident in your skills. It’s likely that you’ll write your first essay and research paper when in high school or college. Then arises the question, “Who will write my paper for me ?” A good essay should always have a creative component, so having good writing skills is a must. Essays often aren’t as scientific as research papers, yet they nevertheless need a clear structure. The basic essay writing guidelines recommend following a five-paragraph structure with an introduction, a body, and a conclusion.
What is a Research Paper?
A research paper is the in-depth study of a chosen scientific topic that aims to generate new scientific findings based on previous studies and experiments. It isn’t enough for students to just state the facts or give their opinion on this topic. Your professor will evaluate your ability to think critically, choose trustworthy sources, and have a solid theoretical grounding in the topic of your research. Writing a research paper takes originality, knowledge, and subject matter expertise. Compared to traditional essay writing, research work has a different objective and structure. Research papers use data from primary sources like books on the topic, academic papers, interviews, web sources, and journals. The basic research writing guidelines recommend following this pattern: introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusions/recommendations. Research papers may also include acknowledgments, a brief biography of the author for some Master’s or Ph.D. works, references, endnotes, footnotes, and so on.
Key Differences Between Essay and Research Paper
The biggest difference between a research paper and an essay is that a research paper must have a strict methodology and set of study objectives. A research paper should outline a problem and the approaches that can be used to solve it effectively. Meanwhile, an essay can present a personal opinion without any references. Now let us go over other key differences between an essay and a research paper. The following comparison table outlines the key differences between essays and research papers:

Similarities Differences Between Essay and Research Paper
It makes sense that you could find it challenging to tell the difference between an essay and a research paper since there’re so many similarities between the two types of academic papers. That’s why it’s important to learn about the similarities of the two as well.
- Research: Basic research is still necessary in both. Even though you don’t need to do in-depth study for an essay, you still need to at least fact-check your information. However, for a research paper, you’ll need to cite more sources to demonstrate that you’re doing more than simply skimming the topic.
- Structure: The research paper has multiple paragraphs, much like an essay. Although the structure is a little different, the material presented in each paragraph should be in an easy-to-follow format to save the reader’s time from having to wade through irrelevant data and concepts. There should be an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion in both types of papers. When you want to conduct research, there’re some differences, but there’re also a few similarities because you need to present the topic properly.
- Thesis statement: Both types of papers should have a thesis statement that presents an opinion, an argument, or a hypothesis. Even though it isn’t always required for an essay, adding a thesis statement will make your essay sound even more scientific.
- Format and Style: Your professor might recommend a specific format for your paper depending on the topic matter and the class itself. The liberal arts and humanities normally utilize the MLA and Chicago/Turabian formats, while the social sciences typically use the APA format. Both research papers and essays must follow specific formatting guidelines for headers, footers, in-text citations, reference pages, and other elements. These forms guarantee consistency and point readers to the relevant sources.
Research papers and essays are two different types of writing. We can draw the conclusion that the key differences between essays and research papers are those relating to purpose, structure, and format. Even though these two types of papers have many things in common, essays and research papers are written for different purposes. The requirements for a research paper are stricter because it must follow the right structure, format, and methodology. However, an essay is more forgiving because it has a descriptive narrative that allows the author to express their own opinions. Please be advised that the views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this blog are solely that of the author or his/her sources and do not necessarily reflect those of English Forward. This includes, but is not limited to, third-party content contained on or accessible through the English Forward websites and web pages or sites displayed as search results or contained within a directory of links on the English Forward network.
7 Common Pitfalls in English Translations
The top 10 slang words of young people nowadays, leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
Essay vs Research Paper: What are the Differences?
by Antony W
September 10, 2021

This is the most comprehensive guide on essay vs research paper .
We’ll look at the differences and similarities between the two papers so that you can approach either assignment with clarity and certainty.
To begin with, essays and research paper examine your research, writing and analytical skills. They also require adherence to strict formatting and the inclusion of citation and bibliography.
What’s an Essay?
An essay is a written academic assignment that requires you to look into an issue and then provide your personal opinion while using credible sources and verifiable evidence to support your work.
In addition to knowing the different types of essays , you need to have excellent research and writing skills to write great essays that earn full marks.
The length of an essay varies from topic to topic. A shorter essay is about 500 words and longer ones can go up to 4,000 words .
Shorter essays don’t require extended research and you can therefore write them in one sitting.
Longer essays, on the other hand, demand in-depth research and attention to details. They can be quite time consuming to write and edit, which part of the reasons why students seek for writing help.
So if you have a longer essay to complete within a short deadline, check our essay writing service and let us help you get the essay completed in time.
What Essays Do Students Write in School?
The following are some of the most common essays that you’ll write in high school, college, or university.
1. Descriptive Essays
If asked to write a descriptive essay, focus on explaining the characteristics of a subject or issue.
Descriptive essays require some literary devices , such as similes and metaphors, to read well and communicate your message. You can check our guide on how to write description essays .
2. Comparison Essays
In a compare and contrast essay , you have to explain the differences and similarities between two subject. You can organize your writing based either on individual points or on the subjects.
3. Analytical Essays
Analytical essays don’t just appear in academic journals, newspapers, and magazines. They’re also common in academic settings.
In analytical essay writing , your work is to provide a substantive analysis of the topic without being biased.
3. Reflective Essays
In reflective essay writing , students have to examine experiences and explore the changes, challenges, developments, and growth that those experiences bring.
The standard format for a reflective essay is the same for all, but the format may change a little depending on the audience.
4. Argumentative Essays
In argumentative essay writing , you have to take a stance on an issue and use objective evidence to support your position.
Check out our argumentative essay hub here to learn more.
5. Academic Essays
Written at college and university levels, academic essay cover content in your coursework to gauge your writing skills and intelligence’s level.
These essays tend to be longer with the word count ranging between 3,000 and 5,000 words.
What’s a Research Paper?

A research paper is an academic assignment that requires students to express their views on a subject using supportive sources such as books and journal articles.
They’re longer than typical essays and therefore take more time to research, write, and proofread.
In the case where you have more demanding assignments and a research paper waiting for you to complete, you can take advantage of our research paper writing service to get the project done in time.
Types of Research Papers
The following are the common types of research papers that you’ll write in college or university:
1. Analytical Research Paper
With this type of research paper, you choose a topic, collect information from credible sources, and use the data to draw your conclusion on the subject.
Maintain a neutral position when writing an analytical research paper.
2. Argumentative Research Paper
In argumentative research paper, you look into two controversial issues in the same document.
While you’ll look into both sides of the argument, you’ll have to take a side and use information from different reliable sources to persuade reader to take your side.
3. Experimental Research
Experimental research papers are practical in form. Your instructor expects you to describe procedures you used in your experiment, accompanied by in-depth data analysis and a written report.
4. Survey Research Paper
With survey research papers, you have to collect information from as many respondents as you can find. Then, you have to analyze the information and write a final report.

In this section, we’ll look at the differences between essays and research papers to give you more insight.
Differences in Writing
Since the primary objective of a research paper is to present a deeper knowledge of the subject, you have to do extensive research from different sources.
You also have to do a deep data analysis before writing so you can make a concrete conclusion.
Moreover, you have to be very conversant with the primary sources on the subject to write a good research paper.
With an essay, your goal is to show your teacher that you have good research and writing skills and can articulate your ideas in a way that shows your understanding of the given topic.
As such, essays won’t require deep research. In essay writing, you don’t necessarily have to be familiar with the main sources on a given subject although it’s important to.
Differences in Outline and Length
An essay has three parts: an introduction, the main body, and a conclusion. The body section has at least 3 paragraphs, but there can be more depending on the subject, research, and the number of ideas you’d like to present.
A research paper has more sections. Your work needs to feature a title page, an abstract (summary of the research), the main body (divided into sections such as methodology and results), a conclusion, references, acknowledgements, and references.
An essay can be as short as one page, especially if it’s on a topic that doesn’t require extensive research. In some cases, you may have to make your essay longer . So check the prompt to know how long your instructor expects you to make the essay.
On the other hand, a research paper is longer than a typical essay’s length and can span up to 8 pages or more.
Differences in Presentation
In essay writing, students present their personal views on a given issue or subject and use reliable academic sources to support their opinions.
In research paper writing, you have to present other scientists and researchers’ point of views of a subject and also add your opinion as a writer. Therefore, you must not only logically organize your ideas but also formulate them academically.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
- Undergraduate courses
- Postgraduate courses
- January starts
- Foundation courses
- Apprenticeships
- Part-time and short courses
- Apply undergraduate
- Apply postgraduate
Search for a course
Search by course name, subject, and more
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- (suspended) - Available in Clearing Not available in Clearing location-sign UCAS
Fees and funding
- Tuition fees
- Scholarships
- Funding your studies
- Student finance
- Cost of living support
Why study at Kent
Student life.
- Careers and employability
- Student support and wellbeing
- Our locations
- Placements and internships
- Year abroad
- Student stories
- Schools and colleges
- International
- International students
- Your country
- Applicant FAQs
- International scholarships
- University of Kent International College
- Campus Tours
- Applicant Events
- Postgraduate events
- Maps and directions
- Research strengths
- Research centres
- Research impact
Research institutes
- Durrell Institute of Conservation and Ecology
- Institute of Cyber Security for Society
- Institute of Cultural and Creative Industries
- Institute of Health, Social Care and Wellbeing
Research students
- Graduate and Researcher College
- Research degrees
- Find a supervisor
- How to apply
Popular searches
- Visits and Open Days
- Jobs and vacancies
- Accommodation
- Student guide
- Library and IT
- Research highlights
- Signature themes
- Partner with us
- Student Guide
- Student Help
- Health & wellbeing
- Student voice
- Living at Kent
- Careers & volunteering
- Diversity at Kent
- Finance & funding
- Life after graduation
These guides have been created for you by the Student Learning Advisory Service . For more detailed guidance and to speak to one of our advisers, please book an appointment or join one of our workshops . Alternatively, have a look at our SkillBuilder skills videos.
The purpose of a report
A report is a practical document that describes, details or analyses something so that the reader can make decisions or take specific action concerning it. A report can be written about anything; a business issue, a recent event, a piece of research, however it is likely to be one or more of the following in character:
Informative Defining or establishing the facts surrounding a current situation
Explanatory Exploring and explaining a situation and suggesting a range of possible actions
Persuasive Investigating a problem and recommending a specific course of action
The difference between reports and essays
As a part of the assessment for your course, you may be required to write both reports and essays; this table highlights the main differences between the two:
LibAnswers: Library and Learning Services
What is the difference between an essay and a report.
Reports are typically used to present the findings from a particular project, experiment, or investigation in a systematic way. Essays are used to develop a discussion of a topic or build an argument.
Reports present information in a different way from an essay. Whilst essays are generally quite fluid in terms of structure, enabling the author to explore a topic through a series of paragraphs, a report will be highly structured with section headings and subheadings that have a clear function. Reports often use tables, bullet points and graphics to present information.
Links & Files
- Learn more about different types of assignment
- Learn more about academic writing
- Academic Writing
- Last Updated Aug 21, 2023
- Answered By Anna Nunn
FAQ Actions
- Share on Facebook
Comments (0)
➔ About the Library
➔ Meet the Team
➔ Customer Service Charter
➔ Library Policies & Regulations
➔ Privacy & Data Protection
Essential Links
➔ Database A-Z
➔ Frequently Asked Questions
➔Discover the Library
➔Referencing Help
➔ Print & Copy Services
➔ Service Updates
Library & Learning Services, University of Suffolk, Library Building, Long Street, Ipswich, IP4 1QJ
✉ Email Us: [email protected]
✆ Call Us: +44 (0)1473 3 38700

7sistershomeschool.com
Homeschool Help and Curriculum
What is the Difference between Essays, Reports and Research Papers?
- Facebook 139
- Pinterest 22
By request: What is the Difference between Essays, Reports and Research Papers?

One of our wonderful 7th Sisters brought up an interesting question in our 7SistersHomeschool Facebook group . What is the difference between essays, reports and research papers ?
That is a marvelous question because lots of parents who are new to homeschooling high school ask the same thing. High school writing can be confusing when you are trying to figure out all the categories and what fits in each one! So let me start with this:
You CAN do this!
And not only that, once you get used to it, homeschooling high school years are the best years yet!
So let’s start with a basic overview of the writing that we have found is best to be covered in ELA (English/Language Arts) credits. We say this gently because there are many different views on what should be covered in writing. These are the things that we have found give our teens good life and college prep. So for each ELA credit our teens cover:
- Research papers
- Short stories
The main question our 7th Sister had was about the difference between essays, short papers/reports and research papers . Let’s dive into it. First, remember: there’s not ONE right way to homeschool high school, so adapt our guidelines to fit your family’s needs!

What are essays?
The current American version of essays is based on the 5-paragraph essay.
At high school level, the 5-paragraph essay is a standard format but is often longer as the student gains writing skills. Beginners often start with
- Persuasive essays
- Compare/contrast essays
- Literature analysis
Intermediate writers build on their introductory skills by working on:
- Literary analysis
- Editorial/letter to the editor
- Essay Tests
Advanced writers can further add to their skills by working on:
- Persuasive Essay
- The Compare/Contrast Essay
- Fiction Literary Analysis
- Non-Fiction Literary Analysis
- Writing An Editorial/Letter to the Editor
- The SAT/ACT Essay
As you can see, many of the topics are the same, but the homeschool high schoolers develop deeper critical thinking and expressive skills with each year they work on essay.
BTW- All 7Sisters essay writing guides include writing prompts, but here are some more prompts that might be relevant to your teens.
High school essays are usually one to two pages but can be longer.
Essay questions
You will notice that in the intermediate level (at least in our 7SistersHomeschool Essay curriculum), one of the topics covered is essay tests. The questions on essay tests are generally long-answers to in-depth kind of questions. In high school, students usually a write paragraph or two. There are some tricks of the trade to writing essay question answers. That is why we included these in the Intermediate Guide to Essay Writing .
Another place homeschool high schoolers will see essay questions is in many of our literature study guides . These essay questions help teens to develop those inferential skills that aid them in getting the most insight from their readings. Our 7th Sister had asked the excellent question: If my teen writes four separate paragraphs on A Scarlet Letter , would you count that as one essay?
What a great question! Here is what I suggested to her:
If it fits your goals for your teen’s writing goals for this year, combine the essay questions in the literature study guide into an essay. (You might want to help her with transition sentences for that.) You are homeschooling and you get to decide what’s best for your teen. That’s why we homeschool, we know what our teens need to learn, where they struggle, what their goals are. Give yourself freedom to make writing work for her.
One of the joys of homeschooling is doing what is best for our teens. Unless you have a supervising organization or umbrella school that tells you otherwise, you get to decide what to do with your teen’s assignments!
One more side note about essays.
In the old days, before someone invented the 5-paragraph format, essays were different. Even currently in England, as our friend, Kat Patrick from Dreaming Spires Home Education, says that they do not use that format at all. For them, essays are more traditional working out of one’s thoughts (essay being from the French word, “to try”) so more what we might call a reflection paper.
What are reports?
You probably remember writing reports when you were in school. Reports are usually introductory experiences in finding information and presenting it. They are simple. Many middle schoolers will write reports to get used to the research and writing processes. However, inexperienced or reluctant high school writers can get the basics down by starting out with a report. We have a freebie to take you step by step through that process.
After a report, teens are often able to move into writing a research paper but if they need more help, work with our Research Paper Readiness Guide .
What are research papers?
Research papers help teens develop their skills in researching, digesting and presenting information. There are a number of different research paper formats. It is good to learn several of them (especially for college-bound teens).
Many teens find it is easiest to start with an APA research paper . It is like an extension of the basic report. However, if teens enjoy writing their 5-paragraph essays, they might enjoy starting their research paper experience with writing an MLA paper . (Our homeschool grads who recently finished college, told us that the Chicago-style papers were important for some of their classes.)
What are short papers, then?
Are you confused yet? It’s okay. Let’s review the four basic kinds of yearly writing projects that we suggest for homeschool high schoolers:
Homeschool high schoolers need to have experiences with long papers (research papers) and short papers (essays, short stories, poetry). However, short papers do not need to be limited to essays, short stories and poetry. Short papers can also include professional writing , creative chronicling , college essay writing , resume writing , mission statements , reflection papers or anything else that interests your teens.
The length of the short papers will be determined by the type of paper, your teens’ age, abilities, interests and goals. Here’s a guide .
Check out this marvelous interview with Janet and Geoff Benge about non-fiction writing .
Remember YOU know what’s best for your teens. There’s not ONE right way to homeschool high school and you CAN do it! Adjust any plan to fit your teens’ needs. We are so thankful for all our 7th Sisters and for your excellent questions and ideas.
7Sisters email subscribers receive periodic practical encouragement, special offers and NO SPAM EVER.

Vicki Tillman
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Difference Between an Essay & a Paper
Jennifer brozak.

Whether you’re in middle school, high school or toiling away at college, paper writing is a fundamental facet of schooling. While essays and other forms of creative writing are common in English classes, you’ll also need to understand how to write informative pieces, such as research or term papers. By understanding the difference between the various types of writing styles, you’ll be able to draft compelling prose that is appropriate for any given assignment.
Explore this article
- What Is an Essay?
- What Is a Research Paper?
- What Is the Difference Between a Research Paper and Term Paper?
- Avoid Getting a Free Essay Writer
1 What Is an Essay?
One of the most common forms of writing is the essay. Starting in your later elementary school years and into middle school, you’ll likely be exposed to the five-paragraph essay, which is a fundamental starting point for creating longer-length writing assignments as you move upward through the higher grades. While they’re typically shorter pieces of writing (often under 1,000 words), they allow teachers to evaluate students on different writing, reading and analysis skills, including the art of persuasion and exposition.
Essays can take on many forms: They can be narrative, or tell a story; expository, or require investigation and evidential support; descriptive, in which a student is required to describe, creatively, a person, place or object; and finally, persuasive, in which a student is asked to argue a specific position on a particular topic.
As a whole, paper essay writing typically allows for more creativity than more formal writing styles, such as research papers.
2 What Is a Research Paper?
The phrase “research paper” can conjure anxiety in even the most adequate student writers. However, this need not be the case. In fact, it’s helpful to think of a research paper as an inflated essay. The structure will basically be the same, but you’ll need a thesis statement (which is not required in some forms of essay writing), significant research and evidence to support your ideas. You’ll also be required to include several credible sources in your paper, which will be listed on a reference page. And consider this: If you choose a subject you’re interested in researching, writing an informative paper can actually be quite a rewarding experience.
3 What Is the Difference Between a Research Paper and Term Paper?
Teachers, especially college professors, sometimes refer to longer research papers as “term papers,” which are similar in their structure and format. They’re expanded essays that will require evidence and credible sources to support your ideas. The difference lies in the subject matter. Research papers may allow you to cover a topic outside of the general subject matter (such as writing a persuasive research paper about global warming in an English class), while term papers will focus solely on the subject matter discussed in the course. High-quality research and term paper examples can be found on numerous sites, such as the Purdue University Online Writing Lab.
4 Avoid Getting a Free Essay Writer
A note of caution about submitting any writing assignment: While the Internet abounds with sources to help you in your quest to write the perfect paper, avoid using “essay generators” or hiring a free essay writer or buying papers from a database. Even if you’re procrastinating and panicking about finishing your assignment, it’s always better to turn in your own work. Not only do many teachers utilize online plagiarism checkers, but they also learn to recognize a student’s specific writing style over the course of an academic year. While it’s perfectly fine to use a term paper example as a guideline, it’s always better to submit your own paper or essay with minor errors than to attempt to pass off someone else’s writing as your own.
- 1 SUNY Empire State College: Research Writing: Elements and Steps
- 2 Enago Academy: How to Avoid Plagiarism in Research Papers (Part1 )
About the Author
Jennifer Brozak earned her state teaching certificate in Secondary English and Communications from St. Vincent College in Latrobe, Pa., and her bachelor's degree in journalism from the University of Pittsburgh. A former high school English teacher, Jennifer enjoys writing articles about parenting and education and has contributed to Reader's Digest, Mamapedia, Shmoop and more.
Related Articles

How to Write a Research Paper in a Day

How to Write a Rough Draft

What Are Good College Essays?

How to Make Your Writing More Interesting for Middle...

Plagiarism Checkers for Students

Challenges Facing Essay Writing

What Is a Narrative Response?

How to Start an Interview Summary Paper

What Is a Lead-in Statement?

What Are the Benefits of Using an Outline When Writing?

How to Write a Spanish Essay

How to Use Contractions in a College Essay

What Is a Subjective Essay?

What Makes Up a Well-Written Essay in High School?

How to Start an Informative Paper

How to Write a Graduate-Level Research paper

Plagiarism Vs. Paraphrasing

What Is an Objective in a Synthesis Paper?

Tips on Writing on Unlined Paper
Regardless of how old we are, we never stop learning. Classroom is the educational resource for people of all ages. Whether you’re studying times tables or applying to college, Classroom has the answers.
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Manage Preferences
© 2020 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved. Based on the Word Net lexical database for the English Language. See disclaimer .
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 27 March 2024
Tweeting your research paper boosts engagement but not citations
- Bianca Nogrady
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Even before complaints about X’s declining quality, posting a paper on the social-media platform did not lead to a boost in citations. Credit: Matt Cardy/Getty
Posting about a research paper on social-media platform X (formerly known as Twitter) doesn’t translate into a bump in citations, according to a study that looked at 550 papers.
The finding comes as scientists are moving away from the platform in the wake of changes after its 2022 purchase by entrepreneur Elon Musk.
An international group of 11 researchers, who by the end of the experiment had between them nearly 230,000 followers on X, examined whether there was evidence that posting about a paper would increase its citation rate.
“There certainly is a correlation, and that’s been found in a lot of papers. But very few people have ever looked to see whether there’s any experimental causation,” says Trevor Branch, a marine ecologist at the University of Washington in Seattle and lead author on the paper, published in PLoS ONE last week 1 .
Every month for ten months, each researcher was allocated a randomly selected primary research article or review from a journal of their choice to post about on their personal account. Four randomly chosen articles from the same edition of the journal served as controls, which the researchers did not post about. They conducted the experiment in the period before Elon Musk took ownership of what was then known as Twitter and complaints of its declining quality increased.
‘Nail in the coffin’
Three years after the initial posts, the team compared the citation rates for the 110 posted articles with those of the 440 control articles, and found no significant difference. The researchers did acknowledge that their followers might not have been numerous enough to detect a statistically significant effect on citations.
The rate of daily downloads for the posted papers was nearly fourfold higher on the day that they were shared, compared with controls. Shared papers also had significantly higher accumulated Altmetric scores both 30 days and three years after the initial post. Calculated by London-based technology company Digital Science, an Altmetric score, says Branch, is a measure of how many people have looked at a paper and are talking about it, but it’s not a reliable indicator of a paper’s scientific worth. “It’s thoroughly biased by how many people with large followings tweet about it,” he says.
The findings echo those of information scientist Stefanie Haustein at the University of Ottawa, whose 2013 study 2 found a low correlation between posts and citations.
Haustein says the problem with using posts as a metric is that, even a decade ago, there was a lot of noise in the signal.
“We actually showed that a lot of the counts on Twitter you would get were bots, it wasn’t even humans,” says Haustein, who wasn’t involved in the new study.
She says the more recent departure of scientists from the platform has been the final nail in the coffin of the idea that posting could increase citations.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00922-y
Branch, T. A. et al. PLoS ONE 19 , e0292201 (2024).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Haustein, S., Peters, I., Sugimoto, C. R., Thelwall, M. & Larivière, V. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 65, 656–669 (2014).
Article Google Scholar
Download references
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles

- Communication
- Scientific community

Divas, captains, ghosts, ants and bumble-bees: collaborator attitudes explained
Career Column 15 MAR 24

Three actions PhD-holders should take to land their next job
Career Column 13 MAR 24

This geologist communicates science from the ski slopes
Career Q&A 11 MAR 24

The corpse of an exploded star and more — March’s best science images
News 28 MAR 24

How OpenAI’s text-to-video tool Sora could change science – and society
News 12 MAR 24

Giant plume of plasma on the Sun’s surface and more — February’s best science images
News 01 MAR 24
How can we make PhD training fit for the modern world? Broaden its philosophical foundations
Correspondence 02 APR 24

Research assessments are still not fit for purpose — here’s how to change things
World View 02 APR 24

Africa’s postdoc workforce is on the rise — but at what cost?
Career Feature 02 APR 24
Postdoctoral Associate- Cell Biology
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Head of ClinicalTrials.gov
National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Library of Medicine (NLM) National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Information Engineering...
Washington D.C. (US)
National Library of Medicine, National Center for Biotechnology Information
POSTDOCTORAL FELLOWSHIP IN SYSTEMS BIOLOGY: PRECISION VACCINE PROGRAM (PVP) - BOSTON CHILDREN'
The Data Management and Analysis Core (DMAC) within the Precision Vaccine Program (PVP) at Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School (H...
Boston, Massachusetts
Boston Children's Hospital - Department of Pediatrics
2024 Recruitment notice Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology: Shenzhen, China
The wide-ranging expertise drawing from technical, engineering or science professions...
Shenzhen,China
Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology
Global Talent Recruitment (Scientist Positions)
Global Talent Gathering for Innovation, Changping Laboratory Recruiting Overseas High-Level Talents.
Beijing, China
Changping Laboratory
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Read our research on: Abortion | Podcasts | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
Most americans favor legalizing marijuana for medical, recreational use, legalizing recreational marijuana viewed as good for local economies; mixed views of impact on drug use, community safety.
Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand the public’s views about the legalization of marijuana in the United States. For this analysis, we surveyed 5,140 adults from Jan. 16 to Jan. 21, 2024. Everyone who took part in this survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for the report and its methodology .
As more states pass laws legalizing marijuana for recreational use , Americans continue to favor legalization of both medical and recreational use of the drug.
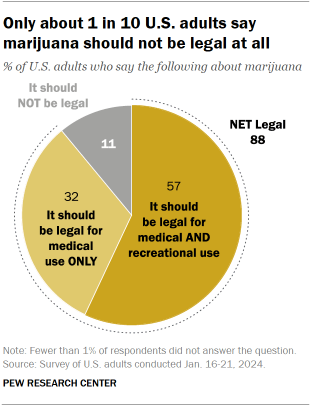
An overwhelming share of U.S. adults (88%) say marijuana should be legal for medical or recreational use.
Nearly six-in-ten Americans (57%) say that marijuana should be legal for medical and recreational purposes, while roughly a third (32%) say that marijuana should be legal for medical use only.
Just 11% of Americans say that the drug should not be legal at all.
Opinions about marijuana legalization have changed little over the past five years, according to the Pew Research Center survey, conducted Jan. 16-21, 2024, among 5,14o adults.
The impact of legalizing marijuana for recreational use
While a majority of Americans continue to say marijuana should be legal , there are varying views about the impacts of recreational legalization.
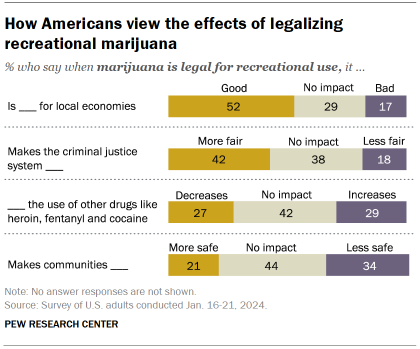
About half of Americans (52%) say that legalizing the recreational use of marijuana is good for local economies; just 17% think it is bad and 29% say it has no impact.
More adults also say legalizing marijuana for recreational use makes the criminal justice system more fair (42%) than less fair (18%); 38% say it has no impact.
However, Americans have mixed views on the impact of legalizing marijuana for recreational use on:
- Use of other drugs: About as many say it increases (29%) as say it decreases (27%) the use of other drugs, like heroin, fentanyl and cocaine (42% say it has no impact).
- Community safety: More Americans say legalizing recreational marijuana makes communities less safe (34%) than say it makes them safer (21%); 44% say it has no impact.
Partisan differences on impact of recreational use of marijuana
There are deep partisan divisions regarding the impact of marijuana legalization for recreational use.
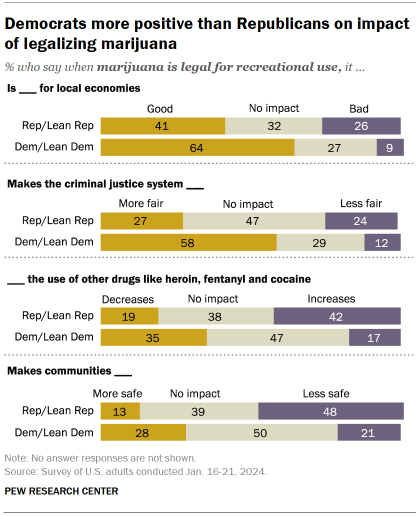
Majorities of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents say legalizing recreational marijuana is good for local economies (64% say this) and makes the criminal justice system fairer (58%).
Fewer Republicans and Republican leaners say legalization for recreational use has a positive effect on local economies (41%) and the criminal justice system (27%).
Republicans are more likely than Democrats to cite downsides from legalizing recreational marijuana:
- 42% of Republicans say it increases the use of other drugs, like heroin, fentanyl and cocaine, compared with just 17% of Democrats.
- 48% of Republicans say it makes communities less safe, more than double the share of Democrats (21%) who say this.
Demographic, partisan differences in views of marijuana legalization
Sizable age and partisan differences persist on the issue of marijuana legalization though small shares of adults across demographic groups are completely opposed to it.
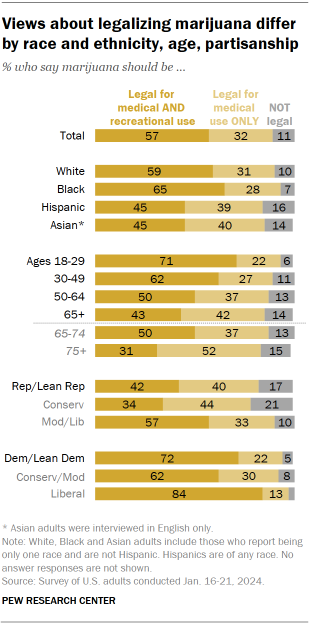
Older adults are far less likely than younger adults to favor marijuana legalization.
This is particularly the case among adults ages 75 and older: 31% say marijuana should be legal for both medical and recreational use.
By comparison, half of adults between the ages of 65 and 74 say marijuana should be legal for medical and recreational use, and larger shares in younger age groups say the same.
Republicans continue to be less supportive than Democrats of legalizing marijuana for both legal and recreational use: 42% of Republicans favor legalizing marijuana for both purposes, compared with 72% of Democrats.
There continue to be ideological differences within each party:
- 34% of conservative Republicans say marijuana should be legal for medical and recreational use, compared with a 57% majority of moderate and liberal Republicans.
- 62% of conservative and moderate Democrats say marijuana should be legal for medical and recreational use, while an overwhelming majority of liberal Democrats (84%) say this.
Views of marijuana legalization vary by age within both parties
Along with differences by party and age, there are also age differences within each party on the issue.
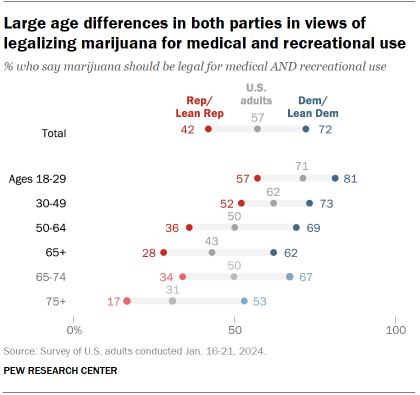
A 57% majority of Republicans ages 18 to 29 favor making marijuana legal for medical and recreational use, compared with 52% among those ages 30 to 49 and much smaller shares of older Republicans.
Still, wide majorities of Republicans in all age groups favor legalizing marijuana at least for medical use. Among those ages 65 and older, just 20% say marijuana should not be legal even for medical purposes.
While majorities of Democrats across all age groups support legalizing marijuana for medical and recreational use, older Democrats are less likely to say this.
About half of Democrats ages 75 and older (53%) say marijuana should be legal for both purposes, but much larger shares of younger Democrats say the same (including 81% of Democrats ages 18 to 29). Still, only 7% of Democrats ages 65 and older think marijuana should not be legalized even for medical use, similar to the share of all other Democrats who say this.
Views of the effects of legalizing recreational marijuana among racial and ethnic groups
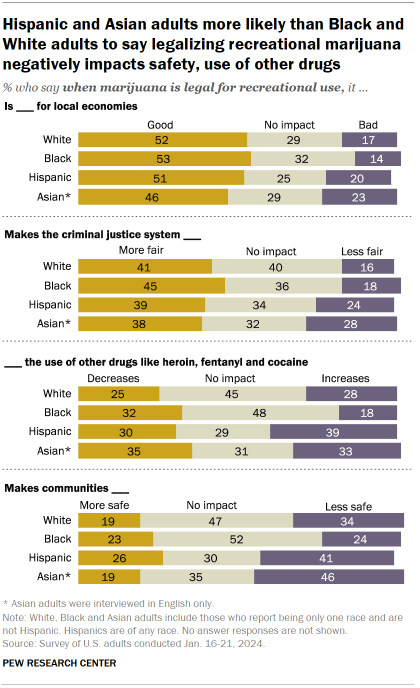
Substantial shares of Americans across racial and ethnic groups say when marijuana is legal for recreational use, it has a more positive than negative impact on the economy and criminal justice system.
About half of White (52%), Black (53%) and Hispanic (51%) adults say legalizing recreational marijuana is good for local economies. A slightly smaller share of Asian adults (46%) say the same.
Criminal justice
Across racial and ethnic groups, about four-in-ten say that recreational marijuana being legal makes the criminal justice system fairer, with smaller shares saying it would make it less fair.
However, there are wider racial differences on questions regarding the impact of recreational marijuana on the use of other drugs and the safety of communities.
Use of other drugs
Nearly half of Black adults (48%) say recreational marijuana legalization doesn’t have an effect on the use of drugs like heroin, fentanyl and cocaine. Another 32% in this group say it decreases the use of these drugs and 18% say it increases their use.
In contrast, Hispanic adults are slightly more likely to say legal marijuana increases the use of these other drugs (39%) than to say it decreases this use (30%); 29% say it has no impact.
Among White adults, the balance of opinion is mixed: 28% say marijuana legalization increases the use of other drugs and 25% say it decreases their use (45% say it has no impact). Views among Asian adults are also mixed, though a smaller share (31%) say legalization has no impact on the use of other drugs.
Community safety
Hispanic and Asian adults also are more likely to say marijuana’s legalization makes communities less safe: 41% of Hispanic adults and 46% of Asian adults say this, compared with 34% of White adults and 24% of Black adults.
Wide age gap on views of impact of legalizing recreational marijuana
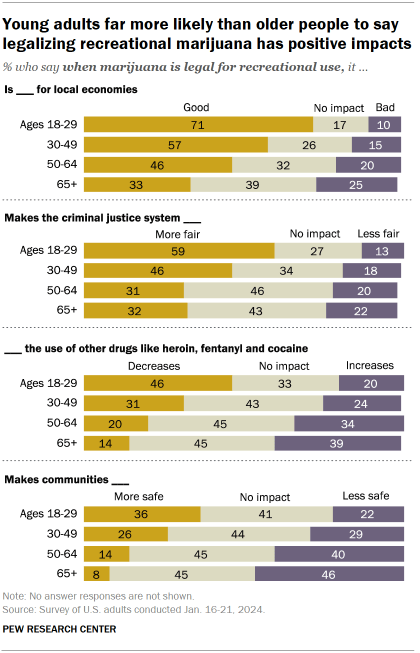
Young Americans view the legalization of marijuana for recreational use in more positive terms compared with their older counterparts.
Clear majorities of adults under 30 say it is good for local economies (71%) and that it makes the criminal justice system fairer (59%).
By comparison, a third of Americans ages 65 and older say legalizing the recreational use of marijuana is good for local economies; about as many (32%) say it makes the criminal justice system more fair.
There also are sizable differences in opinion by age about how legalizing recreational marijuana affects the use of other drugs and the safety of communities.
Facts are more important than ever
In times of uncertainty, good decisions demand good data. Please support our research with a financial contribution.
Report Materials
Table of contents, most americans now live in a legal marijuana state – and most have at least one dispensary in their county, 7 facts about americans and marijuana, americans overwhelmingly say marijuana should be legal for medical or recreational use, clear majorities of black americans favor marijuana legalization, easing of criminal penalties, religious americans are less likely to endorse legal marijuana for recreational use, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The difference Between report and essay is discussed here in detail: An essay is a brief literary composition, which is used to describe, present, argue, and analyse the idea or topic. Conversely, a report is a formal and concise document consisting of findings from the practical research.
Key Takeaways. Essays and reports serve different purposes and require different approaches. Essays are subjective and allow for creativity, while reports are objective and focus on facts and data. Understanding the differences between these two forms of writing is important for effective communication.
The first and main difference between an essay and a research paper is the purpose of writing. An essay as an academic task has the goal of developing students' creative thinking. It also teaches us a structured presentation of thoughts regarding a certain topic.
Difference Between Essays and Reports in a Table. Reports. Essays. Reports are written with a specific purpose and audience in mind. Essays are written to demonstrate that the author fully understands the research question and can answer it with research. All reports start with a purpose but also include details of events/results of research.
Essays don't usually include tables, charts, or diagrams. Reports usually include descriptions of the methods used. Essays don't usually refer to the methods you used to arrive at your conclusions. The discussion in a report often comments on how the report research could be improved and extended, and may evaluate the methods and processes used.
In conclusion, the difference between a research paper and a report is of great significance. Research papers require more in-depth exploration into the subject matter while reports are typically summaries or reviews of relevant information on an issue. It is important to recognize this distinction when approaching any writing assignment that ...
IV. Differences between Reports and Research Papers. In academic writing, reports and research papers have some distinct differences. Both types of documents require the same level of comprehensive evaluation; however, a report will present summaries in an organized fashion while a research paper is more analytical and requires further exploration.
Key Differences: Report vs Essay While both reports and essays involve research, analysis, and communication of ideas, there are key differences in their purpose, structure, and approach: Purpose: Reports aim to present factual information and analysis to inform decision-making, while essays explore ideas, theories, and arguments to provoke ...
Argumentative essays. An argumentative essay presents an extended, evidence-based argument. It requires a strong thesis statement—a clearly defined stance on your topic. Your aim is to convince the reader of your thesis using evidence (such as quotations) and analysis.. Argumentative essays test your ability to research and present your own position on a topic.
For a generalised audience. Meaning is conveyed through text. Meaning constructed through sentences. Students often ask the question, What is the difference between a report and an essay? Here we have a helpful summary of the main differences between essays and reports presented in a table and a video.
A description of the research method used, e.g., qualitative, quantitative, or other. Statistical analysis. Causal (or explanatory) research (i.e., research identifying relationships between two variables) Inductive research, also known as 'theory-building'. Deductive research, such as that used to test theories.
Research papers help in building your knowledge about a given topic, while essays test your writing skills. They both have a thesis statement. A research paper is a long form of writing with about 8 pages or more, while the words in essays range between 500 to 1000. They both have an organizational structure.
Main Difference between Essay and Report. An essay serves as a concise literary composition for presenting and analyzing ideas, while a report is a formal document that communicates research findings. Essays blend subjective analysis with personal ideas, while reports maintain objectivity by relying on past research and current data.
The first main difference lies in the length: research papers tend to be longer than essays, which generally range from 500-800 words while research papers can exceed 5,000 words. Furthermore, the format of a research paper follows specific guidelines that must be adhered to for successful completion; for example they often include sections ...
The biggest difference between a research paper and an essay is that a research paper must have a strict methodology and set of study objectives. A research paper should outline a problem and the approaches that can be used to solve it effectively. Meanwhile, an essay can present a personal opinion without any references.
Differences in Outline and Length. An essay has three parts: an introduction, the main body, and a conclusion. The body section has at least 3 paragraphs, but there can be more depending on the subject, research, and the number of ideas you'd like to present. A research paper has more sections.
Essays are written to present arguments, express opinions, or analyze a topic. They aim to persuade, inform, or entertain the reader. Reports are written to present factual information, findings, or research on a specific topic. They focus on providing objective and detailed analysis without personal opinions or biases. Structure.
Essays can expose a writer's opinion if wanted. In research papers, Writers should abstain from personal opinions and stay in line with facts only. 3. Purpose: The essay's main point is to ...
A report can be written about anything; a business issue, a recent event, a piece of research, however it is likely to be one or more of the following in character: Informative. Defining or establishing the facts surrounding a current situation. Explanatory. Exploring and explaining a situation and suggesting a range of possible actions.
Essays are used to develop a discussion of a topic or build an argument. Reports present information in a different way from an essay. Whilst essays are generally quite fluid in terms of structure, enabling the author to explore a topic through a series of paragraphs, a report will be highly structured with section headings and subheadings that ...
Speaking of the key research paper vs essay elements that help to set an essay apart from other types of writing, these are the rules to remember: An essay is usually a piece of writing that is up to 1,000 words or shorter. Writing an essay usually relates to a particular subject or so-called 'essay prompt'. In certain cases, essays are written ...
Reports are usually introductory experiences in finding information and presenting it. They are simple. Many middle schoolers will write reports to get used to the research and writing processes. However, inexperienced or reluctant high school writers can get the basics down by starting out with a report.
Understanding the difference between the various types of writing styles, including research papers and essays, will help you craft compelling prose that is appropriate. As a whole, paper essay writing typically allows for more creativity than more formal writing styles, such as research papers.
Tweeting your research paper boosts engagement but not citations. Analysis of a random selection of papers shared on social media showed no causative link between posting and citations. Even ...
A 57% majority of Republicans ages 18 to 29 favor making marijuana legal for medical and recreational use, compared with 52% among those ages 30 to 49 and much smaller shares of older Republicans. Still, wide majorities of Republicans in all age groups favor legalizing marijuana at least for medical use. Among those ages 65 and older, just 20% ...