- Notifications 0

- Add Friend ($5)

As a registered member you can:
- View all solutions for free
- Request more in-depth explanations for free
- Ask our tutors any math-related question for free
- Email your homework to your parent or tutor for free
- Grade 5 Eureka - Answer Keys Module 2
Thank you for doing your homework!

Submit Your Question

Home > CC2 > Chapter 5 > Lesson 5.3.2
Lesson 5.1.1, lesson 5.1.2, lesson 5.2.1, lesson 5.2.2, lesson 5.2.3, lesson 5.2.4, lesson 5.2.5, lesson 5.2.6, lesson 5.3.1, lesson 5.3.2, lesson 5.3.3, lesson 5.3.4, lesson 5.3.5.
© 2022 CPM Educational Program. All rights reserved.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
5th grade (Eureka Math/EngageNY)
Unit 1: module 1: place value and decimal fractions, unit 2: module 2: multi-digit whole number and decimal fraction operations, unit 3: module 3: addition and subtractions of fractions, unit 4: module 4: multiplication and division of fractions and decimal fractions, unit 5: module 5: addition and multiplication with volume and area, unit 6: module 6: problem solving with the coordinate plane.
Standards Alignment
Assessments, professional learning, family engagement, case studies.
NEW EUREKA MATH 2 ® PILOT PACKAGE
Are you looking for new ways to advance equity and build knowledge in your math classroom with high-quality instructional materials? EdReports recently reviewed Eureka Math 2 . Scan the QR code or access the final report .
Check out our special pilot package for only $10 per student.
Shop Online

SEE THE SCIENCE OF READING IN ACTION
At Great Minds ® , we’re committed to ensuring our curricula are aligned to the latest research on how students best learn to read, write, and build knowledge.
Explore webinars, blogs, research briefs, and more to discover how we incorporate this important body of research.

FREE CLASSROOM PRINTABLES
At Great Minds®, we’re committed to supporting educators with high-quality curricula and resources.
Explore resources designed to aid students in science and engineering and spark classroom conversation.
Webinar Library
Instructional resources, trending topics, knowledge-building, the science of reading, lesson design, universal design for learning (udl), background knowledge.
Palm Springs, CA
Houston, TX
New Orleans, LA
Eureka Math Student Materials: Grades K–5
Learn, Practice, Succeed
Learn, Practice, and Succeed from Eureka Math™ offer teachers multiple ways to differentiate instruction, provide extra practice, and assess student learning. These versatile companions to A Story of Units® (Grades K–5) guide teachers in response to intervention (RTI), provide extra practice, and inform instruction.
Also available for Grades 6–8 .
Learn, Practice, Succeed can be purchased all together or bundled in any configuration. Contact your account solutions manager for more information and pricing.

The Learn book serves as a student’s in-class companion where they show their thinking, share what they know, and watch their knowledge build every day!
Application Problems: Problem solving in a real-world context is a daily part of Eureka Math , building student confidence and perseverance as students apply their knowledge in new and varied ways.
Problem Sets : A carefully sequenced Problem Set provides an in-class opportunity for independent work, with multiple entry points for differentiation.
Exit Tickets: These exercises check student understanding, providing the teacher with immediate, valuable evidence of the efficacy of that day’s instruction and informing next steps.
Templates: Learn includes templates for the pictures, reusable models, and data sets that students need for Eureka Math activities.

With Practice , students build competence in newly acquired skills and reinforce previously learned skills in preparation for tomorrow’s lesson. Together, Learn and Practice provide all the print materials a student uses for their core instruction.
Eureka Math contains multiple daily opportunities to build fluency in mathematics . Each is designed with the same notion—growing every student’s ability to use mathematics with ease . Fluency experiences are generally fast-paced and energetic, celebrating improvement and focusing on recognizing patterns and connections within the material.
Eureka Math fluency activities provide differentiated practice through a variety of formats—some are conducted orally, some use manipulatives, others use a personal whiteboard, or a handout and paper-and-pencil format.
Sprints: Sprint fluency activities in Eureka Math Practice build speed and accuracy with already acquired skills. Used when students are nearing optimum proficiency, Sprints leverage tempo to build a low-stakes adrenaline boost that increases memory and recall. Their intentional design makes Sprints inherently differentiated – the problems build from simple to complex, with the first quadrant of problems being the simplest, and each subsequent quadrant adding complexity.

Eureka Math Succeed enables students to work individually toward mastery. Teachers and tutors can use Succeed books from prior grade levels as curriculum-consistent tools for filling gaps in foundational knowledge. Students will thrive and progress more quickly, as familiar models facilitate connections to their current, grade-level content.
Additional Problem Sets: Ideal for Homework or extra practice, these additional problem sets align lesson-by-lesson with what is happening in the classroom. These problems are sequenced from simple-to-complex to naturally scaffold student practice. They align with Eureka Math and use the curriculum’s mathematical models and language, ensuring that students feel the connections and relevance to their daily instruction, whether they are working on foundational skills or getting extra practice on the current topic.
Homework Helpers: Each problem set is accompanied by a Homework Helper, a set of worked examples that illustrate how similar problems are solved. The examples, viewed side by side with the homework, support students as they reinforce the day’s learning. Homework Helpers are also a great way to keep parents informed about math class.

Bundles and Class Sets Available
Bundle options are available for all of our materials (print, digital, PD, etc.). Prices vary by grade and size of class set. Certain grade-levels do not include all packets due to the nature of the grade-level content. Student workbooks are available in class sets of 20, 25, and 30. Prices vary by size of class set .

every child is capable of greatness
- Job Openings
- Digital Support
- Print Support
- Media Inquiries
Let’s Connect
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- System Status
- CA Residents: Do Not Sell My Info
Common Core Grade 5 Math (Worksheets, Homework, Lesson Plans)
Looking for video lessons that will help you in your Common Core Grade 5 Math classwork or homework? Looking for Common Core Math Worksheets and Lesson Plans that will help you prepare lessons for Grade 5 students?
The following lesson plans and worksheets are from the New York State Education Department Common Core-aligned educational resources. The Lesson Plans and Worksheets are divided into six modules.
Related Pages Common Core Math Resources, Lesson Plans And Worksheets Common Core Math Video Lessons, Math Worksheets and Games for Grade 5 Common Core Math Video Lessons, Math Worksheets and Games for all grades
Grade 5 Homework, Lesson Plans And Worksheets

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
- 888-309-8227
- 732-384-0146
New User Registration
Forgot Password
enVision MATH Common Core 5, Grade: 5 Publisher: Scott Foresman Addison Wesley
Envision math common core 5, title : envision math common core 5, publisher : scott foresman addison wesley, isbn : 328672637, isbn-13 : 9780328672639, use the table below to find videos, mobile apps, worksheets and lessons that supplement envision math common core 5., textbook resources.
- Call us toll-free
- FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
- Contact Lumos Learning – Proven Study Programs by Expert Teachers
Follow us: Lumos Learning -->
- 2024 © Lumos Learning
- Privacy Policy - Terms of Service - Disclaimers
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc... Read More
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc., the Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any state of the Union. Neither PARCC, Inc., nor The Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any member state has endorsed this product. No portion of any fees or charges paid for any products or services Lumos Learning offers will be paid or inure to the benefit of PARCC, Inc., or any state of the Union
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not aff... Read More
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC, was not... Read More
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC,was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved... Read More
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the prod... Read More
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved... Read More
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved... Read More
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved... Read More
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved... Read More
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
- Barretts Elementary
- Bellerive Elementary
- Carman Trails Elementary
- Claymont Elementary
- Craig Elementary
- Green Trails Elementary
- Hanna Woods Elementary
- Henry Elementary
- Highcroft Ridge Elementary
- Mason Ridge Elementary
- McKelvey Elementary
- McKelvey Primary Elementary
- Oak Brook Elementary
- Pierremont Elementary
- River Bend Elementary
- Ross Elementary
- Shenandoah Valley Elementary
- Sorrento Springs Elementary
- Wren Hollow Elementary
- Central Middle
- Northeast Middle
- South Middle
- Southwest Middle
- West Middle
- Central High
- Fern Ridge High
- Early Childhood Center
- Alumni Association

Higher Expectations. Brighter Futures.
Page Navigation
- 5th Grade Home
- Clever (Parkway Apps)
- Leader In Me Parent Guide
- Social Studies
- MAP Practice
- 5th Grade Schedule
- 5th Grade Curriculum Information
Math Homework Pages and Answers
Topic 1: understand place value.
1-1: Patterns with Exponents and Powers of 10
- Homework Page
1-2: Understand Whole-Number Place Value
1-3: Decimals to Thousandths
1-4: Understand Decimal Place Value
1-5: Compare Decimals
1-6: Round Decimals
Topic 2: Use Models and Strategies to Add and Subtract Decimals
2-2: Estimate Sums and Differences of Decimals
2-3: Use Models to Add and Subtract Decimals
2-4: Use Strategies to Add Decimals
2-5: Use Strategies to Subtract Decimals
2-6: Model with Math
Topic 3: Fluently Multiply Multi-Digit Whole Numbers
3-1: Multiply Greater Numbers by Powers of 10
3-2: Estimate Products
3-3: Multiply by 1-Digit Numbers
3-4: Multiply 2-Digit by 2-Digit Numbers
3-5: Multiply 3-Digit by 2-Digit Numbers
3-6: Multiply Whole Numbers with Zeros
3-7: Practice Multiplying Multi-Digit Numbers
3-8: Solve Word Problems
3-9: Critique Reasoning
Topic 4: Use Models and Strategies to Multiply Decimals
4-1:Multiply Decimals by Powers of 10
4-2: Estimate the Product of a Decimal and a Whole Number
4-3: Use Models to Multiply a Decimal and a Whole Number
4-4: Multiply a Decimal and a Whole Number
4-5: Use Models to Multiply a Decimal and a Decimal
4-6: Multiply Decimals Using Partial Products
4-7: Use Properties to Multiply Decimals
4-8: Use Number Sense to Multiply Decimals
4-9: Model with Math
Topic 5: Use Models and Strategies to Divide Whole Numbers
Topic 5-1: Use Patterns and Mental Math to Divide
Topic 5-2: Estimate Quotients with 2-Digit Divisors
Topic 5-3: Use Models and Properties to Divide with 2-Digit Divisors
Topic 5-4: Use Partial Quotients to Divide
Topic 5-5: Use Sharing to Divide: Two Digit Divisors
Topic 5-6: Use Sharing to Divide: Greater Dividends
Topic 5-7: Choose a Strategy to Divide
Lesson 5-8: Make Sense and Persevere
Topic 6: Use Models and Strategies to Divide Decimals
6-1: Patterns for Dividing with Decimals
6-2: Estimate Decimals Quotients
6-3: Use Models to Divide by a 1-Digit Number
6-4: Divide by a 2-digit Whole Number
6-5: Divide by a Decimal
6-6: Reasoning

Topic 7: Use Equivalent Fractions to Add and Subtract Fractions
7-2: Find Common Denominators
- Answers
7-3: Add Fractions with Unlike Denominators
7-4: Subtract Fractions with Unlike Denominators
7-5: Add and Subtract Fractions
7-6: Estimate Sums and Differences of Mixed Numbers
7-7: Use Models to Add Mixed Numbers
7-8: Add Mixed Numbers
7-9: Use Models to Subtract Mixed Numbers
7-10: Subtract Mixed Numbers
7-11: Add and Subtract Mixed Numbers
Topic 8: Apply Understanding of Multiplication to Multiply Fractions
8-1: Multiply a Fraction by a Whole Number
8-2: Multiply a Whole Number by a Fraction
8-3: Multiply Fractions and Whole Numbers
8-4: Use Models to Multiply Two Fractions
8-5: Multiply Two Fractions
8-6: Area of a Rectangle
8-7: Multiply Mixed Numbers
Topic 9: Apply Understanding of Division to Divide Fractions
Lesson 9-1: Fractions and Division
Lesson 9-2: Fractions and Mixed Numbers as Quotients
Lesson 9-3: Use Multiplication to Divide
Lesson 9-4: Divide Whole Numbers by Unit Fractions
Lesson 9-5: Divide Unit Fractions by Non-Zero Whole Numbers
Lesson 9-6: Divide Whole Numbers and Unit Fractions
Lesson 9-7: Solve Problems Using Division
Lesson 9-8: Repeated Reasoning
Topic 10: Represent and Interpret Data
Lesson 10-1: Analyze Line Plots
Lesson 10-2: Make Line Plots
Lesson 10-3: Solve Word Problems Using Measurement Data
Lesson 10-4: Critique Reasoning
Topic 11: Understand Volume Concepts
Lesson 11-1: Model Volume
Lesson 11-2: Develop a Formula
Lesson 11-3: Combine Volume of Prisms
Lesson 11-4: Solve Word Problems Using Volume
Lesson 11-5: Use Appropriate Tools
5th Grade Homework Policy
We value your family time. therefore, we will be intentional with any homework we send home. students’ daily homework will be required reading of at least 30 minutes., students will have nightly math homework which supports our learning in class. there are a lot of new math concepts in 5th grade and it is important for students' growth and understanding. additionally, study guides and other assignments may be sent home periodically throughout the year., please note: if a student exhibits off-task behaviors, fails to complete an assignment, or is struggling to understand a concept, an assignment will be sent home for completion..
- Questions or Feedback? |
- Web Community Manager Privacy Policy (Updated) |
- AP Calculus
- AP Statistics
- Independent Study
- Second Grade Math
- Third Grade Math
- Fourth Grade Math
- Fifth Grade Math
- Sixth Grade Math
- Sixth Grade Math (CA)
- Seventh Grade Math (CA)
- Eighth Grade Math (CA)
- Integrated Math 1
- Integrated Math 2
- Integrated Math 3
- PreCalculus
- AP Statistics Exam Prep
- Elementary Statistics
- ELM Practice
- Percents and Decimals
- Sixth Grade Math (Big Ideas)
Online Math Class
Mr. Math Blog
Polygons - Lesson 11.1
Triangles - Lesson 11.2
Quadrilaterals - Lesson 11.3
Three Dimensional Figures - Lesson 11.5
Unit Cubes and Solid Figures - Lesson 11.6
Understanding Volume - Lesson 11.7
Estimate Volume - Lesson 11.8
Volume of a Rectangular Prism - Lesson 11.9
Apply Volume Formulas - Lesson 11.10
Finding Volume of Composite Formulas - Lesson 11.12
Find a Part of a Group - Lesson 7.1
Multiply Fractions and Whole Numbers - Lesson 7.2
Fraction and Whole Number Multiplication - Lesson 7.3
Multiply Fractions - Lesson 7.4
Compare Fraction Factor and Product - Lesson 7.5
Fraction Multiplication - Lesson 7.6
Area and Mixed Numbers - Lesson 7.7
Compare Mixed Number Factors and Products - Lesson 7.8
Multiply Mixed Numbers - Lesson 7.9
Problem Solving - Find Unknown Lengths - Lesson 7.10
Please Donate, if you're a regular!
The donate link is below. Thanks so much!!
Line Plots - Lesson 9.1
Ordered Pairs - Lesson 9.2
Graph Data - Lesson 9.3
Line Graphs - Lesson 9.4
Numerical Patterns - Lesson 9.5
Problem Solving - Find a Rule - Lesson 9.6
Graph and Analyze Relationships - Lesson 9.7
Customary Length - Lesson 10.1
Customary Capacity - Lesson 10.2
Weight - Lesson 10.3
Multistep Measurement Problems - Lesson 10.4
Metric Measures - Lesson 10.5
Problem Solving Conversions - Lesson 10.6
Elapsed Time - Lesson 10.7
Division Patterns with Decimals - Lesson 5.1
Divide Decimals by Whole Numbers - Lesson 5.2
Estimate Quotients - lesson 5.3
Division of Decimals by Whole Numbers - Lesson 5.4
Decimal Division - Lesson 5.5
Divide Decimals - Lesson 5.6
Write Zeros in the Dividend - Lesson 5.7
Problem Solving - Decimal Operations - Lesson 5.8
Divide Fractions and Whole Numbers - Lesson 8.1
Problem Solving - Use Multiplication - Lesson 8.2
Connect Fractions to Division - Lesson 8.3
Fraction and Whole Number Division - Lesson 8.4
Interpret Division with Fractions - Lesson 8.5
Addition with Unlike Denominators - Lesson 6.1
Subtraction with Unlike Denominators - Lesson 6.2
Estimate Fraction Sums and Differences - Lesson 6.3
Common Denominators and Equivalent Fractions - Lesson 6.4
Add or Subtract Fractions - Lesson 6.5
Add or Subtract Mixed Numbers - Lesson 6.6
Subtraction with Renaming - Lesson 6.7
Patterns with Fractions - Lesson 6.8
Problem Solving with Addition and Subtraction - Lesson 6.9
Use Properties of Addition - Lesson 6.10
Multiplication Patterns with Decimals - Lesson 4.1
Multiply Decimals and Whole Numbers - Lesson 4.2
Multiply Decimals and Whole Numbers - Lesson 4.3
Multiply Using Expanded Form - Lesson 4.4
Problem Solving - Multiply Money - Lesson 4.5
Decimal Multiplication - Lesson 4.6
Multiply Decimals - Lesson 4.7
Thousandths - Lesson 3.1
Place Value of Decimals - Lesson 3.2
Compare and Order Decimals - Lesson 3.3
Round Decimals - Lesson 3.4
Decimal Addition - Lesson 3.5
Decimal Subtraction - Lesson 3.6
Estimate Decimal Sums and Differences - Lesson 3.7
Add Decimals - Lesson 3.8
Subtract Decimals - Lesson 3.9
Patterns with Decimals - Lesson 3.10
Problem Solving Add and Subtract Money - Lesson 3.11
Choose a Method - Lesson 3.12
Performance Task on Chapter 3
Place the First Digit - Lesson 2.1
Divide by 1-Digit Divisors - Lesson 2.2
Division with 2-Digit Divisors - Lesson 2.3
Partial Quotients - Lesson 2.4
Estimate with 2-Digit Divisors - Lesson 2.5
Divide by 2-Digit Divisors - Lesson 2.6
Interpret the Remainder - Lesson 2.7
Adjust Quotients - Lesson 2.8
Problem Solving - Division - Lesson 2.9
Performance Task on Chapter 2
Fifth Grade
Math
Copyright 2013. All rights reserved.
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- enVision Math
- EngageNY Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 5.3 Answer Key Estimate Fraction Sums and Differences
Refer to our Texas Go Math Grade 5 Answer Key Pdf to score good marks in the exams. Test yourself by practicing the problems from Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 5.3 Answer Key Estimate Fraction Sums and Differences.
Unlock the Problem
Kimberly will be riding her bike to school this year. The distance from her house to the end of the Street is \(\frac{1}{62}\)mile. The distance from the end of the Street to the school is \(\frac{3}{8}\) mile. About how far is Kimberly’s house from school?
You can use benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.

STEP 3: Add the rounded fractions.

Another Way
Use mental math. You can compare the numerator and the denominator to round a fraction and find a reasonable estimate.
Estimate. \(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{5}{8}\) STEP 1: Round \(\frac{9}{10}\). Think: The numerator is about the same as the denominator. Round the fraction \(\frac{9}{10}\) to __________.
Remember A fraction with the same numerator and denominator, such as \(\frac{2}{2}, \frac{5}{5}, \frac{12}{12}\) or \(\frac{96}{96}\), is equal to 1.
STEP 2: Round \(\frac{5}{8}\) Think: The numerator is about half the denominator. Round the fraction \(\frac{5}{8}\) to ___________.

STEP 1: Round \(\frac{9}{10}\). Think: The numerator is about the same as the denominator. Round the fraction \(\frac{9}{10}\) to \(\frac{10}{10}\)
STEP 2: Round \(\frac{5}{8}\) Think: The numerator is about half the denominator. Round the fraction \(\frac{5}{8}\) to \(\frac{4}{8}\)

Math Talk Mathematical Processes
Explain another way you could use benchmarks to estimate \(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{5}{8}\). Answer: \(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{5}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{6}\) \(\frac{1}{6}\) is very near to \(\frac{1}{5}\) Explanation: Used bench marks to find the sum
Share and Show
Estimate the sum or difference.
Question 1. \(\frac{5}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) a. Round \(\frac{5}{6}\) to its closest benchmark. Answer: \(\frac{6}{6}\)
b. Round \(\frac{3}{8}\) to its closest benchmark. Answer: \(\frac{4}{8}\)
c. Add to find the estimate. \(\frac{6}{6}\) +\(\frac{4}{8}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) Answer: 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Go Math Lesson 5.3 5th Grade Answer Key Question 2. \(\frac{5}{9}\) – \(\frac{3}{8}\) Answer: a. Round \(\frac{5}{9}\) to its closest benchmark. Answer: \(\frac{5}{9}\)
c. Add to find the estimate. \(\frac{5}{9}\) – \(\frac{4}{8}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{18}\) Answer: 1\(\frac{1}{18}\) Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 3. \(\frac{5}{6}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) Answer: a. Round \(\frac{5}{6}\) to its closest benchmark. Answer: \(\frac{6}{6}\)
b. Round \(\frac{2}{5}\) to its closest benchmark. Answer: \(\frac{2}{5}\)
c. Add to find the estimate. \(\frac{6}{6}\) +\(\frac{2}{5}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) Answer: 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 4. \(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{1}{9}\) Answer: a. Round \(\frac{9}{10}\) to its closest benchmark. Answer: \(\frac{10}{10}\)
b. Round \(\frac{1}{9}\) to its closest benchmark. Answer: \(\frac{0}{9}\)
c. Add to find the estimate. \(\frac{10}{10}\) – \(\frac{0}{9}\) = 1 Answer: 1 Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Problem Solving
Lesson 5.3 Answer Key 5th Grade Go Math Question 5. How do you know whether your estimate for \(\frac{9}{10}\) + 3\(\frac{6}{7}\) would be greater than or less than the actual sum? Explain. Answer: Greater than the actual sum \(\frac{9}{10}\) + 3\(\frac{6}{7}\) = close to bench marks \(\frac{10}{10}\) + 3\(\frac{7}{7}\) = 4 Explanation: Is greater than the actual sum used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 6. Write Math Nick estimated that \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\) is about 2. Explain how you know his estimate is not reasonable. Answer: \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\) close to benchmarks \(\frac{4}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\) = 1 Explanation: Nick estimated that \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\) is about 2. used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1. so, his estimation is wrong
Question 7. Lisa and Valerie are picnicking in Trough Creek State Park in Pennsylvania. Lisa has brought a salad that she made with \(\frac{3}{4}\) cup of strawberries, \(\frac{7}{8}\) cup of peaches, and \(\frac{1}{6}\) cup of blueberries. About how many total cups of fruit are in the salad? Answer: \(\frac{3}{4}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\) very close to bench marks \(\frac{4}{4}\) + \(\frac{8}{8}\) + \(\frac{0}{6}\) =2 \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation: Lisa and Valerie are picnicking in Trough Creek State Park in Pennsylvania. Lisa has brought a salad that she made with \(\frac{3}{4}\) cup of strawberries, \(\frac{7}{8}\) cup of peaches, and \(\frac{1}{6}\) cup of blueberries. 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) total cups of fruit are in the salad

Go Math 5th Grade Lesson 5.3 How to Estimate Fractions Question 9. H.O.T Explain how you know that \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{6}{10}\) is greater than 1. Answer: No Explanation: Close to the bench marks \(\frac{8}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{10}\) = 1 actual sum is greater than 1
Daily Assessment Task
Fill in the bubble completely to show your answer.
Question 10. Mia uses \(\frac{1}{5}\) of a bag of gravel in the morning and \(\frac{11}{12}\) of a bag in the afternoon. About how much gravel does she use in one day? (A) 0 bags (B) \(\frac{1}{2}\) bag (C) 1 bag (D) 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) bags Answer: C \(\frac{1}{5}\) + \(\frac{11}{12}\) nearest benchmarks are \(\frac{0}{5}\) + \(\frac{12}{12}\) = 1 Explanation: Mia uses \(\frac{1}{5}\) of a bag of gravel in the morning and \(\frac{11}{12}\) of a bag in the afternoon. she use 1 bag of gravel
Question 11. Evaluate Reasonableness Hector and Veronica are going hiking. They made a trail mix that has \(\frac{2}{3}\) cup of almonds, \(\frac{7}{8}\) cup of peanuts, and \(\frac{4}{5}\) cup of raisins in it. Hector estimates that they made about 3 cups of trail mix. Is the estimate greater than or less than the actual sum? How do you know? (A) The estimate is greater because each fraction is rounded up to a benchmark. (B) The estimate is less because each fraction is rounded down to a benchmark. (C) The estimate is greater because they really made more than 3 cups. (D) The estimate is less because each fraction is rounded up to a benchmark. Answer: A Explanation: \(\frac{2}{3}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{5}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks \(\frac{3}{3}\) + \(\frac{8}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{5}\) = 3 Evaluated Reasonableness Hector and Veronica are going hiking. They made a trail mix that has \(\frac{2}{3}\) cup of almonds, ” \(\frac{7}{8}\) cup of peanuts, and \(\frac{4}{5}\) cup of raisins in it. Hector estimates that they made about 3 cups of trail mix.
Lesson 5.3 Go Math 5th Grade Answer Key Question 12. Multi-Step Amanda picked \(\frac{3}{5}\) pound of blueberries at her local farm yesterday. She used \(\frac{3}{8}\) pound of blueberries. Today she picked \(\frac{4}{5}\) pound of blueberries. About how many pounds of blueberries does Amanda have now? (A) \(\frac{1}{5}\)lb (B) 1 lb (C) \(\frac{1}{2}\)lb (D) 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)lbs Answer: B Explanation: what she bought is that she used yesterday in today marked to nearest benchmarks \(\frac{4}{5}\) is \(\frac{5}{5}\) that is 1
Texas Test Prep
Question 13. Jake added \(\frac{1}{8}\) cup of sunflower seeds and \(\frac{4}{5}\) cup of banana chips to his sundae. Which is the best estimate of the total amount of toppings Jake added to his sundae? (A) about 2 cups (B) about 1 cup (C) about 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) cups (D) about \(\frac{1}{2}\) cup Answer: B Explanation: Jake added \(\frac{1}{8}\) cup of sunflower seeds and \(\frac{4}{5}\) cup of banana chips to his sundae. The best estimate of the total amount of toppings Jake added to his sundae is 1 cup
Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 5.3 Homework and Practice Answer Key
Question 1. \(\frac{3}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{5}\) = ___________ Answer: \(\frac{3}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{5}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks \(\frac{4}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{5}\) = 1 \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
5th Grade Go Math Lesson 5.3 Answer Key Question 2. \(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{3}{8}\) = ___________ Answer: \(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{3}{8}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks \(\frac{10}{10}\) – \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 3. \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) = ___________ Answer: \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks \(\frac{4}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) = 1 Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 4. \(\frac{6}{7}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) = ___________ Answer: \(\frac{6}{7}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks \(\frac{7}{7}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 5. \(\frac{3}{8}\) – \(\frac{1}{6}\) = ___________ Answer: \(\frac{3}{8}\) – \(\frac{1}{6}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks \(\frac{4}{8}\) – \(\frac{0}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 6. \(\frac{7}{12}\) + \(\frac{1}{7}\) = ___________ Answer: \(\frac{7}{12}\) + \(\frac{1}{7}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks \(\frac{6}{12}\) + \(\frac{0}{7}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Go Math Lesson 5.3 5th Grade Homework Answer Key Question 7. \(\frac{4}{9}\) – \(\frac{5}{8}\) = ___________ Answer: \(\frac{4}{9}\) – \(\frac{5}{8}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks \(\frac{5}{9}\) – \(\frac{4}{8}\) = 0 Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 8. \(\frac{1}{9}\) + \(\frac{5}{6}\) = ___________ Answer: \(\frac{1}{9}\) + \(\frac{5}{6}\) rounded to the nearest benchmark \(\frac{0}{9}\) + \(\frac{6}{6}\) = 1 Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 9. \(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\) = ___________ Answer: \(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\) rounded to the nearest bench mark \(\frac{8}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\) =1\(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 10. \(\frac{1}{5}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) = ___________ Answer: \(\frac{1}{5}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) rounded to the nearest benchmark \(\frac{0}{5}\) + \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 11. \(\frac{7}{9}\) – \(\frac{2}{6}\) = ___________ Answer: \(\frac{7}{9}\) – \(\frac{2}{6}\) rounded to the nearest benchmark \(\frac{9}{9}\) – \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 5.3 Homework Answer Key Question 12. \(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{7}{8}\) = ___________ Answer: \(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{7}{8}\) rounded to the benchmarks \(\frac{10}{10}\) – \(\frac{8}{8}\) = 0 Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 13. Explain how you can estimate the sum of \(\frac{4}{5}\) and \(\frac{1}{6}\). Answer: \(\frac{4}{5}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\) rounded to the nearest bench marks \(\frac{5}{5}\) + \(\frac{0}{6}\) = 1 Explanation: used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 14. Jena uses \(\frac{7}{8}\) cup of raisins for muffins and \(\frac{5}{8}\) cup of raisins for a bowl of oatmeal. Does lena need more than or less than 1 cup of raisins to make muffins and oatmeal? Explain. Answer: more than 1 cup of raisins Explanation: Jena uses \(\frac{7}{8}\) cup of raisins for muffins and \(\frac{5}{8}\) cup of raisins for a bowl of oatmeal. \(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{8}\) rounded the benhmark \(\frac{8}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{8}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 15. A group of students ate \(\frac{5}{12}\) of a cheese pizza, \(\frac{7}{8}\) of a pepperoni pizza, and \(\frac{5}{8}\) of a veggie pizza. About how many pizzas were eaten? Answer: \(\frac{5}{12}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{8}\) rounded to the nearest benchmark \(\frac{6}{12}\) + \(\frac{8}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{8}\) = 2 Explanation: A group of students ate \(\frac{5}{12}\) of a cheese pizza, \(\frac{7}{8}\) of a pepperoni pizza, and \(\frac{5}{8}\) of a veggie pizza. 2 pizzas were eaten in whole.
Lesson Check
Question 16. On Saturday, the scouts hiked \(\frac{4}{5}\) mile up the mountain. On Sunday, they hiked \(\frac{1}{4}\) mile up the mountain. About how far did the scouts hike up the mountain in all? (A) \(\frac{1}{2}\) mile (B) 1 mile (C) 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) miles (D) 2 miles Answer: \(\frac{4}{5}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\) rounded to nearest benchmark \(\frac{5}{5}\) + \(\frac{0}{4}\) is 1 mile Explanation: On Saturday, the scouts hiked \(\frac{4}{5}\) mile up the mountain. On Sunday, they hiked \(\frac{1}{4}\) mile up the mountain. 1 mile far the scouts hike up the mountain in all
Question 17. Which of the following best describes the difference for \(\frac{11}{12}\) – \(\frac{7}{10}\) ? (A) less than \(\frac{1}{2}\) (B) greater than \(\frac{1}{2}\) (C) greater than 1 (D) greater than 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) Answer: A Explanation: \(\frac{11}{12}\) – \(\frac{7}{10}\) is 0 that is less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Practice and Homework Lesson 5.3 Answer Key 5th Grade Question 18. Which sum is greatest? Use estimation to decide. (A) \(\frac{2}{7}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) (B) \(\frac{1}{10}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) (C) \(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{8}\) (D) \(\frac{2}{9}\) + \(\frac{1}{8}\) Answer: A Explanation: \(\frac{2}{7}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) = 1

Question 20. Multi-Step Michaela has \(\frac{11}{12}\) yard of orange fabric and \(\frac{7}{8}\) yard of green fabric. She uses \(\frac{1}{2}\) yard of each color for her sewing project. About how much fabric does Michaela have left if she combines the two colors? (A) 1 yard (B) \(\frac{1}{2}\) yard (C) 1 \(\frac{1}{2}\) yards (D) 2 yards Answer: D \(\frac{11}{12}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\) rounded to nearest bench marks \(\frac{12}{12}\) + \(\frac{8}{8}\) = 2 Explanation: 2 yards fabric uses Michaela have left if she combines the two colors.
Question 21. Multi-Step Dustin buys \(\frac{9}{10}\) yard of striped fabric. He uses \(\frac{3}{8}\) yard. He buys \(\frac{7}{8}\) yard more. About how much fabric does Dustin have now? (A) 1 yard (B) \(\frac{1}{2}\) yard (C) 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) yards (D) 2 yards Answer: C Explanation: Dustin buys \(\frac{9}{10}\) yard of striped fabric. He uses \(\frac{3}{8}\) yard. He buys \(\frac{7}{8}\) yard more. \(\frac{9}{10}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\) rounded to nearest benchmarks \(\frac{10}{10}\) – \(\frac{4}{8}\) + \(\frac{8}{8}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) yards
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Chapter 5: Ratios and Proportions
Chapter 5 homework solutions.
5.1-5.3 Extra Practice Worksheet
5.1 Ratios and Rates
5.1 Lesson Preso
5.1 Textbook Exercises: page 167
Ba: 1-6, 11-27 odd;
Avg: 1-6, 11-21 odd, 24-28 even, 29, 31;
Adv: 1-6, 18-38 even
5.2 Proportions
5.2 Textbook Exercises page 174
Ba: 1-4, 5-13 odd, 21-27 odd;
Avg 1-4, 5-13 odd, 22-30 even;
Adv: 1-4, 6-14 even, 22-32 even
5.3 Writing Proportions
5.3 Lesson Preso
5.3 Textbook Exercises page 182
Ba: 1-3, 9, 11, 12, 13-23 odd
Avg: 1-3, 8-14 even, 19-23
Adv: 1-3, 8-24 even, 25
5.4 Solving Proportions
5.4 Lesson Preso
5.4 Textbook Exercises page 190
Ba: 1-3, 5-9 odd, 15-21 odd, 22, 23-27 odd
Avg: 1-3, 5-9 odd, 15-21 odd, 22, 29, 30, 32-35
Adv: 1-3, 4-8 even, 14-38 even
5.5 Lesson Preso
5.5 Textbook Exercises page 196
Ba: 1-3, 5-11 odd, 12, 13-17 odd
Avg: 1-3, 5-11 odd, 12, 14-17
Adv: 1-3, 4-18 even
5.6 Direct Variation
5.6 Lesson Preso
5.6 Textbook Exercises page 202
Ba: 1-3, 7-17 odd, 18, 19-25 odd
Avg: 1-3, 7-17 odd, 18-28 even
Adv: 1-3, 8-28 even
Chapter 5 Review
5.1-5.3 Review Quizizz:
5.4-5.6 Review Quizizz:
Chapter 5 Review Quizizz:
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Lesson 7 Answer Key
Engage ny eureka math 5th grade module 3 lesson 7 answer key, eureka math grade 5 module 3 lesson 7 sprint answer key.
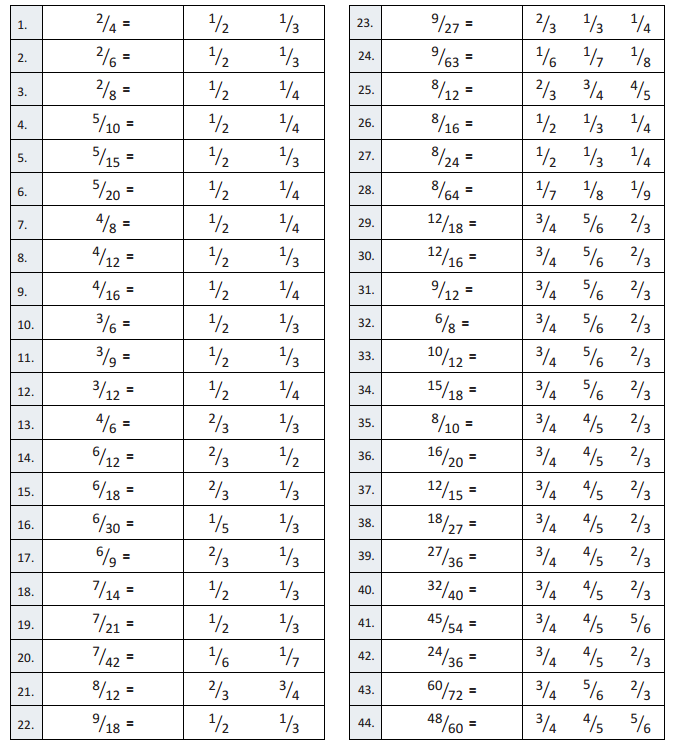
Question 1. \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{2}{4}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 2. \(\frac{2}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{2}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{2}{6}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 3. \(\frac{2}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{2}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{2}{8}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 4. \(\frac{5}{10}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{5}{10}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{5}{10}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 5 we get \(\frac{1}{2}[/latex
Question 5. [latex]\frac{5}{15}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{5}{15}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{5}{15}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 5 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 6. \(\frac{5}{20}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{5}{20}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{5}{20}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 5 we get \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 7. \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{4}{8}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 4 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 8. \(\frac{4}{12}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{4}{12}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{4}{12}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 4 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 9. \(\frac{4}{16}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{4}{16}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{4}{16}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 4 we get \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 10. \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{3}{6}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 3 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 11. \(\frac{3}{9}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{3}{9}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{3}{9}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 3 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 12. \(\frac{3}{12}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{3}{12}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{3}{12}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 3 we get \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 13. \(\frac{4}{6}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{4}{6}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{4}{6}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 14. \(\frac{6}{12}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{2}\) Answer: \(\frac{6}{12}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{6}{12}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 6 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 15. \(\frac{6}{18}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{6}{18}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{6}{18}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 6 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 16. \(\frac{6}{30}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{6}{30}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\) Explanation : \(\frac{6}{30}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 6 we get \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Question 17. \(\frac{6}{9}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{6}{9}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{6}{9}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 3 we get \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 18. \(\frac{7}{14}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{7}{14}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{7}{14}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 7 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 19. \(\frac{7}{21}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{7}{21}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{7}{21}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 7 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 20. \(\frac{7}{42}\) = \(\frac{1}{6}\) \(\frac{1}{7}\) Answer: \(\frac{7}{42}\) = \(\frac{1}{6}\) Explanation : \(\frac{7}{42}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 7 we get \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Question 21. \(\frac{8}{12}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) \(\frac{3}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{8}{12}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{8}{12}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 4 we get \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 22. \(\frac{9}{18}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{9}{18}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{9}{18}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 9 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 23. \(\frac{9}{27}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{9}{27}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{9}{27}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 9 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 24. \(\frac{9}{63}\) = \(\frac{1}{6}\) \(\frac{1}{7}\) \(\frac{1}{8}\) Answer: \(\frac{9}{63}\) = \(\frac{1}{7}\) Explanation : \(\frac{9}{63}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 9 we get \(\frac{1}{7}\)
Question 25. \(\frac{8}{12}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) Answer: \(\frac{8}{12}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{8}{12}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 4 we get \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 26. \(\frac{8}{16}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{8}{16}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{8}{16}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 8 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 27. \(\frac{8}{24}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{8}{24}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{8}{24}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 8 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 28. \(\frac{8}{64}\) = \(\frac{1}{7}\) \(\frac{1}{8}\) \(\frac{1}{9}\) Answer: \(\frac{8}{64}\) = \(\frac{1}{8}\) Explanation : \(\frac{8}{64}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 8 we get \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Question 29. \(\frac{12}{18}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{12}{18}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{12}{18}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 6 we get \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 30. \(\frac{12}{16}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{12}{16}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{12}{16}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 4 we get \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 31. \(\frac{9}{12}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{9}{12}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{9}{12}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 3 we get \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 32. \(\frac{6}{8}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{6}{8}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{6}{8}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 33. \(\frac{10}{12}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{10}{12}\) = \(\frac{5}{6}\) Explanation : \(\frac{10}{12}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Question 34. \(\frac{15}{18}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{15}{18}\) = \(\frac{5}{6}\) Explanation : \(\frac{15}{18}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 3 we get \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Question 35. \(\frac{8}{10}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{8}{10}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\) Explanation : \(\frac{8}{10}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Question 36. \(\frac{16}{20}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{16}{20}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\) Explanation : \(\frac{16}{20}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 4 we get \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Question 37. \(\frac{12}{15}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{12}{15}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\) Explanation : \(\frac{12}{15}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 3 we get \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Question 38. \(\frac{18}{27}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{18}{27}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{18}{27}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 9 we get \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 39. \(\frac{27}{36}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{27}{36}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{27}{36}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 9 we get \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 40. \(\frac{32}{40}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{32}{40}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\) Explanation : \(\frac{32}{40}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 8 we get \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Question 41. \(\frac{45}{54}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) Answer: \(\frac{45}{54}\) = \(\frac{5}{6}\) Explanation : \(\frac{45}{54}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 9 we get \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Question 42. \(\frac{24}{36}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{24}{36}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{24}{36}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 12 we get \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 43. \(\frac{60}{72}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{60}{72}\) = \(\frac{5}{6}\) Explanation : \(\frac{60}{72}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 12 we get \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Question 44. \(\frac{48}{60}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) Answer: \(\frac{48}{60}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\) Explanation : \(\frac{48}{60}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 12 we get \(\frac{4}{5}\)
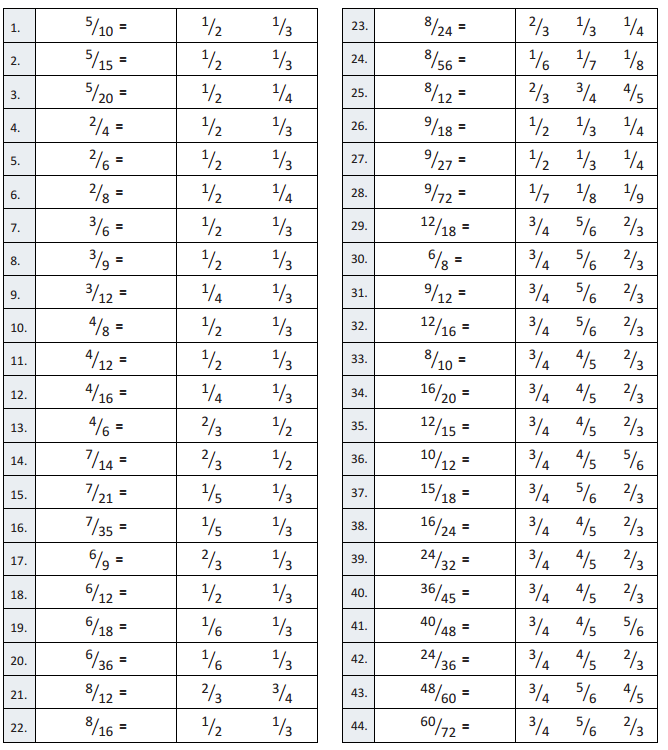
Question 1. \(\frac{5}{10}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{5}{10}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{5}{10}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 5 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 2. \(\frac{5}{15}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{5}{15}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{5}{15}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 5 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 3. \(\frac{5}{20}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{5}{20}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{5}{20}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 5 we get \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 4. \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{2}{4}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 5. \(\frac{2}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{2}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{2}{6}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 6. \(\frac{2}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{2}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{2}{8}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 7. \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{3}{6}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 3 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 8. \(\frac{3}{9}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{3}{9}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{3}{9}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 3 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 9. \(\frac{3}{12}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{3}{12}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{3}{12}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 3 we get \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 10. \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{4}{8}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 4 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 11. \(\frac{4}{12}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{4}{12}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{4}{12}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 4 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 12. \(\frac{4}{16}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{4}{16}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{4}{16}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 4 we get \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 13. \(\frac{4}{6}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{2}\) Answer: \(\frac{4}{6}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{4}{6}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 14. \(\frac{7}{14}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{2}\) Answer: \(\frac{7}{14}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{7}{14}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 7 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 15. \(\frac{7}{21}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{7}{21}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{7}{21}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 7 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 16. \(\frac{7}{35}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{7}{35}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\) Explanation : \(\frac{7}{35}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 7 we get \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Question 18. \(\frac{6}{12}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{6}{12}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{6}{12}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 6 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 19. \(\frac{6}{18}\) = \(\frac{1}{6}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{6}{18}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{6}{18}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 6 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 20. \(\frac{6}{36}\) = \(\frac{1}{6}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{6}{36}\) = \(\frac{1}{6}\) Explanation : \(\frac{6}{36}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 6 we get \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Question 22. \(\frac{8}{16}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{8}{16}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{8}{16}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 8 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 23. \(\frac{8}{24}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{8}{24}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{8}{24}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 8 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 24. \(\frac{8}{56}\) = \(\frac{1}{6}\) \(\frac{1}{7}\) \(\frac{1}{8}\) Answer: \(\frac{8}{24}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{8}{56}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 8 we get \(\frac{1}{7}\)
Question 26. \(\frac{9}{18}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{9}{18}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Explanation : \(\frac{9}{18}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 9 we get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 27. \(\frac{9}{27}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: \(\frac{9}{27}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{9}{27}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 9 we get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 28. \(\frac{9}{72}\) = \(\frac{1}{7}\) \(\frac{1}{8}\) \(\frac{1}{9}\) Answer: \(\frac{9}{72}\) = \(\frac{1}{8}\) Explanation : \(\frac{9}{72}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 9 we get \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Question 30. \(\frac{6}{8}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{6}{8}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{6}{8}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 32. \(\frac{12}{16}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{12}{16}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{12}{16}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 4 we get \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 33. \(\frac{8}{10}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{8}{10}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\) Explanation : \(\frac{8}{10}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Question 34. \(\frac{16}{20}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{16}{20}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\) Explanation : \(\frac{16}{20}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 4 we get \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Question 35. \(\frac{12}{15}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{12}{15}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\) Explanation : \(\frac{12}{15}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 3 we get \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Question 36. \(\frac{10}{12}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) Answer: \(\frac{10}{12}\) = \(\frac{5}{6}\) Explanation : \(\frac{10}{12}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 2 we get \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Question 37. \(\frac{15}{18}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{15}{18}\) = \(\frac{5}{6}\) Explanation : \(\frac{15}{18}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 3 we get \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Question 38. \(\frac{16}{24}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{16}{24}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) Explanation : \(\frac{16}{24}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 8 we get \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 39. \(\frac{24}{32}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{24}{32}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) Explanation : \(\frac{24}{32}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 12 we get \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 40. \(\frac{36}{45}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{36}{45}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\) Explanation : \(\frac{36}{45}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 9 we get \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Question 41. \(\frac{40}{48}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) Answer: \(\frac{40}{48}\) = \(\frac{5}{6}\) Explanation : \(\frac{40}{48}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 8 we get \(\frac{5}{}\)
Question 43. \(\frac{48}{60}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) Answer: \(\frac{48}{60}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\) Explanation : \(\frac{48}{60}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 12 we get \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Question 44. \(\frac{60}{72}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) \(\frac{5}{6}\) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Answer: \(\frac{60}{72}\) = \(\frac{5}{6}\) Explanation : \(\frac{60}{72}\) when its numerator and denominator is divided by 12 we get \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Lesson 7 Problem Set Answer Key
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Lesson 7 Exit Ticket Answer Key
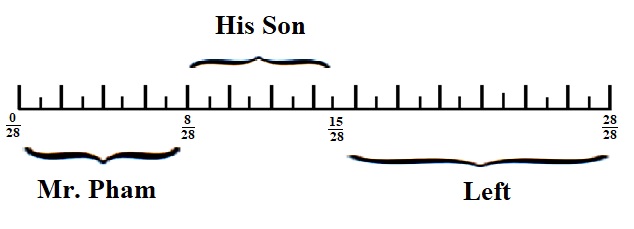
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Lesson 7 Homework Answer Key
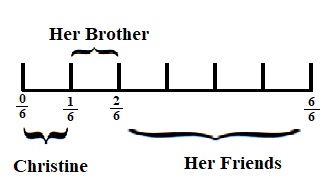
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Lesson 2 Sprint Answer Key. Question 1. x = 2 . Question 2. x = 10 . Question 3. x = 4 . Question 4. x = 6 .
Lesson 5: Multiply decimal fractions with tenths by multi -digit whole numbers using place value understanding to record partial products. A Story of Units 5•2 G5-M2-Lesson 5 1. Draw an area model, and then solve using the standard algorithm. Use arrows to match the partial products from the area model to the partial products in the algorithm. a.
EngageNY/Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 5 Lesson 2For more videos, please visit http://bit.ly/engageportalPLEASE leave a message if a video has a technical diffi...
Module 3: Addition and Subtraction of Fractions 1 Lesson 1 Answer Key 5• 3 Lesson 1 Sprint Side A 1. 2 12. 2 23. 4 34. 7 2. 5 13. 2 24. 7 35. 4 3. 2 14. 2 25. 7 36.
Eureka Math Grade 5. Please share this page with your friends on FaceBook. Lesson 1: Homework Answer Keys. Lesson 2: Homework Answer Keys. Lesson 3: Homework Answer Keys. Lesson 4: Homework Answer Keys. Lesson 5: Homework Answer Keys. Lesson 6:Homework Answer Keys. Lesson 7: Homework Answer Keys.
CPM Education Program proudly works to offer more and better math education to more students.
Unit 5: Module 5: Addition and multiplication with volume and area. 0/1400 Mastery points. Topic A: Concepts of volume Topic B: Volume and the operations of multiplication and addition Topic C: Area of rectangular figures with fractional side lengths. Topic D: Drawing, analysis, and classification of two-dimensional shapes.
GRADE 5 • MODULE 2 Multi-Digit Whole Number and Decimal Fraction Operations A STORY OF UNITS. ... 2 6 Answer Key 5•Lesson 2 Homework 1. a. 972 3. $6,000 b. 18,972 4. $28,466 2. a. 34,397 b. 26,288 c. 34,868 d. 25,392 A STORY OF UNITS. Module 2: Multi-Digit Whole ...
Bundle options are available for all of our materials (print, digital, PD, etc.). Prices vary by grade and size of class set. Certain grade-levels do not include all packets due to the nature of the grade-level content. Student workbooks are available in class sets of 20, 25, and 30. Prices vary by size of class set.
Topic A Overview. Lesson 1: Multiply multi-digit whole numbers and multiples of 10 using place value patterns and the distributive and associative properties. ( Video Lesson) Lesson 2: Estimate multi-digit products by rounding factors to a basic fact and using place value patterns. ( Video Lesson ) B.
5TH GRADE. Go Math! What is the "Go Math!" curriculum? Curriculum - This details what domain, cluster, standard, and essential questions are taught within the math program. ... Homework: Lesson 5.1 Lesson 5.2 Lesson 5.3 Lesson 5.4 Lesson 5.5 Lesson 5.6 Lesson 5.7 Lesson 5.8 Extra Practice.
Chapter 16: Coordinate Geometry. enVision MATH Common Core 5 grade 5 workbook & answers help online. Grade: 5, Title: enVision MATH Common Core 5, Publisher: Scott Foresman Addison Wesley, ISBN: 328672637.
EngageNY/Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Lesson 5For more Eureka Math (EngageNY) videos and other resources, please visit http://EMBARC.onlinePLEASE leave a mes...
Go Math! Practice Book (TE), G5. Name Fraction and Whole Number Multiplication Find the product. Write the product in simplest form. 2. Lesson 7.3 COMMON CORE STANDARD CC5.NF.4a Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to multiply and divide fractions. — or 33ž 27 or 2— —x 9=10' 10 10 3. 6.
Students' daily homework will be required reading of at least 30 minutes. Students will have nightly math homework which supports our learning in class. There are a lot of new math concepts in 5th grade and it is important for students' growth and understanding. Additionally, study guides and other assignments may be sent home periodically ...
Polygons - Lesson 11.1. Triangles - Lesson 11.2. Quadrilaterals - Lesson 11.3. Three Dimensional Figures - Lesson 11.5. Unit Cubes and Solid Figures - Lesson 11.6. Understanding Volume - Lesson 11.7. Estimate Volume - Lesson 11.8. Volume of a Rectangular Prism - Lesson 11.9. Apply Volume Formulas - Lesson 11.10.
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 5 Lesson 15 Problem Set Answer Key. Question 1. The length of a flowerbed is 4 times as long as its width. If the width is " 38 meter, what is the area? Answer: Given, The width of the flower bed = 3/8 meters. The length of the flower bed is 4 times as long as its width. Which means, 3/8 x 4 = 12/ 8 = 3/2.
Engage NY Eureka Math 5th Grade Module 3 Lesson 16 Answer Key Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 3 Lesson 16 Problem Set Answer Key. Question 1. Draw the following ribbons. When finished, compare your work to your partner's. a. 1 ribbon. The piece shown below is only \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the whole. Complete the drawing to show the whole ribbon. b. 1 ...
Test yourself by practicing the problems from Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 5.3 Answer Key Estimate Fraction Sums and Differences. Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 5.3 Answer Key Estimate Fraction Sums and Differences. Unlock the Problem. Kimberly will be riding her bike to school this year.
Chapter 5 Homework Solutions. 5.1-5.3 Extra Practice Worksheet. 5.1 Ratios and Rates . 5.1 Lesson Preso. 5.1 Textbook Exercises: page 167 ... 5.2 Lesson. 5.2 Textbook Exercises page 174 . Ba: 1-4, 5-13 odd, 21-27 odd; Avg 1-4, 5-13 odd, 22-30 even; Adv: 1-4, 6-14 even, 22-32 even. 5.3 Writing Proportions. 5.3 Lesson Preso. 5.3 Textbook ...
The source for the homework pages is available here for free. I used the full module PDF:https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-3-mathematics-module-5
520 when its numerator and denominator is divided by 5 we get 14. Question 7. 48 = 12 14. Answer: 48 = 12. Explanation : 48 when its numerator and denominator is divided by 4 we get 12. Question 8. 412 = 12 13.