An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Elsevier - PMC COVID-19 Collection


Reviving tourism industry post-COVID-19: A resilience-based framework
Gagan deep sharma.
a University School of Management Studies, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, Sector 16C, Dwarka, New Delhi, India
Asha Thomas
b Jagan Institute of Management Studies, Sector 5, Rohini, New Delhi, India
Justin Paul
c University of Puerto Rico, San Juan, PR, USA
The COVID-19 pandemic struck the tourism industry severely. Based on the review of 35 papers that studied the tourism industry in the wake of the pandemic, we propose a resilience-based framework for reviving the global tourism industry post-COVID-19. Our framework outlines four prominent factors for building resilience in the industry: government response, technology innovation, local belongingness, and consumer and employee confidence. We argue that using such inclusive resilience; the tourism industry may transform into a new global economic order characterized by sustainable tourism, society's well-being, climate action, and the involvement of local communities. We also offer directions for future research in the area.
1. Introduction
The outbreak of COVID-19 has posed critical health challenges worldwide. The pandemic is one of the most highly contagious outbreaks in recent human history, with more than 46 million cases and 1.2 million deaths (as on 31st October 2020) ( https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ ). Given the high speed of transmission of the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), governments worldwide have had no other option but to impose lockdowns. The spread of the virus has severely threatened lives, and measures such as lockdowns have posed a critical risk to the masses' livelihoods ( Sharma & Mahendru, 2020 ). The economic shocks of the pandemic are being observed across all industries and sectors worldwide. While some industries can adapt to digital platforms and continue their struggle for survival ( Mehrolia, Alagarsamy, & Solaikutty, 2020 ), a few industries have encountered unprecedented failures due to travel restrictions and social distancing, thereby finding it extremely difficult to survive the pandemic. Tourism is one industry that cannot hold its ground without the mobility of tourists. The fall of 22% in tourist numbers in the first quarter of 2020 (compared to the same quarter of 2019), and the threat of 60% to 80% fall throughout 2020 (compared to 2019), are some indications of the havoc that the COVID-19 pandemic can cause for the global tourism industry ( World Tourism Organization, 2020 ). Tourism is one of the most labour-intensive sectors. Such a slowdown for the industry may put millions of jobs at risk, thereby threatening to roll back the progress made on the front of sustainable development goals ( World Tourism Organization, 2020 ).
As indicated by Rivera (2020) , examining the hospitality and tourism industries in the pandemic context is of paramount importance. Researchers have started to focus on this area, yet there is only limited work available so far. A search query on the Web of Science database yielded no more than 45 results that studied the impact of COVID-19 on the tourism industry. These studies are also observed to be all over the place, which poses a directional challenge for scholarship in the area. Such variance in studies fails to significantly enrich the body of knowledge, thereby proving to be of limited use to policymakers and practitioners.
The WHO (2017) recommends rapid reviews to provide timely evidence for policymakers to respond to the emergency. Since the COVID-19 pandemic threatens to be particularly fatal for the tourism industry, a rapid review of the available literature is highly recommended. Such a review will not merely consolidate the findings of the existing studies but also provide insights and directions for future researchers to focus on the appropriate problems plaguing the sector.
The above discussion drives our motivation to perform a review of the challenges being faced by the global tourism industry in the wake of COVID-19. The research questions for our study are set as follows:
To observe the impact of COVID-19 on the tourism industry by studying the emerging body of knowledge in the field;
To suggest a policy framework that enables market players and governments worldwide to cope with the challenges emerging for the global tourism industry from the outbreak of the pandemic.
Out of the 47 papers found on the Web of Science database, we discovered that 10 do not meet the inclusion criteria (detailed in the methodology section). We rigorously reviewed 37 papers to synthesize their findings and propose a framework for further advancement of the scholarship in this area. Our results reveal that the pandemic has created severe roadblocks for the tourism industry, and the way ahead seems to be rocky. We learn that this challenge may open the doors for local tourism, eco-tourism, and sustainable tourism, which have long been part of the discussion but have failed to take any tangible shape so far. Four significant themes emerge from our work, namely, sustainable tourism, climate action, transformation to the new global economic order, and resilience. We make a significant theoretical and practical contribution to the field by suggesting a coping-up mechanism, which revolves around resilience. Our framework includes resilience from market players, governments, non-government agencies, and all other stakeholders.
The remainder of our paper is organized as follows: The next section discusses the methodology of our work, the third section presents the thematic discussion, the fourth section highlights the future research agenda, and the last section concludes by outlining the policy framework to deal with the challenges emerging from COVID-19 for the tourism industry.
2. Methodology
The systematic reviewing methodology is followed in this paper. The advent of this methodology in the field of management is recent ( Paul & Criado, 2020 ; Tranfield, Denyer, & Smart, 2003 ). This methodology is driven by its merits in the form of systematic, transparent, and replicable review ( Cook, Greengold, Ellrodt, & Weingarten, 1997 ; Cook, Mulrow, & Haynes, 1997 ; Hao & al, 2019 ; Wolf, Shea, & Albanese, 2001 ). It is also inspired by prior review articles ( Bansal, Garg, & Sharma, 2019 ; Dhaliwal, Singh, & Paul, 2020 ; Gilal, Zhang, Paul, & Gilal, 2019 ; Jain, Sharma, & Mahendru, 2019 ; Paul & Feliciano-Cestero, 2020 ; Paul & Mas, 2020 ; Rosado-Serrano, Paul, & Dikova, 2018 ; Talan & Sharma, 2019 ; Thomas & Paul, 2019 ).
Records were searched employing the Web of Science database. The usage of this database ensures a consistent standard for the articles. Using keywords like “COVID-19,” “tourism,” “hospitality,” and “coronavirus,” we found 47 records. Since the problem of COVID-19 pertains to 2020, the records are fewer in number. Nevertheless, given the mandate of the WHO for rapid reviews, we consider it worthwhile to conduct a review in this pivotal field. These records were then screened through titles and abstracts. It was discovered that 37 papers fell within our theme, while the remaining 10 did not. These 37 papers were selected for further analysis. These papers are shown in Table 1 .
Reviewed papers.
To arrive at the appropriate themes studied in the selected papers, we ran a cluster analysis on these papers' keywords through the VOS viewer project developed by Leiden University, the Netherlands. Through this approach, we came up with four clusters, namely, sustainable tourism, climate action, transformation to the new global economic order, and resilience. We use these clusters as the themes for our work, and group the keywords of the 35 records within these themes, which drive the thematic discussion of our study.
This analysis leads to the development of three clusters as detailed in Table 2 .
Keywords and clusters.
3. Thematic discussion
Fig. 1 exhibits the prominent keywords clustered into three groups. First, the focus of research has been around the future of tourism, wherein the body of knowledge is concerned about the future of tourism sector, specifically in the context of communities and the cause of sustainability. Second, the scholarship is engaged in deliberating on the issues of resilience, mobility, degrowth, and sustainable tourism. Finally, there is an ongoing discussion around geopolitics, climate change, and transformation to the new situation through a reset of the sector. We use these keywords to draw two major themes, comprising four sub-themes, as exhibited in Fig. 2 . This thematic discussion is presented below.

Clusters of keywords used by the reviewed literature.

Thematic framework.
3.1. Resilience
The business world recognizes resilience as a crisis management tool/strategy for business stability and adaptability to all types of risks, during natural disasters and emergencies. Furthermore, business resilience is linked to the organization's ability to adapt to the environment and new circumstances to mitigate the effects of the incident ( Supardi, Kudus, Hadi, & Indonesia, 2020 ). Resilience strategies require coordination, various crisis management techniques, good relationships (among all stakeholders), a comprehensive network, recognition of risks and opportunities, and timely and scalable intervention ( Alves, Lok, Luo, & Hao, 2020 ; Fitriasari, 2020 ). The literature on resilience identifies proactive, absorptive/adaptive, reactive, or dynamic attributes of resilience ( Supardi et al., 2020 ).
Historically, the tourism industry has quickly bounced back after disasters, pandemics, and epidemics like Ebola, Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) and severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Local, regional, or national governments are aiding in the industry's recovery by luring investors through tax breaks, lenient land-use rules, etc. ( Brouder, 2020 ; Ioannides & Gyimóthy, 2020 ). Before international travel can resume, domestic tourism will boost the resumption of the tourism industry in the wake of the pandemic. Other factors, including technological resilience, local belongingness, and customer and employee confidence, may help build industry resilience, which is the need of the hour.
3.1.1. Governments' response to COVID-19: A new outlook
Businesses across industries are looking forward to “business as usual”, and the tourism industry is no exception. All the industries are banking largely upon “government stimulus packages and interventions” to improve their productivity. For instance, TUI, the world's most prominent multinational tourism organization, is taking the UK and German governments' aid and has announced cost reduction in its operations across the world ( Higgins-Desbiolles, 2020 ). The government has become a significant role player in the economy of tourism ( Table 3 ). This has resulted in the re-nationalization of airlines, tourism firms, and networks like airports. This is something different in comparison to earlier crises, which created curiosity in research and institutions and had no “policy impact,” particularly in the tourism industry ( Hall et al., 2020 ). Tsionas (2020) discusses post-COVID-19 problems and mentions that “opening at limited capacity” of almost 33% is a good option. He proposes that government subsidies would be needed to support such lower capacities. There has been massive government intervention in the working and operation of the tourism industry during the COVID-19 crisis ( Higgins-Desbiolles, 2020 ). Discussing Macao's reaction to the pandemic in a “3-wave analogy,” McCartney (2020) observes that the wave of recovery will push toward “public-private partnership and cooperation.” In future, the effect of such governmental response on tourism will create a novel outlook.
Government response to COVID-19. (Source : OEDC, 2020)
3.1.2. Technology innovation
Technology is a major force in creating flexibility in the tourism industry ( Hall et al., 2020 ). Disasters help in speeding up changes in technology. During COVID-19, people have taken massive aid from technology experts. There are instances of robots replacing people, applications on mobiles being employed to track people's contacts, or Big Data analytics forecasting COVID-19 spread among the masses. Robot, automation technologies, and artificial intelligence can reduce cost, improve liquidity, and enhance flexibility. This will also help maintain social distancing ( Assaf & Scuderi, 2020 ; Thomas & Chopra, 2020 ), as technology can connect people without any physical contact. Thus, technology can handle pandemic-specific problems such as screening travellers, discovering COVID-19 cases and tracking contacts, ensuring online education for students, etc. ( Hall et al., 2020 ). Many reports show a surge in the public's trust in technology, their readiness to connect, and their willingness to change their attitudes toward technology. People have now started ignoring privacy issues to get a more significant technology benefit ( Stankov et al., 2020 ). Gretzel et al. (2020) has presented the “six transformative e-tourism research pillars” for bringing in changes in e-tourism by proactively using IT resources for short-term and long-term purposes.
3.1.3. Local belongingness
The global aspect seems broken that calls for local belongingness to come to the rescue ( Brouder et al., 2020 ; Chang et al., 2020 ). During the pandemic and post-COVID-19, domestic tourism is poised to dominate the scene with most travellers coming from nearby areas ( Haywood, 2020 ). In many places, domestic travel is limited to visiting friends and relatives, but this will expand to leisure tourism soon. International travel will gradually revive when the borders open and international flights are permitted to operate without any hindrances ( Baum & Hai, 2020 ). Many countries and regions have restricted movements by imposing bans and other stringent requirements on entry and exit, which has subtly impacted the global tourism industry. According to Higgins-Desbiolles (2020) and Baum and Hai (2020) , the right to travel or enjoy gainful employment in the hospitality and tourism industry will not be allowed in the near-immediate future. “Tourism bubbles,” or local links built during the disaster, will act as a flexible plan. Future travel will depend on combined self-care, such as the suggestion to open the Trans-Tasman bubble between Australia and New Zealand ( Carr, 2020 ), or the potential fast-tracking of immigration clearance between the Republic of Korea and China ( Mostafanezhad et al., 2020 ). The feeling of belongingness among locals will dictate terms for the revival of the tourism industry.
3.1.4. Consumer and employee confidence
It is essential to gain consumer confidence to restart the halted industry of tourism. Learning from disaster planning and fighting the drive to turn away from failures experienced in the future are the critical pathways to be followed ( Rivera, 2020 ). The revival of the tourism industry will depend on boosting confidence in travelling and lessening the perception of risk involved ( Assaf & Scuderi, 2020 ). The impact of COVID-19 influences consumers' perception of tourism product and services ( Yu et al., 2020 ). Mao et al. (2020) focuses on human capital and gaining employee confidence.
3.2. Transformation to the new global economic order
Transformations like restarting, reorganizing, and assimilating the tourism industry according to the latest standards and rules are required to revive the industry ( Lew et al., 2020 ). The renewal will be impacted by the government's response to climate change and the need for a carbon-free economy. After the pandemic, the global economic and political systems will encompass changing patterns concerning climate change mitigation, sustainable tourism, local communities, and society's well-being.
3.2.1. Sustainable tourism
The present times are the most appropriate to promote a sustainable and equitable tourism industry ( Benjamin et al., 2020 ). As per Carr (2020) , original cultural sites suggest happiness, physical condition, environmental responsibility, and conventional ecological information. Such sites form the future of “cultural sustainability” and it is essential to manage these prudently for the development of the economy. In the aftermath of COVID-19, the tourism industry is bound to be reorganized based on actual planning and not just paperwork. The industry needs to be oriented toward education, environmental and social justice, and racial healing. There is a need for wary people (For instance, tourists, local communities, SMEs, Government) to take advantage of the present grave situation as it will allow more tourist experiences. The industry's service providers need to be encouraged to push a new demand by changing their unsustainable product offers. Such measures can connect, support, and take care of the whole tourism industry to everyone's advantage ( Stankov et al., 2020 ). The market players should also confront the means and systems that will prevent and transform harmful and weak tourism ( Higgins-Desbiolles, 2020 ). There is an essential requirement for a charter for setting up a stable and sustainable tourism industry. There is a disconnect between what UNWTO (World Tourism Organization) is preaching (sustainability) and what is exercising (growth expansion). These disconnects need to be understood and repaired before considering tourism's future ( Brouder et al., 2020 ; Nepal, 2020 ). The ongoing impermanent process of deglobalization has presented the tourism industry with a unique opportunity to recreate sustainability by leaving aside the “dark sides” of recent years, such as environmental deprivation, economic abuse, or congestion ( Niewiadomski, 2020 ). Sustainability is a continuous procedure to attain positive outcomes and is defined by changing beliefs, wishes, information, skills, and public awareness ( Galvani et al., 2020 ). Expert knowledge and experience ( Chang et al., 2020 ; Prideaux et al., 2020 ) need to be put into practice for shifting toward sustainable tourism.
3.2.2. Well-being of society
The South American concept Buen Vivir was examined by Everingham and Chassagne (2020) . This is a non-Western alternative to neoliberal capitalism for moving tourism priorities from economic growth to the welfare of, and meaningful connections in, the society at large and covering the ecological balance. The impact of COVID-19 is such that how people live and travel has changed completely. Preferences are now shifting toward connecting and shopping locally. The virus has offered an opportunity to the tourism industry to recreate and contribute to society's welfare ( Benjamin et al., 2020 ; Rowen, 2020 ). Life, health, environment, etc., are the focused areas during disasters. According to Benjamin et al. (2020) , it is essential to select a program that encourages sustainable and equitable development where people can acknowledge the planet and shift their current unsustainable views on tourism. In addition, Benjamin et al. (2020) point out that the change should concentrate on equity. This will necessitate positive and slow changes relating to systems' interconnectedness, where economic growth is not considered a default parameter of social and ecological well-being ( Cheer, 2020 ). The scholarship in the field of tourism needs to acknowledge tourism as an industry with a focus on societal well-being ( Benjamin et al., 2020 ).
3.2.3. Climate action
The pandemic's effect is worsening due to global climate changes ( Sharma et al., 2020 ; Sharma & Mahendru, 2020 ; Sharma, Talan, Srivastava, Yadav, & Chopra, 2020 ). Crossley (2020) studies the connection between pandemic and climate change and explores how the damage done to the environment can be repaired and can be attached to ecological grief. Emotional dynamics can further help understand tourists' behavior, covering the constant “attitude-behavior” gap concerning sustainable tourism. COVID-19 offers an opportunity to tackle the impact of climate change by shifting from the present model of “high resource consumption” to one that is “environmentally friendly” ( Gössling et al., 2020 ; Prideaux et al., 2020 ).
3.2.4. Local communities – the centres of transformation.
Local communities are the centres of transformation for the tourism industry during this pandemic. There may be future disagreements in local areas as tourists take the help of these local communities and governments for their business. Changes being considered by tourist destinations relating to modifications in a carbon-free economy are significant (Rideau et al., 2020). Changes at the local level may help restore neocolonial and neoliberal biases ( Everingham & Chassagne, 2020 ; Renaud, 2020 ; Tremblay-Huet, 2020 ).
Since the tourism industry has come to a halt and social distancing acts are relevant, even small-scale local-level activity is considered harmful. People have to think about the local community at large ( Lapointe, 2020 ). According to Renaud (2020) , the industry of cruise tourism should approve a “local mobility” model, which means that large cruise ships will be forbidden, but a fleet of smaller ships will be allowed. During the pandemic, social unity, self-sacrifice, and a sympathetic attitude are as significant as wearing a face mask to protect oneself and others. Post-COVID-19 times will allow service providers to rethink and reset the tourism industry for the future. There is a need for a “community-centered tourism framework” with responsible approaches to reset, redescribe, and refamiliarize the tourism industry in the interest of local communities. A deeper understanding of remote communities' challenges and acts may help transform the sector ( Tremblay-Huet, 2020 ). Some research studies consider these times as a defining moment for resetting the industry of tourism ( Higgins-Desbiolles, 2020 ). Developed countries are considering domestic or “proximity tourism” based on local thought and local acting theory.
4. A resilience-based framework for the new global economic order
Based on literature review, we propose a resilience-based framework for the new global economic order ( Fig. 3 ). This framework stems from the challenges posed by COVID-19 and the containment measures (such as lockdown) to the global tourism industry. The advisories issued to the tourists by various governments have further added fuel to the fire, resulting in the decline of revenues ( World Tourism Organization, 2020 ). The tourism industry seems to have moved from “over-tourism” to “non-tourism” at once ( Gössling et al., 2020 ). The increasing unemployment in other sectors of the global economy will also reflect in the number of tourist visits in the coming years. Segments of the tourism industry, including airlines, hospitality, sports events, restaurants, and cruises, are bound to be hammered by the pandemic. The proposed resilience-based framework can help transform the industry both during and after COVID-19.

Resilience-based framework for the new global economic order.
Organizational studies are focusing on sustainable change deal with resilience and deployment of adaptive capabilities by providing insights into recovery responses. Crises and emergencies such as COVID-19 also extend global visibility and understanding. This pandemic will contribute to creating new business models, which will essentially determine the industry's chances of survival by transforming it into a much more sustainable form. The tourism industry needs to demonstrate resilience from several sides. We broadly propose that three segments, namely, governments, market players, and local communities, need to get their act together to lend resilience to the industry. Technological innovations need to rise to a higher level for speeding up creations in tourism and hospitality. Artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of things (IoT), and technologies relating to location, navigation, drones, and robotics, are a few areas that need enhancements. This can promote flexible thinking within the tourism industry. This pandemic has compelled industry leaders to explore and analyze other better-suited technologies to reboot the industry and regain consumer confidence. Existing literature notes that the tourism industry has previously been quick to bounce back from the shocks of epidemics, pandemics, and global crises. However, governments realize that the shock of COVID-19 is unique since it is not possible to market the unsold capacity in coming years, causing a permanent setback for the industry. Governments should strive to build an atmosphere in which they attract investors through a variety of opportunities in the prevalent spirit of neoliberalism, such as offering tax breaks, relaxing strict land-use laws, etc. ( Brouder, 2020 ). Governments may promote the local embeddedness of tourism businesses to improve the element of belongingness. Supporting these arguments, Di Domenico, Haugh, and Tracey (2010) observe that local economies react to crises by working together and through social work, and Johannisson and Olaison (2007) note that rural firms have better prospects of recovery than their urban counterparts. Henceforth, the support from the government, coupled with local belongingness, may pave the way for the transformation of the tourism industry. The challenge is different for large-scale multinational players in the industry, focusing on local supply chains to minimize the costs. They may need to review their activities and rely on narrower and sub-national supply chains. This may include sourcing more resources locally, be it food, raw materials, service providers, or the composition of the workforce. Post-pandemic times may entail a long-term decrease in the appeal of certain growth spots now deemed too risky. Such a situation may augur well for less popular, less populated regions by providing them the opportunity to improve their appeal as potential tourism destinations.
Resilience from all sides of the value-chain may transform the tourism industry into the new global economic order characterized by sustainable tourism, climate action, societal well-being, and involvement of local communities. Studies have observed that the tourism industry indirectly contributes to pandemics in multiple ways, including food wastages leading to industrialized food production ( Hall & Gössling, 2013 ), human interference with wildlife and deforestation ( Barlow et al., 2016 ; Lade et al., 2020 ), and climate change conditions ( Scott, Hall, & Gössling, 2019 ). The lockdown in many countries and the adoption of significant restrictions on borders has also drastically affected the tourism economy worldwide. The movement from “over-tourism” to “under-tourism” is bound to reverse the scene of climate change to a large extent ( Hall & Gössling, 2013 ). COVID-19 is leading to some positive outcomes for the tourism industry. Declined demand in the aviation industry is already causing airlines to phase out outdated aircraft. Restrictions on overseas travel for international students, business travellers, political leaders, etc., are leading to increased leverage from video-conferencing ( Banister & Stead, 2004 ; Cohen, Hanna, & Gössling, 2018 ). These changes are bound to reorient the global tourism industry in a “sustainable” way, which focuses more on inclusive development, rather than the abstract notion of “growth.” Carbon footprint reductions may gain more traction worldwide, as is already seen across main tourist destinations. Similarly, the mobility of visitors could transform significantly, not only in the immediate future but over a long period. The relentless neophilia and the disturbing desire for (often irresponsible) exploration in distant places may be replaced by recreation and travel much closer to home.
5. Future research agenda
COVID-19 has triggered unprecedented casualties for mankind in life-changing circumstances. The shock and effect of this pandemic are so strong that research work across all fields is subject to pre-COVID-19 and post-COVID-19 classifications. The post-COVID-19 research is bound to be characterized by economic, environmental, and social setbacks, and the policy suggestions to counter those. Given the tourism industry's sensitivity to this pandemic situation, the body of knowledge in the field of tourism needs some quick and sound work to prepare for the future. Following most downloaded review articles ( Dhaliwal et al., 2020 ; Paul & Benito, 2018 ), we provide directions for future research in this section to set up an interesting future research agenda for the research in the tourism industry in the post-COVID-19 period. It is important to examine how businesses can translate this crisis chaos into transformative innovation. Never before has tourism research felt the need to hold its purpose as much as today.
Post-crisis tourism research must align academic and corporate interests. We present the future research agenda in two segments. One, based on the gaps in the existing literature, we present the research questions for tourism research to explore different sub-topics in the context of COVID-19. Two, we present a research agenda to test our resilience-based framework ( Table 4 ) and derive propositions which can be used as testable hypotheses in future studies by others.
Themes and research questions for future scholarship in tourism and COVID-19.
Future researchers may test the resilience-based framework in line with Fig. 3 . Using the tenets included in the resilience framework, we derive propositions in this study which can be used as either research questions or hypotheses in future studies.
Tourism industry has to resort to internal measures, including technology innovation and building consumer and employee confidence, to build resilience to fight COVID-19;
External factors, including government measures and local belongingness, significantly contribute to the tourism industry's quest for resilience to revive from the COVID-19 shock;
Resilience strategies based on internal and external factors mediate the revival of the tourism industry from the shock of COVID-19 by transforming it to the new global economic order, which comprises sustainable tourism, the well-being of society, mitigating climate change, and strengthening of local communities.
These topical ideations can be actualized by applying versatile methodologies. The case-study method is by far the most prominently used method in tourism research in the context of a crisis. However, as suggested by most of the related works ( Haywood, 2020 ; Nepal, 2020 ; Rivera, 2020 ; Tsionas, 2020 ), it would be advisable to employ conceptual, quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods to inform the questions about the contemporary tourism industry.
6. Conclusion
The tourism industry was seen as a major cause and carrier of the novel coronavirus that triggered the outbreak of COVID-19. The unsustainable practices of the industry didn't help the cause of sustainable living worldwide. The pandemic has nearly brought the global tourism industry to a halt. All stakeholders in the industry must work together to make the industry sufficiently resilient to deal with the crisis. Based on the studies conducted to understand the tourism industry in the context of COVID-19, we propose a resilience-based framework for the industry. Through our framework, we argue that with the help of the resilient approach from governments, market players, technology innovators, and the workforce employed in the industry, the tourism sector may end up evolving in a much more sustainable way post-pandemic. The involvement of local communities is going to be immensely critical in this journey, as the restrictions on international travel may stay longer than anticipated. Such developments would widen not only the base of the tourism industry but also present opportunities for less-developed tourism spots to grow further. Large-scale tourism players would need a reboot to survive in post-pandemic times. Still, acting in line with our resilience-based framework, small-scale players certainly can emerge victorious and ensure the well-being of the society at large while also facilitating sustainable tourism.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no funding were received for this research.
Biographies

Gagan Deep Sharma is an Associate Professor at the University School of Management Studies, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, New Delhi, India. His fields of research interest includes Systematic reviewing, Sustainable development, Resliience-based strategy, Neuroeconomics, and Behavioural economics.

Asha Thomas is Assistant Professor at Jagan Institute of Management Studies (JIMS), New Delhi. Her areas of research interest include knowledge management, Organizational behavior, Marketing. She has about 12 years of experience in teaching, as well as over 3 years of experience in IT and Telecom Industry. She is currently pursuing Doctorate program as a Part-time Research Scholar from the prestigious Delhi Technological University. She has several national and international research papers to her credit. She has also presented papers in National and International Conferences. She also serves as reviewer for several top international journals.

Justin Paul , serves as Editor-in-chief of International Journal of Consumer studies and as an Associate Editor of Journal of Business Research. He is a full professor of PHD & MBA programs, University of Puerto Rico, USA. He holds three honorary titles as ‘Distinguished Professor’ with three reputed universities- Indian Institute of Management (IIM—K) and SIBM, Pune and MS university in TN state of India. He has published over 100 articles in SSCI listed journals. He is an author of 8 books. He has served as a faculty member with University of Washington and Rollins college, Florida, USA. His website is drjustinpaul.com.
- Alves J.C., Lok T.C., Luo Y., Hao W. Research Square; 2020. Crisis Management for Small Business during the COVID-19 outbreak: Survival, resilience and renewal strategies of firms in Macau; pp. 1–29. PREPRINT (June) [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Assaf A., Scuderi R. COVID-19 and the recovery of the tourism industry. Tourism Economics. 2020 doi: 10.1177/1354816620933712. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Banister D., Stead D. Impact of information and communications technology on transport. Transport Reviews. 2004 doi: 10.1080/0144164042000206060. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bansal S., Garg I., Sharma G.D. Social entrepreneurship as a path for social change and driver of sustainable development: A systematic review and research agenda. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2019; 11 (4):1091. doi: 10.3390/su11041091. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barlow J., Lennox G.D., Ferreira J., Berenguer E., Lees A.C., Nally R.M.…Gardner T.A. Anthropogenic disturbance in tropical forests can double biodiversity loss from deforestation. Nature. 2016; 535 (7610):144–147. doi: 10.1038/nature18326. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baum T., Hai N.T.T. Hospitality, tourism, human rights and the impact of COVID-19. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management. 2020; 32 (7):2397–2407. doi: 10.1108/IJCHM-03-2020-0242. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Benjamin S., Dillette A., Alderman D.H. “We can’t return to normal”: Committing to tourism equity in the post-pandemic age. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1759130. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brouder P. Reset redux: Possible evolutionary pathways towards the transformation of tourism in a COVID-19 world. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1760928. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brouder P., Teoh S., Salazar N.B., Mostafanezhad M., Pung J.M., Lapointe D.…Clausen H.B. Reflections and discussions: Tourism matters in the new normal post COVID-19. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1770325. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Buckley R. Conservation implications of COVID19: Effects via tourism and extractive industries. Biological Conservation. 2020; 247 doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2020.108640. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carr A. COVID-19, indigenous peoples and tourism: A view from New Zealand. Tourism Geographies. 2020; 0 (0):1–12. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1768433. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chang C.L., McAleer M., Ramos V. A charter for sustainable tourism after COVID-19. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2020; 12 (9) doi: 10.3390/su12093671. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cheer J.M. Human flourishing, tourism transformation and COVID-19: A conceptual touchstone. Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–11. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1765016. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen H., Huang X., Li Z. A content analysis of Chinese news coverage on COVID-19 and tourism. Current Issues in Tourism. 2020:1–8. doi: 10.1080/13683500.2020.1763269. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen S.A., Hanna P., Gössling S. The dark side of business travel: A media comments analysis. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment. 2018 doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2017.01.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook D.J., Greengold N.L., Ellrodt A.G., Weingarten S.R. The relation between systematic reviews and practice guidelines. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1997; 127 :210–216. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-127-3-199708010-00006. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook D.J., Mulrow C.D., Haynes R.B. Systematic reviews: Synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1997; 126 :376–380. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-126-5-199703010-00006. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Crossley É. Ecological grief generates desire for environmental healing in tourism after COVID-19. Tourism Geographies. 2020; 0 (0):1–10. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1759133. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dhaliwal A., Singh D.P., Paul J. The consumer behavior of luxury goods: A review and research agenda. Journal of Strategic Marketing. 2020:1–27. [ Google Scholar ]
- Di Domenico M.L., Haugh H., Tracey P. Social bricolage: Theorizing social value creation in social enterprises. Entrepreneurship: Theory and Practice. 2010 doi: 10.1111/j.1540-6520.2010.00370.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Everingham P., Chassagne N. Post COVID-19 ecological and social reset: Moving away from capitalist growth models towards tourism as Buen Vivir. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1762119. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fitriasari F. How do small and medium-sized enterprises (SME) survive the COVID-19 outbreak? Jurnal Inovasi Ekonomi. 2020; 5 (3):53–62. doi: 10.22219/jiko.v5i3.11838. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gallego I., Font X. Changes in air passenger demand as a result of the COVID-19 crisis: Using Big Data to inform tourism policy. Journal of Sustainable Tourism. 2020 doi: 10.1080/09669582.2020.1773476. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Galvani A., Lew A.A., Perez M.S. COVID-19 is expanding global consciousness and the sustainability of travel and tourism. Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–10. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1760924. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gilal F.G., Zhang J., Paul J., Gilal N.G. The role of self-determination theory in marketing science: An integrative review and agenda for research. European Management Journal. 2019 doi: 10.1016/j.emj.2018.10.004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gössling S., Scott D., Hall C.M. Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. Journal of Sustainable Tourism. 2020:1–20. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2020.1758708. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gretzel U., Fuchs M., Baggio R., Hoepken W., Law R., Neidhardt J.…Xiang Z. e-Tourism beyond COVID-19: A call for transformative research. Information Technology and Tourism. 2020; 22 (2):187–203. doi: 10.1007/s40558-020-00181-3. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hall C.M., Gössling S. Sustainable culinary systems: Local foods, innovation, tourism and hospitality. 2013. Sustainable Culinary Systems: Local foods, innovation, tourism and hospitality; pp. 1–314. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hall C.M., Scott D., Gössling S. Pandemics, transformations and tourism: Be careful what you wish for. Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–22. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1759131. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hao A., al e. Two decades of research on nation branding: A review and future research agenda. International Marketing Review. 2019 doi: 10.1108/IMR-01-2019-0028. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Haywood K.M. A post-COVID future: Tourism community re-imagined and enabled. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1762120. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Higgins-Desbiolles F. Socialising tourism for social and ecological justice after COVID-19. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1757748. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Iaquinto B.L. Tourist as vector: Viral mobilities of COVID-19. Dialogues in Human Geography. 2020; 10 (2):174–177. doi: 10.1177/2043820620934250. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ioannides D., Gyimóthy S. The COVID-19 crisis as an opportunity for escaping the unsustainable global tourism path. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1763445. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jain M., Sharma G.D., Mahendru M. Can i sustain my happiness? A review, critique and research agenda for economics of happiness. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2019; 11 (22):6375. doi: 10.3390/su11226375. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johannisson B., Olaison L. The moment of truth - reconstructing entrepreneurship and social capital in the eye of the storm. Review of Social Economy. 2007 doi: 10.1080/00346760601132188. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lade S.J., Steffen W., de Vries W., Carpenter S.R., Donges J.F., Gerten D.…Rockström J. Human impacts on planetary boundaries amplified by Earth system interactions. Nature Sustainability. 2020; 3 (2):119–128. doi: 10.1038/s41893-019-0454-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lapointe D. Reconnecting tourism after COVID-19: The paradox of alterity in tourism areas. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1762115. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lew A.A., Cheer J.M., Haywood M., Brouder P., Salazar N.B. Visions of travel and tourism after the global COVID-19 transformation of 2020. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1770326. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mao Y., He J., Morrison A.M., Andres Coca-Stefaniak J. Effects of tourism CSR on employee psychological capital in the COVID-19 crisis: From the perspective of conservation of resources theory. Current Issues in Tourism. 2020 doi: 10.1080/13683500.2020.1770706. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McCartney G. The impact of the coronavirus outbreak on Macao. From tourism lockdown to tourism recovery. Current Issues in Tourism. 2020 doi: 10.1080/13683500.2020.1762549. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mehrolia S., Alagarsamy S., Solaikutty V.M. Customers response to online food delivery services during COVID-19 outbreak using binary logistic regression. International Journal of Consumer Studies. 2020 doi: 10.1111/ijcs.12630. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mostafanezhad M., Cheer J.M., Sin H.L. Geopolitical anxieties of tourism: (Im)mobilities of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dialogues in Human Geography. 2020; 10 (2):182–186. doi: 10.1177/2043820620934206. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nepal S.K. Travel and tourism after COVID-19 – Business as usual or opportunity to reset? Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–5. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1760926. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Niewiadomski P. COVID-19: From temporary de-globalisation to a re-discovery of tourism? Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1757749. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul J., Benito G.R. A review of research on outward foreign direct investment from emerging countries, including China: What do we know, how do we know and where should we be heading? Asia Pacific Business Review. 2018; 24 (1):90–115. [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul J., Criado A.R. The art of writing literature review: What do we know and what do we need to know? International Business Review. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.ibusrev.2020.101717. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul J., Feliciano-Cestero M.M. Five decades of research on foreign direct investment by MNEs: An overview and research agenda. Journal of Business Research. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.04.017. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paul J., Mas E. Toward a 7-P framework for international marketing. Journal of Strategic Marketing. 2020; 28 (8):681–701. doi: 10.1080/0965254X.2019.1569111. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Prideaux B., Thompson M., Pabel A. Lessons from COVID-19 can prepare global tourism for the economic transformation needed to combat climate change. Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–12. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1762117. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Renaud L. Reconsidering global mobility–distancing from mass cruise tourism in the aftermath of COVID-19. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1762116. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rivera M.A. Hitting the reset button for hospitality research in times of crisis: Covid19 and beyond. International Journal of Hospitality Management. 2020; 87 doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102528. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Romagosa F. The COVID-19 crisis: Opportunities for sustainable and proximity tourism. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1763447. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosado-Serrano A., Paul J., Dikova D. International franchising: A literature review and research agenda. Journal of Business Research. 2018 doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.12.049. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rowen I. The transformational festival as a subversive toolbox for a transformed tourism: Lessons from Burning Man for a COVID-19 world. Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–8. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1759132. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scott D., Hall C.M., Gössling S. Global tourism vulnerability to climate change. Annals of Tourism Research. 2019; 77 :49–61. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2019.05.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sharma G.D., Ghura A.S., Mahendru M., Erkut B., Kaur T., Bedi D. Panic during COVID-19 pandemic! A qualitative investigation into the psychosocial experiences of a sample of Indian people. Frontiers in Psychology. 2020; 11 (October):1–7. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.575491. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sharma G.D., Mahendru M. Lives or livelihood: Insights from locked-down India due to COVID19. Social Sciences & Humanities Open. 2020; 2 (1) doi: 10.1016/j.ssaho.2020.100036. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sharma G.D., Talan G., Srivastava M., Yadav A., Chopra R. A qualitative enquiry into strategic and operational responses to Covid-19 challenges in South Asia. Journal of Public Affairs. 2020 doi: 10.1002/pa.2195. May. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stankov U., Filimonau V., Vujičić M.D. A mindful shift: An opportunity for mindfulness-driven tourism in a post-pandemic world. Tourism Geographies. 2020:1–10. doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1768432. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Supardi S., Kudus U.M., Hadi S., Indonesia U.I. New perspective on the resilience of SMEs proactive, adaptive, reactive from business turbulence: A systematic review. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology. 2020; XII (V) doi: 10.37896/jxat12.05/1524. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Talan G., Sharma G.D. Doing well by doing good: A systematic review and research agenda for sustainable investment. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2019; 11 (2):353. doi: 10.3390/su11020353. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thomas A., Chopra M. Digital transformation in business and society. Palgrave Macmillan; Cham: 2020. On how big data revolutionizes knowledge management; pp. 39–60. [ Google Scholar ]
- Thomas A., Paul J. Knowledge transfer and innovation through university- industry partnership: An integrated theoretical view. Knowledge Management Research & Practice. 2019; 17 (4):436–448. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tranfield D., Denyer D., Smart P. Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. British Journal of Management. 2003; 14 :207–222. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tremblay-Huet S. COVID-19 leads to a new context for the “right to tourism”: A reset of tourists’ perspectives on space appropriation is needed. Tourism Geographies. 2020 doi: 10.1080/14616688.2020.1759136. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trupp A., Dolezal C. Tourism and the sustainable development goals in Southeast Asia. Austrial Journal of South-East Asian Studies. 2020; 13 (1):1–16. doi: 10.18111/9789284417254. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tsionas M.G. COVID-19 and gradual adjustment in the tourism, hospitality, and related industries. Tourism Economics. 2020 doi: 10.1177/1354816620933039. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wolf F.M., Shea J.A., Albanese M.A. Toward setting a research agenda for systematic reviews of evidence of the effects of medical education. Teaching and Learning in Medicine. 2001; 13 :53–60. doi: 10.1207/s15328015tlm1301_11. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World Health Organization . World Health Organization; 2017. Rapid reviews to strengthen health policy and systems: A practical guide. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World Tourism Organization International tourism numbers could fall 60–80% in 2020. 2020. https://www.unwto.org/news/covid-19-international-tourist-numbers-could-fall-60-80-in-2020 [Press Release −7 May 2020]. Retrieved July 22, 2020, from.
- Yu F., Du L., Ojcius D.M., Pan C., Jiang S. Measures for diagnosing and treating infections by a novel coronavirus responsible for a pneumonia outbreak originating in Wuhan, China. Microbes Infect. 2020; 22 (2):74–79. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2020.01.003. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 13 May 2024
The influence of rural tourism landscape perception on tourists’ revisit intentions—a case study in Nangou village, China
- Yuxiao Kou 1 &
- Xiaojie Xue 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 620 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Environmental studies
Rural tourism development has an important impact on optimizing the rural industrial structure and stimulating local economic growth. China’s Rural Revitalization Strategy has promoted the development of rural tourism nationwide and emphasized Chinese characteristics in the process of local development. Based on the theoretical analysis of landscape perception, this article uses the external Landscape Perception→Satisfaction→Revisit Intention influence path as a theoretical research framework to construct a structural equation model to analyze the willingness of tourists to revisit rural tourism destinations. We selected Nangou Village, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province, as a key model village for rural revitalization, and conducted an empirical analysis. The empirical analysis results show that landscape perception has a significant positive impact on satisfaction and revisit intention. Tourist satisfaction has a significant positive impact on revisit intention and plays an intermediary role between landscape perception and revisit intention. The five dimensions of natural ecology, historical culture, leisure recreation, research experience, and integral route under landscape perception are all significantly positively correlated with revisit intention, with historical culture and integral route having the greatest impact on landscape perception. The survey about Nangou Village verifies the relationship between landscape perception, satisfaction, and tourists’ revisit intention. Based on the objective data analysis results, this study puts forward suggestions for optimizing Nangou Village’s tourism landscapes and improving tourists’ willingness to revisit from three aspects: deeply excavating rural historical and cultural resources, shaping the national red culture brand, and creating rural tourism boutique routes. It is hoped that the quantitative research method of landscape perception theory in Nangou Village can also provide a reference and inspiration for similar rural tourism planning.
Similar content being viewed by others
Impact of ecological presence in virtual reality tourism on enhancing tourists’ environmentally responsible behavior
Evaluating the potential of suburban and rural areas for tourism and recreation, including individual short-term tourism under pandemic conditions
A geographical perspective on the formation of urban nightlife landscape
Introduction.
Rural tourism, which originated in Europe in the mid-19th century (He, 2003 ), has constructed a new type of urban–rural relationship—the attachment of the cities to the countryside and the integration of the countryside with the city (Liu, 2018 ). In the 1990s, with the continuous improvement of China’s urbanization level, rural tourism began to rise in response to the demand for returning to nature and simplicity (Guo and Han, 2010 ). The main body of rural tourism (i.e., the main target) is urban residents, and its object is a combination of enjoying the agricultural ecological environment, agricultural production activities, and traditional folk customs. These are presented through tourism industry planning and landscape product design, which is based on the unique production, life, and ecological resources in the countryside, and integrates sightseeing, participation, leisure, vacation, recuperation, entertainment, shopping, and other tourism activities (Zhang, 2006 ).
Rural tourism development is of great significance for optimizing the industrial structure in rural areas, realizing the linked development of primary, secondary, and tertiary industries, increasing farmers’ income, stimulating rural economic development, and accelerating the integration of urban and rural areas (Lu et al., 2019 ). Since the implementation of the Rural Revitalization Strategy, China has taken increasing rural tourism as one of the important ways to achieve it (Yin and Li, 2018 ) and has launched construction projects nationwide.
Rural tourism in China started with self-organized agritainment, with farming experiences and sightseeing leisure as the main projects (Guo et al., 2000 ). Early studies have found that rural tourism projects embodying regional characteristics, folklore, and participatory farming activities present stronger competitive advantages in terms of higher rates of tourists’ participation and revisit rates (Wang et al., 2005 ). In the process of the “localization” of rural tourism in China, rural tourism has undergone a top-down evolution. Since the central government’s comprehensive deployment of new rural construction in 2006, national departments and local governments have issued a series of policies to promote the development of rural tourism, leisure agriculture, and culture, which have promoted the prosperity of diversified, high-quality, and distinctive practices of rural tourism nationwide (Ma et al., 2007 ). The rural revitalization strategy is a crucial national policy at present in China, driving various initiatives such as the construction of beautiful countryside and the development of the rural tourism industry. This policy has given rise to trends like the inheritance of local culture, the promotion of green ecological concepts, and the integration of industries. However, there are still challenges encountered, such as the homogenization in tourism development and the necessity to coordinate the development of industries, culture, ecology, and economy. Under the policy guidance of developing the agricultural economy and revitalizing national culture, China has explored rural tourism landscape products that fit the national cultural context and market demand of the country. Its characteristics are mainly reflected at two levels: First, it focuses on the integration of ethnic and regional cultural perspectives. Rural tourism planning focuses on identifying geographical cultural aspects (Sun et al., 2008 ), integrating traditional Chinese red culture and local characteristics (Huang, 2003 ) into tourism landscape products, and creating Chinese cultural brands. Second, we should focus on upgrading traditional sightseeing, farming, folk customs, and leisure tourism projects, develop in-depth experiential research projects, and create a comprehensive boutique tourism route (Chen et al., 2021 ).
With the prosperity of rural tourism, the related research has gradually increased. Zhai ( 2015 ) pointed out that unique cultural and geographical landscapes are not only objects that should be emphasized and protected in the construction of the countryside but also important resources for the development of rural tourism. Zhang and Wang ( 2018 ) believed that the essence of rural tourism is the cultural experience of tourists in the countryside. Chen ( 2020 ) studied the “local sentiment” from an anthropological perspective as an important factor in promoting the development of China’s rural tourism market. Xu and Tang ( 2016 ) argued that local characteristics are essential for rural landscape construction, proposing the planning and construction strategy of “livability, suitability for industry, suitability for tourism, and suitability for culture”. Shi ( 2021 ) pointed out the significance of ecological esthetics theory to the planning and design of rural tourism landscapes and proposed the strategy of integrating local characteristics with ecological features and improving the ecosystems through artistic techniques. Most of the research has focused on the development and upgrading strategies of Chinese rural tourism landscapes from the supply-side perspective but lacks studies on what kind of experience and value tourists expect from the demand-side perspective, and the research methods lack scientific quantitative analyses.
Satisfaction and revisit intention are used to evaluate the perception and experience of rural landscapes, which directly reflect tourists’ actual feelings about the resource endowment, operational management effectiveness, social and cultural environment, and rural landscape planning in the area (Zhang et al., 2014 ). Landscape perception emphasizes the mutual influence of tourists’ perception of the tourism environment (Echtner and Ritchie, 1993 ), recognition of the location (Middleton and Hawkins, 1998 ), preferences (Zhang et al., 2017 ), and other aspects, while the revisit intention reflects tourists’ willingness to experience an activity again (Xu et al., 2014 ). Strengthening tourists’ revisit intention in rural tourism is of great significance for stabilizing and increasing rural income and promoting sustainable development in rural areas. It is an important measure of whether the quality and style of rural areas have been improved and whether rural revitalization has been promoted (Li et al., 2022 ). Therefore, based on the objective data analysis results of tourists’ perception and satisfaction with rural tourism landscapes and their revisit intention, we can objectively and reasonably propose upgrading and optimization strategies for rural landscapes. The relationship diagram is shown in Fig. 1 .
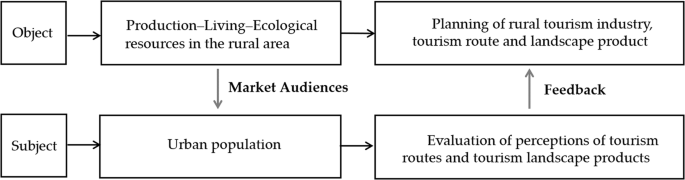
The figure illustrates the interaction between subject and object in rural tourism.
This study selected Nangou Village in Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province, as the research object. Based on the construction of traditional rural tourism facilities, Nangou Village has developed a certain number of distinctive tourism products that integrate production, learning, and research based on the Ansai folk culture and revolutionary humanistic resources in the region. However, as a key model village in China’s rural revitalization strategy, Nangou Village is still exploring a new round of optimization and upgrading. On the basis of the theory of landscape perception and a demonstrated impact mechanism between landscape perception and satisfaction, as well as revisit intention, combined with the perception results, this article proposes feasible strategies for the planning, design, and optimization of the tourism industry in Nangou Village.
Theoretical foundation
Landscape perception theory.
Landscape perception theory originated in the 1950s and is an independent theory developed for environmental psychology research. It combines the research paradigms and methods of environmental psychology and human geography (Deng, 2006 ) and aims to study people’s preferences (Guo et al., 2004 ), perception (Crompton, 1979 ; Fan et al., 2014 ), and satisfaction levels (Tribe and Snaith, 1998 ; Chi and Qu, 2008 ) of the objective environment. Ervin Zube et al. ( 1982 ) integrated the existing research paradigms of landscape perception—expert paradigm, psychophysical paradigm, cognitive paradigm, and empirical paradigm—and further proposed a theoretical model to unify humans, landscapes, and the results of their interaction into a closed loop. Landscape perception is essentially a process in which the human brain acquires environmental information through the sensory systems and then processes it (Purcell, 1987 ). In the interactive relationship between people and landscapes, the landscape is the perceived object while people are the main subjects of the environmental perception. The perception of landscapes is related to individual differences, involving experiences, memories, cognitive level, and social–cultural backgrounds (Qin, 2022 ; Cosgrove, 1984 ).
Based on subjective feelings and psychological evaluations of the surrounding environment, landscape perception further affects individuals’ emotions and environmental behaviors. An emotional state is a psychological product of individuals’ acceptance of external stimuli, combined with their own experiences and cognition, which is an important driving force that can promote individuals’ interactive behavioral responses. Motloch ( 2000 ) proposed that landscape perception will also generate emotional load after observation, recognition, and meaning attribution. Song ( 2013 ) summarizes it as a process of landscape stimulation, generation of feelings, sublimation of cognition, and emotional response. For such emotional reactions, scholars commonly use satisfaction and place identity to measure the positive affective state generated by landscape perception (Baker and Crompton, 2000 ). Behavioral responses are subjective reactions of people to approach or avoid external stimuli, which are especially influenced by their emotional state (Bitner, 1992 ; Mehrabian and Russell, 1974 ). Gobster ( 2008 ) argues that landscape perception is reflected both in cognitive and emotional aspects and that landscape preferences and emotional experiences can affect environmental behavior. Ostoić et al. ( 2017 ) believe that landscape perception emphasizes the mutual influence of tourists’ perceptions, recognition, preferences, and other aspects of the tourism environment, which can directly reflect the effectiveness of the tourism environment’s planning and design, and thus affect tourists’ behavior. In short, there are interactions between landscape environmental stimuli, emotional states, and behavioral responses, and landscape perception has a significant impact on an individual’s sense of environmental responsibility, environmental protection intention, and intention to revisit a destination (Wu et al., 2019 ).
Landscape perception and satisfaction, revisit intention
Satisfaction is a comprehensive feeling experienced by tourists during and after visiting a tourist destination (Chon, 1989 ). It can be an evaluation of a single dimension such as landscape products, tourism services, transportation accessibility, etc., or a comprehensive measure of overall satisfaction in multiple dimensions (Cole and Scott, 2004 ; Sailesh et al., 2023 ). Among them, the physical landscape environment is one of the most important dimensions that affects overall satisfaction (Chi and Qu, 2009 ). Oliver ( 1980 ) proposed the “expectation discrepancy model”, which refers to the process in which tourists form certain expectations based on their previous experiences before traveling, and then compare their expectations with their actual feelings during the travel process to determine their level of satisfaction. If the expectations are met, the tourists are satisfied; otherwise, they are not. The tourism landscape studied in this article is an important component in the study of tourist destination satisfaction, which directly affects the tourists’ selection of tourist destinations, consumption of tourism products and services, and willingness to revisit.
Behavioral intention is the result of rational cognitive processing of situational information by tourists, resulting from psychological comparison and judgment (perception value or satisfaction). In the existing research, tourists’ behavioral intentions are often described as tourists’ recommendation behavior and revisiting intention. Revisit intention refers to the behavioral intention of tourists to visit the destination again in the future (Hung and Petrick, 2011 ). Chen proposed that revisit intention should include two levels of behavioral intention: the intention of the tourists themselves to revisit this place, and the intention to recommend this place to their acquaintances. Xiu, on this basis, included whether tourists would prioritize this attraction in their travel choices into the evaluation indexes of revisit intention (Guo, 2016 ). In addition, some scholars have demonstrated that destination image perception, especially landscape perception, is a direct driver of tourists’ recommendation behavior and intention (Chew and Jahari, 2013 ; Nisco et al., 2015 ; Prayag et al., 2017 ), and satisfaction with the tourism destination is one of the strongest factors affecting revisiting behavior (Campo-Martínez et al., 2010 ; Humagain and Singleton, 2021 ).
In summary, the relationship between landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention has been demonstrated in relevant studies. In spite of this, it remains necessary to further the research on the influence paths of these three factors. For example, Xu et al. ( 2023 ) took the Qilian Village landscape renovation project as the subject of a case study to identify users’ perceptions of landscape characteristics through structural equation modeling. Although they explored the impact of landscape perception on satisfaction, no further study was conducted on users’ behavioral intentions via the influence paths. Similarly, Qu et al. ( 2023 ), referring to the ancient villages in southern Anhui as an example, explored the path to high-quality development of rural tourism from the perspective of the authenticity of rural landscapes. Despite the SPSS data analysis conducted to verify the positive correlation between satisfaction and revisit intention, they ignored the optimization strategies of landscape as the carrier of tourism, which thus affects the applicability of this research. Additionally, in China, there are few papers that quantitatively present tourists’ landscape demands and support planning strategies, with most research focusing on the subjective discussions of tourism landscape planning strategies from the perspective of the supply side. In conclusion, it remains imperative to conduct further research on the strategies of optimizing the design of rural tourism landscapes based on a complete demonstration of the influence paths of landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention, with the results of quantitative data analysis as guidance.

Research hypotheses
Landscape perception theory has been widely applied in tourism-related research and has gradually permeated into the research on rural tourism landscapes (Yang et al., 2022 ; Fan, 2020 ). The rural tourism landscape studied in this article, perceived as a physical environment, usually includes rural ecological landscapes, authentic historical and cultural landscapes, agricultural leisure and entertainment facilities, and experiential red revolutionary landscapes, and it also involves diachronic overall tourism routes.
Some scholars have explored the rationality of the path mechanism of the landscape perception–satisfaction–revisit intention in related studies, and they used the relevant results as a strategic basis for optimizing the development of rural tourism. For example, Acharya et al. ( 2023 ) showed that the better the tourism ecological environment is, the higher the satisfaction and revisit intention of tourists are, and the path from the ecological environment to the revisit intention of tourists needs to be connected by satisfaction. Geng et al. ( 2010 ) analyzed and demonstrated the positive impact of rural natural landscape satisfaction and sightseeing route satisfaction on tourists’ revisit intention using logistic model analysis. Queiroz ( 2017 ) found that cultural experiences can better reflect the authenticity of rural areas, and tourist satisfaction can be improved through the enhancement of cultural facilities, thereby promoting tourists’ willingness to revisit. Yang et al. ( 2022 ) believe that developing recreational activities with rural characteristics can stimulate tourists’ interest and participation, thereby enhancing their satisfaction and willingness to return. Zhou et al. ( 2016 ) posited that recreational facilities and entertainment activities are both important factors that attract tourists to choose rural tourism; in addition, a higher attractiveness of the tourism landscape increases the satisfaction of tourists, creating a greater impact on revisit intention.
Some scholars have further proposed and demonstrated that satisfaction plays a mediating role in the impact path of tourists’ landscape perception on their revisit intention. For example, Kim et al. ( 2013 ) conducted a survey in rural areas and found that satisfaction plays an intermediary role between tourists’ rural image perception and tourists’ revisit intention.Tu et al. ( 2017 )proposed that the internal mechanism of tourists’ behavioral intentions based on destination image perception may be achieved through the mediating effect of positive emotions such as satisfaction. Meng ( 2018 ) argued that in rural tourism, rural landscapes, and related service facilities are important manifestations of rurality, which affect tourists’ satisfaction with their travel experience and indirectly affect their revisit intention.
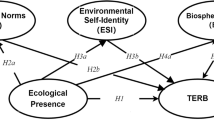
In summary, this study took Nangou Village as a research sample to explore the influence mechanism between rural tourism landscape perception and its associated satisfaction and revisit intention, and the following hypotheses were made (Fig. 2 ).
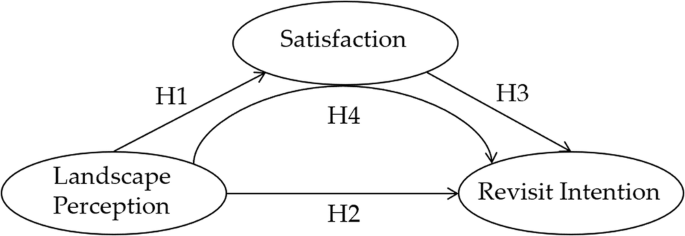
The figure presents the hypothesized relationship between the three variables.
Hypothesis 1 (H1) . Rural tourism landscape perception will positively affect the overall satisfaction of rural tourism.
Hypothesis 2 (H2) . Rural tourism landscape perception will positively affect the rural tourism revisit intention.
Hypothesis 3 (H3) . Rural tourism satisfaction will positively affect the rural tourism revisit intention.
Hypothesis 4 (H4) . Satisfaction will act as a mediator in the relationship between rural tourism landscape perception and revisit intention.
Study design
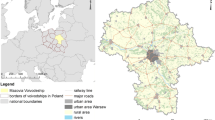
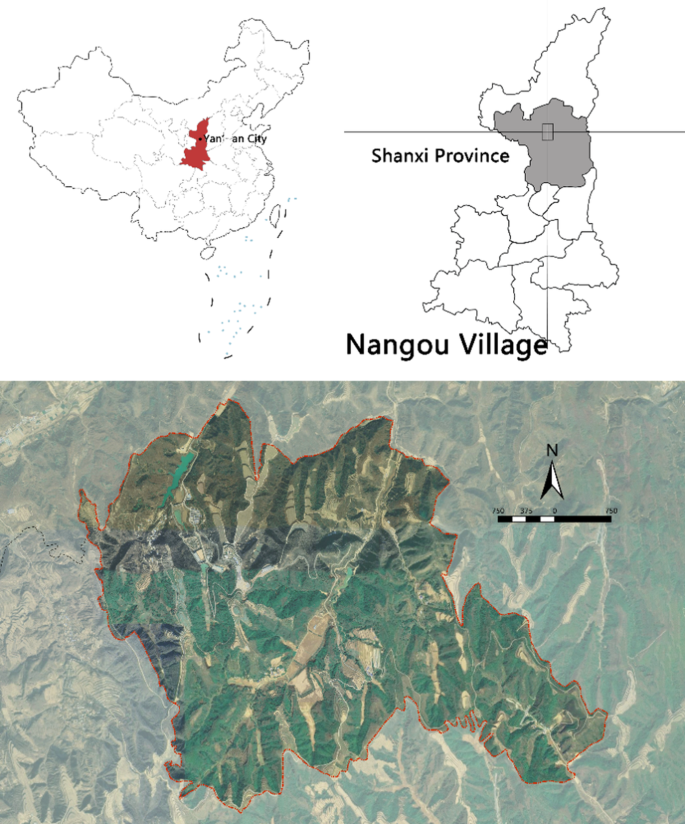
Nangou Village, the research object of this study, is located in Gaoqiao Town, Ansai District, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province, China, covering approximately 1716 hectares with seven natural villages under its jurisdiction, which are typical loess hilly villages (Fig. 3 ). As a key model village for rural revitalization, Nangou Village has a good natural ecological foundation and abundant agricultural and regional culture resources and has achieved preliminary linkages between the primary, secondary, and tertiary industries. In the first rural tourism development, Nangou Village built the Nangou Paradise for sightseeing and its supporting facilities, the Nangou Soil and Water Conservation Demonstration Park of Ansai District of Yan’an City, and the Agricultural Picking Experience Park, the red military camps based on Yan’an Red Culture, and various characteristic landscape pieces under the influence of Ansai’s unique regional culture, which form a comprehensive cultural tourism village. With the deepening of rural revitalization in China, Nangou Village will serve as a key area for the Ansai District to build a five-billion-level cultural tourism industry cluster, further expanding and upgrading the existing tourism landscape facilities. Therefore, this article aims to propose a scientific strategy for the upgrading and transformation of Nangou Village through subjective evaluation methods.
The figure presents the geographic location of the Nangou village.
Evaluation index construction
Based on the analysis and organization of the existing literature and the construction of the theoretical framework mentioned earlier, this study constructed evaluation indicators for three variables: landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention (Table 1 ).
LP—The research on rural tourism landscape perception is not yet perfect; this study tentatively divided the LP scale into five dimensions on the basis of previous research and combined with a review of the literature. Among them, the Natural Ecology sub-dimension involves the evaluation of the rural landscape’s pastoral characteristics, the quality of the ecological environment, and the integration of landscape facilities and natural ecology (Xie et al., 2002 ; Marianna et al., 2023 ). The Historical Culture sub-dimension involves the evaluation of the regional history and culture of the rural tourism landscapes, the recognizability of the cultural symbols, and the authenticity of the cultural preservation (Huang et al., 2015 ). The Leisure Recreation sub-dimension involves the evaluation of the suitability, attractiveness, and abundance of recreational facilities in rural tourism landscapes (Yuan, 2017 ). The Research Experience sub-dimension involves the evaluation of the attractiveness, abundance, brand value, and impressiveness of the research experiences for tourists (Fan and Liu, 2016 ; Wang and Wang, 2010 ; Huang et al., 2018 ). The Integral Route sub-dimension involves the evaluation of the prominent theme features in the routes, an abundance of scenarios and experiences, and the attractiveness of the integral route (Li, 2003 ; Yan, 2021 ).
SA—This is the evaluation of whether the overall quality and experience of the rural tourism landscapes meet expectations. Here, the overall satisfaction, expectation, and competitiveness of rural tourism landscape quality and experience are used as the evaluation indexes (Chen, 2012 ; Wang et al., 2005 ).
RI—This is the evaluation of tourists’ loyalty to rural tourism destinations, with loyalty, willingness to revisit, and recommendation behavior as the evaluation indexes (Wang et al., 2006 ; Stylos et al., 2015 ).
Questionnaire design and collection
The questionnaire was designed in four parts. The first part covers the demographic characteristics, including gender, age, education level, and occupation. The second part is the evaluation of cultural image perception, while the third part is the evaluation of environmental design, and the fourth part is the evaluation of place perception. The items in these last three parts corresponded to the evaluation indexes shown in Tables 2 – 4 , respectively, and a 5-point Likert scale was used to rank the perception level.
In November 2022, the study conducted a field survey in Nangou village, complemented by an online questionnaire from November 15, 2022, through September 12, 2023. The introduction section of the questionnaire included the research objectives, the anticipated societal benefits, and the scope of information that would be collected. Before proceeding, participants were asked to review this introduction; their agreement to participate was taken as informed consent. In total, the study received 344 valid responses, serving as the sample data. The sample size satisfies the requirements for structural equation modeling that a desirable sample size should be over 200, with at least ten responses correlating to each variable under observation (Barrett, 2007 ).
Quantitative analysis methods
The data were analyzed using SPSS (version 27.0) and AMOS 27.0. Frequency analysis of the demographic characteristics and reliability analysis were conducted.
In this study, structural equation modeling (SEM) was used as the core method, and the three concepts of landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention were set as latent variables, and SEM was utilized to verify the hypotheses on the relationship between the three aspects. First, a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was introduced to test whether the relationship between the factors and the corresponding measurement items was as expected, and to further revise the relationship model between the latent variables and the indicator question items and between the indicator question items (Li and Chen, 2010 ). Second, the interaction mechanism between the latent variables was analyzed by SEM to verify or falsify the research hypotheses (Gu et al., 2022 ). Finally, the bootstrap method was used to validate and analyze the indirect effects (Wen and Ye, 2014 ).
Results analysis
Demographic variables and statistical results of travel characteristics.
Using SPSS software to analyze the demographic characteristics of the 354 questionnaires, the sample was found to be well-balanced in terms of gender. The age distribution was broad and predominantly consisted of young and middle-aged people. The occupational status covered various fields, while most respondents had received middle and higher levels of education. The middle-income group accounted for a larger proportion of the sample, which is a good representation of the population (Fig. 4 ).
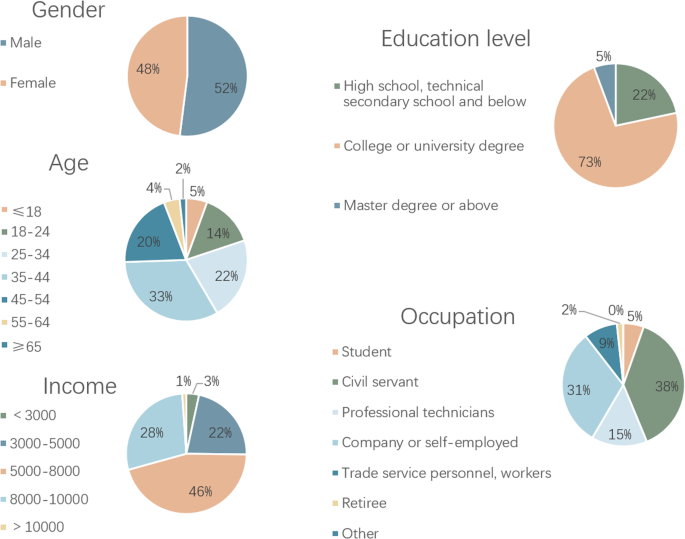
The figure presents the statistical results of the demographic variables for the 354 questionnaires.
The survey results showed that tourists preferred to choose research experience and historical culture landscape projects at the destination, followed by natural ecology and leisure recreation. In terms of tour length and size, tourists who chose one-day and two-person tours accounted for most of the tourists, and very few tourists chose multiday tours. The majority of tourists who came to this destination came as a unit, and the least frequent response was as individual tourists. The majority of tourists visited this village for the first time, and the number of tourists choosing to revisit the place again was very few (Fig. 5 ).
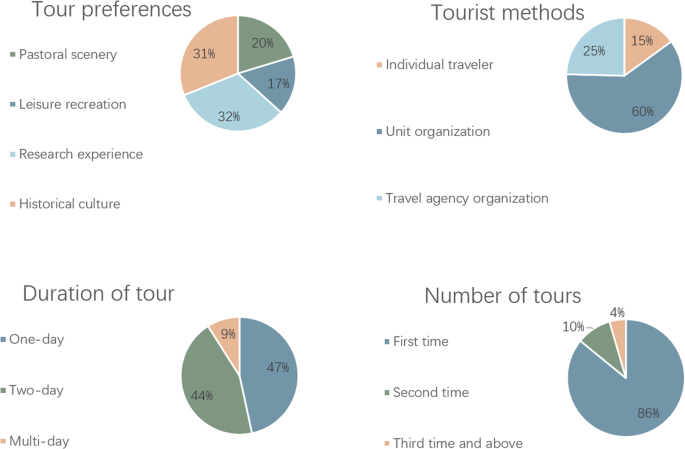
The figure presents the statistical results of the travel characteristics for the 354 questionnaires.
Reliability analysis results
In this study, the latent variables were tested using Cronbach’s α (Table 2 ), which showed that the Cronbach’s α values of landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention were 0.898, 0.803, and 0.845, respectively, and the scales’ overall Cronbach’s α value was 0.913. The Cronbach’s α values of the sub-dimensions under landscape perception ranged from 0.805 to 0.863, which are all greater than 0.8. In summary, the reliability test coefficients of each sub-dimension scale exceed 0.7, which indicates that the internal consistency of the data was good (Eisinga et al., 2013 ).
Latent variable evaluation results
As shown in Fig. 6 , the overall average landscape perception score was 3.748, which is close to a good level. Comparing the average evaluation score, the five latent variables can be ranked as NE > HC > RE > LR > IR, with scores of 3.976, 3.906, 3.889, 3.836, and 3.826, respectively. The overall average score for satisfaction was 3.625, between average and satisfactory. The overall average score for revisit intention was 3.452, between average and willing, but not reaching the desired level.
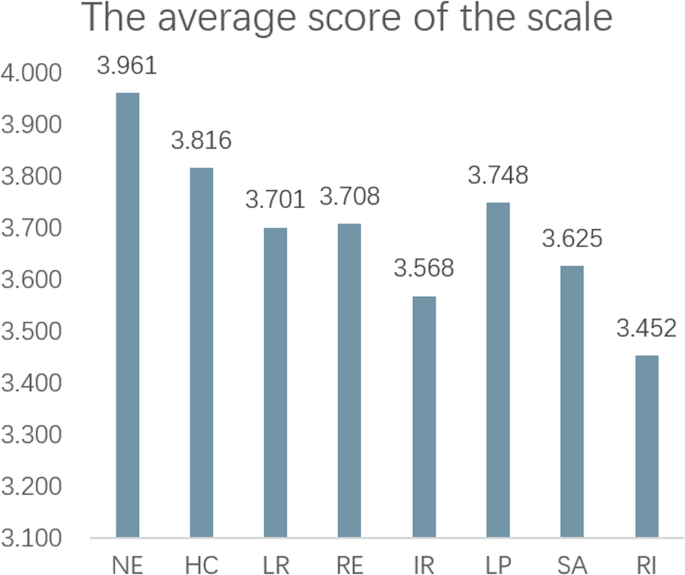
The figure presents the statistical results of the latent variable average scores. NE Natural Ecology, HC Historical Culture, LR Leisure Recreation, RE Research Experience, IR Integral Route, LP Landscape Perception, SA Satisfaction, RI Revisit Intention.
This study examined the relationship between the latent and observed variables in the measurement model through CFA to determine the reasonableness of the scale construction by convergent and discriminant validity. For convergent validity, there are usually three discriminating criteria: (1) standardized factor loadings are all greater than 0.5 (Bailey and Ball, 2006 ); (2) average variance extracted (AVE) is greater than 0.5 (Bagozzi and Yi, 1988 ); and (3) composite reliability (CR) is greater than 0.7 (Fornell and Larcker, 1981 ). Satisfying the above criteria indicates good convergent validity. As shown in Table 3 , the standardized factor loading ranged from 0.686 to 0.891, which meets the criterion of greater than 0.5. The minimum value of CR was greater than 0.8, which is greater than the threshold value of 0.7, and the AVEs were all greater than 0.5, which indicates that the scale has a good convergent validity.
For discriminant validity, if the correlation coefficients between a factor and the other factors are all less than the square root of its AVE value, it indicates good discriminant validity between the factors (Hair et al., 2010 ). As shown in Table 4 , the correlation coefficients between landscape perception and the two factors of its sub-dimension are only slightly larger than the square root of the AVE, and the square root of the AVE values of the rest of the factors is higher than the correlation coefficients between the factor and the other factors, which indicates that the present scale has good discriminant validity.
Theoretical model validation
Under the premise of ensuring the reliability and validity of the measurement model, structural modeling was further performed to verify the hypothesized relationships among the three variables of landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention. First, the results of model fit showed that CMID/DF = 1.097, GFI = 0.949, AGFI = 0.936, CFI = 0.995, TLI (NNFI) = 0.994, RMSEA = 0.017, and SRMR = 0.037 (Table 5 ), and all the indexes were in line with the standard, which indicated that the model had a good fit (Hayduk, 1987 ; Scott and Willits, 1994 ).
This study further used AMOS 27 to establish a structural model and measure the causal relationships between the three latent variables, LP, SA, and RI. As shown in Table 6 and Fig. 7 , (1) Landscape perception has a positive and significant effect on Satisfaction, with a path coefficient of 0.559 ( P < 0.001); (2) Landscape perception has a positive and significant effect on Revisit Intention, with a path coefficient of 0.434 ( P < 0.001); and (3) Landscape Satisfaction had a positive and significant effect on Revisit Intention, with a path coefficient of 0.377 ( P < 0.001) (Cabrera-Nguyen, 2010 ). This proves that hypotheses H1, H2, and H3 are supported.
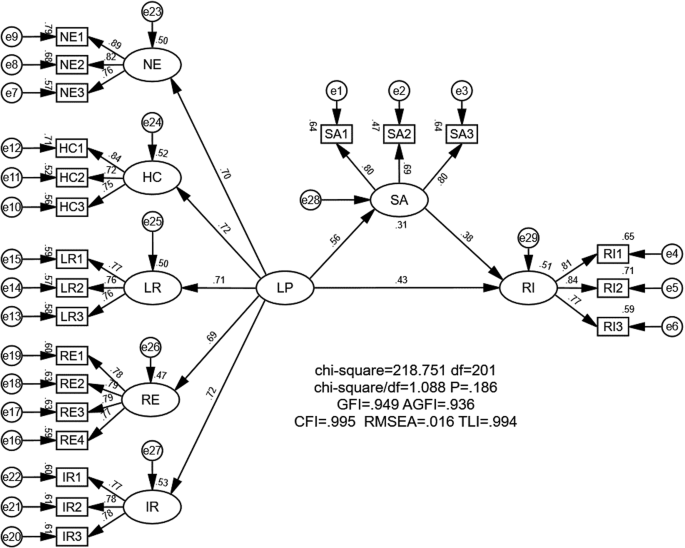
NE Natural Ecology, HC Historical Culture, LR Leisure Recreation, RE Research Experience, IR Integral Route, LP Landscape Perception, SA Satisfaction, RI Revisit Intention.
Mediation analysis of satisfaction
This study adopted the bootstrap method suggested by McKinnom to test the possible mediating effect of SA in the relationship between LP and RI, and the bootstrap sample size was set at 5000 (MacKinnon et al., 2002 ). Usually, if the bootstrap confidence interval does not contain 0, then the corresponding indirect, direct, or total effect exists (MacKinnon et al., 2004 ). The test results show that at a 95% confidence level, the confidence interval of indirect effect was [0.141, 0.314], the confidence interval of direct effect was [0.456, 0.755], and the confidence interval of total effect was [0.682, 0.961], which all exclude 0, indicating that the indirect effect exists, and the ratio of the indirect effect was 0.27. The results of the mediation test support hypothesis H4 (Table 7 ).
Discussion and recommendations
Coupling relationship among lp, sa, and ri.
This study established a hypothesis model based on the a priori theory of the influencing relationship between Landscape Perception→Satisfaction→Revisit Intention, and explored and confirmed the influence paths of LP on SA and RI with Nangou Village as the research object. In the SEM results, the coefficient of LP’s influence path on SA was 0.559, and the coefficient of LP’s influence path on RI was 0.434. LP influences tourists’ revisit intention to the destination through the overall satisfaction of the tourist landscapes, which confirms that the landscape quality and experience of the destination is an important influencing factor that affects tourists’ satisfaction, which then enhances tourists’ revisit intention. This result is consistent with that of many previous studies, such as those conducted by Cao ( 2019 ) and Li ( 2022 ), in which quantitative analysis is conducted under different contexts to investigate the influence paths of landscape perception. Their research also confirms that tourists’ perception of the landscape contributes to enhancing satisfaction and revisiting intention. At present, the intention to revisit Nangou Village has not reached the desired level. Based on the LP → SA → RI influence path, this study concludes that it is necessary to upgrade the tourism landscapes as a whole in the new round of rural tourism planning, to effectively improve the attractiveness of the destination from the environmental level.
Coupling relationship among LP and its sub-variables
Different from previous studies, we defined LP as a second-order variable containing five sub-dimensions: natural ecology, historical culture, leisure recreation, research experience, and integral route. The fitted data showed that the five sub-variables were an accurate representation of the LP structure. In the results of the structural equation, all five latent variables involved in the LP dimension showed significant positive correlations with LP ( P < 0.01), and the influence path was IR > HC > LR > NE > RE. In the correlation analysis, IR, HC, LR, RE, and IR also showed significant positive correlations with revisit intention, with correlation coefficients in the order of NE > IR > HC > LR > RE (Table S1 ), and the correlation coefficients in the order of IR > LR > LR > RE (Table 2 ). All of these results emphasize the important influence of historical culture and integral route on landscape perception and revisit intention. In the actual evaluation of landscape perception, the evaluation results of the five sub-dimensions did not reach a satisfactory level; therefore, in order to further increase the revisit intention of the destination, it is necessary to upgrade the landscapes of Nangou Village in all dimensions as a whole, and in particular, it should focus on upgrading the historical culture, the integral routes, as well as the facilities of the research experience that tourists are more inclined to choose.
Recommendations
Deeply excavating rural historical and cultural resources.
Rural tourism itself is a large-scale cultural exchange; any tourism product or tourism mode has its own cultural connotation, which is a necessary condition to attract tourism (Li and Wang, 1999 ). Rural culture is both productive and fragile; therefore, cultural protection and inheritance in rural tourism development is essential. Emphasizing the characteristic regional culture can not only improve the visibility, dissemination, and attractiveness of rural tourism destinations, but also enhance the vitality, efficiency, and effectiveness of rural development. The rural landscapes are both the end product of rural tourism and the carrier of rural culture. Based on the principle of protecting the authenticity of rural culture, integrating the elements of native culture into the tourism landscape designs of traditional villages and optimizing the tourism content is conducive to strengthening the attractiveness of traditional villages to tourists (Sun and Zhang, 2020 ). The results of the survey on the preference of tourism types in Nangou Village show that the historical culture and landscapes are popular aspects. Meanwhile, the SEM model results show that historical culture is an important factor influencing tourists’ revisit intention. Therefore, future tourism planning in Nangou Village should strengthen the development of vernacular cultural landscapes and highlight its own distinct characteristics. The tourism landscapes developed in the first round in Nangou Village have problems such as low cultural taste and inconspicuous characteristics. The new tourism planning for Nangou Village should sufficiently mobilize the regional cultural resources of the Ansai District, utilizing the region’s primitive village landscapes and folk cultural resources to create a rich “composite vernacular complex” type of landscape facilities. For example, we could introduce traditional activities such as horse riding, cattle riding, and Paper Cuttings with Ansai characteristics to the local culture experience hall; renovate cave dwelling homestays with distinctive Shaanxi characteristics; and integrate agricultural and folk activities such as tasting farmhouse meals and picking agricultural products into the homestay experience. In summary, the new tourism landscape should showcase the inherent qualities of Nangou Village, such as locality, authenticity, and humanity, from four aspects: food, housing, transportation, and work.
Shaping the National Red Culture Brand
Red cultural resources, as the Chinese excellent culture refined during the revolutionary era, play a prominent role in enhancing national self-confidence and building a strong nation. Meanwhile, the red tourism industry, which inherits and carries forward the red culture, has also become a unique path in China’s rural revitalization (Liu, 2020 ). The purpose of rural red tourism is to jointly develop traditional green ecological resources and red resources with humanistic characteristics. Through the development model of red and green integration, we can carry forward the narrative and dissemination power of the red spirit concept. At the same time, based on the comprehensive development of red tourism routes, sites, events, symbols, and other resources, we can enhance the popularity of rural tourism brands, expand market entities, and attract more visitors (Hong, 2021 ). Nangou Village is located in the red Yan’an revolutionary hometown, which occupies a place in China’s revolutionary history. In the first round of development, Nangou Village built red culture experience facilities, mainly serving units with red education and training needs in the surrounding areas. However, Nangou Village has insufficient scheduling of classic resources such as red sites, red stories, red history, and red characters, and has not established a more competitive and penetrating red tourism culture brand that serves a comprehensive audience. Therefore, we suggest that Nangou Village expand the scale of red travel facilities, create multi-dimensional red tourism experience scenarios, enhance the cultural connotation of red tourism scenic spots, and create educational and training routes with prominent themes of the red spirit. In addition, rural culture, red tourism resources, and natural ecological resources should be integrated under specific local conditions, for example, temperature-controlled greenhouses, characteristic agricultural planting, folk culture experiences, and other projects around the red tourism areas can be incorporated. This is conducive to enhancing the “red tourism integration” brand effect for its greater influence on surrounding facilities. Therefore, the connection between the cultural dimension and tourists’ perception of landscapes can be reinforced. In turn, it enhances the favorability and visibility of the “Red Yan’an” brand, which gives full play to its economic potential while promoting the inheritance of red cultural genes.
Creating rural tourism boutique routes
Rural tourism boutique routes are an arrangement and scientific organization of characteristic tourism landscapes, which is an important strategy for rural tourism destinations to attract tourists. The creation of boutique tourism routes is based on the integration of regional resources, forming a “string of points into a line, with a line leading to the surface, the overall promotion” of the joint development of the countryside, which is able to better utilize and display rural resources, and promote the integrated development of industries and the cultivation of new business models (You, 2014 ; Wang, 2015 ). According to the SEM results, it can be seen that the integral route sub-dimension of Nangou Village had the greatest impact on landscape perception. However, at present, tourists gave the lowest rating for aspect, which affected their satisfaction and led to a low willingness to revisit. At present, the tourism landscape projects in Nangou Village have problems, such as dispersion, small scales, individual operations, a single rural tourism product, and imperfect industrial and economic structures. Therefore, the upgrading strategy should incorporate the cultural theme of “Ansai Five Business Cards” into the integral tourism routes, and form the regional tourism development routes, rural tourism routes, and red knowledge education and training routes in the Greater Nangou area, which rely on the characteristic resources of Nangou Village. Moreover, it should connect the regional construction with the routes, and form a diversified tourism industry integrating “agricultural science popularization + folklore experience + parent-child amusement + leisure agriculture”. Finally, the tourism route planning should make full use of the Nangou Village brand, taking rural culture and tourism as the engine to optimize and expand primary industries, achieve coordinated development of the village and urban economy, and focus on the development of tertiary industries, in order to cooperate with the new rural industrial development system in Nangou Village.
Conclusions
With the gradual evolution of urbanization and the extensive promotion of China’s Rural Revitalization Strategy, rural tourism has become more and more popular and has developed rapidly. Landscape perception is the process of human interactions with the landscape, and the positive or negative results of this perception will directly affect the satisfaction of the tourists with the destination, thus affecting the tourists’ revisit intention. This study was based on the theory of landscape perception, and selected Nangou Village as the research object, on the basis of validating the influencing relationship of Landscape Perception→Satisfaction→Revisit Intention, to put forward reasonable suggestions for the optimization and upgrading of Nangou Village. The results of the research show the following: (1) Tourists’ landscape perception significantly influences tourists’ satisfaction and revisit intention. (2) Tourists’ satisfaction with the destination plays an intermediary role in the influence of landscape perception on revisit intention. (3) Landscape perception contains five dimensions (natural ecology, historical culture, leisure recreation, research experience, and integral route), all of which significantly influence tourists’ satisfaction and revisit intention. Among these dimensions, historical culture and integral route have the greatest influence, which indicates that the cultural and integral nature of the landscape is the core element that drives tourists to generate positive emotions. (4) Tourists prefer landscape projects with historical culture and research experience. (5) The overall landscape planning of Nangou Village was not evaluated highly, and it needs to be upgraded in a focused way. Using the empirical results as a reference, this study proposes strategies for upgrading the tourism landscapes of Nangou Village: deeply excavate rural historical and cultural resources, shape the national red culture brand, and create rural tourism boutique routes. Therefore, exploring the factors affecting revisit intention and thinking about the construction of rural tourism landscape perception elements can provide theoretical guidance for solving the next stage of rural tourism planning in Nangou Village and providing a direction for the construction of beautiful villages in the future.
The methodology of empirical research as applied in this study, along with the corresponding data analysis conducted in the case study of Nangou Village, aims to reveal the influencing factors for revisit intention. By adopting a reverse-thinking approach to constructing the elements of rural tourism landscape perception, theoretical guidance is provided for the next phase of rural tourism planning in Nangou Village. Meanwhile, it gains the strategic insights crucial for local governments and collaborative planning agencies to develop, manage, and market rural tourism destinations. Additionally, the research methods used in this study provide a reference for relevant government and planning agencies to carry out rural tourism planning. Firstly, rural tourism relies heavily on tourism landscape facilities as its primary support system. Therefore, rural tourism is supposed to focus on increasing the attention paid to tourists’ demands from the perspective of the supply side. This can be achieved by constructing landscape perception scales that are more tailored to the advantages and characteristics of tourism destinations. Through the surveys of rural tourism landscape perception elements based on combined scale analysis, tourists’ expectations and demands can be better satisfied. Thus, their satisfaction and revisit intention can be enhanced. Secondly, in the practice of rural tourism marketing, the SEM (structural equation modeling) quantitative results of landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention can be referenced to guide targeted promotion and advertising efforts for landscape elements perceived more strongly by tourists. In this way, the attractiveness to tourist groups can be improved. Lastly, planning agencies can apply the scale developed in this study to measure the satisfaction level of rural tourism industries in tourists’ minds at various stages. By assessing the scores in different dimensions, planning agencies can better identify their strengths and weaknesses, which enables them to maintain their advantages while making improvement.
Some limitations should be noted, which need to be addressed in the future. Firstly, the division of landscape perception dimensions in this study was somewhat subjective and innovative, and there are some immaturity issues. Secondly, the data collection time was short, which may not represent the average situation throughout the year. Finally, this article intended to propose optimization suggestions for Nangou Village at the landscape level, but this should be integrated with the industrial transformation, planning and propaganda, and enhancing service quality and other influencing factors of tourism destinations in the overall tourism planning.
Data availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material ( S2 . Dataset), further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Acharya S, Mekker M, Jonas DV (2023) Linking travel behavior and tourism literature: investigating the impacts of travel satisfaction on destination satisfaction and revisit intention. Transp Res Interdiscip Perspect 17:100745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trip.2022.100745
Article Google Scholar
Bagozzi RP, Yi Y (1988) On the evaluation of structural equation models. J Acad Market Sci 16(1):74–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02723327
Bailey R, Ball S (2006) An exploration of the meanings of hotel brand equity. Serv Ind J 26:15–38. https://doi.org/10.1080/02642060500358761
Baker DA, Crompton JL (2000) Quality, satisfaction and behavioral intentions. Ann Tour Res 27:785–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-7383(99)00108-5
Barrett P (2007) Structural equation modelling: adjudging model fit. Pers Individ Differ 42:815–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2006.09.018
Bitner MJ (1992) Servicescapes: the impact of physical surroundings on customers and employees. J Market 56:57–71. https://doi.org/10.1177/002224299205600205
Cabrera-Nguyen P (2010) Author guidelines for reporting scale development and validation results in the Journal of the Society for Social Work and Research. J Soc Soc Work Res 01:99–103. https://doi.org/10.5243/jsswr.2010.8
Campo-Martínez S, Garau-Vadell JB, Martínez-ruiz MP (2010) Factors influencing repeat visits to a destination: the influence of group composition. Tour Manag 31:862–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2009.08.013
Cao YL (2019) A study of the effect of perceived rurality on revisit intention. Master’s Thesis. Xi’an International Studies University, Xi’an, China
Google Scholar
Chen B (2020) Rural complex and rural revitalization: approaches and prospects of Chinese rural anthropology. Guangxi Ethnic Stud 06:94–102. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-454X.2020.06.012
Chen CW, Jin ML, Jin HX, Cheng QY (2021) Beautiful country quality line construction based on region linkage—a case study of the construction practice of Yiwu “Colorful Huaxi”. Chin Landsc Archit 37(2):12–19. https://doi.org/10.19775/j.cla.2021.02.0012
Article CAS Google Scholar
Chen JH (2012) The research of tourist satisfaction in urban wetland park tourism resort based on tourism experience. Master’s Thesis. Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China
Chew YET, Jahari SA (2013) Destination image as a mediator between perceived risks and revisit intention: a case of post-disaster Japan. Tour Manag 40:382–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2013.07.008
Chi CG, Qu H (2008) Examining the structural relationships of destination image, tourist satisfaction and destination loyalty: an integrated approach. Tour Manag 29:624–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2007.06.007
Chi CGQ, Qu H (2009) Examining the relationship between tourists’ attribute satisfaction and overall satisfaction. J Hosp Market Manag 18:4–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/19368620801988891
Chon K (1989) Understanding recreational travelers’ motivation, attitude and satisfaction. Tour Rev 44(1):3–7. https://doi.org/10.1108/eb058009
Cole ST, Scott D (2004) Examining the mediating role of experience quality in a model of tourist experiences. J Travel Tour Market 16:79–90. https://doi.org/10.1300/J073v16n01_08
Cosgrove D (1984) Social formation and symbolic landscape. Groom Helm, London, GBR. pp. 56–84
Crompton JL (1979) An assessment of the image of Mexico as a vacation destination and the influence of geographic allocation upon that image. J Travel Res 17(4):18–23. https://doi.org/10.1177/004728757901700404
Deng W (2006) Landscape perception: towards landscape semiology. World Archit 07:47–50. https://doi.org/10.16414/j.wa.2006.07.009
Echtner CM, Ritchie JRB (1993) The measurement of destination image: an empirical assessment. J Travel Res 31(4):3–13. https://doi.org/10.1177/004728759303100402
Eisinga R, Grotenhuis M, Pelzer B (2013) The reliability of a two-item scale: Pearson, Cronbach, or Spearman-Brown? Int J Public Health 58(4):637–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-012-0416-3
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Fan J, Qiu HL, Wu XF (2014) Tourist destination image, place attachment and tourists’ environmentally responsible behavior: a case of Zhejiang tourist resorts. Tour Trib 29(1):55–66. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-5006.2014.01.006
Fan YH (2020) Research on the evaluation and perception of village landscape in western Sichuan based on the network content analysis method. Master’s Thesis. Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu, China
Fan YM, Liu H (2016) Landscape and village integrated beautiful village planning. Planners 32(04):97–100. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-0022.2016.04.016
Fornell C, Larcker DF (1981) Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J Market Res 18(1):39–50. https://doi.org/10.1177/002224378101800104
Geng XH, Wang XQ, Sun QS (2010) Eco-tourism, tourist satisfaction and revisit will: a case study of future Agro-park in Suzhou China. Ecol Econ 06:119–123
Gobster PH (2008) Yellowstone hotspot: reflections on scenic beauty, aesthetics, and ecology. Landscape J 27:291–308
Gu T, Hao E, Ma L, Liu X, Wang L (2022) Exploring the determinants of residents’ behavior towards participating in the sponge-style old community renewal of China: extending the theory of planned behavior. Land 11:1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081160
Guo HC (2016) Study on the experience value of mountain resort tourism, degree of satisfaction and revisit intention—a case of DaWei Mountain. Master’s Thesis. Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China
Guo HC, Han D (2010) Review on the development of rural tourism in China. Prog Geogr 29(12):1597–1605. https://doi.org/10.11820/dlkxjz.2010.12.018
Guo HC, Liu JP, Wang YC (2000) The study on development of tourism agriculture. Econ Geogr 20:119–124. https://doi.org/10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2000.02.025
Guo YZ, Zhang H, Song SL, Li L, Chen XL, Zhang L (2004) A study of market positioning of China’s outbound travel destinations. Tour Trib 19(4):27–32. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-5006.2004.04.010
Hair JFJ, Black WC, Babin BJ et al. (2010) Multivariate data analysis. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, USA. pp. 785-785
Hayduk LA (1987) Structural equation modeling with LISREL: essentials and advances. JHU Press, Maryland, USA
He JM (2003) A study on rural tourism overseas. Tour Trib 18:76–80. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-5006.2003.01.017
Hong Y (2021) Research on government functions in the integration and development of Yan’an Red Culture and tourism industry, Master’s Thesis, Yan’an University, Yan’an, China
Huang J (2003) Soil complex, family complex and agritourism development. Thinking 29(5):24–26. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-778X.2003.05.006
Huang SS, Fan Y, Xiong HG (2018) Study on the development path for red culture resources under the perspective of rural revitalization strategy. Price Month 09:90–94. https://doi.org/10.14076/j.issn.1006-2025.2018.09.16
Huang ZF, Lu L, Su Q, Zhang JH, Sun JX, Wan XC et al. (2015) Research and development of rural tourism under the background of new urbanization: theoretical reflection and breakthrough of predicament. Geogr Res 34(8):1409–1421. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlyj201508001
Humagain P, Singleton PA (2021) Examining relationships between COVID-19 destination practices, value, satisfaction and behavioral intentions for tourists’ outdoor recreation trips. J Dest Market Manag 22:100665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdmm.2021.100665
Hung K, Petrick JF (2011) The role of self- and functional congruity in cruising intentions. J Travel Res 50:100–112. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287509355321
Kim B, 김용기 GK, Hee Park S (2013) Effects of images of rural tourism on tourists’ satisfaction and revisit intention: case of Changpo and Woiam villages. J Tour Sci 37:303–324
Li D, Wang YQ, You YA, Chen YT (2022) Tourism involvement, destination image and willingness to revisit: a moderated intermediary role model. J Central China Normal University (Natural Sciences) 56(5):871–881. https://doi.org/10.19603/j.cnki.1000-1190.2022.05.017
Li JH (2022) Research on the effects of rurality perception on the tourists’ revisit intentions—taking Nostalgialove Hometown Taihang Water Town in Baoding as a study case. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University, Baoding, China
Li TY, Wang LY (1999) An introduction to tourism principles. Nankai University Press, Tianjin, China. pp. 34–50
Li W (2003) A discussion on the development and plan of rural tourism. Areal Res Dev 22(6):72–75. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-2363.2003.06.018
Article ADS Google Scholar
Li XJ, Chen XZ (2010) Factor analysis under the structural equation model. Sci Technol Eng 10:5708–5711+5727. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2010.23.022
Liu T (2020) Study on the practice path of Honghu Wetland Red Culture promoting rural rejuvenation, Master’s Thesis, Hubei University of Technology, Wuhan, China
Liu YS (2018) Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the new era in China. Acta Geogr Sinica 73(04):637–650. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlxb201804004
Lu L, Ren YS, Zhu DC, Cheng JM, Yang XZ, Yang Z et al. (2019) The research framework and prospect of rural revitalization led by rural tourism. Geogr Res 38(01):102–118. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlyj020180454
Ma Y, Zhao L, Song H, Guo QX, Liu MJ (2007) Study on the Chinese rural tourism development pattern—a case of CHENGDU. Econ Geogr 27(2):336–339. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-8462.2007.02.035
MacKinnon DP, Lockwood CM, Hoffman JM, West SG, Sheets V (2002) A comparison of methods to test mediation and variable effects. Psychol Methods 07:83–104. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989x.7.1.83
MacKinnon DP, Lockwood CM, Willams J (2004) Confidence limits for the indirect effect; distribution of the product and resampling methods. Multivar Behav Res 39(1):99–128. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327906mbr3901_4
Marianna S, Solenè P, Bynum BB (2023) Resident connection to nature and attitudes towards tourism: findings from three different rural nature tourism destinations in Poland. J Sustain Tour 31:664–687. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1995399
Mehrabian A, Russell JA (1974) An approach to environmental psychology. The MIT Press, Cambridge, GBR
Meng XL (2018) Research on rural tourism destination image, perceived value and the relationship between revisit intention: based on the research on rural tourism in Zhejiang province. J Zhejiang Wanli Univ 31(01):8–15. https://doi.org/10.13777/j.cnki.issn1671-2250.2018.01.002
Middleton VTC, Hawkins R (1998) Sustainable tourism: a marketing perspective. Routledge Press, Boston, USA
Motloch JL (2000) Introduction to landscape design. John Wiley & Sons, New York, USA
Nisco AD, Mainolfi G, Marino V, Napolitano MR (2015) Tourism satisfaction effect on general country image, destination image, and post-visit intentions. J Vacat Market 21:305–317. https://doi.org/10.1177/1356766715577502
Oliver RL (1980) A cognitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. J Market Res 17:460–469. https://doi.org/10.1177/002224378001700405
Ostoić SK, Van Den Bosch CCK, Vuletić D, Stevanov M, Živojinović I, Mutabdžija-Bećirović S et al. (2017) Citizens’ perception of and satisfaction with urban forests and green space: results from selected Southeast European cities. Urban Forest Urban Green 23:93–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2017.02.005
Prayag G, Hosany S, Muskat B, Del Chiappa G (2017) Understanding the relationships between tourists’ emotional experiences, perceived overall image, satisfaction, and intention to recommend. J Travel Res 56:41–54. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287515620567
Purcell AT (1987) Landscape perception, preference, and Schema discrepancy. Environ Plann B Plann Design 14:67–92. https://doi.org/10.1068/b140067
Qin R (2022) Research on children’s outdoor activity space design based on Landscape Perception—Take Tongle Bay of Changchun North Lake Park as an example. Master’s Thesis. Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun, China
Queiroz OT (2017) Ruralities as tourist attraction and cultural experience: the Santa Gertrudes farm. Rosa dos Ventos 9(3):447–456. https://doi.org/10.18226/21789061.v9i3p447
Qu GC, Zhao Y, An JH, Xu JY, Qian QQ, Chen MC (2023) Research on the path of high-quality development of rural tourism in southern Anhui based on the original authenticity of nostalgia. Gansu Agri (12):90–95. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-9019.2023.12.017
Sailesh A, Michelle M, Jonas VD (2023) Linking travel behavior and tourism literature: Investigating the impacts of travel satisfaction on destination satisfaction and revisit intention. Transp Res Interdiscip Perspect 17:100745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trip.2022.100745
Scott D, Willits FK (1994) Environmental attitudes and behavior: a Pennsylvania survey. Environ Behav 26(2):239–260. https://doi.org/10.1177/001391659402600206
Shi X (2021) Landscape design for rural tourism under the perspective of ecological aesthetics. Sichuan Drama (10):113–116
Song WY (2013) Outdoor event space landscape perception and its design research. Master’s Thesis. Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China
Stylos N, Vassiliadis AC, Bellou V, Andronikidis A (2015) Destination images, holistic images and personal normative beliefs: predictors of intention to revisit a destination. Tour Manag 53:40–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2015.09.006
Sun XH, Zhang X (2020) Research on adaptive design of traditional village landscape under the background of rural tourism. Design 33:158–160
Sun YH, Chen T, Wang YC (2008) Progress and prospects in research of the traditional rural cultural landscape. Prog Geogr 27(6):90–96. https://doi.org/10.11820/dlkxjz.2008.06.013
Tribe J, Snaith T (1998) From SERVQUAL TO HOLSAT: holiday satisfaction in Varadero, Cuba. Tour Manag 19:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-5177(97)00094-0
Tu HW, Xiong LY, Huang YM, Guo GX (2017) The effect of destination image on tourist behavior intention: an explanation based on the emotion appraisal theory. Tour Trib 32(2):32–41. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-5006.2017.02.009
Wang Q, Ding ZR, Zhang JH, Yang XZ (2006) Study on the model of tourist satisfaction index about tourism environment: a case study of Huangshan Mountain. Geogr Res 25(1):171–181. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2006.01.020
Wang X, Gu CLMei H (2005) Tourist attraction customer satisfaction index model. Acta Geogr Sinica 60(5):807–816. 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2005.05.012
Wang XR, Wang SJ (2010) The research on customer satisfaction of leisure agriculture garden. Chin Agri Sci Bull 26(13):413–419
CAS Google Scholar
Wang YC, Xu CX, Guo HC (2005) Discussions on the new trends of rural tourism development in China. Arid Land Geogr 28(6):862–868. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-6060.2005.06.025
Wang ZJ (2015) Study on the planning and design of beautiful rural top line, Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou, China
Wen ZL, Ye BJ (2014) Analyses of mediating effects: the development of methods and models. Adv Psychol Sci 22(5):731–745. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00731
Wu D, Shen CY, Wang EX, Hou YY, Yang J (2019) Impact of the perceived authenticity of heritage sites on subjective well-being: a study of the mediating role of place attachment and satisfaction. Sustainability 11(21):6148. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11216148
Xie HL, Liu LM, Li L (2002) An inquiry analysis on rural development of ecotourism. Ecol Econ 12:69–71. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-4407.2002.12.022
Xu JQ, Zeng Q, Li C (2023) Perception and evaluation of beautiful rural landscape characteristics from the perspective of regional culture-taking Qilian village landscape improvement project as an example. Agri Technol 43(01):89–94. https://doi.org/10.19754/j.nyyjs.20230115023
Xu WH, Tang LZ (2016) Research on the “Four Desirable” strategy in beautiful countryside planning and construction. Chin Landsc Archit 32(09):20–23
Xu YF, Liu MH, Zhang CY (2014) The influence mechanism of tourist loyalty based on perceived destination attributes. Econ Geogr 34(8):167–172
Yan R (2021) Research and application of tourism route optimization based on improved genetic algorithm, Master’s Thesis, North Minzu University, Yinchuan, China https://doi.org/10.27754/d.cnki.gbfmz.2021.0000944
Yang F, Fen J, Xie SY (2022) A study on the evaluation of tourist satisfaction and its influence on the intention to revisit destination: taking 5A scenic spots in Wuhan as examples. J Central China Normal Univ (Natural Sciences) 56(1):116–126. https://doi.org/10.19603/j.cnki.1000-1190.2022.01.013
Yang W, Fan B, Tan J, Lin J, Shao T (2022) The spatial perception and spatial feature of rural cultural landscape in the context of rural tourism. Sustainability 14:4370
Yin Y, Li XQ (2018) The development of mobile internet and the changes of the elderly life. J Chin Acad Gov 05:182–186+193. https://doi.org/10.14063/j.cnki.1008-9314.20181023.026
You JM (2014) The research on the development of rural tourism resources in Zhejiang province based on the construction of beautiful countryside, Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou, China
Yuan Y (2017) Planning and construction of rural complex oriented tourism areas: Siliangjiang Rural Tourism Area Planning (2017–2021) example. Planners 33(12):136–143. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-0022.2017.12.020
Zhai YZ (2015) Regional Cultural Studies Rural Cultural Tourism Landscape Design. Master’s Thesis. Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, China
Zhang D (2006) Study on tourist perceived value of rural tourism. Master’s Thesis. Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Zhang H, Fu X, Ca LA, LU L (2014) Destination image and tourist loyalty: a meta-analysis. Tour Manag 40(1):213–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2013.06.006
Zhang L, Wang SL (2018) Study on the visitors experience of tourism products in historical and cultural rural tourism. Art Design 06:142–143. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0412-3662.2018.06.037
Zhang Y, Van Den Berg AE, Van Dijk T, Weitkamp G (2017) Quality over quantity: contribution of urban green space to neighborhood satisfaction. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(5):535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14050535
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Zhou Y, He JH, Rong H (2016) Satisfaction evaluation of tourist and influence factors analysis in rural tourism. Bus Manag J 38(07):156–166. https://doi.org/10.19616/j.cnki.bmj.2016.07.014
Zube EH, Sell JL, Taylor JG (1982) Landscape perception: research, application and theory. Landsc Plann 9:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3924(82)90009-0
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Academy of Agricultural Planning and Engineering, MARD of China “Study on the transformation of rural space and planning response in the suburbs of Xi'an from the perspective of social change”, grant number XC2X2DKT-20230916 and by the Shaanxi Provincial Science and Technology Project of China “Study on Reshaping the Spatial Value of Cultural Memory of Industrial Heritage and the Path of Local Identity”, grant number 2022JM-289.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Art and Design, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an, Shaanxi Province, China
Yuxiao Kou & Xiaojie Xue
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization, YK and XX; methodology, XX; software, YK; validation, YK and XX; formal analysis, YK; investigation, YK; resources, XX; data curation, YK; writing—original draft preparation, YK; writing—review and editing, XX; visualization, YK; supervision, XX; project administration, XX; funding acquisition, XX All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xiaojie Xue .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted with approval from the Ethics Committee of the primary author’s institution, School of Art and Design, Xi’an University of Technology. All procedures involving human participants in the research were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable standards.
Informed consent
The informed consent was obtained from all participants before the study started.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supporting material, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kou, Y., Xue, X. The influence of rural tourism landscape perception on tourists’ revisit intentions—a case study in Nangou village, China. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 620 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03129-8
Download citation
Received : 21 December 2023
Accepted : 24 April 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03129-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The journal welcomes papers in any area of tourism and travel, including additional topics of interest such as economics, marketing, sociology and statistics. Online publication from 2024 International Journal of Tourism Research will be published in online-only format effective with the 2024 volume.
Pablo-Romero and Molina (2013) performed a chronological analysis of the empirical research, classifying papers according to the methodology applied (time series, panel data and cross-sectional data). The results of this work mostly confirm the relationship between tourism and growth; from a sample of 87 studies, 55 found a univocal ...
This paper aims to systematically review and analyze the current research on tourism impacts on destinations during 2016-2020. The Scopus database was used to search for tourism impact studies.
A Social Sciences Journal Annals of Tourism Research is a social sciences journal focusing upon academic perspectives on tourism. For the purposes of determining areas of interest, tourism is defined as a global economic activity comprising travel behaviour, the management and marketing activities of service industries that arise to meet consumer demand, the effects of tourism activities on ...
Tourism and Hospitality Research (THR) is firmly established as an influential and authoritative, peer-reviewed journal for tourism and hospitality researchers and professionals. THR covers applied research in the context of Tourism and Hospitality in areas such as policy, planning, performance, development, management, strategy, operations, marketing and consumer behavior…
Annals of Tourism Research is the oldest journal in the publication of papers related to sustainable tourism and occupies the fourth place with an h-index equal to 38. The analysis of the evolution of production by source ( Fig. 3 ) shows that the journal Sustainability (Switzerland) had the highest number of publications.
The current paper makes headway in research on COVID-19 and tourism, as it presents a deep analysis of the research and proposes a way forward in tourism research and practice. Regarding RQ1, the study revealed a corpus of 1303 manuscripts on COVID-19 and the hospitality and tourism sector published between 1 December 2019 and 31 March 2021 ...
This paper aims to study the progress of research on Sustainable Tourism and to outline and identify the key disciplines, journals, articles and authors. This is carried out through a wide, in-depth, and structured examination of published scholarly papers. In recent decades, sustainable tourism has been one of the most significant subjects ...
The paper does not aim to provide a fully comprehensive and inclusive analysis of all the impacts, theories, topics and tourism stakeholders that COVID-19 tourism research can examine. Instead, it aims to provide practical and theoretical implications on how to better research, understand, manage and transformative valorize COVID-19 tourism ...
Journal overview. The Journal of Sustainable Tourism is a leading tourism journal which advances critical understanding of the relationships between tourism and sustainable development. It publishes theoretical, conceptual and empirical research that explores one or more of the economic, social, cultural, political, organisational or ...
Sustainable tourism must maintain a high level of customer satisfaction, raise awareness of sustainability concerns, and spread sustainable tourism practices among them. Several earlier studies have measured sustainable tourism in various regions of the world, but a thorough review of it is rare. Thus, the study is founded on a comprehensive literature review to evaluate the current research ...
Throughout time, the global tourism industry and economy have been significantly affected by disasters and crises. At present, COVID-19 represents one of these disasters as it has been causing a serious economic downturn with huge implications in tourism. In this review paper, we have analysed more than 100 papers regarding the effect and consequences of a pandemic on tourism and related ...
Established in 1976, the Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research (JHTR) plays a major role in incubating, influencing, and inspiring hospitality and tourism research. JHTR publishes original research that clearly advances theoretical development … | View full journal description. This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication ...
It is the aim of this paper to complete past tourism research negligence on the study of alternative tourism by studying the differential characteristics of alternative tourism that are focused on ...
Journal of Travel Research (JTR) is the premier research journal focusing on travel and tourism behavior, management and development. As a top-ranked journal focused exclusively on travel and tourism, JTR provides up-to-date, high quality, international and multidisciplinary research on behavioral trends and management theory.JTR is a category 4 ranked journal by the Association of Business ...
The second paper, addressing tourism workforce research for the period 2005-2014, is brought up-to-date with a separate review covering 2015-2020. These contributions collectively provide a window into the current state of play of research in tourism work and employment.
The COVID-19 pandemic struck the tourism industry severely. Based on the review of 35 papers that studied the tourism industry in the wake of the pandemic, we propose a resilience-based framework for reviving the global tourism industry post-COVID-19. Our framework outlines four prominent factors for building resilience in the industry ...
Landscape perception theory has been widely applied in tourism-related research and has gradually permeated into the research on rural tourism landscapes (Yang et al., 2022; Fan, 2020). The rural ...
This chapter describes the main sectors within the travel, tourism and hosp itality industries. It. provides a good overview of the vertical and horizontal inter-relationships between different. 1 ...
Finally, this research paper identifies the challenges in fulfilling the expectations of tourists and how digitalisation is supporting the same and leading Indian tourism towards a sustainable path. The survey results show that with the current findings and reports it is visibly clear that cultural tourism is the way to move to have sustainable ...
Papers that link unrelated concepts can be seen as bridges between the literature that play an essential strategic role in linking two different fields, ... This study concludes that destination research is a critical branch of tourism research because it considers multiple stakeholder groups, discusses macro-level governance issues, meso ...
This study endeavors to bridge this gap by conducting a systematic review of text analysis research published in the top five journals in tourism and hospitality between 2013 and 2023. From a thematic analysis perspective, this paper provides an elaborate description of how text data can be utilized for prediction and understanding purposes.
Purpose This paper aims to uncover the insights derived from past experimental studies in promoting sustainable tourism. It also advocates for leveraging future experimental designs to position tourism as a catalyst for positive change toward sustainable development goals. Design/methodology/approach A review of previous literature examines the contributions of experimental design in both ...
Articles, working papers, and case studies, among others, about the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the tourism industry have increased in academic and scientific journals in the past few years.
Abstract. Although sustainable tourism research is a rich and diverse field, it still suffers from a few important shortcomings. Negligible attention has been given to various possible pathways to sustainable tourism (as opposed to sustainable tourism as a 'goalpost') and there is an insufficient understanding of how the interconnections and interdependencies within tourism as a complex ...
The review found that the 125 articles were mostly published in tourism-related journals (Tourism Management 15%), Journal of Sustainable Tourism 10%) and Annals of Tourism Research 8%), multidisciplinary journals (Sustainability 13%), and rural-oriented journals (Journal of Rural Studies 4%, and Agricultural Economics 2%).Overall, the majority of the case studies focused on Spain (11% ...
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Hence, understanding of what creates a satisfying tourist experience becomes crucial for e-tourism service environment. This research paper investigates the satisfaction level of tourists in using ...