Skip to content
Read the latest news stories about Mailman faculty, research, and events.

Departments
We integrate an innovative skills-based curriculum, research collaborations, and hands-on field experience to prepare students.
Learn more about our research centers, which focus on critical issues in public health.
Our Faculty
Meet the faculty of the Mailman School of Public Health.
Become a Student
Life and community, how to apply.
Learn how to apply to the Mailman School of Public Health.
Content Analysis
Content analysis is a research tool used to determine the presence of certain words, themes, or concepts within some given qualitative data (i.e. text). Using content analysis, researchers can quantify and analyze the presence, meanings, and relationships of such certain words, themes, or concepts. As an example, researchers can evaluate language used within a news article to search for bias or partiality. Researchers can then make inferences about the messages within the texts, the writer(s), the audience, and even the culture and time of surrounding the text.
Description
Sources of data could be from interviews, open-ended questions, field research notes, conversations, or literally any occurrence of communicative language (such as books, essays, discussions, newspaper headlines, speeches, media, historical documents). A single study may analyze various forms of text in its analysis. To analyze the text using content analysis, the text must be coded, or broken down, into manageable code categories for analysis (i.e. “codes”). Once the text is coded into code categories, the codes can then be further categorized into “code categories” to summarize data even further.
Three different definitions of content analysis are provided below.
Definition 1: “Any technique for making inferences by systematically and objectively identifying special characteristics of messages.” (from Holsti, 1968)
Definition 2: “An interpretive and naturalistic approach. It is both observational and narrative in nature and relies less on the experimental elements normally associated with scientific research (reliability, validity, and generalizability) (from Ethnography, Observational Research, and Narrative Inquiry, 1994-2012).
Definition 3: “A research technique for the objective, systematic and quantitative description of the manifest content of communication.” (from Berelson, 1952)
Uses of Content Analysis
Identify the intentions, focus or communication trends of an individual, group or institution
Describe attitudinal and behavioral responses to communications
Determine the psychological or emotional state of persons or groups
Reveal international differences in communication content
Reveal patterns in communication content
Pre-test and improve an intervention or survey prior to launch
Analyze focus group interviews and open-ended questions to complement quantitative data
Types of Content Analysis
There are two general types of content analysis: conceptual analysis and relational analysis. Conceptual analysis determines the existence and frequency of concepts in a text. Relational analysis develops the conceptual analysis further by examining the relationships among concepts in a text. Each type of analysis may lead to different results, conclusions, interpretations and meanings.
Conceptual Analysis
Typically people think of conceptual analysis when they think of content analysis. In conceptual analysis, a concept is chosen for examination and the analysis involves quantifying and counting its presence. The main goal is to examine the occurrence of selected terms in the data. Terms may be explicit or implicit. Explicit terms are easy to identify. Coding of implicit terms is more complicated: you need to decide the level of implication and base judgments on subjectivity (an issue for reliability and validity). Therefore, coding of implicit terms involves using a dictionary or contextual translation rules or both.
To begin a conceptual content analysis, first identify the research question and choose a sample or samples for analysis. Next, the text must be coded into manageable content categories. This is basically a process of selective reduction. By reducing the text to categories, the researcher can focus on and code for specific words or patterns that inform the research question.
General steps for conducting a conceptual content analysis:
1. Decide the level of analysis: word, word sense, phrase, sentence, themes
2. Decide how many concepts to code for: develop a pre-defined or interactive set of categories or concepts. Decide either: A. to allow flexibility to add categories through the coding process, or B. to stick with the pre-defined set of categories.
Option A allows for the introduction and analysis of new and important material that could have significant implications to one’s research question.
Option B allows the researcher to stay focused and examine the data for specific concepts.
3. Decide whether to code for existence or frequency of a concept. The decision changes the coding process.
When coding for the existence of a concept, the researcher would count a concept only once if it appeared at least once in the data and no matter how many times it appeared.
When coding for the frequency of a concept, the researcher would count the number of times a concept appears in a text.
4. Decide on how you will distinguish among concepts:
Should text be coded exactly as they appear or coded as the same when they appear in different forms? For example, “dangerous” vs. “dangerousness”. The point here is to create coding rules so that these word segments are transparently categorized in a logical fashion. The rules could make all of these word segments fall into the same category, or perhaps the rules can be formulated so that the researcher can distinguish these word segments into separate codes.
What level of implication is to be allowed? Words that imply the concept or words that explicitly state the concept? For example, “dangerous” vs. “the person is scary” vs. “that person could cause harm to me”. These word segments may not merit separate categories, due the implicit meaning of “dangerous”.
5. Develop rules for coding your texts. After decisions of steps 1-4 are complete, a researcher can begin developing rules for translation of text into codes. This will keep the coding process organized and consistent. The researcher can code for exactly what he/she wants to code. Validity of the coding process is ensured when the researcher is consistent and coherent in their codes, meaning that they follow their translation rules. In content analysis, obeying by the translation rules is equivalent to validity.
6. Decide what to do with irrelevant information: should this be ignored (e.g. common English words like “the” and “and”), or used to reexamine the coding scheme in the case that it would add to the outcome of coding?
7. Code the text: This can be done by hand or by using software. By using software, researchers can input categories and have coding done automatically, quickly and efficiently, by the software program. When coding is done by hand, a researcher can recognize errors far more easily (e.g. typos, misspelling). If using computer coding, text could be cleaned of errors to include all available data. This decision of hand vs. computer coding is most relevant for implicit information where category preparation is essential for accurate coding.
8. Analyze your results: Draw conclusions and generalizations where possible. Determine what to do with irrelevant, unwanted, or unused text: reexamine, ignore, or reassess the coding scheme. Interpret results carefully as conceptual content analysis can only quantify the information. Typically, general trends and patterns can be identified.
Relational Analysis
Relational analysis begins like conceptual analysis, where a concept is chosen for examination. However, the analysis involves exploring the relationships between concepts. Individual concepts are viewed as having no inherent meaning and rather the meaning is a product of the relationships among concepts.
To begin a relational content analysis, first identify a research question and choose a sample or samples for analysis. The research question must be focused so the concept types are not open to interpretation and can be summarized. Next, select text for analysis. Select text for analysis carefully by balancing having enough information for a thorough analysis so results are not limited with having information that is too extensive so that the coding process becomes too arduous and heavy to supply meaningful and worthwhile results.
There are three subcategories of relational analysis to choose from prior to going on to the general steps.
Affect extraction: an emotional evaluation of concepts explicit in a text. A challenge to this method is that emotions can vary across time, populations, and space. However, it could be effective at capturing the emotional and psychological state of the speaker or writer of the text.
Proximity analysis: an evaluation of the co-occurrence of explicit concepts in the text. Text is defined as a string of words called a “window” that is scanned for the co-occurrence of concepts. The result is the creation of a “concept matrix”, or a group of interrelated co-occurring concepts that would suggest an overall meaning.
Cognitive mapping: a visualization technique for either affect extraction or proximity analysis. Cognitive mapping attempts to create a model of the overall meaning of the text such as a graphic map that represents the relationships between concepts.
General steps for conducting a relational content analysis:
1. Determine the type of analysis: Once the sample has been selected, the researcher needs to determine what types of relationships to examine and the level of analysis: word, word sense, phrase, sentence, themes. 2. Reduce the text to categories and code for words or patterns. A researcher can code for existence of meanings or words. 3. Explore the relationship between concepts: once the words are coded, the text can be analyzed for the following:
Strength of relationship: degree to which two or more concepts are related.
Sign of relationship: are concepts positively or negatively related to each other?
Direction of relationship: the types of relationship that categories exhibit. For example, “X implies Y” or “X occurs before Y” or “if X then Y” or if X is the primary motivator of Y.
4. Code the relationships: a difference between conceptual and relational analysis is that the statements or relationships between concepts are coded. 5. Perform statistical analyses: explore differences or look for relationships among the identified variables during coding. 6. Map out representations: such as decision mapping and mental models.
Reliability and Validity
Reliability : Because of the human nature of researchers, coding errors can never be eliminated but only minimized. Generally, 80% is an acceptable margin for reliability. Three criteria comprise the reliability of a content analysis:
Stability: the tendency for coders to consistently re-code the same data in the same way over a period of time.
Reproducibility: tendency for a group of coders to classify categories membership in the same way.
Accuracy: extent to which the classification of text corresponds to a standard or norm statistically.
Validity : Three criteria comprise the validity of a content analysis:
Closeness of categories: this can be achieved by utilizing multiple classifiers to arrive at an agreed upon definition of each specific category. Using multiple classifiers, a concept category that may be an explicit variable can be broadened to include synonyms or implicit variables.
Conclusions: What level of implication is allowable? Do conclusions correctly follow the data? Are results explainable by other phenomena? This becomes especially problematic when using computer software for analysis and distinguishing between synonyms. For example, the word “mine,” variously denotes a personal pronoun, an explosive device, and a deep hole in the ground from which ore is extracted. Software can obtain an accurate count of that word’s occurrence and frequency, but not be able to produce an accurate accounting of the meaning inherent in each particular usage. This problem could throw off one’s results and make any conclusion invalid.
Generalizability of the results to a theory: dependent on the clear definitions of concept categories, how they are determined and how reliable they are at measuring the idea one is seeking to measure. Generalizability parallels reliability as much of it depends on the three criteria for reliability.
Advantages of Content Analysis
Directly examines communication using text
Allows for both qualitative and quantitative analysis
Provides valuable historical and cultural insights over time
Allows a closeness to data
Coded form of the text can be statistically analyzed
Unobtrusive means of analyzing interactions
Provides insight into complex models of human thought and language use
When done well, is considered a relatively “exact” research method
Content analysis is a readily-understood and an inexpensive research method
A more powerful tool when combined with other research methods such as interviews, observation, and use of archival records. It is very useful for analyzing historical material, especially for documenting trends over time.
Disadvantages of Content Analysis
Can be extremely time consuming
Is subject to increased error, particularly when relational analysis is used to attain a higher level of interpretation
Is often devoid of theoretical base, or attempts too liberally to draw meaningful inferences about the relationships and impacts implied in a study
Is inherently reductive, particularly when dealing with complex texts
Tends too often to simply consist of word counts
Often disregards the context that produced the text, as well as the state of things after the text is produced
Can be difficult to automate or computerize
Textbooks & Chapters
Berelson, Bernard. Content Analysis in Communication Research.New York: Free Press, 1952.
Busha, Charles H. and Stephen P. Harter. Research Methods in Librarianship: Techniques and Interpretation.New York: Academic Press, 1980.
de Sola Pool, Ithiel. Trends in Content Analysis. Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 1959.
Krippendorff, Klaus. Content Analysis: An Introduction to its Methodology. Beverly Hills: Sage Publications, 1980.
Fielding, NG & Lee, RM. Using Computers in Qualitative Research. SAGE Publications, 1991. (Refer to Chapter by Seidel, J. ‘Method and Madness in the Application of Computer Technology to Qualitative Data Analysis’.)
Methodological Articles
Hsieh HF & Shannon SE. (2005). Three Approaches to Qualitative Content Analysis.Qualitative Health Research. 15(9): 1277-1288.
Elo S, Kaarianinen M, Kanste O, Polkki R, Utriainen K, & Kyngas H. (2014). Qualitative Content Analysis: A focus on trustworthiness. Sage Open. 4:1-10.
Application Articles
Abroms LC, Padmanabhan N, Thaweethai L, & Phillips T. (2011). iPhone Apps for Smoking Cessation: A content analysis. American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 40(3):279-285.
Ullstrom S. Sachs MA, Hansson J, Ovretveit J, & Brommels M. (2014). Suffering in Silence: a qualitative study of second victims of adverse events. British Medical Journal, Quality & Safety Issue. 23:325-331.
Owen P. (2012).Portrayals of Schizophrenia by Entertainment Media: A Content Analysis of Contemporary Movies. Psychiatric Services. 63:655-659.
Choosing whether to conduct a content analysis by hand or by using computer software can be difficult. Refer to ‘Method and Madness in the Application of Computer Technology to Qualitative Data Analysis’ listed above in “Textbooks and Chapters” for a discussion of the issue.
QSR NVivo: http://www.qsrinternational.com/products.aspx
Atlas.ti: http://www.atlasti.com/webinars.html
R- RQDA package: http://rqda.r-forge.r-project.org/
Rolly Constable, Marla Cowell, Sarita Zornek Crawford, David Golden, Jake Hartvigsen, Kathryn Morgan, Anne Mudgett, Kris Parrish, Laura Thomas, Erika Yolanda Thompson, Rosie Turner, and Mike Palmquist. (1994-2012). Ethnography, Observational Research, and Narrative Inquiry. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University. Available at: https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=63 .
As an introduction to Content Analysis by Michael Palmquist, this is the main resource on Content Analysis on the Web. It is comprehensive, yet succinct. It includes examples and an annotated bibliography. The information contained in the narrative above draws heavily from and summarizes Michael Palmquist’s excellent resource on Content Analysis but was streamlined for the purpose of doctoral students and junior researchers in epidemiology.
At Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, more detailed training is available through the Department of Sociomedical Sciences- P8785 Qualitative Research Methods.
Join the Conversation
Have a question about methods? Join us on Facebook
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
Content Analysis | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
Published on 5 May 2022 by Amy Luo . Revised on 5 December 2022.
Content analysis is a research method used to identify patterns in recorded communication. To conduct content analysis, you systematically collect data from a set of texts, which can be written, oral, or visual:
- Books, newspapers, and magazines
- Speeches and interviews
- Web content and social media posts
- Photographs and films
Content analysis can be both quantitative (focused on counting and measuring) and qualitative (focused on interpreting and understanding). In both types, you categorise or ‘code’ words, themes, and concepts within the texts and then analyse the results.
Table of contents
What is content analysis used for, advantages of content analysis, disadvantages of content analysis, how to conduct content analysis.
Researchers use content analysis to find out about the purposes, messages, and effects of communication content. They can also make inferences about the producers and audience of the texts they analyse.
Content analysis can be used to quantify the occurrence of certain words, phrases, subjects, or concepts in a set of historical or contemporary texts.
In addition, content analysis can be used to make qualitative inferences by analysing the meaning and semantic relationship of words and concepts.
Because content analysis can be applied to a broad range of texts, it is used in a variety of fields, including marketing, media studies, anthropology, cognitive science, psychology, and many social science disciplines. It has various possible goals:
- Finding correlations and patterns in how concepts are communicated
- Understanding the intentions of an individual, group, or institution
- Identifying propaganda and bias in communication
- Revealing differences in communication in different contexts
- Analysing the consequences of communication content, such as the flow of information or audience responses
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
- Unobtrusive data collection
You can analyse communication and social interaction without the direct involvement of participants, so your presence as a researcher doesn’t influence the results.
- Transparent and replicable
When done well, content analysis follows a systematic procedure that can easily be replicated by other researchers, yielding results with high reliability .
- Highly flexible
You can conduct content analysis at any time, in any location, and at low cost. All you need is access to the appropriate sources.
Focusing on words or phrases in isolation can sometimes be overly reductive, disregarding context, nuance, and ambiguous meanings.
Content analysis almost always involves some level of subjective interpretation, which can affect the reliability and validity of the results and conclusions.
- Time intensive
Manually coding large volumes of text is extremely time-consuming, and it can be difficult to automate effectively.
If you want to use content analysis in your research, you need to start with a clear, direct research question .
Next, you follow these five steps.
Step 1: Select the content you will analyse
Based on your research question, choose the texts that you will analyse. You need to decide:
- The medium (e.g., newspapers, speeches, or websites) and genre (e.g., opinion pieces, political campaign speeches, or marketing copy)
- The criteria for inclusion (e.g., newspaper articles that mention a particular event, speeches by a certain politician, or websites selling a specific type of product)
- The parameters in terms of date range, location, etc.
If there are only a small number of texts that meet your criteria, you might analyse all of them. If there is a large volume of texts, you can select a sample .
Step 2: Define the units and categories of analysis
Next, you need to determine the level at which you will analyse your chosen texts. This means defining:
- The unit(s) of meaning that will be coded. For example, are you going to record the frequency of individual words and phrases, the characteristics of people who produced or appear in the texts, the presence and positioning of images, or the treatment of themes and concepts?
- The set of categories that you will use for coding. Categories can be objective characteristics (e.g., aged 30–40, lawyer, parent) or more conceptual (e.g., trustworthy, corrupt, conservative, family-oriented).
Step 3: Develop a set of rules for coding
Coding involves organising the units of meaning into the previously defined categories. Especially with more conceptual categories, it’s important to clearly define the rules for what will and won’t be included to ensure that all texts are coded consistently.
Coding rules are especially important if multiple researchers are involved, but even if you’re coding all of the text by yourself, recording the rules makes your method more transparent and reliable.
Step 4: Code the text according to the rules
You go through each text and record all relevant data in the appropriate categories. This can be done manually or aided with computer programs, such as QSR NVivo , Atlas.ti , and Diction , which can help speed up the process of counting and categorising words and phrases.
Step 5: Analyse the results and draw conclusions
Once coding is complete, the collected data is examined to find patterns and draw conclusions in response to your research question. You might use statistical analysis to find correlations or trends, discuss your interpretations of what the results mean, and make inferences about the creators, context, and audience of the texts.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Luo, A. (2022, December 05). Content Analysis | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/content-analysis-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked
How to do thematic analysis | guide & examples, data collection methods | step-by-step guide & examples, qualitative vs quantitative research | examples & methods.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to do a content analysis

What is content analysis?
Why would you use a content analysis, types of content analysis, conceptual content analysis, relational content analysis, reliability and validity, reliability, the advantages and disadvantages of content analysis, a step-by-step guide to conducting a content analysis, step 1: develop your research questions, step 2: choose the content you’ll analyze, step 3: identify your biases, step 4: define the units and categories of coding, step 5: develop a coding scheme, step 6: code the content, step 7: analyze the results, frequently asked questions about content analysis, related articles.
In research, content analysis is the process of analyzing content and its features with the aim of identifying patterns and the presence of words, themes, and concepts within the content. Simply put, content analysis is a research method that aims to present the trends, patterns, concepts, and ideas in content as objective, quantitative or qualitative data , depending on the specific use case.
As such, some of the objectives of content analysis include:
- Simplifying complex, unstructured content.
- Identifying trends, patterns, and relationships in the content.
- Determining the characteristics of the content.
- Identifying the intentions of individuals through the analysis of the content.
- Identifying the implied aspects in the content.
Typically, when doing a content analysis, you’ll gather data not only from written text sources like newspapers, books, journals, and magazines but also from a variety of other oral and visual sources of content like:
- Voice recordings, speeches, and interviews.
- Web content, blogs, and social media content.
- Films, videos, and photographs.
One of content analysis’s distinguishing features is that you'll be able to gather data for research without physically gathering data from participants. In other words, when doing a content analysis, you don't need to interact with people directly.
The process of doing a content analysis usually involves categorizing or coding concepts, words, and themes within the content and analyzing the results. We’ll look at the process in more detail below.
Typically, you’ll use content analysis when you want to:
- Identify the intentions, communication trends, or communication patterns of an individual, a group of people, or even an institution.
- Analyze and describe the behavioral and attitudinal responses of individuals to communications.
- Determine the emotional or psychological state of an individual or a group of people.
- Analyze the international differences in communication content.
- Analyzing audience responses to content.
Keep in mind, though, that these are just some examples of use cases where a content analysis might be appropriate and there are many others.
The key thing to remember is that content analysis will help you quantify the occurrence of specific words, phrases, themes, and concepts in content. Moreover, it can also be used when you want to make qualitative inferences out of the data by analyzing the semantic meanings and interrelationships between words, themes, and concepts.
In general, there are two types of content analysis: conceptual and relational analysis . Although these two types follow largely similar processes, their outcomes differ. As such, each of these types can provide different results, interpretations, and conclusions. With that in mind, let’s now look at these two types of content analysis in more detail.
With conceptual analysis, you’ll determine the existence of certain concepts within the content and identify their frequency. In other words, conceptual analysis involves the number of times a specific concept appears in the content.
Conceptual analysis is typically focused on explicit data, which means you’ll focus your analysis on a specific concept to identify its presence in the content and determine its frequency.
However, when conducting a content analysis, you can also use implicit data. This approach is more involved, complicated, and requires the use of a dictionary, contextual translation rules, or a combination of both.
No matter what type you use, conceptual analysis brings an element of quantitive analysis into a qualitative approach to research.
Relational content analysis takes conceptual analysis a step further. So, while the process starts in the same way by identifying concepts in content, it doesn’t focus on finding the frequency of these concepts, but rather on the relationships between the concepts, the context in which they appear in the content, and their interrelationships.
Before starting with a relational analysis, you’ll first need to decide on which subcategory of relational analysis you’ll use:
- Affect extraction: With this relational content analysis approach, you’ll evaluate concepts based on their emotional attributes. You’ll typically assess these emotions on a rating scale with higher values assigned to positive emotions and lower values to negative ones. In turn, this allows you to capture the emotions of the writer or speaker at the time the content is created. The main difficulty with this approach is that emotions can differ over time and across populations.
- Proximity analysis: With this approach, you’ll identify concepts as in conceptual analysis, but you’ll evaluate the way in which they occur together in the content. In other words, proximity analysis allows you to analyze the relationship between concepts and derive a concept matrix from which you’ll be able to develop meaning. Proximity analysis is typically used when you want to extract facts from the content rather than contextual, emotional, or cultural factors.
- Cognitive mapping: Finally, cognitive mapping can be used with affect extraction or proximity analysis. It’s a visualization technique that allows you to create a model that represents the overall meaning of content and presents it as a graphic map of the relationships between concepts. As such, it’s also commonly used when analyzing the changes in meanings, definitions, and terms over time.
Now that we’ve seen what content analysis is and looked at the different types of content analysis, it’s important to understand how reliable it is as a research method . We’ll also look at what criteria impact the validity of a content analysis.
There are three criteria that determine the reliability of a content analysis:
- Stability . Stability refers to the tendency of coders to consistently categorize or code the same data in the same way over time.
- Reproducibility . This criterion refers to the tendency of coders to classify categories membership in the same way.
- Accuracy . Accuracy refers to the extent to which the classification of content corresponds to a specific standard.
Keep in mind, though, that because you’ll need to code or categorize the concepts you’ll aim to identify and analyze manually, you’ll never be able to eliminate human error. However, you’ll be able to minimize it.
In turn, three criteria determine the validity of a content analysis:
- Closeness of categories . This is achieved by using multiple classifiers to get an agreed-upon definition for a specific category by using either implicit variables or synonyms. In this way, the category can be broadened to include more relevant data.
- Conclusions . Here, it’s crucial to decide what level of implication will be allowable. In other words, it’s important to consider whether the conclusions are valid based on the data or whether they can be explained using some other phenomena.
- Generalizability of the results of the analysis to a theory . Generalizability comes down to how you determine your categories as mentioned above and how reliable those categories are. In turn, this relies on how accurately the categories are at measuring the concepts or ideas that you’re looking to measure.
Considering everything mentioned above, there are definite advantages and disadvantages when it comes to content analysis:
Let’s now look at the steps you’ll need to follow when doing a content analysis.
The first step will always be to formulate your research questions. This is simply because, without clear and defined research questions, you won’t know what question to answer and, by implication, won’t be able to code your concepts.
Based on your research questions, you’ll then need to decide what content you’ll analyze. Here, you’ll use three factors to find the right content:
- The type of content . Here you’ll need to consider the various types of content you’ll use and their medium like, for example, blog posts, social media, newspapers, or online articles.
- What criteria you’ll use for inclusion . Here you’ll decide what criteria you’ll use to include content. This can, for instance, be the mentioning of a certain event or advertising a specific product.
- Your parameters . Here, you’ll decide what content you’ll include based on specified parameters in terms of date and location.
The next step is to consider your own pre-conception of the questions and identify your biases. This process is referred to as bracketing and allows you to be aware of your biases before you start your research with the result that they’ll be less likely to influence the analysis.
Your next step would be to define the units of meaning that you’ll code. This will, for example, be the number of times a concept appears in the content or the treatment of concept, words, or themes in the content. You’ll then need to define the set of categories you’ll use for coding which can be either objective or more conceptual.
Based on the above, you’ll then organize the units of meaning into your defined categories. Apart from this, your coding scheme will also determine how you’ll analyze the data.
The next step is to code the content. During this process, you’ll work through the content and record the data according to your coding scheme. It’s also here where conceptual and relational analysis starts to deviate in relation to the process you’ll need to follow.
As mentioned earlier, conceptual analysis aims to identify the number of times a specific concept, idea, word, or phrase appears in the content. So, here, you’ll need to decide what level of analysis you’ll implement.
In contrast, with relational analysis, you’ll need to decide what type of relational analysis you’ll use. So, you’ll need to determine whether you’ll use affect extraction, proximity analysis, cognitive mapping, or a combination of these approaches.
Once you’ve coded the data, you’ll be able to analyze it and draw conclusions from the data based on your research questions.
Content analysis offers an inexpensive and flexible way to identify trends and patterns in communication content. In addition, it’s unobtrusive which eliminates many ethical concerns and inaccuracies in research data. However, to be most effective, a content analysis must be planned and used carefully in order to ensure reliability and validity.
The two general types of content analysis: conceptual and relational analysis . Although these two types follow largely similar processes, their outcomes differ. As such, each of these types can provide different results, interpretations, and conclusions.
In qualitative research coding means categorizing concepts, words, and themes within your content to create a basis for analyzing the results. While coding, you work through the content and record the data according to your coding scheme.
Content analysis is the process of analyzing content and its features with the aim of identifying patterns and the presence of words, themes, and concepts within the content. The goal of a content analysis is to present the trends, patterns, concepts, and ideas in content as objective, quantitative or qualitative data, depending on the specific use case.
Content analysis is a qualitative method of data analysis and can be used in many different fields. It is particularly popular in the social sciences.
It is possible to do qualitative analysis without coding, but content analysis as a method of qualitative analysis requires coding or categorizing data to then analyze it according to your coding scheme in the next step.

Chapter 17. Content Analysis
Introduction.
Content analysis is a term that is used to mean both a method of data collection and a method of data analysis. Archival and historical works can be the source of content analysis, but so too can the contemporary media coverage of a story, blogs, comment posts, films, cartoons, advertisements, brand packaging, and photographs posted on Instagram or Facebook. Really, almost anything can be the “content” to be analyzed. This is a qualitative research method because the focus is on the meanings and interpretations of that content rather than strictly numerical counts or variables-based causal modeling. [1] Qualitative content analysis (sometimes referred to as QCA) is particularly useful when attempting to define and understand prevalent stories or communication about a topic of interest—in other words, when we are less interested in what particular people (our defined sample) are doing or believing and more interested in what general narratives exist about a particular topic or issue. This chapter will explore different approaches to content analysis and provide helpful tips on how to collect data, how to turn that data into codes for analysis, and how to go about presenting what is found through analysis. It is also a nice segue between our data collection methods (e.g., interviewing, observation) chapters and chapters 18 and 19, whose focus is on coding, the primary means of data analysis for most qualitative data. In many ways, the methods of content analysis are quite similar to the method of coding.

Although the body of material (“content”) to be collected and analyzed can be nearly anything, most qualitative content analysis is applied to forms of human communication (e.g., media posts, news stories, campaign speeches, advertising jingles). The point of the analysis is to understand this communication, to systematically and rigorously explore its meanings, assumptions, themes, and patterns. Historical and archival sources may be the subject of content analysis, but there are other ways to analyze (“code”) this data when not overly concerned with the communicative aspect (see chapters 18 and 19). This is why we tend to consider content analysis its own method of data collection as well as a method of data analysis. Still, many of the techniques you learn in this chapter will be helpful to any “coding” scheme you develop for other kinds of qualitative data. Just remember that content analysis is a particular form with distinct aims and goals and traditions.
An Overview of the Content Analysis Process
The first step: selecting content.
Figure 17.2 is a display of possible content for content analysis. The first step in content analysis is making smart decisions about what content you will want to analyze and to clearly connect this content to your research question or general focus of research. Why are you interested in the messages conveyed in this particular content? What will the identification of patterns here help you understand? Content analysis can be fun to do, but in order to make it research, you need to fit it into a research plan.
Figure 17.1. A Non-exhaustive List of "Content" for Content Analysis
To take one example, let us imagine you are interested in gender presentations in society and how presentations of gender have changed over time. There are various forms of content out there that might help you document changes. You could, for example, begin by creating a list of magazines that are coded as being for “women” (e.g., Women’s Daily Journal ) and magazines that are coded as being for “men” (e.g., Men’s Health ). You could then select a date range that is relevant to your research question (e.g., 1950s–1970s) and collect magazines from that era. You might create a “sample” by deciding to look at three issues for each year in the date range and a systematic plan for what to look at in those issues (e.g., advertisements? Cartoons? Titles of articles? Whole articles?). You are not just going to look at some magazines willy-nilly. That would not be systematic enough to allow anyone to replicate or check your findings later on. Once you have a clear plan of what content is of interest to you and what you will be looking at, you can begin, creating a record of everything you are including as your content. This might mean a list of each advertisement you look at or each title of stories in those magazines along with its publication date. You may decide to have multiple “content” in your research plan. For each content, you want a clear plan for collecting, sampling, and documenting.
The Second Step: Collecting and Storing
Once you have a plan, you are ready to collect your data. This may entail downloading from the internet, creating a Word document or PDF of each article or picture, and storing these in a folder designated by the source and date (e.g., “ Men’s Health advertisements, 1950s”). Sølvberg ( 2021 ), for example, collected posted job advertisements for three kinds of elite jobs (economic, cultural, professional) in Sweden. But collecting might also mean going out and taking photographs yourself, as in the case of graffiti, street signs, or even what people are wearing. Chaise LaDousa, an anthropologist and linguist, took photos of “house signs,” which are signs, often creative and sometimes offensive, hung by college students living in communal off-campus houses. These signs were a focal point of college culture, sending messages about the values of the students living in them. Some of the names will give you an idea: “Boot ’n Rally,” “The Plantation,” “Crib of the Rib.” The students might find these signs funny and benign, but LaDousa ( 2011 ) argued convincingly that they also reproduced racial and gender inequalities. The data here already existed—they were big signs on houses—but the researcher had to collect the data by taking photographs.
In some cases, your content will be in physical form but not amenable to photographing, as in the case of films or unwieldy physical artifacts you find in the archives (e.g., undigitized meeting minutes or scrapbooks). In this case, you need to create some kind of detailed log (fieldnotes even) of the content that you can reference. In the case of films, this might mean watching the film and writing down details for key scenes that become your data. [2] For scrapbooks, it might mean taking notes on what you are seeing, quoting key passages, describing colors or presentation style. As you might imagine, this can take a lot of time. Be sure you budget this time into your research plan.
Researcher Note
A note on data scraping : Data scraping, sometimes known as screen scraping or frame grabbing, is a way of extracting data generated by another program, as when a scraping tool grabs information from a website. This may help you collect data that is on the internet, but you need to be ethical in how to employ the scraper. A student once helped me scrape thousands of stories from the Time magazine archives at once (although it took several hours for the scraping process to complete). These stories were freely available, so the scraping process simply sped up the laborious process of copying each article of interest and saving it to my research folder. Scraping tools can sometimes be used to circumvent paywalls. Be careful here!
The Third Step: Analysis
There is often an assumption among novice researchers that once you have collected your data, you are ready to write about what you have found. Actually, you haven’t yet found anything, and if you try to write up your results, you will probably be staring sadly at a blank page. Between the collection and the writing comes the difficult task of systematically and repeatedly reviewing the data in search of patterns and themes that will help you interpret the data, particularly its communicative aspect (e.g., What is it that is being communicated here, with these “house signs” or in the pages of Men’s Health ?).
The first time you go through the data, keep an open mind on what you are seeing (or hearing), and take notes about your observations that link up to your research question. In the beginning, it can be difficult to know what is relevant and what is extraneous. Sometimes, your research question changes based on what emerges from the data. Use the first round of review to consider this possibility, but then commit yourself to following a particular focus or path. If you are looking at how gender gets made or re-created, don’t follow the white rabbit down a hole about environmental injustice unless you decide that this really should be the focus of your study or that issues of environmental injustice are linked to gender presentation. In the second round of review, be very clear about emerging themes and patterns. Create codes (more on these in chapters 18 and 19) that will help you simplify what you are noticing. For example, “men as outdoorsy” might be a common trope you see in advertisements. Whenever you see this, mark the passage or picture. In your third (or fourth or fifth) round of review, begin to link up the tropes you’ve identified, looking for particular patterns and assumptions. You’ve drilled down to the details, and now you are building back up to figure out what they all mean. Start thinking about theory—either theories you have read about and are using as a frame of your study (e.g., gender as performance theory) or theories you are building yourself, as in the Grounded Theory tradition. Once you have a good idea of what is being communicated and how, go back to the data at least one more time to look for disconfirming evidence. Maybe you thought “men as outdoorsy” was of importance, but when you look hard, you note that women are presented as outdoorsy just as often. You just hadn’t paid attention. It is very important, as any kind of researcher but particularly as a qualitative researcher, to test yourself and your emerging interpretations in this way.
The Fourth and Final Step: The Write-Up
Only after you have fully completed analysis, with its many rounds of review and analysis, will you be able to write about what you found. The interpretation exists not in the data but in your analysis of the data. Before writing your results, you will want to very clearly describe how you chose the data here and all the possible limitations of this data (e.g., historical-trace problem or power problem; see chapter 16). Acknowledge any limitations of your sample. Describe the audience for the content, and discuss the implications of this. Once you have done all of this, you can put forth your interpretation of the communication of the content, linking to theory where doing so would help your readers understand your findings and what they mean more generally for our understanding of how the social world works. [3]
Analyzing Content: Helpful Hints and Pointers
Although every data set is unique and each researcher will have a different and unique research question to address with that data set, there are some common practices and conventions. When reviewing your data, what do you look at exactly? How will you know if you have seen a pattern? How do you note or mark your data?
Let’s start with the last question first. If your data is stored digitally, there are various ways you can highlight or mark up passages. You can, of course, do this with literal highlighters, pens, and pencils if you have print copies. But there are also qualitative software programs to help you store the data, retrieve the data, and mark the data. This can simplify the process, although it cannot do the work of analysis for you.
Qualitative software can be very expensive, so the first thing to do is to find out if your institution (or program) has a universal license its students can use. If they do not, most programs have special student licenses that are less expensive. The two most used programs at this moment are probably ATLAS.ti and NVivo. Both can cost more than $500 [4] but provide everything you could possibly need for storing data, content analysis, and coding. They also have a lot of customer support, and you can find many official and unofficial tutorials on how to use the programs’ features on the web. Dedoose, created by academic researchers at UCLA, is a decent program that lacks many of the bells and whistles of the two big programs. Instead of paying all at once, you pay monthly, as you use the program. The monthly fee is relatively affordable (less than $15), so this might be a good option for a small project. HyperRESEARCH is another basic program created by academic researchers, and it is free for small projects (those that have limited cases and material to import). You can pay a monthly fee if your project expands past the free limits. I have personally used all four of these programs, and they each have their pluses and minuses.
Regardless of which program you choose, you should know that none of them will actually do the hard work of analysis for you. They are incredibly useful for helping you store and organize your data, and they provide abundant tools for marking, comparing, and coding your data so you can make sense of it. But making sense of it will always be your job alone.
So let’s say you have some software, and you have uploaded all of your content into the program: video clips, photographs, transcripts of news stories, articles from magazines, even digital copies of college scrapbooks. Now what do you do? What are you looking for? How do you see a pattern? The answers to these questions will depend partially on the particular research question you have, or at least the motivation behind your research. Let’s go back to the idea of looking at gender presentations in magazines from the 1950s to the 1970s. Here are some things you can look at and code in the content: (1) actions and behaviors, (2) events or conditions, (3) activities, (4) strategies and tactics, (5) states or general conditions, (6) meanings or symbols, (7) relationships/interactions, (8) consequences, and (9) settings. Table 17.1 lists these with examples from our gender presentation study.
Table 17.1. Examples of What to Note During Content Analysis
One thing to note about the examples in table 17.1: sometimes we note (mark, record, code) a single example, while other times, as in “settings,” we are recording a recurrent pattern. To help you spot patterns, it is useful to mark every setting, including a notation on gender. Using software can help you do this efficiently. You can then call up “setting by gender” and note this emerging pattern. There’s an element of counting here, which we normally think of as quantitative data analysis, but we are using the count to identify a pattern that will be used to help us interpret the communication. Content analyses often include counting as part of the interpretive (qualitative) process.
In your own study, you may not need or want to look at all of the elements listed in table 17.1. Even in our imagined example, some are more useful than others. For example, “strategies and tactics” is a bit of a stretch here. In studies that are looking specifically at, say, policy implementation or social movements, this category will prove much more salient.
Another way to think about “what to look at” is to consider aspects of your content in terms of units of analysis. You can drill down to the specific words used (e.g., the adjectives commonly used to describe “men” and “women” in your magazine sample) or move up to the more abstract level of concepts used (e.g., the idea that men are more rational than women). Counting for the purpose of identifying patterns is particularly useful here. How many times is that idea of women’s irrationality communicated? How is it is communicated (in comic strips, fictional stories, editorials, etc.)? Does the incidence of the concept change over time? Perhaps the “irrational woman” was everywhere in the 1950s, but by the 1970s, it is no longer showing up in stories and comics. By tracing its usage and prevalence over time, you might come up with a theory or story about gender presentation during the period. Table 17.2 provides more examples of using different units of analysis for this work along with suggestions for effective use.
Table 17.2. Examples of Unit of Analysis in Content Analysis
Every qualitative content analysis is unique in its particular focus and particular data used, so there is no single correct way to approach analysis. You should have a better idea, however, of what kinds of things to look for and what to look for. The next two chapters will take you further into the coding process, the primary analytical tool for qualitative research in general.
Further Readings
Cidell, Julie. 2010. “Content Clouds as Exploratory Qualitative Data Analysis.” Area 42(4):514–523. A demonstration of using visual “content clouds” as a form of exploratory qualitative data analysis using transcripts of public meetings and content of newspaper articles.
Hsieh, Hsiu-Fang, and Sarah E. Shannon. 2005. “Three Approaches to Qualitative Content Analysis.” Qualitative Health Research 15(9):1277–1288. Distinguishes three distinct approaches to QCA: conventional, directed, and summative. Uses hypothetical examples from end-of-life care research.
Jackson, Romeo, Alex C. Lange, and Antonio Duran. 2021. “A Whitened Rainbow: The In/Visibility of Race and Racism in LGBTQ Higher Education Scholarship.” Journal Committed to Social Change on Race and Ethnicity (JCSCORE) 7(2):174–206.* Using a “critical summative content analysis” approach, examines research published on LGBTQ people between 2009 and 2019.
Krippendorff, Klaus. 2018. Content Analysis: An Introduction to Its Methodology . 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A very comprehensive textbook on both quantitative and qualitative forms of content analysis.
Mayring, Philipp. 2022. Qualitative Content Analysis: A Step-by-Step Guide . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Formulates an eight-step approach to QCA.
Messinger, Adam M. 2012. “Teaching Content Analysis through ‘Harry Potter.’” Teaching Sociology 40(4):360–367. This is a fun example of a relatively brief foray into content analysis using the music found in Harry Potter films.
Neuendorft, Kimberly A. 2002. The Content Analysis Guidebook . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Although a helpful guide to content analysis in general, be warned that this textbook definitely favors quantitative over qualitative approaches to content analysis.
Schrier, Margrit. 2012. Qualitative Content Analysis in Practice . Thousand Okas, CA: SAGE. Arguably the most accessible guidebook for QCA, written by a professor based in Germany.
Weber, Matthew A., Shannon Caplan, Paul Ringold, and Karen Blocksom. 2017. “Rivers and Streams in the Media: A Content Analysis of Ecosystem Services.” Ecology and Society 22(3).* Examines the content of a blog hosted by National Geographic and articles published in The New York Times and the Wall Street Journal for stories on rivers and streams (e.g., water-quality flooding).
- There are ways of handling content analysis quantitatively, however. Some practitioners therefore specify qualitative content analysis (QCA). In this chapter, all content analysis is QCA unless otherwise noted. ↵
- Note that some qualitative software allows you to upload whole films or film clips for coding. You will still have to get access to the film, of course. ↵
- See chapter 20 for more on the final presentation of research. ↵
- . Actually, ATLAS.ti is an annual license, while NVivo is a perpetual license, but both are going to cost you at least $500 to use. Student rates may be lower. And don’t forget to ask your institution or program if they already have a software license you can use. ↵
A method of both data collection and data analysis in which a given content (textual, visual, graphic) is examined systematically and rigorously to identify meanings, themes, patterns and assumptions. Qualitative content analysis (QCA) is concerned with gathering and interpreting an existing body of material.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
What Is Qualitative Content Analysis?
Qca explained simply (with examples).
By: Jenna Crosley (PhD). Reviewed by: Dr Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | February 2021
If you’re in the process of preparing for your dissertation, thesis or research project, you’ve probably encountered the term “ qualitative content analysis ” – it’s quite a mouthful. If you’ve landed on this post, you’re probably a bit confused about it. Well, the good news is that you’ve come to the right place…
Overview: Qualitative Content Analysis
- What (exactly) is qualitative content analysis
- The two main types of content analysis
- When to use content analysis
- How to conduct content analysis (the process)
- The advantages and disadvantages of content analysis
1. What is content analysis?
Content analysis is a qualitative analysis method that focuses on recorded human artefacts such as manuscripts, voice recordings and journals. Content analysis investigates these written, spoken and visual artefacts without explicitly extracting data from participants – this is called unobtrusive research.
In other words, with content analysis, you don’t necessarily need to interact with participants (although you can if necessary); you can simply analyse the data that they have already produced. With this type of analysis, you can analyse data such as text messages, books, Facebook posts, videos, and audio (just to mention a few).
The basics – explicit and implicit content
When working with content analysis, explicit and implicit content will play a role. Explicit data is transparent and easy to identify, while implicit data is that which requires some form of interpretation and is often of a subjective nature. Sounds a bit fluffy? Here’s an example:
Joe: Hi there, what can I help you with?
Lauren: I recently adopted a puppy and I’m worried that I’m not feeding him the right food. Could you please advise me on what I should be feeding?
Joe: Sure, just follow me and I’ll show you. Do you have any other pets?
Lauren: Only one, and it tweets a lot!
In this exchange, the explicit data indicates that Joe is helping Lauren to find the right puppy food. Lauren asks Joe whether she has any pets aside from her puppy. This data is explicit because it requires no interpretation.
On the other hand, implicit data , in this case, includes the fact that the speakers are in a pet store. This information is not clearly stated but can be inferred from the conversation, where Joe is helping Lauren to choose pet food. An additional piece of implicit data is that Lauren likely has some type of bird as a pet. This can be inferred from the way that Lauren states that her pet “tweets”.
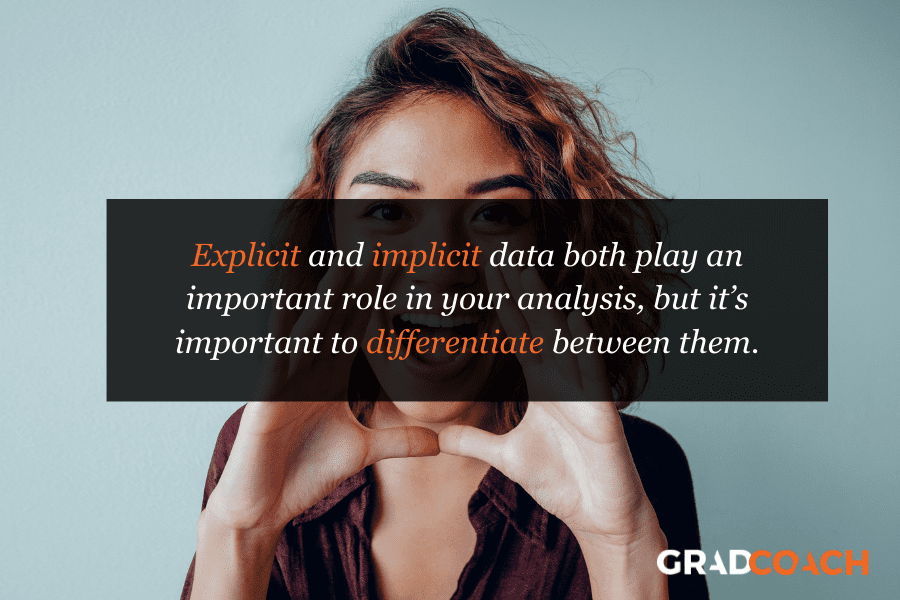
As you can see, explicit and implicit data both play a role in human interaction and are an important part of your analysis. However, it’s important to differentiate between these two types of data when you’re undertaking content analysis. Interpreting implicit data can be rather subjective as conclusions are based on the researcher’s interpretation. This can introduce an element of bias , which risks skewing your results.
2. The two types of content analysis
Now that you understand the difference between implicit and explicit data, let’s move on to the two general types of content analysis : conceptual and relational content analysis. Importantly, while conceptual and relational content analysis both follow similar steps initially, the aims and outcomes of each are different.
Conceptual analysis focuses on the number of times a concept occurs in a set of data and is generally focused on explicit data. For example, if you were to have the following conversation:
Marie: She told me that she has three cats.
Jean: What are her cats’ names?
Marie: I think the first one is Bella, the second one is Mia, and… I can’t remember the third cat’s name.
In this data, you can see that the word “cat” has been used three times. Through conceptual content analysis, you can deduce that cats are the central topic of the conversation. You can also perform a frequency analysis , where you assess the term’s frequency in the data. For example, in the exchange above, the word “cat” makes up 9% of the data. In other words, conceptual analysis brings a little bit of quantitative analysis into your qualitative analysis.
As you can see, the above data is without interpretation and focuses on explicit data . Relational content analysis, on the other hand, takes a more holistic view by focusing more on implicit data in terms of context, surrounding words and relationships.
There are three types of relational analysis:
- Affect extraction
- Proximity analysis
- Cognitive mapping
Affect extraction is when you assess concepts according to emotional attributes. These emotions are typically mapped on scales, such as a Likert scale or a rating scale ranging from 1 to 5, where 1 is “very sad” and 5 is “very happy”.
If participants are talking about their achievements, they are likely to be given a score of 4 or 5, depending on how good they feel about it. If a participant is describing a traumatic event, they are likely to have a much lower score, either 1 or 2.
Proximity analysis identifies explicit terms (such as those found in a conceptual analysis) and the patterns in terms of how they co-occur in a text. In other words, proximity analysis investigates the relationship between terms and aims to group these to extract themes and develop meaning.
Proximity analysis is typically utilised when you’re looking for hard facts rather than emotional, cultural, or contextual factors. For example, if you were to analyse a political speech, you may want to focus only on what has been said, rather than implications or hidden meanings. To do this, you would make use of explicit data, discounting any underlying meanings and implications of the speech.
Lastly, there’s cognitive mapping, which can be used in addition to, or along with, proximity analysis. Cognitive mapping involves taking different texts and comparing them in a visual format – i.e. a cognitive map. Typically, you’d use cognitive mapping in studies that assess changes in terms, definitions, and meanings over time. It can also serve as a way to visualise affect extraction or proximity analysis and is often presented in a form such as a graphic map.
To recap on the essentials, content analysis is a qualitative analysis method that focuses on recorded human artefacts . It involves both conceptual analysis (which is more numbers-based) and relational analysis (which focuses on the relationships between concepts and how they’re connected).
Need a helping hand?
3. When should you use content analysis?
Content analysis is a useful tool that provides insight into trends of communication . For example, you could use a discussion forum as the basis of your analysis and look at the types of things the members talk about as well as how they use language to express themselves. Content analysis is flexible in that it can be applied to the individual, group, and institutional level.
Content analysis is typically used in studies where the aim is to better understand factors such as behaviours, attitudes, values, emotions, and opinions . For example, you could use content analysis to investigate an issue in society, such as miscommunication between cultures. In this example, you could compare patterns of communication in participants from different cultures, which will allow you to create strategies for avoiding misunderstandings in intercultural interactions.
Another example could include conducting content analysis on a publication such as a book. Here you could gather data on the themes, topics, language use and opinions reflected in the text to draw conclusions regarding the political (such as conservative or liberal) leanings of the publication.

4. How to conduct a qualitative content analysis
Conceptual and relational content analysis differ in terms of their exact process ; however, there are some similarities. Let’s have a look at these first – i.e., the generic process:
- Recap on your research questions
- Undertake bracketing to identify biases
- Operationalise your variables and develop a coding scheme
- Code the data and undertake your analysis
Step 1 – Recap on your research questions
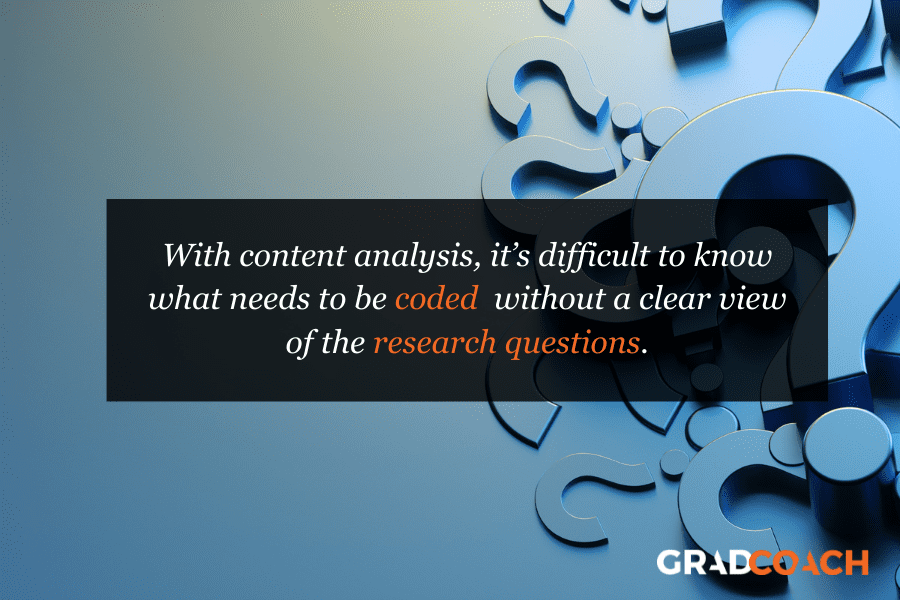
It’s always useful to begin a project with research questions , or at least with an idea of what you are looking for. In fact, if you’ve spent time reading this blog, you’ll know that it’s useful to recap on your research questions, aims and objectives when undertaking pretty much any research activity. In the context of content analysis, it’s difficult to know what needs to be coded and what doesn’t, without a clear view of the research questions.
For example, if you were to code a conversation focused on basic issues of social justice, you may be met with a wide range of topics that may be irrelevant to your research. However, if you approach this data set with the specific intent of investigating opinions on gender issues, you will be able to focus on this topic alone, which would allow you to code only what you need to investigate.
Step 2 – Reflect on your personal perspectives and biases
It’s vital that you reflect on your own pre-conception of the topic at hand and identify the biases that you might drag into your content analysis – this is called “ bracketing “. By identifying this upfront, you’ll be more aware of them and less likely to have them subconsciously influence your analysis.
For example, if you were to investigate how a community converses about unequal access to healthcare, it is important to assess your views to ensure that you don’t project these onto your understanding of the opinions put forth by the community. If you have access to medical aid, for instance, you should not allow this to interfere with your examination of unequal access.

Step 3 – Operationalise your variables and develop a coding scheme
Next, you need to operationalise your variables . But what does that mean? Simply put, it means that you have to define each variable or construct . Give every item a clear definition – what does it mean (include) and what does it not mean (exclude). For example, if you were to investigate children’s views on healthy foods, you would first need to define what age group/range you’re looking at, and then also define what you mean by “healthy foods”.
In combination with the above, it is important to create a coding scheme , which will consist of information about your variables (how you defined each variable), as well as a process for analysing the data. For this, you would refer back to how you operationalised/defined your variables so that you know how to code your data.
For example, when coding, when should you code a food as “healthy”? What makes a food choice healthy? Is it the absence of sugar or saturated fat? Is it the presence of fibre and protein? It’s very important to have clearly defined variables to achieve consistent coding – without this, your analysis will get very muddy, very quickly.

Step 4 – Code and analyse the data
The next step is to code the data. At this stage, there are some differences between conceptual and relational analysis.
As described earlier in this post, conceptual analysis looks at the existence and frequency of concepts, whereas a relational analysis looks at the relationships between concepts. For both types of analyses, it is important to pre-select a concept that you wish to assess in your data. Using the example of studying children’s views on healthy food, you could pre-select the concept of “healthy food” and assess the number of times the concept pops up in your data.
Here is where conceptual and relational analysis start to differ.
At this stage of conceptual analysis , it is necessary to decide on the level of analysis you’ll perform on your data, and whether this will exist on the word, phrase, sentence, or thematic level. For example, will you code the phrase “healthy food” on its own? Will you code each term relating to healthy food (e.g., broccoli, peaches, bananas, etc.) with the code “healthy food” or will these be coded individually? It is very important to establish this from the get-go to avoid inconsistencies that could result in you having to code your data all over again.
On the other hand, relational analysis looks at the type of analysis. So, will you use affect extraction? Proximity analysis? Cognitive mapping? A mix? It’s vital to determine the type of analysis before you begin to code your data so that you can maintain the reliability and validity of your research .
How to conduct conceptual analysis
First, let’s have a look at the process for conceptual analysis.
Once you’ve decided on your level of analysis, you need to establish how you will code your concepts, and how many of these you want to code. Here you can choose whether you want to code in a deductive or inductive manner. Just to recap, deductive coding is when you begin the coding process with a set of pre-determined codes, whereas inductive coding entails the codes emerging as you progress with the coding process. Here it is also important to decide what should be included and excluded from your analysis, and also what levels of implication you wish to include in your codes.
For example, if you have the concept of “tall”, can you include “up in the clouds”, derived from the sentence, “the giraffe’s head is up in the clouds” in the code, or should it be a separate code? In addition to this, you need to know what levels of words may be included in your codes or not. For example, if you say, “the panda is cute” and “look at the panda’s cuteness”, can “cute” and “cuteness” be included under the same code?
Once you’ve considered the above, it’s time to code the text . We’ve already published a detailed post about coding , so we won’t go into that process here. Once you’re done coding, you can move on to analysing your results. This is where you will aim to find generalisations in your data, and thus draw your conclusions .
How to conduct relational analysis
Now let’s return to relational analysis.
As mentioned, you want to look at the relationships between concepts . To do this, you’ll need to create categories by reducing your data (in other words, grouping similar concepts together) and then also code for words and/or patterns. These are both done with the aim of discovering whether these words exist, and if they do, what they mean.
Your next step is to assess your data and to code the relationships between your terms and meanings, so that you can move on to your final step, which is to sum up and analyse the data.
To recap, it’s important to start your analysis process by reviewing your research questions and identifying your biases . From there, you need to operationalise your variables, code your data and then analyse it.

5. What are the pros & cons of content analysis?
One of the main advantages of content analysis is that it allows you to use a mix of quantitative and qualitative research methods, which results in a more scientifically rigorous analysis.
For example, with conceptual analysis, you can count the number of times that a term or a code appears in a dataset, which can be assessed from a quantitative standpoint. In addition to this, you can then use a qualitative approach to investigate the underlying meanings of these and relationships between them.
Content analysis is also unobtrusive and therefore poses fewer ethical issues than some other analysis methods. As the content you’ll analyse oftentimes already exists, you’ll analyse what has been produced previously, and so you won’t have to collect data directly from participants. When coded correctly, data is analysed in a very systematic and transparent manner, which means that issues of replicability (how possible it is to recreate research under the same conditions) are reduced greatly.
On the downside , qualitative research (in general, not just content analysis) is often critiqued for being too subjective and for not being scientifically rigorous enough. This is where reliability (how replicable a study is by other researchers) and validity (how suitable the research design is for the topic being investigated) come into play – if you take these into account, you’ll be on your way to achieving sound research results.
Recap: Qualitative content analysis
In this post, we’ve covered a lot of ground – click on any of the sections to recap:
If you have any questions about qualitative content analysis, feel free to leave a comment below. If you’d like 1-on-1 help with your qualitative content analysis, be sure to book an initial consultation with one of our friendly Research Coaches.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

14 Comments
If I am having three pre-decided attributes for my research based on which a set of semi-structured questions where asked then should I conduct a conceptual content analysis or relational content analysis. please note that all three attributes are different like Agility, Resilience and AI.
Thank you very much. I really enjoyed every word.
please send me one/ two sample of content analysis
send me to any sample of qualitative content analysis as soon as possible
Many thanks for the brilliant explanation. Do you have a sample practical study of a foreign policy using content analysis?
1) It will be very much useful if a small but complete content analysis can be sent, from research question to coding and analysis. 2) Is there any software by which qualitative content analysis can be done?
Common software for qualitative analysis is nVivo, and quantitative analysis is IBM SPSS
Thank you. Can I have at least 2 copies of a sample analysis study as my reference?
Could you please send me some sample of textbook content analysis?
Can I send you my research topic, aims, objectives and questions to give me feedback on them?
please could you send me samples of content analysis?
Yes please send
really we enjoyed your knowledge thanks allot. from Ethiopia
can you please share some samples of content analysis(relational)? I am a bit confused about processing the analysis part
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Content Analysis
- First Online: 02 January 2023
Cite this chapter

- Scott Tunison 4
Part of the book series: Springer Texts in Education ((SPTE))
4131 Accesses
1 Citations
Content analysis emerged from studies of archived texts (Vogt et al., When to use what research design, Guilford Press, 2012), such as newspapers, transcripts of speeches, and magazines. (Ellingson, The SAGE handbook of qualitative research (4th ed., pp. 595–610). Sage, 2011.) noted that content analysis resides in the postpositivist typology which allows researchers to “conduct an inductive analysis of textual data, form a typology grounded in the data … use the derived typology to sort data into categories, and then count the frequencies of each theme or category across data” (p. 596).
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Anderson, G., & Arsenault, N. (1998). Fundamentals of educational research (2nd ed.). Routledge.
Google Scholar
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2018). Research methods in education (8th ed.). Routledge.
Creswell, J. (2011). Controversies in mixed methods research. In N. Denzin & Y. Lincoln (Eds.), The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research (4th ed., pp. 269–283). Sage.
Ellingson, L. (2011). Analysis and representation across the continuum. In N. Denzin & Y. Lincoln (Eds.), The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research (4th ed., pp. 595–610). Sage.
Ezzy, D. (2002). Qualitative analysis: Practice and innovation . Routledge.
Mayring, P. (2004). Qualitative content analysis. In U. Flick, E. von Kardoff, & I. Steinke (Eds.), A companion to qualitative research . Sage.
Newby, P. (2010). Research methods for education . Pearson Education.
Robson, C. (2002). Real world research (2nd ed.). Blackwell.
Vogt, W. P., Gardner, D., & Haeffele, L. (2012). When to use what research design . Guilford Press.
Online Resources
Adu, P. (2016). Qualitative analysis: Coding and categorizing data . https://youtu.be/v_mg7OBpb2Y
Duke University—Mod-U (2016). How to know you are coding correctly: Qualitative research methods . https://youtu.be/iL7Ww5kpnIM
Gramenz, G. (2014). How to code a document and create themes . https://youtu.be/sHv3RzKWNcQ
Shaw, A. (2019). NVivo 12 and thematic/content analysis . https://youtu.be/5s9-rg1ygWs
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Canada
Scott Tunison
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Scott Tunison .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Educational Administration, College of Education, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Janet Mola Okoko
Department of Educational Administration, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Keith D. Walker
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Tunison, S. (2023). Content Analysis. In: Okoko, J.M., Tunison, S., Walker, K.D. (eds) Varieties of Qualitative Research Methods. Springer Texts in Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04394-9_14
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04394-9_14
Published : 02 January 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-04396-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-04394-9
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Am J Pharm Educ
- v.84(1); 2020 Jan
Demystifying Content Analysis
A. j. kleinheksel.
a The Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, Augusta, Georgia
Nicole Rockich-Winston
Huda tawfik.
b Central Michigan University, College of Medicine, Mt. Pleasant, Michigan
Tasha R. Wyatt
Objective. In the course of daily teaching responsibilities, pharmacy educators collect rich data that can provide valuable insight into student learning. This article describes the qualitative data analysis method of content analysis, which can be useful to pharmacy educators because of its application in the investigation of a wide variety of data sources, including textual, visual, and audio files.
Findings. Both manifest and latent content analysis approaches are described, with several examples used to illustrate the processes. This article also offers insights into the variety of relevant terms and visualizations found in the content analysis literature. Finally, common threats to the reliability and validity of content analysis are discussed, along with suitable strategies to mitigate these risks during analysis.
Summary. This review of content analysis as a qualitative data analysis method will provide clarity and actionable instruction for both novice and experienced pharmacy education researchers.

INTRODUCTION
The Academy’s growing interest in qualitative research indicates an important shift in the field’s scientific paradigm. Whereas health science researchers have historically looked to quantitative methods to answer their questions, this shift signals that a purely positivist, objective approach is no longer sufficient to answer pharmacy education’s research questions. Educators who want to study their teaching and students’ learning will find content analysis an easily accessible, robust method of qualitative data analysis that can yield rigorous results for both publication and the improvement of their educational practice. Content analysis is a method designed to identify and interpret meaning in recorded forms of communication by isolating small pieces of the data that represent salient concepts and then applying or creating a framework to organize the pieces in a way that can be used to describe or explain a phenomenon. 1 Content analysis is particularly useful in situations where there is a large amount of unanalyzed textual data, such as those many pharmacy educators have already collected as part of their teaching practice. Because of its accessibility, content analysis is also an appropriate qualitative method for pharmacy educators with limited experience in educational research. This article will introduce and illustrate the process of content analysis as a way to analyze existing data, but also as an approach that may lead pharmacy educators to ask new types of research questions.
Content analysis is a well-established data analysis method that has evolved in its treatment of textual data. Content analysis was originally introduced as a strictly quantitative method, recording counts to measure the observed frequency of pre-identified targets in consumer research. 1 However, as the naturalistic qualitative paradigm became more prevalent in social sciences research and researchers became increasingly interested in the way people behave in natural settings, the process of content analysis was adapted into a more interesting and meaningful approach. Content analysis has the potential to be a useful method in pharmacy education because it can help educational researchers develop a deeper understanding of a particular phenomenon by providing structure in a large amount of textual data through a systematic process of interpretation. It also offers potential value because it can help identify problematic areas in student understanding and guide the process of targeted teaching. Several research studies in pharmacy education have used the method of content analysis. 2-7 Two studies in particular offer noteworthy examples: Wallman and colleagues employed manifest content analysis to analyze semi-structured interviews in order to explore what students learn during experiential rotations, 7 while Moser and colleagues adopted latent content analysis to evaluate open-ended survey responses on student perceptions of learning communities. 6 To elaborate on these approaches further, we will describe the two types of qualitative content analysis, manifest and latent, and demonstrate the corresponding analytical processes using examples that illustrate their benefit.
Qualitative Content Analysis
Content analysis rests on the assumption that texts are a rich data source with great potential to reveal valuable information about particular phenomena. 8 It is the process of considering both the participant and context when sorting text into groups of related categories to identify similarities and differences, patterns, and associations, both on the surface and implied within. 9-11 The method is considered high-yield in educational research because it is versatile and can be applied in both qualitative and quantitative studies. 12 While it is important to note that content analysis has application in visual and auditory artifacts (eg, an image or song), for our purposes we will largely focus on the most common application, which is the analysis of textual or transcribed content (eg, open-ended survey responses, print media, interviews, recorded observations, etc). The terminology of content analysis can vary throughout quantitative and qualitative literature, which may lead to some confusion among both novice and experienced researchers. However, there are also several agreed-upon terms and phrases that span the literature, as found in Table 1 .
Terms and Definitions Used in Qualitative Content Analysis

There is more often disagreement on terminology in the methodological approaches to content analysis, though the most common differentiation is between the two types of content: manifest and latent. In much of the literature, manifest content analysis is defined as describing what is occurring on the surface, what is and literally present, and as “staying close to the text.” 8,13 Manifest content analysis is concerned with data that are easily observable both to researchers and the coders who assist in their analyses, without the need to discern intent or identify deeper meaning. It is content that can be recognized and counted with little training. Early applications of manifest analysis focused on identifying easily observable targets within text (eg, the number of instances a certain word appears in newspaper articles), film (eg, the occupation of a character), or interpersonal interactions (eg, tracking the number of times a participant blinks during an interview). 14 This application, in which frequency counts are used to understand a phenomenon, reflects a surface-level analysis and assumes there is objective truth in the data that can be revealed with very little interpretation. The number of times a target (ie, code) appears within the text is used as a way to understand its prevalence. Quantitative content analysis is always describing a positivist manifest content analysis, in that the nature of truth is believed to be objective, observable, and measurable. Qualitative research, which favors the researcher’s interpretation of an individual’s experience, may also be used to analyze manifest content. However, the intent of the application is to describe a dynamic reality that cannot be separated from the lived experiences of the researcher. Although qualitative content analysis can be conducted whether knowledge is thought to be innate, acquired, or socially constructed, the purpose of qualitative manifest content analysis is to transcend simple word counts and delve into a deeper examination of the language in order to organize large amounts of text into categories that reflect a shared meaning. 15,16 The practical distinction between quantitative and qualitative manifest content analysis is the intention behind the analysis. The quantitative method seeks to generate a numerical value to either cite prevalence or use in statistical analyses, while the qualitative method seeks to identify a construct or concept within the text using specific words or phrases for substantiation, or to provide a more organized structure to the text being described.
Latent content analysis is most often defined as interpreting what is hidden deep within the text. In this method, the role of the researcher is to discover the implied meaning in participants’ experiences. 8,13 For example, in a transcribed exchange in an office setting, a participant might say to a coworker, “Yeah, here we are…another Monday. So exciting!” The researcher would apply context in order to discover the emotion being conveyed (ie, the implied meaning). In this example, the comment could be interpreted as genuine, it could be interpreted as a sarcastic comment made in an attempt at humor in order to develop or sustain social bonds with the coworker, or the context might imply that the sarcasm was meant to convey displeasure and end the interaction.
Latent content analysis acknowledges that the researcher is intimately involved in the analytical process and that the their role is to actively use mental schema, theories, and lenses to interpret and understand the data. 10 Whereas manifest analyses are typically conducted in a way that the researcher is thought to maintain distance and separation from the objects of study, latent analyses underscore the importance of the researcher co-creating meaning with the text. 17 Adding nuance to this type of content, Potter and Levine‐Donnerstein argue that within latent content analysis, there are two distinct types: latent pattern and latent projective . 14 Latent pattern content analysis seeks to establish a pattern of characteristics in the text itself, while latent projective content analysis leverages the researcher’s own interpretations of the meaning of the text. While both approaches rely on codes that emerge from the content using the coder’s own perspectives and mental schema, the distinction between these two types of analyses are in their foci. 14 Though we do not agree, some researchers believe that all qualitative content analysis is latent content analysis. 11 These disagreements typically occur where there are differences in intent and where there are areas of overlap in the results. For example, both qualitative manifest and latent pattern content analyses may identify patterns as a result of their application. Though in their research design, the researcher would have approached the content with different methodological approaches, with a manifest approach seeking only to describe what is observed, and the latent pattern approach seeking to discover an unseen pattern. At this point, these distinctions may seem too philosophical to serve a practical purpose, so we will attempt to clarify these concepts by presenting three types of analyses for illustrative purposes, beginning with a description of how codes are created and used.
Creating and Using Codes
Codes are the currency of content analysis. Researchers use codes to organize and understand their data. Through the coding process, pharmacy educators can systematically and rigorously categorize and interpret vast amounts of text for use in their educational practice or in publication. Codes themselves are short, descriptive labels that symbolically assign a summative or salient attribute to more than one unit of meaning identified in the text. 18 To create codes, a researcher must first become immersed in the data, which typically occurs when a researcher transcribes recorded data or conducts several readings of the text. This process allows the researcher to become familiar with the scope of the data, which spurs nascent ideas about potential concepts or constructs that may exist within it. If studying a phenomenon that has already been described through an existing framework, codes can be created a priori using theoretical frameworks or concepts identified in the literature. If there is no existing framework to apply, codes can emerge during the analytical process. However, emergent codes can also be created as addenda to a priori codes that were identified before the analysis begins if the a priori codes do not sufficiently capture the researcher’s area of interest.
The process of detecting emergent codes begins with identification of units of meaning. While there is no one way to decide what qualifies as a meaning unit, researchers typically define units of meaning differently depending on what kind of analysis is being conducted. As a general rule, when dialogue is being analyzed, such as interviews or focus groups, meaning units are identified as conversational turns, though a code can be as short as one or two words. In written text, such as student reflections or course evaluation data, the researcher must decide if the text should be divided into phrases or sentences, or remain as paragraphs. This decision is usually made based on how many different units of meaning are expressed in a block of text. For example, in a paragraph, if there are several thoughts or concepts being expressed, it is best to break up the paragraph into sentences. If one sentence contains multiple ideas of interest, making it difficult to separate one important thought or behavior from another, then the sentence can be divided into smaller units, such as phrases or sentence fragments. These phrases or sentence fragments are then coded as separate meaning units. Conversely, longer or more complex units of meaning should be condensed into shorter representations that still retain the original meaning in order to reduce the cognitive burden of the analytical process. This could entail removing verbal ticks (eg, “well, uhm…”) from transcribed data or simplifying a compound sentence. Condensation does not ascribe interpretation or implied meaning to a unit, but only shortens a meaning unit as much as possible while preserving the original meaning identified. 18 After condensation, a researcher can proceed to the creation of codes.
Many researchers begin their analyses with several general codes in mind that help guide their focus as defined by their research question, even in instances where the researcher has no a priori model or theory. For example, if a group of instructors are interested in examining recorded videos of their lectures to identify moments of student engagement, they may begin with using generally agreed upon concepts of engagement as codes, such as students “raising their hands,” “taking notes,” and “speaking in class.” However, as the instructors continue to watch their videos, they may notice other behaviors which were not initially anticipated. Perhaps students were seen creating flow charts based on information presented in class. Alternatively, perhaps instructors wanted to include moments when students posed questions to their peers without being prompted. In this case, the instructors would allow the codes of “creating graphic organizers” and “questioning peers” to emerge as additional ways to identify the behavior of student engagement.
Once a researcher has identified condensed units of meaning and labeled them with codes, the codes are then sorted into categories which can help provide more structure to the data. In the above example of recorded lectures, perhaps the category of “verbal behaviors” could be used to group the codes of “speaking in class” and “questioning peers.” For complex analyses, subcategories can also be used to better organize a large amount of codes, but solely at the discretion of the researcher. Two or more categories of codes are then used to identify or support a broader underlying meaning which develops into themes. Themes are most often employed in latent analyses; however, they are appropriate in manifest analyses as well. Themes describe behaviors, experiences, or emotions that occur throughout several categories. 18 Figure 1 illustrates this process. Using the same videotaped lecture example, the instructors might identify two themes of student engagement, “active engagement” and “passive engagement,” where active engagement is supported by the category of “verbal behavior” and also a category that includes the code of “raising their hands” (perhaps something along the lines of “pursuing engagement”), and the theme of “passive engagement” is supported by a category used to organize the behaviors of “taking notes” and “creating graphic organizers.”

The Process of Qualitative Content Analysis
To more fully demonstrate the process of content analysis and the generation and use of codes, categories, and themes, we present and describe examples of both manifest and latent content analysis. Given that there are multiple ways to create and use codes, our examples illustrate both processes of creating and using a predetermined set of codes. Regardless of the kind of content analysis instructors want to conduct, the initial steps are the same. The instructor must analyze the data using codes as a sense-making process.
Manifest Content Analysis
The first form of analysis, manifest content analysis, examines text for elements that exist on the surface of the text, the meaning of which is taken at face value. Schools and colleges of pharmacy may benefit from conducting manifest content analyses at a programmatic level, including analysis of student evaluations to determine the value of certain courses, or analysis of recruitment materials for addressing issues of cultural humility in a uniform manner. Such uses for manifest content analysis may help administrators make more data-based decisions about students and courses. However, for our example of manifest content analysis, we illustrate the use of content analysis in informing instruction for a single pharmacy educator ( Figure 2 ).

A Student’s Completed Beta-blocker Case with Codes in Underlined Bold Text
In the example, a pharmacology instructor is trying to assess students’ understanding of three concepts related to the beta-blocker class of drugs: indication of the drug, relevance of family history, and contraindications and precautions. To do so, the instructor asks the students to write a patient case in which beta-blockers are indicated. The instructor gives the students the following prompt: “Reverse-engineer a case in which beta-blockers would be prescribed to the patient. Include a history of the present illness, the patients’ medical, family, and social history, medications, allergies, and relevant lab tests.” Figure 2 is a hypothetical student’s completed assignment, in which they demonstrate their understanding of when and why a beta-blocker would be prescribed.
The student-generated cases are then treated as data and analyzed for the presence of the three previously identified indicators of understanding in order to help the instructor make decisions about where and how to focus future teaching efforts related to this drug class. Codes are created a priori out of the instructor’s interest in analyzing students’ understanding of the concepts related to beta-blocker prescriptions. A codebook ( Table 2 ) is created with the following columns: name of code, code description, and examples of the code. This codebook helps an individual researcher to approach their analysis systematically, but it can also facilitate coding by multiple coders who would apply the same rules outlined in the codebook to the coding process.
Example Code Book Created for Manifest Content Analysis

Using multiple coders introduces complexity to the analysis process, but it is oftentimes the only practical way to analyze large amounts of data. To ensure that all coders are working in tandem, they must establish inter-rater reliability as part of their training process. This process requires that a single form of text be selected, such as one student evaluation. After reviewing the codebook and receiving instruction, everyone on the team individually codes the same piece of data. While calculating percentage agreement has sometimes been used to establish inter-rater reliability, most publication editors require more rigorous statistical analysis (eg, Krippendorf’s alpha, or Cohen’s kappa). 19 Detailed descriptions of these statistics fall outside the scope of this introduction, but it is important to note that the choice depends on the number of coders, the sample size, and the type of data to be analyzed.
Latent Content Analysis
Latent content analysis is another option for pharmacy educators, especially when there are theoretical frameworks or lenses the educator proposes to apply. Such frameworks describe and provide structure to complex concepts and may often be derived from relevant theories. Latent content analysis requires that the researcher is intimately involved in interpreting and finding meaning in the text because meaning is not readily apparent on the surface. 10 To illustrate a latent content analysis using a combination of a priori and emergent codes, we will use the example of a transcribed video excerpt from a student pharmacist interaction with a standardized patient. In this example, the goal is for first-year students to practice talking to a customer about an over-the-counter medication. The case is designed to simulate a customer at a pharmacy counter, who is seeking advice on a medication. The learning objectives for the pharmacist in-training are to assess the customer’s symptoms, determine if the customer can self-treat or if they need to seek out their primary care physician, and then prescribe a medication to alleviate the patient’s symptoms.
To begin, pharmacy educators conducting educational research should first identify what they are looking for in the video transcript. In this case, because the primary outcome for this exercise is aimed at assessing the “soft skills” of student pharmacists, codes are created using the counseling rubric created by Horton and colleagues. 20 Four a priori codes are developed using the literature: empathy, patient-friendly terms, politeness, and positive attitude. However, because the original four codes are inadequate to capture all areas representing the skills the instructor is looking for during the process of analysis, four additional codes are also created: active listening, confidence, follow-up, and patient at ease. Figure 3 presents the video transcript with each of the codes assigned to the meaning units in bolded parentheses.

A Transcript of a Student’s (JR) Experience with a Standardized Patient (SP) in Which the Codes are Bolded in Parentheses
Following the initial coding using these eight codes, the codes are consolidated to create categories, which are depicted in the taxonomy in Figure 4 . Categories are relationships between codes that represent a higher level of abstraction in the data. 18 To reach conclusions and interpret the fundamental underlying meaning in the data, categories are then organized into themes ( Figure 1 ). Once the data are analyzed, the instructor can assign value to the student’s performance. In this case, the coding process determines that the exercise demonstrated both positive and negative elements of communication and professionalism. Under the category of professionalism, the student generally demonstrated politeness and a positive attitude toward the standardized patient, indicating to the reviewer that the theme of perceived professionalism was apparent during the encounter. However, there were several instances in which confidence and appropriate follow-up were absent. Thus, from a reviewer perspective, the student's performance could be perceived as indicating an opportunity to grow and improve as a future professional. Typically, there are multiple codes in a category and multiple categories in a theme. However, as seen in the example taxonomy, this is not always the case.

Example of a Latent Content Analysis Taxonomy
If the educator is interested in conducting a latent projective analysis, after identifying the construct of “soft skills,” the researcher allows for each coder to apply their own mental schema as they look for positive and negative indicators of the non-technical skills they believe a student should develop. Mental schema are the cognitive structures that provide organization to knowledge, which in this case allows coders to categorize the data in ways that fit their existing understanding of the construct. The coders will use their own judgement to identify the codes they feel are relevant. The researcher could also choose to apply a theoretical lens to more effectively conceptualize the construct of “soft skills,” such as Rogers' humanism theory, and more specifically, concepts underlying his client-centered therapy. 21 The role of theory in both latent pattern and latent projective analyses is at the discretion of the researcher, and often is determined by what already exists in the literature related to the research question. Though, typically, in latent pattern analyses theory is used for deductive coding, and in latent projective analyses underdeveloped theory is used to first deduce codes and then for induction of the results to strengthen the theory applied. For our example, Rogers describes three salient qualities to develop and maintain a positive client-professional relationship: unconditional positive regard, genuineness, and empathetic understanding. 21 For the third element, specifically, the educator could look for units of meaning that imply empathy and active listening. For our video transcript analysis, this is evident when the student pharmacist demonstrated empathy by responding, "Yeah, I understand," when discussing aggravating factors for the patient's condition. The outcome for both latent pattern and latent projective content analysis is to discover the underlying meaning in a text, such as social rules or mental models. In this example, both pattern and projective approaches can discover interpreted aspects of a student’s abilities and mental models for constructs such as professionalism and empathy. The difference in the approaches is where the precedence lies: in the belief that a pattern is recognizable in the content, or in the mental schema and lived experiences of the coder(s). To better illustrate the differences in the processes of latent pattern and projective content analyses, Figure 5 presents a general outline of each method beginning with the creation of codes and concluding with the generation of themes.

Flow Chart of the Stages of Latent Pattern and Latent Projective Content Analysis
How to Choose a Methodological Approach to Content Analysis
To determine which approach a researcher should take in their content analysis, two decisions need to be made. First, researchers must determine their goal for the analysis. Second, the researcher must decide where they believe meaning is located. 14 If meaning is located in the discrete elements of the content that are easily identified on the surface of the text, then manifest content analysis is appropriate. If meaning is located deep within the content and the researcher plans to discover context cues and make judgements about implied meaning, then latent content analysis should be applied. When designing the latent content analysis, a researcher then must also identify their focus. If the analysis is intended to identify a recognizable truth within the content by uncovering connections and characteristics that all coders should be able to discover, then latent pattern content analysis is appropriate. If, on the other hand, the researcher will rely heavily on the judgment of the coders and believes that interpretation of the content must leverage the mental schema of the coders to locate deeper meaning, then latent projective content analysis is the best choice.
To demonstrate how a researcher might choose a methodological approach, we have presented a third example of data in Figure 6 . In our two previous examples of content analysis, we used student data. However, faculty data can also be analyzed as part of educational research or for faculty members to improve their own teaching practices. Recall in the video data analyzed using latent content analysis, the student was tasked to identify a suitable over-the-counter medication for a patient complaining of heartburn symptoms. We have extended this example by including an interview with the pharmacy educator supervising the student who was videotaped. The goal of the interview is to evaluate the educator’s ability to assess the student’s performance with the standardized patient. Figure 6 is an excerpt of the interview between the course instructor and an instructional coach. In this conversation, the instructional coach is eliciting evidence to support the faculty member’s views, judgements, and rationale for the educator’s evaluation of the student’s performance.

A Transcript of an Interview in Which the Interviewer (IN) Questions a Faculty Member (FM) Regarding Their Student’s Standardized Patient Experience
Manifest content analysis would be a valid choice for this data if the researcher was looking to identify evidence of the construct of “instructor priorities” and defined discrete codes that described aspects of performance such as “communication,” “referrals,” or “accurate information.” These codes could be easily identified on the surface of the transcribed interview by identifying keywords related to each code, such as “communicate,” “talk,” and “laugh,” for the code of “communication.” This would allow coders to identify evidence of the concept of “instructor priorities” by sorting through a potentially large amount of text with predetermined targets in mind.
To conduct a latent pattern analysis of this interview, researchers would first immerse themselves in the data to identify a theoretical framework or concepts that represent the area of interest so that coders could discover an emerging truth underneath the surface of the data. After immersion in the data, a researcher might believe it would be interesting to more closely examine the strategies the coach uses to establish rapport with the instructor as a way to better understand models of professional development. These strategies could not be easily identified in the transcripts if read literally, but by looking for connections within the text, codes related to instructional coaching tactics emerge. A latent pattern analysis would require that the researcher code the data in a way that looks for patterns, such as a code of “facilitating reflection,” that could be identified in open-ended questions and other units of meaning where the coder saw evidence of probing techniques, or a code of “establishing rapport” for which a coder could identify nonverbal cues such as “[IN leans forward in chair].”
Conducting latent projective content analysis might be useful if the researcher was interested in using a broader theoretical lens, such as Mezirow’s theory of transformative learning. 22 In this example, the faculty member is understood to have attempted to change a learner’s frame of reference by facilitating cognitive dissonance or a disorienting experience through a standardized patient simulation. To conduct a latent projective analysis, the researcher could analyze the faculty member’s interview using concepts found in this theory. This kind of analysis will help the researcher assess the level of change that the faculty member was able to perceive, or expected to witness, in their attempt to help their pharmacy students improve their interactions with patients. The units of meaning and subsequent codes would rely on the coders to apply their own knowledge of transformative learning because of the absence in the theory of concrete, context-specific behaviors to identify. For this analysis, the researcher would rely on their interpretations of what challenging educational situations look like, what constitutes cognitive dissonance, or what the faculty member is really expecting from his students’ performance. The subsequent analysis could provide evidence to support the use of such standardized patient encounters within the curriculum as a transformative learning experience and would also allow the educator to self-reflect on his ability to assess simulated activities.
OTHER ASPECTS TO CONSIDER
Navigating terminology.
Among the methodological approaches, there are other terms for content analysis that researchers may come across. Hsieh and Shannon 10 proposed three qualitative approaches to content analysis: conventional, directed, and summative. These categories were intended to explain the role of theory in the analysis process. In conventional content analysis, the researcher does not use preconceived categories because existing theory or literature are limited. In directed content analysis, the researcher attempts to further describe a phenomenon already addressed by theory, applying a deductive approach and using identified concepts or codes from exiting research to validate the theory. In summative content analysis, a descriptive approach is taken, identifying and quantifying words or content in order to describe their context. These three categories roughly map to the terms of latent projective, latent pattern, and manifest content analyses respectively, though not precisely enough to suggest that they are synonyms.
Graneheim and colleagues 9 reference the inductive, deductive, and abductive methods of interpretation of content analysis, which are data-driven, concept-driven, and fluid between both data and concepts, respectively. Where manifest content produces phenomenological descriptions most often (but not always) through deductive interpretation, and latent content analysis produces interpretations most often (but not always) through inductive or abductive interpretations. Erlingsson and Brysiewicz 23 refer to content analysis as a continuum, progressing as the researcher develops codes, then categories, and then themes. We present these alternative conceptualizations of content analysis to illustrate that the literature on content analysis, while incredibly useful, presents a multitude of interpretations of the method itself. However, these complexities should not dissuade readers from using content analysis. Identifying what you want to know (ie, your research question) will effectively direct you toward your methodological approach. That said, we have found the most helpful aid in learning content analysis is the application of the methods we have presented.
Ensuring Quality
The standards used to evaluate quantitative research are seldom used in qualitative research. The terms “reliability” and “validity” are typically not used because they reflect the positivist quantitative paradigm. In qualitative research, the preferred term is “trustworthiness,” which is comprised of the concepts of credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability, and researchers can take steps in their work to demonstrate that they are trustworthy. 24 Though establishing trustworthiness is outside the scope of this article, novice researchers should be familiar with the necessary steps before publishing their work. This suggestion includes exploration of the concept of saturation, the idea that researchers must demonstrate they have collected and analyzed enough data to warrant their conclusions, which has been a focus of recent debate in qualitative research. 25
There are several threats to the trustworthiness of content analysis in particular. 14 We will use the terms “reliability and validity” to describe these threats, as they are conceptualized this way in the formative literature, and it may be easier for researchers with a quantitative research background to recognize them. Though some of these threats may be particular to the type of data being analyzed, in general, there are risks specific to the different methods of content analysis. In manifest content analysis, reliability is necessary but not sufficient to establish validity. 14 Because there is little judgment required of the coders, lack of high inter-rater agreement among coders will render the data invalid. 14 Additionally, coder fatigue is a common threat to manifest content analysis because the coding is clerical and repetitive in nature.
For latent pattern content analysis, validity and reliability are inversely related. 14 Greater reliability is achieved through more detailed coding rules to improve consistency, but these rules may diminish the accessibility of the coding to consumers of the research. This is defined as low ecological validity. Higher ecological validity is achieved through greater reliance on coder judgment to increase the resonance of the results with the audience, yet this often decreases the inter-rater reliability. In latent projective content analysis, reliability and validity are equivalent. 14 Consistent interpretations among coders both establishes and validates the constructed norm; construction of an accurate norm is evidence of consistency. However, because of this equivalence, issues with low validity or low reliability cannot be isolated. A lack of consistency may result from coding rules, lack of a shared schema, or issues with a defined variable. Reasons for low validity cannot be isolated, but will always result in low consistency.
Any good analysis starts with a codebook and coder training. It is important for all coders to share the mental model of the skill, construct, or phenomenon being coded in the data. However, when conducting latent pattern or projective content analysis in particular, micro-level rules and definitions of codes increase the threat of ecological validity, so it is important to leave enough room in the codebook and during the training to allow for a shared mental schema to emerge in the larger group rather than being strictly directed by the lead researcher. Stability is another threat, which occurs when coders make different judgments as time passes. To reduce this risk, allowing for recoding at a later date can increase the consistency and stability of the codes. Reproducibility is not typically a goal of qualitative research, 15 but for content analysis, codes that are defined both prior to and during analysis should retain their meaning. Researchers can increase the reproducibility of their codebook by creating a detailed audit trail, including descriptions of the methods used to create and define the codes, materials used for the training of the coders, and steps taken to ensure inter-rater reliability.
In all forms of qualitative analysis, coder fatigue is a common threat to trustworthiness, even when the instructor is coding individually. Over time, the cases may start to look the same, making it difficult to refocus and look at each case with fresh eyes. To guard against this, coders should maintain a reflective journal and write analytical memos to help stay focused. Memos might include insights that the researcher has, such as patterns of misunderstanding, areas to focus on when considering re-teaching specific concepts, or specific conversations to have with students. Fatigue can also be mitigated by occasionally talking to participants (eg, meeting with students and listening for their rationale on why they included specific pieces of information in an assignment). These are just examples of potential exercises that can help coders mitigate cognitive fatigue. Most researchers develop their own ways to prevent the fatigue that can seep in after long hours of looking at data. But above all, a sufficient amount of time should be allowed for analysis, so that coders do not feel rushed, and regular breaks should be scheduled and enforced.
Qualitative content analysis is both accessible and high-yield for pharmacy educators and researchers. Though some of the methods may seem abstract or fluid, the nature of qualitative content analysis encompasses these concerns by providing a systematic approach to discover meaning in textual data, both on the surface and implied beneath it. As with most research methods, the surest path towards proficiency is through application and intentional, repeated practice. We encourage pharmacy educators to ask questions suited for qualitative research and to consider the use of content analysis as a qualitative research method for discovering meaning in their data.
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >
4 Qualitative Content Analysis
- Published: November 2015
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This chapter examines qualitative content analysis, a recent methodological innovation. Qualitative content analysis is defined and distinguished here from basic and interpretive approaches to content analysis. Qualitative content analysis is also distinguished from other qualitative research methods, though features and techniques overlap with other qualitative methods. Key differences in the predominant use of newly collected data and use of non-quantitative analysis techniques are detailed. Differences in epistemology and the role of researcher self-awareness and reflexivity are also discussed. Methods of graphic data presentation are illustrated. Three short exemplar studies using qualitative content analysis are described and examined. Qualitative content analysis is explored in detail in terms of its characteristic components: (1) the research purposes of content analysis, (2) target audiences, (3) epistemological issues, (4) ethical issues, (5) research designs, (6) sampling issues and methods, (7) collecting data, (8) coding and categorization methods, (9) data analysis methods, and (10) the role of researcher reflection.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
- Google Scholar Indexing
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
About a third of U.S. workers who can work from home now do so all the time

Roughly three years after the COVID-19 pandemic upended U.S. workplaces, about a third (35%) of workers with jobs that can be done remotely are working from home all of the time, according to a new Pew Research Center survey. This is down from 43% in January 2022 and 55% in October 2020 – but up from only 7% before the pandemic.
While the share working from home all the time has fallen off somewhat as the pandemic has gone on, many workers have settled into hybrid work. The new survey finds that 41% of those with jobs that can be done remotely are working a hybrid schedule – that is, working from home some days and from the office, workplace or job site other days. This is up from 35% in January 2022.
Among hybrid workers who are not self-employed, most (63%) say their employer requires them to work in person a certain number of days per week or month. About six-in-ten hybrid workers (59%) say they work from home three or more days in a typical week, while 41% say they do so two days or fewer.
Related: How Americans View Their Jobs
Many hybrid workers would prefer to spend more time working from home than they currently do. About a third (34%) of those who are currently working from home most of the time say, if they had the choice, they’d like to work from home all the time. And among those who are working from home some of the time, half say they’d like to do so all (18%) or most (32%) of the time.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to study how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected the workplace and specifically how workers with jobs that can be done from home have adapted their work schedules. To do this, we surveyed 5,775 U.S. adults who are working part time or full time and who have only one job or who have more than one job but consider one of them to be their primary job. All the workers who took part are members of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses.
Address-based sampling ensures that nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for this analysis, along with responses, and the survey’s methodology .
The majority of U.S. workers overall (61%) do not have jobs that can be done from home. Workers with lower incomes and those without a four-year college degree are more likely to fall into this category. Among those who do have teleworkable jobs, Hispanic adults and those without a college degree are among the most likely to say they rarely or never work from home.
When looking at all employed adults ages 18 and older in the United States, Pew Research Center estimates that about 14% – or roughly 22 million people – are currently working from home all the time.
The advantages and disadvantages of working from home
Workers who are not self-employed and who are teleworking at least some of the time see one clear advantage – and relatively few downsides – to working from home. By far the biggest perceived upside to working from home is the balance it provides: 71% of those who work from home all, most or some of the time say doing so helps them balance their work and personal lives. That includes 52% who say it helps them a lot with this.
About one-in-ten (12%) of those who are at least occasionally working from home say it hurts their ability to strike the right work-life balance, and 17% say it neither helps nor hurts. There is no significant gender difference in these views. However, parents with children younger than 18 are somewhat more likely than workers without children in that age range to say working from home is helpful in this regard (76% vs. 69%).
A majority of those who are working from home at least some of the time (56%) say this arrangement helps them get their work done and meet deadlines. Only 7% say working from home hurts their ability to do these things, and 37% say it neither helps nor hurts.
There are other aspects of work – some of them related to career advancement – where the impact of working from home seems minimal:
- When asked how working from home affects whether they are given important assignments, 77% of those who are at least sometimes working from home say it neither helps nor hurts, while 14% say it helps and 9% say it hurts.
- When it comes to their chances of getting ahead at work, 63% of teleworkers say working from home neither helps or hurts, while 18% say it helps and 19% say it hurts.
- A narrow majority of teleworkers (54%) say working from home neither helps nor hurts with opportunities to be mentored at work. Among those who do see an impact, it’s perceived to be more negative than positive: 36% say working from home hurts opportunities to be mentored and 10% say it helps.
One aspect of work that many remote workers say working from home makes more challenging is connecting with co-workers: 53% of those who work from home at least some of the time say working from home hurts their ability to feel connected with co-workers, while 37% say it neither helps nor hurts. Only 10% say it helps them feel connected.
In spite of this, those who work from home all the time or occasionally are no less satisfied with their relationship with co-workers than those who never work from home. Roughly two-thirds of workers – whether they are working exclusively from home, follow a hybrid schedule or don’t work from home at all – say they are extremely or very satisfied with these relationships. In addition, among those with teleworkable jobs, employed adults who work from home all the time are about as likely as hybrid workers to say they have at least one close friend at work.
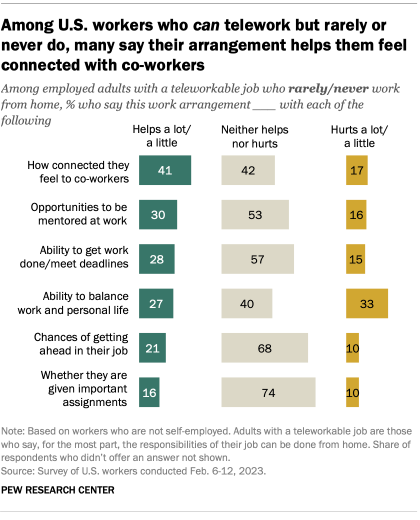
Feeling connected with co-workers is one area where many workers who rarely or never work from home see an advantage in their setup. About four-in-ten of these workers (41%) say the fact that they rarely or never work from home helps in how connected they feel to their co-workers. A similar share (42%) say it neither helps nor hurts, and 17% say it hurts.
At the same time, those who rarely or never work from home are less likely than teleworkers to say their current arrangement helps them achieve work-life balance. A third of these workers say the fact that they rarely or never work from home hurts their ability to balance their work and personal lives, while 40% say it neither helps nor hurts and 27% say it helps.
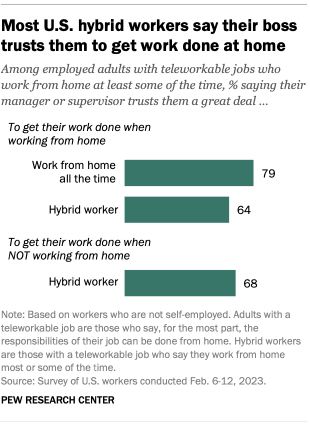
When it comes to other aspects of work, many of those who rarely or never work from home say their arrangement is neither helpful nor hurtful. This is true when it comes to opportunities to be mentored (53% say this), their ability to get work done and meet deadlines (57%), their chances of getting ahead in their job (68%) and whether they are given important assignments (74%).
Most adults with teleworkable jobs who work from home at least some of the time (71%) say their manager or supervisor trusts them a great deal to get their work done when they’re doing so. Those who work from home all the time are the most likely to feel trusted: 79% of these workers say their manager trusts them a great deal, compared with 64% of hybrid workers.
Hybrid workers feel about as trusted when they’re not working from home: 68% say their manager or supervisor trusts them a great deal to get their work done when they’re not teleworking.
Note: Here are the questions used for this analysis, along with responses, and the survey’s methodology .
- Business & Workplace
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)

Majorities of adults see decline of union membership as bad for the U.S. and working people
A look at black-owned businesses in the u.s., from businesses and banks to colleges and churches: americans’ views of u.s. institutions, 2023 saw some of the biggest, hardest-fought labor disputes in recent decades, older workers are growing in number and earning higher wages, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- Open access
- Published: 15 April 2024
Construction and application of the core competence course training system for infectious disease specialist nurses
- Chao Wu 1 na1 ,
- Hongli Zhang 1 , 2 na1 ,
- Yawei Lin 3 na1 ,
- Weiyun Yuan 4 ,
- Jing He 5 ,
- Donglei Jiang 7 ,
- Zhaohua Ji 8 &
- Hongjuan Lang 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 410 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
170 Accesses
Metrics details
This study aims to construct and apply a training course system which was scientific and comprehensive to foster the core competence of infectious disease specialist nurses.
A two-round Delphi consultation survey was carried out to collect feedback from experts on constructing the training course system of core competence for infectious disease specialist nurses. Besides, a non-randomized controlled experimental study was adopted to check the application effect of the courses.
This study adopted a series of methods including group discussion, theoretical analysis and Delphi consultation to draft the training course content of core competence of infectious disease specialist nurses. Twenty-one Chinese experts were invited to participate in the Delphi consultation from November 2021 to December 2021. From October 2022 to January 2023, a total of 105 infectious disease specialist nurses from two training bases were selected by the convenience sampling method, of which the nurses in one training base were the control group and the nurses in the other training base were the observation group. The observation group was trained by the constructed core competence training course. Questionnaire evaluation was used to compare the core competence of infectious disease specialist nurses and the training effect.
The experts, regarded as the authorities on the subject, were highly motivated in this study. Besides, they reached a consensus on the results. The final training course system of core competence for infectious disease specialist nurses focused on 5 competence modules and was composed of 12 categories of courses with 66 classes and corresponding objectives. The core competence scores of the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group after training ( P < 0.05), which proved the training system can effectively enhance the core competence of infectious disease specialist nurses.
Conclusions
The research methods embodied scientific and precise properties. The course system was comprehensive in content and reliable in results. It could serve as a reference for training infectious disease specialist nurses.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
With the rapid development of medical treatment, especially in the era of knowledge, nurses must continue to learn in order to meet the needs of professional development [ 1 , 2 ]. It is reported that continuing education and vocational learning are the main ways for nurses to acquire knowledge [ 3 ]. Continuing education and scientific training can help post-qualification nurses to master new knowledge [ 4 , 5 ]. Specialist nurses refer to expert clinical nurses with high competence and expertise in a specialized nursing field, who can use their knowledge, expertise and technology to provide nursing services for patients and social groups [ 6 , 7 ]. As the backbone of the nursing team, specialist nurses play a critical role in team dynamics [ 8 , 9 ]. Therefore, continuing education for this group is particularly important. In China, however, infectious disease specialist nurse training and infection control education are still in the initial stage, we need to further optimize the teaching arrangements, teaching methods and training procedures [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. Since nurse specialization is a field that does not share the same standardization as medical specialties do, a lot of heterogeneity exists.
Infection prevention has always been a very important field even before the COVID-19 pandemic. It is essential for preventing healthcare-associated infections, and particularly the spread of multidrug resistant bacteria [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 ]. Nurses’ infection prevention and infection nursing ability not only guarantees their own safety, but also greatly affects the quality and efficiency of infectious disease nursing. As an important way of cultivation, nursing training ensures the sustainability of the nursing team [ 17 ]. Therefore, how to train infectious disease specialist nurses effectively to meet the practical needs is of great importance and urgency. More and more studies focus on the ability of infectious disease nurses [ 18 , 19 , 20 ]. But it is noticeable that there are no mature, systematic and scientific training courses for Chinese infectious disease specialist nurses. In fact, the training of Chinese specialist infectious disease professionals has been carried out in the training base established by different hospitals, which has then been assessed by their own standards. After passing the assessment, trainees will be awarded the qualification. Owing to the different training standards at individual hospitals, the curriculum, training materials and methods are not uniform. Besides, the medical development in different regions of China is unbalanced. It is not conducive to the homogeneous development of infectious disease specialist nurses. Taking the frequent occurrence of emerging infectious diseases into consideration, the existing training system of infectious disease nursing cannot meet the urgent clinical needs for the development of nursing. The implementation of a standardized curriculum may be the prerequisite for comprehensively improving the core competence of infectious disease nurses, with the courses being the training core.
Therefore, our study aims at constructing and applying a set of scientific training courses for infectious disease specialist nurses which can regulate the training of infectious disease specialist nurses in different hospitals, improve the training quality and enhance the development of infectious disease specialist nursing so as to better respond to the infectious diseases.
Construction of a core competence course training system for infectious disease specialist nurses
Establishment of the research group.
The research group was set up before the research, including one professor, one associate professor, two lecturers, one nurse-in-charge and one postgraduate. The draft of the course training system was constructed on the basis of the index system of core competence assessment for infectious disease specialist nurses constructed in the early stage [ 19 ]. The research group analyzed and categorized all the indicators and translated them into competence modules, course categories and class contents, and then compiled the expert consultation questionnaires, distributed the questionnaires and analyzed the feedback.
Selection of the experts
We developed a pool of potential participants who met our inclusion criteria and had expertise in infection control. By using the random sampling method and sending invitation, 21 experts out of the expert resources were selected to engage in the consultation. The research group explained the research contents and purposes to the experts before the consultation. Besides, consultation would not be conducted until the consent was got from each expert. The expert panel contained three types of professionals and the inclusion criteria were as follows: (a) for experts on infectious disease health care: they should be engaged in infectious disease health care or infectious disease medical supervision for more than 15 years, obtain the intermediate or advanced level of certificate, have a bachelor degree or above, sign the informed consent form and voluntarily participate in this study; (b) for experts on infectious disease nursing: they should be engaged in infectious disease nursing or infectious disease nursing supervision for more than 15 years, obtain the intermediate or advanced level of certificate, have a bachelor degree or above, sign the informed consent form and voluntarily participate in this study; (c) for experts on infectious disease nursing education, they should be engaged in the teaching of infectious disease nursing in the training class of infectious disease specialist nurses for more than 3 years or in institutions of higher education for more than 15 years, obtain the intermediate or advanced level of certificate, have a bachelor degree or above, sign the informed consent form and voluntarily participate in this study.
Construction of the expert consultation questionnaire
The expert consultation questionnaire was composed of three parts: (a) basic information of the experts which included name, age, professional title, years of engaging in infectious disease specialist nurse training and working unit, etc.; (b) the first draft of the course training system of core competence of infectious disease specialist nurses consisting of 5 competence modules, 12 course categories, 46 class contents and their corresponding objectives. The importance of course system was evaluated by way of Likert 5-level scoring method, 5 = very important, 4 = important, 3 = general, 2 = unimportant, 1 = completely unimportant, and the column for suggestions and supplements was provided; (c) expert familiarity with content of the survey and judgement.
Questionnaire distribution and analysis
The consultation questionnaires were sent via e-mail. To ensure the quality of the consultation questionnaire, the experts had two weeks to fill in the questionnaire. We revised the questionnaire according to the results of the first-round consultation and issued the revised questionnaire to the experts for the second round. Two rounds of Delphi consultation were carried out during November and December of 2021. In the process, the training courses were refined and revised until the final version of the training course system of core competence for infectious disease specialist nurses was eventually formed.
The statistical software SPSS26.0 was applied in the process of data analysis. Variable distribution was checked for continuous variables and was parametrically distributed variables. Data measurement and data calculation were expressed in the form of mean ± standard deviation, frequency, and percentage respectively. The enthusiasm of the experts was also expressed in the form of questionnaire response rate. The authority degree of the expert opinion was shown by the authority coefficient. The coordination degree of expert opinion was displaced by variable coefficient and Kendall harmony coefficient. It indicated that the difference was statistically significant ( P < 0.05).
Quality control
The research group selected experts from 5 different provinces and cities to participate in the consultation. And the experts were from 3 different fields, namely infectious disease health care, infectious disease nursing and infectious disease nursing education.
Application of the core competence course training system for infectious disease specialist nurses
Participants.
A non-randomized controlled experimental study design was adopted in our research and the required sample size was calculated by software G*Power 2.1. Repeated measures analysis of variance statistic method was chosen to estimate the sample size, and with the effect size being 0.8, α being 0.05, power being 0.95, allocation ratio being 1, the total sample size was at least 84.
From October 2022 to January 2023, a total of 105 infectious disease specialist nurses from two training bases were selected by convenience sampling method, the selected nurses in one training base were the control group (50) while the selected ones in the other training bases (55) were the observation group.
Research implementation
In the empirical study, the control group did not apply the core competence course training system, and they only participated in the relevant traditional training courses, while the observation group was trained with the core competence course training system.
Evaluation methodology
Core competence of infectious disease specialist nurses is measured by self-report questionnaire measurement. We used the infectious disease specialist nurses’ core competence scale [ 21 ] which was specifically developed by the research group in the early stage to evaluate their core competence before and after the training. The scale has good reliability and validity. It contained 5 dimensions and 34 items: Professional Development Abilities (11 items), Infection Prevention and Control Abilities (9 items), Nursing Abilities for Infectious Diseases (6 items), Professionalism and Humanistic Accomplishment (5 items) and Responsiveness to Emergency Infectious Diseases (3 items). The scale adopted the 5-level scoring method, ranging from “fully consistent with the item” to “completely disagree with the item”, the scale was scored from “5 points” to “1 point”. The higher the score of the questionnaire was, the higher the infectious disease specialist nurses’ core competence was.
From October 2022 to January 2023, before the start of the study and after the implementation of the course, we distributed questionnaires to the two groups of infectious disease specialist nurses to investigate their core competence. After we collected the questionnaire, the differences in the core competence of the two groups before and after training were identified. The entire process was shown in Fig. 1 .
The entire process of the study
Qualifications of lecturers
In order to ensure the quality of training, lecturers needed to have the following qualifications: obtaining a bachelor degree or above, having intermediate or above professional titles. When the course content was settled, qualified lecturers were selected and given half a year to prepare for the lectures before they carried out the training.
Ethical consideration
This study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki [ 22 , 23 ]. The purpose and significance of the study were explained to the participants and informed consent of participants was obtained. During the investigation, the participants could terminate and withdraw from the consultation at any time. And their personal information was completely confidential. The inquiry data was only used for this study and not open for other purposes.
Basic information of the experts
The age of the experts ranged from 34 to 51 years old, with an average of 42.48 (SD 4.63). Their length of service varied from 3 to 24 years, with an average of 14.05 (SD 6.36) years. The details were shown in Table 1 .
Experts’ interest in the topic
The enthusiasm of the experts was assessed on the basis of the return rate of the questionnaires. In this study, during the two rounds of consultation, 21 questionnaires were distributed and 21 valid questionnaires were returned with a response rate of 100%. The details were shown in Table 2 .
Experts’ authority coefficient
The authority of the expert opinions was illustrated by the authority coefficient. It was the arithmetic average of the judgement coefficient and familiarity coefficient. The authority coefficient over 0.7 indicated that the result of consultation was reliable. The experts’ judgement was based on practical experience, theoretical analysis, domestic and foreign reference materials and intuitive perception. The degree of expert familiarity was divided into four categories, and each item was referred to a different value shown in Tables 3 and 4 .
In this study, the experts exhibited a judgement coefficient of 0.952, a degree of expert familiarity of 0.962, and an authority coefficient of 0.957, as evidenced in Tables 5 and 6 .
Experts’ opinion coordination degree
The experts’ opinion coordination degree was used to judge whether the experts had disagreements on the importance of the items. It was normally expressed by Kendall’s coefficient of concordance (Kendall’s W). The Kendall’s W ranged from 0 to 1. The closer to 1 it was, the higher the degree of experts’ opinion coordination was.
In the first round of consultation, the Kendall’s W of competence module, course category and class content were 0.280, 0.292 and 0.303 respectively while in the second round of consultation, the data were 0.301, 0.350 and 0.253 respectively. The Kendall’s W test showed statistical significance ( P <0.05), indicating that the experts’ opinion coordination degree in the two rounds of consultation was satisfactory, as shown in Table 7 .
Results of the Delphi consultation
In the first round of questionnaire consultation, 18 experts put forward their suggestions on the revision of the course system. After group discussion, we modified the course system: revising 2 course categories, deleting 1 class content, revising 10 class contents, adding 10 class contents, splitting 1 class content into 2 parts, revising 12 class objectives and adding 22 class objectives. The specific modifications were as follows. II-1 Introduction to Infectious Diseases and II-2 Responding to Infectious Diseases were respectively revised to II-1 The ability of predicting epidemics and conducting emergency drills and II-2 The ability of responding to infectious disease epidemics. I-1-3 Questionnaire designing and data collection was revised to How to prepare questionnaire and select data. I-1-5 Common medical statistical approaches was revised to Medical statistics. I-3-1 Good curriculum design was revised to How to design classes and conduct teaching methodology. II-1-3 Emergency plan and response procedures for public health emergencies of the infectious diseases was revised to How to compile emergency plan and drill for public health emergencies of the infectious diseases. II-2-2 Treatment and prevention to SARS, Ebola hemorrhagic fever and COVID-19 was revised to How to respond to public health of the infectious diseases such as SARS, Ebola hemorrhagic fever and COVID-19. III-2-1 Collection of the infectious disease patients’ blood culture specimen was revised to How to collect different specimen from infectious disease patients and transport blood culture specimen. IV-1-2 Coping with vocational stress in nursing was revised to How to adjust and cope with vocational stress in infectious disease nursing. IV-1-4 Prevention and coping with disputes in nursing was revised to Nursing and corresponding laws. IV-2-2 Promoting psychological healthcare for infectious disease patients from the perspective of positive psychology was revised to psychological nursing of infectious disease patients, and V-1-2 disinfection to infectious diseases was revised to How to disinfect the environment and instrument in infectious disease section.
I-2-4 Management of refined nursing and patients’ safety in infectious disease section was split into How to conduct refined nursing management and How to carry out safety management for infectious disease patients.
How to analyze key nationwide infectious diseases and epidemic trends, How to predict and recognize public health emergencies of the infectious diseases, How to compile emergency plan and drill for public health emergencies of the infectious diseases and Laws and regulations related to major infectious diseases were integrated into The ability of predicting epidemics and conducting emergency drills. How to respond to public health of the infectious diseases such as SARS, Ebola hemorrhagic fever and COVID-19 was integrated into The ability of responding to infectious disease epidemics.
I-1-1 Research progress of infectious disease nursing was deleted on the principle that the item should be deleted if its average was lower than 3.5 and variable coefficient was higher than 0.25. How to apply research project and declare project achievement, How to cultivate scientific research literacy, How to solve clinical issues and transform patent, How to manage nursing personnel in infectious disease section, How to manage materials such as drugs, consumable items and instruments in infectious disease section, How to carry out clinical teaching and practical teaching, How to train nurses in general department under the circumstance of infectious disease emergencies, How to predict and recognize public health emergencies of the infectious disease, Laws and regulations related to major infectious diseases and Nursing care to patients with multiple resistant bacteria were added to the system.
In the second round of questionnaire consultation, 4 experts put forward their suggestions on the revision of the course system: revising 1 class content and 4 class objectives. The specific modifications were as follows. How to analyze key nationwide infectious diseases and epidemic trends was revised to How to analyze key worldwide infectious diseases and epidemic trends while its class objective was revised as “to know the epidemic distribution of the worldwide infectious disease and its trends”. The objective “to master the principles of dosage and route, method of common medication” was revised as “to master the principles of dosage, route and method of common medication, observation of curative effect, and precaution of toxic and side effect”. The objective “to know the nursing care to patients with virus infectious diseases such as mumps, Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome, epidemic encephalitis B, hand-foot-and-mouth disease and rabies” was revised as “to know the nursing care to patients with virus infectious diseases such as mumps, Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome, epidemic encephalitis B, hand-foot-and-mouth disease, rabies and HFRS”. The objective “to master correct put-on and removal procedures of protective equipment” was revised as “to master the selection of medical protective equipment under different protection levels and correct put-on and removal procedures of protective equipment”.
Finally, core competence training courses for infectious diseases specialist nurses focused on 5 competence modules (professional development abilities, responsiveness to infectious diseases, nursing abilities for infectious diseases, professionalism and humanistic accomplishment, and infection prevention and control abilities). The courses were divided into 12 categories and composed of 66 classes, as shown in Table 8 .
The general information of infectious disease specialist nurses in the two groups were shown in Table 9 . The general demographic baseline data of the two groups were balancing and comparable.
Before the training, the core competence of the infectious disease specialist nurses between the two groups had no statistical significance. After the training, the scores in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group ( P < 0.05). Comparing the nurses in the same group before and after the training, the observation group demonstrated significant improvements in professional development abilities, infection prevention and control abilities, nursing abilities for infectious diseases, and responsiveness to emergency infectious diseases ( P < 0.05). These results indicate that the training courses are both scientifically designed and effective, as depicted in Table 10 .
Reliability and scientific validity of Delphi expert consultation results
Under the guidance of the previous index system of core competence assessment for infectious disease specialist nurses [ 19 ] and on the basis of fully reviewing the core competence training course of specialist nurses [ 24 , 25 , 26 ] and core competence theory [ 27 , 28 , 29 ], after rigorous Delphi expert consultation, this study constructed the training course system for infectious disease specialist nurses. The system contained 4 aspects, such as the training competence modules, course categories, class contents and class objectives.
Before class contents were formulated, the research group held group meeting, consulted and drew feedback from the experts, and invited them to assess the feasibility of the first draft of the course system so as to ensure the practicability of the class contents. The experts involved in the research belonged to level-A tertiary hospitals, infectious disease specialist hospitals and School of Nursing in high educational institutions in 5 provinces and cities around China. They all had rich clinical and nursing education experience of infectious diseases. The Kendall’s coefficient of concordance of the two rounds of Delphi expert consultation after significance testing ( P < 0.05) indicated that the experts’ opinion coordination degree was preferable and the results of the study were reliable. As there was no standardized training course system of core competence of infectious disease specialist nurses, our study scientifically constructed a comprehensive training course system.
Analysis of course system contents
The training course system of in this study focused on 5 competence modules and was divided into 12 course categories which involved 66 class contents and corresponding objectives. The competence module of professional development was the key point of this training course system. Scientific research on nursing was the biggest problem that had always plagued the clinical nurses [ 30 , 31 ]. Compared with ordinary nurses, the specialist nurses should have a more systematic and comprehensive scientific research knowledge system and capability [ 32 ]. Besides, a high level of scientific research could improve efficiency and quality of nursing [ 33 ]. Our study targeted on the weaknesses of clinical nurses and problems that urgently needed to be solved. Scientific research on nursing was regarded as the priority of the training course system. The system not only covered such contents as scientific research selection and design, literature review and statistical analysis and paper writing, but also extended to the related contents such as research project application and achievement declaration, clinical issues and patent transformation so that the system could effectively guarantee the improvement of the specialist nurses’ core competence. Although scientific research is important to nursing practices, it should not be the sole focus or priority of training and education programs which should virtually focus on ability development and practical approaches. In the competence modules of professional development, the weighting target of classes of nursing management accounted for the largest proportion, around 0.082. It covered the contents of management of nursing quality, management of refined nursing and so on, aiming to improve the nursing management capabilities of the infectious disease specialist nurses through comprehensive management training classes so that the specialist nurses could play the role of nursing managers in clinical work and improve the quality of infectious disease nursing. Specialist nurses not only needed to play such important roles as nursing staff and nursing managers, but also needed to act as nursing educators who could deliver lectures on infectious diseases to ordinary nurses, nursing students and nursing staff in other departments [ 34 , 35 ]. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, nurses in infectious disease department proffered great help to nurses in other departments in quickly responding to the pandemic [ 36 ].
The infectious disease specialist nurses should not only be proficient in infectious disease nursing, but also have the ability to deal with infectious diseases. Considering the infectious disease specialist nurses lacked the ability of response to infectious diseases, the competence module of response to infectious disease was regarded as a relatively important part of this training course system. Starting with the two course categories, including prediction and emergency drills and response to infectious disease epidemics, this module elaborated on the distribution of the current key global infectious diseases and analysis of their development trend, prediction and recognition of the public health emergencies, interpretation of laws and regulations related to major infectious diseases, and China’s experience in responding to major outbreaks of infectious diseases in the past ten years. The contents of this module ranged from theory to practice, and from macro analysis to specific operations. This kind of setting aimed to yield effective measures and meet the needs of responding to future infectious disease emergencies.
Nursing abilities for infectious disease were the basic abilities that infectious disease specialist nurses should acquire. The weighting target of this competence module was 0.204, ranking the second. This competence module of nursing for infectious disease included three categories, namely nursing capabilities, commonly used diagnosis and treatment technology in infectious disease department and critical thinking capabilities, with nursing capabilities accounting for the largest proportion of 0.086. Infectious disease specialist nurses should be proficient in the symptoms and signs of different types of infectious disease patients and corresponding nursing skills, and should take targeted nursing measures so as to provide patients with high-quality nursing service [ 20 ]. They should also be proficient in commonly used diagnosis and treatment techniques in infectious disease nursing process. At the same time, they should foster their critical thinking capability in the process of training [ 37 ], which was important in nursing work because it could help avoid nursing errors and accidents and improve work efficiency. The classes of critical thinking aimed to strengthen the specialist nurses’ critical thinking abilities in the nursing of clinical infectious disease.
The competence module of professionalism and humanistic accomplishment consisted of two categories, professionalism and humanistic care, with respective weightings of 0.080 and 0.082. The classes of professionalism aimed at improving the infectious disease specialist nurses’ professionalism through the study of career planning and vocational stress coping in infectious disease nursing. The classes of humanistic accomplishment encompassed humanistic care in nursing, health education and health promotion, and application of hospice among infectious disease patients. The classes reflected the humanistic feelings in infectious disease nursing, including the care to infectious disease patients and the health education to the public, as well as the hospice care to infectious disease patients at the terminal stage.
The competence module of infection prevention and control made up the largest proportion of the expert questionnaire consultation in this training course system. Infection prevention and control ability was the most important ability which affected the continuation of the combat effectiveness of nursing staff. The competence module of infection prevention and control included two categories, disinfection and quarantine, and occupational protection. These categories had equal weighting targets, accounting for approximately 0.090 each. The disinfection and quarantine classes, as well as the occupational protection classes, were structured to cover both theoretical and practical aspects so as to provide comprehensive lectures on infectious disease disinfection and quarantine, improvement and standardization of infectious disease specialist nurses’ occupational protection ability.
Significance of the training course system
At present, great differences lie in training contents, objectives, resources and management among infectious disease specialist nurses. Our study established a comprehensive, scientific and standardized training course system which covered both the competence requirements that general nurses need to meet and the contents that infectious disease specialist nurses should learn. The study has practical significance in training specialist nurses and especially in improving both the overall training quality and core competence of infectious disease specialist nurses. Homogeneous training of infectious disease specialist nurses plays an important role in responses to public health emergencies of major infectious diseases. If nurses get homogeneous training with the uniform standards and nursing procedures, they can definitely cooperate better and fulfil their work faster when they gather together from different provinces and cities to fight against the epidemics. In this study, the training course system has been developed through group discussions and expert consultations to better meet the expectations of infectious disease specialist nurses. Through training course system, infectious disease specialist nurses can systematically learn the professional knowledge, master new nursing skills and techniques, and improve the accuracy and proficiency of actual practice. And it may serve as a reference for the homogeneous training of infectious disease specialist nurses in the future.
Limitations
There are some limitations in the construction of the training course system of core competence of infectious disease specialist nurses by way of Delphi expert consultation. The Delphi study is prone to subjective factors and may lack profound theoretical and logical arguments. Besides, it lasts for a long period of time. Although the expert participants were selected from three different fields such as infectious disease health care, infectious disease nursing and infectious disease nursing education, and from five different provinces and cities, it would be more representative if the experts belonged to more fields, and more provinces and cities. In the subsequent study, we will explore the duration of the acquisitions and implement the training course in diverse geographical contexts.
In this study, through two rounds of Delphi expert questionnaire consultation, we establish the training course system of core competence for infectious disease specialist nurses which focuses on 5 competence modules and consists of 12 course categories with 66 class contents and corresponding objectives. On the basis of the scientific and rigorous research methods, as well as the comprehensive content of the training course system, we have obtained the reliable research results. In conclusion, the training course system can serve as a valuable reference for training infectious disease specialist nurses.
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to the protection of the privacy of consulting experts but are available from the corresponding author ([email protected]) on reasonable request.
Mahan JD, Clinchot D. Why medical education is being (inexorably) re-imagined and re-designed. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2014;44(6):137–40.
Article Google Scholar
Drake RL. A retrospective and prospective look at medical education in the United States: trends shaping anatomical sciences education. J Anat. 2014;224(3):256–60.
Longhini J, Rossettini G, Palese A. Massive open online courses for nurses’ and healthcare professionals’ continuous education: a scoping review. Int Nurs Rev. 2021;68(1):108–21.
Yao X, Cheng G, Shao J, Wang Y, Lin Y, Zhang C. Development and implementation of a standardized training program for newly graduated mental health nurses: process and preliminary outcomes. Nurse Educ Today. 2021;104:104953.
Holt SL, Vivian SR, Brown H. Training and preparedness of clinical coaches for their role in Training Student Veterinary nurses in the United Kingdom: an exploratory Inquiry. J Vet Med Educ 2021:e20200100.
Brennan EJ. Towards resilience and wellbeing in nurses. Br J Nurs. 2017;26(1):43–7.
Forsell L, Forsberg A, Kisch A, Rantala A. Specialist Ambulance Nurses’ Perceptions of Nursing: A Phenomenographic Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17(14).
Latter KA, Purser S, Chisholm S, Robinson E. Divisional review of the nurse specialist role. Nurs Standard (Royal Coll Nurs (Great Britain): 1987). 2019;34(5):31–4.
Mayo AM, Ray MM, Chamblee TB, Urden LD, Moody R. The Advanced Practice Clinical Nurse specialist. Nurs Adm Q. 2017;41(1):70–6.
Ling DL, Hu J, Zhong MY, Li WT, Yu HJ. Attitudes and beliefs towards implementation of nurse prescribing among general nurses and nurse specialists in China: a cross-sectional survey study. Nurs open. 2021;8(5):2760–72.
Cheng Q, Zhang Q, Liu X, Chen Y. Initial exploration of training for palliative care specialist nurses in mainland China. Nurse Educ Today. 2021;101:104869.
Tong Y, Zhu H, Wang J, Zou Y, Gao H, Cheng M. The effect of training orthopedic nurse specialists in Jiangsu Province of China. Annals Palliat Med. 2021;10(9):9488–96.
Salian VS, Wright JA, Vedell PT, Nair S, Li C, Kandimalla M, Tang X, Carmona Porquera EM, Kalari KR, Kandimalla KK. COVID-19 transmission, current treatment, and future therapeutic strategies. Mol Pharm. 2021;18(3):754–71.
Ejaz H, Alsrhani A, Zafar A, Javed H, Junaid K, Abdalla AE, Abosalif KOA, Ahmed Z, Younas S. COVID-19 and comorbidities: deleterious impact on infected patients. J Infect Public Health. 2020;13(12):1833–9.
White EM, Wetle TF, Reddy A, Baier RR. Front-line nursing Home Staff experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2021;22(1):199–203.
Mo Y, Deng L, Zhang L, Lang Q, Liao C, Wang N, Qin M, Huang H. Work stress among Chinese nurses to support Wuhan in fighting against COVID-19 epidemic. J Nurs Adm Manag. 2020;28(5):1002–9.
Spatz DL, Pugh LC. The integration of the use of human milk and breastfeeding in baccalaureate nursing curricula. Nurs Outlook. 2007;55(5):257–63.
Zhou Y, Asante EA, Zhuang Y, Wang J, Zhu Y, Shen L. Surviving an infectious disease outbreak: how does nurse calling influence performance during the COVID-19 fight? J Nurs Adm Manag. 2021;29(3):421–31.
Wu C, Wu P, Li P, Cheng F, Du Y, He S, Lang H. Construction of an index system of core competence assessment for infectious disease specialist nurse in China: a Delphi study. BMC Infect Dis. 2021;21(1):791.
Fryk JJ, Tong S, Marshall C, Rajkhowa A, Buising K, MacIsaac C, Walsham N, Thevarajan I. Knowledge, attitudes and practices of healthcare workers within an Australian tertiary hospital to managing high-consequence infectious diseases. Infect Disease Health. 2021;26(2):95–103.
Wu C, Yan J, Wu J, Wu P, Cheng F, Du L, Du Y, Lei S, Lang H. Development, reliability and validity of infectious disease specialist nurse’s core competence scale. BMC Nurs. 2021;20(1):231.
Issue Information-Declaration of Helsinki. J bone Mineral Research: Official J Am Soc Bone Mineral Res. 2019;34(3):BMi–BMii.
Halonen JI, Erhola M, Furman E, Haahtela T, Jousilahti P, Barouki R, Bergman Å, Billo NE, Fuller R, Haines A, et al. The Helsinki Declaration 2020: Europe that protects. Lancet Planet Health. 2020;4(11):e503–5.
Apatu E, Sinnott W, Piggott T, Butler-Jones D, Anderson LN, Alvarez E, Dobbins M, Harrison L, Neil-Sztramko SE. Where are we now? A Content Analysis of Canadian Master of Public Health Course Descriptions and the Public Health Agency of Canada’s core competencies. J Public Health Manage Practice: JPHMP. 2021;27(2):201–7.
Fitzgerald A, McNelis AM, Billings DM. NLN Core competencies for nurse educators: are they present in the course descriptions of academic nurse Educator Programs? Nurs Educ Perspect. 2020;41(1):4–9.
Dickmann P, Abraham T, Sarkar S, Wysocki P, Cecconi S, Apfel F, Nurm ÜK. Risk communication as a core public health competence in infectious disease management: development of the ECDC training curriculum and programme. Euro Surveillance: Bull Europeen sur les maladies Transmissibles = Eur Commun Disease Bull 2016, 21(14).
Davies A, Mueller J, Moulton G. Core competencies for clinical informaticians: a systematic review. Int J Med Informatics. 2020;141:104237.
Lavoie P, Michaud C, Bélisle M, Boyer L, Gosselin É, Grondin M, Larue C, Lavoie S, Pepin J. Learning theories and tools for the assessment of core nursing competencies in simulation: a theoretical review. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74(2):239–50.
Sturm EC, Mellinger JD, Koehler JL, Wall JCH. An appreciative Inquiry Approach to the Core competencies: taking it from theory to practice. J Surg Educ. 2020;77(2):380–9.
Jokiniemi K, Korhonen K, Kärkkäinen A, Pekkarinen T, Pietilä AM. Clinical nurse specialist role implementation structures, processes and outcomes: participatory action research. J Clin Nurs. 2021;30(15–16):2222–33.
Fitzgerald M, Milberger P, Tomlinson PS, Peden-Mcalpine C, Meiers SJ, Sherman S. Clinical nurse specialist participation on a collaborative research project. Barriers and benefits. Clin Nurse Spec CNS. 2003;17(1):44–9.
French B. Evaluating research for use in practice: what criteria do specialist nurses use? J Adv Nurs. 2005;50(3):235–43.
Gullick JG, West SH. Building research capacity and productivity among advanced practice nurses: an evaluation of the community of practice model. J Adv Nurs. 2016;72(3):605–19.
Boeykens K, Van Hecke A. Advanced practice nursing: Nutrition Nurse specialist role and function. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2018;26:72–6.
García-Goñi M. Specializing nurses as an Indirect Education Program for Stoma Patients. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2019, 16(13).
Saseedharan S, Karanam R, Kadam V, Shirsekar S. Smart secretion management to protect nurses from COVID19 and other infectious diseases. Nursing in critical care 2021.
Lam SKK, Kwong EWY, Hung MSY, Chien WT. Investigating the strategies adopted by Emergency nurses to address uncertainty and change in the event of emerging infectious diseases: a grounded theory study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17(7).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our heartfelt gratitude to the 21 experts for their participation in the two rounds of questionnaire consultation and for their precious suggestions on the construction of the training course system.
Establishment and cultivation of teaching achievements of Air Force Medical University (2019-36).
Author information
Chao Wu, Hongli Zhang and Yawei Lin contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Nursing Department, Air Force Medical University, No. 169 Changle West Road, 710032, Shaanxi, Shaanxi, China
Chao Wu, Hongli Zhang & Hongjuan Lang
School of Nursing, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang, China
Hongli Zhang
Department of Anesthesiology, 956Th Hospital of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army, Nyingchi, China
Xijing Hospital of Air Force Medical University, Shaanxi, China
Weiyun Yuan
Laboratory Department, Yan’an University Affiliated Hospital, Yan’an, China
Tangdu Hospital of Air Force Medical University, Shaanxi, China
Department of Foreign Languages, School of Basic Medicine, Air Force Medical University, No. 169 Changle West Road, 710032, Shaanxi, Shaanxi, China
Donglei Jiang
Department of Epidemiology, Ministry of Education Key Lab of Hazard Assessment and Control in Special Operational Environment, School of Public Health, Air Force Medical University, Shaanxi, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Chao Wu wrote the main manuscript. Hongli Zhang and Hongjuan Lang distributed questionnaires to experts and infectious disease specialist nurses. Yawei Lin contributed to the analysis and processing of data. Weiyun Yuan, Jing He and Donglei Jiang contributed to the writing and revision of the manuscript. Lu Li and Zhaohua Ji contributed to the design of manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Donglei Jiang , Zhaohua Ji or Hongjuan Lang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was conducted in compliance with the ethical standards in the Declaration of Helsinki and those followed at Air Force Medical University. The study was part of the project to improve the core competence of infectious disease specialist nurses which received approval from the Institutional Review Board of Air Force Medical University. The panelists provided written informed consent before they took part in the study. They have the right to withdraw at any stage of the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Wu, C., Zhang, H., Lin, Y. et al. Construction and application of the core competence course training system for infectious disease specialist nurses. BMC Med Educ 24 , 410 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05405-2
Download citation
Received : 27 October 2023
Accepted : 09 April 2024
Published : 15 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05405-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Training course system
- Infectious disease specialist nurses
- Core competence
- Delphi study
- Empirical research
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Skip to main content
- Skip to FDA Search
- Skip to in this section menu
- Skip to footer links

The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- Search
- Menu
- Science & Research
- About Science & Research at FDA
- The FDA Science Forum
Dynamic headspace GC-MS method to detect volatile extractables from medical device materials
2023 FDA Science Forum
Volatile extractables, released from medical devices during use, are a concern as they may expose patients to harmful levels of toxic compounds. According to ISO 10993-18:2020, the Analytical Evaluation Threshold (AET) is used to determine the analytical sensitivity required to detect extractables from medical devices. Compounds, at or above the AET, need to be reported for toxicological risk assessment. Currently, volatile analysis by static headspaces is used as a supplementary technique for medical device or material extracts. Variation of signal response in static headspace led to undefined AET for the volatile analysis method. Therefore, investigating new technologies that generate reproducible data for volatile quantification is needed for improved hazards identification. This study was designed to evaluate the performance of dynamic headspace (DHS) gas chromatography-mass spectrometric (GC-MS) analysis to achieve the sensitivity levels suitable for proper toxicological risk assessment for volatiles extracted from medical devices. DHS method development was conducted using residual solvents class 3 - mix A standard and the initial method development and analyses were done using GERSTEL MPS attached to Agilent GC-MS system. Two different methods were designed to address both volatile and semi volatile compounds. The efficiency of DHS extraction was optimized based on incubation temperature, trapping volume/ time, adsorbent type (Carbopack B/ Carbopack X (Carbopack B/X) and Tenax TA), and drying time for low volume samples. Method performance was compared with commonly used static headspace GC-MS analysis. To further improve the headspace concentration of more water-soluble compounds such as alcohols, and ketones, the effect of surfactants addition to the sample matrix was also investigated. Application of developed methods were tested using saline extracts of various medical device materials such as ABS, Buna and PVC. Preliminary results showed improved efficiency in detecting volatile extractable in ABS material extracts with semi volatile method with increased peak area responses compared to the volatile method. This sensitive dynamic headspace GC-MS method may facilitate improved toxicological risk assessment for the volatiles detected in medical devices.
Download the Poster (PDF; 2.24 MB)
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Bayesian maximum entropy interpolation analysis for rapid assessment of seismic intensity using station and ground motion prediction equations provisionally accepted.

- 1 Lanzhou Earthquake Research Institute, China Earthquake Administration, China
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
The Bayesian maximum entropy (BME) spatial interpolation analysis method is used to explore the effective combination of seismic station data and the ground motion prediction equation (GMPE) is applied to establish a seismic intensity assessment map based on the obtained results. The results indicate that: (1) According to the intensity analysis results. Soft data in the Japanese earthquake analysis caused overestimation of affected areas, but BME corrected this, especially at the epicenter. Similarly, U.S. earthquakes improved rupture direction predictions. (2) Compared with other spatial interpolation methods, the profile results show that the BME results of the Japanese earthquake and the Turkey earthquake are more consistent with the ShakeMap results than IDW and Kriging, and IDW has low intensity anomaly areas. (3) The BME method overcomes the significant deviation between the intensity assessment results and the actual damage situation when moment magnitudes are small, accurately delineates the scope of the earthquake-stricken areas and enriches the postearthquake processing of information and data in disaster areas. The proposed method is broadly applicable, and when there are only soft data or few stations with data, the BME method can still be effectively used for interpolation analysis.
Keywords: spatial interpolation1, Bayesian maximum entropy2, GMPE3, seismic intensity4, disaster information service5
Received: 02 Mar 2024; Accepted: 22 Apr 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Kang, Chen and Jia. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Dr. Wenkai Chen, Lanzhou Earthquake Research Institute, China Earthquake Administration, Lanzhou, China
People also looked at

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Content analysis is a research method used to identify patterns in recorded communication. To conduct content analysis, you systematically collect data from a set of texts, which can be written, oral, or visual: Books, newspapers and magazines. Speeches and interviews. Web content and social media posts. Photographs and films.
When done well, is considered a relatively "exact" research method. Content analysis is a readily-understood and an inexpensive research method. A more powerful tool when combined with other research methods such as interviews, observation, and use of archival records. It is very useful for analyzing historical material, especially for ...
Content analysis is a research method used to identify patterns in recorded communication. To conduct content analysis, you systematically collect data from a set of texts, which can be written, oral, or visual: Books, newspapers, and magazines; Speeches and interviews;
Content analysis is a research method used to analyze and interpret the characteristics of various forms of communication, such as text, images, or audio. It involves systematically analyzing the content of these materials, identifying patterns, themes, and other relevant features, and drawing inferences or conclusions based on the findings.
Many articles and books are available that describe qualitative research methods and provide overviews of content analysis procedures , , , , , ... When reflecting on the proposed study aim together with the student, we often suggest content analysis methodology as the best fit for the study and the student, especially the novice researcher. ...
In research, content analysis is the process of analyzing content and its features with the aim of identifying patterns and the presence of words, themes, and concepts within the content. Simply put, content analysis is a research method that aims to present the trends, patterns, concepts, and ideas in content as objective, quantitative or ...
Abstract. In this chapter, the focus is on ways in which content analysis can be used to investigate and describe interview and textual data. The chapter opens with a contextualization of the method and then proceeds to an examination of the role of content analysis in relation to both quantitative and qualitative modes of social research.
Interpretive content analysis may overlap with some not very well-articulated qualitative research methods such as "thematic analysis" (Boyatzis, 2000). Ginger (2006) calls interpretive content analysis a flexible research method that may explore key story lines, subjects and objects of texts, normative positions, and the methods used to ...
Content analysis is a widely used qualitative research technique. Rather than being a single method, current applications of content analysis show three distinct approaches: conventional, directed, or summative. All three approaches are used to interpret meaning from the content of text data and, hence, adhere to the naturalistic paradigm.
Content analysis is a research method that has been used increasingly in social and health research, including quality of life and well-being. Content analysis has been generally defined as a systematic technique for compressing many words of text into fewer content categories based on explicit rules of coding (Berelson 1952; Krippendorff 1980 ...
Chapter 17. Content Analysis Introduction. Content analysis is a term that is used to mean both a method of data collection and a method of data analysis. Archival and historical works can be the source of content analysis, but so too can the contemporary media coverage of a story, blogs, comment posts, films, cartoons, advertisements, brand packaging, and photographs posted on Instagram or ...
Content analysis is a qualitative analysis method that focuses on recorded human artefacts such as manuscripts, voice recordings and journals. Content analysis investigates these written, spoken and visual artefacts without explicitly extracting data from participants - this is called unobtrusive research. In other words, with content ...
These problems underscore a need for a qualitative content analysis method that is not only well-defined but also clearly applicable within qualitative research frameworks. This method should enable the effective reduction and description of data, while establishing a clear distinction from other qualitative methods.
Downe-Wambolt (1992) underlines that content analysis is more than a counting process, as the goal is to link the results to their context or to the environment in which they were produced: "Content analysis is a research method that provides a systematic and objective means to make valid inferences from verbal, visual, or written data in ...
As is the case with so many aspects of the academic research enterprise, the method of content analysis is not without controversy. For example, Creswell argued that content analysis is a quantitative method misappropriated by mixed-methods researchers as a qualitative process. He observed that content analysis is "a quantitative procedure ...
Abstract. Content analysis is a highly fl exible research method that has been. widely used in library and infor mation science (LIS) studies with. varying research goals and objectives. The ...
Content analysis (CA) is a research methodology to make sense of the (often unstructured) content of messages - b e they texts, images, sym bols or audio data. In s hort it could be sa id to
Several research studies in pharmacy education have used the method of content analysis. 2-7 Two studies in particular offer noteworthy examples: Wallman and colleagues employed manifest content analysis to analyze semi-structured interviews in order to explore what students learn during experiential rotations, 7 while Moser and colleagues ...
This article characterizes content analysis as a systematic, rigorous approach to analyzing documents obtained or generated in the course of research, distinguishes between quantitative and qualitative content analysis, and shows that content analysis serves the purposes of both quantitative research and qualitative research. Content analysis is a highly flexible research method that has been ...
Qualitative methods. In qualitative research, your analysis will be based on language, images, and observations (often involving some form of textual analysis). Specific methods might include: Content analysis: Categorizing and discussing the meaning of words, phrases and sentences
Qualitative content analysis is explored in detail in terms of its characteristic components: (1) the research purposes of content analysis, (2) target audiences, (3) epistemological issues, (4) ethical issues, (5) research designs, (6) sampling issues and methods, (7) collecting data, (8) coding and categorization methods, (9) data analysis ...
Content analysis is a widely used qualitative research technique. Rather than being a single method, current applications of content analysis show three distinct approaches: conventional, directed ...
We identified 37 scholarly works including peer-reviewed journal articles, books ,and chapters. Using mixed methods content analysis, we analyze and synthesize the contributions of this literature in terms of theoretical development about therapeutic effectiveness in MFT, MFT training, research, and practice.
Many articles and books are available that describe qualitative research methods and provide overviews of content analysis procedures [1], [2], ... When reflecting on the proposed study aim together with the student, we often suggest content analysis methodology as the best fit for the study and the student, especially the novice researcher. ...
Here are the questions used for this analysis, along with responses, and the survey's methodology. The majority of U.S. workers overall (61%) do not have jobs that can be done from home. Workers with lower incomes and those without a four-year college degree are more likely to fall into this category.
Besides, a non-randomized controlled experimental study was adopted to check the application effect of the courses. This study adopted a series of methods including group discussion, theoretical analysis and Delphi consultation to draft the training course content of core competence of infectious disease specialist nurses.
This study was designed to evaluate the performance of dynamic headspace (DHS) gas chromatography-mass spectrometric (GC-MS) analysis to achieve the sensitivity levels suitable for proper ...
The Bayesian maximum entropy (BME) spatial interpolation analysis method is used to explore the effective combination of seismic station data and the ground motion prediction equation (GMPE) is applied to establish a seismic intensity assessment map based on the obtained results. The results indicate that: (1) According to the intensity analysis results. Soft data in the Japanese earthquake ...