
Essays About Science: Top 12 Examples and Prompts
Science can explain almost every aspect of our lives; if you want to write essays about science , start by reading our guide.
The word “science” comes from the Latin word Scientia or “ knowledge ,” It does indeed leave us with no shortage of knowledge as it advances to extraordinary levels. It is present in almost every aspect of our lives, allowing us to live the way we do today and helping us improve society.
In the 21st century, we see science everywhere. It has given us the technology we deem “essential” today, from our mobile phones to air conditioning units to lightbulbs and refrigerators. Yet, it has also allowed us to learn so much about the unknown, such as the endless vacuum of space and the ocean’s mysterious depths. It is, without a doubt, a vehicle for humanity to obtain knowledge and use this knowledge to flourish.
To start writing essays about science , look at some of our featured essay examples below.
| IMAGE | PRODUCT | |
|---|---|---|
| Grammarly | ||
| ProWritingAid |
1. The challenging environment for science in the 21st century by Nithaya Chetty
2. disadvantages of science by ella gray, 3. reflections from a nobel winner: scientists need time to make discoveries by donna strickland.
- 4. The fact of cloning by Cesar Hill
5. T. Rex Like You Haven’t Seen Him: With Feathers by Jason Farago
6. common, cheap ingredients can break down some ‘forever chemicals’ by jude coleman, 1. what is science, 2. a noteworthy scientist, 3. why is it important to study science, 4. are robots a net positive for society, 5. types of sciences, 6. science’s role in warfare.
“Open-ended, unfettered science in its purest form has, over the centuries, been pursued in the interests of understanding nature in a fundamental way, and long may that continue. Scientific ideas and discoveries have often been very successfully exploited for commercial gain and societal improvements, and much of the science system today the world over is designed to push scientists in the direction of more relevance.”
For South Africa to prosper, Chetty encourages cooperation and innovation among scientists. He discusses several problems the country faces, including the politicization of research, a weak economy, and misuse of scientific discoveries. These challenges, he believes, can be overcome if the nation works as one and with the international community and if the education system is improved.
“Technology can make people lazy. Many people are already dependent and embrace this technology. Like students playing computer games instead of going to school or study. Technology also brings us privacy issues. From cell phone signal interceptions to email hacking, people are now worried about their once private information becoming public knowledge and making profit out of video scandals.”
Gray discusses the adverse effects technology, a science product, has had on human life and society. These include pollution, the inability to communicate properly, and laziness.
She also acknowledges that technology has made life easier for almost everyone but believes that technology, as it is used now, is detrimental; more responsible use of technology is ideal.
“We must give scientists the opportunity through funding and time to pursue curiosity-based, long-term, basic-science research. Work that does not have direct ramifications for industry or our economy is also worthy. There’s no telling what can come from supporting a curious mind trying to discover something new.”
Strickland, a Nobel Prize winner, explains that a great scientific discovery can only come with ample time for scientists to research, using her work as an example. She describes her work on chirped pulse amplification and its possible applications, including removing brain tumors. Her Nobel-awarded work was done over a long time, and scientists must be afforded ample time and funding to make breakthroughs like hers.
4. The fact of cloning by Cesar Hill
“Any research into human cloning would eventually need to be tested on humans. Cloning might be used to create a “perfect human”. Cloning might have a detrimental effect family relationship. However the debate over cloning has more pros out weighting the cons, giving us a over site of the many advantages cloning has and the effects of it as well. Cloning has many ups and downs nevertheless there are many different ways in which it can be used to adapt and analyse new ways of medicine.”
Hill details both the pros and cons of cloning. It can be used for medical purposes and help us understand genetics more, perhaps even allowing us to prevent genetic diseases in children. However, it is expensive, and many oppose it on religious grounds. Regardless, Hill believes that the process has more advantages than disadvantages and is a net good.
“For the kids who will throng this new exhibition, and who will adore this show’s colorful animations and fossilized dino poop, T. rex may still appear to be a thrilling monster. But staring in the eyes of the feather-flecked annihilators here, adults may have a more uncanny feeling of identification with the beasts at the pinnacle of the food chain. You can be a killer of unprecedented savagery, but the climate always takes the coup de grâce.”
In his essay , Farago reviews an exhibition on the Tyrannosaurus Rex involving an important scientific discovery: it was a feathered dinosaur. He details the different displays in the exhibition, including models of other dinosaurs that helped scientists realize that the T-Rex had feathers.
“Understanding this mechanism is just one step in undoing forever chemicals, Dichtel’s team said. And more research is needed: There are other classes of PFAS that require their own solutions. This process wouldn’t work to tackle PFAS out in the environment, because it requires a concentrated amount of the chemicals. But it could one day be used in wastewater treatment plants, where the pollutants could be filtered out of the water, concentrated and then broken down.”
Coleman explains a discovery by which scientists were able to break down a perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substance, a “forever chemical” dangerous to the environment. He explains how they could break the chemical bond and turn the “forever chemical” into something harmless. This is important because pollution can be reduced significantly, particularly in the water.
Writing Prompts on Essays about Science
“Science” is quite a broad term and encompasses many concepts and definitions. Define science, explain what it involves and how we can use it, and give examples of how it is present in the world. If you want, you can also briefly discuss what science means to you personally.
Many individuals have made remarkable scientific discoveries, contributing to the wealth of knowledge we have acquired through science. For your essay , choose one scientist you feel has made a noteworthy contribution to their field. Then, give a brief background on the scientists and explain the discovery or invention that makes them essential.
Consider what it means to study science: how is it relevant now? What lessons can we learn from science? Then, examine the presence of science in today’s world and write about the importance of science in our day-to-day lives- be sure to give examples to support your points. Finally, in your essay , be sure to keep in mind the times we are living in today.

When we think of science, robots are often one of the first things that come to mind. However, there is much to discuss regarding safety, especially artificial intelligence. Discuss the pros and cons of robots and AI , then conclude whether or not the benefits outweigh the disadvantages. Finally, provide adequate evidence to reinforce your argument and explain it in detail.
From biology to chemistry to physics, science has many branches, each dealing with different aspects of the world and universe. Choose one branch of science and then explain what it is, define basic concepts under this science, and give examples of how it is applied: Are any inventions requiring it? How about something we know today thanks to scientific discovery? Answer these questions in your own words for a compelling essay .
Undoubtedly, technology developed using science has had devastating effects, from nuclear weapons to self-flying fighter jets to deadly new guns and tanks. Examine scientific developments’ role in the war: Do they make it more brutal? Or do they reduce the casualties? Make sure to conduct ample research before writing your essay ; this topic is debatable.
For help with your essays, check out our round-up of the best essay checkers .
If you’re looking for inspiration, check out our round-up of essay topics about nature .
Essay on Science for Students and Children
500+ words essay on science.
Essay on science: As we look back in our ancient times we see so much development in the world. The world is full of gadgets and machinery . Machinery does everything in our surroundings. How did it get possible? How did we become so modern? It was all possible with the help of science. Science has played a major role in the development of our society. Furthermore, Science has made our lives easier and carefree.

Science in our Daily Lives
As I have mentioned earlier Science has got many changes in our lives. First of all, transportation is easier now. With the help of Science it now easier to travel long distances . Moreover, the time of traveling is also reduced. Various high-speed vehicles are available these days. These vehicles have totally changed. The phase of our society. Science upgraded steam engines to electric engines. In earlier times people were traveling with cycles. But now everybody travels on motorcycles and cars. This saves time and effort. And this is all possible with the help of Science.
Secondly, Science made us reach to the moon. But we never stopped there. It also gave us a glance at Mars. This is one of the greatest achievements. This was only possible with Science. These days Scientists make many satellites . Because of which we are using high-speed Internet. These satellites revolve around the earth every day and night. Even without making us aware of it. Science is the backbone of our society. Science gave us so much in our present time. Due to this, the teacher in our schools teaches Science from an early age.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Science as a Subject
In class 1 only a student has Science as a subject. This only tells us about the importance of Science. Science taught us about Our Solar System. The Solar System consists of 9 planets and the Sun. Most Noteworthy was that it also tells us about the origin of our planet. Above all, we cannot deny that Science helps us in shaping our future. But not only it tells us about our future, but it also tells us about our past.
When the student reaches class 6, Science gets divided into three more subcategories. These subcategories were Physics, Chemistry, and Biology. First of all, Physics taught us about the machines. Physics is an interesting subject. It is a logical subject.
Furthermore, the second subject was Chemistry . Chemistry is a subject that deals with an element found inside the earth. Even more, it helps in making various products. Products like medicine and cosmetics etc. result in human benefits.
Last but not least, the subject of Biology . Biology is a subject that teaches us about our Human body. It tells us about its various parts. Furthermore, it even teaches the students about cells. Cells are present in human blood. Science is so advanced that it did let us know even that.
Leading Scientists in the field of Science
Finally, many scientists like Thomas Edison , Sir Isaac Newton were born in this world. They have done great Inventions. Thomas Edison invented the light bulb. If he did not invent that we would stay in dark. Because of this Thomas Edison’s name marks in history.
Another famous Scientist was Sir Isaac Newton . Sir Isaac Newton told us about Gravity. With the help of this, we were able to discover many other theories.
In India Scientists A..P.J Abdul was there. He contributed much towards our space research and defense forces. He made many advanced missiles. These Scientists did great work and we will always remember them.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Our Writers
- How to Order
- Assignment Writing Service
- Report Writing Service
- Buy Coursework
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Research Paper Writing Service
- All Essay Services
Science Essay
Learn How to Write an A+ Science Essay
11 min read

People also read
150+ Engaging Science Essay Topics To Hook Your Readers
Read 13 Impressive Science Essay Examples And Get Inspired
Science Fiction Essay: Examples & Easy Steps Guide
Essay About Science and Technology| Tips & Examples
Essay About Science in Everyday Life - Samples & Writing Tips
Check Out 5 Impressive Essay About Science Fair Examples
Did you ever imagine that essay writing was just for students in the Humanities? Well, think again!
For science students, tackling a science essay might seem challenging, as it not only demands a deep understanding of the subject but also strong writing skills.
However, fret not because we've got your back!
With the right steps and tips, you can write an engaging and informative science essay easily!
This blog will take you through all the important steps of writing a science essay, from choosing a topic to presenting the final work.
So, let's get into it!
- 1. What Is a Science Essay?
- 2. How To Write a Science Essay?
- 3. How to Structure a Science Essay?
- 4. Science Essay Examples
- 5. How to Choose the Right Science Essay Topic
- 6. Science Essay Topics
- 7. Science Essay Writing Tips
What Is a Science Essay?
A science essay is an academic paper focusing on a scientific topic from physics, chemistry, biology, or any other scientific field.
Science essays are mostly expository. That is, they require you to explain your chosen topic in detail. However, they can also be descriptive and exploratory.
A descriptive science essay aims to describe a certain scientific phenomenon according to established knowledge.
On the other hand, the exploratory science essay requires you to go beyond the current theories and explore new interpretations.
So before you set out to write your essay, always check out the instructions given by your instructor. Whether a science essay is expository or exploratory must be clear from the start. Or, if you face any difficulty, you can take help from a science essay writer as well.
Moreover, check out this video to understand scientific writing in detail.
Now that you know what it is, let's look at the steps you need to take to write a science essay.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How To Write a Science Essay?
Writing a science essay is not as complex as it may seem. All you need to do is follow the right steps to create an impressive piece of work that meets the assigned criteria.
Here's what you need to do:
Choose Your Topic
A good topic forms the foundation for an engaging and well-written essay. Therefore, you should ensure that you pick something interesting or relevant to your field of study.
To choose a good topic, you can brainstorm ideas relating to the subject matter. You may also find inspiration from other science essays or articles about the same topic.
Conduct Research
Once you have chosen your topic, start researching it thoroughly to develop a strong argument or discussion in your essay.
Make sure you use reliable sources and cite them properly . You should also make notes while conducting your research so that you can reference them easily when writing the essay. Or, you can get expert assistance from an essay writing service to manage your citations.
Create an Outline
A good essay outline helps to organize the ideas in your paper. It serves as a guide throughout the writing process and ensures you don’t miss out on important points.
An outline makes it easier to write a well-structured paper that flows logically. It should be detailed enough to guide you through the entire writing process.
However, your outline should be flexible, and it's sometimes better to change it along the way to improve your structure.
Start Writing
Once you have a good outline, start writing the essay by following your plan.
The first step in writing any essay is to draft it. This means putting your thoughts down on paper in a rough form without worrying about grammar or spelling mistakes.
So begin your essay by introducing the topic, then carefully explain it using evidence and examples to support your argument.
Don't worry if your first draft isn't perfect - it's just the starting point!
Proofread & Edit
After finishing your first draft, take time to proofread and edit it for grammar and spelling mistakes.
Proofreading is the process of checking for grammatical mistakes. It should be done after you have finished writing your essay.
Editing, on the other hand, involves reviewing the structure and organization of your essay and its content. It should be done before you submit your final work.
Both proofreading and editing are essential for producing a high-quality essay. Make sure to give yourself enough time to do them properly!
After revising the essay, you should format it according to the guidelines given by your instructor. This could involve using a specific font size, page margins, or citation style.
Most science essays are written in Times New Roman font with 12-point size and double spacing. The margins should be 1 inch on all sides, and the text should be justified.
In addition, you must cite your sources properly using a recognized citation style such as APA , Chicago , or Harvard . Make sure to follow the guidelines closely so that your essay looks professional.
Following these steps will help you create an informative and well-structured science essay that meets the given criteria.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How to Structure a Science Essay?
A basic science essay structure includes an introduction, body, and conclusion.
Let's look at each of these briefly.
- Introduction
Your essay introduction should introduce your topic and provide a brief overview of what you will discuss in the essay. It should also state your thesis or main argument.
For instance, a thesis statement for a science essay could be,
"The human body is capable of incredible feats, as evidenced by the many athletes who have competed in the Olympic games."
The body of your essay will contain the bulk of your argument or discussion. It should be divided into paragraphs, each discussing a different point.
For instance, imagine you were writing about sports and the human body.
Your first paragraph can discuss the physical capabilities of the human body.
The second paragraph may be about the physical benefits of competing in sports.
Similarly, in the third paragraph, you can present one or two case studies of specific athletes to support your point.
Once you have explained all your points in the body, it’s time to conclude the essay.
Your essay conclusion should summarize the main points of your essay and leave the reader with a sense of closure.
In the conclusion, you reiterate your thesis and sum up your arguments. You can also suggest implications or potential applications of the ideas discussed in the essay.
By following this structure, you will create a well-organized essay.
Check out a few example essays to see this structure in practice.
Science Essay Examples
A great way to get inspired when writing a science essay is to look at other examples of successful essays written by others.
Here are some examples that will give you an idea of how to write your essay.
Science Essay About Genetics - Science Essay Example
Environmental Science Essay Example | PDF Sample
The Science of Nanotechnology
Science, Non-Science, and Pseudo-Science
The Science Of Science Education
Science in our Daily Lives
Short Science Essay Example
Let’s take a look at a short science essay:
As we step into the 21st century, it is evident that the chalkboard and textbook are no longer the sole tools of education. Technology has fundamentally reshaped education by offering improved learning experiences, enhancing accessibility, and equipping students with essential digital skills. Technology enhances learning experiences by providing interactive and engaging educational content. Digital platforms offer multimedia resources, simulations, and virtual laboratories, enabling students to grasp complex concepts more effectively. For example, in the field of science, students can virtually dissect organisms, observe chemical reactions, and explore outer space—all from the comfort of their devices. These immersive experiences not only make learning more enjoyable but also deepen understanding and retention of the subject matter. Lastly, technology equips students with essential digital skills vital for success in the modern workforce. Proficiency in using digital tools, software, and online research is becoming increasingly necessary in almost every career path. By incorporating technology into education, students not only acquire subject-specific knowledge but also develop crucial digital literacy and problem-solving skills that are highly sought after by employers. In conclusion, technology's impact on modern education cannot be overstated. It enhances learning experiences, broadens access to education, and equips students with the digital skills they need to thrive in today's interconnected world. While traditional teaching methods still hold value, integrating technology into education is essential to prepare students for the challenges and opportunities of the digital age. As we move forward, it is crucial to strike a balance between technology and traditional pedagogy to provide a well-rounded education that prepares students for a diverse and dynamic future. |
Want to read more essay examples? Here, you can find more science essay examples to learn from.
How to Choose the Right Science Essay Topic
Choosing the right science essay topic is a critical first step in crafting a compelling and engaging essay. Here's a concise guide on how to make this decision wisely:
- Consider Your Interests: Start by reflecting on your personal interests within the realm of science. Selecting a topic that genuinely fascinates you will make the research and writing process more enjoyable and motivated.
- Relevance to the Course: Ensure that your chosen topic aligns with your course or assignment requirements. Read the assignment guidelines carefully to understand the scope and focus expected by your instructor.
- Current Trends and Issues: Stay updated with the latest scientific developments and trends. Opting for a topic that addresses contemporary issues not only makes your essay relevant but also demonstrates your awareness of current events in the field.
- Narrow Down the Scope: Science is vast, so narrow your topic to a manageable scope. Instead of a broad subject like "Climate Change," consider a more specific angle like "The Impact of Melting Arctic Ice on Global Sea Levels."
- Available Resources: Ensure that there are sufficient credible sources and research materials available for your chosen topic. A lack of resources can hinder your research efforts.
- Discuss with Your Instructor: If you're uncertain about your topic choice, don't hesitate to consult your instructor or professor. They can provide valuable guidance and may even suggest specific topics based on your academic goals.
Science Essay Topics
Choosing an appropriate topic for a science essay is one of the first steps in writing a successful paper.
Here are a few science essay topics to get you started:
- How space exploration affects our daily lives?
- How has technology changed our understanding of medicine?
- Are there ethical considerations to consider when conducting scientific research?
- How does climate change affect the biodiversity of different parts of the world?
- How can artificial intelligence be used in medicine?
- What impact have vaccines had on global health?
- What is the future of renewable energy?
- How do we ensure that genetically modified organisms are safe for humans and the environment?
- The influence of social media on human behavior: A social science perspective
- What are the potential risks and benefits of stem cell therapy?
Important science topics can cover anything from space exploration to chemistry and biology. So you can choose any topic according to your interests!
Need more topics? We have gathered 100+ science essay topics to help you find a great topic!
Continue reading to find some tips to help you write a successful science essay.
Science Essay Writing Tips
Once you have chosen a topic and looked at examples, it's time to start writing the science essay.
Here are some key tips for a successful essay:
- Research thoroughly
Make sure you do extensive research before you begin writing your paper. This will ensure that the facts and figures you include are accurate and supported by reliable sources.
- Use clear language
Avoid using jargon or overly technical language when writing your essay. Plain language is easier to understand and more engaging for readers.
- Referencing
Always provide references for any information you include in your essay. This will demonstrate that you acknowledge other people's work and show that the evidence you use is credible.
Make sure to follow the basic structure of an essay and organize your thoughts into clear sections. This will improve the flow and make your essay easier to read.
- Ask someone to proofread
It’s also a good idea to get someone else to proofread your work as they may spot mistakes that you have missed.
These few tips will help ensure that your science essay is well-written and informative!
You've learned the steps to writing a successful science essay and looked at some examples and topics to get you started.
Make sure you thoroughly research, use clear language, structure your thoughts, and proofread your essay. With these tips, you’re sure to write a great science essay!
Do you still need expert help writing a science essay? Our science essay writing service is here to help. With our team of professional writers, you can rest assured that your essay will be written to the highest standards.
Contact our essay service now to get started!
Also, do not forget to try our essay typer tool for quick and cost-free aid with your essays!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Betty is a freelance writer and researcher. She has a Masters in literature and enjoys providing writing services to her clients. Betty is an avid reader and loves learning new things. She has provided writing services to clients from all academic levels and related academic fields.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Science: Sample for Students in 100,200 Words
- Updated on
- Oct 28, 2023

Science, the relentless pursuit of knowledge and understanding, has ignited the flames of human progress for centuries. It’s a beacon guiding us through the uncharted realms of the universe, unlocking secrets that shape our world. In this blog, we embark on an exhilarating journey through the wonders of science. We’ll explore the essence of science and its profound impact on our lives. With this we will also provide you with sample essay on science in 100 and 200 words.

Must Read: Essay On Internet
What Is Science?
Science is a systematic pursuit of knowledge about the natural world through observation, experimentation, and analysis. It aims to understand the underlying principles governing the universe, from the smallest particles to the vast cosmos. Science plays a crucial role in advancing technology, improving our understanding of life and the environment, and driving innovation for a better future.
Branches Of Science
The major branches of science can be categorized into the following:
- Physical Science: This includes physics and chemistry, which study the fundamental properties of matter and energy.
- Biological Science : Also known as life sciences, it encompasses biology, genetics, and ecology, focusing on living organisms and their interactions.
- Earth Science: Geology, meteorology, and oceanography fall under this category, investigating the Earth’s processes, climate, and natural resources.
- Astronomy : The study of celestial objects, space, and the universe, including astrophysics and cosmology.
- Environmental Science : Concentrating on environmental issues, it combines aspects of biology, chemistry, and Earth science to address concerns like climate change and conservation.
- Social Sciences : This diverse field covers anthropology, psychology, sociology, and economics, examining human behavior, society, and culture.
- Computer Science : Focused on algorithms, data structures, and computing technology, it drives advancements in information technology.
- Mathematics : A foundational discipline, it underpins all sciences, providing the language and tools for scientific analysis and modeling.
Wonders Of Science
Science has numerous applications that profoundly impact our lives and society: Major applications of science are stated below:
- Medicine: Scientific research leads to the development of vaccines, medicines, and medical technologies, improving healthcare and saving lives.
- Technology: Science drives technological innovations, from smartphones to space exploration.
- Energy: Advances in physics and chemistry enable the development of renewable energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Agriculture: Biology and genetics improve crop yields, while chemistry produces fertilizers and pesticides.
- Environmental Conservation : Scientific understanding informs efforts to protect ecosystems and combat climate change.
- Transportation : Physics and engineering create efficient and sustainable transportation systems.
- Communication : Physics and computer science underpin global communication networks.
- Space Exploration : Astronomy and physics facilitate space missions, expanding our understanding of the cosmos.
Must Read: Essay On Scientific Discoveries
Sample Essay On Science in 100 words
Science, the bedrock of human progress, unveils the mysteries of our universe through empirical investigation and reason. Its profound impact permeates every facet of modern life. In medicine, it saves countless lives with breakthroughs in treatments and vaccines. Technology, a child of science, empowers communication and innovation. Agriculture evolves with scientific methods, ensuring food security. Environmental science guides conservation efforts, preserving our planet. Space exploration fuels dreams of interstellar travel.
Yet, science requires responsibility, as unchecked advancement can harm nature and society. Ethical dilemmas arise, necessitating careful consideration. Science, a double-edged sword, holds the potential for both salvation and destruction, making it imperative to harness its power wisely for the betterment of humanity.
Sample Essay On Science in 250 words
Science, often regarded as humanity’s greatest intellectual endeavor, plays an indispensable role in shaping our world and advancing our civilization.
At its core, science is a methodical pursuit of knowledge about the natural world. Through systematic observation, experimentation, and analysis, it seeks to uncover the underlying principles that govern our universe. This process has yielded profound insights into the workings of the cosmos, from the subatomic realm to the vastness of space.
One of the most remarkable contributions of science is to the field of medicine. Through relentless research and experimentation, scientists have discovered vaccines, antibiotics, and groundbreaking treatments for diseases that once claimed countless lives.
Furthermore, science has driven technological advancements that have reshaped society. The rapid progress in computing, for instance, has revolutionized communication, industry, and research. From the ubiquitous smartphones in our pockets to the complex algorithms that power our digital lives, science, and technology are inseparable partners in progress.
Environmental conservation is another critical arena where science is a guiding light. Climate change, a global challenge, is addressed through rigorous scientific study and the development of sustainable practices. Science empowers us to understand the impact of human activities on our planet and to make informed decisions to protect it.
In conclusion, science is not just a field of study; it is a driving force behind human progress. As we continue to explore the frontiers of knowledge, science will remain the beacon guiding us toward a brighter future.
Science is a boon due to innovations, medical advancements, and a deeper understanding of nature, improving human lives exponentially.
Galileo Galilei is known as the Father of Science.
Science can’t address questions about personal beliefs, emotions, ethics, or matters of subjective experience beyond empirical observation and measurement.
We hope this blog gave you an idea about how to write and present an essay on science that puts forth your opinions. The skill of writing an essay comes in handy when appearing for standardized language tests. Thinking of taking one soon? Leverage Edu provides the best online test prep for the same via Leverage Live . Register today to know more!
Amisha Khushara
Hey there! I'm a content writer who turns complex ideas into clear, engaging stories. Think of me as your translator, taking expert knowledge and making it interesting and relatable for everyone.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
Science Definition & Meaning Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
The problem of science and its meaning is addressed by J. Revatz. The article explains different perspectives of science, its role, and its functions in modern society. The author singles out different notions and approaches to science and its management practices for both researchers and the community. The three images of science selected for analysis are science as techniques, the pursuit of truth, and science as dirty work. Revatz claims that science is about the explanation of facts and the environment, and since researchers are human beings, the scientific project is a human one. For people, it is crucial to interpret the readings of instruments to themselves and other human beings. Revatz explains that it is thus important to distinguish between what happens inside a process and the interpretation of these happenings or experiences. The human experience does not depend on active intellect, whereas explanation certainly does. In other words, knowledge is the result of a scientist-independent reality, whereas theory is a product of the human mind. The insights into the nature of matter and living organisms that scientific questions have given researchers also tell them what is not possible.
The article “When All You Have Left Is Your Pride” by Carey describes everyday interaction between people and communication patterns. Despite its simplicity and plainness, this article uses science as “dirty work” to explain and defend social interaction mechanisms. All this is to say that though there may be no limit to the number of exciting new facts and theories that will come from social science, this plethora of wonders should not lead the readers to the false assumption that anything is possible. What technology does do, is bring people ever closer to the inherent limits of materials. For instance, all social human beings are composed of identical and similar habits and traditions. It’s because of this modularity, and the mathematics of complexity, that the world is predictable, and it’s because science has the keys to this knowledge that society values science and science instruction. Using science as “dirty work”, the author tries to explain social preferences and causes of social behavior. “To the extent that it sustains good habits and reflects personal pride, they say, this kind of play-acting can be an extremely effective social strategy, especially in uncertain times” (Carey 2009). Even a correctly controlled experiment that used sticks of equal diameter and uneven length would not advance a scientist’s understanding of stability, because such understanding requires a theoretical structure well beyond second graders and second-grade teachers.
The article “Wheat genome project to underpin food security” sees science as the pursuit of truth The author gives a detailed analysis of cells composed of identical and similar protein molecules which have an impact on crops and genetic modifications. “The wheat genome is five times larger than the human genome and is composed of three essentially separate yet closely related genomes. It therefore represents a major challenge in genome sequencing and analysis” (Wheat genome project 2009). Likewise, the base pairs of DNA can form an unlimited collection of living organisms, all of which exist within a limited range of heat because they are all made of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. In science, there may never be a way to know–even in principle the structure and properties of all probable substances or organisms, just as there is no way to know all the facts and scientific studies that can be written. This is just to say that the ways of combining even a few basic entities can be inconceivably vast, albeit still finite.
“The Most Powerful Volcanic Eruption of the 20th Century” sees science as a technique that helps researchers to investigate and explain the problem. The article vividly portrays that science makes endless combinations of the elements, materials, and pressure, limited in density, tensile strength, and so on by the maximum mass of nuclei and the intrinsic strength of the chemical bond between atoms. To some extent, science limits the hope that there will always be another technological fix for humanity’s problems. It just maybe that people can get themselves into trouble earlier than science can bail them out. To this end, scientific values might be useful tools of the trade, but he refused to concede that they were true, or about true, descriptions of an extrasensory world. The logical positivists, influenced by the developments of relativity and quantum mechanics which had overthrown some of the basic notions of space, time, and causality assumed by Newton, wanted to develop a foundation for science that would never be overthrown by future discoveries. And as some extrasensory entities, such as atoms and genes, became ever more visible, they were less inclined to deny their reality.
In sum, science is a unique field that helps researchers to investigate, analyze and evaluate natural phenomena and facts. Indeed, the reality of most events, from the internal temperature of a moon to the age of the molecule, is linked to observations only through a long chain of the deductive way of thinking. Nothing significant can be concluded from such a mixture experiment and the implication that it can be only reinforced unscientific thoughts. It’s this group that has excitedly endorsed science because it allows them to speak only about the process (whatever is described) rather than consequences and real initial causes (of which they are ignorant).
Bibliography
Carey, B. 2009, When All You Have Left Is Your Pride. The New York Times. Web.
T he Most Powerful Volcanic Eruption of the 20th Century. 2009. Geology.Com. Web.
Wheat genome project to underpin food security. 2009. BBSRC . Web.
- Discussion: Human Genome Sequencing
- Human Genome Sequencing and Experiments
- Wheat Supply and Demand in the Global Market
- Case Study Methodology in Special Educational Settings
- Popper's Falsification Science
- The Interpretive Frameworks Used in the Qualitative and Proposed Study
- How to Become an Accomplished Critical Thinker
- Work-Life Balance Development in the UK Retail Stores
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, November 16). Science Definition & Meaning. https://ivypanda.com/essays/science-definition-amp-meaning/
"Science Definition & Meaning." IvyPanda , 16 Nov. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/science-definition-amp-meaning/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Science Definition & Meaning'. 16 November.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Science Definition & Meaning." November 16, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/science-definition-amp-meaning/.
1. IvyPanda . "Science Definition & Meaning." November 16, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/science-definition-amp-meaning/.
IvyPanda . "Science Definition & Meaning." November 16, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/science-definition-amp-meaning/.
- BiologyDiscussion.com
- Follow Us On:
- Google Plus
- Publish Now

Essay on Science: Meaning, Scope, Nature, Technology and Society
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Essay on Science:- 1. Meaning and Definitions of Science 2. Scope of Science 3. Nature of Science 4. Physical Science 5. Science and Social Environment 6. Science and Technology 7. Science and Society 8. Scientific Method and Its Steps.
- Essay on Scientific Method and Its Steps
Essay # 1. Meaning and Definitions of Science :
Meaning of Science:
The English word Science is derived from a Latin Verb ‘Scire’, which means ‘to know’ and Latin Noun ‘Scientia’ which means ‘knowledge’. Meaning of Science is based on German word ‘ Wissenchaft’, which means systematic, organized knowledge. Thus, Science is a systematized knowledge.
The necessity and curiosity of man to know about himself and his surroundings has led him to investigate, find and to know about living beings and nature, which to verifiable knowledge of facts. But Science is not always about the collection of facts or development of new concepts or ideas. It is all about the passion for the discovery that drives one to explore the environment and the nature in every aspect.
Science is basically founded to investigate the nature and its processes. Although there are a number of other methods that can be utilized to acquire the knowledge about nature, but science is considered as the only one that results in the acquisition of reliable knowledge. Hence, Rene Descartes said, “Science is a method of investigating nature that discovers reliable knowledge about it.”
Science is the investigation of unknown phenomena and it also looks and compares with existing principles, theories and practices. Science is both a particular kind of activity and also the result of that activity. Science uses tools like observation, measurement and scientific experimentation and is entirely based on the observable facts.
Science is observation, identification, description, experimentation, investigation and theoretical explanation of the phenomenon that occur in nature.
Science could be described as the study, which attempts to perceive and understand the nature of the universe both living and non-living in its part and as a whole.
Definitions of Science :
During early times people perceived Science, as what the scientist does. There are many definitions available, though not a single definition could be universally accepted.
Some of the definitions are mentioned here to understand it from different angles:
1. According to Columbian Dictionary:
“Science is an accumulated and systematized learning in general usage restricted to natural phenomenon”.
2. Einstein (1879-1955):
“Science is an attempt to make the chaotic diversity of our sense experience corresponds to logically uniform system of thought”.
3. Fitzpatrick (1960):
“Science is a cumulative and endless series of empirical observations, which results in the formation of concepts and theories, with both concepts and theories being subject to modification in the light of further empirical observations. Science is both a body of knowledge and the process of acquiring it”.
4. Bronowski, J. (1956):
“Science as the organization of our knowledge in such a way that it commands or makes possible the explanation of more of the hidden potentialities found in the environment”.
5. Conant (1957):
“An interconnected series of concepts and conceptual schemes that have developed as a result of experimentation and observation and are fruitful of further experimentation and observation”.
6. Fisher (1975):
“Science is the body of Knowledge obtained by methods, based upon observation”.
The above definitions clearly reveal that Science is both a process and product. A comprehensive definition of Science would be “science is a systematized knowledge gained through human observation and experimentation of cause revealing the unknown phenomenon of nature and universe both living and non-living involving the process of critical, creative thinking and investigation including sometimes sudden insights too.”
Science = Process + Product
= Methods + Knowledge
= Scientific Method + Scientific Attitude + Scientific Knowledge
Essay # 2. Scope of Science :
Science is a body of knowledge obtained by methods based upon observation. Observation is authentic and that it is only through the senses of man that observations can be made. Thus, anything outside the limits of man’s senses is outside the limits of science. In other words, science deals with the universe and galaxies in the forms of matter and energy which is in the form of living and non-living.
Science employs a number of instruments to extend mail’s senses to the extremely minute to very vast, to the short-time duration or long-time duration, to dilute or to concentrate and so on and so forth which does not alter the conclusion that science is limited to that which is observable.
Thus, as in any other discipline contemporary experimental techniques set up some practical limitations but these are not to be confused with the intrinsic limitations inherent in the very nature of science. The knowledge of science is tested and retested and also reinvented.
Today the disciplines of Science and Social Sciences are drawing into each other. Behavioural zoologists study the sociology and psychology of animals. Archaeologists derive new insights from the rapid advances in chemical and physical analysis. Hence sciences should be understood with interdisciplinary approach within science as a whole. Biology draws on chemistry, physics and geology.
ADVERTISEMENTS: (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); Essay # 3. Nature of Science:
Human by birth has quest for knowledge as they are curious of knowing about nature. They have a highly developed brain because of which they can observe precisely, correlate observations and predict future happenings on the basis of their observation. This ability helped humans to adjust to nature. The process of observing, describing, exploring and using the physical world is science.
Science has certain characteristics which distinguish it from other spheres of human endeavour.
These characteristics define the nature of science as discussed below:
Science is a Particular way of Looking at Nature :
1. Science is a way of learning about what the nature is, how the nature behaves and how the nature got to be the way it is.
2. Science focuses exclusively on the nature.
3. It is not simply a collection of facts; rather it is a path to understand the phenomenon underlying.
(i) Science is, just the nature existing around you.
(ii) Every day we look at the rising sun and pay great respect to it for bestowing the earth with its light in energy form.
(iii) The knowledge of all that is in the universe from the tiniest subatomic particles in an atom to universe and galaxies.
Science as a Rapidly Expanding Body of Knowledge :
1. Science is the dynamic, ever expanding knowledge, covering every new domain of experiences.
2. Knowledge refers to the product of science, such as the concepts and explanations.
3. Research being carried out in the field of science resulted in developing more knowledge at a faster pace sometimes by replacing old concepts, ideas or principles.
The technological developments that took place in recent times enhanced the acceleration of knowledge.
Science as an Interdisciplinary Area of Learning:
1. In the last two decades there have been studies claiming that science is becoming even more an interdisciplinary area of learning.
2. Science cannot be taught in isolation. All the branches of science are interdependent upon all other and there are a number of facts and principles which are common to various science subjects.
3. Knowledge started expanding day by day; scientists started specialising in certain areas. Hence the knowledge has been organized for convenience into different disciplines.
Environmental science is an interdisciplinary academic field that integrates physics, biological and information sciences (including ecology, biology, physics, chemistry, zoology, mineralogy, oceanology, limnology, soil science, geology of atomospheric science and geodesy).
Science as a Truly International Enterprise :
1. International collaboration in most of the projects is the order of the day.
2. In collaborative research, visibility among the peer and active exploitation of complementary capabilities increase.
3. Share the costs of the projects that are large in scale and scope.
4. Able to access expensive physical resources.
5. Exchange ideas in order to encourage greater creativity.
The large Hadron collides; at the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) has been build up by scientists drawn from many countries including India. The experiment on this machine is being conducted by scientists from many countries including many Indian scientists. In this sense, science do not belong to any single country or a group of countries and it would be morally and ethically wrong to deny the fruits of scientific development to any country in the world.
Science as Always Tentative :
Scientific models are always being questioned. Up-and-coming scientists always find gaps or errors in existing scientific models and develop a new one in place of them. In scientific field models have been tested and refined to such an extent that errors are likely to be minor. The real evidences need to be scrutinized carefully.
Marine researchers have expressed concern about the effect of global warming on the future of coral reefs because increasing sea temperature cause coral bleaching. Bleaching happens; the corals expel the algae that live within their cells die, when temperature rises. Recent research have tentatively showed that some algae may be able to adapt to temperature rises, consequently improved the chances that corals can survive.
Tentative Nature of Scientific Theories :
1. Scientific theories took decades in their development.
2. When two competing theories explain their observations related to a certain phenomenon, Scientists prefer to accept a theory which explains larger number of observations with few assumptions.
There was a time when both the geocentric and the heliocentric theories explained all the planetary observations. However geocentric theory had to introduce a new assumption every time. On the other hand, the heliocentric theory with just one assumption that all the planets revolve round the sun, it explained every available observation and eventually survived.
The fact remains that scientific theories are tentative and are always subject to change.
Science Promotes Skepticism :
“In science, keeping an open mind is a virtue just not so open that your brains fall out”-James Oberg.
1. Skepticism does not mean doubting the validity of everything, rather to judge the validity of a claim based on objective empirical evidences.
2. David Hume, the 18th century philosopher viewed that we should accept nothing as true unless the evidences available makes the non-existence of the thing more miraculous than its existence.
3. We examine the available evidences before reaching a decision until sufficient evidences are found.
Scientists are Highly Skeptic People :
‘Science is what scientists do’.
1. The scientists in different fields try to describe the phenomena in nature and establish their relationships.
2. After having described the phenomena, scientists attempt to find out the reason behind and make predictions.
3. Scientists use ideas of their own and of others as tools for testing and gaining knowledge. They use many resources to get valid answers to their questions and problems, by designing their own experiments and invent new tools with which they observe and check different phenomena. Hence, scientists are highly skeptic people.
For instances, if we look at Newton’s story the way he was inspired to formulate his theory of gravitation by watching the fall of an apple from a tree speaks his skeptic nature. Though many scientists and other common men were aware that all the objects descend perpendicularly to the ground, they never pondered upon it. This incident prompted Newton to explore the possibility of connecting gravity with the force that kept the moon on its orbit. This led him to the universal law of gravity.
Charles Goodyear (1800) a chemist and manufacturing engineer who developed vulcanized rubber. His discovery was accidental, where he explored the situation and after five years of searching for a more stable rubber and stumbling upon the effectiveness of heating.
Science Demands Perseverance from its Practitioners :
1. The important characteristic of science that brings development and progress is perseverance of scientists.
2. Scientists getting an inspirational idea or a creative thought have to persist with the idea to take it to its logical conclusions, based on facts or observations.
3. Scientists may work alone or join with others in developing the idea further to find out ways to discover or invention, While at other times the scientists can make only a beginning and then others join them in developing the idea further.
The discovery of the wonder drug pencillin by Alexander Fleming in 1929 is the result of an incident happened by a chance which led to serious observation followed by hard work paved the way for discovery of many other antibiotics like Streptomycin and Erythromycin.
Science as an Approach to Investigate and as a Process of Constructing Knowledge :
1. The investigations in science involve some form of scientific method.
2. Scientists for seeking solution to a problem use different methods like observation, prediction and sometimes experimentation to study the cause and effect relationship.
3. Whatever we observe through our senses (information) is sent to the brain and the brain processes the information by registering, classifying, generalising etc., and converts into knowledge. Sensory perception is primary in knowledge development.
4. Here, the individual constructs the knowledge on his own by applying their own mental abilities and intelligence to process the information received through senses.
5. The basic unit of knowledge is fact. In science any repeatedly verifiable observation becomes a fact.
6. Scientific approach always is based on cause and effect relation.
Examples of facts are:
i. Solids have definite shape and volume.
ii. The rainbow is seen in a direction opposite to that of the sun.
Essay # 4. Physical Science :
The child is interested to learn things which are related to his experiences. This could be possible only when the subjects are integrated and correlated rather than in isolation. The other physical sciences also have equally contributed a lot to the field of biological studies.
Obviously we can’t teach and understand each and every thing about a particular branch of science without the help of other sciences. The child on the other hand can’t appreciate and understand the branches of science in isolation from others. The study of interrelatedness helps the child to understand the concepts easily, more interesting and natural.
Science cannot be taught in isolation. All the branches of science are interdependent upon each other and there are a number of facts and principles which are common to various science subjects. This however does not mean that the teacher of one branch of science ought to know everything of other branches of science.
But it is very much essential that he should have sufficient knowledge of other sciences so as to bring about integration of subjects. He should also know where to depart from his own subject and how much should he venture into areas which are not his own.
The following example may be taken:
1. A teacher while teaching the sense organs says an eye should make a parallelism with a camera, which the student has learnt in physics. To understand the images, knowledge of image formation by the convex lens is essential.
E.g. (a) The rays which pass through the centre of the lens travel straight without any change in direction.
(b) The rays which run parallel to the principal axis pass through the focus of the lens after refraction from the lens.
Again when the teacher is teaching the same topic in the period of human physiology, the defects in the eye i.e., short sightedness (by the elongation of the eyeball and the image in formed a little in front of the retina and not exactly on the retina) he should know other factors also which cause the shifting of the image.
E.g. (a) By changing the distance between the lens and object.
(b) By changing the distance between the lens and the screen.
(c) By changing the total length of lens.
If the teacher possesses knowledge of physics he can most successfully correlate his topic with other branches of science and make the whole knowledge easily acceptable to the children.
2. Similarly while teaching digestive system the teacher should have adequate knowledge of chemistry without the help of which he cannot justify the topic.
The teacher must correlate it by telling about:
(a) Soluble and insoluble constituents of our diet.
(b) Chemistry of different digestive juices and their effect on the constituents of food that we take.
(c) The final products and the process of assimilation of products by the membranes of different organs. This will involve the reference of concepts of osmosis, density and the pressure etc.
Science is universal; it has no barrier of any kind as too has no barriers. The recent advances in the field of science and technology and its wide application as well as their use in daily life situation justify the utilitarian value of science. Taxonomy reveals the unity in diversity. Evolution and mutation theories help us understand the relation of living forms.
Motion, Mass and Energy related theories relate Universe, Sun, Earth and all other planets and their existence. Further their relation to life forms. Hence in nature everything is in relation and co-existence. This is what has to be understood by the student in the study of scientific theories and phenomenon.
Essay # 5. Science and Social Environment:
Relating science education with the environment of a child has been the prime concern of educationists. The environment of the child includes natural and social environment.
In science we learn about the nature’s phenomena. Human is a part of nature. Therefore, every effort should be made to integrate science with learning the environment. The science curriculum should address issues and concerns related to environment such as climate change, acid rain, growth of water, eutrophication and various types of pollutions etc. Further, it should be applied to society to understand social phenomenon in a scientific way and solve all social problems with all objectivity and universal application.
Science teachers should aim to enlighten the young minds with the wonders of science. They should be engaged to construct the knowledge through an interdisciplinary approach appreciating its relation and impact on the social and natural environment. They can recognize the competence of science by doing activities related to their everyday life.
Current issues and events in science like new technological innovations, scientific discoveries, can be examined through social, economic and ethical perspectives to help students in relating these issues with one another and explore their areas of interest.
The significance of chemistry to society can be highlighted by discussing the chemical components used in products that have altered agriculture, food, health, medicine, electronics, transportation, technology and the natural environments. To understand its relevance to home economics, one can think what happens to the electricity bill if solar cooker, solar heater, solar lanterns and CFL (compact fluorescent lamp) are used.
For Instances- Bhopal Tragedy Unforgettable Industrial Disaster :
Industries are the symbols of development, but other side of the coin is lack of safety measures and irresponsibility of emitting pollutants. On 2 nd December 1984 about 3000 human beings died and 5000 were effected seriously, thousands of cattle, birds, dogs, and cats died in just one night at Bhopal tragedy.
These mass deaths were due to the leakage of Methyle Isocyanate (MIC) into the air from an insecticide factory managed by union carbide. Thousands of lives helplessly crushed in this incident. This is unforgettable industrial disaster towards air pollution.
Essay # 6. Science and Technology :
Technology is often equated to applied sciences and its domain is generally thought to include mechanical, electrical, optical, electronic devices and instruments, the house hold and commercial gadgets, equipment used in physics, chemistry, biology, nuclear science etc. These various sub-domains of technology are interrelated. Modern technology is an applied science because the basic principles of sciences are applied to develop the technology.
Science and technology are linked to each other. Discoveries in science have paved the way for the evolution of new technologies. At the same time technology has been instrumental in the development of science.
Han’s Christian Oersted, one of the leading scientists of the 19 th century, played a crucial role in understanding electromagnetism. In 1820 he discovered that a compass needle got deflected when an electric current passed through a metallic wire placed nearby. Through this he showed that electricity and magnetism were related phenomena. His research later created technologies such as radio, television and fiber optics.
The development of microscope by Antony Van Leeuwenhock, where he interwined optical principles with astronomical and biological understanding which further led to the development of the telescope.
Thus, science influences technology by providing knowledge and methodology. But on the other hand technology also influences science by providing equipments to find out the unknown phenomenon of the nature. This shows interdependence of science and technology.
In science we inquire how a natural phenomenon occurs, while in technology we deal with how the scientific processes can also be used for human welfare. Technology as a discipline has its own autonomy and should not be regarded as a mere extension of science.
Basically science is an open ended exploration; its end results are not fixed in advance. Technology on the other hand, is also an exploration but usually with a definite goal in mind. Science is universal; technology is goal oriented and often local specific.
People today are faced with an increasingly fast-changing world where the most important skills are flexibility in adapting to new demands and creativity in taking advantages of new opportunities. These imperatives have to be kept in mind in shaping science education.
Essay # 7. Science and Society :
The applications of science and technology have led to the remarkable improvement in the quality of human life. It has given lot of comfort and leisure to the human kind on one side and equipped it with skills needed for problem solving and decision making on the other side. It has changed the outlook of the individual on different beliefs, myths, taboos and superstitions.
People started working with logical thinking, objectivity and open mindedness. Modern society believed in the co-existence of diversity in social and political thinking. Science always works for the welfare of our future generations by talking about sustainable development. Society is also showing its concern using the scientific knowledge for peace and prosperity of the society.
For instances, consuming tobacco (Gutkha, cigarettes, beedi, khaini) damages the internal organs of the body. The numbers of addicted people at the age of 15 or below are 57.57 lakhs (68%) both in Telengana and Andhra. When they reach 30 yrs. of age thin internal organs becomes damaged, this may lead to several problems and sometimes lead to death.
It is a dangerous trend in our country. So, we have to inculcate healthy habits in children by teaching science. Many youth are also addicted to alcohol which damages the liver and other body organs which in turn also affects human resource development.
Let Us Think It Over:
Do you know that our eyes can live even after our death? By donating our eyes after we die, we can give sight to a blind person.
About 35 million people in the developing world are blind and most of them can be cured. About 4.5 million people are with corneal blindness, can be cured by corneal transplantation of donated eyes. Out of these 4.5 million, 60% are children below the age of 12 yrs. So, if we got the gift of vision, let us pass it on to somebody who does not have it.
Essay # 8. Scientific Method and Its Steps:
1. The development of scientific attitude and training in scientific method are two cardinal aims for the teaching of science. In other words it is a method of solving a problem scientifically.
2. Scientific method involves reflective thinking, reasoning and results from the achievement of certain abilities, skills and attitudes.
Definition of Scientific Method :
Carl Pearson says, ‘The scientific method is marked by the following features:
1. Careful and accurate classification of facts.
2. Observation of their co-relation and sequence.
3. Discovery of scientific law by creative imagination, and self-criticism.
4. The final touch-stone of equal validity for all normally constituted needs.
Steps of Scientific Method:
Observation :
Observation is the base for science. It knows the phenomenon through senses. Without control of external or internal situations.
1. It is the way we perceive the nature and using the senses and processed through the faculty of brain.
2. It is a process of checking conclusions. After observation we try to explain what we have seen based on cause and effect relation. In science repeatedly verifiable observations becomes a fact.
Facts are specific verifiable information obtained through observation and measurement. They are verifiable with reference to time and place.
Some facts do not require the time and place to be mentioned. Ex- Iron is a greyish hard metal.
Some facts are specific like ‘water boils at 100°C at 760mm Hg of pressure.
A concept is an idea or a mental image of an object is generalised forms of specific relevant direct experiences interpreted in a language or word form for communication.
1. Concepts. Ex. plant, animal etc.
2. According to Bruner, every concept has five elements i.e. name, example (positive & negative), attributes (characteristics) attribute value and rule (definition).
3. Concepts formed without direct experiences may lead to misconceptions. Hence, care should be taken in provide direct experiences in learning process.
Principles :
Principles are based on several concepts. They are the representation of phenomena on which the activities or behaviour can be generalised to some extent.
A number of concepts combine in a way to convey meaning which can be tested and verified universally, becomes a principle.
Ex- Mytosis, Meiosis, Glycolysis, Photosynthe sis, Mutations, Evolution etc.
Scientific Inquiry :
It occupies a prominent place in science as it helps pupils to understand how scientific ideas are developed.
1. It is broadly defined as a search for truth or knowledge. Emphasis is placed on the aspects of search rather than on the mere acquisition of knowledge.
2. Empirical testing, reasoning and controlled experimenting are some of the methods of science inquiry.
The steps in scientific methods are illustrated with a specific example:
The teacher demonstrates an experiment to the students to show that water boils at low temperature under low pressure.
1. Sensing the Problem:
The teacher provides a situation in which the students feel the need of asking some questions. Teacher may also put questions which require reflective thinking and reasoning on the part of the students, this may become a problem to solve. The interest of the students, availability of the material and its utility should be considered.
A flask was taken and filled it half with water. Boil the water over a flame. Remove the flame. Cork the flask. Invert it and pour cold water on the flask. The students observe the process carefully and saw that water has begun to boil again when cold water is poured on the bottom of the inverted flask. They at once sense a problem for themselves finding out the reason and explanation of what they have seen.
2. Defining the Problem:
The student now defines the problem in a concise, definite and clear language. There should be some key-words in the statement of the problem, which may help in better understanding the problem.
The student can give different statements such as:
(i) Why is water boiling?
(ii) Why did the water boil first?
(iii) Why was the flask corked and then inverted?
(iv) Why was cold water poured over the bottom of the inverted flask?
(v) Why did the water boil in the flask when cold water is poured over the inverted flask?
Of all these statements, the last one is in fact the problem which should be solved.
3. Analysis of the Problem:
The student now fined the key words and phrases in the problem which provide clue to further study of the problem. At the same time, the students must have knowledge of every key word and the understanding of the whole problem. In our selected problem ‘water boil’ or the boiling of the water are the key words which gives us clue to find information regarding the boiling of water under different conditions.
Collection of Data :
After analysis of the problem the teacher suggests references on the problem. The student needs to plan the subsequent activities. They have to discuss, consult references, use audio-visual aids such as models, pictures, specimens, organise field trips and do the experimentation carefully. Unnecessary data should also be discarded.
Formulation of Tentative Solutions or Hypothesis :
After collection of data, the students are asked to formulate some tentative hypothesis. A hypothesis is the probable solution to the problem in hand, which should be free from bias and self-inclination.
The students can suggest the hypothesis like:
Water will also boil:
(i) When flask is not inverted.
(ii) When water is not boiled but only warmed.
(iii) When hot water is poured over the inverted flask containing cold water.
(iv) When hot water is poured over the inverted flask containing boiled water.
(v) When cold water is poured over the flask containing cold water.
(vi) When cold water is poured over the inverted flask containing boiled water.
These are some of the hypothesis the students can suggest.
Selecting and Testing the Most Appropriate Hypothesis :
The students can select the most tenable hypothesis by rejecting others through experimentation and discussion.
The students have found out that water begins to boil again in an inverted flask when cold water is poured over it. In no other condition this was possible and so all other hypothesis were rejected.
Drawing Conclusions and Making Generalisations :
In this step, conclusions are drawn from the experiments. The results should support the expected solution. Experiments can be repeated to verify the consistency and correctness of the conclusion drawn and should be properly reported. When some conclusions are drawn from different sets of experimentation under similar situations, they may go for generalisation of their conclusion.
The generalisation can be made by arranging a set of experiments which also show the same conclusion already reached at.
The effect of varying pressure on boiling point of water can be found out by conducting experiments. From these conditions, one can generalise that pressure has a direct effect on the boiling point of water i.e. the increase in pressure raises the boiling point of water and vice-versa.
Application of Generalization to New Situations :
The student should apply generalization under new situations in his daily life minimising the gap between classroom situation and real life situation.
The student will apply the generalization that increase in pressure increases the boiling point of water and vice-versa, to explain the reason of – ‘why’ is it difficult to cook meat and pulses at higher altitudes.
Why do the pulses take lesser time for cooking in pressure cooker.
In this way the student will apply the generalization to other life situations.
Scientific Method- A Critical View :
A few points about the scientific method need to be emphasized.
Scientific method is not a prescribed pathing for making discoveries in science. Very rarely the method has remained a key to discovery in science. It is the attitude of inquiry, investigation and experimentation rather than following set steps of a particular method that leads to discoveries and advancement in science.
Sometimes a theory may suggest a new experiment at other times an experiment may suggest a new theoretical model. Scientists do not always go through all the steps of the method and not necessarily in the order we have outlines above. Investigation in science often involves repeated action on any one or all steps of the scientific method in any order.
Many important and path breaking discoveries in science have been made by trial and error, experimentation and accidental observation. The Rontgen and Fleming both of them did not set out the following scientific steps to discover X-rays and penicillin, but they had qualities of healthy intuition and perseverance which took them to their goals. Besides intuition informed guesswork, creativity, an eye for an unusual occurrence, all played a significant role in developing new theories, and there by progress in science.
The validity of a hypothesis depends solely on the experimental test and not on any other attributes. There is no authority in science that tells you what you can criticize and what you cannot criticize. Thus, science is highly objective discipline.
A scientific method with its linear steps makes us feel that science is a ‘closed box approach’ of thinking. However in practice science is more about thinking ‘out of the box’. There is tremendous scope for creativity in science. Many times in science an idea or a solution to a vexing problem appears to arise out of creativity and imagination. Ex- The stories of Archimedes, Newton, Robert Hook, Fleming and Madam Curie etc.
People keep floating all kinds of theories; often they narrow their arguments in scientific terms. This may create lot of confusion among them, but we should remember that a theory is valid only if it passes the test of experimentation, otherwise it may just be a matter of faith.
The scientific method imposes operational limitation on science. It does not help us to make aesthetic or value judgment. For example, frequency of the colour of paintings may be determined but there is no scientific method to label the paintings of two artists as great or not so great. Scientific method does not prove or refute the ideas such as existence of God and existence of life after death.
Following scientific method does not ensure that a discovery can be made. However, the skills learnt in making observation, analysis, hypothesis, prediction from a hypothesis and it’s testing by experimentation help us in developing scientific attitude.
All of us will benefit immensely if we imbibe the spirit of scientific method in our personal lives. The scientific method tells us to be honest in reporting our observations or experimental results, keep an open mind and to be ready to accept other points of view. If our own view is proved wrong.
Scientific method is a logical approach to problem-solving.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Environmental Science
- Content-cum-Methodology in Teaching: Concept, Nature, Need and Steps
Science , Meaning , Meaning of Science
- Anybody can ask a question
- Anybody can answer
- The best answers are voted up and rise to the top
Forum Categories
- Animal Kingdom
- Biodiversity
- Biological Classification
- Biology An Introduction 11
- Biology An Introduction
- Biology in Human Welfare 175
- Biomolecules
- Biotechnology 43
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Cell- Structure and Function
- Chemical Coordination
- Digestion and Absorption
- Diversity in the Living World 125
- Environmental Issues
- Excretory System
- Flowering Plants
- Food Production
- Genetics and Evolution 110
- Human Health and Diseases
- Human Physiology 242
- Human Reproduction
- Immune System
- Living World
- Locomotion and Movement
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Mineral Nutrition
- Molecualr Basis of Inheritance
- Neural Coordination
- Organisms and Population
- Photosynthesis
- Plant Growth and Development
- Plant Kingdom
- Plant Physiology 261
- Principles and Processes
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Reproduction 245
- Reproduction in Animals
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Reproductive Health
- Respiration
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Transport in Plants
- Trending 14
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
- School Guide
- English Grammar Free Course
- English Grammar Tutorial
- Parts of Speech
- Figure of Speech
- Tenses Chart
- Essay Writing
- Email Writing
- NCERT English Solutions
- English Difference Between
- SSC CGL English Syllabus
- SBI PO English Syllabus
- SBI Clerk English Syllabus
- IBPS PO English Syllabus
- IBPS CLERK English Syllabus
Essay on Science in English: Check 200, 300 & 500 Words Essay
Science is the study of logic. It explains why the world is round, why stars twinkle, why light travels faster than sound, why hawks soar higher than crows, why sunflowers face the sun and other phenomena. Science answers every question logically rather than offering mystical interpretations. Students are very interested in science as a topic. This subject is indeed crucial for those hoping to pursue careers in science and related professions.
People who are knowledgeable in science are more self-assured and aware of their environment. Knowing the cause and origin of natural events, a person knowledgeable in science will not be afraid of them.
However, science also has a big impact on a country’s technological advancement and illiteracy.
Table of Content
English-language Long and Short Science Essay
Essay on science (200 words), essay on science (300 words), essay on science (400 words), essay on science (500 words), essay on science (600 words).
We have included a brief and lengthy English essay on science below for your knowledge and convenience. The writings have been thoughtfully crafted to impart to you the relevance and meaning of science. You will understand what science is, why it matters in daily life, and how it advances national progress after reading the writings. These science essays can be used for essay writing, debate, and other related activities at your institution or school.
Science entails a thorough examination of the behavior of the physical and natural world. Research, experimentation, and observation are used in the study.
The scientific disciplines are diverse. The social sciences, formal sciences, and natural sciences are some of them. Subcategories and sub-sub-categories have been created from these basic categories. The natural sciences include physics, chemistry, biology, earth science, and astronomy; the social sciences include history, geography, economics, political science, sociology, psychology, social studies, and anthropology; and the formal sciences include computer science, logic, statistics, decision theory, and mathematics.
The world has positively transformed because of science. Throughout history, science has produced several inventions that have improved human convenience. We cannot fathom our lives without several of these inventions since they have become essential parts of them.
Global scientists persist in their experiments and occasionally produce more advanced innovations, some of which spark global revolutions. Even if science is helpful, some people have abused knowledge, usually those in positions of authority, to drive an arms race and destroy the environment.
There is no common ground between the ideologies of science and religion. These seeming opposite viewpoints have historically led to a number of confrontations and still do.
Science is a way to learn about, comprehend, examine, and experiment with the physical and natural features of the world in order to apply it to the development of newer technologies that improve human convenience. In science, observation and experimentation are broad and not restricted to a specific concept or area of study.
Applications of Science
Science has given us almost everything we use on a daily basis. Everything, from laptops to washing machines, microwaves to cell phones, and refrigerators to cars, is the result of scientific experimentation. Here are some ways that science affects our daily lives:
Not only are refrigerators, grills, and microwaves examples of scientific inventions, but gas stoves, which are frequently used for food preparation, are as well.
Medical Interventions
Scientific advancements have made it feasible to treat a number of illnesses and conditions. Thus, science encourages healthy living and has helped people live longer.
Interaction
These days, mobile phones and internet connections are necessities in our life and were all made possible by scientific advancements. These innovations have lowered barriers to communication and widened global connections.
E nergy Source
The creation and application of numerous energy forms have been facilitated by the discovery of atomic energy. One of its greatest innovations is electricity, and everyone is aware of the effects it has on daily life.
Variety in Cuisine
There has also been an increase in food diversity. These days, a wide variety of fruits and vegetables are available year-round. It’s not necessary to wait for a given season to enjoy a certain meal. This modification is the result of scientific experimentation.
So, science is a part of our daily existence. Without scientific advancements, our lives would have been considerably more challenging and varied. Nonetheless, we cannot ignore the fact that a great deal of scientific innovation has contributed to environmental deterioration and a host of health issues for humankind.
There are essentially three main disciplines of science. The Natural Sciences, Social Sciences, and Formal Sciences are some of them. To examine different aspects, these branches are further divided into subcategories. This is a thorough examination of these groups and their subgroups.
Scientific Subdisciplines
Natural Science
This is the study of natural phenomena, as the name implies. It investigates how the cosmos and the world function. Physical science and life science are subcategories of natural science.
a) Science of Physics
The subcategories of physical science comprise the following:
- Physics is the study of matter’s and energy’s properties.
- Chemistry is the study of the materials that make up matter.
- The study of space and celestial bodies is called astronomy.
- Ecology is the study of how living things interact with their natural environments and with one another.
- Geology: It studies the composition and physical makeup of Earth.
- Earth science is the study of the atmosphere and the physical makeup of the planet.
- The study of the physical and biological components and phenomena of the ocean is known as oceanography.
- Meteorology: It studies the atmospheric processes.
The subcategories of life science include the following:
- The study of living things is called biology.
- The study of plants is known as botany.
- The study of animals is known as zoology.
c) Social Science
This includes examining social patterns and behavioral patterns in people. It is broken down into more than one subcategory. Among them are:
- History: The examination of past occurrences
- Political science is the study of political processes and governmental structures.
- Geographic: Study of the atmospheric and physical characteristics of Earth.
- Human society is studied in social studies.
- Sociology: The study of how societies form and operate.
Academic Sciences
It is the area of study that examines formal systems like logic and mathematics. It encompasses the subsequent subcategories:
- Numbers are studied in mathematics.
- Reasoning is the subject of logic.
- Statistics: It is the study of numerical data analysis.
- Mathematical analysis of decision-making in relation to profit and loss is known as decision theory.
- The study of abstract organization is known as systems theory.
- Computer science is the study of engineering and experimentation as a foundation for computer design and use.
Scientists from several fields have been doing in-depth research and testing numerous facets of the subject matter in order to generate novel ideas, innovations, and breakthroughs. Although these discoveries and technologies have made life easier for us, they have also permanently harmed both the environment and living things.
Introduction
Science is the study of various physical and natural phenomena’ structures and behaviors. Before drawing any conclusions, scientists investigate these factors, make extensive observations, and conduct experiments. In the past, science has produced a number of inventions and discoveries that have been beneficial to humanity.
I deas in Religion and Science
In science, new ideas and technologies are developed through a methodical and rational process; in religion, however, beliefs and faith are the only factors considered. In science, conclusions are reached by careful observation, analysis, and experimentation; in religion, however, conclusions are rarely reached through reason. As a result, they have very different perspectives on things.
Science and Religion at Odds
Because science and religion hold different opinions on many issues, they are frequently perceived as being at odds. Unfortunately, these disputes occasionally cause social unrest and innocent people to suffer. These are a few of the most significant disputes that have happened.
The World’s Creation
The world was formed in six days, according to many conservative Christians, sometime between 4004 and 8000 BCE. However, cosmologists assert that the Earth originated about 4.5 billion years ago and that the cosmos may be as old as 13.7 billion years.
The Earth as the Universe’s Center
Among the most well-known clashes is this one. Earth was considered to be the center of the universe by the Roman Catholic Church. They say that it is surrounded by the Sun, Moon, stars, and other planets. Famous Italian mathematician and astronomer Galileo Galilei’s discovery of the heliocentric system—in which the Sun is at the center of the solar system and the Earth and other planets orbit it—led to the conflict.
Eclipses of the Sun and Moon
Iraq was the scene of one of the first wars. The locals were informed by the priests that the moon eclipse was caused by the gods’ restlessness. These were seen as foreboding and intended to overthrow the kings. When the local astronomers proposed a scientific explanation for the eclipse, a disagreement arose.
There are still many myths and superstitions concerning solar and lunar eclipses around the world, despite astronomers providing a compelling and rational explanation for their occurrence.
In addition to these, there are a number of other fields in which religious supporters and scientists hold divergent opinions. While scientists, astronomers, and biologists have evidence to support their claims, the majority of people adhere closely to religious beliefs.
Not only do religious activists frequently oppose scientific methods and ideas, but many other facets of society have also taken issue with science since its discoveries are leading to a host of social, political, environmental, and health problems. Nuclear weapons are one example of a scientific invention that threatens humanity. In addition, the processes involved in preparation and the utilization of the majority of scientifically created equipment contribute to pollution, making life more difficult for all.
In the previous few decades, a number of scientific advancements and discoveries have greatly eased people’s lives. The previous ten years were not an anomaly. A good number of important scientific discoveries were acknowledged. The top ten most amazing recent scientific inventions are shown below.
New Developments and Findings in Science
Amputee Gains Control of Biomechanical Hand via Mental After a tragic accident took away his forearm, Pierpaolo Petruzziello, an Italian, used his mind to control a biomechanical hand attached to his arm. The hand used wires and electrodes to connect to the nerves in his arm. He became the first to become skilled at doing motions like gripping objects, wriggling his fingers, and moving.
The Global Positioning System
In 2005, the Global Positioning System, or GPS as it is more often known, went into commercial use. It was incorporated into mobile devices and worked wonders for tourists all over the world. Traveling to more recent locations and needing instructions couldn’t be simpler.
The Self-Driving Car Toyota debuted Prius shortly after Google launched its own self-driving car experiment in 2008. The accelerator, steering wheel, and brake pedals are absent from this vehicle. It runs without the need for user input because it is driven by an electric motor. To guarantee that the driverless experience is seamless and secure, it is integrated with specialized software, a collection of sensors, and precise digital maps.
Android, widely regarded as one of the most significant innovations of the decade, revolutionized the market by flooding it with devices running Java and Symbian earlier on. These days, Android is the operating system used by the majority of smartphones. Millions of applications are supported by it.
c) Computer Vision
A number of sub-domains fall under the umbrella of computer vision, including learning, video tracking, object recognition, object pose estimation, event detection, indexing, picture restoration, and scene reconstruction. In order to produce symbolic information, the field includes methods for processing, analyzing, obtaining, and understanding images in high-dimensional data from the real world.
d) Touch Screen Technology
It appears that touch screen technology has taken over the planet. The popularity of touch screen gadgets can be attributed to their ease of use. These gadgets are becoming quite popular everywhere.
e) Method of 3D Printing
The 3D printer is capable of producing a wide range of items, such as lamps, cookware, accessories, and much more. Alternatively referred to as additive manufacturing, this process uses digital model data from electronic data sources like Additive Manufacturing Files (AMF) to construct three-dimensional items of any shape.
Git Hub is an online hosting service and version control repository that was founded in 2008. It provides features including bug tracking, task management, feature requests, and the sharing of codes, apps, and other materials. The GitHub platform was first developed in 2007, and the website went live in 2008.
f) Smart Timepieces
The market for smart watches has been around for a while. The more recent models, like the one introduced by Apple, have garnered enormous popularity and come with a number of extra capabilities. Nearly all of the functionality found on smartphones are included in these watches, which are also more convenient to wear and use.
g) Websites for Crowdfunding
The emergence of crowdsourcing websites like Indiegogo, Kickstarter, and GoFundMe has been a blessing for innovators. Inventors, artists, and other creative people can share their ideas and gain the funding they need to put them into action by using these websites.
Global scientists constantly observe and experiment to develop new scientific discoveries that improve people’s lives. Not only do they consistently create new technologies, but they also adapt the ones that already exist whenever there is an opportunity. Even while these innovations have made life easier for humans, you are all aware of the numerous environmental, social, and political risks they have brought about.
500+ Words Essay on Mother Teresa in English For Students 500+ Words Essay on Swami Vivekananda in English for Students Rabindranath Tagore Essay in English For Students APJ Abdul Kalam Essay For Students: Check 500 Words Essay
Essay on Science- FAQs
Who is father of science.
Galileo is the father of science.
Why is it called science?
The word “scientia” has Latin origins and originally meant “knowledge,” “an expertness,” or “experience.”
What is science for students?
Science is the study of the world by observation, recording, listening, and watching. Science is the application of intellectual inquiry into the nature of the world and its behavior. Think like a scientist, anyone can.
What is science’s primary goal or objective?
Science’s primary goal is to provide an explanation for the facts. Moreover, science does not prohibit the explanation of facts in an arbitrary manner. Additionally, science organizes the data and develops theories to explain the data.
Describe what a scientific fact is.
Repeatable, meticulous observations or measurements made through experiments or other methods are referred to as scientific facts. Furthermore, empirical evidence is another name for a scientific fact. Most importantly, the development of scientific hypotheses depends on scientific facts.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- English Blogs
- School English

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Definition and Examples of Science Writing
Glossary of Grammatical and Rhetorical Terms
Serge Kozak/Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
The term science writing refers to writing about a scientific subject matter, often in a non-technical manner for an audience of non-scientists (a form of journalism or creative nonfiction ). Also called popular science writing . (Definition No. 1)
Science writing may also refer to writing that reports scientific observations and results in a manner governed by specific conventions (a form of technical writing ). More commonly known as scientific writing . (Definition No. 2)
Examples and Observations
- "Because science writing is intended to be entertaining enough to capture the continued interest of potential readers, its style is much less somber than the usual scientific writing [i.e., definition No. 2, above]. The use of slang , puns , and other word plays on the English language are accepted and even encouraged. . . . "Distinguishing between science writing and scientific writing is reasonable—they have different purposes and a different audience . However, one would be ill-advised to use the term 'science writing' or 'popular writing' in a disparaging way. Writing (or providing consultation for others who are writing) popularized accounts based on scientific research should be an important part of every scientists' outreach activities. The wider community is essential to adequate support for scientific endeavors."
- An Example of Science Writing: "Stripped for Parts": "Sustaining a dead body until its organs can be harvested is a tricky process requiring the latest in medical technology. But it's also a distinct anachronism in an era when medicine is becoming less and less invasive. Fixing blocked coronary arteries, which not long ago required prying a patient's chest open with a saw and spreader, can now be accomplished with a tiny stent delivered to the heart on a slender wire threaded up the leg. Exploratory surgery has given way to robot cameras and high-resolution imaging. Already, we are eyeing the tantalizing summit of gene therapy, where diseases are cured even before they do damage. Compared with such microscale cures, transplants—which consist of salvaging entire organs from a heart-beating cadaver and sewing them into a different body—seem crudely mechanical, even medieval."
On Explaining Science
"The question is not "should" you explain a concept or process, but "how" can you do so in a way that is clear and so readable that it is simply part of the story?
"Use explanatory strategies such as ...
- "People who study what makes an explanation successful have found that while giving examples is helpful, giving nonexamples is even better. "Nonexamples are examples of what something is not . Often, that kind of example will help clarify what the thing is . If you were trying to explain groundwater, for instance, you might say that, while the term seems to suggest an actual body of water, such as a lake or an underground river, that would be an inaccurate image. Groundwater is not a body of water in the traditional sense; rather, as Katherine Rowan, communications professor, points out, it is water moving slowly but relentlessly through cracks and crevices in the ground below us... "Be acutely aware of your readers' beliefs. You might write that chance is the best explanation of a disease cluster; but this could be counterproductive if your readers reject chance as an explanation for anything. If you are aware that readers' beliefs may collide with an explanation you give, you may be able to write in a way that doesn't cause these readers to block their minds to the science you explain."
The Lighter Side of Science Writing
"In this paragraph I will state the main claim that the research makes, making appropriate use of ' scare quotes ' to ensure that it's clear that I have no opinion about this research whatsoever.
"In this paragraph, I will briefly (because no paragraph should be more than one line) state which existing scientific ideas this new research 'challenges.'
"If the research is about a potential cure or a solution to a problem, this paragraph will describe how it will raise hopes for a group of sufferers or victims.
"This paragraph elaborates on the claim, adding weasel-words like 'the scientists say' to shift responsibility for establishing the likely truth or accuracy of the research findings on to absolutely anybody else but me, the journalist. ..."
(Janice R. Matthews and Robert W. Matthews, Successful Scientific Writing: A Step-by-Step Guide for the Biological and Medical Sciences , 4th ed. Cambridge University Press, 2014)
(Jennifer Kahn, "Stripped for Parts." Wired. March 2003. Reprinted in The Best American Science Writing 2004 , edited by Dava Sobel. HarperCollins, 2004)
(Sharon Dunwoody, "On Explaining Science." A Field Guide for Science Writers , 2nd ed., ed. by Deborah Blum, Mary Knudson, and Robin Marantz Henig. Oxford University Press, 2006)
(Martin Robbins, "This Is a News Website Article About a Scientific Paper." The Guardian , September 27, 2010)
- Examples of Great Introductory Paragraphs
- Topic In Composition and Speech
- Definition and Examples of Explication (Analysis)
- Definition and Examples of Paragraphing in Essays
- Definition and Examples of a Transition in Composition
- Understanding Organization in Composition and Speech
- Theory Definition in Science
- Supporting Detail in Composition and Speech
- Definition and Examples of Paragraph Breaks in Prose
- Second Grade Writing Prompts
- Premise Definition and Examples in Arguments
- Genres in Literature
- Definition and Examples of Body Paragraphs in Composition
- Development in Composition: Building an Essay
- Conciseness for Better Composition
- Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
Write Like a Scientist
A Guide to Scientific Communication
What is scientific writing ?
Scientific writing is a technical form of writing that is designed to communicate scientific information to other scientists. Depending on the specific scientific genre—a journal article, a scientific poster, or a research proposal, for example—some aspects of the writing may change, such as its purpose , audience , or organization . Many aspects of scientific writing, however, vary little across these writing genres. Important hallmarks of all scientific writing are summarized below. Genre-specific information is located here and under the “By Genre” tab at the top of the page.
What are some important hallmarks of professional scientific writing?
1. Its primary audience is other scientists. Because of its intended audience, student-oriented or general-audience details, definitions, and explanations — which are often necessary in lab manuals or reports — are not terribly useful. Explaining general-knowledge concepts or how routine procedures were performed actually tends to obstruct clarity, make the writing wordy, and detract from its professional tone.
2. It is concise and precise . A goal of scientific writing is to communicate scientific information clearly and concisely. Flowery, ambiguous, wordy, and redundant language run counter to the purpose of the writing.
3. It must be set within the context of other published work. Because science builds on and corrects itself over time, scientific writing must be situated in and reference the findings of previous work . This context serves variously as motivation for new work being proposed or the paper being written, as points of departure or congruence for new findings and interpretations, and as evidence of the authors’ knowledge and expertise in the field.
All of the information under “The Essentials” tab is intended to help you to build your knowledge and skills as a scientific writer regardless of the scientific discipline you are studying or the specific assignment you might be working on. In addition to discussions of audience and purpose , professional conventions like conciseness and specificity, and how to find and use literature references appropriately, we also provide guidelines for how to organize your writing and how to avoid some common mechanical errors .
If you’re new to this site or to professional scientific writing, we recommend navigating the sub-sections under “The Essentials” tab in the order they’re provided. Once you’ve covered these essentials, you might find information on genre- or discipline-specific writing useful.
- Authentic custom writing service
- Confidential and secure
- Only custom written work
- Essay on what science means to you
Sample Essay On What Science Means to You
The word 'science' is derived from the Latin word 'scientia' which means knowledge. Therefore, science is about gaining knowledge either through observing, studying, experience, or practice. Entire knowledge acquired through science is about discovering truths, finding facts, uncovering phenomenon hidden by the nature. Observations and experimentation, in science, support in describing truth and realities through systematic processes and procedures. For me, science is an intellectual set of activities designed to uncover information about anything related to this world in which we live. The information gathered is organized through scientific methods to form eloquent patterns. In my opinion the primary objective of science is to gather information and to distinguish the order found between facts.
What Science Means to Me as an Upcoming Scientist
Science exposes several ideas along with significant themes so that I could test them independently and without any bias to arrive at solid conclusion. For this purpose exchange of data and materials is necessary. I am able to generate real and tangible facts supported by reliable evidence. Work of scientist is based on theoretical science. It means, in theoretical science, there is only a sign, just a hint on which discoveries could be made, facts could be found. While studying science I am always working for determining truth, based on my perceptions, judgment, observation, experience, and knowledge collected through several means. It is pertinent to mention that science, in fact, has practical limits, however it is beneficial in almost every areas of human beings. Through science, I have the opportunity to test and verify ideas. I feel myself as an upcoming scientist because of my probing aptitude always ready to help people by producing useful things which great scientists have been able to accomplish like producing products such as cars, computers, airplanes, satellites etc.
In fact, science involves more than just gathering knowledge. I as a scientist can make systematic and well-organized inquiry to search for the realities and develop deeper understanding of the world. As an upcoming scientist I am of the view that reality exists and it is science through which I can learn about it. By applying scientific methods, I am sure that nature has not misguided me to know anything which is vital or critical for human beings. Science is building something that is useful, practical and realistic.
As explained above, science is all about collecting information to gain knowledge. Information collected is used to replace old ideas with new ones. Through new ideas, I can discover new things. As a scientist I shall be able to know the unknown, discover what has not yet been discovered and explain what previously has not been explained. By studying world around us it is easy to establish there is a lawmaker above us- the God- who has established the laws of nature. This idea is relevant to thinking of historians as well as philosophers, and also the past thinkers and forms the basis of modern science and discoveries being made today.
It is pertinent to mention that heavy resources are assigned to developing of new knowledge and scientists devote their entire life to explore the realities of nature for finding and discovering things that are useful for the human beings. The high a society is concerned about the well-being of its people; the more it will be making efforts in scientific areas to find new ways of making people's lives better. As I am interested in exploring realities, finding truths, and discovering the hidden phenomena, I am inclined towards research activities, whether in lab or in the field, making contributions towards discovering knowledge. This thinking forms the basis of my thoughts to be an upcoming scientist.
I believe that the basis of discoveries is trying continuously discovering, developing, and deducing new themes, concepts, theories, and ideas. Knowledge is not static rather dynamic as such change towards developing better understanding of the world is the fundamental idea in science. The theme of change is vital in developing new ideas and discovering innovative realities. However, understanding new concepts, and uncovering new realities requires constant questioning about current ideas, challenging their authenticity.
Becoming a scientist in future I want to develop a systematic approach for creating awareness about the phenomenon that observation, tests, and falsifiable experiments are necessary to understand how nature works. For example, scientists, through observations and experiments, are able to know about DNA codes and involve in stem cell research for the purpose of cure and support medical treatment of incurable diseases. As science challenges current and existing ideas discovered in the past which is not directly testable or observable, therefore, interpreting and challenging past ideas pose huge challenge to reject previous ideas and discover new things. Scientific theories enable us to engage continuously in the process of discovering.
Using Science in Everyday Life
I am a proponent of using science and benefit from it. It not only extends but also enriches and improves my life. It expands my vision, create imagination and release me from ghosts of false notion and ignorance. By using science I systematically can collect knowledge about laws and theories by testing the ideas and derived results. The previously concluded results and theses can be confronted to discover more reliable ideas and concepts. In fact, science is about studying every thing and anything. It is significant for the daily use as its study makes huge contributions towards understanding life and the opportunities offered by life. It enables us to acknowledge and appreciate matters related to betterment of ordinary people in everyday life.
Science heavily supports in economic and social development of human beings. For instance scientists work to discover natural resources like petroleum being a vital requirement in daily life. Scientists strive to find new ways in agriculture sector to keep us nutritionally enrich. New chemical substances are being discovered by the scientists, developing new phenomena to support economic development. Almost every nation in the world is involved in competing with others on economic fronts, discoveries through science as well as technological developments provides huge support to meet this objective.
Scientists are working continuously to serve humanity by increasing their control over world and its environment. Scientific knowledge makes us understand as to how continuous changes have caused the oceans and atmosphere to transform, altering the climate of world. Science supports us in controlling the main source of our being- food and water. Science, in our daily lives, is a huge blessing of God as it relieves us from ignorance, pain, and feeling of distress. It provides us the opportunity to control our world, acquire wisdom, and gain knowledge through valuable inventions. It is, in fact, providing precious service to human beings, only if we use it instead of misusing it. Science has changed entire course of human life. Although, it is a fact that everybody is not able to reap benefits of science, yet the comfort created by it benefits everyone, to some more, while for others less. In daily life, for example, it is necessary to communicate with each other including friends, relatives, colleagues etc. We need to contact several persons during routine life. Through mobiles, wireless, telephones, and internet, it has become immensely easy to communicate with each other even in seconds. Cheap methods of entertainment are available to us through scientific innovations. For example in music, science has opened new avenues of enjoying life at a very low cost. Radios, cinemas, televisions, DVDs, and different other modes of entertainment has opened new doors of recreation as well as effective modes of communications. Life of human beings today is, therefore, significantly different compared to almost a decade ago and this continuous change will be affecting and altering our daily lives in the future.
Another important area of our daily life is fast and convenience methods of traveling. The advent and invention of new as well as innovative ways of traveling have enabled us to cover huge distances in a very short span of time. Airplanes and railways have made the journey, thanks to science, comfortable, safe, convenient, and swift. In fact, world has shrunk to become a global village in which distances do not matter.
In the area of health, with the support of medical research, science has provided new ways to probe human body for making a better diagnosis and curing the disease effectively. This is one of the main reasons as to why average rate of life has increased, whereas death rate has significantly decreased. Complicated operations are being done with great ease supported by technological advancements in the medical field. New medicines are being introduced almost everyday to provide better cure and fight illness making life comfortable and healthy. Environment in offices and homes have become more comfortable with electricity, air-conditioners and fans in summer while heaters are used in winter to protect from cold.
Efforts have been made in the paper to describe role of science in daily life. Importance of science in my life has been highlighted and thoughts have been presented of my becoming a scientist. Science, in fact, has benefited us in almost every area of life and has changed our entire course of life.

Essay on Importance of Science in Our Life
Science is a systematic process in which various theories, formulas, laws, and thoughts are analysed and evaluated in order to determine the truth about the facts of anything.
This systematic process studies and generates new knowledge from any kind of activity that occurs in the nature around us or in the universe, of which we are a tiny part.
Table of Contents
Science is essential.
- Importance of Science in Society
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Science is a methodical process of extracting true facts from any given thought by adhering to a set of rules known as methodology.
It includes the following:
- Observation: The observations are made based on the collected data and measurements.
- Evidence: If any evidence is gathered for further processing of data evaluation.
- Experiment : Using the data and evidence gathered, experiments are carried out to test the assumption.
- Initiation: Identify the facts based on data and evidence analysis.
- Re-examination and complex analysis: To ensure the veracity and authenticity of the results, the data and evidence are examined several times and critically analysed.
- Verification and review of the results: The results of the experiment are verified and tested by experts to ensure that they are correct.
Science is concerned with generating new knowledge and proving new hypotheses by collecting and analysing data in a systematic manner.
There are numerous scientific disciplines:
- Astrophysics
- Climate science
- Atmospheric science
Importance of science in society
Science and technology play an important role in today’s changing world. Everything from the road to the buildings, the shop to the educational instructions is the result of modern science and technology. Almost everything we see in society is the result of applied science and technology. Even the toothpaste we use to clean our teeth after waking up in the morning and before going to bed at night are products of science and technology.
Electricity
The discovery of electricity was the first modern scientific marvel. It has altered our way of life, society, and culture. It’s a fantastic source of power and energy.
The radio and television Lights, fans, electric irons, mills, factories, and refrigerators are all powered by electricity.
Transport and Communication
Science has simplified and shortened our communication. Ships, boats, trains, buses, and cars can be found on the seas, rivers, and roads. All of these are scientific gifts.
Telegraph, telephone, fax, and wireless communication are also important modes of communication. Trains, steamers, aeroplanes, buses, and other modes of transportation make communication quick and easy.
Medicine and Surgery
- It elevates one’s overall standard of living, quality of life, and life expectancy.
- It aids in detecting and treating diseases, ailments, and conditions.
- It dissects the molecular mechanism of any disease and helps to develop drugs and pharmaceuticals.
- Basic Medical Sciences, in addition to curative care, sow the seeds of preventive care.
- It teaches researchers, doctors, scientists, and even laypeople about living a healthy lifestyle.
- It fosters a fundamental understanding of medical science principles, which may be useful in the future.
Agriculture
A great deal of agricultural research was conducted, which resulted in the production of artificial fertilisers, which are now a basic requirement for all agricultural activities. Agricultural education is now taught in schools across the country. Scientists have gone so far as to study the genomic makeup of plants to select crops that can withstand harsh climate changes. Improved farming techniques have been developed using new technologies such as computer science and biotechnology.
Science has played an important role in agriculture, and the two cannot be separated. Science must be used to help produce better yields on a small piece of land for the world to be able to provide enough food for all of its citizens.
Read more: Chemistry of Life
New scientific understanding may result in new applications.
The discovery of the structure of DNA, for example, was a major breakthrough. It served as the foundation for research that would eventually lead to many practical applications, such as DNA fingerprinting, genetically engineered crops, and genetic disease tests.
New technological developments may result in new scientific discoveries.
For example, the development of DNA copying and sequencing technologies has resulted in significant advances in many areas of science.
Scientific research may be motivated by potential applications.
For example, the possibility of engineering microorganisms to produce drugs for diseases such as malaria motivates many microbe genetics researchers to continue their research.
Frequently Asked Questions on Essay on Importance of Science in Our Life
What role does science play in our lives.
It helps us live a longer and healthier life by monitoring our health, providing medicine to cure our diseases, alleviating aches and pains, assisting us in providing water for our basic needs – including our food – providing energy and making life more enjoyable by including sports, music, entertainment, and cutting-edge communication technology.
How has science influenced our daily lives?
Science has changed how we live and what we believe since the invention of the plough. Science has allowed man to pursue societal concerns such as ethics, aesthetics, education, and justice, to create cultures, and to improve human conditions by making life easier.
How has science made our lives easier?
When scientific discoveries are combined with technological advancements, machines make managing our lives easier. Science has created everything from household appliances to automobiles and aeroplanes. Farmers can now save their crops from pests and other problems thanks to advances in science.
What is the social significance of science and technology?
The essence of how science and technology contribute to society is the creation of new knowledge and then the application of that knowledge to improve human life and solve societal problems.
Why is science education important in the 21st century?
Exemplary science education can offer a rich context for developing many 21st-century skills, such as critical thinking, problem solving, and information literacy, especially when instruction addresses the nature of science and promotes the use of science practices.
| CHEMISTRY Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Social History
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- Ethnic Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Politics of Development
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Qualitative Political Methodology
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous
- Next chapter >

Introduction to the Science of Meaning
- Published: July 2018
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This Introduction aims to acquaint the reader with some of the main views on the foundations of natural language semantics, to discuss the type of phenomena semanticists study, and to give some basic technical background in compositional model-theoretic semantics necessary to understand the chapters in this collection. Topics discussed include truth conditions, compositionality, context-sensitivity, dynamic semantics, the relation of formal semantic theories to the theoretical apparatus of reference and propositions current in much philosophy of language, what semantic theories aim to explain, realism, the metaphysics of language and different views of the relation between languages and speakers, and the epistemology of semantics.
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| October 2022 | 3 |
| November 2022 | 6 |
| January 2023 | 5 |
| February 2023 | 2 |
| April 2023 | 3 |
| May 2023 | 6 |
| July 2023 | 2 |
| August 2023 | 3 |
| October 2023 | 8 |
| November 2023 | 2 |
| February 2024 | 2 |
| March 2024 | 3 |
| April 2024 | 2 |
| May 2024 | 3 |
| June 2024 | 1 |
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
Understanding Science
How science REALLY works...
- Science is deeply interwoven with society and changes along with society.
- The Internet and other technological advances have changed how scientific information is distributed and the process of scrutiny within science.
Modern science: What’s changing?
When Gregor Mendel began his investigations of plant genetics in the 1800s, he worked alone — a middle-aged European monk counting peas in the abbey garden. One hundred and fifty years later, modern plant genetics laboratories, like Chelsea Specht’s below, look a lot more diverse and employ the latest DNA sequencing techniques. When J.J. Thomson discovered a new particle of matter — the electron — at the turn of the century, his lab equipment mainly consisted of vacuum tubes, magnets, and some simple wiring. One hundred years later, scientists searching for new particles like the Higgs boson use a supercollider — a 17-mile-long machine that costs several billion dollars and will produce data to be analyzed by the most powerful supercomputer in the world. Science has come a long way in the last 150 years! We now have more powerful data analysis techniques, more sophisticated equipment for making observations and running experiments , and a much greater breadth and depth of scientific knowledge. And as the attitudes of the broader society have progressed, science has benefited from the expanding diversity of perspectives offered by its participants. But what about the process of science itself? Has this fundamental aspect of the scientific enterprise changed over time?
Science will always look for explanations for what goes on in the natural world and test those explanations against evidence from the natural world — but exactly how this gets done may evolve. The scientific enterprise is not static. Science is deeply interwoven with society, and as it has changed, so too has science. Here are just a few examples of how modern scientific practices have been transformed by increasing knowledge, changing societal concerns, and advances in communication and technology .
Publication and peer review
- Take a sidetrip
To learn more about evaluating scientific messages check out our section on A Scientific Approach to Life: A Science Toolkit .
The rise of the Internet has enabled scientific results to be publicized more rapidly than ever before possible. Journal articles are often made available online even before they are printed. This swift distribution of information can speed the pace of science since the latest studies can be scrutinized, replicated , and/or built upon with very little lag time. And as more and more journals provide records of reader comments on e-published articles, the process of peer review is being extended: many more scientists can provide feedback on a particular article and they may do it long after the article’s original publication. But the information flow doesn’t stop there. Journalists can also quickly access the latest scientific findings and begin to publicize them to the broader population. Scientific information on a wide variety of topics is now available to anyone with an Internet connection — which makes staying informed convenient, but also carries responsibilities. Consumers of this information must remember that, in science, the first report of a finding is never the last word. Many years and multiple rounds of testing may be required before science can be confident about a particular conclusion. With so much information, from so many different sources, it is now more important than ever to be a critical consumer of media messages about science.
VIRTUAL SCIENCE
- The Public Library of Science , where all articles are free
- The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , where articles more than six months old are available for free
- The Directory of Open Access Journals , where you can find free journals on many different topics
In fact, scientists (especially young scientists) are beginning to change the way they communicate, more freely sharing information and sometimes making it available online before it is published. Read about this new trend in an article from the Boston Globe .
New media are also playing an increasingly important role in modern science. Check out a new movement in scientific publishing: video!
- The Journal of Visualized Experiments publishes biological research in a video format and is especially useful for learning new lab techniques.
You can even listen in on scientists’ coffee break discussions of recent papers, problems, and ideas by checking out online forums like:
- Cosmocoffee on cosmology and high-energy physics
- BioForum on biology lab techniques
Technological advances have also added an additional step to the review that many scientific articles undergo: image analysis. In 2004, Woo Suk Hwang announced to the scientific community and the rest of the world that he had reached a milestone of biology — cloning a human embryonic stem cell. Over the next two years, partly through the close scrutiny of images in his published work that appeared to be duplicated and manipulated, this so-called breakthrough was revealed to be a fraud. As cases like Huang’s have come to light, many journals have begun to more carefully scrutinize the images in scientific papers, often using computer programs to digitally analyze pictures and hunt for manipulation.
Specialization and collaboration
As our scientific knowledge has advanced and the questions we seek to answer have become more complex, science has become more specialized. While Charles Darwin’s research in the 1800s seems to have known no bounds — he studied everything from evolutionary theory, to geology, to human emotions, to soil ecology, to tropical corals, to barnacles and botany — a modern scientist is much more likely to focus on a narrower topic: salamander development, for example, or ancient climate changes in aquatic ecosystems. It’s not that modern scientists’ interests range less widely, but that our knowledge has expanded to such a degree that developing the expertise (and resources) necessary to conduct research at the cutting edge of a field can represent a huge investment of time and effort. Because of this, modern scientists tend to be more specialized than their predecessors.
This specialization (along with the complexity of the questions modern science investigates) has necessitated more cross-disciplinary collaboration than in the past. For example, a recent project investigating desertification in Southern Europe involved collaboration between sociologists, anthropologists, archaeologists, agronomists, biologists, and mathematical modelers. 1 In addition, scientists today are now more likely to work in large teams — regardless of disciplinary specialization. In 1960, the average number of authors on science and engineering articles was around 1.9. As of 2000, that number had reached 3.5 and appeared to be on the rise. 2 The most extreme examples of modern scientific teamwork are truly astounding. The paper reporting the initial sequence of the human genome had more than a thousand authors, 3 and a similar number of physicists are involved with the Large Hadron Collider, a recent project in particle physics. Happily, advances in communications, especially the Internet, have smoothed the water for this transition to team science. Ideas, plans, and data can now be easily shared regardless of distance or political and institutional boundaries. In fact, many of the largest projects make their raw data publically available via the Internet for anyone to scrutinize or use in an investigation.
See the data for yourself. Visit the Human Genome Project website for a tutorial on accessing free genetic data online.
In the 1830s, while travelling on the Beagle , Charles Darwin amassed for scientific study a vast collection of animal and plant specimens from around the world. In the 1880s, Louis Pasteur tested a vaccine by exposing groups of vaccinated and unvaccinated sheep to anthrax bacteria. In the 1890s, Marie and Pierre Curie’s studies of radiation were carried out without any environmental or safety precautions — and, in fact, their research notes from those years are still so radioactive that scholars wishing to study them must sign a risk waiver! Today, each of these studies would be subject to significant regulation from government agencies and scientific bodies — but historically, relatively few guidelines and rules have pertained to the ethics, safety, and environmental impact of scientific research. As society and the scientific community have become increasingly concerned about these ramifications, scientific and governmental organizations have set up guidelines to minimize potentially negative impacts and ensure that research is carried out ethically.
Learn more about the many ways in which modern science is regulated. Visit Great Expectations in our unit on the Social Side of Science .
The process of science clearly evolves along with advances in knowledge and technology and with societal concerns. The Internet has opened up new ways for scientists to share information and work on projects together. Our expanding knowledge base has influenced the degree to which scientists specialize in sub-disciplines and, correspondingly, how much they collaborate. And, of course, as both the scientific community and the broader society in which it is embedded have become increasingly concerned about safety, environmental protection, and the treatment of animal and human study participants, new limits have been placed on how research is carried out. These shifts don’t suggest any fundamental changes in how science works — it’s still about finding explanations for phenomena in the natural world that hold up against multiple lines of evidence and the scrutiny of the scientific community — they do highlight the flexibility of the process of science to accommodate new concerns and build upon new opportunities.
- Science was once dominated by men and most recently by men living in Western nations. However, this situation is changing along with science itself. To learn more, visit Science around the world .
- Advanced: Visit the Visionlearning website to learn about how scientific institutions have changed over time and evolved into their current forms .
1 Jeffrey, P. 2003. Smoothing the waters: Observations on the process of cross-disciplanary research collaboration. Social Studies of Science 33:539-562. 2 Wuchty, S., B.F. Jones, and B. Uzzi. 2007. The increasing dominance of teams in production of knowledge. Science 316(5827):1036-1039. 3 International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. 2001. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409:860-921.
Subscribe to our newsletter
- Understanding Science 101
- The science flowchart
- Science stories
- Grade-level teaching guides
- Teaching resource database
- Journaling tool
- Misconceptions

Human Consciousness Is an Illusion, Scientists Say
The entire universe may have an internal mind—or the whole idea of consciousness could be a sham. Here’s why scientists still can’t agree.
The concept of panpsychism has been around for hundreds of years. Italian philosopher Francesco Patrizi coined the term in the late 16th century. He combined the Greek words παν (pronounced “pan,” and meaning everything) and ψυχή (psyche, meaning “soul” or “mind”) to describe a distinctive soulfulness inherent to each and every order of creation. The idea dates back even further, though, to ancient Greece, when astronomer, mathematician, and pre-Socratic philosopher Thales said “that everything is full of gods,” and one of the world’s best-studied philosophers, Plato, said that the world is indeed a living being endowed with a soul and intelligence.
In the 19th century, panpsychism took off in the West, championed by the likes of the great philosopher of pessimism, Arthur Schopenhauer, and the father of modern psychology, William James. Then came the philosophical movement that emerged in Vienna, Italy, in the 1920s, called logical positivism: the idea that scientific knowledge—empirically proven knowledge—was the only kind of acceptable knowledge, the rest being metaphysical mumbo-jumbo. It was game over for panpsychism.
Until recently.
The inability of empirical sciences to figure out why and how matter gives rise to the experiences of consciousness has recently rekindled an interest in panpsychism. So have developments in the fields of neuroscience, psychology, and quantum physics.
In 2004, Italian neuroscientist and psychiatrist Giulio Tononi, Ph.D., proposed the integrated information theory of consciousness, which says that consciousness is widespread and can be found even in some simple systems. In his article in Scientific American , leading American neuroscientist Christof Koch, Ph.D., bashed materialism and its view of emerging consciousness 10 years later. The notion of subjective feelings springing from physical stuff is at odds with a commonly applied axiom in philosophy and modern science: the “ ex nihilo nihil fit ,” or that “out of nothing, nothing comes, ” Koch wrote . He argued that elementary particles either have some charge, or they have none; similarly, where there are organized lumps of matter, consciousness follows.
.css-2l0eat{font-family:UnitedSans,UnitedSans-roboto,UnitedSans-local,Helvetica,Arial,Sans-serif;font-size:1.625rem;line-height:1.2;margin:0rem;padding:0.9rem 1rem 1rem;}@media(max-width: 48rem){.css-2l0eat{font-size:1.75rem;line-height:1;}}@media(min-width: 48rem){.css-2l0eat{font-size:1.875rem;line-height:1;}}@media(min-width: 64rem){.css-2l0eat{font-size:2.25rem;line-height:1;}}.css-2l0eat b,.css-2l0eat strong{font-family:inherit;font-weight:bold;}.css-2l0eat em,.css-2l0eat i{font-style:italic;font-family:inherit;} “Consciousness doesn’t exist, and we only think it does because we are under a sort of illusion about our own minds.”
Not everyone agrees though. Keith Frankish, Ph.D., a professor of philosophy at the University of Sheffield, believes today’s panpsychism is in a “metaphysical limbo,” a direct result of what he calls the “ depsychologization of consciousness .” This means that we try to grasp consciousness through what our senses perceive or through our immediate experiences, and that we refuse to acknowledge it as a psychological function. “The thought is that, if consciousness is not essentially connected to brain processes, then there’s no reason to think it must be restricted to brains . Maybe everything has a little inner glow to it, ” Frankish says. But it is exactly this view that tends to undermine the significance of consciousness. “If my consciousness makes no difference to how I react, why should I or anyone else care about it?” he asks. Frankish proposes a mirror image of panpsychism.
“Whereas panpsychists think that consciousness is everywhere, I think that consciousness—of the non-functional, inner glow kind—is nowhere,” he explains. “Consciousness doesn’t exist, and we only think it does because we are under a sort of illusion about our own minds, a view I call illusionism,” he continues. In other words, we humans have vastly extended the power of our biological brains and, through powerful tricks like self-manipulation or solid problem-solving skills, we have convinced ourselves we have a unified, conscious mind, a self, a soul—but it’s all an illusion, according to Frankish.
But illusionism is a view antithetical to what well-known biologist and author Rupert Sheldrake, Ph.D., believes. For Sheldrake, it’s an irrefutable fact that not only do we humans have consciousness, but the whole galaxy has consciousness, too. Sheldrake is best known for his hypothesis of morphic resonance, a process through which self-organizing systems (picture termite colonies or insulin molecules) inherit a memory from previous, similar systems. Similar organisms share mysterious telepathic interconnections, and species share collective memories: this is how your dog foretells when you’re coming home and why you feel awkward when someone is staring at you, according to Sheldrake. In a paper he published in the Journal of Consciousness Studies in 2021, Sheldrake asked “Is the sun conscious?” For him, it most certainly is.
“Consciousness does not need to be confined to brains,” Sheldrake says. “The link between minds and physical systems seems to be through rhythmic electromagnetic fields, which of course are present in our brains. They are also present in and around the sun, and these could be the interface between the solar mind and the body of the sun.” So, if the sun is conscious, it’s likely to be aware of activities within the solar system, continues Sheldrake, including here on Earth, and also of its relationship with other stars within the galaxy and the galaxy as a whole.
Perhaps it’s a matter of personal positioning in the world. Is nothing around me conscious? Is everything around me conscious? If the latter is true, where does my consciousness end and yours begin, and why is an intact brain conscious, whereas the same brain, pureed to goo inside a blender, is not ( as Koch ponders )? Will we ever know? No wonder scientists describe consciousness as the granddaddy of all mysteries of human behavior. If you subscribe to the panpsychist view, however, you may be startled to know that the conscious sun makes choices. “It may be able to choose in which direction to send out solar flares or coronal mass ejections, which can have an enormous effect on life on Earth, and to which our technologies are very vulnerable,” Sheldrake says.
Stav Dimitropoulos’s science writing has appeared online or in print for the BBC, Discover, Scientific American, Nature, Science, Runner’s World, The Daily Beast and others. Stav disrupted an athletic and academic career to become a journalist and get to know the world.

.css-cuqpxl:before{padding-right:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;} Pop Mech Pro: Science .css-xtujxj:before{padding-left:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;}
The CIA’s Plan to Deploy an Army of Super Spies

She Was Pronounced Dead—Then Found Gasping for Air

Every Single Cell in Your Body Could Be Conscious

How to Live Forever, or Die Trying

A Groundbreaking Discovery For Interstellar Travel
Dark Matter Could Unlock a Limitless Energy Source

The Source of All Consciousness May Be Black Holes
Could Freezing Your Brain Help You Live Forever?

The Universe Could Be Eternal, This Theory Says

Immortality Is Impossible Until We Beat Physics
How Vacuum Energy Could Help Us Reach Light Speed
Scientific breakthroughs: 2024 emerging trends to watch

December 28, 2023
Across disciplines and industries, scientific discoveries happen every day, so how can you stay ahead of emerging trends in a thriving landscape? At CAS, we have a unique view of recent scientific breakthroughs, the historical discoveries they were built upon, and the expertise to navigate the opportunities ahead. In 2023, we identified the top scientific breakthroughs , and 2024 has even more to offer. New trends to watch include the accelerated expansion of green chemistry, the clinical validation of CRISPR, the rise of biomaterials, and the renewed progress in treating the undruggable, from cancer to neurodegenerative diseases. To hear what the experts from Lawrence Liverpool National Lab and Oak Ridge National Lab are saying on this topic, join us for a free webinar on January 25 from 10:00 to 11:30 a.m. EDT for a panel discussion on the trends to watch in 2024.
The ascension of AI in R&D

While the future of AI has always been forward-looking, the AI revolution in chemistry and drug discovery has yet to be fully realized. While there have been some high-profile set-backs , several breakthroughs should be watched closely as the field continues to evolve. Generative AI is making an impact in drug discovery , machine learning is being used more in environmental research , and large language models like ChatGPT are being tested in healthcare applications and clinical settings.
Many scientists are keeping an eye on AlphaFold, DeepMind’s protein structure prediction software that revolutionized how proteins are understood. DeepMind and Isomorphic Labs have recently announced how their latest model shows improved accuracy, can generate predictions for almost all molecules in the Protein Data Bank, and expand coverage to ligands, nucleic acids, and posttranslational modifications . Therapeutic antibody discovery driven by AI is also gaining popularity , and platforms such as the RubrYc Therapeutics antibody discovery engine will help advance research in this area.
Though many look at AI development with excitement, concerns over accurate and accessible training data , fairness and bias , lack of regulatory oversight , impact on academia, scholarly research and publishing , hallucinations in large language models , and even concerns over infodemic threats to public health are being discussed. However, continuous improvement is inevitable with AI, so expect to see many new developments and innovations throughout 2024.
‘Greener’ green chemistry

Green chemistry is a rapidly evolving field that is constantly seeking innovative ways to minimize the environmental impact of chemical processes. Here are several emerging trends that are seeing significant breakthroughs:
- Improving green chemistry predictions/outcomes : One of the biggest challenges in green chemistry is predicting the environmental impact of new chemicals and processes. Researchers are developing new computational tools and models that can help predict these impacts with greater accuracy. This will allow chemists to design safer and more environmentally friendly chemicals.
- Reducing plastics: More than 350 million tons of plastic waste is generated every year. Across the landscape of manufacturers, suppliers, and retailers, reducing the use of single-use plastics and microplastics is critical. New value-driven approaches by innovators like MiTerro that reuse industrial by-products and biomass waste for eco-friendly and cheaper plastic replacements will soon be industry expectations. Lowering costs and plastic footprints will be important throughout the entire supply chain.
- Alternative battery chemistry: In the battery and energy storage space, finding alternatives to scarce " endangered elements" like lithium and cobalt will be critical. While essential components of many batteries, they are becoming scarce and expensive. New investments in lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries that do not use nickel and cobalt have expanded , with 45% of the EV market share being projected for LFP in 2029. Continued research is projected for more development in alternative materials like sodium, iron, and magnesium, which are more abundant, less expensive, and more sustainable.
- More sustainable catalysts : Catalysts speed up a chemical reaction or decrease the energy required without getting consumed. Noble metals are excellent catalysts; however, they are expensive and their mining causes environmental damage. Even non-noble metal catalysts can also be toxic due to contamination and challenges with their disposal. Sustainable catalysts are made of earth-abundant elements that are also non-toxic in nature. In recent years, there has been a growing focus on developing sustainable catalysts that are more environmentally friendly and less reliant on precious metals. New developments with catalysts, their roles, and environmental impact will drive meaningful progress in reducing carbon footprints.
- Recycling lithium-ion batteries: Lithium-ion recycling has seen increased investments with more than 800 patents already published in 2023. The use of solid electrolytes or liquid nonflammable electrolytes may improve the safety and durability of LIBs and reduce their material use. Finally, a method to manufacture electrodes without solvent s could reduce the use of deprecated solvents such as N-methylpyrrolidinone, which require recycling and careful handling to prevent emissions.
Rise of biomaterials

New materials for biomedical applications could revolutionize many healthcare segments in 2024. One example is bioelectronic materials, which form interfaces between electronic devices and the human body, such as the brain-computer interface system being developed by Neuralink. This system, which uses a network of biocompatible electrodes implanted directly in the brain, was given FDA approval to begin human trials in 2023.
- Bioelectronic materials: are often hybrids or composites, incorporating nanoscale materials, highly engineered conductive polymers, and bioresorbable substances. Recently developed devices can be implanted, used temporarily, and then safely reabsorbed by the body without the need for removal. This has been demonstrated by a fully bioresorbable, combined sensor-wireless power receiver made from zinc and the biodegradable polymer, poly(lactic acid).
- Natural biomaterials: that are biocompatible and naturally derived (such as chitosan, cellulose nanomaterials, and silk) are used to make advanced multifunctional biomaterials in 2023. For example, they designed an injectable hydrogel brain implant for treating Parkinson’s disease, which is based on reversible crosslinks formed between chitosan, tannic acid, and gold nanoparticles.
- Bioinks : are used for 3D printing of organs and transplant development which could revolutionize patient care. Currently, these models are used for studying organ architecture like 3D-printed heart models for cardiac disorders and 3D-printed lung models to test the efficacy of drugs. Specialized bioinks enhance the quality, efficacy, and versatility of 3D-printed organs, structures, and outcomes. Finally, new approaches like volumetric additive manufacturing (VAM) of pristine silk- based bioinks are unlocking new frontiers of innovation for 3D printing.
To the moon and beyond

The global Artemis program is a NASA-led international space exploration program that aims to land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon by 2025 as part of the long-term goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the Moon. Additionally, the NASA mission called Europa Clipper, scheduled for a 2024 launch, will orbit around Jupiter and fly by Europa , one of Jupiter’s moons, to study the presence of water and its habitability. China’s mission, Chang’e 6 , plans to bring samples from the moon back to Earth for further studies. The Martian Moons Exploration (MMX) mission by Japan’s JAXA plans to bring back samples from Phobos, one of the Mars moons. Boeing is also expected to do a test flight of its reusable space capsule Starliner , which can take people to low-earth orbit.
The R&D impact of Artemis extends to more fields than just aerospace engineering, though:
- Robotics: Robots will play a critical role in the Artemis program, performing many tasks, such as collecting samples, building infrastructure, and conducting scientific research. This will drive the development of new robotic technologies, including autonomous systems and dexterous manipulators.
- Space medicine: The Artemis program will require the development of new technologies to protect astronauts from the hazards of space travel, such as radiation exposure and microgravity. This will include scientific discoveries in medical diagnostics, therapeutics, and countermeasures.
- Earth science: The Artemis program will provide a unique opportunity to study the Moon and its environment. This will lead to new insights into the Earth's history, geology, and climate.
- Materials science: The extreme space environment will require new materials that are lightweight, durable, and radiation resistant. This will have applications in many industries, including aerospace, construction, and energy.
- Information technology: The Artemis program will generate a massive amount of data, which will need to be processed, analyzed, and shared in real time. This will drive the development of new IT technologies, such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
The CRISPR pay-off

After years of research, setbacks, and minimal progress, the first formal evidence of CRISPR as a therapeutic platform technology in the clinic was realized. Intellia Therapeutics received FDA clearance to initiate a pivotal phase 3 trial of a new drug for the treatment of hATTR, and using the same Cas9 mRNA, got a new medicine treating a different disease, angioedema. This was achieved by only changing 20 nucleotides of the guide RNA, suggesting that CRISPR can be used as a therapeutic platform technology in the clinic.
The second great moment for CRISPR drug development technology came when Vertex and CRISPR Therapeutics announced the authorization of the first CRISPR/Cas9 gene-edited therapy, CASGEVY™, by the United Kingdom MHRA, for the treatment of sickle cell disease and transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia. This was the first approval of a CRISPR-based therapy for human use and is a landmark moment in realizing the potential of CRISPR to improve human health.
In addition to its remarkable genome editing capability, the CRISPR-Cas system has proven to be effective in many applications, including early cancer diagnosis . CRISPR-based genome and transcriptome engineering and CRISPR-Cas12a and CRISPR-Cas13a appear to have the necessary characteristics to be robust detection tools for cancer therapy and diagnostics. CRISPR-Cas-based biosensing system gives rise to a new era for precise diagnoses of early-stage cancers.
MIT engineers have also designed a new nanoparticle DNA-encoded nanosensor for urinary biomarkers that could enable early cancer diagnoses with a simple urine test. The sensors, which can detect cancerous proteins, could also distinguish the type of tumor or how it responds to treatment.
Ending cancer

The immuno-oncology field has seen tremendous growth in the last few years. Approved products such as cytokines, vaccines, tumor-directed monoclonal antibodies, and immune checkpoint blockers continue to grow in market size. Novel therapies like TAC01-HER2 are currently undergoing clinical trials. This unique therapy uses autologous T cells, which have been genetically engineered to incorporate T cell Antigen Coupler (TAC) receptors that recognize human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) presence on tumor cells to remove them. This could be a promising therapy for metastatic, HER2-positive solid tumors.
Another promising strategy aims to use the CAR-T cells against solid tumors in conjunction with a vaccine that boosts immune response. Immune boosting helps the body create more host T cells that can target other tumor antigens that CAR-T cells cannot kill.
Another notable trend is the development of improved and effective personalized therapies. For instance, a recently developed personalized RNA neoantigen vaccine, based on uridine mRNA–lipoplex nanoparticles, was found effective against pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Major challenges in immuno-oncology are therapy resistance, lack of predictable biomarkers, and tumor heterogenicity. As a result, devising novel treatment strategies could be a future research focus.
Decarbonizing energy

Multiple well-funded efforts are underway to decarbonize energy production by replacing fossil fuel-based energy sources with sources that generate no (or much less) CO2 in 2024.
One of these efforts is to incorporate large-scale energy storage devices into the existing power grid. These are an important part of enabling the use of renewable sources since they provide additional supply and demand for electricity to complement renewable sources. Several types of grid-scale storage that vary in the amount of energy they can store and how quickly they can discharge it into the grid are under development. Some are physical (flywheels, pumped hydro, and compressed air) and some are chemical (traditional batteries, flow batteries , supercapacitors, and hydrogen ), but all are the subject of active chemistry and materials development research. The U.S. government is encouraging development in this area through tax credits as part of the Inflation Reduction Act and a $7 billion program to establish regional hydrogen hubs.
Meanwhile, nuclear power will continue to be an active R&D area in 2024. In nuclear fission, multiple companies are developing small modular reactors (SMRs) for use in electricity production and chemical manufacturing, including hydrogen. The development of nuclear fusion reactors involves fundamental research in physics and materials science. One major challenge is finding a material that can be used for the wall of the reactor facing the fusion plasma; so far, candidate materials have included high-entropy alloys and even molten metals .
Neurodegenerative diseases

Neurodegenerative diseases are a major public health concern, being a leading cause of death and disability worldwide. While there is currently no cure for any neurodegenerative disease, new scientific discoveries and understandings of these pathways may be the key to helping patient outcomes.
- Alzheimer’s disease: Two immunotherapeutics have received FDA approval to reduce both cognitive and functional decline in individuals living with early Alzheimer's disease. Aducannumab (Aduhelm®) received accelerated approval in 2021 and is the first new treatment approved for Alzheimer’s since 2003 and the first therapy targeting the disease pathophysiology, reducing beta-amyloid plaques in the brains of early Alzheimer’s disease patients. Lecanemab (Leqembi®) received traditional approval in 2023 and is the first drug targeting Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology to show clinical benefits, reducing the rate of disease progression and slowing cognitive and functional decline in adults with early stages of the disease.
- Parkinson’s disease: New treatment modalities outside of pharmaceuticals and deep brain stimulation are being researched and approved by the FDA for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease symptoms. The non-invasive medical device, Exablate Neuro (approved by the FDA in 2021), uses focused ultrasound on one side of the brain to provide relief from severe symptoms such as tremors, limb rigidity, and dyskinesia. 2023 brought major news for Parkinson’s disease research with the validation of the biomarker alpha-synuclein. Researchers have developed a tool called the α-synuclein seeding amplification assay which detects the biomarker in the spinal fluid of people diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease and individuals who have not shown clinical symptoms.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): Two pharmaceuticals have seen FDA approval in the past two years to slow disease progression in individuals with ALS. Relyvrio ® was approved in 2022 and acts by preventing or slowing more neuron cell death in patients with ALS. Tofersen (Qalsody®), an antisense oligonucleotide, was approved in 2023 under the accelerated approval pathway. Tofersen targets RNA produced from mutated superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) genes to eliminate toxic SOD1 protein production. Recently published genetic research on how mutations contribute to ALS is ongoing with researchers recently discovering how NEK1 gene mutations lead to ALS. This discovery suggests a possible rational therapeutic approach to stabilizing microtubules in ALS patients.
Gain new perspectives for faster progress directly to your inbox.
Drive industry-leading advancements and accelerate breakthroughs by unlocking your data’s full potential. Contact our CAS Custom Services SM experts to find the digital solution to your information challenges.

2024’s violent tornado season has been one of the most active on record − a meteorologist explains the weather behind the outbreaks
Professor of Atmospheric Science, Iowa State University
Disclosure statement
William Gallus receives funding from the National Science Foundation, Department of Energy, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Iowa State University provides funding as a member of The Conversation US.
View all partners
Spring 2024 was unnerving for people across large parts of the U.S. as tornado warnings and sirens sent them scrambling for safety.
More than 1,100 tornadoes were reported through May − a preliminary number but nearly twice the 30-year average at that point and behind only 2011 , when deadly tornado outbreaks tore across the southeastern U.S.
The U.S. experienced several multistate outbreaks in 2024. Tornadoes damaged homes from Texas to Minnesota and east to West Virginia and Georgia . They caused widespread destruction in several towns, including Greenfield, Iowa ; Westmoreland, Kansas ; and Bartlesville, Oklahoma . Barnsdall, Oklahoma, was hit twice in two months .
In May, at least one tornado occurred somewhere in the country almost every day .
What causes some years to have so many tornadoes? I’m a meteorologist who studies tornadoes and thunderstorms . Here’s what created the perfect conditions for these violent storms.
2 key tornado ingredients, on steroids
The hyperactive season has been due to an abundance of two key ingredients for tornadoes: wind shear and instability.
The jet stream − a band of strong upper-level winds that mostly blows west to east, flowing between warm air to its south and cool air to its north − plays an important role in how and where weather systems evolve, and in wind shear.
During April and May 2024 , the jet stream often dipped southward in the western U.S. before turning back to the northeast across the Plains. That’s a pattern favorable for producing tornadoes in the central U.S.
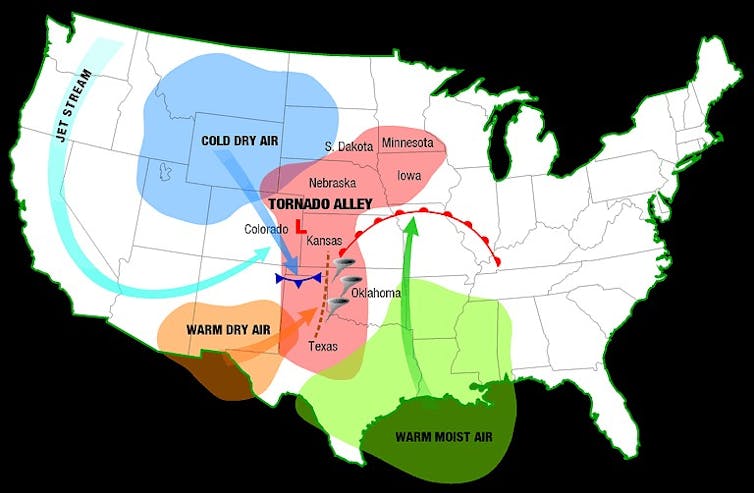
In the area east of the jet stream’s southern dip, air rises. That creates a strong low-pressure system, which causes winds near the ground to blow from a different direction than winds higher up, contributing to wind shear.
Making this year even more active, persistent record heat waves were common over Mexico and Texas, while the Rockies and far northern United States stayed cool. The sharp temperature difference created a stronger jet stream than normal, leading to strong changes in wind speed with elevation. As a result, wind shear has been on steroids.
The change in wind speed with elevation can cause air to have a rolling motion . The rapidly rising air in a thunderstorm can then tilt the rolling motion to create a spinning thunderstorm that can concentrate the spin into a tornado.
The Gulf of Mexico was also much warmer than normal , producing abundant heat and moisture that could be transported northward to fuel thunderstorms. That creates atmospheric instability , the other key ingredient for tornadoes.
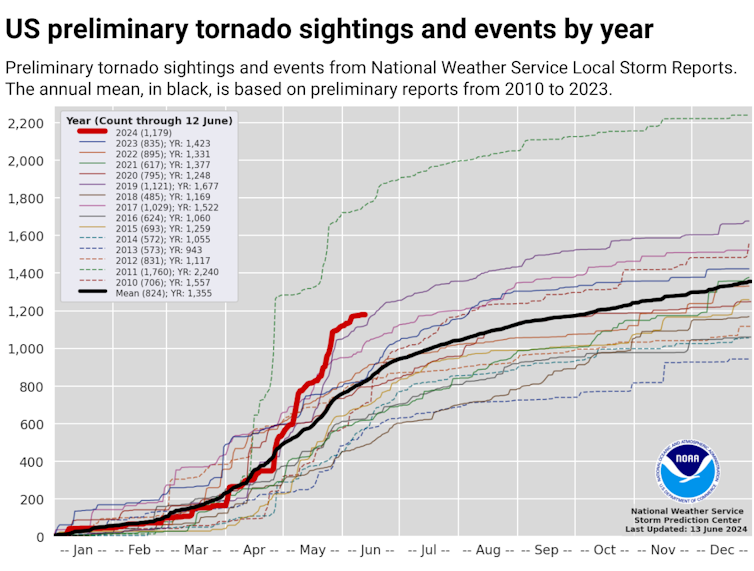
El Niño’s weakening was a warning
This perfect combination of ingredients for tornadoes wasn’t a complete surprise.
El Niño and La Niña – opposing climate patterns centered in the Pacific Ocean – can affect winds and weather around the world. A 2016 study found that when El Niño is shifting to La Niña , the number of tornadoes in the central Plains and Upper Midwest is often larger than normal.
That’s exactly what was happening in spring 2024 . The tornadoes mostly occurred in the traditional Tornado Alley, from northern Texas to South Dakota, with an extension across the Corn Belt through Iowa and as far east as Ohio, matching the findings of that study.
How is tornado activity changing?
The active spring in the Great Plains was a bit unusual, however. Studies show a long-term trend of decreasing tornado numbers in this region and an increase in tornadoes farther east , near or just east of the Mississippi River.
That shift is consistent with what climate models suggest is likely to happen throughout the remainder of the century as global temperatures rise.
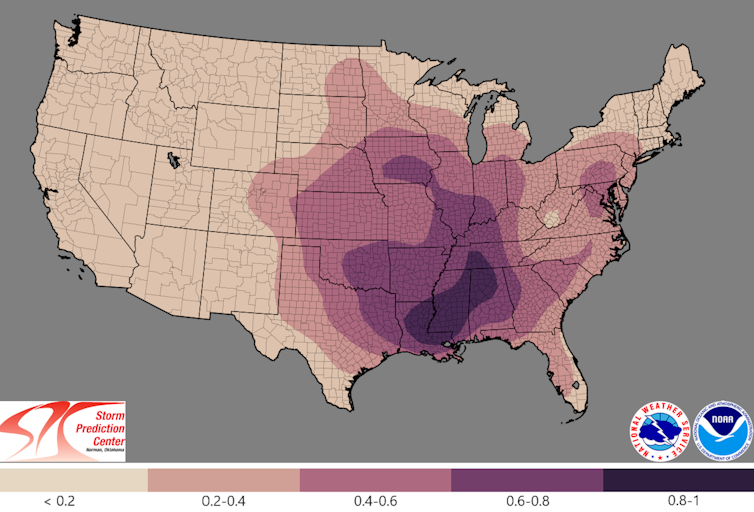
The expected decline in the number of tornadoes in the Plains is likely related to increasing heat over the high ground of the desert Southwest and Mexico. That heat flows over the Great Plains a few thousand feet above ground, creating a cap, or lid. The cap lets heat and moisture build up until it punches through to form a thunderstorm. This hot, moist air is why the central U.S. is home to the most violent tornadoes on Earth.
One theory is that, with climate change, the cap will likely be harder to break through, reducing the number of tornadoes in the Plains. At the same time, increasing heat and moisture elsewhere will fuel more tornadoes in the East.
Long-term trends and climate model predictions also suggest that more tornadoes are occurring during the cooler months , particularly in the Southeast . Tornadoes are also occurring on fewer days each year, but on the days when they do form, there is more likely to be an outbreak with several tornadoes
- Climate change
- Extreme weather
- Atmospheric science
- Thunderstorms
- El Niño Southern Oscillation
- Extreme storms

Clinical Trial Database Support Officer

PhD Scholarship

Senior Lecturer, HRM or People Analytics

Centre Director, Transformative Media Technologies

Postdoctoral Research Fellowship

- Games & Quizzes
- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions
- Ancient Middle Eastern and Greek astronomy
- Greek physics
- Islamic and medieval science
- Impact of Newtonian theory
- New discoveries
- Electricity and magnetism
- Evolution of stars and formation of chemical elements
- Solar-system astronomy and extrasolar planets
- Radioactivity and the transmutation of elements
- The nucleus
- Einstein’s 1905 trilogy
- Quantum mechanics

Is mathematics a physical science?
- Why is light important for life on Earth?
- What are Earth sciences?
- What do the Earth sciences entail?
- What are Earth science topics?

physical science
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Table Of Contents

What is physical science?
Physical science is the study of the inorganic world. That is, it does not study living things. (Those are studied in biological, or life, science.) The four main branches of physical science are astronomy , physics , chemistry , and the Earth sciences , which include meteorology and geology .
What are some of the physical sciences?
Among the physical sciences are astronomy , which studies the universe beyond Earth ; physics , which studies matter and energy and their interactions; chemistry , which studies the properties of substances and how they change; and the Earth sciences , which study Earth itself as well as its atmosphere and waters .
Is biology one of the physical sciences?
No. Biology , the study of living things, is not one of the physical sciences. The physical sciences do not study living things (though the principles and methods of the physical sciences are used in biophysics to investigate biological phenomena).
Although mathematics is used throughout the physical sciences, it is often debated whether mathematics is itself a physical science. Those who include it as a physical science point out that physical laws can be expressed in mathematical terms and that the concept of number arises in counting physical objects. Those who say mathematics is not a physical science consider numbers as abstract concepts that are helpful in describing groups of objects but do not arise from the physical objects themselves.
physical science , the systematic study of the inorganic world, as distinct from the study of the organic world, which is the province of biological science . Physical science is ordinarily thought of as consisting of four broad areas: astronomy , physics , chemistry , and the Earth sciences . Each of these is in turn divided into fields and subfields. This article discusses the historical development—with due attention to the scope, principal concerns, and methods—of the first three of these areas. The Earth sciences are discussed in a separate article.
Physics, in its modern sense, was founded in the mid-19th century as a synthesis of several older sciences—namely, those of mechanics , optics , acoustics , electricity , magnetism , heat , and the physical properties of matter . The synthesis was based in large part on the recognition that the different forces of nature are related and are, in fact, interconvertible because they are forms of energy .
The boundary between physics and chemistry is somewhat arbitrary. As it developed in the 20th century, physics is concerned with the structure and behaviour of individual atoms and their components, while chemistry deals with the properties and reactions of molecules . These latter depend on energy, especially heat, as well as on atoms; hence, there is a strong link between physics and chemistry. Chemists tend to be more interested in the specific properties of different elements and compounds , whereas physicists are concerned with general properties shared by all matter. ( See chemistry: The history of chemistry .)
Astronomy is the science of the entire universe beyond Earth ; it includes Earth’s gross physical properties, such as its mass and rotation, insofar as they interact with other bodies in the solar system . Until the 18th century, astronomers were concerned primarily with the Sun , Moon , planets , and comets . During the following centuries, however, the study of stars , galaxies , nebulas , and the interstellar medium became increasingly important. Celestial mechanics , the science of the motion of planets and other solid objects within the solar system, was the first testing ground for Newton’s laws of motion and thereby helped to establish the fundamental principles of classical (that is, pre-20th-century) physics. Astrophysics, the study of the physical properties of celestial bodies, arose during the 19th century and is closely connected with the determination of the chemical composition of those bodies. In the 20th century physics and astronomy became more intimately linked through cosmological theories, especially those based on the theory of relativity . ( See astronomy: History of astronomy .)

Heritage of antiquity and the Middle Ages
The physical sciences ultimately derive from the rationalistic materialism that emerged in classical Greece , itself an outgrowth of magical and mythical views of the world. The Greek philosophers of the 6th and 5th centuries bce abandoned the animism of the poets and explained the world in terms of ordinarily observable natural processes. These early philosophers posed the broad questions that still underlie science: How did the world order emerge from chaos ? What is the origin of multitude and variety in the world? How can motion and change be accounted for? What is the underlying relation between form and matter? Greek philosophy answered these questions in terms that provided the framework for science for approximately 2,000 years.
Why genetic testing can't always reveal the sex of a baby
Gender and sex are more complicated than X and Y chromosomes.
Gender reveal parties are best known as celebrations involving pink and blue, cake and confetti, and the occasional wildfire . Along with being social media hits, gender reveals are a testament to how society is squeezing children into one of two predetermined gender boxes before they are even born.
These parties are often based on the 18- to 20-week ultrasound , otherwise known as the anatomy scan . This is the point during fetal development when the genitals are typically observed and the word "boy" or "girl" can be secretly written on a piece of paper and placed into an envelope for the planned reveal.
Now there is a new player in the gender reveal game: genetic screening.
Advancements in genetic research have led to the development of a simple blood test called cell-free DNA prenatal screening that screens for whether a baby has extra or missing pieces of genetic information — chromosomes — as early as 10 weeks into pregnancy. Included in this test are the sex chromosomes, otherwise known as X and Y, that play a role in the development and function of the body.
This blood test is more informally called noninvasive prenatal testing, or NIPT. Many people refer to it as "the gender test." But this blood test cannot determine gender.
As genetic counselors and clinical researchers working to improve genetic services for gender-diverse and intersex people, we emphasize the significance of using precise and accurate language when discussing genetic testing. This is critical for providing affirming counseling to any patient seeking pregnancy-related genetic testing and resisting the erasure of transgender and intersex people in health care .
Distinguishing sex and sex chromosomes
Sex and gender are often used interchangeably, but they represent entirely different concepts.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Typically when people think of sex, they think of the categories female or male. Most commonly, sex is assigned by health care providers at birth based on the genitals they observe on the newborn. Sex may also be assigned based on the X and Y chromosomes found on a genetic test. Commonly, people with XX chromosomes are assigned female at birth, and people with XY chromosomes are assigned male. Since cell-free DNA, or cfDNA, prenatal screening can report on sex chromosomes months before birth, babies are receiving sex assignments much sooner than previously possible.
While cfDNA prenatal screening can offer insights into what sex chromosomes an infant may have, sex determination is much more complicated than just X’s and Y’s.
For one, sex chromosomes don’t exactly determine someone’s sex . Other chromosomes, hormone receptors, neural pathways, reproductive organs and environmental factors contribute to sex determination as well, not unlike an orchestra with its ensemble of instruments. Each cello, flute, tympani and violin plays a crucial role in the performance of the final musical score. There is no single instrument that defines the entirety of the symphony.
RELATED: Fetal testosterone may program boys' behavior
Intersex people , or those with variations in sex characteristics that deviate from societal norms of binary sex, exemplify the complexities of sex. These variations can manifest in various ways beyond X and Y chromosomes, such as differences in hormone levels, genitalia or secondary sexual characteristics.
The oversimplification of sex based on societal norms has led many to believe that there are only two discrete sexes. The binary framework of sex excludes intersex people and perpetuates their erasure and mistreatment within both health care and society at large.
For instance, many intersex individuals face unnecessary surgeries , such as nonconsensual genital procedures, to conform to binary norms, violating their bodily autonomy .
Where gender comes in
While sex typically describes someone’s anatomical characteristics, gender is an umbrella term that encompasses the way someone views and presents themselves to the world. Countless aspects influence how someone defines their own gender and how the world views their gender, including clothing, haircuts and voice tone. Similar to how Western cultures have historically confined sex to two buckets, it has also created two gender categories: man and woman.
Gender is not dependent on anatomical parts or chromosomes . People are not math equations, and having certain combinations of biological parts does not equal someone’s gender. For example, some people may be transgender , meaning their assigned sex is not congruent with their socially or self-defined gender. Nonbinary people do not identify exclusively with either of the two genders in the binary, regardless of their assigned sex.
Just like sex diversity, gender diversity is not rare. A 2022 Pew Research Center analysis found that approximately 5% of adults in the U.S. under the age of 30 are transgender or nonbinary.
These estimates will likely increase as societal awareness and acceptance of gender-diverse individuals increases. Anti-transgender legislation often oversimplifies gender as strictly binary, conflating it solely with sex assigned at birth.
Intersex and gender-diverse people show that sex and gender are both multidimensional . Gender is not solely determined by biology, and it is erroneous to define someone’s gender by their sex, much less by their sex chromosomes.

Challenging sex and gender norms
The idea that biology plays the largest role in determining who an individual is, or bioessentialism, has governed misconceptions about sex and gender for many years. This concept is used to confine people to buckets and limit their self-determination .
For instance, societal norms dictate that women should be nurturing and gentle, while men are expected to be protective and assertive. Such rigid gender roles, often enforced through the lens of biology, serve to uphold notions of evolutionary destiny and a purported natural order.
Marketing strategies for children’s toys often adhere strictly to gender roles, steering girls toward dolls and domestic play sets while steering boys toward action figures and construction sets.
Educational systems often reinforce gender norms by directing girls toward subjects such as literature and arts while steering boys toward science and mathematics. This perpetuates the notion that certain traits and interests are inherently linked to one’s sex and gender, thereby reinforcing societal norms and sustaining inequality.
Upholding binary constructs of sex and gender does not allow for individuality and gender fluidity. Categorizing people from the time their chromosomes are analyzed or the moment their genitals are observed at birth restricts their autonomy and authenticity. These simple assumptions set expectations that can be harmful.
Letting children define themselves
If you’re a parent offered cfDNA prenatal screening during pregnancy, remember that it is commenting only on one instrument in the orchestra of sex. It cannot examine all of the other factors that determine sex as a whole. And it most certainly cannot determine gender, which is an entirely different concert.
— Pregnancy causes dramatic changes in the brain, study confirms
— Caster Semenya, testosterone and the history of gender segregation in sports
— Scientists made mice with Y chromosomes female by deleting just 6 tiny molecules
In recent years, Jenna Karvunidis , the mother considered the inventor of gender reveal parties, shared her regrets for starting the trend and noted that her views on sex and gender have shifted. In a 2019 Facebook post, Karvunidis wrote, "PLOT TWIST. The world’s first gender reveal party baby is a girl who wears suits!" She had also gone on to say , "Celebrate the baby … Let’s just have a cake."
When the envelope is opened, the balloons are popped and the crafty cake is cut, consider how these practices perpetuate social confinements and a gendered destiny for your little bundle of joy. Perhaps opt simply for a celebration that leaves space for your child to one day define who they are.
This edited article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article .
Maggie Ruderman, MS, CGC (she/her) is a genetic counselor, clinical researcher, and assistant professor at Boston University Chobanian and Avedisian School of Medicine. Through presentations, research, and blog posts, she has done work focusing on improving genetic services for gender diverse and BIPOC people.
Restless legs syndrome tied to 140 'hotspots' in the genome
'Fossil viruses' embedded in the human genome linked to psychiatric disorders
If alien life exists on Europa, we may find it in hydrothermal vents
Most Popular
- 2 Argyle mine: Earth's treasure trove of pink diamonds born during a supercontinent's break up
- 3 Tasselled wobbegong: The master of disguise that can eat a shark almost as big as itself
- 4 Newly discovered asteroid larger than the Great Pyramid of Giza will zoom between Earth and the moon on Saturday
- 5 NASA offers SpaceX $843 million to destroy the International Space Station
- 2 Newly discovered asteroid larger than the Great Pyramid of Giza will zoom between Earth and the moon on Saturday
- 3 James Webb Space Telescope spies strange shapes above Jupiter's Great Red Spot
- 4 Shattered Russian satellite forces ISS astronauts to take shelter in stricken Starliner capsule
- 5 What causes you to get a 'stitch in your side'?
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Judge in Trump classified docs case grants his request for hearing on key evidence in indictment
FILE - Republican presidential candidate former President Donald Trump speaks at a campaign rally, June 22, 2024, at Temple University in Philadelphia. The federal judge presiding over Trump’s classified documents prosecution is hearing arguments Monday, June 24, on whether to bar him from public comments that prosecutors say could endanger the lives of FBI agents working on the case. Special counsel Jack Smith’s team says the restrictions are necessary in light of Trump’s false comments that the FBI agents who searched his Mar-a-Lago estate for classified documents were out to kill him and his family. (AP Photo/Chris Szagola, File)

- Copy Link copied
WASHINGTON (AP) — The federal judge presiding over the classified documents case of former President Donald Trump granted his request Thursday for a hearing on whether prosecutors had been permitted to improperly breach attorney-client privilege when they obtained crucial evidence from one of his ex-lawyers.
The order from U.S. District Judge Aileen Cannon ensures further delays in a criminal case that has already been snarled by significant postponements, resulting in the indefinite cancelation of trial date that had been set for May 20 in Fort Pierce, Florida. It means that Cannon will revisit a different judge’s order from last year that permitted prosecutors to get testimony and other evidence from a Trump attorney that wound up being repeatedly cited in the indictment of the former president.
Trump faces dozens of felony counts accusing him of illegally hoarding classified documents from his presidency at his Mar-a-Lago estate and obstructing the FBI’s efforts to recover them. He has pleaded not guilty.
Defense lawyers are ordinarily shielded from being forced to testify about their confidential conversations with their client but can be compelled to do so if prosecutors can show that their legal services were used in furtherance of a crime — a doctrine known as the crime-fraud exception.
The then-chief federal judge in the District of Columbia, Beryl Howell, agreed last year with special counsel Jack Smith’s team that the exception applied and ordered grand jury testimony from a Trump attorney, M. Evan Corcoran, who represented the former president when the FBI on Aug. 8, 2022, searched Mar-a-Lago for classified documents and seized boxes of classified records.
She also directed Corcoran to turn over audio recordings he made that documented his impressions of conversations he had had with Trump about returning the documents. Those conversations form the basis of key portions of the indictment, including one quote in which Trump proposed not cooperating with the FBI and Justice Department as they sought the return of classified documents that he took with him to Mar-a-Lago after he left the White House.
“Wouldn’t it be better if we just told them we don’t have anything here?” Corcoran quoted him as saying.
AP AUDIO: Judge in Trump classified docs case grants his request for hearing on key evidence in indictment
AP correspondent Jackie Quinn reports on a ruling that further delays Donald Trump’s classified documents case, and reaction from the attorney general.
In her order Thursday, Cannon said there was “nothing unduly prejudicial or legally erroneous about Defendant Trump’s fact-development request,” even as she sought to deflect the Smith team’s concerns that the hearing could be a “mini-trial.”
“There is a difference between a resource-wasting and delay-producing ‘mini-trial,’ on the one hand, and an evidentiary hearing geared to adjudicating the contested factual and legal issues on a given pre-trial motion to suppress, on the other,” she said.
Cannon said it was “the obligation of this Court to make factual findings afresh on the crime-fraud issue.”
The judge also denied a request for a hearing on a separate Trump team claim that the Justice Department had submitted false or misleading information in an application to search Mar-a-Lago. They argued, for instance, that the application should have noted that a senior FBI official proposed seeking the consent of Trump’s lawyers for a search rather than obtaining a court-authorized search warrant.
But Cannon sided with Smith team in finding that neither that nor any other of the alleged omissions raised by the defense had any bearing on whether or not prosecutors had sufficient probable cause to search the property. She had signaled that position during a hearing earlier this week.
“Even accepting those statements by the high-level FBI official, the Motion offers an insufficient basis to believe that inclusion in the affidavit of that official’s perspective (or of the dissenting views of other FBI agents as referenced generally in his testimony) would have altered the evidentiary calculus in support of probable cause for the alleged offenses,” Cannon wrote.

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
How Can Biden Win the Debate? Trump? Five Tips for Each Candidate.

By New York Times Opinion
Joe Biden and Donald Trump will face off Thursday night for the first general-election debate of the 2024 presidential election cycle. Below, two political experts weigh in on what each candidate needs to do to win.
The Five Things Biden Needs to Do
By Chris Whipple
Chris Whipple is the author of “The Fight of His Life: Inside Joe Biden’s White House” and “The Gatekeepers: How the White House Chiefs of Staff Define Every Presidency.”
1. Be energetic and engaged. Mr. Trump and his MAGA allies have tried to portray the president as a doddering geriatric who can’t complete a sentence. Simply appearing engaged, alert and coherent will be a victory for Mr. Biden. Mr. Biden would also do well to remember this fact: Incumbent presidents almost always lose the first debate. That’s true of even superlative political talents like Ronald Reagan and Barack Obama. Among the reasons for this are hubris and lack of practice; incumbent presidents are used to being saluted, not challenged.
2. Drive the contrast with Mr. Trump. Mr. Biden must recast the race from a referendum on his presidency to a stark choice between himself and Mr. Trump. “I used to say to President Obama, ‘If you’re on defense about your record, we’re losing,’” says Jim Messina, who ran Mr. Obama’s winning 2012 campaign. Mr. Biden should remind voters that his predecessor lost more jobs than any president since Herbert Hoover and cut taxes for the ultrawealthy and corporations. He should emphasize: “Donald Trump said he was going to pass an infrastructure bill. He couldn’t. I did. Donald Trump said he was going to bring back manufacturing jobs. He couldn’t. I did . ”
3. Outline a second-term agenda. Voters don’t reward presidents for what they’ve done; they want to know what they’ll do in the future. Mr. Biden should pick up on the American comeback narrative from his State of the Union speech and detail his priorities for a second term: codifying Roe v. Wade; cutting taxes for the middle class; extending student loans; combating climate change; and perhaps above all, making goods and housing affordable for working families. Admit that prices are too high and explain how he’ll bring them down. Mr. Biden can frame the election as a choice between a president who cares about the common good and a felon who cares only about himself and retribution.
4. Stress the threat to reproductive rights and democracy. These have been potent issues for Democrats in recent elections across the country. In November, they will be potent again. Mr. Biden should repeat Mr. Trump’s own words, like the former president’s boast, “ I was able to kill Roe v. Wade ,” and his remark that there should be “some form of punishment” for women who have abortions. If Mr. Trump asserts that he’s leaving abortion to the states, Mr. Biden can reply: “When he says ‘states’ rights’, he really means taking away a woman’s right. It’s code for outlawing abortion.”
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
science, any system of knowledge that is concerned with the physical world and its phenomena and that entails unbiased observations and systematic experimentation. In general, a science involves a pursuit of knowledge covering general truths or the operations of fundamental laws. Science can be divided into different branches based on the ...
Science is a way of discovering what's in the universe and how those things work today, how they worked in the past, and how they are likely to work in the future. Scientists are motivated by the thrill of seeing or figuring out something that no one has before. Science is useful. The knowledge generated by science is powerful and reliable.
Science is a rigorous, systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the world. Modern science is typically divided into three major branches: the natural sciences (e.g., physics, chemistry, and biology), which study the physical world; the social sciences (e.g., economics, psychology, and sociology), which study individuals ...
Science as a collective institution aims to produce more and more accurate natural explanations of how the natural world works, what its components are, and how the world got to be the way it is now. Classically, science's main goal has been building knowledge and understanding, regardless of its potential applications — for example, investigating the chemical reactions that an organic ...
3. Reflections from a Nobel winner: Scientists need time to make discoveries by Donna Strickland. "We must give scientists the opportunity through funding and time to pursue curiosity-based, long-term, basic-science research. Work that does not have direct ramifications for industry or our economy is also worthy.
Science defined simply as knowledge of natural processes is universal among humankind, and it has existed since the dawn of human existence. The mere recognition of regularities does not exhaust the full meaning of science, however. In the first place, regularities may be simply constructs of the human mind.
Science is the backbone of our society. Science gave us so much in our present time. Due to this, the teacher in our schools teaches Science from an early age. Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas. Science as a Subject. In class 1 only a student has Science as a subject. This only tells us about the importance of Science.
Most science essays are written in Times New Roman font with 12-point size and double spacing. The margins should be 1 inch on all sides, and the text should be justified. In addition, you must cite your sources properly using a recognized citation style such as APA, Chicago, or Harvard. Make sure to follow the guidelines closely so that your ...
Sample Essay On Science in 100 words. Science, the bedrock of human progress, unveils the mysteries of our universe through empirical investigation and reason. Its profound impact permeates every facet of modern life. In medicine, it saves countless lives with breakthroughs in treatments and vaccines. Technology, a child of science, empowers ...
Science is a body of knowledge that belongs to humanity as a whole. Its emergence and success over the past 400 years is a miracle. Science aims at, and thus attains at least approximately, objective and universal knowledge and it is thereby limited to those questions that can have universal answers.
The process of science is a way of building knowledge about the universe — constructing new ideas that illuminate the world around us. Those ideas are inherently tentative, but as they cycle through the process of science again and again and are tested and retested in different ways, we become increasingly confident in them. Furthermore, through this same iterative process, ideas are ...
Science means something that happens in a laboratory: the very word calls up a picture of graphs, test-tubes, balances, Bunsen burners, microscopes. A biologist, and astronomer, perhaps a psychologist or a mathematician is described as a 'man of science': no one would think of applying this term to a statesman, a poet, a journalist or even ...
This essay, "Science Definition & Meaning" is published exclusively on IvyPanda's free essay examples database. You can use it for research and reference purposes to write your own paper. However, you must cite it accordingly. Donate a paper. Removal Request.
Essay # 1. Meaning and Definitions of Science: Meaning of Science: The English word Science is derived from a Latin Verb 'Scire', which means 'to know' and Latin Noun 'Scientia' which means 'knowledge'. Meaning of Science is based on German word ' Wissenchaft', which means systematic, organized knowledge. Thus, Science is a ...
These science essays can be used for essay writing, debate, and other related activities at your institution or school. Essay On Science (200 words) Science entails a thorough examination of the behavior of the physical and natural world. Research, experimentation, and observation are used in the study. The scientific disciplines are diverse.
Examples and Observations "Because science writing is intended to be entertaining enough to capture the continued interest of potential readers, its style is much less somber than the usual scientific writing [i.e., definition No. 2, above]. The use of slang, puns, and other word plays on the English language are accepted and even encouraged. . . . ...
Scientific writing is a technical form of writing that is designed to communicate scientific information to other scientists. Depending on the specific scientific genre—a journal article, a scientific poster, or a research proposal, for example—some aspects of the writing may change, such as its purpose, audience, or organization. Many ...
Science is building something that is useful, practical and realistic. As explained above, science is all about collecting information to gain knowledge. Information collected is used to replace old ideas with new ones. Through new ideas, I can discover new things. As a scientist I shall be able to know the unknown, discover what has not yet ...
philosophy of science, the study, from a philosophical perspective, of the elements of scientific inquiry. This article discusses metaphysical, epistemological, and ethical issues related to the practice and goals of modern science. For treatment of philosophical issues raised by the problems and concepts of specific sciences, see biology ...
Essay on Importance of Science in Our Life - Science has unquestionably done a great service to humanity. Man has led to many discoveries in various parts of the world. The study of animals, chemicals, the force, the earth, and plants, among other things, are within various branches of science such as physics, chemistry, and biology.
Semantics is the study of meaning. But what exactly is "meaning"? What is the target of semantic theory? There is a very wide range of views on the issue, ranging from the claim that semantics studies something psychological (e.g. a semantic faculty or brain processing), to the claim that semantics studies something about conventions of the linguistic community, to the claim that semantics ...
Science will always look for explanations for what goes on in the natural world and test those explanations against evidence from the natural world — but exactly how this gets done may evolve. The scientific enterprise is not static. Science is deeply interwoven with society, and as it has changed, so too has science.
Stav Dimitropoulos's science writing has appeared online or in print for the BBC, Discover, Scientific American, Nature, Science, Runner's World, The Daily Beast and others.
Earth science: The Artemis program will provide a unique opportunity to study the Moon and its environment. This will lead to new insights into the Earth's history, geology, and climate. Materials science: The extreme space environment will require new materials that are lightweight, durable, and radiation resistant. This will have applications ...
William Gallus receives funding from the National Science Foundation, Department of Energy, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Spring 2024 was unnerving for people across ...
physical science, the systematic study of the inorganic world, as distinct from the study of the organic world, which is the province of biological science. Physical science is ordinarily thought of as consisting of four broad areas: astronomy, physics, chemistry, and the Earth sciences. Each of these is in turn divided into fields and ...
Mr. Hari is a British journalist and the author of "Magic Pill: The Extraordinary Benefits — and Disturbing Risks — of the New Weight Loss Drugs."
Gender and sex are more complicated than X and Y chromosomes. Gender reveal parties are best known as celebrations involving pink and blue, cake and confetti, and the occasional wildfire. Along ...
WASHINGTON (AP) — The federal judge presiding over the classified documents case of former President Donald Trump granted his request Thursday for a hearing on whether prosecutors had been permitted to improperly breach attorney-client privilege when they obtained crucial evidence from one of his ex-lawyers.. The order from U.S. District Judge Aileen Cannon ensures further delays in a ...
3. Outline a second-term agenda. Voters don't reward presidents for what they've done; they want to know what they'll do in the future. Mr.