How to find Research Papers: A Cheat Sheet for Graduate Students
- July 23, 2022
- PRODUCTIVITY

“I will read this paper later.” I thought to myself before adding another paper to my overflowing internet browser.
Of course, I didn’t read it later.
Since my workflow was unorganized, I missed out on reading many important papers.
This was a crucial period in my undergraduate career. I had been working with a company for my final year project and knew success would require a solid intellectual foundation. For many hours, I read papers, determined to master the literature in my field.
“How to find research papers quickly?” has been a never-ending question for me.

However, I was unable to succeed despite my best intentions, largely due to inefficiency. In addition, I did not have a system in place for keeping track of new papers being published daily in my topic area or checking if I had missed key studies.
Nothing is worse than forgetting where you saved an important research paper. If I couldn’t find that specific paper, I couldn’t do anything else, and sometimes a day would pass before I found it.
As I was about to begin my PhD, I convinced myself that I should be more organized.
This is the first post of the four-part blog series: The Bulletproof Literature Management System . Follow the links below to read the other posts in the series:
- How to How to find Research Papers (You are here)
- How to Manage Research Papers
- How to Read Research Papers
- How to Organize Research Papers
My workflow has evolved through many iterations, and I have finally found a system that suits my needs after lots of trial and error.
These tips will help you how to find research papers quickly and more efficiently.

Get recommendations from your supervisor
You may have already received a folder of information from your supervisor regarding your thesis topic. Your supervisor should have already been working on the proposal before you were hired for a funded project.
My supervisor, for example, has a folder named “Literature” for each project folder that contains all the important papers one might need to complete that project.
Therefore, asking your supervisor is one of the most straightforward ways to find research papers.
Even though your supervisor has not put up a folder like that, you can still ask them for recommendations, and they can point out a couple of pertinent articles. From there, you can find the references in the papers they recommended.
Use feed aggregators
Feed aggregators, such as Feedly , Inoreader , and NewsBlur , help me organize my feeds. In the morning, I dedicate five minutes to scanning my feed. For most papers, I just glance at the title and scroll past. Whenever I come across something interesting, I add it to my ‘Read Later’ folder.
Instead of storing papers in an unsecured location, my papers are more secure. As a result, it is much easier for me to look at that folder later on.
Use literature mapping tools
ResearchRabbit , Inciteful , Litmaps , and Connected Papers are literature-mapping tools you can use to dig deeper into a topic. It lets you see which papers are the most groundbreaking in a given field based on their citation networks.
This might not be very helpful if you’re doing research in a relatively new area. Finding relevant research papers in such cases may be more challenging.
This is why checking research databases would be a better option.
Use standard research databases
Scopus has strong searching capabilities and publishes metrics that can measure the relative importance of papers in their fields. However, it may take up to 2 years before an article is included in Scopus.
It has more features for sorting and filtering, so you might not feel overwhelmed when searching.
Therefore, if you are just starting your research, SCOPUS might be an excellent option for finding research papers.
ResearchGate
In addition to traditional searching for publications, ResearchGate offers the following features:
- Follow researchers in your field, so you can keep up with their work.
- Keep up-to-date with the research projects of other researchers by following their research projects, and
- Comment on publications, ask questions, and send direct messages to interact with others.
As most of the comments on ResearchGate are coming from experts in their respective fields, the QnA section may be a great resource for finding the right paper for your research.
An RSS(Really Simple Syndication) feed, as the name implies, is a straightforward solution. By subscribing to RSS, users can access content from specific websites.
You can find RSS feeds for nearly every major journal and preprint server on their home pages – just look for the orange icon. As new articles are added to PubMed or Google Scholar, you can even subscribe to specific keywords.
Use academic textbooks the right way
If you are new to a particular research area, it would be best to start by reading textbooks to understand the topic better.
Despite the lack of depth and detail in a textbook, it can provide you with the basic concepts you need to read further. Furthermore, textbooks often include extensive lists of references as well as this information to get you started . Download the relevant articles from these references.
You might feel overwhelmed if you try to read an academic textbook from beginning to end. For this reason, read only the sections which contain the information you need for your project.
Review papers are game changers
A review paper on your topic is a great starting point for finding good references and getting a broad overview of your research topic.
After reading the review paper, you can read the references cited therein.
You are reading a much more comprehensive summary of the topic than you would have found reading ten individual research papers on the same topic if you found a highly relevant review paper for your research.
Look for technical reports and theses
Make sure you don’t limit yourself to research papers when looking for references. A technical report or code document on your topic may contain important citations (as well as practical information).
There is nothing that compares to a PhD thesis when it comes to the depth and extent of analytical work. See which references students have cited in their theses on your topic.
If you find a relevant thesis for your literature review, you will have extensive information about the research topic in one place, saving you a ton of time.
Google Scholar
The best for the last!
Due to its versatility and efficiency in finding academic papers, I decided to include Google Scholar separately from the database section.
I enjoy using Google Scholar among all the fancy databases available. One drawback to Google Scholar is that it lacks the ability to search for keywords and filter results.
Therefore, if you are just starting your research and aren’t sure what “keywords” to search for, Google Scholar might not be your first choice.
The advantage of Google Scholar is that if you are already familiar with your field of study and already know what you are doing, you will be able to find relevant research papers more quickly.
Use Google Scholar’s search function to locate relevant articles. Furthermore, you can subscribe to updates from colleagues in your field to access the latest references. The publisher of a journal paper may also report an article faster to Google Scholar than another database, which can take up to two years to include an article.
Images courtesy: Internet marketing vector created by jcomp – www.freepik.com
Aruna Kumarasiri
Founder at Proactive Grad, Materials Engineer, Researcher, and turned author. In 2019, he started his professional carrier as a materials engineer with the continuation of his research studies. His exposure to both academic and industrial worlds has provided many opportunities for him to give back to young professionals.
Did You Enjoy This?
Then consider getting the ProactiveGrad newsletter. It's a collection of useful ideas, fresh links, and high-spirited shenanigans delivered to your inbox every two weeks.
I accept the Privacy Policy
Hand-picked related articles

Why do graduate students struggle to establish a productive morning routine? And how to handle it?
- March 17, 2024

How to stick to a schedule as a graduate student?
- October 10, 2023

The best note-taking apps for graduate students: How to choose the right note-taking app
- September 20, 2022
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Post Comment
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
How to Find Sources | Scholarly Articles, Books, Etc.
Published on June 13, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on May 31, 2023.
It’s important to know how to find relevant sources when writing a research paper , literature review , or systematic review .
The types of sources you need will depend on the stage you are at in the research process , but all sources that you use should be credible , up to date, and relevant to your research topic.
There are three main places to look for sources to use in your research:
Research databases
- Your institution’s library
- Other online resources
Table of contents
Library resources, other online sources, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about finding sources.
You can search for scholarly sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar . These provide a range of search functions that can help you to find the most relevant sources.
If you are searching for a specific article or book, include the title or the author’s name. Alternatively, if you’re just looking for sources related to your research problem , you can search using keywords. In this case, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the scope of your project and of the most relevant keywords.
Databases can be general (interdisciplinary) or subject-specific.
- You can use subject-specific databases to ensure that the results are relevant to your field.
- When using a general database or search engine, you can still filter results by selecting specific subjects or disciplines.
Example: JSTOR discipline search filter

Check the table below to find a database that’s relevant to your research.
Google Scholar
To get started, you might also try Google Scholar , an academic search engine that can help you find relevant books and articles. Its “Cited by” function lets you see the number of times a source has been cited. This can tell you something about a source’s credibility and importance to the field.
Example: Google Scholar “Cited by” function
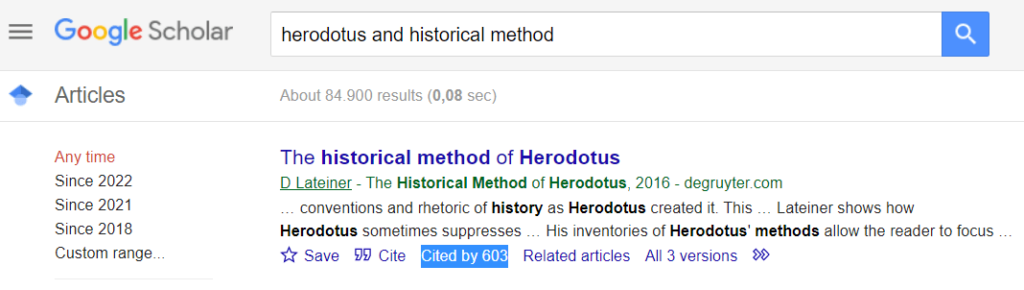
Boolean operators
Boolean operators can also help to narrow or expand your search.
Boolean operators are words and symbols like AND , OR , and NOT that you can use to include or exclude keywords to refine your results. For example, a search for “Nietzsche NOT nihilism” will provide results that include the word “Nietzsche” but exclude results that contain the word “nihilism.”
Many databases and search engines have an advanced search function that allows you to refine results in a similar way without typing the Boolean operators manually.
Example: Project Muse advanced search

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
You can find helpful print sources in your institution’s library. These include:
- Journal articles
- Encyclopedias
- Newspapers and magazines
Make sure that the sources you consult are appropriate to your research.
You can find these sources using your institution’s library database. This will allow you to explore the library’s catalog and to search relevant keywords. You can refine your results using Boolean operators .
Once you have found a relevant print source in the library:
- Consider what books are beside it. This can be a great way to find related sources, especially when you’ve found a secondary or tertiary source instead of a primary source .
- Consult the index and bibliography to find the bibliographic information of other relevant sources.
You can consult popular online sources to learn more about your topic. These include:
- Crowdsourced encyclopedias like Wikipedia
You can find these sources using search engines. To refine your search, use Boolean operators in combination with relevant keywords.
However, exercise caution when using online sources. Consider what kinds of sources are appropriate for your research and make sure the sites are credible .
Look for sites with trusted domain extensions:
- URLs that end with .edu are educational resources.
- URLs that end with .gov are government-related resources.
- DOIs often indicate that an article is published in a peer-reviewed , scientific article.
Other sites can still be used, but you should evaluate them carefully and consider alternatives.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
You can find sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar . Use Boolean operators or advanced search functions to narrow or expand your search.
For print sources, you can use your institution’s library database. This will allow you to explore the library’s catalog and to search relevant keywords.
It is important to find credible sources and use those that you can be sure are sufficiently scholarly .
- Consult your institute’s library to find out what books, journals, research databases, and other types of sources they provide access to.
- Look for books published by respected academic publishing houses and university presses, as these are typically considered trustworthy sources.
- Look for journals that use a peer review process. This means that experts in the field assess the quality and credibility of an article before it is published.
When searching for sources in databases, think of specific keywords that are relevant to your topic , and consider variations on them or synonyms that might be relevant.
Once you have a clear idea of your research parameters and key terms, choose a database that is relevant to your research (e.g., Medline, JSTOR, Project MUSE).
Find out if the database has a “subject search” option. This can help to refine your search. Use Boolean operators to combine your keywords, exclude specific search terms, and search exact phrases to find the most relevant sources.
There are many types of sources commonly used in research. These include:
You’ll likely use a variety of these sources throughout the research process , and the kinds of sources you use will depend on your research topic and goals.
Scholarly sources are written by experts in their field and are typically subjected to peer review . They are intended for a scholarly audience, include a full bibliography, and use scholarly or technical language. For these reasons, they are typically considered credible sources .
Popular sources like magazines and news articles are typically written by journalists. These types of sources usually don’t include a bibliography and are written for a popular, rather than academic, audience. They are not always reliable and may be written from a biased or uninformed perspective, but they can still be cited in some contexts.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, May 31). How to Find Sources | Scholarly Articles, Books, Etc.. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/finding-sources/
Is this article helpful?


Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, types of sources explained | examples & tips, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, boolean operators | quick guide, examples & tips, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Eight Ways (and More) To Find and Access Research Papers
This blog is part of our Research Smarter series. You’ll discover the various search engines, databases and data repositories to help you along the way. Click on any of the following links for in an in-depth look at how to find relevant research papers, journals , and authors for your next project using the Web of Science™. You can also check out our ultimate guides here , which include tips to speed up the writing process.
If you’re in the early stages of your research career, you’re likely struggling to learn all you can about your chosen field and evaluate your options. You also need an easy and convenient way to find the right research papers upon which to build your own work and keep you on the proper path toward your goals.
Fortunately, most institutions have access to thousands of journals, so your first step should be to be to check with library staff and find out what is available via your institutional subscriptions.
For those who may be unfamiliar with other means of access, this blog post – the first in a series devoted to helping you “research smarter” – will provide a sampling of established data sources for scientific research. These include search engines, databases, and data repositories.
Search Engines and Databases
You may have already discovered that the process of searching for research papers offers many choices and scenarios. Some search engines, for example, can be accessed free of charge. Others require a subscription. The latter group generally includes services that index the contents of thousands of published journals, allowing for detailed searches on data fields such as author name, institution, title or keyword, and even funding sources. Because many journals operate on a subscription model too, the process of obtaining full-text versions of papers can be complicated.
On the other hand, a growing number of publishers follow the practice of Open Access (OA) , making their journal content freely available. Similarly, some authors publish their results in the form of preprints, posting them to preprint servers for immediate and free access. These repositories, like indexing services, differ in that some concentrate in a given discipline or broad subject area, while others cover the full range of research.
Search Engines
Following is a brief selection of reputable search engines by which to locate articles relevant to your research.
Google Scholar is a free search engine that provides access to research in multiple disciplines. The sources include academic publishers, universities, online repositories, books, and even judicial opinions from court cases. Based on its indexing, Google Scholar provides citation counts to allow authors and others to track the impact of their work.
The Directory of Open Access Journals ( DOAJ ) allows users to search and retrieve the article contents of nearly 10,000 OA journals in science, technology, medicine, social sciences, and humanities. All journals must adhere to quality-control standards, including peer review.
PubMed , maintained by the US National Library of Medicine, is a free search engine covering the biomedical and life sciences. Its coverage derives primarily from the MEDLINE database, covering materials as far back as 1951.
JSTOR affords access to more than 12 million journal articles in upwards of 75 disciplines, providing full-text searches of more than 2,000 journals, and access to more than 5,000 OA books.
Selected Databases
The following selection samples a range of resources, including databases which, as discussed above, index the contents of journals either in a given specialty area or the full spectrum of research. Others listed below offer consolidated coverage of multiple databases. Your institution is likely subscribed to a range of research databases, speak to your librarian to see which databases you have access to, and how to go about your search.
Web of Science includes The Web of Science Core Collection, which covers more than 20,000 carefully selected journals, along with books, conference proceedings, and other sources. The indexing also captures citation data, permitting users to follow the thread of an idea or development over time, as well as to track a wide range of research-performance metrics. The Web of Science also features EndNote™ Click , a free browser plugin that offers one-click access to the best available legal and legitimate full-text versions of papers. See here for our ultimate guide to finding relevant research papers on the Web of Science .
Science.gov covers the vast territory of United States federal science, including more than 60 databases and 2,200-plus websites. The many allied agencies whose research is reflected include NASA, the US Department of Agriculture, and the US Environmental Protection Agency.
CiteSeerx is devoted primarily to information and computer science. The database includes a feature called Autonomous Citation Indexing, designed to extract citations and create a citation index for literature searching and evaluation.
Preprint and Data Repositories
An early form of OA literature involved authors, as noted above, making electronic, preprint versions of their papers freely available. This practice has expanded widely today. You can find archives devoted to a single main specialty area, as well as general repositories connected with universities and other institutions.
The specialty archive is perhaps best exemplified by arXiv (conveniently pronounced “archive,” and one of the earliest examples of a preprint repository). Begun in 1991 as a physics repository, ArXiv has expanded to embrace mathematics, astronomy, statistics, economics, and other disciplines. The success of ArXiv spurred the development of, for example, bioArXiv devoted to an array of topics within biology, and for chemistry, ChemRxiv .
Meanwhile, thousands of institutional repositories hold a variety of useful materials. In addition to research papers, these archives store raw datasets, graphics, notes, and other by-products of investigation. Currently, the Registry of Open Access Repositories lists more than 4,700 entries.
Reach Out Yourself?
If the resources above don’t happen to result in a free and full-text copy of the research you seek, you can also try reaching out to the authors yourself.
To find who authored a paper, you can search indexing platforms like the Web of Science , or research profiling systems like Publons™ , or ResearchGate , then look to reach out to the authors directly.
So, although the sheer volume of research can pose a challenge to identifying and securing needed papers, plenty of options are available.
Related posts
Unlocking u.k. research excellence: key insights from the research professional news live summit.

For better insights, assess research performance at the department level

Getting the Full Picture: Institutional unification in the Web of Science

Reference management. Clean and simple.
The top list of academic search engines
1. Google Scholar
4. science.gov, 5. semantic scholar, 6. baidu scholar, get the most out of academic search engines, frequently asked questions about academic search engines, related articles.
Academic search engines have become the number one resource to turn to in order to find research papers and other scholarly sources. While classic academic databases like Web of Science and Scopus are locked behind paywalls, Google Scholar and others can be accessed free of charge. In order to help you get your research done fast, we have compiled the top list of free academic search engines.
Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles
- Abstracts: only a snippet of the abstract is available
- Related articles: ✔
- References: ✔
- Cited by: ✔
- Links to full text: ✔
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, Vancouver, RIS, BibTeX
BASE is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany. That is also where its name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles (contains duplicates)
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✘
- References: ✘
- Cited by: ✘
- Export formats: RIS, BibTeX

CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open-access research papers. For each search result, a link to the full-text PDF or full-text web page is provided.
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles
- Links to full text: ✔ (all articles in CORE are open access)
- Export formats: BibTeX
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need anymore to query all those resources separately!
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles and reports
- Links to full text: ✔ (available for some databases)
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX (available for some databases)
Semantic Scholar is the new kid on the block. Its mission is to provide more relevant and impactful search results using AI-powered algorithms that find hidden connections and links between research topics.
- Coverage: approx. 40 million articles
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, BibTeX

Although Baidu Scholar's interface is in Chinese, its index contains research papers in English as well as Chinese.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 100 million articles
- Abstracts: only snippets of the abstract are available
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX

RefSeek searches more than one billion documents from academic and organizational websites. Its clean interface makes it especially easy to use for students and new researchers.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 1 billion documents
- Abstracts: only snippets of the article are available
- Export formats: not available
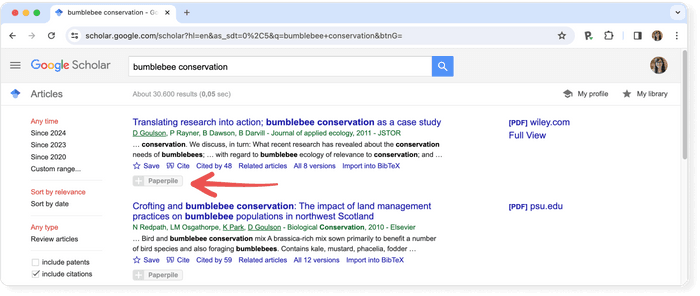
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to save, organize, and cite your references. Paperpile integrates with Google Scholar and many popular databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons:
Google Scholar is an academic search engine, and it is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only let's you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free, but also often provides links to full text PDF file.
Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature developed at the Allen Institute for AI. Sematic Scholar was publicly released in 2015 and uses advances in natural language processing to provide summaries for scholarly papers.
BASE , as its name suggest is an academic search engine. It is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany and that's where it name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open access research papers. For each search result a link to the full text PDF or full text web page is provided.
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need any more to query all those resources separately!
Literature Searching
In this guide.
- Introduction
- Steps for searching the literature in PubMed
- Step 1 - Formulate a search question
- Step 2- Identify primary concepts and gather synonyms
- Step 3 - Locate subject headings (MeSH)
- Step 4 - Combine concepts using Boolean operators
- Step 5 - Refine search terms and search in PubMed
- Step 6 - Apply limits

Steps for Searching the Literature
Searching is an iterative process and often requires re-evaluation and testing by adding or changing keywords and the ways they relate to each other. To guide your search development, you can follow the search steps below. For more information on each step, navigate to its matching tab on the right menu.
1. Formulate a clear, well-defined, answerable search question
Generally, the basic literature search process begins with formulating a clear, well-defined research question. Asking the right research question is essential to creating an effective search. Your research question(s) must be well-defined and answerable. If the question is too broad, your search will yield more information than you can possibly look through.
2. Identify primary concepts and gather synonyms
Your research question will also help identify the primary search concepts. This will allow you to think about how you want the concepts to relate to each other. Since different authors use different terminology to refer to the same concept, you will need to gather synonyms and all the ways authors might express them. However, it is important to balance the terms so that the synonyms do not go beyond the scope of how you've defined them.
3. Locate subject headings (MeSH)
Subject databases like PubMed use 'controlled vocabularies' made up of subject headings that are preassigned to indexed articles that share a similar topic. These subject headings are organized hierarchically within a family tree of broader and narrower concepts. In PubMed and MEDLINE, the subject headings are called Medical Subject Headings (MeSH). By including MeSH terms in your search, you will not have to think about word variations, word endings, plural or singular forms, or synonyms. Some topics or concepts may even have more than one appropriate MeSH term. There are also times when a topic or concept may not have a MeSH term.
4. Combine concepts using Boolean operators AND/OR
Once you have identified your search concepts, synonyms, and MeSH terms, you'll need to put them together using nesting and Boolean operators (e.g. AND, OR, NOT). Nesting uses parentheses to put search terms into groups. Boolean operators are used to combine similar and different concepts into one query.
5. Refine search terms and search in PubMed
There are various database search tactics you can use, such as field tags to limit the search to certain fields, quotation marks for phrase searching, and proximity operators to search a number of spaces between terms to refine your search terms. The constructed search string is ready to be pasted into PubMed.
6. Apply limits (optional)
If you're getting too many results, you can further refine your search results by using limits on the left box of the results page. Limits allow you to narrow your search by a number of facets such as year, journal name, article type, language, age, etc.
Depending on the nature of the literature review, the complexity and comprehensiveness of the search strategies and the choice of databases can be different. Please contact the Lane Librarians if you have any questions.
The type of information you gather is influenced by the type of information source or database you select to search. Bibliographic databases contain references to published literature, such as journal articles, conference abstracts, books, reports, government and legal publications, and patents. Literature reviews typically synthesis indexed, peer-reviewed articles (i.e. works that generally represent the latest original research and have undergone rigorous expert screening before publication), and gray literature (i.e. materials not formally published by commercial publishers or peer-reviewed journals). PubMed offers a breadth of health sciences literature and is a good starting point to locate journal articles.
What is PubMed?
PubMed is a free search engine accessing primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. Available to the public online since 1996, PubMed was developed and is maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) , at the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM) , located at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) .
MEDLINE is the National Library of Medicine’s (NLM) premier bibliographic database that contains more than 27 million references to journal articles from more than 5,200 worldwide journals in life sciences with a concentration on biomedicine. The Literature Selection Technica Review Committee (LSTRC) reviews and selects journals for MEDLINE based on the research quality and impact of the journals. A distinctive feature of MEDLINE is that the records are indexed with NLM Medical Subject Headings (MeSH).
PubMed also contains citations for PubMed Central (PMC) articles. PMC is a full-text archive that includes articles from journals reviewed and selected by NLM for archiving (current and historical), as well as individual articles collected for archiving in compliance with funder policies. PubMed allows users to search keywords in the bibliographic data, but not the full text of the PMC articles.

How to Access PubMed?
To access PubMed, go to the Lane Library homepage and click PubMed in "Top Resources" on the left. This PubMed link is coded with Find Fulltext @ Lane Library Stanford that links you to Lane's full-text articles online.

- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: Step 1 - Formulate a search question >>
- Last Updated: Jan 9, 2024 10:30 AM
- URL: https://laneguides.stanford.edu/LitSearch
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER COLUMN
- 07 July 2022
How to find, read and organize papers
- Maya Gosztyla 0
Maya Gosztyla is a PhD student in biomedical sciences at the University of California, San Diego.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
“I’ll read that later,” I told myself as I added yet another paper to my 100+ open browser tabs.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-022-01878-7
This is an article from the Nature Careers Community, a place for Nature readers to share their professional experiences and advice. Guest posts are encouraged .
Competing Interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Related Articles

- Research management

Africa’s postdoc workforce is on the rise — but at what cost?
Career Feature 02 APR 24

Research assessments are still not fit for purpose — here’s how to change things
World View 02 APR 24

How scientists are making the most of Reddit
Career Feature 01 APR 24
Adopt universal standards for study adaptation to boost health, education and social-science research
Correspondence 02 APR 24
How can we make PhD training fit for the modern world? Broaden its philosophical foundations
Allow researchers with caring responsibilities ‘promotion pauses’ to make research more equitable
Postdoctoral Associate- Cell Biology
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Head of ClinicalTrials.gov
National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Library of Medicine (NLM) National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Information Engineering...
Washington D.C. (US)
National Library of Medicine, National Center for Biotechnology Information
POSTDOCTORAL FELLOWSHIP IN SYSTEMS BIOLOGY: PRECISION VACCINE PROGRAM (PVP) - BOSTON CHILDREN'
The Data Management and Analysis Core (DMAC) within the Precision Vaccine Program (PVP) at Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School (H...
Boston, Massachusetts
Boston Children's Hospital - Department of Pediatrics
2024 Recruitment notice Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology: Shenzhen, China
The wide-ranging expertise drawing from technical, engineering or science professions...
Shenzhen,China
Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology
Global Talent Recruitment (Scientist Positions)
Global Talent Gathering for Innovation, Changping Laboratory Recruiting Overseas High-Level Talents.
Beijing, China
Changping Laboratory
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Google Scholar includes journal and conference papers, theses and dissertations, academic books, pre-prints, abstracts, technical reports and other scholarly literature from all broad areas of research. You'll find works from a wide variety of academic publishers, professional societies and university repositories, as well as scholarly articles ...
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
ResearchRabbit, Inciteful, Litmaps, and Connected Papers are literature-mapping tools you can use to dig deeper into a topic. It lets you see which papers are the most groundbreaking in a given field based on their citation networks. This might not be very helpful if you’re doing research in a relatively new area.
Research databases. You can search for scholarly sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar. These provide a range of search functions that can help you to find the most relevant sources. If you are searching for a specific article or book, include the title or the author’s name. Alternatively, if you’re just ...
To find who authored a paper, you can search indexing platforms like the Web of Science, or research profiling systems like Publons™, or ResearchGate, then look to reach out to the authors directly. So, although the sheer volume of research can pose a challenge to identifying and securing needed papers, plenty of options are available.
Find the research you need | With 160+ million publications, 1+ million questions, and 25+ million researchers, this is where everyone can access science
Get 30 days free. 1. Google Scholar. Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
To guide your search development, you can follow the search steps below. For more information on each step, navigate to its matching tab on the right menu. 1. Formulate a clear, well-defined, answerable search question. Generally, the basic literature search process begins with formulating a clear, well-defined research question.
Step 1: find. I used to find new papers by aimlessly scrolling through science Twitter. But because I often got distracted by irrelevant tweets, that wasn’t very efficient. I also signed up for ...
Elsevier Journal Finder helps you find journals that could be best suited for publishing your scientific article. Journal Finder uses smart search technology and field-of-research specific vocabularies to match your paper’s abstract to scientific journals.