- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
By: History.com Editors
Updated: February 20, 2024 | Original: November 9, 2009

Rosa Parks (1913—2005) helped initiate the civil rights movement in the United States when she refused to give up her seat to a white man on a Montgomery, Alabama bus in 1955. Her actions inspired the leaders of the local Black community to organize the Montgomery Bus Boycott . Led by a young Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. , the boycott lasted more than a year—during which Parks not coincidentally lost her job—and ended only when the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that bus segregation was unconstitutional. Over the next half-century, Parks became a nationally recognized symbol of dignity and strength in the struggle to end entrenched racial segregation .

Rosa Parks’ Early Life
Rosa Louise McCauley was born in Tuskegee, Alabama , on February 4, 1913. She moved with her parents, James and Leona McCauley, to Pine Level, Alabama, at age 2 to reside with Leona’s parents. Her brother, Sylvester, was born in 1915, and shortly after that her parents separated.
Did you know? When Rosa Parks refused to give up her bus seat in 1955, it wasn’t the first time she’d clashed with driver James Blake. Parks stepped onto his very crowded bus on a chilly day 12 years earlier, paid her fare at the front, then resisted the rule in place for Black people to disembark and re-enter through the back door. She stood her ground until Blake pulled her coat sleeve, enraged, to demand her cooperation. Parks left the bus rather than give in.
Rosa’s mother was a teacher, and the family valued education. Rosa moved to Montgomery, Alabama, at age 11 and eventually attended high school there, a laboratory school at the Alabama State Teachers’ College for Negroes. She left at 16, early in 11th grade, because she needed to care for her dying grandmother and, shortly thereafter, her chronically ill mother. In 1932, at 19, she married Raymond Parks, a self-educated man 10 years her senior who worked as a barber and was a long-time member of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People ( NAACP ). He supported Rosa in her efforts to earn her high-school diploma, which she ultimately did the following year.
Rosa Parks: Roots of Activism
Raymond and Rosa, who worked as a seamstress, became respected members of Montgomery’s large African American community. Co-existing with white people in a city governed by “ Jim Crow ” (segregation) laws, however, was fraught with daily frustrations: Black people could attend only certain (inferior) schools, could drink only from specified water fountains and could borrow books only from the “Black” library, among other restrictions.
Although Raymond had previously discouraged her out of fear for her safety, in December 1943, Rosa also joined the Montgomery chapter of the NAACP and became chapter secretary . She worked closely with chapter president Edgar Daniel (E.D.) Nixon. Nixon was a railroad porter known in the city as an advocate for Black people who wanted to register to vote, and also as president of the local branch of the Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters union .
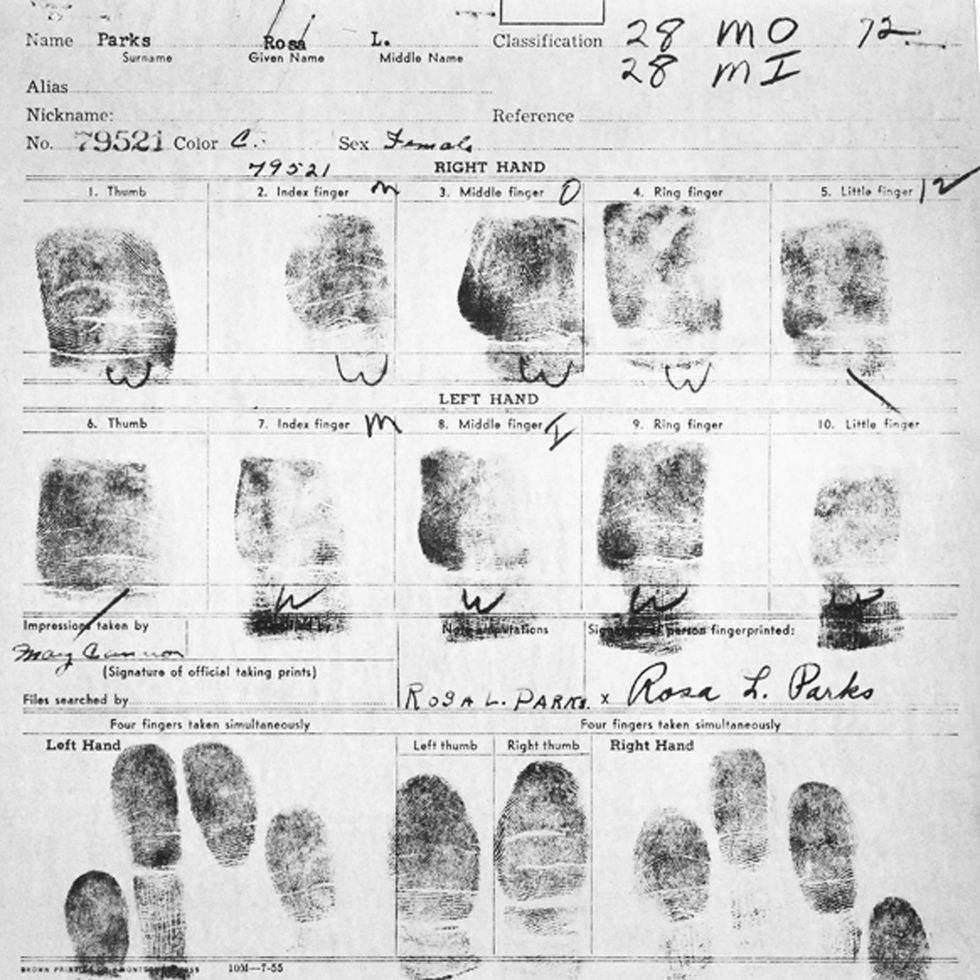
December 1, 1955: Rosa Parks Is Arrested
On Thursday, December 1, 1955, the 42-year-old Rosa Parks was commuting home from a long day of work at the Montgomery Fair department store by bus. Black residents of Montgomery often avoided municipal buses if possible because they found the Negroes-in-back policy so demeaning. Nonetheless, 70 percent or more riders on a typical day were Black, and on this day Rosa Parks was one of them.
Segregation was written into law; the front of a Montgomery bus was reserved for white citizens, and the seats behind them for Black citizens. However, it was only by custom that bus drivers had the authority to ask a Black person to give up a seat for a white rider. There were contradictory Montgomery laws on the books: One said segregation must be enforced, but another, largely ignored, said no person (white or Black) could be asked to give up a seat even if there were no other seat on the bus available.
Nonetheless, at one point on the route, a white man had no seat because all the seats in the designated “white” section were taken. So the driver told the riders in the four seats of the first row of the “colored” section to stand, in effect adding another row to the “white” section. The three others obeyed. Parks did not.
“People always say that I didn’t give up my seat because I was tired,” wrote Parks in her autobiography, “but that isn’t true. I was not tired physically… No, the only tired I was, was tired of giving in.”
Eventually, two police officers approached the stopped bus, assessed the situation and placed Parks in custody.
Rosa Parks and the Montgomery Bus Boycott
Although Parks used her one phone call to contact her husband, word of her arrest had spread quickly and E.D. Nixon was there when Parks was released on bail later that evening. Nixon had hoped for years to find a courageous Black person of unquestioned honesty and integrity to become the plaintiff in a case that might become the test of the validity of segregation laws. Sitting in Parks’ home, Nixon convinced Parks—and her husband and mother—that Parks was that plaintiff. Another idea arose as well: The Black population of Montgomery would boycott the buses on the day of Parks’ trial, Monday, December 5. By midnight, 35,000 flyers were being mimeographed to be sent home with Black schoolchildren, informing their parents of the planned boycott.
On December 5, Parks was found guilty of violating segregation laws, given a suspended sentence and fined $10 plus $4 in court costs. Meanwhile, Black participation in the boycott was much larger than even optimists in the community had anticipated. Nixon and some ministers decided to take advantage of the momentum, forming the Montgomery Improvement Association (MIA) to manage the boycott, and they elected Reverend Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.–new to Montgomery and just 26 years old—as the MIA’s president.
As appeals and related lawsuits wended their way through the courts, all the way up to the U.S. Supreme Court , the Montgomery Bus Boycott engendered anger in much of Montgomery’s white population as well as some violence, and Nixon’s and Dr. King’s homes were bombed . The violence didn’t deter the boycotters or their leaders, however, and the drama in Montgomery continued to gain attention from the national and international press.
On November 13, 1956, the Supreme Court ruled that bus segregation was unconstitutional; the boycott ended December 20, a day after the Court’s written order arrived in Montgomery. Parks—who had lost her job and experienced harassment all year—became known as “the mother of the civil rights movement.”
Rosa Parks's Life After the Boycott
Facing continued harassment and threats in the wake of the boycott, Parks, along with her husband and mother, eventually decided to move to Detroit, where Parks’ brother resided. Parks became an administrative aide in the Detroit office of Congressman John Conyers Jr. in 1965, a post she held until her 1988 retirement. Her husband, brother and mother all died of cancer between 1977 and 1979. In 1987, she co-founded the Rosa and Raymond Parks Institute for Self-Development, to serve Detroit’s youth.
In the years following her retirement, she traveled to lend her support to civil-rights events and causes and wrote an autobiography, Rosa Parks: My Story . In 1999, Parks was awarded the Congressional Gold Medal, the highest honor the United States bestows on a civilian. (Other recipients have included George Washington , Thomas Edison , Betty Ford and Mother Teresa.) When she died at age 92 on October 24, 2005, she became the first woman in the nation’s history to lie in honor at the U.S. Capitol.

HISTORY Vault: Black History
Watch acclaimed Black History documentaries on HISTORY Vault.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
- Did You Know?
- Photo Gallery
ROSA LOUISE PARKS BIOGRAPHY
Rosa Louise Parks was nationally recognized as the “mother of the modern day civil rights movement” in America. Her refusal to surrender her seat to a white male passenger on a Montgomery, Alabama bus, December 1, 1955, triggered a wave of protest December 5, 1955 that reverberated throughout the United States. Her quiet courageous act changed America, its view of black people and redirected the course of history.
Mrs. Parks was born Rosa Louise McCauley, February 4, 1913 in Tuskegee, Alabama. She was the first child of James and Leona Edwards McCauley. Her brother, Sylvester McCauley, now deceased, was born August 20, 1915. Later, the family moved to Pine Level, Alabama where Rosa was reared and educated in the rural school. When she completed her education in Pine Level at age eleven, her mother, Leona, enrolled her in Montgomery Industrial School for Girls (Miss White’s School for Girls), a private institution. After finishing Miss White’s School, she went on to Alabama State Teacher’s College High School. She, however, was unable to graduate with her class, because of the illness of her grandmother Rose Edwards and later her death.
As Rosa Parks prepared to return to Alabama State Teacher’s College, her mother also became ill, therefore, she continued to take care of their home and care for her mother while her brother, Sylvester, worked outside of the home. She received her high school diploma in 1934, after her marriage to Raymond Parks, December 18, 1932. Raymond, now deceased was born in Wedowee, Alabama, Randolph County, February 12, 1903, received little formal education due to racial segregation. He was a self-educated person with the assistance of his mother, Geri Parks. His immaculate dress and his thorough knowledge of domestic affairs and current events made most think he was college educated. He supported and encouraged Rosa’s desire to complete her formal education.
Mr. Parks was an early activist in the effort to free the “Scottsboro Boys,” a celebrated case in the 1930′s. Together, Raymond and Rosa worked in the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP’s) programs. He was an active member and she served as secretary and later youth leader of the local branch. At the time of her arrest, she was preparing for a major youth conference.
After the arrest of Rosa Parks, black people of Montgomery and sympathizers of other races organized and promoted a boycott of the city bus line that lasted 381 days. Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. was appointed the spokesperson for the Bus Boycott and taught nonviolence to all participants. Contingent with the protest in Montgomery, others took shape throughout the south and the country. They took form as sit-ins, eat-ins, swim-ins, and similar causes. Thousands of courageous people joined the “protest” to demand equal rights for all people.
Mrs. Parks moved to Detroit, Michigan in 1957. In 1964 she became a deaconess in the African Methodist Episcopal Church (AME).
Congressman John Conyers First Congressional District of Michigan employed Mrs. Parks, from 1965 to 1988. In February, 1987, she co-founded the Rosa and Raymond Parks Institute for Self Development with Ms. Elaine Eason Steele in honor of her husband, Raymond (1903-1977). The purpose is to motivate and direct youth not targeted by other programs to achieve their highest potential. Rosa Parks sees the energy of young people as a real force for change. It is among her most treasured themes of human priorities as she speaks to young people of all ages at schools, colleges, and national organizations around the world.
The Rosa and Raymond Parks Institute for Self Development’s “Pathways to Freedom program, traces the underground railroad into the civil rights movement and beyond. Youth, ages 11 through 17, meet and talk with Mrs. Parks and other national leaders as they participate in educational and historical research throughout the world. They journey primarily by bus as “freedom riders” did in the 1960′s,the theme: “Where have we been? Where are we going?”
As a role model for youth she was stimulated by their enthusiasm to learn as much about her life as possible. A modest person, she always encourages them to research the lives of other contributors to world peace. The Institute and The Rosa Parks Legacy are her legacies to people of good will.
Mrs. Parks received more than forty-three honorary doctorate degrees, including one from SOKA UNIVERSITY, Tokyo Japan, hundreds of plaques, certificates, citations, awards and keys to many cities. Among them are the NAACP’s Spingarn Medal, the UAW’s Social Justice Award, the Martin Luther King, Jr. Non – Violent Peace Prize and the ROSA PARKS PEACE PRIZE in 1994, Stockholm Sweden, to name a few. In September 1996 President William J. Clinton, the forty second President of the United States of America gave Mrs. Parks the MEDAL OF FREEDOM, the highest award given to a civilian citizen.
Published Act no.28 of 1997 designated the first Monday following February 4, as Mrs Rosa Parks’ Day in the state of Michigan, her home state. She is the first living person to be honored with a holiday.
She was voted by Time Magazine as one of the 100 most Influential people of the 20th century. A Museum and Library is being built in her honor, in Montgomery, AL and will open in the fall of the year 2000 (ground breaking April 21, 1998). On September 2, 1998 The Rosa L. Parks Learning Center was dedicated at Botsford Commons, a senior community in Michigan. Through the use of computer technology, youth will mentor seniors on the use of computers. (Mrs. Parks was a member of the first graduating class on November 24, 1998). On September 26, 1998 Mrs. Parks was the recipient of the first International Freedom Conductor’s Award by the National Underground Railroad Freedom Center in Cincinnati, Ohio.
She attended her first “State of the Union Address” in January 1999. Mrs. Parks received a unanimous bipartisan standing ovation when President William Jefferson Clinton acknowledged her. Representative Julia Carson of Indianapolis, Indiana introduced H. R. Bill 573 on February 4, 1999, which would award Mrs. Rosa Parks the Congressional Gold Medal of Honor if it passed the House of Representatives and the Senate by a majority. The bill was passed unanimously in the Senate on April 19, and with one descenting vote in the House of Representatives on April 20. President Clinton signed it into law on May 3, 1999. Mrs. Parks was one of only 250 individuals at the time, including the American Red Cross to receive this honor. President George Washington was the first to receive the Congressional Gold Medal of Honor. President Nelson Mandela is also listed among the select few of world leaders who have received the medal.
In the winter of 2000 Mrs. Parks met Pope John-Paul II in St. Louis, MO and read a statement to him asking for racial healing. She received the NAACP Image Award for Best Supporting Actress in the Television series, TOUCHED BY AN ANGEL, “Black like Monica”. Troy State University at Montgomery opened The Rosa Parks Library and Museum on the site where Mrs. Parks was arrested December 1, 1955. It opened on the 45th Anniversary of her arrest and the Montgomery Bus Boycott.
“The Rosa Parks Story” was filmed in Montgomery, Alabama May 2001, an aired February 24, 2002 on the CBS television network. Mrs. Parks continues to receive numerous awards including the very first Lifetime Achievement Award ever given by The Institute for Research on Women & Gender, Stanford University. She received the Gandhi, King, Ikeda award for peace and on October 29, 2003 Mrs. Parks was an International Institute Heritage Hall of fame honoree. On February 4, 2004 Mrs. Parks 91st birthday was celebrated at the Charles H. Wright Museum of African American History. On December 21, 2004 the 49th Anniversary of the Mrs. Parks’ arrest was commemorated with a Civil Rights and Hip-Hop Forum at the Franklin Settlement in Detroit, Michigan.
On February 4, 2005 Mrs. Parks’ 92nd birthday was celebrate at Calvary Baptist Church in Detroit, MI. Students from the Detroit Public Schools did “Willing to be Arrested,” a reenactment of Mrs. Parks arrest. February 6, 2005 Mrs. Parks received the first annual Cardinal Dearden Peace Award at Holy Trinity Catholic Church in Detroit, MI. February 19 – 20, composer Hannibal Lokumbe premiered an original symphony “Dear Mrs. Parks.” Mr. Lokumbe did this original work as part of the Detroit Symphony Orchestra’s ” Classical Roots Series.” The beginning of many events that will commemorate the 50th Anniversary of Mrs. Parks’ arrest December 1, 1955.
Mrs. Parks has written four books, Rosa Parks: My Story: by Rosa Parks with Jim Haskins, Quiet Strength by Rosa Parks with Gregory J. Reed, Dear Mrs. Parks: A Dialogue With Today’s Youth by Rosa Parks with Gregory J, Reed, this book received the NAACP’s Image Award for Outstanding Literary Work, (Children’s) in 1996 and her latest book, I AM ROSA PARKS by Rosa Parks with Jim Haskins, for preschoolers.
A quiet exemplification of courage, dignity, and determination; Rosa Parks was a symbol to all to remain free. Rosa Parks made her peaceful transition October 24, 2005.
Find Us On Facebook
REACH THE INSTITUTE
Rosa parks institute for self development.

On December 1, 1955, Rosa Parks boarded a bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Instead of going to the back of the bus, which was designated for African Americans, she sat in the front. When the bus started to fill up with white passengers, the bus driver asked Parks to move. She refused. Her resistance set in motion one of the largest social movements in history, the Montgomery Bus Boycott .
Rosa Louise McCauley was born on February 4th, 1913 in Tuskegee, Alabama. As a child, she went to an industrial school for girls and later enrolled at Alabama State Teachers College for Negroes (present-day Alabama State University). Unfortunately, Parks was forced to withdraw after her grandmother became ill. Growing up in the segregated South, Parks was frequently confronted with racial discrimination and violence. She became active in the Civil Rights Movement at a young age.
Parks married a local barber by the name of Raymond Parks when she was 19. He was actively fighting to end racial injustice. Together the couple worked with many social justice organizations. Eventually, Rosa was elected secretary of the Montgomery chapter of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP).
By the time Parks boarded the bus in 1955, she was an established organizer and leader in the Civil Rights Movement in Alabama. Parks not only showed active resistance by refusing to move she also helped organize and plan the Montgomery Bus Boycott. Many have tried to diminish Parks’ role in the boycott by depicting her as a seamstress who simply did not want to move because she was tired. Parks denied the claim and years later revealed her true motivation:
“People always say that I didn’t give up my seat because I was tired, but that isn’t true. I was not tired physically, or no more tired than I usually was at the end of a working day. I was not old, although some people have an image of me as being old then. I was forty-two. No, the only tired I was, was tired of giving in.”
Parks courageous act and the subsequent Montgomery Bus Boycott led to the integration of public transportation in Montgomery. Her actions were not without consequence. She was jailed for refusing to give up her seat and lost her job for participating in the boycott.
After the boycott, Parks and her husband moved to Hampton, Virginia and later permanently settled in Detroit, Michigan. Parks work proved to be invaluable in Detroit’s Civil Rights Movement. She was an active member of several organizations which worked to end inequality in the city. By 1980, after consistently giving to the movement both financially and physically Parks, now widowed, suffered from financial and health troubles. After almost being evicted from her home, local community members and churches came together to support Parks. On October 24th, 2005, at the age of 92, she died of natural causes leaving behind a rich legacy of resistance against racial discrimination and injustice.
- Parks, Rosa. Rosa Parks: My Story. New York: Puffin Books, 1999.
- Theoharis, Jeanne. The Rebellious Life of Mrs.Rosa Parks. New York: Beacon Press, 2014.
- “An Act of Courage, The Arrest Records of Rosa Parks” National Archives, Accessed 23 March 2017. https://www.archives.gov/education/lessons/rosa-parks
- PHOTO: Library of Congress
MLA – Norwood, Arlisha. "Rosa Parks." National Women's History Museum. National Women's History Museum, 2017. Date accessed.
Chicago- Norwood, Arlisha. "Rosa Parks." National Women's History Museum. 2017. www.womenshistory.org/education-resources/biographies/rosa-parks.
- Robinson, Jo Ann. Montgomery Bus Boycott and the Women Who Started It: The Memoir of Jo Ann Gibson Robison. Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 1987.
- “Rosa Parks: How I Fought for Civil Rights.” Scholastic Teacher’s Activity Guide. Accessed 23 March 2017.
- “What If: I Don’t Move to the Back of The Bus?” The Henry Ford Foundation : Stories of Innovation, Accessed March 23 2017.
Related Biographies

Stacey Abrams

Abigail Smith Adams

Jane Addams


Toshiko Akiyoshi
Related background, mary church terrell , belva lockwood and the precedents she set for women’s rights, women’s rights lab: black women’s clubs, educational equality & title ix:.
Rosa Parks: Timeline of Her Life, Montgomery Bus Boycott and Death

After the bus boycott, Parks continued to participate in the civil rights movement. She attended the March on Washington in 1963 and in 1965 witnessed the signing of the Voting Rights Act . Her later years saw Parks' work recognized with the Presidential Medal of Freedom and the Congressional Gold Medal.
The following timeline covers notable events and achievements in Parks' long and remarkable life:
February 4, 1913: Rosa Louise McCauley born in Tuskegee, Alabama to James and Leona McCauley
1919: A six-year-old Parks begins picking cotton alongside her grandparents. She also starts attending a segregated school in Pine Level, Alabama.
1924: As there is no local school for Black children to attend after the sixth grade, McCauley goes to Miss White’s Montgomery Industrial School for Girls in Montgomery, Alabama.
1929: Parks leaves school in the 11th grade to care for her ill grandmother and mother.
1931: While Parks is working as a housekeeper for a white family, a white neighbor attempts to rape her .
1931: Parks is introduced to Raymond Parks, whom she later described as being the first activist she encountered.
December 18, 1932: Rosa weds Raymond Parks

1933: Parks returns to school and obtains her high school diploma, a notable accomplishment at a time when very few Black people in Alabama held this degree.
1941: Parks starts work at Maxwell Air Force Base, which has an integrated cafeteria and trolley system.
December 1943: Parks joins the Montgomery branch of the NAACP
As the only woman at her first meeting, she is named secretary of the group. Parks' work for the NAACP will also include investigating crimes against Black people such as murder, assaults and police brutality.
Parks attempts to register to vote but is told she failed the literacy test required of Black voters.
September 1944: Recy Taylor, a Black woman, is gang-raped by six white men. The Montgomery NAACP dispatches Parks to investigate the case.
Parks helps establish the Committee for Equal Justice for the Rights of Mrs. Recy Taylor to advocate for legal action against Taylor's assailants. The case becomes national news but the rapists are never convicted.

1945: After taking the required literacy test for a third time, Parks becomes a registered voter. Yet before she can cast a ballot, she must pay a retroactive poll tax of $1.50 for every year since she reached the voting age of 21.
1948 : Parks becomes the Alabama state secretary for the NAACP.
1949: Parks steps back as NAACP secretary to take care of her mother.
1952: Parks returns to the Montgomery NAACP and once more becomes a branch secretary.
August 1955: Parks attends a two-week training session at the Highlander Folk School in Tennessee. Alongside other civil rights activists, both Black and white, she discusses how to integrate schools following the Supreme Court's Brown v. Board of Education decision of 1954.
December 1, 1955: In Montgomery, Parks defies a bus driver's order to let a white man take her seat
The driver, who had treated Parks rudely and evicted her from his bus in 1943, contacts the police and she is arrested.
December 5, 1955: Though Parks was not the first Black woman arrested for defying segregation on city buses, news of her case spurs the Black community to begin a boycott of Montgomery buses .
Parks' trial takes place. She is found guilty and fined $10, plus $4 in court costs. Her lawyers file an appeal.
January 7, 1956: Parks is let go from her job as a tailor's assistant at the Montgomery Fair department store.
January 1956: Raymond quits his barbershop job after discussion of his wife and the boycott is forbidden.
February 21, 1956: Along with dozens of other civil rights leaders, including Martin Luther King Jr. , Parks is indicted for violating a Montgomery law outlawing boycotts.
February 22, 1956: Parks is among a group of indicted boycott leaders who present themselves for arrest. She is quickly released. The case against Parks is eventually dismissed.
1956: During the boycott, Parks serves as a dispatcher to coordinate carpools. She also travels across the country to speak about the boycott.
December 21, 1956: Following a Supreme Court ruling that segregated buses are unconstitutional, the 381-day boycott ends. Parks is photographed sitting at the front of a bus for Look magazine.
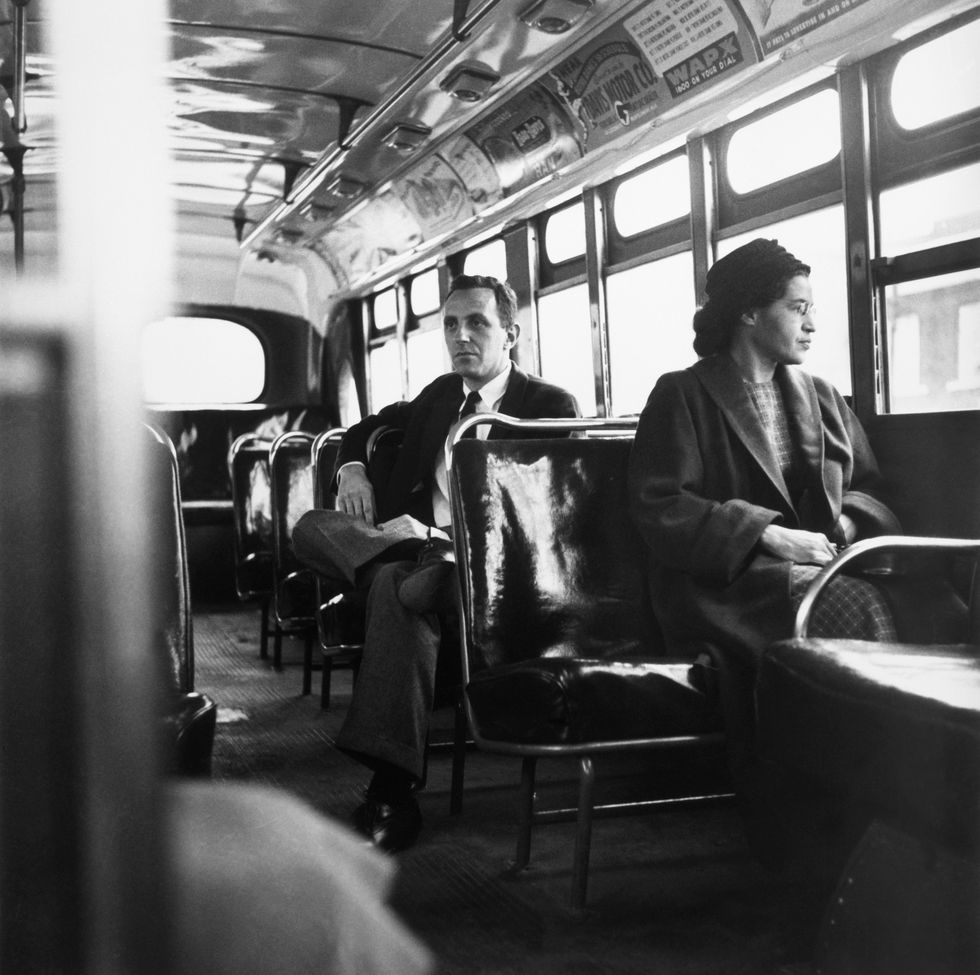

August 1957: Unable to find work in Montgomery and still facing threats for her role in the bus boycott, Parks and her family depart for Detroit
October 1957: Parks becomes a hostess at the Holly Tree Inn, part of the Hampton Institute in Virginia, but leaves after the fall semester in 1958 to rejoin her husband and mother in Detroit.
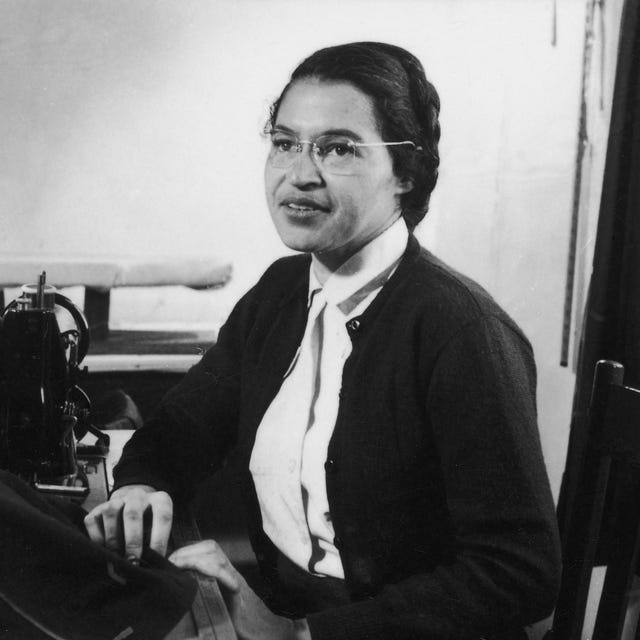
1959: Parks begins doing piecework for Detroit's Stockton Sewing Company, a job she holds through 1964.
July 1960: A Jet magazine article reveals that Parks and her family have been struggling financially, due in part to her health problems.
August 28, 1963: Parks attends the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom . No women are invited to speak at the event, but Parks is among those singled out for a "Tribute to Women" in the civil rights movement.
March 1, 1965: Parks takes a job in the Detroit office of newly elected Congressman John Conyers, where her tasks include answering phones and aiding constituents. She stays in this position until her retirement in 1988.
March 25, 1965: Parks joins the march to Montgomery for equal voting rights. Many of the marchers do not recognize her but in the end she is acknowledged and invited to speak at the capitol building.
August 6, 1965: Parks is among those present to witness President Lyndon Johnson's signing of the Voting Rights Act.
July 23, 1967: Parks is in Detroit during five days of rioting. Amid the upheaval, her husband's barbershop is destroyed.
August 30, 1967: A "People's Tribunal" is held regarding the deaths of three young Black men during the Detroit riots. Parks serves on the jury, which finds the police who were at the scene guilty (the officers faced no such repercussions in the legal system).
August 19, 1977: Parks' husband, Raymond, dies.
August 1979: The NAACP presents Parks with its highest accolade, the Spingarn Medal.
January 14, 1980: Parks is given the Martin Luther King Jr. Nonviolent Peace Prize
1987: Parks establishes the Rosa and Raymond Parks Institute for Self Development, intended to help young people better understand the past and prepare for their futures.
1992: Rosa Parks: My Story , an autobiography for younger readers, is published.
August 30, 1994: Parks is robbed and beaten by a mugger inside her home.
October 16, 1995: At the invitation of Nation of Islam leader Louis Farrakhan, Parks attends the Million Man March in Washington, D.C.
1994: Another book by Parks, entitled Quiet Strength , is published.
September 15, 1996: Parks is presented with the Presidential Medal of Freedom by Bill Clinton .
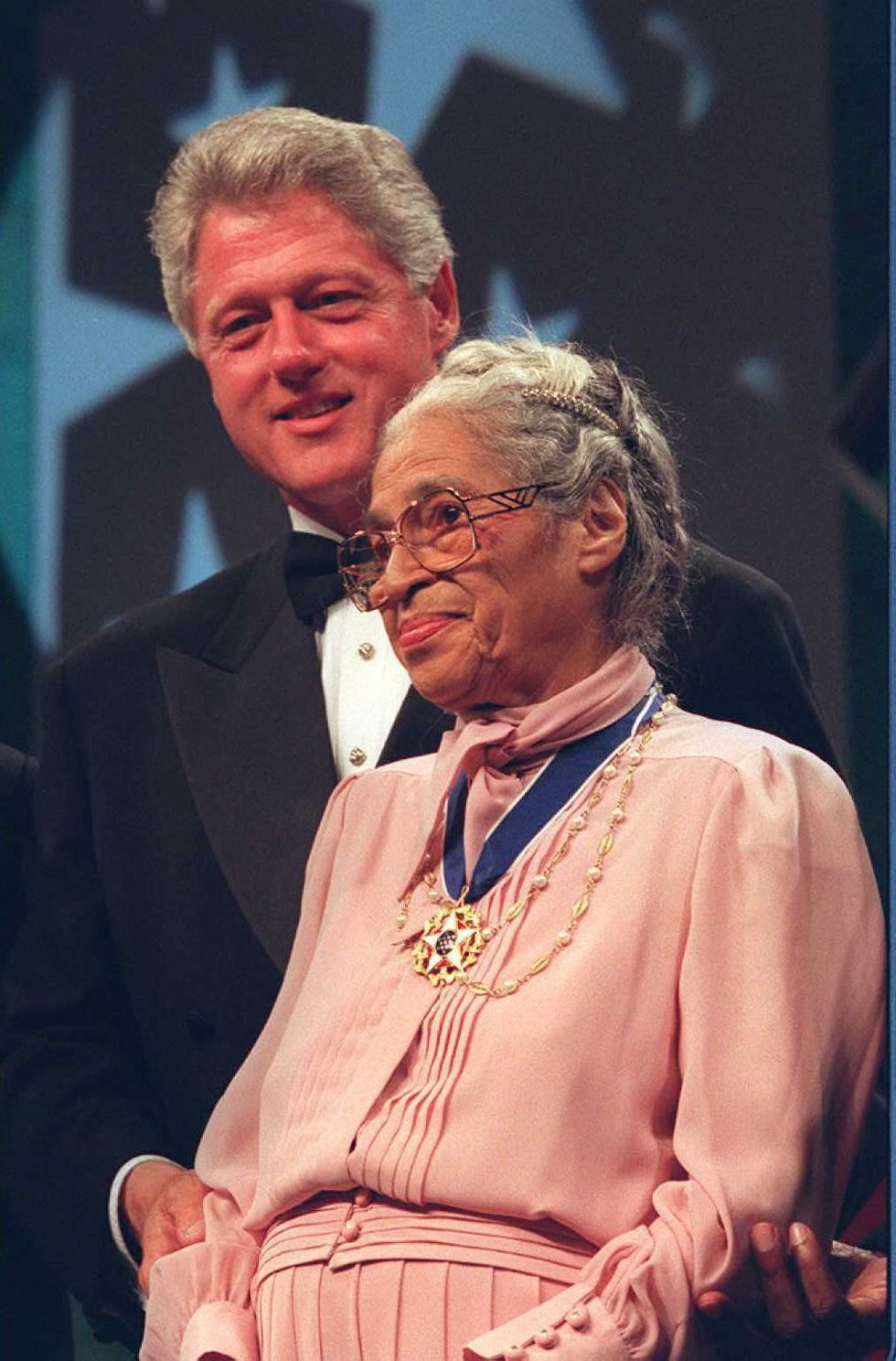

June 15, 1999: Parks receives the Congressional Gold Medal, the highest legislative honor in the United States.
April 14, 2005: Parks and the hip-hop group Outkast reach an out-of-court settlement regarding their 1998 song "Rosa Parks."
October 24, 2005: Parks dies at the age of 92
Her body is brought to lie in honor at the U.S. Capitol Rotunda, the first time for a woman to receive this recognition.
Watch “Rosa Parks: Mother Of A Movement” on History Vault
Black History

Jesse Owens

Alice Coachman

Wilma Rudolph

Tiger Woods

Deb Haaland

10 Famous Langston Hughes Poems

5 Crowning Achievements of Maya Angelou

Ava DuVernay

Octavia Spencer
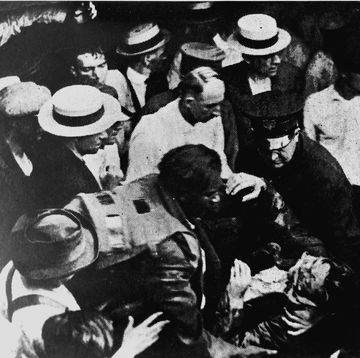
Inventor Garrett Morgan’s Lifesaving 1916 Rescue

Get to Know 5 History-Making Black Country Singers

- Member Interviews
- Science & Exploration
- Public Service
- Achiever Universe
- Summit Overview
- About The Academy
- Academy Patrons
- Delegate Alumni
- Directors & Our Team
- Golden Plate Awards Council
- Golden Plate Awardees
- Preparation
- Perseverance
- The American Dream
- Recommended Books
- Find My Role Model
All achievers
Pioneer of civil rights.

Download our free multi-touch iBook The Road to Civil Rights — available for your Mac or iOS device on Apple Books
The Road to Civil Rights iBook takes readers on a journey through one of the most significant periods in America’s history. Travel through the timeline and listen to members of the American Academy of Achievement as they discuss the key events that shaped the future of the country.

Listen to this achiever on What It Takes
What It Takes is an audio podcast produced by the American Academy of Achievement featuring intimate, revealing conversations with influential leaders in the diverse fields of endeavor: public service, science and exploration, sports, technology, business, arts and humanities, and justice.
Two policemen came on the bus, and one asked me if the driver had told me to stand. He wanted to know why I didn’t stand, and I told him I didn’t think I should have to stand up. I asked him, why did they push us around? He said, I don’t know, but the law is the law and you are under arrest.
Most historians date the beginning of the modern civil rights movement in the United States to December 1, 1955. That was the day when an unknown seamstress in Montgomery, Alabama refused to give up her bus seat to a white passenger. This brave woman, Rosa Parks, was arrested and fined for violating a city ordinance, but her lonely act of defiance began a movement that ended legal segregation in America, and made her an inspiration to freedom-loving people everywhere.

Rosa Parks was born Rosa Louise McCauley in Tuskegee, Alabama to James McCauley, a carpenter, and Leona McCauley, a teacher. At the age of two she moved to her grandparents’ farm in Pine Level, Alabama with her mother and younger brother, Sylvester. At the age of 11 she enrolled in the Montgomery Industrial School for Girls, a private school founded by liberal-minded women from the northern United States.

The school’s philosophy of self-worth was consistent with Leona McCauley’s advice to “take advantage of the opportunities, no matter how few they were.” Opportunities were few indeed. “Back then,” Mrs. Parks recalled in an interview, “we didn’t have any civil rights. It was just a matter of survival, of existing from one day to the next. I remember going to sleep as a girl hearing the Klan ride at night and hearing a lynching and being afraid the house would burn down.” In the same interview, she cited her lifelong acquaintance with fear as the reason for her relative fearlessness in deciding to appeal her conviction during the bus boycott. “I didn’t have any special fear,” she said. “It was more of a relief to know that I wasn’t alone.” After attending Alabama State Teachers College, the young Rosa settled in Montgomery, with her husband, Raymond Parks. The couple joined the local chapter of the NAACP and worked quietly for many years to improve the lot of African Americans in the segregated South.

“I worked on numerous cases with the NAACP,” Mrs. Parks recalled, “but we did not get the publicity. There were cases of flogging, peonage, murder, and rape. We didn’t seem to have too many successes. It was more a matter of trying to challenge the powers that be, and to let it be known that we did not wish to continue being second-class citizens.”

The bus incident led to the formation of the Montgomery Improvement Association, led by the young pastor of the Dexter Avenue Baptist Church, Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. The association called for a boycott of the city-owned bus company. The boycott lasted 381 days and brought Mrs. Parks, Dr. King, and their cause to the attention of the world. A Supreme Court decision struck down the Montgomery ordinance under which Mrs. Parks had been fined, and outlawed racial segregation on public transportation.

In 1957, Mrs. Parks and her husband moved to Detroit, Michigan, where Mrs. Parks served on the staff of U.S. Representative John Conyers. The Southern Christian Leadership Council established an annual Rosa Parks Freedom Award in her honor.

After the death of her husband in 1977, Mrs. Parks founded the Rosa and Raymond Parks Institute for Self-Development. The Institute sponsors an annual summer program for teenagers called Pathways to Freedom. The young people tour the country in buses, under adult supervision, learning the history of their country and of the civil rights movement. President Clinton presented Rosa Parks with the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 1996. She received a Congressional Gold Medal in 1999.

When asked if she was happy living in retirement, Rosa Parks replied, “I do the very best I can to look upon life with optimism and hope and looking forward to a better day, but I don’t think there is any such thing as complete happiness. It pains me that there is still a lot of Klan activity and racism. I think when you say you’re happy, you have everything that you need and everything that you want, and nothing more to wish for. I haven’t reached that stage yet.”
Mrs. Parks spent her last years living quietly in Detroit, where she died in 2005 at the age of 92. After her death, her casket was placed in the rotunda of the United States Capitol for two days, so the nation could pay its respects to the woman whose courage had changed the lives of so many. She was the first woman and the second African American to lie in honor at the Capitol, a distinction usually reserved for Presidents of the United States.
View and listen to Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr.’s historic “I Have a Dream” speech, delivered on the steps of Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., August 28, 1963.
Member of the American Academy of Achievement, poet and best-selling author, Maya Angelou shares her interpretation of Dr. Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream” speech.

Rosa Parks, the “Mother of the Civil Rights Movement” was one of the most important citizens of the 20th century. Mrs. Parks was a seamstress in Montgomery, Alabama when, in December of 1955, she refused to give up her seat on a city bus to a white passenger. The bus driver had her arrested. She was tried and convicted of violating a local ordinance.
Her act sparked a citywide boycott of the bus system by blacks that lasted more than a year. The boycott raised an unknown clergyman named Martin Luther King, Jr., to national prominence and resulted in the U.S. Supreme Court decision outlawing segregation on city buses. Over the next four decades, she helped make her fellow Americans aware of the history of the civil rights struggle. This pioneer in the struggle for racial equality was the recipient of innumerable honors, including the Martin Luther King Jr. Nonviolent Peace Prize and the Presidential Medal of Freedom. Her example remains an inspiration to freedom-loving people everywhere.
In 1955, you refused to give up your seat to a white passenger on a public bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Your act inspired the Montgomery Bus Boycott, the event historians call the beginning of the modern Civil Rights Movement. Could you tell us exactly what happened that day?
Rosa Parks: I was arrested on December 1, 1955 for refusing to stand up on the orders of the bus driver, after the white seats had been occupied in the front. And of course, I was not in the front of the bus as many people have written and spoken that I was — that I got on the bus and took the front seat, but I did not. I took a seat that was just back of where the white people were sitting, in fact, the last seat. A man was next to the window, and I took an aisle seat and there were two women across. We went on undisturbed until about the second or third stop when some white people boarded the bus and left one man standing. And when the driver noticed him standing, he told us to stand up and let him have those seats. He referred to them as front seats. And when the other three people — after some hesitancy — stood up, he wanted to know if I was going to stand up, and I told him I was not. And he told me he would have me arrested. And I told him he may do that. And of course, he did. Two policemen came on the bus and one asked me if the driver had told me to stand and I said, “Yes.” And he wanted to know why I didn’t stand, and I told him I didn’t think I should have to stand up. And then I asked him, why did they push us around? And he said, and I quote him, “I don’t know, but the law is the law and you are under arrest.” And with that, I got off the bus, under arrest.

Did they take you down to the police station?
Rosa Parks: Yes. A policeman wanted the driver to swear out a warrant, if he was willing, and he told him that he would sign a warrant when he finished his trip and delivered his passengers, and he would come straight down to the City Hall to sign a warrant against me.

Did he do that?
Rosa Parks: Yes, he did.

Did the public response begin immediately?
Rosa Parks: Actually, it began as soon as it was announced.
It was put in the paper that I had been arrested. Mr. E.D. Nixon was the legal redress chairman of the Montgomery branch of the NAACP, and he made a number of calls during the night, called a number of ministers. I was arrested on a Thursday evening, and on Friday evening is when they had the meeting at the Dexter Avenue Baptist Church, where Dr. Martin Luther King was the pastor. A number of citizens came, and I told them the story and from then on, it became news about my being arrested. My trial was December 5, when they found me guilty. The lawyers Fred Gray and Charles Langford, who represented me, filed an appeal and, of course, I didn’t pay any fine. We set a meeting at the Holt Street Baptist Church on the evening of December 5th, because December 5th was the day the people stayed off in large numbers and did not ride the bus. In fact, most of the buses, I think all of them were just about empty with the exception of maybe very, very few people. When they found out that one day’s protest had kept people off the bus, it came to a vote and unanimously, it was decided that they would not ride the buses anymore until changes for the better were made.

When you refused to stand up, did you have a sense of anger at having to do it?
Rosa Parks: I don’t remember feeling that anger, but I did feel determined to take this as an opportunity to let it be known that I did not want to be treated in that manner and that people have endured it far too long. However, I did not have at the moment of my arrest any idea of how the people would react. And since they reacted favorably, I was willing to go with that. We formed what was known as the Montgomery Improvement Association, on the afternoon of December 5th. Dr. Martin Luther King became very prominent in this movement, so he was chosen as a spokesman and the president of the Montgomery Improvement Association.

What are your thoughts when you look back on that time in your life. Any regrets?
As I look back on those days, it’s just like a dream. The only thing that bothered me was that we waited so long to make this protest and to let it be known wherever we go that all of us should be free and equal and have all opportunities that others should have.
What personal characteristics do you think are most important to accomplish something?
Rosa Parks: I think it’s important to believe in yourself and when you feel like you have the right idea, to stay with it. And of course, it all depends upon the cooperation of the people around. People were very cooperative in getting off the buses. And from that, of course, we went on to other things. I, along with Mrs. Field, who was here with me, organized the Rosa and Raymond Parks Institute for Self-Development. Raymond, my husband—he is now deceased—was another person who inspired me, because he believed in freedom and equality himself.

You were married during the bus incident.
Rosa Parks: Yes, I was.

How old were you?
Rosa Parks: When I was arrested, I was 42 years old. There were so many needs for us to continue to work for freedom, because I didn’t think that we should have to be treated in the way we were, just for the sake of white supremacy, because it was designed to make them feel superior, and us feel inferior. That was the whole plan of racially enforced segregation.
What was it like in Montgomery when you were growing up?
Rosa Parks: Back in Montgomery during my growing up there, it was completely legally enforced racial segregation, and of course, I struggled against it for a long time. I felt that it was not right to be deprived of freedom when we were living in the Home of the Brave and Land of the Free. Of course, when I refused to stand up, on the orders of the bus driver, for a white passenger to take the seat, and I was not sitting in the front of the bus, as so many people have said, and neither was my feet hurting, as many people have said. But I made up my mind that I would not give in any longer to legally-imposed racial segregation and of course my arrest brought about the protests for more than a year. And in doing so, Dr. Martin Luther King became prominent because he was the leader of our protests along with many other people. And I’m very glad that this experience I had then brought about a movement that triggered across the United States and in other places.
- 26 photos
The Rebellious Life of Mrs. Rosa Parks
By jeanne theoharis, “treading the tightrope of jim crow”.
Portrait of Rosa Parks. Library of Congress, courtesy of Rosa and Raymond Parks Institute for Self Development. Retrieved from: www.loc.gov/teachers
Born on February 4, 1913 in Tuskegee, AL, Rosa Parks was raised by her mother and grandparents in Pine Level, Alabama. Her grandfather supported the Garvey movement and, when Klan violence escalated after World War I, would sit out on the porch with his shotgun to protect the family home. A 6-year-old Rosa would sometimes sit vigil with him. Rosa McCauley was a shy young woman but she had a feisty side, picking up a brick when a white bully threatened her and her brother and pushing back when a white boy pushed her. Her grandmother worried about her granddaughter’s determined spirit and her ways of “talking biggety to white folks”. An older Rosa Parks recounted how her grandmother grew very angry when a young Rosa told her about the brick incident and worried for her safety. Rosa told her grandmother: “I would rather be lynched than live to be mistreated than not be allowed to say ‘I don’t like it.’”
Rosa Parks framed the power of speaking back as fundamental. Full personhood required the option “to say ‘I don’t like it,’” and key to the functioning of white supremacy was shutting down the right and space to assert this. Nonetheless, Parks’ “determination never to accept it, even if it must be endured” led her to “search for a way of working for freedom and first class citizenship.”
Related primary source: Early childhood incidents and experiences and family, Rosa Parks’ recollections. Library of Congress, courtesy of Rosa and Raymond Parks Institute for Self Development.

IMAGES
VIDEO