Home » 8 Parts of Speech | 8 Types, Definition and Examples

8 Parts of Speech | 8 Types, Definition and Examples

Are you curious to Speak or Learn the English Language? well, Every word in the English language is referred to as a component of speech. A word’s function in a sentence indicates the portion of speech to which it belongs. The “8 Parts of Speech,” which have distinct roles in sentence formation, are some of these building elements. To assist you in understanding the fundamentals of grammar, we will go over the various parts of speech in this tutorial, along with their definitions, types, and instances. This article explains the various parts of speech and provides examples and a definition.
The parts of speech are the conventional grammatical categories to which words are assigned based on their syntactic roles, such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, and so forth. Stated differently, they talk about the varied roles that words might play in a sentence and the connections that words have to one another as defined by syntax and grammar.
Every single English word can be classified into one of the eight components of speech. A word’s part of speech is the purpose it fulfills in a sentence. These jobs were also designed to work as a team, much like any workplace or ensemble cast television series.
Table of Contents
What Is a Part of Speech?
Before delving into the specifics, let’s clarify what we mean by a “Part of speech.” In grammar, a part of speech is a category of words with similar grammatical properties. These categories help us understand how words function within sentences.
8 Parts of Speech:
- Preposition
- Conjunction
- Interjection
Let us now dissect each of the 8 parts of speech:
Noun: the foundation of sentences.
- Types: Common nouns, proper nouns, abstract nouns, concrete nouns. See more…
- Definition: A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea.
- Example: cat , London , happiness , desk
Pronoun: Substitutes for Nouns
- Types: Personal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, indefinite pronouns.
- Definition: A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun to avoid repetition.
- Example: he , she , it , they
Verb: The Action Words
- Types: Action verbs, linking verbs, helping verbs.
- Definition: A verb expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being.
- Example: She runs every morning. The flowers smell delightful.
Adjective: Describing Words
- Types: Descriptive adjectives, limiting adjectives.
- Definition: An adjective describes or modifies a noun or pronoun.
- Example: The blue sky, tall trees, delicious food.
Adverb: Modifiers of Verbs
- Types: Adverbs of manner, place, time, degree.
- Definition: An adverb modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb
- Example: He ran quickly , She sings beautifully .
Preposition: Indicators of Position or Relationship
- Types: Simple prepositions, compound prepositions.
- Definition: A preposition shows the relationship between its object and another word in the sentence.
- Example: The book is on the table. She walked across the bridge.
Conjunction: Joining Words
- Types: Coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions.
- Definition: A conjunction connects words, phrases, or clauses.
- Example: She likes tea and coffee. He went to the store because he needed groceries.
Interjection: Expressions of Emotion
- Types: Expressive interjections, introductory interjections.
- Definition: An interjection expresses strong emotions or sudden bursts of feeling.
- Example: Wow! That was amazing! Ouch! That hurt.
You may also like

Past indefinite Tense Example Sentences in English

Example Sentences of Present Continuous Tense

Present indefinite Tense Examples Sentences in English

Abstract Nouns List A to Z in English | 500+ Abstract...

Proper Nouns List A to Z | 500+ Proper Nouns

Common Nouns List A to Z | 500+ Common Nouns
About the author.
mrmrsenglish.com
Leave a comment x.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech
The 8 Parts of Speech | Chart, Definition & Examples

A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, “laugh” can be a noun (e.g., “I like your laugh”) or a verb (e.g., “don’t laugh”).
Table of contents
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Other parts of speech
Interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., “jump”), occurrence (e.g., “become”), or state of being (e.g., “exist”). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., simple past), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding“-ed” to the end of the word (or “-d” if the word already ends in “e”). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
“I’ve already checked twice.”
“I heard that you used to sing .”
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., “a red hat”), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like “to be” (e.g., “the hat is red ”).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding “-ly” to the end of an adjective (e.g., “slow” becomes “slowly”), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., “at”) or phrase (e.g., “on top of”) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
- Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., “the door,” “the energy,” “the mountains”).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., “a poster,” “an engine”).
There’s a concert this weekend.
If you want to know more about nouns , pronouns , verbs , and other parts of speech, make sure to check out some of our language articles with explanations and examples.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Types of verbs
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., “a dog,” “an island”).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., “ in the field”)
- Noun (e.g., “I have an in with that company”)
- Adjective (e.g., “Tim is part of the in crowd”)
- Adverb (e.g., “Will you be in this evening?”)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., “a cup and plate”), or two adjectives (e.g., “strong and smart”). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use "The", "A" or "An"
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, understanding the 8 parts of speech: definitions and examples.
General Education
If you’re trying to learn the grammatical rules of English, you’ve probably been asked to learn the parts of speech. But what are parts of speech and how many are there? How do you know which words are classified in each part of speech?
The answers to these questions can be a bit complicated—English is a difficult language to learn and understand. Don’t fret, though! We’re going to answer each of these questions for you with a full guide to the parts of speech that explains the following:
- What the parts of speech are, including a comprehensive parts of speech list
- Parts of speech definitions for the individual parts of speech. (If you’re looking for information on a specific part of speech, you can search for it by pressing Command + F, then typing in the part of speech you’re interested in.)
- Parts of speech examples
- A ten question quiz covering parts of speech definitions and parts of speech examples
We’ve got a lot to cover, so let’s begin!
Feature Image: (Gavina S / Wikimedia Commons)

What Are Parts of Speech?
The parts of speech definitions in English can vary, but here’s a widely accepted one: a part of speech is a category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences.
To make that definition even simpler, a part of speech is just a category for similar types of words . All of the types of words included under a single part of speech function in similar ways when they’re used properly in sentences.
In the English language, it’s commonly accepted that there are 8 parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions, interjections, and prepositions. Each of these categories plays a different role in communicating meaning in the English language. Each of the eight parts of speech—which we might also call the “main classes” of speech—also have subclasses. In other words, we can think of each of the eight parts of speech as being general categories for different types within their part of speech . There are different types of nouns, different types of verbs, different types of adjectives, adverbs, pronouns...you get the idea.
And that’s an overview of what a part of speech is! Next, we’ll explain each of the 8 parts of speech—definitions and examples included for each category.

There are tons of nouns in this picture. Can you find them all?
Nouns are a class of words that refer, generally, to people and living creatures, objects, events, ideas, states of being, places, and actions. You’ve probably heard English nouns referred to as “persons, places, or things.” That definition is a little simplistic, though—while nouns do include people, places, and things, “things” is kind of a vague term. I t’s important to recognize that “things” can include physical things—like objects or belongings—and nonphysical, abstract things—like ideas, states of existence, and actions.
Since there are many different types of nouns, we’ll include several examples of nouns used in a sentence while we break down the subclasses of nouns next!
Subclasses of Nouns, Including Examples
As an open class of words, the category of “nouns” has a lot of subclasses. The most common and important subclasses of nouns are common nouns, proper nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, collective nouns, and count and mass nouns. Let’s break down each of these subclasses!
Common Nouns and Proper Nouns
Common nouns are generic nouns—they don’t name specific items. They refer to people (the man, the woman), living creatures (cat, bird), objects (pen, computer, car), events (party, work), ideas (culture, freedom), states of being (beauty, integrity), and places (home, neighborhood, country) in a general way.
Proper nouns are sort of the counterpart to common nouns. Proper nouns refer to specific people, places, events, or ideas. Names are the most obvious example of proper nouns, like in these two examples:
Common noun: What state are you from?
Proper noun: I’m from Arizona .
Whereas “state” is a common noun, Arizona is a proper noun since it refers to a specific state. Whereas “the election” is a common noun, “Election Day” is a proper noun. Another way to pick out proper nouns: the first letter is often capitalized. If you’d capitalize the word in a sentence, it’s almost always a proper noun.
Concrete Nouns and Abstract Nouns
Concrete nouns are nouns that can be identified through the five senses. Concrete nouns include people, living creatures, objects, and places, since these things can be sensed in the physical world. In contrast to concrete nouns, abstract nouns are nouns that identify ideas, qualities, concepts, experiences, or states of being. Abstract nouns cannot be detected by the five senses. Here’s an example of concrete and abstract nouns used in a sentence:
Concrete noun: Could you please fix the weedeater and mow the lawn ?
Abstract noun: Aliyah was delighted to have the freedom to enjoy the art show in peace .
See the difference? A weedeater and the lawn are physical objects or things, and freedom and peace are not physical objects, though they’re “things” people experience! Despite those differences, they all count as nouns.
Collective Nouns, Count Nouns, and Mass Nouns
Nouns are often categorized based on number and amount. Collective nouns are nouns that refer to a group of something—often groups of people or a type of animal. Team , crowd , and herd are all examples of collective nouns.
Count nouns are nouns that can appear in the singular or plural form, can be modified by numbers, and can be described by quantifying determiners (e.g. many, most, more, several). For example, “bug” is a count noun. It can occur in singular form if you say, “There is a bug in the kitchen,” but it can also occur in the plural form if you say, “There are many bugs in the kitchen.” (In the case of the latter, you’d call an exterminator...which is an example of a common noun!) Any noun that can accurately occur in one of these singular or plural forms is a count noun.
Mass nouns are another type of noun that involve numbers and amount. Mass nouns are nouns that usually can’t be pluralized, counted, or quantified and still make sense grammatically. “Charisma” is an example of a mass noun (and an abstract noun!). For example, you could say, “They’ve got charisma, ” which doesn’t imply a specific amount. You couldn’t say, “They’ve got six charismas, ” or, “They’ve got several charismas .” It just doesn’t make sense!

Verbs are all about action...just like these runners.
A verb is a part of speech that, when used in a sentence, communicates an action, an occurrence, or a state of being . In sentences, verbs are the most important part of the predicate, which explains or describes what the subject of the sentence is doing or how they are being. And, guess what? All sentences contain verbs!
There are many words in the English language that are classified as verbs. A few common verbs include the words run, sing, cook, talk, and clean. These words are all verbs because they communicate an action performed by a living being. We’ll look at more specific examples of verbs as we discuss the subclasses of verbs next!
Subclasses of Verbs, Including Examples
Like nouns, verbs have several subclasses. The subclasses of verbs include copular or linking verbs, intransitive verbs, transitive verbs, and ditransitive or double transitive verbs. Let’s dive into these subclasses of verbs!
Copular or Linking Verbs
Copular verbs, or linking verbs, are verbs that link a subject with its complement in a sentence. The most familiar linking verb is probably be. Here’s a list of other common copular verbs in English: act, be, become, feel, grow, seem, smell, and taste.
So how do copular verbs work? Well, in a sentence, if we said, “Michi is ,” and left it at that, it wouldn’t make any sense. “Michi,” the subject, needs to be connected to a complement by the copular verb “is.” Instead, we could say, “Michi is leaving.” In that instance, is links the subject of the sentence to its complement.
Transitive Verbs, Intransitive Verbs, and Ditransitive Verbs
Transitive verbs are verbs that affect or act upon an object. When unattached to an object in a sentence, a transitive verb does not make sense. Here’s an example of a transitive verb attached to (and appearing before) an object in a sentence:
Please take the clothes to the dry cleaners.
In this example, “take” is a transitive verb because it requires an object—”the clothes”—to make sense. “The clothes” are the objects being taken. “Please take” wouldn’t make sense by itself, would it? That’s because the transitive verb “take,” like all transitive verbs, transfers its action onto another being or object.
Conversely, intransitive verbs don’t require an object to act upon in order to make sense in a sentence. These verbs make sense all on their own! For instance, “They ran ,” “We arrived ,” and, “The car stopped ” are all examples of sentences that contain intransitive verbs.
Finally, ditransitive verbs, or double transitive verbs, are a bit more complicated. Ditransitive verbs are verbs that are followed by two objects in a sentence . One of the objects has the action of the ditransitive verb done to it, and the other object has the action of the ditransitive verb directed towards it. Here’s an example of what that means in a sentence:
I cooked Nathan a meal.
In this example, “cooked” is a ditransitive verb because it modifies two objects: Nathan and meal . The meal has the action of “cooked” done to it, and “Nathan” has the action of the verb directed towards him.

Adjectives are descriptors that help us better understand a sentence. A common adjective type is color.
#3: Adjectives
Here’s the simplest definition of adjectives: adjectives are words that describe other words . Specifically, adjectives modify nouns and noun phrases. In sentences, adjectives appear before nouns and pronouns (they have to appear before the words they describe!).
Adjectives give more detail to nouns and pronouns by describing how a noun looks, smells, tastes, sounds, or feels, or its state of being or existence. . For example, you could say, “The girl rode her bike.” That sentence doesn’t have any adjectives in it, but you could add an adjective before both of the nouns in the sentence—”girl” and “bike”—to give more detail to the sentence. It might read like this: “The young girl rode her red bike.” You can pick out adjectives in a sentence by asking the following questions:
- Which one?
- What kind?
- How many?
- Whose’s?
We’ll look at more examples of adjectives as we explore the subclasses of adjectives next!
Subclasses of Adjectives, Including Examples
Subclasses of adjectives include adjective phrases, comparative adjectives, superlative adjectives, and determiners (which include articles, possessive adjectives, and demonstratives).
Adjective Phrases
An adjective phrase is a group of words that describe a noun or noun phrase in a sentence. Adjective phrases can appear before the noun or noun phrase in a sentence, like in this example:
The extremely fragile vase somehow did not break during the move.
In this case, extremely fragile describes the vase. On the other hand, adjective phrases can appear after the noun or noun phrase in a sentence as well:
The museum was somewhat boring.
Again, the phrase somewhat boring describes the museum. The takeaway is this: adjective phrases describe the subject of a sentence with greater detail than an individual adjective.
Comparative Adjectives and Superlative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives are used in sentences where two nouns are compared. They function to compare the differences between the two nouns that they modify. In sentences, comparative adjectives often appear in this pattern and typically end with -er. If we were to describe how comparative adjectives function as a formula, it might look something like this:
Noun (subject) + verb + comparative adjective + than + noun (object).
Here’s an example of how a comparative adjective would work in that type of sentence:
The horse was faster than the dog.
The adjective faster compares the speed of the horse to the speed of the dog. Other common comparative adjectives include words that compare distance ( higher, lower, farther ), age ( younger, older ), size and dimensions ( bigger, smaller, wider, taller, shorter ), and quality or feeling ( better, cleaner, happier, angrier ).
Superlative adjectives are adjectives that describe the extremes of a quality that applies to a subject being compared to a group of objects . Put more simply, superlative adjectives help show how extreme something is. In sentences, superlative adjectives usually appear in this structure and end in -est :
Noun (subject) + verb + the + superlative adjective + noun (object).
Here’s an example of a superlative adjective that appears in that type of sentence:
Their story was the funniest story.
In this example, the subject— story —is being compared to a group of objects—other stories. The superlative adjective “funniest” implies that this particular story is the funniest out of all the stories ever, period. Other common superlative adjectives are best, worst, craziest, and happiest... though there are many more than that!
It’s also important to know that you can often omit the object from the end of the sentence when using superlative adjectives, like this: “Their story was the funniest.” We still know that “their story” is being compared to other stories without the object at the end of the sentence.
Determiners
The last subclass of adjectives we want to look at are determiners. Determiners are words that determine what kind of reference a noun or noun phrase makes. These words are placed in front of nouns to make it clear what the noun is referring to. Determiners are an example of a part of speech subclass that contains a lot of subclasses of its own. Here is a list of the different types of determiners:
- Definite article: the
- Indefinite articles : a, an
- Demonstratives: this, that, these, those
- Pronouns and possessive determiners: my, your, his, her, its, our, their
- Quantifiers : a little, a few, many, much, most, some, any, enough
- Numbers: one, twenty, fifty
- Distributives: all, both, half, either, neither, each, every
- Difference words : other, another
- Pre-determiners: such, what, rather, quite
Here are some examples of how determiners can be used in sentences:
Definite article: Get in the car.
Demonstrative: Could you hand me that magazine?
Possessive determiner: Please put away your clothes.
Distributive: He ate all of the pie.
Though some of the words above might not seem descriptive, they actually do describe the specificity and definiteness, relationship, and quantity or amount of a noun or noun phrase. For example, the definite article “the” (a type of determiner) indicates that a noun refers to a specific thing or entity. The indefinite article “an,” on the other hand, indicates that a noun refers to a nonspecific entity.
One quick note, since English is always more complicated than it seems: while articles are most commonly classified as adjectives, they can also function as adverbs in specific situations, too. Not only that, some people are taught that determiners are their own part of speech...which means that some people are taught there are 9 parts of speech instead of 8!
It can be a little confusing, which is why we have a whole article explaining how articles function as a part of speech to help clear things up .

Adverbs can be used to answer questions like "when?" and "how long?"
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives (including determiners), clauses, prepositions, and sentences. Adverbs typically answer the questions how?, in what way?, when?, where?, and to what extent? In answering these questions, adverbs function to express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty . Adverbs can answer these questions in the form of single words, or in the form of adverbial phrases or adverbial clauses.
Adverbs are commonly known for being words that end in -ly, but there’s actually a bit more to adverbs than that, which we’ll dive into while we look at the subclasses of adverbs!
Subclasses Of Adverbs, Including Examples
There are many types of adverbs, but the main subclasses we’ll look at are conjunctive adverbs, and adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency.
Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs look like coordinating conjunctions (which we’ll talk about later!), but they are actually their own category: conjunctive adverbs are words that connect independent clauses into a single sentence . These adverbs appear after a semicolon and before a comma in sentences, like in these two examples:
She was exhausted; nevertheless , she went for a five mile run.
They didn’t call; instead , they texted.
Though conjunctive adverbs are frequently used to create shorter sentences using a semicolon and comma, they can also appear at the beginning of sentences, like this:
He chopped the vegetables. Meanwhile, I boiled the pasta.
One thing to keep in mind is that conjunctive adverbs come with a comma. When you use them, be sure to include a comma afterward!
There are a lot of conjunctive adverbs, but some common ones include also, anyway, besides, finally, further, however, indeed, instead, meanwhile, nevertheless, next, nonetheless, now, otherwise, similarly, then, therefore, and thus.
Adverbs of Place, Time, Manner, Degree, and Frequency
There are also adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency. Each of these types of adverbs express a different kind of meaning.
Adverbs of place express where an action is done or where an event occurs. These are used after the verb, direct object, or at the end of a sentence. A sentence like “She walked outside to watch the sunset” uses outside as an adverb of place.
Adverbs of time explain when something happens. These adverbs are used at the beginning or at the end of sentences. In a sentence like “The game should be over soon,” soon functions as an adverb of time.
Adverbs of manner describe the way in which something is done or how something happens. These are the adverbs that usually end in the familiar -ly. If we were to write “She quickly finished her homework,” quickly is an adverb of manner.
Adverbs of degree tell us the extent to which something happens or occurs. If we were to say “The play was quite interesting,” quite tells us the extent of how interesting the play was. Thus, quite is an adverb of degree.
Finally, adverbs of frequency express how often something happens . In a sentence like “They never know what to do with themselves,” never is an adverb of frequency.
Five subclasses of adverbs is a lot, so we’ve organized the words that fall under each category in a nifty table for you here:
It’s important to know about these subclasses of adverbs because many of them don’t follow the old adage that adverbs end in -ly.
Here's a helpful list of pronouns. (Attanata / Flickr )
#5: Pronouns
Pronouns are words that can be substituted for a noun or noun phrase in a sentence . Pronouns function to make sentences less clunky by allowing people to avoid repeating nouns over and over. For example, if you were telling someone a story about your friend Destiny, you wouldn’t keep repeating their name over and over again every time you referred to them. Instead, you’d use a pronoun—like they or them—to refer to Destiny throughout the story.
Pronouns are typically short words, often only two or three letters long. The most familiar pronouns in the English language are they, she, and he. But these aren’t the only pronouns. There are many more pronouns in English that fall under different subclasses!
Subclasses of Pronouns, Including Examples
There are many subclasses of pronouns, but the most commonly used subclasses are personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, indefinite pronouns, and interrogative pronouns.
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are probably the most familiar type of pronoun. Personal pronouns include I, me, you, she, her, him, he, we, us, they, and them. These are called personal pronouns because they refer to a person! Personal pronouns can replace specific nouns in sentences, like a person’s name, or refer to specific groups of people, like in these examples:
Did you see Gia pole vault at the track meet? Her form was incredible!
The Cycling Club is meeting up at six. They said they would be at the park.
In both of the examples above, a pronoun stands in for a proper noun to avoid repetitiveness. Her replaces Gia in the first example, and they replaces the Cycling Club in the second example.
(It’s also worth noting that personal pronouns are one of the easiest ways to determine what point of view a writer is using.)
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are used to indicate that something belongs to or is the possession of someone. The possessive pronouns fall into two categories: limiting and absolute. In a sentence, absolute possessive pronouns can be substituted for the thing that belongs to a person, and limiting pronouns cannot.
The limiting pronouns are my, your, its, his, her, our, their, and whose, and the absolute pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs . Here are examples of a limiting possessive pronoun and absolute possessive pronoun used in a sentence:
Limiting possessive pronoun: Juan is fixing his car.
In the example above, the car belongs to Juan, and his is the limiting possessive pronoun that shows the car belongs to Juan. Now, here’s an example of an absolute pronoun in a sentence:
Absolute possessive pronoun: Did you buy your tickets ? We already bought ours .
In this example, the tickets belong to whoever we is, and in the second sentence, ours is the absolute possessive pronoun standing in for the thing that “we” possess—the tickets.
Demonstrative Pronouns, Interrogative Pronouns, and Indefinite Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns include the words that, this, these, and those. These pronouns stand in for a noun or noun phrase that has already been mentioned in a sentence or conversation. This and these are typically used to refer to objects or entities that are nearby distance-wise, and that and those usually refer to objects or entities that are farther away. Here’s an example of a demonstrative pronoun used in a sentence:
The books are stacked up in the garage. Can you put those away?
The books have already been mentioned, and those is the demonstrative pronoun that stands in to refer to them in the second sentence above. The use of those indicates that the books aren’t nearby—they’re out in the garage. Here’s another example:
Do you need shoes? Here...you can borrow these.
In this sentence, these refers to the noun shoes. Using the word these tells readers that the shoes are nearby...maybe even on the speaker’s feet!
Indefinite pronouns are used when it isn’t necessary to identify a specific person or thing . The indefinite pronouns are one, other, none, some, anybody, everybody, and no one. Here’s one example of an indefinite pronoun used in a sentence:
Promise you can keep a secret?
Of course. I won’t tell anyone.
In this example, the person speaking in the second two sentences isn’t referring to any particular people who they won’t tell the secret to. They’re saying that, in general, they won’t tell anyone . That doesn’t specify a specific number, type, or category of people who they won’t tell the secret to, which is what makes the pronoun indefinite.
Finally, interrogative pronouns are used in questions, and these pronouns include who, what, which, and whose. These pronouns are simply used to gather information about specific nouns—persons, places, and ideas. Let’s look at two examples of interrogative pronouns used in sentences:
Do you remember which glass was mine?
What time are they arriving?
In the first glass, the speaker wants to know more about which glass belongs to whom. In the second sentence, the speaker is asking for more clarity about a specific time.

Conjunctions hook phrases and clauses together so they fit like pieces of a puzzle.
#6: Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that are used to connect words, phrases, clauses, and sentences in the English language. This function allows conjunctions to connect actions, ideas, and thoughts as well. Conjunctions are also used to make lists within sentences. (Conjunctions are also probably the most famous part of speech, since they were immortalized in the famous “Conjunction Junction” song from Schoolhouse Rock .)
You’re probably familiar with and, but, and or as conjunctions, but let’s look into some subclasses of conjunctions so you can learn about the array of conjunctions that are out there!
Subclasses of Conjunctions, Including Examples
Coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions are three subclasses of conjunctions. Each of these types of conjunctions functions in a different way in sentences!
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions are probably the most familiar type of conjunction. These conjunctions include the words for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so (people often recommend using the acronym FANBOYS to remember the seven coordinating conjunctions!).
Coordinating conjunctions are responsible for connecting two independent clauses in sentences, but can also be used to connect two words in a sentence. Here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two independent clauses in a sentence:
He wanted to go to the movies, but he couldn’t find his car keys.
They put on sunscreen, and they went to the beach.
Next, here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two words:
Would you like to cook or order in for dinner?
The storm was loud yet refreshing.
The two examples above show that coordinating conjunctions can connect different types of words as well. In the first example, the coordinating conjunction “or” connects two verbs; in the second example, the coordinating conjunction “yet” connects two adjectives.
But wait! Why does the first set of sentences have commas while the second set of sentences doesn’t? When using a coordinating conjunction, put a comma before the conjunction when it’s connecting two complete sentences . Otherwise, there’s no comma necessary.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are used to link an independent clause to a dependent clause in a sentence. This type of conjunction always appears at the beginning of a dependent clause, which means that subordinating conjunctions can appear at the beginning of a sentence or in the middle of a sentence following an independent clause. (If you’re unsure about what independent and dependent clauses are, be sure to check out our guide to compound sentences.)
Here is an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears at the beginning of a sentence:
Because we were hungry, we ordered way too much food.
Now, here’s an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears in the middle of a sentence, following an independent clause and a comma:
Rakim was scared after the power went out.
See? In the example above, the subordinating conjunction after connects the independent clause Rakim was scared to the dependent clause after the power went out. Subordinating conjunctions include (but are not limited to!) the following words: after, as, because, before, even though, one, since, unless, until, whenever, and while.
Correlative Conjunctions
Finally, correlative conjunctions are conjunctions that come in pairs, like both/and, either/or, and neither/nor. The two correlative conjunctions that come in a pair must appear in different parts of a sentence to make sense— they correlate the meaning in one part of the sentence with the meaning in another part of the sentence . Makes sense, right?
Here are two examples of correlative conjunctions used in a sentence:
We’re either going to the Farmer’s Market or the Natural Grocer’s for our shopping today.
They’re going to have to get dog treats for both Piper and Fudge.
Other pairs of correlative conjunctions include as many/as, not/but, not only/but also, rather/than, such/that, and whether/or.

Interjections are single words that express emotions that end in an exclamation point. Cool!
#7: Interjections
Interjections are words that often appear at the beginning of sentences or between sentences to express emotions or sentiments such as excitement, surprise, joy, disgust, anger, or even pain. Commonly used interjections include wow!, yikes!, ouch!, or ugh! One clue that an interjection is being used is when an exclamation point appears after a single word (but interjections don’t have to be followed by an exclamation point). And, since interjections usually express emotion or feeling, they’re often referred to as being exclamatory. Wow!
Interjections don’t come together with other parts of speech to form bigger grammatical units, like phrases or clauses. There also aren’t strict rules about where interjections should appear in relation to other sentences . While it’s common for interjections to appear before sentences that describe an action or event that the interjection helps explain, interjections can appear after sentences that contain the action they’re describing as well.
Subclasses of Interjections, Including Examples
There are two main subclasses of interjections: primary interjections and secondary interjections. Let’s take a look at these two types of interjections!
Primary Interjections
Primary interjections are single words, like oh!, wow!, or ouch! that don’t enter into the actual structure of a sentence but add to the meaning of a sentence. Here’s an example of how a primary interjection can be used before a sentence to add to the meaning of the sentence that follows it:
Ouch ! I just burned myself on that pan!
While someone who hears, I just burned myself on that pan might assume that the person who said that is now in pain, the interjection Ouch! makes it clear that burning oneself on the pan definitely was painful.
Secondary Interjections
Secondary interjections are words that have other meanings but have evolved to be used like interjections in the English language and are often exclamatory. Secondary interjections can be mixed with greetings, oaths, or swear words. In many cases, the use of secondary interjections negates the original meaning of the word that is being used as an interjection. Let’s look at a couple of examples of secondary interjections here:
Well , look what the cat dragged in!
Heck, I’d help if I could, but I’ve got to get to work.
You probably know that the words well and heck weren’t originally used as interjections in the English language. Well originally meant that something was done in a good or satisfactory way, or that a person was in good health. Over time and through repeated usage, it’s come to be used as a way to express emotion, such as surprise, anger, relief, or resignation, like in the example above.

This is a handy list of common prepositional phrases. (attanatta / Flickr)
#8: Prepositions
The last part of speech we’re going to define is the preposition. Prepositions are words that are used to connect other words in a sentence—typically nouns and verbs—and show the relationship between those words. Prepositions convey concepts such as comparison, position, place, direction, movement, time, possession, and how an action is completed.
Subclasses of Prepositions, Including Examples
The subclasses of prepositions are simple prepositions, double prepositions, participle prepositions, and prepositional phrases.
Simple Prepositions
Simple prepositions appear before and between nouns, adjectives, or adverbs in sentences to convey relationships between people, living creatures, things, or places . Here are a couple of examples of simple prepositions used in sentences:
I’ll order more ink before we run out.
Your phone was beside your wallet.
In the first example, the preposition before appears between the noun ink and the personal pronoun we to convey a relationship. In the second example, the preposition beside appears between the verb was and the possessive pronoun your.
In both examples, though, the prepositions help us understand how elements in the sentence are related to one another. In the first sentence, we know that the speaker currently has ink but needs more before it’s gone. In the second sentence, the preposition beside helps us understand how the wallet and the phone are positioned relative to one another!
Double Prepositions
Double prepositions are exactly what they sound like: two prepositions joined together into one unit to connect phrases, nouns, and pronouns with other words in a sentence. Common examples of double prepositions include outside of, because of, according to, next to, across from, and on top of. Here is an example of a double preposition in a sentence:
I thought you were sitting across from me.
You see? Across and from both function as prepositions individually. When combined together in a sentence, they create a double preposition. (Also note that the prepositions help us understand how two people— you and I— are positioned with one another through spacial relationship.)
Prepositional Phrases
Finally, prepositional phrases are groups of words that include a preposition and a noun or pronoun. Typically, the noun or pronoun that appears after the preposition in a prepositional phrase is called the object of the preposition. The object always appears at the end of the prepositional phrase. Additionally, prepositional phrases never include a verb or a subject. Here are two examples of prepositional phrases:
The cat sat under the chair .
In the example above, “under” is the preposition, and “the chair” is the noun, which functions as the object of the preposition. Here’s one more example:
We walked through the overgrown field .
Now, this example demonstrates one more thing you need to know about prepositional phrases: they can include an adjective before the object. In this example, “through” is the preposition, and “field” is the object. “Overgrown” is an adjective that modifies “the field,” and it’s quite common for adjectives to appear in prepositional phrases like the one above.
While that might sound confusing, don’t worry: the key is identifying the preposition in the first place! Once you can find the preposition, you can start looking at the words around it to see if it forms a compound preposition, a double preposition of a prepositional phrase.

10 Question Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples
Since we’ve covered a lot of material about the 8 parts of speech with examples ( a lot of them!), we want to give you an opportunity to review and see what you’ve learned! While it might seem easier to just use a parts of speech finder instead of learning all this stuff, our parts of speech quiz can help you continue building your knowledge of the 8 parts of speech and master each one.
Are you ready? Here we go:
1) What are the 8 parts of speech?
a) Noun, article, adverb, antecedent, verb, adjective, conjunction, interjection b) Noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, determiner, clause, adjective, preposition c) Noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, conjunction, interjection, preposition
2) Which parts of speech have subclasses?
a) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs b) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, and prepositions c) All of them! There are many types of words within each part of speech.
3) What is the difference between common nouns and proper nouns?
a) Common nouns don’t refer to specific people, places, or entities, but proper nouns do refer to specific people, places, or entities. b) Common nouns refer to regular, everyday people, places, or entities, but proper nouns refer to famous people, places, or entities. c) Common nouns refer to physical entities, like people, places, and objects, but proper nouns refer to nonphysical entities, like feelings, ideas, and experiences.
4) In which of the following sentences is the emboldened word a verb?
a) He was frightened by the horror film . b) He adjusted his expectations after the first plan fell through. c) She walked briskly to get there on time.
5) Which of the following is a correct definition of adjectives, and what other part of speech do adjectives modify?
a) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns and noun phrases. b) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify verbs and adverbs. c) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns, verbs, and adverbs.
6) Which of the following describes the function of adverbs in sentences?
a) Adverbs express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty. b) Adverbs express an action performed by a subject. c) Adverbs describe nouns and noun phrases.
7) Which of the following answers contains a list of personal pronouns?
a) This, that, these, those b) I, you, me, we, he, she, him, her, they, them c) Who, what, which, whose
8) Where do interjections typically appear in a sentence?
a) Interjections can appear at the beginning of or in between sentences. b) Interjections appear at the end of sentences. c) Interjections appear in prepositional phrases.
9) Which of the following sentences contains a prepositional phrase?
a) The dog happily wagged his tail. b) The cow jumped over the moon. c) She glared, angry that he forgot the flowers.
10) Which of the following is an accurate definition of a “part of speech”?
a) A category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences. b) A category of words that are of similar length and spelling. c) A category of words that mean the same thing.
So, how did you do? If you got 1C, 2C, 3A, 4B, 5A, 6A, 7B, 8A, 9B, and 10A, you came out on top! There’s a lot to remember where the parts of speech are concerned, and if you’re looking for more practice like our quiz, try looking around for parts of speech games or parts of speech worksheets online!

What’s Next?
You might be brushing up on your grammar so you can ace the verbal portions of the SAT or ACT. Be sure you check out our guides to the grammar you need to know before you tackle those tests! Here’s our expert guide to the grammar rules you need to know for the SAT , and this article teaches you the 14 grammar rules you’ll definitely see on the ACT.
When you have a good handle on parts of speech, it can make writing essays tons easier. Learn how knowing parts of speech can help you get a perfect 12 on the ACT Essay (or an 8/8/8 on the SAT Essay ).
While we’re on the topic of grammar: keep in mind that knowing grammar rules is only part of the battle when it comes to the verbal and written portions of the SAT and ACT. Having a good vocabulary is also important to making the perfect score ! Here are 262 vocabulary words you need to know before you tackle your standardized tests.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Page Content
- Sidebar Content
- Main Navigation
- Quick links
- All TIP Sheets
The Eight Parts of Speech
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
- Basic Sentence Structure
- Sentence Fragments
- Run-on Sentences and Comma Splices
- Sentence Type and Purpose
- Independent and Dependent Clauses: Coordination and Subordination
- Subject Verb Agreement
- Consistent Verb Tense
- Other Phrases: Verbal, Appositive, Absolute
- Pronoun Reference
- Relative Pronouns: Restrictive and Nonrestrictive Clauses
- Avoiding Modifier Problems
- Transitions
- Would, Should, Could
- Achieving Parallelism
- Definite and Indefinite Articles
- Two-Word Verbs
TIP Sheet THE EIGHT PARTS OF SPEECH
There are eight parts of speech in the English language: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. The part of speech indicates how the word functions in meaning as well as grammatically within the sentence. An individual word can function as more than one part of speech when used in different circumstances. Understanding parts of speech is essential for determining the correct definition of a word when using the dictionary.
1. NOUN
- A noun is the name of a person, place, thing, or idea.
man... Butte College... house... happiness
A noun is a word for a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are often used with an article ( the , a , an ), but not always. Proper nouns always start with a capital letter; common nouns do not. Nouns can be singular or plural, concrete or abstract. Nouns show possession by adding 's . Nouns can function in different roles within a sentence; for example, a noun can be a subject, direct object, indirect object, subject complement, or object of a preposition.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher , and then she quickly disappeared. Oh my!
See the TIP Sheet on "Nouns" for further information.
2. PRONOUN
- A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun.
She... we... they... it
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. A pronoun is usually substituted for a specific noun, which is called its antecedent. In the sentence above, the antecedent for the pronoun she is the girl. Pronouns are further defined by type: personal pronouns refer to specific persons or things; possessive pronouns indicate ownership; reflexive pronouns are used to emphasize another noun or pronoun; relative pronouns introduce a subordinate clause; and demonstrative pronouns identify, point to, or refer to nouns.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher, and then she quickly disappeared. Oh my!
See the TIP Sheet on "Pronouns" for further information.
3. VERB
- A verb expresses action or being.
jump... is... write... become
The verb in a sentence expresses action or being. There is a main verb and sometimes one or more helping verbs. (" She can sing." Sing is the main verb; can is the helping verb.) A verb must agree with its subject in number (both are singular or both are plural). Verbs also take different forms to express tense.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher, and then she quickly disappeared . Oh my!
See the TIP Sheet on "Verbs" for more information.
4. ADJECTIVE
- An adjective modifies or describes a noun or pronoun.
pretty... old... blue... smart
An adjective is a word used to modify or describe a noun or a pronoun. It usually answers the question of which one, what kind, or how many. (Articles [a, an, the] are usually classified as adjectives.)
See the TIP Sheet on "Adjectives" for more information.
5. ADVERB
- An adverb modifies or describes a verb, an adjective, or another adverb.
gently... extremely... carefully... well
An adverb describes or modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb, but never a noun. It usually answers the questions of when, where, how, why, under what conditions, or to what degree. Adverbs often end in -ly.
See the TIP Sheet on "Adverbs" for more information.
6. PREPOSITION
- A preposition is a word placed before a noun or pronoun to form a phrase modifying another word in the sentence.
by... with.... about... until
(by the tree, with our friends, about the book, until tomorrow)
A preposition is a word placed before a noun or pronoun to form a phrase modifying another word in the sentence. Therefore a preposition is always part of a prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase almost always functions as an adjective or as an adverb. The following list includes the most common prepositions:
See the TIP Sheet on "Prepositions" for more information.
7. CONJUNCTION
- A conjunction joins words, phrases, or clauses.
and... but... or... while... because
A conjunction joins words, phrases, or clauses, and indicates the relationship between the elements joined. Coordinating conjunctions connect grammatically equal elements: and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet. Subordinating conjunctions connect clauses that are not equal: because, although, while, since, etc. There are other types of conjunctions as well.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher, and then she quickly disappeared. Oh my!
See the TIP Sheet on "Conjunctions" for more information.
8. INTERJECTION
- An interjection is a word used to express emotion.
Oh!... Wow!... Oops!
An interjection is a word used to express emotion. It is often followed by an exclamation point.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher, and then she quickly disappeared. Oh my !
See the TIP Sheet on "Interjections" for more information.
Home | Calendars | Library | Bookstore | Directory | Apply Now | Search for Classes | Register | Online Classes | MyBC Portal MyBC -->
Butte College | 3536 Butte Campus Drive, Oroville CA 95965 | General Information (530) 895-2511
- Types of Verbs
- Types of Adjectives
- Types of Noun
- Participles
- Phrases and Clauses
- Parts of Speech
- Parts of a Sentence
- Determiners
- Parallelism
- Direct & Indirect Speech
- Modal Verbs
- Relative Clauses
- Nominalisation
- Substitution & Ellipsis
- Demonstratives
- Pronoun Reference
- Confusing Words
- Online Grammar Quizzes
- Printable Grammar Worksheets
- Courses to purchase
- Grammar Book
- Grammar Blog
8 Parts of Speech
The 8 parts of speech in English are: Nouns, Adjectives, Adverbs, Verbs, Prepositions, Pronouns, Conjunctions, and Interjections.
A part of speech is a category of words that have similar grammatical functions or properties. In other words, they play similar roles in a sentence. For instance, a verb shows the action of a subject or the subject's state of being.

We'll now look in more detail at the function of each of these parts of speech.
Understanding the 8 Parts of Speech
Nouns are words used to talk about people, places, things, or ideas/concepts. Here are some examples:
- Person: The President
- Place: London
- Thing: Table
- Idea/concept: Neo-liberalism
So it may be naming something we can touch ( e.g. table; book; car ) or something we cannot touch ( e.g. Neo-liberalism; happiness; wish ).
There are both common nouns, used for classes of people, places, things, or ideas/concepts, and proper nouns, which is their given name, always with a capital letter.
Common Nouns
- political party
Proper Nouns
- Chester Avenue
Learn more about the various types of noun >>
Another of the 8 parts of speech are adjectives. They describe nouns or pronouns. They can come before or after the noun/pronoun they describe:
Absolute Adjectives
- The large shopping complex
- The excited child
- She is happy
- It was a shocking film
- Her dress was lovely
- He's a good-looking man
These are absolute adjectives , but they can also be comparative (comparing two or more things) or superlative (showing degree or quality):
Comparative Adjectives
- She's fitter than the others
- Their house is bigger
- I ran faster than you
- Cats are more agile than dogs
- Sue's more tired than Tim
Superlative Adjectives
- She's the fittest
- Their house is the biggest
- I ran the fastest
- Cats are the most agile
- Sue's the most tired
There are various other types of adjective. Learn more about the different types of adjectives >>
Adverbs modify verbs, other adverbs, and adjectives. There are adverbs of manner, time, place and degree . Here are examples of each being modified in relation to verbs, adverbs, and adjectives (the word being modified is underlined):
Adverbs Modifying Verbs
- He runs fast
- Ian quickly left the room
- She spoke slowly
Adverbs Modifying Other Adverbs
- He runs exceptionally fast
- Ian very quickly left the room
- She spoke extremely slowly
Adverbs Modifying Adjectives
- She's really excited
- He's happily married
- The elegantly designed dress is mine
Verbs form part of the predicate of a sentence.
In relation to the subject, they are used to express a physical action (e.g. walk; speak; show) or a mental action (e.g. think; feel; want). They can also express a state of being , mainly with the verb 'to be' but also some others.
Here are some examples:
Physical Action
- He ran home
- They chose the blue one
Mental Activity
- I am thinking about it
- Ian guessed the answer
- She believes in ghosts
State of Being
- She is a police woman
- They seem worried
These though are main verbs. They have many other uses in a sentence so you should read about all the types of verbs further.
Prepositions
Another of the 8 parts of speech are prepositions. These show the relationship between two words or phrases in a sentence. They precede a noun or pronoun.
Commons examples of prepositions are above, up, upon, at, before, behind, since, to, through, under, until, with, within, about, against, along, around, beside, between, down, during, below, by, except, for, from, in, into, like, near, of, off, on, toward.
In these example sentences with prepositions, the two words whose relationship is being expressed are underlined and the prepositions are in bold:
- The book is on the table
- He is the leader of the conservative party
- The boy picked up the toy under the sofa
- This is a present for your mother
Pronouns replace nouns and they prevent us from repeating the noun in a sentence. These are the types of pronouns with some examples:
- Personal e.g. I; you; they; she
- Possessive e.g. mine; yours; his; theirs
- Relative e.g. who; which; that; whom
- Demonstrative e.g. this; these; those
- Reciprocal e.g. one another; each other
- Emphatic / Reflexive e.g. myself; herself; itself; ourselves
- Interrogative e.g. what; which; whom; whose
Here are some examples of these words used in sentences:
- Martha decided she would leave
- Why don't you use his car instead of mine
- Mick is a person who learns quickly
- Shall we buy some of these ?
- They began to argue with each other
- Jenny is pleased with herself
- What time is he coming?
Conjunctions
Conjunctions are the of the 8 parts of speech responsible for joining together words, phrases, or clauses. There are three types:
- Coordinating: and; or; but; so; yet; for; nor
- Correlative: neither/nor; either/or; not only/but also
- Subordinating: e.g. although; because; while; which; where; until
Coordinating Conjunctions
Used to connect like for like words (e.g. noun+noun):
- I like apples and oranges ( 2 nouns )
- His speech was slow but effective ( 2 adjectives )
- Shall I say it loudly or quietly? ( 2 adverbs )
Or simple sentences (independent clauses):
- I find the music annoying but she finds It pleasant
- She came to the lecture late so she missed everything important
- She took her umbrella for it was raining hard
Correlative Conjunctions
Used to join alternative or equal elements:
- He felt neither happy nor sad about it
- Sue had to decide to either quit or carry on
- I went not only to Australia but also to New Zealand
Subordinating Conjunctions
Used to join subordinate clauses to main clauses:
- The government won't vote on the bill until both parties agree
- I'm still not tired although it is late
- I'll eat the dish which you don't like
Interjections
Interjections are words used to express an emotion or a sentiment such as surprise, joy, disgust, fear, excitement, pain, or enthusiasm.
They usually appear at the start of a sentence and are not connected to it grammatically. Here are some examples of interjections in sentences:
- Wow , that's an amazing score!
- Oh , I didn't know you failed the exam
- Well , we better not leave too late
- Ow , that really hurt!
- Ah , I understand now
- Oops , I've forgotten to bring the sandwiches
Are there only 8 Parts of Speech?
Sometimes rather than 8 parts of speech, you may see 9 or 10 listed. This is because some people treat articles and determiners as separate categories.
However, when there are only 8 parts of speech considered (as above), this is because as these two types of word modify nouns, they are classified under adjectives.
Now practice what you have learned in our identifying parts of speech quiz
More on Sentence Structure:

Parallelism Grammar Rules (Parallel Structure)
Parallelism is about balancing the grammatical structure of words, phrases and clauses in your sentences. Parallel structure will improve your writing's coherence.

Direct and Indirect Objects: The Differences
Direct and indirect objects are key parts of most sentences. A direct object is the receiver of action while indirect object identifies to or for whom or what the action of the verb is performed.

Subject Complements: Predicate Adjectives and Predicate Nominatives
Here we demystify subject complements, predicate adjectives, and predicate nominatives with simple explanations and examples.

Examples of Parallelism in English Grammar
View examples of parallelism in English grammar that show you correct and incorrect parallel sentences.

Types of Clauses in English Grammar - Independent and Dependent Clause
The two types of clauses in English grammar are the independent and dependent clause. Both have a subject and verb which makes them clauses, but while independent clauses express a complete thought, dependent clauses do not. This is the main distinction.

Nominalisation in English Grammar: High Level Writing Tips
Nominalisation is an important aspect of academic writing. This lesson teachers you what this is and how you can use it effectively in your writing.

Parts of a Sentence: Subject, Verbs, Objects, Predicates, Complements
The main parts of a sentence are subjects, verbs, objects, predicates, and subject complements. All of these have a specific purpose within the structure of a sentence.

How to Use Either and Neither with Examples
Advice on how to use either and neither in English grammar. They can be adjectives, adverbs, pronouns and conjunctions.

Phrases and Clauses - Building good sentences
Phrases and clauses are the key building blocks of sentences. A clause contains a subject and a verb and can express a complete thought. A phrase does not contain a subject or verb.

Using Object Complements in a Sentence
Using object complements in a sentence enhances your ability to convey specific information about actions and their outcomes.
Sign up for free grammar tips, quizzes and lessons, straight into your inbox
New! Comments
Any questions or comments about the grammar discussed on this page?
Post your comment here.

Grammar Rules
Subscribe to grammar wiz:, grammar ebook.

This is an affiliate link
Recent Articles
Zero Article Rules with Examples
Apr 13, 24 02:33 AM
Definite, Indefinite and Zero Articles Explained
Apr 05, 24 09:40 AM
Definite and Indefinite Articles Quiz
Mar 30, 24 12:58 PM
Important Pages
Online Quizzes Courses Blog
Connect with Us
Search Site
Privacy Policy / Disclaimer / Terms of Use
- English Grammar
- Parts of Speech
Parts of Speech - Definition, 8 Types and Examples
In the English language , every word is called a part of speech. The role a word plays in a sentence denotes what part of speech it belongs to. Explore the definition of parts of speech, the different parts of speech and examples in this article.
Table of Contents
Parts of speech definition, different parts of speech with examples.
- Sentences Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
A Small Exercise to Check Your Understanding of Parts of Speech
Frequently asked questions on parts of speech, what is a part of speech.
Parts of speech are among the first grammar topics we learn when we are in school or when we start our English language learning process. Parts of speech can be defined as words that perform different roles in a sentence. Some parts of speech can perform the functions of other parts of speech too.
- The Oxford Learner’s Dictionary defines parts of speech as “one of the classes into which words are divided according to their grammar, such as noun, verb, adjective, etc.”
- The Cambridge Dictionary also gives a similar definition – “One of the grammatical groups into which words are divided, such as noun, verb, and adjective”.
Parts of speech include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections.
8 Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples:
1. Nouns are words that are used to name people, places, animals, ideas and things. Nouns can be classified into two main categories: Common nouns and Proper nouns . Common nouns are generic like ball, car, stick, etc., and proper nouns are more specific like Charles, The White House, The Sun, etc.
Examples of nouns used in sentences:
- She bought a pair of shoes . (thing)
- I have a pet. (animal)
- Is this your book ? (object)
- Many people have a fear of darkness . (ideas/abstract nouns)
- He is my brother . (person)
- This is my school . (place)
Also, explore Singular Nouns and Plural Nouns .
2. Pronouns are words that are used to substitute a noun in a sentence. There are different types of pronouns. Some of them are reflexive pronouns, possessive pronouns , relative pronouns and indefinite pronouns . I, he, she, it, them, his, yours, anyone, nobody, who, etc., are some of the pronouns.
Examples of pronouns used in sentences:
- I reached home at six in the evening. (1st person singular pronoun)
- Did someone see a red bag on the counter? (Indefinite pronoun)
- Is this the boy who won the first prize? (Relative pronoun)
- That is my mom. (Possessive pronoun)
- I hurt myself yesterday when we were playing cricket. (Reflexive pronoun)
3. Verbs are words that denote an action that is being performed by the noun or the subject in a sentence. They are also called action words. Some examples of verbs are read, sit, run, pick, garnish, come, pitch, etc.
Examples of verbs used in sentences:
- She plays cricket every day.
- Darshana and Arul are going to the movies.
- My friends visited me last week.
- Did you have your breakfast?
- My name is Meenakshi Kishore.
4. Adverbs are words that are used to provide more information about verbs, adjectives and other adverbs used in a sentence. There are five main types of adverbs namely, adverbs of manner , adverbs of degree , adverbs of frequency , adverbs of time and adverbs of place . Some examples of adverbs are today, quickly, randomly, early, 10 a.m. etc.
Examples of adverbs used in sentences:
- Did you come here to buy an umbrella? (Adverb of place)
- I did not go to school yesterday as I was sick. (Adverb of time)
- Savio reads the newspaper everyday . (Adverb of frequency)
- Can you please come quickly ? (Adverb of manner)
- Tony was so sleepy that he could hardly keep his eyes open during the meeting. (Adverb of degree)
5. Adjectives are words that are used to describe or provide more information about the noun or the subject in a sentence. Some examples of adjectives include good, ugly, quick, beautiful, late, etc.
Examples of adjectives used in sentences:
- The place we visited yesterday was serene .
- Did you see how big that dog was?
- The weather is pleasant today.
- The red dress you wore on your birthday was lovely.
- My brother had only one chapati for breakfast.
6. Prepositions are words that are used to link one part of the sentence to another. Prepositions show the position of the object or subject in a sentence. Some examples of prepositions are in, out, besides, in front of, below, opposite, etc.
Examples of prepositions used in sentences:
- The teacher asked the students to draw lines on the paper so that they could write in straight lines.
- The child hid his birthday presents under his bed.
- Mom asked me to go to the store near my school.
- The thieves jumped over the wall and escaped before we could reach home.
7. Conjunctions are a part of speech that is used to connect two different parts of a sentence, phrases and clauses . Some examples of conjunctions are and, or, for, yet, although, because, not only, etc.
Examples of conjunctions used in sentences:
- Meera and Jasmine had come to my birthday party.
- Jane did not go to work as she was sick.
- Unless you work hard, you cannot score good marks.
- I have not finished my project, yet I went out with my friends.
8. Interjections are words that are used to convey strong emotions or feelings. Some examples of interjections are oh, wow, alas, yippee, etc. It is always followed by an exclamation mark.
Examples of interjections used in sentences:
- Wow ! What a wonderful work of art.
- Alas ! That is really sad.
- Yippee ! We won the match.
Sentence Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
- Noun – Tom lives in New York .
- Pronoun – Did she find the book she was looking for?
- Verb – I reached home.
- Adverb – The tea is too hot.
- Adjective – The movie was amazing .
- Preposition – The candle was kept under the table.
- Conjunction – I was at home all day, but I am feeling very tired.
- Interjection – Oh ! I forgot to turn off the stove.
Let us find out if you have understood the different parts of speech and their functions. Try identifying which part of speech the highlighted words belong to.
- My brother came home late .
- I am a good girl.
- This is the book I was looking for.
- Whoa ! This is amazing .
- The climate in Kodaikanal is very pleasant.
- Can you please pick up Dan and me on your way home?
Now, let us see if you got it right. Check your answers.
- My – Pronoun, Home – Noun, Late – Adverb
- Am – Verb, Good – Adjective
- I – Pronoun, Was looking – Verb
- Whoa – Interjection, Amazing – Adjective
- Climate – Noun, In – Preposition, Kodaikanal – Noun, Very – Adverb
- And – Conjunction, On – Preposition, Your – Pronoun
What are parts of speech?
The term ‘parts of speech’ refers to words that perform different functions in a sentence in order to give the sentence a proper meaning and structure.
How many parts of speech are there?
There are 8 parts of speech in total.
What are the 8 parts of speech?
Nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections are the 8 parts of speech.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech
The 8 Parts of Speech | Definition & Examples
A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyse how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, ‘laugh’ can be a noun (e.g., ‘I like your laugh’) or a verb (e.g., ‘don’t laugh’).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, other parts of speech, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., ‘jump’), occurrence (e.g., ‘become’), or state of being (e.g., ‘exist’). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., past simple ), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding’-ed’ to the end of the word (or ‘-d’ if the word already ends in ‘e’). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
‘I’ve already checked twice’.
‘I heard that you used to sing ‘.
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., ‘a red hat’), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like ‘to be’ (e.g., ‘the hat is red ‘).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding ‘-ly’ to the end of an adjective (e.g., ‘slow’ becomes ‘slowly’), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., ‘at’) or phrase (e.g., ‘on top of’) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., ‘the door’, ‘the energy’, ‘the mountains’).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., ‘a poster’, ‘an engine’).
There’s a concert this weekend.
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., ‘a dog’, ‘an island’).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., ‘ in the field’)
- Noun (e.g., ‘I have an in with that company’)
- Adjective (e.g., ‘Tim is part of the in crowd’)
- Adverb (e.g., ‘Will you be in this evening?’)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., ‘a cup and plate’), or two adjectives (e.g., ‘strong and smart’). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use 'The', 'A' or 'An'
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types

The 8 Parts of Speech
You probably began learning about the eight parts of speech in second grade. You learned that your big sister, Disney World, and the duckbilled platypus are all nouns, for example. The thing is, you’ve probably also forgotten much of what you learned in elementary school. Seriously, how many dinosaurs can you name? Because pint-sized you could rattle off a dozen theropods faster than present-day you can Google “What the heck’s a theropod?”
If the 8 parts of speech are currently occupying a dusty corner of your mind, right alongside the dilophosaurus, then this refresher is for you.

What Are the 8 Parts of Speech?
There are, in fact, eight parts of speech. That’s not too many, right? Here is a simple guide to the 8 parts of speech and examples of each.
1. Adjectives
Adjectives modify nouns and pronouns. You probably know that they’re used to describe, but they can also quantify, identify, and limit.
Check out the examples of this part of speech:
Brett ate nine tacos.
In this example, nine quantifies tacos . It also limits the number of tacos — even if Brett knows no limits when it comes to portion control.
The disgruntled grandma threw snowballs at the teenagers next door.
Disgruntled describes the grandma who wants the kids to turn down the Cardi B already, for crying out loud.
Just like its cousin the adjective, adverbs are used to describe. The difference? Adverbs can modify verbs, adjectives, and even other adverbs. Oh, the power!
Here are some examples of this part of speech:
After eating nine tacos, Brett threw up violently.
In this example, violently describes the verb phrase threw up . Gross.
The extremely disgruntled grandma threw snowballs at the teenagers next door.
Here, the adverb extremely describes the adjective disgruntled . Because Grandma, frankly, has had it.
Adverbs often end in – ly , but they don’t have to. In fact, adverbs can be phrases, too. Generally speaking, adverbs are expertly deployed to answer one of the following questions:
- When? (tomorrow; when the mayor called; now)
- Where? (there; to Target; in your ear)
- How? (sneakily; slowly; angrily)
- To what extent? (highest; most attractive)
- In what manner? (backwards; like he hadn’t eaten in a year)
3. Conjunctions
Conjunctions are used to connect words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence. Think of them like duct tape or that friend from high school who thought that if she joined every single club, she’d get into Princeton. (Hi, Emily!)
There are three types of conjunctions:
- Coordinating conjunctions , which link words, phrases, and clauses together
- Subordinating conjunctions , which link two clauses together
- Correlative conjunctions, which are pairs of conjunctions that work in tandem to join equal sentence components
Let’s check out an example of each of these parts of speech:
JC and Justin were my favorite members of *NSYNC.
In this example, the coordinating conjunction and links JC and Justin , just as their shared love of bedazzled denim once did.
When he remembered that he can’t skate, Evan decided not to try out for the ice hockey team after all.
Here, the subordinating conjunction when links the dependent clause that opens the sentence with the independent clause that comes after the comma.
Neither Donna nor Kaitie could believe that their geometry professor used to play drums for The Snots.
In this example, nor is a correlative conjunction used to link Donna and Kaitie , which are both nouns.

4. Interjections
Interjections are the most dramatic part of speech. They’re used to express emotion, and they often interrupt the flow of a paragraph. Literally any phrase can be an interjection. Here are five examples of interjections as a part of speech:
- Holy guacamole!
Nouns are the granddaddy of the eight parts of speech. The boss. The Big Kahuna. The High Priestess of — well, you get it. You probably learned about these first, and you probably remember that a noun is a person, place, or thing.
Here are three examples of nouns to use the next time you encounter a stranger on the street who demands that you help her complete some Mad Libs before you can pass:
- Kelly Clarkson
6. Prepositions
Prepositions are used to hook up a noun or a pronoun with another word in the sentence. You might think of them like wingmen. Or not.
Either way, they’re never seen without an object. Check out this example to see a preposition and its object in action.
Maria dropped her phone in the toilet.
Here, the preposition in links the nouns phone and toilet . Toilet is the object of the preposition, and in the toilet is a prepositional phrase. (Ten points to Gryffindor if you just screamed, “And the is an adjective!”)
Other common prepositions include words/phrases such as the following:
7. Pronouns
Just as found footage is a subgenre of horror movies, pronouns are a subgenre of nouns — you know, but without all the grainy, black-and-white footage of little girl ghosts. Keeping the whole movie analogy going, you might think of a pronoun as a noun’s stand-in. Generally speaking, these parts of speech are used to avoid repetition.
Here’s a paragraph with zero pronouns:
Dean works out seven days a week. Dean’s training for a 5K and wants to be a famous knee model someday. Since Dean began his fitness regimen, Dean has lost 75 pounds. Dean’s modeling agency is very proud of Dean.
Here’s what happens when pronouns are plugged in:
My brother, Dean, works out seven days a week. He’s training for a 5K and wants to be a famous knee model someday. Since my brother began his fitness regimen, he has lost 75 pounds. His modeling agency is very proud of him.
The paragraph no longer sounds like it was written by robots. Score!

Back in the day, you probably learned that verbs express an action. If that’s all you learned, then your second-grade teacher was a big, fat liar.
In addition to action verbs, such as screams or sneezed , verbs come in a handful of other useful varieties:
- Linking verbs, which link the sentence’s subject to information about it (Brett is nauseated.)
- Helping verbs , which team up with the main verb in the sentence to make a verb phrase (Grandma’s neighbors have been playing Cardi B songs for six hours straight.)
No matter what form it takes, the humble verb is a must-have – even if it’s irregular . In order to truly be a sentence, that sentence needs to include a verb.
Conclusion: The Eight Parts of Speech at a Glance
Real talk: There’s much, much more to the eight parts of speech. Each part of the 8 parts of speech can be broken down into myriad subclasses. (Okay, maybe not interjections.) If you have any tips for telling count nouns from mass nouns or remembering the most common prepositions, sound off in the comments below!
Amber Morris
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
8 Parts of Speech | Definitions, Types, and Examples
8 parts of speech definitions and examples.
Quick Navigation
This lesson will analyze the ‘8 Parts of Speech’ in English with definitions, types, and examples. Parts of Speech are part and parcel of English grammar. We can’t think of a sentence without using Parts of Speech. There are 8 Parts of Speech in English.
However, if you want to learn English, you must know the Parts of Speech. Otherwise, it won’t be easy to learn English grammar more accurately. Let us know the definition of ‘Parts of Speech in English grammar. Just follow the below sentence.
- Wow! I see a very stunning bird flying in the sky.
This sentence will get a clear picture of the 8 Parts of Speech in English.
Every word underlined in the sentence is called Parts of Speech.
Definition of Parts of Speech by Different Scholars
J.C. Nesfield: The different kinds of words are called P arts of Speech. Wren & Martin: Words are divided into different kinds of classes, called Parts of speech, according to their use; that is, according to the work they do in the sentence.
Types of Parts of Speech
There are eight types of Parts of Speech in English grammar. They are:

- Preposition
- Conjunction
- Interjection .
- Stages of child language development
- Definition of language
- Characteristics of language
- Ten best English learning websites
- How to learn English quickly
- Visit this website to have speeches written by experts
Any naming word (person, place, thing, or idea) is called a Noun. Sometimes many students think a noun is the name of a person or place only, but it can be a thing, idea, feeling, etc.
Let us see some examples of nouns; John, boy, country, United Kingdom, New York City, cow, army, iron, honesty, etc. Nouns are underlined in the below sentences for easy identification:
- John is a good boy .
- The United Kingdom is my favorite country.
- My brother lives in New York City .
- The Cow is roaming in the field .
- The army protects their homeland .
- Iron is beneficial for human life.
- Honesty is a good virtue.
There are five types of nouns in English. They are:
- Proper noun
- Common noun
- Material noun
- Abstract noun
A word that is placed instead of a noun is called a Pronoun. If we use a single noun for every sentence, it doesn’t look good. For example, James goes to meet with his friends, and James is enjoying the party, and James recollects his old memories.
Here we use a single noun for every sentence, and that’s why it looks weird. But if we use the pronoun ‘he’ for the last two sentences instead of ‘James,’ it seems pretty good.
That’s why we need to use a pronoun instead of a noun. Let us see examples of pronouns; he, she, they, I, we, it, etc. Pronouns are underlined in the below sentences for easy identification:
- He is going to the market to buy a t-shirt.
- She plays with her classmate.
- I am the only man who understands the matter.
- We are going to arrange a free campaign.
- It was considered that he would be won the trophy.
There are nine types of pronouns. They are:
- Personal pronoun
- Possessive pronoun
- Reflexive pronoun
- Demonstrative pronoun
- Indefinite pronoun
- Relative pronoun
- Interrogative pronoun
- Distributive pronoun
- Reciprocal pronoun.
3. Adjective
A word used to describe a noun or pronoun is called an Adjective . In other words, we can say an adjective usually modifies a noun or a pronoun.
For example, happy, good, clever, intelligent, lazy, large, etc. Adjectives are underlined in the below sentences for easy identification:
- He looks like he is happy now.
- They had been playing good cricket at a time.
- Don’t try to be more clever .
- Undoubtedly he is an intelligent person.
- This animal is so lazy .
- I saw a large building.
There are nine types of adjectives. They are:
- Proper Adjectives
- Adjectives of Quality
- Adjectives of Quantity
- Numeral Adjectives
- Demonstrative Adjectives
- Distributive Adjectives
- Interrogative Adjectives
- Possessive Adjectives
A word that expresses an action or doing something is called a Verb. For example, am, is, are, was, were, have, has had, can, could, should, will, go, play, read, want, sing, etc.
Verbs are underlined in the below sentences for easy identification:
- I am good at English.
- He is a good boy.
- They are playing in the field.
- She was suffering from a fever.
- These two boys were going to catch fish.
- I have a beautiful doll.
- They have gone to this place.
- He has done his job successfully.
- My sister had a sweet dog.
- He can do this work.
- You could attend this meeting.
- His father shall go to the field.
- You should be attentive to your study.
- She will go to meet her friends.
- He would claim a better job.
- Read the book carefully.
- The boy wants to sing a song.
There are four types of verbs. They are:
- Auxiliary verb
- Principal verb
- Transitive verb
- Intransitive verb
A word that is used to add something to the meaning or modify a verb, an adjective, or another adverb is called an Adverb.
For example, about, after, before, fast, slow, etc. Adverbs are underlined in the below sentences for easy identification:
- Tell me something about you.
- Pass the book after him.
- He has done his task before the boy.
- They want to run fast .
- The tortoise walks slowly .
There are three types of Adverbs. They are:
- Simple adverb
- Relative adverb
- Interrogative adverb
6. Preposition
A word that is placed before a noun or a pronoun or a noun-equivalent to show its relation to any other term of the sentence is called a Preposition.
For example, on, in, to, for, with, within, above over, etc. Prepositions are underlined in the below sentences for easy identification:
- He stores his books on his bookshelf.
- They have been playing football on the field since morning.
- He goes to the market to buy some clothes.
- She is dancing with her mates.
- The plane was flying above my head.
- He couldn’t succeed in this plan over the years.
There are three types of prepositions. They are:
- Simple preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
7. Conjunction
A word that is usually used to join one word to another, one word to a clause, or one sentence to another is called a Conjunction.
Conjunctions are of three types. They are:
- Coordinating Conjunctions
- Subordinating Conjunctions
- Correlative Conjunctions
For example; and, but, or, if, though, than, since, so–that, as soon as, either–or, neither–nor, etc. Conjunctions are underlined in the below sentences for easy identification:
- Janny and Jammy are good friends.
- He is rich but cheap-minded.
- Please read more, or you will fail the exam.
- They will be good doctors if they work hard.
- He could attend the meeting though he had enough time.
- The boy is tall than the girl.
- It has been raining since morning.
- The older man is so poor that he can’t buy enough food.
- He left the place as soon as they came.
- Either Jack or John will do the task.
- She will neither come here nor her friend.
8. Interjection
A word used to express a short sudden emotion or excitement is called an Interjection. For example, hurrah! alas! oops! Etc. Interjections are underlined in the below sentences for easy identification:
- Hurrah ! We won the match.
- Alas ! She is no more.
- Oops ! They can’t do this job correctly.
There are three kinds of Interjections. They are:
- Volitive Interjection
- Emotive Interjection
- Cognitive Interjection.
To sum up, we may say without parts of speech; we can’t make a sentence. These eight parts of speech are the fundamental parts of English grammar.
Please share this article with your friends to get a helpful guideline about these eight parts of speech with definitions and examples.
Parts of Speech Quiz
Your answer:
Correct answer:
Your Answers

Azizul Hakim is the founder & CEO of englishfinders.com . He is a passionate writer, English instructor, and content creator. He has completed his graduation and post-graduation in English language and literature.
Related Posts

Future Continuous Tense | Definition, Structure, and Examples
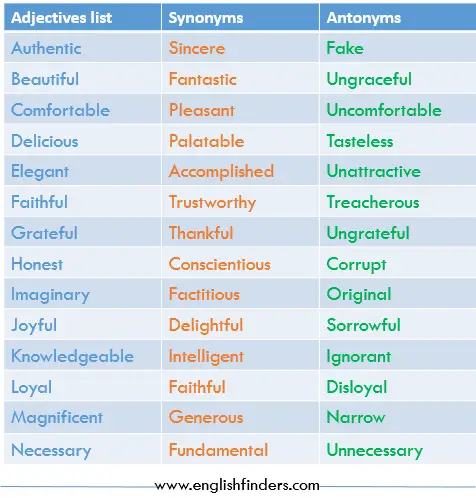
100 Most Useful Adjectives List with Meanings and Examples

Simple Sentences | Definition and Examples
Their functions
i love this

GREAT!!!!!!!!!!!
I appreciate
Okay, I joint
I like this grammar even my teacher also like this
Helped me thanks!
U are really a good tutor I wsh to see u
Thank you so much
You’re welcome!
Types should be discussed
We have separate lessons for each part of speech. Kindly check them out.
Define all types of noun
Very helpful! with this info, I can complete my school project. thank you so much for this!
Insert/edit link
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content

Parts of Speech Definition (8)Types and Examples

Parts of Speech in English refer to words that are into eight categories according to their use and function in sentences. Explore Parts of Speech: Definition, (8)Types, Examples, and Explanation to get a clear idea.
Parts of Speech
Parts of Speech are words used in sentences to make different functions and meanings. Without parts of speech, a sentence can not be expressed.
Parts of Speech Definition
Words are divided into different kinds or classes according to the purpose that they are used for. The different kinds of words are called Parts of Speech. – J.C. Nesfield
Different Parts of Speech with Examples
Parts of Speech can be divided into eight classes the function they perform in sentences.
1. Noun: The Taj Mahal is one of the seven wonders.
2. Pronoun: He can make it easier.
3. Adjective: She is as beautiful as a rose.
4. Verb: Mother cooks food.
5. Adverb: Barking dog seldom bites.
6. Preposition: The book is on the table.
7. Conjunction: Do or die
8. Interjection: Hurrah! we have won the match.
(8)Types of Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples:
1. noun: .
A noun is a word that names a thing, person, or place.
(a) Ram is a good boy .
(b) India is our motherland .
(c) Oil floats on water .
(d) kindness is a great quality .
(e) The committee has approved the decision.
All the above italic words in sentences are nouns .
2. Pronoun:
A pronoun is a word that is used in place of a noun.
(a) Vinod is studying. He has a test tomorrow.
(b) It is going to rain. I don’t have an umbrella.
(c) My parents and I are in Munnar. We like this place.
(d) That is a nice sari! you look very pretty in it .
(e) Nilima is a good girl. She reads in a college.
3. Adjective:
An adjective is a word that adds something to the meaning of a Noun or Pronoun.
(a) This is a pretty house.
(b) The small boy is crying.
(c) He seems angry .
(d) There are four candles on the table.
(e) Many men were present.
All the above italic words in sentences are Adjectives .
4. Verb:
A verb is doing a word. It is used to express an action or state about people, animals, or things.
(a) I am angry.
(b) Mr ram drives a motorcycle.
(c) They push the suitcase under the cot.
(d) The Rose smells sweet.
(e) Iron and copper are useful metals.
All the above italic words in sentences are Verbs .
5. Adverb:
An adverb is a word that tells us more about verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs.
a) He walks fast .
(b) He is very clever.
(c) She pronounced the word quite correctly .
(d) Some people spell badly .
(e) They asked me to wait here .
All the above italic words in sentences are Adverbs .
6. Preposition:
A preposition is a word placed before a Noun or a noun-equivalent or a pronoun to show its relation to some other word in the sentence.
(a) The book is on the table.
(b) He came to me.
(c) She is in the garden.
(d) The girl is fond of music.
(e) The little girl sat under a tree.
All the above italic words in sentences are Prepositions .
7. Conjunction:
A conjunction is a word that is used to join words, phrases, clauses, and sentences.
(a) It is very hot, and everybody is sweating.
(b) We can go to a film or we can go to the beach.
(c) He sat behind you, but in front of me.
(d) As he was ill, he did not go to his school.
(e) Ram as well as Karim went there.
All the above italic words in sentences are Conjunctions .
8. Interjection :
An interjection is a word that is used to show a strong or sudden feeling of happiness, sadness, surprise, or hurt.
(a) Hurrah! I did very well in maths.
(b) Alas! we lost the battle.
(c) Oh dear! how did they catch the thief?
(d) Ouch! you stepped on my toe.
(e) Goodness! He should not have said that.
All the above italic words in sentences are Interjections .
Some Examples of Parts of Speech in Sentences
1. The sun shines bright. ( Noun )
2. He is a brave boy. ( Pronoun )
3. She is absent because she is ill. ( Pronoun )
4. The girl wrote a letter to her father. ( Verb )
5. Kolkata is a big city. ( Adjective )
6. He worked the sum quickly . ( Adverb )
7. This flower is very beautiful. ( Adverb )
8. There is a cow in the garden. ( Preposition )
9. Rama and Hari are cousins. ( Conjunction )
10. Two and two make four. ( Conjunction )
11. Alas! He is dead. ( Interjection )
12. I can run fast, but miss the train. ( Conjunction )
13. Iron and copper are useful metals. ( Adjective )
14. His courage won him honour. ( Noun )
15. She pronounced the word quiet correctly. ( Adverb )
16. The girl is fond of music. ( Preposition )
Same Word used as different Parts of Speech
Frequently asked questions on parts of speech.
Q1 What are parts of speech? Ans: Parts of Speech are words used in a sentence. Those words make a sentence meaningful.
Q2 How many parts of speech are there? Ans: There are 8 parts of speech according to function and meaning in sentences..
Q3 W hat are the 8 parts of speech grammar?
Ans: Nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections are the 8 parts of speech Grammar.
Related posts:

- School Guide
- English Grammar Free Course
- English Grammar Tutorial
- Parts of Speech
- Figure of Speech
- Tenses Chart
- Essay Writing
- Email Writing
- NCERT English Solutions
- English Difference Between
- SSC CGL English Syllabus
- SBI PO English Syllabus
- SBI Clerk English Syllabus
- IBPS PO English Syllabus
- IBPS CLERK English Syllabus
- English Grammar : Learn Rules of Grammar and Basics
- Parts of Speech: Definitions, Examples & 8 Types
- What is a Noun? Types, Definitions and Examples (List)
- Proper Noun - Definition, Examples, & Rules
- Common Noun - Definition, Examples, List & Usage
- Plural Noun - Rules and Examples
- Possessive Noun - Meaning, Usage, Rules and Examples
- What is Collective Noun? List of Examples, Uses and Exercises
- Abstract Nouns - Definition, Examples, List, Usage
- What is a Compound Noun? Definition, Types & Examples
- What are Countable Noun?
- What are Uncountable Noun - How to use them?
- Material Noun: Definition, Examples, Rules & Exercises
- Pronoun Definition - Rules and Types of Pronouns
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Subject Pronouns - Definition, Example and Exercise
- Relative Pronouns - Definition, Uses and Examples
- Demonstrative Pronouns - Definition and Examples
- Possessive Pronouns - Definition, Usage and Examples
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Personal Pronoun - Definition, Rules and Examples
- Interrogative Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronouns - Definition, Examples & Uses
- What is a Verb? Types, Uses, Examples
- Main Verbs - Meaning, Types and Examples
- Helping Verb: Definition, Types and Examples
- Auxiliary Verbs: Definition, Examples & List
- Irregular Verbs
- What Are Modal Verbs? – Definition, Usage & Examples
- What is A Gerund? Definition and Examples
- Adjective - Definition, List, Types, Uses and Examples
- Proper Adjectives Definition and Examples
- Possessive Adjectives - Definition, Example and List
- Interrogative Adjective - Meaning, Definition and Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, List & Examples
- Conjunctive Adverbs - Meaning, Examples and Exercises
- Adverbs of Time - Examples, Meaning, and Definition
- Adverbs of Frequency - Definition, Examples, and Usage
- Adverbs of Place - Definition, List and Examples
- What are Adverbs of Degree? Definition, List and Examples
- Adverbs of Manner - Meaning, Definition and Examples
Conjunction
- What is a Conjunction - Meaning, Definition, Types & Exercises
- Subordinating Conjunction - Meaning, Definition, Types and Examples
Preposition
Interjection.
- Interjections - Definition, Types, Rules and Examples
- Definite and Indefinite Articles ( A, An, The)
- Subject-Verb Agreement Rules: Examples & Exercises
- Active and Passive Voice Rules for Competitive Exams
- What is Tense? Types, Definitions & Examples
- Tense Chart in English - Rules, Examples, Types & Mind map
Parts of Speech: Definitions, Examples & 8 Types
Every word is a part of speech playing a specific role in sentences or paragraphs. Parts of speech provide an organized way to align words and phrases, it is a fundamental meaning for a language to become more understandable and serve a specific purpose. Here, in this article, we will see what is Part of Speech, its types, and its uses. So let us dive in deeper to learn more about it!

Table of Content
What is Part of Speech?
Parts of speech chart.
- Different Types of Parts of Speech :
- Parts of Speech Examples Using Sentences
- Quiz to practice Parts of Speech

Parts of Speech – FAQs
The English language has thousands of words and every word has some function to perform. Some words are there to show action, some to join, and some to name something. There are 8 different parts of speech including nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunction, and interjection. And together, all the functions performed by words in the English language fall under Parts of speech.
Parts of Speech Definition
The parts of speech are the “traditional grammatical categories to which words are assigned in accordance with their syntactic functions, such as noun, verb, adjective, adverb, and so on.” In other words, they refer to the different roles that words can play in a sentence and how they relate to one another based on grammar and syntax.
All Parts of Speech with Examples
There are 8 different types of parts of speech i.e., Nouns, Pronouns, Adjectives, Verbs, Adverb, prepositions, Conjunction, and Interjection.
Noun –
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, state, or quality. It can be singular or plural. Nouns are a part of speech.
- Function: Refers to Things or person
- Examples: Pen, Chair, Ram, Honesty
- Sentences: Cars are expensive, This chair is made of wood, and Ram is a topper, Honesty is the best policy.
Pronoun –
The word used in place of a noun or a noun phrase is known as a pronoun. A pronoun is used in place of a noun to avoid the repetition of the noun.
- Function: Replaces a noun
- Examples: I, you, he, she, it, they
- Sentences: They are expensive, It is of wood, He is a topper, It is the best policy
Adjective –
A word that modifies a noun or a pronoun is an adjective. Generally, an adjective’s function is to further define and quantify a noun or pronoun.
- Function: Describes a noun
- Examples: Super, Red, Our, Big, Great, class
- Sentences: Supercars are expensive, The red chair is for kids, Ram is a class topper, and Great things take time.
Verb –
A word or a group of words that describes an action, a state, or an event is called a verb. A verb is a word that says what happens to somebody or what somebody or something does.
- Function: Describes action or state
- Sentences: I play football, I will be a doctor, I like to work, I love writing poems.
Adverb –
A verb, adjective, another adverb, determiner, clause, preposition, or sentence is typically modified by an adverb . Adverbs often answer questions like “how,” “in what way,” “when,” “where,” and “to what extent” by expressing things like method, place, time, frequency, degree, level of certainty, etc
- Function: Describes a verb, adjective, or adverb
- Examples: Silently, too, very
- Sentences: I love reading silently, It is too tough to handle, He can speak very fast.
Preposition –
A preposition is called a connector or linking word which has a very close relationship with the noun, pronoun or adjective that follows it . Prepositions show position in space, movement, direction, etc.
- Function: Links a noun to another word
- Examples: at, in, of, after, under,
- Sentences: The ball is under the table, I am at a restaurant, she is in trouble, I am going after her, It is so nice of him
Conjunction –
A conjunction is a word that connects clauses, sentences, or other words. Conjunctions can be used alone or in groups of two.
- Function: Joins clauses and sentences
- Examples: and, but, though, after
- Sentences: First, I will go to college and then I may go to Fest, I don’t have a car but I know how to drive, She failed the exam though she worked hard, He will come after he finishes his match.
Interjection –
An interjection is a word or phrase expressing some sudden feelings of sadness or emotions.
- Function: Shows exclamation
- Examples: oh! wow!, alas! Hurray!
- Sentences: Oh! I got fail again, Wow! I got the job, Alas! She is no more, Hurray! We are going to a party.
These are the main parts of speech, but there are additional subcategories and variations within each. Understanding the different parts of speech can help construct grammatically correct sentences and express ideas clearly.
Sentence Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
- Examples: Luggage, Cattle.
- Sentence: Never leave your luggage unattended.
- In some places, cattle are fed barely.
- Examples: who, either, themselves
- Sentence: I know a man who plays the guitar very well.
- Either of the two cars is for sale.
- They enjoyed themselves at the party.
- Examples: kind, moving, wounder.
- Sentence:
- She is a kind person.
- Boarding a moving bus can be dangerous.
- Never poke a wounded animal.
- Examples: Praise, Hate, Punish
- Sentence: She always praises her friends.
- I don’t hate anybody.
- The boy has been punished by his teacher
- Examples: Always, enough, immediately
- Sentence: we should always help each other.
- We should be wise enough to understand what is good for us.
- We should leave bad habits immediately.
- Examples: Off, Below, From. to
- He plunged off the cliff
- I live below the 9th floor.
- I travel daily from Delhi to Noida.
- Examples: whereas, as well as, so,
- Sentence: The new software is fairly simple whereas the old one was a bit complicated.
- The finance company is not performing well as well as some of its competitors.
- He was ready so he may come.
- Examples: oops! whoa! phew!
- Sentence: Oops! I forgot to mention her name.
- Whoa! you drive fast.
- Phew! That was a close call, we had a narrow escape.
Parts of Speech Exercise – Test your Knowledge of Part of speech
Choose the correct Parts of Speech of the BOLD word from the following questions.
1. Let us play, Shall We?
a. Conjunction b. Pronoun c. Verb
2. I t is a good practice to arrange books on shelves.
a. Verb b. Noun c. Adjective
3. Whose books are these?
a. Pronoun b. Preposition c. verb
4. Father, please get me that toy.
a. Pronoun b. Adverb c. Adjective
5. His mentality is rather obnoxious.
a. Adverb b. Adjective c. Noun
6. He is the guy whose money got stolen.
a. Pronoun b. Conjunction c. Adjective
7. I will have finished my semester by the end of this year.
a. Interjection b. Conjunction c. Preposition
8. Bingo! That’s the one I have been looking for
a. Interjection b. Conjunctio c. Preposition
Quiz Answers:
1. c, 2. b, 3. a, 4. c, 5. a, 6. b, 7. c, 8. a
Also Check:
- English Grammar
- Figures of Speech
- Learn English Grammar Online
- Difference Between Adjective and Verb
Q1. What are Parts of Speech?
A word is assigned to a category as per its function, and those categories are together known as Parts of Speech.
Q2. What are the 8 Parts of Speech?
Noun, Pronoun, Adjective, Verb, Adverb, Preposition, Conjunction, Interjection.
Q3. How many Parts of Speech are there?
There are a total of 8 parts of Speech.
Q4. What Part of Speech is “our”?
“Our” is a adjective type of Part of Speech. Eg. Our car.
Q5. What Part of Speech is “Quickly”?
Adverb. let us understand it with this example – Milk sours quickly in warm weather.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- SSC/Banking
- 10 Ways to Use Microsoft OneNote for Note-Taking
- 10 Best Yellow.ai Alternatives & Competitors in 2024
- 10 Best Online Collaboration Tools 2024
- 10 Best Autodesk Maya Alternatives for 3D Animation and Modeling in 2024
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

The 8 Parts of Speech: Definition, Types, Functions & Examples
In the English language, there are eight parts of speech: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. Part of speech indicates the word’s meaning and grammatical role in the sentence.
It is possible for a single word to serve multiple purposes depending on the context in which it is used. When looking up a word in a dictionary, it’s critical to know the different parts of speech and how they fit together.
Parts of Speech: Definition, Types, Functions, and Examples
People, places, things, and ideas are all examples of nouns.
a man, a college, a house, and a sense of happiness
People, places, things, and ideas are all examples of nouns. Using an article (the, a, or an) before a noun is common, but it isn’t required in all cases. Common nouns don’t begin with a capital letter, but the proper nouns they describe do.
Concrete and abstract nouns are both examples of nouns. ‘s is added to nouns to indicate that they are in someone’s possession. A noun can be a subject, direct object, indirect object, subject complement, or the object of a preposition in a sentence.
I was given a lengthy letter from my high school teacher by a young girl who then vanished. What a shock!
A pronoun is a term that replaces a noun in a sentence.
The she/we/they/it
Words that can be used in place of nouns are called pronouns. The antecedent of a pronoun is usually a specific noun, which is known as its predicate. The girl is the antecedent of the pronoun she in the preceding phrase.
The types of pronouns are further defined: There are four types of pronouns: personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, reflexive pronouns, relative pronouns, and demonstrative pronouns, which identity, point to, or refer to specific nouns or pronouns.
I was given a lengthy letter from my high school instructor by a young girl who then vanished. What a shock!
3. Verb
A verb is a word that describes what someone is doing or who they are.
is… write… become… jump
An action or state of being can be expressed by the verb in a sentence. A primary verb and one or more supporting verbs are often present. (“She has a good voice.”) can serve as a supporting verb to sing.) The number of the verb’s subject must match the subject’s (both are singular or both are plural). Verbs can also communicate tensely in a variety of ways.
4. Adjective
adverbs are used to describe or modify nouns and pronouns.
lovely… vintage… azure… shrewd
A noun or pronoun can be described by an adjective. In most cases, it answers the question of how many or which one. Adjectives are commonly used to describe articles [a, an, the].
5. The Adverb
Abbreviation: An abbreviation is any word that is used to describe or modify another word (adjective).
slowly… incredibly… cautiously…
In contrast to nouns, an adverb only describes or modifies a verb or adjective or another adverb. Most often, it provides answers to the following questions: how long ago, where, how much, why, and under what circumstances. Most adverbs have a -ly suffix.
6. Preposition
It is customary to use a preposition before a noun or pronoun to create a phrase that alters the meaning of the preceding word(s).
until the end of time (by the tree, with our friends, about the book, until tomorrow)
When a preposition precedes a noun or pronoun, it creates a phrase that describes another word in the sentence. This means that every prepositional phrase has a preposition as part of it. Adjectives and adverbs are the most common uses of the prepositional phrase. List of most frequently used prepositions:
7. Conjunctions
Words, phrases, and clauses can be joined by a conjunction.
and… but… or… even so… since
Cohesion is a term used to describe the relationship between two or more parts. Corresponding conjunctions join grammatically equivalent parts of the sentence. Because, although, while, since, etc. are examples of subordinating conjunctions. Conjunctions come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
8. Interjections
The last but not least Parts of Speech on our list. Emotion is conveyed through the use of an interjection.
“Wow!” “Oops!” “Oh!”
Using an interjection is a way to express your feelings in a succinct manner. An exclamation point is frequently used after it.
Read Also: 10 Tips to Study Late at Night without Sleeping
Similar Posts

Summary Writing: Skills and Techniques on How to Write a Good Summary

Question Tags and Answer Tags: Meaning, Examples, and Rules of Tags

9 Common Figures of Speech You Need to be Familiar With

Major Differences Between Upon and Apon

How and Why Latin is a Dead Language

Emphatic Stress
Basic English Grammar
Helping People Understand the Eight Parts of Speech!
Parts of Speech

8 Parts of Speech Definitions With Examples
The 8 parts of speech definitions with examples include nouns, verbs, adjectives, pronouns, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections. By using proper grammar in your writing and speaking, you will communicate clearly and effectively … [Read More...]
Grammar Tips

What are the 7 Subjective Pronouns?
Pronouns replace nouns within English sentences in order to avoid repetition. Subjective pronouns replace … [Read More...]

Possessive Adjectives vs Possessive Pronouns
The key differences between possessive adjectives and possessive pronouns relate mainly to their grammatical … [Read More...]

What are the 7 Possessive Adjectives?
Possessive adjectives are adjectives that modify nouns by identifying who has ownership or possession of them. … [Read More...]

What is a Simple Sentence With Examples?
Simple sentences are the foundation of clear and effective communication. Simple sentences are easy to … [Read More...]

Predicate Nominative Vs Predicate Adjective
The predicate is the part of a sentence that gives us more information about the subject. The subject of the … [Read More...]

4 Types of Sentence Structures With Examples
The significance of sentence structure lies in its ability to affect the clarity and coherence of written and … [Read More...]

4 Types of Sentences With Examples
Incorporating diverse sentence forms can enhance your writing and capture the reader's attention. There are … [Read More...]

Examples of Possessive Pronouns in Sentences!
Possessive pronouns are personal pronouns in the possessive case which have the grammatical function of nouns. … [Read More...]

What are the 7 possessive pronouns?
Pronouns are words that are used in place of nouns in a sentence. We used these pronouns in speech and writing … [Read More...]

How to Use Multiple Adjectives in a Sentence?
Adjectives are words that modify a noun or pronoun. Adjectives provide information that will help your reader … [Read More...]

What is the Word Order of Cumulative Adjectives?
We use adjectives to help the reader experience more precisely what we want to convey about a person, place, … [Read More...]

What are some examples of cumulative adjectives?
Here are some examples of cumulative adjectives in sentences. Cumulative adjectives follow a specific order. … [Read More...]

What are Cumulative Adjectives With Examples?
Cumulative adjectives are two or more adjectives that work together as a unit in order to modify a noun by … [Read More...]

What are Coordinate Adjectives With Examples?
Coordinate adjectives are adjectives that independently modify the same noun. These coordinate adjectives are … [Read More...]

8 Simple Comma Rules With Examples
There are 8 simple comma rules with examples that will help you take the guess work out of comma placement in … [Read More...]

5 Types of Adverbs in English Grammar With Examples
The 5 types of adverbs in English grammar with examples include time, manner, place, degree and frequency. … [Read More...]

8 Types of Adjectives in English Grammar With Examples
There are 8 types of adjectives in English grammar with examples and they include proper, descriptive, … [Read More...]

8 Types of Pronouns In English Grammar With Examples
The 8 types of pronouns in English grammar with examples include 1) personal, 2) interrogative, 3) possessive, … [Read More...]

The 8 parts of speech definitions with examples include nouns, verbs, adjectives, pronouns, adverbs, … [Read More...]

10 Types of Nouns in English Grammar With Examples
10 Types of Nouns in English Grammar With Examples: The 10 types of nouns in English grammar with examples … [Read More...]

8 Types of Nouns in English Grammar and Examples
8 Types of Nouns in English Grammar and Examples: The 8 types of nouns in English grammar and examples include … [Read More...]

8 Types of Prepositions in English Grammar With Examples
8 Types of Prepositions in English Grammar With Examples: The 8 types of prepositions in English grammar with … [Read More...]

4 Types of Conjunctions in English Grammar With Examples
4 Types of Conjunctions in English Grammar With Examples: The 4 types of conjunctions in English grammar are: … [Read More...]

8 Noun Functions In English Grammar With Examples
How do nouns function in English sentences? In this article I will explain and illustrate the 8 noun functions … [Read More...]

What is a Personal Pronoun
What is a personal pronoun? First of all pronouns are words that take the place of nouns. Therefore, pronouns … [Read More...]

What are the Rules for Commas?
What are the Rules for Commas? A comma is a punctuation mark, which is used for several reasons, but mostly … [Read More...]

What is an Interjection?
What is an interjection? An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses emotion. Interjections have no … [Read More...]

What is a Preposition?
What is a preposition? A preposition is a word or group of words that shows relationship of a noun or pronoun … [Read More...]

What is a Conjunction?
What is a conjunction? A conjunction is a part of speech that is used to join words, phrases, clauses and … [Read More...]

How To Identify Verbs With Examples
There are many ways to identify verbs. I have found using a simple chart (see below) with verb kinds, verb … [Read More...]

Worksheet For Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
A Worksheet For Transitive and Intransitive Verbs provides transitive and intransitive verb exercises in order … [Read More...]

What is a Definite Article and an Indefinite Article
What is a Definite Article and an Indefinite Article explains the grammatical significance of definite … [Read More...]

Sentences of Troublesome Words
Sentences of troubesome words look at troublesome verb pairs - lie and lay, sit and set, and rise and … [Read More...]

Types of English Sentence Structure
There are four (4) types of English sentence structure. Once you master these four types of English sentence … [Read More...]

Diagramming English Sentences
Diagramming English Sentences: I have found that sentence diagramming is an effective way to learn grammar. … [Read More...]

What is An Adverb?
What is an adverb? An Adverb is a word or group of words (phrase or clause) that modifies a verb, an adjective … [Read More...]

What is An Adjective?
What is an adjective explains how to recognize an adjective and where it is placed in an English … [Read More...]

Understanding the Eight Parts of Speech
Understanding the Eight Parts of Speech: Using proper grammar is an important part of communicating clearly … [Read More...]

There are seven types of pronouns. A brief explanation of each type of pronouns will help you understand how … [Read More...]

English Verbs
English verbs provide a basic understanding of how verbs are used in sentences. Verbs - How Verbs are … [Read More...]

Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
Learning to recognize Transitive and Intransitive Verbs will help you understand the functions of verbs and … [Read More...]

Extended List of Irregular Verbs
Extended List of Irregular Verbs provides a list of irregular verbs and defines the difference between regular … [Read More...]

Linking Verb
Linking Verb helps you understand the hidden linking verbs in a sentence. Once you know the usual linking … [Read More...]

A List of Helping Verbs
A list of helping verbs will help you identify helping or auxiliary verbs in English sentences and improve … [Read More...]

Functions of a Noun
Functions of a Noun provides the eight different noun functions with examples so that you can understand how … [Read More...]

Different Types of Nouns
Different types of nouns provide 6 types of nouns that make up a sentence in the English language. … [Read More...]
Articles of Interest

Home » University Of Oklahoma » What Are The 8 Types Of Speech?
What Are The 8 Types Of Speech?
Table of Contents
There are eight parts of speech in the English language: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection . The part of speech indicates how the word functions in meaning as well as grammatically within the sentence.
What type of speech is eight?
Eight can be a numeral or a noun .
What are the 8 parts of speech with examples PDF?
The eight parts of speech are noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, adjective, conjunction, preposition and interjections .
What sentence has all 8 parts of speech?
Conjunction: Words that connect words, phrases and sentences in form and meaning. I am very hungry, but the fridge is empty. I was watching tv when she came in. Other Example Sentences;
- Looks ugly (Adjective)
- It plays quite well (Envelope)
- What a coincidence!
- His eyes filled up when he entered the room (Verb)
What are the eight parts of speech and their functions?
Words are important elements of each sentence and based on their function, words are classified into eight types of parts of speech. However, 8 important parts of speech are noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, adjective, preposition, conjunction and interjection . Noun: This is the easiest one among the eight parts of speech.
What are the types of speeches?
Types of speeches
- Informative speech. Informative speeches aim to educate an audience on a particular topic or message.
- Entertaining speech. Entertaining speeches aim to amuse a crowd of people.
- Demonstrative speech.
- Persuasive speech.
- Oratorical speech.
- Debate speech.
- Special occasion speech.
- Pitch speech.
What do you mean by 8?
Definition of eight 1 : a number that is one more than seven — see Table of Numbers. 2 : the eighth in a set or series the eight of spades. 3 : something having eight units or members: such as.
What are the types of speech in English language PDF?
It is a category to which a word is assigned in accordance with its syntactic functions. English has eight main parts of speech, namely, Nouns, Pronouns, Adjectives, Verbs, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions & Interjections .
What are the part of speech and their examples?
For example, “work” can be a verb and a noun; “but” can be a conjunction and a preposition; “well” can be an adjective, an adverb and an interjection. Words with More Than One Job.
What are the types of speech in English language in computer?
In English you use various words with different functions to make sentences much like each computer component has a certain role in the information process. Words are categorized into eight types called parts of speech: noun, pronoun, adjective, verb, adverb, conjunction, interjection, and preposition .
What is a sentence for eight?
1, Eight massive stone pillars supported the roof. 2, The two buildings are eight metres apart. 3, Of eight starters, only three finished the race. 4, I work eight hours a day.
How many figures of speech are there?
The five major categories. In European languages, figures of speech are generally classified in five major categories : (1) figures of resemblance or relationship, (2) figures of emphasis or understatement, (3) figures of sound, (4) verbal games and gymnastics, and (5) errors.
What is speech grammar?
Definition of speech 1a : the communication or expression of thoughts in spoken words . b : exchange of spoken words : conversation. 2a : something that is spoken : utterance. b : a usually public discourse : address. 3a : language, dialect.
Why is it important to know the 8 parts of speech?
Understanding the 8 parts of speech is beneficial for analyzing the meaning of each word . By learning the 8 parts of speech, you can easily identify a grammatical problem in the sentence, and see whether there is a run-on sentence, a misused pronoun or a problem of the verb agreement.
What are the 8 parts of speech with 5 examples?
Check your answers.
- My – Pronoun, Home – Noun, Late – Adverb.
- Am – Verb, Good – Adjective.
- I – Pronoun, Was looking – Verb.
- Whoa – Interjection, Amazing – Adjective.
- Climate – Noun, In – Preposition, Kodaikanal – Noun, Very – Adverb.
- And – Conjunction, On – Preposition, Your – Pronoun.
What are the functions of speech?
the various purposes for which spoken language is used, primarily the communication of ideas or information, the maintenance of social relationships, and the expression of feelings or emotions .
What are the 10 types of speech?
10 Types of Speeches
- Emotional Speech.
- Explanation Speech.
- Oratory Speech.
- Motivational Speech.
- Funny Speech.
- Factual Speech.
- Selling Speech.
- Special Occassion Speech.
What are the 9 types of speeches?
Below, let’s take a look at 9 different types of speeches.
- DEMONSTRATIVE SPEECH.
- INFORMATIVE SPEECH.
- ENTERTAINING SPEECH.
- PERSUASIVE SPEECH.
- ORATORICAL SPEECH.
- MOTIVATIONAL SPEECH.
- INTRODUCTORY SPEECH.
- ACCEPTANCE SPEECH.
What are the 5 types of speech style?
According to Joos (1976), speech style is divided into five forms. They are frozen style, formal style, consultative style, casual style and intimate style . It means that people have five options of styles when they want to communicate with other people. For example, people use formal language in a formal place.
What is the meaning of this emoji _?
The emoticon . _. means “Apathy,” “Disappointment,” or “Resignation.”
How do you spell 12?
In English, the spelling of 12 is Twelve .

By Antonia Leonard
Antonia Leonard is an education expert who has dedicated her life to helping students achieve their academic goals. She has worked in schools all over the world, and has developed groundbreaking curricula that have helped countless students excel.
Antonia is a firm believer in the power of education, and she is passionate about helping students reach their full potential. She is also a strong advocate for equal opportunity, and she works tirelessly to ensure that all students have access to quality education regardless of their socioeconomic status or race.
Antonia is a gifted educator, and she is widely respected within the education community. She has received numerous awards and accolades for her work, including being named one of the "Top 10 Educators to Watch" by Education Week magazine.
You might also like:
Can a hurricane hit oklahoma, does oklahoma have tornadoes, how much are ou dorms.
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- Types of speeches
The 4 types of speeches
Informative, demonstrative, persuasive and special occasion.
By: Susan Dugdale | Last modified: 01-31-2024
There are four main types of speeches or types of public speaking.
- Demonstrative
- Special occasion or Entertaining
To harness their power a speaker needs to be proficient in all of them: to understand which speech type to use when, and how to use it for maximum effectiveness.
What's on this page:
An overview of each speech type, how it's used, writing guidelines and speech examples:
- informative
- demonstrative
- special occasion/entertaining
- how, and why, speech types overlap

Return to Top
Informative speeches
An informative speech does as its name suggests: informs. It provides information about a topic. The topic could be a place, a person, an animal, a plant, an object, an event, or a process.
The informative speech is primarily explanatory and educational.
Its purpose is not to persuade or influence opinion one way or the other. It is to provide sufficient relevant material, (with references to verifiable facts, accounts, studies and/or statistics), for the audience to have learned something.
What they think, feel, or do about the information after they've learned it, is up to them.
This type of speech is frequently used for giving reports, lectures and, sometimes for training purposes.
Examples of informative speech topics:
- the number, price and type of dwellings that have sold in a particular suburb over the last 3 months
- the history of the tooth brush
- how trees improves air quality in urban areas
- a brief biography of Bob Dylan
- the main characteristics of Maine Coon cats
- the 1945 US bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
- the number of, and the work of local philanthropic institutions
- the weather over the summer months
- the history of companion planting
- how to set up a new password
- how to work a washing machine

Click this link if you'd like more informative topic suggestions . You'll find hundreds of them.
And this link to find out more about the 4 types of informative speeches : definition, description, demonstration and explanation. (Each with an example outline and topic suggestions.)

Demonstration, demonstrative or 'how to' speeches
A demonstration speech is an extension of an informative process speech. It's a 'how to' speech, combining informing with demonstrating.
The topic process, (what the speech is about), could either be demonstrated live or shown using visual aids.
The goal of a demonstrative speech is to teach a complete process step by step.
It's found everywhere, all over the world: in corporate and vocational training rooms, school classrooms, university lecture theatres, homes, cafes... anywhere where people are either refreshing or updating their skills. Or learning new ones.
Knowing to how give a good demonstration or 'how to' speech is a very valuable skill to have, one appreciated by everybody.
Examples of 'how to' speech topics are:
- how to braid long hair
- how to change a car tire
- how to fold table napkins
- how to use the Heimlich maneuver
- how to apply for a Federal grant
- how to fill out a voting form
- how to deal with customer complaints
- how to close a sale
- how to give medicine to your cat without being scratched to bits!

Resources for demonstration speeches
1 . How to write a demonstration speech Guidelines and suggestions covering:
- choosing the best topic : one aligning with your own interests, the audience's, the setting for the speech and the time available to you
- how to plan, prepare and deliver your speech - step by step guidelines for sequencing and organizing your material plus a printable blank demonstration speech outline for you to download and complete
- suggestions to help with delivery and rehearsal . Demonstration speeches can so easily lurch sideways into embarrassment. For example: forgetting a step while demonstrating a cake recipe which means it won't turn out as you want it to. Or not checking you've got everything you need to deliver your speech at the venue and finding out too late, the very public and hard way, that the lead on your laptop will not reach the only available wall socket. Result. You cannot show your images.

2. Demonstration speech sample outline This is a fully completed outline of a demonstration speech. The topic is 'how to leave an effective voice mail message' and the sample covers the entire step by step sequence needed to do that.
There's a blank printable version of the outline template to download if you wish and a YouTube link to a recording of the speech.
3. Demonstration speech topics 4 pages of 'how to' speech topic suggestions, all of them suitable for middle school and up.

Persuasive speeches
The goal of a persuasive speech is to convince an audience to accept, or at the very least listen to and consider, the speaker's point of view.
To be successful the speaker must skillfully blend information about the topic, their opinion, reasons to support it and their desired course of action, with an understanding of how best to reach their audience.
Everyday examples of persuasive speeches
Common usages of persuasive speeches are:
- what we say when being interviewed for a job
- presenting a sales pitch to a customer
- political speeches - politicians lobbying for votes,
- values or issue driven speeches e.g., a call to boycott a product on particular grounds, a call to support varying human rights issues: the right to have an abortion, the right to vote, the right to breathe clean air, the right to have access to affordable housing and, so on.
Models of the persuasive process
The most frequently cited model we have for effective persuasion is thousands of years old. Aristotle, the Greek philosopher, 384–322 BC , explained it as being supported by three pillars: ethos, pathos and logos.

Briefly, ethos is the reliability and credibility of the speaker. How qualified or experienced are they talk on the topic? Are they trustworthy? Should we believe them? Why?
Pathos is the passion, emotion or feeling you, the speaker, bring to the topic. It's the choice of language you use to trigger an emotional connection linking yourself, your topic and the audience together, in a way that supports your speech purpose.
(We see the echo of Pathos in words like empathy: the ability to understand and share the feels of another, or pathetic: to arouse feelings of pity through being vulnerable and sad.)
Logos is related to logic. Is the information we are being presented logical and rational? Is it verifiable? How is it supported? By studies, by articles, by endorsement from suitably qualified and recognized people?
To successfully persuade all three are needed. For more please see this excellent article: Ethos, Pathos, Logos: 3 Pillars of Public Speaking and Persuasion
Monroe's Motivated Sequence of persuasion
Another much more recent model is Monroe's Motivated Sequence based on the psychology of persuasion.

It consists of five consecutive steps: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization and action and was developed in the 1930s by American Alan H Monroe, a lecturer in communications at Purdue University. The pattern is used extensively in advertising, social welfare and health campaigns.
Resources for persuasive speeches
1. How to write a persuasive speech Step by step guidelines covering:
- speech topic selection
- setting speech goals
- audience analysis
- empathy and evidence
- balance and obstacles
- 4 structural patterns to choose from
2. A persuasive speech sample outline using Monroe's Motivated Sequence
3. An example persuasive speech written using Monroe's Motivated Sequence
4. Persuasive speech topics : 1032+ topic suggestions which includes 105 fun persuasive ideas , like the one below.☺

Special occasion or entertaining speeches
The range of these speeches is vast: from a call 'to say a few words' to delivering a lengthy formal address.
This is the territory where speeches to mark farewells, thanksgiving, awards, birthdays, Christmas, weddings, engagements and anniversaries dwell, along with welcome, introduction and thank you speeches, tributes, eulogies and commencement addresses.
In short, any speech, either impromptu or painstakingly crafted, given to acknowledge a person, an achievement, or an event belongs here.
You'll find preparation guidelines, as well as examples of many special occasion speeches on my site.
Resources for special occasion speeches
How to prepare:
- an acceptance speech , with an example acceptance speech
- a birthday speech , with ongoing links to example 18th, 40th and 50th birthday speeches
- an office party Christmas speech , a template with an example speech
- an engagement party toast , with 5 examples
- a eulogy or funeral speech , with a printable eulogy planner and access to 70+ eulogy examples
- a farewell speech , with an example (a farewell speech to colleagues)
- a golden (50th) wedding anniversary speech , with an example speech from a husband to his wife
- an impromptu speech , techniques and templates for impromptu speaking, examples of one minute impromptu speeches with a printable outline planner, plus impromptu speech topics for practice
- an introduction speech for a guest speaker , with an example
- an introduction speech for yourself , with an example
- a maid of honor speech for your sister , a template, with an example
- a retirement speech , with an example from a teacher leaving to her students and colleagues
- a student council speech , a template, with an example student council president, secretary and treasurer speech
- a Thanksgiving speech , a template, with an example toast
- a thank you speech , a template, with an example speech expressing thanks for an award, also a business thank you speech template
- a tribute (commemorative) speech , with a template and an example speech
- a welcome speech for an event , a template, an example welcome speech for a conference, plus a printable welcome speech planner
- a welcome speech for new comers to a church , a template with an example speech
- a welcome speech for a new member to the family , a template with an example
Speech types often overlap
Because speakers and their speeches are unique, (different content, purposes, and audiences...), the four types often overlap. While a speech is generally based on one principal type it might also have a few of the features belonging to any of the others.
For example, a speech may be mainly informative but to add interest, the speaker has used elements like a demonstration of some sort, persuasive language and the brand of familiar humor common in a special occasion speech where everybody knows each other well.
The result is an informative 'plus' type of speech. A hybrid! It's a speech that could easily be given by a long serving in-house company trainer to introduce and explain a new work process to employees.
Related pages:
- how to write a good speech . This is a thorough step by step walk through, with examples, of the general speech writing process. It's a great place to start if you're new to writing speeches. You'll get an excellent foundation to build on.
- how to plan a speech - an overview of ALL the things that need to be considered before preparing an outline, with examples
- how to outline a speech - an overview, with examples, showing how to structure a speech, with a free printable blank speech outline template to download
- how to make and use cue cards - note cards for extemporaneous speeches
- how to use props (visual aids)
And for those who would like their speeches written for them:
- commission me to write for you

speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
- Nanoparticles For Cancer Imaging – A New Avenue to Explore!
- Moana: The Disney Movie Set In Polynesia You Cannot Miss Out!
- Day Trips from Wilmington, NC
- ChatGPT Use Cases: Making the Most Use of ChatGPT in Daily Life
- What Is Hyssop In The Bible And Its Modern Significance
- How To Wash Wool Blanket? The 4-Step Guide For You!
- Where To Watch Ugliest House In America?
- 10 Hottest Video Game Characters You Cannot Miss Out On!
- Triangle Tattoo Meaning: Exploring The Secrets Here!
- 10 Best American History Books That You Must Read!

Home » 8 Types Of Figure Of Speech And Their Examples
8 Types Of Figure Of Speech And Their Examples
There are mainly 8 types of figure of speech we will discuss in this post. The list of figures of speech is very long. However, there are only eight that are used most often to embellish the English language. These are the literary tools in the English language that can make the language more effective and engaging. Many of them have existed for 100 years, whereas many of them are being essentially added every day. In this post, we will discuss the main 8 types of figure of speech. However, you need to keep in mind that the types are endless and are used in different forms in the English language. Let’s explore!
Table of Contents
What Does Figure Of Speech Mean?
A figure of speech is a way to make the language more interesting and engaging. If you say something in plain words, no one wants to listen to you. However, when you make some exciting comparisons or add wit to the talk, people become all ears to your words. The figure of speech works magic when it comes to making a conversion more exciting. Whether you want to be sarcastic, make comparisons, or introduce literary elements in language, you can use different figures of speech. So, you can conclude it as a tool to embellish a language that enables the speakers/writers to become more expressive and interesting.
Types of Figure of Speech
The English language has many figures of speech; each has its unique qualities. In this post, we will discuss 8 of them, which are most commonly used in speaking or writing the English language:
In the first place, we have Simile on our list. This figure of speech is used for comparison purposes. It is used to compare one thing with the other using “As” or “Like.” However, it is effortless to determine in a sentence. The moment you see any of the two words, you can tell that Simile is used in the sentence. It is widely used in English literature, poetry, and other places. There is another figure of speech, which is also used for making comparisons, same as Simile, we will discuss in the next points. If you are a writer, you can make your writing pieces using Simile.
2: Metaphor
As we have discussed above, another figure of speech used for the comparison is the Metaphor. It serves the same function; however, the application of Metaphor is different in a sentence. It doesn’t involve the use of the words “As” and “Like.” It directly imposes the characteristics of one object on the other without using any comparison words. Metaphor is figurative, wherein the indicated meaning of a word or phrase is not the same as its literal meaning. So, it can add an artistic twist in the language that readers or listeners can thoroughly enjoy.

3: Personification
Personification is a figure of speech wherein non-living things are being given human attributes. In personification, human emotions are imposed on non-living things. The non-living things are described as if the author is talking about a human. If you look closely, you will notice that personification is also a kind of Metaphor. Here too comparison is being made without using the words, as or like. However, it has different characteristics of addressing non-human things as humans. In this figure of speech, these non-living things are shown to have life and motion. For instance, in “Angry Sun,” the sun can’t be angry; however, the fierce nature of the sun can be compared to human anger.

4: Hyperbole
Hyperbole is among the 8 types of figure of speech, used commonly in English literature. It is figurative language used to exaggerate a person, thing, or event. You can take it as an overstatement about something. If you want to give emphasis on something, you can use this figure of speech. The authors and poets use it to enhance the magnificence of a thing or event.

Imagery is also a figurative language that creates a scenic image when reading the text. It can take the readers to the particular scenario the author is talking about. The writers used to evoke the senses by the elements of taste, touch, smell, and various others. This figure of speech gives a strong description of an incident so that readers can fully visualize the situation. Reading this figurative language, you can reach an old mental memory or feel the most profound emotions. Physical feelings are also involved in it, such as sensuality, pain, tiresomeness, and several others. All of these can be established merely with words.

6: Alliteration
Alliteration is a literary device that creates a symphonic effect on the reader. It involves the repetition of the same consonant sound in two or more consecutive words. It takes place when two or more nearby words start with the same consonant letter. However, not necessarily the same letters in the beginning, but the alphabets that create the same sound. For instance, “Kids Coat.”

7: Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is when a word describes a sound and actually imitates the sound of the object or action it refers to when it is spoken. It appeals to the sense of hearing, and writers use it to bring a story or poem to life in the reader’s head. This one is really unique among the list of the 8 types of figure of speech described in this post.

The irony is a literary device in which seemingly contradictory claims or situations show a fact that isn’t what it appears to be. In literature, there are several different types of irony. The reader’s perceptions and interpretation plays a crucial role. Irony is based on the difference of of the difference between what “should” happen and what “really” happens. This can be in the form of an unforeseen outcome of an event, a character’s unanticipated behavior, or something incongruous that is said.

The world of figures of speech is fascinating. Besides, reading the examples of these 8 types of figure of speech can surely make you read more about them. If you liked this post, find more in our blog section.
You may also like:

6 Impulse Control Activities For Kids That Parents Must Know!

Is Psychology A Social Science? Get Your Doubts Cleared!

Leverage AI-Driven e-learning for professional upskilling

How do I create a featured post on Blogger? Follow the 7 steps!
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Transparency Center
Facebook Community Standards
Policies that outline what is and isn't allowed on the Facebook app.
Instagram Community Guidelines
Policies that outline what is and isn't allowed on the Instagram app.
Meta Advertising Standards
Policies for ad content and business assets.
Other policies
Other policies that apply to Meta technologies.
How Meta improves
How we update our policies, measure results, work with others, and more.
Enforcement
Detecting violations
How technology and review teams help us detect and review violating content and accounts.
Taking action
Our three-part approach to content enforcement: remove, reduce and inform.
Threat disruptions
How we take down coordinated adversarial networks to protect people using our services
Security threats
Challenges we investigate and counter around the globe
Threat reporting
Security research into the adversarial networks we’ve taken down since 2017
Our approach to the opioid epidemic
How we support communities in the face of the opioid epidemic.
Our approach to elections
How we help prevent interference, empower people to vote and more.
Our approach to misinformation
How we work with independent fact-checkers, and more, to identify and take action on misinformation.
Our approach to newsworthy content
How we assess content for newsworthiness.
Our approach to Facebook Feed ranking
How we reduce problematic content in News Feed.
Our approach to explaining ranking
How we build AI systems.
Governance innovation
Oversight Board overview
How to appeal to the Oversight Board
Oversight Board cases
Oversight Board recommendations
Creating the Oversight Board
Oversight Board: Further asked questions
Meta’s Quarterly Updates on the Oversight Board
Research tools
Content Library and Content Library API
Comprehensive access to public data from Facebook and Instagram
Ad Library tools
Comprehensive and searchable database of all ads currently running across Meta technologies
Other research tools and datasets
Additional tools for in-depth research on Meta technologies and programs
Community Standards Enforcement Report
Quarterly report on how well we're doing at enforcing our policies on the Facebook app and Instagram.
Intellectual Property
Report on how well we're helping people protect their intellectual property.
Government Requests for User Data
Report on government request for people's data.
Content Restrictions Based on Local Law
Report on when we restrict content that's reported to us as violating local law.
Internet Disruptions
Report on intentional internet restrictions that limit people's ability to access the internet.
Widely Viewed Content Report
Quarterly report on what people see on Facebook, including the content that receives the widest distribution during the quarter.
Regulatory and Other Transparency Reports
Download current and past regulatory reports for Facebook and Instagram.
Hate Speech
Policy details.
Current version
Mar 1, 2024
May 26, 2023, nov 24, 2022, jul 29, 2022, jul 1, 2022, nov 25, 2021, oct 29, 2021, jun 24, 2021, jan 29, 2021, nov 19, 2020, oct 13, 2020, sep 24, 2020, aug 12, 2020, jul 31, 2020, jun 23, 2020, mar 27, 2020, feb 28, 2020, dec 17, 2019, oct 31, 2019, aug 27, 2019, jul 31, 2019, jul 2, 2019, mar 21, 2019, sep 1, 2018, may 26, 2018.
We believe that people use their voice and connect more freely when they don’t feel attacked on the basis of who they are. That is why we don’t allow hate speech on Facebook, Instagram, or Threads. It creates an environment of intimidation and exclusion, and in some cases may promote offline violence.
We define hate speech as direct attacks against people — rather than concepts or institutions— on the basis of what we call protected characteristics (PCs): race, ethnicity, national origin, disability, religious affiliation, caste, sexual orientation, sex, gender identity, and serious disease. Additionally, we consider age a protected characteristic when referenced along with another protected characteristic. We also protect refugees, migrants, immigrants, and asylum seekers from the most severe attacks, though we do allow commentary on and criticism of immigration policies. Similarly, we provide some protections for non- protected characteristics, such as occupation, when they are referenced along with a protected characteristic. Sometimes, based on local nuance, we consider certain words or phrases as frequently used proxies for PC groups.
We define a hate speech attack as dehumanizing speech; statements of inferiority, expressions of contempt or disgust; cursing; and calls for exclusion or segregation. We also prohibit the use of harmful stereotypes, which we define as dehumanizing comparisons that have historically been used to attack, intimidate, or exclude specific groups, and that are often linked with offline violence. We also prohibit the usage of slurs that are used to attack people on the basis of their protected characteristics. Attacks are separated into two tiers of severity, described below.
We have additional restrictions for paid content.
However, we recognize that people sometimes share content that includes slurs or someone else’s hate speech in order to condemn the speech or report on it. In other cases, speech, including slurs, that might otherwise violate our standards is used self-referentially or in an empowering way. People also sometimes express contempt or curse at a gender in the context of a romantic break-up. Other times, they use gender-exclusive language to control membership in a health or positive support group, such as a breastfeeding group for women only. Our policies are designed to allow room for these types of speech but require people to clearly indicate their intent. Where intention is unclear, we may remove content.
Note: Violent speech targeting people on the basis of their protected characteristics is covered in our Violence and Incitement Policy.
Learn more about our approach to hate speech.
Content targeting a person or group of people (including all groups except those who are considered non-protected groups described as having carried out violent crimes or sexual offenses or representing less than half of a group) on the basis of their aforementioned protected characteristic(s) or immigration status in written or visual form with:
- Dehumanizing speech in the form of comparisons to or generalizations about:
- Animals and pathogens
- Insects (including but not limited to: cockroaches, locusts)
- Animals in general or specific types of animals that are culturally perceived as inferior (including but not limited to: Black people and apes or ape-like creatures; Jewish people and rats; Muslim people and pigs; Mexican people and worms)
- Certain Inanimate Objects and Non-Human States:
- Certain objects (women as household objects or property or objects in general; Black people as farm equipment; transgender or non-binary people as “it”)
- Feces (including but not limited to: shit, crap)
- Filth (including but not limited to: dirt, grime, or saying "[protected characteristic or quasi-protected characteristic] has bad hygiene")
- Bacteria, viruses, or microbes
- Disease (including but not limited to: cancer, sexually transmitted diseases)
- Subhumanity (including but not limited to: savages, devils, monsters, primitives)
- Sexual predators (including but not limited to: Muslim people having sex with goats or pigs)
- Violent criminals (including but not limited to: terrorists, murderers, members of hate or criminal organizations)
- Other criminals (including but not limited to “thieves,” “bank robbers,” or saying “All [protected characteristic or quasi-protected characteristic] are ‘criminals’”).
- Statements in the form of calls for action or statements of intent to inflict, aspirational or conditional statements about, or statements advocating or supporting harm in the following ways:
- In favor of contracting a disease
- In favor of experiencing a natural disaster
- Calls for self-injury or suicide
- Calls for death without a perpetrator or method
- Calls for accidents and other physical harms caused either by no perpetrator or by a deity
- Statements denying existence (including but not limited to: "[protected characteristic(s) or quasi-protected characteristic] do not exist", "no such thing as [protected charactic(s) or quasi-protected characteristic]" or “[protected characteristic(s) or quasi-protected characteristic] shouldn’t exist”)
- Harmful stereotypes historically linked to intimidation, exclusion, or violence on the basis of a protected characteristic, such as Blackface; Holocaust denial; claims that Jewish people control financial, political, or media institutions; and references to Dalits as menial laborers
- Mocking the concept, events or victims of hate crimes even if no real person is depicted in an image.
- Mocking people on the basis of their Protected Characteristics or Quasi-Protected Characteristics for having or experiencing a disease.
- Content that describes or negatively targets people with slurs, where slurs are defined as words that inherently create an atmosphere of exclusion and intimidation against people on the basis of a protected characteristic, often because these words are tied to historical discrimination, oppression, and violence. They do this even when targeting someone who is not a member of the PC group that the slur inherently targets.
- Physical appearance, including but not limited to: ugly, hideous.
- Intellectual capacity, including but not limited to: dumb, stupid, idiots.
- Education, including but not limited to: illiterate, uneducated.
- Mental health, including but not limited to: mentally ill, retarded, crazy, insane.
- Character traits culturally perceived as negative, including but not limited to: coward, liar, arrogant, ignorant.
- Derogatory terms related to sexual activity, including but not limited to: whore, slut, perverts.
- Expressions about being less than adequate, including but not limited to: worthless, useless.
- Expressions about being better/worse than another protected characteristic, including but not limited to: "I believe that males are superior to females."
- Expressions about deviating from the norm, including but not limited to: freaks, abnormal.
- Self-admission to intolerance on the basis of a protected characteristics, including but not limited to: homophobic, islamophobic, racist.
- Expressions of hate, including but not limited to: "I despise","I hate", " I can't stand".
- Expressions of dismissal, including but not limited to: "I don´t respect", "I don't like", " I don´t care for"
- Expressions that suggest the target causes sickness, including but not limited to: vomit, throw up.
- Expressions of repulsion or distaste, including but not limited to: vile, disgusting, yuck.
- Referring to the target as genitalia or anus, including but not limited to: cunt, dick, asshole.
- Profane terms or phrases or other curses with the intent to insult, including but not limited to: fuck, bitch, motherfucker.
- Terms or phrases calling for engagement in sexual activity, or contact with genitalia, anus, feces or urine, including but not limited to: suck my dick, kiss my ass, eat shit.
- Exclusion or segregation in the form of calls for action, statements of intent, aspirational or conditional statements, or statements advocating or supporting defined as:
- Explicit exclusion, which means things like expelling certain groups or saying they are not allowed or segregation.
- Political exclusion, which means denying the right to political participation.
- Economic exclusion, which means denying access to economic entitlements and limiting participation in the labor market.
- Social exclusion, which means things like denying access to spaces (physical and online)and social services, except for gender-based exclusion in health and positive support Groups.
Do not post:
- Content explicitly providing or offering to provide products or services that aim to change people’s sexual orientation or gender identity.
- Content attacking concepts, institutions, ideas, practices, or beliefs associated with protected characteristics, which are likely to contribute to imminent physical harm, intimidation or discrimination against the people associated with that protected characteristic. Meta looks at a range of signs to determine whether there is a threat of harm in the content. These include but are not limited to: content that could incite imminent violence or intimidation; whether there is a period of heightened tension such as an election or ongoing conflict; and whether there is a recent history of violence against the targeted protected group. In some cases, we may also consider whether the speaker is a public figure or occupies a position of authority.
- Content targeting a person or group of people on the basis of their protected characteristic(s) with claims that they have or spread the novel coronavirus, are responsible for the existence of the novel coronavirus, are deliberately spreading the novel coronavirus.
In certain cases, we will allow content that may otherwise violate the Community Standards when it is determined that the content is satirical. Content will only be allowed if the violating elements of the content are being satirized or attributed to something or someone else in order to mock or criticize them.
See some examples of what enforcement looks like for people on Facebook, such as: what it looks like to report something you don’t think should be on Facebook, to be told you’ve violated our Community Standards and to see a warning screen over certain content.
Note: We’re always improving, so what you see here may be slightly outdated compared to what we currently use.
USER EXPERIENCE
Post-report communication, takedown experience, warning screens.
Percentage of times people saw violating content
Content actioned
Number of pieces of violating content we took action on
Proactive rate
Percentage of violating content we found before people reported it
Appealed content
Number of pieces of content people appealed after we took action on it
Restored content
Number of pieces of content we restored after we originally took action on it
Universal entry point
We have an option to report, whether it’s on a post, a comment, a story, a message or something else.

Get started
We help people report things that they don’t think should be on our platform.

Select a problem
We ask people to tell us more about what’s wrong. This helps us send the report to the right place.

Report submitted
After these steps, we submit the report. We also lay out what people should expect next.

Update via notifications
After we’ve reviewed the report, we’ll send the reporting user a notification.

More detail in the Support Inbox
We’ll share more details about our review decision in the Support Inbox. We’ll notify people that this information is there and send them a link to it.

Appeal option
If people think we got the decision wrong, they can request another review.

Post-appeal communication
We’ll send a final response after we’ve re-reviewed the content, again to the Support Inbox.

Immediate notification
When someone posts something that doesn't follow our rules, we’ll tell them.

Additional context
We’ll also address common misperceptions and explain why we made the decision to enforce.

Policy Explanation
We’ll give people easy-to-understand explanations about the relevant rule.

Option for review
If people disagree with the decision, they can ask for another review and provide more information.

Final decision
We set expectations about what will happen after the review has been submitted.

Warning screens in context
We cover certain content in News Feed and other surfaces, so people can choose whether to see it.

More information
In this example, we give more context on why we’ve covered the photo with more context from independent fact-checkers

We have the same policies around the world, for everyone on Facebook.
Review teams
Our global team of over 15,000 reviewers work every day to keep people on Facebook safe.
Stakeholder engagement
Outside experts, academics, NGOs and policymakers help inform the Facebook Community Standards.
Learn what you can do if you see something on Facebook that goes against our Community Standards.
Visit our Help Center
Privacy violations, violent and graphic content, enforcement.
Crowdtangle
Facebook Open Research and Transparency
RESEARCH TOOLS
Ad Library Tools
Privacy Policy
Terms of Service

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Answers for Types of speech (8) crossword clue, 8 letters. Search for crossword clues found in the Daily Celebrity, NY Times, Daily Mirror, Telegraph and major publications. Find clues for Types of speech (8) or most any crossword answer or clues for crossword answers.
8 Articles. A pear. The brick house. An exciting experience. These bolded words are known as articles. Articles come in two flavors: definite articles and indefinite articles. And similarly to the two types of nouns, the type of article you use depends on how specific you need to be about the thing you're discussing.
Interjection: Expressions of Emotion. Types: Expressive interjections, introductory interjections. Definition: An interjection expresses strong emotions or sudden bursts of feeling. Example: Wow! That was amazing! Ouch! That hurt. 8 Parts of Speech 8 Types Definition and Examples eight parts of speech.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles. Many words can function as different parts of ...
In the English language, it's commonly accepted that there are 8 parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions, interjections, and prepositions. Each of these categories plays a different role in communicating meaning in the English language. Each of the eight parts of speech—which we might also call the "main ...
The Eight Parts of Speech. There are eight parts of speech in the English language: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. The part of speech indicates how the word functions in meaning as well as grammatically within the sentence. An individual word can function as more than one part of speech when ...
The 8 parts of speech in English are: Nouns, Adjectives, Adverbs, Verbs, Prepositions, Pronouns, Conjunctions, and Interjections. A part of speech is a category of words that have similar grammatical functions or properties. In other words, they play similar roles in a sentence. For instance, a verb shows the action of a subject or the subject ...
Knowing the different parts of speech is essential for good grammar. Become an expert at knowing when and what parts of speech to use with these examples.
Understand the 8 parts of speech with examples: 1. Nouns 2. Pronouns 3. Verbs 4. Adjectives 5. Adverbs 6. Conjunctions 7. Prepositions 8. interjections
There are eight different parts of speech. Think of them as team members, each working together by fulfilling specific tasks to develop coherent sentences. The eight parts of speech are nouns ...
8 Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples: 1. Nouns are words that are used to name people, places, animals, ideas and things. Nouns can be classified into two main categories: Common nouns and Proper nouns. Common nouns are generic like ball, car, stick, etc., and proper nouns are more specific like Charles, The White House, The Sun, etc.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles. Many words can function as different parts of ...
Here is a simple guide to the 8 parts of speech and examples of each. 1. Adjectives. Adjectives modify nouns and pronouns. You probably know that they're used to describe, but they can also quantify, identify, and limit. Check out the examples of this part of speech: Brett ate nine tacos. In this example, nine quantifies tacos.
Preposition. 7. Conjunction. 8. Interjection. Conclusion. This lesson will analyze the '8 Parts of Speech' in English with definitions, types, and examples. Parts of Speech are part and parcel of English grammar. We can't think of a sentence without using Parts of Speech.
Different Parts of Speech with Examples. Parts of Speech can be divided into eight classes the function they perform in sentences. 1. Noun: The Taj Mahal is one of the seven wonders. 2. Pronoun: He can make it easier. 3. Adjective: She is as beautiful as a rose. 4.
There are 8 different types of parts of speech i.e., Nouns, Pronouns, Adjectives, Verbs, Adverb, prepositions, Conjunction, and Interjection. Noun -. A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, state, or quality. It can be singular or plural. Nouns are a part of speech.
Do you know the 8 parts of speech? Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions and prepositions? 📝 *GET THE FREE LESSON PDF* _here_ 👉🏼 https...
The 8 Parts of Speech: Definition, Types, Functions & Examples. In the English language, there are eight parts of speech: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. Part of speech indicates the word's meaning and grammatical role in the sentence. It is possible for a single word to serve multiple ...
The 8 parts of speech definitions with examples include nouns, verbs, adjectives, pronouns, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections. By using proper grammar in your writing and speaking, you will communicate clearly and effectively …
Words are important elements of each sentence and based on their function, words are classified into eight types of parts of speech. However, 8 important parts of speech are noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, adjective, preposition, conjunction and interjection. Noun: This is the easiest one among the eight parts of speech.
This type of speech is frequently used for giving reports, lectures and, sometimes for training purposes. Examples of informative speech topics: the number, price and type of dwellings that have sold in a particular suburb over the last 3 months; the history of the tooth brush; how trees improves air quality in urban areas; a brief biography of ...
Informative speech. Informative speeches aim to educate an audience on a particular topic or message. Unlike demonstrative speeches, they don't use visual aids. They do, however, use facts, data and statistics to help audiences grasp a concept. These facts and statistics help back any claims or assertions you make.
4: Hyperbole. Hyperbole is among the 8 types of figure of speech, used commonly in English literature. It is figurative language used to exaggerate a person, thing, or event. You can take it as an overstatement about something. If you want to give emphasis on something, you can use this figure of speech.
We believe that people use their voice and connect more freely when they don't feel attacked on the basis of who they are. That is why we don't allow hate speech on Facebook, Instagram, or Threads. It creates an environment of intimidation and exclusion, and in some cases may promote offline violence. We define hate speech as direct attacks ...
This pattern was reversed for gesture production. Speech and gesture production also varied by discourse context. Adults with either type of aphasia used a lower amount of and less diverse speech in third-person than in first-person narratives; this pattern was also reversed for gesture production.
Broca's Aphasia is characterized by: A struggle to form words. Leaving out words such as "is" or "the.". Saying something that doesn't resemble a sentence. Trouble understanding sentences. Making mistakes in following directions like "left, right, under and after.". Using a word that's close to what you intend, but not the ...