- Mattress Education Mattress Sizes Mattress Types Choosing the Best Mattress Replacing a Mattress Caring for a Mattress Mattress Disposal Mattress Accessories Adjustable Beds Mattress Sizes Mattress Types Choosing the Best Mattress Replacing a Mattress Caring for a Mattress Mattress Disposal Mattress Accessories Adjustable Beds
- Better Sleep Sleep Positions Better Sleep Guide How to Sleep Better Tips for Surviving Daylight Saving Time The Ideal Bedroom Survey: Relationships & Sleep Children & Sleep Sleep Myths
- Resources Blog Research Press Releases
- Extras The Science of Sleep Stages of Sleep Sleep Disorders Sleep Safety Consequences of Poor Sleep Bedroom Evolution History of the Mattress

- December 12, 2018

Teens, Sleep and Homework Survey Results
Better sleep council research finds that too much homework can actually hurt teens' performance in school.
- Press Releases
ALEXANDRIA, Va. , Dec. 11, 2018 – According to new research from the Better Sleep Council (BSC) – the nonprofit consumer-education arm of the International Sleep Products Association – homework, rather than social pressure, is the number one cause of teenage stress, negatively affecting their sleep and ultimately impacting their academic performance.
American teenagers said they spend 15+ hours a week on homework, and about one-third (34%) of all teens spend 20 or more hours a week. This is more than time spent at work, school clubs, social activities and sports. When asked what causes stress in their lives, about three-quarters of teens said grades/test scores (75%) and/or homework (74%) cause stress, more than self-esteem (51%), parental expectations (45%) and even bullying (15%). In fact, according to the American Psychological Association’s Stress in America™ Survey, during the school year, teenagers say they experience stress levels higher than those reported by adults.
Further, more than half (57%) of all teenagers surveyed do not feel they get enough sleep. Seventy-nine percent reported getting 7 hours of sleep or less on a typical school night, more than two-thirds (67%) say they only get 5 to 7 hours of sleep on a school night, and only about one in five teens is getting 8 hours of sleep or more. Based on the BSC’s findings, the more stressed teenagers feel, the more likely they are to get less sleep, go to bed later and wake up earlier. They are also more likely to have trouble going to sleep and staying asleep – more often than their less-stressed peers.
“We’re finding that teenagers are experiencing this cycle where they sacrifice their sleep to spend extra time on homework, which gives them more stress – but they don’t get better grades,” said Mary Helen Rogers , vice president of marketing and communications for the Better Sleep Council. “The BSC understands the impact sleep has on teenagers’ overall development, so we can help them reduce this stress through improved sleep habits.”
The BSC recommends that teens between the ages of 13-18 get 8-10 hours of sleep per night. For teens to get the sleep their bodies need for optimal school performance, they should consider the following tips:
- Establish a consistent bedtime routine . Just like they set time aside for homework, they should schedule at least 8 hours of sleep into their daily calendars. It may be challenging in the beginning, but it will help in the long run.
- Keep it quiet in the bedroom. It’s easier to sleep when there isn’t extra noise. Teens may even want to wear earplugs if their home is too noisy.
- Create a relaxing sleep environment. Make sure the bedroom is clutter-free, dark and conducive to great sleep. A cool bedroom, between 65 and 67 degrees , is ideal to help teens sleep.
- Cut back on screen time. Try cutting off screen time at least an hour before bed. The blue light emitted from electronics’ screens disturbs sleep.
- Examine their mattress. Since a mattress is an important component of a good night’s sleep, consider replacing it if it isn’t providing comfort and support, or hasn’t been changed in at least seven years.
Other takeaways on the relationship between homework, stress and sleep in teenagers include:
- Teens who feel more stress (89%) are more likely than less-stressed teens (65%) to say homework causes them stress in their lives.
- More than three-quarters (76%) of teens who feel more stress say they don’t feel they get enough sleep – which is significantly higher than teens who are not stressed, since only 42% of them feel they don’t get enough sleep.
- Teens who feel more stress (51%) are more likely than less-stressed teens (35%) to get to bed at 11 p.m. or later. Among these teens who are going to bed later, about 33% of them said they are waking up at 6:00 a.m. or earlier.
- Students who go to bed earlier and awaken earlier perform better academically than those who stay up late – even to do homework.
About the BSC The Better Sleep Council is the consumer-education arm of the International Sleep Products Association, the trade association for the mattress industry. With decades invested in improving sleep quality, the BSC educates consumers on the link between sleep and health, and the role of the sleep environment, primarily through www.bettersleep.org , partner support and consumer outreach.
Related Posts

The State of America’s Sleep: COVID-19 and Sleep
The state of america’s sleep: isolation and sleep, the state of america’s sleep.

ABOUT THE BETTER SLEEP COUNCIL
- Mattress Education
- Better Sleep
- Privacy Policy
- Confidentiality Statement
- Our Mission
Homework, Sleep, and the Student Brain

At some point, every parent wishes their high school aged student would go to bed earlier as well as find time to pursue their own passions -- or maybe even choose to relax. This thought reemerged as I reread Anna Quindlen's commencement speech, A Short Guide to a Happy Life. The central message of this address, never actually stated, was: "Get a life."
But what prevents students from "getting a life," especially between September and June? One answer is homework.
Favorable Working Conditions
As a history teacher at St. Andrew's Episcopal School and director of the Center for Transformative Teaching and Learning , I want to be clear that I both give and support the idea of homework. But homework, whether good or bad, takes time and often cuts into each student's sleep, family dinner, or freedom to follow passions outside of school. For too many students, homework is too often about compliance and "not losing points" rather than about learning.
Most schools have a philosophy about homework that is challenged by each parent's experience doing homework "back in the day." Parents' common misconception is that the teachers and schools giving more homework are more challenging and therefore better teachers and schools. This is a false assumption. The amount of homework your son or daughter does each night should not be a source of pride for the quality of a school. In fact, I would suggest a different metric when evaluating your child's homework. Are you able to stay up with your son or daughter until he or she finishes those assignments? If the answer is no, then too much homework is being assigned, and you both need more of the sleep that, according to Daniel T. Willingham , is crucial to memory consolidation.
I have often joked with my students, while teaching the Progressive Movement and rise of unions between the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries, that they should consider striking because of how schools violate child labor laws. If school is each student's "job," then students are working hours usually assigned to Washington, DC lawyers (combing the hours of the school day, school-sponsored activities, and homework). This would certainly be a risky strategy for changing how schools and teachers think about homework, but it certainly would gain attention. (If any of my students are reading this, don't try it!)
So how can we change things?
The Scientific Approach
In the study "What Great Homework Looks Like" from the journal Think Differently and Deeply , which connects research in how the brain learns to the instructional practice of teachers, we see moderate advantages of no more than two hours of homework for high school students. For younger students, the correlation is even smaller. Homework does teach other important, non-cognitive skills such as time management, sustained attention, and rule following, but let us not mask that as learning the content and skills that most assignments are supposed to teach.
Homework can be a powerful learning tool -- if designed and assigned correctly. I say "learning," because good homework should be an independent moment for each student or groups of students through virtual collaboration. It should be challenging and engaging enough to allow for deliberate practice of essential content and skills, but not so hard that parents are asked to recall what they learned in high school. All that usually leads to is family stress.
But even when good homework is assigned, it is the student's approach that is critical. A scientific approach to tackling their homework can actually lead to deepened learning in less time. The biggest contributor to the length of a student's homework is task switching. Too often, students jump between their work on an assignment and the lure of social media. But I have found it hard to convince students of the cost associated with such task switching. Imagine a student writing an essay for AP English class or completing math proofs for their honors geometry class. In the middle of the work, their phone announces a new text message. This is a moment of truth for the student. Should they address that text before or after they finish their assignment?
Delayed Gratification
When a student chooses to check their text, respond and then possibly take an extended dive into social media, they lose a percentage of the learning that has already happened. As a result, when they return to the AP essay or honors geometry proof, they need to retrace their learning in order to catch up to where they were. This jump, between homework and social media, is actually extending the time a student spends on an assignment. My colleagues and I coach our students to see social media as a reward for finishing an assignment. Delaying gratification is an important non-cognitive skill and one that research has shown enhances life outcomes (see the Stanford Marshmallow Test ).
At my school, the goal is to reduce the barriers for each student to meet his or her peak potential without lowering the bar. Good, purposeful homework should be part of any student's learning journey. But it takes teachers to design better homework (which can include no homework at all on some nights), parents to not see hours of homework as a measure of school quality, and students to reflect on their current homework strategies while applying new, research-backed ones. Together, we can all get more sleep -- and that, research shows, is very good for all of our brains and for each student's learning.
Login to your account
If you don't remember your password, you can reset it by entering your email address and clicking the Reset Password button. You will then receive an email that contains a secure link for resetting your password
If the address matches a valid account an email will be sent to __email__ with instructions for resetting your password
Access provided by

Download started.
- PDF [1 MB] PDF [1 MB]
- Figure Viewer
- Download Figures (PPT)
- Add To Online Library Powered By Mendeley
- Add To My Reading List
- Export Citation
- Create Citation Alert
Associations of time spent on homework or studying with nocturnal sleep behavior and depression symptoms in adolescents from Singapore
- Sing Chen Yeo, MSc Sing Chen Yeo Affiliations Center for Cognitive Neuroscience, Program in Neuroscience and Behavioral Disorders, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore Search for articles by this author
- Jacinda Tan, BSc Jacinda Tan Affiliations Center for Cognitive Neuroscience, Program in Neuroscience and Behavioral Disorders, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore Search for articles by this author
- Joshua J. Gooley, PhD Joshua J. Gooley Correspondence Corresponding author: Joshua J. Gooley, Center for Cognitive Neuroscience, Neuroscience and Behavioral Disorders Program, Duke-NUS Medical School Singapore, 8 College Road, Singapore 117549, Singapore Contact Affiliations Center for Cognitive Neuroscience, Program in Neuroscience and Behavioral Disorders, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore Search for articles by this author
Participants
Measurements, conclusions.
- Sleep deprivation
Introduction
- Dewald J.F.
- Meijer A.M.
- Kerkhof G.A.
- Scopus (1010)
- Google Scholar
- Gooley J.J.
- Scopus (222)
- Chaput J.P.
- Poitras V.J.
- Scopus (515)
- Crowley S.J.
- Wolfson A.R.
- Carskadon M.A
- Scopus (370)
- Roenneberg T.
- Pramstaller P.P.
- Full Text PDF
- Scopus (1116)
- Achermann P.
- Scopus (346)
- Gradisar M.
- Scopus (77)
- Watson N.F.
- Martin J.L.
- Scopus (83)
- Robinson J.C.
- Scopus (656)
- Street N.W.
- McCormick M.C.
- Austin S.B.
- Scopus (16)
- Scopus (292)
- Scopus (297)
- Twenge J.M.
- Scopus (142)
- Galloway M.
- Scopus (63)
- Huang G.H.-.C.
- Scopus (66)
- Scopus (116)
Participants and methods
Participants and data collection, assessment of sleep behavior and time use.
- Scopus (1322)
- Carskadon M.A.
- Scopus (557)
Assessment of depression symptoms
- Brooks S.J.
- Krulewicz S.P.
- Scopus (60)
Data analysis and statistics
- Fomberstein K.M.
- Razavi F.M.
- Scopus (56)
- Fuligni A.J.
- Scopus (234)
- Miller L.E.
- Scopus (424)
- Preacher K.J.
- Scopus (22856)
- Open table in a new tab

- View Large Image
- Download Hi-res image
- Download (PPT)

- Scopus (33)
- Scopus (17)
- Scopus (58)
- Scopus (164)
- Maddison R.
- Lushington K.
- Pallesen S.
- Stormark K.M.
- Jakobsen R.
- Lundervold A.J.
- Sivertsen B
- Scopus (345)
- Scopus (30)
- Afzali M.H.
- Scopus (218)
- Abramson L.Y
- Scopus (1179)
- Spaeth A.M.
- Scopus (106)
- Gillen-O'Neel C.
- Fuligni A.J
- Scopus (76)
- Felden E.P.
- Rebelatto C.F.
- Andrade R.D.
- Beltrame T.S
- Scopus (72)
- Twan D.C.K.
- Karamchedu S.
- Scopus (25)
Conflict of interest
Acknowledgments, appendix. supplementary materials.
- Download .docx (.51 MB) Help with docx files
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
Article info
Publication history, identification.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2020.04.011
User license

For non-commercial purposes:
- Read, print & download
- Redistribute or republish the final article
- Text & data mine
- Translate the article (private use only, not for distribution)
- Reuse portions or extracts from the article in other works
Not Permitted
- Sell or re-use for commercial purposes
- Distribute translations or adaptations of the article
ScienceDirect
- Download .PPT
Related Articles
- Access for Developing Countries
- Articles & Issues
- Articles In Press
- Current Issue
- List of Issues
- Special Issues
- Supplements
- For Authors
- Author Information
- Download Conflict of Interest Form
- Researcher Academy
- Submit a Manuscript
- Style Guidelines for In Memoriam
- Download Online Journal CME Program Application
- NSF CME Mission Statement
- Professional Practice Gaps in Sleep Health
- Journal Info
- About the Journal
- Activate Online Access
- Information for Advertisers
- Career Opportunities
- Editorial Board
- New Content Alerts
- Press Releases
- More Periodicals
- Find a Periodical
- Go to Product Catalog
The content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Accessibility
- Help & Contact


We don't ship to your address!
- Choose your country
- Czech Republic
- Liechtenstein
- The Netherlands
- The United Kingdom
- kr. DANSK KRONE
- € EURO
- Ft MAGYAR FORINT
- £ POUND
- kr SVENSK KRONA
- zł ZłOTY
We're here to help
- Customer service
- Business-to-Business
- Shipping information
- Frequently asked questions
- Terms and Conditions
No products
You have to add to cart at least 0 bottles or any program to make checkout.
We are here to help you
How Does Homework Affect Students Sleep?
Published: June 21st, 2023
Exploring how homework affects students' sleep is an essential part of understanding the overall health and academic performance of our youth. The correlation between heavy workload from assignments and sleep deprivation has been a subject of multiple studies, with compelling findings.
Understanding the correlation between homework and teenage stress
Exploring the impact on quality sleep due to excessive homework, how late-night study impacts the circadian rhythm, the link between disturbed sleep patterns and academic performance, unpacking research findings linking heavy homework load with mental health issues, implications for future educational policies regarding home-based tasks, evaluating pros & cons related to assigning extensive workloads at elementary levels, suggesting alternatives for effective learning without compromising children's wellbeing, alfie kohn's perspective on education system practices, proposing changes toward balanced school schedules, assessing potential benefits shifting school start times based upon nsf recommendations, effective time management strategies, the impact of sleep deprivation on students, does homework affect sleep schedules, what percentage of students lose sleep due to homework, why does school cause sleep deprivation, why is sleep more important than homework.
This blog post delves into the impact that excessive homework can have on high school students' quality sleep, and how it might disrupt their natural circadian rhythm or sleep cycle. We will also explore its implications on mental health issues among younger kids who are often encouraged to go to bed earlier but struggle due to late-night study sessions.
The role of American education system practices in contributing to student's lack of adequate rest will be examined along with Alfie Kohn’s perspective about current education policies. Additionally, we'll discuss early school start times as another potential burden leading towards disturbed sleeping patterns.
Finally, we aim at proposing some changes for more balanced school schedules and providing tips for effectively managing time amidst academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities without being sleep deprived.

The Impact of Homework on Teenage Stress and Sleep
Homework is a major source of stress for teenagers, affecting their sleep patterns. According to studies, about 75% of high school students report grades and homework as significant stressors. This anxiety can lead to sleep deprivation, with over 50% of students reporting insufficient rest.
A heavy workload not only affects academic performance but also disrupts the normal sleep cycle. The pressure to excel academically leads many students into a vicious cycle where they stay up late completing tasks, wake up early for school, and end up being sleep deprived.
This lack of rest impairs cognitive functions like memory retention and problem-solving skills - both crucial for academic success. Furthermore, inadequate sleep may lead to ailments such as reduced immunity or persistent tiredness.
Sleep experts recommend that younger kids should go to bed earlier than teens because their biological clock naturally prompts them to feel sleepy around 8-9 PM. However, this becomes challenging when burdened with loads of assignments which extend their screen time significantly beyond recommended limits.
The blue light emitted by electronic devices used for studying suppresses melatonin production - a hormone that regulates our body's internal clock determining when we feel sleepy or awake (National Sleep Foundation). Consequently, these factors combined make falling asleep more difficult leading towards disrupted sleeping patterns ultimately affecting overall well-being including mental health status alongside academic performance negatively.
In conclusion, there needs to be an urgent reevaluation of how much work is assigned outside class hours considering potential adverse effects upon student's health, especially concerning adequate rest necessary for optimal functioning throughout day-to-day activities, whether within academia or other extracurricular responsibilities undertaken during leisure periods post-school schedules.
Analyzing Sleep Patterns Among Stressed Students
High schoolers are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of sleep deprivation due to the demands of juggling academics and extracurriculars. The pressure of balancing academics with extracurricular activities can lead to late nights and early mornings, leaving them feeling perpetually tired and impacting their academic performance.
The human body operates on a 24-hour internal clock known as the circadian rhythm. This biological process regulates our sleep-wake cycle, among other things. When students stay up late studying or completing homework, they disrupt this natural rhythm which can result in a range of health issues including chronic fatigue and weakened immunity.
Screen time is another factor that exacerbates this issue. Many students use electronic devices for research or writing assignments before bed, exposing themselves to blue light which further interferes with their circadian rhythms.
Regular slumber is a must for cognitive functions, such as memory consolidation and problem-solving aptitude - fundamental aspects of learning. Multiple studies have shown that when these patterns are disturbed due to excessive homework or late-night study sessions, it can negatively affect academic performance.
- Poor Concentration: Lack of adequate rest makes focusing on tasks more difficult, leading to decreased productivity during study hours.
- Inability To Retain Information: During deep stages of sleep, information from short-term memory gets transferred into long-term storage enabling better recall later; deprived individuals miss out on this critical process.
- Deteriorating Mental Health: Chronic lack of rest has been linked with increased levels of anxiety and depression amongst teenagers, impacting overall wellbeing and indirectly affecting grades too.
A report by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) suggests there's an urgent need for schools to address these concerns seriously, considering the potential repercussions over students' physical and mental health alongside scholastic achievements. Making sure they get enough quality rest each night is essential for optimal functioning throughout the day, both inside and outside the classroom environments.
Investigating Time Spent on Homework and Its Effects on Mental Health
The amount of time spent on homework and studying significantly affects students' mental health. Multiple studies have shown that an excessive workload can lead to depression, stress, and sleep deprivation .
A comprehensive study involving 2386 adolescents assessed various aspects, including self-rated health, overweight status, and depression symptoms, alongside time spent on homework/studying. The researchers used ten different multiple linear regression models to test the association with the global Kutcher Adolescent Depression Scale score. This approach allowed them to analyze how each aspect correlates with the others.
The results were revealing: there was a clear correlation between increased hours dedicated to home-based tasks and higher levels of depressive tendencies among high school students . These effects weren't limited only to academic performance but extended into their personal lives as well, affecting relationships, participation rates in extracurricular activities , and more.
This data suggests that we need a more balanced approach when it comes to assigning workloads at schools. Instead of piling up assignments indiscriminately, educators should aim for an optimal balance where learning is enhanced rather than hindered by excessive amounts of homework.
In light of this information, some countries are already taking steps towards reducing screen time requirements, especially during after-school hours. This allows younger kids to go to bed earlier, improving their sleep cycle quality significantly, which ultimately leads to better cognitive functioning the next day at school or other engagements they might have outside the academic context, like part-time jobs or family duties.
To sum up, a healthy balance between academic and other life obligations is essential to avoid potential repercussions in all aspects of a student's life. Neglecting to strike a balance between academic and other responsibilities can have severe repercussions, not only in terms of grades but also emotionally, socially, and mentally. Therefore, it is imperative to address this issue promptly and effectively with all stakeholders involved in the education sector worldwide today, tomorrow, and onwards too.
Excessive Workload Strain from Assignments in Younger Kids
The ongoing discussion about the implications of homework for younger students has drawn attention from educators, parents, and researchers. While assignments can reinforce what students learn during school hours, evidence supporting benefits from home-based tasks remains scarce before high-school levels. This is concerning considering the potential adverse effects an excessive workload can have on young minds.
On one hand, homework can instill discipline and help develop good study habits. On the other hand, too much of it could lead to sleep deprivation among younger kids who should ideally be going to bed earlier. The AAP suggests that 6-12 year olds should have 9-12 hours of rest, however this can be hard to attain when they are inundated with assignments.
Besides affecting their sleep cycle, overburdening them with academic responsibilities also leaves little room for extracurricular activities which play a crucial role in their overall development. It may even result in screen time replacing physical activity as children turn towards digital platforms to complete their assignments.
Rather than piling up work indiscriminately, schools could consider adopting strategies aimed at enhancing learning while ensuring the well-being of students. For instance, project-based learning could be an effective alternative where students actively explore real-world problems and challenges, thereby gaining deeper knowledge.
In addition to this approach would be limiting daily homework duration per grade level or introducing "homework-free" days during weekends or holidays providing ample rest periods essential for growth development amongst younger kids.
This shift not only ensures that our future generations aren't sleep deprived due to unnecessary academic pressure but also fosters a love for lifelong learning - something far more valuable than mere grades obtained through rote memorization.
American Education's Role In Student Sleep Deprivation
It's common for students in the US to be sleep deprived , not just because of academic pressures but also due to extracurricular activities . Late nights and early mornings disrupt a healthy sleep cycle , affecting student wellbeing.
Educational critic Alfie Kohn argues that the American education system emphasizes homework without considering its impact on student wellbeing. Many tasks assigned do not enhance learning but rather contribute towards stress and sleep deprivation among students. You can read more about his thoughts in his article titled " The Truth About Homework: Needless Assignments Persist Because of Widespread Misconceptions About Learning. "
Kohn suggests a shift towards assigning work aimed at enhancing learning rather than piling it up indiscriminately. Schools should recognize the importance of adequate rest for optimal functioning.
- Reduce homework loads: Lightening the load could help alleviate some of the pressure students feel, allowing them time to relax and get enough sleep each night.
- Consider late start times: Multiple studies suggest that starting school later in the morning could have numerous benefits including improved attendance rates and higher alertness, reducing instances of depressive tendencies significantly. (National Sleep Foundation (NSF))
- Promote good sleep hygiene: Schools can educate students about good sleep habits such as maintaining consistent bedtimes and wake-up times, limiting screen time before bedtime, and creating quiet, dark sleeping environments.
The key takeaway here is balance - between academics, extracurricular activities, family responsibilities, and personal downtime - which includes getting sufficient restful sleep every night.
Early School Start Times - An Additional Burden
Many adolescents in the US are finding that having to get up at sunrise is more of an encumbrance than a blessing. Parents and educators alike have reported that these early start times are inhibiting productivity throughout daytime schedules.
The National Sleep Foundation (NSF), an organization dedicated to improving health and well-being through sleep education and advocacy, suggests shifting school timings as one possible solution. This adjustment could result in improved attendance rates along with higher alertness among students during class hours.
The NSF study indicated that adjusting the school start time from 7:30 AM to 8:30 AM produced tangible improvements in student performance. The extra hour allowed teenagers' natural sleep cycle to align better with their academic schedule leading them to feel less sleep deprived.
- Better Attendance: Schools noted fewer tardies and absences after implementing later start times.
- Increase In Grades: Students showed improvement in core subjects like Math and English.
- Mental Health Benefits: A decrease was observed in instances of depressive tendencies significantly among students.
This shift not only helped improve academic outcomes but also had positive effects on mental health as teens were able to get adequate rest without having to sacrifice extracurricular activities or family duties.
The idea of starting schools later isn't new; however, its implementation has been slow due largely because changing such ingrained societal norms takes time. But if we want our younger kids performing optimally while avoiding unnecessary strain caused by excessive workload or screen time then we need to rethink how we structure our day-to-day lives. Research has demonstrated that inadequate rest can detrimentally affect our health and wellness, so it is essential to ensure we are getting enough sleep by retiring earlier and limiting screen time before bed.
Balancing Academic Responsibilities With Other Duties
As a student, you're expected to juggle academic responsibilities with other duties. Yet, it can be a challenge to effectively manage such a hectic schedule. Homework alone can take up to four hours a day, and that's not counting extracurricular activities or part-time jobs. So, how can you manage your time effectively amidst these multifarious responsibilities?
The key to managing your diverse obligations lies in effective time management strategies . Here are some tips that could help:
- Prioritize tasks: Not all assignments are created equal. Some require more effort and attention than others. Prioritizing your work can help you focus on what's most important first.
- Create a schedule: Having a set routine for studying can make it easier to stick to your commitments and avoid procrastination.
- Leverage technology: There are numerous apps available designed specifically for helping students manage their workload efficiently.
- Avoid multitasking: Multitasking often leads to mistakes and decreased productivity. Rather than attempting to juggle multiple tasks, give your full attention to one task until it is finished before progressing onto the next.
Sleep deprivation among high school students is a serious issue that needs urgent addressing. Multiple studies reveal that the majority of teenagers receive only six to eight hours of sleep per night despite needing more for optimal functioning. This lack of sleep not only affects academic performance but also overall health and wellbeing.
In addition, extracurricular activities and screen time can also affect younger kids' sleep cycle. The American education system has been criticized for promoting this unhealthy trend by assigning excessive amounts of homework without considering individual capacities or needs.
To combat this problem, parents need support from schools in ensuring children go to bed earlier while limiting their exposure to electronic devices during evening hours. This can significantly improve the quality of rest received each night, reducing instances of depressive tendencies associated with inadequate slumber patterns amongst adolescents today.
FAQs in Relation to How Does Homework Affect Students Sleep
Yes, excessive homework can lead to late-night studying, causing students to have inadequate sleep.
Around 56% of students reported losing sleep over schoolwork according to a Stanford study .
Schools may contribute to students' sleep deprivation through early start times and heavy academic loads.
Sleep is crucial for cognitive functions , including memory consolidation which aids in learning; overworking could hinder these processes.
Is Homework Ruining Your Sleep?
Excessive homework can negatively impact students' mental and physical health, leading to stress and lack of sleep.
Teachers can help by coordinating assignment deadlines and exploring alternatives like home-based tasks for younger children.
It's important for educators to recognize the effects of heavy academic loads on student productivity and well-being.
According to a study by the National Sleep Foundation, teenagers need 8-10 hours of sleep per night to function at their best.
Don't let homework rob you of your Z's - prioritize your health and well-being!
Check our wiki for more articles
Sign up to our newsletter and enjoy 10% off one order
Related blog posts
Lack of sleep effects on brain, dementia and sleep, sleeping on the couch, why do i feel sleepy all the tim..., menopause and sleep, how to function after sleepless ..., the best temperature for sleep i..., side effects of sleeping with a ..., why do i roll around in my sleep..., sleep latency, sleep deprivation headache, rhythmic movement disorder, sleep texting : causes and preve..., sleeping with pets: sleep qualit..., military sleep method for better..., improve sleep: the exercise and ..., paradoxical insomnia: causes and..., why you shouldn't always sleep w..., fasting and sleep, sudden tiredness during the day, sms sleep disorder, causes of insomnia in females, ostpartum insomnia, why do men sleep so much, elpenor syndrome, non-24 sleep wake disorder: caus..., daylight savings, how to relax before bed when str..., is it bad to eat before bed, short sleeper syndrome, sleeping with window open, boost sleep and productivity, minimizing screen time before bed, how sleep affects immunity, benefits of yoga for sleep, circadian rhythm fasting, how is sleep quality calculated, obesity and sleep: what is the c..., sleep deprivation and reaction time, sleeping in the dark, insomnia in elderly, do moon phases affect sleep, how to cool a room during summer, nightmare disorder: symptoms and..., fibromyalgia and sleeping too much, can too much exercise cause inso..., improve sleep and athletic perfo..., are we showering the right way f..., at what age do adults start taki..., is insomnia genetic, nightmares in children, the structure of sleeping patterns, how does technology affect sleep, watching tv before sleep: health..., is snoring harmless risks and t..., sleep and memory: a crucial conn..., daytime sleeping: better health,..., diet and sleep, can dogs have sleep apnea, what would happen if we get rid ..., how much sleep do athletes need ..., connection between gaming and sleep, seasonal insomnia, drinks to avoid sleep disruptions, why i sleep better away from home, sleep divorce, sleeping while working from home, exploring the best and worst cit..., sleep inequality, wildfire smoke and sleep, treatment strategies for chronic..., infradian rhythm for optimal wel..., how to not be tired all the time, what causes sleep apnea, 7 night sleep habit builder: gui..., how to improve sleep posture for..., how does social media affect sleep, how much sleep do we lose on tha..., how to achieve good sleep when y..., how working from home has change..., covid insomnia: causes, impacts ..., why do old people wake up so early, how long can you go without sleep, how to beat insomnia and anxiety, can sleep apnea be cured, can you die from lack of sleep, how many spiders do you swallow ..., do power naps work, best sleeping position for breat..., what to do when someone is snori..., how to sleep on a plane, teeth falling out dream, night eating syndrome, why is hyperthyroidism worse at ..., allergies and sleep, coffee naps : boost your energy, insomnia hypnosis, sleep and mental health, how to get more rem sleep, baby sleep cycles, shift work sleep disorder, sleep and epilepsy, the best breathing exercises for..., is dreaming a sign of good sleep, meditation and sleep, benefits of waking up early, how to fall back asleep, doe sleeping make you taller, how to prevent stuffy nose in th..., melatonin and birth control, nose bleeds at night, can lack of sleep cause nausea, 7 effective stretches to do befo..., can you sleep if you have a conc..., disturbed sleep, why do i keep yawning, how to interpret dreams, does turkey make you sleepy, sleep and weight loss, sleeping with socks: health bene..., pregnancy insomnia, sudden excessive sleepiness in e..., is lucid dreaming dangerous, how to hydrate overnight, what causes snoring in females, why you feel sleepy after workout, false awakening: causes and mana..., eating before bed: pros and cons, how long do dreams last, somniphobia: causes and treatments, parasomnia: causes, and treatments, how many calories do you burn sl..., how long does it take to fall as..., what causes snoring in kids, recurring dreams, sleeping upright, precognitive dreams, cold shower before bed, waking up gasping for breath, nightmares during pregnancy, ideal sleeping position during p..., how to wake up in the morning, how to stay awake when tired, fetal position sleep, why do i fart so much in the mor..., gaba for sleep, narcolepsy symptoms, how to wake up early, hypersomnia: causes and symptoms, staying up all night: effects an..., how to become a morning person, why shouldn't you workout before..., melatonin nightmares, what is pink noise, sleeping with eyes open, do blind people dream, cataplexy: symptoms and causes, valerian root for sleep, is sleep apnea genetic, headache from sleeping, micro sleep, binaural beats, foods that help you sleep, why is it so hard to wake up, woke up with blurry vision that ..., why do i moan in my sleep when s..., cbd oil for sleep, what is the 90 minute sleep stra..., what is the ultimate sleep pattern, how to fall asleep fast, master your bedtime routine for ....

- Close Menu Search
- Recommend a Story

The Lion's Roar
March 15 2023-2024 NFL Playoffs: Playoff Schedule And Results
February 23 The Timeline of Shirley Chisholm
February 23 Black Musicians’ Influences on Modern Music
February 23 Chiefs Win Super Bowl 58
February 23 6 Influential Black Americans That Schools Failed to Teach You About
The Effects Homework Can Have On Teens’ Sleeping Habits

Jess Amabile '24 and February 25, 2021
Ever wonder why you feel like you never get enough sleep? Here’s a pretty good reason: large amounts of homework can be detrimental to a teen’s sleeping habits, even more so with high schoolers.
There have been many studies recently about the damage homework has to students’ health, mainly concerning lack of sleep in teenagers. According to an article published by US News called “The Importance of Sleep for Teen Mental Health” , it states that “ surveys show that less than 9 percent of teens get enough sleep”. This fact is devastating, especially considering the fact that teenagers take up about thirteen percent of the country’s population.
Also mentioned in “The Importance of Sleep for Teen Mental Health” , “ about forty-one million Americans get six or fewer hours of sleep per night”. If teenagers see their parents not getting enough sleep, it can convince them that there are things more important than sleep, such as something almost every teenager in America has to deal with–homework.
Homework is pretty stressful for teens, especially if they have other things to do. Many teens have long hours at school, which limits the time for them to do their insane amount of homework, attend extra-curricular activities, eat, do whatever they need to around the house, and sleep. And usually, sleeping is the last thing on the list of things to do before school the next day. Another article, “What’s preventing adequate teen sleep” , states that, “Homework is possibly the biggest factor that keeps teens from getting enough sleep…The sheer quantity of homework absorbs hours that should be dedicated to sleep”. Students generally have so much homework that they don’t have enough time to do everything else they need to do that day. So, sleeping is often the first thing teens eliminate from their schedule.
According to Oxford Learning , homework can have other negative effects on students. In their article, Oxford Learning remarks, “56 percent of students considered homework a primary source of stress. Too much homework can result in lack of sleep, headaches, exhaustion, and weight loss”.
Similarly, Stanford Medicine News Center reports that the founder of the Stanford Sleep Disorders Clinic stated, “‘I think high school is the real danger spot in terms of sleep deprivation,’ said William Dement, MD, Ph.D.”. Sleep deprivation is a real problem for high school students, and Stanford Medicine News Center continues on this topic by commenting, “Sleep deprivation increases the likelihood teens will suffer myriad negative consequences, including an inability to concentrate, poor grades, drowsy-driving incidents, anxiety, depression, thoughts of suicide and even suicide attempts. It’s a problem that knows no economic boundaries”. If students are constantly battling sleep deprivation, how can they concentrate on schoolwork, or even be able to perform everyday tasks? This shows that homework greatly affects students in both mental and physical ways. If something is supposed to continue a lesson that was learned in school, why is it negatively affecting students’ lives?
Ask yourself: is homework really worth the extremely negative effects?
“What’s preventing adequate teen sleep”
http://sleepeducation.org/news/2017/07/26/what-is-preventing-adequate-teen-sleep
“The Importance of Sleep for Teen Mental Health”
https://health.usnews.com/health-care/for-better/articles/2018-07-02/the-importance-of-sleep-for-teen-mental-health
Oxford Learning
https://www.oxfordlearning.com/how-does-homework-affect-students/#:~:text=How%20Does%20Homework%20Affect%20Students,headaches%2C%20exhaustion%20and%20weight%20loss.
Stanford Medicine News Center
https://med.stanford.edu/news.html
What time should high school should start?
- 7:00 AM or earlier
- 7:30 AM (Current Start Time)
- After 9:00 AM
View Results
- Polls Archive
The Timeline of Shirley Chisholm

6 Influential Black Americans That Schools Failed to Teach You About
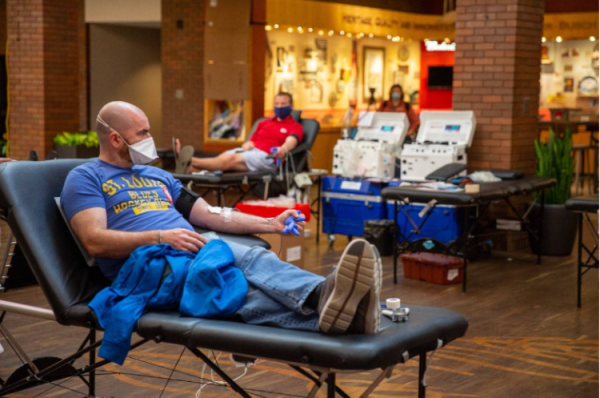
West Lions Save Lives: SGO’s 2024 Blood Drive
TIMELINE: The College Application Process

Santa Claus: Has He Become a Fraud and Only a Model for Greed to Children?
George Santos Expelled From House of Representatives
Interview with Ms. Roskoph: Introducing the New Grade 12 Principal
Mr. Burt Talks About His New Role at Cherry Hill West

Meeting the Principal: Interview with Dr. Burns

Katherine Johnson: Contributions to space exploration through math
Comments (0)
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Search form
- Find Stories
- For Journalists
Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework
A Stanford researcher found that students in high-achieving communities who spend too much time on homework experience more stress, physical health problems, a lack of balance and even alienation from society. More than two hours of homework a night may be counterproductive, according to the study.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
• Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
• Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
• Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
Improving lives through learning
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
share this!
August 16, 2021
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
by Sara M Moniuszko

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Dune: What the climate of Arrakis can tell us about the hunt for habitable exoplanets
6 hours ago

Saturday Citations: The volcanoes of Mars; Starship launched; 'Try our new menu item,' say Australian researchers
10 hours ago

Researchers take deep dive into how much water is stored in snow
12 hours ago

Ultra-flat optics for broadband thermal imaging
Mar 15, 2024

Shark-bitten orcas in the Northeastern Pacific could be a new population of killer whale

Einasto Supercluster: The new heavyweight contender in the universe

Protein fragments ID two new 'extremophile' microbes—and may help find alien life

Bridging the gap: Computer scientists develop model to enhance water data from satellites
Researchers develop a new strategy to enhance blue perovskite LED performance

Brighter, cheaper blue light could revolutionize screen technology
Relevant physicsforums posts, the new california math framework: another step backwards.
Mar 14, 2024
The changing physics curriculum in 1961
Feb 26, 2024
Rant about working in the tutoring lab: How should I deal with this?
Feb 25, 2024
Are Degree Apprenticeships a Good idea
Feb 23, 2024
Opinion: When Pro Scientists Explain Using Pop Science
Feb 15, 2024
Various Intuitions and Conceptualizations of Measurable Cardinals.
Feb 14, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you

Gender and racial discrimination uncovered in leadership positions at Australia's leading universities

Study finds children in Flint experienced educational declines even if they did not have lead pipes

Could iPhones replace microscopes in early STEM education?

Research finds a college degree remains a sound investment despite rising tuition
Mar 12, 2024

Research unveils effective STEM program models for high school students from historically marginalized communities
Mar 8, 2024

Doing more but learning less: Addressing the risks of AI in research
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Nat Sci Sleep
Causes and consequences of sleepiness among college students
Shelley d hershner.
Department of Neurology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
Ronald D Chervin
Daytime sleepiness, sleep deprivation, and irregular sleep schedules are highly prevalent among college students, as 50% report daytime sleepiness and 70% attain insufficient sleep. The consequences of sleep deprivation and daytime sleepiness are especially problematic to college students and can result in lower grade point averages, increased risk of academic failure, compromised learning, impaired mood, and increased risk of motor vehicle accidents. This article reviews the current prevalence of sleepiness and sleep deprivation among college students, contributing factors for sleep deprivation, and the role of sleep in learning and memory. The impact of sleep and sleep disorders on academics, grade point average, driving, and mood will be examined. Most importantly, effective and viable interventions to decrease sleepiness and sleep deprivation through sleep education classes, online programs, encouragement of naps, and adjustment of class time will be reviewed. This paper highlights that addressing sleep issues, which are not often considered as a risk factor for depression and academic failure, should be encouraged. Promotion of university and college policies and class schedules that encourage healthy and adequate sleep could have a significant impact on the sleep, learning, and health of college students. Future research to investigate effective and feasible interventions, which disseminate both sleep knowledge and encouragement of healthy sleep habits to college students in a time and cost effective manner, is a priority.
Introduction
The college experience is of great value in providing emerging adults with a structured environment in which they can gain the knowledge, skills, and independence to chart their own path, become successfully employed, and contribute to society. However, this experience comes at great cost given rising tuition fees and ballooning student debt, and thus, it is vital that the college years be as efficacious as possible. A potential obstacle to maximizing success in college is the high prevalence of daytime sleepiness, sleep deprivation, and irregular sleep schedules among college students.
Daytime sleepiness is a major problem, exhibited by 50% of college students compared to 36% of adolescents and adults. 1 At least 3 days a week, 60% of students report that they are dragging, tired, or sleepy. 2 Sleepiness is defined as the inability or difficulty in maintaining alertness during the major wake period of the day, resulting in unintended lapses into drowsiness or sleep. 3 It is important to note that sleepiness is often circumstance-dependent, with many aspects of the students’ learning environment exacerbating sleepiness. 4 For example, a lecture that does not require active participation and may be in a dark, warm lecture hall can unmask underlying sleepiness. Sleep deprivation is defined as obtaining inadequate sleep to support adequate daytime alertness. 4 How much sleep a young adult needs is not clearly known, but is thought to be 8 hours. 5 , 6 Most college students are sleep deprived, as 70.6% of students report obtaining less than 8 hours of sleep. 7 The impact of educational major on sleepiness and sleep duration is not well studied, but the effect may be substantial. As reported at an Architecture School in the Midwest, only 4% of students obtained at least 7 hours of sleep at night; the average sleep duration was 5.7 hours, with 2.7 “all-nighters” per month. 8 Eighty-two percent of college students believe that inadequate sleep and sleepiness impact their school performance. 9 Students rank sleep problems second only to stress in factors that negatively impact academic performance. 10
Sleep deprivation and sleepiness are caused by a host of reasons and have numerous negative consequences. In the literature, sleep deprivation is often termed either acute sleep deprivation or chronic partial sleep deprivation. Colloquially for students, acute sleep deprivation is termed “pulling an all-nighter”, meaning that a person stays up for 24 hours or longer. More typically, sleep deprivation consists of chronic partial sleep deprivation, where a student obtains some, but not adequate sleep. Sleepiness can be an obvious consequence of sleep deprivation, but sleepiness can be caused by other circumstances, most commonly sleep disorders. To understand the consequences of sleepiness and sleep deprivation, knowledge of normal sleep and its impact on learning, memory, and performance are necessary. Equally important are potential interventions, as these may offer an opportunity to improve health and educational outcomes for this demographic. This article reviews the prevalence of sleepiness and sleep deprivation among college students, the impact of sleep on memory, contributing factors for sleep deprivation, potential consequences with a focus on those particularly applicable to college students, and available interventions to improve sleep among college students.
Regulation of normal sleep: the circadian rhythm and homeostatic sleep drive
Many college students are sleep deprived because they go to sleep late and wake up for classes or employment before adequate sleep is obtained. Two primary processes govern how much sleep is obtained, the homeostatic sleep drive and the circadian rhythm. The circadian system (internal clock) helps to regulate sleep/wake cycles and hormonal secretions while the homeostatic sleep drive increases the need for sleep as the period of wakefulness lengthens. The interaction of these two systems is described by the Two-Process Model of Sleep Regulation. 11
Physiologically, adolescents and young adults tend to have a delayed circadian preference, and are “night owls”. 12 This change occurs in association with puberty; more physically mature adolescents have a preference for later bedtimes and may have a lower homeostatic sleep drive, and consequently, are less sleepy at night. 13 – 15 The typical adult circadian period is 24.1 hours, compared to an adolescent’s circadian period of 24.27 hours; this longer period makes it easier for the bedtime to shift later. 15 , 16 A cardinal sign of a delayed circadian system is an irregular sleep schedule, where students have catch-up sleep on the weekend. Both high school and college students demonstrate a 1–3 hour sleep deficit on school nights, with a much longer sleep duration and often a later wake time on the weekends. 7 , 17 , 18
How the circadian rhythm and homeostatic sleep drive change with puberty is not well understood, but the cumulative effect is that adolescents and young adults feel more awake in the evening, have a difficult time falling asleep until later, and consequently, have insufficient sleep during the school week and catch-up on sleep on the weekend.
Exactly when this nocturnal preference or “night owl” tendency diminishes, remains unclear. When evaluated longitudinally, weekday bedtimes continued to delay until around 19 years of age, with weekend bedtimes remaining later until the early 20s, although other studies have shown this delay persisting until the junior year. 19 The transition from high school to college also has an impact; college students go to bed 75 minutes later than high school students. 7 In this study, freshman students’ bedtime was 12.22 am and 1.58 am with a rise time of 8.08 am and 10.26 am on weekdays and the weekend, respectively.
Learning, memory, and sleep cycles
Sleepiness and irregular sleep schedules have many unintended consequences, one of which is to negatively impact learning, memory, and performance. The precise details of the relationship between sleep and memory formation are not yet completely understood. The dual process theory maintains that certain types of memory are dependent on specific sleep states, such that procedural memory (knowing how) may be dependent on REM (rapid eye movement) sleep and declarative memory (knowing what) on NREM (non-REM) sleep. The sequential processing theory suggests that memories require an orderly succession of sleep stages, ie, memory formation may be prompted by slow-wave sleep and consolidated by REM sleep (see Figure 1 ). 20

The interaction of sleep and memory.
Notes: The dual process theory suggests that certain types of memory are dependent on specific sleep states, such as REM sleep, or slow-wave sleep (a stage of NREM sleep). The sequential processing theory suggests that memories require an orderly succession of sleep stages, eg, slow-wave sleep followed by REM sleep. 20
Abbreviations: NREM, non-rapid eye movement; REM, rapid eye movement.
Both theories may help to explain how a student’s sleep pattern could impact learning. 21 In one study, REM sleep deprivation eliminated sleep-induced improvement on a visual perceptual learning (procedural) task; the same effect was not found with selective slow-wave sleep deprivation. 22 REM sleep normally occurs every 90–120 minutes, approximately 4–5 times in a typical night, with each REM sleep period growing progressively longer, with the last episode near rise time. 23 Therefore, college students with early morning classes may not attain the last 1–2 REM sleep periods, thus adversely affecting procedural memory. However, other studies suggest that NREM rather than REM sleep enhances procedural memories, while other studies correlated improvement with slow-wave sleep followed by REM sleep. 24 – 26 Both of these theories support that sleep deprivation may limit the amount of REM sleep and/or slow-wave sleep that students obtain, which may compromise both learning and memory, but further research is required to clarify this.
Many studies investigating the interaction of sleep, memory, and learning use scenarios of a specific memory task and then alter subjects’ sleep pattern or duration to determine the impact that sleep had on the subject’s performance. These scenarios often may not directly correlate with the memory and learning that college students are expected to perform or the alterations in their sleep schedule they experience. Despite these limitations, these studies illuminate the impact of sleep on students’ memory, learning, and potential academic performance.
Some students may “pull an all-nighter” (24 hours or more of sleep deprivation) before examinations in the hope of improved grades. The literature suggests that all-night study sessions are the wrong plan for improved grades and learning. Subjects were taught a visual discrimination task to identify the presence of “T” or “L” and the orientation of three diagonal bars on a screen. Subjects who were sleep deprived for 30 hours showed no improvement in performance, even after 2 days of post-recovery sleep. 26 Non-sleep-deprived subjects’ performance improved for the next 4 days. In another study investigating if improvement correlated with time or time spent in sleep, subjects were taught a motor task and then tested either after a 12-hour period of wakefulness or a 12-hour period that included sleep. 24 Subjects tested at 10 am and then retested at 10 pm without sleep showed no significant change in performance. After a night of sleep, subjects’ performance improved by 18%. Subjects tested at 10 pm initially, then retested after sleep, also had a significant improvement in performance. This supports the concept that sleep, and not just time, is required for learning and memory consolidation. It may be possible that there is a window for potential learning that requires sleep, and that this opportunity for learning may not be salvaged even after sleep is recovered.
Sleep before learning may also be necessary. To investigate this concept, subjects were tested on an episodic memory encoding task, which involved viewing a series of images with a recognition test 48 hours later. 27 Subjects were tested after 35 hours of sleep deprivation; memory performance was approximately two letter grades (19%; P =0.031) worse when compared to the non-sleep-deprived subjects. This difference did not seem to be due to alertness, as there was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of response rate, which has been correlated with alertness.
Looking at more global functions, total sleep deprivation showed a significant decrease of performance in cognitive tasks assessing inference, recognition of assumptions, and deduction. 28 Although this study was not carried out on college-aged students, subjects aged 10–14 years of age restricted to 5 hours of sleep, had impaired performance on verbal creativity and abstract thinking. 29 Less complex cognitive functions did not appear impaired; this has been shown in other studies and may indicate that motivation, individual response to sleep deprivation, or certain tasks may be less impacted by sleep. 20 , 30
Learning may also affect the intrinsic aspects of sleep. Procedural tasks prior to sleep increased slow-wave activity in the right parietal lobe, an area that is responsible for visual-spatial skills. 31 This increased right parietal activity correlated with improvement in the task. Other studies have found an increase in spindles, a defining feature of stage 2 sleep, after procedural memory training. 32 In an intensive 6-week French language immersion course, improvement was correlated with an increase in subjects’ percentage of REM sleep. 33
In summary, these finding suggest that sleep, likely before and after specific memory tasks, plays an integral part in memory consolidation. Many of these studies isolate memory into specific areas such as visual, declarative, or procedural; however, college students’ learning, memory, and performance in classes rarely would have such a narrow memory domain. Further research with real-life circumstances of students would better help clarify these important issues.
Causes of sleep deprivation and sleepiness
Among college-aged students, one of the most common causes of daytime sleepiness is sleep deprivation, ie, students get inadequate sleep because they go to bed late and wake up early. This occurs for multiple reasons; some are physiologic and others behavioral. The behavioral components may be particularly problematic on college campuses. However, sleep deprivation is not the only cause of sleepiness as college students are not immune to sleep disorders, which may also cause sleepiness. This section will review common causes of sleep deprivation as well as the prevalence of sleep disorders among college students, and the influence of sleep disorders on sleepiness.
Inadequate sleep hygiene
Sleep deprivation can arise from poor sleep behaviors; sleep hygiene encourages habits conducive to restorative sleep and avoidance of substances or behaviors that are not. Good sleep hygiene includes a regular sleep–wake schedule, quiet sleep environment, and avoidance of caffeine after lunch and stimulating activities before bed. 34 , 35 Substances are not the only aspect of inadequate sleep hygiene, as the ubiquitous use of technology before bed may also adversely affect sleep. Many students have inadequate sleep hygiene that, in conjunction with their delayed circadian rhythm, encourages sleep deprivation.
Approximately four out of five college students drink alcohol, with nearly 40% of men and women reporting “binge drinking” at least 4–5 drinks in a row within the last 14 days. 36 , 37 Alcohol shortens sleep latency, but then promotes fragmented sleep in the latter half of the night. 23 One study found that 11.6% of students who drank used alcohol as a sleep aid. 7 , 38 Alcohol may also increase the risk for obstructive sleep apnea. 39
Caffeine and energy drinks
Caffeine, equivalent to 2–4 cups of coffee taken at night, can increase sleep latency on average from 6.3 to 12.1 minutes, reduce sleepiness, and improve the ability to sustain wakefulness. 40 In this study, the effects of caffeine lasted 5.5–7.5 hours, suggesting that caffeine consumed even in the afternoon could impair the ability to fall asleep. Caffeine is an adenosine receptor antagonist and can increase arousal. Caffeine also may act on gamma-aminobutyric acid neurons of the posterior hypothalamus to suppress sleep-promoting pathways. 23 The net effect is that caffeine increases vigilance, alertness, and decreases sleepiness.
Energy drinks are becoming increasingly popular and 34% of 18–24-year-olds consume them regularly. In 2006, Americans spent more than $3.2 billion on energy drinks. 41 The majority (67%) of users consumed energy drinks to help compensate for insufficient sleep. 42 The contents of energy drinks are variable and depend on the individual product, but usually contain caffeine, herbal products, and sometimes vitamins and other supplements. Caffeine is the primary constituent responsible for the effect of increased energy. The amount of caffeine varies widely from 45–500 mg. Use of energy drinks is associated with higher use of alcohol and possibly other drugs, including stimulants. 43
Use of either prescribed or nonprescribed stimulants is a growing problem in young adults. The most commonly reported reason is to “stay awake to study” or increase concentration. 44 Students may utilize these drugs more than age-matched non-students. 45 A survey at 119 colleges and universities across the US found a 6.9% lifetime prevalence for the use of stimulants. 46 Other studies show prevalence as high as 14%. 44 , 47 Men are more likely than women to use stimulants, as well as caffeine and energy drinks. Nonprescribed use of stimulants is associated with increased use of alcohol, cocaine, and marijuana. 46 Not all stimulant use is illicit, as between 2%–8% of college students’ self-reported symptoms are consistent with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). 48 However, when parents of college students were asked to report such symptoms in their children, the prevalence of ADHD decreased to around 1%. Stimulants increase sleep latency and suppress REM sleep; subjects who use stimulant medications report worse sleep quality. 23 , 47
Inadequate sleep hygiene also encompasses the use of technology prior to bed. Relevant data often must be extrapolated from literature on adolescents, as few studies have focused on college students. The 2011 Sleep in America Poll addressed technology available in the bedroom. “Generation Y’ers” (adults aged 19–29 years old) are heavy users of technology prior to bed: 67% use cell phones, 43% music devices, 60% computers, and 18% video games. The majority (51%) report rarely getting a good night’s sleep and often wake unrefreshed. Computer use in the hour before bed is associated with less restful sleep, higher Epworth Sleepiness Scales, and drowsy driving. 49 Frequent use of cell phones around bedtime is associated with difficulties falling asleep, repeated awakenings, or waking up too early. 50 Most young adults (57%) leave their phone on during sleep, with only 33% turning it to silent or vibrate modes ( Table 1 ). Playing video games before bed can increase sleep latency, an average of 21.6 minutes. 51 Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) shows that video game playing heightens cognitive alertness, especially during violent scenes ( Table 1 ). 52
Frequent use of technology before bed is associated with sleep difficulties and daytime sleepiness
Note: Data from National Sleep Foundation; 49 Dworak et al. 51
Light exposure from various sources, including computers, tablet computers (eg, iPads; Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA, USA), and cell phones may also impact sleep. Melatonin, secreted by the pineal gland, helps regulate the circadian rhythm to the environment. 15 Normally, it is low or absent during the day and starts to rise about 2 hours before the habitual bedtime. Melatonin is suppressed by light, and light sources as low 200–300 lux (room lights) can cause suppression. 53 The amount of light from technologic devices is variable; for example, a tablet computer generated 50 lux suppressed melatonin in a cohort of college students after 2 hours of use. 54 A case report describes a student in Brazil who had a 40-minute delay in sleep on the weekends when electric lights were installed. 55 Bright light (8,000 lux) given at 7 pm or at 9 pm reduced nighttime sleepiness in students who had an evening preference and those with a later onset of melatonin. 56 One of the effects of technology may be to suppress melatonin, resulting in a delay in sleep onset.
In summary, many students engage in behaviors, such as those described above, which increase stimulation and alertness prior to bed. This, in conjunction with their delayed circadian rhythm, encourages late bedtimes and insufficient sleep. To combat sleepiness, students often drink caffeine and energy drinks, compromising sleep and ensuring a vicious cycle of sleep deprivation ( Table 2 ).
Challenges to good sleep hygiene in college students
Note: Data from. 41 , 43 , 47 , 49 , 54
Sleep disorders
Sleep deprivation is not the only cause of sleepiness on campus, as sleep disorders may also play a role. A survey of 1,845 students in introductory psychology labs suggested that 27% were at risk for at least one sleep disorder or sleep-related problem, including obstructive sleep apnea (4%), insomnia (12%), restless legs disorder and periodic limb movement disorder (8%), circadian rhythm sleep disorders (7%), and hypersomnia (4%). 57
Obstructive sleep apnea can be associated with significant sleepiness. 58 The prevalence of snoring may be more common than expected, as 30% of non-overweight students in a California school reported snoring. Men more commonly reported snoring (42%) than women (25%). 59 Asian students (37%) more often reported snoring than African-American (24%) or Caucasian (27%) students. Although such observations of snoring frequency do not reveal the prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea among college students, they do suggest that this disorder may not be as infrequent among young, otherwise healthy college students as is sometimes assumed.
Consequences of sleep deprivation and sleepiness
College is a time of intellectual growth and development as young adults’ transition from adolescence to adulthood. Although the worth of college in terms of increased productivity and higher earning potential is rarely debated, there is a significant personal and societal cost of college both in terms of time and money. For optimal return on the investment of time, effort, and money, students need to maximize their learning, academic, and personal growth. Sleepiness from any cause can compromise these goals, through impact on learning, memory, grades, perception of effort, driving performance, and mood. Although sleep deprivation has effects on many aspects of health, this article will focus on areas that may be particularly problematic for college students.
Grade point average (GPA) and academic performance
Despite growing evidence of the relationships between sleep, learning, and memory, a direct connection between learning and GPA has not yet been established. 60 A student’s GPA is not just an indication of learning, but instead involves a complex interaction between the student and their environment. 61 Intelligence, motivation, work ethic, personality, socioeconomic status, health problems, current and past school systems, course load, academic program, and test-taking abilities all may influence GPA.
Existing evidence does suggest an association between sleep and GPA. Students who obtained more sleep (long sleepers, ≥9 hours) had higher GPAs than short sleepers (≤6 hours): GPAs were 3.24 vs 2.74 on average, respectively. 62 More evidence exists to support an influence of sleep patterns rather than sleep duration on GPA. Students at a community college near Washington DC showed no difference in total sleep time (TST), sleepiness, or morning preference between high (GPA >3.5) and low (GPA <2.7) academic performers. 63 High academic performers instead showed earlier bed and rise times, though with similar overall TST. No difference was present between the two groups with regards to a morning preference, but a validated questionnaire was not used.
Among first-year university students, sleep patterns also influenced GPA; each hour delay in weekday or weekend rise time decreased the GPA by 0.132/4.0 and 0.115/4.0, respectively. 60 Bedtimes were also influential, with later bedtimes associated with lower GPAs. TST or circadian factors were not evaluated. These results do not explain why an earlier rise time was associated with better grades; it could arise from the sleep schedule itself, but many potential confounders exist. For example, early risers may also be more motivated or organized. Another possibility is that negative influences arise when students who have a nocturnal preference are unable to wake up earlier. In a study of medical students, subjects with an evening preference on the Horne–Ostberg Questionnaire had a more irregular sleep pattern than students with a morning or indifferent-type preference. Sleep duration was not different between the groups, but subjects with a more irregular sleep pattern had lower academic performance. 64 This suggests that sleep patterns influence academic performance more than sleep duration, with the caveat that students who have an evening preference may have a more irregular sleep schedule.
Extreme forms of irregular sleep schedules include all-night study sessions. No literature appears to address the association between all-nighter study sessions and GPA, but the absence of sleep is known to affect learning and performance improvement. Subjects taught a visual discrimination task who were then sleep deprived for 30 hours showed no improvement in the task, even after 2 days of post-recovery sleep. 26 Non-sleep-deprived subjects’ performance improved for the next 4 days. Similar results were demonstrated with a finger-tapping motor task; without sleep, no significant improvement occurred. 24 All-nighter study sessions may also alter motivation and perceived effort. Students’ self-perceived effort and performance were evaluated following two sleep scenarios: 24 hours of sleep deprivation or 8 hours of sleep. 28 Despite performing worse, sleep-deprived subjects felt they had better concentration, effort, and performance than did non-sleep-deprived subjects. Why sleep-deprived subjects rated their effort as higher is not known, and could be due to sleep deprivation itself, or relate to other unknown factors. This perception of improved performance following sleep deprivation may in part explain why it can be challenging to get students to change their sleep behavior. If students perceive no impairment in performance due to lack of sleep, they have little motivation to change.
Sleep disorders and academic performance
Students with sleep disorders probably do not achieve optimal academic performance, and up to 27% of students may be at risk for at least one sleep disorder. 57 Students at risk for academic failure (GPA <2.0) were at a disproportionately high risk for sleep disorders. Among those who screened positive for obstructive sleep apnea, 30% were at risk for academic failure. Medical students classified as frequent snorers more frequently failed their Internal Medicine examination (47%) than did occasional snorers (22.2%) or non-snorers (12.8%). After adjustment for age, BMI, and sex, the relative risk for snorers to fail the examination was 1.26 (95% confidence interval: 1.01–1.57). 65 Obstructive sleep apnea is suspected to have cognitive effects in both children and adults. 66 A higher percentage of students at risk for academic failure screened positive for other sleep disorders including: periodic limb movement disorder/restless legs syndrome (21%), 67 insomnia (22%), circadian rhythm sleep disorders (26%), and hypersomnia (21%). 57 As nearly one in four students is at risk for a sleep disorder, screening for sleep disorders among students with poor academic performance may well be advisable.
Although many students have a nocturnal preference, this preference can progress to delayed sleep-phase disorder (DSPD), a circadian rhythm disorder characterized by sleep-onset insomnia and difficulty waking at the desired time. 3 Consequences of DSPD may include missed morning classes, increased sleepiness, and decreased concentration, especially in morning classes. Students with DSPD have lower grades. 68 The prevalence of DSPD in the US college population may be as high as 6.7%–17%. 68 , 69
One of the most concerning consequences of sleep deprivation and sleepiness is drowsy driving. In the 2011 Sleep in America Poll, 66% of young adults reported drowsy driving. 49 However, few studies have evaluated drowsy driving specifically in college students. Among 1,039 undergraduate students, 16% reported falling asleep while driving and 2% had had a motor vehicle accident due to sleepiness. Men were more likely to fall asleep while driving than women. 38 A school in Utah had 86 student deaths due to motor vehicle accidents over a 15-year period; dozing/sleepiness was thought to be causative in 44%–72% of the cases. In a retrospective review of students’ “closest calls” for a motor vehicle accident due to sleepiness, most near accidents occurred between 11 pm and 1 am and often (39%) during the first hour of driving. Nearly half (48%) of students had a less intense dozing episode earlier in the same drive, with 68% of students continuing their drive despite feeling sleepy. 70 The findings overall suggest that drowsy driving accidents or near accidents are too frequent and that students may minimize the warning signs of drowsiness.
Driving, sleep deprivation, and alcohol
The impact of sustained wakefulness on driving performance has been compared to the impairment of performance that is produced by specific blood alcohol levels. In adults, sustained wakefulness of 17 hours was equivalent to a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) of 0.05%, and 24 hours was equivalent to 0.1%, above the legal level for intoxication in the US and most countries worldwide. 71 , 72 Similar findings were found in males aged 19–35 years of age, in whom 18.5 and 21 hours of wakefulness produced changes in driving performance mimicking a 0.08% BAC. 73 Sleep deprivation in combination with alcohol has a synergistic detrimental effect on driving performance. To evaluate these effects, young male college students were sleep restricted to 4 hours in bed; they then consumed alcohol until they attained BACs of 0.025 g/dL or 0.035 g/dL, equivalent to about 1–2 drinks. 74 A simulated driving task at 2 pm monitored crashes, speed variability, and lane deviations. Crashes occurred in 23% and 33% of the subjects (BAC 0.025 g/dL and 0.035 g/dL, respectively), compared to only 4.7% in the controls and 19% in sleep-restricted subjects who had no alcohol.
Driving after drinking is commonplace during college, as up to 34% of students reported driving after drinking within the last 30 days. 75 The combination of sleep deprivation and drinking may be especially common at the end of the semester, when sleep-deprived students celebrate the end of exams with drinks before driving home for the holiday break. The dangerous combination of sleep loss and alcohol could impair driving performance even in students who are not legally intoxicated.
Mood effects
Depression and sleep are interrelated. A cardinal feature of depression is disturbed sleep. 76 , 77 Depression is common during the college years: 14.8% of students report a diagnosis of depression and an estimated 11% have suicidal ideation. 78 Insufficient sleep can increase depressive symptoms. In a study of female college students, sleep debt of 2 hours per night and/or a bedtime after 2 am was associated with greater depressive symptoms. 79 Irregular sleep schedules have been associated with greater depressive symptoms. Prolonged sleep latency was associated with loss of pleasure, punishment feelings, and self-dislike. 80 Differences between sex were apparent, as women went to bed earlier, slept longer, had more nocturnal awakenings, and reported more depressive symptoms. However, when the sleep variable was removed by deleting the question, “Have you experienced changes in sleep?”, no significant difference in sex persisted, suggesting the greater incidence of depression in college-aged women may be due in part to the greater number of reported sleep difficulties. 80 , 81
Improving sleep may improve depressive symptoms. Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) administered via email to college students with poor sleep quality produced greater improvement in depressive symptoms than did an intervention focused on mood and stress reduction. 67 A study on college students without reported sleepiness or depression found that sleep extension significantly improved scores on the Profile of Mood States. 82 Increased total sleep in teenagers has also been shown to improve mood. When school start time was delayed by 30 minutes, fewer students rated themselves as “at least somewhat unhappy or depressed”. 83 As sleep may be a modifiable risk factor for depression, further research is needed on ways to improve sleep and sleep quality in depressed subjects.
Complex relationships exist between suicide, mood disorders, and sleep. Insomnia may be a risk factor for suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, and death by suicide. 84 Conflicting results have been reported on whether both insomnia and nightmares increase the risk of suicidal ideation. 85 , 86 A confounder is that post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) may account for these associations. A study among college students found that insomnia and nightmares were independently associated with suicidal ideation. However, after depression, anxiety, and PTSD were taken into account, nightmares, but not insomnia, retained an association with suicidal ideation. The presence of nightmares in a student with depression may be a warning sign of increased risk for suicidal ideation that warrants further evaluation. 87
Potential interventions
While sleep deprivation, irregular sleep schedules and sleepiness are highly prevalent among college students, little information is available on effective ways for schools to successfully disseminate information on the importance of sleep and to potentially improve the sleep of their students. In general, the few programs that have been tried are expensive, time consuming, and available for only a limited number of students. A recent review of sleep education programs for children and adolescents found only twelve studies, of which four were available only as abstracts. 81
Educational programs
Improved sleep hygiene, which is widely believed to be beneficial, has been the focus of most educational programs on sleep, although there is little published support. An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Practice Parameter concluded in 1999 that insufficient evidence exists to recommend sleep hygiene as a single therapy or in combination with other treatments. 88 A study evaluating sleep hygiene awareness and sleep hygiene practice found only a weak association between knowledge and practice. However, good sleep hygiene practice was strongly correlated with good sleep quality. 35 Adequate sleep knowledge does not necessarily translate into practice. Many sleep hygiene recommendations, such as a quiet environment and use of the bedroom only for sleep, may be challenging in college dormitories.
One educational campaign with a focus on sleep hygiene included a “Go to Bed” poster, a 2-page “Snooze letter”, and sleep educational information in the school newspaper. An earlier bedtime, shorter sleep latency, longer sleep duration, and improved sleep quality, as measured by the Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index, was noted in 9% of students. 89 Although this intervention did not affect a large percentage of the student population, it was relatively inexpensive and did produce a measurable benefit ( Table 3 ).
Components in sleep educational programs
Note: Data from. 67 , 89 – 91 , 93
Sleep courses
In another study, a two-credit, 18-week course included group discussion, lectures, and self-evaluation. Topics included circadian rhythms, sleep hygiene, muscle relaxation, and public sleep education. 90 Participants had improved sleep quality over the semester and women reported decreased nap time. However, despite this intensive intervention, only a limited effect on sleep patterns was observed.
The Sleep Treatment and Education Program (STEPS) consisted of a 30-minute oral presentation and handouts on various aspects of sleep, provided to students attending introductory psychology classes. 91 Six weeks later, participants showed improved sleep quality and sleep hygiene. These results may be more robust than suggested, as sleep quality and sleep behaviors typically worsen as the semester progresses; therefore, this intervention not only halted this deterioration, but resulted in improvement. 92 Four supplementary sleep-learning modules, offered as extra credit, improved sleep knowledge and encouraged some sleep-related behavior changes, as 55% reported a change in their sleep hygiene as compared to 45% of control students ( P <0.01). 93 Students in the intervention reported specific behavior changes such as having a more “consistent wake time” versus a more general “trying to get more sleep” as indicated by the control students. However, all of these interventions are time consuming, involve only a select number of students, and may not be practicable on a large university scale.
Electronic cognitive behavioral therapy
More feasible options are under development. A modified form of cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) was emailed to students over an 8-week period. 67 Each weekly email contained an attachment to address several aspects of sleep, such as stabilizing the circadian rhythm by anchoring wake time, relaxation techniques, and a protocol for self-administered sleep restriction. This was compared to an alternative program (Breathe), which was created to reduce depressive symptoms and improve coping skills for stress. Participants in the sleep program (Refresh) had improvement in sleep quality and a decrease in depressive symptoms. Although the study involved only a small number (19 and 15, respectively), results showed promise as an effective electronic program that could be widely accessible and economically feasible for colleges and universities.
Class scheduling
The amount of sleep that students obtain is often dictated by the first obligation of the day, typically their first class. This is one reason why students often sleep longer and later on a vacation or summer schedule. 15 Therefore, class start times are an opportunity for intervention, but available information must be extrapolated from adolescent literature. A study at an independent college preparatory school showed increased sleep duration after a delay in school start time. The majority of students were boarders (81.5%) with structured lights-out schedules ranging from 10.30–11.30 pm. 83 When school was started at 8.30 am, 30 minutes later than usual, sleep duration was increased by 45 minutes on school days. An unexpected effect was that bedtime shifted earlier by 15 minutes. Following the time change, fewer students reported daytime sleepiness (49.1% to 20.0%), sleepiness in class (85.1% to 60.5%), and falling asleep in class (38% to 18%). A positive effect on mood was found, with a decrease in the Depressed Mood Scale. 83 Students continued to have significant “oversleeping” on the weekend, by nearly 3 hours. A study of eighth graders (mean age 13.7 years) who had 1 hour of sleep extension for 5 days through delays in the school start time, documented improved attention and performance. 94 This growing evidence from adolescents suggests that later school start times do increase total sleep duration, attention, and performance, but the data needs to be replicated in college students ( Table 4 ).
Potential interventions to reduce sleep deprivation and sleepiness
Although not often considered as an intervention for sleep deprivation, daytime naps may offer a potential remedy that may also help academic performance. Interestingly, in light of how napping may improve certain memory tasks, high academic performers were more likely to nap than low academic performers (52% vs 29%, respectively). 63 In a study of non-sleep-deprived subjects, deterioration in the performance of a visual perception task occurred during the day. 95 Intervening naps of 60 or 90 minutes halted this deterioration, but only naps with both REM and slow-wave sleep resulted in improvement compared to baseline. Sustained wakefulness can impair performance. In an episodic memory-encoding task (face and name recognition), significant deterioration at 6 pm occurred in all subjects, except those who had had a 100-minute nap. In the nap group, not only was performance deterioration abated, but improvement was noted. 27 Following training to recognize phonetically similar words, subjects showed an increase in accuracy, but 12 hours of sustained wakefulness reduced improvements by half. A nap prevented this decrement in performance. 96 , 97 In short, naps may enhance certain cognitive and performance tasks, but further research is still needed in this important area.
The college years are a time of critical transition from adolescence to adulthood. For many individuals, this transition is associated with inadequate sleep and daytime sleepiness. Many factors contribute to this, including the students’ own circadian physiology. Class times are often scheduled without consideration of young adults’ circadian patterns. Inadequate sleep hygiene is common, as students often use technology and substances that compromise sleep quality and quantity. This chronic sleep deprivation may impair academic performance, mood regulation, and driving safety. Students who attain sufficient sleep may still struggle with sleepiness due to sleep disorders.
Further research is needed to not only determine how to best educate students about the importance of sleep and the consequences of sleep deprivation, but also how to translate this knowledge into practice. Electronic or web-based interventions may be economically feasible and attractive to an electronically savvy demographic. Universities and colleges need to understand, acknowledge, and publicize that policies and class schedules may have substantial impacts on the sleep, learning, and health of their students. Investigation of new approaches to promote good sleep and sleep habits could have significant public health impact and should be prioritized.
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.

Hi, what are you looking for?
Digital Journal
- TECH & SCIENCE
- SOCIAL MEDIA
- ENTERTAINMENT
How homework is affecting students’ sleep
In most of the world school has been in session for a few months now, with many students starting to eye-up the upcoming holiday breaks. One reason for this is tiredness. The extent of how tired many students are comes via a survey from Sleep Cycle , who produce an app to help people to monitor the quality of the sleep they are receiving. Multiple studies have shown that present day high school students do not receive an optimal amount of sleep.
The new survey has found that children are seldom getting the recommended 8-10 hours of sleep each night. Nearly half (46 percent) of parents have reported that their children get 7 hours or less of sleep each night. One factor influencing this is homework. The survey found that the vast majority (88 percent) of teens have reported how they regularly need to stay up late to finish school projects. Here some 59 percent state they need to have these late night cramming sessions on a weekly or daily basis.
The survey was conducted of over 1,000 U.S. adults and teens, with interviewed conducted by Propeller Research on behalf of Sleep Cycle, and provided to Digital Journal. The questionnaires took place in September 2018, and the results have not been published elsewhere. The headline finding is that homework keeps students up too late. Coupled with early school start times leads to many students falling asleep in class.
Without sufficient sleep, parents report that their children:
Are moody — 64 percent, Are grumpy and disagreeable — 61 percent, Get into more trouble at school — 28 percent, Make worse life choices — 20 percent.
A factor that both parents and teens report as not helping the situation is the school start time. Here 52 percent of parents and 61 percent of teens are of the view that school starts too early. The students report that their school work suffers because of the early start time and that early school start times inhibit them from being productive later in the day. Conversely a alter start time as seen as something that would lead to more productive class work.
According to the National Sleep Foundation : “When schools shift their schedules, teens benefit. For example, seven high schools in Minneapolis moved their start times from 7:25 a.m. to 8:30 a.m. and tested the outcomes for their students. As a result of the change, the teens got five or more extra hours of sleep per week, and attendance and enrollment rates went up, as did alertness. Meanwhile, student-reported depression went down.”
Sleep Cycle, along with many parents and teens, is pushing for a change to schooling policy.

Dr. Tim Sandle is Digital Journal's Editor-at-Large for science news. Tim specializes in science, technology, environmental, business, and health journalism. He is additionally a practising microbiologist; and an author. He is also interested in history, politics and current affairs.

Zelensky claims Russian advance in Ukraine ‘halted’

Problems posed by the edited Princess of Wales image

Entertainment
Oscars ratings climb to almost 20 mn as ‘oppenheimer’ reigns.

NATO prepares for Russian threat in harsh Arctic

Tech & Science
Cybersecurity: time to strengthen the data broker ecosystem, you may also like:.

Social Media
Op-ed: tiktok tech threat — let’s not get too simplistic..
The genuine risks are increasing by the second. That’s what this ban is really about.
Op-Ed: Worldwide neuro-catastrophe will be mismanaged ASAP
Well? No, you’re not. What are you going to do about it?

Putin will lead until ‘end of his natural life’: activist
US-born British financier and political activist Bill Browder has long campaigned against Russian corruption - Copyright AFP Daniel LEALCaroline TAIXVladimir Putin is likely to...

UN demands unimpeded aid access to Sudan as famine looms
The war has since April last year killed tens of thousands, destroyed infrastructure and crippled the economy - Copyright AFP JOHN WESSELSThe United Nations...
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Put this information right at your fingertips with my book, It’s Never Too Late To Sleep Train
Craig Canapari, MD
Proven advice for better sleep in kids and parents
Too Much Homework, Too Little Sleep: Structural Sleep Deprivation in Teens
posted on October 11, 2012
NOTE: The American Academy of Pediatrics has recommended school start times no earlier than 8:30 for teens. Read more here.
A few years ago, I had a sixteen year old come into sleep clinic for insomnia. He was a hard-working student in a good school district. I asked him to describe his sleep problems to me. “I finish my homework at midnight every night,” he said, “and I can’t fall asleep by 12:10 AM.” Each of his Advanced Placement classes had 1-2 hours of assigned homework per night and he was not routinely finishing homework until 11 PM or 12 AM. This may be an exaggerated case [and note that the details have been changed a bit to protect patient privacy.] However, let’s do the math. The typical school day for a high school student in this country is between 6.5-7 hours per day. Most school districts start between 7-8 AM for high school students. Thus, kids are getting out of school between 2-3 PM. Many students do extracurriculars for a few hours after school and cannot start homework until after dinner (say 6:30 PM). The maximum recommended homework for a high school senior is three hours per night ; for younger children, it is ten minutes per grade. If the student goes to sleep at 10 PM and gets up at 6 AM ( a typical wake time around here for high school students), this allows 8 hours of sleep. However, the typical teenager requires between 8.5-9 hours of sleep per night, so even a teen with good sleep habits generally sleep deprived. In Boston, this problem is frequently exaggerated by school choice where some children are assigned to better schools which are a long bus ride away. (These issues exist elsewhere. My friend Trapper Markelz grew up in Alaska and regularly took 45 minute bus trips twice a day to school.)
In their recent article, “ To Study or to Sleep? The Academic Costs of Extra Studying at the Expense of Sleep “, Cari Gillen-O’Neel and colleagues studied the effects of staying up late on students. They studied 535 kids through high school. The average sleep time for these teens diminished from 7.6 to 6.9 hours of sleep from 9th to 12th grade. When they examined what happened when teens stayed up late to study for finish a project, they found that
Results suggest that regardless of how much a student generally studies each day, if that student sacrifices sleep time to study more than usual, he or she will have more trouble understanding material taught in class and be more likely to struggle on an assignment or test the following day.
Essentially, staying up late to cram tends not to help and actually worsens performance. This emphasizes the importance of encouraging good study habits in kids .
Excessive homework is not the only factor squeezing teenager’s sleep. My friend Lauren Daisley had a great video on CBS Sunday Morning several weeks ago discussing early school start times. Sleepiness in teenagers is a major public health issue and early school start times contribute to this. To highlight some recent research:
- Short sleep makes children obese .
- A recent study showed that teenagers who did not get enough sleep were more likely to develop insulin resistance , which is the precursor to type 2 diabetes.
- Sleepiness is a significant cause of automobile accidents which is the most common cause of death in teenagers.
- Depression, anxiety, and irritability are all associated with insufficient sleep.
There is a significant body of research showing the benefits of moving school start times later. Demonstrated benefits have included less tardiness and absenteeism, lower levels of depression, and, most significantly, lower levels of car accidents in teenagers . (There are several great summaries here from the National Sleep Foundation , the New York Times , the Wall Street Journal , and Psychology Today .)
I also think that there are more abstract benefits to avoiding overscheduling for children and teens. In William Deresiewicz’s 2009 essay, “ Solitude and Leadership ,” he writes about his experience as an admission officer at Yale (full disclosure: my alma mater.) He writes,
Well, it turned out that a student who had six or seven extracurriculars was already in trouble. Because the students who got in—in addition to perfect grades and top scores—usually had 10 or 12. So what I saw around me were great kids who had been trained to be world-class hoop jumpers. Any goal you set them, they could achieve. Any test you gave them, they could pass with flying colors. They were, as one of them put it herself, “excellent sheep.”
He argues, however, that for real leadership and problem solvers, you need people who can think and innovate. And that solitude and time for reflection is critical for developing this faculty. Allowing teens extra time may not even hurt their college admission chances. I really enjoy the blog Study Hacks by Cal Newport, a computer science professor who been writing since he was a grad student. He wrote a great article (and a book as well) on how working against the conventional wisdom (e.g. doing a few extracurriculars instead of 10-12) can be a winning strategy for a motivated high school student. I highly recommend reading this: Want to Get into Harvard? Spend More Time Staring at the Clouds: Rethinking the Role of Extracurricular Activities in College Admissions.
Obviously, teenagers are not blameless. Screen time and social media shares some of the blame. But I am most concerned about these structural issues which do not allow enough of a sleep opportunity for kids. These issues are determined at the level of the school district. However, there are some actions that parents can take:
- The US is a relatively homework intense country compared to other industrialized countries with higher standardized test scores. Whether your child is in third grade or twelfth, keep an eye on the amount of homework they are receiving. The rule of thumb is ten minutes/grade level. Have a frank discussion with your child’s teachers or principal if it seems excessive. Be aware that excessive homework times can also reflect difficulties like attention deficit hyperactivity disorder or learning disabilities.
- School start times are typically addressed at the town or district level. As you can imagine, this is a difficult issue to move at the national or state level. If you are concerned by the school start times in your district, go to school board meetings. Also, get involved with Start School Later , an organization dedicating to addressing this issue.
- Make sure that your child has an age appropriate bedtime allowing for enough sleep (10-11 hours in elementary school, 9-10 hours middle school, 9 hours high school). Limit screen time in the evenings before bedtime.
- Prolonged napping can result in s ignificant difficulty at bedtime.
- Keeping screens out of the bedroom except when absolutely necessary can help avoid sleep problems in kids and teens.
- Going on a “light diet” to limit night time light exposure is important for limiting the impact of late night homework sessions on overall sleep patterns.
It is also important to understand the biology of when you fall asleep. This is comprised of a two part system: a) the homeostatic sleep drive (the longer you are awake, the quicker you fall asleep) and b) the circadian or body clock system which helps keep you awake in the evenings.
For more on the topic of homework vs sleep, here is an article I just wrote on the controversy about the value of homework .
You May Also Be Interested In...
- Busting Sleep Myths: From Wake Windows to Sleepy…
- The Top Ten Sleep Training Mistakes You Need to…
- Lack of Sleep is A Cause of Childhood Obesity
Need More Help Getting Your Kid to Fall Asleep (and Stay Asleep)?

Get help with your child’s sleep!
Success! Now check your email to confirm your subscription.
There was an error submitting your subscription. Please try again.
DrCraigCanapari.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means to earn fees when linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
Come say hi on social!
- Close Menu Search
- PR4PR Podcast
- Owlwitness News
- Media Center
- School Store
- YouTube Channel
- The Owl’s Eye

PRHS Night Watch
Homework: The Cause of Sleep Deprivation? Or is it More Than That?
Michelle Galdi , Chief Editor | January 26, 2019

A typical day at Park Ridge High School consists of sitting in various classrooms from 7:45 to 2:44. However, school carries on much longer than those designated times.
Students are constantly preoccupied with homework after school, and, to delve into just how much work students have, I interviewed Sandra Ortega, Alex Uva, Isabella Wise, Susie Rubenstein, and Josh Zdanowicz about the after-school obligations that consume their time, like homework.
All students stated that they feel like they have too much homework, taking an average of 3-4 hours to complete
All students stated that they feel like they have too much homework, taking an average of 3-4 hours to complete. Sandra said that the bulk of her homework comes from her Calculus, Anatomy and French classes. Considering all of those classes are Honors courses, it is reasonable that the homework requirement would be considerable. Additionally, AP classes often prove to be even harder, considering they are similar to college level classes. Alex’s AP English and AP European History homework takes him the longest, along with Susie’s AP Psychology class. Even without the added expectations of Honors and AP courses, students are still preoccupied with other time-consuming activities.
Along with homework, students juggle additional obligations after school, including sports and clubs. Izzy told me that she is “a dancer and an assistant dance teacher” so she “is always at the studio for an hour, then [goes] home to eat dinner, then [goes] back to dance for another 3 hours.” Her long day of dance finally finishes around 10:30 when she gets home and starts her homework. Josh is one of the many students who participate in school sports. He stated that, “during cross country season, it was impossible to get homework done.” When he got home from practice, all he wanted to do was go to bed, unmotivated to do any work. However, sometimes obligations do not always revolve around sports. Everyday after school, Sandra has to pick up her younger sister and her friends from school and she has work occasionally, which tends to eat up her time. Sports, homework, family, and work responsibilities tend to pile up on students.
Similar to the data provided by the Nationwide Children’s hospital, the majority of Park Ridge High School receive between six and eight hours of sleep.
As a result of staying up late to complete their daily tasks, students lose precious hours of sleep. According to the Nationwide Children’s Hospital, teenagers need between nine and nine and a half hours of sleep. However, teenagers only get an average of 7 hours. Investigating further in this statistic, I reached out to a random sample of students and recorded their average hours of sleep over a few days. Similar to the data provided by the Nationwide Children’s hospital, the majority of Park Ridge High School receive between six and eight hours of sleep.
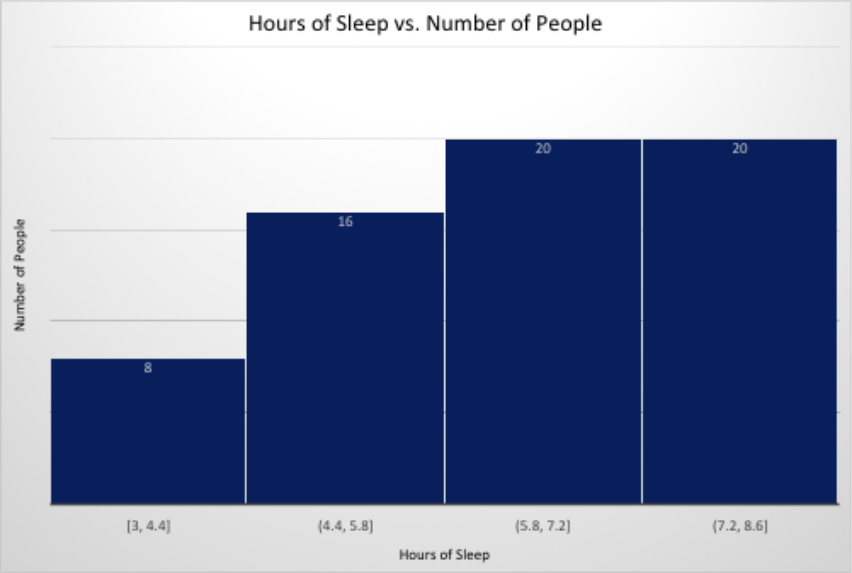
Being sleep deprived can lead to feeling incredibly irritable and tired the next day. Additionally, if a lack of sleep continues, it can affect one’s overall health, making them susceptible to serious medical conditions like obesity, heart disease, and high blood pressure. Sleep is one of the most important things for developing teens. So, how could this conflict be resolved?
I asked the students what they think should be done to change the issue of having too much responsibilities. A few weeks ago, myself and a few of my classmates had to take four tests in one day, resulting in us staying up late in order to study. Sandra, one of my classmates who had to take those four tests, wished that, “teachers [would] coordinate better with each other when they are giving large assignments or tests. The lack of this can cause scheduling issues.” One of those four tests was taken in Mr. Wilson’s Anatomy Honors class, so I spoke to him about the issue. He stated that “kids need to be their own advocates.” If they notice that a bunch of assignments or tests are racking up on their schedules, they need to reach out to their teachers and let them know of their other obligations. If they fail to do so, then it is no longer the teacher’s fault, but that of the student. Izzy came up with the suggestion that homework being optional if you understand what is going on in a class. However, she argued that “if you are struggling with the material, it should be mandatory.” These alternatives might possibly be able to solve some of the problems with homework.
Kids need to be their own advocates.
— Mr. Wilson, Science Teacher
On the other hand, the problem does not solely sit in the issue of homework. Mr. Wilson argued that “time management comes into play,” since students, “wait until the last second to complete things, instead of doing it in small increments over a longer time.” Additionally, “kids feel like they have to join all the clubs and sports.” He stated that there are just too many things going on and so many plates to juggle, eventually something is going to drop. To help solve the overall problem of not only having too much homework, but also the time that sports and clubs consume, Mr. Wilson thinks that having a block schedule can alleviate some of the conflict. Whether the issue is homework or sports, students and teachers both agree that there is a problem. Time management is a large factor that impacts students sleeping time and performance in school. Solutions like homework being more optional, teachers coordinating the scheduling of projects and tests, students advocating for themselves, and block scheduling can all be effective.
- Block Schedule
- Sleep Deprivation
- Time Management

Park Ridge Marching Band: A New Era

Owls defeat St. Mary’s 40-12 in Home Opener

2023 Park Ridge Football Preview

Smriti Gounder Reflects on Park Ridge Robotics Team’s Success
October Sports Summary: Soccer & Football
October Sports Summary (10/22/21) Owls Football The Park Ridge Owls football team is off to a red-hot start so far to begin their 2021 campaign. The...

5 Things to Make a Team Successful
Winter vocal photography highlights.

It’s All About Us

BESTOF2020: Interview with Joker Cinematographer, Lawrence Sher

BESTOF2020: Current Editor in Chief Interviews Last Year’s Editor in Chief
BESTOF2020: Current Events: One Story at a Time with Mr. Farrell
Olivia Interviews: Mrs. Haake
The Student News Site of Park Ridge High School
Comments (2)
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Grace Booras • Jan 24, 2020 at 12:49 pm
Despite homework being useful for practice, middle school students should not have homework. Studies show that homework reduces the amount of physical activity for students, the scold of not doing homework is stressful and frustrating, and students do not get enough sleep at night. First of all, homework reduces the amount of physical activity for students. Too much homework given to students can result in lack of sleep at night, headaches daily, exhaustion, and weight loss. Excessive homework can also result in poor eating habits, which can result in weight loss. According to a school psychiatrist in Oregon, “a low amount of physical activity can result in a change in behavior in a teen, and even make them more disrespectful.” If students are stuck inside, sitting at a desk, staring down at the same paper for hours on end, they can’t have any time or motivation for outside physical activities. Physical activity can also help reduce health problems when the kids are older. The article “Kids need more exercise, less homework” says: “When people ask me, ‘What’s the biggest thing I can do to avoid dementia?’ my answer is ‘exercise,’” said Margaret Gatz, a professor of psychology at USC who has published studies on the connection between diabetes diagnoses in middle age and later Alzheimer’s diagnosis. This shows that not having homework would give students more time to be physical and stay active. Second, the scold of not doing homework is stressful and frustrating for students. Because kids have outside of school activities and are being scolded for not doing homework, when in fact they have other things they need to do, they are missing out on physical and emotional connections. According to the child psychologist Kenneth Barish, “battles over homework rarely result in an improvement in school.” She proved that students and parents argue over doing homework, which can stress both parties out and create tension in families. Parents scold their children for not doing homework, and then the teacher scolds them. Teachers and parents scolding students can make them feel bad about themselves and reduce the want to learn. “It’s disrespectful to tell me that you don’t have time for homework. You can find the time.” Says the teacher. This can make the students feel pressured to cancel after school activities and make them feel stressed out and busy all the time. According to a study done at Stanford University, “56 percent of students considered homework a primary source of stress.” The hours spent everyday in classes plus the hours spent doing homework leads to students feeling overwhelmed and unmotivated. Homework can help students with time management, but it also teaches them to worry and stress about things. When students are stressed out, it can lower their grade, and cause them to zone out during class. Last of all, students don’t get enough sleep at night due to staying up late doing homework. “All students stated that they feel like they have too much homework, taking an average of 3-4 hours to complete.” (Homework: The Cause Of Sleep Deprivation) In the 2006 pole, it has been shown that 80% of middle school students don’t get enough sleep at night because of staying up doing homework, and at least 28% fall asleep in school. Students all over America stay up for hours on end trying to finish their homework. Studies show that Middle school students should get no less than 9 ½ hours of sleep per night. “Similar to the data provided by the Nationwide Children’s hospital, the majority of Park Ridge High School receive between six and eight hours of sleep.” The amount of homework that kids have has increased by 11% since the 1990’s. With 6 different classes to try and juggle, taking home their work is stressful; students need breaks. A student once said “If I can’t sleep at school, then I shouldn’t have to do school work at home.” Even though homework can help students practice the skills they are learning in their classes, students should not lose sleep, lose physical activity, or be stressed out over so much homework at a young age.
This is my essay I am writing for my language arts class. I do agree that homework can be useful in many situations, but I do stand by my point in saying that if you can’t sleep at school and do the things you do at home at school, then you should have to do SCHOOLwork at home 🙂
Cench • Jan 28, 2019 at 1:36 pm
Hi! I’m interested to see how many students have their devices near them and check social media, answer texts, etc. while they are doing homework. I agree with Mr. Wilson that especially in PR, students over commit and overwhelm themselves being involved in too much. Lack of sleep is caused by more than homework and school activities. Many students have expressed they have a hard time actually falling asleep – most likely due to over stimulation of the brain with devices prior to going to bed, binge watching shows or gaming. How long would homework take without distractions? Just a thought 🙂
Forgotten password
Please enter the email address that you use to login to TeenInk.com, and we'll email you instructions to reset your password.
- Poetry All Poetry Free Verse Song Lyrics Sonnet Haiku Limerick Ballad
- Fiction All Fiction Action-Adventure Fan Fiction Historical Fiction Realistic Fiction Romance Sci-fi/Fantasy Scripts & Plays Thriller/Mystery All Novels Action-Adventure Fan Fiction Historical Fiction Realistic Fiction Romance Sci-fi/Fantasy Thriller/Mystery Other
- Nonfiction All Nonfiction Bullying Books Academic Author Interviews Celebrity interviews College Articles College Essays Educator of the Year Heroes Interviews Memoir Personal Experience Sports Travel & Culture All Opinions Bullying Current Events / Politics Discrimination Drugs / Alcohol / Smoking Entertainment / Celebrities Environment Love / Relationships Movies / Music / TV Pop Culture / Trends School / College Social Issues / Civics Spirituality / Religion Sports / Hobbies All Hot Topics Bullying Community Service Environment Health Letters to the Editor Pride & Prejudice What Matters
- Reviews All Reviews Hot New Books Book Reviews Music Reviews Movie Reviews TV Show Reviews Video Game Reviews Summer Program Reviews College Reviews
- Art/Photo Art Photo Videos
- Summer Guide Program Links Program Reviews
- College Guide College Links College Reviews College Essays College Articles
Summer Guide
College guide.
- Song Lyrics
All Fiction
- Action-Adventure
- Fan Fiction
- Historical Fiction
- Realistic Fiction
- Sci-fi/Fantasy
- Scripts & Plays
- Thriller/Mystery
All Nonfiction
- Author Interviews
- Celebrity interviews
- College Articles
- College Essays
- Educator of the Year
- Personal Experience
- Travel & Culture
All Opinions
- Current Events / Politics
- Discrimination
- Drugs / Alcohol / Smoking
- Entertainment / Celebrities
- Environment
- Love / Relationships
- Movies / Music / TV
- Pop Culture / Trends
- School / College
- Social Issues / Civics
- Spirituality / Religion
- Sports / Hobbies
All Hot Topics
- Community Service
- Letters to the Editor
- Pride & Prejudice
- What Matters
All Reviews
- Hot New Books
- Book Reviews
- Music Reviews
- Movie Reviews
- TV Show Reviews
- Video Game Reviews
Summer Program Reviews
- College Reviews
- Writers Workshop
- Regular Forums
- Program Links
- Program Reviews
- College Links
Does Too Much Homework Cause Sleep Deprivation?
People say that homework is supposed to help children in school. Homework,however actually can worsen a child’s grades. Homework has many side effects, some of which are dangerous. A clear side effect of too much homework is lack of sleep. Many students do poorly on exams because of sleep deprivation.
Research showed that students did not think homework was useful and regarded homework as a burden. Students felt pressured to do homework instead of visiting family and participating in activities they used to enjoy. According to research, “56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source[of sleep deprivation]. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.”(healthline.com)Ms. Pope; a researcher said that said the “magic number when it comes to homework is 'nothing over two hours' for highs school and 'no more than 90 minutes' in middle school.”(dailymail.co)As the diagram on the left shows, most students surveyed spent one to two hours each night doing homework. At Wilmington High School and other schools in Massachusetts, that was not always the case.
To prove what research says is true there, was an informal study I conducted that proves students spend too much time on homework and do not always get enough sleep. There was a survey given out to various students in different grades. The results were varied, depending on grade and school. The survey was given out to students both at Wilmington High School and other schools and towns. Students from Wilmington High School said that they did not get enough sleep and knew they needed more sleep. Students at Wilmington High School did around two to three hours of homework per night. Most students were still able to do activities, but by doing extra curricular activities students said they were up later doing their homework. Most Wilmington students got six to seven hours of sleep, but studies show that kids should get eight hours of sleep. See table below for more data.
Wilmington High School Time spent on homework Time for activities time spent sleeping 4-5 hours no 6-7 hours 2 ½- 3 ½ hours yes 5 hours 5 hours heavy 3 hours light yes 6-7 hours 3-4 on heavy 1-2 on light yes, but doesn't do a lot of extra curricular activities 5-6 hours need more 1 unless have projects yes 6-7 hours 3 hours yes, can only do one extra thing a day 6-7 hours 2-4 hours yes 5-6 hours 3-5 hours yes 6-9 hours 3-4 hours yes 6-8 hours 3 hours no 5-6 hours 5-6 hours no 5 hours 1-2 hours yes 8 hours
Students from other towns got roughly the same amount of homework as kids from Wilmington High School, which was two to three hours. All of the students said that they had time for activities, but sometimes they had to spend extra time on homework. The students that go to other schools got around six to seven hours of sleep per night. Wilmington High School students and other students from other schools did not differ in terms of homework, activities, and sleeping. They both spent around two to three hours on homework with time for activities and got around six to seven hours of sleep. See table below for more data.
Other Schools Time spent on homework Time for activities time spent sleeping 2 hours yes 6.5 hours 3-4 hours yes depending on the day, has to spend more time on homework 6-7 hours 1-2 hours sometimes 7-8 hours 1-2 hours yes 8 hours One researcher showed the number of hours spent doing homework and the number of hours spent sleeping.This researcher surveyed sophomores. Most sophomores surveyed did two to under four hours of homework, but some students did have more than that. Four students surveyed had eight or more hours of homework to do. The researcher also surveyed the sophomores on how many hours of sleep they got. More than half of the sophomores got seven or less hours of sleep per night.(see diagram to the right) Another researcher surveyed 102 students. 52 students said that they got five to six hours of sleep on a weeknight. Only one student said that he or she got more than nine hours of sleep. On a weekend 48 students got seven to eight hours of sleep. Students spent the weekend catching up on homework and sleep. The researcher also asked the students what were their reason for giving up sleep was. 86 out of the 102 students said that it was because they were finishing up homework. 57 students said they lost sleep because they were studying for a test. For more information look at the picture to the right. Teachers give students too much homework. Students do not get enough sleep because they are trying to finish homework or they are studying. Researchers say high school students should get no more than two hours of homework per night. Most students got more than two hours of homework per night and this caused them to lose precious sleep time.
Homework also causes students mental and physical health to deteriorate. Students are putting their health at risk trying to finish homework. “Teens who have more homework than they can handle may become disillusioned with school and may lose the motivation to work hard,” says Gerald LeTendre, head of Penn State’s Education Policy Studies department.( livestrong.com) Research done by Australian researchers clearly suggested that placing too much homework can cause lower grades and even lead pupils to begin suffering from depression.(factualfacts.com) Homework also causes scholars to become less physically active. When teens are not physically active it can lead to obesity and other health related problems.(livestrong.com) Homework affects teens mental and physical health. Homework causes many problems for students. These problems include sleep deprivation, lack of physical activity, and poor mental health. Students should get about two hours of homework and eight hours of sleep. Some of the homework assigned, is found useless by students. Homework would be more beneficial if the homework assigned was usefull.
For my english class I had to write a muckraking essay. I choose to do mine on Homework and It's effects;mostly sleep deprivation.
Similar Articles
Join the discussion.
This article has 0 comments.
- Subscribe to Teen Ink magazine
- Submit to Teen Ink
- Find A College
- Find a Summer Program
Share this on
Send to a friend.
Thank you for sharing this page with a friend!
Tell my friends
Choose what to email.
Which of your works would you like to tell your friends about? (These links will automatically appear in your email.)
Send your email
Delete my account, we hate to see you go please note as per our terms and conditions, you agreed that all materials submitted become the property of teen ink. going forward, your work will remain on teenink.com submitted “by anonymous.”, delete this, change anonymous status, send us site feedback.
If you have a suggestion about this website or are experiencing a problem with it, or if you need to report abuse on the site, please let us know. We try to make TeenInk.com the best site it can be, and we take your feedback very seriously. Please note that while we value your input, we cannot respond to every message. Also, if you have a comment about a particular piece of work on this website, please go to the page where that work is displayed and post a comment on it. Thank you!
Pardon Our Dust
Teen Ink is currently undergoing repairs to our image server. In addition to being unable to display images, we cannot currently accept image submissions. All other parts of the website are functioning normally. Please check back to submit your art and photography and to enjoy work from teen artists around the world!

Our advice is expert-vetted and based on independent research, analysis and hands-on testing from our team of Certified Sleep Coaches. If you buy through our links, we may get a commission. Reviews ethics statement
Stop Sabotaging Your Sleep Quality by Dropping These 7 Common Habits
Every little thing you do leading up to climbing in bed can affect the quality of sleep you get at night. Here are the top habits you should break tonight for better sleep.

Bad habits like using your phone too close to bedtime can harm your sleep.
I'd need way more than two hands to count the number of restless nights I've spent waking up several times before morning. I'm not alone in this frustrating sleep disturbance -- one study showed that 35% of Americans woke up at least three nights a week.
Bad sleep leaves you feeling groggy and cranky, with less energy to dedicate to your day. Not to mention several long-term health risks, such as weight gain, weakened immunity and memory issues.

If sleep is so critical, why can it be difficult to sleep through the night without waking?
Waking up in the night is a form of insomnia , and it can be caused by anything from stress to eating spicy foods too close to bedtime. While insomnia can sometimes be a serious problem needing medical attention, its causes can also often be treated with natural sleep aids or simple lifestyle changes. Here are several reasons why you may not be sleeping through the night, and what to do about it.
For better sleep, also check out our rundown of the best cooling mattresses , the best pillows and the best alarm clocks of the year.

1. Middle-of-the-night bathroom trips

Running to the restroom is no way to spend the middle of the night.
One common cause of interrupted sleep is nighttime bathroom trips . Most people wake up throughout the night to go relieve themselves, but if you stay awake for too long after, it can disrupt your sleep cycle. Causes of this frustrating phenomenon range from simply drinking too much water to more serious complications, including diabetes.
If your bladder wakes you up at night, first try to cut down on evening fluid intake. Don't drink anything for two hours before bedtime, especially alcohol or any caffeinated beverages. Alcohol and caffeine are both diuretics, meaning they make your body lose more water, and you have to take more bathroom trips.
Also, if you're on a diuretic medication, like the ones used to treat blood pressure, this could be the culprit of more frequent urination. Nighttime urination can also be a symptom of a UTI or diabetes. If cutting down on fluid intake doesn't help with your problem, you may want to take a trip to the doctor to rule out these problems.
2. A high thermostat
One easy-to-fix culprit of nighttime awakening is simply that your room, or internal body temperature, may be too warm. Your body temperature fluctuates throughout the day -- when it rises in the morning and early afternoon, you become more alert, and as it falls at night it signals that it's time for bed. If your room is too warm in the middle of the night, your body might think that it's time to be awake and alert. Plus, if it's hot, you could wake up with night sweats, and no one likes being jolted awake by sticky sheets.
If you live in a warm area and don't have the luxury of simply turning on air conditioning, there are things you can do to cool down at night . Taking a cold shower, using a bedroom fan and putting your sheets in the freezer for a little bit before bed can all help.
3. Snoring or sleep apnea

If you have sleep apnea, breathing machines can help you get your life back.
Another cause of nighttime awakening is snoring. Snoring can be harmless (besides the noise that wakes up your partner), but frequent intense snoring could be a sign of sleep apnea -- a medical disorder where breathing starts and stops throughout the night. If you wake up with a dry mouth or wake yourself up by snoring loudly, or your partner tells you that you stop breathing in the night, you may have sleep apnea . Sleep apnea is no fun -- it causes restless nights, daytime fatigue and a host of other health issues stemming from long-term sleep deprivation.
A doctor will help decide the best course of treatment for you, including the use of breathing machines , lifestyle changes such as losing weight and maybe surgery.
4. Untreated anxiety or depression

Worrying about the next day can keep you up at night.
Mental health and sleep have a cyclical relationship -- anxiety and depression can worsen sleep quality, and sleep deprivation worsens mental health. It can be hard to escape this loop, especially when sleep deprivation comes along with a lack of motivation.
If you wake up during the night, anxious racing thoughts can make it impossible to fall back asleep. Plus, depression has been strongly associated with waking up too early and being unable to drift back off.
For people who experience both anxiety and sleep disturbances, cognitive behavioral therapy has shown to be effective at treating both. CBT instills lifelong strategies for managing mental health, and targets the root of the behavior rather than the symptoms. Nutritional and herbal supplements have also been suggested to be helpful in treating anxiety disorders.
Other methods of relaxation and stress relief may be helpful, such as meditation, exercise and finding time for meaningful hobbies. If anxious thoughts are keeping you up, try jotting down a to-do list before you doze off. That way, you can forget about what you have to do tomorrow until the morning actually comes.

5. Scrolling on your phone

Scrolling through Instagram may feel relaxing, but it's really keeping you from a good night's sleep.
If you've ever found yourself frantically checking emails before bed, you're not the only one, especially if you're part of a younger crowd. Four out of 5 teens report sleeping with their phone in the room, and countless adults do as well. Many people admit they check a mobile device after they've gone to bed.
The artificial blue light emitted from screens may delay your circadian rhythm and suppress melatonin , a natural chemical that tells your body it's time to sleep. When you stare at your phone right before bed, it causes your body to wake up and become more alert. Your natural rhythm is disrupted, and you're much more likely to wake often throughout the night and experience a lower quality of sleep.
There's a simple fix to this blue light phenomenon, though it's not easy: Don't use your phone or computer right before bed. Two hours before you want to fall asleep, put all the screens away and focus on relaxing activities, like reading, light cleaning and spending time with loved ones. If you use your phone as an alarm, buy a cheap clock to use instead so that you can leave your phone outside of the bedroom for the whole night.
6. Heartburn or indigestion

Heartburn usually gets worse when you lie down.
Here's another yucky one -- according to one source, 14% to 20% of Americans experience heartburn at least once a week, and 70% to 75% of those people have it at night. Nighttime heartburn can wake you up with a burning or choking sensation in your throat, and the pain and discomfort makes it hard to fall back asleep.
Common culprits of heartburn are spicy foods, chocolate, citrus and alcohol. If you can't narrow down what's causing your indigestion, try keeping a food journal along with noting your symptoms. You can eliminate various suspects from your diet to find out what's causing you discomfort. Once you figure it out, try to avoid this food as much as possible. You'll thank yourself for it in the morning.
Heartburn may be simply diet-related, but it could also be an indicator of a relatively common disorder known as gastroesophageal reflux disease , aka GERD or acid reflux. People with GERD typically experience heartburn, choking and coughing more often while lying down at night. If your symptoms are more severe or you think you may have acid reflux, seek medical attention and treatment.
7. Alcohol or nicotine before bed

The nicotine in e-cigarettes can also keep you up.
Many people turn to alcohol to relax, but it disrupts your rest once you've fallen asleep. Alcohol increases a chemical in your brain, adenosine, that helps you fall asleep. However, the rush of that chemical subsides as quickly as it came, and you wake up before you feel rested. A nightcap can also cause bathroom trips during the night. Another unfortunate consequence is that alcohol relaxes your throat muscles, leading to increased snoring, which can also wake you up.
While smoking cigarettes or vaping can similarly be a calming mechanism, it also hinders your rest. Nicotine is a stimulant , so it disrupts your circadian rhythm and makes your body feel more alert throughout the night. Also, it has been suggested that smokers experience nicotine withdrawal while asleep, leading to more sleep disturbances.
Juul e-cigarettes have been painted by some as a healthy alternative to cigarettes, but the high nicotine content in a vaporizer will likely keep you tossing and turning throughout the night.
Want more sleep tips? Learn more about staying cool while you sleep and how to regulate your circadian rhythm to get the best sleep possible.
More recs for better sleep
- Night Sweats: 7 Common Causes and How to Stop Sweating While Sleeping
- Alcohol Can Give You a Bad Night's Sleep. Here's What to Know
- 6 Ways Exhausted Moms Can Get More Sleep With a Newborn at Home
- Interpret Your Dreams: What It Means to Dream About Fire, Death, Falling and More
- Why You Should Rethink Letting Your Pets Sleep With You
- The Secret to Taking a True Power Nap
Mattress Buying Guides
- Best Mattress
- Best Air Mattress
- Best Adjustable Mattress
- Best Mattress in a Box
- Best Memory Foam Mattress
- Best Mattress for Side Sleepers
- Best Mattress for Stomach Sleepers
- Best Mattress for Back Pain
- Best Mattress for Heavy People
- Best Mattress for Kids
- Best Cooling Mattress
- Best Cheap Mattress
- Best Firm Mattress
- Best Soft Mattress
- Best King Mattress
- Purple Mattress
- Dreamcloud Mattress
- Nectar Mattress
- Casper Mattress
- TempurPedic Mattress
- Saatva Mattress
- Tuft & Needle Mattress
- Helix Mattress
- Avocado Mattress
Other Sleep Guides
- Best Pillow
- Best Weighted Blanket
- Best Sleep Mask
- Best Sheets
- Best Mattress Toppers
- Best Mattress Pads
- Best Headphones for Sleeping
- Best Alarm Clock
- Best Earplugs for Sleeping
- Best White Noise Machines
- Best Products for Snoring

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
ALEXANDRIA, Va., Dec. 11, 2018 - According to new research from the Better Sleep Council (BSC) - the nonprofit consumer-education arm of the International Sleep Products Association - homework, rather than social pressure, is the number one cause of teenage stress, negatively affecting their sleep and ultimately impacting their academic performance.
Homework, Sleep, and the Student Brain. At some point, every parent wishes their high school aged student would go to bed earlier as well as find time to pursue their own passions -- or maybe even choose to relax. This thought reemerged as I reread Anna Quindlen's commencement speech, A Short Guide to a Happy Life.
The present study aimed to address these gaps in knowledge by examining how students in a highly-competitive academic setting allocate their time on school days and weekends, and the degree to which homework/studying may displace sleep and affect mood. Our first objective was to evaluate students' time use on school days and weekends.
Background. Sleep is an inseparable part of human health and life, and is pivotal to learning and practice as well as physical and mental health. 1 Studies have suggested that insufficient sleep, increased frequency of short-term sleep, and going to sleep late and getting up early affect the learning capacity, academic performance, and neurobehavioral functions. 2, 3 Previous studies have ...
The Impact of Homework on Teenage Stress and Sleep. Homework is a major source of stress for teenagers, affecting their sleep patterns. According to studies, about 75% of high school students report grades and homework as significant stressors. This anxiety can lead to sleep deprivation, with over 50% of students reporting insufficient rest.
According to Oxford Learning, homework can have other negative effects on students. In their article, Oxford Learning remarks, "56 percent of students considered homework a primary source of stress. Too much homework can result in lack of sleep, headaches, exhaustion, and weight loss". Similarly, Stanford Medicine News Center reports that ...
• Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they ...
A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope, a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a
Elementary and middle school students typically need to sleep for nine to 11 hours each night, and early start times for schools can leave them with less time to complete their homework and relax in the evening. In recent years, some education experts have suggested starting classes later in the morning to help students feel less tired and more ...
The effect of sleep quality on academic performance has been previously investigated. Only a few studies, however, have examined the influence of mental well-being and working memory on this relationship, specifically, since working memory and mental health are well-known predictors of academic performance [33,34]. Therefore, our study aimed to ...
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health ...
On mediation effects of sleep durations on weekdays, as presented in Fig. 2, significant indirect effects of sleep durations were observed at each grade (P-values for indirect effects < 0.05), especially at the 7th and 9th grades, suggesting that high homework burdens were associated with shorter sleep durations, which in turn were associated ...
Around the beginning of puberty, most adolescents experience later sleep onset and wake times, also called "phase delay". This phase delay can shift the body's internal clock back by up to two hours. As a result, the average teenager cannot fall asleep until 11:00 p.m. and would do best waking up at 8:00 a.m. or even later.
Homework stresses kids out; there is no way around this fact. The combination of heavy homework loads and early school start times is a major cause of sleep deprivation and consequent stress in teens, but this can be a problem even in younger kids. When we moved to Connecticut, I was struck by the perception of some parents that my son's ...
The consequences of sleep deprivation and daytime sleepiness are especially problematic to college students and can result in lower grade point averages, increased risk of academic failure, compromised learning, impaired mood, and increased risk of motor vehicle accidents. This article reviews the current prevalence of sleepiness and sleep ...
Nearly half (46 percent) of parents have reported that their children get 7 hours or less of sleep each night. One factor influencing this is homework. The survey found that the vast majority (88 ...
Homework can affect both students' physical and mental health. According to a study by Stanford University, 56 per cent of students considered homework a primary source of stress. Too much homework can result in lack of sleep, headaches, exhaustion and weight loss. Excessive homework can also result in poor eating habits, with families ...
The Academic Costs of Extra Studying at the Expense of Sleep", Cari Gillen-O'Neel and colleagues studied the effects of staying up late on students. They studied 535 kids through high school. The average sleep time for these teens diminished from 7.6 to 6.9 hours of sleep from 9th to 12th grade.
Sports, homework, family, and work responsibilities tend to pile up on students. ". Similar to the data provided by the Nationwide Children's hospital, the majority of Park Ridge High School receive between six and eight hours of sleep. As a result of staying up late to complete their daily tasks, students lose precious hours of sleep.
Getting enough sleep is essential for people's mental and physical wellbeing. However, there are times when a person needs to stay up all night for homework, studying, or work.
On school days, adolescents spent an average of about 6.5 hours each on nocturnal time in bed for sleep and classroom lessons, 3 hours for homework/studying, 2 hours for media use, and approximately 1 hour each for face-to-face family time, transportation, and co-curricular (school-based) activities (Table 1).As expected, students' time use differed substantially on weekends, when little or ...
Homework,however actually can worsen a child's grades. Homework has many side effects, some of which are dangerous. A clear side effect of too much homework is lack of sleep. Many students do ...
Taking a cold shower, using a bedroom fan and putting your sheets in the freezer for a little bit before bed can all help. 3. Snoring or sleep apnea. If you have sleep apnea, breathing machines ...
Yes. Losing an hour of sleep certainly makes everybody a little bit cranky and it can have real world consequences. The Monday after daylight saving time kicks in is actually known as "Sleepy Monday.". Many people can probably relate to feeling groggy the next morning but it carries some real risks: There's about a 6% increase in fatal ...
On average, U.S. adults spend 3.5 hours on social media before bed every night, comprising 74.7% of their daily use, according to a February 2023 survey by Sleep Doctor, the parent company of SleepFoundation.org. Three-quarters of survey respondents say they use at least one of the major social-media platforms before going to sleep each night.