How to conduct qualitative interviews (tips and best practices)
Last updated
18 May 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
However, conducting qualitative interviews can be challenging, even for seasoned researchers. Poorly conducted interviews can lead to inaccurate or incomplete data, significantly compromising the validity and reliability of your research findings.
When planning to conduct qualitative interviews, you must adequately prepare yourself to get the most out of your data. Fortunately, there are specific tips and best practices that can help you conduct qualitative interviews effectively.
- What is a qualitative interview?
A qualitative interview is a research technique used to gather in-depth information about people's experiences, attitudes, beliefs, and perceptions. Unlike a structured questionnaire or survey, a qualitative interview is a flexible, conversational approach that allows the interviewer to delve into the interviewee's responses and explore their insights and experiences.
In a qualitative interview, the researcher typically develops a set of open-ended questions that provide a framework for the conversation. However, the interviewer can also adapt to the interviewee's responses and ask follow-up questions to understand their experiences and views better.
- How to conduct interviews in qualitative research
Conducting interviews involves a well-planned and deliberate process to collect accurate and valid data.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to conduct interviews in qualitative research, broken down into three stages:

1. Before the interview
The first step in conducting a qualitative interview is determining your research question . This will help you identify the type of participants you need to recruit . Once you have your research question, you can start recruiting participants by identifying potential candidates and contacting them to gauge their interest in participating in the study.
After that, it's time to develop your interview questions. These should be open-ended questions that will elicit detailed responses from participants. You'll also need to get consent from the participants, ideally in writing, to ensure that they understand the purpose of the study and their rights as participants. Finally, choose a comfortable and private location to conduct the interview and prepare the interview guide.
2. During the interview
Start by introducing yourself and explaining the purpose of the study. Establish a rapport by putting the participants at ease and making them feel comfortable. Use the interview guide to ask the questions, but be flexible and ask follow-up questions to gain more insight into the participants' responses.
Take notes during the interview, and ask permission to record the interview for transcription purposes. Be mindful of the time, and cover all the questions in the interview guide.
3. After the interview
Once the interview is over, transcribe the interview if you recorded it. If you took notes, review and organize them to make sure you capture all the important information. Then, analyze the data you collected by identifying common themes and patterns. Use the findings to answer your research question.
Finally, debrief with the participants to thank them for their time, provide feedback on the study, and answer any questions they may have.
Free AI content analysis generator
Make sense of your research by automatically summarizing key takeaways through our free content analysis tool.
- What kinds of questions should you ask in a qualitative interview?
Qualitative interviews involve asking questions that encourage participants to share their experiences, opinions, and perspectives on a particular topic. These questions are designed to elicit detailed and nuanced responses rather than simple yes or no answers.
Effective questions in a qualitative interview are generally open-ended and non-leading. They avoid presuppositions or assumptions about the participant's experience and allow them to share their views in their own words.
In customer research , you might ask questions such as:
What motivated you to choose our product/service over our competitors?
How did you first learn about our product/service?
Can you walk me through your experience with our product/service?
What improvements or changes would you suggest for our product/service?
Have you recommended our product/service to others, and if so, why?
The key is to ask questions relevant to the research topic and allow participants to share their experiences meaningfully and informally.
- How to determine the right qualitative interview participants
Choosing the right participants for a qualitative interview is a crucial step in ensuring the success and validity of the research . You need to consider several factors to determine the right participants for a qualitative interview. These may include:
Relevant experiences : Participants should have experiences related to the research topic that can provide valuable insights.
Diversity : Aim to include diverse participants to ensure the study's findings are representative and inclusive.
Access : Identify participants who are accessible and willing to participate in the study.
Informed consent : Participants should be fully informed about the study's purpose, methods, and potential risks and benefits and be allowed to provide informed consent.
You can use various recruitment methods, such as posting ads in relevant forums, contacting community organizations or social media groups, or using purposive sampling to identify participants who meet specific criteria.
- How to make qualitative interview subjects comfortable
Making participants comfortable during a qualitative interview is essential to obtain rich, detailed data. Participants are more likely to share their experiences openly when they feel at ease and not judged.
Here are some ways to make interview subjects comfortable:
Explain the purpose of the study
Start the interview by explaining the research topic and its importance. The goal is to give participants a sense of what to expect.
Create a comfortable environment
Conduct the interview in a quiet, private space where the participant feels comfortable. Turn off any unnecessary electronics that can create distractions. Ensure your equipment works well ahead of time. Arrive at the interview on time. If you conduct a remote interview, turn on your camera and mute all notetakers and observers.
Build rapport
Greet the participant warmly and introduce yourself. Show interest in their responses and thank them for their time.
Use open-ended questions
Ask questions that encourage participants to elaborate on their thoughts and experiences.
Listen attentively
Resist the urge to multitask . Pay attention to the participant's responses, nod your head, or make supportive comments to show you’re interested in their answers. Avoid interrupting them.
Avoid judgment
Show respect and don't judge the participant's views or experiences. Allow the participant to speak freely without feeling judged or ridiculed.
Offer breaks
If needed, offer breaks during the interview, especially if the topic is sensitive or emotional.
Creating a comfortable environment and establishing rapport with the participant fosters an atmosphere of trust and encourages open communication. This helps participants feel at ease and willing to share their experiences.
- How to analyze a qualitative interview
Analyzing a qualitative interview involves a systematic process of examining the data collected to identify patterns, themes, and meanings that emerge from the responses.
Here are some steps on how to analyze a qualitative interview:
1. Transcription
The first step is transcribing the interview into text format to have a written record of the conversation. This step is essential to ensure that you can refer back to the interview data and identify the important aspects of the interview.
2. Data reduction
Once you’ve transcribed the interview, read through it to identify key themes, patterns, and phrases emerging from the data. This process involves reducing the data into more manageable pieces you can easily analyze.
The next step is to code the data by labeling sections of the text with descriptive words or phrases that reflect the data's content. Coding helps identify key themes and patterns from the interview data.
4. Categorization
After coding, you should group the codes into categories based on their similarities. This process helps to identify overarching themes or sub-themes that emerge from the data.
5. Interpretation
You should then interpret the themes and sub-themes by identifying relationships, contradictions, and meanings that emerge from the data. Interpretation involves analyzing the themes in the context of the research question .
6. Comparison
The next step is comparing the data across participants or groups to identify similarities and differences. This step helps to ensure that the findings aren’t just specific to one participant but can be generalized to the wider population.
7. Triangulation
To ensure the findings are valid and reliable, you should use triangulation by comparing the findings with other sources, such as observations or interview data.
8. Synthesis
The final step is synthesizing the findings by summarizing the key themes and presenting them clearly and concisely. This step involves writing a report that presents the findings in a way that is easy to understand, using quotes and examples from the interview data to illustrate the themes.
- Tips for transcribing a qualitative interview
Transcribing a qualitative interview is a crucial step in the research process. It involves converting the audio or video recording of the interview into written text.
Here are some tips for transcribing a qualitative interview:
Use transcription software
Transcription software can save time and increase accuracy by automatically transcribing audio or video recordings.
Listen carefully
When manually transcribing, listen carefully to the recording to ensure clarity. Pause and rewind the recording as necessary.
Use appropriate formatting
Use a consistent format for transcribing, such as marking pauses, overlaps, and interruptions. Indicate non-verbal cues such as laughter, sighs, or changes in tone.
Edit for clarity
Edit the transcription to ensure clarity and readability. Use standard grammar and punctuation, correct misspellings, and remove filler words like "um" and "ah."
Proofread and edit
Verify the accuracy of the transcription by listening to the recording again and reviewing the notes taken during the interview.
Use timestamps
Add timestamps to the transcription to reference specific interview sections.
Transcribing a qualitative interview can be time-consuming, but it’s essential to ensure the accuracy of the data collected. Following these tips can produce high-quality transcriptions useful for analysis and reporting.
- Why are interview techniques in qualitative research effective?
Unlike quantitative research methods, which rely on numerical data, qualitative research seeks to understand the richness and complexity of human experiences and perspectives.
Interview techniques involve asking open-ended questions that allow participants to express their views and share their stories in their own words. This approach can help researchers to uncover unexpected or surprising insights that may not have been discovered through other research methods.
Interview techniques also allow researchers to establish rapport with participants, creating a comfortable and safe space for them to share their experiences. This can lead to a deeper level of trust and candor, leading to more honest and authentic responses.
- What are the weaknesses of qualitative interviews?
Qualitative interviews are an excellent research approach when used properly, but they have their drawbacks.
The weaknesses of qualitative interviews include the following:
Subjectivity and personal biases
Qualitative interviews rely on the researcher's interpretation of the interviewee's responses. The researcher's biases or preconceptions can affect how the questions are framed and how the responses are interpreted, which can influence results.
Small sample size
The sample size in qualitative interviews is often small, which can limit the generalizability of the results to the larger population.
Data quality
The quality of data collected during interviews can be affected by various factors, such as the interviewee's mood, the setting of the interview, and the interviewer's skills and experience.
Socially desirable responses
Interviewees may provide responses that they believe are socially acceptable rather than truthful or genuine.
Conducting qualitative interviews can be expensive, especially if the researcher must travel to different locations to conduct the interviews.
Time-consuming
The data analysis process can be time-consuming and labor-intensive, as researchers need to transcribe and analyze the data manually.
Despite these weaknesses, qualitative interviews remain a valuable research tool . You can take steps to mitigate the impact of these weaknesses by incorporating the perspectives of other researchers or participants in the analysis process, using multiple data sources , and critically analyzing your biases and assumptions.
Mastering the art of qualitative interviews is an essential skill for businesses looking to gain deep insights into their customers' needs , preferences, and behaviors. By following the tips and best practices outlined in this article, you can conduct interviews that provide you with rich data that you can use to make informed decisions about your products, services, and marketing strategies.
Remember that effective communication, active listening, and proper analysis are critical components of successful qualitative interviews. By incorporating these practices into your customer research, you can gain a competitive edge and build stronger customer relationships.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

Qualitative Research 101: Interviewing
5 Common Mistakes To Avoid When Undertaking Interviews
By: David Phair (PhD) and Kerryn Warren (PhD) | March 2022
Undertaking interviews is potentially the most important step in the qualitative research process. If you don’t collect useful, useable data in your interviews, you’ll struggle through the rest of your dissertation or thesis. Having helped numerous students with their research over the years, we’ve noticed some common interviewing mistakes that first-time researchers make. In this post, we’ll discuss five costly interview-related mistakes and outline useful strategies to avoid making these.
Overview: 5 Interviewing Mistakes
- Not having a clear interview strategy /plan
- Not having good interview techniques /skills
- Not securing a suitable location and equipment
- Not having a basic risk management plan
- Not keeping your “ golden thread ” front of mind
1. Not having a clear interview strategy
The first common mistake that we’ll look at is that of starting the interviewing process without having first come up with a clear interview strategy or plan of action. While it’s natural to be keen to get started engaging with your interviewees, a lack of planning can result in a mess of data and inconsistency between interviews.
There are several design choices to decide on and plan for before you start interviewing anyone. Some of the most important questions you need to ask yourself before conducting interviews include:
- What are the guiding research aims and research questions of my study?
- Will I use a structured, semi-structured or unstructured interview approach?
- How will I record the interviews (audio or video)?
- Who will be interviewed and by whom ?
- What ethics and data law considerations do I need to adhere to?
- How will I analyze my data?
Let’s take a quick look at some of these.
The core objective of the interviewing process is to generate useful data that will help you address your overall research aims. Therefore, your interviews need to be conducted in a way that directly links to your research aims, objectives and research questions (i.e. your “golden thread”). This means that you need to carefully consider the questions you’ll ask to ensure that they align with and feed into your golden thread. If any question doesn’t align with this, you may want to consider scrapping it.
Another important design choice is whether you’ll use an unstructured, semi-structured or structured interview approach . For semi-structured interviews, you will have a list of questions that you plan to ask and these questions will be open-ended in nature. You’ll also allow the discussion to digress from the core question set if something interesting comes up. This means that the type of information generated might differ a fair amount between interviews.
Contrasted to this, a structured approach to interviews is more rigid, where a specific set of closed questions is developed and asked for each interviewee in exactly the same order. Closed questions have a limited set of answers, that are often single-word answers. Therefore, you need to think about what you’re trying to achieve with your research project (i.e. your research aims) and decided on which approach would be best suited in your case.
It is also important to plan ahead with regards to who will be interviewed and how. You need to think about how you will approach the possible interviewees to get their cooperation, who will conduct the interviews, when to conduct the interviews and how to record the interviews. For each of these decisions, it’s also essential to make sure that all ethical considerations and data protection laws are taken into account.
Finally, you should think through how you plan to analyze the data (i.e., your qualitative analysis method) generated by the interviews. Different types of analysis rely on different types of data, so you need to ensure you’re asking the right types of questions and correctly guiding your respondents.
Simply put, you need to have a plan of action regarding the specifics of your interview approach before you start collecting data. If not, you’ll end up drifting in your approach from interview to interview, which will result in inconsistent, unusable data.

2. Not having good interview technique
While you’re generally not expected to become you to be an expert interviewer for a dissertation or thesis, it is important to practice good interview technique and develop basic interviewing skills .
Let’s go through some basics that will help the process along.
Firstly, before the interview , make sure you know your interview questions well and have a clear idea of what you want from the interview. Naturally, the specificity of your questions will depend on whether you’re taking a structured, semi-structured or unstructured approach, but you still need a consistent starting point . Ideally, you should develop an interview guide beforehand (more on this later) that details your core question and links these to the research aims, objectives and research questions.
Before you undertake any interviews, it’s a good idea to do a few mock interviews with friends or family members. This will help you get comfortable with the interviewer role, prepare for potentially unexpected answers and give you a good idea of how long the interview will take to conduct. In the interviewing process, you’re likely to encounter two kinds of challenging interviewees ; the two-word respondent and the respondent who meanders and babbles. Therefore, you should prepare yourself for both and come up with a plan to respond to each in a way that will allow the interview to continue productively.
To begin the formal interview , provide the person you are interviewing with an overview of your research. This will help to calm their nerves (and yours) and contextualize the interaction. Ultimately, you want the interviewee to feel comfortable and be willing to be open and honest with you, so it’s useful to start in a more casual, relaxed fashion and allow them to ask any questions they may have. From there, you can ease them into the rest of the questions.
As the interview progresses , avoid asking leading questions (i.e., questions that assume something about the interviewee or their response). Make sure that you speak clearly and slowly , using plain language and being ready to paraphrase questions if the person you are interviewing misunderstands. Be particularly careful with interviewing English second language speakers to ensure that you’re both on the same page.
Engage with the interviewee by listening to them carefully and acknowledging that you are listening to them by smiling or nodding. Show them that you’re interested in what they’re saying and thank them for their openness as appropriate. This will also encourage your interviewee to respond openly.
Need a helping hand?
3. Not securing a suitable location and quality equipment
Where you conduct your interviews and the equipment you use to record them both play an important role in how the process unfolds. Therefore, you need to think carefully about each of these variables before you start interviewing.
Poor location: A bad location can result in the quality of your interviews being compromised, interrupted, or cancelled. If you are conducting physical interviews, you’ll need a location that is quiet, safe, and welcoming . It’s very important that your location of choice is not prone to interruptions (the workplace office is generally problematic, for example) and has suitable facilities (such as water, a bathroom, and snacks).
If you are conducting online interviews , you need to consider a few other factors. Importantly, you need to make sure that both you and your respondent have access to a good, stable internet connection and electricity. Always check before the time that both of you know how to use the relevant software and it’s accessible (sometimes meeting platforms are blocked by workplace policies or firewalls). It’s also good to have alternatives in place (such as WhatsApp, Zoom, or Teams) to cater for these types of issues.
Poor equipment: Using poor-quality recording equipment or using equipment incorrectly means that you will have trouble transcribing, coding, and analyzing your interviews. This can be a major issue , as some of your interview data may go completely to waste if not recorded well. So, make sure that you use good-quality recording equipment and that you know how to use it correctly.
To avoid issues, you should always conduct test recordings before every interview to ensure that you can use the relevant equipment properly. It’s also a good idea to spot check each recording afterwards, just to make sure it was recorded as planned. If your equipment uses batteries, be sure to always carry a spare set.

4. Not having a basic risk management plan
Many possible issues can arise during the interview process. Not planning for these issues can mean that you are left with compromised data that might not be useful to you. Therefore, it’s important to map out some sort of risk management plan ahead of time, considering the potential risks, how you’ll minimize their probability and how you’ll manage them if they materialize.
Common potential issues related to the actual interview include cancellations (people pulling out), delays (such as getting stuck in traffic), language and accent differences (especially in the case of poor internet connections), issues with internet connections and power supply. Other issues can also occur in the interview itself. For example, the interviewee could drift off-topic, or you might encounter an interviewee who does not say much at all.
You can prepare for these potential issues by considering possible worst-case scenarios and preparing a response for each scenario. For instance, it is important to plan a backup date just in case your interviewee cannot make it to the first meeting you scheduled with them. It’s also a good idea to factor in a 30-minute gap between your interviews for the instances where someone might be late, or an interview runs overtime for other reasons. Make sure that you also plan backup questions that could be used to bring a respondent back on topic if they start rambling, or questions to encourage those who are saying too little.
In general, it’s best practice to plan to conduct more interviews than you think you need (this is called oversampling ). Doing so will allow you some room for error if there are interviews that don’t go as planned, or if some interviewees withdraw. If you need 10 interviews, it is a good idea to plan for 15. Likely, a few will cancel , delay, or not produce useful data.

5. Not keeping your golden thread front of mind
We touched on this a little earlier, but it is a key point that should be central to your entire research process. You don’t want to end up with pages and pages of data after conducting your interviews and realize that it is not useful to your research aims . Your research aims, objectives and research questions – i.e., your golden thread – should influence every design decision and should guide the interview process at all times.
A useful way to avoid this mistake is by developing an interview guide before you begin interviewing your respondents. An interview guide is a document that contains all of your questions with notes on how each of the interview questions is linked to the research question(s) of your study. You can also include your research aims and objectives here for a more comprehensive linkage.
You can easily create an interview guide by drawing up a table with one column containing your core interview questions . Then add another column with your research questions , another with expectations that you may have in light of the relevant literature and another with backup or follow-up questions . As mentioned, you can also bring in your research aims and objectives to help you connect them all together. If you’d like, you can download a copy of our free interview guide here .
Recap: Qualitative Interview Mistakes
In this post, we’ve discussed 5 common costly mistakes that are easy to make in the process of planning and conducting qualitative interviews.
To recap, these include:
If you have any questions about these interviewing mistakes, drop a comment below. Alternatively, if you’re interested in getting 1-on-1 help with your thesis or dissertation , check out our dissertation coaching service or book a free initial consultation with one of our friendly Grad Coaches.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Topic Guides
- Research Methods Guide
- Interview Research
Research Methods Guide: Interview Research
- Introduction
- Research Design & Method
- Survey Research
- Data Analysis
- Resources & Consultation
Tutorial Videos: Interview Method
Interview as a Method for Qualitative Research

Goals of Interview Research
- Preferences
- They help you explain, better understand, and explore research subjects' opinions, behavior, experiences, phenomenon, etc.
- Interview questions are usually open-ended questions so that in-depth information will be collected.
Mode of Data Collection
There are several types of interviews, including:
- Face-to-Face
- Online (e.g. Skype, Googlehangout, etc)
FAQ: Conducting Interview Research
What are the important steps involved in interviews?
- Think about who you will interview
- Think about what kind of information you want to obtain from interviews
- Think about why you want to pursue in-depth information around your research topic
- Introduce yourself and explain the aim of the interview
- Devise your questions so interviewees can help answer your research question
- Have a sequence to your questions / topics by grouping them in themes
- Make sure you can easily move back and forth between questions / topics
- Make sure your questions are clear and easy to understand
- Do not ask leading questions
- Do you want to bring a second interviewer with you?
- Do you want to bring a notetaker?
- Do you want to record interviews? If so, do you have time to transcribe interview recordings?
- Where will you interview people? Where is the setting with the least distraction?
- How long will each interview take?
- Do you need to address terms of confidentiality?
Do I have to choose either a survey or interviewing method?
No. In fact, many researchers use a mixed method - interviews can be useful as follow-up to certain respondents to surveys, e.g., to further investigate their responses.
Is training an interviewer important?
Yes, since the interviewer can control the quality of the result, training the interviewer becomes crucial. If more than one interviewers are involved in your study, it is important to have every interviewer understand the interviewing procedure and rehearse the interviewing process before beginning the formal study.
- << Previous: Survey Research
- Next: Data Analysis >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 10:42 AM
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Twelve tips for conducting qualitative research interviews
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Learning, Informatics, Management and Ethics, Karolinska Institutet , Stockholm , Sweden.
- 2 Department of Education, Stockholm University , Stockholm , Sweden.
- 3 Primary Health Care Unit, Institute of Medicine, The Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg , Gothenburg , Sweden.
- PMID: 30261797
- DOI: 10.1080/0142159X.2018.1497149
The qualitative research interview is an important data collection tool for a variety of methods used within the broad spectrum of medical education research. However, many medical teachers and life science researchers undergo a steep learning curve when they first encounter qualitative interviews, both in terms of new theory but also regarding new methods of inquiry and data collection. This article introduces the concept of qualitative research interviews for novice researchers within medical education, providing 12 tips for conducting qualitative research interviews.
PubMed Disclaimer
Similar articles
- Preparing and conducting interviews to collect data. Doody O, Noonan M. Doody O, et al. Nurse Res. 2013 May;20(5):28-32. doi: 10.7748/nr2013.05.20.5.28.e327. Nurse Res. 2013. PMID: 23687846
- Series: Practical guidance to qualitative research. Part 3: Sampling, data collection and analysis. Moser A, Korstjens I. Moser A, et al. Eur J Gen Pract. 2018 Dec;24(1):9-18. doi: 10.1080/13814788.2017.1375091. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Eur J Gen Pract. 2018. PMID: 29199486 Free PMC article.
- Using qualitative interviews in CAM research: a guide to study design, data collection and data analysis. Broom A. Broom A. Complement Ther Med. 2005 Mar;13(1):65-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2005.01.001. Epub 2005 Apr 26. Complement Ther Med. 2005. PMID: 15907681
- The qualitative research interview. Dicicco-Bloom B, Crabtree BF. Dicicco-Bloom B, et al. Med Educ. 2006 Apr;40(4):314-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2929.2006.02418.x. Med Educ. 2006. PMID: 16573666 Review.
- Skype interviewing: the new generation of online synchronous interview in qualitative research. Janghorban R, Latifnejad Roudsari R, Taghipour A. Janghorban R, et al. Int J Qual Stud Health Well-being. 2014 Apr 15;9:24152. doi: 10.3402/qhw.v9.24152. eCollection 2014. Int J Qual Stud Health Well-being. 2014. PMID: 24746247 Free PMC article. Review.
- Pre-implementation planning for a sepsis intervention in a large learning health system: a qualitative study. Eaton TA, Kowalkowski M, Burns R, Tapp H, O'Hare K, Taylor SP. Eaton TA, et al. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Aug 28;24(1):996. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-11344-x. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 39192331 Free PMC article.
- Guidelines to support the design, and selection and appraisal of multimedia teaching aids for microbiology education. Van Beek R, Spijkerman DJC, van der Burgt N, Hermanns B, Barendse S, Sainsbury PD, Timmis KN, Timmis JK. Van Beek R, et al. Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Aug;17(8):e14553. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14553. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39163108 Free PMC article.
- Intravenous ferric carboxymaltose versus oral ferrous sulphate for the treatment of moderate to severe postpartum anaemia in Nigerian women (IVON-PP): protocol for an open-label randomised controlled type 1 hybrid effectiveness-implementation trial. Afolabi BB, Adaramoye VO, Adeyemo TA, Balogun M, Mitchell EJ, Walker K, Akinajo OR, Abioye IA, Banke-Thomas A, Babah OA, Chieme CF, Oshodi Y, Quao R, Eboreime EA, Ogunsola F. Afolabi BB, et al. BMJ Open. 2024 Aug 17;14(8):e086553. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-086553. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39153791 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
- Exploring perceptions of sexuality among youth with physical disabilities in Gweru, Zimbabwe. Mashanyare T, Garutsa TC, Odhav K. Mashanyare T, et al. Afr J Disabil. 2024 Jul 24;13:1363. doi: 10.4102/ajod.v13i0.1363. eCollection 2024. Afr J Disabil. 2024. PMID: 39114453 Free PMC article.
- Nursing students' perceptions of interaction in a multiplayer virtual reality simulation: A qualitative descriptive study. Piispanen N, Haavisto E, Hublin L, Ikonen R, Koivisto JM. Piispanen N, et al. Nurs Open. 2024 Aug;11(8):e2245. doi: 10.1002/nop2.2245. Nurs Open. 2024. PMID: 39083574 Free PMC article.
- Search in MeSH
Related information
- Cited in Books
LinkOut - more resources
Full text sources.
- Taylor & Francis
Other Literature Sources
- scite Smart Citations
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Qualitative Research Interviews
Try Qualtrics for free
How to carry out great interviews in qualitative research.
11 min read An interview is one of the most versatile methods used in qualitative research. Here’s what you need to know about conducting great qualitative interviews.
What is a qualitative research interview?
Qualitative research interviews are a mainstay among q ualitative research techniques, and have been in use for decades either as a primary data collection method or as an adjunct to a wider research process. A qualitative research interview is a one-to-one data collection session between a researcher and a participant. Interviews may be carried out face-to-face, over the phone or via video call using a service like Skype or Zoom.
There are three main types of qualitative research interview – structured, unstructured or semi-structured.
- Structured interviews Structured interviews are based around a schedule of predetermined questions and talking points that the researcher has developed. At their most rigid, structured interviews may have a precise wording and question order, meaning that they can be replicated across many different interviewers and participants with relatively consistent results.
- Unstructured interviews Unstructured interviews have no predetermined format, although that doesn’t mean they’re ad hoc or unplanned. An unstructured interview may outwardly resemble a normal conversation, but the interviewer will in fact be working carefully to make sure the right topics are addressed during the interaction while putting the participant at ease with a natural manner.
- Semi-structured interviews Semi-structured interviews are the most common type of qualitative research interview, combining the informality and rapport of an unstructured interview with the consistency and replicability of a structured interview. The researcher will come prepared with questions and topics, but will not need to stick to precise wording. This blended approach can work well for in-depth interviews.
Free eBook: The qualitative research design handbook
What are the pros and cons of interviews in qualitative research?
As a qualitative research method interviewing is hard to beat, with applications in social research, market research, and even basic and clinical pharmacy. But like any aspect of the research process, it’s not without its limitations. Before choosing qualitative interviewing as your research method, it’s worth weighing up the pros and cons.
Pros of qualitative interviews:
- provide in-depth information and context
- can be used effectively when their are low numbers of participants
- provide an opportunity to discuss and explain questions
- useful for complex topics
- rich in data – in the case of in-person or video interviews , the researcher can observe body language and facial expression as well as the answers to questions
Cons of qualitative interviews:
- can be time-consuming to carry out
- costly when compared to some other research methods
- because of time and cost constraints, they often limit you to a small number of participants
- difficult to standardize your data across different researchers and participants unless the interviews are very tightly structured
- As the Open University of Hong Kong notes, qualitative interviews may take an emotional toll on interviewers
Qualitative interview guides
Semi-structured interviews are based on a qualitative interview guide, which acts as a road map for the researcher. While conducting interviews, the researcher can use the interview guide to help them stay focused on their research questions and make sure they cover all the topics they intend to.
An interview guide may include a list of questions written out in full, or it may be a set of bullet points grouped around particular topics. It can prompt the interviewer to dig deeper and ask probing questions during the interview if appropriate.
Consider writing out the project’s research question at the top of your interview guide, ahead of the interview questions. This may help you steer the interview in the right direction if it threatens to head off on a tangent.
Avoid bias in qualitative research interviews
According to Duke University , bias can create significant problems in your qualitative interview.
- Acquiescence bias is common to many qualitative methods, including focus groups. It occurs when the participant feels obliged to say what they think the researcher wants to hear. This can be especially problematic when there is a perceived power imbalance between participant and interviewer. To counteract this, Duke University’s experts recommend emphasizing the participant’s expertise in the subject being discussed, and the value of their contributions.
- Interviewer bias is when the interviewer’s own feelings about the topic come to light through hand gestures, facial expressions or turns of phrase. Duke’s recommendation is to stick to scripted phrases where this is an issue, and to make sure researchers become very familiar with the interview guide or script before conducting interviews, so that they can hone their delivery.
What kinds of questions should you ask in a qualitative interview?
The interview questions you ask need to be carefully considered both before and during the data collection process. As well as considering the topics you’ll cover, you will need to think carefully about the way you ask questions.
Open-ended interview questions – which cannot be answered with a ‘yes’ ‘no’ or ‘maybe’ – are recommended by many researchers as a way to pursue in depth information.
An example of an open-ended question is “What made you want to move to the East Coast?” This will prompt the participant to consider different factors and select at least one. Having thought about it carefully, they may give you more detailed information about their reasoning.
A closed-ended question , such as “Would you recommend your neighborhood to a friend?” can be answered without too much deliberation, and without giving much information about personal thoughts, opinions and feelings.
Follow-up questions can be used to delve deeper into the research topic and to get more detail from open-ended questions. Examples of follow-up questions include:
- What makes you say that?
- What do you mean by that?
- Can you tell me more about X?
- What did/does that mean to you?
As well as avoiding closed-ended questions, be wary of leading questions. As with other qualitative research techniques such as surveys or focus groups, these can introduce bias in your data. Leading questions presume a certain point of view shared by the interviewer and participant, and may even suggest a foregone conclusion.
An example of a leading question might be: “You moved to New York in 1990, didn’t you?” In answering the question, the participant is much more likely to agree than disagree. This may be down to acquiescence bias or a belief that the interviewer has checked the information and already knows the correct answer.
Other leading questions involve adjectival phrases or other wording that introduces negative or positive connotations about a particular topic. An example of this kind of leading question is: “Many employees dislike wearing masks to work. How do you feel about this?” It presumes a positive opinion and the participant may be swayed by it, or not want to contradict the interviewer.
Harvard University’s guidelines for qualitative interview research add that you shouldn’t be afraid to ask embarrassing questions – “if you don’t ask, they won’t tell.” Bear in mind though that too much probing around sensitive topics may cause the interview participant to withdraw. The Harvard guidelines recommend leaving sensitive questions til the later stages of the interview when a rapport has been established.
More tips for conducting qualitative interviews
Observing a participant’s body language can give you important data about their thoughts and feelings. It can also help you decide when to broach a topic, and whether to use a follow-up question or return to the subject later in the interview.
Be conscious that the participant may regard you as the expert, not themselves. In order to make sure they express their opinions openly, use active listening skills like verbal encouragement and paraphrasing and clarifying their meaning to show how much you value what they are saying.
Remember that part of the goal is to leave the interview participant feeling good about volunteering their time and their thought process to your research. Aim to make them feel empowered , respected and heard.
Unstructured interviews can demand a lot of a researcher, both cognitively and emotionally. Be sure to leave time in between in-depth interviews when scheduling your data collection to make sure you maintain the quality of your data, as well as your own well-being .
Recording and transcribing interviews
Historically, recording qualitative research interviews and then transcribing the conversation manually would have represented a significant part of the cost and time involved in research projects that collect qualitative data.
Fortunately, researchers now have access to digital recording tools, and even speech-to-text technology that can automatically transcribe interview data using AI and machine learning. This type of tool can also be used to capture qualitative data from qualitative research (focus groups,ect.) making this kind of social research or market research much less time consuming.
Data analysis
Qualitative interview data is unstructured, rich in content and difficult to analyze without the appropriate tools. Fortunately, machine learning and AI can once again make things faster and easier when you use qualitative methods like the research interview.
Text analysis tools and natural language processing software can ‘read’ your transcripts and voice data and identify patterns and trends across large volumes of text or speech. They can also perform khttps://www.qualtrics.com/experience-management/research/sentiment-analysis/
which assesses overall trends in opinion and provides an unbiased overall summary of how participants are feeling.
Another feature of text analysis tools is their ability to categorize information by topic, sorting it into groupings that help you organize your data according to the topic discussed.
All in all, interviews are a valuable technique for qualitative research in business, yielding rich and detailed unstructured data. Historically, they have only been limited by the human capacity to interpret and communicate results and conclusions, which demands considerable time and skill.
When you combine this data with AI tools that can interpret it quickly and automatically, it becomes easy to analyze and structure, dovetailing perfectly with your other business data. An additional benefit of natural language analysis tools is that they are free of subjective biases, and can replicate the same approach across as much data as you choose. By combining human research skills with machine analysis, qualitative research methods such as interviews are more valuable than ever to your business.
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Five Tips for Conducting Effective Qualitative Interviews

An interviewer conducts household survey in rural El Salvador for a Center for Health Policy and Inequalities Research study. Photo by Hy V. Huynh.
Published March 12, 2018 under Research News
In qualitative research, in-depth interviews can be an immensely helpful investigative tool. However, the nuances of one-on-one interviewing can sometimes make it difficult to obtain useful results. Rae Jean Proeschold-Bell , associate research professor and founding director of the Evidence Lab at the Duke Global Health Institute, frequently integrates qualitative interviews into her research. In this article, she shares five interviewing tips that have served her well.
1. Convey Intent
Proeschold-Bell says it’s important for the interviewer to know the intent behind each question so that it can be clearly conveyed to the interviewee. Understanding the intent of a question, she’s found, helps interviewers decide whether or not the participant has fully answered the question. This way, they can ask follow-up questions and not leave gaps at the time of data collection. Proeschold-Bell recommends writing the intent of each question below it in italics on the interview script.
Proeschold-Bell also suggests a few more subtle techniques for helping interviewees understand what is really being asked and soliciting pertinent and thorough responses. Asking the question in several different ways can help clarify its meaning. Follow-up prompts such as “That’s really helpful; tell me more about that,” or “Can you describe what was unpleasant about it?” can also give interviewees helpful guidance in crafting their responses.
“You can also convey intent by explaining more broadly why you’re doing the research, so interviewees will be more likely to give you relevant information,” Proeschold-Bell said.
2. Don’t Sway the Participants
Acquiescence bias, which occurs when interviewees agree with what they think the interviewer wants to hear instead of giving their unbiased answer, can often prevent interviewees from sharing all relevant information. Research from Focus Groups: A Practical Guide for Applied Research shows that when power dynamics are present in an interview, it may be especially difficult for an interviewee to give an honest answer.
To minimize acquiescence bias, interviewers can emphasize that the participant is the expert in the subject matter of the interview. For example, they can start the interview by saying, “I’ve asked you to talk with me today because you are an expert in what it’s like to be a patient in Eldoret.”
Interviewers should also avoid nodding or other body language that expresses agreement with the participant. Instead, interviewers should say, “That’s very helpful,” or “Thank you for those thoughts.” Otherwise, participants might elaborate on a point that isn’t actually very important to them just because the interviewer seemed to agree.
Proeschold-Bell also recommends that interviewers pay attention to—and record—interviewees’ non-verbal responses, which often communicate feelings and attitudes that the verbal response doesn’t capture.
3. Eliminate Interviewer Bias
Proeschold-Bell says it’s critically important to eliminate interviewer bias through the interview process. Knowing the interview guide extremely well helps an interviewer pace the interview to avoid running out of time, and adhering to the scripted wording for each question helps maintain unbiased prompting across all interviews. Additionally, if an interviewee starts answering a question that is going to be asked later, the interviewer can ask them to wait.
It’s best to ask interview questions in a specific order because covering certain questions first may influence how interviewees think during later questions. Finally, she recommends, “Ask all questions of all respondents, even if you think you know what they’ll say. They will surprise you sometimes!”
4. Consider a “Test Run” Period
Proeschold-Bell sees her first several interviews for a study as pilots. Learning from these first few test runs and improving questions and interview techniques for future interviews can have a significant impact on the quality of the study. This means that data quality from the first few interviews may not be as strong since some of the questions change, but the data from the interviews later on will be more useful. Proeschold-Bell recommends numbering interviews chronologically to link interviews to the phase of development in which they were conducted.
5. Make Time for Post-Interview Reflection
After an interview, Proeschold-Bell recommends immediately reviewing the data. “This helps capture good ideas that may otherwise be forgotten,” she says. In fact, she suggests creating a review form with a few open-ended questions that can help capture strong reactions and flag questions that didn’t work well or questions that should be added.
It’s also helpful, she says, to note responses that were different from those given in previous interviews. Doing this may generate ideas to analyze more carefully later on.
Looking for more research design tools? Check out Proeschold-Bell’s recent article, “ Five Tips for Designing an Effective Survey .”
Proeschold-Bell recommends that interviewers pay attention to—and record—interviewees’ non-verbal responses, which often communicate feelings and attitudes that the verbal response doesn’t capture.
- Rae Jean Proeschold-Bell
Related News

Education News
New Global Health Students Bring International Flavor
August 23, 2024

Around DGHI
'Rockstar Women' Build Leadership in East Africa
August 13, 2024

Student Stories
Notes from the Field: Tobenna Ndulue MS’25
August 8, 2024

- Account Logins

What We Offer
With a comprehensive suite of qualitative and quantitative capabilities and 55 years of experience in the industry, Sago powers insights through adaptive solutions.
- Recruitment
- Communities
- Methodify® Automated research
- QualBoard® Digital Discussions
- QualMeeting® Digital Interviews
- Global Qualitative
- Global Quantitative
- In-Person Facilities
- Healthcare Solutions
- Research Consulting
- Europe Solutions
- Neuromarketing Tools
- Trial & Jury Consulting
Who We Serve
Form deeper customer connections and make the process of answering your business questions easier. Sago delivers unparalleled access to the audiences you need through adaptive solutions and a consultative approach.
- Consumer Packaged Goods
- Financial Services
- Media Technology
- Medical Device Manufacturing
- Marketing Research
With a 55-year legacy of impact, Sago has proven we have what it takes to be a long-standing industry leader and partner. We continually advance our range of expertise to provide our clients with the highest level of confidence.
- Global Offices
- Partnerships & Certifications
- News & Media
- Researcher Events

Take Your Research to the Next Level with Multi-Video AI Summaries

Steve Schlesinger Inducted Into 2024 Market Research Council Hall of Fame

Sago Announces Launch of Sago Health to Elevate Healthcare Research
Drop into your new favorite insights rabbit hole and explore content created by the leading minds in market research.
- Case Studies
- Knowledge Kit

When Europe Hits Pause: The Summer Slowdown and What It Means for Business

The Swing Voters Project, August 2024: Wisconsin
- Partner with us
- Join our panel
A Step-by-Step Guide for a Successful Qualitative Interview
- Resources , Blog

Key Takeaways:
- Qualitative interviews provide in-depth insights from individual respondents, and are useful when follow-up or clarification is needed
- Clarity of objectives and audience is essential to gathering actionable insights from your qualitative research project
- Build a strong researcher-respondent relationship to elicit honest and engaged responses
Qualitative research uses in-depth interviews to gain rich non-numerical data from individuals. This data helps researchers understand concepts, opinions, and personal experiences. Interviews are an excellent method to discover the “why” behind people’s preferences or behaviors, but they require a thoughtful approach.
Continue reading as we explore use cases and define the steps to follow for a successful qualitative interview.
In this Article:
When Should I Use Qualitative Interviews? Conducting a Successful Qualitative Interview – Step by Step Guide
1. Determine Your Objective 2. Understand Your Audience 3. Design Appropriate Questions 4. Organize and Prepare for the Interview 5. Conduct the Interview 6. Transcribe and Analyze Responses 7. Learn, Adapt, and Evolve Your Interviews
Start Conducting Qualitative Interviews with Sago
Ready to conduct your qualitative interviews.
Book a consultation with our team for help with recruitment, facilities, and more.
Book a consultation
When Should I Use Qualitative Interviews?
Qualitative research is used to obtain context and describe underlying factors. It describes “how” and “why.”
Perhaps a business wants to understand what product features are most or least important to each target segment. They could ask:
“Between product A and product B, how would the features in each product influence your buying decision?”
This creates an opportunity for the respondent to reveal what features are personally important and unimportant for them. In an interview setting, researchers can go deeper into why these features are important, and how important each feature is in comparison to others.
Qualitative interviews are best when:
- You need in-depth insights
- You want answers to a range of follow-up questions, building on prior responses
- Your questions require significant explanation and reasoning
- You explore complex and confusing topics with respondents
- You want to understand what drives consumer decisions
- You want to hear the unique voice of your audience first-hand
Conducting a Successful Qualitative Interview – Step by Step Guide
Knowing when to use a qualitative interview is a great first step, but now you need to understand how best to conduct one. Our experts share a range of steps to follow as you embark on a qualitative interview and best practices for each.
1. Determine Your Objective
What are you trying to understand? The answer to this is critical in guiding your qualitative research process.
Some common examples:
- Understand consumer perceptions of products, services, or brand
- Reveal strengths and weaknesses in product or service portfolios
- Understand consumer buying behaviors
- Test the usability of a website or digital service
- Emotional reactions to packaging design and marketing assets
2. Understand Your Audience
Who is your target audience for this project? Have a clear understanding of who you need to hear from to meet your research objective.
Here are some examples of objectives, and the sample that is most suited to each:
- If you want to understand how existing customers perceive the quality of your products, you need a sample of existing customers.
- If you want to understand why consumers choose competitor products over yours, you need a sample of non-customers who buy products from your primary competitor.
- If you want to understand how the average person perceives your brand, you need a combination of existing customers, non-customers with awareness of your brand, and unaware non-customers.
3. Design Appropriate Questions
The questions you ask must align with the objectives of your research without being leading or introducing bias.
Here are some best practices when designing research questions:
- Keep questions open-ended. This increases the depth of insight obtained.
- Follow a structure. For instance, a tree diagram where every question has pre-determined follow-up questions based on anticipated answers. A planned structure increases the quality and validity of responses and reduces distractions.
- Design questions that simplify data collection and analysis. Format the responses collected to be compatible with your tools during data ingestion.
- Keep it simple. Focus on clarity when designing research questions to improve respondent understanding and engagement.
4. Organize and Prepare for the Interview
Relationships are essential to the interview process. Preparation beforehand helps build the respondent-researcher relationship. This relationship creates trust and elicits more honest and in-depth answers from participants. Here are some ways to prepare for an interview:
- Give respondents as much information as possible—such as question lists and question intent. Put this into an interview handbook to improve engagement and effectiveness.
- Conduct the interview in a suitable environment with minimal distractions and stressors.
- Have the necessary materials to record information.
- Interview yourself to identify and fix problems before you start interviewing others.
5. Conduct the Interview
With a structure in place, researchers have a clear plan of action throughout the interview.
During the interview, stay attuned to emotional reactions and body language with the following techniques:
- Create a relaxed atmosphere. Ask respondents about their lives, work, and passions to establish a connection.
- Give respondents your full attention. An engaged researcher encourages an engaged respondent. Plus, they gave up their personal time to help you out.
- Read body language. Is the respondent crossing their arms, looking down to the floor, or not making eye contact? These reactions may signal discomfort or anxiety, offering an opportunity to build rapport.
- Follow the questions but be flexible when listening. Deviations from the script may lead to unexpected and valuable insights.
6. Transcribe and Analyze Responses
Convert recorded audio responses to text. Decide early which tool or solution will work best for your needs.
Similarly, researchers may need to annotate video responses to describe behaviors and surrounding context before analysis; e.g., this person gritted their teeth during that response, that person’s vocal tone was anxious and uncertain, etc.
Transcribe responses into a format ready for analysis upon ingestion into your business intelligence tools.
7. Learn, Adapt, and Evolve Your Interviews
Each interview is an opportunity to improve the process. Take time after a project to evaluate how it went.
What did you learn about the process? Was it easy or confusing? Was the respondent comfortable or on edge? Did you get the responses you needed?
Scrutinize your interview approach. Look for ways to improve and innovate the process for better outcomes next time.
Now, you should have a good idea of when to use and how to approach qualitative interviews.
Sago has decades of experience across both quantitative and qualitative research. Our experts find interviews ideal for in-depth qualitative insights that guide new product and service development or improve market positioning for existing offerings. We offer both in-person facilities and online spaces to conduct qualitative interviews.
If you still have questions, get in touch with Sago for help with your next research project.

Efficiency Unleashed: Quick Insights with QualBoard’s Multi-video AI Summaries

Enhancing Efficiency with All-in-One Digital Qual

How Connecting with Gen C Can Help Your Brand Grow

The Deciders, July 2024: Former Nikki Haley Voters

OnDemand: Crack the Code: Evolving Panel Expectations

Pioneering the Future of Pediatric Health

The Swing Voter Project, July 2024: Florida

Exploring Travel Trends and Behaviors for Summer 2024
Take a deep dive into your favorite market research topics

How can we help support you and your research needs?

BEFORE YOU GO
Have you considered how to harness AI in your research process? Check out our on-demand webinar for everything you need to know

- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Faculty of Arts & Sciences Libraries

Library Support for Qualitative Research
- Interview Research
General Handbooks and Overviews
Qualitative research communities.
- Types of Interviews
- Recruiting & Engaging Participants
- Interview Questions
- Conducting Interviews
- Recording & Transcription
- Data Analysis
- Managing Interview Data
- Finding Extant Interviews
- Past Workshops on Interview Research
- Methodological Resources
- Remote & Virtual Fieldwork
- Data Management & Repositories
- Campus Access
- Interviews as a Method for Qualitative Research (video) This short video summarizes why interviews can serve as useful data in qualitative research.
- InterViews by Steinar Kvale Interviewing is an essential tool in qualitative research and this introduction to interviewing outlines both the theoretical underpinnings and the practical aspects of the process. After examining the role of the interview in the research process, Steinar Kvale considers some of the key philosophical issues relating to interviewing: the interview as conversation, hermeneutics, phenomenology, concerns about ethics as well as validity, and postmodernism. Having established this framework, the author then analyzes the seven stages of the interview process - from designing a study to writing it up.
- Practical Evaluation by Michael Quinn Patton Surveys different interviewing strategies, from, a) informal/conversational, to b) interview guide approach, to c) standardized and open-ended, to d) closed/quantitative. Also discusses strategies for wording questions that are open-ended, clear, sensitive, and neutral, while supporting the speaker. Provides suggestions for probing and maintaining control of the interview process, as well as suggestions for recording and transcription.
- The SAGE Handbook of Interview Research by Amir B. Marvasti (Editor); James A. Holstein (Editor); Jaber F. Gubrium (Editor); Karyn D. McKinney (Editor) The new edition of this landmark volume emphasizes the dynamic, interactional, and reflexive dimensions of the research interview. Contributors highlight the myriad dimensions of complexity that are emerging as researchers increasingly frame the interview as a communicative opportunity as much as a data-gathering format. The book begins with the history and conceptual transformations of the interview, which is followed by chapters that discuss the main components of interview practice. Taken together, the contributions to The SAGE Handbook of Interview Research: The Complexity of the Craft encourage readers simultaneously to learn the frameworks and technologies of interviewing and to reflect on the epistemological foundations of the interview craft.
- International Congress of Qualitative Inquiry They host an annual confrerence at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, which aims to facilitate the development of qualitative research methods across a wide variety of academic disciplines, among other initiatives.
- METHODSPACE An online home of the research methods community, where practicing researchers share how to make research easier.
- Social Research Association, UK The SRA is the membership organisation for social researchers in the UK and beyond. It supports researchers via training, guidance, publications, research ethics, events, branches, and careers.
- Social Science Research Council The SSRC administers fellowships and research grants that support the innovation and evaluation of new policy solutions. They convene researchers and stakeholders to share evidence-based policy solutions and incubate new research agendas, produce online knowledge platforms and technical reports that catalog research-based policy solutions, and support mentoring programs that broaden problem-solving research opportunities.
- << Previous: Taguette
- Next: Types of Interviews >>
Except where otherwise noted, this work is subject to a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which allows anyone to share and adapt our material as long as proper attribution is given. For details and exceptions, see the Harvard Library Copyright Policy ©2021 Presidents and Fellows of Harvard College.

- Learn How to Use the Library
- Providers & Employees
- Research Help
- All Research Guides
Conducting Research Interviews
The interviewer mindset, quick tips for preparing, developing questions.
- Conducting the Interview
- Applying & Using the Interview
While the research interview is a one-on-one interaction, it's not a normal conversation. As the interviewer, it's expected that you:
- Are knowledgeable on the topic of the interview (this may require some background research)
- Are able to structure and guide the interview to keep it relevant but flexible
- Are able to remember and interpret the information gained in the interview
- Are sensitive to the interviewee's position and their rights
- Do preliminary research on the topic and the interviewee so that you enter the interview with an understanding of what will be discussed.
- Reflect on your goals. What should the interview accomplish? What is important to have recorded in the interview, and why is it important? How can you make the process easy for the interviewee?
- Create a list of topics and questions to explore during the interview. This should not be a strict checklist or a script; rather, it should function as a guide to ensure that you cover all of the content and that the interview stays focused.
- Create an open line of dialog with your interviewee before the interview so that you are comfortable with each other. This can involve going over the process, offering to answer any of their questions, verifying your time and place for the interview, etc.
- Choose and thoroughly familiarize yourself with your recording equipment to minimize any potential issues that may arise during the actual interview.
- Choose an interview space that is relaxed, comfortable, and quiet. You are having a conversation with your interviewee, not an interrogation.
- If you have never interviewed before, feel free to practice for the interview with friends, family, or peers. This will make sure you are prepared for the real thing.
Characteristics of good interview questions
- Open-ended and elicit a long response from the interviewee (can't be answered yes/no or with one word)
- Focus on the experience of the interviewee
- Don't lead the interviewee toward a particular response
- Address a single issue/point (i.e. don't ask multi-part questions)
Writing interview questions
Harvard's Department of Sociology provides some steps to help guide you in the process of writing interview questions (see the link to the guide below).
- Write down the larger research questions of the study. Outline the broad areas of knowledge that are relevant to answering these questions.
- Develop questions within each of these major areas, shaping them to fit particular kinds of respondents. The goal here is to tap into their experiences and expertise.
- Adjust the language of the interview according to the respondent (child, professional, etc.).
- Take care to word questions so that respondents are motivated to answer as completely and honestly as possible.
- Ask “how” questions rather than “why” questions to get stories of process rather than acceptable “accounts” of behavior. “How did you come to join this group . . .?”
- Develop probes that will elicit more detailed and elaborate responses to key questions. The more detail, the better!
- Begin the interview with a “warm-up” question—something that the respondent can answer easily and at some length (though not too long). It doesn’t have to pertain directly to what you are trying to find out (although it might), but this initial rapport-building will put you more at ease with one another and thus will make the rest of the interview flow more smoothly.
- Think about the logical flow of the interview. What topics should come first? What follows more or less “naturally”? This may take some adjustment after several interviews.
- Difficult or potentially embarrassing questions should be asked toward the end of the interview, when rapport has been established.
- The last question should provide some closure for the interview, and leave the respondent feeling empowered, listened to, or otherwise glad that they talked to you.
- Strategies for Qualitative Interviews This handy guide from Harvard's Department of Sociology provides guidance on getting into the interviewer mindset as well as developing and writing interview questions.
Depending on the nature of your assignment or research, you may or may not need to record and transcribe the interview. Review the pros and cons to determine whether recording and transcribing will be worthwhile for you.
- Helps you to recall more details of the interview
- Helps you to thoroughly examine the interview
- It allows other researchers to interpret and reuse the data in new ways
- May be off-putting to interviewees or make them feel pressured
- Transcribing is a time-consuming process; even using a transcription software requires a detailed review of the text
"Strategies for Qualitative Interviews" (n.d.) Harvard. See link above..
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Conducting the Interview >>
- Last Updated: Mar 25, 2024 8:55 AM
- URL: https://aultman.libguides.com/interviews
Aultman Health Sciences Library
Aultman Education Center, C2-230, 2600 Sixth St SW, Canton, OH 44710 | 330-363-5000 | [email protected]

Chapter 11. Interviewing
Introduction.
Interviewing people is at the heart of qualitative research. It is not merely a way to collect data but an intrinsically rewarding activity—an interaction between two people that holds the potential for greater understanding and interpersonal development. Unlike many of our daily interactions with others that are fairly shallow and mundane, sitting down with a person for an hour or two and really listening to what they have to say is a profound and deep enterprise, one that can provide not only “data” for you, the interviewer, but also self-understanding and a feeling of being heard for the interviewee. I always approach interviewing with a deep appreciation for the opportunity it gives me to understand how other people experience the world. That said, there is not one kind of interview but many, and some of these are shallower than others. This chapter will provide you with an overview of interview techniques but with a special focus on the in-depth semistructured interview guide approach, which is the approach most widely used in social science research.
An interview can be variously defined as “a conversation with a purpose” ( Lune and Berg 2018 ) and an attempt to understand the world from the point of view of the person being interviewed: “to unfold the meaning of peoples’ experiences, to uncover their lived world prior to scientific explanations” ( Kvale 2007 ). It is a form of active listening in which the interviewer steers the conversation to subjects and topics of interest to their research but also manages to leave enough space for those interviewed to say surprising things. Achieving that balance is a tricky thing, which is why most practitioners believe interviewing is both an art and a science. In my experience as a teacher, there are some students who are “natural” interviewers (often they are introverts), but anyone can learn to conduct interviews, and everyone, even those of us who have been doing this for years, can improve their interviewing skills. This might be a good time to highlight the fact that the interview is a product between interviewer and interviewee and that this product is only as good as the rapport established between the two participants. Active listening is the key to establishing this necessary rapport.
Patton ( 2002 ) makes the argument that we use interviews because there are certain things that are not observable. In particular, “we cannot observe feelings, thoughts, and intentions. We cannot observe behaviors that took place at some previous point in time. We cannot observe situations that preclude the presence of an observer. We cannot observe how people have organized the world and the meanings they attach to what goes on in the world. We have to ask people questions about those things” ( 341 ).
Types of Interviews
There are several distinct types of interviews. Imagine a continuum (figure 11.1). On one side are unstructured conversations—the kind you have with your friends. No one is in control of those conversations, and what you talk about is often random—whatever pops into your head. There is no secret, underlying purpose to your talking—if anything, the purpose is to talk to and engage with each other, and the words you use and the things you talk about are a little beside the point. An unstructured interview is a little like this informal conversation, except that one of the parties to the conversation (you, the researcher) does have an underlying purpose, and that is to understand the other person. You are not friends speaking for no purpose, but it might feel just as unstructured to the “interviewee” in this scenario. That is one side of the continuum. On the other side are fully structured and standardized survey-type questions asked face-to-face. Here it is very clear who is asking the questions and who is answering them. This doesn’t feel like a conversation at all! A lot of people new to interviewing have this ( erroneously !) in mind when they think about interviews as data collection. Somewhere in the middle of these two extreme cases is the “ semistructured” interview , in which the researcher uses an “interview guide” to gently move the conversation to certain topics and issues. This is the primary form of interviewing for qualitative social scientists and will be what I refer to as interviewing for the rest of this chapter, unless otherwise specified.
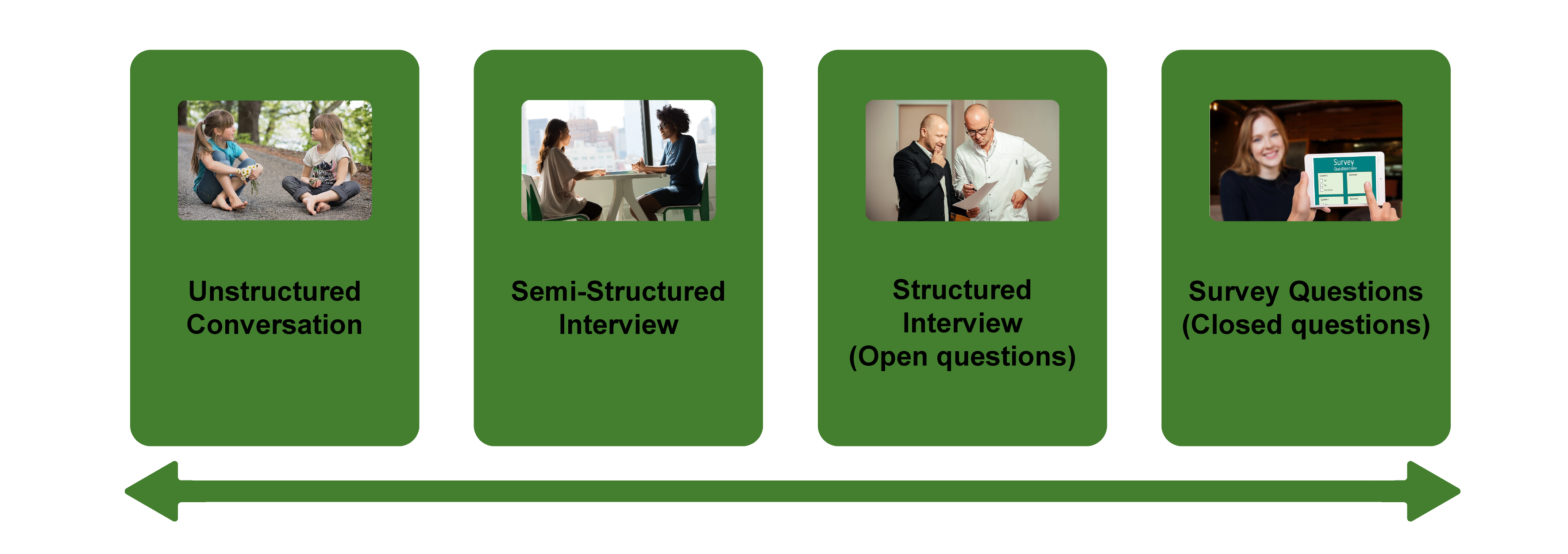
Informal (unstructured conversations). This is the most “open-ended” approach to interviewing. It is particularly useful in conjunction with observational methods (see chapters 13 and 14). There are no predetermined questions. Each interview will be different. Imagine you are researching the Oregon Country Fair, an annual event in Veneta, Oregon, that includes live music, artisan craft booths, face painting, and a lot of people walking through forest paths. It’s unlikely that you will be able to get a person to sit down with you and talk intensely about a set of questions for an hour and a half. But you might be able to sidle up to several people and engage with them about their experiences at the fair. You might have a general interest in what attracts people to these events, so you could start a conversation by asking strangers why they are here or why they come back every year. That’s it. Then you have a conversation that may lead you anywhere. Maybe one person tells a long story about how their parents brought them here when they were a kid. A second person talks about how this is better than Burning Man. A third person shares their favorite traveling band. And yet another enthuses about the public library in the woods. During your conversations, you also talk about a lot of other things—the weather, the utilikilts for sale, the fact that a favorite food booth has disappeared. It’s all good. You may not be able to record these conversations. Instead, you might jot down notes on the spot and then, when you have the time, write down as much as you can remember about the conversations in long fieldnotes. Later, you will have to sit down with these fieldnotes and try to make sense of all the information (see chapters 18 and 19).
Interview guide ( semistructured interview ). This is the primary type employed by social science qualitative researchers. The researcher creates an “interview guide” in advance, which she uses in every interview. In theory, every person interviewed is asked the same questions. In practice, every person interviewed is asked mostly the same topics but not always the same questions, as the whole point of a “guide” is that it guides the direction of the conversation but does not command it. The guide is typically between five and ten questions or question areas, sometimes with suggested follow-ups or prompts . For example, one question might be “What was it like growing up in Eastern Oregon?” with prompts such as “Did you live in a rural area? What kind of high school did you attend?” to help the conversation develop. These interviews generally take place in a quiet place (not a busy walkway during a festival) and are recorded. The recordings are transcribed, and those transcriptions then become the “data” that is analyzed (see chapters 18 and 19). The conventional length of one of these types of interviews is between one hour and two hours, optimally ninety minutes. Less than one hour doesn’t allow for much development of questions and thoughts, and two hours (or more) is a lot of time to ask someone to sit still and answer questions. If you have a lot of ground to cover, and the person is willing, I highly recommend two separate interview sessions, with the second session being slightly shorter than the first (e.g., ninety minutes the first day, sixty minutes the second). There are lots of good reasons for this, but the most compelling one is that this allows you to listen to the first day’s recording and catch anything interesting you might have missed in the moment and so develop follow-up questions that can probe further. This also allows the person being interviewed to have some time to think about the issues raised in the interview and go a little deeper with their answers.
Standardized questionnaire with open responses ( structured interview ). This is the type of interview a lot of people have in mind when they hear “interview”: a researcher comes to your door with a clipboard and proceeds to ask you a series of questions. These questions are all the same whoever answers the door; they are “standardized.” Both the wording and the exact order are important, as people’s responses may vary depending on how and when a question is asked. These are qualitative only in that the questions allow for “open-ended responses”: people can say whatever they want rather than select from a predetermined menu of responses. For example, a survey I collaborated on included this open-ended response question: “How does class affect one’s career success in sociology?” Some of the answers were simply one word long (e.g., “debt”), and others were long statements with stories and personal anecdotes. It is possible to be surprised by the responses. Although it’s a stretch to call this kind of questioning a conversation, it does allow the person answering the question some degree of freedom in how they answer.
Survey questionnaire with closed responses (not an interview!). Standardized survey questions with specific answer options (e.g., closed responses) are not really interviews at all, and they do not generate qualitative data. For example, if we included five options for the question “How does class affect one’s career success in sociology?”—(1) debt, (2) social networks, (3) alienation, (4) family doesn’t understand, (5) type of grad program—we leave no room for surprises at all. Instead, we would most likely look at patterns around these responses, thinking quantitatively rather than qualitatively (e.g., using regression analysis techniques, we might find that working-class sociologists were twice as likely to bring up alienation). It can sometimes be confusing for new students because the very same survey can include both closed-ended and open-ended questions. The key is to think about how these will be analyzed and to what level surprises are possible. If your plan is to turn all responses into a number and make predictions about correlations and relationships, you are no longer conducting qualitative research. This is true even if you are conducting this survey face-to-face with a real live human. Closed-response questions are not conversations of any kind, purposeful or not.
In summary, the semistructured interview guide approach is the predominant form of interviewing for social science qualitative researchers because it allows a high degree of freedom of responses from those interviewed (thus allowing for novel discoveries) while still maintaining some connection to a research question area or topic of interest. The rest of the chapter assumes the employment of this form.
Creating an Interview Guide
Your interview guide is the instrument used to bridge your research question(s) and what the people you are interviewing want to tell you. Unlike a standardized questionnaire, the questions actually asked do not need to be exactly what you have written down in your guide. The guide is meant to create space for those you are interviewing to talk about the phenomenon of interest, but sometimes you are not even sure what that phenomenon is until you start asking questions. A priority in creating an interview guide is to ensure it offers space. One of the worst mistakes is to create questions that are so specific that the person answering them will not stray. Relatedly, questions that sound “academic” will shut down a lot of respondents. A good interview guide invites respondents to talk about what is important to them, not feel like they are performing or being evaluated by you.
Good interview questions should not sound like your “research question” at all. For example, let’s say your research question is “How do patriarchal assumptions influence men’s understanding of climate change and responses to climate change?” It would be worse than unhelpful to ask a respondent, “How do your assumptions about the role of men affect your understanding of climate change?” You need to unpack this into manageable nuggets that pull your respondent into the area of interest without leading him anywhere. You could start by asking him what he thinks about climate change in general. Or, even better, whether he has any concerns about heatwaves or increased tornadoes or polar icecaps melting. Once he starts talking about that, you can ask follow-up questions that bring in issues around gendered roles, perhaps asking if he is married (to a woman) and whether his wife shares his thoughts and, if not, how they negotiate that difference. The fact is, you won’t really know the right questions to ask until he starts talking.
There are several distinct types of questions that can be used in your interview guide, either as main questions or as follow-up probes. If you remember that the point is to leave space for the respondent, you will craft a much more effective interview guide! You will also want to think about the place of time in both the questions themselves (past, present, future orientations) and the sequencing of the questions.
Researcher Note
Suggestion : As you read the next three sections (types of questions, temporality, question sequence), have in mind a particular research question, and try to draft questions and sequence them in a way that opens space for a discussion that helps you answer your research question.
Type of Questions
Experience and behavior questions ask about what a respondent does regularly (their behavior) or has done (their experience). These are relatively easy questions for people to answer because they appear more “factual” and less subjective. This makes them good opening questions. For the study on climate change above, you might ask, “Have you ever experienced an unusual weather event? What happened?” Or “You said you work outside? What is a typical summer workday like for you? How do you protect yourself from the heat?”
Opinion and values questions , in contrast, ask questions that get inside the minds of those you are interviewing. “Do you think climate change is real? Who or what is responsible for it?” are two such questions. Note that you don’t have to literally ask, “What is your opinion of X?” but you can find a way to ask the specific question relevant to the conversation you are having. These questions are a bit trickier to ask because the answers you get may depend in part on how your respondent perceives you and whether they want to please you or not. We’ve talked a fair amount about being reflective. Here is another place where this comes into play. You need to be aware of the effect your presence might have on the answers you are receiving and adjust accordingly. If you are a woman who is perceived as liberal asking a man who identifies as conservative about climate change, there is a lot of subtext that can be going on in the interview. There is no one right way to resolve this, but you must at least be aware of it.
Feeling questions are questions that ask respondents to draw on their emotional responses. It’s pretty common for academic researchers to forget that we have bodies and emotions, but people’s understandings of the world often operate at this affective level, sometimes unconsciously or barely consciously. It is a good idea to include questions that leave space for respondents to remember, imagine, or relive emotional responses to particular phenomena. “What was it like when you heard your cousin’s house burned down in that wildfire?” doesn’t explicitly use any emotion words, but it allows your respondent to remember what was probably a pretty emotional day. And if they respond emotionally neutral, that is pretty interesting data too. Note that asking someone “How do you feel about X” is not always going to evoke an emotional response, as they might simply turn around and respond with “I think that…” It is better to craft a question that actually pushes the respondent into the affective category. This might be a specific follow-up to an experience and behavior question —for example, “You just told me about your daily routine during the summer heat. Do you worry it is going to get worse?” or “Have you ever been afraid it will be too hot to get your work accomplished?”
Knowledge questions ask respondents what they actually know about something factual. We have to be careful when we ask these types of questions so that respondents do not feel like we are evaluating them (which would shut them down), but, for example, it is helpful to know when you are having a conversation about climate change that your respondent does in fact know that unusual weather events have increased and that these have been attributed to climate change! Asking these questions can set the stage for deeper questions and can ensure that the conversation makes the same kind of sense to both participants. For example, a conversation about political polarization can be put back on track once you realize that the respondent doesn’t really have a clear understanding that there are two parties in the US. Instead of asking a series of questions about Republicans and Democrats, you might shift your questions to talk more generally about political disagreements (e.g., “people against abortion”). And sometimes what you do want to know is the level of knowledge about a particular program or event (e.g., “Are you aware you can discharge your student loans through the Public Service Loan Forgiveness program?”).
Sensory questions call on all senses of the respondent to capture deeper responses. These are particularly helpful in sparking memory. “Think back to your childhood in Eastern Oregon. Describe the smells, the sounds…” Or you could use these questions to help a person access the full experience of a setting they customarily inhabit: “When you walk through the doors to your office building, what do you see? Hear? Smell?” As with feeling questions , these questions often supplement experience and behavior questions . They are another way of allowing your respondent to report fully and deeply rather than remain on the surface.
Creative questions employ illustrative examples, suggested scenarios, or simulations to get respondents to think more deeply about an issue, topic, or experience. There are many options here. In The Trouble with Passion , Erin Cech ( 2021 ) provides a scenario in which “Joe” is trying to decide whether to stay at his decent but boring computer job or follow his passion by opening a restaurant. She asks respondents, “What should Joe do?” Their answers illuminate the attraction of “passion” in job selection. In my own work, I have used a news story about an upwardly mobile young man who no longer has time to see his mother and sisters to probe respondents’ feelings about the costs of social mobility. Jessi Streib and Betsy Leondar-Wright have used single-page cartoon “scenes” to elicit evaluations of potential racial discrimination, sexual harassment, and classism. Barbara Sutton ( 2010 ) has employed lists of words (“strong,” “mother,” “victim”) on notecards she fans out and asks her female respondents to select and discuss.
Background/Demographic Questions
You most definitely will want to know more about the person you are interviewing in terms of conventional demographic information, such as age, race, gender identity, occupation, and educational attainment. These are not questions that normally open up inquiry. [1] For this reason, my practice has been to include a separate “demographic questionnaire” sheet that I ask each respondent to fill out at the conclusion of the interview. Only include those aspects that are relevant to your study. For example, if you are not exploring religion or religious affiliation, do not include questions about a person’s religion on the demographic sheet. See the example provided at the end of this chapter.
Temporality
Any type of question can have a past, present, or future orientation. For example, if you are asking a behavior question about workplace routine, you might ask the respondent to talk about past work, present work, and ideal (future) work. Similarly, if you want to understand how people cope with natural disasters, you might ask your respondent how they felt then during the wildfire and now in retrospect and whether and to what extent they have concerns for future wildfire disasters. It’s a relatively simple suggestion—don’t forget to ask about past, present, and future—but it can have a big impact on the quality of the responses you receive.
Question Sequence
Having a list of good questions or good question areas is not enough to make a good interview guide. You will want to pay attention to the order in which you ask your questions. Even though any one respondent can derail this order (perhaps by jumping to answer a question you haven’t yet asked), a good advance plan is always helpful. When thinking about sequence, remember that your goal is to get your respondent to open up to you and to say things that might surprise you. To establish rapport, it is best to start with nonthreatening questions. Asking about the present is often the safest place to begin, followed by the past (they have to know you a little bit to get there), and lastly, the future (talking about hopes and fears requires the most rapport). To allow for surprises, it is best to move from very general questions to more particular questions only later in the interview. This ensures that respondents have the freedom to bring up the topics that are relevant to them rather than feel like they are constrained to answer you narrowly. For example, refrain from asking about particular emotions until these have come up previously—don’t lead with them. Often, your more particular questions will emerge only during the course of the interview, tailored to what is emerging in conversation.
Once you have a set of questions, read through them aloud and imagine you are being asked the same questions. Does the set of questions have a natural flow? Would you be willing to answer the very first question to a total stranger? Does your sequence establish facts and experiences before moving on to opinions and values? Did you include prefatory statements, where necessary; transitions; and other announcements? These can be as simple as “Hey, we talked a lot about your experiences as a barista while in college.… Now I am turning to something completely different: how you managed friendships in college.” That is an abrupt transition, but it has been softened by your acknowledgment of that.
Probes and Flexibility
Once you have the interview guide, you will also want to leave room for probes and follow-up questions. As in the sample probe included here, you can write out the obvious probes and follow-up questions in advance. You might not need them, as your respondent might anticipate them and include full responses to the original question. Or you might need to tailor them to how your respondent answered the question. Some common probes and follow-up questions include asking for more details (When did that happen? Who else was there?), asking for elaboration (Could you say more about that?), asking for clarification (Does that mean what I think it means or something else? I understand what you mean, but someone else reading the transcript might not), and asking for contrast or comparison (How did this experience compare with last year’s event?). “Probing is a skill that comes from knowing what to look for in the interview, listening carefully to what is being said and what is not said, and being sensitive to the feedback needs of the person being interviewed” ( Patton 2002:374 ). It takes work! And energy. I and many other interviewers I know report feeling emotionally and even physically drained after conducting an interview. You are tasked with active listening and rearranging your interview guide as needed on the fly. If you only ask the questions written down in your interview guide with no deviations, you are doing it wrong. [2]
The Final Question
Every interview guide should include a very open-ended final question that allows for the respondent to say whatever it is they have been dying to tell you but you’ve forgotten to ask. About half the time they are tired too and will tell you they have nothing else to say. But incredibly, some of the most honest and complete responses take place here, at the end of a long interview. You have to realize that the person being interviewed is often discovering things about themselves as they talk to you and that this process of discovery can lead to new insights for them. Making space at the end is therefore crucial. Be sure you convey that you actually do want them to tell you more, that the offer of “anything else?” is not read as an empty convention where the polite response is no. Here is where you can pull from that active listening and tailor the final question to the particular person. For example, “I’ve asked you a lot of questions about what it was like to live through that wildfire. I’m wondering if there is anything I’ve forgotten to ask, especially because I haven’t had that experience myself” is a much more inviting final question than “Great. Anything you want to add?” It’s also helpful to convey to the person that you have the time to listen to their full answer, even if the allotted time is at the end. After all, there are no more questions to ask, so the respondent knows exactly how much time is left. Do them the courtesy of listening to them!
Conducting the Interview
Once you have your interview guide, you are on your way to conducting your first interview. I always practice my interview guide with a friend or family member. I do this even when the questions don’t make perfect sense for them, as it still helps me realize which questions make no sense, are poorly worded (too academic), or don’t follow sequentially. I also practice the routine I will use for interviewing, which goes something like this:
- Introduce myself and reintroduce the study
- Provide consent form and ask them to sign and retain/return copy
- Ask if they have any questions about the study before we begin
- Ask if I can begin recording
- Ask questions (from interview guide)
- Turn off the recording device
- Ask if they are willing to fill out my demographic questionnaire
- Collect questionnaire and, without looking at the answers, place in same folder as signed consent form
- Thank them and depart
A note on remote interviewing: Interviews have traditionally been conducted face-to-face in a private or quiet public setting. You don’t want a lot of background noise, as this will make transcriptions difficult. During the recent global pandemic, many interviewers, myself included, learned the benefits of interviewing remotely. Although face-to-face is still preferable for many reasons, Zoom interviewing is not a bad alternative, and it does allow more interviews across great distances. Zoom also includes automatic transcription, which significantly cuts down on the time it normally takes to convert our conversations into “data” to be analyzed. These automatic transcriptions are not perfect, however, and you will still need to listen to the recording and clarify and clean up the transcription. Nor do automatic transcriptions include notations of body language or change of tone, which you may want to include. When interviewing remotely, you will want to collect the consent form before you meet: ask them to read, sign, and return it as an email attachment. I think it is better to ask for the demographic questionnaire after the interview, but because some respondents may never return it then, it is probably best to ask for this at the same time as the consent form, in advance of the interview.
What should you bring to the interview? I would recommend bringing two copies of the consent form (one for you and one for the respondent), a demographic questionnaire, a manila folder in which to place the signed consent form and filled-out demographic questionnaire, a printed copy of your interview guide (I print with three-inch right margins so I can jot down notes on the page next to relevant questions), a pen, a recording device, and water.
After the interview, you will want to secure the signed consent form in a locked filing cabinet (if in print) or a password-protected folder on your computer. Using Excel or a similar program that allows tables/spreadsheets, create an identifying number for your interview that links to the consent form without using the name of your respondent. For example, let’s say that I conduct interviews with US politicians, and the first person I meet with is George W. Bush. I will assign the transcription the number “INT#001” and add it to the signed consent form. [3] The signed consent form goes into a locked filing cabinet, and I never use the name “George W. Bush” again. I take the information from the demographic sheet, open my Excel spreadsheet, and add the relevant information in separate columns for the row INT#001: White, male, Republican. When I interview Bill Clinton as my second interview, I include a second row: INT#002: White, male, Democrat. And so on. The only link to the actual name of the respondent and this information is the fact that the consent form (unavailable to anyone but me) has stamped on it the interview number.
Many students get very nervous before their first interview. Actually, many of us are always nervous before the interview! But do not worry—this is normal, and it does pass. Chances are, you will be pleasantly surprised at how comfortable it begins to feel. These “purposeful conversations” are often a delight for both participants. This is not to say that sometimes things go wrong. I often have my students practice several “bad scenarios” (e.g., a respondent that you cannot get to open up; a respondent who is too talkative and dominates the conversation, steering it away from the topics you are interested in; emotions that completely take over; or shocking disclosures you are ill-prepared to handle), but most of the time, things go quite well. Be prepared for the unexpected, but know that the reason interviews are so popular as a technique of data collection is that they are usually richly rewarding for both participants.
One thing that I stress to my methods students and remind myself about is that interviews are still conversations between people. If there’s something you might feel uncomfortable asking someone about in a “normal” conversation, you will likely also feel a bit of discomfort asking it in an interview. Maybe more importantly, your respondent may feel uncomfortable. Social research—especially about inequality—can be uncomfortable. And it’s easy to slip into an abstract, intellectualized, or removed perspective as an interviewer. This is one reason trying out interview questions is important. Another is that sometimes the question sounds good in your head but doesn’t work as well out loud in practice. I learned this the hard way when a respondent asked me how I would answer the question I had just posed, and I realized that not only did I not really know how I would answer it, but I also wasn’t quite as sure I knew what I was asking as I had thought.
—Elizabeth M. Lee, Associate Professor of Sociology at Saint Joseph’s University, author of Class and Campus Life , and co-author of Geographies of Campus Inequality
How Many Interviews?
Your research design has included a targeted number of interviews and a recruitment plan (see chapter 5). Follow your plan, but remember that “ saturation ” is your goal. You interview as many people as you can until you reach a point at which you are no longer surprised by what they tell you. This means not that no one after your first twenty interviews will have surprising, interesting stories to tell you but rather that the picture you are forming about the phenomenon of interest to you from a research perspective has come into focus, and none of the interviews are substantially refocusing that picture. That is when you should stop collecting interviews. Note that to know when you have reached this, you will need to read your transcripts as you go. More about this in chapters 18 and 19.
Your Final Product: The Ideal Interview Transcript
A good interview transcript will demonstrate a subtly controlled conversation by the skillful interviewer. In general, you want to see replies that are about one paragraph long, not short sentences and not running on for several pages. Although it is sometimes necessary to follow respondents down tangents, it is also often necessary to pull them back to the questions that form the basis of your research study. This is not really a free conversation, although it may feel like that to the person you are interviewing.
Final Tips from an Interview Master
Annette Lareau is arguably one of the masters of the trade. In Listening to People , she provides several guidelines for good interviews and then offers a detailed example of an interview gone wrong and how it could be addressed (please see the “Further Readings” at the end of this chapter). Here is an abbreviated version of her set of guidelines: (1) interview respondents who are experts on the subjects of most interest to you (as a corollary, don’t ask people about things they don’t know); (2) listen carefully and talk as little as possible; (3) keep in mind what you want to know and why you want to know it; (4) be a proactive interviewer (subtly guide the conversation); (5) assure respondents that there aren’t any right or wrong answers; (6) use the respondent’s own words to probe further (this both allows you to accurately identify what you heard and pushes the respondent to explain further); (7) reuse effective probes (don’t reinvent the wheel as you go—if repeating the words back works, do it again and again); (8) focus on learning the subjective meanings that events or experiences have for a respondent; (9) don’t be afraid to ask a question that draws on your own knowledge (unlike trial lawyers who are trained never to ask a question for which they don’t already know the answer, sometimes it’s worth it to ask risky questions based on your hypotheses or just plain hunches); (10) keep thinking while you are listening (so difficult…and important); (11) return to a theme raised by a respondent if you want further information; (12) be mindful of power inequalities (and never ever coerce a respondent to continue the interview if they want out); (13) take control with overly talkative respondents; (14) expect overly succinct responses, and develop strategies for probing further; (15) balance digging deep and moving on; (16) develop a plan to deflect questions (e.g., let them know you are happy to answer any questions at the end of the interview, but you don’t want to take time away from them now); and at the end, (17) check to see whether you have asked all your questions. You don’t always have to ask everyone the same set of questions, but if there is a big area you have forgotten to cover, now is the time to recover ( Lareau 2021:93–103 ).
Sample: Demographic Questionnaire
ASA Taskforce on First-Generation and Working-Class Persons in Sociology – Class Effects on Career Success
Supplementary Demographic Questionnaire
Thank you for your participation in this interview project. We would like to collect a few pieces of key demographic information from you to supplement our analyses. Your answers to these questions will be kept confidential and stored by ID number. All of your responses here are entirely voluntary!
What best captures your race/ethnicity? (please check any/all that apply)
- White (Non Hispanic/Latina/o/x)
- Black or African American
- Hispanic, Latino/a/x of Spanish
- Asian or Asian American
- American Indian or Alaska Native
- Middle Eastern or North African
- Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander
- Other : (Please write in: ________________)
What is your current position?
- Grad Student
- Full Professor
Please check any and all of the following that apply to you:
- I identify as a working-class academic
- I was the first in my family to graduate from college
- I grew up poor
What best reflects your gender?
- Transgender female/Transgender woman
- Transgender male/Transgender man
- Gender queer/ Gender nonconforming
Anything else you would like us to know about you?
Example: Interview Guide
In this example, follow-up prompts are italicized. Note the sequence of questions. That second question often elicits an entire life history , answering several later questions in advance.
Introduction Script/Question
Thank you for participating in our survey of ASA members who identify as first-generation or working-class. As you may have heard, ASA has sponsored a taskforce on first-generation and working-class persons in sociology and we are interested in hearing from those who so identify. Your participation in this interview will help advance our knowledge in this area.
- The first thing we would like to as you is why you have volunteered to be part of this study? What does it mean to you be first-gen or working class? Why were you willing to be interviewed?
- How did you decide to become a sociologist?
- Can you tell me a little bit about where you grew up? ( prompts: what did your parent(s) do for a living? What kind of high school did you attend?)
- Has this identity been salient to your experience? (how? How much?)
- How welcoming was your grad program? Your first academic employer?
- Why did you decide to pursue sociology at the graduate level?
- Did you experience culture shock in college? In graduate school?
- Has your FGWC status shaped how you’ve thought about where you went to school? debt? etc?
- Were you mentored? How did this work (not work)? How might it?
- What did you consider when deciding where to go to grad school? Where to apply for your first position?
- What, to you, is a mark of career success? Have you achieved that success? What has helped or hindered your pursuit of success?
- Do you think sociology, as a field, cares about prestige?
- Let’s talk a little bit about intersectionality. How does being first-gen/working class work alongside other identities that are important to you?
- What do your friends and family think about your career? Have you had any difficulty relating to family members or past friends since becoming highly educated?
- Do you have any debt from college/grad school? Are you concerned about this? Could you explain more about how you paid for college/grad school? (here, include assistance from family, fellowships, scholarships, etc.)
- (You’ve mentioned issues or obstacles you had because of your background.) What could have helped? Or, who or what did? Can you think of fortuitous moments in your career?
- Do you have any regrets about the path you took?
- Is there anything else you would like to add? Anything that the Taskforce should take note of, that we did not ask you about here?
Further Readings
Britten, Nicky. 1995. “Qualitative Interviews in Medical Research.” BMJ: British Medical Journal 31(6999):251–253. A good basic overview of interviewing particularly useful for students of public health and medical research generally.
Corbin, Juliet, and Janice M. Morse. 2003. “The Unstructured Interactive Interview: Issues of Reciprocity and Risks When Dealing with Sensitive Topics.” Qualitative Inquiry 9(3):335–354. Weighs the potential benefits and harms of conducting interviews on topics that may cause emotional distress. Argues that the researcher’s skills and code of ethics should ensure that the interviewing process provides more of a benefit to both participant and researcher than a harm to the former.
Gerson, Kathleen, and Sarah Damaske. 2020. The Science and Art of Interviewing . New York: Oxford University Press. A useful guidebook/textbook for both undergraduates and graduate students, written by sociologists.
Kvale, Steiner. 2007. Doing Interviews . London: SAGE. An easy-to-follow guide to conducting and analyzing interviews by psychologists.
Lamont, Michèle, and Ann Swidler. 2014. “Methodological Pluralism and the Possibilities and Limits of Interviewing.” Qualitative Sociology 37(2):153–171. Written as a response to various debates surrounding the relative value of interview-based studies and ethnographic studies defending the particular strengths of interviewing. This is a must-read article for anyone seriously engaging in qualitative research!
Pugh, Allison J. 2013. “What Good Are Interviews for Thinking about Culture? Demystifying Interpretive Analysis.” American Journal of Cultural Sociology 1(1):42–68. Another defense of interviewing written against those who champion ethnographic methods as superior, particularly in the area of studying culture. A classic.
Rapley, Timothy John. 2001. “The ‘Artfulness’ of Open-Ended Interviewing: Some considerations in analyzing interviews.” Qualitative Research 1(3):303–323. Argues for the importance of “local context” of data production (the relationship built between interviewer and interviewee, for example) in properly analyzing interview data.
Weiss, Robert S. 1995. Learning from Strangers: The Art and Method of Qualitative Interview Studies . New York: Simon and Schuster. A classic and well-regarded textbook on interviewing. Because Weiss has extensive experience conducting surveys, he contrasts the qualitative interview with the survey questionnaire well; particularly useful for those trained in the latter.
- I say “normally” because how people understand their various identities can itself be an expansive topic of inquiry. Here, I am merely talking about collecting otherwise unexamined demographic data, similar to how we ask people to check boxes on surveys. ↵
- Again, this applies to “semistructured in-depth interviewing.” When conducting standardized questionnaires, you will want to ask each question exactly as written, without deviations! ↵
- I always include “INT” in the number because I sometimes have other kinds of data with their own numbering: FG#001 would mean the first focus group, for example. I also always include three-digit spaces, as this allows for up to 999 interviews (or, more realistically, allows for me to interview up to one hundred persons without having to reset my numbering system). ↵
A method of data collection in which the researcher asks the participant questions; the answers to these questions are often recorded and transcribed verbatim. There are many different kinds of interviews - see also semistructured interview , structured interview , and unstructured interview .
A document listing key questions and question areas for use during an interview. It is used most often for semi-structured interviews. A good interview guide may have no more than ten primary questions for two hours of interviewing, but these ten questions will be supplemented by probes and relevant follow-ups throughout the interview. Most IRBs require the inclusion of the interview guide in applications for review. See also interview and semi-structured interview .
A data-collection method that relies on casual, conversational, and informal interviewing. Despite its apparent conversational nature, the researcher usually has a set of particular questions or question areas in mind but allows the interview to unfold spontaneously. This is a common data-collection technique among ethnographers. Compare to the semi-structured or in-depth interview .
A form of interview that follows a standard guide of questions asked, although the order of the questions may change to match the particular needs of each individual interview subject, and probing “follow-up” questions are often added during the course of the interview. The semi-structured interview is the primary form of interviewing used by qualitative researchers in the social sciences. It is sometimes referred to as an “in-depth” interview. See also interview and interview guide .
The cluster of data-collection tools and techniques that involve observing interactions between people, the behaviors, and practices of individuals (sometimes in contrast to what they say about how they act and behave), and cultures in context. Observational methods are the key tools employed by ethnographers and Grounded Theory .
Follow-up questions used in a semi-structured interview to elicit further elaboration. Suggested prompts can be included in the interview guide to be used/deployed depending on how the initial question was answered or if the topic of the prompt does not emerge spontaneously.
A form of interview that follows a strict set of questions, asked in a particular order, for all interview subjects. The questions are also the kind that elicits short answers, and the data is more “informative” than probing. This is often used in mixed-methods studies, accompanying a survey instrument. Because there is no room for nuance or the exploration of meaning in structured interviews, qualitative researchers tend to employ semi-structured interviews instead. See also interview.
The point at which you can conclude data collection because every person you are interviewing, the interaction you are observing, or content you are analyzing merely confirms what you have already noted. Achieving saturation is often used as the justification for the final sample size.
An interview variant in which a person’s life story is elicited in a narrative form. Turning points and key themes are established by the researcher and used as data points for further analysis.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Research Interviews: An effective and insightful way of data collection
Research interviews play a pivotal role in collecting data for various academic, scientific, and professional endeavors. They provide researchers with an opportunity to delve deep into the thoughts, experiences, and perspectives of an individual, thus enabling a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena. It is important for researchers to design an effective and insightful method of data collection on a particular topic. A research interview is typically a two-person meeting conducted to collect information on a certain topic. It is a qualitative data collection method to gain primary information.
The three key features of a research interview are as follows:
Table of Contents
The Significance of Research Interviews in Gathering Primary Data
The role of research interviews in gathering first-hand information is invaluable. Additionally, they allow researchers to interact directly with participants, enabling them to collect unfiltered primary data.
1. Subjective Experience
Research interviews facilitate in-depth exploration of a research topic. Thus, by engaging in one-to-one conversation with participants, researchers can delve into the nuances and complexities of their experiences, perspectives, and opinions. This allows comprehensive understanding of the research subject that may not be possible through other methods. Also, research interviews offer the unique advantage of capturing subjective experiences through personal narratives. Moreover, participants can express their thoughts, feelings, and beliefs, which add depth to the findings.
2. Personal Insights
Research interviews offer an opportunity for participants to share their views and opinions on the objective they are being interviewed for. Furthermore, participants can express their thoughts and experiences, providing rich qualitative data . Consequently, these personal narratives add a human element to the research, thus enhancing the understanding of the topic from the participants’ perspectives. Research interviews offer the opportunity to uncover unanticipated insights or emerging themes. Additionally, open-ended questions and active listening can help the researchers to identify new perspectives, ideas, or patterns that may not have been initially considered. As a result, these factors can lead to new avenues for exploration.
3. Clarification and Validation
Researchers can clarify participants’ responses and validate their understanding during an interview. This ensures accurate data collection and interpretation. Additionally, researchers can probe deeper into participants’ statements and seek clarification on any ambiguity in the information.
4. Contextual Information
Research interviews allow researchers to gather contextual information that offers a comprehensive understanding of the research topic. Additionally, participants can provide insights into the social, cultural, or environmental factors that shape their experiences, behaviors, and beliefs. This contextual information helps researchers place the data in a broader context and facilitates a more nuanced analysis.
5. Non-verbal Cues
In addition to verbal responses, research interviews allow researchers to observe non-verbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice. Additionally, non-verbal cues can convey information, such as emotions, attitudes, or levels of comfort. Furthermore, integrating non-verbal cues with verbal responses provides a more holistic understanding of participants’ experiences and enriches the data collection process.
Research interviews offer several advantages, making them a reliable tool for collecting information. However, choosing the right type of research interview is essential for collecting useful data.
Types of Research Interviews
There are several types of research interviews that researchers can use based on their research goals , the nature of their study, and the data they aim to collect. Here are some common types of research interviews:
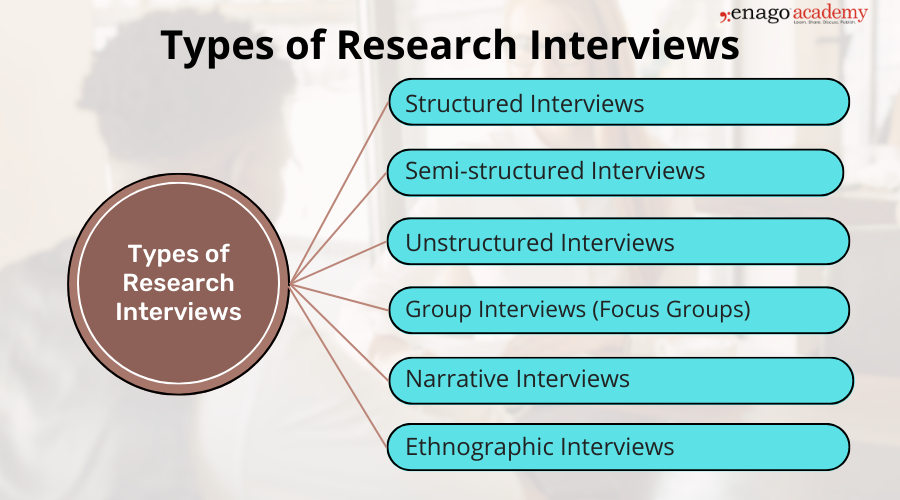
1. Structured Interviews
- Structured interviews are standardized and follow a fixed format.
- Therefore, these interviews have a pre-determined set of questions.
- All the participants are asked the same set of questions in the same order.
- Therefore, this type of interview facilitates standardization and allows easy comparison and quantitative analysis of responses.
- As a result, structured interviews are used in surveys or studies which aims for a high level of standardization and comparability.
2. Semi-structured Interviews
- Semi-structured interviews offer a flexible framework by combining pre-determined questions.
- So, this gives an opportunity for follow-up questions and open-ended discussions.
- Researchers have a list of core questions but can adapt the interview depending on the participant’s responses.
- Consequently, this allows for in-depth exploration while maintaining some level of consistency across interviews.
- As a result, semi-structured interviews are widely used in qualitative research, where content-rich data is desired.
3. Unstructured Interviews
- Unstructured interviews provide the greatest flexibility and freedom in the interview process.
- This type do not have a pre-determined set of questions.
- Thus, the conversation flows naturally based on the participant’s responses and the researcher’s interests.
- Moreover, this type of interview allows for open-ended exploration and encourages participants to share their experiences, thoughts, and perspectives freely.
- Unstructured interviews useful to explore new or complex research topics, with limited preconceived questions.
4. Group Interviews (Focus Groups)
- Group interviews involve multiple participants who engage in a facilitated discussion on a specific topic.
- This format allows the interaction and exchange of ideas among participants, generating a group dynamic.
- Therefore, group interviews are beneficial for capturing diverse perspectives, and generating collective insights.
- They are often used in market research, social sciences, or studies demanding shared experiences.
5. Narrative Interviews
- Narrative interviews focus on eliciting participants’ personal stories, views, experiences, and narratives. Researchers aim to look into the individual’s life journey.
- As a result, this type of interview allows participants to construct and share their own narratives, providing rich qualitative data.
- Qualitative research, oral history, or studies focusing on individual experiences and identities uses narrative interviews.
6. Ethnographic Interviews
- Ethnographic interviews are conducted within the context of ethnographic research, where researchers immerse themselves in a specific social or cultural setting.
- These interviews aim to understand participants’ experiences, beliefs, and practices within their cultural context, thereby understanding diversity in different ethnic groups.
- Furthermore, ethnographic interviews involve building rapport, observing the participants’ daily lives, and engaging in conversations that capture the nuances of the culture under study.
It must be noted that these interview types are not mutually exclusive. Therefore, researchers often employ a combination of approaches to gather the most comprehensive data for their research. The choice of interview type depends on the research objectives and the nature of the research topic.
Steps of Conducting a Research Interview
Research interviews offer several benefits, and thus careful planning and execution of the entire process are important to gather in-depth information from the participants. While conducting an interview, it is essential to know the necessary steps to follow for ensuring success. The steps to conduct a research interview are as follows:
- Identify the objectives and understand the goals
- Select an appropriate interview format
- Organize the necessary materials for the interview
- Understand the questions to be addressed
- Analyze the demographics of interviewees
- Select the interviewees
- Design the interview questions to gather sufficient information
- Schedule the interview
- Explain the purpose of the interview
- Analyze the interviewee based on his/her responses
Considerations for Research Interviews
Since the flexible nature of research interviews makes them an invaluable tool for data collection, researchers must consider certain factors to make the process effective. They should avoid bias and preconceived notion against the participants. Furthermore, researchers must comply with ethical considerations and respect the cultural differences between them and the participants. Also, they should ensure careful tailoring of the questions to avoid making them offensive or derogatory. The interviewers must respect the privacy of the participants and ensure the confidentiality of their details.

By ensuring due diligence of these considerations associated with research interviews, researchers can maximize the validity and reliability of the collected data, leading to robust and meaningful research outcomes.
Have you ever conducted a research interview? What was your experience? What factors did you consider when conducting a research interview? Share it with researchers worldwide by submitting your thought piece on Enago Academy’s Open Blogging Platform .
Frequently Asked Questions
• Identify the objectives of the interview • State and explain the purpose of the interview • Select an appropriate interview format • Organize the necessary materials for the Interview • Check the demographics of the participants • Select the Interviewees or the participants • Prepare the list of questions to gather maximum useful data from the participants • Schedule the Interview • Analyze the participant based on his/ her Responses
Interviews are important in research as it helps to gather elaborative first-hand information. It helps to draw conclusions from the non-verbal views and personal experiences. It reduces the ambiguity of data through detailed discussions.
The advantages of research interviews are: • It offers first-hand information • Offers detailed assessment which can result in elaborate conclusions • It is easy to conduct • Provides non-verbal cues The disadvantages of research interviews are: • There is a risk of personal bias • It can be time consuming • The outcomes might be unpredictable
The difference between structured and unstructured interview are: • Structured interviews have well-structured questions in a pre-determined order; while unstructured interviews are flexible and do not have a pre-planned set of questions. • Structured interview is more detailed; while unstructured interviews are exploratory in nature. • Structured interview is easier to replicate as compared to unstructured interview.
Focus groups is a group of multiple participants engaging in a facilitated discussion on a specific topic. This format allows for interaction and exchange of ideas among participants.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Promoting Research
Graphical Abstracts Vs. Infographics: Best practices for using visual illustrations for increased research impact
Dr. Sarah Chen stared at her computer screen, her eyes staring at her recently published…

- Publishing Research
10 Tips to Prevent Research Papers From Being Retracted
Research paper retractions represent a critical event in the scientific community. When a published article…

- Industry News
Google Releases 2024 Scholar Metrics, Evaluates Impact of Scholarly Articles
Google has released its 2024 Scholar Metrics, assessing scholarly articles from 2019 to 2023. This…
![to conduct an effective research interview you should What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Demystifying the Role of Confounding Variables in Research

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- AI in Academia
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

In your opinion, what is the most effective way to improve integrity in the peer review process?
How to Conduct an Effective Interview; A Guide to Interview Design in Research Study
International Journal of Academic Research in Management, 11(1):39-51, 2022 https://elvedit.com/journals/IJARM/wp-content/uploads/How-to-Conduct-an-Effective-Interview-A-Guide-to-Interview-Design
13 Pages Posted: 18 Aug 2022
Hamed Taherdoost
Hamta Group
Date Written: August 1, 2022
Interviews are one of the most promising ways of collecting qualitative data through establishment of a communication between researcher and the interviewee. Researcher in a face to face, phone or online conversation tries to understand and explore respondents’ opinions and behavior in a specific subject. Despite the significant importance of interviews to collect data in a research study, it may look challenging to design an effective interview that provides unbiased, enough and accurate data. This article provides the common steps of designing and conducting effective interviews and lists the main ethical issues that researchers, interviewers, and participants need to consider in the interview process of a research study.
Keywords: Data Collection, Interview Design, Data Collection Methods, Academic Research Paper, Effective Interview.
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Hamed Taherdoost (Contact Author)
Hamta group ( email ).
Vancouver Canada
Do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on SSRN?
Paper statistics, related ejournals, development economics: microeconomic issues in developing economies ejournal.
Subscribe to this fee journal for more curated articles on this topic
- EXPLORE Random Article
- Happiness Hub
How to Conduct Interviews for Research
Last Updated: July 7, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Jeremiah Kaplan . Jeremiah Kaplan is a Research and Training Specialist at the Center for Applied Behavioral Health Policy at Arizona State University. He has extensive knowledge and experience in motivational interviewing. In addition, Jeremiah has worked in the mental health, youth engagement, and trauma-informed care fields. Using his expertise, Jeremiah supervises Arizona State University’s Motivational Interviewing Coding Lab. Jeremiah has also been internationally selected to participate in the Motivational Interviewing International Network of Trainers sponsored Train the Trainer event. Jeremiah holds a BS in Human Services with a concentration in Family and Children from The University of Phoenix. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 30,620 times.
If you’re putting together a news report, a documentary film, or gathering oral history for any kind of personal project, you’ll likely need to perform 1 or more research interviews to gather the information you need. While these interviews can be relatively informal (unless they’re being broadcast live), you’ll need to make a few preparations beforehand, including having a written list of questions to ask. Let the interviewee answer the questions as they see fit, and guide the interview so that all of your questions are adequately answered.
Laying Groundwork for an Interview

- For example, if you’re interviewing a local biologist about declining frog populations, read up on what types of frogs and frog predators inhabit the area, and find out how much of the frog population has died off.

- If you set up the interview over the phone or via email, say something like, “Thank you for agreeing to answer a few questions. I’m mostly interested in asking you about your extensive knowledge of the publishing industry. I have about 10 questions, but I don’t think this will take more than 30 minutes.”

- If you’re conducting the interview over the phone, find a time when you and the interviewee are both free.

- Don’t tell yourself that you’ll remember the interview! If you don’t record the questions and answers, you’re likely to forget details.
Writing and Asking Effective Questions

- “How did you get your start in the industry?”
- “What’s your favorite type of book to see published?”
- “What would you recommend for any young men or women who’d like to get into publishing?”

- For example, if you ask something like, “Do you think the city planners have done a good job of laying out the new downtown area?” the subject can just answer “yes” or “no.”
- Instead, ask, “What do you think are some of the strengths and weaknesses of the ways the city planners laid out the new downtown area?”

- For example, avoid a question like, “Isn’t it true that the publishing industry refuses to pay women as much as it pays men?”
- Try asking instead: “What are your views on what some people perceive to be a gender pay gap in the industry?”

- For example, avoid asking, “Do pay-to-print or vanity presses hurt the fiscal state of big publishing houses?”
- Instead, ask something like, “Are there any trends within publishing that you think are harmful to the industry overall?”
Behaving During the Interview

- If you'd rather not ask immediately before the interview, ask the interviewee to fill out a consent form a week before the interview takes place. If the subject refuses to give their consent, you'll be unable to legally do the interview.
- For a sample consent form, look online at: https://managementhelp.org/businessresearch/consent-form.htm .

- If the interviewee lingers too long on a specific question, try moving things along. Say something like, “I appreciate your insights. I’d like to turn to a different topic at this point: what’s the best college major for a career in publishing?”

- For example, even if the interviewee says something surprising like: “I think it’s good that the frogs are dying!” avoid jumping up or shouting “What!?”

- For example, say that the interviewee says, “I became interested in city planning after a friend was killed in a poorly-designed intersection.” It would be inappropriate to say, “So what?” or “That sucks.” Instead, say something like, “I’m sorry to hear that; it’s a real tragedy.”

- This would also be a good time to scroll through the audio or video file that you recorded and make sure that it’s all clear and audible.
Expert Q&A
- Always speak clearly when you ask questions and speak to the interviewee, especially if you’re recording with a tape recorder. Ask the interviewee to do the same. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Give your interviewee enough time to answer each question. Don’t rush them on to answer another question while they’re still thinking of an answer for the first one. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Always interview your subjects face-to-face when it’s possible. If a face-to-face interview is impractical, a telephone interview is a decent substitute. Avoid conducting interviews over email except as a last resort. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.csus.edu/indiv/o/obriene/art116/readings/guide%20for%20conducting%20interviews.pdf
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/interviewing/research-interview
- ↑ https://managementhelp.org/businessresearch/interviews.htm
- ↑ https://aultman.libguides.com/c.php?g=974169&p=7042440
- ↑ https://guides.lib.vt.edu/researchmethods/interviews
- ↑ https://uk.indeed.com/career-advice/interviewing/research-interview
About this article

Did this article help you?

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Types of Interviews in Research | Guide & Examples
Types of Interviews in Research | Guide & Examples
Published on March 10, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on June 22, 2023.
An interview is a qualitative research method that relies on asking questions in order to collect data . Interviews involve two or more people, one of whom is the interviewer asking the questions.
There are several types of interviews, often differentiated by their level of structure.
- Structured interviews have predetermined questions asked in a predetermined order.
- Unstructured interviews are more free-flowing.
- Semi-structured interviews fall in between.
Interviews are commonly used in market research, social science, and ethnographic research .
Table of contents
What is a structured interview, what is a semi-structured interview, what is an unstructured interview, what is a focus group, examples of interview questions, advantages and disadvantages of interviews, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about types of interviews.
Structured interviews have predetermined questions in a set order. They are often closed-ended, featuring dichotomous (yes/no) or multiple-choice questions. While open-ended structured interviews exist, they are much less common. The types of questions asked make structured interviews a predominantly quantitative tool.
Asking set questions in a set order can help you see patterns among responses, and it allows you to easily compare responses between participants while keeping other factors constant. This can mitigate research biases and lead to higher reliability and validity. However, structured interviews can be overly formal, as well as limited in scope and flexibility.
- You feel very comfortable with your topic. This will help you formulate your questions most effectively.
- You have limited time or resources. Structured interviews are a bit more straightforward to analyze because of their closed-ended nature, and can be a doable undertaking for an individual.
- Your research question depends on holding environmental conditions between participants constant.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Semi-structured interviews are a blend of structured and unstructured interviews. While the interviewer has a general plan for what they want to ask, the questions do not have to follow a particular phrasing or order.
Semi-structured interviews are often open-ended, allowing for flexibility, but follow a predetermined thematic framework, giving a sense of order. For this reason, they are often considered “the best of both worlds.”
However, if the questions differ substantially between participants, it can be challenging to look for patterns, lessening the generalizability and validity of your results.
- You have prior interview experience. It’s easier than you think to accidentally ask a leading question when coming up with questions on the fly. Overall, spontaneous questions are much more difficult than they may seem.
- Your research question is exploratory in nature. The answers you receive can help guide your future research.
An unstructured interview is the most flexible type of interview. The questions and the order in which they are asked are not set. Instead, the interview can proceed more spontaneously, based on the participant’s previous answers.
Unstructured interviews are by definition open-ended. This flexibility can help you gather detailed information on your topic, while still allowing you to observe patterns between participants.
However, so much flexibility means that they can be very challenging to conduct properly. You must be very careful not to ask leading questions, as biased responses can lead to lower reliability or even invalidate your research.
- You have a solid background in your research topic and have conducted interviews before.
- Your research question is exploratory in nature, and you are seeking descriptive data that will deepen and contextualize your initial hypotheses.
- Your research necessitates forming a deeper connection with your participants, encouraging them to feel comfortable revealing their true opinions and emotions.
A focus group brings together a group of participants to answer questions on a topic of interest in a moderated setting. Focus groups are qualitative in nature and often study the group’s dynamic and body language in addition to their answers. Responses can guide future research on consumer products and services, human behavior, or controversial topics.
Focus groups can provide more nuanced and unfiltered feedback than individual interviews and are easier to organize than experiments or large surveys . However, their small size leads to low external validity and the temptation as a researcher to “cherry-pick” responses that fit your hypotheses.
- Your research focuses on the dynamics of group discussion or real-time responses to your topic.
- Your questions are complex and rooted in feelings, opinions, and perceptions that cannot be answered with a “yes” or “no.”
- Your topic is exploratory in nature, and you are seeking information that will help you uncover new questions or future research ideas.
Depending on the type of interview you are conducting, your questions will differ in style, phrasing, and intention. Structured interview questions are set and precise, while the other types of interviews allow for more open-endedness and flexibility.
Here are some examples.
- Semi-structured
- Unstructured
- Focus group
- Do you like dogs? Yes/No
- Do you associate dogs with feeling: happy; somewhat happy; neutral; somewhat unhappy; unhappy
- If yes, name one attribute of dogs that you like.
- If no, name one attribute of dogs that you don’t like.
- What feelings do dogs bring out in you?
- When you think more deeply about this, what experiences would you say your feelings are rooted in?
Interviews are a great research tool. They allow you to gather rich information and draw more detailed conclusions than other research methods, taking into consideration nonverbal cues, off-the-cuff reactions, and emotional responses.
However, they can also be time-consuming and deceptively challenging to conduct properly. Smaller sample sizes can cause their validity and reliability to suffer, and there is an inherent risk of interviewer effect arising from accidentally leading questions.
Here are some advantages and disadvantages of each type of interview that can help you decide if you’d like to utilize this research method.
| Type of interview | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Structured interview | ||
| Semi-structured interview | , , , and | |
| Unstructured interview | , , , and | |
| Focus group | , , and , since there are multiple people present |
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Student’s t -distribution
- Normal distribution
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Data cleansing
- Reproducibility vs Replicability
- Peer review
- Prospective cohort study
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Placebo effect
- Hawthorne effect
- Hindsight bias
- Affect heuristic
- Social desirability bias
The four most common types of interviews are:
- Structured interviews : The questions are predetermined in both topic and order.
- Semi-structured interviews : A few questions are predetermined, but other questions aren’t planned.
- Unstructured interviews : None of the questions are predetermined.
- Focus group interviews : The questions are presented to a group instead of one individual.
The interviewer effect is a type of bias that emerges when a characteristic of an interviewer (race, age, gender identity, etc.) influences the responses given by the interviewee.
There is a risk of an interviewer effect in all types of interviews , but it can be mitigated by writing really high-quality interview questions.
Social desirability bias is the tendency for interview participants to give responses that will be viewed favorably by the interviewer or other participants. It occurs in all types of interviews and surveys , but is most common in semi-structured interviews , unstructured interviews , and focus groups .
Social desirability bias can be mitigated by ensuring participants feel at ease and comfortable sharing their views. Make sure to pay attention to your own body language and any physical or verbal cues, such as nodding or widening your eyes.
This type of bias can also occur in observations if the participants know they’re being observed. They might alter their behavior accordingly.
A focus group is a research method that brings together a small group of people to answer questions in a moderated setting. The group is chosen due to predefined demographic traits, and the questions are designed to shed light on a topic of interest. It is one of 4 types of interviews .
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, June 22). Types of Interviews in Research | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 30, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/interviews-research/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, unstructured interview | definition, guide & examples, structured interview | definition, guide & examples, semi-structured interview | definition, guide & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
How to Conduct Interviews in Qualitative Research: Interview Guidelines for Qualitative Research
Rev › Blog › Market Research › How to Conduct Interviews in Qualitative Research: Interview Guidelines for Qualitative Research
Qualitative research interviews are depth interviews. They elicit detailed feedback from your leads and customers. Unstructured interviews reveal why people react in a certain way or make certain decisions. According to The Hartford , qualitative research provides an anecdotal look into your business. That provides an important form of data.
Why Your Business Should Use a Qualitative Interview Process
Qualitative research helps business owners:
- Identify customer needs
- Clarify marketing messages
- Generate ideas for improvements of a product
- Decide to extend a line or brand
- Gain perspective on how a product fits into a customer’s lifestyle
How Is Conducting Qualitative Research & Quantitative Research Different?
Quantitative research concerns measurable quantities and numbers. It involves close-ended questions. Answer possibilities include yes or no, true or false, or various set choices. Qualitative research is descriptive and concerned with understanding behavior. It invites people to tell their stories in their own words.
Examples of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research helps researchers understand the social reality of individuals, groups and cultures. Qualitative research for businesses involves understanding consumer behavior. It can involve ethnographic techniques, including participant observation and field research. It also includes phenomenology, understanding life experiences using written or recorded narratives. Qualitative research also includes in-depth interviews.
What Is a Qualitative Interview?
A qualitative interview is a more personal form of research compared to questionnaires. The interviewer can probe or ask follow-up research questions of the interview participant. In some cases, subjects may start to interview the interviewer. This fosters deep discussion of the interview topic.
Why Are Interview Techniques in Qualitative Research Effective?
Qualitative research interviews help you explain, understand and explore opinions, behavior and experiences. Qualitative research can provide insights into a phenomenon. Qualitative research discoveries can be further researched and analyzed to influence business decisions.
How Are Interviews in Qualitative Research Formatted?
Qualitative research interviews may take place one-on-one or in focus groups. Learn how to run a successful focus group . Interviews span around 30 to 90 minutes. The interview can take place in person, over the phone or through video chat. The interviewer collects information about opinions, behavior, attitudes, feelings, preferences and knowledge.
How to Conduct Interviews in Qualitative Research
1. determine your goal., 2. target people to interview., 3. design interview questions., 4. prep the interview., 5. conduct the interview., 6. transcribe and analyze the interview., 7. optimize and evolve your interview guide., the first step in qualitative research: determine your goal.
Determine what you want to study:
- A current or potential product, service or brand positioning
- Strengths and weaknesses in products
- Purchasing decisions
- Reactions to advertising or marketing campaigns
- Usability of a website or other interactive services
- Perceptions about the company, brand or product
- Reactions to packaging and design
How Can You Decide a Goal for a Qualitative Interview?
Have your business team ask the following questions:
- What information do you want to get?
- Why do you want to pursue in-depth information about this research topic?
- Why is a qualitative interview process the best solution for this research?
- How will you use qualitative data to improve your business?
How to Determine the Right Interview Participants
When looking for people to talk to for a qualitative interview, consider your goal. If you want to expand a product line, interview existing customers about their needs. If you’re researching marketing, ask new customers how they found your business. Match interview subjects with the goal of the interview.
How to Design Interview Questions for Qualitative Research
When you’re creating an interview guide, it’s a good idea to:
- Plan structured interviews with open ended questions.
- Avoid leading questions.
- Create interview questions that are clear and easy to understand.
- Make research questions focused but flexible.
- Design questions that align with data collection and data analysis goals.
Tips for Preparing a Qualitative Research Interview
Preparation improves interview effectiveness. Tips to prepare include:
- Create an interview guide. The guide should include questions, question intent and answer-based paths to take.
- Choose a setting where the subject feels comfortable.
- Build rapport with interview participants.
- Have a reliable way to record the interview.
- Rehearse the interview first.
Environmental Concerns for Qualitative Interviews
The setting of a qualitative interview also affects the quality of the interview. Consider the needs of the subject. For example, if you’re interviewing a teenager, a formal boardroom may not be the best setting. Some cultures may not value direct eye contact. An interview that’s non-face-to-face may be better.
How to Make Qualitative Interview Subjects Comfortable
For long interviews, offer water and breaks to participants. Be polite and respectful when interacting with interview subjects. Let interview participants know the purpose of the research. Explain exactly how you’ll use their answers. Address terms of confidentiality if necessary. Thank participants after the interview and let them know what to expect next.
What Are Interview Techniques in Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research techniques include:
- Start interviews with “get-to-know-you” questions to put the interview participant at ease.
- Pay attention.
- Use active listening techniques.
- Watch for body language cues.
- Pivot questions as needed.
- Acknowledge emotions.
- Avoid interrogation.
- Ending interviews, ask subjects if they have anything to add.
What Is Active Listening in Interviews in Qualitative Research?
Active listening techniques include:
- Make eye contact.
- Lean in and use body language to show you’re listening.
- Don’t get distracted by devices.
- Use verbal affirmation.
- Paraphrase answers for reflection.
- Reference earlier answers.
- Avoid interrupting.
- Embrace pauses.
- Ask for clarification.
- Pay attention in the moment.
Tips for Transcribing a Qualitative Interview
It’s best to transcribe and analyze a qualitative research interview right away. This helps you optimize future interviews. Transcribe the interview word for word. Note non-verbal interactions in your transcription. Interactions like pauses and laughter can provide deeper insights into responses.
How to Analyze a Qualitative Interview
Analyze your qualitative research data early. That way, you can identify emerging themes to shape future interviews. Consider adding these to each interview report:
- The goal of the interview
- Details about the interview participant
- Questions asked, summarized responses and key findings
- Recommendations
Relate the analysis to the goal of the qualitative research interview.
Optimize the Interview Guide for Qualitative Research
Each interview can help you improve the efficiency and effectiveness of future ones. Adjust your interview guide based on insights from each previous interview. Keep all versions of your transcriptions and interview guides with notes on them. You can reference these for future qualitative research.
Get Reliable Transcription Services for Qualitative Research Interviews
As mentioned, you should transcribe qualitative research interviews as soon as possible. There are several reasons for this.
- You can gain insights that help you shape your interview guide. You might identify questions to add or questions to clarify.
- Your interview participants may not be appropriate for this type of qualitative research. Finding more targeted interview subjects may be better.
- Answers may evolve the qualitative research goal and/or data analysis.
At Rev, we understand the need for fast transcription for accurate market research. We provide a turnaround time of as few as 12 hours, no matter how big your project is. We guarantee 99%+ accuracy. Learn about Rev’s market research transcription . We can help make your qualitative research project a success.
Download our FREE Qualitative Research Interview Checklist
Everybody’s favorite speech-to-text blog.
We combine AI and a huge community of freelancers to make speech-to-text greatness every day. Wanna hear more about it?
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 05 October 2018
Interviews and focus groups in qualitative research: an update for the digital age
- P. Gill 1 &
- J. Baillie 2
British Dental Journal volume 225 , pages 668–672 ( 2018 ) Cite this article
32k Accesses
63 Citations
20 Altmetric
Metrics details
Highlights that qualitative research is used increasingly in dentistry. Interviews and focus groups remain the most common qualitative methods of data collection.
Suggests the advent of digital technologies has transformed how qualitative research can now be undertaken.
Suggests interviews and focus groups can offer significant, meaningful insight into participants' experiences, beliefs and perspectives, which can help to inform developments in dental practice.
Qualitative research is used increasingly in dentistry, due to its potential to provide meaningful, in-depth insights into participants' experiences, perspectives, beliefs and behaviours. These insights can subsequently help to inform developments in dental practice and further related research. The most common methods of data collection used in qualitative research are interviews and focus groups. While these are primarily conducted face-to-face, the ongoing evolution of digital technologies, such as video chat and online forums, has further transformed these methods of data collection. This paper therefore discusses interviews and focus groups in detail, outlines how they can be used in practice, how digital technologies can further inform the data collection process, and what these methods can offer dentistry.
You have full access to this article via your institution.
Similar content being viewed by others

Interviews in the social sciences

Professionalism in dentistry: deconstructing common terminology
A review of technical and quality assessment considerations of audio-visual and web-conferencing focus groups in qualitative health research, introduction.
Traditionally, research in dentistry has primarily been quantitative in nature. 1 However, in recent years, there has been a growing interest in qualitative research within the profession, due to its potential to further inform developments in practice, policy, education and training. Consequently, in 2008, the British Dental Journal (BDJ) published a four paper qualitative research series, 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 to help increase awareness and understanding of this particular methodological approach.
Since the papers were originally published, two scoping reviews have demonstrated the ongoing proliferation in the use of qualitative research within the field of oral healthcare. 1 , 6 To date, the original four paper series continue to be well cited and two of the main papers remain widely accessed among the BDJ readership. 2 , 3 The potential value of well-conducted qualitative research to evidence-based practice is now also widely recognised by service providers, policy makers, funding bodies and those who commission, support and use healthcare research.
Besides increasing standalone use, qualitative methods are now also routinely incorporated into larger mixed method study designs, such as clinical trials, as they can offer additional, meaningful insights into complex problems that simply could not be provided by quantitative methods alone. Qualitative methods can also be used to further facilitate in-depth understanding of important aspects of clinical trial processes, such as recruitment. For example, Ellis et al . investigated why edentulous older patients, dissatisfied with conventional dentures, decline implant treatment, despite its established efficacy, and frequently refuse to participate in related randomised clinical trials, even when financial constraints are removed. 7 Through the use of focus groups in Canada and the UK, the authors found that fears of pain and potential complications, along with perceived embarrassment, exacerbated by age, are common reasons why older patients typically refuse dental implants. 7
The last decade has also seen further developments in qualitative research, due to the ongoing evolution of digital technologies. These developments have transformed how researchers can access and share information, communicate and collaborate, recruit and engage participants, collect and analyse data and disseminate and translate research findings. 8 Where appropriate, such technologies are therefore capable of extending and enhancing how qualitative research is undertaken. 9 For example, it is now possible to collect qualitative data via instant messaging, email or online/video chat, using appropriate online platforms.
These innovative approaches to research are therefore cost-effective, convenient, reduce geographical constraints and are often useful for accessing 'hard to reach' participants (for example, those who are immobile or socially isolated). 8 , 9 However, digital technologies are still relatively new and constantly evolving and therefore present a variety of pragmatic and methodological challenges. Furthermore, given their very nature, their use in many qualitative studies and/or with certain participant groups may be inappropriate and should therefore always be carefully considered. While it is beyond the scope of this paper to provide a detailed explication regarding the use of digital technologies in qualitative research, insight is provided into how such technologies can be used to facilitate the data collection process in interviews and focus groups.
In light of such developments, it is perhaps therefore timely to update the main paper 3 of the original BDJ series. As with the previous publications, this paper has been purposely written in an accessible style, to enhance readability, particularly for those who are new to qualitative research. While the focus remains on the most common qualitative methods of data collection – interviews and focus groups – appropriate revisions have been made to provide a novel perspective, and should therefore be helpful to those who would like to know more about qualitative research. This paper specifically focuses on undertaking qualitative research with adult participants only.
Overview of qualitative research
Qualitative research is an approach that focuses on people and their experiences, behaviours and opinions. 10 , 11 The qualitative researcher seeks to answer questions of 'how' and 'why', providing detailed insight and understanding, 11 which quantitative methods cannot reach. 12 Within qualitative research, there are distinct methodologies influencing how the researcher approaches the research question, data collection and data analysis. 13 For example, phenomenological studies focus on the lived experience of individuals, explored through their description of the phenomenon. Ethnographic studies explore the culture of a group and typically involve the use of multiple methods to uncover the issues. 14
While methodology is the 'thinking tool', the methods are the 'doing tools'; 13 the ways in which data are collected and analysed. There are multiple qualitative data collection methods, including interviews, focus groups, observations, documentary analysis, participant diaries, photography and videography. Two of the most commonly used qualitative methods are interviews and focus groups, which are explored in this article. The data generated through these methods can be analysed in one of many ways, according to the methodological approach chosen. A common approach is thematic data analysis, involving the identification of themes and subthemes across the data set. Further information on approaches to qualitative data analysis has been discussed elsewhere. 1
Qualitative research is an evolving and adaptable approach, used by different disciplines for different purposes. Traditionally, qualitative data, specifically interviews, focus groups and observations, have been collected face-to-face with participants. In more recent years, digital technologies have contributed to the ongoing evolution of qualitative research. Digital technologies offer researchers different ways of recruiting participants and collecting data, and offer participants opportunities to be involved in research that is not necessarily face-to-face.
Research interviews are a fundamental qualitative research method 15 and are utilised across methodological approaches. Interviews enable the researcher to learn in depth about the perspectives, experiences, beliefs and motivations of the participant. 3 , 16 Examples include, exploring patients' perspectives of fear/anxiety triggers in dental treatment, 17 patients' experiences of oral health and diabetes, 18 and dental students' motivations for their choice of career. 19
Interviews may be structured, semi-structured or unstructured, 3 according to the purpose of the study, with less structured interviews facilitating a more in depth and flexible interviewing approach. 20 Structured interviews are similar to verbal questionnaires and are used if the researcher requires clarification on a topic; however they produce less in-depth data about a participant's experience. 3 Unstructured interviews may be used when little is known about a topic and involves the researcher asking an opening question; 3 the participant then leads the discussion. 20 Semi-structured interviews are commonly used in healthcare research, enabling the researcher to ask predetermined questions, 20 while ensuring the participant discusses issues they feel are important.
Interviews can be undertaken face-to-face or using digital methods when the researcher and participant are in different locations. Audio-recording the interview, with the consent of the participant, is essential for all interviews regardless of the medium as it enables accurate transcription; the process of turning the audio file into a word-for-word transcript. This transcript is the data, which the researcher then analyses according to the chosen approach.
Types of interview
Qualitative studies often utilise one-to-one, face-to-face interviews with research participants. This involves arranging a mutually convenient time and place to meet the participant, signing a consent form and audio-recording the interview. However, digital technologies have expanded the potential for interviews in research, enabling individuals to participate in qualitative research regardless of location.
Telephone interviews can be a useful alternative to face-to-face interviews and are commonly used in qualitative research. They enable participants from different geographical areas to participate and may be less onerous for participants than meeting a researcher in person. 15 A qualitative study explored patients' perspectives of dental implants and utilised telephone interviews due to the quality of the data that could be yielded. 21 The researcher needs to consider how they will audio record the interview, which can be facilitated by purchasing a recorder that connects directly to the telephone. One potential disadvantage of telephone interviews is the inability of the interviewer and researcher to see each other. This is resolved using software for audio and video calls online – such as Skype – to conduct interviews with participants in qualitative studies. Advantages of this approach include being able to see the participant if video calls are used, enabling observation of non-verbal communication, and the software can be free to use. However, participants are required to have a device and internet connection, as well as being computer literate, potentially limiting who can participate in the study. One qualitative study explored the role of dental hygienists in reducing oral health disparities in Canada. 22 The researcher conducted interviews using Skype, which enabled dental hygienists from across Canada to be interviewed within the research budget, accommodating the participants' schedules. 22
A less commonly used approach to qualitative interviews is the use of social virtual worlds. A qualitative study accessed a social virtual world – Second Life – to explore the health literacy skills of individuals who use social virtual worlds to access health information. 23 The researcher created an avatar and interview room, and undertook interviews with participants using voice and text methods. 23 This approach to recruitment and data collection enables individuals from diverse geographical locations to participate, while remaining anonymous if they wish. Furthermore, for interviews conducted using text methods, transcription of the interview is not required as the researcher can save the written conversation with the participant, with the participant's consent. However, the researcher and participant need to be familiar with how the social virtual world works to engage in an interview this way.
Conducting an interview
Ensuring informed consent before any interview is a fundamental aspect of the research process. Participants in research must be afforded autonomy and respect; consent should be informed and voluntary. 24 Individuals should have the opportunity to read an information sheet about the study, ask questions, understand how their data will be stored and used, and know that they are free to withdraw at any point without reprisal. The qualitative researcher should take written consent before undertaking the interview. In a face-to-face interview, this is straightforward: the researcher and participant both sign copies of the consent form, keeping one each. However, this approach is less straightforward when the researcher and participant do not meet in person. A recent protocol paper outlined an approach for taking consent for telephone interviews, which involved: audio recording the participant agreeing to each point on the consent form; the researcher signing the consent form and keeping a copy; and posting a copy to the participant. 25 This process could be replicated in other interview studies using digital methods.
There are advantages and disadvantages of using face-to-face and digital methods for research interviews. Ultimately, for both approaches, the quality of the interview is determined by the researcher. 16 Appropriate training and preparation are thus required. Healthcare professionals can use their interpersonal communication skills when undertaking a research interview, particularly questioning, listening and conversing. 3 However, the purpose of an interview is to gain information about the study topic, 26 rather than offering help and advice. 3 The researcher therefore needs to listen attentively to participants, enabling them to describe their experience without interruption. 3 The use of active listening skills also help to facilitate the interview. 14 Spradley outlined elements and strategies for research interviews, 27 which are a useful guide for qualitative researchers:
Greeting and explaining the project/interview
Asking descriptive (broad), structural (explore response to descriptive) and contrast (difference between) questions
Asymmetry between the researcher and participant talking
Expressing interest and cultural ignorance
Repeating, restating and incorporating the participant's words when asking questions
Creating hypothetical situations
Asking friendly questions
Knowing when to leave.
For semi-structured interviews, a topic guide (also called an interview schedule) is used to guide the content of the interview – an example of a topic guide is outlined in Box 1 . The topic guide, usually based on the research questions, existing literature and, for healthcare professionals, their clinical experience, is developed by the research team. The topic guide should include open ended questions that elicit in-depth information, and offer participants the opportunity to talk about issues important to them. This is vital in qualitative research where the researcher is interested in exploring the experiences and perspectives of participants. It can be useful for qualitative researchers to pilot the topic guide with the first participants, 10 to ensure the questions are relevant and understandable, and amending the questions if required.
Regardless of the medium of interview, the researcher must consider the setting of the interview. For face-to-face interviews, this could be in the participant's home, in an office or another mutually convenient location. A quiet location is preferable to promote confidentiality, enable the researcher and participant to concentrate on the conversation, and to facilitate accurate audio-recording of the interview. For interviews using digital methods the same principles apply: a quiet, private space where the researcher and participant feel comfortable and confident to participate in an interview.
Box 1: Example of a topic guide
Study focus: Parents' experiences of brushing their child's (aged 0–5) teeth
1. Can you tell me about your experience of cleaning your child's teeth?
How old was your child when you started cleaning their teeth?
Why did you start cleaning their teeth at that point?
How often do you brush their teeth?
What do you use to brush their teeth and why?
2. Could you explain how you find cleaning your child's teeth?
Do you find anything difficult?
What makes cleaning their teeth easier for you?
3. How has your experience of cleaning your child's teeth changed over time?
Has it become easier or harder?
Have you changed how often and how you clean their teeth? If so, why?
4. Could you describe how your child finds having their teeth cleaned?
What do they enjoy about having their teeth cleaned?
Is there anything they find upsetting about having their teeth cleaned?
5. Where do you look for information/advice about cleaning your child's teeth?
What did your health visitor tell you about cleaning your child's teeth? (If anything)
What has the dentist told you about caring for your child's teeth? (If visited)
Have any family members given you advice about how to clean your child's teeth? If so, what did they tell you? Did you follow their advice?
6. Is there anything else you would like to discuss about this?
Focus groups
A focus group is a moderated group discussion on a pre-defined topic, for research purposes. 28 , 29 While not aligned to a particular qualitative methodology (for example, grounded theory or phenomenology) as such, focus groups are used increasingly in healthcare research, as they are useful for exploring collective perspectives, attitudes, behaviours and experiences. Consequently, they can yield rich, in-depth data and illuminate agreement and inconsistencies 28 within and, where appropriate, between groups. Examples include public perceptions of dental implants and subsequent impact on help-seeking and decision making, 30 and general dental practitioners' views on patient safety in dentistry. 31
Focus groups can be used alone or in conjunction with other methods, such as interviews or observations, and can therefore help to confirm, extend or enrich understanding and provide alternative insights. 28 The social interaction between participants often results in lively discussion and can therefore facilitate the collection of rich, meaningful data. However, they are complex to organise and manage, due to the number of participants, and may also be inappropriate for exploring particularly sensitive issues that many participants may feel uncomfortable about discussing in a group environment.
Focus groups are primarily undertaken face-to-face but can now also be undertaken online, using appropriate technologies such as email, bulletin boards, online research communities, chat rooms, discussion forums, social media and video conferencing. 32 Using such technologies, data collection can also be synchronous (for example, online discussions in 'real time') or, unlike traditional face-to-face focus groups, asynchronous (for example, online/email discussions in 'non-real time'). While many of the fundamental principles of focus group research are the same, regardless of how they are conducted, a number of subtle nuances are associated with the online medium. 32 Some of which are discussed further in the following sections.
Focus group considerations
Some key considerations associated with face-to-face focus groups are: how many participants are required; should participants within each group know each other (or not) and how many focus groups are needed within a single study? These issues are much debated and there is no definitive answer. However, the number of focus groups required will largely depend on the topic area, the depth and breadth of data needed, the desired level of participation required 29 and the necessity (or not) for data saturation.
The optimum group size is around six to eight participants (excluding researchers) but can work effectively with between three and 14 participants. 3 If the group is too small, it may limit discussion, but if it is too large, it may become disorganised and difficult to manage. It is, however, prudent to over-recruit for a focus group by approximately two to three participants, to allow for potential non-attenders. For many researchers, particularly novice researchers, group size may also be informed by pragmatic considerations, such as the type of study, resources available and moderator experience. 28 Similar size and mix considerations exist for online focus groups. Typically, synchronous online focus groups will have around three to eight participants but, as the discussion does not happen simultaneously, asynchronous groups may have as many as 10–30 participants. 33
The topic area and potential group interaction should guide group composition considerations. Pre-existing groups, where participants know each other (for example, work colleagues) may be easier to recruit, have shared experiences and may enjoy a familiarity, which facilitates discussion and/or the ability to challenge each other courteously. 3 However, if there is a potential power imbalance within the group or if existing group norms and hierarchies may adversely affect the ability of participants to speak freely, then 'stranger groups' (that is, where participants do not already know each other) may be more appropriate. 34 , 35
Focus group management
Face-to-face focus groups should normally be conducted by two researchers; a moderator and an observer. 28 The moderator facilitates group discussion, while the observer typically monitors group dynamics, behaviours, non-verbal cues, seating arrangements and speaking order, which is essential for transcription and analysis. The same principles of informed consent, as discussed in the interview section, also apply to focus groups, regardless of medium. However, the consent process for online discussions will probably be managed somewhat differently. For example, while an appropriate participant information leaflet (and consent form) would still be required, the process is likely to be managed electronically (for example, via email) and would need to specifically address issues relating to technology (for example, anonymity and use, storage and access to online data). 32
The venue in which a face to face focus group is conducted should be of a suitable size, private, quiet, free from distractions and in a collectively convenient location. It should also be conducted at a time appropriate for participants, 28 as this is likely to promote attendance. As with interviews, the same ethical considerations apply (as discussed earlier). However, online focus groups may present additional ethical challenges associated with issues such as informed consent, appropriate access and secure data storage. Further guidance can be found elsewhere. 8 , 32
Before the focus group commences, the researchers should establish rapport with participants, as this will help to put them at ease and result in a more meaningful discussion. Consequently, researchers should introduce themselves, provide further clarity about the study and how the process will work in practice and outline the 'ground rules'. Ground rules are designed to assist, not hinder, group discussion and typically include: 3 , 28 , 29
Discussions within the group are confidential to the group
Only one person can speak at a time
All participants should have sufficient opportunity to contribute
There should be no unnecessary interruptions while someone is speaking
Everyone can be expected to be listened to and their views respected
Challenging contrary opinions is appropriate, but ridiculing is not.
Moderating a focus group requires considered management and good interpersonal skills to help guide the discussion and, where appropriate, keep it sufficiently focused. Avoid, therefore, participating, leading, expressing personal opinions or correcting participants' knowledge 3 , 28 as this may bias the process. A relaxed, interested demeanour will also help participants to feel comfortable and promote candid discourse. Moderators should also prevent the discussion being dominated by any one person, ensure differences of opinions are discussed fairly and, if required, encourage reticent participants to contribute. 3 Asking open questions, reflecting on significant issues, inviting further debate, probing responses accordingly, and seeking further clarification, as and where appropriate, will help to obtain sufficient depth and insight into the topic area.
Moderating online focus groups requires comparable skills, particularly if the discussion is synchronous, as the discussion may be dominated by those who can type proficiently. 36 It is therefore important that sufficient time and respect is accorded to those who may not be able to type as quickly. Asynchronous discussions are usually less problematic in this respect, as interactions are less instant. However, moderating an asynchronous discussion presents additional challenges, particularly if participants are geographically dispersed, as they may be online at different times. Consequently, the moderator will not always be present and the discussion may therefore need to occur over several days, which can be difficult to manage and facilitate and invariably requires considerable flexibility. 32 It is also worth recognising that establishing rapport with participants via online medium is often more challenging than via face-to-face and may therefore require additional time, skills, effort and consideration.
As with research interviews, focus groups should be guided by an appropriate interview schedule, as discussed earlier in the paper. For example, the schedule will usually be informed by the review of the literature and study aims, and will merely provide a topic guide to help inform subsequent discussions. To provide a verbatim account of the discussion, focus groups must be recorded, using an audio-recorder with a good quality multi-directional microphone. While videotaping is possible, some participants may find it obtrusive, 3 which may adversely affect group dynamics. The use (or not) of a video recorder, should therefore be carefully considered.
At the end of the focus group, a few minutes should be spent rounding up and reflecting on the discussion. 28 Depending on the topic area, it is possible that some participants may have revealed deeply personal issues and may therefore require further help and support, such as a constructive debrief or possibly even referral on to a relevant third party. It is also possible that some participants may feel that the discussion did not adequately reflect their views and, consequently, may no longer wish to be associated with the study. 28 Such occurrences are likely to be uncommon, but should they arise, it is important to further discuss any concerns and, if appropriate, offer them the opportunity to withdraw (including any data relating to them) from the study. Immediately after the discussion, researchers should compile notes regarding thoughts and ideas about the focus group, which can assist with data analysis and, if appropriate, any further data collection.
Qualitative research is increasingly being utilised within dental research to explore the experiences, perspectives, motivations and beliefs of participants. The contributions of qualitative research to evidence-based practice are increasingly being recognised, both as standalone research and as part of larger mixed-method studies, including clinical trials. Interviews and focus groups remain commonly used data collection methods in qualitative research, and with the advent of digital technologies, their utilisation continues to evolve. However, digital methods of qualitative data collection present additional methodological, ethical and practical considerations, but also potentially offer considerable flexibility to participants and researchers. Consequently, regardless of format, qualitative methods have significant potential to inform important areas of dental practice, policy and further related research.
Gussy M, Dickson-Swift V, Adams J . A scoping review of qualitative research in peer-reviewed dental publications. Int J Dent Hygiene 2013; 11 : 174–179.
Article Google Scholar
Burnard P, Gill P, Stewart K, Treasure E, Chadwick B . Analysing and presenting qualitative data. Br Dent J 2008; 204 : 429–432.
Gill P, Stewart K, Treasure E, Chadwick B . Methods of data collection in qualitative research: interviews and focus groups. Br Dent J 2008; 204 : 291–295.
Gill P, Stewart K, Treasure E, Chadwick B . Conducting qualitative interviews with school children in dental research. Br Dent J 2008; 204 : 371–374.
Stewart K, Gill P, Chadwick B, Treasure E . Qualitative research in dentistry. Br Dent J 2008; 204 : 235–239.
Masood M, Thaliath E, Bower E, Newton J . An appraisal of the quality of published qualitative dental research. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2011; 39 : 193–203.
Ellis J, Levine A, Bedos C et al. Refusal of implant supported mandibular overdentures by elderly patients. Gerodontology 2011; 28 : 62–68.
Macfarlane S, Bucknall T . Digital Technologies in Research. In Gerrish K, Lathlean J (editors) The Research Process in Nursing . 7th edition. pp. 71–86. Oxford: Wiley Blackwell; 2015.
Google Scholar
Lee R, Fielding N, Blank G . Online Research Methods in the Social Sciences: An Editorial Introduction. In Fielding N, Lee R, Blank G (editors) The Sage Handbook of Online Research Methods . pp. 3–16. London: Sage Publications; 2016.
Creswell J . Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five designs . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1998.
Guest G, Namey E, Mitchell M . Qualitative research: Defining and designing In Guest G, Namey E, Mitchell M (editors) Collecting Qualitative Data: A Field Manual For Applied Research . pp. 1–40. London: Sage Publications, 2013.
Chapter Google Scholar
Pope C, Mays N . Qualitative research: Reaching the parts other methods cannot reach: an introduction to qualitative methods in health and health services research. BMJ 1995; 311 : 42–45.
Giddings L, Grant B . A Trojan Horse for positivism? A critique of mixed methods research. Adv Nurs Sci 2007; 30 : 52–60.
Hammersley M, Atkinson P . Ethnography: Principles in Practice . London: Routledge, 1995.
Oltmann S . Qualitative interviews: A methodological discussion of the interviewer and respondent contexts Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung/Forum: Qualitative Social Research. 2016; 17 : Art. 15.
Patton M . Qualitative Research and Evaluation Methods . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2002.
Wang M, Vinall-Collier K, Csikar J, Douglas G . A qualitative study of patients' views of techniques to reduce dental anxiety. J Dent 2017; 66 : 45–51.
Lindenmeyer A, Bowyer V, Roscoe J, Dale J, Sutcliffe P . Oral health awareness and care preferences in patients with diabetes: a qualitative study. Fam Pract 2013; 30 : 113–118.
Gallagher J, Clarke W, Wilson N . Understanding the motivation: a qualitative study of dental students' choice of professional career. Eur J Dent Educ 2008; 12 : 89–98.
Tod A . Interviewing. In Gerrish K, Lacey A (editors) The Research Process in Nursing . Oxford: Blackwell Publishing, 2006.
Grey E, Harcourt D, O'Sullivan D, Buchanan H, Kipatrick N . A qualitative study of patients' motivations and expectations for dental implants. Br Dent J 2013; 214 : 10.1038/sj.bdj.2012.1178.
Farmer J, Peressini S, Lawrence H . Exploring the role of the dental hygienist in reducing oral health disparities in Canada: A qualitative study. Int J Dent Hygiene 2017; 10.1111/idh.12276.
McElhinney E, Cheater F, Kidd L . Undertaking qualitative health research in social virtual worlds. J Adv Nurs 2013; 70 : 1267–1275.
Health Research Authority. UK Policy Framework for Health and Social Care Research. Available at https://www.hra.nhs.uk/planning-and-improving-research/policies-standards-legislation/uk-policy-framework-health-social-care-research/ (accessed September 2017).
Baillie J, Gill P, Courtenay P . Knowledge, understanding and experiences of peritonitis among patients, and their families, undertaking peritoneal dialysis: A mixed methods study protocol. J Adv Nurs 2017; 10.1111/jan.13400.
Kvale S . Interviews . Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage, 1996.
Spradley J . The Ethnographic Interview . New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 1979.
Goodman C, Evans C . Focus Groups. In Gerrish K, Lathlean J (editors) The Research Process in Nursing . pp. 401–412. Oxford: Wiley Blackwell, 2015.
Shaha M, Wenzell J, Hill E . Planning and conducting focus group research with nurses. Nurse Res 2011; 18 : 77–87.
Wang G, Gao X, Edward C . Public perception of dental implants: a qualitative study. J Dent 2015; 43 : 798–805.
Bailey E . Contemporary views of dental practitioners' on patient safety. Br Dent J 2015; 219 : 535–540.
Abrams K, Gaiser T . Online Focus Groups. In Field N, Lee R, Blank G (editors) The Sage Handbook of Online Research Methods . pp. 435–450. London: Sage Publications, 2016.
Poynter R . The Handbook of Online and Social Media Research . West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons, 2010.
Kevern J, Webb C . Focus groups as a tool for critical social research in nurse education. Nurse Educ Today 2001; 21 : 323–333.
Kitzinger J, Barbour R . Introduction: The Challenge and Promise of Focus Groups. In Barbour R S K J (editor) Developing Focus Group Research . pp. 1–20. London: Sage Publications, 1999.
Krueger R, Casey M . Focus Groups: A Practical Guide for Applied Research. 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE; 2009.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Senior Lecturer (Adult Nursing), School of Healthcare Sciences, Cardiff University,
Lecturer (Adult Nursing) and RCBC Wales Postdoctoral Research Fellow, School of Healthcare Sciences, Cardiff University,
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to P. Gill .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Gill, P., Baillie, J. Interviews and focus groups in qualitative research: an update for the digital age. Br Dent J 225 , 668–672 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.2018.815
Download citation
Accepted : 02 July 2018
Published : 05 October 2018
Issue Date : 12 October 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.2018.815
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Assessment of women’s needs and wishes regarding interprofessional guidance on oral health in pregnancy – a qualitative study.
- Merle Ebinghaus
- Caroline Johanna Agricola
- Birgit-Christiane Zyriax
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2024)
Translating brand reputation into equity from the stakeholder’s theory: an approach to value creation based on consumer’s perception & interactions
- Olukorede Adewole
International Journal of Corporate Social Responsibility (2024)
Perceptions and beliefs of community gatekeepers about genomic risk information in African cleft research
- Abimbola M. Oladayo
- Oluwakemi Odukoya
- Azeez Butali
BMC Public Health (2024)
Assessment of women’s needs, wishes and preferences regarding interprofessional guidance on nutrition in pregnancy – a qualitative study
‘baby mamas’ in urban ghana: an exploratory qualitative study on the factors influencing serial fathering among men in accra, ghana.
- Rosemond Akpene Hiadzi
- Jemima Akweley Agyeman
- Godwin Banafo Akrong
Reproductive Health (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to conduct effective and ethical qualitative research interviews? This article provides twelve tips for researchers who want to collect rich and trustworthy data from their interviewees. The tips cover topics such as preparation, rapport, probing, recording, and analysis. The article draws on examples from various disciplines and contexts to illustrate the practical and ethical issues ...
Vancouver, Canada. Abstract. Interviews are one of the most promising ways of collecting qualitative data throug h establishment of a. communication between r esearcher and the interviewee. Re ...
Here are some steps on how to analyze a qualitative interview: 1. Transcription. The first step is transcribing the interview into text format to have a written record of the conversation. This step is essential to ensure that you can refer back to the interview data and identify the important aspects of the interview.
5. Not keeping your golden thread front of mind. We touched on this a little earlier, but it is a key point that should be central to your entire research process. You don't want to end up with pages and pages of data after conducting your interviews and realize that it is not useful to your research aims.
Develop an interview guide. Introduce yourself and explain the aim of the interview. Devise your questions so interviewees can help answer your research question. Have a sequence to your questions / topics by grouping them in themes. Make sure you can easily move back and forth between questions / topics. Make sure your questions are clear and ...
Abstract. The qualitative research interview is an important data collection tool for a variety of methods used within the broad spectrum of medical education research. However, many medical teachers and life science researchers undergo a steep learning curve when they first encounter qualitative interviews, both in terms of new theory but also ...
A qualitative research interview is a one-to-one data collection session between a researcher and a participant. Interviews may be carried out face-to-face, over the phone or via video call using a service like Skype or Zoom. There are three main types of qualitative research interview - structured, unstructured or semi-structured.
In this article, she shares five interviewing tips that have served her well. 1. Convey Intent. Proeschold-Bell says it's important for the interviewer to know the intent behind each question so that it can be clearly conveyed to the interviewee. Understanding the intent of a question, she's found, helps interviewers decide whether or not ...
Conducting a Successful Qualitative Interview - Step by Step Guide. Knowing when to use a qualitative interview is a great first step, but now you need to understand how best to conduct one. Our experts share a range of steps to follow as you embark on a qualitative interview and best practices for each. 1. Determine Your Objective
InterViews by Steinar Kvale Interviewing is an essential tool in qualitative research and this introduction to interviewing outlines both the theoretical underpinnings and the practical aspects of the process. After examining the role of the interview in the research process, Steinar Kvale considers some of the key philosophical issues relating ...
Developing Questions. Characteristics of good interview questions. Open-ended and elicit a long response from the interviewee (can't be answered yes/no or with one word) Focus on the experience of the interviewee. Don't lead the interviewee toward a particular response. Address a single issue/point (i.e. don't ask multi-part questions) Writing ...
Introduction. Interviewing people is at the heart of qualitative research. It is not merely a way to collect data but an intrinsically rewarding activity—an interaction between two people that holds the potential for greater understanding and interpersonal development. Unlike many of our daily interactions with others that are fairly shallow ...
While conducting an interview, it is essential to know the necessary steps to follow for ensuring success. The steps to conduct a research interview are as follows: Identify the objectives and understand the goals. Select an appropriate interview format. Organize the necessary materials for the interview.
This article provides the common steps of designing and conducting effective interviews and lists the main ethical issues that researchers, interviewers, and participants need to consider in the interview process of a research study.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to conduct a productive research interview: 1. Define your objectives. Identify what you want to achieve and the information you'd like to gather. This helps you guide your questions and gain as much information as possible. Remember, every research assignment has an objective based on what the company or ...
5. Jot down any final notes after the interview has concluded. Take 5 minutes after the interview to gather your thoughts and make any follow-up notes to the information discussed in the interview. Write a note if, for example, the interviewee used any strange body language that could convey discomfort.
Advantages and disadvantages of interviews. Interviews are a great research tool. They allow you to gather rich information and draw more detailed conclusions than other research methods, taking into consideration nonverbal cues, off-the-cuff reactions, and emotional responses.. However, they can also be time-consuming and deceptively challenging to conduct properly.
Qualitative research interviews are depth interviews. They elicit detailed feedback from your leads and customers. Unstructured interviews reveal why people react in a certain way or make certain decisions. According to The Hartford, qualitative research provides an anecdotal look into your business. That provides an important form of data.
The following is a step-‐by-‐step guide to conducting a productive interview. Before the Interview. • Ask the person you would like to interview for an appointment as quickly as you can. This gives you the best chance of getting a "yes" in answer to your request because the window of opportunity for meeting with the person is the ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The reliability of Internet information can be evaluated in which of the following ways?, Internet search tips include, To conduct an effective research interview, you should and more.
7 interview methods in research. Here's a list of seven major interview methods that you can use in your research: 1. Focus group. One popular research interview method is conducting a focus group interview, which involves a group of individuals interviewed at the same time.
A research interview is typically a two-person interview conducted to increase knowledge on a given topic for an organization. Your company may select you to interview people in search of the best possible answers to inform you and your team in ways to improve the company. For instance, you may interview a group of people and compare their ...
Qualitative research is an approach that focuses on people and their experiences, behaviours and opinions. 10,11 The qualitative researcher seeks to answer questions of 'how' and 'why', providing ...