
The Research Problem & Statement
What they are & how to write them (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | March 2023
If you’re new to academic research, you’re bound to encounter the concept of a “ research problem ” or “ problem statement ” fairly early in your learning journey. Having a good research problem is essential, as it provides a foundation for developing high-quality research, from relatively small research papers to a full-length PhD dissertations and theses.
In this post, we’ll unpack what a research problem is and how it’s related to a problem statement . We’ll also share some examples and provide a step-by-step process you can follow to identify and evaluate study-worthy research problems for your own project.
Overview: Research Problem 101
What is a research problem.
- What is a problem statement?
Where do research problems come from?
- How to find a suitable research problem
- Key takeaways
A research problem is, at the simplest level, the core issue that a study will try to solve or (at least) examine. In other words, it’s an explicit declaration about the problem that your dissertation, thesis or research paper will address. More technically, it identifies the research gap that the study will attempt to fill (more on that later).
Let’s look at an example to make the research problem a little more tangible.
To justify a hypothetical study, you might argue that there’s currently a lack of research regarding the challenges experienced by first-generation college students when writing their dissertations [ PROBLEM ] . As a result, these students struggle to successfully complete their dissertations, leading to higher-than-average dropout rates [ CONSEQUENCE ]. Therefore, your study will aim to address this lack of research – i.e., this research problem [ SOLUTION ].
A research problem can be theoretical in nature, focusing on an area of academic research that is lacking in some way. Alternatively, a research problem can be more applied in nature, focused on finding a practical solution to an established problem within an industry or an organisation. In other words, theoretical research problems are motivated by the desire to grow the overall body of knowledge , while applied research problems are motivated by the need to find practical solutions to current real-world problems (such as the one in the example above).
As you can probably see, the research problem acts as the driving force behind any study , as it directly shapes the research aims, objectives and research questions , as well as the research approach. Therefore, it’s really important to develop a very clearly articulated research problem before you even start your research proposal . A vague research problem will lead to unfocused, potentially conflicting research aims, objectives and research questions .

What is a research problem statement?
As the name suggests, a problem statement (within a research context, at least) is an explicit statement that clearly and concisely articulates the specific research problem your study will address. While your research problem can span over multiple paragraphs, your problem statement should be brief , ideally no longer than one paragraph . Importantly, it must clearly state what the problem is (whether theoretical or practical in nature) and how the study will address it.
Here’s an example of a statement of the problem in a research context:
Rural communities across Ghana lack access to clean water, leading to high rates of waterborne illnesses and infant mortality. Despite this, there is little research investigating the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects within the Ghanaian context. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the effectiveness of such projects in improving access to clean water and reducing rates of waterborne illnesses in these communities.
As you can see, this problem statement clearly and concisely identifies the issue that needs to be addressed (i.e., a lack of research regarding the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects) and the research question that the study aims to answer (i.e., are community-led water supply projects effective in reducing waterborne illnesses?), all within one short paragraph.
Need a helping hand?
Wherever there is a lack of well-established and agreed-upon academic literature , there is an opportunity for research problems to arise, since there is a paucity of (credible) knowledge. In other words, research problems are derived from research gaps . These gaps can arise from various sources, including the emergence of new frontiers or new contexts, as well as disagreements within the existing research.
Let’s look at each of these scenarios:
New frontiers – new technologies, discoveries or breakthroughs can open up entirely new frontiers where there is very little existing research, thereby creating fresh research gaps. For example, as generative AI technology became accessible to the general public in 2023, the full implications and knock-on effects of this were (or perhaps, still are) largely unknown and therefore present multiple avenues for researchers to explore.
New contexts – very often, existing research tends to be concentrated on specific contexts and geographies. Therefore, even within well-studied fields, there is often a lack of research within niche contexts. For example, just because a study finds certain results within a western context doesn’t mean that it would necessarily find the same within an eastern context. If there’s reason to believe that results may vary across these geographies, a potential research gap emerges.
Disagreements – within many areas of existing research, there are (quite naturally) conflicting views between researchers, where each side presents strong points that pull in opposing directions. In such cases, it’s still somewhat uncertain as to which viewpoint (if any) is more accurate. As a result, there is room for further research in an attempt to “settle” the debate.
Of course, many other potential scenarios can give rise to research gaps, and consequently, research problems, but these common ones are a useful starting point. If you’re interested in research gaps, you can learn more here .
How to find a research problem
Given that research problems flow from research gaps , finding a strong research problem for your research project means that you’ll need to first identify a clear research gap. Below, we’ll present a four-step process to help you find and evaluate potential research problems.
If you’ve read our other articles about finding a research topic , you’ll find the process below very familiar as the research problem is the foundation of any study . In other words, finding a research problem is much the same as finding a research topic.
Step 1 – Identify your area of interest
Naturally, the starting point is to first identify a general area of interest . Chances are you already have something in mind, but if not, have a look at past dissertations and theses within your institution to get some inspiration. These present a goldmine of information as they’ll not only give you ideas for your own research, but they’ll also help you see exactly what the norms and expectations are for these types of projects.
At this stage, you don’t need to get super specific. The objective is simply to identify a couple of potential research areas that interest you. For example, if you’re undertaking research as part of a business degree, you may be interested in social media marketing strategies for small businesses, leadership strategies for multinational companies, etc.
Depending on the type of project you’re undertaking, there may also be restrictions or requirements regarding what topic areas you’re allowed to investigate, what type of methodology you can utilise, etc. So, be sure to first familiarise yourself with your institution’s specific requirements and keep these front of mind as you explore potential research ideas.
Step 2 – Review the literature and develop a shortlist
Once you’ve decided on an area that interests you, it’s time to sink your teeth into the literature . In other words, you’ll need to familiarise yourself with the existing research regarding your interest area. Google Scholar is a good starting point for this, as you can simply enter a few keywords and quickly get a feel for what’s out there. Keep an eye out for recent literature reviews and systematic review-type journal articles, as these will provide a good overview of the current state of research.
At this stage, you don’t need to read every journal article from start to finish . A good strategy is to pay attention to the abstract, intro and conclusion , as together these provide a snapshot of the key takeaways. As you work your way through the literature, keep an eye out for what’s missing – in other words, what questions does the current research not answer adequately (or at all)? Importantly, pay attention to the section titled “ further research is needed ”, typically found towards the very end of each journal article. This section will specifically outline potential research gaps that you can explore, based on the current state of knowledge (provided the article you’re looking at is recent).
Take the time to engage with the literature and develop a big-picture understanding of the current state of knowledge. Reviewing the literature takes time and is an iterative process , but it’s an essential part of the research process, so don’t cut corners at this stage.
As you work through the review process, take note of any potential research gaps that are of interest to you. From there, develop a shortlist of potential research gaps (and resultant research problems) – ideally 3 – 5 options that interest you.

Step 3 – Evaluate your potential options
Once you’ve developed your shortlist, you’ll need to evaluate your options to identify a winner. There are many potential evaluation criteria that you can use, but we’ll outline three common ones here: value, practicality and personal appeal.
Value – a good research problem needs to create value when successfully addressed. Ask yourself:
- Who will this study benefit (e.g., practitioners, researchers, academia)?
- How will it benefit them specifically?
- How much will it benefit them?
Practicality – a good research problem needs to be manageable in light of your resources. Ask yourself:
- What data will I need access to?
- What knowledge and skills will I need to undertake the analysis?
- What equipment or software will I need to process and/or analyse the data?
- How much time will I need?
- What costs might I incur?
Personal appeal – a research project is a commitment, so the research problem that you choose needs to be genuinely attractive and interesting to you. Ask yourself:
- How appealing is the prospect of solving this research problem (on a scale of 1 – 10)?
- Why, specifically, is it attractive (or unattractive) to me?
- Does the research align with my longer-term goals (e.g., career goals, educational path, etc)?
Depending on how many potential options you have, you may want to consider creating a spreadsheet where you numerically rate each of the options in terms of these criteria. Remember to also include any criteria specified by your institution . From there, tally up the numbers and pick a winner.
Step 4 – Craft your problem statement
Once you’ve selected your research problem, the final step is to craft a problem statement. Remember, your problem statement needs to be a concise outline of what the core issue is and how your study will address it. Aim to fit this within one paragraph – don’t waffle on. Have a look at the problem statement example we mentioned earlier if you need some inspiration.
Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- A research problem is an explanation of the issue that your study will try to solve. This explanation needs to highlight the problem , the consequence and the solution or response.
- A problem statement is a clear and concise summary of the research problem , typically contained within one paragraph.
- Research problems emerge from research gaps , which themselves can emerge from multiple potential sources, including new frontiers, new contexts or disagreements within the existing literature.
- To find a research problem, you need to first identify your area of interest , then review the literature and develop a shortlist, after which you’ll evaluate your options, select a winner and craft a problem statement .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

I APPRECIATE YOUR CONCISE AND MIND-CAPTIVATING INSIGHTS ON THE STATEMENT OF PROBLEMS. PLEASE I STILL NEED SOME SAMPLES RELATED TO SUICIDES.
Very pleased and appreciate clear information.
Your videos and information have been a life saver for me throughout my dissertation journey. I wish I’d discovered them sooner. Thank you!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.
For Business
For Individuals
Effective problem statements have these 5 components

We’ve all encountered problems on the job. After all, that’s what a lot of work is about. Solving meaningful problems to help improve something.
Developing a problem statement that provides a brief description of an issue you want to solve is an important early step in problem-solving .
It sounds deceptively simple. But creating an effective problem statement isn’t that easy, even for a genius like Albert Einstein. Given one hour to work on a problem, he’d spend 55 minutes thinking about the problem and five minutes finding solutions. (Or so the story goes.)
Einstein was probably exaggerating to make a point. But considering his success in solving complex problems, we think he was on to something.
As humans, we’re wired to jump past the problem and go directly to the solution stage. In emergencies, this behavior can be lifesaving, as in leaping out of the way of a speeding car. But when dealing with longer-range issues in the workplace, this can lead to bad decisions or half-baked solutions.
That’s where problem statements come in handy. They help to meaningfully outline objectives to reach effective solutions. Knowing how to develop a great problem statement is also a valuable tool for honing your management skills .
But what exactly is a problem statement, when should you use one, and how do you go about writing one? In this article, we'll answer those questions and give you some tips for writing effective problem statements. Then you'll be ready to take on more challenges large and small.
What is a problem statement?
First, let’s start by defining a problem statement.
A problem statement is a short, clear explanation of an issue or challenge that sums up what you want to change. It helps you, team members, and other stakeholders to focus on the problem, why it’s important, and who it impacts.
A good problem statement should create awareness and stimulate creative thinking . It should not identify a solution or create a bias toward a specific strategy.
Taking time to work on a problem statement is a great way to short-circuit the tendency to rush to solutions. It helps to make sure you’re focusing on the right problem and have a well-informed understanding of the root causes. The process can also help you take a more proactive than reactive approach to problem-solving . This can help position you and your team to avoid getting stuck in constant fire-fighting mode. That way, you can take advantage of more growth opportunities.
When to use a problem statement
The best time to create a problem statement is before you start thinking of solutions. If you catch yourself or your team rushing to the solution stage when you’re first discussing a problem, hit the brakes. Go back and work on the statement of the problem to make sure everyone understands and agrees on what the real problem is.
Here are some common situations where writing problem statements might come in handy:
- Writing an executive summary for a project proposal or research project
- Collaborating on a cross-functional project with several team members
- Defining the customer issue that a proposed product or service aims to solve
- Using design thinking to improve user experience
- Tackling a problem that previous actions failed to solve
How to identify a problem statement
Like the unseen body of an iceberg, the root cause of a specific problem isn’t always obvious. So when developing a problem statement, how do you go about identifying the true, underlying problem?
These two steps will help you uncover the root cause of a problem :
- Collect information from the research and previous experience with the problem
- Talk to multiple stakeholders who are impacted by the problem
People often perceive problems differently. Interviewing stakeholders will help you understand the problem from diverse points of view. It can also help you develop some case studies to illustrate the problem.
Combining these insights with research data will help you identify root causes more accurately. In turn, this methodology will help you craft a problem statement that will lead to more viable solutions.
What are problem statements used for?
You can use problem statements for a variety of purposes. For an organization, it might be solving customer and employee issues. For the government, it could be improving public health. For individuals, it can mean enhancing their own personal well-being . Generally, problem statements can be used to:
- Identify opportunities for improvement
- Focus on the right problems or issues to launch more successful initiatives – a common challenge in leadership
- Help you communicate a problem to others who need to be involved in finding a solution
- Serve as the basis for developing an action plan or goals that need to be accomplished to help solve the problem
- Stimulate thinking outside the box and other types of creative brainstorming techniques
3 examples of problem statements
When you want to be sure you understand a concept or tool, it helps to see an example. There can also be some differences in opinion about what a problem statement should look like. For instance, some frameworks include a proposed solution as part of the problem statement. But if the goal is to stimulate fresh ideas, it’s better not to suggest a solution within the problem statement.
In our experience, an effective problem statement is brief, preferably one sentence. It’s also specific and descriptive without being prescriptive.
Here are three problem statement examples. While these examples represent three types of problems or goals, keep in mind that there can be many other types of problem statements.
Example Problem Statement 1: The Status Quo Problem Statement
Example:
The average customer service on-hold time for Example company exceeds five minutes during both its busy and slow seasons.
This can be used to describe a current pain point within an organization that may need to be addressed. Note that the statement specifies that the issue occurs during the company’s slow time as well as the busy season. This is helpful in performing the root cause analysis and determining how this problem can be solved.
The average customer service on-hold time for Example company exceeds five minutes during both its busy and slow seasons. The company is currently understaffed and customer service representatives are overwhelmed.
Background:
Example company is facing a significant challenge in managing their customer service on-hold times. In the past, the company had been known for its efficient and timely customer service, but due to a combination of factors, including understaffing and increased customer demand, the on-hold times have exceeded five minutes consistently. This has resulted in frustration and dissatisfaction among customers, negatively impacting the company's reputation and customer loyalty.
Reducing the on-hold times for customer service callers is crucial for Example company. Prolonged waiting times have a detrimental effect on customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to potential customer churn and loss of revenue. Additionally, the company's declining reputation in terms of customer service can have a lasting impact on its competitive position in the market. Addressing this problem is of utmost importance to improve customer experience and maintain a positive brand image.
Objectives:
The primary objective of this project is to reduce the on-hold times for customer service callers at Example company. The specific objectives include:
- Analyzing the current customer service workflow and identifying bottlenecks contributing to increased on-hold times.
- Assessing the staffing levels and resource allocation to determine the extent of understaffing and its impact on customer service.
- Developing strategies and implementing measures to optimize the customer service workflow and reduce on-hold times.
- Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the implemented measures through key performance indicators (KPIs) such as average on-hold time, customer satisfaction ratings, and customer feedback.
- Establishing a sustainable approach to maintain reduced on-hold times, taking into account both busy and slow seasons, through proper resource planning, training, and process improvements.
Example Problem Statement 2: The Destination Problem Statement
Leaders at Example company want to increase net revenue for its premium product line of widgets by 5% for the next fiscal year.
This approach can be used to describe where an organization wants to be in the future. This type of problem statement is useful for launching initiatives to help an organization achieve its desired state.
Like creating SMART goals , you want to be as specific as possible. Note that the statement specifies “net revenue” instead of “gross revenue." This will help keep options open for potential actions. It also makes it clear that merely increasing sales is not an acceptable solution if higher marketing costs offset the net gains.
Leaders at Example company aim to increase net revenue for its premium product line of widgets by 5% for the next fiscal year. However, the company currently lacks the necessary teams to tackle this objective effectively. To achieve this growth target, the company needs to expand its marketing and PR teams, as well as its product development teams, to prepare for scaling.
Example company faces the challenge of generating a 5% increase in net revenue for its premium product line of widgets in the upcoming fiscal year. Currently, the company lacks the required workforce to drive this growth. Without adequate staff in the marketing, PR, and product development departments, the company's ability to effectively promote, position, and innovate its premium product line will be hindered. To achieve this kind of growth, it is essential that Example company expands teams, enhances capabilities, and strategically taps into the existing pool of loyal customers.
Increasing net revenue for the premium product line is crucial for Example company's overall business success. Failure to achieve the targeted growth rate can lead to missed revenue opportunities and stagnation in the market. By expanding the marketing and PR teams, Example company can strengthen its brand presence, effectively communicate the value proposition of its premium product line, and attract new customers.
Additionally, expanding the product development teams will enable the company to introduce new features and innovations, further enticing existing and potential customers. Therefore, addressing the workforce shortage and investing in the necessary resources are vital for achieving the revenue growth objective.
The primary objective of this project is to increase net revenue for Example company's premium product line of widgets by 5% in the next fiscal year. The specific objectives include:
- Assessing the current workforce and identifying the gaps in the marketing, PR, and product development teams.
- Expanding the marketing and PR teams by hiring skilled professionals who can effectively promote the premium product line and engage with the target audience.
- Strengthening the product development teams by recruiting qualified individuals who can drive innovation, enhance product features, and meet customer demands.
- Developing a comprehensive marketing and PR strategy to effectively communicate the value proposition of the premium product line and attract new customers.
- Leveraging the existing base of loyal customers to increase repeat purchases, referrals, and brand advocacy.
- Allocating sufficient resources, both time and manpower, to support the expansion and scaling efforts required to achieve the ambitious revenue growth target.
- Monitoring and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) such as net revenue, customer acquisition, customer retention, and customer satisfaction to measure the success of the growth initiatives.
- Establishing a sustainable plan to maintain the increased revenue growth beyond the next fiscal year by implementing strategies for continuous improvement and adaptation to market dynamics.
Example Problem Statement 3 The Stakeholder Problem Statement
In the last three quarterly employee engagement surveys , less than 30% of employees at Eample company stated that they feel valued by the company. This represents a 20% decline compared to the same period in the year prior.
This strategy can be used to describe how a specific stakeholder group views the organization. It can be useful for exploring issues and potential solutions that impact specific groups of people.
Note the statement makes it clear that the issue has been present in multiple surveys and it's significantly worse than the previous year. When researching root causes, the HR team will want to zero in on factors that changed since the previous year.
In the last three quarterly employee engagement surveys, less than 30% of employees at the Example company stated that they feel valued by the company. This indicates a significant decline of 20% compared to the same period in the previous year.
The company aspires to reduce this percentage further to under 10%. However, achieving this goal would require filling specialized roles and implementing substantial cultural changes within the organization.
Example company is facing a pressing issue regarding employee engagement and perceived value within the company. Over the past year, there has been a notable decline in the percentage of employees who feel valued. This decline is evident in the results of the quarterly employee engagement surveys, which consistently show less than 30% of employees reporting a sense of value by the company.
This decline of 20% compared to the previous year's data signifies a concerning trend. To address this problem effectively, Example company needs to undertake significant measures that go beyond superficial changes and necessitate filling specialized roles and transforming the company culture.
Employee engagement and a sense of value are crucial for organizational success. When employees feel valued, they tend to be more productive, committed, and motivated. Conversely, a lack of perceived value can lead to decreased morale, increased turnover rates, and diminished overall performance.
By addressing the decline in employees feeling valued, Example company can improve employee satisfaction, retention, and ultimately, overall productivity. Achieving the desired reduction to under 10% is essential to restore a positive work environment and build a culture of appreciation and respect.
The primary objective of this project is to increase the percentage of employees who feel valued by Example company, aiming to reduce it to under 10%. The specific objectives include:
- Conducting a comprehensive analysis of the factors contributing to the decline in employees feeling valued, including organizational policies, communication practices, leadership styles, and cultural norms.
- Identifying and filling specialized roles, such as employee engagement specialists or culture change agents, who can provide expertise and guidance in fostering a culture of value and appreciation.
- Developing a holistic employee engagement strategy that encompasses various initiatives, including training programs, recognition programs, feedback mechanisms, and communication channels, to enhance employee value perception.
- Implementing cultural changes within the organization that align with the values of appreciation, respect, and recognition, while fostering an environment where employees feel valued.
- Communicating the importance of employee value and engagement throughout all levels of the organization, including leadership teams, managers, and supervisors, to ensure consistent messaging and support.
- Monitoring progress through regular employee surveys, feedback sessions, and key performance indicators (KPIs) related to employee satisfaction, turnover rates, and overall engagement levels.
- Providing ongoing support, resources, and training to managers and supervisors to enable them to effectively recognize and appreciate their teams and foster a culture of value within their respective departments.
- Establishing a sustainable framework for maintaining high employee value perception in the long term, including regular evaluation and adaptation of employee engagement initiatives to address evolving needs and expectations.

What are the 5 components of a problem statement?
In developing a problem statement, it helps to think like a journalist by focusing on the five Ws: who, what, when, where, and why or how. Keep in mind that every statement may not explicitly include each component. But asking these questions is a good way to make sure you’re covering the key elements:
- Who: Who are the stakeholders that are affected by the problem?
- What: What is the current state, desired state, or unmet need?
- When: When is the issue occurring or what is the timeframe involved?
- Where: Where is the problem occurring? For example, is it in a specific department, location, or region?
- Why: Why is this important or worth solving? How is the problem impacting your customers, employees, other stakeholders, or the organization? What is the magnitude of the problem? How large is the gap between the current and desired state?
How do you write a problem statement?
There are many frameworks designed to help people write a problem statement. One example is outlined in the book, The Conclusion Trap: Four Steps to Better Decisions, ” by Daniel Markovitz. A faculty member at the Lean Enterprise Institute, the author uses many case studies from his work as a business consultant.
To simplify the process, we’ve broken it down into three steps:
1. Gather data and observe
Use data from research and reports, as well as facts from direct observation to answer the five Ws: who, what, when, where, and why.
Whenever possible, get out in the field and talk directly with stakeholders impacted by the problem. Get a firsthand look at the work environment and equipment. This may mean spending time on the production floor asking employees questions about their work and challenges. Or taking customer service calls to learn more about customer pain points and problems your employees may be grappling with.
2. Frame the problem properly
A well-framed problem will help you avoid cognitive bias and open avenues for discussion. It will also encourage the exploration of more options.
A good way to test a problem statement for bias is to ask questions like these:
3. Keep asking why (and check in on the progress)
When it comes to problem-solving, stay curious. Lean on your growth mindset to keep asking why — and check in on the progress.
Asking why until you’re satisfied that you’ve uncovered the root cause of the problem will help you avoid ineffective band-aid solutions.
Refining your problem statements
When solving any sort of problem, there’s likely a slew of questions that might arise for you. In order to holistically understand the root cause of the problem at hand, your workforce needs to stay curious.
An effective problem statement creates the space you and your team need to explore, gain insight, and get buy-in before taking action.
If you have embarked on a proposed solution, it’s also important to understand that solutions are malleable. There may be no single best solution. Solutions can change and adapt as external factors change, too. It’s more important than ever that organizations stay agile . This means that interactive check-ins are critical to solving tough problems. By keeping a good pulse on your course of action, you’ll be better equipped to pivot when the time comes to change.
BetterUp can help. With access to virtual coaching , your people can get personalized support to help solve tough problems of the future.
Cultivate your creativity
Foster creativity and continuous learning with guidance from our certified Coaches.
Madeline Miles
Madeline is a writer, communicator, and storyteller who is passionate about using words to help drive positive change. She holds a bachelor's in English Creative Writing and Communication Studies and lives in Denver, Colorado. In her spare time, she's usually somewhere outside (preferably in the mountains) — and enjoys poetry and fiction.
18 excellent educational podcasts to fuel your love of learning
The future of ai: where does your job stand, 6 ai prompt generator tools to boost your creativity, 20 ai tools to help boost productivity in 2023, 4 benefits of ai and 4 potential disadvantages, how to use 100% of your brain: is it possible, the 10 best work productivity tools to maximize your time, applications of ai: 10 common examples, squirrel how to increase attention span so you get stuff done, similar articles, 10 problem-solving strategies to turn challenges on their head, writing a value statement: your guide to keeping your team aligned, 10 personal brand statements to put all eyes on you, discover 4 types of innovation and how to encourage them, what is organizational structure and why is it important, create smart kpis to strategically grow your business, what is customer satisfaction and how can you improve it, what is a career statement, and should you write one, how to craft an impactful company mission statement, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences

- Research Process
What is a Problem Statement? [with examples]
- 5 minute read
Table of Contents
The statement of the problem is one of the first things that a colleague or potential client will read. With the vastness of the information available at one’s fingertips in the online9 world, your work may have just a few seconds to draw in a reader to take a deeper look at your proposal before moving on to the next option. It explains quickly to the reader, the problem at hand, the need for research, and how you intend to do it.
A strong, clear description of the problem that drew you to your research has to be straightforward, easy to read and, most important, relevant. Why do you care about this problem? How can solving this problem impact the world? The problem statement is your opportunity to explain why you care and what you propose to do in the way of researching the problem.
A problem statement is an explanation in research that describes the issue that is in need of study . What problem is the research attempting to address? Having a Problem Statement allows the reader to quickly understand the purpose and intent of the research. The importance of writing your research proposal cannot be stressed enough. Check for more information on Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal .
It is expected to be brief and concise , and should not include the findings of the research or detailed data . The average length of a research statement is generally about one page . It is going to define the problem, which can be thought of as a gap in the information base. There may be several solutions to this gap or lack of information, but that is not the concern of the problem statement. Its purpose is to summarize the current information and where a lack of knowledge may be presenting a problem that needs to be investigated .
The purpose of the problem statement is to identify the issue that is a concern and focus it in a way that allows it to be studied in a systematic way . It defines the problem and proposes a way to research a solution, or demonstrates why further information is needed in order for a solution to become possible.
What is Included in a Problem Statement?
Besides identifying the gap of understanding or the weakness of necessary data, it is important to explain the significance of this lack.
-How will your research contribute to the existing knowledge base in your field of study?
-How is it significant?
-Why does it matter?
Not all problems have only one solution so demonstrating the need for additional research can also be included in your problem statement. Once you identify the problem and the need for a solution, or for further study, then you can show how you intend to collect the needed data and present it.
How to Write a Statement of Problem in Research Proposal
It is helpful to begin with your goal. What do you see as the achievable goal if the problem you outline is solved? How will the proposed research theoretically change anything? What are the potential outcomes?
Then you can discuss how the problem prevents the ability to reach your realistic and achievable solution. It is what stands in the way of changing an issue for the better. Talk about the present state of affairs and how the problem impacts a person’s life, for example.
It’s helpful at this point to generally layout the present knowledge and understanding of the subject at hand, before then describing the gaps of knowledge that are currently in need of study. Your problem statement is a proposed solution to address one of these gaps.
A good problem statement will also layout the repercussions of leaving the problem as it currently stands. What is the significance of not addressing this problem? What are the possible future outcomes?
Example of Problem Statement in Research Proposal
If, for example , you intended to research the effect of vitamin D supplementation on the immune system , you would begin with a review of the current knowledge of vitamin D’s known function in relation to the immune system and how a deficiency of it impacts a person’s defenses.
You would describe the ideal environment in the body when there is a sufficient level of vitamin D. Then, begin to identify the problems associated with vitamin D deficiency and the difficulty of raising the level through supplementation, along with the consequences of that deficiency. Here you are beginning to identify the problem of a common deficiency and the current difficulty of increasing the level of vitamin D in the blood.
At this stage, you may begin to identify the problem and narrow it down in a way that is practical to a research project. Perhaps you are proposing a novel way of introducing Vitamin D in a way that allows for better absorption by the gut, or in a combination with another product that increases its level in the blood.
Describe the way your research in this area will contribute to the knowledge base on how to increase levels of vitamin D in a specific group of subjects, perhaps menopausal women with breast cancer. The research proposal is then described in practical terms.
How to write a problem statement in research?
Problem statements differ depending on the type and topic of research and vary between a few sentences to a few paragraphs.
However, the problem statement should not drag on needlessly. Despite the absence of a fixed format, a good research problem statement usually consists of three main parts:
Context: This section explains the background for your research. It identifies the problem and describes an ideal scenario that could exist in the absence of the problem. It also includes any past attempts and shortcomings at solving the problem.
Significance: This section defines how the problem prevents the ideal scenario from being achieved, including its negative impacts on the society or field of research. It should include who will be the most affected by a solution to the problem, the relevance of the study that you are proposing, and how it can contribute to the existing body of research.
Solution: This section describes the aim and objectives of your research, and your solution to overcome the problem. Finally, it need not focus on the perfect solution, but rather on addressing a realistic goal to move closer to the ideal scenario.
Here is a cheat sheet to help you with formulating a good problem statement.
1. Begin with a clear indication that the problem statement is going to be discussed next. You can start with a generic sentence like, “The problem that this study addresses…” This will inform your readers of what to expect next.
2. Next, mention the consequences of not solving the problem . You can touch upon who is or will be affected if the problem continues, and how.
3. Conclude with indicating the type of research /information that is needed to solve the problem. Be sure to reference authors who may have suggested the necessity of such research.
This will then directly lead to your proposed research objective and workplan and how that is expected to solve the problem i.e., close the research gap.
Language Editing Plus
Elsevier Language Editing Plus service will provide you with a thorough language review of your thesis, article or presentation. It offers review of logic and flow, reference checks, document formatting, a customized cover letter and more.

- Manuscript Preparation
What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research?

How to Use Tables and Figures effectively in Research Papers
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

Research Problem Statement — Find out how to write an impactful one!
Table of Contents
What Is a Research Problem Statement?
A research problem statement is a clear, concise, and specific statement that describes the issue or problem that the research project addresses. It should be written in a way that is easily understandable to both experts and non-experts in the field.
To write a research problem statement, you should:
- Identify the general area of interest: Start by identifying the general area of research that interests you.
- Define the specific problem: Narrow down the general area of interest to a specific problem or issue.
- Explain the significance of the problem: Provide context for the problem by explaining why it is important to study and what gap in current knowledge or understanding it fills.
- Provide a clear and concise statement: State the problem in a clear and concise manner, making sure to use language that is easily understood by your intended audience.
- Use a scientific and objective tone: The problem statement should be written in a neutral and objective tone, avoiding any subjective language and personal bias .
An Example of a Research Problem Statement
“The increasing prevalence of obesity in children is a growing public health concern. Despite the availability of information on healthy eating and physical activity, many children are still not engaging in healthy lifestyle behaviors. The problem this study addresses is the lack of understanding of the barriers and facilitators to healthy lifestyle behaviors in children.”
When to Write a Problem Statement in Research?
A research problem statement should be written at the beginning of the research process, before any data collection or analysis takes place. This is because the statement sets the foundation for the entire research project by clearly defining the problem that the research is trying to address.
Writing a problem statement early in the research process helps to guide the research design and methodology , and ensures that the research is focused on addressing the specific problem at hand. It also helps to ensure that the research is relevant and addresses a gap in current knowledge or understanding.
In addition, a well-written problem statement effectively communicates the purpose and significance of the research to potential funders, collaborators, and other stakeholders. It also generates interest and support for the research project.
It’s also important to note that, during the research process, the statement can be refined or updated as new information is discovered or as the research progresses. This is normal and it’s a good idea to revise the statement as needed to ensure that it remains clear and concise and that it accurately reflects the current focus of the research project.
What Does a Research Problem Statement Include?
A research problem statement typically includes the following elements:
1. The research topic:
The general area of interest or field of study that the research project addresses.
2. The specific problem or issue:
A clear and concise statement of the problem or issue that the research project aims to address.
3. The significance of the problem:
A discussion of why the problem is important and what gap in current knowledge or understanding it fills.
4. The research questions:
A set of questions that the research project aims to answer, in order to address the problem or issue.
5. The research objectives:
A set of specific and measurable objectives that the research project aims to achieve.
6. The scope of the research:
A description of the specific population, setting, or context that the research project will focus on.
7. The theoretical framework:
A discussion of the theoretical concepts and principles that inform the research project.
8. The research design:
A description of the research methodologies that will be used to collect and analyze data in order to address the research questions and objectives.
It’s important to note that the problem statement is usually brief and concise, typically a few sentences or a short paragraph. But it should provide enough information to convey the main idea of the research project.
Important Features of Research Problem Statement
The problem statement should be clear and easy to understand. Write it in a way that is accessible to both experts and non-experts in the field.
2. Specificity
The statement should be specific and clearly define the problem or issue that the research project aims to address. It should be narrow enough to be manageable, but broad enough to be of interest to others in the field.
3. Significance
The statement should explain why the problem is important and what gap in current knowledge or understanding it fills. It should provide context for the research project and help to justify its importance.
4. Relevance
The statement should be relevant to the field of study and address an issue that is currently of concern to researchers.
5. Research questions
The statement should include a set of research questions that the research project aims to answer in order to address the problem or issue.
6. Research objectives
The statement should include a set of specific and measurable objectives that the research project aims to achieve.
The statement should define the specific population, setting, or context that the research project will focus on.
8. Theoretical framework
The statement should provide an overview of the theoretical concepts and principles that inform the research project.
9. Research design
The statement should provide an overview of the research methodologies. This will be useful collect and analyze data in order to address the research questions and objectives.
Difference Between a Thesis Statement and a Problem Statement
A thesis statement and a problem statement are related but distinct elements of a research project.
A thesis statement is a statement that summarizes the central argument or claim of a research paper or essay. It presents the main idea of the paper and sets the direction for the rest of the content. It’s usually located at the end of the introduction, and it’s often one sentence.
A problem statement, on the other hand, is a statement that describes a specific problem or issue that the research project aims to address. It sets the foundation for the entire research project by clearly defining the research problem. It is usually located at the beginning of a research paper or proposal, and is of one or a few paragraphs.
In summary, a thesis statement is a summary of the main point or key argument of the research paper. A problem statement describes the specific issue that the research project aims to address. A thesis statement is more focused on the final outcome of the research. While a problem statement is focused on the current state of knowledge and the gap in understanding that the research project aims to fill.
In Conclusion
A problem statement is a critical component of the research project, as it provides a clear and concise roadmap for the research, and helps to ensure that the research is well-designed and addresses a significant and relevant issue.
We hope this blog has clarified your doubts and confusion associated with research problem statement and helps you write an effective statement for your research project!
comprehensive contents. thanks!
Very good writing and easy to understand
WOW..its easy to understand…
This has opened up my mind, Systematically outlined steps.
Wow I’ve gained Alot from this!
WOW…This was much helpful.
Good and straightforward explanations with ease of understanding for all the students and teachers alike.
Beautiful work
I enjoy and understand every bit of the explanations on each topic. Kudos to the team.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Diversity and Inclusion
The Silent Struggle: Confronting gender bias in science funding
In the 1990s, Dr. Katalin Kariko’s pioneering mRNA research seemed destined for obscurity, doomed by…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Demystifying the Role of Confounding Variables in Research

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
Write a Compelling Problem Statement + Examples & Templates
- November 1, 2023
Ever stared at a blank page, feeling like you’re about to tackle the world’s most confusing jigsaw puzzle, only without the picture on the box to guide you?
Welcome to the club, and trust me, it’s a large one!
But here’s the silver lining: armed with the right problem statement examples, that perplexing puzzle morphs from ‘Mission Impossible’ to ‘Hey, I got this!’.
Maybe not as delightful as a slice of cake, but definitely less hair-pulling.
Ready to decode the mystery? Let’s journey through it together!
What is a Problem Statement?
When you embark on a project or dive into research, understanding the core issue you’re addressing is essential. Enter the problem statement. Think of it as a concise description of a challenge you’re facing . It’s not just about saying, “Here’s an issue”; it’s about defining the problem in clear, actionable terms.
Whether you’re working on a business project or a research paper, crafting a compelling problem statement can set the direction for your work. It’s like a compass, guiding you and ensuring that you stay focused.
So, when you’re looking for examples of problem statements or wondering how to write a problem statement for a project, remember it’s all about clarity and precision .
By the end, anyone reading your problem statement should grasp the essence of the challenge at hand.
What Does a Problem Statement Define Overall?
A problem statement is more than just a sentence detailing an issue. At its core, it paints a clear picture of the specific challenge you’re looking to tackle . You might be thinking it’s just about identifying the problem, but it goes deeper. It provides context, zooms in on the obstacles, and highlights why the problem is worth solving.
Whether you’re defining a problem statement in a business context or within research, its essence remains the same: to present a clear snapshot of the issue at hand.
So, when you come across examples of a problem statement or explore problem statement templates, understand that they aim to capture the heart of the problem, making it clear to anyone involved. By the end, the statement will lay the foundation for the journey ahead, ensuring you and your team know the destination.
Key Elements of an Effective Problem Statement
Creating an effective problem statement isn’t just about stating an issue; it’s about being precise, concise, and actionable . It’s like laying the foundation for a building; if done right, everything else falls into place.
Wondering what goes into crafting one? Let’s break it down for you. Here are the key elements that should be part of any good problem statement:
- Clarity : Ensure the problem is described in simple and straightforward terms. No jargon, no fluff.
- Context : Provide some background or a brief explanation about why this issue matters.
- Specificity : Avoid being vague. Dive into the details and get to the root of the issue.
- Actionability : Frame the problem in a way that points towards a potential solution or direction.
- Relevance : Highlight why it's crucial to address this problem now. What's at stake?
When you incorporate these elements into your problem statement, you’re not just setting the stage but guiding your entire approach to a solution. Remember, the clearer your problem statement, the smoother your journey to finding answers.
Best Practices of Writing a Problem Statement
When diving into the art of crafting a problem statement, it’s essential you’re clued in on some best practices. After all, mastering these will ensure you’re not only clear and concise but truly impactful .
So, for those keen on understanding what makes a good problem statement, or hoping to peek at problem statement examples and derive some inspiration, here are a few practices to adopt:
- Stay Specific : Avoid vagueness. Dive straight into the heart of the issue, detailing it with precision.
- Keep it Short : While details matter, brevity is key. Aim for clarity without the fluff.
- Use Data if Possible : Quantifying the problem can make it more tangible and pressing.
- Highlight the Impact : Convey why solving this problem matters, which aids in gaining stakeholders' buy-in.
- Ensure it's Solvable : A problem statement should present an issue that is, in theory, fixable. After all, what's the point of pinpointing a problem if it's not actionable?
So, there you have it! Whether you’re penning a problem statement for a project, business, or research, these best practices will be your guiding light.
Diverse Applications of Problem Statements
In our daily professional endeavors, the importance of clarity cannot be overstated. One of the tools that lend this clarity is the problem statement.
From guiding corporate strategies to shaping public policies, the significance of crafting a precise problem statement stretches across domains. Let’s explore the diverse arenas where problem statements play a pivotal role:
Business Projects
In the bustling world of business, clarity is paramount , and this is where problem statements anchor themselves. As companies tread the path of innovation, launching new products or tweaking existing processes, it becomes imperative to pinpoint the exact challenges they’re up against.
This clarity ensures teams move cohesively towards a shared objective. Dive into some problem statement examples in business, and you’ll often notice a pattern: they’re geared towards enhancing customer experiences, optimizing operational efficiencies, or catapulting sales figures.
In essence, they form the bedrock of impactful corporate strategies .
Here’s an example problem statement:
Research Endeavors
The academic and research landscapes are vast, teeming with questions waiting to be answered. Here, the problem statement acts as the North Star . Be it a comprehensive thesis, a case study, or a detailed research paper, everything commences with a well-defined problem statement.
This not only provides the research with a sense of direction but also underpins its very purpose. From commonplace research problem statements to those tailored for specific research proposals, they all play a crucial role in determining the course of academic exploration .
Product Management
In the realm of product development, customer-centricity is key . And the process begins much before the first prototype is created. By crafting accurate problem statements, product managers and teams can hone in on genuine customer challenges.
These statements act as guidelines, ensuring that solutions being designed align perfectly with user requirements and market demands . As they delve deeper into the nuances of product management, they discover that the endgame is not just about creating a product, but about designing an experience that resonates.
Policy Framing
The world of public policy is intricate, often dealing with multifaceted societal challenges. Here, problem statements stand out as invaluable tools, helping policymakers delineate the very issues they seek to address .
By offering a crystal-clear picture of the challenges, these statements pave the way for crafting solutions that can bring about tangible change.
Policy problem statement examples could be as varied as tackling environmental degradation, addressing public health anomalies, or bridging educational divides. Through these, policymakers can enact changes that resonate at the grassroots level.
More Examples to Illustrate the Concept
Alright, so you’re diving deeper into the world of problem statements and might be craving a few more examples to cement your understanding. Perfect! It’s always easier when you have a variety of scenarios to reference.
Let’s check out some more examples to illustrate the concept:
- Customer Service
“Despite our efforts to provide efficient support, customer feedback consistently points to a 15-minute wait time on our customer support line. This prolonged waiting period is adversely affecting user satisfaction and potentially leading to the loss of valuable clients.”
- Digital Marketing
“Over the past quarter, our website analytics reflect a concerning 10% increase in the bounce rate. This trend suggests that either our content isn’t resonating with visitors or there are design elements that are hampering the user experience, ultimately impacting our site’s engagement and conversion metrics.”
- Supply Chain Management
“In the last six months, reports indicate that our current logistics partner has had a 7% surge in delivery delays. This inconsistency not only threatens our promise of timely product deliveries to customers but also jeopardizes our brand’s reliability and trustworthiness.”
“An analysis of this year’s hospital data reveals a 5% uptick in patient readmission rates. Such a trend implies potential gaps in either our post-care instructions or the overall efficacy of our treatments, which demands immediate evaluation and rectification to ensure the best patient outcomes.”
Each of these statements identifies a specific issue and hints at the broader implications or consequences, setting the groundwork for solution development.
Templates to Get You Started
Navigating the process of writing a problem statement can feel daunting, right? Fear not! We’ve got you covered with some handy templates to give you a head start. Let’s break it down for you:
General Template
This is your foundational template, ideal for most scenarios. It succinctly captures the essence of the problem, offering a clear view of the challenge faced. Think of it as your jack-of-all-trades template, adaptable across sectors and subjects.
Here’s a template:
Despite [existing solutions/methods], there remains a significant challenge in [specific area/problem]. This [specific area/problem] impacts [group/sector], resulting in [consequences/outcomes].
Business Specific
If you’re in the business domain, this one’s for you. It not only pinpoints the core challenge but also emphasizes the potential impact on corporate goals, stakeholders, and profitability.
This template provides a structure that factors in growth objectives, competition, and market dynamics, ensuring your problem statement resonates with your business strategy.
In the context of [industry/business area], while [current practices or products] have been implemented, a prevailing issue remains: [specific business problem]. This directly influences [stakeholder group/business function], potentially leading to [business consequences, e.g., reduced revenue, unsatisfied customers].
Research-Focused
For all the academic enthusiasts and scholars out there, this is your guiding star. Crafted with research endeavors in mind, it accentuates the research question, relevance, and potential outcomes.
Whether you’re delving into a thesis or crafting a study, this template ensures your problem statement provides clarity and direction, setting the tone for your entire research journey.
In the academic study of [subject/discipline], prior research has delved into [previous studies or areas], yet a gap persists in understanding [specific research problem/phenomenon]. Addressing this gap is crucial, as it holds implications for [broader context or field relevance].
Product Development
Product managers and designers, take note! This template is all about the end-user. It helps you identify user pain points, market gaps, and potential design challenges.
By focusing on the user experience and market needs, it ensures that your product stands out and truly meets the expectations of your target audience.
In the world of [specific product category/industry], users frequently encounter the challenge of [specific user problem/pain point]. While [existing product/features] aim to solve it, there is still a marked need for [desired feature/solution], which would greatly enhance the user experience.
Public Policy
Tailored for the world of public policy and governance, this template zeroes in on societal and community challenges. It underscores the societal implications, potential solutions, and long-term impacts.
Whether addressing environmental issues, public health concerns, or educational challenges, this template guides policymakers in crafting statements that resonate with the larger community and have lasting impact.
In the realm of [specific policy area, e.g., environmental policy or healthcare], the community grapples with [specific societal problem]. Although [current policies or practices] are in place, they fall short in addressing [specific aspect of the problem], which has widespread implications for [affected group or broader society].
Frequently Asked Questions on These Problem Statement Examples
Navigating the realm of problem statements, you’ve probably stumbled across a few common questions. And trust me, you’re not alone! Many folks are eager to better understand these examples and templates, diving deeper into their practical applications.
Let’s tackle some of the frequently asked questions that might be swirling around in your mind:
What is the difference between a problem statement and an issue statement?
Great question! A problem statement pinpoints a specific challenge , outlining what needs improvement. It seeks to bridge the current situation with an ideal one. On the other hand, an issue statement highlights a topic for debate or discussion , not necessarily a problem.
In essence, a problem statement asks, “What needs fixing?” while an issue statement probes, “What are we discussing?” Each serves its unique purpose, so knowing the distinction can be quite handy.
What are the tools I can use in writing a problem statement?
There’s an array of tools available to assist you in crafting a sharp problem statement. One of the most notable advancements in recent times is the rise of AI writing tools . For instance, Jasper AI is a leading tool that not only aids in generating content but can help refine and focus your problem statements .
These AI-driven platforms can take your initial thoughts and transform them into coherent, focused statements, making the writing process smoother and more efficient . It’s like having a digital writing assistant by your side!
How often should I revisit and refine my problem statement?
It’s a good practice to revisit your problem statement at various stages of your project or research . As you gather more data or insights, you might find nuances or aspects of the problem that weren’t apparent initially.
Periodically reviewing ensures that you remain focused on addressing the most pressing and relevant aspects of the challenge. Think of it as a guiding star; as you navigate, you might need to adjust your course based on new information or changing circumstances.
Key Takeaways on These Problem Statement Examples
We dived deep into the world of problem statements, a critical tool that sets the direction for projects, research, and innovation.
At its core, a problem statement is a clear, concise description of an issue which prompts actionable solutions.
We explored its diverse applications, from business projects to policy framing, and even provided examples and templates to steer you right. Remember, it’s not just about identifying the issue; it’s about defining it in a way that invites effective solutions .
One crucial distinction we noted was between problem and issue statements: while both address challenges, the former is more solution-oriented, while the latter tends to be more observational.
And as with all things, there are best practices to adhere to: always keep it concise , specific, and actionable. With these insights in hand, you’re now better equipped to craft problem statements that pave the way for meaningful solutions.
Edgar Abong
Table of contents.
Expert level sales and marketing guides and unbiased software reviews.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
Copyright © 2024 influno. All rights reserved.
Last Updated on November 1, 2023 by Edgar Abong

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment Chapter 1 This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window
Jump to DSE Guide
Problem statement overview.
The dissertation problem needs to be very focused because everything else from the dissertation research logically flows from the problem. You may say that the problem statement is the very core of a dissertation research study. If the problem is too big or too vague, it will be difficult to scope out a purpose that is manageable for one person, given the time available to execute and finish the dissertation research study.
Through your research, your aim is to obtain information that helps address a problem so it can be resolved. Note that the researcher does not actually solve the problem themselves by conducting research but provides new knowledge that can be used toward a resolution. Typically, the problem is solved (or partially solved) by practitioners in the field, using input from researchers.
Given the above, the problem statement should do three things :
- Specify and describe the problem (with appropriate citations)
- Explain the consequences of NOT solving the problem
- Explain the knowledge needed to solve the problem (i.e., what is currently unknown about the problem and its resolution – also referred to as a gap )
What is a problem?
The world is full of problems! Not all problems make good dissertation research problems, however, because they are either too big, complex, or risky for doctorate candidates to solve. A proper research problem can be defined as a specific, evidence-based, real-life issue faced by certain people or organizations that have significant negative implications to the involved parties.
Example of a proper, specific, evidence-based, real-life dissertation research problem:
“Only 6% of CEOs in Fortune 500 companies are women” (Center for Leadership Studies, 2019).
Specific refers to the scope of the problem, which should be sufficiently manageable and focused to address with dissertation research. For example, the problem “terrorism kills thousands of people each year” is probably not specific enough in terms of who gets killed by which terrorists, to work for a doctorate candidate; or “Social media use among call-center employees may be problematic because it could reduce productivity,” which contains speculations about the magnitude of the problem and the possible negative effects.
Evidence-based here means that the problem is well-documented by recent research findings and/or statistics from credible sources. Anecdotal evidence does not qualify in this regard. Quantitative evidence is generally preferred over qualitative ditto when establishing a problem because quantitative evidence (from a credible source) usually reflects generalizable facts, whereas qualitative evidence in the form of research conclusions tend to only apply to the study sample and may not be generalizable to a larger population. Example of a problem that isn’t evidence-based: “Based on the researcher’s experience, the problem is that people don’t accept female leaders;” which is an opinion-based statement based on personal (anecdotal) experience.
Real-life means that a problem exists regardless of whether research is conducted or not. This means that “lack of knowledge” or “lack of research” cannot be used as the problem for a dissertation study because it’s an academic issue or a gap; and not a real-life problem experienced by people or organizations. Example of a problem that doesn’t exist in real life: “There is not enough research on the reasons why people distrust minority healthcare workers.” This type of statement also reveals the assumption that people actually do mistrust minority healthcare workers; something that needs to be supported by actual, credible evidence to potentially work as an underlying research problem.
What are consequences?
Consequences are negative implications experienced by a group of people or organizations, as a result of the problem. The negative effects should be of a certain magnitude to warrant research. For example, if fewer than 1% of the stakeholders experience a negative consequence of a problem and that consequence only constitutes a minor inconvenience, research is probably not warranted. Negative consequences that can be measured weigh stronger than those that cannot be put on some kind of scale.
In the example above, a significant negative consequence is that women face much larger barriers than men when attempting to get promoted to executive jobs; or are 94% less likely than men to get to that level in Corporate America.
What is a gap?
To establish a complete basis for a dissertation research study, the problem has to be accompanied by a gap . A gap is missing knowledge or insights about a particular issue that contributes to the persistence of the problem. We use gaps to “situate” new research in the existing literature by adding to the knowledge base in the business research field, in a specific manner (determined by the purpose of the research). Identifying gaps requires you to review the literature in a thorough fashion, to establish a complete understanding of what is known and what isn’t known about a certain problem. In the example from above about the underrepresentation of female CEOs, a gap may be that male-dominated boards have not been studied extensively in terms of their CEO hiring decisions, which might then warrant a study of such boards, to uncover implicit biases and discriminatory practices against female candidates.
How to Write a Problem Statement
How to write a problem statement.
- Here is one way to construct a problem section (keep in mind you have a 250-300 word limit, but you can write first and edit later):
It is helpful to begin the problem statement with a sentence : “The problem to be addressed through this study is… ” Then, fill out the rest of the paragraph with elaboration of that specific problem, making sure to “document” it, as NU reviewers will look for research-based evidence that it is indeed a problem (emphasis also on timeliness of the problem, supported by citations within the last 5 years).
Next, write a paragraph explaining the consequences of NOT solving the problem. Who will be affected? How will they be affected? How important is it to fix the problem? Again, NU reviewers will want to see research-based citations and statistics that indicate the negative implications are significant.
In the final paragraph, you will explain what information (research) is needed in order to fix the problem. This paragraph shows that the problem is worthy of doctoral-level research. What isn’t known about the problem? Ie, what is the gap? Presumably, if your problem and purpose are aligned, your research will try to close or minimize this gap by investigating the problem. Have other researchers investigated the issue? What has their research left unanswered?
- Another way to tackle the Statement of the Problem:
The Statement of the Problem section is a very clear, concise identification of the problem. It must stay within the template guidelines of 250-300 words but more importantly, must contain four elements as outlined below. A dissertation worthy problem should be able to address all of the following points:
-->identification of the problem itself--what is "going wrong" (Ellis & Levy, 2008)
-->who is affected by the problem
-->the consequences that will result from a continuation of the problem
-->a brief discussion of 1) at least 3 authors’ research related to the problem; and 2) their stated suggestion/recommendation for further research related to the problem
Use the following to work on the Statement of the Problem by first outlining the section as follows:
1. One clear, concise statement that tells the reader what is not working, what is “going wrong”. Be specific and support it with current studies.
2. Tell who is affected by the problem identified in #1.
3. Briefly tell what will happen if the problem isn’t addressed.
4. Find at least 3 current studies and write a sentence or two for each study that
i. briefly discusses the author(s)’ work, what they studied, and
ii. state their recommendation for further research about the problem
- Finally, you can follow this simple 3-part outline when writing the statement of the problem section:
Your problem statement is a short (250-300 words), 3 paragraph section, in which you
- Explain context and state problem (“the problem is XYZ”), supported by statistics and/or recent research findings
- Explain the negative consequences of the problem to stakeholders, supported by statistics and/or recent research findings
- Explain the gap in the literature.
Example of a problem statement that follows the 3-part outline (295 words):
The problem to be addressed by this study is the decline of employee well-being for followers of novice mid-level managers and the corresponding rise in employee turnover faced by business leaders across the financial services industry (Oh et al., 2014). Low levels of employee well-being are toxic for morale and result in expensive turnover costs, dysfunctional work environments, anemic corporate cultures, and poor customer service (Compdata, 2018; Oh et al., 2014). According to Ufer (2017), the financial services industry suffers from one of the highest turnover rates among millennial-aged employees in all industries in the developed world, at 18.6% annually. Starkman (2015) reported that 50% of those surveyed in financial services were not satisfied with a single one of the four key workplace aspects: job, firm, pay or career path.
Low levels of employee well-being interrupt a financial services’ company’s ability to deliver outstanding customer service in a world increasingly dependent on that commodity (Wladawsky-Berger, 2018).Mid-level managers play an essential role in support of the success of many of top businesses today (Anicich & Hirsh, 2017).
The current body of literature does not adequately address the well-being issue in the financial services industry from the follower’s perspective (Uhl-Bien, Riggio, Lowe, & Carsten, 2014). Strategic direction flows top-down from senior executives and passes through mid-level leadership to individual contributors at more junior grades. The mid-level managers’ teams are tasked with the achievement of core tasks and the managers themselves are expected to maintain the workforce’s morale, motivation and welfare (Anicich & Hirsh, 2017). Unless industry leaders better understand the phenomenon of employee well-being from the follower perspective and its role in positioning employees to provide a premium client experience, they may be handicapped from preserving their most significant principal market differentiator: customer service (Wladawsky-Berger, 2018).
Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Next: Purpose Statement >>
- Last Updated: May 3, 2024 8:12 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools

- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Problem Statement in Research
What is a Research Problem Statement?
A research problem statement is a concise statement describing the problem or issue addressed by the research study. The research problem should be composed in a way that both experts and non-experts in the field can understand.
Every research paper describes the investigation of a problem: by adding knowledge to the existing literature, revisiting known observations, or finding concrete solutions. What contribution your publication makes to your field or the scientific community at large depends on whether your research is “basic” (i.e., mainly interested in providing further knowledge that researchers can later apply to specific problems) or “applied” (i.e., developing new techniques, processes, and products).
In any case, a research proposal or research paper must clearly identify and describe the “problem” that is being investigated, so that the reader understands where the research comes from, why the study is relevant, if the applied methods are appropriate, and if the presented results are valid and answer the stated questions. This is known as the “statement of the problem.”
Table of Contents:
- What is a Research Problem?
How to Write a Problem Statement in a Research Paper
- Statement of the Problem Example
- Where Does the Problem Statement Go in Your Paper?
Consider Using Professional Editing Services
Understanding how to write a research problem.
Your research problem defines the gap in existing knowledge you want to address (e.g., global warming causes), an issue with a certain process (e.g., voter registration) or practices (e.g., patient treatment) that is known and well documented and needs a solution, or some surprising phenomena or earlier findings that point to the need for further investigation. Your approach can be theoretical or practical, and the specific type of problem you choose to address depends on the type of research you want to do.
In any case, your paper should not repeat what other studies have already said. It also should not ask a question that is too broad in scope to be answered within your study, nor should it be so vague that your reader cannot grasp your motivation or focus. To avoid such problems, you need to clearly define your research question, put it into context, and emphasize its significance for your field of research, the wider research community, or even the general public.
When including your statement of the research problem, several key factors must be considered in order to make a statement that is clear, concise, relevant, and convincing to readers. Think about the following elements not as “steps” to writing your problem statement, but as necessary conditions on which your statement can be firmly grounded and stand out.
Provide context for your study
Putting your research problem in context means providing the reader with the background information they need to understand why you want to study or solve this particular problem and why it is relevant. If there have been earlier attempts at solving the problem or solutions that are available but seem imperfect and need improvement, include that information here.
If you are doing applied research, this part of the problem statement (or “research statement”) should tell the reader where a certain problem arises and who is affected by it. In basic or theoretical research, you make a review of relevant literature on the topic that forms the basis for the current work and tells the reader where your study fits in and what gap in existing knowledge you are addressing.
Establish the relevance of this research
The problem statement also needs to clearly state why the current research matters, or why future work matters if you are writing a research proposal. Ask yourself (and tell your readers) what will happen if the problem continues and who will feel the consequences the most. If the solution you search for or propose in your study has wider relevance outside the context of the subjects you have studied, then this also needs to be included here. In basic research, the advancement of knowledge does not always have clear practical consequences—but you should clearly explain to the reader how the insights your study offers fit into the bigger picture, and what potential future research they could inspire.
Define specific aims and Objectives
Now that the reader knows the context of your research and why it matters, briefly introduce the design and the methods you used or are planning to use. While describing these, you should also formulate your precise aims more clearly, and thereby bring every element in your paper together so that the reader can judge for themselves if they (a) understand the rationale behind your study and (b) are convinced by your approach.
This last part could maybe be considered the actual “statement of the problem” of your study, but you need to prepare the reader by providing all the necessary details before you state it explicitly. If the background literature you cite is too broad and the problem you introduced earlier seems a bit vague, then the reader will have trouble understanding how you came up with the specific experiments you suddenly describe here. Make sure your readers can follow the logical structure of your presentation and that no important details are left out.
Research Problem Statement Example
The following is a sample statement of the problem for a practical research study on the challenges of online learning. Note that your statement might be much longer (especially the context section where you need to explain the background of the study) and that you will need to provide sources for all the claims you make and the earlier literature you cite. You will also not include the headers “context”, “relevance” and “aims and objectives” but simply present these parts as different paragraphs. But if your problem statement follows this structure, you should have no problem convincing the reader of the significance of your work.
Providing context: Since the beginning of the Covid pandemic, most educational institutions around the world have transitioned to a fully online study model, at least during peak times of infections and social distancing measures. This transition has not been easy and even two years into the pandemic, problems with online teaching and studying persist (reference needed) . While the increasing gap between those with access to technology and equipment and those without access has been determined to be one of the main challenges (reference needed) , others claim that online learning offers more opportunities for many students by breaking down barriers of location and distance (reference needed) .
Establishing relevance: Since teachers and students cannot wait for circumstances to go back to normal, the measures that schools and universities have implemented during the last two years, their advantages and disadvantages, and the impact of those measures on students’ progress, satisfaction, and well-being need to be understood so that improvements can be made and demographics that have been left behind can receive the support they need as soon as possible.
Defining aims and objectives: To identify what changes in the learning environment were considered the most challenging and how those changes relate to a variety of student outcome measures, we conducted surveys and interviews among teachers and students at ten institutions of higher education in four different major cities, two in the US (New York and Chicago), one in South Korea (Seoul), and one in the UK (London). Responses were analyzed with a focus on different student demographics and how they might have been affected differently by the current situation.
Where Does the Problem Statement Go in Your Paper?
If you write a statement of the problem for a research proposal, then you could include it as a separate section at the very beginning of the main text (unless you are given a specific different structure or different headings, however, then you will have to adapt to that). If your problem statement is part of a research paper manuscript for publication in an academic journal, then it more or less constitutes your introduction section , with the context/background being the literature review that you need to provide here.
If you write the introduction section after the other parts of your paper, then make sure that the specific research question and approach you describe here are in line with the information provided in the research paper abstract , and that all questions you raise here are answered at the end of the discussion section —as always, consistency is key. Knowing where to put the research question can depend on several important contextual factors.
Receive instant editing with Wordvice.AI, our automated grammar checker . Then hand over your manuscript or paper to a professional English editing service for paper editing , thesis editing , or other academic editing services .
And if you need advice on how to write the other parts of your research paper , on how to make a research paper outline if you are struggling with putting everything you did together, or on how to come up with a good research question in case you are not even sure where to start, then head over to the Wordvice academic resources website where we have a lot more articles and videos for you.
How to Write a Statement of the Problem for Your Research Proposal
Defining your research problem is essential when conducting an experiment. In this article, you will learn how to write a statement of the problem for your research proposal. Learn about the characteristics of a good statement of the problem and examples of research questions.
Updated on May 17, 2022

You are a great researcher. You are full of ideas and questions as to where to go next with your work. You would not be in this position if you were not good at coming up with interesting questions within your area.
One problem, though, is knowing where to spend your time, energy, and money. Which ideas, questions, and problems are worthwhile?
You need to be able to define a good research problem. A research problem addresses an existing gap in knowledge in your field and leads to further investigations by you and other researchers. Inspiring others with your research problem will lead to citations, enhancing your and your institution's impact.
In order to write a clear and useful problem statement, you need to describe a question and its consequences.
One key way to assess the ‘usefulness' of your research ideas is to learn how to express them as clear problems.
In this article, we will talk about how to write a statement of the problem for your next research proposal. This is important not just for assessing the ‘usefulness' of research ideas, but also for formulating a grant application or proposal. We'll talk about how to explain your research ideas to others in the form of a problem statement in your proposal.
What is a statement of the problem in research?
All research projects should start with a clear problem statement. A problem statement is a formulation of an issue which is usually a ‘gap' within your area. A research gap is an unanswered question, an issue, controversy, or untested hypothesis that has not yet been addressed.
The trick with research problems is working out whether they are actually worth investing the time, energy, and money to figure out. This comes with experience, or you could just read on!
Since a clear problem statement is going to form the basis of your next research project, the question is: How can I write one?
How is this done? The first step is to become familiar with the basic elements of a problem statement in effective research.
Characteristics of a problem statement
A research problem statement has two key attributes:
- The problem must be challenging and original, but also potentially achievable by your team.
- The problem must not be incremental. In other words, don't try to address a small change or advance on an existing study that leads to no new scientific insight. This could be damaging to your and your team's reputation, and will likely not lead to a meaningful publication.
Developing a ‘good' research problem statement, therefore, involves systematic planning and setting time-based, realistic objectives. Your problem has to be achievable.
You'll also need to apply feasible research methods based on an approach that best suits the research question. Your methods have to make sense. They must be usable. In other words, you must be able to acquire statistically sufficient and relevant data that is reproducible.
Finally, the problem you define means you'll need to train team members in this particular research area and methods.
Writing a statement of the problem
Stating a research problem is done by defining it within the general area of your research. This depends on your previous work and experience. It may be an area you want to move into or a topic related to what you have already worked on as a researcher. Examples could include a question in astrophysics within physics, robotics within engineering, nutrition within medicine, or marine biology within ocean and Earth science.
Once you've determined your overall area (and you'll know this already of course), it's time to drill down, decide, and define a research problem within that field.
First , your statement should identify a problem that needs to be addressed within your selected sub-area.
This will almost certainly require literature work, but the idea may arise from:
- Discussions you've had with colleagues;
- Discussions at a conference;
- A paper you've read.
Second , your problem statement should be a “good research problem.” This will require further investigation and reading as you consider “what has been done?” and “what needs to be done?”
Third , search for more information, perhaps by:
- Locating relevant books, papers and other materials;
- Evaluating the quality and authority of the information collected;
- Maintaining a regular literature review throughout the project;
- Making regular notes on background material;
- Deciding how this literature search will be carried out within the research group;
- Deciding how information gained will be disseminated to the group (e.g., via each researcher carrying out a regular literature review in their sub-area and information disseminated at group meetings or via email at regular intervals).
This process may well change or modify how your research problem is stated or formulated.
Once your research problem has been identified, research questions within the problem need to be specified.
How long should your statement of the problem be?
Not too long. One page is more than enough for a clear and effective problem statement.
Research questions within your problem
The first stage of writing your research problem statement involves formulating your questions in a meaningful way. In the context of important questions, we are looking for things that many readers across different disciplines find to be interesting. But at the same time, set your question within your field.
Thus, once a research problem has been established, several questions can be written down. These questions should specify exactly what needs to be determined to address the problem.
These questions should also be specific enough that they can be answered using appropriate available research methods - or methods that could be made available to the research group (e.g. by buying or borrowing equipment).
These questions should require complex in-depth investigation, analysis, and argument. They should not be simple enough that they can be answered easily with well-established facts or yes/no answers.
All research questions should be focused, specific, appropriately complex, and relevant to the overall aims of the project.
Examples of questions and next steps
- How do government regulations prevent companies from polluting water systems?
- What factors have influenced population growth in the fastest growing countries?
- How can a bespoke thermal desorption unit be designed and built for use in detection of trace particulate matter in a polluted environment (e.g., a busy city street)?
- What methods and procedures can be used to understand, and hence control, fundamental chemical processes that occur in flames?
- How can measurement protocols used in mass spectrometry in a university research laboratory be developed and standardized to enable direct comparison with related measurements in a government laboratory?
Once the problem and questions have been identified, the resources required to carry out the research will need to be assessed. This will involve:
- Identifying the equipment needed. Find out what is available and what needs to be purchased.
- Assessing which consumables (e.g., chemicals) are needed for the project, and determining if they can be obtained on a regular basis (i.e., in the right quantities at the appropriate times).
- Identifying the software, data-analyses and other computer support needed. Assess what needs to be purchased.
- Assessing what laboratory and office space is needed. And if more is required, discuss this with the relevant laboratory manager.
- Identifying what support for travel is needed for the group, as well as what resources are required for the group to attend relevant conferences and training of group personnel.
Final thoughts
Defining and writing a clear statement of a problem as the basis of a project is the first - and most important - step in any research. The tips and ideas in this article will help you clearly identify the purpose of the research you are developing.
A clear research problem statement will likely form the skeleton of the Introduction of your final article. If you are able to clearly direct your reader (the most important person in the publishing process) to an important and interesting question, they will likely stay engaged, and use and cite your article in the future.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
- How to Write a Problem Statement for your Research

Every research starts with identifying a problem which is usually an existing gap in your field of study. Once you do this, the next step is to craft a statement of the problem that captures this issue and how you plan to resolve it. A statement of problem forms the basis of every systematic investigation.
Seeing as a problem statement forms the core of your research, it makes sense to know how to write an effective one. So how do you go about this? First, you need to get acquainted with the features of a good problem statement plus its elements and structure.
Use this guide to know how to write an effective statement of the problem for your systematic investigation.
What is the Statement of the Problem in Research?
A statement of problem refers to the critical issue that your research seeks to address. In other words, it captures the existing knowledge gap that your study aims to bridge using reliable results or outcomes. A problem statement can be as little as a few sentences or go all the way to several paragraphs—what matters is it communicates the central focus of your study.
As your study bridges this gap, it also leaves room for future investigations. The implication is that your problem statement should not be too broad; instead, it should address one specific issue and contribute to the knowledge pool for further research.
Use for Free: Research Form Templates
What are the Features of a Good Problem Statement?
A good problem statement captures the core purpose of your study in simple, clear, and direct terms. Some other tell-tale signs of a well-written research statement of problem include:
- A good problem statement is concrete and concise. It doesn’t capture ideas vaguely or ambiguously.
- It allows you to contextualize the research problem.
- A good problem statement helps you to set the aims and objectives of your systematic investigation.
- It justifies your research and draws attention to the study’s significance.
Why is a Problem Statement Important in Research Writing?
Writing a good problem statement serves both the researcher and the readers. For the researcher, the problem statement helps you visualize the scope of your project and outline it accordingly. Also, it allows you to map out specific aims and objectives for your study.
On the flip side, the problem statement helps the reader identify the core reason for your research and see how your work fits into the existing body of knowledge. It helps them get on the same page as you regarding the importance and significance of your systematic investigation.
If you require funding for your research, a problem statement can help potential financiers to see why investing in your project is the right move to make. It gives them an overview of the existing problem, your solution, and the impact of your solution on the field of study.
Elements and Structure of a Problem Statement
In its most basic form, a problem statement comprises three(3) elements which are:
- The research problem
- The claim or working thesis
- The significance of the study
In other words, it tells the reader what you’re trying to solve, how you plan to solve it, and why you want to solve it.
1. The Research Problem
Your research problem is the reason for your systematic investigation. It is the gap you identified and planned to fill based on the results of your study. You can also think of this as the primary research question.
A few questions you should ask yourself here include:
- Is it clear what’s being described in this problem statement?
- Do I understand the main problem being described here?
- Do I have a good grasp of what the main issue is here?
2. The Claim or Working Thesis
Your working thesis is the first attempt at asserting your position, and it spells out your stance on the matter at a specific point in time. It’s called a “working” thesis because it is subject to change as your study progresses. In your working thesis, you have the chance to justify your position by providing primary and secondary claims that support your position.

3. The Significance of the Study
This is the point where you communicate the value of your research and show readers why it is necessary in the first place. Here, you can discuss the impact of your work and its relevance to your field of study. Don’t forget to highlight the contributions of your work to existing knowledge and how others will benefit from it.
Read: Research Report: Definition, Types + [Writing Guide]
What is the Difference Between a Thesis Statement and a Problem Statement?
A problem statement focuses on the specific issue you’ve identified and hope to resolve with your research. It comprises the research problem, claim, or working statement and the significance of your research. On the other hand, a thesis statement makes a specific claim or assertion open for debate.
For example, the statement “writing is more of a science than an art” is an excellent example of a thesis statement because it proposes an idea that may be true or false. Once you establish the thesis statement for your research, you are expected to provide evidence and build a strong argument that supports this claim.
What are the Steps for Writing a Problem Statement?
- Define Your Research Context
- State Why The Problem Matters
- State the Financial Cost
- Back Up Your Claims
- Propose A Solution
- Conclude By Summarizing the Problem and Solution
1. Define Your Research Context
The first thing you need to do is build a solid context that makes it easier for readers to understand the problem. A hack for this is to describe an ideal world where the problem doesn’t exist. In other words, help your readers to visualize how different things would be if they didn’t have to deal with this problem in the first place.
For example, if you’re researching the rise in the number of train accidents in London, start by describing how the process would function if the current problem didn’t exist. When you’ve done this, you can refer to the research problem at the end of your explanation.
2. State Why the Problem Matters
You should let readers in on why the problem matters and why you must address it at this point. In other words, answer the question, “why is it important that we fix this particular problem?” What difference would it make?
Your job here is to show the reader why your research problem is the biggest elephant in the room. You may also consider including what attempts have already been made to solve the problem and why they didn’t work out.
3. State the Financial Cost
If there’s a financial implication of not fixing the problem, then it’s a good idea to state it here. This is more useful if you’re pitching for funding for your research.
4. Back Up Your Claims
It’s not enough to say that the problem has some negative impact on other people or your organization; you must back up all of these claims with well-researched data. This is the point where you pull up information from relevant secondary data sources and reference them in your work.
5. Proffer a Solution
Now that we know the problem, the next question is, “what can be done about it”? To answer this, you need to propose a practical solution to the research problem. Take time to demonstrate why this is the most pragmatic solution and why it will work. More importantly, focus on the impact of your solution and hint at its benefits.
6. Conclude By Summarizing the Problem and Solution
Your conclusion should consist of the problem, why it needs to be fixed, and a summarized argument of why your solution is the best answer to the problem.
Sample Problem Statement
Problem : The use of hard drugs amongst teenagers in the District of Columbia has increased significantly over the past decade.
Background : According to the Drug Abuse Statistics Organization data, 50% of teenagers have misused a drug at least once. Teenagers in the District of Columbia are 11.94% more likely to have used drugs in the last month than the average American teen. Existing data shows that this is a significant problem but fails to address the root causes of rising teenage drug abuse in the state. Therefore, more research is required to identify why teenagers in Colombia abuse drugs and proffer solutions to this menace.
Relevance : Young people who abuse drugs expose themselves to many risks, including life-threatening conditions and mental health-related problems. Drug abuse can impact the brain’s ability to function in the short term and prevent proper growth and development in the long term. Data shows that teenagers who use hard drugs are more likely to be disillusioned. Addressing this problem will give concerned parties the much-needed insights to help them curtail drug abuse.
Objectives : This research aims to identify the root causes of teenage drug abuse and map out actionable solutions to address this.
Mistakes to Avoid when Writing Problem Statements
A good problem statement sets the tone for the rest of your dissertation, so you want to get it right. That said, here are some things you should have at the back of your mind as you craft a problem statement for your research paper.
1. Make sure your problem statement is straight to the point. Every sentence should reinforce the importance of your study.
2. Narrow the scope of your problem statement.
3. Avoid unnecessary jargon and highly technical language.
4. Build a logical argument that will convince the reader
5. Emphasize the “why” of the problem
FAQ About Writing a Statement of the Problem
How do you identify a research problem?
The best way to identify a research problem is to read through existing studies to discover any gaps in knowledge. You can also discover research problems by observing your environment and identifying any contradictions that exist among perspectives.
Conclusion
Whether you’re seeking funding for your research or approval from your professor, you need to write a well-defined statement of the problem. A problem statement allows you to pitch the core idea of your study and show others why it is worth being addressed. It should draw attention to the core idea of your research, and convince others to invest in your systematic investigation.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- abstract in research papers
- Applied research methods
- problem statements
- research context
- research problems
- research report
- busayo.longe

You may also like:
Research Questions: Definitions, Types + [Examples]
A comprehensive guide on the definition of research questions, types, importance, good and bad research question examples

21 Chrome Extensions for Academic Researchers in 2022
In this article, we will discuss a number of chrome extensions you can use to make your research process even seamless
15 Reasons to Choose Quantitative over Qualitative Research
This guide tells you everything you need to know about qualitative and quantitative research, it differences,types, when to use it, how...
What is Applied Research? + [Types, Examples & Method]
Simple guide on applied research; its types, examples, characteristics, methods, and advantages
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
- Privacy Policy

Home » Problem Statement – Writing Guide, Examples and Types
Problem Statement – Writing Guide, Examples and Types
Table of Contents

Problem Statement
Definition:
Problem statement is a clear, concise, and well-defined statement that outlines the issue or challenge that needs to be addressed. It is a crucial element in any project or research as it provides a clear understanding of the problem, its context, and its potential impact.
Types of Problem Statements
There are various types of problem statements, and the type of problem statement used depends on the context and purpose of the project or research. Some common types of problem statements are:
Business Problem Statement
Business Problem Statement identifies a problem or challenge within an organization that needs to be solved. It typically includes the impact of the problem on the organization and its stakeholders, such as customers, employees, or shareholders.
Research Problem Statement
Research Problem Statement outlines the research question or problem that the study aims to address. It describes the research objectives, the significance of the research, and the potential impact of the research findings.
Design Problem Statement
Design Problem Statement defines the problem or challenge that a design project aims to solve. It includes the user’s needs, the design constraints, and the desired outcomes of the design project.
Social Problem Statement
Social Problem Statement describes a problem or challenge in society that needs to be addressed. It typically includes the social, economic, or political impact of the problem and its effect on individuals or communities.
Technical Problem Statement
Technical Problem Statement defines a problem or challenge related to technology or engineering. It includes the technical requirements, constraints, and potential solutions to the problem.
Components of Problem Statement
The components of a problem statement may vary depending on the context and purpose of the project or research, but some common components include:
- Problem description : This component provides a clear and concise description of the problem, its context, and its impact. It should explain what the problem is, who is affected by it, and why it needs to be addressed.
- Background information : This component provides context for the problem by describing the current state of knowledge or practice related to the problem. It may include a review of relevant literature, data, or other sources of information.
- Objectives : This component outlines the specific objectives that the project or research aims to achieve. It should explain what the project or research team hopes to accomplish by addressing the problem.
- Scope : This component defines the boundaries of the problem by specifying what is included and excluded from the problem statement. It should clarify the limits of the project or research and ensure that the team remains focused on the core problem.
- Methodology : This component outlines the approach or methodology that the project or research team will use to address the problem. It may include details about data collection, analysis, or other methods used to achieve the objectives.
- Expected outcomes : This component describes the potential impact or outcomes that the project or research aims to achieve. It should explain how the solution or findings will address the problem and benefit the stakeholders.
How to write Problem Statement
Here are some general steps to follow when writing a problem statement:
- Identify the problem : Clearly identify the problem that needs to be addressed. Consider the context, stakeholders, and potential consequences of the problem.
- Research the problem: Conduct research to gather data and information about the problem. This may involve reviewing literature, analyzing data, or consulting with experts.
- Define the problem: Define the problem clearly and concisely, using specific language and avoiding vague or ambiguous terms. Be sure to include the impact of the problem and the context in which it occurs.
- State the objectives : Clearly state the objectives that the project or research aims to achieve. This should be specific and measurable, with clear outcomes that can be evaluated.
- Identify the scope: Identify the boundaries of the problem, including what is included and excluded from the problem statement. This helps to ensure that the team remains focused on the core problem.
- Outline the methodology : Outline the approach or methodology that the project or research team will use to address the problem. This should be based on research and best practices, and should be feasible and realistic.
- Describe the expected outcomes : Describe the potential impact or outcomes that the project or research aims to achieve. Be specific about how the solution or findings will address the problem and benefit the stakeholders.
- Revise and refine : Review the problem statement and revise it as needed to ensure clarity, accuracy, and completeness.
Applications of Problem Statement
Here are some of the applications of problem statements:
- Research : In academic research, problem statements are used to clearly define the research problem, identify the research question, and justify the need for the study. A well-crafted problem statement is essential for the success of any research project.
- Project management: In project management, problem statements are used to identify the issues or challenges that a project team needs to address. Problem statements help project managers to define project scope, set project goals, and develop project plans.
- Business strategy: In business strategy, problem statements are used to identify business challenges and opportunities. Problem statements help businesses to define their strategic objectives, develop action plans, and allocate resources.
- Product development : In product development, problem statements are used to identify customer needs and develop new products that address those needs. Problem statements help product developers to define product requirements, develop product features, and test product prototypes.
- Policy-making: In public policy-making, problem statements are used to identify social, economic, and environmental issues that require government intervention. Problem statements help policymakers to define policy objectives, develop policy options, and evaluate policy outcomes.
Examples of Problem Statements
Examples of Problem Statements are as follows:
- High student-to-teacher ratios are leading to decreased individualized attention and lower academic achievement.
- Limited funding for extracurricular activities is limiting opportunities for student development and engagement.
- The lack of diversity and inclusion in curriculum is limiting cultural understanding and perpetuating inequalities.
- The need for continuous professional development for teachers is crucial to improving teaching quality and student outcomes.
- Unequal access to education due to socio-economic status, geographical location, or other factors is contributing to disparities in academic achievement.
- The shortage of healthcare professionals is leading to increased patient wait times and decreased quality of care.
- Limited access to mental health services is contributing to the high prevalence of mental health issues and suicides.
- The over-prescription of opioids is contributing to the current opioid epidemic and increasing rates of addiction and overdose.
- Limited access to affordable and nutritious food is leading to poor nutrition and increased rates of chronic diseases.
- The lack of standardized electronic health record systems is limiting coordination of care and leading to medical errors.
Environmental Science
- Pollution from industrial and agricultural practices is contributing to climate change and increased health risks.
- The overexploitation of natural resources is leading to decreased biodiversity and ecological imbalance.
- Limited access to clean water is leading to health issues and affecting agriculture and economic development.
- The destruction of natural habitats is leading to the extinction of many species and disrupting ecosystems.
- Climate change is leading to more frequent and severe natural disasters, causing significant damage to infrastructure and displacement of populations.
Engineering
- The inadequate design and maintenance of bridges and roads is leading to increased accidents and fatalities.
- The lack of reliable and sustainable energy sources is contributing to environmental degradation and limiting economic growth.
- The lack of cybersecurity measures in critical infrastructure is making it vulnerable to cyber attacks and compromising public safety.
- The lack of efficient waste management systems is contributing to pollution and environmental degradation.
- The need for developing technologies that are environmentally friendly and sustainable is crucial to addressing climate change.
Social Work
- The lack of resources for mental health and social services is contributing to homelessness and the need for emergency assistance.
- The high prevalence of child abuse and neglect is leading to long-term physical and emotional harm to children.
- The lack of affordable and accessible childcare is limiting the opportunities for working parents, especially mothers.
- The stigmatization of mental health issues is limiting access to mental health services and perpetuating discrimination.
- The limited access to education, employment, and housing opportunities is contributing to poverty and social inequality.
- The increasing use of ad-blocking software is limiting the effectiveness of traditional digital advertising.
- The lack of transparency in digital advertising is leading to ad fraud and decreased trust in online marketing.
- The need to adapt marketing strategies to changing consumer behaviors and preferences is crucial to reaching target audiences effectively.
- The high competition in the marketplace is making it challenging for small businesses to compete with larger corporations.
- The need to balance marketing goals with ethical considerations is crucial to maintaining consumer trust and avoiding negative publicity.
- The high prevalence of anxiety and depression is leading to decreased productivity and increased healthcare costs.
- The limited access to mental health services in certain geographic areas is limiting access to care and contributing to disparities in mental health outcomes.
- The need for effective prevention and intervention programs for substance abuse and addiction is crucial to reducing rates of addiction and overdose.
- The lack of awareness and understanding of mental health issues is perpetuating stigma and limiting access to care.
- The need for culturally sensitive mental health services that are tailored to the needs of diverse populations is crucial to improving mental health outcomes.
Purpose of Problem Statement
The purpose of a problem statement is to clearly and concisely describe a specific problem or issue that needs to be addressed. It serves as a clear and succinct explanation of the problem, its context, and its importance, providing the necessary information to understand why the problem is worth solving. A well-crafted problem statement also helps to define the scope of the problem, which in turn helps to guide the research or problem-solving process. In essence, a problem statement sets the stage for identifying potential solutions and determining the best approach to solve the problem.
Characteristics of Problem Statement
The characteristics of a good problem statement include:
- Clear and concise : A problem statement should be written in clear and concise language, free of technical jargon, and easily understandable to the intended audience.
- Specific : The statement should clearly define the problem and its scope. It should identify the who, what, where, when, and why of the problem.
- Measurable : A problem statement should be measurable in some way, whether through quantitative or qualitative methods. This allows for objective assessment of progress towards solving the problem.
- Relevant : The problem statement should be relevant to the context in which it is presented. It should relate to the needs and concerns of stakeholders and the broader community.
- Feasible : The problem statement should be realistic and achievable, given the available resources and constraints.
- Innovative: A good problem statement should inspire creative and innovative solutions.
- Actionable : The problem statement should lead to actionable steps that can be taken to address the problem. It should provide a roadmap for moving forward.
Advantages of Problem Statement
Advantages of Problem Statement are as follows:
- Focus : A problem statement helps to clearly define the problem at hand and provides focus to the problem-solving process. It helps to avoid wasting time and resources on issues that are not relevant.
- Alignment : A well-written problem statement ensures that everyone involved in the problem-solving process is on the same page and understands the issue at hand. This alignment helps to ensure that efforts are focused in the right direction and that everyone is working towards the same goal.
- Clarity : A problem statement provides clarity about the nature of the problem and its impact. This clarity helps to facilitate communication and decision-making, making it easier to develop effective solutions.
- Innovation : A well-crafted problem statement can inspire creativity and encourage innovative thinking. By clearly defining the problem, it can help to identify new approaches and solutions that may not have been considered before.
- Measurability : A problem statement that is clear and specific can be used to measure progress and success. It helps to ensure that efforts are focused on addressing the root cause of the problem and that progress towards a solution can be tracked and evaluated.
Limitations of Problem Statement
While problem statements have many advantages, they also have some limitations, such as:
- Limited Scope: A problem statement is usually focused on a specific issue or challenge. As a result, it may not capture the full complexity of a larger problem, which can limit the effectiveness of the solutions developed.
- Lack of Detail : In some cases, problem statements may be too broad or lack sufficient detail, which can make it difficult to develop effective solutions. It’s important to ensure that the problem statement is specific enough to guide the problem-solving process.
- Bias : The way in which a problem statement is written can sometimes reflect the biases or assumptions of the person or group writing it. This can lead to a narrow or incomplete understanding of the problem and limit the effectiveness of the solutions developed.
- Inflexibility : A problem statement may be too rigid or inflexible, which can limit the exploration of alternative solutions. It’s important to keep an open mind and be willing to adapt the problem statement as new information or perspectives emerge.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
Free Problem Statement Templates: All Formats
By Kate Eby | March 4, 2024
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
We've collected the top problem statement templates to help you identify and articulate challenges clearly and concisely in any business context. Download any of these free templates that align with your needs, and customize it for your organization.
On this page, you’ll find a customer problem statement template , a problem and solution slide template , a problem statement document template , and more. You’ll also find information on different types of problem statement templates and related problem-solving tools .
5 Ws Problem Statement Template
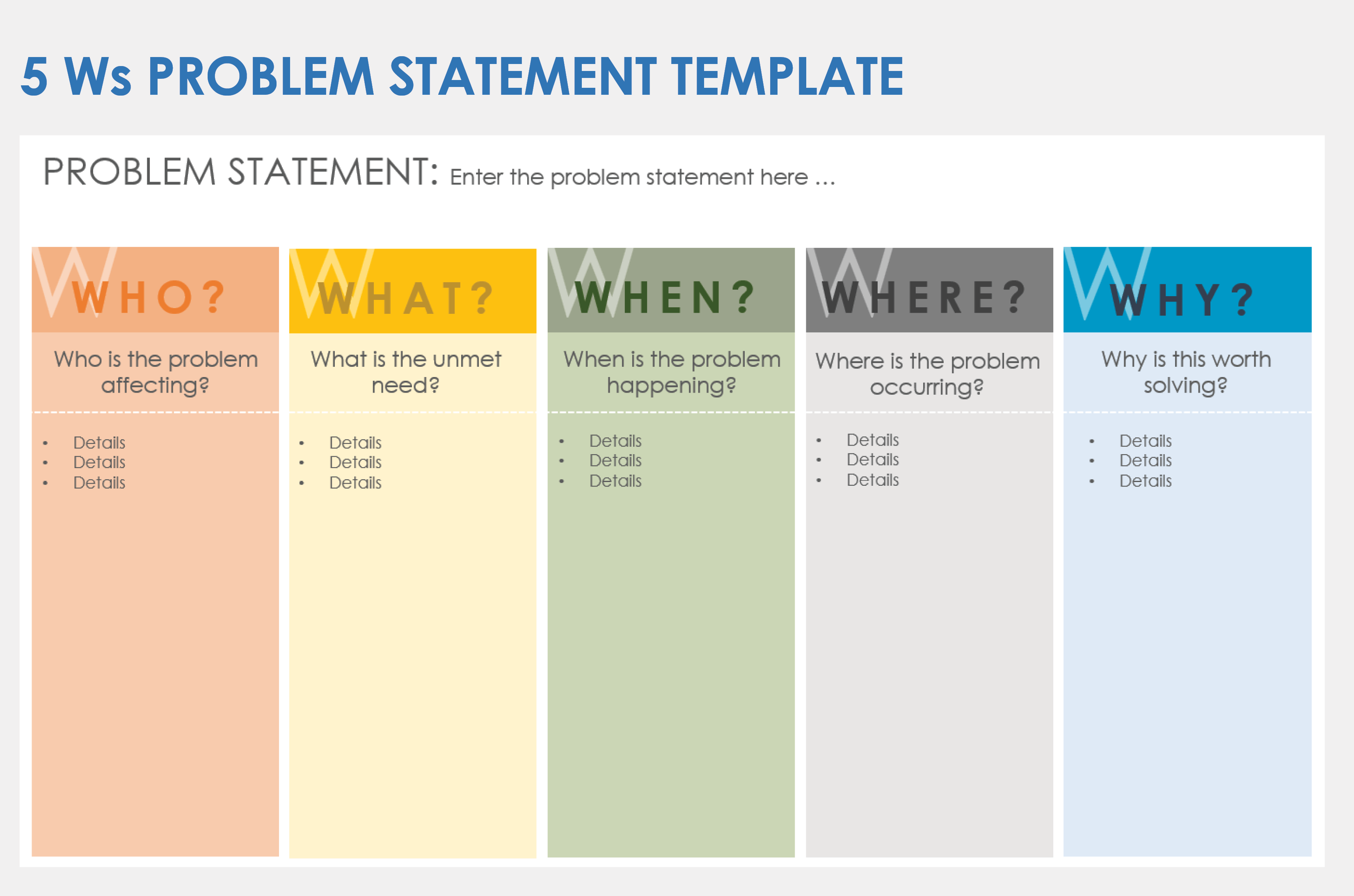
Download a 5 Ws Problem Statement Template for
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | PowerPoint | Google Slides
When to Use This Template: Use this 5 Ws problem statement template to create a methodical breakdown of issues at team meetings or brainstorming sessions. Ensure that nothing is overlooked by answering who, what, when, where, and why questions about a problem. By doing so, you can create a clear and concise problem statement.
Notable Template Features: Using five key questions to explore a problem fosters a comprehensive understanding of the issue while helping to narrow the focus of your final problem statement. Each segment of the template is color-coded and provides bullet points to delve into specifics, such as who is affected and the problem's scope and significance.
Customer Problem Statement Template
Download a Customer Problem Statement Template for
When to Use This Template: This template provides a structured approach to translating client issues into an effective problem statement. It is especially useful for customer experience teams, marketing personnel, and product developers who are tasked with turning customer feedback into actionable insights.
Notable Template Features: This template takes you through the steps of clarifying customer issues and perspectives to help teams find customer-focused solutions. Download the template in PowerPoint or Google Slides for presentations, or try the Microsoft Word or Adobe PDF versions to create a printable worksheet.
Three-Part Problem Statement Slide Template
Download a Three-Part Problem Statement Slide Template for
PowerPoint | Google Slides
When to Use This Template: Use this slide template to present key points to stakeholders in project reviews or strategic planning sessions. Teams can also use this template to facilitate problem-solving meetings.
Notable Template Features: This template guides the audience from problem to solution to result, promoting a thorough understanding of the problem’s context. Each section includes bullet points to organize and present complex details in a simple yet engaging format.
Single-Problem Statement and Solution Slide Template
Download a Single-Problem Statement and Solution Slide Template for
When to Use This Template: This problem statement slide template allows you to clearly outline a problem and propose a viable solution in one visually dynamic slide, making it a perfect addition to business proposals, project pitches, and strategy meetings.
Notable Template Features: This slide template separates the problem on the left from the solution on the right, using a clear layout and colorful symbols to grab the viewer's attention. This simple design ensures that the audience grasps the core issue quickly, facilitating a focused and efficient discussion.
For more slide template resources like this one, see this collection of free PowerPoint problem statement templates .
Project Problem Statement Document Template
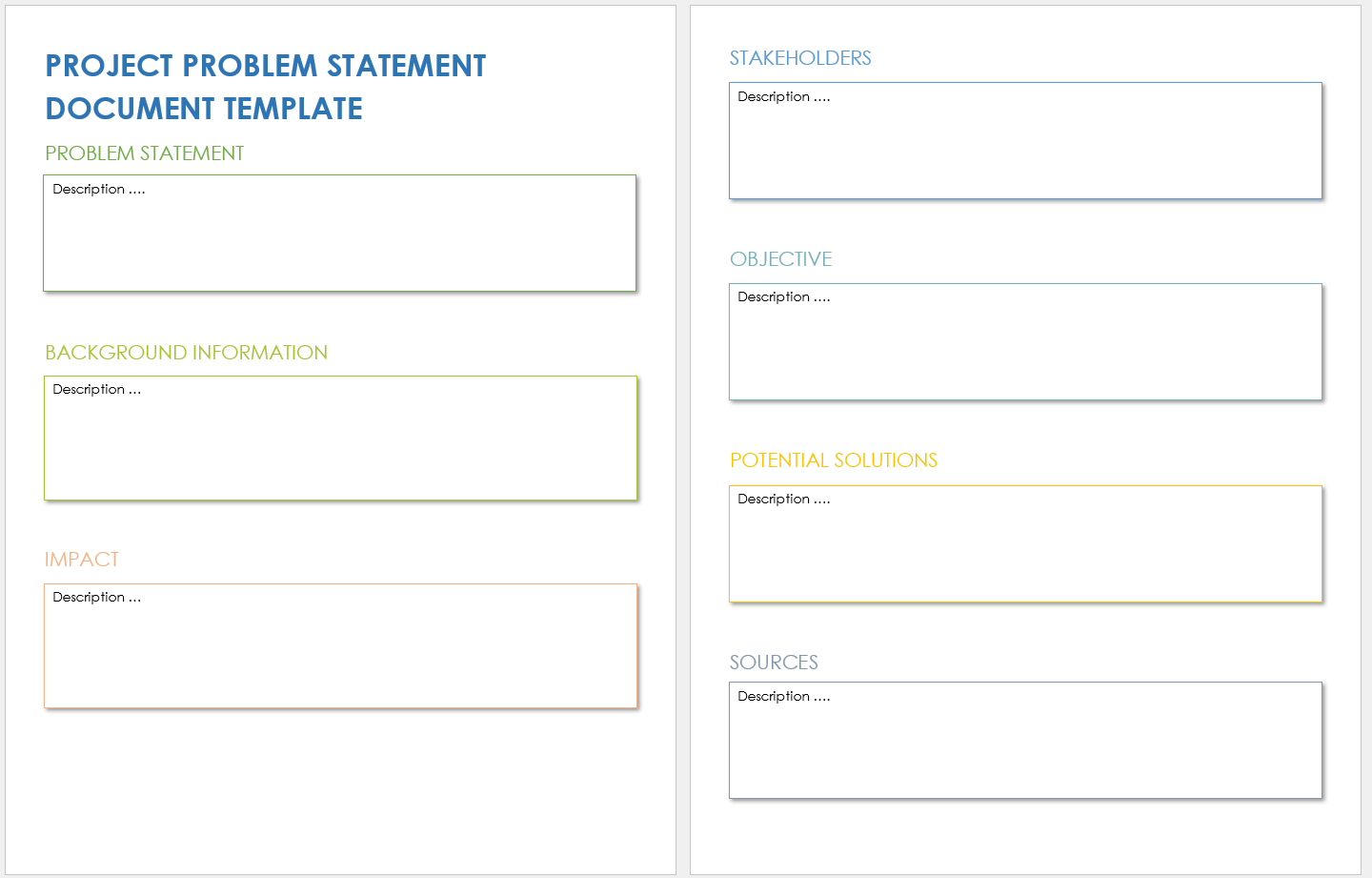
Download a Project Problem Statement Document Template for
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
When to Use This Template: Use this document template to draft a comprehensive problem statement report. The template is best for individuals or teams tasked with in-depth analysis and documentation of business issues, ensuring that they cover all relevant aspects of the problem.
Notable Template Features: This template features a structured outline with labeled sections for documenting the problem statement, background information, impact, and potential solutions. The outline takes readers through a logical progression — from identifying the problem to proposing solutions — for a clear and persuasive presentation.
Problem Statement Worksheet Template

Download a Problem Statement Worksheet Template for
Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
When to Use This Template: Use this worksheet to create an effective problem statement when starting a new project. The template is particularly useful for project teams that need to align on the specifics of a problem, set measurable goals, and identify obstacles and solutions.
Notable Template Features: This problem statement worksheet guides you through a step-by-step process to craft a concise and impactful problem statement. The template includes clear sections where you can provide details about the problem, the gap between the current state and the goal, and the people or processes affected. It includes space for setting SMART goals related to the problem, identifying barriers, and formulating a plan to overcome these challenges.
Problem Statement Matrix Template
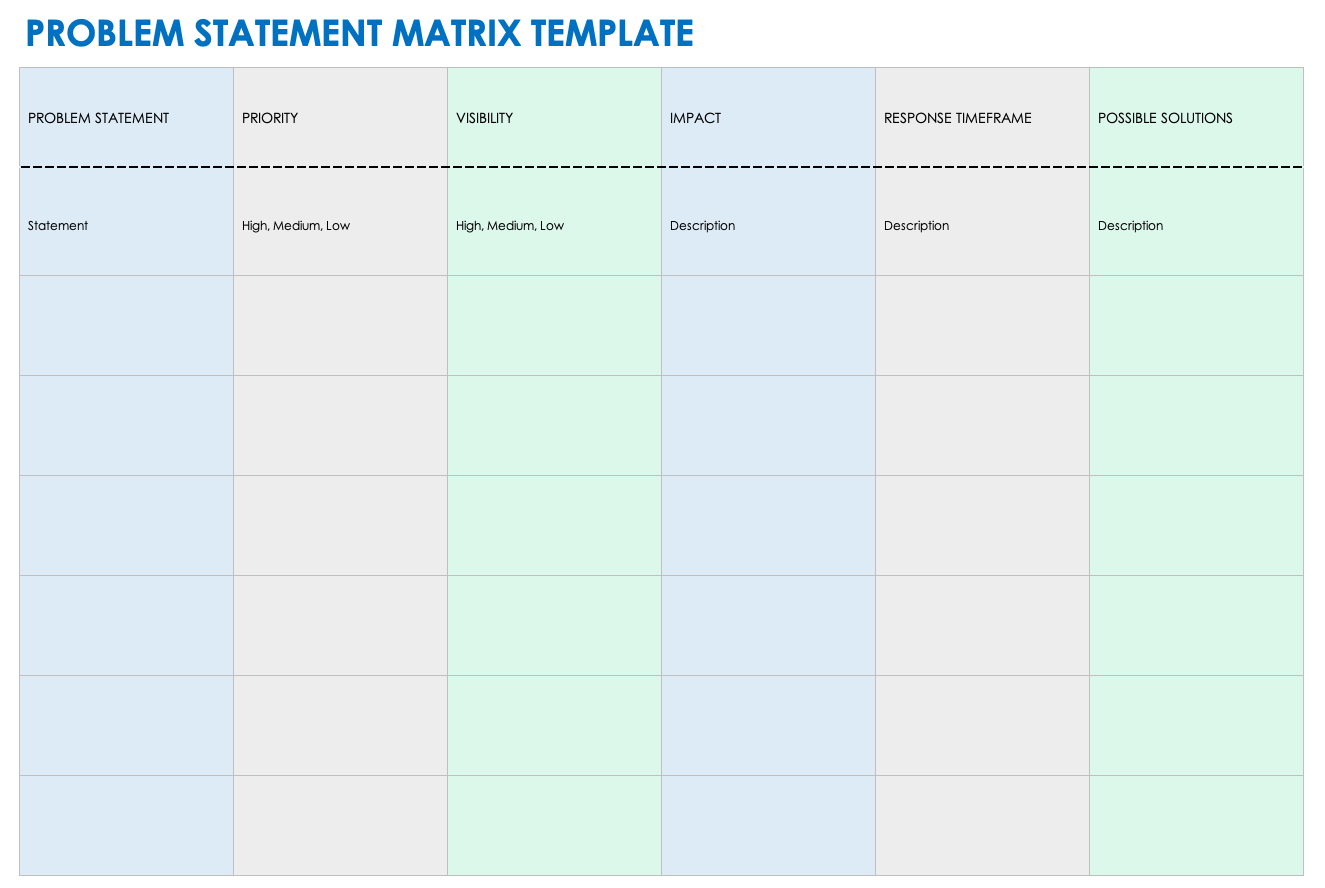
Download a Problem Statement Matrix Template for
When to Use This Template: This template helps teams and managers prioritize multiple problems. Teams can assess and sort problems based on urgency and potential impact to effectively guide strategic action plans.
Notable Template Features: This template organizes essential aspects of each problem into a simple matrix, including a problem statement, priority, visibility, impact, response timeframe, and proposed solutions. The matrix format is useful when you want an overview of problems with key details highlighted.
Types of Problem Statement Templates
Problem statements are used in business settings and academic research to clearly define a problem that needs to be solved. A well-written statement is concise, narrow in focus, and based on evidence. While all problem statements include similar elements, they will vary depending on the context and type of issue. There are many tools that can aid in this process.
Here’s a closer look at the different types of problem statement templates for project and product management:
Customer Problem Statement Templates
Customer problem statement templates guide you through the process of viewing issues from the customer’s perspective. They provide a structured approach to mapping out the customer journey, pinpointing the underlying cause of problems, and understanding their emotional impacts on customers.
Customer problem statement templates typically organize information into five key elements:
- I Am: Who is the customer? This could be as broad as a demographic group or as specific as a user persona. Clearly defining your customer sets the foundation for a more targeted analysis.
- I Am Trying To: What is the customer trying to achieve? Articulate the customer's goal or what they hope to accomplish with your product or service. This helps in aligning your solutions with customer needs.
- But: What is getting in their way? Identify the challenges that prevent the customer from achieving their goals. These could be related to product features, service limitations, or external factors.
- Because: What is the root of the issue? Analyze the internal and external factors that contribute to the problem to uncover the underlying causes.
- Which Makes Me Feel: What is the customer's emotional response to this issue? Emotions can affect how customers perceive your product or service. If they're feeling frustration, disappointment, or confusion, they might be less likely to engage positively with your brand or recommend your services to others. Knowing this helps convey the urgency of addressing the problem.
Using a customer problem statement template shifts the focus from internal perceptions of what the problem might be to a clearer understanding of the customer's experience. The process involves gathering and analyzing customer feedback, conducting market research, and possibly engaging directly with customers through interviews or surveys.
Product Problem Statement Templates
Since having a customer-centric perspective is vital for developing successful products, there is overlap between product and customer problem statement templates. However, understanding customer issues is just one step in the development process. Product teams must consider whether the solutions they come up with will truly benefit the customer, what value a product will bring to the company, what steps are needed to solve the problem, and how to measure success.
One common structure for product problem statement templates is the 5 Ws framework, which involves answering the following questions:
- Who: Who is the problem affecting?
- What: What is the unmet need?
- When: When is the problem happening?
- Where: Where is the problem occurring?
- Why: Why is this worth solving?
Some templates might include a sixth question: How are you going to solve the problem?
These templates can help teams identify initial product opportunities, refine product concepts, and diagnose issues in existing products. They help in prioritizing features, making strategic adjustments, and communicating the product vision and challenges internally.
Project Problem Statement Templates
Similar to customer and product templates, project problem statement templates help teams articulate the core issue they aim to address with their project. They are often used at early planning stages to gain clarity and consensus among stakeholders on the project's direction.
A project problem statement template typically includes the following elements:
- Problem: Clearly define the issue at hand with a precise description of the gap between the current state and the desired state.
- Background: Provide context for the problem by offering insights into its origins and scope. This helps stakeholders understand the complexity and nuances of the issue.
- Relevance: Highlight the significance of the problem, its potential impacts, and why addressing it matters to the organization or stakeholders.
- Objectives: Outline the objectives of the project with SMART goals that guide the project's direction and help in measuring its success.
Some templates, such as a problem statement worksheet, are designed to help you craft an effective statement, while others are suitable for presentations or reports to stakeholders. For some helpful options, see this collection of free problem statement slide templates .
Related Problem-Solving Templates
Fully understanding a problem and finding effective solutions requires in-depth analysis. Here is a list of problem-solving templates that can help with that process:
Fishbone Diagram Template
A fishbone diagram template organizes the causes of a problem into categories, enabling teams to identify, analyze, and address root causes by branching out possible contributing factors from a central problem statement.
8D Report Template
An 8D report template guides teams through a structured eight-step process to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems. This problem-solving approach emphasizes root cause analysis and long-term solutions.

A3 Template
An A3 template offers a concise framework for problem solving, encouraging teams to identify issues, find root causes, and develop solutions on a single A3-sized sheet of paper for clarity and efficiency.
Simple Root Cause Analysis Template
Use our simple root cause analysis template to map out symptoms, effects, causes, and suggested solutions in a color-coded spreadsheet. Each section includes important details, such as urgency, risks, and success criteria for a systematic approach to analyzing problems.

DMAIC Root Cause Analysis Template
A DMAIC analysis template outlines a structured, five-phase approach to problem solving
— define, measure, analyze, improve, control — guiding teams through a detailed process to identify problems, analyze causes, and improve processes.
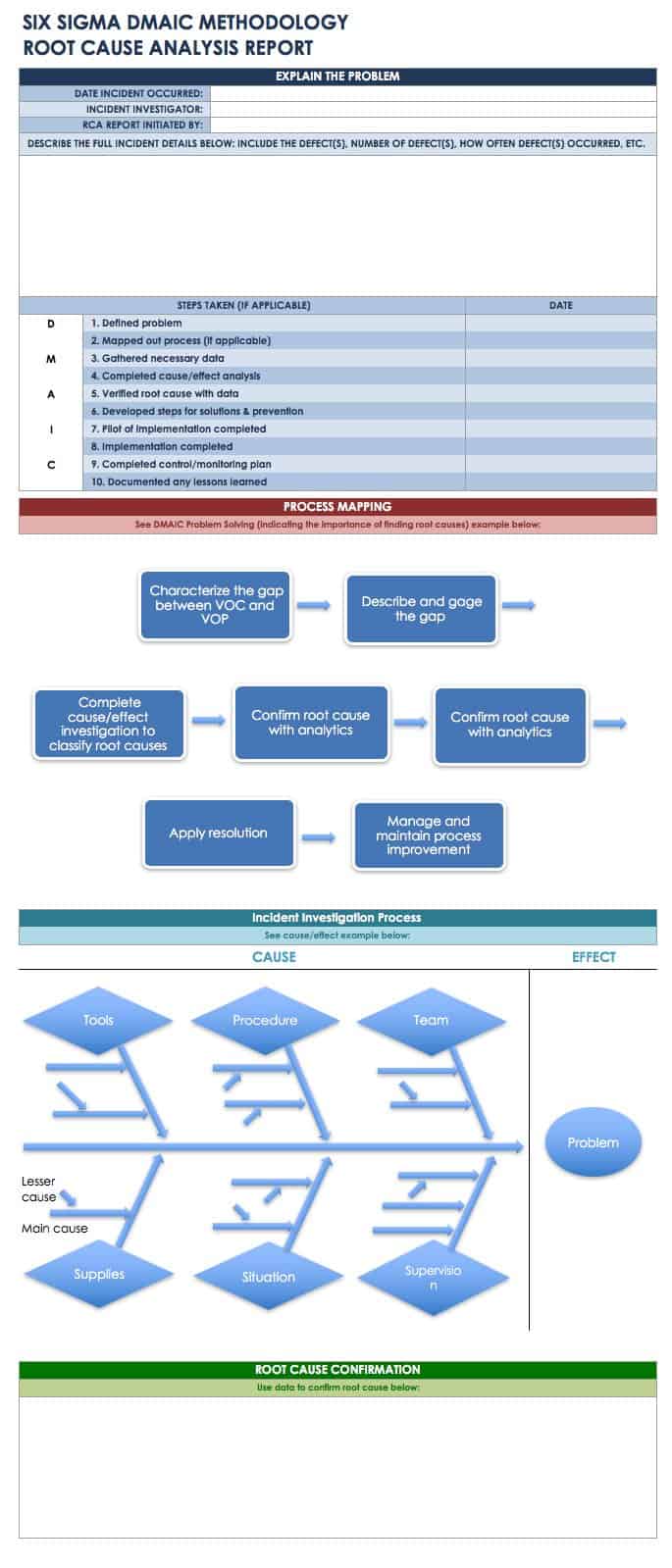
For more problem-solving templates, see this collection of free root cause analysis templates and Lean Six Sigma templates .
Solve Organizational Issues with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Problem Statement Example – A Comprehensive Guide
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

The problem statement poses a crucial section of any dissertation, research project, and thesis, providing a concise and clear outline of the issue the study seeks to address. A well-written problem statement serves as a cornerstone in guiding the research process and sets the foundation for your methodology , findings, and research questions . This article will provide problem statement examples that can serve as models for articulating the critical issues your research aims to resolve.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 In a Nutshell – Problem Statement Example
- 2 Definition: Problem statement example
- 3 Writing a problem statement with examples
- 4 Final problem statement example
- 5 Do’s and don’ts for an effective problem statement
In a Nutshell – Problem Statement Example
- A problem statement is essential in guiding and targeting research efforts.
- This section provides an overview of the study’s context and its relevance.
- The purpose and existence of the research are explained and justified.
- The section forms a crucial link between the literature review and the whole study.
Definition: Problem statement example
A problem statement is like a lighthouse in the vast sea of research. Its purpose is to provide a brief and straightforward statement that outlines the issue or problem that the study seeks to solve. It highlights the gap in current knowledge or context that the research aims to fill.
Writing a problem statement with examples
Step 1: identify the problem, step 2: provide context, step 3: state the consequences, step 4: propose a solution.
The first step in writing a problem statement is to identify the problem. The problem could be an unmet need, a gap in knowledge, or an issue that has not been properly addressed. It’s essential that the problem is not just a symptom of another problem, but the actual issue that needs to be addressed.
Suppose you’re conducting a research study about nutrition in public schools. After some preliminary research, you’ve identified that many students are not eating the provided school meals, resulting in poor nutrition and concentration.
Once you have identified the problem, the next step is to provide context for the problem. This includes information about who is affected by the problem, where the problem occurs, and what consequences the problem may have if not addressed.
“Many students in our city’s public schools are not consuming the meals provided at school. This is leading to poor nutrition, affecting their concentration and overall academic performance negatively.”
The next step is to explicitly state what will happen if the problem is not solved. This helps readers understand the seriousness of the issue and the importance of finding a solution.
“If this problem is not addressed, we risk our city’s students continuing to underperform academically, affecting their future prospects and overall health.”
The last step in writing a problem statement is to propose a potential solution to the problem or an approach to finding a solution. The solution doesn’t have to be definitive; it could be what you aim to achieve through your research.
“This study aims to explore the reasons behind students’ reluctance to consume school meals and develop strategies to improve meal consumption and nutritional intake. We will use a combination of surveys and interviews to gather data from students, parents, and school administrators.”
Final problem statement example
Considering all four step, the final problem statement could look like this:
“Many students in our city’s public schools are not consuming the school-provided meals, leading to poor nutrition and affecting their concentration and overall academic performance. If this problem is not addressed, we risk our city’s students continuing to underperform academically, affecting their future prospects and overall health. This study aims to explore the reasons behind students’ reluctance to consume school meals and develop strategies to improve meal consumption and nutritional intake. We will use a combination of surveys and interviews to gather data from students, parents, and school administrators.”
This problem statement clearly states the problem, provides context, discusses the consequences of inaction, and proposes a research approach to find solutions. Following these steps will guide you in writing a comprehensive, clear, and effective problem statement for your research.
Do’s and don’ts for an effective problem statement
- Be concise: Stick to the point for a direct problem statement example.
- What, why, how: What is the problem? Why is it important? How is it solved?
- Be specific: Specify your problem statement and address a real issue.
- Avoid vagueness: Steer clear from vague and ambiguous statements.
- Don’t overcomplicate: Keep the language simple and straightforward.
- Avoid jargon: Use plain, accessible, and comprehensive language.
Is a problem statement always necessary?
Yes, a problem statement is crucial in any type of research paper or study, as it outlines the focus and direction of the research.
Can a problem statement change during the research?
Although it’s best to stick to your initial problem statement, research is an exploratory process. Thus, minor adjustments may be made as long as they do not significantly alter the research’s direction.
Is there a length requirement for a problem statement?
No, there is no strict length requirement. However, a problem statement should be as concise as possible while still adequately addressing the problem, its relevance, and the proposed method to address it.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
Filter by Keywords
10 Free Problem Statement Templates in Word & ClickUp
Praburam Srinivasan
Growth Marketing Manager
February 13, 2024
No matter what your position title is, solving problems is likely part of your job description. From project managers to IT team leads to administrative agents at government organizations, we all have to address issues that threaten to derail our objectives.
One of the best ways to achieve success is to have a process in place to identify and respond to potential risks. Many business owners and managers choose problem statements as an effective option. These tools highlight existing problems, offer context, and are designed to generate discussion for solutions.
Here, we’ll explain what problem statement templates do and discuss when to use them. Plus, we’ll show you what to look for when choosing one and share 10 free problem statement templates to use in ClickUp and Word. 👀
What is a Problem Statement Template?
What makes a good problem statement template , 1. clickup customer problem statement template, 2. clickup root cause analysis template, 3. clickup a3 action plan template, 4. clickup remediation action plan template, 5. clickup after action report template, 6. clickup report work incident template, 7. clickup incident response report template, 8. clickup it incident report template, 9. word problem statement template by sample.net, 10. google docs research problem statement template by template.net.
A problem statement is a project management tool that describes an existing issue that needs to be solved. It explains the current status, lays out a desired solution, and analyzes the scope of the process required to reach the end goal.
It’s a process tool that encourages creativity when developing potential solutions to issues, rather than highlighting a specific solution.
A problem statement template makes it easier to compile the necessary information and present it to relevant team members. That way everyone on the project knows the goal and can play a part in creating a road map to solve the problem. 💡
Here are four key elements of a problem statement:
- Current status: Briefly explain the current problem as succinctly as possible and outline a statement of work blueprint
- Ideal goal: What would the situation look like without the existing problem? Describe what your end goal is in finding a viable solution
- The reason it matters: Analyze how the problem affects different team members and the company goals. Also, determine the consequences of not addressing the problem
- Proposal: A problem statement doesn’t have to list solutions. Instead, focus on providing context for research so the team can develop answers creatively
Not all problem statement templates are created equal. You want to choose one that briefly explains the problem, highlights the end goal, and offers room for creative discussion.
A good problem statement template will:
- Start with a goal: Give your team an objective to aim for. Highlight multiple outcomes and provide context for what an ideal solution will be using an effective problem statement template
- Explain the specific problem and current state : A good problem-solving template will highlight how the issue prevents you from reaching the stated objective
- Identify knowledge gaps: You can’t find a solution if you don’t have all the relevant data. Use the template to describe what information you’re missing and what data you need to come up with possible solutions
- Avoid proposing a specific solution: The goal here is to generate ideas and creative discussion. There’s more than one solution to a problem, so instead of laying out one solution, offer a framework for coming up with answers and ideas
10 Problem Statement Templates to Use in 2024
Problem statements take time to draft, especially if you’re using them repeatedly as part of your workflows. To cut down on time creating these useful documents, turn to problem statement templates.
These handy tools make it easy to outline the problem and turn it into actionable insights while getting input from your team.
Ready to start improving your processes? We’ve gathered 10 of the best problem statement templates to streamline how you respond and adapt to issues. From incident reports and remediation plans to addressing customer problems, you’ll find what you need to address issues that matter at your company.
Here are the best problem statement templates to use whether you work in IT for the government, run a small product agency, or head human resources at a midsize firm. 🛠️
Use ClickUp’s Customer Problem Statement Template to identify common customer issues to develop products and services that better address customers’ needs. Fill in the customer profile section to keep track of different audience needs.
Next, break down what that type of customer wants, and what roadblocks prevent them from their goals during the customer journey . Be sure to give context on why those issues are present—as well as a proposed solution.
Create new pages for each problem and share each one with the relevant team members. Generate tasks to break down the teamwork based on department, and use the different ClickUp views to keep the team on schedule and monitor results across problem statements. ✅
Before you can lay out a road map to success, you need to anticipate the root cause of a problem. Create a concise problem statement and improve your decision-making process by using the Root Cause Analysis Template from ClickUp .
This problem statement template breaks the bigger problem down into a list of issues, making them easier to assign to various team members. It’s an effective tool for predicting issues and laying the groundwork to prevent them from derailing a project.
Use the nine custom fields to draft problem statement examples and tasks for the team to tackle. Add priority to the most pressing issues, and hop into the Needs Action view to see what’s in progress and to track issues that still need to be addressed.
As a project lead, an action plan is your best friend. It highlights stakeholders, provides a roadmap to success, and offers metrics to gauge performance.
With ClickUp’s A3 Action Plan Template , map out long-term projects while staying organized and improving productivity. When using this problem statement template, start by brainstorming to identify and define your business problem statement.
You can collaborate with other team members through ClickUp Docs . After this step, you can gather data, develop a solution, and then create an action plan.
With the view types in ClickUp’s problem statements, you can monitor goals, timelines, and action steps. Plus, the four custom fields let you manage tasks with breakdowns by department, complexity, progress, and type. 📝
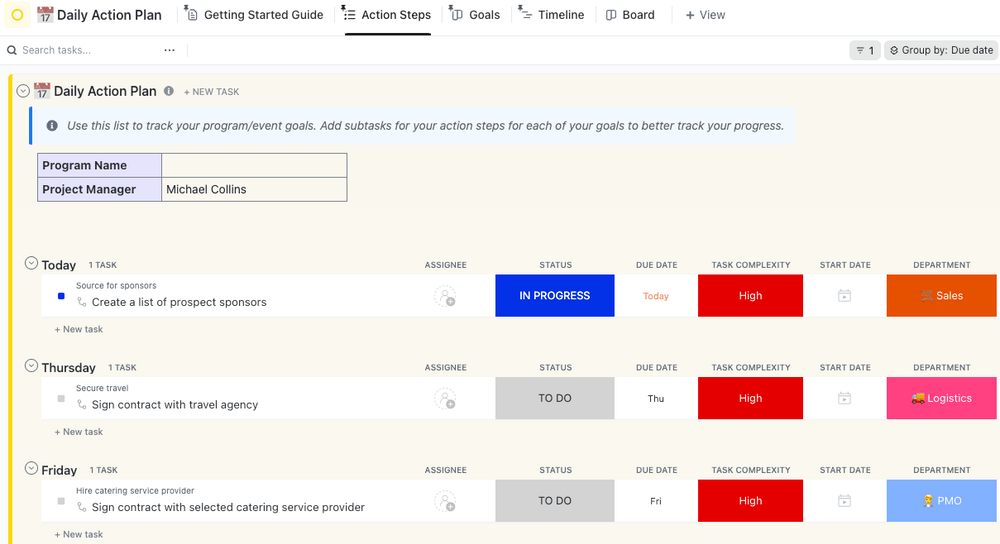
Create an action plan for corrective action using ClickUp’s Remediation Action Plan Template . From ideation and methodology processes to execution and integration in workflows, this template makes it easy to come up with solutions for even the most complex problems.
Use the template to identify remediation steps and to automate assigning the tasks to the relevant team members. Assess risk levels, and add priority tags to tasks that need to be addressed immediately.
Develop an action plan by using custom fields for each risk, and track progress using ClickUp Checklists . These to-do lists populate within the task, making it easy to break down repetitive tasks and incorporate company procedures in your remediation workflows.
Whether you’re midway through a long project or one has just wrapped, you need to assess the process and make adjustments for the future. The After Action Report Template from ClickUp is useful in determining what went well, deciding what needs improvement, and generating new workflows to streamline the process.
This simple one-page template highlights project participants, the basics of the project, the project scope, and results based on project data.
Incorporate this template into your workflows as part of a review step. The template is an excellent tool when preparing for employee reviews since it lists the actions they took and documents the overall team workflow. Use this tool to evaluate how well your workflows performed and if anything broke down during the process.
The ClickUp After Action Report Template also helps you celebrate team success. While it’s easy to focus on what went wrong, this template highlights things that went well and team members that performed .
You can emphasize areas where employees avoided budget issues, overcame resource management issues, and adjusted their workflows to keep the project on track. 🌻
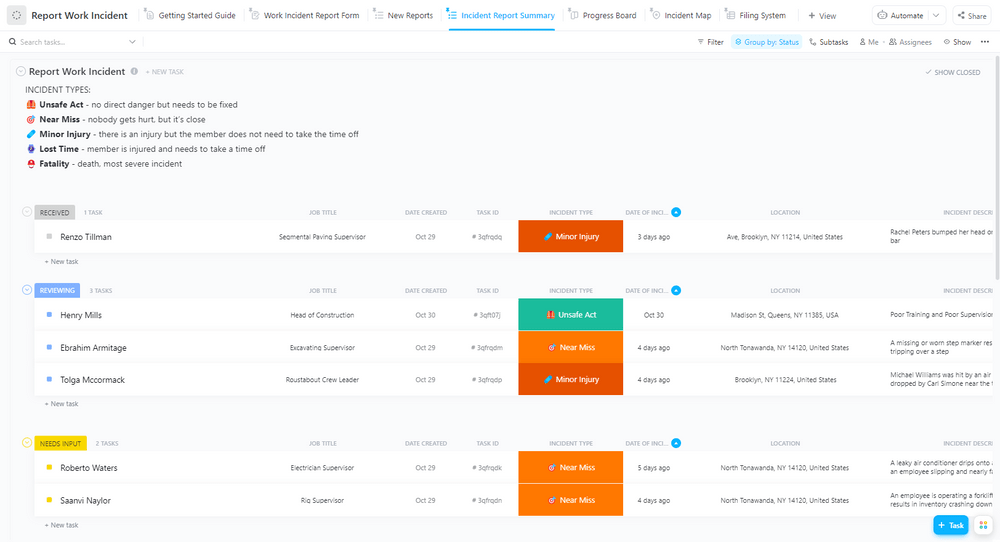
One of the biggest project management challenges is managing safety and correctly recording workplace incidents. With ClickUp’s Report Work Incident Template , you can gather incident reports and compile mitigation procedures in one easy-to-access space.
In the task card, collect information about a specific incident, and choose from 13 custom fields—including basics like the date of the incident, parties involved, and location. If the local authorities were involved, you can add information on officer contact information and police report filing details.
In addition to recording the pertinent information, you can suggest a corrective action to improve the processes and prevent a repeat incident.
This template also features seven different view types, so you can get the information you need at a glance. For example, the Incident Report Summary view is excellent for getting a quick overview of what occurred.
The Progress Board and Reports views keep you on top of solutions and how things are getting worked out.
With the Incident Response Report Template from ClickUp , it’s easier than ever to identify threats, draft steps to address the risk, and develop insights from the incident response process. The template includes a simple step-by-step approach to creating an incident report, including sections for risks, next steps, containment, eradication, recovery, and lessons learned.
With this template, report existing incidents, track proposed solutions, and gather intel so that you can adjust your procedures to better address future incidents. Plus, with its five custom fields, you can easily track supporting documents and keep an audit trail of who created, approved, or reviewed an incident report.
The documentation is also invaluable when responding to legal issues. 👩🏿⚖️
Whether you work in product management or lead an IT team, you know how important it is to stay on top of risks. With ClickUp’s IT Incident Report Template , you can easily track bugs and software issues that affect the performance of your IT system.
The 14 custom fields offer a high degree of personalization. That means that you can truly leverage this template to meet your specific company needs.
When using this template, get insight into the IT threat by filling out the basics of the problem, including affected software systems, platforms, and build versions. Next, highlight the severity of each incident and explain the reasons for the incident as well as the impact.
Finally, lay out a path for solutions, and use the data gathered to inform your incident management process.
Problem statements are a great way to generate new ideas, support a creative-thinking process, and get buy-in from various team members in different departments.
This Problem Statement Template from Sample.Net is compatible with MS Word, Google Docs, and Powerpoint. It features a one-page layout explaining the existing problem, a description of the issue, risks, and ideas for solutions.
Use this template to design thinking processes and creatively brainstorm solutions with your team. Each person can share their specific point of view as you work together to develop solutions to the issue and hand. 🏆

This simple Research Problem Statement Template makes it easy to draft a quick breakdown of an existing issue and offers support for coming up with solutions. It’s available as a Google Doc, Apple Pages, or MS Word file.
Save time formatting and use this template to quickly fill out the sections for the description, risks, and solution for your problem statement examples.
The template features branding customization in such a way that you can add a company logo and contact information if you’re sharing this document with an outside agency that’s supporting your resolution process. Change the color scheme and font style to match other company documentation and to meet branding standards.
Solve Problems Fast and Effectively With ClickUp
With these problem statement templates, you’re well on your way to being a more effective leader and employee. From reporting incidents and tracking IT issues to generating discussions on how to solve common customer problems, these templates are sure to make your work life easier.
Try ClickUp today to create a problem statement that propels your business forward and builds the basis for better products and services. Browse hundreds of free templates to improve your project management style, assist with incident reporting and track performance on all of your objectives. ✨
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples
Published on 8 November 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George.
A problem statement is a concise and concrete summary of the research problem you seek to address. It should:
- Contextualise the problem. What do we already know?
- Describe the exact issue your research will address. What do we still need to know?
- Show the relevance of the problem. Why do we need to know more about this?
- Set the objectives of the research. What will you do to find out more?
Table of contents
When should you write a problem statement, step 1: contextualise the problem, step 2: show why it matters, step 3: set your aims and objectives.
Problem statement example
Frequently asked questions about problem statements
There are various situations in which you might have to write a problem statement.
In the business world, writing a problem statement is often the first step in kicking off an improvement project. In this case, the problem statement is usually a stand-alone document.
In academic research, writing a problem statement can help you contextualise and understand the significance of your research problem. It is often several paragraphs long, and serves as the basis for your research proposal . Alternatively, it can be condensed into just a few sentences in your introduction .
A problem statement looks different depending on whether you’re dealing with a practical, real-world problem or a theoretical issue. Regardless, all problem statements follow a similar process.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
The problem statement should frame your research problem, giving some background on what is already known.
Practical research problems
For practical research, focus on the concrete details of the situation:
- Where and when does the problem arise?
- Who does the problem affect?
- What attempts have been made to solve the problem?
Theoretical research problems
For theoretical research, think about the scientific, social, geographical and/or historical background:
- What is already known about the problem?
- Is the problem limited to a certain time period or geographical area?
- How has the problem been defined and debated in the scholarly literature?
The problem statement should also address the relevance of the research. Why is it important that the problem is addressed?
Don’t worry, this doesn’t mean you have to do something groundbreaking or world-changing. It’s more important that the problem is researchable, feasible, and clearly addresses a relevant issue in your field.
Practical research is directly relevant to a specific problem that affects an organisation, institution, social group, or society more broadly. To make it clear why your research problem matters, you can ask yourself:
- What will happen if the problem is not solved?
- Who will feel the consequences?
- Does the problem have wider relevance? Are similar issues found in other contexts?
Sometimes theoretical issues have clear practical consequences, but sometimes their relevance is less immediately obvious. To identify why the problem matters, ask:
- How will resolving the problem advance understanding of the topic?
- What benefits will it have for future research?
- Does the problem have direct or indirect consequences for society?
Finally, the problem statement should frame how you intend to address the problem. Your goal here should not be to find a conclusive solution, but rather to propose more effective approaches to tackling or understanding it.
The research aim is the overall purpose of your research. It is generally written in the infinitive form:
- The aim of this study is to determine …
- This project aims to explore …
- This research aims to investigate …
The research objectives are the concrete steps you will take to achieve the aim:
- Qualitative methods will be used to identify …
- This work will use surveys to collect …
- Using statistical analysis, the research will measure …
The aims and objectives should lead directly to your research questions.
Learn how to formulate research questions
You can use these steps to write your own problem statement, like the example below.
Step 1: Contextualise the problem A family-owned shoe manufacturer has been in business in New England for several generations, employing thousands of local workers in a variety of roles, from assembly to supply-chain to customer service and retail. Employee tenure in the past always had an upward trend, with the average employee staying at the company for 10+ years. However, in the past decade, the trend has reversed, with some employees lasting only a few months, and others leaving abruptly after many years.
Step 2: Show why it matters As the perceived loyalty of their employees has long been a source of pride for the company, they employed an outside consultant firm to see why there was so much turnover. The firm focused on the new hires, concluding that a rival shoe company located in the next town offered higher hourly wages and better “perks”, such as pizza parties. They claimed this was what was leading employees to switch. However, to gain a fuller understanding of why the turnover persists even after the consultant study, in-depth qualitative research focused on long-term employees is also needed. Focusing on why established workers leave can help develop a more telling reason why turnover is so high, rather than just due to salaries. It can also potentially identify points of change or conflict in the company’s culture that may cause workers to leave.
Step 3: Set your aims and objectives This project aims to better understand why established workers choose to leave the company. Qualitative methods such as surveys and interviews will be conducted comparing the views of those who have worked 10+ years at the company and chose to stay, compared with those who chose to leave.
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarise the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2022, November 08). How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/write-a-problem-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, how to write a strong hypothesis | guide & examples.
Problem statement template
Define a clearly articulated problem statement
.webp)
Use the problem statement template to clearly define and communicate a problem that needs to be addressed. This template helps to identify the scope, context, and significance of the problem with stakeholders in a structured workshop.
Identify the customer or user having the problem, where the problem occurs, what the problem is, and what’s causing the issue. Then, take these insights and turn them into an actionable, concise problem statement.
The problem statement template helps to:
- Improve problem-solving and team decision-making
- Define expected outcomes for a proposed solution
- Create a guiding principle for a project
- Collaborate with stakeholders and build teamwork
- Build empathy with the end-user
How to use the problem statement workshop
This template can be used in both solo and group settings, either as a solo brainstorming exercise or a guided workshop with team members. Use these steps as a guide to the elements of a problem statement.
1. Identify the target audience
Who is affected by the problem at hand? Is this who will benefit from the solution? What do we know or assume about them?
You may want to conduct a brainstorming session to define the user persona and list out any facts or assumptions you have about them and the problem they’re experiencing.
Pro-tip: Be sure to include any user research or data that can provide further background information.
2. Define the problem
Take some time to ideate and address these questions:
- What is the problem from the user or customer’s point of view?
- Is it easy to explain?
- Is it an actual/real problem?
- What evidence or examples exist of the problem?
3. Provide context for the problem
Describe when and where the problem occurs. Be sure to identify root causes and downstream effects of the problem. What is the context where the user is experiencing the problem? Include any examples or proof of the specific problem.
4. Explain why it matters
Explain why this is a real problem for your customers or users and why the problem is worth solving. Ask the following questions:
- What is the most important value for the user?
- What pain points would a solution help get rid of?
- Why is it worth our investment?
- How does it meet or align to business goals or KPIs?
5. Review each section in the template and draft your problem statement
Use the data, ideas, and work from the previous sections to draft an effective problem statement. Now that you have a clear understanding of the problem, your team can get started on brainstorming a viable solution.
Note: Read our full guide on creating problem statements with problem statement examples .
Tips for running a successful problem statement workshop
- While brainstorming with other team members, turn on Mural's private mode feature to prevent groupthink.
- Use the built-in timer feature to time-block each activity and stay on schedule.
- Problem statements are good for more than just project management! Try using the template for internal uses like strategic planning.
How to create a Problem statement template
Get started with this template right now.
Build better problem statements with Mural

Sticky notes & text
Add ideas, action items, and more as a sticky note or text box — then change the colors and cluster to identify patterns and new solutions.

Real-time collaboration
Add more productivity and engagement to meetings and calls with features to guide collaboration.

Find & filter
Search and filter by color, last edited by, and more to unlock patterns and enhance visual collaboration.

Tags on sticky notes
Customizable labels make it easy to find, organize, and categorize your work in a mural.

Flexible permissions
Control access to collaboration features with view-only, edit, and facilitator settings.

Mapping and diagramming
Build quick and easy visualizations of flows, maps, processes, hierarchies, journeys, and more.
Problem statement template frequently asked questions
What is a problem statement, why should you create a problem statement, can a problem statement be a question.

Template by Design Sprint Academy
Design Sprint Academy helps organizations build sustainable products, discover opportunities for innovation & solve their toughest business challenges.

Mural is the only platform that offers both a shared workspace and training on the LUMA System™, a practical way to collaborate that anyone can learn and apply.
More Education templates

Learning experience canvas

Storyboard the student journey

Team breakout
45 Research Problem Examples & Inspiration
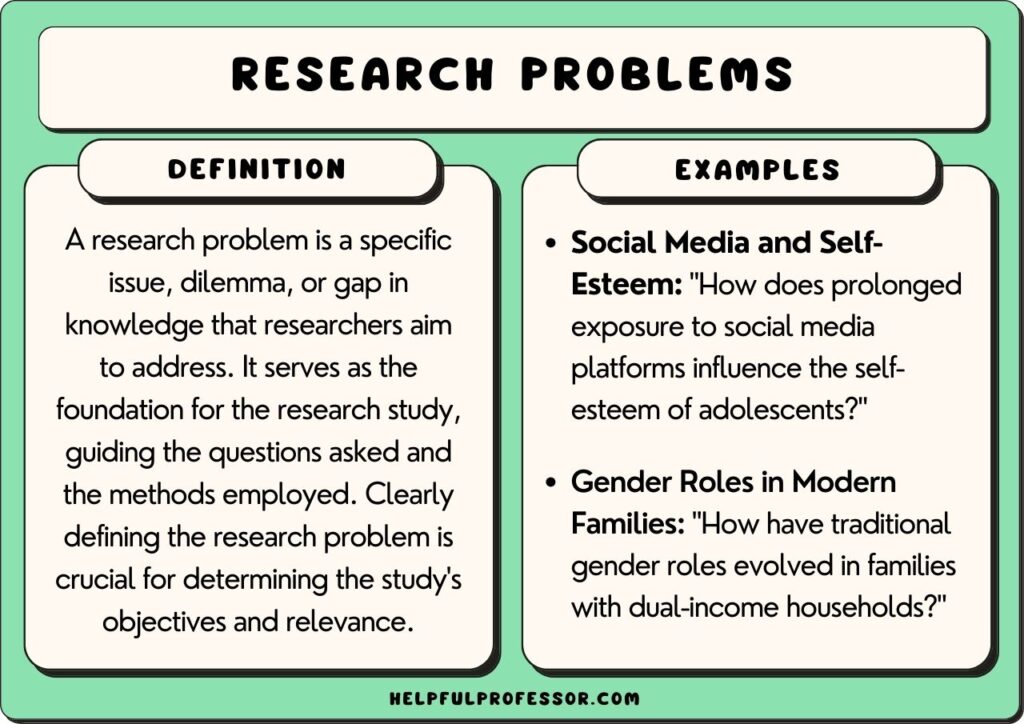
A research problem is an issue of concern that is the catalyst for your research. It demonstrates why the research problem needs to take place in the first place.
Generally, you will write your research problem as a clear, concise, and focused statement that identifies an issue or gap in current knowledge that requires investigation.
The problem will likely also guide the direction and purpose of a study. Depending on the problem, you will identify a suitable methodology that will help address the problem and bring solutions to light.
Research Problem Examples
In the following examples, I’ll present some problems worth addressing, and some suggested theoretical frameworks and research methodologies that might fit with the study. Note, however, that these aren’t the only ways to approach the problems. Keep an open mind and consult with your dissertation supervisor!

Psychology Problems
1. Social Media and Self-Esteem: “How does prolonged exposure to social media platforms influence the self-esteem of adolescents?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Comparison Theory
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking adolescents’ social media usage and self-esteem measures over time, combined with qualitative interviews.
2. Sleep and Cognitive Performance: “How does sleep quality and duration impact cognitive performance in adults?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Psychology
- Methodology : Experimental design with controlled sleep conditions, followed by cognitive tests. Participant sleep patterns can also be monitored using actigraphy.
3. Childhood Trauma and Adult Relationships: “How does unresolved childhood trauma influence attachment styles and relationship dynamics in adulthood?
- Theoretical Framework : Attachment Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of attachment styles with qualitative in-depth interviews exploring past trauma and current relationship dynamics.
4. Mindfulness and Stress Reduction: “How effective is mindfulness meditation in reducing perceived stress and physiological markers of stress in working professionals?”
- Theoretical Framework : Humanist Psychology
- Methodology : Randomized controlled trial comparing a group practicing mindfulness meditation to a control group, measuring both self-reported stress and physiological markers (e.g., cortisol levels).
5. Implicit Bias and Decision Making: “To what extent do implicit biases influence decision-making processes in hiring practices?
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Dissonance Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design using Implicit Association Tests (IAT) to measure implicit biases, followed by simulated hiring tasks to observe decision-making behaviors.
6. Emotional Regulation and Academic Performance: “How does the ability to regulate emotions impact academic performance in college students?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Theory of Emotion
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys measuring emotional regulation strategies, combined with academic performance metrics (e.g., GPA).
7. Nature Exposure and Mental Well-being: “Does regular exposure to natural environments improve mental well-being and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression?”
- Theoretical Framework : Biophilia Hypothesis
- Methodology : Longitudinal study comparing mental health measures of individuals with regular nature exposure to those without, possibly using ecological momentary assessment for real-time data collection.
8. Video Games and Cognitive Skills: “How do action video games influence cognitive skills such as attention, spatial reasoning, and problem-solving?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cognitive Load Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design with pre- and post-tests, comparing cognitive skills of participants before and after a period of action video game play.
9. Parenting Styles and Child Resilience: “How do different parenting styles influence the development of resilience in children facing adversities?”
- Theoretical Framework : Baumrind’s Parenting Styles Inventory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of resilience and parenting styles with qualitative interviews exploring children’s experiences and perceptions.
10. Memory and Aging: “How does the aging process impact episodic memory , and what strategies can mitigate age-related memory decline?
- Theoretical Framework : Information Processing Theory
- Methodology : Cross-sectional study comparing episodic memory performance across different age groups, combined with interventions like memory training or mnemonic strategies to assess potential improvements.
Education Problems
11. Equity and Access : “How do socioeconomic factors influence students’ access to quality education, and what interventions can bridge the gap?
- Theoretical Framework : Critical Pedagogy
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative data on student outcomes with qualitative interviews and focus groups with students, parents, and educators.
12. Digital Divide : How does the lack of access to technology and the internet affect remote learning outcomes, and how can this divide be addressed?
- Theoretical Framework : Social Construction of Technology Theory
- Methodology : Survey research to gather data on access to technology, followed by case studies in selected areas.
13. Teacher Efficacy : “What factors contribute to teacher self-efficacy, and how does it impact student achievement?”
- Theoretical Framework : Bandura’s Self-Efficacy Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys to measure teacher self-efficacy, combined with qualitative interviews to explore factors affecting it.
14. Curriculum Relevance : “How can curricula be made more relevant to diverse student populations, incorporating cultural and local contexts?”
- Theoretical Framework : Sociocultural Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of curricula, combined with focus groups with students and teachers.
15. Special Education : “What are the most effective instructional strategies for students with specific learning disabilities?
- Theoretical Framework : Social Learning Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing different instructional strategies, with pre- and post-tests to measure student achievement.
16. Dropout Rates : “What factors contribute to high school dropout rates, and what interventions can help retain students?”
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking students over time, combined with interviews with dropouts.
17. Bilingual Education : “How does bilingual education impact cognitive development and academic achievement?
- Methodology : Comparative study of students in bilingual vs. monolingual programs, using standardized tests and qualitative interviews.
18. Classroom Management: “What reward strategies are most effective in managing diverse classrooms and promoting a positive learning environment?
- Theoretical Framework : Behaviorism (e.g., Skinner’s Operant Conditioning)
- Methodology : Observational research in classrooms , combined with teacher interviews.
19. Standardized Testing : “How do standardized tests affect student motivation, learning, and curriculum design?”
- Theoretical Framework : Critical Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative analysis of test scores and student outcomes, combined with qualitative interviews with educators and students.
20. STEM Education : “What methods can be employed to increase interest and proficiency in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields among underrepresented student groups?”
- Theoretical Framework : Constructivist Learning Theory
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing different instructional methods, with pre- and post-tests.
21. Social-Emotional Learning : “How can social-emotional learning be effectively integrated into the curriculum, and what are its impacts on student well-being and academic outcomes?”
- Theoretical Framework : Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of student well-being with qualitative interviews.
22. Parental Involvement : “How does parental involvement influence student achievement, and what strategies can schools use to increase it?”
- Theoretical Framework : Reggio Emilia’s Model (Community Engagement Focus)
- Methodology : Survey research with parents and teachers, combined with case studies in selected schools.
23. Early Childhood Education : “What are the long-term impacts of quality early childhood education on academic and life outcomes?”
- Theoretical Framework : Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development
- Methodology : Longitudinal study comparing students with and without early childhood education, combined with observational research.
24. Teacher Training and Professional Development : “How can teacher training programs be improved to address the evolving needs of the 21st-century classroom?”
- Theoretical Framework : Adult Learning Theory (Andragogy)
- Methodology : Pre- and post-assessments of teacher competencies, combined with focus groups.
25. Educational Technology : “How can technology be effectively integrated into the classroom to enhance learning, and what are the potential drawbacks or challenges?”
- Theoretical Framework : Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK)
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing classrooms with and without specific technologies, combined with teacher and student interviews.
Sociology Problems
26. Urbanization and Social Ties: “How does rapid urbanization impact the strength and nature of social ties in communities?”
- Theoretical Framework : Structural Functionalism
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative surveys on social ties with qualitative interviews in urbanizing areas.
27. Gender Roles in Modern Families: “How have traditional gender roles evolved in families with dual-income households?”
- Theoretical Framework : Gender Schema Theory
- Methodology : Qualitative interviews with dual-income families, combined with historical data analysis.
28. Social Media and Collective Behavior: “How does social media influence collective behaviors and the formation of social movements?”
- Theoretical Framework : Emergent Norm Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of social media platforms, combined with quantitative surveys on participation in social movements.
29. Education and Social Mobility: “To what extent does access to quality education influence social mobility in socioeconomically diverse settings?”
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking educational access and subsequent socioeconomic status, combined with qualitative interviews.
30. Religion and Social Cohesion: “How do religious beliefs and practices contribute to social cohesion in multicultural societies?”
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys on religious beliefs and perceptions of social cohesion, combined with ethnographic studies.
31. Consumer Culture and Identity Formation: “How does consumer culture influence individual identity formation and personal values?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Identity Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining content analysis of advertising with qualitative interviews on identity and values.
32. Migration and Cultural Assimilation: “How do migrants negotiate cultural assimilation and preservation of their original cultural identities in their host countries?”
- Theoretical Framework : Post-Structuralism
- Methodology : Qualitative interviews with migrants, combined with observational studies in multicultural communities.
33. Social Networks and Mental Health: “How do social networks, both online and offline, impact mental health and well-being?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Network Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys assessing social network characteristics and mental health metrics, combined with qualitative interviews.
34. Crime, Deviance, and Social Control: “How do societal norms and values shape definitions of crime and deviance, and how are these definitions enforced?”
- Theoretical Framework : Labeling Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of legal documents and media, combined with ethnographic studies in diverse communities.
35. Technology and Social Interaction: “How has the proliferation of digital technology influenced face-to-face social interactions and community building?”
- Theoretical Framework : Technological Determinism
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative surveys on technology use with qualitative observations of social interactions in various settings.
Nursing Problems
36. Patient Communication and Recovery: “How does effective nurse-patient communication influence patient recovery rates and overall satisfaction with care?”
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys assessing patient satisfaction and recovery metrics, combined with observational studies on nurse-patient interactions.
37. Stress Management in Nursing: “What are the primary sources of occupational stress for nurses, and how can they be effectively managed to prevent burnout?”
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative measures of stress and burnout with qualitative interviews exploring personal experiences and coping mechanisms.
38. Hand Hygiene Compliance: “How effective are different interventions in improving hand hygiene compliance among nursing staff, and what are the barriers to consistent hand hygiene?”
- Methodology : Experimental design comparing hand hygiene rates before and after specific interventions, combined with focus groups to understand barriers.
39. Nurse-Patient Ratios and Patient Outcomes: “How do nurse-patient ratios impact patient outcomes, including recovery rates, complications, and hospital readmissions?”
- Methodology : Quantitative study analyzing patient outcomes in relation to staffing levels, possibly using retrospective chart reviews.
40. Continuing Education and Clinical Competence: “How does regular continuing education influence clinical competence and confidence among nurses?”
- Methodology : Longitudinal study tracking nurses’ clinical skills and confidence over time as they engage in continuing education, combined with patient outcome measures to assess potential impacts on care quality.
Communication Studies Problems
41. Media Representation and Public Perception: “How does media representation of minority groups influence public perceptions and biases?”
- Theoretical Framework : Cultivation Theory
- Methodology : Content analysis of media representations combined with quantitative surveys assessing public perceptions and attitudes.
42. Digital Communication and Relationship Building: “How has the rise of digital communication platforms impacted the way individuals build and maintain personal relationships?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Penetration Theory
- Methodology : Mixed methods, combining quantitative surveys on digital communication habits with qualitative interviews exploring personal relationship dynamics.
43. Crisis Communication Effectiveness: “What strategies are most effective in managing public relations during organizational crises, and how do they influence public trust?”
- Theoretical Framework : Situational Crisis Communication Theory (SCCT)
- Methodology : Case study analysis of past organizational crises, assessing communication strategies used and subsequent public trust metrics.
44. Nonverbal Cues in Virtual Communication: “How do nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions and gestures, influence message interpretation in virtual communication platforms?”
- Theoretical Framework : Social Semiotics
- Methodology : Experimental design using video conferencing tools, analyzing participants’ interpretations of messages with varying nonverbal cues.
45. Influence of Social Media on Political Engagement: “How does exposure to political content on social media platforms influence individuals’ political engagement and activism?”
- Theoretical Framework : Uses and Gratifications Theory
- Methodology : Quantitative surveys assessing social media habits and political engagement levels, combined with content analysis of political posts on popular platforms.
Before you Go: Tips and Tricks for Writing a Research Problem
This is an incredibly stressful time for research students. The research problem is going to lock you into a specific line of inquiry for the rest of your studies.
So, here’s what I tend to suggest to my students:
- Start with something you find intellectually stimulating – Too many students choose projects because they think it hasn’t been studies or they’ve found a research gap. Don’t over-estimate the importance of finding a research gap. There are gaps in every line of inquiry. For now, just find a topic you think you can really sink your teeth into and will enjoy learning about.
- Take 5 ideas to your supervisor – Approach your research supervisor, professor, lecturer, TA, our course leader with 5 research problem ideas and run each by them. The supervisor will have valuable insights that you didn’t consider that will help you narrow-down and refine your problem even more.
- Trust your supervisor – The supervisor-student relationship is often very strained and stressful. While of course this is your project, your supervisor knows the internal politics and conventions of academic research. The depth of knowledge about how to navigate academia and get you out the other end with your degree is invaluable. Don’t underestimate their advice.
I’ve got a full article on all my tips and tricks for doing research projects right here – I recommend reading it:
- 9 Tips on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
All Formats
Table of Contents
Statement template bundle, 1. research problem statement template, 2. nursing research problem statement template, 3. community health nursing research problem statement template, 4. medical surgical nursing research problem statement template, 5. pediatric nursing research problem statement template, 6. covid 19 research problem statement template, 7. bsc nursing research problem statement sample, 8. general quantitative research problem statement template, 9. effective research paper problem statement template, 10. qualitative research problem purpose statement template, 11. marketing research problem statement required format, 12. business research problem statement template, 13. research study problem statement template, how to write a good research problem statement, what is the benefit of developing a research statement, what is the writing style of a research statement, what are the elements of research problems, problem statement vs purpose statement, what are the types of research question, 5 tips to formulate a research problem, statement templates, 12+ research problem statement templates in pdf | ms word | google docs | apple pages.
A research problem statement is that statement which outlines the problem that is addressed by the research study. A good research problem is one that mentions the gap in the knowledge that leads to further research. Here are some problem statement templates that can provide you with more information.

- Google Docs

- Apple Pages

Step 1: You Own Vision
Step 2: write your issue statement, step 3: the organization of the method, step 4: focus on 5ws, 1. specifying the research objective:, 2. the context of the research problem:, 3. the nature of the problem:, 4. the variable relationships:, 5. usage of alternative couse of action:, more in statement templates, editable research flowchart template, sample research template, research poster template for keynote, education research agenda template, research agenda template, legal research methodology ppt template, medical research template, high school research template, research proposal template, detailed financial research template.
- 11+ Statement of Termination Templates in PDF | DOC
- 24+ Research Statement Templates in PDF | DOC
- 21+ Suitability Statement Templates in DOC | PDF
- 17+ Expense Statement Templates in Google Docs | Word | Pages | PDF
- 18+ Written Statement Templates in PDF | DOC
- 25+ Disclosure Statement Templates in PDF | DOC
- 5+ Cash Flow Statement Analysis Templates in PDF | DOC
- 9+ Salary Statement Templates in PDF | DOC | XLS
- 18+ Personal Statement Worksheet Templates in PDF | DOC
- 22+ Impact Statement Templates in PDF | DOC
- 10+ Expenditure Statement Templates in Google Docs | Word | Pages | PDF | DOC
- 22+ Sworn Statement Templates in Google Docs | Word | Pages | PDF
- 19+ Purpose Statement Templates in PDF | DOC
- 13+ Clearance Statement Templates in PDF | DOC
- 23+ Verification Statement Templates in PDF | DOC
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.
- Business Templates
- Sample Statements
FREE 11+ Research Problem Statement Samples [ Marketing, Quantitative, Nursing ]

When you are going to come across researches in social sciences or even in humanities, you will notice that their research problems usually answers questions with “so what”. This type of question usually refers to surviving the quality of a measurement procedure. When you are going to answer questions having a “so what”, it simply implies that you don’t only have to show your available research materials, but also the thought of the significance of your research. In this article analysis , you will be able to know more about research problem statements and how to create a good one.
Research Problem Statement
11+ research problem statement samples, 1. research problem statement template, 2. sample research problem statement template, 3. research problem purpose statement template, 4. sample research problem statement template, 5. research problem title statement template, 6. standard research problem statement template, 7. printable research problem statement template, 8. research solicitation problem statement template, 9. research problem statement review form template, 10. statement of research problem template, 11. sample research proposal problem statement template, 12. editable research problem statement template, process of writing a research problem statement, example research problem statement, what is the criteria when reviewing for your problem statement, what should an effective problem statement do.
Research problem statement is defined as something that explains the problem in which your process improvement will address. In other words, it outlines all the negative points of the current situation and ultimately explains the reason why it actually matters. It is also a good tool used for communication which helps you in gaining total support from others. One of the major goals of a problem statement is to simply define the problem that is being addressed in a clear and precise manner. It focuses on the improvement of every processes and in steering every project scope .

- Google Docs

Size: 27 KB
Problem statements must possess the following attributes: clarity and precision, identification of what needs to be studied, identification of the key factors and variables, identification of key concepts and terms, articulation of the boundaries and parameters of the research study plan , generalizability to making use of the results or outcome, conveyance of the importance of the research study, benefits, and justification, does not have jargons, and conveyance to gathering descriptive type of data.

Size: 145 KB

Size: 599 KB

Size: 79 KB
Size: 403 KB

Size: 102 KB
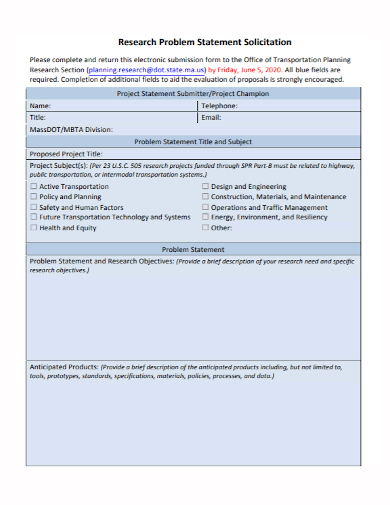
Size: 334 KB
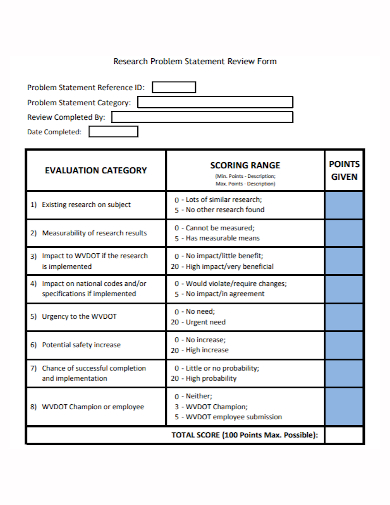
Size: 100 KB

Size: 63 KB

Size: 589 KB

Size: 14 KB
Step 1: Conceptualize the problem – the problem statement itself must be able to contain within our research problem and be able to provide a background on what should be known. For practical research, you should focus more on the details of the situation. For theoretical research, you should think about anything scientific, social, or a history background.
Step 2: Why it matters? – your problem statement should be able to address the importance of your research essay outline . What is more essential in this process is that you know exactly that it is researchable and feasible. For practical research problems, it should be relevant to the problem that directly affects the entire organization. For theoretical research problems, their relevance is not quite obvious.
Step 3: Know your objectives – ask yourself on how can you manage to address the problem. Your objective here is to seek for reasons behind the occurrence of the problem and propose effective and solid solutions.
“The staffing model in the Process Improvement Unit (PIU) has changed (we have more staff, and some of the staff have different working patterns) we need to have a clear way of recording status and sta ge of our business activities (projects, workshops and training) that will be used by all PIU staff, so that we can work effectively and provide good service to our customers. A member of staff is due to go on annual leave in two weeks time and we have no visibility or way of easily sharing information about their work analysis , this will make it hard for the rest of the team to cover the work during staff absence.” sheffield.ac.uk
It should only focus on one problem, should be 1-2 sentences long, and should not suggest a solution.
It puts the problem in the context, describe the present issue, show the importance of the problem, and set the objectives for your research.
If you want to see more samples and format, check out some of the research problem statement samples and templates provided in the article for your sample reference.
Related Posts
Free 10+ research worksheet samples, free 10+ analytical thesis statement samples, free 10+ educational impact statement samples, free 10+ internship statement of purpose samples, free 10+ product compliance statement samples, free 10+ safe work method statement samples, free 10+ community impact statement samples, free 5+ employee impact statement samples, how to write a a+ research paper, free 36+ statement examples & templates, free 28+ statement samples, free 10+ construction method statement samples, free 10+ graduate statement of purpose samples, free 8+ research agenda samples, free 10+ human resource statement of purpose samples, free 10+ quality management statement samples, free 9+ undergraduate research statement samples, free 35+ statement samples, free 10+ racial impact statement samples.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 3: Set your aims and objectives. Finally, the problem statement should frame how you intend to address the problem. Your goal here should not be to find a conclusive solution, but rather to propose more effective approaches to tackling or understanding it. The research aim is the overall purpose of your research.
From there, tally up the numbers and pick a winner. Step 4 - Craft your problem statement. Once you've selected your research problem, the final step is to craft a problem statement. Remember, your problem statement needs to be a concise outline of what the core issue is and how your study will address it.
Example Problem Statement 3 The Stakeholder Problem Statement. Example: In the last three quarterly employee engagement surveys, less than 30% of employees at Eample company stated that they feel valued by the company. This represents a 20% decline compared to the same period in the year prior.
The purpose of the problem statement is to identify the issue that is a concern and focus it in a way that allows it to be studied in a systematic way. It defines the problem and proposes a way to research a solution, or demonstrates why further information is needed in order for a solution to become possible.
A research problem statement typically includes the following elements: 1. The research topic: The general area of interest or field of study that the research project addresses. 2. The specific problem or issue: A clear and concise statement of the problem or issue that the research project aims to address. 3.
A research problem statement is the descriptive statement which conveys the issue a researcher is trying to address through the study with the aim of informing the reader the context and significance of performing the study at hand. The research problem statement is crucial for researchers to focus on a particular component of a vast field of ...
When you embark on a project or dive into research, understanding the core issue you're addressing is essential. Enter the problem statement. Think of it as a concise description of a challenge you're facing. It's not just about saying, "Here's an issue"; it's about defining the problem in clear, actionable terms.
Here is one way to construct a problem section (keep in mind you have a 250-300 word limit, but you can write first and edit later): It is helpful to begin the problem statement with a sentence: "The problem to be addressed through this study is…". Then, fill out the rest of the paragraph with elaboration of that specific problem, making ...
Establish the relevance of this research. The problem statement also needs to clearly state why the current research matters, or why future work matters if you are writing a research proposal. Ask yourself (and tell your readers) what will happen if the problem continues and who will feel the consequences the most.
Developing a 'good' research problem statement, therefore, involves systematic planning and setting time-based, realistic objectives. Your problem has to be achievable. You'll also need to apply feasible research methods based on an approach that best suits the research question. Your methods have to make sense.
That said, here are some things you should have at the back of your mind as you craft a problem statement for your research paper. 1. Make sure your problem statement is straight to the point. Every sentence should reinforce the importance of your study. 2. Narrow the scope of your problem statement.
Here are some general steps to follow when writing a problem statement: Identify the problem: Clearly identify the problem that needs to be addressed. Consider the context, stakeholders, and potential consequences of the problem. Research the problem: Conduct research to gather data and information about the problem.
Download free problem statement templates for Microsoft Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Adobe PDF, and Google Slides. Find project and customer problem statements. ... Problem statements are used in business settings and academic research to clearly define a problem that needs to be solved. A well-written statement is concise, narrow in focus, and ...
The answer is yes, for at least three reasons. 1) branding is important - a good title will help the reviewer establish a connection with your proposal 2) a negative first impression will likely linger with the reviewer while reading the rest of the problem statement, and 3) if the title is confusing, chances are the rest of the problem ...
The problem statement poses a crucial section of any dissertation, research project, and thesis, providing a concise and clear outline of the issue the study seeks to address. A well-written problem statement serves as a cornerstone in guiding the research process and sets the foundation for your methodology, findings, and research questions.This article will provide problem statement examples ...
10. Google Docs Research Problem Statement Template by Template.net. via Template.net. This simple Research Problem Statement Template makes it easy to draft a quick breakdown of an existing issue and offers support for coming up with solutions. It's available as a Google Doc, Apple Pages, or MS Word file.
52. Statement of Problem Template. Haidy Henry Dusim. Universiti Teknologi Mara (UiTM) Sabah. [email protected]. ABSTRACT. Writing a clear problem statement in rese arch helps the rea der to ...
Step 3: Set your aims and objectives. Finally, the problem statement should frame how you intend to address the problem. Your goal here should not be to find a conclusive solution, but rather to propose more effective approaches to tackling or understanding it. The research aim is the overall purpose of your research.
Use the problem statement template to clearly define and communicate a problem that needs to be addressed. This template helps to identify the scope, context, and significance of the problem with stakeholders in a structured workshop. ... Pro-tip: Be sure to include any user research or data that can provide further background information. 2 ...
45 Research Problem Examples & Inspiration. A research problem is an issue of concern that is the catalyst for your research. It demonstrates why the research problem needs to take place in the first place. Generally, you will write your research problem as a clear, concise, and focused statement that identifies an issue or gap in current ...
Step 1: You Own Vision. To formulate a good research problem statement it is essential that you establish your own vision board for the research problem. It is important to understand the benefits of solving the problem. That is when you will be able to establish a proper statement.
Process of Writing a Research Problem Statement. Step 1: Conceptualize the problem - the problem statement itself must be able to contain within our research problem and be able to provide a background on what should be known. For practical research, you should focus more on the details of the situation. For theoretical research, you should think about anything scientific, social, or a ...