Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Open access
- Published: 02 October 2023

Mapping crisis communication in the communication research: what we know and what we don’t know
- Shalini Upadhyay 1 &
- Nitin Upadhyay 2
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 10 , Article number: 632 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
3304 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Business and management
This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of crisis communication research from 1968 to 2022, utilizing bibliometric methods to illuminate its trajectories, thematic shifts, and future possibilities. Additionally, it presents foundational themes such as crisis communication and social media, health communication, crisis and leadership, and reputation and advertising. This analysis offers not only historical insights but also serves as a roadmap for future research endeavors. Furthermore, this study critically evaluates over five decades of scholarship by unveiling the intellectual, social, and conceptual contours of the field while highlighting thematic evolutions. Employing diverse bibliometric indices, this research quantifies authors’ and nations’ productivity and impact. Through co-word analysis, four thematic clusters emerge, capturing the dynamic nature of crisis communication research. However, the study also reveals limited collaboration among authors, primarily localized, indicating room for enhanced cross-border cooperation and exploration of emerging themes. The study’s social network analysis sheds light on key actors and entities within the crisis communication realm, underscoring opportunities to fortify global networks for a robust crisis communication spectrum. Beyond academic curiosity, these insights hold practical implications for policymakers, scholars, and practitioners, offering a blueprint to enhance crisis communication’s effectiveness. This study’s findings can be considered as a reference point for future studies in crisis communication.
Similar content being viewed by others
Worldwide divergence of values
Joshua Conrad Jackson & Danila Medvedev
Increase in concerns about climate change following climate strikes and civil disobedience in Germany
Johannes Brehm & Henri Gruhl
Persistent interaction patterns across social media platforms and over time
Michele Avalle, Niccolò Di Marco, … Walter Quattrociocchi
Introduction
Although crisis communication as such is not a new phenomenon (Coombs, 2021 ), it’s role has become more prominent in recent times because of the events such as 9/11, SARS, COVID-19 pandemic (Avraham and Beirman, 2022 ; Watkins and Walker, 2021 ). Such events have posed unprecedented challenges to crisis management teams and necessitated effective communication and appropriate response strategies. At the same time, these events have revived scholarly interest in the topic (Coombs, 2021 ). As a result, it becomes essential for the scholars to perform timely review of the literature, to explore and understand the diversity of the specific field (Tranfield et al., 2003 ). Not only such reviews help to consolidate the research but also establish connections between disparate bodies of research and understand the diversity of the field (Crossan and Apaydin, 2010 ; Tranfield et al., 2003 ).
Coombs ( 1998 ) defines crisis as “an event that is an unpredictable, a major threat that can have a negative effect on the organization, industry, or stakeholders if handled improperly.” Since a crisis can cause financial and reputational damage to the company, a considerable attention has been given to the research on crisis, crisis management and crisis communication (Coombs and Holladay, 2002 ) and also on appropriate crisis response strategies so as to enable the organizations to manage crisis and reduce harm (Coombs, 2007a ). Our results depict that crisis communication received recognition during late 1960s, and the first studies on “crisis communication” were published only in 1968. The field had limited contribution until late 1990s. However, the double digit annual publication began in the early 2000s and in the recent years the contribution has grown with over 150 publications annually. Between 1991 and 2009, the image restoration theory (Benoit, 1995 ; Benoit, 1997 ) and the situational crisis communication theory (Avery et al., 2010 ; Coombs, 1995 ; Coombs 2007b ) dominated crisis communication research. The image restoration theory was applied to analyze and study several case-based situations while the situational crisis communication theory was extensively utilized for experimental research. Both the theories have been adopted for qualitative and quantitative analyses with an aim to prevent reputational harm and thus these theories became organization centric. The current trend is more towards understanding stakeholders’ perspectives with a multivocal approach (Frandsen and Johansen, 2017 ). Additionally the dominance of social media increases the complexity of crisis communication (Bukar et al., 2020 ; Eriksson, 2018 ).
In the extensive literature on crisis communication, scholars have approached the study of crisis communication from various perspectives and have examined it through multiple lenses. Several recent literature (For e.g., Seeger et al., 2016 ; Zhao, 2020 ) have shed light on these perspectives. The research encompasses different stakeholders involved in crisis communication, including the supply side (such as destinations, cruise lines, hotels, and airlines), the demand side (including tourists, prospective visitors, and general public), as well as other relevant stakeholders like government entities, local residents, and employees. Moreover, the research has explored crisis issues across a wide spectrum, ranging from natural disasters like hurricanes, tsunamis, earthquakes, and wildfires, to human-made crises such as terrorist attacks and service failures (Avraham and Beirman, 2022 ; Watkins and Walker, 2021 ). Furthermore, the literature has also addressed the unprecedented crisis brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has had far-reaching implications for crisis communication. Importantly, the body of research takes a global perspective, encompassing various regions and countries. For instance, studies have examined crisis communication practices in diverse regions, including Asia, the Middle East, coastal destinations, as well as Western countries like Australia, the United States, and the United Kingdom. This global lens provides valuable insights into the different cultural, social, and contextual factors that shape crisis communication strategies and outcomes across different regions. However, the recent trends related to crisis communication scholarly research have gained traction, particularly in the past decade, especially in the US region (For e.g., Barbe and Pennington-Gray, 2018 ; Beck et al., 2016 ; Briones et al., 2011 ; Kwak et al., 2021 ; Liu et al., 2015a , 2015b ; Seeger et al., 2016 ; Sellnow and Seeger, 2013 ; Zhao, 2020 ).
Moreover, crisis communication research has been fragmented over the past two decades due to the emergence of several new sub-fields (Coombs, 2010 ; Coombs, 2021 ). This poses challenges to the researchers to cope up with the pace and volume of corpora (Yuan et al., 2015 ). Scholars (e.g., Lim et al., 2022 ; Mukherjee et al., 2022 ) recommend capturing scientific progress of a field by means of a systematic and comprehensive review. There are several review techniques that may be used to trace the scientific growth and potential research domains of a field. Various such review techniques have been employed in the crisis communication field to integrate and synthesize the existing knowledge. However, these studies have limited coverage and context of crisis communication. For example, previous studies have focused on organizational crisis communication (Fischer et al., 2016 ) and crisis communication in public relations (Avery et al., 2010 ). Few papers have intensively reviewed crisis communication during the pandemic and infectious disease outbreaks (MacKay et al., 2022 ; Malecki et al., 2021 ; Sadri et al., 2021 ) or captured risk and disaster communication (Bradley et al., 2014 ; Goerlandt et al., 2020 ). Lately, the focus has shifted toward using virtual channels and space (Eriksson, 2018 ; Liu-Lastres, 2022 ; Tornero et al., 2021 ; Wang and Dong, 2017 ; Yang, 2016 ).
However, these studies have dealt with the development of the field either through the qualitative approach in structured literature review (e.g., Valackiene and Virbickaite, 2011 ) or through the quantitative content analysis method (e.g., Li, 2017 ). Zupic and Čater ( 2015 ) claim that though structured literature review analysis deals with an in-depth examination, it insinuates subjective biases thereby constraining the scope of works. Additionally, despite its broader coverage in exploring key authors, topics, theories and methodologies, the content analysis is unable to capture the socio-cognitive structure. Suffice it to say that a comprehensive literature review which may capture intellectual, social and conceptual structures along with the thematic evolution of the crisis communication field has not been attempted (Ha and Boynton, 2014 ; Sarmiento and Poblete, 2021 ).
To overcome this gap bibliometric analysis is recommended which comprehensively captures the literature and traces its thematic evolution (An and Cheng, 2010 ; Moreno-Fernández and Fuentes-Lara, 2019 ; Zurro-Antón et al., 2021 ). Moreover, it facilitates the exploration of various performance metrics and mapping of the intellectual, social, and conceptual structures (Harker and Saffer, 2018 ; Lazzarotti et al., 2011 ). Wamba and Queiroz ( 2020 ) argue that bibliometric analysis examines large corpora of literature in an objective and evidence-based outcomes and it is more effective than the traditional methods (e.g., systematic literature review, meta-analysis, narrative analysis, etc.), which are labor-intensive and subjective. Additionally, bibliometric methods and visualization examinations are scalable and can be easily applied to a large corpora of literature covering authors and articles (Ki et al., 2019 ; Morgan and Wilk, 2021 ).
There are two approaches in bibliometric techniques—evaluative and relational. The evaluative review uses qualitative and quantitative methods covering aspects of the field’s ranking and contribution of different elements (e.g., sources, documents, institutions, and authors) (Benckendorff, 2009 ). The evaluative review focuses on productivity and impact (McKercher, 2012 ; Park et al., 2011 ). In contrast, relational review investigates relationships within the structures of the research field. It explores thematic evolution, co-authorship patterns, and co-citation (Benckendorff and Zehrer, 2013 ). Cobo et al. ( 2012 ) propose four different relational techniques for different contexts that answer who, when, where, what, and with whom questions by performing suitable analyses such as profiling, temporal, geospatial, topical, and network. It also facilitates a three-level analysis- micro (individual researchers), meso (regional-groups- journals), and macro (entire field). Overall, the relational analysis provides an in-depth coverage of the field, however, in the crisis communication area, it has not been utilized to explore and understand crisis communication research activity. Thus there is an inadequate synthetization of numerous aspects of the field in a single paper.
This paper utilizes relational analysis to explore and investigate the broad structure of crisis communication research. It aims at mapping crisis communication field by exploring its social, intellectual and conceptual structures over the past 50 years. Subsequently, the paper’s specific objectives are- determining the influential authors, countries and sources; and identifying major thematic areas affecting thematic evolution. Therefore, the process and outcomes of this paper are different from the studies that have either used or use traditional methods, as discussed above. However, the study’s outcomes complement those review articles that focus on specific contexts and aspects of crisis communication.
Methodology
In this study, we aim to map crisis communication in the communication research. The study also seeks to find the field’s social, intellectual and conceptual structures over the past 50 years. Additionally the future directions need to be explored.
Research questions
We defined the following research questions to map crisis communication in the following way:
RQ1: Who are the prominent contributors to the literature on crisis communication discipline?
RQ2: What is the social structure (or collaboration patterns) in crisis communication literature?
RQ3: What is the conceptual structure (or main research themes) in crisis communication literature?
RQ4: What is the intellectual structure in crisis communication literature?
RQ5: What are the future research directions in crisis communication scholarship?
The first research question was aimed at identifying the core contributors (author, document, source, institution and country) to the literature on crisis communication discipline, while the second question was designed to examine the collaboration pattern across levels—individual, institution, and country-level. The purpose of the third question was to gain more in-depth insights into the themes that have received attention in the literature. While the fourth research questions was aimed at identifying the intellectual patterns across levels—individual, document, and source. Finally, the fifth question was to identify the future directions in the crisis communication field.
We prepared the data considering two steps. First, we selected the source of data and then extracted the relevant articles based on the search query. We selected Scopus database to extract the relevant articles. The Scopus database includes all authors in cited references. This gives accuracy to the author-based citation and co-citation analysis. Further, we searched for the term “crisis communication” to extract relevant articles, and subsequently gathered 2487 documents. However, to explore the growth, contributions, and thematic areas we limited our search only to the journal articles in the English language. The search fields focus on covering abstracts, titles and keywords. Moreover, the search also had a criteria of limiting extraction of only articles (research and review) from peer-reviewed journals and excluding documents such as opinion pieces, book reviews, and commentaries. Finally, a sample of 1850 papers were included for further analyses.
Bibliometric methods for addressing RQs
We addressed RQ1 by performing descriptive analysis to identify core sources, authors, countries, publications, affiliations and prominent contributors to the literature on crisis communication. Measurements such as source impact (h-index and m-index), total citations (TC), and annual net publications (NP) were used to determine core sources and core authors. We used Bradford’s law to identify the core sources which are categorized into three zones. Zone 1 (the nuclear zone) is considered highly productive, while zones 2 and 3 represent moderate and low productions respectively (Zupic and Čater, 2015 ). Further, publication frequency and total citations were used to determine the top countries and affiliations.
We addressed RQ2 by using co-author analysis as it provides evidence of co-authorship when the authors jointly contribute to papers. Social structures are created when authors collaborate to develop and create articles. Moreover, when two authors co-publish a paper, they establish social ties or relationships (Lu and Wolfram, 2012 ). Co-authorship analysis can examine social structure at the level of the institute and the country. Co-authorship networks play a significant role in analyzing scientific collaboration and assessing the status of individual researchers. While they bear some resemblance to extensively studied citation networks, co-authorship networks signify a more robust social connection than mere citations. Unlike citations, which can occur between authors who are unfamiliar with each other and extend over time, co-authorship signifies a collegial and time-bound relationship, making it a focal point of Social Network Analysis (SNA) (Acedo et al., 2006 ; Fischbach and Schoder, 2011 ). To build the collaboration network, Louvain method was used as a clustering algorithm (Lu and Wolfram, 2012 ). The threshold of 50 as the number of nodes and 2 as the minimum edges were considered to avoid isolated and “one-time” collaboration. The nodes depicting isolation due to a lack of ties or relationships were removed.
Furthermore, in the field of social network analysis, centrality measures are crucial when examining the status of actors within a network. While various methods and measures are employed in SNA, centrality provides valuable insights into an actor’s position. One commonly used measure is degree centrality, which captures the basic essence of centrality by quantifying the number of connections an actor has with its immediate neighbors in the network. It reflects the total number of edges adjacent to a node and represents the incoming and outgoing links of an actor. Another significant measure is closeness centrality, which focuses on an actor’s proximity to all other actors in the network. While authors may be well-connected within their immediate neighborhood, they could still be part of partially isolated groups. Despite having strong local connections, their overall centrality might be limited. Closeness centrality extends the concept of degree centrality by emphasizing an author’s closeness to all other authors. Calculating closeness centrality requires determining the shortest distances between a node and all other authors, and then converting these values into a metric of closeness. A central author in the network is identified by having multiple short links to other authors. In addition, betweenness centrality offers a distinct perspective on centrality. It measures how often a particular node lies on the shortest path between pairs of nodes in the network. Nodes that frequently appear on these paths are considered highly central as they regulate the flow of information within the network. Although betweenness centrality can be applied to disconnected networks, it may result in numerous nodes with zero centrality since many nodes may not act as bridges within the network. This measure is based on the number of shortest routes passing through an actor. Actors with high betweenness centrality act as “middlemen,” linking different groups together.
Network analysis software enables the computation of centrality measures such as degree, betweenness, and closeness. These measures hold varying significance based on the specific network under examination. For instance, within a co-authorship network, an author’s degree centrality reflects the number of co-authored papers with other authors (Fischbach and Schoder, 2011 ). High betweenness centrality suggests that an author serves as a crucial link between distinct research streams. Furthermore, authors with high closeness centrality can establish connections with other authors in the network through shorter paths. UCINET (Borgatti et al., 2002 ) and Pajek (Batagelj and Mrvar, 1998 ) are the predominant software packages employed for network visualization purposes. For the present study, Pajek was employed to examine the social network and conduct centrality analyses.
We addressed RQ3 by using co-word analysis to gather concept space knowledge by utilizing the co-occurrence frequency of keywords. A co-word network is prepared based on the co-occurrence of words to examine specific areas of interest in crisis communication. We performed co-occurrence network analysis and hierarchical clustering to identify clusters that represent common concepts. The results were then described on the thematic map and theme evolution space. We considered 50 nodes as a threshold and a minimum of two edges for each node. Further, we chose the Louvain method for the clustering algorithm and the association as the normalization parameter for the analysis. Thematic mapping, built upon the keyword co-occurrence network and clusters, was performed to study the conceptual structure. We divided the evolution of thematic areas into four distinct periods (1968–1999, 2000–2007, 2008–2014, 2015–2022). These thematic areas represent a group of evolved themes across different subperiods. The evolution of key themes helps to understand variations in the research stream as well as provide necessary directions for future research., while interconnections link one theme with another thematic area. We also developed a thematic map representing four different themes based on their placement in the quadrant (Cobo et al., 2012 ), for example,
Themes placed in the upper-right quadrant are based on strong centrality and high density. These are the motor themes which are well developed and are important for shaping the research field.
Themes placed in the upper-left quadrant refer to the niche themes that are specialized and that depict peripheral characteristics.
Themes placed in the lower-left quadrant refer to the emerging or disappearing themes. They depict weak centrality and low density. Such themes are weakly developed.
Themes placed in the lower-right quadrant refer to the basic themes. These themes are important to the research field but are underdeveloped.
For addressing the RQ4, we performed co-citation analysis to develop clusters depicting the intellectual base of the field. Co-citation refers to the citation of two (or more than two) articles in the third article, which is the counterpart of bibliographic coupling. The Louvain method was used as a clustering algorithm to develop the co-citation network considering articles, authors, and sources. A threshold of 50 for a number of nodes, and 20 as the minimum edge strength (representing approximately 5% of the corpora in crisis communication) was considered. This as a whole aided in performing cluster level analysis.
Finally, the synthesis of the results of RQ1, RQ2, RQ3, and RQ4 helped to address the RQ5.
Scientific output (RQ1)
This section elaborates on the research landscape of crisis communication from 1968 to 2022. We gathered a total of 1850 articles by 3277 authors from 1222 institutions published in 646 journals as per the set criteria.
Publication output
The contribution to the field is highest through journal articles with over 95%, followed by review articles (4.7%). Moreover, around 28% of the articles are single-authored publications, while 72% are published in collaboration. The overall annual production of articles in crisis communication shows an exponential growth (Supplementary Fig. S1 ). The growth of the articles is stagnant between 1968 and 2000, with a few publications until 2000. However, growth is evident from the early 2000s, crossing double-digit publications annually. From 2015 onwards, annual publication growth improves by over 100 publications. Between 2020 and 2022, the annual publication count increases by over 200. Since 2015, the number of annual publications has been larger than the cumulative number of articles published before 2015. Overall, the annual growth rate of the research articles is 15% (the calculation does not include the period 1968–2000 and 2022 due to sensitivity).
Source output
A total of 1850 articles have appeared in 646 journals. The leading journals are the Public Relations Review which has hosted 249 publications, followed by the Journal of Contingencies and Crisis Management with 65 publications. Subsequently, the Journal of Communication Management has hosted 51 publications, followed by Corporate Communications with 48 publications, and then the Journal of Public Relations Research with 37 publications, respectively (Supplementary Table S2 ). The subject of crisis communication also belongs to the broader area of public relations and communication, which matches with the aims and scope of these journals. Additionally, the most cited sources, showcasing that the Public Relations Review has fetched the highest citations of 8284, followed by Journal of Contingencies and Crisis Management with 1539 citations. Subsequently, the Journal of Applied Communications Research has fetched 1522 citations, followed by the Journal of Public Relations Research with 1333 citations, and Corporate Reputation Review with 1158 citations, respectively. The Public Relations Review is identified as the top outlet for publication having the highest impact in the crisis communication field.
Most productive authors
Considering our dataset, 3277 authors from 1222 organizations have published articles on crisis communication. Sellnow has published the maximum number of articles with 35 publications on crisis communication, followed by Jin with 34 articles (Supplementary Table S3 ). Subsequently, Liu has published 33 articles followed by Spence with 28 articles, and then Lachlan has published 27 articles.
The author’s productivity and impact are measured considering the number of published articles and citations per year. It can be noted that Sellnow, Jin, Liu, Spence, and Lachlan are the most productive authors. While Coombs, Jin, Holladay, Liu, and Sellnow have received the highest citations (Supplementary Fig. S4 ). Scholars argue that the total citations received is not the only metric that determines the author’s production (Forliano et al., 2021 ; Huang and Hsu, 2005 ). Thus, we used three indicators—m-index, h-index, and the total citations (Supplementary Table S5 ). The most cited authors having more than 1000 citations in the database are Coombs (with 3418 citations), Jin (with 1914 citations), Holladay (1833 with citations), Liu (with 1655 citations), Sellnow (with 1299 citations), Spence (with 1200 citations), and Seeger (with 1095 citations). However, Coombs (TC = 3418 and h index = 18), Jin (TC = 1914 and h-index = 20) and Liu (TC = 1299 and h-index = 18) and Sellnow (TC = 1299 and h-index = 20) have the best combination of productivity and impact (Hirsch, 2005 ). For example, Coombs with h-index 18 has published 18 articles that have received at least 18 citations. Out of the top 20 contributors, 11 authors have h-index of at least 10. Hirsch ( 2007 ) suggests considering the contribution of young authors by the metric m-index, which determines the h-index weighted for the activity period of an author. Hence, young authors such as Claeys, Cauberghie, Kim, and Liu who started publishing from 2009 can be counted amongst the most influential authors.
Most productive institution
The most active organizations in this field are the University of Maryland (with 79 publications), the University of Kentucky (with 75 publications), the University of Florida (with 51 publications), the University of Georgia (with 50 publications), and Nanyang Technological University (with 49 publications) (Supplementary Table S6 ).
Most productive countries
Scholars argue that multi-authored publications might not represent the open collaborations dimensions of the most prolific countries publishing the articles. Thus, three different metrics are considered: SCP (single-country publication; intra-country publications), MCP (multiple-country publications; inter-country publications) and MCP ratio (ratio between MCPs and the total number of publications in the database TC; Supplementary Table S7 ). The MCP ratio determines the level of openness of the country to collaborate. It is noted that the intra-country publications are highest in the USA (SCP = 589), Germany (SCP = 51), China (SCP = 42), Sweden (SCP = 42), and the United Kingdom (SCP = 41) while inter-country publications are highest in the USA (MCP = 41), Korea (MCP = 23), the United Kingdom (MCP = 20), China (MCP = 17), and Hong Kong (MCP = 15). However, considering the MCP ratio, Hong Kong (MCP ratio = 0.555), Korea (MCP ratio = 0.54), Finland (MCP ratio = 0.33), the United Kingdom (MCP ratio = 0.32), and China (MCP ratio = 0.28) showcase openness in collaborations. It is surprising to note that the top 2 countries (USA and Germany) despite publishing the highest number of articles have limited openness in international collaborations as per the MCP ratio.
Additionally, considering total citations and production, the US emerges as the leader in production and impact; however, Korea, Netherlands, and Australia show a rising trend in terms of the impact, while China and Sweden, a declining trend (Supplementary Table S8 ).
Social structure (RQ2)
In this section, we performed analysis of collaborations patterns across three levels: author, institution, and country. Crisis communication has received contributions from 75 countries and 1222 different institutions publishing 1850 articles that depict global attention given to the field. In the database, multiple-authored articles (72% of the total published articles) are higher than single-authored articles.
Authors’ social structure
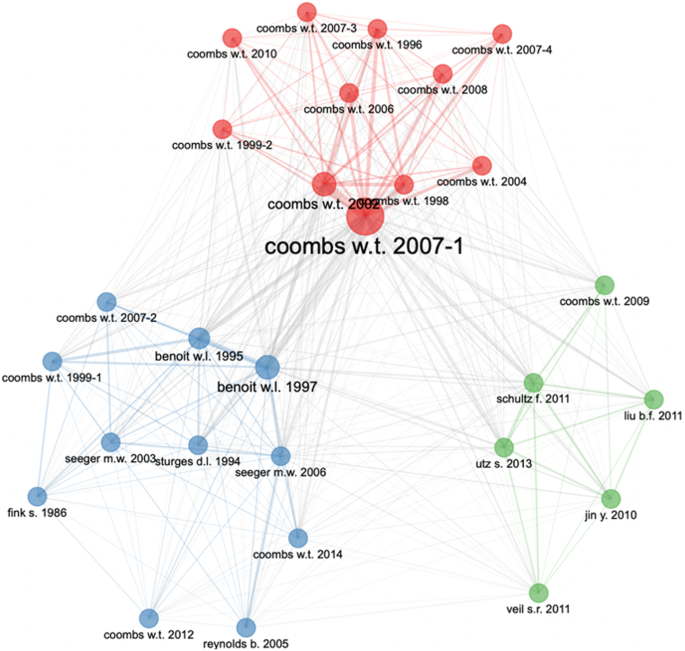
Figure 1 shows 11 clusters (in different colors) of the 36 most influential authors. Out of these 11 clusters, 6 are dominated by double authors while rest have more than two authors. Among the double author collaborations clusters, the one including Coombs and Holladay leads in terms of contribution and impact.
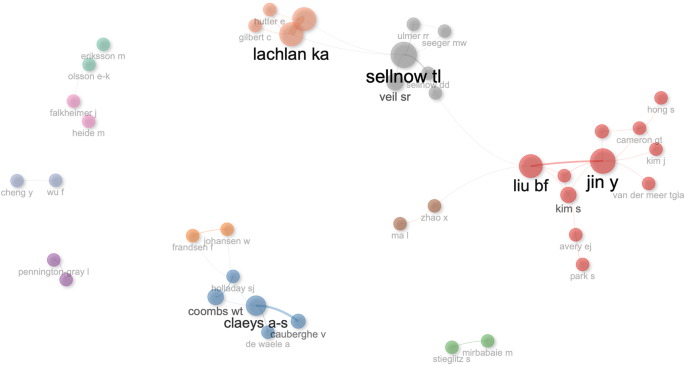
The network depicts 11 clusters.
Institutions’ social structure
Figure 2 shows the collaborations among the institutions. The institutional social structure is dominated by two clusters—cluster 1 (red color) and cluster 2 (blue color)—are led by University of Maryland and University of Kentucky, respectively.
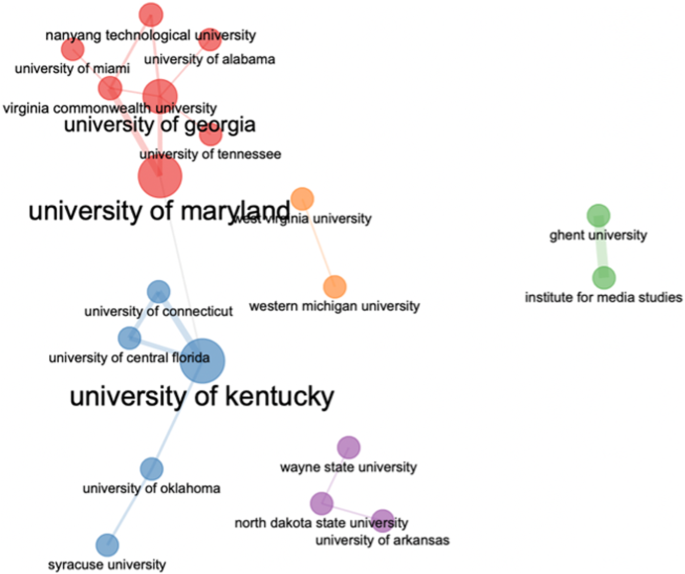
The network depicts five clusters.
Countries’ social structure
Figure 3 depicts country-wise social collaborations. The USA leads in terms of contribution and collaboration while countries like Malaysia and Nigeria show minimal collaborations. This indicates that there is a dearth of contributions from developing economies. Thus, investigating crisis communication in this context may be considered for further research.
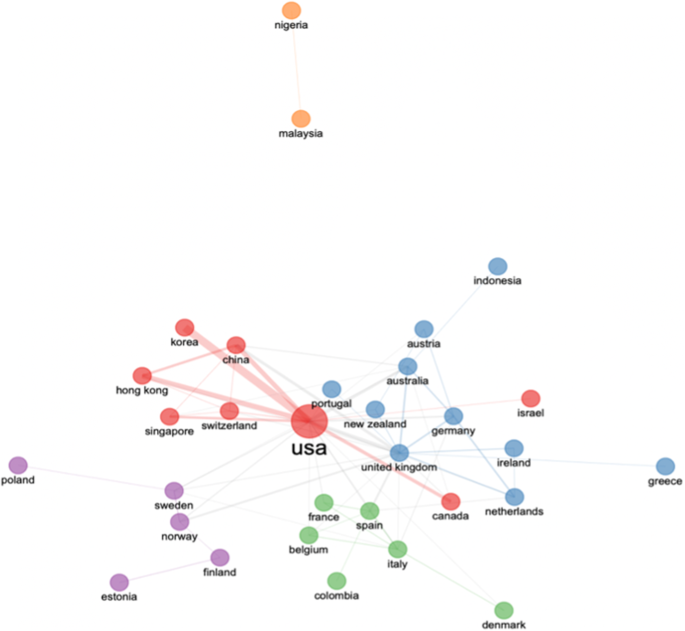
Social network perspective
We gathered a total of 1850 articles by 3277 authors from 1222 institutions published in 646 journals as per the set criteria. For a deeper insights, we examined the social network measures at two levels. Firstly, at the cluster level network for authors (Fig. 1 ), institutes (Fig. 2 ), and countries (Fig. 3 ). Secondly, for the complete social network for authors, institutes and countries, See Fig. S10 .
Betweenness centrality is a measure that quantifies the number of shortest routes passing through an actor in a network. Actors with high betweenness centrality play a crucial role in linking different groups together, acting as “middlemen”. In Table S9 , we observed that Liu for cluster 1, has the highest betweenness centrality (140), followed by Jin (89.7), Besides, Herovic for cluster 8, has the highest betweenness centrality (114), followed by Sellnow (104) in the studied network. This indicates that they serves as a central figure, connecting authors within the network in the field of crisis communication in Scopus from 1968 to 2022.
Furthermore, authors with a high closeness centrality are connected to all other authors through a small number of routes or paths, indicating their strong proximity to the entire network. A central author is distinguished by having numerous short connections to other authors within the network. According to the closeness centrality values presented in Table S9 where each clusters has more than 5 nodes, Liu in cluster 1, Claeys in cluster 2 and Herovic in cluster 8 exhibits the highest closeness centrality in their cluster network.
In Table S10 , we observed that University of Georgia for cluster 2, has the highest betweenness centrality (144.90), followed by University of Maryland (122.32). Besides, University of Tennessee takes the third place (112.32) in the studied network. This indicates that they serve as a central figure/point, connecting institutions within the network in the field of crisis communication in Scopus from 1968 to 2022. Furthermore, considering cluster nodes greater than 5, University of Maryland in cluster 2, and University of Kentucky in cluster 4 exhibit the highest closeness centrality in the their cluster network.
In Table S11 , we observed that USA for cluster 2, has the highest betweenness centrality (377.40), followed by United Kingdom (180.57), Besides, Italy takes the third place (68) in the studied network. This indicates that they act as a central figure, connecting country’s within the network in the field of crisis communication in Scopus from 1968 to 2022. Furthermore, considering cluster nodes greater than 5, USA in cluster 2, and “Italy” in cluster 1 exhibit the highest closeness centrality in the their cluster network.
Furthermore, when we examined the complete social network (Fig. S10 ) of authors, institutes and country based on the degree centrality, closeness and betweenness metrics, we identified significant insights and patterns. For example, as per Table S12 , among the authors listed, Lachlan has the highest author centrality score of 37, indicating a significant level of influence or importance within the field. Sellnow closely follows with a centrality score of 31, while Spence, Jin, and Claeys have scores of 34, 29, and 24, respectively. In terms of university centrality, the University of Kentucky has the highest score of 24, suggesting it holds a prominent position within the academic network. The University of Maryland and the University of Georgia share the second-highest centrality score of 20, followed by Virginia Commonwealth University with 15 and the University of Central Florida with 14. The country with the highest centrality score is the USA, with a score of 159. It is followed by the UK with a score of 91, China with 49, Australia with 41, and Spain with 37.
Based on the closeness centrality values presented in Table S13 , notable patterns emerged in the author, institutes, and country networks. In the author network, Jiu takes the lead with the highest closeness centrality score of 0.206531, closely followed by Herovic with 0.194615, Jin with 0.180714, and Sellnow and Kim with 0.171525. Shifting focus to the institutes network, the University of Maryland claims the top position with a score of 0.340000 in closeness centrality. Following closely behind is the University of Kentucky with 0.330000, the University of Tennessee with 0.325217, the University of Georgia with 0.320571, and the University of Central Florida with 0.295263. These institutions exhibit high closeness centrality, indicating their efficient access to information and strong connectivity within their respective networks. In the country network, the USA secures the highest closeness score of 0.660000, showcasing its exceptional accessibility and connectivity within the network. The United Kingdom follows closely with a score of 0.628571, demonstrating its strong network presence. Spain exhibits a score of 0.557746, Italy with 0.542466, and Australia and Sweden share a closeness score of 0.535135, all highlighting their significant connectivity and influence within the country network.
In Table S14 , a comprehensive view of betweenness centrality scores revealed significant insights into the network of authors and universities, along with their respective countries. Liu emerges as the most influential figure with the highest betweenness centrality score of 0.119048, followed closely by Sellnow with a score of 0.088435, and then Jin with 0.076288. These authors hold crucial positions, acting as central connectors within the field of crisis communication. Examining the betweenness centrality scores for universities, the University of Kentucky stands out with the highest score of 0.176513, occupying a prominent central position within the institution network. Following closely, the University of Georgia secures a score of 0.123216, and the University of Maryland follows suit with a score of 0.104022. Additionally, the University of Central Florida and the Nanyang Technological University both showcase their relevance, claiming positions in the top 5 among university betweenness centrality scores. Analyzing country betweenness centrality, the USA leads with the highest score of 0.320927, indicating its pivotal role in connecting various entities within the global network. The UK follows with a score of 0.153552, showcasing its significant influence as well. Australia, Italy, and Spain also demonstrate their bridging capacities, garnering respective scores of 0.082574, 0.058308, and 0.045895.
Conceptual structures (RQ3)
Scholars have argued the utility of keywords and co-occurrence analysis to develop prevalent themes in the underlying research field. The year wise cumulative occurrences of keywords depict dominance of “crisis communication” (Supplementary Fig. S9 ). The outcome of co-occurrence analysis is theme clusters. To explore the scientific knowledge structure of the field, in this study, a threshold of 500 author keywords was deployed. To explore the thematic evolution of crisis communication, four “time-slicing” periods were examined considering the publications growth, (Supplementary Fig. 1 ). These time periods are considered for the overall time distribution of publications: 1968–1999, 2000–2007, 2008–2014, 2015–2022. The time based thematic coverage analysis is based on four different quadrants (Cobo et al., 2012 ): motor themes, basic themes, niche themes, and emerging or disappearing themes.
First period (1968–1999)
During the period between 1968 and 1999, there is a limited development of the intellectual base depicting the emergence of only a few major themes. Crisis communication in the basic theme, plays a foundational role in defining the structure of the field during the first period. The basic theme indicates that “crisis communication” provided the foundation for exploring crisis management and issue management, which are important basic terms during this period. Advertising is identified as an emerging theme, with the focus on branding, e-communication, effective communication, image building, positioning, and reputation. The motor theme that emerges in this period is crisis focusing on crisis management and image restoration. However, this period does not identify niche themes.
During this period, several scholars have discussed the purpose and importance of reputation and advertising during crisis communication. Williams and Treadaway ( 1992 ) attribute the failure of Exxon’s crisis communication to the delay in the initial response and ineffective use of burden-sharing and scapegoating strategies. Argenti ( 1997 ), while exploring the “Dow Corning’s Breast Implant Controversy” case, identifies that the corporate (Dow Corning) failed to consider the reputation as a strategic tool during the crisis and poorly communicated with the stakeholders. Versailles ( 1999 ) argues the role of effective communication in shaping and building a reputation for Hydro-Québec’s crisis communication. Likewise, U.S. airlines gained public support and confidence after the 9/11 crisis by using timely and honest communication, and by utilizing appropriate crisis response strategies such as suffering (Coombs, 1995 ; Massey, 2005 ). Saliou ( 1994 ) advocates using an adaptive crisis communication strategy to defuse panic, avoid rumors and vulnerability, manage local and global stakeholders, and disseminate information to target groups. Advertising, on the other hand, plays a critical role in building reputation during crises (Versailles, 1999 ).
Second period (2000–2007)
The thematic focus during 2000 and 2007 indicates an expansion of the intellectual base with a diverse set of concepts.This suggests a slight paradigm shift toward recognizing crisis communication as a multi-dimensional theme. Motor themes in this period are: risk assessment, leadership, attribution, and public health. In the motor theme, public health and attribution dominate the theme. For the public health theme the focus is on the exploration of disaster communication, flu pandemic communication and terrorism management, while the attribution theme focuses on responsibility and accountability. Surprisingly, the basic themes have a large coverage focusing on corporate image, public relations, crisis communication and crisis. Crisis communication dominates the basic theme by having a larger coverage on risk communication, media relations, image repair, political communication, crisis management, and response strategies. The theme public relations focuses on crisis planning, conflict management, corporate image, and corporate communication. The presence of niche theme - attribution and emerging theme - communication strategies is also evident.
During this period, the focus is majorly on the developments of appropriate theoretical frameworks. Hearit’s ( 2001 ) theory of corporate apologia proposes the rhetorical concept of self-defense, wherein organizations are seen as possessing public characters, and this provides momentum to the term reputation. Kauffman ( 2001 ) argues that NASA’s timely, honest, and open communication regarding the Apollo 13 crisis with the public and stakeholders, bolstered its image and attracted public and congress support for further manned space explorations. Coombs ( 2007a , 2007b ) attribution theory and Situational Crisis Communication Theory (SCCT) suggest embracing the field’s evolution and the influx of empirical methods in the context of crisis communication (Arpan and Roskos-Ewoldsen, 2005 ). More emphasis is given to prescriptive, rather than descriptive methods of investigation and analysis. Attribution is directly linked to people’s need to search for causes of the event (Weiner, 1986 ), making it logical to connect crisis with attribution theory (Coombs, 2007a ). Cowden and Sellnow ( 2002 ) explores the role of attribution as part of the image restoration strategies for Northwest Airlines (NWA) in proactively reducing the culpability of the strike. Gallagher et al. ( 2007 ) argue that an organization’s decision to acknowledge its role in the crisis is vital for crisis communication and for establishing public relations. It is important to be in sync with health systems to share relevant and appropriate information. For example, Mebane et al. ( 2003 ) find that a deviation of media and information shared by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) related to Anthrax caused panic. Various empirical studies have attempted a prescriptive approach to analyzing the crisis. Additionally, public segmentation in communicating (Rawlins and Bowen, 2005 ) enhances the organization’s public relations. By doing so, organizations become aware of customers’ perceptions of the crisis response, thereby offering appropriate public relations communication.
Third period (2008–2014)
In this period, the number of annually published articles increases remarkably. Seven major themes emerge and their spread is evident in the four quadrants. There is a presence of a niche theme in terms of risk and crisis communication, focusing on health communication, pandemic, flu, H1N1, influenza, and risk perception. However, strong linkages are witnessed between health communication, and response strategy. The theme risk and crisis communication focuses on organizational communication, political communication, internal communication, and corporate communication. In addition, response strategy is closely linked to organizational communication, and crisis response. The emerging theme identifies situational crisis communication as a collective theme that focuses on leadership, contingency, crisis response strategy, ethos, crisis responsibility, image repair, and threats. The basic theme is dominated by crisis communication and communication. The motor themes include corporate communication, corporate social responsibility, communications and emotions.
Avery et al. ( 2009 ) attribute crisis communication to multiple contexts (e.g., delay, use of scapegoating strategies). Crisis communication, built around the concept of corporate apologia, aims to develop rhetorical strategies to reduce reputational harm and help organizations build images and restore order (Coombs et al., 2010 ). Gallagher et al. ( 2007 ) argue that an organization’s decision to acknowledge its role in the crisis is vital for crisis communication and for establishing public relations. However, when an organization responds in a timely manner and follows transparency in communication, it attracts the trust and support of stakeholders. Identifying the type of response and understanding its consequences also plays a critical role in managing crisis communication. For example, an organization in crisis struggles to choose the correct answer as the choices vary— defensive vs. offensive, reactive vs. proactive, vague vs. transparent, etc. However, to effectively manage crisis communication, an organization must consider reputational, legal and financial outcomes (Avery et al., 2009 ). Internal communication in health organizations is critical for health practices. For example, Schmidt et al. ( 2013 ) identify a lack of correct perception of influenza by healthcare workers, thereby limiting the execution of timely vaccination. Kim and Atkinson ( 2014 ) identify critical factors such as brand ownership, exposure to media, and involvement with the crisis and consider advertising as a tool to communicate with consumers during the crisis to shape reputation.
Fourth period (2015–2022)
In this period, the field grows multidimensionally, including all the four themes. The motor theme includes COVID-19, and crisis management. The emerging theme focuses on crisis. The basic theme represents crisis communication and the emerging theme depicts the importance of public relations, and crisis. The niche theme focuses on risk communication. An interesting insight is the inclusion of the pandemic COVID-19 under the motor theme, which is strongly related to the niche theme in the earlier period. This shows that this period witnessed a dramatic shift in the themes and focal interest.
During this period, both scholars and practitioners consider the use of social media as a new-age communication tool, as it helps to offer direct and personalized communication to social media consumers. Such communication helps to shape and build reputation during a crisis. For example, Wang ( 2016 ) argues that social media is an effective crisis communication tool for turning crises into opportunities. Ho et al. ( 2017 ) propose a corporate crisis advertising framework and validate its applicability in managing and restoring an organization’s reputation. The authors also focus on the role of omni-channel (e.g., social media, print media, TV, radio) and short-, medium-, and long-term crisis communication plans to manage and shape their reputations. Additionally, Claeys and Opgenhaffen ( 2021 ) argue that to manage crisis communication effectively impact of reputational consequences and legal and financial outcomes needs to be considered. Hyland-Wood et al. ( 2021 ) argue on deploying crisis communication responses by including clear messages shared through appropriate channels and trusted sources. Such messages are customized to attract diverse audience members. Additionally, public segmentation in communicating (Rawlins and Bowen, 2005 ) enhances the organization’s public relations (Wen et al., 2021 ). By doing so, organizations become aware of customers’ perceptions of the crisis response and thereby offer appropriate public relations communication. Santosa et al. ( 2021 ) argue using varied public relations professionals’ communication strategies based on gender. Moreover, Malik et al. ( 2021 ) highlight the role of health organizations in countering misinformation on social media. They suggest that few elements such as timely and accurate information, and inclusion of credible sources help to streamline the facts.
Overall themes
Figure 4 shows the development of the four major clusters. The number of times the term is used is proportional to the size of the node. The nodes that are closely linked are the proximate nodes, while the thickness of the links connecting the nodes is proportional to the strength of the connection.

The network depicts four clusters.
Cluster 1: crisis communication and social media
The largest cluster (in red) includes 23 items and is mainly related to crisis response strategies, strategic communication, situational crisis communication, and communication on social media. The linkages to terms such as image repair, internal communication, and corporate communication may indicate that crisis communication concerns related to organizations can provide multiple co-benefits and strengthen public relations (Coombs, 2021 ; Tornero et al., 2021 ).
Cluster 2: health communication
Cluster 2 (in blue) consists of ten items and mainly covers issues related to public health and health communication. This cluster has strong links to infectious disease outbreaks, pandemics, and associated risk communication. Moreover, the inclusion of political communication to deal with the level of severity of the threat or risk is found to be critical.
Cluster 3: crisis and leadership
Cluster 3 (in green) includes ten items and focuses on two major areas: crisis and leadership. Other terms, such as disaster, risk, apology, resilience, and reputation are closely related to crisis and leadership.
Cluster 4: reputation and advertising
Cluster 4 (in purple) includes seven items and focuses on two major aspects: reputation and advertising for brand building. This cluster has strong links to corporate reputation, media, trust, advertising, and leadership. Related terms are closely linked to reputation that may indicate strategic alignment of leadership to communicate effectively (Coombs and Holladay, 2002 ).
Intellectual structure (RQ4)
In this section, we examined the intellectual collaborations patterns across three levels: author, sources, and documents. We performed the co-citation network analyses to explore the intellectual structure. Figure 5 presents two clusters that dominate the intellectual structure based on the authors. Cluster 1 (in blue color) is driven by Kim, Jin, Liu, Lee, Veil Smith, and Schultz, while cluster 2 (in red color) is driven by the contributions of Coombs, Benoit, Seeger, Heath, and Ullmer. Cluster segmentation depicts diverse dominant areas of research interests among the authors.
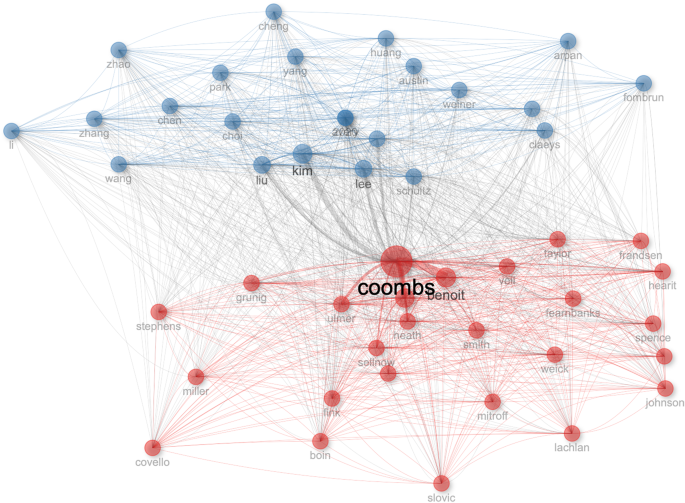
The network depicts two clusters.
Figure 6 presents the development of three major clusters showcasing the intellectual structure of the research in crisis communication based on sources. Cluster 1 (in red color) is dominated by Public Relations Review, Journal of Public Relations Research , and Journal of Applied Communication Research . Cluster 2 (in green) is driven by Corporate Reputation review, Journal of Personality and Psychology, Journal of Business Research and Business Horizons . However, Cluster 3 (in blue), is driven by Management Communication Quarterly, Corporate Communications: An International Journal, and Journal of Business Communication .
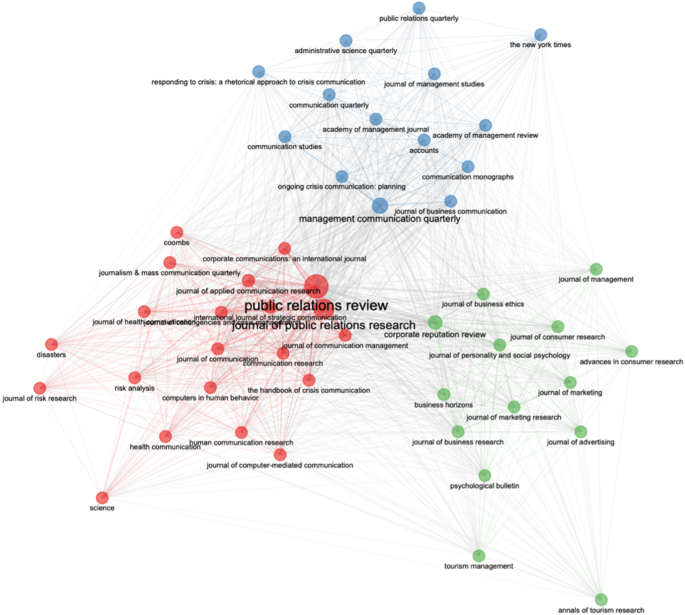
The network depicts three clusters.
Figure 7 presents the development of three major clusters showcasing the intellectual structure of the research in crisis communication based on contributed papers. Cluster 1 (in red color) is dominated by Coombs ( 2007b ), Coombs and Holladay ( 2002 ), and Coombs ( 1998 ). Cluster 2 (in blue color) is driven by Benoit ( 1995 ), Benoit ( 1997 ), Seeger ( 2006 ) and Schultz et al. ( 2011 ). Cluster 3 (in green color) is driven by Schultz et al. ( 2011 ), Coombs ( 2009 ), and Jin ( 2010 ). The cluster segmentation depicts the diverse dominant areas of research interests among the authors.
Crisis communication is one of the most important critical elements of the communication research. The availability of large corpora of literature on crisis communication necessitated a bibliometric approach to study its evolution and growth in the communication field. We adopted bibliometric visualization techniques to understand the trajectory of crisis communication scholarship. First, we used descriptive analysis to study the prominent contributors to the field with respect to the authors, sources, institutions, and countries. We portrayed the growth trajectory and presented the trend analysis including the most productive and impactful authors, sources, countries and institutions. Second, the co-authorship analysis was done to project the social structures of the crisis communication research. This enabled us to present the social collaboration relationship of different, authors institutions and countries. Besides, we performed the analysis of social network measures to explore valuable insights into the dynamics of collaboration within the crisis communication domain. To delve deeper into the networks, we examined the cluster-level networks for authors, institutes, and countries, as well as the complete social network. The network measures (degree centrality, closeness and betweenness) shed light on the pivotal actors, institutes, and countries within the crisis communication domain, illustrating their roles as central connectors and influential figures. The findings have provided valuable insights into the collaborative landscape, facilitating a deeper understanding of the dynamics and relationships that shape the field of crisis communication in Scopus from 1968 to 2022.
Third, we performed the co-word analysis to gather concept space knowledge by utilizing the co-occurrence frequency of keywords. Subsequently, co-occurrence network analysis and clustering were used to identify clusters that represent common concepts. The keywords co-occurrence network and clusters developed the thematic mapping and thus presented the conceptual structure. Fourth, we performed the co-citation analysis of author, reference and sources to develop the intellectual structure of the field. This projected the network relationship among the authors.
Theoretical implications and roadmap for future research
This paper is one of its own kind, in which co-occurrence, co-authorship and co-citation analyses were performed to understand the growth and development of crisis communication research in the communication field. This paper presents the advantages of bibliometric analysis over the traditional methods in the study of crisis communication literature. For example, bibliometric analysis not only covers the full spectrum of the available literature, but it also objectively navigates the development of the field by exploring the social, conceptual and intellectual structures of the crisis communication research, while, traditional methods are unable to capture and synthesize large datasets of authors and articles (García-Lillo et al., 2016 ).
By utilizing bibliometric visualization, this study examines the patterns of interactions among key authors and articles; and develops clusters of research themes. The interaction patterns and relationships provide insights into the knowledge domain (Hu and Racherla, 2008 ), while clustering technique depicts key papers with similarities in topics (Chen, 2006 ). Bibliometric visualizations facilitate a display of temporal data in different colors. Additionally, a longitudinal view in the form of four quadrants provides the thematic evolution of crisis communication research and presents the evolution and growth of major themes. These projections aid researchers in identifying research boundaries and display recent themes (Chen, 2006 ).
This paper presents insights into the intellectual, social and conceptual structures of the crisis communication field. The other major contribution of the study is the formulation of the research questions which are mentioned in the methodology section. RQ1 findings identified core sources, authors, countries, publications, and affiliations to examine prominent contributors to the literature on crisis communication. We observed that 3277 authors from 1222 institutions published 1850 articles in 646 journals addressing crisis communication within more than 50 years (with the first publication being released in 1968). Though Sellnow appeared to be contributing the highest number of articles with the most extended unbroken series of publications from 1993 to 2022, Coombs received the best combination of productivity and impact (TC = 3418 and h-index = 18). Our results also corroborate with other bibliometric studies where the author’s production and impact are measured considering the number of articles published, total citations, and h-index (for example, Forliano et al., 2021 ). Moreover, among the young and influential authors the works of Claeys, Cauberghie, Kim and Lin are noteworthy. Further the annual scientific publication growth was stagnant in Period 1 and increased in Period 2. However, rapid growth was evident after 2015, in Period 4. This may be attributed to the wide availability of information channels and global events (Maal and Wilson-North, 2019 ). Public Relations Review outranks all other journals by publishing the highest number of articles (249) on crisis communication. This journal published thrice more than the number of articles published by the Journal of Contingencies and Crisis Management which stood second in the list. These results are in concurrence with the earlier studies that found Public Relations Review published the highest number of articles (e.g., An and Cheng, 2010 ; Avery et al., 2010 ).
RQ2 examined the social structure of the crisis communication research domain. Borgatti et al. ( 2013 ) and Grace et al. ( 2020 ) suggest that social collaborations are majorly driven by geographic and institutional proximity. This is corroborated in the current study as well. Country collaboration depicts network of authors and we observed that the concentration of the publication corpora was within a few countries, out of which the USA depicted a huge presence. We also observed that the most productive countries do not always have high openness in collaborations. This observation should encourage more scholars to consider contributing to the present debate and enhance cross country collaborations (Massaro et al., 2016 ). We noticed that the contributions in crisis communication were fragmented despite receiving increased attention in the recent years. Hence a proper synthesis and systemization of work is potent to expand the crisis communication production and impact. We identified 11 co-author clusters depicting the most influential scholars with confined collaborations. Out of these, 6 clusters had collaborations of only two influential scholars. We observed that 28% of contributions were from single-authored publications. We suggest that more scholars should contribute to the crisis communication space. The results from the co-authorship network present the current state of collaboration and the most influential authors on crisis communication. Our evidence suggests that there is relatively little collaboration among authors, and much of this is localized. We noticed that the social structure at the level of institutions is dominated by the universities in the USA (e.g., University of Maryland and University of Kentucky). According to the social collaboration structure, the contribution of developing countries is minimal in the crisis communication space. Thus, more collaborations and empirical evidence may be solicited from the developing countries.
RQ3 explored popular themes in the crisis communication literature with the help of keywords and co-occurrence (or co-word) analysis. Overall, four major themes emerged: (a) crisis communication and social media (b) health communication, (c) crisis and leadership, and (d) reputation and advertising. The keywords related to the themes were a part of the crisis communication evolution during the study period (1968–2022). The results of our citation analysis suggest that a limited number of articles have shaped the field. We observed a clear shift in crisis communication and response strategies with the onset of omni-channels, such as social media platforms.
RQ4 examined the emergence of two main groups in the intellectual structure (co-citation analysis). Despite having a relatively low number of relational ties, they act as knowledge brokers among the groups. This may be due to closed group collaborations, and thus, better collaborative efforts among scholars are needed. Coombs ( 2007b , 2002 , 1998 ) dominate the intellectual space in terms of the document-based intellectual structure. The thematic development and its evolution are helpful for scholars, sources (journals), institutions and countries to acquire knowledge on specialized and highly relevant topics. More specifically, niche and emerging themes may address the immediate call for research and collaborations. Journals are encouraged to announce special issues on these themes. Additionally, journals may increase the number of publications as they are ranked among the most impactful ones but have relatively low number of publications.
The findings of the paper has implications for crisis communication research in terms of examining the social, conceptual and intellectual structures of the field. Given the large corpora and growth of crisis communication research over the last 50 years, Biblioshiny, serves as a useful tool to objectively capture the social and intellectual collaborations, growth and evolution of concept and knowledge space of this field (Denyer and Tranfield, 2006 ). These insights, therefore, may be extremely useful to the early scholars or researchers from outside the field (Benckendorff and Zehrer, 2013 ).
The overall findings and analysis of this paper present several opportunities for future research in the field of crisis communication. A list of potential research questions is prepared as the outcome of RQ5 which was accomplished by collating the results of RQ1, RQ2, RQ3, and RQ4.
While research opportunities are immense in crisis communication, the following research questions can be considered for further understanding, see Table 1 :
The findings from our study on social network measures at two levels, namely, cluster-level networks for authors, institutes, and countries, as well as the complete social network for authors, institutes, and countries, have provided valuable insights into the field of crisis communication from 1968 to 2022. The application of network metrics, such as degree centrality, betweenness centrality and closeness centrality, has enabled us to identify key actors, institutions, and countries that play pivotal roles in linking different entities within the crisis communication domain. Figure 8 represents the framework enhancing social collaboration based on the social network analyses.
Identifying Key Connectors: The analysis of betweenness centrality in Tables S9 , S10 , and S11 has revealed central figures, such as Liu and Herovic in the author network, University of Georgia and University of Maryland in the institute network, and USA in the country network. These individuals and entities act as “middlemen,” connecting various clusters and facilitating efficient information flow between different groups. Researchers and policymakers can leverage this insight to foster collaboration and knowledge exchange among the identified central figures, thereby enhancing crisis communication efforts globally.
Enhancing Network Proximity: Authors with high closeness centrality scores, like Liu in cluster 1, Claeys in cluster 2, and Herovic in cluster 8, have strong proximity to the entire network. Similarly, institutes with high closeness centrality scores, such as University of Maryland, University of Kentucky, and University of Tennessee, exhibit efficient access to information within their respective clusters. Policymakers and practitioners can focus on strengthening ties and communication channels among these authors and institutions to foster a more cohesive and well-connected crisis communication community.
Promoting Global Collaboration: The country network analysis based on betweenness centrality in Table S11 has highlighted the significant role of countries like the USA, United Kingdom, and Italy in connecting various nations in the crisis communication research domain. This implies that these countries have the potential to facilitate global collaboration and knowledge dissemination. Encouraging international conferences, joint research initiatives, and exchange programs can further strengthen ties between these influential countries and foster a more inclusive and comprehensive approach to crisis communication worldwide.
Identifying Influential Authors and Universities: Table S12 has provided a comprehensive view of the author and university centrality scores. Researchers can collaborate with authors like Lachlan and Sellnow who hold substantial influence and importance within their field. Additionally, universities like University of Kentucky and University of Maryland stand out as prominent knowledge hubs, making them potential partners for collaborative research and academic exchanges.
Leveraging Network Insights for Crisis Management: The identification of influential actors, institutes, and countries through betweenness centrality can be instrumental in strategic crisis management. By collaborating with central figures, crisis communication efforts can be streamlined, and rapid response systems can be developed, ensuring effective handling of crises and their aftermath.
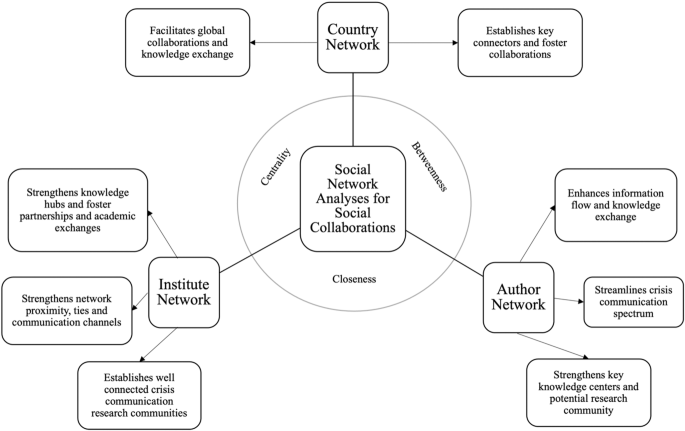
Framework for enhancing social collaboration based on the social network analyses.
Limitations
This study is not devoid of limitations. First, the Scopus database is used to gather a quality dataset for the study. This limits the analysis of publications as other databases such as Google Scholar, WOS, PubMed, etc., might include more publications. Additionally, some conditions were applied to improve the performance analysis (e.g., year of publication, type of document, language). Therefore, future research can address this gap by retrieving datasets from all popular databases for further analysis. Second, the inherent complexity of certain metrics, such as the usage of h-index or comparable metrics, might induce some inconsistencies. As such, future research can provide comparisons of metrics while performing an analysis. Third, a mixed approach (quantitative and qualitative) may be considered in future work to provide more specific analysis in terms of theory, context, and implications. Fourth, currently the social network analyses was limited to two levels—cluster and a complete network considering three measures degree centrality, betweenness, and closeness—to explain social collaborations. However, future research can perform an extensive and detailed social network analyses.
Lastly, Biblioshiny software presents some limitations in terms of database selection, division of periods, threshold selection and adjustment of suitable nodes and links for analysis. These parameters are generally selected by researchers on the basis of past papers, which may yield slightly different networks on account of different settings. However, Biblioshiny with its high stability in running the data provides consistent results for the same data and parameters. This enhances the reliability of the results. Though Biblioshiny offers visualization of data and networks at different depths by zooming-in and zooming-out, such dynamic visualizations are not present in the paper. We recommend inclusion of three-dimensional visualizations for improving visibility and exploring relationships as a separate supplementary material.
Conclusions
This paper presents the first bibliometric study of crisis communication between 1968 and 2022. We critically appraised more than 50 years of crisis communication scholarship, described its intellectual, social, and conceptual structure and its thematic evolution over time, and identified many opportunities and directions for future research. With the publications in the highly reputable journals, the research in crisis communication field has grown exponentially since 1968. Various bibliometric indicators were used to capture the productivity (e.g. total publications) and impact (total citations received, h-index, m-index, citations per year) of authors, sources and countries. We identified four thematic clusters under the conceptual structure by using co-word analysis, such as, crisis communication and social media, health communication, crisis and leadership, and reputation and advertising . The presence of crisis communication as a basic theme in all the four periods demonstrate that though the theme is important to the research field but it is underdeveloped. Collaboration analysis showed that the most productive countries do not always have high openness in collaborations. Further, the findings depicted relatively little collaboration among authors, and much of it was localized. More openness in country-wise collaborations along with examination of niche and emerging themes may provide immense opportunities for future research. Our study on social network measures has shed light on key actors, institutes, and countries in the field of crisis communication. The implications of this research extend beyond academic curiosity, as the identified central figures and well-connected entities offer potential avenues for strengthening global crisis communication networks and enhancing collaborative efforts in times of need. Policymakers, researchers, and practitioners should capitalize on these insights to create a more resilient and responsive crisis communication landscape for the future.Thus, this paper attempts to make a prominent contribution by presenting the growth of the field along with future research opportunities.This paper will help both the scholars and the practitioners with a comprehensive review of the scholarly literature on crisis communication to address the future needs and to explore proposed avenues for further research.
Data availability
The data analyzed in this study is subject to the licenses/restrictions: original data were sourced where indicated from the Scopus. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to https://www.scopus.com/home.uri .
Acedo FJ, Barroso C, Casanueva C, Galan JL (2006) Co-authorship in management and organizational studies: an empirical and network analysis. J Manag Stud 43(5):957–983. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6486.2006.00625.x
Article Google Scholar
An SK, Cheng, IH (2010). Crisis communication research in public relations journals: tracking research trends over thirty years. In: The handbook of crisis communication. Wiley-Blackwell, p 65–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444314885.ch3
Argenti P (1997) Dow Corning’s breast implant controversy: managing reputation in the face of ‘junk science’. Corp Reputation Rev 1(2):126–131. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.crr.1540031
Arpan LM, Roskos-Ewoldsen DR (2005) Stealing thunder: analysis of the effects of proactive disclosure of crisis information. Public Relat Rev 31(3):425–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2005.05.003
Avery DR, Richeson JA, Hebl MR, Ambady N (2009) It does not have to be uncomfortable: the role of behavioral scripts in Black–White interracial interactions. J Appl Psychol 94(6):1382–1393. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0016208
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Avery E, Lariscy R, Kim S, Hocke T (2010) A quantitative review of crisis communication research in public relations from 1991 to 2009. Public Relat Rev 36:190–192. pp:
Avery, E (2017) Public information officers’ social media monitoring during the Zika virus crisis, a global health threat surrounded by public uncertainty. Public Relat Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2017.02.018
Avraham E, Beirman, D (2022) From SARS through Zika and up to Covid-19: destination recovery marketing campaigns in response to pandemics. Ann Leis Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/11745398.2022.2070511
Barbe D, Pennington-Gray L (2018) Using situational crisis communication theory to understand Orlando hotels’ Twitter response to three crises in the summer of 2016. J Hosp Tour Insights 1(3):258–275. https://doi.org/10.1108/JHTI-02-2018-0009
Barbe D, Pennington-Gray L, Schroeder A (2018) Destinations’ response to terrorism on Twitter. Int J Tour Cities 4(4):495–512. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJTC-04-2018-0027
Batagelj V, Mrvar A (1998) Pajek - program for large network analysis. Connections 21(2):47–57
MATH Google Scholar
Beck M, Foster W, Kenney C, O’Rourke J (2016) Airbnb: crisis communication in the sharing economy. J Organ Behav Educ 9:1–15
Google Scholar
Benckendorff P (2009) Themes and trends in Australian and New Zealand tourism research: a social network analysis of citations in two leading journals (1994–2007). J Hosp Tour Manag 16(1):1–15
Benckendorff P, Zehrer A (2013) A network analysis of tourism research. Ann Tour Res 43:121–149
Benoit WL (1995) Accounts, excuses and apologies: a theory of image restoration strategies. State University of New York Press, Albany, NY
Benoit WL (1995) Sears’ repair of its auto service image: image restoration discourse in the corporate sector. Commun Stud 46(1-2):89–105. https://doi.org/10.1080/10510979509368441
Benoit WL (1997) Image repair discourse and crisis communication. Public Relat Rev 23(2):177–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0363-8111(97)90023-0
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Borgatti SP, Everett MG, Freeman LC (2002) UCINET for windows: software for social network analysis. Analytic Technologies, Harvard, MA
Borgatti SP, Everett MG, Johnson JC (2013) Analyzing social networks. London: Sage
Bradley D, Mcfarland M, Clarke M (2014) The effectiveness of disaster risk communication: a systematic review of intervention studies. PLoS Curr. https://doi.org/10.1371/currents.dis.349062e0db1048bb9fc3a3fa67d8a4f8
Briones RL, Kuch B, Liu BF, Jin Y (2011) Keeping up with the digital age: how the American Red Cross uses social media to build relationships. Public Relat Rev 37(1):37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2010.12.006
Bukar U, Jabar M, Sidi F, Nor R, Abdullah S, Othman M (2020) Crisis informatics in the context of social media crisis communication: theoretical models, taxonomy, and open issues. IEEE Access 8:185842–185869. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3030184
Chen C (2006) Citespace II: detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 57(3):359–377
Claeys A-S, Opgenhaffen M (2021) Changing perspectives: managerial and legal considerations regarding crisis communication. Public Relat Rev 47(4):102080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2021.102080
Cobo MJ, Lopez-Herrera AG, Herrera-Viedma E, Herrera F (2012) SciMAT: a new science mapping analysis software tool. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 63(8):1609–1630. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22688
Coombs W, Frandsen F, Holladay S, Johansen W (2010) Why a concern for apologia and crisis communication. Corp Commun Int J 15:337–349. https://doi.org/10.1108/13563281011085466
Coombs WT (2021) Ongoing crisis communication: planning, managing, and responding. Sage
Coombs WT (1995) Choosing the right words: the development of guidelines for the selection of the “appropriate” crisis-response strategies. Manag Commun Q 8(4):447–476
Coombs WT (1998) The Internet as potential equalizer: new leverage for confronting social irresponsibility. Public Relat Rev 24(3):289–303
Coombs WT (2007a) Attribution theory as a guide for post-crisis communication research. Public Relat Rev 33:135–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2006.11.016
Coombs WT (2007b) Protecting organization reputations during a crisis: the development and application of situational crisis communication theory. Corp Reputation Rev 10(3):163–176. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.crr.1550049
Coombs WT (2009) Conceptualizing crisis communication. In: Heath RL, O’Hair HD (eds) Handbook of crisis and risk communication. Routledge, New York, p 100–119
Coombs WT (2010). Parameters for crisis communication. The handbook of crisis communication. Wiley, p 17–53
Coombs WT, Holladay SJ (2002) Helping crisis managers protect reputational assets: initial tests of the situational crisis communication theory. Manag Commun Q 16(2):165–186. https://doi.org/10.1177/089331802237233
Coombs WT, Laufer D (2018) Global crisis management – current research and future directions. J Int Manag 24(3):199–203
Cowden K, Sellnow TL (2002) Issues Advertising as Crisis Communication: Northwest Airlines’ Use of Image Restoration Strategies During the 1998 Pilot’s Strike. J Bus Commun 39(2):193–219
Crijns H, Cauberghe V, Hudders L, Claeys A (2017) How to deal with online consumer comments during a crisis? The impact of personalized organizational responses on organizational reputation. Comput Hum Behav 75:619–631
Crossan M, Apaydin M (2010) A multi-dimensional framework of organizational innovation: a systematic review of the literature. J Manag Stud 47:1154–1191
Denyer D, Tranfield D (2006) Using qualitative research synthesis to build an actionable knowl- edge base. Manag Decis 44(2):213–227
Eriksson M (2018) Lessons for crisis communication on social media: a systematic review of what research tells the practice. Int J Strateg Commun 12(5):526–551
Fischbach P, Schoder (2011) Co-authorship networks in electronic markets research. Electron Mark 21(1):19–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12525-011-0051-5
Fischer D, Posegga O, Fischbach K (2016) Communication barriers in crisis management: a literature review. Res Pap 168. https://aisel.aisnet.org/ecis2016_rp/168
Frandsen F, Johansen W (2017) Organizational crisis communication: A multivocal approach, London, UK: Sage
Forliano C, Bernardi, D P, Yahiaoui D (2021) Entrepreneurial universities: a bibliometric analysis within the business and management domains. Technol Forecast Soc Change 165:120522
Gallagher P, Barry P, O’Mahony D (2007) Inappropriate prescribing in the elderly. J Clin Pharm Ther 32(2):113–121. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2710.2007.00793.x
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
García-Lillo F, Úbeda-García M, Marco-Lajara B (2016) The intellectual structure of research in hospitality management: a literature review using bibliometric methods of the journal. Int J Hosp Manag 52:121–130
Goerlandt F, Li J, Reniers G (2020) The landscape of risk communication research: a scientometric analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(9):3255
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Grace JY, Weiting T, Hyejoon R (2020) Mapping corporate social responsibility research in communication: A network and bibliometric analysis. Public Relat Rev. 46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2020.101963
Ha JH, Boynton L (2014) Has crisis communication been studied using an interdisciplinary approach? A 20-year content analysis of communication journals. Int J Strateg Commun 8(1):29–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/1553118X.2013.850694
Hagen L, Keller T, Neely S, DePaula N, Robert-Cooperman C (2018) Crisis communications in the age of social media: a network analysis of Zika-related tweets. Soc Sci Comput Rev 36(5):523–541
Harker JL, Saffer AJ (2018) Mapping a subfield’s sociology of science: a 25-year network and bibliometric analysis of the knowledge construction of sports crisis communication. J Sport Soc Issues 42(5):369–392. https://doi.org/10.1177/0193723518790011
Hearit KM (2001) Corporate apologia. When an organization speaks in defense of itself. In: Heath RL (ed) Handbook of public relations. Sage, Thousand Oaks, p 501–511
Hirsch JE (2005) An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(46):16569–16572
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central MATH ADS Google Scholar
Hirsch JE (2007) Does the h index have predictive power? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19193–19198
Ho B, Shin W, Pang A (2017) Corporate crisis advertising : a framework examining the use and effects of corporate advertising before and after crises. J Mark Commun 23(6):537–551. https://doi.org/10.1080/13527266.2015.1136349
Hu C, Racherla P (2008) Visual representation of knowledge networks: a social network analy- sis of hospitality research domain. Int J Hosp Manag 27:302–312
Huang H-H, Hsu JS-C (2005) An evaluation of publication productivity in information systems: 1999-2003,”. Commun Assoc Inf Syst 15:555–564
Hyland-Wood B, Gardner J, Leask J, Ecker UKH (2021) Toward effective government communication strategies in the era of COVID-19. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 8(1):30. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-020-00701-w
Jin Y (2010) Making sense sensibly in crisis communication: how publics’ crisis appraisals influence their negative emotions, coping strategy preferences, and crisis response acceptance. Commun Res 37(4):522–552. https://doi.org/10.1177/0093650210368256
Article ADS Google Scholar
Kauffman J (2001) A successful failure: NASA’s crisis communications regarding Apollo 13. Public Relat Rev 27(4):437–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0363-8111(01)00099-6
Ki E-J, Pasadeos Y, Ertem-Eray T (2019) Growth of public relations research networks: a bibliometric analysis. J Public Relat Res 31(1–2):5–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/1062726X.2019.1577739
Kim S, Atkinson LJ (2014) Responses toward corporate crisis and corporate advertising. J Promot Manag 20(5):647–665. https://doi.org/10.1080/10496491.2014.946201
Kim Y (2018) Enhancing employee communication behaviors for sensemaking and sensegiving in crisis situations: strategic management approach for effective internal crisis communication. J Commun Manag 22:451–475
Kwok L, Lee J, Han SH (2021) Crisis communication on social media: what types of COVID-19 messages get the attention? Cornell Hosp Q. https://doi.org/10.1177/19389655211028143
Lazzarotti F, Dalfovo MS, Hoffmann VE (2011) A bibliometric study of innovation based on Schumpeter. J Technol Manag Innov 6(4):121–135. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-27242011000400010
Li M-N (2017) Analyzing intellectual structure of related topics to blockchain and bitcoin: from co-citation clustering and bibliographic coupling perspectives. Zidonghua Xuebao/Acta Autom Sin 43(9):1509–1519. https://doi.org/10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160648
Lim WM, Kumar S, Ali F (2022) Advancing knowledge through literature reviews: “what”, “why”, and “how to contribute”. Serv Ind J 42:7–8
Liu-Lastres B (2022) Beyond simple messaging: a review of crisis communication research in hospitality and tourism. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 34(5):1959–1983
Liu B, Kim H, Pennington-Gray L (2015) Responding to the bed bug crisis in social media. Int J Hosp Manag 47:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2015.03.005
Article CAS Google Scholar
Liu B, Pennington-Gray L, Donohoe H, Omodior O (2015) New York City bed bug crisis as framed by tourists on Trip Advisor. Tour Anal 20(2):243–250. https://doi.org/10.3727/108354215X14265319207597
Liu W, Lai C-H, Xu W (2018) Tweeting about emergency: a semantic network analysis of government organizations’ social media messaging during Hurricane Harvey. Public Relat Rev 44:807–819
Lu K, Wolfram D (2012) Measuring author research relatedness: a comparison of word-based, topic- based, and author cocitation approaches. J Am Soc Inf Sci 63(10):1973–1986. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22628
Luo Q, Zhai X (2017) “I will never go to Hong Kong again!” How the secondary crisis communication of “Occupy Central” on Weibo shifted to a tourism boycott. Tour Manag 62:159–172
Lwin MO, Lu J, Sheldenkar A, Schulz PJ (2018) Strategic uses of Facebook in Zika outbreak communication: implications for the crisis and emergency risk communication model. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(9):1974
Maal M, Wilson-North M (2019) Social media in crisis communication – the “do’s” and “don’ts. Int J Disaster Resil Built Environ 10(5):379–391. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJDRBE-06-2014-0044
MacKay M, Ford C, Colangeli T et al. (2022) A content analysis of Canadian influencer crisis messages on Instagram and the public’s response during COVID-19. BMC Public Health 22:763
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Malecki K, Keating JA, Safdar N (2021) Crisis communication and public perception of COVID-19 risk in the era of social media. Clin Infect Dis 72(4):697–702
Malik A, Khan ML, Quan-Haase A (2021) Public health agencies outreach through Instagram during the COVID-19 pandemic: crisis and emergency risk communication perspective. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 61:102346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2021.102346
Massaro M, Dumay J, Guthrie J (2016) On the shoulders of giants: undertaking a structured literature review in accounting. Account Audit Account J 29(5):767–801
Massey JE (2005) Public relations in the airline industry: the crisis response to the September 11th attacks. J Hosp Leis Mark 12(1-2):97–114. https://doi.org/10.1300/J150v12n01_07 . pp
McKercher B (2012) Influence ratio: an alternate means to assess the relative influence of hospitality and tourism journals on research. Int J Hosp Manag 31(3):962–971
Mebane F, Temin S, Parvanta CF (2003) Communicating anthrax in 2001: a comparison of CDC information and print media accounts. J Health Commun 8(1):50–82
Moreno-Fernández A, Fuentes-Lara MC (2019) Engagement and social media. Bibliometric analysis from the scientific field of public relations. Tripodos 45:49–72. https://doi.org/10.51698/TRIPODOS.2019.45P49-72
Morgan A, Wilk V (2021) Social media users’ crisis response: a lexical exploration of social media content in an international sport crisis. Public Relat Rev 47(4):102057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2021.102057
Mukherjee D, Lim WM, Kumar S, Donthu N (2022) Guidelines for advancing theory and practice through bibliometric research. J Bus Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.04.042
Park K, Phillips WJ, Canter DD, Abbott J (2011) Hospitality and tourism research rankings by author, university, and country using six major journals: the first decade of the new millennium. J Hosp Tour Res 35(3):381–416. https://doi.org/10.1177/1096348011400743
Ratzan SC, Sommariva S, Rauh L (2020) Enhancing global health communication during a crisis: lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic. Public Health Res Pract 30(2):3022010
Rawlins B, Bowen S (2005) Encyclopaedia of public relations. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA, p 718–721
Sadri AM, Ukkusuri S, Ahmed MdA (2021) Review of social influence in crisis communications and evacuation decision-making. Transp Res Interdiscip Perspect 9:100325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trip.2021.100325
Saliou P (1994) Crisis communication in the event of a flu pandemic. Eur J Epidemiol 10:515–517
Santoso NR, Dewi EASK, Arviani H, Achmad ZA (2021) Public relations professionals’ communication strategies in responding to the COVID-19 pandemic based on gender. Plaridel 18(1):295–315. https://doi.org/10.52518/2021.18.1-08saderac
Schmidt S, Saulle R, Di Thiene D, Boccia A, La Torre G (2013) Do the quality of the trials and the year of publication affect the efficacy of intervention to improve seasonal influenza vaccination among healthcare workers?: results of a systematic review. Hum Vaccin Immunother 9(2):349–361. https://doi.org/10.4161/hv.2273
Schultz F, Utz S, Göritz A (2011) Is the medium the message? Perceptions of and reactions to crisis communication via twitter, blogs and traditional media. Public Relat Rev 37(1):20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2010.12.001
Seeger MW (2006) Best Practices in Crisis Communication: An Expert Panel Process. J Appl Commun Res 34(3):232–244
Seeger MW, Sloan AG, Sellnow TL (2016) Crisis communication research in the United States. In: Schwarz A, Seeger MW, Auer C (eds) The handbook of international crisis communication research, 1st edn. John Wiley & Sons
Sellnow TL, Seeger MW (2013) Theorizing crisis communication. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Chichester
Smith B, Smith S, Knighton D (2018) Social media dialogues in a crisis: a mixed-methods approach to identifying publics on social media. Public Relat Rev 44(4):562–573
Stolow JA, Moses LM, Lederer AM, Carter R (2020) How fear appeal approaches in COVID-19 health communication may be harming the global community. Health Educ Behav 47(4):531–535
Sarmiento H, Poblete B (2021) Crisis communication: a comparative study of communication patterns across crisis events in social media, SAC '21: Proceedings of the 36th Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, p 1711–1720
Tan ML, Prasanna R, Stock K, Doyle HE, Leonard G, Johnston D (2017) Mobile applications in crisis informatics literature: a systematic review. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 24:297–311
Tandoc E, Takahashi B (2016) Log in if you survived: collective coping on social media in the aftermath of Typhoon Haiyan in the Philippines. New Media Soc. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444816642755
Tornero JMP, Lladó CM, Cervi L (2021) Pandemic and war: crisis narrative and leadership. analysis of the presidential speeches at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. Rev Latina Comun Soc 79:1–21. https://doi.org/10.4185/RLCS-2021-1500
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence- informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag 14(3):207–222
Valackiene A, Virbickaite R (2011) Conceptualization of crisis situation in a company. J Bus Econ Manag 12(2):317–331. https://doi.org/10.3846/16111699.2011.575192
Versailles G (1999) Surviving the ice storm: the communication manager’s perspective. Corp Reputation Rev 2(2):166–175
Wamba SF, Queiroz MM (2020) Blockchain in the operations and supply chain management: benefits, challenges and future research opportunities. Int J Inf Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.102064
Wang B, Zhuang J (2018) Rumor, response, debunking response, and decision makings of misinformed Twitter users during disasters Nat Hazards 93:1145–1162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3344-6
Wang Y (2016) Brand crisis communication through social media: a dialogue between brand competitors on Sina Weibo. Corp Commun 21(1):56–72. https://doi.org/10.1108/CCIJ-10-2014-0065
Wang Y, Dong C (2017) Applying social media in crisis communication: a quantitative review of social media- related crisis communication research from 2009 to 2017. Int J Crisis Commun 1(1):29–37
Watkins D, Walker S (2021) Leadership crisis communication during the pandemic of 2020. J Leadersh Account Ethics 18(1):53–67
Weiner B (1986) An attributional theory of motivation and emotion. Springer, New York
Book Google Scholar
Wen TJ, Li J-Y, Song B (2021) Does public segmentation matter in crisis communication? The interplay between public segmentation and crisis response strategies. Corp Commun 26(3):622–635. https://doi.org/10.1108/CCIJ-11-2020-0158
Williams DE, Treadaway G (1992) Exxon and the Valdez accident: a failure in crisis communication. Commun Stud 43(1):56–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/10510979209368359
Xie Y, Qiao R, Shao G, Chen H (2017) Research on Chinese social media users’ communication behaviors during public emergency events. Telemat Inform 34:740–754
Xu W, Zhang C (2018) Sentiment, richness, authority, and relevance model of information sharing during social crises—the case of #MH370 tweets. Comput Hum Behav 89:199–206
Yang C (2016) How social media is changing crisis communication strategies: evidence from updated literature. J Contingencies Crisis Manag 26:58–68
Yuan Y, Gretzel U, Tseng YH (2015) Revealing the nature of contemporary tourism research: extracting common subject areas through bibliographic coupling. Int J Tourism Res 17(5):417–431
Zhao H (2020) Explicating the social constructionist perspective on crisis communication and crisis management research: a review of communication and business journals. J Public Relat Res 32(3-4):98–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/1062726X.2020.1802732
Zheng B, Liu H, Davison R (2017) Exploring the relationship between corporate reputation and the public’s crisis communication on social media. Public Relat Rev 44:56–64
Zhu L, Anagondahalli D, Zhang A (2017) Social media and culture in crisis communication: McDonald’s and KFC crises management in China. Public Relat Rev 43:487–492
Zupic I, Čater T (2015) Bibliometric methods in management and organization. Organ Res Methods 18(3):429–472. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428114562629
Zurro-Antón N, Fuentes-Lara M-C, Moreno M-Á (2021) Crisis communication (2008-2018). Review of the main advances in empirical knowledge in communication management. Profes Inf 30(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.3145/epi.2021.ene.07
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Humanities and Social Science Department, BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa Campus, Goa, 403726, India
Shalini Upadhyay
IT Systems and Analytics, Indian Institute of Management Jammu, Jammu, 180016, India
Nitin Upadhyay
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nitin Upadhyay .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Additional information.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions

About this article
Cite this article.
Upadhyay, S., Upadhyay, N. Mapping crisis communication in the communication research: what we know and what we don’t know. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10 , 632 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-02069-z
Download citation
Received : 29 December 2022
Accepted : 29 August 2023
Published : 02 October 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-02069-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
ScholarWorks at University of Montana
Home > Humanities and Sciences > Communication Studies > Communication Studies ETDs
Communication Studies Theses, Dissertations, and Professional Papers
This collection includes theses, dissertations, and professional papers from the University of Montana Department of Communication Studies. Theses, dissertations, and professional papers from all University of Montana departments and programs may be searched here.
Theses/Dissertations from 2023 2023
COMEDY, CAMARADERIE, AND CONFLICT: USING HUMOR TO DEFUSE DISPUTES AMONG FRIENDS , Sheena A. Bringa
Navigating Toxic Identities Within League of Legends , Jeremy Thomas Miner
Theses/Dissertations from 2022 2022
UNDERSTANDING MEDIA RICHNESS AND SOCIAL PRESENCE: EXPLORING THE IMPACTS OF MEDIA CHANNELS ON INDIVIDUALS’ LEVELS OF LONELINESS, WELL-BEING, AND BELONGING , Ashley M. Arsenault
CANCELING VS. #CANCEL CULTURE: AN ANALYSIS ON THE SURVEILLANCE AND DISCIPLINE OF SOCIAL MEDIA BEHAVIOR THROUGH COMPETING DISCOURSES OF POWER , Julia G. Bezio
DISTAL SIBLING GRIEF: EXPLORING EMOTIONAL AFFECT AND SALIENCE OF LISTENER BEHAVIORS IN STORIES OF SIBLING DEATH , Margaret C. Brock
Is Loss a Laughing Matter?: A Study of Humor Reactions and Benign Violation Theory in the Context of Grief. , Miranda B. Henrich
The Request Is Not Compatible: Competing Frames of Public Lands Discourse in the Lolo Peak Ski Resort Controversy , Philip A. Sharp
Patient Expectations, Satisfaction, and Provider Communication Within the Oncology Experience , Elizabeth Margaret Sholey
Psychological Safety at Amazon: A CCO Approach , Kathryn K. Zyskowski
Theses/Dissertations from 2021 2021
Discourse of Renewal: A Qualitative Analysis of the University of Montana’s COVID-19 Crisis Communication , Haley Renae Gabel
Activating Hope: How Functional Support Can Improve Hope in Unemployed Individuals , Rylee P. Walter
Theses/Dissertations from 2020 2020
THE HOME AS A SITE OF FAMILY COMMUNICATED NARRATIVE SENSE-MAKING: GRIEF, MEANING, AND IDENTITY THROUGH “CLEANING OUT THE CLOSET” , Kendyl A. Barney
CRISIS AS A CONSTANT: UNDERSTANDING THE COMMUNICATIVE ENACTMENT OF COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE WITHIN THE EXTENSION DISASTER EDUCATION NETWORK (EDEN) , Danielle Maria Farley
FOSTERING COMMUNITIES OF PRACTICE IN COMPREHENSIVE SEX EDUCATION: EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS ON THE FOUNDATIONS TRAINING , Shanay L. Healy
Belonging for Dementia Caregivers , Sabrina Singh
Theses/Dissertations from 2019 2019
Making the Most of People We Do Not Like: Capitalizing on Negative Feedback , Christopher Edward Anderson
Understanding the Relationship Between Discursive Resources and Risk-Taking Behaviors in Outdoor Adventure Athletes , Mira Ione Cleveland
Service Failure Management in High-End Hospitality Resorts , Hunter A. Dietrich
Fear, Power, & Teeth (2007) , Olivia Hockenbroch
The climate change sublime: Leveraging the immense awe of the planetary threat of climate change , Sean D. Quartz
Theses/Dissertations from 2018 2018
The Relationship Between Memorable Messages and Identity Construction , Raphaela P. Barros Campbell
Wonder Woman: A Case Study for Critical Media Literacy , Adriana N. Fehrs
Curated Chaos: A Rhetorical Study of Axmen , Rebekah A. McDonald
THE ROLE OF BIPOLAR DISORDER, STIGMA, AND HURTFUL MESSAGES IN ROMANTIC RELATIONSHIPS , Callie Parrish
Cruising to be a Board Gamer: Understanding Socialization Relating to Board Gaming and The Dice Tower , Benjamin Wassink
Theses/Dissertations from 2017 2017
STEAMED: EXAMINATIONS OF POWER STRUGGLES ON THE VALUE FORUM , richard E. babb
Beyond the Bike; Identity and Belonging of Free Cycles Members , Caitlyn Lewis
Adherence and Uncertainty Management: A Test Of The Theory Of Motivated Information Management , Ryan Thiel
Theses/Dissertations from 2016 2016
Redskins Revisited: Competing Constructions of the Washington Redskins Mascot , Eean Grimshaw
A Qualitative Analysis of Belonging in Communities of Practice: Exploring Transformative Organizational Elements within the Choral Arts , Aubrielle J. Holly
Training the Professoraite of Tomorrow: Implementing the Needs Centered Training Model to Instruct Graduate Teaching Assistants in the use of Teacher Immediacy , Leah R. Johnson
Beyond Blood: Examining the Communicative Challenges of Adoptive Families , Mackensie C. Minniear
Attitudes Toward Execution: The Tragic and Grotesque Framing of Capital Punishment in the News , Katherine Shuy
Knowledge and Resistance: Feminine Style and Signifyin[g] in Michelle Obama’s Public Address , Tracy Valgento
Theses/Dissertations from 2015 2015
BLENDED FRAMEWORK: BILL MCKIBBEN'S USE OF MELODRAMA AND COMEDY IN ENVIRONMENTAL RHETORIC , Megan E. Cullinan
THE INFLUENCE OF MEDICAL DRAMAS ON PATIENT EXPECTATIONS OF PHYSICIAN COMMUNICATION , Kayla M. Fadenrecht
Diabesties: How Diabetic Support on Campus can Alleviate Diabetic Burnout , Kassandra E. Martin
Resisting NSA Surveillance: Glenn Greenwald and the public sphere debate about privacy , Rebecca Rice
Rhetoric, participation, and democracy: The positioning of public hearings under the National Environmental Policy Act , Kevin C. Stone
Socialization and Volunteers: A Training Program for Volunteer Managers , Allison M. Sullivan
Theses/Dissertations from 2014 2014
THIRD PARTY EFFECTS OF AFFECTIONATE COMMUNICATION IN FAMILY SUBSYSTEMS: EXAMINING INFLUENCE ON AFFECTIONATE COMMUNICATION, MENTAL WELL-BEING, AND FAMILY SATISFACTION , Timothy M. Curran
Commodity or Dignity? Nurturing Managers' Courtesy Nurtures Workers' Productivity , Montana Rafferty Moss
"It Was My Job to Keep My Children Safe": Sandra Steingraber and the Parental Rhetoric of Precaution , Mollie Katherine Murphy
Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Free Markets: ALEC's Populist Constructions of "the People" in State Politics , Anne Sherwood
Theses/Dissertations from 2013 2013
COMMUNICATIVE CONSTRUCTION OF EXPECTATIONS: AN EXAMINATION OF EXPECTATIONS REGARDING MOTHERS IN NARRATIVE CONSTRUCTION , Jordan A. Allen
Let’s talk about sex: A training program for parents of 4th and 5th grade children , Elizabeth Kay Eickhoff
"You Is The Church": Identity and Identification in Church Leadership , Megan E. Gesler
This land is your land, this land is my land: A qualitative study of tensions in an environmental decision making group , Gabriel Patrick Grelle
The Constitution of Queer Identity in the 1972 APA Panel, "Psychiatry: Friend or Foe to Homosexuals? A Dialogue" , Dustin Vern Edward Schneider
The Effect of Religious Similarity on the Use of Relational Maintenance Strategies in Marriages , Jamie Karen Taylor
Justice, Equality, and SlutWalk: The Rhetoric of Protesting Rape Culture , Dana Whitney Underwood
Theses/Dissertations from 2012 2012
Collective Privacy Boundary Turbulence and Facework Strategies: A Cross-Cultural Comparison of South Korea and the United States , Min Kyong Cho
COMMUNICATING ARTIFACTS: AN ANALYSIS OF HOW MUSEUMS COMMUNICATE ORGANIZATIONAL IDENTITY DURING TIMES OF CONTROVERSY AND FINANCIAL STRAIN , Amanda Renee Cornuke
Communication Apprehension and Perceived Responsiveness , Elise Alexandra Fanney
Improving Patient-Provider Communication in the Health Care context , Charlotte M. Glidden
What They Consider, How They Decide: Best Practices of Technical Experts in Environmental Decision-Making , Cassandra J. Hemphill
Rebuilding Place: Exploring Strategies to Align Place Identity During Relocation , Brigette Renee McKamey
Sarah Palin, Conservative Feminism, and the Politics of Family , Jasmine Rose Zink
Theses/Dissertations from 2011 2011
Salud, Dignidad, Justicia: Articulating "Choice" and "Reproductive Justice" for Latinas in the United States , Kathleen Maire de Onis
Environmental Documentary Film: A Contemporary Tool For Social Movement , Rachel Gregg
In The Pink: The (Un)Healthy Complexion of National Breast Cancer Awareness Month , Kira Stacey Jones
Jihad as an Ideograph: Osama bin Laden's rhetorical weapon of choice , Faye Lingarajan
The Heart of the Matter: The Function and Relational Effects of Humor for Cardiovascular Patients , Nicholas Lee Lockwood
Feeling the Burn: A Discursive Analysis of Organizational Burnout in Seasonal Wildland Firefighters , Whitney Eleanor Marie Maphis
Making A Comeback: An Exploration of Nontraditional Students & Identity Support , Jessica Kate McFadden
In the Game of Love, Play by the Rules: Implications of Relationship Rule Consensus over Honesty and Deception in Romantic Relationships , Katlyn Elise Roggensack
Assessing the balance: Burkean frames and Lil' Bush , Elizabeth Anne Sills
Theses/Dissertations from 2010 2010
The Discipline of Identity: Examining the Challenges of Developing Interdisciplinary Identities Within the Science Disciplines , Nicholas Richard Burk
Occupational Therapists: A Study of Managing Multiple Identities , Katherine Elise Lloyd
Discourse, Identity, and Culture in Diverse Organizations: A Study of The Muslim Students Association (University of Montana) , Burhanuddin Bin Omar
The Skinny on Weight Watchers: A Critical Analysis of Weight Watcher's Use of Metaphors , Ashlynn Laura Reynolds-Dyk
You Got the Job, Now What?: An Evaluation of the New Employee Orientation Program at the University of Montana , Shiloh M. A. Sullivan
Theses/Dissertations from 2009 2009
Because We Have the Power to Choose: A Critical Analysis of the Rhetorical Strategies Used in Merck's Gardasil Campaign , Brittney Lee Buttweiler
Communicative Strategies Used in the Introduction of Spirituality in the Workplace , Matthew Alan Condon
Cultures in Residence: Intercultural Communication Competence for Residence Life Staff , Bridget Eileen Flaherty
The Influence of Sibling Support on Children's Post-Divorce Adjustment: A Turning Point Analysis , Kimberly Ann Jacobs
TALK ABOUT “HOOKING UP”: HOW COLLEGE STUDENTS‟ ACCOUNTS OF “HOOKING UP” IN SOCIAL NETWORKS INFLUENCES ENGAGING IN RISKY SEXUAL BEHAVIOR , Amanda J. Olson
The Effect of Imagined Interactions on Secret Revelation and Health , Adam Stephens Richards
Teaching Intercultural Communication Competence in the Healthcare Context , Jelena Stojakovic
Quitting versus Not Quitting: The Process and Development of an Assimilation Program Within Opportunity Resources, Inc. , Amanda N. Stovall
Theses/Dissertations from 2008 2008
IMAGES AS A LAYER OF POSITIVE RHETORIC: A VALUES-BASED CASE STUDY EXPLORING THE INTERACTION BETWEEN VISUAL AND VERBAL ELEMENTS FOUND ON A RURAL NATURAL RESOURCES NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATION WEBSITE , Vailferree Stilwell Brechtel
Relational Transgressions in Romantic Relationships: How Individuals Negotiate the Revelation and Concealment of Transgression Information within the Social Network , Melissa A. Maier
Theses/Dissertations from 2007 2007
THE SOCIALIZATION OF SEASONAL EMPLOYEES , Maria Dawn Blevins
Friends the family you choose (no matter what: An investigation of fictive kin relationships amoung young adults. , Kimberly Anne Clinger
Public relations in nonprofit organizations: A guide to establishing public relations programs in nonprofit settings , Megan Kate Gale
Negotiated Forgiveness in Parent-Child Relationships: Investigating Links to Politeness, Wellness and Sickness , Jennifer Lynn Geist
Developing and Communicating Better Sexual Harassment Policies Through Ethics and Human Rights , Thain Yates Hagan
Managing Multiple Identities: A Qualitative Study of Nurses and Implications for Work-Family Balance , Claire Marie Spanier
BEYOND ORGANIC: DEFINING ALTERNATIVES TO USDA CERTIFIED ORGANIC , Jennifer Ann von Sehlen
Theses/Dissertations from 2006 2006
Graduate Teaching Assistant Interpretations and Responses to Student Immediacy Cues , Clair Owen Canfield
Verbal negotiation of affection in romantic relationships , Andrea Ann Richards
Theses/Dissertations from 2005 2005
Art of forgiveness , Carrie Benedict
"We shall fight for the things we have always held nearest our hearts": Rhetorical strategies in the U.S. woman suffrage movement , Stephanie L. Durnford
War on Terror Middle-East peace and a drive around the ranch: The rhetoric of US-Saudi diplomacy in the post-911 period , J. Robert Harper
What do you mean by competence?: A comparison of perceived communication competence among North Americans and Chinese , Chao He
Rhetoric of public interest in an inter-organizational environmental debate: The Fernie mining controversy. , Shelby Jo. Long
Investigation of the initiation of short-term relationships in a vacation setting. , Aneta Milojevic
"It 's the other way around"| Sustainability, promotion, and the shaping of identity in nonprofit arts organizations , Georgi A. Rausch
Child left behind: An examination of comforting strategies goals and outcomes following the death of a child , Kelly R. Rossetto
Profile of the modern smokejumper| A tension-centered lens on identity and identification , Cade Wesley Spaulding
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Collections
- Disciplines
Author Corner
- University of Montana
- Maureen and Mike Mansfield Library
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
About UM | Accessibility | Administration | Contact UM | Directory | Employment | Safety
The Journal of the NPS Center for Homeland Defense and Security
Crisis Communication for Law Enforcement: Crafting a Successful Strategy Using Social Media
By Angela Coonce

Angela Coonce's thesis
– Executive Summary –
The police-involved shooting that occurred in Ferguson, Missouri in the summer of 2014 was a watershed moment that launched the national Black Lives Matter movement into the public spotlight around the world. The depth and breadth of the influence of social media platforms, such as Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube on the incident is discussed in this thesis. This influence highlights the need for law enforcement agencies to have a strategy for the use of social media in crisis communication, especially after use of force incidents. This thesis examines a two-fold research question: (1) What best practices or principles of crisis communication from the private sector might be applicable to law enforcement? (2) What should a social media crisis communication strategy for law enforcement look like? The socialization or increased accessibility of information through technology advances has enabled more people to share information instantly and across global systems. This sharing is a change from the older, “top-down” structure of information dissemination and provides an opportunity for narratives to be influenced by a larger population. The increased speed with which information can be shared has created opportunities for law enforcement to respond more quickly in crises, but doubles as an obstacle when this pace is accessible to individuals in the community as well. Social media allows agencies to communicate quickly in times of crisis, which may lead to improved control of the narrative. It is important that law enforcement agencies consider accuracy of information, not just the quickness of the response. Agencies that have a social media communication strategy in place prior to crisis events will be better equipped to balance speed and accuracy. With social media moving from a communication platform to one that drives community action, this strategy becomes even more vital. It could be argued that law enforcement officers are especially well-suited for communication due to their training as storytellers. Part of an officer’s duty is to craft a police report that captures all the details of a given scene; a record that may end up impacting the lives of those affected by the incident described. Capitalizing on this skill should allow agencies to craft stories that help influence narratives, especially after use of force events. However, hurdles arise that are sometimes genuine and other times self-inflicted. The Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) provides law enforcement guidance on what information must be released, when requested, and allows for exclusions designed to protect the integrity of ongoing investigations. Sometimes agencies use the exclusion clause to delay or avert the release of information that may be outside the scope of the intention of FOIA. This inclination to withhold information, while appropriate in some cases, may work against agencies in other instances when releasing information can provide the community with much-needed transparency. A majority of law enforcement agencies lack goals for social media use. Only one third of the agencies polled by the International Association of the Chiefs of Police indicated they had goals in place related to social media. More than 80 percent of these same agencies find it somewhat challenging to very challenging to adapt to new social media trends and train personnel on the effective use of social media. Regulations and guidelines for users producing content on social media are lax to non-existent, which creates an environment where information is shared almost instantly and is often considered to be accurate, regardless of the source. Social media content, especially images, can trigger strong emotions and can have a mobilizing effect on individuals and groups. This mentality can have real consequences on the street for law enforcement and is a motivating factor in understanding how crisis communication can influence narratives. An evaluation of crisis communication theory provides some insight into human emotions during crisis. Situational crisis communication theory was derived from attribution theory, which describes a need to make sense of events and behaviors by assigning cause and striving to determine motivation. This theory highlights the importance of providing information to the community after a use of force incident to help citizens make sense of the crisis. Image repair theory informs that a damaged reputation, which can occur after a use of force incident, will require repair as a part of the recovery process. Research has shown that the perception of law enforcement can be improved through the use of social media. Social information processing theory suggests that computer-mediated communication can be as effective as face-to-face communication, which allows law enforcement to use social media to reach members of the community not otherwise be accessible in person. However, social presence theory warns that social media interactions should retain a human voice to maintain an effective connection. An evaluation of the existing research on social media-specific crisis communication found the best practices to be very similar to traditional crisis communication. The platform from which someone communicates after a crisis is evidently less important than the content of that communication. The best practices identified in the research closely resemble those garnered from an evaluation of successful crisis communication strategies employed by the private sector. While reputation management in the private sector is conducted to improve sales, the public sector is typically driven to improve or repair credibility. The strategies to regain either customers or credibility after crises are similar, even across disparate organizations. Southwest Airlines, Taco Bell, and GitLab were all able to leverage social media to navigate crises successfully. Southwest Airlines prepares for crises with extensive training and foresight. That preparation was likely the biggest driver in their ability to respond to their first passenger fatality; an event that passengers began to record and report within minutes. The speed of their response, coupled with their compassionate and honest voice, were other keys to its success. Taco Bell focused on honesty and transparency when faced with a lawsuit questioning the quality of their beef; potentially, a huge blow to their reputation. It used an aggressive social media strategy to communicate a defense of its reputation that ultimately led to a restoration, and perhaps an improvement, in its status. GitLab was the first to admit an error on its part that negatively impacted customers and used language that was open and apologetic throughout its social media response. Accepting blame circumvented the customers’ need to assign blame, per attribution theory, and allowed GitLab to begin the image repair process. Private sector examples of crisis response failures were uncovered in incidents at Papa John’s and BP. Papa John’s released a written statement that was perceived as inauthentic and remorseless in response to racist language used by the company’s CEO. A video later posted to social media offered no apology or expression of understanding that the language used was wrong. The image of Papa John’s was tarnished and was not successfully repaired with its social media response. BP had no strategic crisis communication plan in place to handle a crisis that occurred when the Deepwater Horizon oil rig exploded, which caused employee fatalities. The response showed indifference to the loss of life, did not accept blame, and failed to use compassionate language. BP did, however, seem to learn from the misstep and subsequently used social media to increase communication and outline plans for improvements moving forward. The analysis of private sector crisis communication case studies revealed seven common threads that can be applied to a social media strategy for law enforcement. Agencies should establish protocols and form a crisis communication team with specific team members identified and a reporting structure that includes management. Law enforcement should identify high-risk incidents, such as use of force incidents, and prepare through training and scenario-based drills. Crisis communication teams should respond quickly and regularly after crises. Agencies should utilize the experience and technological savvy of digital natives for their social media communication team. Organizations should engage in both social monitoring, to ensure direct responses are accurate and timely, and social listening, to allow for a broader understanding of the concerns of a community after crisis. The language used by law enforcement on social media should be a human voice, as opposed to an organizational language, to allow agencies to connect with their audience. Finally, communication teams should emphasize compassion and honesty in their content and strive for transparency. The importance of influencing narratives is critical for law enforcement during crises. After the Ferguson demonstrations, the Department of Justice (DOJ) found that law enforcement needed a “better and more immediate grasp on the use of social media during emergency situations” if they wanted to handle crises more effectively moving forward. Obstacles to overcome include procuring funding, securing resources that can be available at a moment’s notice, and deciding the appropriate personnel, law enforcement versus civilian employees. The tension that exists between the media and law enforcement may be abetted by agencies circumventing the traditional approach to communicating with the public through an increased use of social media. Social media allows agencies a faster and more effective communication platform with the public after use of force incidents. Law enforcement should embrace the opportunity that the digitalization of society offers through social media. With the creation of a social media crisis communication strategy that incorporates the seven common threads, law enforcement leaders can tell their own stories firsthand, in a thoughtful and transparent manner.
Find all CHDS Theses
Homeland Security Digital Library's Thesis Repository
More Articles

Beyond the Border: The Impact of Flawed Migration Strategies in South and Central America on U.S. Immigration
Do the dutch know much a comparative analysis of gender and use of force in law enforcement in the netherlands and the united states, all hands on deck: a preparedness analysis of municipal fire department mutual aid during fires aboard u.s. navy vessels, legitimation of the police: a practitioner’s framework, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *


- USF Research
- USF Libraries
Digital Commons @ USF > College of Arts and Sciences > Department of Communication > Theses and Dissertations
Communication Theses and Dissertations
Theses/dissertations from 2023 2023.
Consumer Purchase Intent in Opinion Leader Live Streaming , Jihong Huo
Organizing and Communicating Health: A Culture-centered and Necrocapitalist Inquiry of Groundwater Contamination in Rural West Bengal , Parameswari Mukherjee
HIV Stalks Bodies Like Mine: An Autoethnography of Self-Disclosure, Stigmatized Identity, and (In)Visibility in Queer Lived Experience , Steven Ryder
Theses/Dissertations from 2022 2022
Reviving the Christian Left: A Thematic Analysis of Progressive Christian Identity in American Politics , Adam Blake Arledge
Organizing Economies: Narrative Sensemaking and Communciative Resilience During Economic Disruption , Timothy Betts
The Tesla Brake Failure Protestor Scandal: A Case Study of Situational Crisis Communication Theory on Chinese Media , Jiajun Liu
Inflammatory Bowel Disease & Social (In)Visibility: An Interpretive Study of Food Choice, Self-Blame and Coping in Women Living with IBD , Jessica N. Lolli
Florida Punks: Punk, Performance, and Community at Gainesville’s Fest , Michael Anthony Mcdowell Ii
Re-centering and De-centering ‘Race’: an Analysis of Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Organizational Websites , Beatriz Nieto-Fernandez
The Labors of Professional Wrestling: The Dream, the Drive, and Debility , Brooks Oglesby
Outside the Boundaries of Biomedicine: A Culture-Centered Approach to Female Patients Living Undiagnosed and Chronically Ill , Bianca Siegenthaler
The Effect of Racial and Ethnic Identity Salience on Online Political Expression and Political Participation in the United States , Jonathon Smith
Grey’s Anatomy and End of Life Ethics , Sean Micheal Swenson
Informal Communication, Sensemaking, and Relational Precarity: Constituting Resilience in Remote Work During COVID , Tanya R.M. Vomacka
Making a Way: An Auto/ethnographic Exploration of Narratives of Citizenship, Identity, (Un)Belonging and Home for Black Trinidadian[-]American Women , Anjuliet G. Woodruffe
Theses/Dissertations from 2021 2021
When I Rhyme It’s Sincerely Yours: Burkean Identification and Jay-Z’s Black Sincerity Rhetoric in the Post Soul Era , Antoine Francis Hardy
Explicating the Process of Communicative Disenfranchisement for Women with Chronic Overlapping Pain Conditions (COPCs) , Elizabeth A. Hintz
Mitigating Negativity Bias in Media Selection , Gabrielle R. Jarmoszko
Blue Rage: A Critical Cultural Analysis of Policing, Whiteness, and Racial Surveillance , Wesley T. Johnson
Narratives of Success: How Honors College Newcomers Frame the Entrance to College , Cayla Lanier
Peminist Performance in/as Filipina Feminist Praxis: Collaging Stand-Up Comedy and the Narrative Points in Between , Christina-Marie A. Magalona
¿De dónde eres?: Negotiating identity as third culture kids , Sophia Margulies
The Rise of the "Gatecrashers": The Growing Impact of Athletes Breaking News on Mainstream Media through Social Media , Michael Nabors
Learning From The Seed: Illuminating Black Girlhood in Sustainable Living Paradigms , Toni Powell Powell Young
A Comparative Thematic Analysis of Newspaper Articles in France after the Bataclan and in the United States of America after Pulse , Simon Rousset
This is it: Latina/x Representation on One Day at a Time , Camille Ruiz Mangual
STOP- motion as theory, method, and praxis: ARRESTING moments of racialized gender in the academy , Sasha J. Sanders
Advice as Metadiscourse: On the gendering of women's leadership in advice-giving practices , Amaly Santiago
The Communicative Constitution of Environment: Land, Weather, Climate , Leanna K. Smithberger
Women Entrepreneurs in China: Dialectical Discourses, Situated Activities, and the (Re)production of Gender and Entrepreneurship , Zhenyu Tian
Theses/Dissertations from 2020 2020
Constructing a Neoliberal Youth Culture in Postcolonial Bangladeshi Advertising , Md Khorshed Alam
Communication, Learning and Social Support at the Speaking Center: A Communities of Practice Perspective , Ann Marie Foley Coats
A Visit to Cuba: Performance Ethnography of Place , Adolfo Lagomasino
Elemental Climate Disaster Texts and Queer Ecological Temporality , Laura Mattson
When the Beat Drops: Exploring Hip Hop, Home and Black Masculinity , Marquese Lamont McFerguson
Communication Skills in Medical Education: A Discourse Analysis of Simulated Patient Practices , Grace Ellen Peters
Hiding Under the Sun: Health, Access, and Discourses of Representation in Undocumented Communities , Jaime Shamado Robb
Theses/Dissertations from 2019 2019
Walking Each Other Home: Sensemaking of Illness Identity in an Online Metastatic Cancer Community , Ariane B. Anderson
Widow Narratives on Film and in Memoirs: Exploring Formula Stories of Grief and Loss of Older Women After the Death of a Spouse , Jennifer R. Bender
Life as a Reluctant Immigrant: An Autoethnographic Inquiry , Dionel Cotanda
“It’s A Broken System That’s Designed to Destroy”: A Critical Narrative Analysis of Healthcare Providers’ Stories About Race, Reproductive Health, and Policy , Brianna Rae Cusanno
Representations of Indian Christians in Bollywood Movies , Ryan A. D'souza
(re)Making Worlds Together: Rooster Teeth, Community, and Sites of Engagement , Andrea M. M. Fortin
In Another's Voice: Making Sense of Reproductive Health as Women of Color , Nivethitha Ketheeswaran
Communication as Constitutive of Organization: Practicing Collaboration in and English Language Program , Ariadne Miranda
Interrogating Homonationalism in Love, Simon , Jessica S. Rauchberg
Making Sense at the Margins: Describing Narratives on Food Insecurity Through Hip-hop , Lemuel Scott
Theses/Dissertations from 2018 2018
Telling a Rape Joke: Performing Humor in a Victim Help Center , Angela Mary Candela
Becoming a Woman of ISIS , Zoe D. Fine
The Uses of Community in Modern American Rhetoric , Cody Ryan Hawley
Opening Wounds and Possibilities: A Critical Examination of Violence and Monstrosity in Horror TV , Amanda K. Leblanc
As Good as it Gets: Redefining Survival through Post-Race and Post-Feminism in Apocalyptic Film and Television , Mark R. McCarthy
Managing a food health crisis: Perceptions and reactions to different response strategies , Yifei Ren
Everything is Fine: Self-Portrait of a Caregiver with Chronic Depression and Other Preexisting Conditions , Erin L. Scheffels
Lives on the (story)Line: Group Facilitation with Men in Recovery at The Salvation Army , Lisa Pia Zonni Spinazola
Theses/Dissertations from 2017 2017
Breach: Understanding the Mandatory Reporting of Title IX Violations as Pedagogy and Performance , Jacob G. Abraham
Documenting an Imperfect Past: Examining Tampa's Racial Integration through Community, Film, and Remembrance of Central Avenue , Travis R. Bell
Chemotherapy-Induced Alopecia and Quality-of-Life: Ovarian and Uterine Cancer Patients and the Aesthetics of Disease , Meredith L. Clements
Full-Time Teleworkers Sensemaking Process for Informal Communication , Sheila A. Gobes-Ryan
Volunteer Tourism: Fulfilling the Needs for God and Medicine in Latin America , Erin Howell
Practical Theology in an Interpretive Community: An Ethnography of Talk, Texts and Video in a Mediated Women's Bible Study , Nancie Hudson
Performing Narrative Medicine: Understanding Familial Chronic Illness through Performance , Alyse Keller
Second-Generation Bruja : Transforming Ancestral Shadows into Spiritual Activism , Lorraine E. Monteagut
The Rhetoric of Scientific Authority: A Rhetorical Examination of _An Inconvenient Truth_ , Alexander W. Morales
Daniel Bryan & The Negotiation of Kayfabe in Professional Wrestling , Brooks Oglesby
Improvising Close Relationships: A Relational Perspective on Vulnerability , Nicholas Riggs
Theses/Dissertations from 2016 2016
When Maps Ignore the Territory: An Examination of Gendered Language in Cancer Patient Literature , Joanna Bartell
From Portraits to Selfies: Family Photo-making Rituals , Krystal M. Bresnahan
Spiritual Frameworks in Pediatric Palliative Care: Understanding Parental Decision-making , Lindy Grief Davidson
Blue-Collar Scholars: Bridging Academic and Working-Class Worlds , Nathan Lee Hodges
The Communication Constitution of Law Enforcement in North Carolina’s Efforts Against Human Trafficking , Elizabeth Hampton Jeter
“Black Americans and HIV/AIDS in Popular Media” Conforming to The Politics of Respectability , Alisha Lynn Menzies
Selling the American Body: The Construction of American Identity Through the Slave Trade , Max W. Plumpton
In Search of Solidarity: Identification Participation in Virtual Fan Communities , Jaime Shamado Robb
Theses/Dissertations from 2015 2015
Straight Benevolence: Preserving Heterosexual Authority and White Privilege , Robb James Bruce
A Semiotic Phenomenology of Homelessness and the Precarious Community: A Matter of Boundary , Heather Renee Curry
Heart of the Beholder: The Pathos, Truths and Narratives of Thermopylae in _300_ , James Christopher Holcom
Was It Something They Said? Stand-up Comedy and Progressive Social Change , David M. Jenkins
The Meaning of Stories Without Meaning: A Post-Holocaust Experiment , Tori Chambers Lockler
Half Empty/Half Full: Absence, Ethnicity, and the Question of Identity in the United States , Ashley Josephine Martinez
Feeling at Home with Grief: An Ethnography of Continuing Bonds and Re-membering the Deceased , Blake Paxton
"In Heaven": Christian Couples' Experiences of Pregnancy Loss , Grace Ellen Peters
“You Better Redneckognize”: White Working-Class People and Reality Television , Tasha Rose Rennels
Designing Together with the World Café: Inviting Community Ideas for an Idea Zone in a Science Center , William Travis Thompson
Theses/Dissertations from 2014 2014
Crisis Communication: Sensemaking and Decision-making by the CDC Under Conditions of Uncertainty and Ambiguity During the 2009-2010 H1N1 Pandemic , Barbara Bennington
Communication as Yoga , Kristen Caroline Blinne
Love and (M)other (Im)possibilities , Summer Renee Cunningham
The Rhetoric of Corporate Identity: Corporate Social Responsibility, Creating Shared Value, and Globalization , Carolyn Day
"Is That What You Dream About? Being a Monster?": Bella Swan and the Construction of the Monstrous-Feminine in The Twilight Saga , Amanda Jayne Firestone
Organizing Disability: Producing Knowledge in a University Accommodations Office , Shelby Forbes
Emergency Medicine Triage as the Intersection of Storytelling, Decision-Making, and Dramaturgy , Colin Ainsworth Forde
Changing Landscapes: End-of-Life Care & Communication at a Zen Hospice , Ellen W. Klein
"We're Taking Slut Back": Analyzing Racialized Gender Politics in Chicago's 2012 Slutwalk March , Aphrodite Kocieda
Informing, Entertaining and Persuading: Health Communication at The Amazing You , David Haldane Lee
(Dis)Abled Gaming: An Autoethnographic Analysis of Decreasing Accessibility For Disabled Gamers , Kyle David Romano
Theses/Dissertations from 2013 2013
African Americans and Hospice: A Culture-Centered Exploration of Disparities in End-of-Life Care , Patrick Dillon
Polysemy, Plurality, & Paradigms: The Quixotic Quest for Commensurability of Ethics and Professionalism in the Practices of Law , Eric Paul Engel
Examining the Ontoepistemological Underpinnings of Diversity Education Found in Interpersonal Communication Textbooks , Tammy L. Jeffries
The 2008 Candlelight Protest in South Korea: Articulating the Paradox of Resistance in Neoliberal Globalization , Huikyong Pang
Compassionate Storytelling with Holocaust Survivors: Cultivating Dialogue at the End of an Era , Chris J. Patti
Advanced Search
- Email Notifications and RSS
- All Collections
- USF Faculty Publications
- Open Access Journals
- Conferences and Events
- Theses and Dissertations
- Textbooks Collection
Useful Links
- Department of Communication
- Rights Information
- SelectedWorks
- Submit Research
Home | About | Help | My Account | Accessibility Statement | Language and Diversity Statements
Privacy Copyright
- Bibliography
- More Referencing guides Blog Automated transliteration Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Automated transliteration
- Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Referencing guides
Dissertations / Theses on the topic 'Communication in crisis management'
Create a spot-on reference in apa, mla, chicago, harvard, and other styles.
Consult the top 50 dissertations / theses for your research on the topic 'Communication in crisis management.'
Next to every source in the list of references, there is an 'Add to bibliography' button. Press on it, and we will generate automatically the bibliographic reference to the chosen work in the citation style you need: APA, MLA, Harvard, Chicago, Vancouver, etc.
You can also download the full text of the academic publication as pdf and read online its abstract whenever available in the metadata.
Browse dissertations / theses on a wide variety of disciplines and organise your bibliography correctly.
Abrache, Cassandra. "Crisis Communication Management: -A Case Study of Oxfam’s 2018 Credibility Crisis." Thesis, Örebro universitet, Institutionen för humaniora, utbildnings- och samhällsvetenskap, 2019. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:oru:diva-75154.
Martin, Damion R. "Culture and crisis communication : the use of intercultural communication in public relations crisis management planning." Scholarly Commons, 2011. https://scholarlycommons.pacific.edu/uop_etds/787.
Hlela, Nomfundo. "Exploring best practices for crisis communication." Thesis, Nelson Mandela Metropolitan University, 2017. http://hdl.handle.net/10948/15060.
Zhao, Jingyang. "Chinese Government, Weibo, Crisis Management." Ohio University / OhioLINK, 2013. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=ohiou1368019728.
Choi, Jihee. "Brand Crisis Management in the Restaurant Industry." The Ohio State University, 2017. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=osu1502924048683273.
Dorward, Rebecca, and Amanda Kling. "Crisis management from an embassy point of view : A qualitative study on internal crisis communication." Thesis, Karlstads universitet, 2018. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:kau:diva-66563.
Thompson, Enid Alane. "Managing Effective Communication After a Crisis." ScholarWorks, 2016. https://scholarworks.waldenu.edu/dissertations/2698.
Lin, Ying-Hsuan. "Testing the effects of apology and compassion response in product-harm crises in situational crisis communication theory." online access from Digital Dissertation Consortium, 2007. http://libweb.cityu.edu.hk/cgi-bin/er/db/ddcdiss.pl?1451577.
Mbolekwano, Veliswa A. "Middle management communication in the midst of a crisis." Thesis, Rhodes University, 2017. http://hdl.handle.net/10962/52477.
Wright, Courtney. "Responding to Crises: A Test of the Situational Crisis Communication Theory." Scholar Commons, 2008. https://scholarcommons.usf.edu/etd/91.
Kriyantono, Rachmat. "A critical ethnography of crisis management dealing with a mudflow crisis in Sidoarjo, Indonesia [thesis]." Thesis, Edith Cowan University, Research Online, Perth, Western Australia, 2011. https://ro.ecu.edu.au/theses/407.
Michaels, Olufunke. "Strategic relational communication in crisis : the humanitarian example." Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2013. http://hdl.handle.net/1721.1/80693.
Mohammed, Zuhura. "Crisis Communication and Management using SocialMedia: a Crisis Response to Ethiopian Airlines ET302 Crash." Thesis, Örebro universitet, Institutionen för humaniora, utbildnings- och samhällsvetenskap, 2020. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:oru:diva-85637.
Lindström, Petter, and Viktor Petersson. "Crisis Management - Influencing factors, implementation and preparedness." Thesis, Internationella Handelshögskolan, Högskolan i Jönköping, IHH, Företagsekonomi, 2011. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:hj:diva-15559.
Horsley, J. Suzanne Boynton Lois A. "Reliability in chaos crisis communication in state emergency management agencies /." Chapel Hill, N.C. : University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, 2006. http://dc.lib.unc.edu/u?/etd,412.
Williams, Tomicka Nicole. "Crisis Communication Systems Among K-12 School Principals." ScholarWorks, 2019. https://scholarworks.waldenu.edu/dissertations/6704.
Pang, Augustine. "Conflict positioning in crisis communication integrating contingency stance with image repair strategies /." Diss., Columbia, Mo. : University of Missouri-Columbia, 2006. http://hdl.handle.net/10355/5858.
Stránská, Adriana. "Crisis Management on the social network Facebook." Master's thesis, Vysoká škola ekonomická v Praze, 2013. http://www.nusl.cz/ntk/nusl-192424.
Horner, Tomas, and David Palmkvist. "Crisis Management: The Moment of Truth : A Case Study of Kommunal." Thesis, Luleå tekniska universitet, Institutionen för ekonomi, teknik och samhälle, 2016. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:ltu:diva-59923.
Ullström, Camilla. "Det är det här mittenläget som är väldigt knepigt : En komparativ fallstudie om svenska universitets interna kommunikation med medarbetare." Thesis, Umeå universitet, Institutionen för kultur- och medievetenskaper, 2016. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:umu:diva-119109.
Smith, Joshua L. "When it hits the fan a public relations practitioners' guide to crisis communication /." unrestricted, 2007. http://etd.gsu.edu/theses/available/etd-04192007-161900/.
Harrison, Gordon Alan. "Communication Strategies as a Basis for Crisis Management Including Use of the Internet as a Delivery Platform." Digital Archive @ GSU, 2007. http://digitalarchive.gsu.edu/english_diss/22.
Ericsson, Marika, and Sara Olofsson. "När kommunikationen krisar : En studie av myndigheters informations- och kommuniktionssamverkan under beredskapsövningar." Thesis, Linnéuniversitetet, Institutionen för samhällsvetenskaper, SV, 2012. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:lnu:diva-20562.
Suydam, Martin. "Instant learning for crisis response." Fairfax, VA : George Mason University, 2008. http://hdl.handle.net/1920/3217.
Oliveira, Maria de Fatima. "Multicultural Environments and their Challenges to Crisis Communication." Diss., Temple University Libraries, 2010. http://cdm16002.contentdm.oclc.org/cdm/ref/collection/p245801coll10/id/92288.
Hale, Susan. "Communicating a Crisis: The Public Information Officer's Perspective." unrestricted, 2007. http://etd.gsu.edu/theses/available/etd-11282007-150038/.
Francová, Martina. "Krizová komunikace jako důležitý nástroj managementu podniku." Master's thesis, Vysoká škola ekonomická v Praze, 2009. http://www.nusl.cz/ntk/nusl-10941.
Shumilova, Elizaveta, Asanee Börjesson, and Do Gyoon Kim. "Organisational Crisis Interpretations: analysing communicational tactics and its consequenses." Thesis, Internationella Handelshögskolan, Högskolan i Jönköping, IHH, Företagsekonomi, 2014. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:hj:diva-23865.
Gannon, Patrick J. "The impact of social media on crisis communication." Scholarly Commons, 2011. https://scholarlycommons.pacific.edu/uop_etds/775.
Söderlund, Malin. "Governmental Crisis Response – To be On Top of the Frame : The Case of Norway 22/7 2011 - Crisis communication and news management." Thesis, Försvarshögskolan, 2013. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:fhs:diva-4148.
Hansson, Anna, and Tomas Vikström. "Successful Crisis Management in the Airline Industry : A Quest for Legitimacy Through Communication?" Thesis, Uppsala universitet, Företagsekonomiska institutionen, 2010. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:uu:diva-144082.
Drumheller, Kristina D. "Vehicles for entertainment or for legitimacy crisis? : revisting legitimacy and image restoration efforts after film depictions of organizational crisis /." free to MU campus, to others for purchase, 2004. http://wwwlib.umi.com/cr/mo/fullcit?p3144413.
Narducci, Cassandra. "Social Media and Reputation Management During Crisis: A Case Study of the 2012-2013 NHL Lockout." Thesis, Université d'Ottawa / University of Ottawa, 2016. http://hdl.handle.net/10393/34226.
Giblin, Patrick J. "Social media's impact on higher education crisis communication plans." Scholarly Commons, 2011. https://scholarlycommons.pacific.edu/uop_etds/776.
Chinn, Mo-sum Sammy George, and 陳務森. "A study of organizational effectiveness in crisis management in amodern system control centre." Thesis, The University of Hong Kong (Pokfulam, Hong Kong), 1987. http://hub.hku.hk/bib/B31263732.
Adebayo, O. "The application of Facebook to crisis communication management : a case study of Malaysia Airlines." Thesis, University of Salford, 2017. http://usir.salford.ac.uk/42319/.
Nazem, Ghanai Ramona, Malin Forss, and Gabriella Sundkvist. "Let's Make Better Mistakes Tomorrow : Brand Management and Crisis Communication for Social Media Influencers." Thesis, Internationella Handelshögskolan, Jönköping University, IHH, Företagsekonomi, 2020. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:hj:diva-48973.
Jonsson, Hanna, and Josefin Davidsson. ""A company is never better than its latest mistake" : A consumer perspective on crisis communication." Thesis, Internationella Handelshögskolan, Högskolan i Jönköping, IHH, Företagsekonomi, 2017. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:hj:diva-35669.
Park, Sun-A. "Using conflict positioning as a pretreatment in the public's evaluation of crisis management." Diss., Columbia, Mo. : University of Missouri-Columbia, 2007. http://hdl.handle.net/10355/5984.
Lonk, David. "Úloha krizového managementu při reorganizaci podniku MSV Metal Studénka, a.s." Master's thesis, Vysoká škola ekonomická v Praze, 2010. http://www.nusl.cz/ntk/nusl-194137.
Hellman, Malin, and Sofia Löfgren. "Mellanchefen skapar mening genom att agera kommunikationsfilter. : En studie om intern kommunikation och sensemaking under exceptionell kris." Thesis, Linnéuniversitetet, Institutionen för organisation och entreprenörskap (OE), 2020. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:lnu:diva-95825.
Abuhajaj, Ayham, and George Lampis. "Strategy Formulation Process in Crisis Management : Volkswagen Case Study." Thesis, Högskolan Dalarna, Företagsekonomi, 2017. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:du-25266.
Hysenlika, Vjollca. "Communicating During an Organizational Crisis: Using Facebook as a Relationship Management Tool." Scholar Commons, 2012. http://scholarcommons.usf.edu/etd/4337.
Pettersson, Henrik, and Marcus Sundling. "VAG-koncernens utsläppsskandal : En kvalitativ studie inom kriskommunikatioin." Thesis, Mittuniversitetet, Avdelningen för ekonomivetenskap och juridik, 2018. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:miun:diva-34684.
Massey, Joseph Eric 1964. "Maintaining legitimacy through public organizational discourse: Crisis and communication in the United States airline industry." Diss., The University of Arizona, 1997. http://hdl.handle.net/10150/282482.
Golway, Danielle. "Relationship, trust and crisis communication on social media with millennials and generation Z." Thesis, Kansas State University, 2017. http://hdl.handle.net/2097/35551.
HERZBERGER, JONATHAN D. ""Can you hear me now?" Experimental research on the efficacy of pre-crisis messages in a severe weather context." Cleveland State University / OhioLINK, 2014. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=csu1408374541.
Hunt, Kathleen P. "From Prophecy to Advocacy: A Rhetorical Analysis of Al Gore's Enactment of Climate Crisis Management." Cincinnati, Ohio : University of Cincinnati, 2009. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view.cgi?acc_num=ucin1243353239.
Keene, Andrea. "An exploratory Q-sort of crisis communications performed by public relations professionals." CardinalScholar 1.0, 2009. http://liblink.bsu.edu/uhtbin/catkey/1540702.
Tapia, Herrera Johnny Edson. "Modelo de gestión de crisis para organizaciones políticas del Perú." Master's thesis, Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas (UPC), 2020. http://hdl.handle.net/10757/652968.
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this study, we aim to map crisis communication in the communication research. The study also seeks to find the field's social, intellectual and conceptual structures over the past 50 years.
The Importance of Crisis Communication. Dr. Michael S. Wilson; Dr. James Biteman. This business honors thesis investigates intra-organizational crisis communication. during "unique crises ...
In a study of examining the usage of situational crisis communication theory by non-. profit organizations, Fussell, Sisco, Collins, and Zoch (2010) coded news reports related to. American Red Cross and critics of its crisis management into four crises and three situational crisis communication response strategies.
Abstract. This article introduces the special issue on crisis communication, whose aim is to bring together diverse approaches and methods of analysis in the field. The article overviews the field by discussing two main frameworks, dealing with postcrisis (reputation management) and precrisis (issue management) communication, respectively.
Effective crisis communication management: Perspectives from public relations and communications practitioners (Doctoral dissertation, University of Pretoria). Google Scholar Kamruzzaman, M. (2020).
The types of responses, as described in Situational Crisis Communication Theory (Coombs, 2007), have been studied in conjunction with both the responses' crisis types and the communicator delivering the message. However, studies on the source of the crisis response have rarely gone past investigating the traditional response personnel.
The Geertshuis et al. (2015), study is similar to Coombs and Holladay (1996) study of SCCT because communication affects people's perceptions and reactions to a. crisis. The perceptions and reactions of employees after a crisis are important. The. leader-employee relationship is a vital piece of the recovery process.
Matthew W. Seeger (PhD, Indiana University) is Professor and Chair of the Department of Communication at Wayne State University in Detroit, Michigan. Seeger's research interests concern crisis and risk communication, crisis response and agency coordination, health communication, and ethics.
CHALLENGES TO CRISIS COMMUNICATION A Dissertation Submitted to the Temple University Graduate Board in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY by Maria de Fatima Oliveira August, 2010 Examining Committee Members: Priscilla Murphy, PhD, Advisory Chair, Mass Media and Communication
communication, but extensive theories on crisis communication itself, this paper tries to analyze if existing crisis communication guidelines could be used also in social media. This is done by combining a literature review that looks into existing research on crisis communication and social media with interviews conducted with crisis
Master's Thesis The Use of Social Media in Risk Communication during COVID-19: An Analysis of Stakeholders' Messages on Social Media Thesis Type: Review Article ... have further demonstrated the centrality of communities in risk and crisis communication. The terms 'risk communication' and 'crisis communication' have been used ...
The crisis communication literature ranges from the theoretical to the applied and includes rhetorical, quantitative, and interpretive approaches. A communicative response to crisis defines possibilities for human action in a particular historical moment, providing meaningful engagement with uncertainty and the unknown.
SOCIAL MEDIA IN CRISIS COMMUNICATIONS. Abstract. Today, social media is increasing its influence on the communication environment. The. toolkit of online platforms creates new opportunities for ...
Each of these has as its foundation a vigorous strategic communication plan. Crisis plans are necessary in today's business environment, and effective communication is an essential element of any crisis plan. This dissertation will focus on communication methodology as a means of crisis avoidance and crisis mitigation.
Video (online) Consult the top 50 dissertations / theses for your research on the topic 'Crisis communication.'. Next to every source in the list of references, there is an 'Add to bibliography' button. Press on it, and we will generate automatically the bibliographic reference to the chosen work in the citation style you need: APA, MLA ...
Master's Thesis Author: Marlies Nittmann Date: 31.3.2021 Title of thesis: Crisis Communication: The case of the airline industry during the COVID-19 pandemic Abstract: Due to the increasing frequency of crises and the diversification of their causes, a wide range of research has been completed in this field. However, the crisis communication
Crisis communication systems (CCS) are critical in assuring school security and safety. Currently, schools are challenged with crises ranging from mass shootings to natural disasters. Recent figures reported that 65% of K-12 schools in the United States reported a crisis that involved violent actions and deaths (Musu-Gillette, Zhang, Wang,
Theses/Dissertations from 2021 PDF. Discourse of Renewal: A Qualitative Analysis of the University of Montana's COVID-19 Crisis Communication, Haley Renae Gabel. PDF. Activating Hope: How Functional Support Can Improve Hope in Unemployed Individuals, Rylee P. Walter. Theses/Dissertations from 2020 PDF
The analysis of private sector crisis communication case studies revealed seven common threads that can be applied to a social media strategy for law enforcement. Agencies should establish protocols and form a crisis communication team with specific team members identified and a reporting structure that includes management.
Theses/Dissertations from 2014 PDF. Crisis Communication: Sensemaking and Decision-making by the CDC Under Conditions of Uncertainty and Ambiguity During the 2009-2010 H1N1 Pandemic, Barbara Bennington. PDF. Communication as Yoga, Kristen Caroline Blinne. PDF. Love and (M)other (Im)possibilities, Summer Renee Cunningham. PDF
This Dissertation is brought to you for free and open access by the Walden Dissertations and Doctoral Studies Collection at ScholarWorks. It has been accepted for inclusion in Walden Dissertations and Doctoral Studies by an
This thesis explores how the legitimacy and reputation of firms that have experienced severe crises can be restored through the means of crisis management and crisis communication strategies. Our focus is on the airline industry, analyzing how three European airlines have communicated and acted towards important shareholders during and ...
A balanced approach to crisis communication, which includes media relations, social media, and other communication channels, can help ensure that a company's side about a crisis is told ...
American universities and colleges are beefing up their strategic communications efforts given the onslaught of public backlash and political scrutiny that shows no signs of tapering off.. Why it matters: Higher ed is the latest industry to learn the hard lessons about crisis communications and how no institution is immune from big, divisive issues. ...
With Princess Kate's surgery, absence, and altered photo, the Kensington Palace communications team needs a new playbook. The internet has been buzzing with chatter and conspiracy theories ...
UnitedHealth Group 's communications moves during the hack of its Change Healthcare unit show the difficulty of balancing regulatory obligations, informing customers and handling sensitive ...
The US has also accused the army of war crimes. Last month, World Food Programme Executive Director Cindy McCain called the war in Sudan "the forgotten crisis," a sentiment echoed by US ...
This capstone study's purpose explored how social workers used ethics for. decision-making during crisis mitigation in a nonurban community. Enck's (2014) biomedical ethical decision-making model, along with the NASW Code of Ethics (2021), was used to understand what guides social work practice when social workers in a.
April 18, 2024 at 9:00 PM PDT. Listen. 2:00. The European Union 's demand for liquefied natural gas, which provided a key lifeline during the energy crisis, will likely peak this year as the ...
April 15, 2024 at 7:27 PM PDT. Listen. 2:11. Surging ocean temperatures have triggered a second global coral bleaching event in a decade, threatening crucial marine ecosystems that underpin an ...