Likes, Shares, and Beyond: Exploring the Impact of Social Media in Essays
Table of contents
- 1 Definition and Explanation of a Social Media Essay
- 2.1 Topics for an Essay on Social Media and Mental Health
- 2.2 Social Dynamics
- 2.3 Social Media Essay Topics about Business
- 2.4 Politics
- 3 Research and Analysis
- 4 Structure Social Media Essay
- 5 Tips for Writing Essays on Social Media
- 6 Examples of Social Media Essays
- 7 Navigating the Social Media Labyrinth: Key Insights
In the world of digital discourse, our article stands as a beacon for those embarking on the intellectual journey of writing about social media. It is a comprehensive guide for anyone venturing into the dynamic world of social media essays. Offering various topics about social media and practical advice on selecting engaging subjects, the piece delves into research methodologies, emphasizing the importance of credible sources and trend analysis. Furthermore, it provides invaluable tips on structuring essays, including crafting compelling thesis statements and hooks balancing factual information with personal insights. Concluding with examples of exemplary essays, this article is an essential tool for students and researchers alike, aiding in navigating the intricate landscape of its impact on society.

Definition and Explanation of a Social Media Essay

Essentially, when one asks “What is a social media essay?” they are referring to an essay that analyzes, critiques, or discusses its various dimensions and effects. These essays can range from the psychological implications of its use to its influence on politics, business strategies, and social dynamics.
A social media essay is an academic or informational piece that explores various aspects of social networking platforms and their impact on individuals and society.
In crafting such an essay, writers blend personal experiences, analytical perspectives, and empirical data to paint a full picture of social media’s role. For instance, a social media essay example could examine how these platforms mold public opinion, revolutionize digital marketing strategies, or raise questions about data privacy ethics. Through a mix of thorough research, critical analysis, and personal reflections, these essays provide a layered understanding of one of today’s most pivotal digital phenomena.
Great Social Media Essay Topics
When it comes to selecting a topic for your essay, consider its current relevance, societal impact, and personal interest. Whether exploring the effects on business, politics, mental health, or social dynamics, these social media essay titles offer a range of fascinating social media topic ideas. Each title encourages an exploration of the intricate relationship between social media and our daily lives. A well-chosen topic should enable you to investigate the impact of social media, debate ethical dilemmas, and offer unique insights. Striking the right balance in scope, these topics should align with the objectives of your essays, ensuring an informative and captivating read.
Topics for an Essay on Social Media and Mental Health
- The Impact of Social Media on Self-Esteem.
- Unpacking Social Media Addiction: Causes, Effects, and Solutions.
- Analyzing Social Media’s Role as a Catalyst for Teen Depression and Anxiety.
- Social Media and Mental Health Awareness: A Force for Good?
- The Psychological Impacts of Cyberbullying in the Social Media Age.
- The Effects of Social Media on Sleep and Mental Health.
- Strategies for Positive Mental Health in the Era of Social Media.
- Real-Life vs. Social Media Interactions: An Essay on Mental Health Aspects.
- The Mental Well-Being Benefits of a Social Media Detox.
- Social Comparison Psychology in the Realm of Social Media.
Social Dynamics
- Social Media and its Impact on Interpersonal Communication Skills: A Cause and Effect Essay on Social Media.
- Cultural Integration through Social Media: A New Frontier.
- Interpersonal Communication in the Social Media Era: Evolving Skills and Challenges.
- Community Building and Social Activism: The Role of Social Media.
- Youth Culture and Behavior: The Influence of Social Media.
- Privacy and Personal Boundaries: Navigating Social Media Challenges.
- Language Evolution in Social Media: A Dynamic Shift.
- Leveraging Social Media for Social Change and Awareness.
- Family Dynamics in the Social Media Landscape.
- Friendship in the Age of Social Media: An Evolving Concept.
Social Media Essay Topics about Business
- Influencer Marketing on Social Media: Impact and Ethics.
- Brand Building and Customer Engagement: The Power of Social Media.
- The Ethics and Impact of Influencer Marketing in Social Media.
- Measuring Business Success Through Social Media Analytics.
- The Changing Face of Advertising in the Social Media World.
- Revolutionizing Customer Service in the Social Media Era.
- Market Research and Consumer Insights: The Social Media Advantage.
- Small Businesses and Startups: The Impact of Social Media.
- Ethical Dimensions of Social Media Advertising.
- Consumer Behavior and Social Media: An Intricate Relationship.
- The Role of Social Media in Government Transparency and Accountability
- Social Media’s Impact on Political Discourse and Public Opinion.
- Combating Fake News on Social Media: Implications for Democracy.
- Political Mobilization and Activism: The Power of Social Media.
- Social Media: A New Arena for Political Debates and Discussions.
- Government Transparency and Accountability in the Social Media Age.
- Voter Behavior and Election Outcomes: The Social Media Effect.
- Political Polarization: A Social Media Perspective.
- Tackling Political Misinformation on Social Media Platforms.
- The Ethics of Political Advertising in the Social Media Landscape.
- Memes as a Marketing Tool: Successes, Failures, and Pros of Social Media.
- Shaping Public Opinion with Memes: A Social Media Phenomenon.
- Political Satire and Social Commentary through Memes.
- The Psychology Behind Memes: Understanding Their Viral Nature.
- The Influence of Memes on Language and Communication.
- Tracing the History and Evolution of Internet Memes.
- Memes in Online Communities: Culture and Subculture Formation.
- Navigating Copyright and Legal Issues in the World of Memes.
- Memes as a Marketing Strategy: Analyzing Successes and Failures.
- Memes and Global Cultural Exchange: A Social Media Perspective.
Research and Analysis
In today’s fast-paced information era, the ability to sift through vast amounts of data and pinpoint reliable information is more crucial than ever. Research and analysis in the digital age hinge on identifying credible sources and understanding the dynamic landscape. Initiating your research with reputable websites is key. Academic journals, government publications, and established news outlets are gold standards for reliable information. Online databases and libraries provide a wealth of peer-reviewed articles and books. For websites, prioritize those with domains like .edu, .gov, or .org, but always critically assess the content for bias and accuracy. Turning to social media, it’s a trove of real-time data and trends but requires a discerning approach. Focus on verified accounts and official pages of recognized entities.
Analyzing current trends and user behavior is crucial for staying relevant. Platforms like Google Trends, Twitter Analytics, and Facebook Insights offer insights into what’s resonating with audiences. These tools help identify trending topics, hashtags, and the type of content that engages users. Remember, it reflects and influences public opinion and behavior. Observing user interactions, comments, and shares can provide a deeper understanding of consumer attitudes and preferences. This analysis is invaluable for tailoring content, developing marketing strategies, and staying ahead in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Structure Social Media Essay
In constructing a well-rounded structure for a social media essay, it’s crucial to begin with a strong thesis statement. This sets the foundation for essays about social media and guides the narrative.
Thesis Statements
A thesis statement is the backbone of your essay, outlining the main argument or position you will explore throughout the text. It guides the narrative, providing a clear direction for your essay and helping readers understand the focus of your analysis or argumentation. Here are some thesis statements:
- “Social media has reshaped communication, fostering a connected world through instant information sharing, yet it has come at the cost of privacy and genuine social interaction.”
- “While social media platforms act as potent instruments for societal and political transformation, they present significant challenges to mental health and the authenticity of information.”
- “The role of social media in contemporary business transcends mere marketing; it impacts customer relationships, shapes brand perception, and influences operational strategies.”
Social Media Essay Hooks
Social media essay hooks are pivotal in grabbing the reader’s attention right from the beginning and compelling them to continue reading. A well-crafted hook acts as the engaging entry point to your essay, setting the tone and framing the context for the discussion that will follow.
Here are some effective social media essay hooks:
- “In a world where a day without social media is unimaginable, its pervasive presence is both a testament to its utility and a source of various societal issues.”
- “Each scroll, like, and share on social media platforms carries the weight of influencing public opinion and shaping global conversations.”
- “Social media has become so ingrained in our daily lives that its absence would render the modern world unrecognizable.”
Introduction:
Navigating the digital landscape, an introduction for a social media essay serves as a map, charting the terrain of these platforms’ broad influence across various life aspects. This section should briefly summarize the scope of the essay, outlining both the benefits and the drawbacks, and segue into the thesis statement.
When we move to the body part of the essay, it offers an opportunity for an in-depth exploration and discussion. It can be structured first to examine the positive aspects of social media, including improved communication channels, innovative marketing strategies, and the facilitation of social movements. Following this, the essay should address the negative implications, such as issues surrounding privacy, the impact on mental health, and the proliferation of misinformation. Incorporating real-world examples, statistical evidence, and expert opinions throughout the essay will provide substantial support for the arguments presented.
Conclusion:
It is the summit of the essay’s exploration, offering a moment to look back on the terrain covered. The conclusion should restate the thesis in light of the discussions presented in the body. It should summarize the key points made, reflecting on the multifaceted influence of social media in contemporary society. The essay should end with a thought-provoking statement or question about the future role of social media, tying back to the initial hooks and ensuring a comprehensive and engaging end to the discourse.
Tips for Writing Essays on Social Media
In the ever-evolving realm of digital dialogue, mastering the art of essay writing on social media is akin to navigating a complex web of virtual interactions and influences. Writing an essay on social media requires a blend of analytical insight, factual accuracy, and a nuanced understanding of the digital landscape. Here are some tips to craft a compelling essay:
- Incorporate Statistical Data and Case Studies
Integrate statistical data and relevant case studies to lend credibility to your arguments. For instance, usage statistics, growth trends, and demographic information can provide a solid foundation for your points. Case studies, especially those highlighting its impact on businesses, politics, or societal change, offer concrete examples that illustrate your arguments. Ensure your sources are current and reputable to maintain the essay’s integrity.
- Balance Personal Insights with Factual Information
While personal insights can add a unique perspective to your essay, balancing them with factual information is crucial. Personal observations and experiences can make your essay relatable and engaging, but grounding these insights in factual data ensures credibility and helps avoid bias.
- Respect Privacy
When discussing real-world examples or case studies, especially those involving individuals or specific organizations, be mindful of privacy concerns. Avoid sharing sensitive information, and always respect the confidentiality of your sources.
- Maintain an Objective Tone
It is a polarizing topic, but maintaining an objective tone in your essay is essential. Avoid emotional language and ensure that your arguments are supported by evidence. An objective approach allows readers to form opinions based on the information presented.
- Use Jargon Wisely
While using social media-specific terminology can make your essay relevant and informed, it’s important to use jargon judiciously. Avoid overuse and ensure that terms are clearly defined for readers who might not be familiar with their lingo.
Examples of Social Media Essays
Title: The Dichotomy of Social Media: A Tool for Connection and a Platform for Division
Introduction
In the digital era, social media has emerged as a paradoxical entity. It serves as a bridge connecting distant corners of the world and a battleground for conflicting ideologies. This essay explores this dichotomy, utilizing statistical data, case studies, and real-world examples to understand its multifaceted impact on society.
Section 1 – Connection Through Social Media:
Social media’s primary allure lies in its ability to connect. A report by the Pew Research Center shows that 72% of American adults use some form of social media, where interactions transcend geographical and cultural barriers. This statistic highlights the platform’s popularity and role in fostering global connections. An exemplary case study of this is the #MeToo movement. Originating as a hashtag on Twitter, it grew into a global campaign against sexual harassment, demonstrating its power to mobilize and unify people for a cause.
However, personal insights suggest that while it bridges distances, it can also create a sense of isolation. Users often report feeling disconnected from their immediate surroundings, hinting at the platform’s double-edged nature. Despite enabling connections on a global scale, social media can paradoxically alienate individuals from their local context.
Section 2 – The Platform for Division
Conversely, social media can amplify societal divisions. Its algorithm-driven content can create echo chambers, reinforcing users’ preexisting beliefs. A study by the Knight Foundation found that it tends to polarize users, especially in political contexts, leading to increased division. This is further exacerbated by the spread of misinformation, as seen in the 2016 U.S. Presidential Election case, where it was used to disseminate false information, influencing public opinion and deepening societal divides.
Respecting privacy and maintaining an objective tone, it is crucial to acknowledge that social media is not divisive. Its influence is determined by both its usage and content. Thus, it is the obligation of both platforms to govern content and consumers to access information.
In conclusion, it is a complex tool. It has the unparalleled ability to connect individuals worldwide while possessing the power to divide. Balancing the personal insights with factual information presented, it’s clear that its influence is a reflection of how society chooses to wield it. As digital citizens, it is imperative to use it judiciously, understanding its potential to unite and divide.
Delving into the intricacies of social media’s impact necessitates not just a keen eye for detail but an analytical mindset to dissect its multifaceted layers. Analysis is paramount because it allows us to navigate through the vast sea of information, distinguishing between mere opinion and well-supported argumentation.
This essay utilizes tips for writing a social media essay. Statistical data from the Pew Research Center and the Knight Foundation lend credibility to the arguments. The use of the #MeToo movement as a case study illustrates its positive impact, while the reference to the 2016 U.S. Presidential Election demonstrates its negative aspects. The essay balances personal insights with factual information, respects privacy, maintains an objective tone, and appropriately uses jargon. The structure is clear and logical, with distinct sections for each aspect of its impact, making it an informative and well-rounded analysis of its role in modern society.
Navigating the Social Media Labyrinth: Key Insights
In the digital age, the impact of social media on various aspects of human life has become a critical area of study. This article has provided a comprehensive guide for crafting insightful and impactful essays on this subject, blending personal experiences with analytical rigor. Through a detailed examination of topics ranging from mental health and social dynamics to business and politics, it has underscored the dual nature of social media as both a unifying and divisive force. The inclusion of statistical data and case studies has enriched the discussion, offering a grounded perspective on the nuanced effects of these platforms.
The tips and structures outlined serve as a valuable framework for writers to navigate the complex interplay between social media and societal shifts. As we conclude, it’s clear that understanding social media’s role requires a delicate balance of critical analysis and open-mindedness. Reflecting on its influence, this article guides the creation of thoughtful essays and encourages readers to ponder the future of digital interactions and their implications for the fabric of society.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Why social media has changed the world — and how to fix it
Press contact :, media download.

*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."

Previous image Next image
Are you on social media a lot? When is the last time you checked Twitter, Facebook, or Instagram? Last night? Before breakfast? Five minutes ago?
If so, you are not alone — which is the point, of course. Humans are highly social creatures. Our brains have become wired to process social information, and we usually feel better when we are connected. Social media taps into this tendency.
“Human brains have essentially evolved because of sociality more than any other thing,” says Sinan Aral, an MIT professor and expert in information technology and marketing. “When you develop a population-scale technology that delivers social signals to the tune of trillions per day in real-time, the rise of social media isn’t unexpected. It’s like tossing a lit match into a pool of gasoline.”
The numbers make this clear. In 2005, about 7 percent of American adults used social media. But by 2017, 80 percent of American adults used Facebook alone. About 3.5 billion people on the planet, out of 7.7 billion, are active social media participants. Globally, during a typical day, people post 500 million tweets, share over 10 billion pieces of Facebook content, and watch over a billion hours of YouTube video.
As social media platforms have grown, though, the once-prevalent, gauzy utopian vision of online community has disappeared. Along with the benefits of easy connectivity and increased information, social media has also become a vehicle for disinformation and political attacks from beyond sovereign borders.
“Social media disrupts our elections, our economy, and our health,” says Aral, who is the David Austin Professor of Management at the MIT Sloan School of Management.
Now Aral has written a book about it. In “The Hype Machine,” published this month by Currency, a Random House imprint, Aral details why social media platforms have become so successful yet so problematic, and suggests ways to improve them.
As Aral notes, the book covers some of the same territory as “The Social Dilemma,” a documentary that is one of the most popular films on Netflix at the moment. But Aral’s book, as he puts it, "starts where ‘The Social Dilemma’ leaves off and goes one step further to ask: What can we do about it?”
“This machine exists in every facet of our lives,” Aral says. “And the question in the book is, what do we do? How do we achieve the promise of this machine and avoid the peril? We’re at a crossroads. What we do next is essential, so I want to equip people, policymakers, and platforms to help us achieve the good outcomes and avoid the bad outcomes.”
When “engagement” equals anger
“The Hype Machine” draws on Aral’s own research about social networks, as well as other findings, from the cognitive sciences, computer science, business, politics, and more. Researchers at the University of California at Los Angeles, for instance, have found that people obtain bigger hits of dopamine — the chemical in our brains highly bound up with motivation and reward — when their social media posts receive more likes.
At the same time, consider a 2018 MIT study by Soroush Vosoughi, an MIT PhD student and now an assistant professor of computer science at Dartmouth College; Deb Roy, MIT professor of media arts and sciences and executive director of the MIT Media Lab; and Aral, who has been studying social networking for 20 years. The three researchers found that on Twitter, from 2006 to 2017, false news stories were 70 percent more likely to be retweeted than true ones. Why? Most likely because false news has greater novelty value compared to the truth, and provokes stronger reactions — especially disgust and surprise.
In this light, the essential tension surrounding social media companies is that their platforms gain audiences and revenue when posts provoke strong emotional responses, often based on dubious content.
“This is a well-designed, well-thought-out machine that has objectives it maximizes,” Aral says. “The business models that run the social-media industrial complex have a lot to do with the outcomes we’re seeing — it’s an attention economy, and businesses want you engaged. How do they get engagement? Well, they give you little dopamine hits, and … get you riled up. That’s why I call it the hype machine. We know strong emotions get us engaged, so [that favors] anger and salacious content.”
From Russia to marketing
“The Hype Machine” explores both the political implications and business dimensions of social media in depth. Certainly social media is fertile terrain for misinformation campaigns. During the 2016 U.S. presidential election, Russia spread false information to at least 126 million people on Facebook and another 20 million people on Instagram (which Facebook owns), and was responsible for 10 million tweets. About 44 percent of adult Americans visited a false news source in the final weeks of the campaign.
“I think we need to be a lot more vigilant than we are,” says Aral.
We do not know if Russia’s efforts altered the outcome of the 2016 election, Aral says, though they may have been fairly effective. Curiously, it is not clear if the same is true of most U.S. corporate engagement efforts.
As Aral examines, digital advertising on most big U.S. online platforms is often wildly ineffective, with academic studies showing that the “lift” generated by ad campaigns — the extent to which they affect consumer action — has been overstated by a factor of hundreds, in some cases. Simply counting clicks on ads is not enough. Instead, online engagement tends to be more effective among new consumers, and when it is targeted well; in that sense, there is a parallel between good marketing and guerilla social media campaigns.
“The two questions I get asked the most these days,” Aral says, “are, one, did Russia succeed in intervening in our democracy? And two, how do I measure the ROI [return on investment] from marketing investments? As I was writing this book, I realized the answer to those two questions is the same.”
Ideas for improvement
“The Hype Machine” has received praise from many commentators. Foster Provost, a professor at New York University’s Stern School of Business, says it is a “masterful integration of science, business, law, and policy.” Duncan Watts, a university professor at the University of Pennsylvania, says the book is “essential reading for anyone who wants to understand how we got here and how we can get somewhere better.”
In that vein, “The Hype Machine” has several detailed suggestions for improving social media. Aral favors automated and user-generated labeling of false news, and limiting revenue-collection that is based on false content. He also calls for firms to help scholars better research the issue of election interference.
Aral believes federal privacy measures could be useful, if we learn from the benefits and missteps of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and a new California law that lets consumers stop some data-sharing and allows people to find out what information companies have stored about them. He does not endorse breaking up Facebook, and suggests instead that the social media economy needs structural reform. He calls for data portability and interoperability, so “consumers would own their identities and could freely switch from one network to another.” Aral believes that without such fundamental changes, new platforms will simply replace the old ones, propelled by the network effects that drive the social-media economy.
“I do not advocate any one silver bullet,” says Aral, who emphasizes that changes in four areas together — money, code, norms, and laws — can alter the trajectory of the social media industry.
But if things continue without change, Aral adds, Facebook and the other social media giants risk substantial civic backlash and user burnout.
“If you get me angry and riled up, I might click more in the short term, but I might also grow really tired and annoyed by how this is making my life miserable, and I might turn you off entirely,” Aral observes. “I mean, that’s why we have a Delete Facebook movement, that’s why we have a Stop Hate for Profit movement. People are pushing back against the short-term vision, and I think we need to embrace this longer-term vision of a healthier communications ecosystem.”
Changing the social media giants can seem like a tall order. Still, Aral says, these firms are not necessarily destined for domination.
“I don’t think this technology or any other technology has some deterministic endpoint,” Aral says. “I want to bring us back to a more practical reality, which is that technology is what we make it, and we are abdicating our responsibility to steer technology toward good and away from bad. That is the path I try to illuminate in this book.”
Share this news article on:
Press mentions.
Prof. Sinan Aral’s new book, “The Hype Machine,” has been selected as one of the best books of the year about AI by Wired . Gilad Edelman notes that Aral’s book is “an engagingly written shortcut to expertise on what the likes of Facebook and Twitter are doing to our brains and our society.”
Prof. Sinan Aral speaks with Danny Crichton of TechCrunch about his new book, “The Hype Machine,” which explores the future of social media. Aral notes that he believes a starting point “for solving the social media crisis is creating competition in the social media economy.”
New York Times
Prof. Sinan Aral speaks with New York Times editorial board member Greg Bensinger about how social media platforms can reduce the spread of misinformation. “Human-in-the-loop moderation is the right solution,” says Aral. “It’s not a simple silver bullet, but it would give accountability where these companies have in the past blamed software.”
Prof. Sinan Aral speaks with Kara Miller of GBH’s Innovation Hub about his research examining the impact of social media on everything from business re-openings during the Covid-19 pandemic to politics.
Prof. Sinan Aral speaks with NPR’s Michael Martin about his new book, “The Hype Machine,” which explores the benefits and downfalls posed by social media. “I've been researching social media for 20 years. I've seen its evolution and also the techno utopianism and dystopianism,” says Aral. “I thought it was appropriate to have a book that asks, 'what can we do to really fix the social media morass we find ourselves in?'”
Previous item Next item
Related Links
- MIT Sloan School of Management
Related Topics
- Business and management
- Social media
- Books and authors
- Behavioral economics
Related Articles

The catch to putting warning labels on fake news

Our itch to share helps spread Covid-19 misinformation

Better fact-checking for fake news

Study: On Twitter, false news travels faster than true stories

Social networking
More mit news.

Three from MIT awarded 2024 Guggenheim Fellowships
Read full story →

A musical life: Carlos Prieto ’59 in conversation and concert

Two from MIT awarded 2024 Paul and Daisy Soros Fellowships for New Americans

MIT Emerging Talent opens pathways for underserved global learners

The MIT Edgerton Center’s third annual showcase dazzles onlookers
3 Questions: A shared vocabulary for how infectious diseases spread
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
Digital Doughnut
The Future of Social Media: Key Trends and Predictions for 2023
In this article, we explore the key trends expected to shape the world of social media in 2023 and beyond. From the continued growth of visual content to the rise of micro-influencers, we examine the trends set to transform how we use social media and interact with brands.
Whether you're a seasoned social media marketer or just getting started, this article offers valuable insights and predictions for the future of social media – and the steps you can take to stay ahead of the curve and succeed in the ever-changing world of online marketing. So if you're ready to learn more about the future of social media, read on!

As we look toward the future, it's clear that social media will continue to play a pivotal role in our daily lives and in the world of marketing. In 2023, we can expect to see several exciting trends emerge, including a few key trends in social media that marketers should be aware of:
1. Continued Growth of Visual Content
With the proliferation of platforms like Instagram and TikTok, visual content is more popular than ever. In 2023, we can expect more emphasis on visually appealing content, including photos, videos, and graphics. Marketers must prioritize creating visually appealing content that resonates with their target audience to stand out on social media.
2. Rise of Micro-Influencers
While traditional celebrities have long been famous on social media, in recent years, there has been a shift towards "micro-influencers" – everyday people with smaller but highly engaged followings.
In 2023, we can expect more brands to partner with micro-influencers as they offer a more authentic and relatable form of social media marketing.
3. Increased Focus on Ecommerce
Social media platforms are increasingly used for consumers to discover and purchase products.
In 2023, we can expect to see more emphasis on ecommerce on platforms like Instagram and Facebook, with the development of new features and tools to facilitate online shopping. Marketers will need to consider leveraging social media to drive ecommerce sales.
4. Greater use of Chatbots
Chatbots – automated software programs that can communicate with users in real-time – are expected to become even more prevalent on social media in 2023.
These tools can help brands provide quick and efficient customer service, answer frequently asked questions, and even make recommendations to users. Marketers must consider incorporating chatbots into their social media strategy to improve customer experience and drive engagement.
5. Rise of Ephemeral Content
Social media platforms increasingly embrace brief content, which disappears after a certain period. Examples include Stories on Instagram and Snapchat and Fleets on Twitter. In 2023, we can expect more brands to experiment with ephemeral content to create a sense of urgency and build anticipation around their products and services.
Overall, the future of social media in 2023 looks bright, with new opportunities for visual content, micro-influencers, e-commerce, chatbots, ephemeral content, and AI. By staying up-to-date on the latest trends and adapting their strategy accordingly, marketers will be well-positioned to succeed on social media in the year ahead.
Author Profile
Dr. Islam Gouda is a young professional with a passion for marketing. Dr. Gouda has an honorary doctorate from the University of California in Strategic Marketing as a result of the many articles, research studies and publications in that field. He also has a masters degree from the University of Wollongong in Strategic Marketing, and an organizational leadership training from Lehigh in USA, and an American University of Sharjah graduate in Marketing and Management. Dr. Gouda is a marketing focused business experience with a strong analytical ability of using available market data for strategic marketing, business development, product development purposes along with the identification of new business opportunities and measurement of ROI. Dr. Gouda's specialties include, leadership and communications skills with the ability to adapt to a wide variety of cultures and to manage and work part of cross-functional teams. Dr. Gouda has a strong track of success on the definition and execution of the whole marketing mix for both consumer and enterprise segments: market intelligence, product management, demand generation, press, advertising, alliances - with a proven channel expertise, campaigns setup, channel enablement programs, execution, tracking, reporting.
B2B and B2C Marketing, marketing research, branding, online marketing, business development, product development and marketing events management.
Previous Experience
This user has not entered their Previous Experience
Education & Qualifications
This user has not entered their Education & Qualifications
Contribute Now!
Loving our articles? Do you have an insightful post that you want to shout about? Well, you've come to the right place! We are always looking for fresh Doughnuts to be a part of our community.
Popular Articles
The Impact of New Technology on Marketing
Technology has impacted every part of our lives. From household chores to business disciplines and etiquette, there's a gadget or app for it. Marketing has changed dramatically over the years, but what is the...
Infographic: The State of B2B Lead Generation 2024
A new report from London Research and Demand Exchange looks at the latest trends in B2B lead generation, with clear insights around how lead gen leaders are generating the quality and quantity of leads they require.
How much has marketing really changed in the last 30 years?
Have the principles of marketing changed in the age of the Internet? Or have many of the key fundamentals of the discipline stayed the same?
How to Review a Website — A Guide for Beginners
A company website is crucial for any business's digital marketing strategy. To keep up with the changing trends and customer buying behaviors, it's important to review and make necessary changes regularly...
7 Reasons Why Social Media Marketing is Important For Your Business
In the past two decades social media has become a crucial tool for marketers, enabling businesses to connect with potential customers. If your business has yet to embrace social media and you want to know why it is...
Social Media in Future: Twitter, Instagram and Tango Essay
Social media was originally meant to cater for the peculiar communication needs of young people. However, social media soon became a global revolution that has since changed the way individuals, businesses, and governments go about their activities. In addition, social media has created a parallel society that has a new set of norms. The revolution surrounding social media has also had unexpected changes and impacts on the society. However, the changes that have characterized the use of social media are set to continue in future. The past changes in social media have changed modes of conducting business and altered the path of globalization.
People are increasingly depending on the virtual crowds on social media for political and commercial purposes. The future of social media will not have distinct differences from its current form. The confusion that characterizes the current social media players where thousands of developers are seeking to establish themselves as the dominant stakeholders in the market is likely to decline in future.
Social media will continue to have a great impact on peoples’ lives especially their interactions and entertainment habits. This paper attempts to explore the future of social media in respect to the lives of individuals. The paper will focus on some of the leading social media providers including Twitter, Instagram, and Tango.
The future of social media will incorporate the current and new modes of doing things. First, the information that is accessed by social media users is likely to become more specific. Most social media companies are currently gathering information about their users. Companies such as Facebook and Google are currently gathering information about their users’ preferences and purchasing habits. Therefore, in future the companies will customize the data that they submit to their customers using the data that they have been collecting.
Most social media platforms are constantly gathering information about “our likes and dislikes, our interests and disdains…soon…we will no longer need to search for information on the Web as information will find us based on all this data” (Kietzmann 248). Contrary to the popular belief that people will be bombarded with mountains of data, the information that will be served to social media users will coincide with their specific needs. Therefore, in future people will not spend considerable amounts of time while searching for information via social media.
The future of social media will be characterized by the fact that “the right information will be served to the right people at the right time” (Benkler 56). Most of the people who shun social media platforms do so because they find social media to be a confusing avenue where too much ‘useless’ information is supplied to them.
To attract more users, social media platforms are engineering methods of cutting down the transmission of unnecessary data to their users. This intention will be a major determinant of how social media will look like in future. The future social media look is lean and simple to avoid burdening individuals with unnecessary information.
Currently, the social media platform is littered with over 123,000 apps. The future of social media will not have this big number of platforms. In future, social media avenues will be ‘branched’. Therefore, the major social media platforms will act as ‘dashboards’ for the smaller apps. For instance, small start-up companies will rely on companies such as Twitter. The current dominant social media platforms will act as “social channels on which other companies will grow and develop their own technologies and businesses in future” (Asur and Huberman 51). For example, a company such as Tango is not gaining market share quickly.
In future, Tango might partner with other dominant companies such as Facebook and Skype and be providing these platforms with a voice-chat option to the more than 700 million Facebook users. Therefore, in future, most companies will have merged or they will be operating in clusters. Furthermore, the dominance that is being pursued by the leading companies will be achieved easily. For instance, in future Instagram might provide its users with a wide array of apps that have the potential to enhance the experiences of its users.
Future social media platforms will be complete in nature and they will cater to every possible need that users might have (Culnan, McHugh and Zubillaga 256). A user might want to combine the instantaneous experience of Instagram with the interactive nature of Facebook. Future social media platforms will focus on a wider range of consumer needs. Furthermore, upcoming app developers will develop platforms that complement the current leading providers and not ones that compete against the market leaders.
For example, companies such as Tweetdeck and Stocktwits have always operated under the Twitter platform although they started out as independent companies. This trend will dominate the future of social media. In future, several independent social media platforms will congregate under one umbrella. It is also probable that more than half of the existing social media platforms will have died out in the next ten to twenty years.
Most companies factor in a market-entry period and this means they do not expect to make any profits in their initial stages. Currently, part of the over 123,000 apps are in their market-entry phase. However, if this phase is completed without a company realizing any profits, the company might be forced to shut down its operations.
Advertising has become a major part of social media platforms. In future, the advertising techniques will change and become more user-driven as opposed to them being provider-driven. People will be able to turn off advertisements in their social media apps, albeit at a fee. Alternatively, consumers will have the option of switching social media adverts on or off whenever they wish to. The trend of for-pay applications is also likely to take root in future. The current success of the Whatsapp messaging tool is enough evidence that social media platforms that make revenues through advertising will not dominate the future.
The issue of privacy will also change in future. In future, social media platforms are likely to embrace advanced privacy technologies so as to entice security-conscious individuals. In twenty years, most companies will have mastered the art of ensuring maximum privacy for their users. The current tendency by social media companies to embrace transparency as opposed to privacy is driven by existing inadequacies. However, these inadequacies will be overcome in future and we shall all embrace privacy.
I am not afraid of the changes that will happen to social media in future mostly because all of them are market-driven. Furthermore, the future of social media means that I will spend less time perusing through heaps of information. Furthermore, I will also be less worried about my privacy being compromised by capitalistic social media companies and aggressive advertisers. I am optimistic about the future of social media and the direction that is being taken by the companies that provide these services.
Works Cited
Asur, Sitaram, and Bernardo A. Huberman. “Predicting the future with social media.” Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology 9.1 (2010): 43-59. Print.
Benkler, Yochai. The wealth of networks: How social production transforms markets and freedom , Yale: Yale University Press, 2006. Print.
Culnan, Mary J., Patrick J. McHugh and Jesus I. Zubillaga. “How large US companies can use Twitter and other social media to gain business value.” MIS Quarterly Executive 9.4 (2010): 243-259. Print.
Kietzmann, Jan. “Social media? Get serious! Understanding the functional building blocks of social media.” Business horizons 54.3 (2011): 241-251. Print.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, July 30). Social Media in Future: Twitter, Instagram and Tango. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-in-future-twitter-instagram-and-tango/
"Social Media in Future: Twitter, Instagram and Tango." IvyPanda , 30 July 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-in-future-twitter-instagram-and-tango/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Social Media in Future: Twitter, Instagram and Tango'. 30 July.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Social Media in Future: Twitter, Instagram and Tango." July 30, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-in-future-twitter-instagram-and-tango/.
1. IvyPanda . "Social Media in Future: Twitter, Instagram and Tango." July 30, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-in-future-twitter-instagram-and-tango/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Social Media in Future: Twitter, Instagram and Tango." July 30, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-media-in-future-twitter-instagram-and-tango/.
- Market-Entry and Channel Strategy
- Tango: Origin, History, and Characteristics
- "In Strangers' Arms: The Magic of the Tango"
- Gender Roles in Tango: Cultural Aspects
- Controversy of “And Tango Makes Three” by Parnell & Richardson
- Argentine Tango Dance for Cancer Survivors: A Feasibility Study
- Astor Piazzolla: Biography, Career, and Legacy
- "Rebellions in Everynight Life" by Delgado and Muñoz
- Classical Music: Attending a Concert
- Latin American Music
- Social Media Benefits: Twitter, Instagram, and Google Plus
- People’s Responsibility in the Social Media World and Its Effects on the Reputation
- Social Media Platforms Effects on Social identity
- The Role of Social Media
- Censorship of Social Networking Sites in Developing Countries

The rise of social media
Social media sites are used by more than two-thirds of internet users. how has social media grown over time.
This article is an archived version of an article published in 2019. Due to data availability, the article and charts will not be updated.
Facebook, the largest social media platform in the world, had 2.4 billion users in 2019. Other social media platforms, including YouTube and WhatsApp, also had over one billion users each.
These numbers are huge – in 2019, there were 7.7 billion people worldwide, with at least 3.5 billion online . This means social media platforms were used by one in three people worldwide and more than two-thirds of all Internet users.
Social media has changed the world. The rapid and vast adoption of these technologies is changing how we find partners , access information from the news, and organize to demand political change .
Who uses social media? When did the rise of social media start, and how has the number of users changed over time? Here we answer these and other key questions to understand the history of social media worldwide.
We begin with an outline of key trends and conclude with a perspective on the social media adoption rate relative to other modern communication technologies.
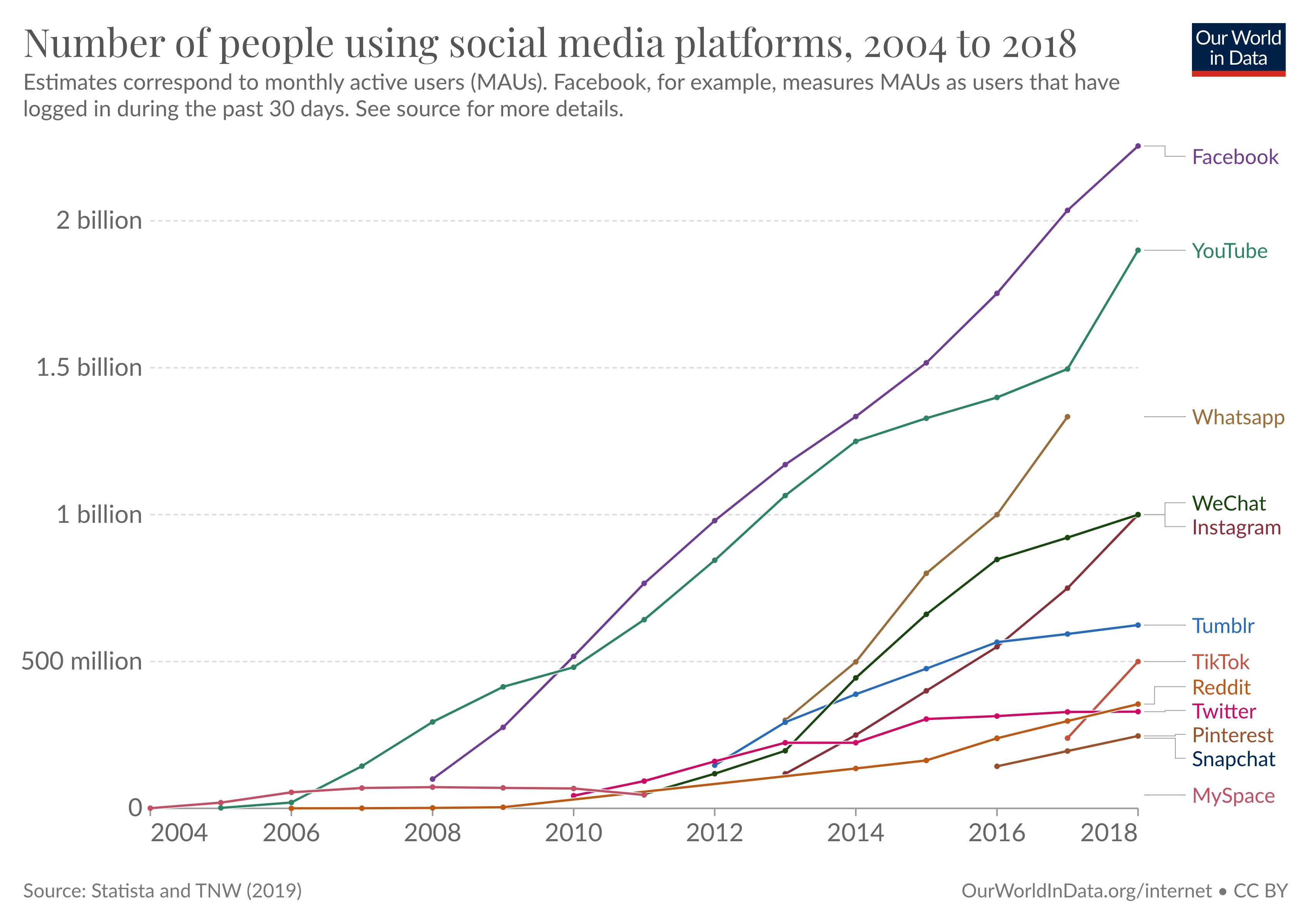
Social media started in the early 2000s
MySpace was the first social media site to reach a million monthly active users – it achieved this milestone around 2004. This is arguably the beginning of social media as we know it. 1
In the chart, we plot monthly active users across various platforms since 2004.
Some large social media sites, such as Facebook, YouTube, and Reddit, have been around for ten or more years, but others are much newer.
TikTok, for example, launched in September 2016, and by mid-2018, it had already reached half a billion users. To put this in perspective: TikTok gained, on average, about 20 million new users per month over this period.
The data also shows rapid changes in the opposite direction. Once-dominant platforms have disappeared. In 2008, Hi5, MySpace, and Friendster were close competitors to Facebook, yet by 2012 they had virtually no market share. The case of MySpace is remarkable, considering that in 2006 it temporarily surpassed Google as the most visited website in the US.
Most social media platforms that survived the last decade have shifted significantly in what they offer users. Twitter, for example, didn’t allow users to upload videos or images initially. Since 2011 this has been possible, and today, more than 50% of the content viewed on Twitter includes images and videos.
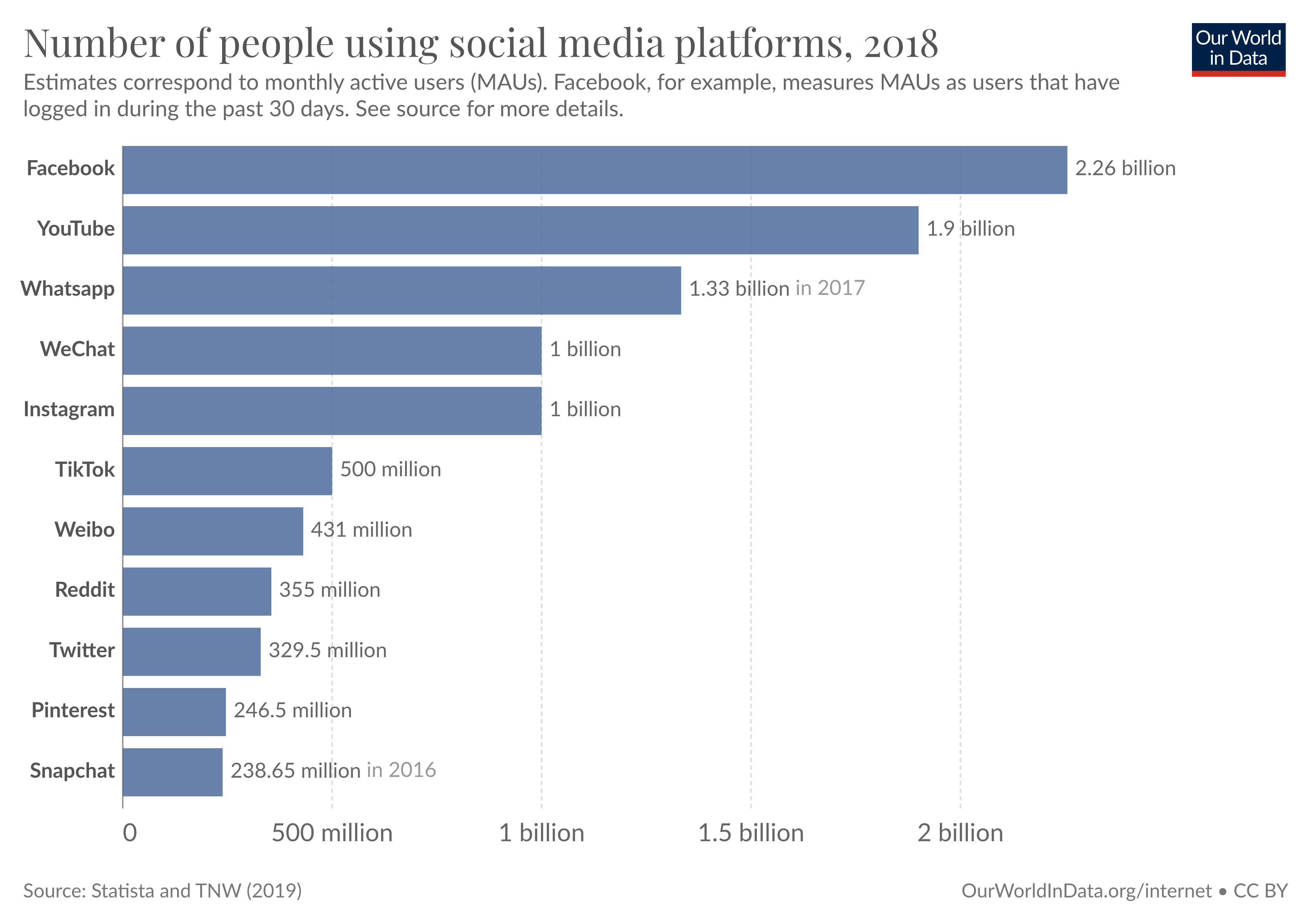
Facebook dominated the social media market for a decade, but five other platforms also have more than half a billion users
With 2.3 billion users, Facebook was the most popular social media platform in 2019. YouTube, Instagram, and WeChat followed, with over a billion users. Tumblr and TikTok came next, with over half a billion users.
The bar chart shows a ranking of the top social media platforms.
Some social media sites are particularly popular among specific population groups
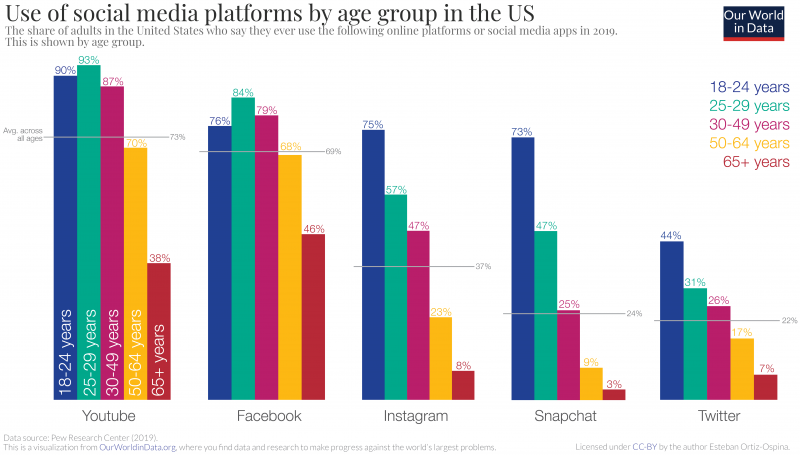
The aggregate numbers mask a great deal of heterogeneity across platforms. Some social media sites are much more popular than others among specific population groups.
In general, young people are more likely to use social media than older people. But some platforms are much more popular among younger people. This is shown in the chart where we plot the breakdown of social media use by age group in the US.
For Snapchat and Instagram, the ‘age gradient’ is exceptionally steep – the popularity of these platforms drops much faster with age. Most people under 25 use Snapchat (73%), while only 3% of people over 65 use it.
Since these platforms are relatively new, it’s hard to know how much of this age gradient results from a “cohort effect”. In other words: it’s unclear whether today’s young people will continue using Snapchat as they age. If they do, the age gradient will narrow.
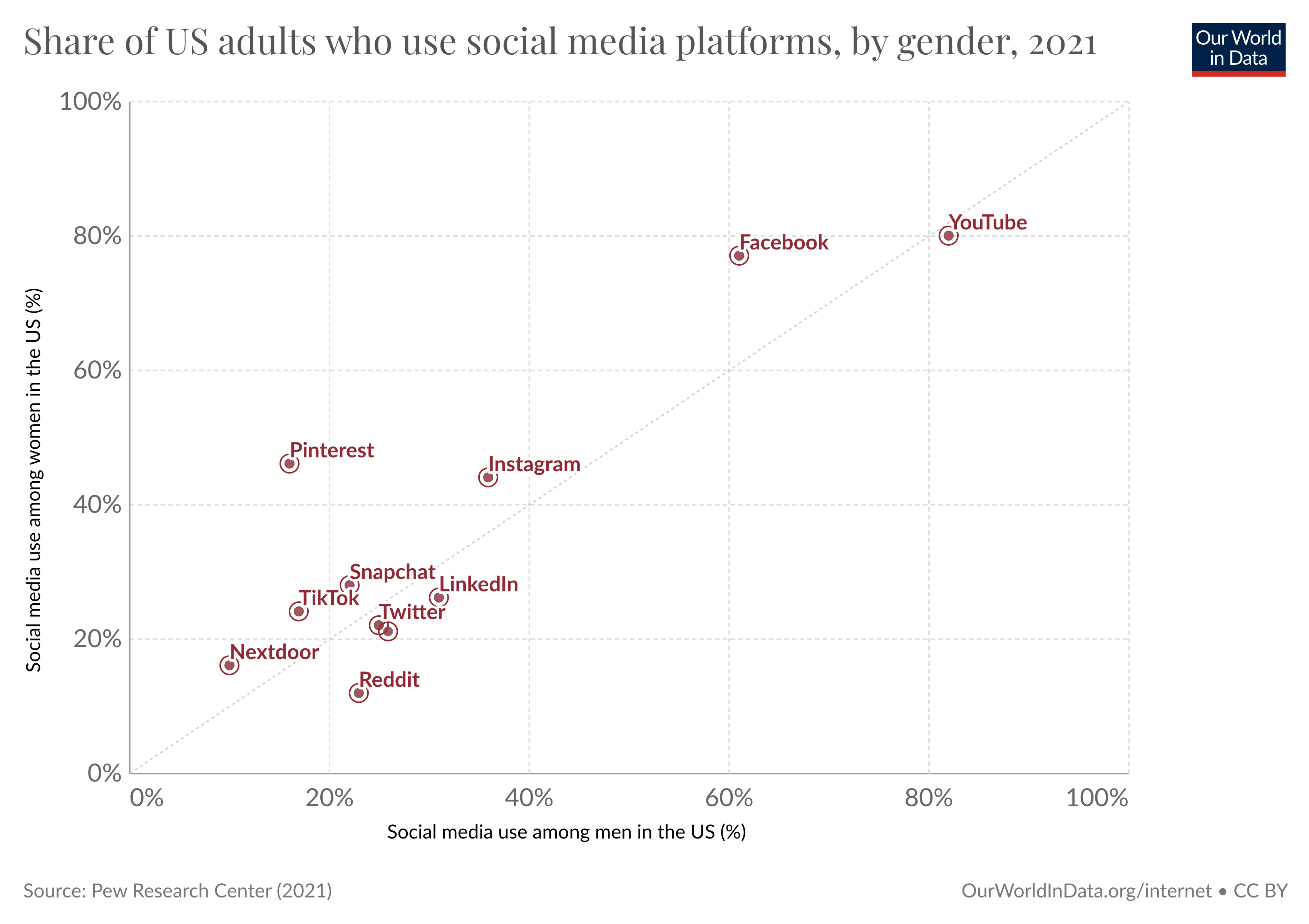
Let’s now look at gender differences.
This chart shows the percentage of men and women that used different platforms in the US in 2021—the diagonal line marks parity. Sites above the diagonal line are more popular among women, and those below are more popular among men.
For some platforms, the gender differences are substantial. The share of women who used Pinterest was 3 times as high as that of men using this platform. For Reddit, it was the other way around: the share of men was twice as high.
In rich countries, almost all young people use social media
From a back-of-the-envelope calculation, we know that if Facebook had 2.3 billion users in 2019, then at least 30% of the world was using social media. 2 This is just an average – usage rates were much higher for some world regions, specifically for some population groups.
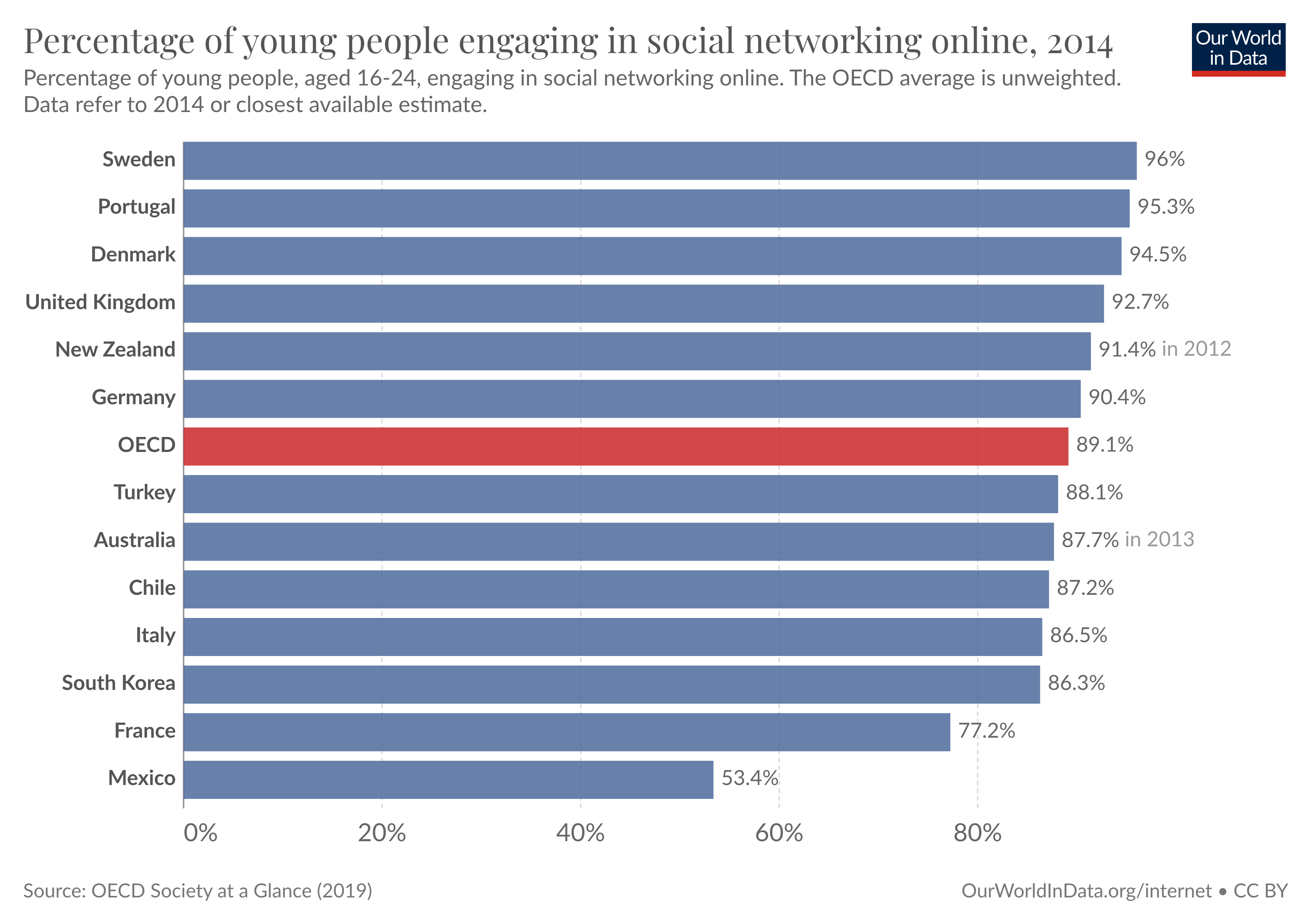
Young people tend to use social media more frequently. In fact, in rich countries where access to the Internet is nearly universal , the vast majority of young adults use it.
Our chart shows the proportion of people aged 16 to 24 who used social networks across various countries. As we can see, the average for the OECD is close to 90%.
If today’s young adults continue using social media throughout their lives, then it’s likely that social media will continue growing rapidly as Internet adoption expands throughout lower-income countries .
The rise of social media in rich countries has come together with an increase in the amount of time spent online
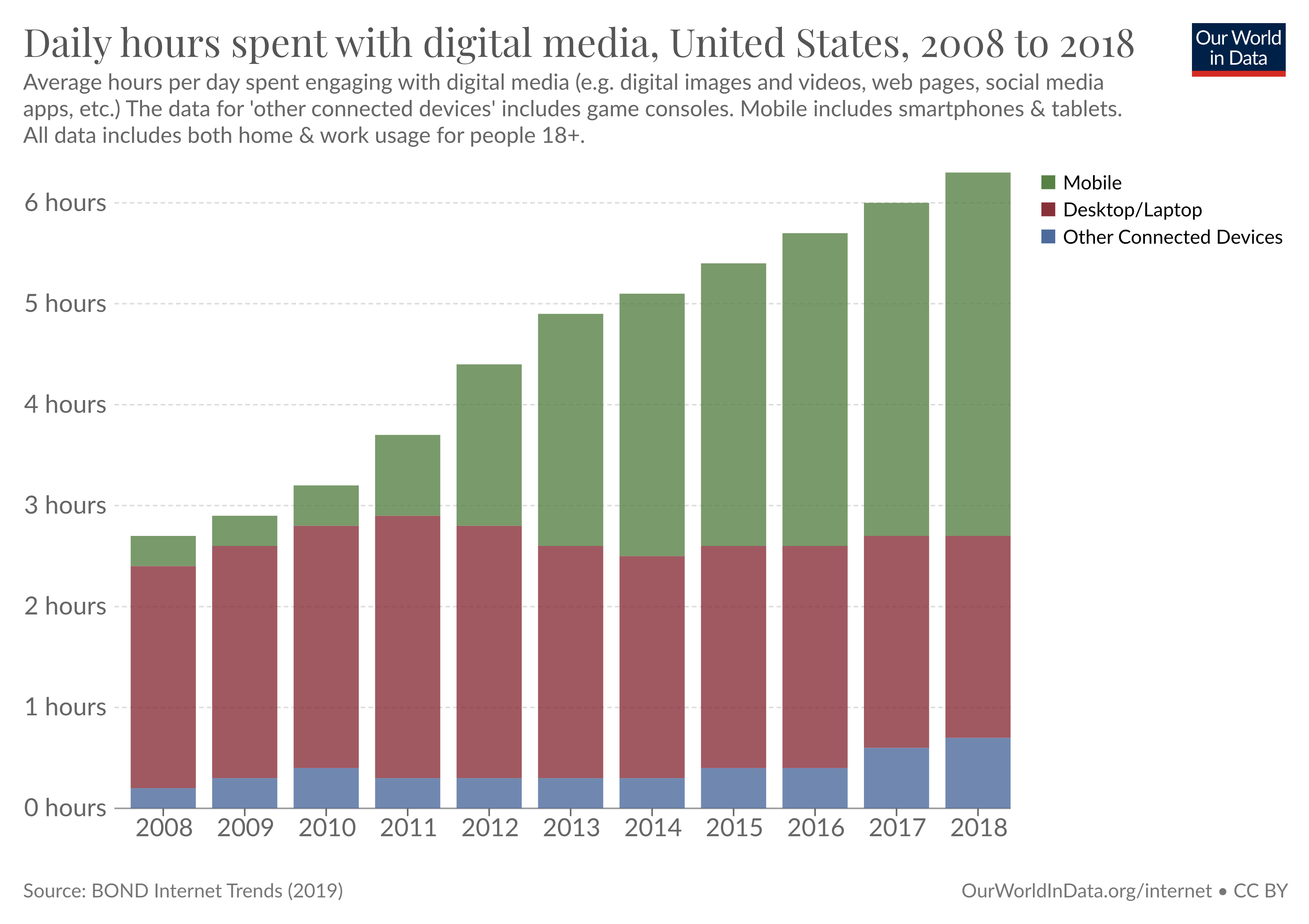
The increase in social media use over the last decade has, of course, come together with a large increase in the amount of time people spend online.
In the US, adults spend more than 6 hours daily on digital media (apps and websites accessed through mobile phones, tablets, computers, and other connected devices such as game consoles). As the chart shows, this growth has been driven almost entirely by additional time spent on smartphones and tablets. 3
According to a survey from the Pew Research Center, adults aged 18 to 29 in the US are more likely to get news indirectly via social media than directly from print newspapers or news sites. They also report being online “almost constantly” . 4
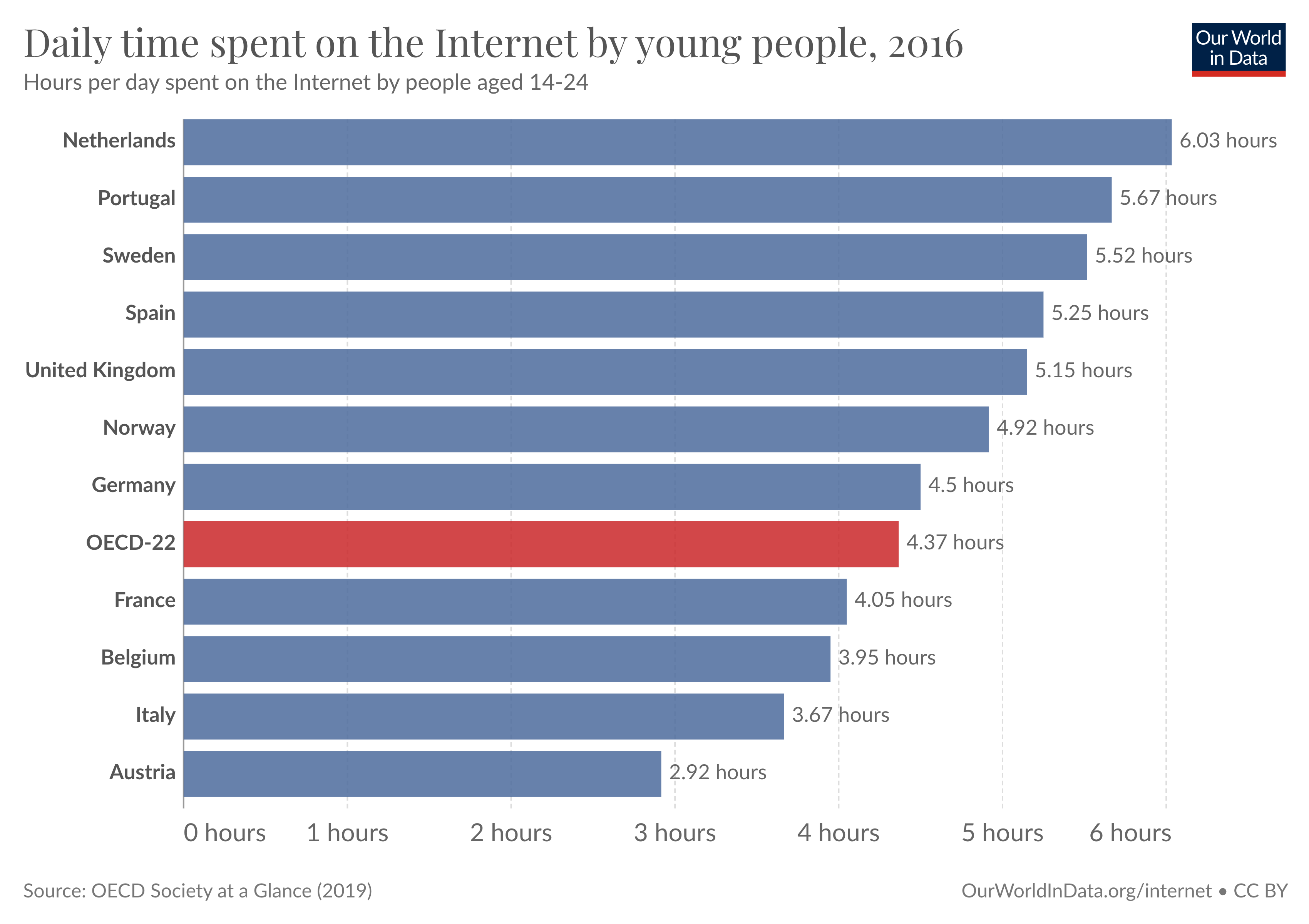
Evidence shows that in other rich countries, people also spend many hours per day online. The following chart shows how many hours young people spend online across various rich countries. As we can see, the average for the OECD is more than 4 hours per day; in some countries, the average is above 6 hours per day.
Some perspective on how fast and profound these rapid changes are
The percentage of US adults who use social media increased from 5% in 2005 to 79% in 2019. Even on a global stage, the speed of diffusion is striking: Facebook surged from covering around 1.5% of the world population in 2008 to around 30% in 2018. 5
How does this compare to the diffusion of other communication technologies in today's everyday life?
The following chart provides some perspective.
Social media’s growth in the US is comparable – in speed and, to some extent, reach – to most modern communication-enabling technologies, including computers, smartphones, and the Internet.
The rise of social media is an extraordinary example of how quickly and drastically social behaviors can change: Something that is today part of the everyday life of one-third of the world population was unthinkable less than a generation ago.
Rapid changes like those brought about by social media always spark fears about possible negative effects. Specifically, in the context of social media, a key question is whether these new communication technologies are harming our mental health – this is an important question and we cover the evidence in another article on Our World in Data.
There were, of course, earlier, much smaller predecessors of social networking websites. The first recognizable social media site, in the format we know today, was Six Degrees – a platform created in 1997 that enabled users to upload a profile and make friends with other users. At the core, the features that define a social media platform are (i) profiles for users, (ii) the ability for users to upload content constantly, and (iii) the ability for users to discuss content and connect with other users.
To be precise, Facebook had 2.3 billion ‘active users.’ There may be some discrepancies between the number of ‘active users’ and the number of people since one person could, in theory, maintain multiple accounts. In practice, these discrepancies are likely small because most social media platforms, including Facebook, have policies and checks to avoid multiple accounts per person.
Digital media contrasts with print media (including books, newspapers, and magazines) and other traditional or analog media (including TV, movies, and radio).
According to the survey from Pew Research, 36% of adults 18 to 29 in the US say they ‘often get news via social media,’ which is higher than the share saying they ‘often get news via other platforms,’ such as news sites, TV, radio or print newspapers. From the same survey, we also know that 48% of adults 18 to 29 say they go online almost constantly, and 46% say they go online multiple times daily.
The US social media adoption data is here . Regarding Facebook’s global numbers: In 2018, Facebook had 2.26 billion users, and in 2008 it had 100 million; the world population in 2008 was 6.8 billion, and in 2018 it was 7.63 billion (you can check the population data here .)
Cite this work
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this article, please also cite the underlying data sources. This article can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
What the debate over TikTok means for the future of social media
Subscribe to the center for technology innovation newsletter, mishaela robison and mishaela robison research assistant @mishaelarobison jack karsten jack karsten former senior research analyst, center for technology innovation - the brookings institution @jtkarsten.
October 12, 2020
It has been an eventful few months for TikTok: The social media platform recently won an injunction against a nationwide ban while it negotiates a deal with Oracle and Walmart to satisfy President Trump’s executive orders demanding a sale to a U.S. company. With the November deadline for a deal upcoming, the shifting contours of the transaction and concerns over the app’s security will have important ramifications for future technology policy.
The TikTok app has consistently topped worldwide download charts and recently celebrated the best quarter of downloads in app history. Yet this very popularity fueled concerns about data security and potential foreign espionage from China, where TikTok’s current parent company ByteDance is located. Though some TikTok users have speculated that the executive orders have been in retaliation to the platform’s role in organizing opposition to Trump’s reelection campaign , the app has been under national security review since 2019 due to its rising influence in the U.S., which suggests several overlapping motivations.
Other social media platforms have benefitted from the pandemonium surrounding TikTok’s current legal challenges, lessening the focus on their own products and services and attracting TikTok users. But the perceived political motivation to ban TikTok based on its Chinese origins sets a damaging precedent for other social media platforms balancing global ambitions with the U.S.’s broader handling of foreign relations.
Ties to China
Prior to issuing his executive order, Trump stated that he did not mind if “a very American company buys [TikTok.]” His sentiments were rooted in the administration’s growing distrust of Chinese technology companies. TikTok had previously attempted to allay the president’s concerns by storing Americans’ data on U.S. soil, hiring an American CEO, and employing lobbyists in Washington. Further, TikTok’s founder chose to create separate apps for the Chinese and global markets so that users around the world could avoid censorship requirements from the Chinese Communist Party. Still, efforts to assure the U.S. government that TikTok would not give data to the Chinese government have not been sufficient enough to quell concerns over Chinese influence and interference through the app.
Despite Trump’s initial demand that TikTok be acquired by an American company, the current deal proposal still allows ByteDance an 80% ownership stake in the newly established entity, TikTok Global, with 20% ownership from potential buyers Oracle and Walmart. It also remains unclear if such a proposal will be enough to eliminate other lingering concerns about the social media giant. Several lawmakers, including Senator Josh Hawley (R-MO,) criticized prior deals for not sufficiently severing ties with China. Trump himself has expressed similar sentiment in the past by vowing not to sign off if ByteDance maintains any organizational control. For now, American companies appear likely to acquire a minority of the social media giant with Trump’s “blessing” in spite of the majority control left to a company which has previously censored anti-China content on TikTok.
Reflected in both the president’s executive orders and his business guidance is the absence of coherent policy around Chinese technology, leaving TikTok as a precedent for future actions. Ongoing negotiations between TikTok and other companies signal a need for a comprehensive strategy for dealing with Chinese-based technology firms operating in the U.S. In March, similar scrutiny lead to the sale of the gay dating app Grindr after the Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States (CFIUS) determined that Chinese ownership of the app was a national security risk, though the Committee did not publicly share the evidence underlying that decision. Comparatively, the U.S. government has raised few concerns about data protection on the popular Swedish-based music app Spotify, despite major privacy concerns arising in Sweden. As questions of Chinese-owned tech companies continue to emerge, the U.S. government needs much clearer policies going forward to avoid making decisions an ad hoc manner.
Algorithmic transparency
By many accounts, TikTok’s power comes from its algorithm , which tailors an infinite feed of videos to each individual user’s preferences. As a result, the average TikTok user spends more time on the platform than its competitors. Recent trade restrictions by China have highlighted the value that the country places on the development of powerful algorithms.
Artificial intelligence can be a double-edged sword for social media, providing potential for increased engagement while creating echo chambers, bias, and manipulation. In light of these concerns, TikTok pledged to share their algorithm with external experts, a move that came days before the House Antitrust Hearing confronted Big Tech CEOs for their lack of transparency. In a blog post announcing this decision, former CEO Kevin Mayer called on other social media companies to do the same, emphasizing TikTok’s commitment to accountability. Mayer vowed to use TikTok’s time in the spotlight to “drive deeper conversations around algorithms, transparency, and content moderation, and to develop stricter rules of the road.”
TikTok’s openness may set a new benchmark for other social media companies, challenging them to be more transparent about their algorithms or risk losing trust. Though experts have debated the degree to which algorithms should be made transparent, research from the Stanford Department of Communication found that users trust algorithms more when presented with at least some information on how they work. These factors point to a need for algorithmic transparency, and the urgency of policy to enforce it.
Privacy enhancements
When asked about a potential Microsoft acquisition, co-founder Bill Gates described “being big in the social media business” as “a poison chalice” due to questions of encryption and privacy. Similarly, implicit in concerns that China may have access to TikTok users’ data are questions about data security and privacy. TikTok has previously faced criticism—and a lawsuit —for failing to protect the data privacy of minors, resulting in heightened privacy measures that they have only partially implemented.
Though, as a viral TikTok video pointed out, Facebook currently tracks more user data than TikTok, despite the latter engaging in concerning several data acquisition tactics . Since the ban was announced, major employers such as Wells Fargo and the federal government , and the Biden campaign have prohibited their staff from using the app due to security concerns. If ByteDance retains any part of U.S. operations, they could still be required to send data to Chinese companies under the country’s national security law. In the past, critics have also accused Oracle of selling personal user data , which suggests a need for greater privacy regulation for all companies in the United States, regardless of national origin.
Vanessa Pappas, TikTok’s new global head, has said her primary focus will be the app’s creators and users . If that is the case, she must first address the security of their data and institute appropriate privacy mechanisms.
TikTok exemplifies the necessity for comprehensive policies regarding foreign tech companies. While the fate of the imminent deal remains ambiguous, the tech world will be watching to determine if the company’s partnership with Oracle and Walmart can ameliorate the concerns that prompted calls for its removal from app stores. Reflexive condemnation of Chinese-based technology companies without a systematic policy basis is likely to prove ineffective and confusing in the long run. The current policy ambiguity misses an opportunity to pursue greater transparency and accountability from all technology companies.
No matter the ultimate outcome, TikTok has left an indelible mark on the social media industry. The questions raised by recent action are not new and illuminate gaps in policy which concern the future of the entire tech sector.
Facebook is a general, unrestricted donor to the Brookings Institution. The findings, interpretations, and conclusions posted in this piece are solely those of the author and not influenced by any donation.
Related Content
Darrell M. West, Nicol Turner Lee, Tom Wheeler
September 17, 2020
Geoffrey Gertz
August 7, 2020
November 15, 2019
Cybersecurity Internet & Telecommunications Privacy
Governance Studies
Center for Technology Innovation
Julian Jacobs, Francesco Tasin, AJ Mannan
April 25, 2024
Elaine Kamarck, Darrell M. West
August 27, 2024
Jolynn Dellinger, Stephanie K. Pell
April 18, 2024
The future of social media in marketing
- Conceptual/Theoretical Paper
- Open access
- Published: 12 October 2019
- Volume 48 , pages 79–95, ( 2020 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Gil Appel 1 ,
- Lauren Grewal 2 ,
- Rhonda Hadi 3 &
- Andrew T. Stephen 3 , 4
887k Accesses
661 Citations
81 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
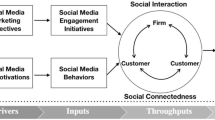
Social media allows people to freely interact with others and offers multiple ways for marketers to reach and engage with consumers. Considering the numerous ways social media affects individuals and businesses alike, in this article, the authors focus on where they believe the future of social media lies when considering marketing-related topics and issues. Drawing on academic research, discussions with industry leaders, and popular discourse, the authors identify nine themes, organized by predicted imminence (i.e., the immediate, near, and far futures), that they believe will meaningfully shape the future of social media through three lenses: consumer, industry, and public policy. Within each theme, the authors describe the digital landscape, present and discuss their predictions, and identify relevant future research directions for academics and practitioners.
Similar content being viewed by others
Social media marketing strategy: definition, conceptualization, taxonomy, validation, and future agenda

Online influencer marketing
Social media influencer marketing: foundations, trends, and ways forward
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Social media is used by billions of people around the world and has fast become one of the defining technologies of our time. Facebook, for example, reported having 2.38 billion monthly active users and 1.56 billion daily active users as of March 31, 2019 (Facebook 2019 ). Globally, the total number of social media users is estimated to grow to 3.29 billion users in 2022, which will be 42.3% of the world’s population (eMarketer 2018 ). Given the massive potential audience available who are spending many hours a day using social media across the various platforms, it is not surprising that marketers have embraced social media as a marketing channel. Academically, social media has also been embraced, and an extensive body of research on social media marketing and related topics, such as online word of mouth (WOM) and online networks, has been developed. Despite what academics and practitioners have studied and learned over the last 15–20 years on this topic, due to the fast-paced and ever-changing nature of social media—and how consumers use it—the future of social media in marketing might not be merely a continuation of what we have already seen. Therefore, we ask a pertinent question, what is the future of social media in marketing?
Addressing this question is the goal of this article. It is important to consider the future of social media in the context of consumer behavior and marketing, since social media has become a vital marketing and communications channel for businesses, organizations and institutions alike, including those in the political sphere. Moreover, social media is culturally significant since it has become, for many, the primary domain in which they receive vast amounts of information, share content and aspects of their lives with others, and receive information about the world around them (even though that information might be of questionable accuracy). Vitally, social media is always changing. Social media as we know it today is different than even a year ago (let alone a decade ago), and social media a year from now will likely be different than now. This is due to constant innovation taking place on both the technology side (e.g., by the major platforms constantly adding new features and services) and the user/consumer side (e.g., people finding new uses for social media) of social media.
What is social media?
Definitionally, social media can be thought of in a few different ways. In a practical sense, it is a collection of software-based digital technologies—usually presented as apps and websites—that provide users with digital environments in which they can send and receive digital content or information over some type of online social network. In this sense, we can think of social media as the major platforms and their features, such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. We can also in practical terms of social media as another type of digital marketing channel that marketers can use to communicate with consumers through advertising. But we can also think of social media more broadly, seeing it less as digital media and specific technology services, and more as digital places where people conduct significant parts of their lives. From this perspective, it means that social media becomes less about the specific technologies or platforms, and more about what people do in these environments. To date, this has tended to be largely about information sharing, and, in marketing, often thought of as a form of (online) word of mouth (WOM).
Building on these definitional perspectives, and thinking about the future, we consider social media to be a technology-centric—but not entirely technological—ecosystem in which a diverse and complex set of behaviors, interactions, and exchanges involving various kinds of interconnected actors (individuals and firms, organizations, and institutions) can occur. Social media is pervasive, widely used, and culturally relevant. This definitional perspective is deliberately broad because we believe that social media has essentially become almost anything—content, information, behaviors, people, organizations, institutions—that can exist in an interconnected, networked digital environment where interactivity is possible. It has evolved from being simply an online instantiation of WOM behaviors and content/information creation and sharing. It is pervasive across societies (and geographic borders) and culturally prominent at both local and global levels.
Throughout the paper we consider many of the definitional and phenomenological aspects described above and explore their implications for consumers and marketing in order to address our question about the future of marketing-related social media. By drawing on academic research, discussions with industry leaders, popular discourse, and our own expertise, we present and discuss a framework featuring nine themes that we believe will meaningfully shape the future of social media in marketing. These themes by no means represent a comprehensive list of all emerging trends in the social media domain and include aspects that are both familiar in extant social media marketing literature (e.g., online WOM, engagement, and user-generated content) and emergent (e.g., sensory considerations in human-computer interaction and new types of unstructured data, including text, audio, images, and video). The themes we present were chosen because they capture important changes in the social media space through the lenses of important stakeholders, including consumers, industry/practice, and public policy.
In addition to describing the nature and consequences of each theme, we identify research directions that academics and practitioners may wish to explore. While it is infeasible to forecast precisely what the future has in store or to project these on a specific timeline, we have organized the emergent themes into three time-progressive waves, according to imminence of impact (i.e., the immediate, near, and far future). Before presenting our framework for the future of social media in marketing and its implications for research (and practice and policy), we provide a brief overview of where social media currently stands as a major media and marketing channel.
Social media at present
The current social media landscape has two key aspects to it. First are the platforms—major and minor, established and emerging—that provide the underlying technologies and business models making up the industry and ecosystem. Second are the use cases; i.e., how various kinds of people and organizations are using these technologies and for what purposes.
The rise of social media, and the manner in which it has impacted both consumer behavior and marketing practice, has largely been driven by the platforms themselves. Some readers might recall the “early days” of social media where social networking sites such as MySpace and Friendster were popular. These sites were precursors to Facebook and everything else that has developed over the last decade. Alongside these platforms, we continue to have other forms of social media such as messaging (which started with basic Internet Relay Chat services in the 1990s and the SMS text messaging built into early digital mobile telephone standards in the 2000s), and asynchronous online conversations arranged around specific topics of interest (e.g., threaded discussion forums, subreddits on Reddit). More recently, we have seen the rise of social media platforms where images and videos replace text, such as Instagram and Snapchat.
Across platforms, historically and to the present day, the dominant business model has involved monetization of users (audiences) by offering advertising services to anyone wishing to reach those audiences with digital content and marketing communications. Prior research has examined the usefulness of social media (in its various forms) for marketing purposes. For example, work by Trusov et al. ( 2009 ) and Stephen and Galak ( 2012 ) demonstrated that certain kinds of social interactions that now happen on social media (e.g., “refer a friend” features and discussions in online communities) can positively affect important marketing outcomes such as new customer acquisition and sales. More recently, the value of advertising on social media continues to be explored (e.g., Gordon et al. 2019 ), as well as how it interacts with other forms of media such as television (e.g., Fossen and Schweidel 2016 , 2019 ) and affects new product adoption through diffusion of information mechanisms (e.g., Hennig-Thurau et al. 2015 ).
Although the rise (and fall) of various kinds of social media platforms has been important for understanding the social media landscape, our contention is that understanding the current situation of social media, at least from a marketing perspective, lies more in what the users do on these platforms than the technologies or services offered by these platforms. Presently, people around the world use social media in its various forms (e.g., news feeds on Facebook and Twitter, private messaging on WhatsApp and WeChat, and discussion forums on Reddit) for a number of purposes. These can generally be categorized as (1) digitally communicating and socializing with known others, such as family and friends, (2) doing the same but with unknown others but who share common interests, and (3) accessing and contributing to digital content such as news, gossip, and user-generated product reviews.
All of these use cases are essentially WOM in one form or another. This, at least, is how marketing scholars have mainly characterized social media, as discussed by Lamberton and Stephen ( 2016 ). Indeed, online WOM has been—and, we contend, will continue to be—important in marketing (e.g., in the meta-analysis by Babić Rosario et al. 2016 the authors found, on average, a positive correlation between online WOM and sales). The present perspective on social media is that people use it for creating, accessing, and spreading information via WOM to various types of others, be it known “strong ties” or “weak ties” in their networks or unknown “strangers.” Some extant research has looked at social media from the WOM perspective of the consequences of the transmission of WOM (e.g., creating a Facebook post or tweeting) on others (e.g., Herhausen et al. 2019 ; Stephen and Lehmann 2016 ), the impact of the type of WOM content shared on others’ behavior (e.g., Villarroel Ordenes et al. 2017 ; Villarroel Ordenes et al. 2018 ), and on the motivations that drive consumer posting on social media, including considerations of status and self-presentation (e.g., Grewal et al. 2019 ; Hennig-Thurau et al. 2004 ; Hollenbeck and Kaikati 2012 ; Toubia and Stephen 2013 ; Wallace et al. 2014 ).
While this current characterization of WOM appears reasonable, it considers social media only from a communications perspective (and as a type of media channel). However, as social media matures, broader social implications emerge. To appropriately consider the future, we must expand our perspective beyond the narrow communicative aspects of social media and consider instead how consumers might use it. Hence, in our vision for the future of social media in marketing in the following sections, we attempt to present a more expansive perspective of what social media is (and will become) and explain why this perspective is relevant to marketing research and practice.
Overview of framework for the future of social media in marketing
In the following sections we present a framework for the immediate, near, and far future of social media in marketing when considering various relevant stakeholders. Themes in the immediate future represent those which already exist in the current marketplace, and that we believe will continue shaping the social media landscape. The near future section examines trends that have shown early signs of manifesting, and that we believe will meaningfully alter the social media landscape in the imminent future. Finally, themes designated as being in the far future represent more speculative projections that we deem capable of long-term influence on the future of social media. The next sections delve into each of the themes in Table 1 , organized around the predicted imminence of these theme’s importance to marketing (i.e., the immediate, near, and far futures).
The immediate future
To begin our discussion on the direction of social media, in this section, we highlight three themes that have surfaced in the current environment that we believe will continue to shape the social media landscape in the immediate future. These themes—omni-social presence, the rise of influencers, and trust and privacy concerns—reflect the ever-changing digital and social media landscape that we presently face. We believe that these different areas will influence a number of stakeholders such as individual social media users, firms and brands that utilize social media, and public policymakers (e.g., governments, regulators).
Omni-social presence
In its early days, social media activity was mostly confined to designated social media platforms such as Facebook and Twitter (or their now-defunct precursors). However, a proliferation of websites and applications that primarily serve separate purposes have capitalized on the opportunity to embed social media functionality into their interfaces. Similarly, all major mobile and desktop operating systems have in-built social media integration (e.g., sharing functions built into Apple’s iOS). This has made social media pervasive and ubiquitous—and perhaps even omnipotent—and has extended the ecosystem beyond dedicated platforms.
Accordingly, consumers live in a world in which social media intersects with most aspects of their lives through digitally enabled social interactivity in such domains as travel (e.g., TripAdvisor), work (e.g., LinkedIn), food (e.g., Yelp), music (e.g., Spotify), and more. At the same time, traditional social media companies have augmented their platforms to provide a broader array of functionalities and services (e.g., Facebook’s marketplace, Chowdry 2018 ; WeChat’s payment system, Cheng 2017 ). These bidirectional trends suggest that the modern-day consumer is living in an increasingly “omni-social” world.
From a marketing perspective, the “omni-social” nature of the present environment suggests that virtually every part of a consumer’s decision-making process is prone to social media influence. Need recognition might be activated when a consumer watches their favorite beauty influencer trying a new product on YouTube. A consumer shopping for a car might search for information by asking their Facebook friends what models they recommend. A hungry employee might sift through Yelp reviews to evaluate different lunch options. A traveler might use Airbnb to book future accommodation. Finally, a highly dissatisfied (or delighted) airline passenger might rant (rave) about their experience on Twitter. While the decision-making funnel is arguably growing flatter than the aforementioned examples would imply (Cortizo-Burgess 2014 ), these independent scenarios illustrate that social media has the propensity to influence the entire consumer-decision making process, from beginning to end.
Finally, perhaps the greatest indication of an “omni-social” phenomenon is the manner in which social media appears to be shaping culture itself. YouTube influencers are now cultural icons, with their own TV shows (Comm 2016 ) and product lines (McClure 2015 ). Creative content in television and movies is often deliberately designed to be “gifable” and meme-friendly (Bereznak 2018 ). “Made-for-Instagram museums” are encouraging artistic content and experiences that are optimized for selfie-taking and posting (Pardes 2017 ). These examples suggest that social media’s influence is hardly restricted to the “online” world (we discuss the potential obsolescence of this term later in this paper), but is rather consistently shaping cultural artifacts (television, film, the arts) that transcend its traditional boundaries. We believe this trend will continue to manifest, perhaps making the term “social media” itself out-of-date, as it’s omni-presence will be the default assumption for consumers, businesses, and artists in various domains.
This omni-social trend generates many questions to probe in future research. For example, how will social interactivity influence consumer behavior in areas that had traditionally been non-social? From a practitioner lens, it might also be interesting to explore how marketers can strategically address the flatter decision-making funnel that social media has enabled, and to examine how service providers can best alter experiential consumption when anticipating social media sharing behavior.
The rise of new forms of social influence (and influencers)
The idea of using celebrities (in consumer markets) or well-known opinion leaders (in business markets), who have a high social value, to influence others is a well-known marketing strategy (Knoll and Matthes 2017 ). However, the omnipresence of social media has tremendously increased the accessibility and appeal of this approach. For example, Selena Gomez has over 144 million followers on Instagram that she engages with each of her posts. In 2018, the exposure of a single photo shared by her was valued at $3.4 million (Maxim 2018 ). However, she comes at a high price: one post that Selena sponsors for a brand can cost upwards of $800,000 (Mejia 2018 ). However, putting high valuations on mere online exposures or collecting “likes” for specific posts can be somewhat speculative, as academic research shows that acquiring “likes” on social media might have no effect on consumers’ attitudes or behaviors (John et al. 2017 ; Mochon et al. 2017 ). Moreover, Hennig-Thurau et al. ( 2015 ), show that while garnering positive WOM has little to no effect on consumer preferences, negative WOM can have a negative effect on consumer preferences.
While celebrities like Selena Gomez are possible influencers for major brands, these traditional celebrities are so expensive that smaller brands have begun, and will continue to, capitalize on the popularity and success of what are referred to as “micro-influencers,” representing a new form of influencers. Micro-influencers are influencers who are not as well-known as celebrities, but who have strong and enthusiastic followings that are usually more targeted, amounting anywhere between a few thousand to hundreds of thousands of followers (Main 2017 ). In general, these types of influencers are considered to be more trustworthy and authentic than traditional celebrities, which is a major reason influencer marketing has grown increasingly appealing to brands (Enberg 2018 ). These individuals are often seen as credible “experts” in what they post about, encouraging others to want to view the content they create and engage with them. Furthermore, using these influencers allows the brand via first person narration (compared to ads), which is considered warmer and more personal, and was shown to be more effective in engaging consumers (Chang et al. 2019 ).
Considering the possible reach and engagement influencers command on social media, companies have either begun embracing influencers on social media, or plan to expand their efforts in this domain even more. For example, in recent conversations we had with social media executives, several of them stated the growing importance of influencers and mentioned how brands generally are looking to incorporate influencer marketing into their marketing strategies. Further, recent conversations with executives at some globally leading brands suggest that influencer marketing spending by big brands continues to rise.
While influencer marketing on social media is not new, we believe it has a lot of potential to develop further as an industry. In a recent working paper, Duani et al. ( 2018 ) show that consumers enjoy watching a live experience much more and for longer time periods than watching a prerecorded one. Hence, we think live streaming by influencers will continue to grow, in broad domains as well as niche ones. For example, streaming of video game playing on Twitch, a platform owned by Amazon, may still be niche but shows no signs of slowing down. However, live platforms are limited by the fact that the influencers, being human, need to sleep and do other activities offline. Virtual influencers (i.e., “CGI” influencers that look human but are not), on the other hand, have no such limitations. They never get tired or sick, they do not even eat (unless it is needed for a campaign). Some brands have started exploring the use of virtual influencers (Nolan 2018 ), and we believe that in coming years, along with stronger computing power and artificial intelligence algorithms, virtual influencers will become much more prominent on social media, being able to invariably represent and act on brand values and engage with followers anytime.
There are many interesting future research avenues to consider when thinking about the role of influencers on social media. First, determining what traits and qualities (e.g., authenticity, trust, credibility, and likability) make sponsored posts by a traditional celebrity influencer, versus a micro-influencer, or even compared to a CGI influencer, more or less successful is important to determine for marketers. Understanding whether success has to do with the actual influencer’s characteristics, the type of content being posted, whether content is sponsored or not, and so on, are all relevant concerns for companies and social media platforms when determining partnerships and where to invest effort in influencers. In addition, research can focus on understanding the appeal of live influencer content, and how to successfully blend influencer content with more traditional marketing mix approaches.
Privacy concerns on social media
Consumer concerns regarding data privacy, and their ability to trust brands and platforms are not new (for a review on data privacy see Martin and Murphy 2017 ). Research in marketing and related disciplines has examined privacy and trust concerns from multiple angles and using different definitions of privacy. For example, research has focused on the connections between personalization and privacy (e.g., Aguirre et al. 2015 ; White et al. 2008 ), the relationship of privacy as it relates to consumer trust and firm performance (e.g., Martin 2018 ; Martin et al. 2017 ), and the legal and ethical aspects of data and digital privacy (e.g., Culnan and Williams 2009 ; Nill and Aalberts 2014 ). Despite this topic not seeming novel, the way consumers, brands, policy makers, and social media platforms are all adjusting and adapting to these concerns are still in flux and without clear resolution.
Making our understanding of privacy concerns even less straightforward is the fact that, across extant literature, a clear definition of privacy is hard to come by. In one commentary on privacy, Stewart ( 2017 ), defined privacy as “being left alone,” as this allows an individual to determine invasions of privacy. We build from this definition of privacy to speculate on a major issue in privacy and trust moving forward. Specifically, how consumers are adapting and responding to the digital world, where “being left alone” isn’t possible. For example, while research has shown benefits to personalization tactics (e.g., Chung et al. 2016 ), with eroding trust in social platforms and brands that advertise through them, many consumers would rather not share data and privacy for a more personalized experiences, are uncomfortable with their purchases being tracked and think it should be illegal for brands to be able to buy their data (Edelman 2018 ). These recent findings seem to be in conflict with previously established work on consumer privacy expectations. Therefore, understanding if previously studied factors that mitigated the negative effects of personalization (e.g., perceived utility; White et al. 2008 ) are still valued by consumers in an ever-changing digital landscape is essential for future work.
In line with rising privacy concerns, the way consumers view brands and social media is becoming increasingly negative. Consumers are deleting their social media presence, where research has shown that nearly 40% of digitally connected individuals admitted to deleting at least one social media account due to fears of their personal data being mishandled (Edelman 2018 ). This is a negative trend not only for social media platforms, but for the brands and advertisers who have grown dependent on these avenues for reaching consumers. Edelman found that nearly half of the surveyed consumers believed brands to be complicit in negative aspects of content on social media such as hate speech, inappropriate content, or fake news (Edelman 2018 ). Considering that social media has become one of the best places for brands to engage with consumers, build relationships, and provide customer service, it’s not only in the best interest of social media platforms to “do better” in terms of policing content, but the onus of responsibility has been placed on brands to advocate for privacy, trust, and the removal of fake or hateful content.
Therefore, to combat these negative consumer beliefs, changes will need to be made by everyone who benefits from consumer engagement on social media. Social media platforms and brands need to consider three major concerns that are eroding consumer trust: personal information, intellectual property and information security (Information Technology Faculty 2018 ). Considering each of these concerns, specific actions and initiatives need to be taken for greater transparency and subsequent trust. We believe that brands and agencies need to hold social media accountable for their actions regarding consumer data (e.g., GDPR in the European Union) for consumers to feel “safe” and “in control,” two factors shown necessary in cases of privacy concerns (e.g., Tucker 2014 ; Xu et al. 2012 ). As well, brands need to establish transparent policies regarding consumer data in a way that recognizes the laws, advertising restrictions, and a consumer’s right to privacy (a view shared by others; e.g., Martin et al. 2017 ). All of this is managerially essential for brands to engender feelings of trust in the increasingly murky domain of social media.
Future research can be conducted to determine consumer reactions to different types of changes and policies regarding data and privacy. As well, another related and important direction for future research, will be to ascertain the spillover effects of distrust on social media. Specifically, is all content shared on social media seen as less trustworthy if the platform itself is distrusted? Does this extend to brand messages displayed online? Is there a negative spillover effect to other user-generated content shared through these platforms?
The near future
In the previous section, we discussed three areas where we believe social media is immediately in flux. In this section, we identify three trends that have shown early signs of manifesting, and which we believe will meaningfully alter the social media landscape in the near, or not-too-distant, future. Each of these topics impact the stakeholders we mentioned when discussing the immediate social media landscape.
Combatting loneliness and isolation
Social media has made it easier to reach people. When Facebook was founded in 2004, their mission was “to give people the power to build community and bring the world closer together... use Facebook to stay connected with friends and family, to discover what’s going on in the world, and to share and express what matters to them” (Facebook 2019 ). Despite this mission, and the reality that users are more “connected” to other people than ever before, loneliness and isolation are on the rise. Over the last fifty years in the U.S., loneliness and isolation rates have doubled, with Generation Z considered to be the loneliest generation (Cigna 2018 ). Considering these findings with the rise of social media, is the fear that Facebook is interfering with real friendships and ironically spreading the isolation it was designed to conquer something to be considered about (Marche 2012 )?
The role of social media in this “loneliness epidemic” is being hotly debated. Some research has shown that social media negatively impacts consumer well-being. Specifically, heavy social media use has been associated with higher perceived social isolation, loneliness, and depression (Kross et al. 2013 ; Primack et al. 2017 ; Steers et al. 2014 ). Additionally, Facebook use has been shown to be negatively correlated with consumer well-being (Shakya and Christakis 2017 ) and correlational research has shown that limiting social media use to 10 min can decrease feelings of loneliness and depression due to less FOMO (e.g., “fear of missing out;” Hunt et al. 2018 ).
On the other hand, research has shown that social media use alone is not a predictor of loneliness as other factors have to be considered (Cigna 2018 ; Kim et al. 2009 ). In fact, while some research has shown no effect of social media on well-being (Orben et al. 2019 ), other research has shown that social media can benefit individuals through a number of different avenues such as teaching and developing socialization skills, allowing greater communication and access to a greater wealth of resources, and helping with connection and belonging (American Psychological Association 2011 ; Baker and Algorta 2016 ; Marker et al. 2018 ). As well, a working paper by Crolic et al. ( 2019 ) argues that much of the evidence of social media use on consumer well-being is of questionable quality (e.g., small and non-representative samples, reliance on self-reported social media use), and show that some types of social media use are positively associated with psychological well-being over time.
Managerially speaking, companies are beginning to respond as a repercussion of studies highlighting a negative relationship between social media and negative wellbeing. For example, Facebook has created “time limit” tools (mobile operating systems, such as iOS, now also have these time-limiting features). Specifically, users can now check their daily times, set up reminder alerts that pop up when a self-imposed amount of time on the apps is hit, and there is the option to mute notifications for a set period of time (Priday 2018 ). These different features seem well-intentioned and are designed to try and give people a more positive social media experience. Whether these features will be used is unknown.
Future research can address whether or not consumers will use available “timing” tools on one of many devices in which their social media exists (i.e., fake self-policing) or on all of their devices to actually curb behavior. It could also be the case that users will actually spend less time on Facebook and Instagram, but possibly spend that extra time on other competing social media platforms, or attached to devices, which theoretically will not help combat loneliness. Understanding how (and which) consumers use these self-control tools and how impactful they are is a potentially valuable avenue for future research.
One aspect of social media that has yet to be considered in the loneliness discussion through empirical measures, is the quality of use (versus quantity). Facebook ads have begun saying, “The best part of Facebook isn’t on Facebook. It’s when it helps us get together” (Facebook 2019 ). There have been discussions around the authenticity of this type of message, but at its core, in addition to promoting quantity differences, it’s speaking to how consumers use the platform. Possibly, to facilitate this message, social media platforms will find new ways to create friend suggestions between individuals who not only share similar interests and mutual friends to facilitate in-person friendships (e.g., locational data from the mobile app service). Currently there are apps that allow people to search for friends that are physically close (e.g., Bumble Friends), and perhaps social media will go in this same direction to address the loneliness epidemic and stay current.
Future research can examine whether the quantity of use, types of social media platforms, or the way social media is used causally impacts perceived loneliness. Specifically, understanding if the negative correlations found between social media use and well-being are due to the demographics of individuals who use a lot of social media, the way social media works, or the way users choose to engage with the platform will be important for understanding social media’s role (or lack of role) in the loneliness epidemic.

Integrated customer care
Customer care via digital channels as we know it is going to change substantially in the near future. To date, many brands have used social media platforms as a place for providing customer care, addressing customers’ specific questions, and fixing problems. In the future, social media-based customer care is expected to become even more customized, personalized, and ubiquitous. Customers will be able to engage with firms anywhere and anytime, and solutions to customers’ problems will be more accessible and immediate, perhaps even pre-emptive using predictive approaches (i.e., before a customer even notices an issue or has a question pop into their mind).
Even today, we observe the benefits that companies gain from connecting with customers on social media for service- or care-related purposes. Customer care is implemented in dedicated smartphone apps and via direct messaging on social media platforms. However, it appears that firms want to make it even easier for customers to connect with them whenever and wherever they might need. Requiring a customer to download a brand specific app or to search through various social media platforms to connect with firms through the right branded account on a platform can be a cumbersome process. In those cases, customers might instead churn or engage in negative WOM, instead of connecting with the firm to bring up any troubles they might have.
The near future of customer care on social media appears to be more efficient and far-reaching. In a recent review on the future of customer relationship management, Haenlein ( 2017 ) describes “invisible CRM” as future systems that will make customer engagement simple and accessible for customers. New platforms have emerged to make the connection between customer and firm effortless. Much of this is via instant messaging applications for businesses, which several leading technology companies have recently launched as business-related features in existing platforms (e.g., contact business features in Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp or Apple’s Business Chat).
These technologies allow businesses to directly communicate via social media messaging services with their customers. Amazon, Apple, Facebook, and Google are in the process, or have already released early versions of such platforms (Dequier 2018 ). Customers can message a company, ask them questions, or even order products and services through the messaging system, which is often built around chatbots and virtual assistants. This practice is expected to become more widespread, especially because it puts brands and companies into the social media messaging platforms their customers already use to communicate with others, it provides quicker—even instantaneous—responses, is economically scalable through the use of AI-driven chatbots, and, despite the use of chatbots, can provide a more personalized level of customer service.
Another area that companies will greatly improve upon is data collection and analysis. While it is true that data collection on social media is already pervasive today, it is also heavily scrutinized. However, we believe that companies will adapt to the latest regulation changes (e.g., GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California) and improve on collecting and analyzing anonymized data (Kakatkar and Spann 2018 ). Furthermore, even under these new regulations, personalized data collection is still allowed, but severely limits firm’s abilities to exploit consumers’ data, and requires their consent for data collection.
We believe that in the future, companies will be able recognize early indications of problems within customer chatter, behavior, or even physiological data (e.g., monitoring the sensors in our smart watches) before customers themselves even realize they are experiencing a problem. For example, WeWork, the shared workspace company, collects data on how workers move and act in a workspace, building highly personalized workspaces based on trends in the data. Taking this type of approach to customer care will enable “seamless service,” where companies would be able to identify and address consumer problems when they are still small and scattered, and while only a small number of customers are experiencing problems. Customer healthcare is a pioneer in this area, where using twitter and review sites were shown to predict poor healthcare quality (Greaves et al. 2013 ), listen to patients to analyze trending terms (Baktha et al. 2017 ; Padrez et al. 2016 ), or even predict disease outbreaks (Schmidt 2012 ).
Companies, wanting to better understand and mimic human interactions, will invest a lot of R&D efforts into developing better Natural Language Processing, voice and image recognition, emotional analysis, and speech synthesis tools (Sheth 2017 ). For example, Duplex, Google’s latest AI assistant, can already call services on its own and seamlessly book reservations for their users (Welch 2018 ). In the future, AI systems will act as human ability augmenters, allowing us to accomplish more, in less time, and better results (Guszcza 2018 ).
For marketers, this will reduce the need for call centers and agents, reducing points of friction in service and increasing the convenience for customers (Kaplan and Haenlein 2019 ). However, some raise the question that the increased dependence on automation may result in a loss of compassion and empathy. In a recent study, Force (2018) shows that interacting with brands on social media lowered people’s empathy. In response to such concerns, and to educate and incentivize people to interact with machines in a similar way they do with people, Google programmed their AI assistant to respond in a nicer way if you use a polite, rather than a commanding approach (Kumparak 2018 ). While this might help, more research is needed to understand the effect of an AI rich world on human behavior. As well, future research can examine how consumer generated data can help companies preemptively predict consumer distress. Another interesting path for research would be to better understand the difference in consumer engagement between the various platforms, and the long-term effects of service communications with non-human AI and IoT.
Social media as a political tool
Social media is a platform to share thoughts and opinions. This is especially true in the case of disseminating political sentiments. Famously, President Barack Obama’s victory in the 2008 election was partially attributed to his ability to drive and engage voters on social media (Carr 2008 ). Indeed, Bond et al. ( 2012 ) have shown that with simple interventions, social media platforms can increase targeted audiences’ likelihood of voting. Social media is considered one of the major drivers of the 2010 wave of revolutions in Arab countries, also known as the Arab Spring (Brown et al. 2012 ).
While social media is not new to politics, we believe that social media is transitioning to take a much larger role as a political tool in the intermediate future. First evidence for this could be seen in the 2016 U.S. presidential election, as social media took on a different shape, with many purported attempts to influence voter’s opinions, thoughts, and actions. This is especially true for then-candidate and now-President Donald Trump. His use of Twitter attracted a lot of attention during the campaign and has continued to do so during his term in office. Yet, he is not alone, and many politicians changed the way they work and interact with constituents, with a recent example of Congresswoman Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez that even ran a workshop for fellow congress members on social media (Dwyer 2019 ).
While such platforms allow for a rapid dissemination of ideas and concepts (Bonilla and Rosa 2015 ; Bode 2016 ), there are some, both in academia and industry that have raised ethical concerns about using social media for political purposes. Given that people choose who to follow, this selective behavior is said to potentially create echo chambers, wherein, users are exposed only to ideas by like-minded people, exhibiting increased political homophily (Bakshy et al. 2015 ). People’s preference to group with like-minded people is not new. Social in-groups have been shown to promote social identification and promote in-group members to conform to similar ideas (Castano et al. 2002 ; Harton and Bourgeois 2004 ). Furthermore, it was also shown that group members strongly disassociate and distance themselves from outgroup members (Berger and Heath 2008 ; White and Dahl 2007 ). Thus, it is not surprising to find that customized newsfeeds within social media exacerbate this problem by generating news coverage that is unique to specific users, locking them in their purported echo chambers (Oremus 2016 ).
While social media platforms admit that echo chambers could pose a problem, a solution is not clear (Fiegerman 2018 ). One reason that echo chambers present such a problem, is their proneness to fake news. Fake news are fabricated stories that try to disguise themselves as authentic content, in order to affect other social media users. Fake news was widely used in the 2016 U.S. elections, with accusations that foreign governments, such as Iran and Russia, were using bots (i.e., online automatic algorithms), to spread falsified content attacking Hillary Clinton and supporting President Trump (Kelly et al. 2018 ). Recent research has furthermore shown how the Chinese government strategically uses millions of online comments to distract the Chinese public from discussing sensitive issues and promote nationalism (King et al. 2017 ). In their latest incarnation, fake news uses an advanced AI technique called “Deep Fake” to generate ultra-realistic forged images and videos of political leaders while manipulating what those leaders say (Schwartz 2018 ). Such methods can easily fool even the sharpest viewer. In response, research has begun to explore ways that social media platforms can combat fake news through algorithms that determine the quality of shared content (e.g., Pennycook and Rand 2019 ).
One factor that has helped the rise of fake news is echo chambers. This occurs as the repeated sharing of fake news by group members enhance familiarity and support (Schwarz and Newman 2017 ). Repetition of such articles by bots can only increase that effect. Recent research has shown that in a perceived social setting, such as social media, participants were less likely to fact-check information (Jun et al. 2017 ), and avoided information that didn’t fit well with their intuition (Woolley and Risen 2018 ). Schwarz and Newman ( 2017 ) state that misinformation might be difficult to correct, especially if the correction is not issued immediately and the fake news has already settled into the minds of users. It was also shown that even a single exposure to fake news can create long term effect on users, making their effect larger than previously thought (Pennycook et al. 2019 ).
Notably, some research has found that exposure to opposing views (i.e., removing online echo chambers) may in fact increase (versus decrease) polarization (Bail et al. 2018 ). Accordingly, more work from policy makers, businesses, and academics is needed to understand and potentially combat political extremism. For example, policy makers and social media platforms will continually be challenged to fight “fake news” without censoring free speech. Accordingly, research that weighs the risk of limited freedom of expression versus the harms of spreading fake news would yield both theoretical and practically meaningful insights.
The far future
In this section, we highlight three emerging trends we believe will have a have long-term influence on the future of social media. Note that although we label these trends as being in the “far” future, many of the issues described here are already present or emerging. However, they represent more complex issues that we believe will take longer to address and be of mainstream importance for marketing than the six issues discussed previously under the immediate and near futures.
Increased sensory richness
In its early days, the majority of social media posts (e.g., on Facebook, Twitter) were text. Soon, these platforms allowed for the posting of pictures and then videos, and separate platforms dedicated themselves to focus on these specific forms of media (e.g., Instagram and Pinterest for pictures, Instagram and SnapChat for short videos). These shifts have had demonstrable consequences on social media usage and its consequences as some scholars suggest that image-based posts convey greater social presence than text alone (e.g., Pittman and Reich 2016 ). Importantly however, a plethora of new technologies in the market suggest that the future of social media will be more sensory-rich.
One notable technology that has already started infiltrating social media is augmented reality (AR). Perhaps the most recognizable examples of this are Snapchat’s filters, which use a device’s camera to superimpose real-time visual and/or video overlays on people’s faces (including features such as makeup, dog ears, etc.). The company has even launched filters to specifically be used on users’ cats (Ritschel 2018 ). Other social media players quickly joined the AR bandwagon, including Instagram’s recent adoption of AR filters (Rao 2017 ) and Apple’s Memoji messaging (Tillman 2018 ). This likely represents only the tip of the iceberg, particularly given that Facebook, one of the industry’s largest investors in AR technology, has confirmed it is working on AR glasses (Constine 2018 ). Notably, the company plans to launch a developer platform, so that people can build augmented-reality features that live inside Facebook, Instagram, Messenger and Whatsapp (Wagner 2017 ). These developments are supported by academic research suggesting that AR often provides more authentic (and hence positive) situated experiences (Hilken et al. 2017 ). Accordingly, whether viewed through glasses or through traditional mobile and tablet devices, the future of social media is likely to look much more visually augmented.
While AR allows users to interact within their current environments, virtual reality (VR) immerses the user in other places, and this technology is also likely to increasingly permeate social media interactions. While the Facebook-owned company Oculus VR has mostly been focusing on the areas of immersive gaming and film, the company recently announced the launch of Oculus Rooms where users can spend time with other users in a virtual world (playing games together, watching media together, or just chatting; Wagner 2018 ). Concurrently, Facebook Spaces allows friends to meet online in virtual reality and similarly engage with one another, with the added ability to share content (e.g., photos) from their Facebook profiles (Whigham 2018 ). In both cases, avatars are customized to represent users within the VR-created space. As VR technology is becoming more affordable and mainstream (Colville 2018 ) we believe social media will inevitably play a role in the technology’s increasing usage.
While AR and VR technologies bring visual richness, other developments suggest that the future of social media might also be more audible. A new player to the social media space, HearMeOut, recently introduced a platform that enables users to share and listen to 42-s audio posts (Perry 2018 ). Allowing users to use social media in a hands-free and eyes-free manner not only allows them to safely interact with social media when multitasking (particularly when driving), but voice is also said to add a certain richness and authenticity that is often missing from mere text-based posts (Katai 2018 ). Given that podcasts are more popular than ever before (Bhaskar 2018 ) and voice-based search queries are the fastest-growing mobile search type (Robbio 2018 ), it seems likely that this communication modality will accordingly show up more on social media use going forward.
Finally, there are early indications that social media might literally feel different in the future. As mobile phones are held in one’s hands and wearable technology is strapped onto one’s skin, companies and brands are exploring opportunities to communicate to users through touch. Indeed, haptic feedback (technology that recreates the sense of touch by applying forces, vibrations, or motions to the user; Brave et al. 2001 ) is increasingly being integrated into interfaces and applications, with purposes that go beyond mere call or message notifications. For example, some companies are experimenting with integrating haptics into media content (e.g., in mobile ads for Stoli vodka, users feel their phone shake as a woman shakes a cocktail; Johnson 2015 ), mobile games, and interpersonal chat (e.g., an app called Mumble! translates text messages into haptic outputs; Ozcivelek 2015 ). Given the high levels of investment into haptic technology (it is predicted to be a $20 billion industry by 2022; Magnarelli 2018 ) and the communicative benefits that stem from haptic engagement (Haans and IJsselsteijn 2006 ), we believe it is only a matter of time before this modality is integrated into social media platforms.
Future research might explore how any of the new sensory formats mentioned above might alter the nature of content creation and consumption. Substantively-focused researchers might also investigate how practitioners can use these tools to enhance their offerings and augment their interactions with customers. It is also interesting to consider how such sensory-rich formats can be used to bridge the gap between the online and offline spaces, which is the next theme we explore.
Online/offline integration and complete convergence
A discussion occurring across industry and academia is on how marketers can appropriately integrate online and offline efforts (i.e., an omnichannel approach). Reports from industry sources have shown that consumers respond better to integrated marketing campaigns (e.g., a 73% boost over standard email campaigns; Safko 2010 ). In academia meanwhile, the majority of research considering online promotions and advertisements has typically focused on how consumers respond to these strategies through online only measures (e.g., Manchanda et al. 2006 ), though this has begun to change in recent years with more research examining offline consequences to omnichannel strategies (Lobschat et al. 2017 ; Kumar et al. 2017 ).
Considering the interest in integrated marketing strategies over the last few years, numerous strategies have been utilized to follow online and offline promotions and their impacts on behavior such as the usage of hashtags to bring conversations online, call-to-actions, utilizing matching strategies on “traditional” avenues like television with social media. While there is currently online/offline integration strategies in marketing, we believe the future will go even further in blurring the lines between what is offline and online to not just increase the effectiveness of marketing promotions, but to completely change the way customers and companies interact with one another, and the way social media influences consumer behavior not only online, but offline.
For brands, there are a number of possible trends in omnichannel marketing that are pertinent. As mentioned earlier, a notable technology that has begun infiltrating social media is augmented reality (AR). In addition to what already exists (e.g., Snapchat’s filters, Pokémon Go), the future holds even more possibilities. For example, Ikea has been working to create an AR app that allows users to take photos of a space at home to exactly , down to the millimeter size and lighting in the room, showcase what a piece of furniture would look like in a consumer’s home (Lovejoy 2017 ). Another set of examples of AR comes from beauty company L’Oréal. In 2014 for the flagship L’Oréal Paris brand they released a mobile app called Makeup Genius that allowed consumers to virtually try on makeup on their phones (Stephen and Brooks 2018 ). Since then, they have developed AR apps for hair color and nail polish, as well as integrating AR into mobile ecommerce webpages for their luxury beauty brand Lancôme. AR-based digital services such as these are likely to be at the heart of the next stage of offline/online integration.
AR, and similar technology, will likely move above and beyond being a tool to help consumers make better decisions about their purchases. Conceivably, similar to promotions that currently exist to excitse consumers and create communities, AR will be incorporated into promotions that integrate offline and online actions. For example, contests on social media will advance to the stage where users get to vote on the best use of AR technology in conjunction with a brand’s products (e.g., instead of users submitting pictures of their apartments to show why they should win free furniture, they could use AR to show how they would lay out the furniture if they were to win it from IKEA).
Another way that the future of online/offline integration on social media needs to be discussed is in the sense of a digital self. Drawing on the extended self in the digital age (Belk 2013 ), the way consumers consider online actions as relevant to their offline selves may be changing. For example, Belk ( 2013 ) spoke of how consumers may be re-embodied through avatars they create to represent themselves online, influencing their offline selves and creating a multiplicity of selves (i.e., consumers have more choice when it comes to their self-representation). As research has shown how digital and social media can be used for self-presentation, affiliation, and expression (Back et al. 2010 ; Gosling et al. 2007 ; Toubia and Stephen 2013 ; Wilcox and Stephen 2012 ), what does it mean for the future if consumers can create who they want to be?
In addition, when considering digital selves, what does this mean for how consumers engage with brands and products? Currently, social media practice is one where brands encourage consumer engagement online (Chae et al. 2017 ; Godes and Mayzlin 2009 ), yet the implications for how these types of actions on the part of the brand to integrate online social media actions and real-life behavior play out are unclear. Research has begun to delve into the individual-level consequences of a consumer’s social media actions on marketing relevant outcomes (Grewal et al. 2019 ; John et al. 2017 ; Mochon et al. 2017 ; Zhang et al. 2017 ), however much is still unknown. As well, while there is recent work examining how the device used to create and view content online impacts consumer perceptions and behaviors (e.g., Grewal and Stephen 2019 ), to date research has not examined these questions in the context of social media. Therefore, future research could address how digital selves (both those held offline and those that only exist online), social media actions, and if the way consumers reach and use various platforms (i.e., device type, app vs. webpage, etc.) impact consumer behavior, interpersonal relationships, and brand-related measures (e.g., well-being, loyalty, purchase behaviors).
Social media by non-humans
The buzz surrounding AI has not escaped social media. Indeed, social bots (computer algorithms that automatically produce content and interact with social media users; Ferrara et al. 2016 ) have inhabited social media platforms for the last decade (Lee et al. 2011 ), and have become increasingly pervasive. For example, experts estimate that up to 15% of active Twitter accounts are bots (Varol et al. 2017 ), and that percentage appears to be on the rise (Romano 2018 ). While academics and practitioners are highly concerned with bot detection (Knight 2018 ), in the vast majority of current cases, users do not appear to recognize when they are interacting with bots (as opposed to other human users) on social media (Stocking and Sumida 2018 ). While some of these bots are said to be benign, and even useful (e.g., acting as information aggregators), they have also been shown to disrupt political discourse (as mentioned earlier), steal personal information, and spread misinformation (Ferrara et al. 2016 ).
Of course, social bots are not only a problem for social media users but are also a nagging concern plaguing marketers. Given that companies often assess marketing success on social media through metrics like Likes, Shares, and Clicks, the existence of bots poses a growing threat to accurate marketing metrics and methods for ROI estimation, such as attribution modelling (Bilton 2014 ). Similarly, when these bots act as “fake followers,” it can inflate the worth of influencers’ audiences (Bogost 2018 ). This can also be used nefariously by individuals and firms, as shown in a New York Times Magazine expose that documented the market used by some influencers to purchase such “fake” followers to inflate their social media reach (Confessore et al. 2018 ). As discussed above in relation to influencer marketing, where it has been commonplace for influencers to be paid for posts at rates proportionate to their follower counts, there have been perverse incentives to game the system by having non-human “fake” bot followers. This, however, erodes consumer trust in the social media ecosystem, which is a growing issue and a near-term problem for many firms using social media channels for marketing purposes.
However, there are instances when consumers do know they are interacting with bots, and do not seem to mind. For example, a number of virtual influencers (created with CGI, as mentioned earlier) seem to be garnering sizeable audiences, despite the fact they are clearly non-human (Walker 2018 ). One of the most popular of these virtual influencers, Lil Miquela, has over 1.5 million followers on Instagram despite openly confessing, “I am not a human being... I’m a robot” (Yurieff 2018 ). Future research might try to understand the underlying appeal of these virtual influencers, and the potential boundary conditions of their success.
Another category of social bots gaining increasing attention are therapy bots. These applications (e.g., “Woebot;” Molteni 2017 ) aim to support the mental health of users by proactively checking in on them, “listening” and chatting to users at any time and recommending activities to improve users’ wellbeing (de Jesus 2018 ). Similar bots are being used to “coach” users, and help them quit maladaptive behaviors, like smoking (e.g., QuitGenius; Crook 2018 ). Interestingly, by being explicitly non-human, these agents are perceived to be less judgmental, and might accordingly be easier for users to confide in.
Finally, the Internet of Things revolution has ushered in with it the opportunity for a number of tangible products and interfaces to “communicate” via social media. For example, in what started as a design experiment, “Brad,” a connected toaster, was given the ability to “communicate” with other connected toasters, and to tweet his “feelings” when neglected or under-used (Vanhemert 2014 ). While this experiment was deliberately designed to raise questions about the future of consumer-product relationships (and product-product “relationships”), the proliferation of autonomous tangible devices does suggest a future in which they have a “voice,” even in the absence of humans (Hoffman and Novak 2018 ).
Going forward, we believe the presence of bots on social media will be more normalized, but also more regulated (e.g., a recent law passed in California prevents bots from masquerading as humans; Smith 2018 ). Further, consumers and companies alike will be become increasingly interested in how bots communicate and interact with each other outside of human involvement. This brings up interesting potential research questions for academics and practitioners alike. How will the presence of non-humans change the nature of content creation and conversation in social media? And how should companies best account for the presence of non-humans in their attribution models?
Future research directions and conclusion
This article has presented nine themes pertinent to the future of social media as it relates to (and is perhaps influenced by) marketing. The themes have implications for individuals/consumers, businesses and organizations, and also public policymakers and governments. These themes, which represent our own thinking and a synthesis of views from extant research, industry experts, and popular public discourse, are of course not the full story of what the future of social media will entail. They are, however, a set of important issues that we believe will be worth considering in both academic research and marketing practice.
To stimulate future research on these themes and related topics, we present a summary of suggested research directions in Table 2 . These are organized around our nine themes and capture many of the suggested research directions mentioned earlier. As a sub-field within the field of marketing, social media is already substantial and the potential for future research—based on identified needs for new knowledge and answers to perplexing questions—suggests that this sub-field will become even more important over time. We encourage researchers to consider the kinds of research directions in Table 2 as examples of issues they could explore further. We also encourage researchers in marketing to treat social media as a place where interesting (and often very new) consumer behaviors exist and can be studied. As we discussed earlier in the paper, social media as a set of platform businesses and technologies is interesting, but it is how people use social media and the associated technologies that is ultimately of interest to marketing academics and practitioners. Thus, we urge scholars to not be overly enticed by the technological “shiny new toys” at the expense of considering the behaviors associated with those technologies and platforms.
Finally, while we relied heavily (though not exclusively) on North American examples to illustrate the emergent themes, there are likely interesting insights to be drawn by explicitly exploring cross-cultural differences in social media usage. For example, variations in regulatory policies (e.g., GDPR in the European Union) may lead to meaningful differences in how trust and privacy concerns manifest. Further, social media as a political tool might be more influential in regions where the mainstream media is notoriously government controlled and censored (e.g., as was the case in many of the Arab Spring countries). While such cross-cultural variation is outside the scope of this particular paper, we believe it represents an area of future research with great theoretical and practical value.
In reviewing the social media ecosystem and considering where it is heading in the context of consumers and marketing practice, we have concluded that this is an area that is very much still in a state of flux. The future of social media in marketing is exciting, but also uncertain. If nothing else, it is vitally important that we better understand social media since it has become highly culturally relevant, a dominant form of communication and expression, a major media type used by companies for advertising and other forms of communication, and even has geopolitical ramifications. We hope that the ideas discussed here stimulate many new ideas and research, which we ultimately hope to see being mentioned and shared across every type of social media platform.
Aguirre, E., Mahr, D., Grewal, D., Ruyter, K. D., & Wetzels, M. (2015). Unraveling the personalization paradox: The effect of information collection and trust-building strategies on online advertisement effectiveness. Journal of Retailing, 91 (1), 34–59.
Google Scholar
American Psychological Association. (2011). Social networking's good and bad impacts on kids . American Psychological Association.
Babić Rosario, A., Sotgiu, F., De Valck, K., & Bijmolt, T. H. A. (2016). The effect of electronic word of mouth on sales: A meta-analytic review of platform, product, and metric factors. Journal of Marketing Research, 53 (3), 297–318.
Back, M., Stopfer, J., Vazire, S., Gaddis, S., Schmukle, S., Egloff, B., & Gosling, S. (2010). Facebook profiles reflect actual personality, not self-idealization. Psychological Science, 21 (3), 372–374.
Bail, C. A., Argyle, L. P., Brown, T. W., Bumpus, J. P., Chen, H., Hunzaker, M. F., Lee, J., Mann, M., Merhout, F., & Volfovsky, A. (2018). Exposure to opposing views on social media can increase political polarization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115 (37), 9216–9221.
Baker, D. A., & Algorta, G. P. (2016). The relationship between online social networking and depression: A systematic review of quantitative studies. Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 19 (11), 638–648.
Bakshy, E., Messing, S., & Adamic, L. A. (2015). Exposure to ideologically diverse news and opinion on Facebook. Science, 348 (6239), 1130–1132.
Baktha, K., Dev, M., Gupta, H., Agarwal, A., & Balamurugan, B. (2017). Social network analysis in healthcare. In Internet of Things and Big Data Technologies for Next Generation Healthcare (pp. 309–334). Springer, Cham.
Belk, R. W. (2013). Extended self in a digital world. Journal of Consumer Research, 40 (October), 477–500.
Bereznak, A. (2018). A Meme Is Born: How Internet Jokes Turned ‘A Star Is Born’ Into a Hit. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y7b9xfym .
Berger, J., & Heath, C. (2008). Who drives divergence? Identity signaling, outgroup dissimilarity, and the abandonment of cultural tastes. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 95 (3), 593–607.
Bhaskar, S. (2018). How Podcasts Became So Popular (And Why That’s a Good Thing). Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/yczfmzue .
Bilton, N. (2014). Social media bots offer phony friends and real profit. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y93z3wdj .
Bode, L. (2016). Political news in the news feed: Learning politics from social media. Mass Communication and Society, 19 (1), 24–48.
Bogost, I. (2018). All followers are fake followers. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ybxblkek .
Bond, R. M., Fariss, C. J., Jones, J. J., DI Kramer, A., Marlow, C., Settle, J. E., & Fowler, J. H. (2012). A 61-million-person experiment in social influence and political mobilization. Nature, 489 (7415), 295–298.
Bonilla, Y., & Rosa, J. (2015). # Ferguson: Digital protest, hashtag ethnography, and the racial politics of social media in the United States. American Ethnologist, 42 (1), 4–17.
Brave, S., Nass C., & Sirinian E. (2001). Force-feedback in computer-mediated communication. Proceedings of HCI International 2001 (9 th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction , Constantine Stephanidis, Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum), 145–149.
Brown, H., Guskin, E., & Mitchell A. (2012). The role of social Media in the Arab Uprising. Retreived from https://tinyurl.com/y7d8t7je .
Carr, D. (2008) How Obama Tapped into Social Networks’ Power. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ydyvtocj .
Castano, E., Yzerbyt, V., Paladino, M. P., & Sacchi, S. (2002). I belong, therefore, I exist: Ingroup identification, ingroup entitativity, and ingroup bias. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 28 (2), 135–143.
Chae, I., Stephen, A. T., Bart, Y., & Yao, D. (2017). Spillover effects in seeded word-of-mouth marketing campaigns. Marketing Science, 36 (1), 89–104.
Chang, Y., Li, Y., Yan, J., & Kumar, V. (2019). Getting more likes: The impact of narrative person and brand image on customer–brand interactions. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science , 1–19.
Cheng, E. (2017). China is living the future of mobile pay right now. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y8hm6vlo .
Chowdry, A., (2018). Facebook launches ads in marketplace. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y8kf5g4t .
Chung, T. S., Wedel, M., & Rust, R. T. (2016). Adaptive personalization using social networks. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 44 , 66–87.
Cigna (2018). New Cigna Study Reveals Loneliness at Epidemic Levels in American. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y9e7gl2u .
Colville W. (2018). Facebook VR leader talk about the future of virtual marketing. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y8kdd4cr .
Comm J. (2016). 9 Social media influencers who are killing it on TV. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y76wyo8j .
Confessore, N., Dance, G. J. X., Harris, R., & Hansen, M. (2018). The Follower Factory. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/yaym3e69 .
Constine, J. (2018). Facebook confirms its building augmented reality glasses. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y82et9tw .
Cortizo-Burgess, P. (2014). The traditional purchase funnel is kaput. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y7azj7oc .
Crolic, C., Stephen, A. T., Zubcsek, P. P., & Brooks, G. (2019). Staying connected: The positive effect of social media consumption on psychological well-being. Working Paper.
Crook, J. (2018). Quit Genius, backed by Y combinator, wants to help you quit smoking. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y7hhfzf8 .
Culnan, M. J., & Williams, C. C. (2009). How ethics can enhance organization privacy: Lessons from the choice point and TJX data breaches. MIS Quarterly, 33 , 673–687.
de Jesus, A. (2018). Chatbots for mental health and therapy – Comparing 5 current apps and use cases. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/yc5c6qco .
Dequier, S. (2018). Everything You Need to Know about Apple Business Chat (and what to expect from it). Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/yd4dmtgw .
Duani, N., Barasch, A., & Ward A. (2018). “Brought to you live”: On the consumption experience of live social media streams. Working paper.
Dwyer, D., (2019). Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez’s Twitter lesson for House Democrats. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ydgy9suw .
Edelman, K. (2018). Trust Barometer Brands Social Media. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ycrm23gf .
eMarketer (2018). Social Network Users and Penetration in Worldwide. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ycr2d3v9 .
Enberg, J. (2018). Global Influencer Marketing. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y7srumpm .
Facebook (2019). Company Info. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/n544jrt .
Ferrara, E., Varol, O., Davis, C., Menczer, F., & Flammini, A. (2016). The rise of social bots. Communications of the ACM, 59 (7), 96–104.
Fiegerman, S. (2018). Facebook admits social media can 'corrode democracy'. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y9f7hxju .
Fossen, B. L., & Schweidel, D. A. (2016). Television advertising and online word-of-mouth: An empirical investigation of social TV activity. Marketing Science, 36 (1), 105–123.
Fossen, B. L., & Schweidel, D. A. (2019). Social TV, advertising, and sales: Are social shows good for advertisers? Marketing Science, 38 (2), 274–295.
Godes, D., & Mayzlin, D. (2009). Firm-created word-of-mouth communication: Evidence from a field test. Marketing Science, 28 (4), 721–739.
Gordon, B. R., Zettelmeyer, F., Bhargava, N., & Chapsky, D. (2019). A comparison of approaches to advertising measurement: Evidence from big field experiments at Facebook. Marketing Science, 38 (2), 193–225.
Gosling, S., Gaddis, S., & Vazire, S. (2007). Personality Impressions Based on Facebook Profiles. ICWSM , 1–4.
Greaves, F., Ramirez-Cano, D., Millett, C., Darzi, A., & Donaldson, L. (2013). Harnessing the cloud of patient experience: Using social media to detect poor quality healthcare. BMJ Quality and Safety, 22 (3), 251–255.
Grewal, L., & Stephen, A. T. (2019). In mobile we trust: The effects of mobile versus nonmobile reviews on consumer purchase intentions. Journal of Marketing Research, 56 (5), 791–808.
Grewal, L., Stephen, A. T., & Coleman, N. V. (2019). When posting about products in social media backfires: The negative effects of consumer identity-signaling on product interest. Journal of Marketing Research, 56 (2), 197–210.
Guszcza, J. (2018). Smarter together. Deloitte Review, 22 , 36–45.
Haans, A., & IJsselsteijn, W. (2006). Mediated social touch: A review of current research and future directions. Virtual Reality, 9 (2), 149–159.
Haenlein, M. (2017). How to date your clients in the 21st century: Challenges in managing customer relationships in today's world. Business Horizons, 60 , 577–586.
Harton, H. C., & Bourgeois, M. J. (2004). Cultural elements emerge from dynamic social impact. The Psychological Foundations of Culture , 41–75.
Hennig-Thurau, T., Gwinner, K. P., Walsh, G., & Gremler, D. D. (2004). Electronic word-of-mouth via consumer-opinion platforms: What motivates consumers to articulate themselves on the internet? Journal of Interactive Marketing, 18 (1), 38–52.
Hennig-Thurau, T., Wiertz, C., & Feldhaus, F. (2015). Does twitter matter? The impact of microblogging word of mouth on consumers’ adoption of new movies. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43 (3), 375–394.
Herhausen, D., Ludwig, S., Grewal, D., Wulf, J., & Schoegel, M. (2019). Detecting, preventing, and mitigating online firestorms in brand communities. Journal of Marketing, 83 (3), 1–21.
Hilken, T., de Ruyter, K., Chylinski, M., Mahr, D., & Keeling, D. I. (2017). Augmenting the eye of the beholder: Exploring the strategic potential of augmented reality to enhance online service experiences. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (6), 884–905.
Hoffman, D. L., & Novak, T. P. (2018). Consumer and object experience in the internet of things: An assemblage theory approach. Journal of Consumer Research, 44 (6), 1178–1204.
Hollenbeck, C. R., & Kaikati, A. M. (2012). Consumers’ use of brands to reflect their actual and ideal selves on Facebook. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 29 (4), 395–405.
Hunt, M. G., Marx, R., Lipson, R., & Young, J. (2018). No more FOMO: Limiting social media decreases loneliness and depression. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 37 (10), 751–768.
Information Technology Faculty (2018). Building Trust in the Digital Age Report. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y9rkxbxu .
John, L. K., Emrich, O., Gupta, S., & Norton, M. I. (2017). Does “liking” lead to loving? The impact of joining a brand’s social network on marketing outcomes. Journal of Marketing Research, 54 (1), 144–155.
Johnson, L. (2015). Stoli's Mobile Ads Let You Actually Feel a Cocktail Being Made in Your Hand. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y72uud3c .
Jun, Y., Meng, R., & Johar, G. V. (2017). Perceived social presence reduces fact-checking. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114 (23), 5976–5981.
Kakatkar, C., & Spann, M. (2018). Marketing analytics using anonymized and fragmented tracking data. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 36 (1), 117–136.
Kaplan, A., & Haenlein, M. (2019). Siri, Siri, in my hand: Who’s the fairest in the land? On the interpretations, illustrations, and implications of artificial intelligence. Business Horizons, 62 (1), 15–25.
Katai L. (2018). 3 Reasons why audio will conquer all social media. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y9q6bvjr .
Kelly, H., Horowitz, J., O'Sullivan, D. (2018). Facebook takes down 652 pages after finding disinformation campaigns run from Iran and Russia. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ybte3bp4 .
Kim, J., LaRose, R., & Peng, W. (2009). Loneliness as the cause and the effect of problematic internet use: The relationship between internet use and psychological well-being. Cyberpsychology & Behavior, 12 (4), 451–455.
King, G., Pan, J., & Roberts, M. E. (2017). How the Chinese government fabricates social media posts for strategic distraction, not engaged argument. American Political Science Review, 111 (3), 484–501.
Knight, T. (2018). How to tell if you are talking to a bot. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ycamg4p8 .
Knoll, J., & Matthes, J. (2017). The effectiveness of celebrity endorsements: A meta-analysis. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (1), 55–75.
Kross, E., Verduyn, P., Demiralp, E., Park, J., Lee, D. S., Lin, N., Shablack, H., Jonides, J., & Ybarra, O. (2013). Facebook use predicts declines in subjective well-being in young adults. PLoS One, 8 (8), e69841.
Kumar, V., Choi, J. B., & Greene, M. (2017). Synergistic effects of social media and traditional marketing on brand sales: Capturing the time-varying effects. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (2), 268–288.
Kumparak, G. (2018). Google Assistant will now be nicer if you say ‘Please’ and ‘Thank you’. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ybcfdztv .
Lamberton, C., & Stephen, A. T. (2016). A thematic exploration of digital, social media, and mobile marketing research's evolution from 2000 to 2015 and an agenda for future research. Journal of Marketing, 80 (6), 146–172.
Lee, K., Eoff, B.D., & Caverlee, J. (2011), Seven months with the devils: A long-term study of content polluters on twitter. In Proceedings of the 5th International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, 185–192.
Lobschat, L., Osinga, E. C., & Reinartz, W. J. (2017). What happens online stays online? Segment-specific online and offline effects of banner advertisements. Journal of Marketing Research, 54 (6), 901–913.
Lovejoy, B. (2017). Ikea to be Apple launch partner for AR, showing virtual furniture in your own home. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/yarzpz8n .
Magnarelli, M. (2018). The Next Marketing Skill You Need to Master: Touch. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y7tybx4d .
Main, S. (2017). Micro-Influencers Are More Effective with Marketing Campaigns Than Highly Popular Accounts. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/moww4p4 .
Manchanda, P., Dubé, J. P., Goh, K. Y., & Chintagunta, P. K. (2006). The effect of banner advertising on internet purchasing. Journal of Marketing Research, 43 (1), 98–108.
Marche. T. (2012). Is Facebook making us lonely? Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ybyje7ol .
Marker, C., Gnambs, T., & Appel, M. (2018). Active on Facebook and failing at school? Meta-analytic findings on the relationship between online social networking activities and academic achievement. Educational Psychology Review , 651–677.
Martin, K. (2018). The penalty for privacy violations: How privacy violations impact trust online. Journal of Business Research, 82 , 103–116.
Martin, K. D., & Murphy, P. E. (2017). The role of data privacy in marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (2), 135–155.
Martin, K. D., Borah, A., & Palmatier, R. W. (2017). Data privacy: Effects on customer and firm performance. Journal of Marketing, 81 (1), 36–58.
Maxim (2018). Every Selena Gomez Instagram post for puma is worth $3.4 million. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ybr6nzok .
McClure, E. (2015). 11 Youtube Stars with Makeup Collections We Can’t Get Enough Of. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ybwzz6mm .
Mejia, Z., (2018). Kylie Jenner reportedly makes $1 million per paid Instagram post—here's how much other top influencers get. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y7khetcu .
Mochon, D., Johnson, K., Schwartz, J., & Ariely, D. (2017). What are likes worth? A Facebook page field experiment. Journal of Marketing Research, 54 (2), 306–317.
Molteni, S., (2017). The Chatbot Therapist Will See You Now. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y8g9b3oq .
Nill, A., & Aalberts, R. J. (2014). Legal and ethical challenges of online behavioral targeting in advertising. Journal of Current Issues and Research in Advertising, 35 , 126–146.
Nolan, H. (2018), Brands are creating virtual influencers, Which could make the Kardashians a thing of the past. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y7gu7t26 .
Orben, A., Dienlin, T., & Przybylski, A. K. (2019). Social media’s enduring effect on adolescent life satisfaction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116 (21), 10226–10228.
Oremus, W. (2016). Who Controls Your Facebook Feed. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y745c2ap .
Ozcivelek, A. (2015). The future of wearable tech. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y88kf554 .
Padrez, K. A., Ungar, L., Schwartz, H. A., Smith, R. J., Hill, S., Antanavicius, T., Brown, D. M., Crutchley, P., Asch, D. A., & Merchant, R. M. (2016). Linking social media and medical record data: A study of adults presenting to an academic, urban emergency department. BMJ Quality and Safety, 25 (6), 414–423.
Pardes, A. (2017). Selfie Factories: The rise of the Made-for-Instagram Museum. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ycqswbz2 .
Pennycook, G., & Rand, D. G. (2019). Fighting misinformation on social media using crowdsourced judgments of news source quality. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116 (7), 2521–2526.
Pennycook, G., Cannon, T. D., & Rand, D. G. (2019). Prior exposure increases perceived accuracy of fake news . Journal of Experimental Psychology: General In press.
Perry, E. (2018). Meet HearMeOut: the social media platform looking to bring audio back into the mainstream. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y8yxbzah .
Pittman, M., & Reich, B. (2016). Social media and loneliness: Why an Instagram picture may be worth more than a thousand twitter words. Computers in Human Behavior, 62 , 155–167.
Priday, R. (2018). How to use Instagram and Facebooks new time limit tools. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y8allnxe .
Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Sidani, J. E., Whaite, E. O., Lin, L. Y., Rosen, D., Colditz, J. B., Radovic, A., & Miller, E. (2017). Social media use and perceived social isolation among young adults in the US. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 53 (1), 1–8.
Rao, L., (2017). Instagram Copies Snapchat Once Again with Face Filters. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ybcuxxdv .
Ritschel, C. (2018). Snapchat Introduces New Filters for Cats. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y8shdhpl .
Robbio, A. (2018). The hyper-adoption of voice technology. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y9zzqpan .
Romano, A. (2018). Two-thirds of links on twitter come from bots. The good news? They’re Mostly Bland. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y8hpyldc .
Safko, L. (2010). The social media bible: Tactics, tools, and strategies for business success. John Wiley & Sons.
Schmidt, C. W. (2012). Trending now: Using social media to predict and track disease outbreaks.
Schwartz, O. (2018). You thought fake news was bad? Deep fakes are where truth goes to die. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y7mcrysq .
Schwarz, N., & Newman, E. J. (2017). How does the gut know truth? Psychological Science Agenda, 31 (8).
Shakya, H. B., & Christakis, N. A. (2017). Association of Facebook use with compromised well-being: A longitudinal study. American Journal of Epidemiology, 185 (3), 203–211.
Sheth, J. (2017). The future history of consumer research: Will the discipline rise to the opportunity? Advances in Consumer Research, 45 , 17–20.
Smith, A. (2018). California Law Bans Bots from Pretending to Be Human. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/y78qdkpu .
Steers, M. L. N., Wickham, R. E., & Acitelli, L. K. (2014). Seeing everyone else's highlight reels: How Facebook usage is linked to depressive symptoms. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 33 (8), 701–731.
Stephen, A. T. & G. Brooks (2018). L’Oréal Paris Makeup Genius. Saïd Business School Case Study, University of Oxford.
Stephen, A. T., & Galak, J. (2012). The effects of traditional and social earned media on sales: A study of a microlending marketplace. Journal of Marketing Research, 49 (5), 624–639.
Stephen, A. T., & Lehmann, D. R. (2016). How word-of-mouth transmission encouragement affects consumers’ transmission decisions, receiver selection, and diffusion speed. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 33 (4), 755–766.
Stewart, D. W. (2017). A comment on privacy. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45 (2), 156–159.
Stocking, G. & Sumida, N. (2018). Social Media Bots Draw Public’s Attention and Concern. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ybabbeu4 .
Tillman, M. (2018). What are Memoji? How to create an Animoji that looks like you. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/yakqjqdf .
Toubia, O., & Stephen, A. T. (2013). Intrinsic vs. image-related utility in social media: Why do people contribute content to twitter? Marketing Science, 32 (3), 368–392.
Trusov, M., Bucklin, R. E., & Pauwels, T. (2009). Effects of word-of mouth versus traditional marketing: Findings from an internet social networking site. Journal of Marketing, 73 (5), 90–102.
Tucker, C. E. (2014). Social networks, personalized advertising and privacy controls. Journal of Marketing Research, 51 (5), 546–562.
Vanhemert, K. (2014). Needy robot toaster sells itself if neglected. Retrieved from https://bit.ly/2ROGvt3 .
Varol. O., Ferrara, E., Davis, C. A., Menczer, F., & Flammini, A. (2017). Online Human-Bot Interactions: Detection, Estimation and Characterization. Retrieved from https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.03107 .
Villarroel Ordenes, F., Ludwig, S., De Ruyter, K., Grewal, D., & Wetzels, M. (2017). Unveiling what is written in the stars: Analyzing explicit, implicit, and discourse patterns of sentiment in social media. Journal of Consumer Research, 43 (6), 875–894.
Villarroel Ordenes, F., Grewal, D., Ludwig, S., Ruyter, K. D., Mahr, D., & Wetzels, M. (2018). Cutting through content clutter: How speech and image acts drive consumer sharing of social media brand messages. Journal of Consumer Research, 45 (5), 988–1012.
Wagner, K. (2017). Mark Zuckerberg, In His Own Words, On why AR is Facebook’s next big platform bet. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/yagf24e4 .
Wagner, K. (2018). Oculus Go, the virtual reality headset Facebook hopes will bring VR to the mainstream, is finally here. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ycnz468q .
Walker, H. (2018). Meet Lil Miquela, the Instagram star created by CGI. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/yc32k25l .
Wallace, E., Buil, I., de Chernatony, L., & Hogan, M. (2014). Who “Likes” You … and Why? A Typology of Facebook Fans. Journal of Advertising Research, 54 (1), 92–109.
Welch, C., (2018). How to use Google Duplex to make a restaurant reservation. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/yaup796a .
Whigham, N. (2018). The way we hang out on social media could look (and feel) very different soon. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ycs3efqv .
White, K., & Dahl, D. W. (2007). Are all out-groups created equal? Consumer identity and dissociative influence. Journal of Consumer Research, 34 (4), 525–536.
White, T. B., Zahay, D. L., Thorbjørnsen, H., & Shavitt, S. (2008). Getting too personal: Reactance to highly personalized email solicitations. Marketing Letters, 19 (1), 39–50.
Wilcox, K., & Stephen, A. T. (2012). Are close friends the enemy? Online social networks, self-esteem, and self-control. Journal of Consumer Research, 40 (1), 90–103.
Woolley, K., & Risen, J. L. (2018). Closing your eyes to follow your heart: Avoiding information to protect a strong intuitive preference. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 114 (2), 230–245.
Xu, H., Teo, H. H., Tan, B. C. Y., & Agarwal, R. (2012). Effects of individual self-protection industry self-regulation, and government regulation on privacy concerns: A study of location based services. Information Systems Research, 23 , 1342–1363.
Yurieff, K. (2018). Instagram star isn’t what she seems. But brands are buying in. Retrieved from https://tinyurl.com/ycqnf72c .
Zhang, Y., Trusov, M., Stephen, A. T., & Jamal, Z. (2017). Online shopping and social media: Friends or foes? Journal of Marketing, 81 (6), 24–41.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the special issue editors and reviewers for their comments, and the Oxford Future of Marketing Initiative for supporting this research. The authors contributed equally and are listed in alphabetical order or, if preferred, order of Marvel superhero fandom from highest to lowest and order of Bon Jovi fandom from lowest to highest.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Marshall School of Business, University of Southern California, 701 Exposition Blvd, Los Angeles, CA, 90089, USA
Tuck School of Business, Dartmouth College, 100 Tuck Hall, Hanover, NH, 03755, USA
Lauren Grewal
Saïd Business School, University of Oxford, Park End Street, Oxford, OX1 1HP, UK
Rhonda Hadi & Andrew T. Stephen
Monash Business School, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia
Andrew T. Stephen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Rhonda Hadi or Andrew T. Stephen .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Mark Houston served as accepting editor for this article.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Appel, G., Grewal, L., Hadi, R. et al. The future of social media in marketing. J. of the Acad. Mark. Sci. 48 , 79–95 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-019-00695-1
Download citation
Published : 12 October 2019
Issue Date : January 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-019-00695-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Social media
- Digital marketing
- Future of marketing
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- The Future of Digital Spaces and Their Role in Democracy
Many experts say public online spaces will significantly improve by 2035 if reformers, big technology firms, governments and activists tackle the problems created by misinformation, disinformation and toxic discourse. Others expect continuing troubles as digital tools and forums are used to exploit people’s frailties, stoke their rage and drive them apart
Table of contents.
- 1. A sampling of some of the key overarching views
- 2. Public digital spaces will be improved: Tech can be fixed, governments and corporations can reorient incentives and people can band together to work for reform
- 3. Large improvement of digital spaces is unlikely by 2035: Human frailties will remain the same; corporations, governments and the public will not be able to make reforms
- 4. Work is needed now to prepare for a mind-bending future
- 5. Closing thoughts
- 6. About this canvassing of experts
- Acknowledgments

This is the 13th “ Future of the Internet ” canvassing Pew Research Center and Elon University’s Imagining the Internet Center have conducted together to gather expert views about important digital issues. In this report, the questions focused on the prospects for improvements in the tone and activities of the digital public sphere by 2035. This is a nonscientific canvassing based on a nonrandom sample; this broad array of opinions about where current trends may lead in the next decade represents only the points of view of the individuals who responded to the queries. Pew Research Center and Elon’s Imagining the Internet Center built a database of experts to canvass from a wide range of fields, inviting professionals and policy people based in government bodies, nonprofits and foundations, technology businesses and think tanks, as well as interested academics and technology innovators. The predictions reported here came in response to a set of questions in an online canvassing conducted between June 29 and Aug. 2, 2021. In all, 862 technology innovators and developers, business and policy leaders, researchers and activists responded to at least one of the questions covered in this report. More on the methodology underlying this canvassing and the participants can be found in the section titled “ About this canvassing of experts .”
Those who worry about the future of democracy focus a lot of their anxiety on the way that the things that happen in online public spaces are harming deliberation and the fabric of society. To be sure, billions of users appreciate what the internet does for them. But the climate in some segments of social media and other online spaces has been called a “ dumpster fire ” of venom, misinformation, conspiracy theories and goads to violence.
Social media platforms are drawing fire for their role in all of this. After the Jan. 6, 2021, attack on the U.S. Capitol, a congressional panel requested that Facebook, Google, Twitter, Parler, 4chan, Twitch and TikTok release all records related to misinformation around the 2020 election, including efforts to influence or overturn the presidential election results. In September 2021, a five-part series in The Wall Street Journal exposed details that seem to show that Facebook has allowed the diffusion of misinformation, disinformation and toxicity that has resulted in ethnic violence and harm to teenage girls and has undermined COVID-19 vaccination efforts. And The Journal’s source, Facebook whistleblower Frances Haugen, followed up by telling the U.S. Senate that she had gone public with her explosive material “because I believe that Facebook’s products harm children, stoke division and weaken our democracy.”
Worries over the rise in the acrid tone and harmful and manipulative interactions in some online spaces, and concerns over the role of technology firms in all of this, have spawned efforts by tech activists to try to redesign online spaces in ways that facilitate debate, enhance civility and provide personal security. A selection of these initiatives were described in a spring 2021 article in The Atlantic Monthly by Anne Applebaum and Peter Pomerantsev. Among the suggested solutions documented in the piece:
- The creation of an internet version of public media along the lines of PBS and NPR;
- “ Middleware ” that could allow people to set an algorithm to give them the kind of internet experience they want, perhaps without the dystopian side effects;
- Online upvoting systems that favor content that could push partisans toward consensus, rather than polarizing them;
- An internet “bill of rights” allowing “self-sovereign identity” that lets people stay anonymous online, but weeds out bots; and
- “ Constructive communication ” systems set up to dial down anger and bridge divides.
In light of the current conversations about the need to rethink and redesign online public spaces, Pew Research Center and Elon University’s Imagining the Internet Center asked experts how they expect the digital public sphere to evolve by 2035. Some 862 technology innovators, developers, business and policy leaders, researchers and activists responded to this specific question:
Looking ahead to 2035, will digital spaces and people’s use of them be changed in ways that significantly serve the public good?
Some 61% chose the option declaring that, “yes,” by 2035, digital spaces and people’s uses of them will change in ways that significantly serve the public good; 39% chose the “no” option, positing that by 2035, digital spaces and people’s uses of them will not change in ways that significantly serve the public good.
It is important to note that a large share of who chose “yes” – that online public spaces would improve by 2035 – also wrote in their answers that the changes between now and then could go either way. They often listed one or more difficult hurdles to overcome before that outcome can be achieved. Thus, the numeric findings reported here are not fully indicative of the troubles that they think lie between now and 2035.
In fact, in answer to a separate question in which they were asked how they see digital spaces generally evolving now, a majority ( 70% ), said current technological evolution has both positives and negatives , 18% said digital spaces are evolving in a mostly negative way that is likely to lead to a worse future for society, 10% said the online world is evolving in a mostly positive way that is likely to lead to a better society, and about 3% said digital spaces are not evolving in one direction or another .
It is also worth noting that the responses were gathered in mid-summer of 2021. People’s responses came in the cultural context of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, and at a time when rising concerns over climate change , racial justice and social inequality were particularly prominent – and half a year after the Jan. 6, 2021, attack at the U.S. Capitol in the aftermath of one of the most highly contentious U.S. presidential elections in recent history.
This is a nonscientific canvassing, based on a nonrandom sample. The results represent only the opinions of the individuals who responded to the queries and are not projectable to any other population.
The bulk of this report covers these experts’ written answers explaining their responses to our questions. They sounded many broad themes in sharing their insights about the evolution of the digital “town squares” most people frequent.
The themes are outlined in the tables that follow below:

As they considered these questions, some of these experts predicted that changes of a different order of magnitude are also in store by 2035. Some of the most compelling ideas include:
- Brad Templeton advanced a “new moral theory [that] it is wrong to exploit known flaws in the human psyche.” He argues that the embrace of “psyche-exploitation avoidance” would lead to a new design of online spaces.
- Mike Liebhold outlined a future with applied machine intelligence everywhere, continuous pervasive cybersecurity vulnerabilities, ubiquitous conversational bot agents, holographic media and telepresence and cobotics (collaborative robotics), among other things.
- Carolina Rossini predicted that a regulatory agency to monitor technology’s impact on health – a Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for algorithms – will arise as increasing numbers of digital technology tools are placed in people’s bodies.
- Raashi Saxena urged, “We do not have a global, agreed-upon list of digital harms that can be inflicted upon us … We first need to define the rights to be protected.”
- Jerome Glenn said a new civilization will emerge as the “Information Age” gives way to the “Conscious-Technology Age” through the force of two megatrends: “First, humans will become cyborgs, as our biology becomes integrated with technology. Second, our built environment will incorporate more artificial intelligence.”
- Cory Doctorow said the “tyranny of network effects” will be broken if interoperability is imposed on tech companies so that, for instance, people could move their social media networks from one platform to another and easily abandon online spaces they do not like.
- Robin Raskin predicted, “The metaverse – digital twins of real worlds or entirely fabricated worlds – will be a large presence by 2035, unfortunately with some of the same bad practices on the internet today such as personal-identity infringements.”
- Beth Simone Noveck expects new “governance models” for public online spaces that allow citizens and groups to participate directly in policymaking and provision of services.
- James Hendler believes there will be tech advances that allow people to control their online identities and privacy preferences in ways that thwart omnipresent surveillance schemes.
- Barry Chudakov predicts “the self will go digital” and exist in the flesh and in its digital avatar. “Identity is thereby multiple and fluid: Roles, sexual orientation and self-presentation evolve from solely in-person to in-space.”
In the next chapter, there is a collection of responses from technology and academic experts that cover a range of issues tied to online public spaces and are noteworthy for their insights, and for the prominence of the respondents. It closes with two essay-style responses to these questions from internet sages Barry Chudakov and Judith Donath .
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Politics Online
Most Americans favor restrictions on false information, violent content online
#blacklivesmatter turns 10, a profile of the top-ranked podcasts in the u.s., support for the black lives matter movement has dropped considerably from its peak in 2020, on alternative social media sites, many prominent accounts seek financial support from audiences, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

Essay on The Power of Social Media
Students are often asked to write an essay on The Power of Social Media in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on The Power of Social Media
Introduction to social media.
Social media is a powerful tool that connects people globally. It’s like a virtual meeting place where you can share ideas and experiences.
The Influence of Social Media
Social media has a significant influence on our lives. It shapes our thoughts, opinions, and even our behaviors.
Benefits of Social Media
Social media offers many benefits. It helps us connect with friends, learn new things, and express ourselves creatively.
Challenges of Social Media
Despite its benefits, social media can also pose challenges. It can lead to cyberbullying and misinformation.
In conclusion, social media has both positive and negative aspects. It’s important to use it responsibly.
250 Words Essay on The Power of Social Media
The ubiquity of social media.
Social media has become a pervasive force in contemporary society, transforming the way we communicate, interact, and perceive the world. It’s not just a tool for connecting with friends and family; it’s a platform that influences public opinion, shapes political landscapes, and even drives consumer behavior.
Amplifying Voices
One of the most profound impacts of social media is its ability to amplify voices that were once marginalized. It has democratized information, enabling anyone with internet access to share their views, stories, and experiences. This has led to a surge in social movements, from Black Lives Matter to #MeToo, which have leveraged social media to raise awareness and effect change.
Shaping Public Opinion
However, the power of social media is a double-edged sword. While it can be a force for good, it can also be a platform for misinformation and manipulation. The Cambridge Analytica scandal highlighted how personal data can be exploited to sway public opinion, raising ethical questions about the role of social media in our democratic processes.
The Future of Social Media
The future of social media lies in its ability to adapt and evolve. As we become more aware of its potential pitfalls, there is a growing demand for more transparency, accountability, and ethical standards. The power of social media is undeniable, but it is up to us to harness it responsibly.
In conclusion, social media has reshaped our world in myriad ways. It has the power to amplify voices, shape public opinion, and even influence our democratic processes. As we navigate this digital landscape, it’s essential to use this power responsibly.
500 Words Essay on The Power of Social Media
In the contemporary digital age, social media platforms have become an integral part of our lives. They are not merely tools for communication and entertainment, but have evolved into platforms for education, business, and social change. Social media’s power lies in its ability to connect, inform, and influence, transcending geographical boundaries and cultural divides.
The Power to Connect and Inform
Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn have revolutionized communication. They enable individuals to connect with others across the globe in real time, fostering a sense of global community. Information dissemination has also been greatly enhanced by social media. News, whether it’s about local events or international crises, can reach millions within seconds. This immediacy of information exchange has reshaped our perception of the world, making it more interconnected and accessible.
The Power to Influence
The influence of social media is another facet of its power. It has become a significant platform for marketing and advertising. Businesses, both large and small, leverage social media to reach their target audience, promote products, and build brand identity. Furthermore, influencers use these platforms to sway public opinion, whether it’s about fashion, politics, or social issues.
Driving Social Change
Perhaps the most profound illustration of social media’s power is its role in driving social change. It has provided a platform for marginalized voices, enabling them to share their stories and rally support. Movements like #BlackLivesMatter and #MeToo gained momentum through social media, leading to global awareness and significant societal change.
The Double-Edged Sword
However, the power of social media is a double-edged sword. While it can promote positive change, it can also spread misinformation and fuel polarization. The Cambridge Analytica scandal highlighted how data from social media can be used to manipulate public opinion. Similarly, the proliferation of fake news on these platforms has become a major concern.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power Responsibly
In conclusion, social media is a powerful tool with the potential to connect, inform, influence, and instigate change. However, its power can be both constructive and destructive. As users and beneficiaries of social media, it is incumbent upon us to use these platforms responsibly. The power of social media, when harnessed correctly, can be a catalyst for positive change, fostering global understanding and cooperation.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Positive Effects of Social Media
- Essay on Social Media and Students
- Essay on Role of Social Media
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
You’re Not Imagining It: Social Media Is in Chaos

By Sriram Krishnan
Mr. Krishnan is a general partner at Andreessen Horowitz, a venture capital firm.
War is breaking out on social media, and it could radically change how the internet works and how we experience it.
Last week, Meta rolled out Threads, a social media product similar to Twitter that quickly got over 100 million sign-ups. This is more than just a tech founder cage match ; it is the latest incident in a pattern of increasing chaos. Large parts of the internet community site Reddit went dark recently in a user protest over its decision to charge other companies more for using its data. This came right after the livestreaming platform Twitch walked back restrictions on creators after boycott threats. There’s change in the air in social media, and it is spreading fast.
I spent most of the past decade working at large social media companies. I briefly helped Elon Musk after his acquisition of Twitter, in which my firm is an investor . My firm is also an investor in Substack , Reddit and other social media companies , and our general partner Marc Andreessen is on the board of Meta.
I believe the skirmishes of the past few weeks are connected to one another and are worth paying attention to. They represent a fundamental rejection of how the internet and large tech companies have worked for several decades. Instead of being limited to a few large companies, we may be at the start of an era of many online spaces, where consumers could have more power and rights than they’ve ever had.
Think of the current large social networks as various European nations at the dawn of the 20th century. Often ruled by monarchs and autocrats (C.E.O.s), they exist in an uneasy balance with their own users and with one another.
Users and social networks have an unspoken agreement: In return for entertainment, utility and an audience, users hand over control. If the network chooses to kick you out, you’re out in the cold. Choosing to leave one platform means losing your audience forever. You can’t take it with you.
Large social networks act like geopolitical neighbors in an uneasy Westphalian peace with one another. They often move in lock step, swiftly introducing similar features. Stories on Snap? Copied by Instagram and YouTube. TikTok reels? See Reels and YouTube Shorts.
They are also aligned ideologically on what content to censor. Major companies agreed on how to handle theories on the origin of Covid or stories about Hunter Biden’s laptop, leading to what Evelyn Douek, a Stanford law professor, calls “content cartels.” In many ways, there has been a prevailing monolithic culture on how things get done.
In 1914, Europe seemed to be at relative peace, but there were cracks and tensions emerging. All it took was an assassination, initially seen as insignificant, to plunge the world into conflict. Similarly, in the first half of 2023 there has been a succession of online dominoes smashing the status quo of social media to smithereens, causing uprisings in several places.
The first domino was economic. As interest rates started to rise, social media companies discovered they weren’t immune to macroeconomic forces. C.E.O.s reacted with an increased emphasis on products that make money directly from the consumer and reducing employee head count.
The second domino was the introduction of A.I. assistants like ChatGPT. While many were blown away by their possibilities, they forced social media websites to re-evaluate how their data is used externally. Historically many websites like Reddit and Stack Overflow allowed some of their content — especially the discussions among their users on various topics — to be available free. This was typically done to allow search engines to find this content and send users back to these sites. Want to compare two highly recognized San Francisco restaurants? Enter their names and “Reddit” in Google, and recent Reddit conversations are likely to appear. Click on one of the links, and you’re now in Reddit (thereby boosting its business). Third-party developers also tapped this data to build useful tools on top of this content.
A.I. assistants rely on enormous amounts of such data and would hoover up that conversation about San Francisco restaurants. So if you ask an A.I. assistant for the names of San Francisco’s best restaurants, it could well use that Reddit discussion to generate its answer. But it won’t tell you that Reddit was a source for its answer. It won’t send you to Reddit. And as of now, it pays Reddit nothing for the help.
The third domino was Elon Musk’s purchase of Twitter. Whether or not you agree with his moves after he bought Twitter, they have sparked a chain reaction. Reddit’s C.E.O. cited Twitter as a template for how to cut costs. Meta’s Facebook and Instagram followed Twitter in charging for verification of individual users. Meta introduced Threads. While it’s early days to see how this plays out, it is clear the social media landscape has shifted quickly and profoundly.
This takes us to the first key shift that may reshape how the internet works: decentralization. For over a decade, all major internet platforms have been centralized: Services are run by a central team, often based in Silicon Valley.
Decentralized services try to bring modern democratic ideas to internet platforms. While social media giants endure a constant stream of accusations that they curate their content in a way that furthers political agendas, the goal of decentralization is a network that is credibly neutral in the way it works. The network should be able to resist attempts by any party to seize power and become centralized. Most important, no centralized gatekeeper can delete a user’s account or data — and you should be able to take your audience with you wherever you go.
Interest in decentralized services has been increasing for some time, as various groups have disagreed with the management of the platforms they use. One such service is Farcaster, a decentralized social network in which I’m a direct investor. Others are apps like Bluesky and Mastodon. Instagram has said Threads will support some flavor of this in the future.
The second major development is that large internet sites are fighting back against A.I. models with the internet equivalent of raising the castle drawbridge. The coding site Stack Overflow, Reddit and others have raised the prices for their data to be used. In Reddit’s case, the change had the effect of blocking some popular third-party applications , setting off continuing protests and blackouts.
We will need a fundamentally different mechanism for websites to exchange value with A.I. assistants. Otherwise, expect more raised drawbridges and more user protests. Some industry experts believe the answers are in legal action and older sites forming content alliances .
As a technologist, my hope is that the answers lie in code rather than lawyers and that we see creative technology solutions to help keep the internet open.
For far too long, the online world has been in stasis, limited to a few options dominated by a few large companies. Technological breakthroughs and unrest were needed to shake things up, and that has happened. A pessimist might say that this is going to lead to chaos and challenges. As an optimist who invests in technology entrepreneurs for a living, I believe we are in for an age of major innovation, with all of us having more options and say in how things are run online.
Either way, it’s going to be one heck of a ride.
Sriram Krishnan is a general partner at Andreessen Horowitz, a venture capital firm, and a co-host of the podcast “The Aarthi and Sriram Show.”
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow The New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Twitter (@NYTopinion) and Instagram .
Feb 15, 2023
6 Example Essays on Social Media | Advantages, Effects, and Outlines
Got an essay assignment about the effects of social media we got you covered check out our examples and outlines below.
Social media has become one of our society's most prominent ways of communication and information sharing in a very short time. It has changed how we communicate and has given us a platform to express our views and opinions and connect with others. It keeps us informed about the world around us. Social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn have brought individuals from all over the world together, breaking down geographical borders and fostering a genuinely global community.
However, social media comes with its difficulties. With the rise of misinformation, cyberbullying, and privacy problems, it's critical to utilize these platforms properly and be aware of the risks. Students in the academic world are frequently assigned essays about the impact of social media on numerous elements of our lives, such as relationships, politics, and culture. These essays necessitate a thorough comprehension of the subject matter, critical thinking, and the ability to synthesize and convey information clearly and succinctly.
But where do you begin? It can be challenging to know where to start with so much information available. Jenni.ai comes in handy here. Jenni.ai is an AI application built exclusively for students to help them write essays more quickly and easily. Jenni.ai provides students with inspiration and assistance on how to approach their essays with its enormous database of sample essays on a variety of themes, including social media. Jenni.ai is the solution you've been looking for if you're experiencing writer's block or need assistance getting started.
So, whether you're a student looking to better your essay writing skills or want to remain up to date on the latest social media advancements, Jenni.ai is here to help. Jenni.ai is the ideal tool for helping you write your finest essay ever, thanks to its simple design, an extensive database of example essays, and cutting-edge AI technology. So, why delay? Sign up for a free trial of Jenni.ai today and begin exploring the worlds of social networking and essay writing!
Want to learn how to write an argumentative essay? Check out these inspiring examples!
We will provide various examples of social media essays so you may get a feel for the genre.
6 Examples of Social Media Essays
Here are 6 examples of Social Media Essays:
The Impact of Social Media on Relationships and Communication
Introduction:.
The way we share information and build relationships has evolved as a direct result of the prevalence of social media in our daily lives. The influence of social media on interpersonal connections and conversation is a hot topic. Although social media has many positive effects, such as bringing people together regardless of physical proximity and making communication quicker and more accessible, it also has a dark side that can affect interpersonal connections and dialogue.
Positive Effects:
Connecting People Across Distances
One of social media's most significant benefits is its ability to connect individuals across long distances. People can use social media platforms to interact and stay in touch with friends and family far away. People can now maintain intimate relationships with those they care about, even when physically separated.
Improved Communication Speed and Efficiency
Additionally, the proliferation of social media sites has accelerated and simplified communication. Thanks to instant messaging, users can have short, timely conversations rather than lengthy ones via email. Furthermore, social media facilitates group communication, such as with classmates or employees, by providing a unified forum for such activities.
Negative Effects:
Decreased Face-to-Face Communication
The decline in in-person interaction is one of social media's most pernicious consequences on interpersonal connections and dialogue. People's reliance on digital communication over in-person contact has increased along with the popularity of social media. Face-to-face interaction has suffered as a result, which has adverse effects on interpersonal relationships and the development of social skills.
Decreased Emotional Intimacy
Another adverse effect of social media on relationships and communication is decreased emotional intimacy. Digital communication lacks the nonverbal cues and facial expressions critical in building emotional connections with others. This can make it more difficult for people to develop close and meaningful relationships, leading to increased loneliness and isolation.
Increased Conflict and Miscommunication
Finally, social media can also lead to increased conflict and miscommunication. The anonymity and distance provided by digital communication can lead to misunderstandings and hurtful comments that might not have been made face-to-face. Additionally, social media can provide a platform for cyberbullying , which can have severe consequences for the victim's mental health and well-being.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the impact of social media on relationships and communication is a complex issue with both positive and negative effects. While social media platforms offer many benefits, such as connecting people across distances and enabling faster and more accessible communication, they also have a dark side that can negatively affect relationships and communication. It is up to individuals to use social media responsibly and to prioritize in-person communication in their relationships and interactions with others.
The Role of Social Media in the Spread of Misinformation and Fake News
Social media has revolutionized the way information is shared and disseminated. However, the ease and speed at which data can be spread on social media also make it a powerful tool for spreading misinformation and fake news. Misinformation and fake news can seriously affect public opinion, influence political decisions, and even cause harm to individuals and communities.
The Pervasiveness of Misinformation and Fake News on Social Media
Misinformation and fake news are prevalent on social media platforms, where they can spread quickly and reach a large audience. This is partly due to the way social media algorithms work, which prioritizes content likely to generate engagement, such as sensational or controversial stories. As a result, false information can spread rapidly and be widely shared before it is fact-checked or debunked.
The Influence of Social Media on Public Opinion
Social media can significantly impact public opinion, as people are likelier to believe the information they see shared by their friends and followers. This can lead to a self-reinforcing cycle, where misinformation and fake news are spread and reinforced, even in the face of evidence to the contrary.
The Challenge of Correcting Misinformation and Fake News
Correcting misinformation and fake news on social media can be a challenging task. This is partly due to the speed at which false information can spread and the difficulty of reaching the same audience exposed to the wrong information in the first place. Additionally, some individuals may be resistant to accepting correction, primarily if the incorrect information supports their beliefs or biases.
In conclusion, the function of social media in disseminating misinformation and fake news is complex and urgent. While social media has revolutionized the sharing of information, it has also made it simpler for false information to propagate and be widely believed. Individuals must be accountable for the information they share and consume, and social media firms must take measures to prevent the spread of disinformation and fake news on their platforms.
The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health and Well-Being
Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of people around the world using platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter to stay connected with others and access information. However, while social media has many benefits, it can also negatively affect mental health and well-being.
Comparison and Low Self-Esteem
One of the key ways that social media can affect mental health is by promoting feelings of comparison and low self-esteem. People often present a curated version of their lives on social media, highlighting their successes and hiding their struggles. This can lead others to compare themselves unfavorably, leading to feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem.
Cyberbullying and Online Harassment
Another way that social media can negatively impact mental health is through cyberbullying and online harassment. Social media provides a platform for anonymous individuals to harass and abuse others, leading to feelings of anxiety, fear, and depression.
Social Isolation
Despite its name, social media can also contribute to feelings of isolation. At the same time, people may have many online friends but need more meaningful in-person connections and support. This can lead to feelings of loneliness and depression.
Addiction and Overuse
Finally, social media can be addictive, leading to overuse and negatively impacting mental health and well-being. People may spend hours each day scrolling through their feeds, neglecting other important areas of their lives, such as work, family, and self-care.
In sum, social media has positive and negative consequences on one's psychological and emotional well-being. Realizing this, and taking measures like reducing one's social media use, reaching out to loved ones for help, and prioritizing one's well-being, are crucial. In addition, it's vital that social media giants take ownership of their platforms and actively encourage excellent mental health and well-being.
The Use of Social Media in Political Activism and Social Movements
Social media has recently become increasingly crucial in political action and social movements. Platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram have given people new ways to express themselves, organize protests, and raise awareness about social and political issues.
Raising Awareness and Mobilizing Action
One of the most important uses of social media in political activity and social movements has been to raise awareness about important issues and mobilize action. Hashtags such as #MeToo and #BlackLivesMatter, for example, have brought attention to sexual harassment and racial injustice, respectively. Similarly, social media has been used to organize protests and other political actions, allowing people to band together and express themselves on a bigger scale.
Connecting with like-minded individuals
A second method in that social media has been utilized in political activity and social movements is to unite like-minded individuals. Through social media, individuals can join online groups, share knowledge and resources, and work with others to accomplish shared objectives. This has been especially significant for geographically scattered individuals or those without access to traditional means of political organizing.
Challenges and Limitations
As a vehicle for political action and social movements, social media has faced many obstacles and restrictions despite its many advantages. For instance, the propagation of misinformation and fake news on social media can impede attempts to disseminate accurate and reliable information. In addition, social media corporations have been condemned for censorship and insufficient protection of user rights.
In conclusion, social media has emerged as a potent instrument for political activism and social movements, giving voice to previously unheard communities and galvanizing support for change. Social media presents many opportunities for communication and collaboration. Still, users and institutions must be conscious of the risks and limitations of these tools to promote their responsible and productive usage.
The Potential Privacy Concerns Raised by Social Media Use and Data Collection Practices
With billions of users each day on sites like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, social media has ingrained itself into every aspect of our lives. While these platforms offer a straightforward method to communicate with others and exchange information, they also raise significant concerns over data collecting and privacy. This article will examine the possible privacy issues posed by social media use and data-gathering techniques.
Data Collection and Sharing
The gathering and sharing of personal data are significant privacy issues brought up by social media use. Social networking sites gather user data, including details about their relationships, hobbies, and routines. This information is made available to third-party businesses for various uses, such as marketing and advertising. This can lead to serious concerns about who has access to and uses our personal information.
Lack of Control Over Personal Information
The absence of user control over personal information is a significant privacy issue brought up by social media usage. Social media makes it challenging to limit who has access to and how data is utilized once it has been posted. Sensitive information may end up being extensively disseminated and may be used maliciously as a result.
Personalized Marketing
Social media companies utilize the information they gather about users to target them with adverts relevant to their interests and usage patterns. Although this could be useful, it might also cause consumers to worry about their privacy since they might feel that their personal information is being used without their permission. Furthermore, there are issues with the integrity of the data being used to target users and the possibility of prejudice based on individual traits.
Government Surveillance
Using social media might spark worries about government surveillance. There are significant concerns regarding privacy and free expression when governments in some nations utilize social media platforms to follow and monitor residents.
In conclusion, social media use raises significant concerns regarding data collecting and privacy. While these platforms make it easy to interact with people and exchange information, they also gather a lot of personal information, which raises questions about who may access it and how it will be used. Users should be aware of these privacy issues and take precautions to safeguard their personal information, such as exercising caution when choosing what details to disclose on social media and keeping their information sharing with other firms to a minimum.
The Ethical and Privacy Concerns Surrounding Social Media Use And Data Collection
Our use of social media to communicate with loved ones, acquire information, and even conduct business has become a crucial part of our everyday lives. The extensive use of social media does, however, raise some ethical and privacy issues that must be resolved. The influence of social media use and data collecting on user rights, the accountability of social media businesses, and the need for improved regulation are all topics that will be covered in this article.
Effect on Individual Privacy:
Social networking sites gather tons of personal data from their users, including delicate information like search history, location data, and even health data. Each user's detailed profile may be created with this data and sold to advertising or used for other reasons. Concerns regarding the privacy of personal information might arise because social media businesses can use this data to target users with customized adverts.
Additionally, individuals might need to know how much their personal information is being gathered and exploited. Data breaches or the unauthorized sharing of personal information with other parties may result in instances where sensitive information is exposed. Users should be aware of the privacy rules of social media firms and take precautions to secure their data.
Responsibility of Social Media Companies:
Social media firms should ensure that they responsibly and ethically gather and use user information. This entails establishing strong security measures to safeguard sensitive information and ensuring users are informed of what information is being collected and how it is used.
Many social media businesses, nevertheless, have come under fire for not upholding these obligations. For instance, the Cambridge Analytica incident highlighted how Facebook users' personal information was exploited for political objectives without their knowledge. This demonstrates the necessity of social media corporations being held responsible for their deeds and ensuring that they are safeguarding the security and privacy of their users.
Better Regulation Is Needed
There is a need for tighter regulation in this field, given the effect, social media has on individual privacy as well as the obligations of social media firms. The creation of laws and regulations that ensure social media companies are gathering and using user information ethically and responsibly, as well as making sure users are aware of their rights and have the ability to control the information that is being collected about them, are all part of this.
Additionally, legislation should ensure that social media businesses are held responsible for their behavior, for example, by levying fines for data breaches or the unauthorized use of personal data. This will provide social media businesses with a significant incentive to prioritize their users' privacy and security and ensure they are upholding their obligations.
In conclusion, social media has fundamentally changed how we engage and communicate with one another, but this increased convenience also raises several ethical and privacy issues. Essential concerns that need to be addressed include the effect of social media on individual privacy, the accountability of social media businesses, and the requirement for greater regulation to safeguard user rights. We can make everyone's online experience safer and more secure by looking more closely at these issues.
In conclusion, social media is a complex and multifaceted topic that has recently captured the world's attention. With its ever-growing influence on our lives, it's no surprise that it has become a popular subject for students to explore in their writing. Whether you are writing an argumentative essay on the impact of social media on privacy, a persuasive essay on the role of social media in politics, or a descriptive essay on the changes social media has brought to the way we communicate, there are countless angles to approach this subject.
However, writing a comprehensive and well-researched essay on social media can be daunting. It requires a thorough understanding of the topic and the ability to articulate your ideas clearly and concisely. This is where Jenni.ai comes in. Our AI-powered tool is designed to help students like you save time and energy and focus on what truly matters - your education. With Jenni.ai , you'll have access to a wealth of examples and receive personalized writing suggestions and feedback.
Whether you're a student who's just starting your writing journey or looking to perfect your craft, Jenni.ai has everything you need to succeed. Our tool provides you with the necessary resources to write with confidence and clarity, no matter your experience level. You'll be able to experiment with different styles, explore new ideas , and refine your writing skills.
So why waste your time and energy struggling to write an essay on your own when you can have Jenni.ai by your side? Sign up for our free trial today and experience the difference for yourself! With Jenni.ai, you'll have the resources you need to write confidently, clearly, and creatively. Get started today and see just how easy and efficient writing can be!
Try Jenni for free today
Create your first piece of content with Jenni today and never look back
Opinion: Does social media rewire kids’ brains? Here’s what the science really says

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
America’s young people face a mental health crisis, and adults constantly debate how much to blame phones and social media. A new round of conversation has been spurred by Jonathan Haidt’s book “The Anxious Generation,” which contends that rising mental health issues in children and adolescents are the result of social media replacing key experiences during formative years of brain development.
The book has been criticized by academics , and rightfully so. Haidt’s argument is based largely on research showing that adolescent mental health has declined since 2010, coinciding roughly with mass adoption of the smartphone. But of course, correlation is not causation. The research we have to date suggests that the effects of phones and social media on adolescent mental health are probably much more nuanced.

Opinion: Troubled youth? Contrary to stereotypes, much of Gen Z is doing just fine
Perceptions of younger generations as broadly suffering from mental health problems are exaggerated and potentially harmful.
Feb. 16, 2024
That complex picture is less likely to get attention than Haidt’s claims because it doesn’t play as much into parental fears. After all, seeing kids absorbed in their phones, and hearing that their brains are being “rewired,” calls to mind an alien world-domination plot straight from a sci-fi film.
And that’s part of the problem with the “rewiring the brain” narrative of screen time. It reflects a larger trope in public discussion that wields brain science as a scare tactic without yielding much real insight.
First, let’s consider what the research has shown so far . Meta-analyses of the links between mental health and social media give inconclusive or relatively minor results. The largest U.S. study on childhood brain development to date did not find significant relationships between the development of brain function and digital media use . This month, an American Psychological Assn. health advisory reported that the current state of research shows “ using social media is not inherently beneficial or harmful to young people” and that its effects depend on “pre-existing strengths or vulnerabilities, and the contexts in which they grow up.”

Editorial: Social media companies refuse to safeguard kids. It’s up to lawmakers now
State and federal lawmakers are trying to create regulations to protect kids from potential harms from social media use. It’s not easy to find balance.
April 22, 2024
So why the insistence from Haidt and others that smartphones dangerously rewire the brain? It stems from misunderstandings of research that I have encountered frequently as a neuroscientist studying emotional development, behavioral addictions and people’s reactions to media.
Imaging studies in neuroscience typically compare some feature of the brain between two groups: one that does not do a specific behavior (or does it less frequently) and one that does the behavior more frequently. When we find a relationship, all it means is either that the behavior influences something about the functioning of this brain feature, or something about this feature influences whether we engage in the behavior.
In other words, an association between increased brain activity and using social media could mean that social media activates the identified pathways, or people who already have increased activity in those pathways tend to be drawn to social media, or both.
Fearmongering happens when the mere association between an activity such as social media use and a brain pathway is taken as a sign of something harmful on its own. Functional and structural research on the brain cannot give enough information to objectively identify increases or decreases in neural activity, or in a brain region’s thickness, as “good” or “bad.” There is no default healthy status quo that everybody’s brains are measured against, and doing nearly any activity involves many parts of the brain.

Opinion: The surprising way to help your brain remember
Testing, not rote memorization, is key to learning. But it works only under the right circumstances.
Feb. 19, 2024
“The Anxious Generation” neglects these subtleties when, for example, it discusses a brain system known as the default mode network. This system decreases in activity when we engage with spirituality, meditation and related endeavors, and Haidt uses this fact to claim that social media is “not healthy for any of us” because studies suggest that it by contrast increases activity in the same network.
But the default mode network is just a set of brain regions that tend to be involved in internally focused thinking, such as contemplating your past or making a moral judgment, versus externally focused thinking such as playing chess or driving an unfamiliar route. Its increased activity does not automatically mean something unhealthy.
This type of brain-related scare tactic is not new. A common version, which is also deployed for smartphones , involves pathways in the brain linked to drug addiction, including areas that respond to dopamine and opioids. The trope says that any activity associated with such pathways is addictive, like drugs, whether it’s Oreos , cheese , God , credit card purchases , sun tanning or looking at a pretty face . These things do involve neural pathways related to motivated behavior — but that does not mean they damage our brains or should be equated with drugs.

The week’s bestselling books, April 21
The Southern California Independent Bookstore Bestsellers list for Sunday, April 21, 2024, including hardcover and paperback fiction and nonfiction.
April 17, 2024
Adolescence is a time when the brain is particularly plastic, or prone to change. But change doesn’t have to be bad. We should take advantage of plasticity to help teach kids healthy ways to self-manage their own use of, and feelings surrounding, smartphones.
Do I expect future findings on the adolescent brain to immediately quell parents’ fears on this issue? Of course not — and the point is that they shouldn’t. Brain imaging data is a fascinating way to explore interactions between psychology, neuroscience and social factors. It’s just not a tool for declaring behaviors to be pathological. Feel free to question whether social media is good for kids — but don’t misuse neuroscience to do so.
Anthony Vaccaro is a postdoctoral research associate at the University of Southern California’s Psychology department.
More to Read

A little too obsessed with Taylor Swift? It might be a coping mechanism
April 11, 2024

Opinion: Think life just keeps getting worse? Try being nostalgic — for the present
April 10, 2024

Letters to the Editor: Give ‘Generation Alpha’ a break. Millennial offspring can’t be that bad
March 28, 2024
A cure for the common opinion
Get thought-provoking perspectives with our weekly newsletter.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Op-Comic: You can cry if you want to

Opinion: The Supreme Court just showed us that Trump is not incompetent. He’s a master of corruption
April 26, 2024

Granderson: Arizona’s indictment of Trump allies follows a sordid, racist history

Opinion: Is planting trees on Arbor Day one way we can all fight climate change? Not so much

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Current trending social media topics. 7 predictions on the future of social media. AR and VR will become mainstream with high adoption. Search will increase on social media. Influencers will weigh in more. Users will seek personalized content. Authenticity will be the key.
Essay. Predicting the future in the development of social media applications can be very difficult because it depends on the IT brains all over the world. Who would have thought that one day we would have online banks where we can store our money and make purchase without physical more (He, Zha and Li 469). Twenty years ago, nobody would have ...
Social Media Essay Hooks. ... The essay should end with a thought-provoking statement or question about the future role of social media, tying back to the initial hooks and ensuring a comprehensive and engaging end to the discourse. Tips for Writing Essays on Social Media.
The shift helps explain why some social networking companies, which continue to have billions of users and pull in billions of dollars in revenue, are now exploring new avenues of business ...
Prof. Sinan Aral speaks with Danny Crichton of TechCrunch about his new book, "The Hype Machine," which explores the future of social media. Aral notes that he believes a starting point "for solving the social media crisis is creating competition in the social media economy."
The Future Of Social Media Essay. 2362 Words10 Pages. Social Media and Its Future Since its creation, the world is in a continuous evolution; an evolution that has been marked by many revolutions changing the way in which the human eye perceives the world, mainly the industrial revolution in the XVIII century, the atomic bomb in the XX century ...
The Future of Social Media Thesis. Social media has changed the manner in which individuals interact with each other. Prior to the 21 st century, the most common means through which people would communicate to each other was through sending of letters. Telephones were also the preferred means through which people would communicate instantly ...
Overall, the future of social media in 2023 looks bright, with new opportunities for visual content, micro-influencers, e-commerce, chatbots, ephemeral content, and AI. By staying up-to-date on the latest trends and adapting their strategy accordingly, marketers will be well-positioned to succeed on social media in the year ahead. Share:
In this article, the authors present the results from a structured review of the literature, identifying and analyzing the most quoted and dominant definitions of social media (SM) and alternative terms that were used between 1994 and 2019 to identify their major applications. Similarities and differences in the definitions are highlighted to provide guidelines for researchers and managers who ...
This paper attempts to explore the future of social media in respect to the lives of individuals. The paper will focus on some of the leading social media providers including Twitter, Instagram, and Tango. The future of social media will incorporate the current and new modes of doing things. First, the information that is accessed by social ...
Some perspective on how fast and profound these rapid changes are. The percentage of US adults who use social media increased from 5% in 2005 to 79% in 2019. Even on a global stage, the speed of diffusion is striking: Facebook surged from covering around 1.5% of the world population in 2008 to around 30% in 2018. 5.
What the debate over TikTok means for the future of social media. It has been an eventful few months for TikTok: The social media platform recently won an injunction against a nationwide ban while ...
This study discusses the findings of 132 papers (in selected IS journals) on social media and social networking published between 1997 and 2017. ... Future researchers can look to overcome such exclusions and focus on the overall review of literature on social media platforms. Future reviews may focus on reviewing articles published in a larger ...
Social media allows people to freely interact with others and offers multiple ways for marketers to reach and engage with consumers. Considering the numerous ways social media affects individuals and businesses alike, in this article, the authors focus on where they believe the future of social media lies when considering marketing-related topics and issues. Drawing on academic research ...
Social media platforms are drawing fire for their role in all of this. After the Jan. 6, 2021, attack on the U.S. Capitol, a congressional panel requested that Facebook, Google, Twitter, Parler, 4chan, Twitch and TikTok release all records related to misinformation around the 2020 election, including efforts to influence or overturn the ...
The future of social media lies in its ability to adapt and evolve. As we become more aware of its potential pitfalls, there is a growing demand for more transparency, accountability, and ethical standards. The power of social media is undeniable, but it is up to us to harness it responsibly. In conclusion, social media has reshaped our world ...
Last week, Meta rolled out Threads, a social media product similar to Twitter that quickly got over 100 million sign-ups. This is more than just a tech founder cage match; it is the latest ...
These include mobile marketing, stand-alone applications, wearables, and visual social media. Video and photo-sharing applications such as Vine, Instagram and Snapchat have also grown in popularity, while social media sites such as Twitter and Facebook have redesigned so that their text-based status update features can be more compatible with ...
People's reliance on digital communication over in-person contact has increased along with the popularity of social media. Face-to-face interaction has suffered as a result, which has adverse effects on interpersonal relationships and the development of social skills. Decreased Emotional Intimacy.
"Social media provides a lot of opportunities for young people to discover new information, learn about current events, engage with issues, and have their voices heard," Nesi added. ... An updated agenda for the study of digital media use and adolescent development: Future directions following Odgers & Jensen (2020) Prinstein, M. J., et al.,
Current and Future T rends in Social Media. Enkh-Amgalan Baatarjav and Ram Dantu. Department of Computer Science and Engineering. University of North Texas. Denton, Te xas, 76203, USA. Email ...
The purpose of this study is to understand the role of social media content on users' engagement behavior. More specifically, we investigate: (i)the direct effects of format and platform on users' passive and active engagement behavior, and (ii) we assess the moderating effect of content context on the link between each content type (rational, emotional, and transactional content) and ...
Hypersensitivity to social feedback. Brain development starting at ages 10-13 (i.e., the outset of puberty) until approximately the mid-twenties is linked with hypersensitivity to social feedback/stimuli. iv In other words, youth become especially invested in behaviors that will help them get personalized feedback, praise, or attention from peers.. AI-recommended content has the potential to ...
Feb. 16, 2024. That complex picture is less likely to get attention than Haidt's claims because it doesn't play as much into parental fears. After all, seeing kids absorbed in their phones ...
In December 2022, the Board of Directors of the Association for Psychological Science (APS) became aware of specific concerns about the editorial practices of Klaus Fiedler, then the editor-in-chief (EIC) of the APS journal Perspectives on Psychological Science.These concerns were not reported directly to APS; rather, a manuscript detailing these issues was publicly disseminated by its author ...