Elements of an Essay
Definition of elements of an essay.
An essay is a piece of composition that discusses a thing, a person, a problem, or an issue in a way that the writer demonstrates his knowledge by offering a new perspective , a new opinion, a solution, or new suggestions or recommendations. An essay is not just a haphazard piece of writing. It is a well-organized composition comprising several elements that work to build an argument , describe a situation, narrate an event, or state a problem with a solution. There are several types of essays based on the purpose and the target audience . Structurally, as an essay is an organized composition, it has the following elements:
- Introduction
- Body Paragraphs

Nature of Elements of an Essay
An essay has three basic elements as given above. Each of these elements plays its respective role to persuade the audience, convince the readers, and convey the meanings an author intends to convey. For example, an introduction is intended to introduce the topic of the essay. First it hooks the readers through the ‘ hook ,’ which is an anecdote , a good quote, a verse , or an event relevant to the topic. It intends to attract the attention of readers.
Following the hood, the author gives background information about the topic, which is intended to educate readers about the topic. The final element of the introduction is a thesis statement. This is a concise and compact sentence or two, which introduces evidence to be discussed in the body paragraphs.
Body paragraphs of an essay discuss the evidences and arguments introduced in the thesis statement . If a thesis statement has presented three evidences or arguments about the topic, there will be three body paragraphs. However, if there are more arguments or evidences, there could be more paragraphs.
The structure of each body paragraph is the same. It starts with a topic sentence, followed by further explanation, examples, evidences, and supporting details. If it is a simple non-research essay, then there are mostly examples of what is introduced in the topic sentences. However, if the essay is research-based, there will be supporting details such as statistics, quotes, charts, and explanations.
The conclusion is the last part of an essay. It is also the crucial part that sums up the argument, or concludes the description, narration, or event. It is comprised of three major parts. The first part is a rephrasing of the thesis statement given at the end of the introduction. It reminds the readers what they have read about. The second part is the summary of the major points discussed in the body paragraphs, and the third part is closing remarks, which are suggestions, recommendations, a call to action, or the author’s own opinion of the issue.
Function of Elements of an Essay
Each element of an essay has a specific function. An introduction not only introduces the topic, but also gives background information, in addition to hooking the readers to read the whole essay. Its first sentence, which is also called a hook, literally hooks readers. When readers have gone through the introduction, it is supposed that they have full information about what they are going to read.
In the same way, the function of body paragraphs is to give more information and convince the readers about the topic. It could be persuasion , explanation, or clarification as required. Mostly, writers use ethos , pathos , and logos in this part of an essay. As traditionally, it has three body paragraphs, writers use each of the rhetorical devices in each paragraph, but it is not a hard and fast rule. The number of body paragraphs could be increased, according to the demand of the topic, or demand of the course.
As far as the conclusion is concerned, its major function is to sum up the argument, issue, or explanation. It makes readers feel that now they are going to finish their reading. It provides them sufficient information about the topic. It gives them a new perspective, a new sight, a new vision, or motivates them to take action. The conclusion needs to also satisfy readers that they have read something about some topic, have got something to tell others, and that they have not merely read it for the sake of reading.
Related posts:
- Important Elements of Poetry
- Narrative Essay
- Definition Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Types of Essay
- Analytical Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Cause and Effect Essay
- Critical Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Process Essay
- Explicatory Essay
- An Essay on Man: Epistle I
- Comparison and Contrast Essay
Post navigation

Successful University Writing
- Before You Start Writing...
Structuring an essay
- Report writing
- Annotated bibliography
- Literature review
- Reflective writing
- Using Ideas from sources in your writing
- Writing concisely and editing your work
- Student Success study support

Thesis statements
Most academic writing at university will require you to argue a position. This means including a thesis statement upfront in the first paragraph that concisely states the central argument and purpose of the essay. This video addresses the key features of a thesis statement.
- Parts of an essay
- Writing introductions and conclusions
- Writing paragraphs
- Making your writing flow
Academic writing structures may vary, but the main sections are the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. Here is an overview of what these sections contain:
Introduction
- The introduction tells the reader what your writing is about.
- Start by defining the topic and any terms which will be crucial for your discussion.
- The introduction should also state what position you will argue and how you will do it. This is the thesis statement .
- Use words and phrases which are in the assignment question to help the reader see that you are directly addressing the main issues.
- It can help to write the introduction last. This is particularly helpful if you have not yet fully determined what your document is going to say and what your arguments will be.
- This is the most important part of your writing. Begin each sentence with a "topic sentence" which is then discussed and explained.
- Each paragraph must discuss a different point. Each paragraph should be a discussion on the point you have made in the first sentence.
- Paraphrase or summarise the sources you have read in your research. If using direct quotes, ensure they are relevant and impactful. Evaluate what is being said. Never assume the reader knows what you are talking about.
- Always reference any ideas you have used in your writing.
- Paragraphs should flow in an organised and logical sequence. One way to do this is by introducing the next paragraph (topic) in the last sentence of the previous paragraph.
- Avoid repetition and rewriting another version of what you have already said.
- Transition or linking words , such as however, therefore, and although tell the reader about the direction you are arguing or when there is a change of direction.
- Avoid using first person point of view.
- Avoid slang or jargon (use academic language).
- Avoid using long and complicated sentences. Make your point obvious and easy to read.
- The work should read as one organised discussion, not a mix of unrelated information. Make sure each sentence in the paragraphs has a role in the discussion and contributes to the overall argument and topic you are addressing.
- Restate what you planned to do in your introduction and discuss how you have done it. You should tell the reader that your discussion led to the conclusion that your thesis (argument/position) supported.
- No new information should be included in the conclusion.
An essay introduction usually:
- clearly states the topic that will be the focus of the essay;
- offers a preview of main aspects that will addressed, or the particular angle that will be taken in; and
- clearly articulates the position that will be argued. This is known as the thesis statement.
Consider this introduction:
Leadership has been defined as “the process of influencing the activities of an organized group toward goal achievement” (Block & Tackle, 2019 , p. 46). This essay compares and contrasts two approaches to leadership from Western and Eastern traditions. The first is Fayol’s Administrative Principles approach, considered to be one of the foundations of the study of Management. The second approach is Confucianism, which is said to continue to guide leadership and management across China and much of South-East Asia (Shih, Wong, Han, Zheng, & Xin, 2004). It will be argued that these two approaches share certain core values, and a critical understanding of both approaches can support management decision-making.
The first sentence clearly states the topic. Leadership has been defined as “the process of influencing the activities of an organized group toward goal achievement” (Block & Tackle, 2019 , p. 46).
The middle sentences preview the aspects that will be addressed and hints at the approach (compare and contrast). This essay compares and contrasts two approaches to leadership from Western and Eastern traditions. The first is Fayol’s Administrative Principles approach, considered to be one of the foundations of the study of Management. The second approach is Confucianism, which is said to continue to guide leadership and management across China and much of South-East Asia (Shih, Wong, Han, Zheng, & Xin, 2004).
The final sentence clearly states the thesis, or position that will be argued. This is essentially a succinct version of the response to the essay question. It will be argued that these two approaches share certain core values, and a critical understanding of both approaches can support management decision-making.
In any academic essay, the paragraphs should follow the key points that have been outlined in the introduction. Each paragraph then contextualises and expands upon these points in relation the thesis statement of the essay. Having a paragraph plan is an effective way to map out your essay and ensure that you address the key points of the essay in detail – especially for longer forms of essays and academic writing that students engage with at university.
An basic paragraph plan would generally contain:
- The thesis statement (for an essay)
- A topic heading for each paragraph
- The claim of argument to be made in each paragraph (this will be, or will inform, your topic sentence)
- The evidence that will be presented to support the claim
- Summary of the conclusion paragraph
Consider this example of a paragraph plan:
Paragraph plans provide an overview of your essay and provide an effective starting point for structured writing. The next step is using this plan to expand on the points as you write your essay.
Getting your writing to flow.
In almost all cases, written assignments call for students to explore complex topics or aspects of an area of study. Any academic writing task is an opportunity to show how well you understand a particular topic, theme or area. Usually this means demonstrating how various ideas, knowledge, information or ways of thinking are connected within the context of the task or area of focus.
This means that successful academic writing presents ideas logically, and that there is high connectivity within the writing. In other words, the aim should be for writing to have high flow to help make the connections clear.
Three ways to achieve this include:
- ensuring that there is good connection from one paragraph to another;
- ensuring that there is good connection from one sentence to another; and
- using transition words effectively to make the logical connections between ideas clear.
Flow from one paragraph to another
Topic sentences, or the leading sentences of a paragraph, play a key role in connecting the ideas of an essay. High-flow topic sentences should look to include three key elements:
- An explicit reference to the topic of the essay.
- A reference to the main aspect of the previous paragraph
- An introduction to the topic of the new paragraph
Consider the following examples of topic sentences in response to an essay question about Virtue Ethics.
A low-flow topic sentence : Aristotle defined phronesis as practical wisdom.
This sentence does not reference the topic (virtue ethics), nor does it link to an idea from a previous paragraph. It does however, introduce the sub-topic of the paragraph (phronesis).
A high-flow topic sentence: Another fundamental concept in Virtue Ethics is phronesis.
This sentence refers to the essay topic (virtue ethics), acknowledges that this is an additional concept that build on the previous paragraph, and introduces the topic of this paragraph (phronesis).
Flow from one sentence to another
Well-constructed paragraphs have high connections between sentences. In general sentences that promote flow should:
- reference the topic of the previous sentence;
- add new information in the second half; and
- use topic words.
The following paragraph example can be considered high-flow. It includes sentences that reference the previous sentence ( underlined ), add new information ( maroon ) and use topic words ( green ).
Another fundamental concept in Virtue Ethics is phronesis. According to Aristotle, phronesis is a form of practical wisdom through which individuals make principled decisions in line with virtues such as courage and honesty (reference). Its practical nature means that phronesis can only be developed over a lifetime of carefully considered actions and sober reflection . This practice builds a person’s moral character, allowing them to make morally-defensible choices even in unfamiliar and complex situations (reference). In other words, it is a kind of social and professional skill, which at first requires conscious effort and can still result in mistakes. However, through discipline and persistence, it becomes second nature. As a result, practitioners consistently act wisely and in accordance with the virtues they uphold . Their wise actions further strengthen their own character and contribute to human fulfilment at both individual and community levels (reference).
Transition words that improve flow
Transition words help make the relationships and connections between ideas clear. Some examples of helpful transition words and phrases for various types of connections include:
Success Now! workshops and consultations
Success Now! workshops are available live online or on campus. Register here for workshops on research and writing . You can also organise an individual consultation here to talk to a learning advisor about planning your assignments.
- << Previous: Types of university academic writing
- Next: Report writing >>
- Last Updated: Feb 1, 2024 10:25 AM
- URL: https://library.nd.edu.au/writing
Mastering the Elements of a Perfect Essay Structure

Table of Contents
Essay writing has always been a tough task for writers, no matter how much experience they have in the field. It is because new topics and research areas come with new sets of problems and issues. Not to mention different types of essays demand different focal points, tone, voice, and other aspects of writing.
Still, there is one thing that remains the same – structure. While keeping variations and formats in mind, the structure of essays often remains the same. That’s why it pays students and novice writers to learn the mechanics and dynamics of essay structure.
In this post, we will dig deeper into how to lay out an essay, its importance, and then a detailed account of its elements.
What Is The Structure of An Essay?
The essay structure or the essay layout format is the arrangement of different variables in the writing. It is about picking a different tone, in the beginning, to lure the readers in and then ease them into the subject through background information. The structure is also about the size of the margins, spacing between lines, font style, and size. However, in this blog, we will cover more of the contextual and structural issues with writing an essay.
In practice, it all boils down to developing and balancing different sections of an essay so that they have more value. Readers often find it difficult to understand the contents of the essay when the structure is not sound. That’s why it is necessary to understand how it works and how it can be leveraged to get more value for the essay .
Importance of A Good Essay Structure
The primary purpose behind writing an essay is about connecting with the readers and helping them understand a subject. That’s where the structure plays an important role. If you spread the same information throughout the essay with no structure at all, your readers will end up more confused than they were in the beginning. On the other hand, if you pick different elements of the structure with care, you will end up with an essay that checks all the boxes of being a great one.
Keeping that in mind, experts have identified different elements in a traditional essay.
Elements of An Essay Set-Up Structure
Whether you are writing a narrative essay or trying your hand at an argumentative one, it is necessary to set up a structure where relevant things are aligned perfectly with their intended purpose. Three major elements constitute the whole essay:
Introduction/ Opening
- Closing/ Conclusion
The writer’s job is simple – balance all the information in these three sections in such a way that the value of the whole becomes more than the sum of individual sections.
Let us go through each of the elements in detail to ensure that students can understand them better, and can apply the theory in practice.
This is where things get started – literally. The introduction or opening of an essay lets the readers know what they are about to read. Instead of getting right on the topic, it is best to start light and then ease readers into the subject.
Easing Readers Into The Subject
To do that, writers employ tactics including a hook. It is a literary device that is not directly related to the subject but can help readers understand the point of the writer. After setting up a great hook, it is best to provide background information on the subject before closing the introduction with a thesis statement.
Essentials of A Solid Introduction
Following are some of the essentials for a good introduction:
Brief & bold
Opens with a hook
Context for readers
To the point thesis statement
Main Body/ Body Paragraphs
When it comes to the real value of the essay, this is where the magic happens. Introductions have their agenda and conclusions are more about revisiting the things discussed in the main body. That’s why the main body paragraphs are considered the essence of the essay.
Heart & Soul of An Essay
No matter the type of essay you are writing, the main body should get the most word count. According to common standards, it takes no less than 66% of the total word count. Whether writers are dealing with arguments, facts, details, and description, this is where all the action takes place. Still, writers should mind the length and focal points of the essay.
What Makes A Good Essay Main Body
There are many ways to make a good essay main body, but we are taking a standard route containing insights for all types of essays. In the narrative and descriptive essays, all the elements should play out in this section. As for expository and argumentative essays, they must cover all the factual information and arguments in the main body.
Conclusion/ Closing
A conclusion is one of the most important sections of the essay. Logically, it is what readers will read in the end and will remember the most. So, the conclusion should be written with extreme care so that all the bases are covered.
Rationale Behind Closing
Even though writers have made a great impact with the introduction and solid body paragraphs, it is necessary to close things logically. Also, many readers do not have the time to read the essay in its entirety. So, a comprehensive summary, in the end, is not too much to ask for.
Best Practices For Essay Conclusions
Here are some of the best practices that writers should keep in mind to compose riveting conclusions:
Restating the thesis
Summarizing all the main points
Closing with catchy sentences
Never adding new to the main arguments/ points
For the last point, many novice writers make this mistake which leads to poor reception of the essay. So, steer clear of that one to ensure that the structure of your essay is sound.
Tips For Enticing Readers With A Simple Essay Format
Students often learn more from tips than from a comprehensive guide. If that’s the case with our readers, we have put up some of the best tips on capturing the readers’ imagination with a solid essay.
Starting With A Hook
A hook is a literary device that grabs readers’ attention. It can be a question, a statistic, or a bold or shocking statement about the subject of the essay. Whatever it is, writers should cover all the bases in its case. Otherwise, it will be a miss for them and their readers.
Chat With A Writer
Stating A Bold & Brief Thesis A thesis statement is the summary of the main point or theme of the essay. It is an essential part of the essay as no essay is complete without it. In most cases, it comes in the closing lines of the introduction, but expository essays can even open with a thesis statement. It should be bold and brief so that the point becomes clear to the readers without any fluff.
Main Points & Arguments In The Body
The main body does not have the space or logic to beat around the bush. It is the place where writers should go all in with their material. Whether it is a narrative essay or an expository one, it should cover all the main points, arguments, and counterarguments in this section.
Anticipating Counter Points
While writing argumentative essays, writers often need to anticipate counterpoints or arguments in the body. This helps them in persuading peers and other researchers that indeed their ideas were better. For instance, if they are supporting one side of the argument, they can better illuminate their rationale by explaining why they are not supporting the other side.
Closing On A High Note
If writers want to close on a high note, they need to come up with a winning conclusion. A conclusion is nothing more than a short but effective summary of the whole essay. Many experts believe that it should be treated as such to get the best value out of it.
Revisiting the Main Points of The Essay
A good conclusion is not about merely attracting or keeping the attention of the readers. The real value comes from revisiting all the main points from the body paragraphs. This not only helps readers but also aids writers in steering their essays in the right direction.
Key Takeaways
In the beginning, many students are not concerned about the structure and format of an essay, even though it is one of the most important aspects of it. The structure of an essay is about connecting with the readers at a deeper level through tangible assets. The action in essay starts with the introduction and then the main body takes over before things come to a logical end.
We have shed ample light on how is an essay structured in this resource so that students can become better writers. But if they cannot write their essays before the deadline, PerfectEssay can help them with submission-ready essays. We have a team of academic writers with experience in writing essays in all subjects and disciplines. So, place your order now and get a 15% discount on your first order!
Courtesy of PerfectEssay
Related articles.

How To Write A Short Essay Read More »

How To Write a Informative Essay Read More »

How Many Words is a Perfect Essay? Read More »


Writing Help
- Writing Process
Starting an Essay
Essay structure, writing a thesis statement, introduction paragraphs, body paragraphs, conclusions.
- Paragraph Structure
- Paraphrase, Summarize, and Synthesize
- Writing Genres
- Sentence Structure
- Punctuation and Grammar
- Using Bias-Free Language
- Revision, Editing, and Proofreading
- Mastering the Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Annotated Bibliography
- Help This link opens in a new window
Note: This guide was used/adapted with the permission of Baker College. For more information please visit the Baker College Writing Guide .
Almost every course you will encounter in college will include writing assignments. One of the most common writing assignments is known as an essay. While the content and style of essay projects will vary across the disciplines, there are several key components that all good essays include. This section of the guide walks you through some of the basic components of the essay genre. Here are some general thoughts before you get started.
- A good essay is well-organized and structured. Good essays have a clear introduction, thesis, and conclusion. Body paragraphs in the essay connect back to the thesis.
- Essays should be cohesive and have a good flow. We can create this flow by using transition words and phrases to connect one point to the next.
- Remember to review the directions before you start. One can produce a wonderfully written essay, but if it does not meet the project's parameters, it will not usually receive a passing grade.
- Tips for Writing Your Thesis Drafting a thesis statement can be intimidating, but there are a variety of resources to help.
- Strong Introduction Paragraphs Review tips on starting your paper strong.
- Creating Body Paragraphs This resource walks you through paragraph creation including how to implement good topic sentences, proper organization, and excellent development.
- Crafting a Strong Conclusion We often focus on creating a strong introduction, but crafting a well-written conclusion is just as important.
- << Previous: Writing Process
- Next: Paragraph Structure >>
- Last Updated: Nov 30, 2023 1:00 PM
- URL: https://bethelu.libguides.com/writinghelp
Gordon Harvey’s Elements of the Academic Essay
The “Elements of the Academic Essay” is a taxonomy of academic writing by Gordon Harvey. It identifies the key components of academic writing across the disciplines and has been widely influential. Below is a complete list (with descriptions).
Elements of an Essay
“Your main insight or idea about a text or topic, and the main proposition that your essay demonstrates. It should be true but arguable (not obviously or patently true, but one alternative among several), be limited enough in scope to be argued in a short composition and with available evidence, and get to the heart of the text or topic being analyzed (not be peripheral). It should be stated early in some form and at some point recast sharply (not just be implied), and it should govern the whole essay (not disappear in places).” — Gordon Harvey, “Elements of the Academic Essay”
- See this fuller discussion of some of the scholarly debates about the thesis statement: The Thesis Statement
- See this piece on the pros and cons of having a thesis statement: Pros and Cons of Thesis Statements
- See this piece on working with students without a thesis: What To Do When There’s No Thesis
- And see this piece for working with students with varied levels of thesis development: A Pseudo-Thesis
“The intellectual context that you establish for your topic and thesis at the start of your essay, in order to suggest why someone, besides your instructor, might want to read an essay on this topic or need to hear your particular thesis argued—why your thesis isn’t just obvious to all, why other people might hold other theses (that you think are wrong). Your motive should be aimed at your audience: it won’t necessarily be the reason you first got interested in the topic (which could be private and idiosyncratic) or the personal motivation behind your engagement with the topic. Indeed it’s where you suggest that your argument isn’t idiosyncratic, but rather is generally interesting. The motive you set up should be genuine: a misapprehension or puzzle that an intelligent reader (not a straw dummy) would really have, a point that such a reader would really overlook. Defining motive should be the main business of your introductory paragraphs, where it is usually introduced by a form of the complicating word ‘But.'” — Gordon Harvey, “The Elements of the Academic Essay”
“The data—facts, examples, or details—that you refer to, quote, or summarize to support your thesis. There needs to be enough evidence to be persuasive; it needs to be the right kind of evidence to support the thesis (with no obvious pieces of evidence overlooked); it needs to be sufficiently concrete for the reader to trust it (e.g. in textual analysis, it often helps to find one or two key or representative passages to quote and focus on); and if summarized, it needs to be summarized accurately and fairly.” –Gordon Harvey, “The Elements of the Academic Essay
“The work of breaking down, interpreting, and commenting upon the data, of saying what can be inferred from the data such that it supports a thesis (is evidence for something). Analysis is what you do with data when you go beyond observing or summarizing it: you show how its parts contribute to a whole or how causes contribute to an effect; you draw out the significance or implication not apparent to a superficial view. Analysis is what makes the writer feel present, as a reasoning individual; so your essay should do more analyzing than summarizing or quoting.” — Gordon Harvey, “The Elements of the Academic Essay”
“The recurring terms or basic oppositions that an argument rests upon, usually literal but sometimes a ruling metaphor. These terms usually imply certain assumptions—unstated beliefs about life, history, literature, reasoning, etc. that the essayist doesn’t argue for but simply assumes to be true. An essay’s keyterms should be clear in their meaning and appear throughout (not be abandoned half-way); they should be appropriate for the subject at hand (not unfair or too simple—a false or constraining opposition); and they should not be inert clichés or abstractions (e.g. “the evils of society”). The attendant assumptions should bear logical inspection, and if arguable they should be explicitly acknowledged.” — Gordon Harvey, “The Elements of the Academic Essay”
One of the most common issues we address in the writing center is the issue of structure. Many students never consciously address structure in the way that they consciously formulate a thesis. This is ironic because the two are inseparable – that is, the way you formulate an argument (structure) is essential to the argument itself (thesis). Thus, when emphasizing the importance of structure to students, it is important to remind them that structure cannot be developed in the absence of a strong thesis: you have to know what you’re arguing before you decide how to argue it.
As a writing tutor, your first task in addressing issues of structure will be to try and gauge if the student writer has an idea of what good structure looks like. Some students understand good structure, even if it’s just at an intuitive level, while others do not. If comprehension seems lacking, it may be useful to actually stop and explain what good structure looks like.
Some Ways of Thinking about Structure:
The structure of the paper should be progressive; the paper should “build” throughout. That is, there should be a logical order to the paper; each successive paragraph should build on the ideas presented in the last. In the writing center we are familiar with the scattershot essay in which the student throws out ten arguments to see what sticks. Such essays are characterized by weak or nonexistent transitions such as “My next point…” or “Another example of this…”.
Some students will understand structure better with the help of a metaphor. One particularly nice metaphor (courtesy of Dara) is to view the structure of an academic paper as a set of stairs. The paper begins with a small step; the first paragraph gives the most simple assumption or support for the argument. The paper then builds, slowly and gradually towards the top of the staircase. When the paper reaches its conclusion, it has brought the reader up to the top of the staircase to a point of new insight. From the balcony the reader can gaze out upon the original statement or question from higher ground.
How Gordon Harvey describes structure in his “Elements of the Academic Essay”:
“The sections should follow a logical order, and the links in that order should be apparent to the reader (see “stitching”). But it should also be a progressive order—there should have a direction of development or complication, not be simply a list or a series of restatements of the thesis (“Macbeth is ambitious: he’s ambitious here; and he’s ambitious here; and he’s ambitions here, too; thus, Macbeth is ambitious”). And the order should be supple enough to allow the writer to explore the topic, not just hammer home a thesis.”
“Words that tie together the parts of an argument, most commonly (a) by using transition (linking or turning) words as signposts to indicate how a new section, paragraph, or sentence follows from the one immediately previous; but also (b) by recollection of an earlier idea or part of the essay, referring back to it either by explicit statement or by echoing key words or resonant phrases quoted or stated earlier. The repeating of key or thesis concepts is especially helpful at points of transition from one section to another, to show how the new section fits in.” — Gordon Harvey, “The Elements of the Academic Essay”
Persons or documents, referred to, summarized, or quoted, that help a writer demonstrate the truth of his or her argument. They are typically sources of (a) factual information or data, (b) opinions or interpretation on your topic, (c) comparable versions of the thing you are discussing, or (d) applicable general concepts. Your sources need to be efficiently integrated and fairly acknowledged by citation.” — Gordon Harvey, “The Elements of the Academic Essay”
When you pause in your demonstration to reflect on it, to raise or answer a question about it—as when you (1) consider a counter-argument—a possible objection, alternative, or problem that a skeptical or resistant reader might raise; (2) define your terms or assumptions (what do I mean by this term? or, what am I assuming here?); (3) handle a newly emergent concern (but if this is so, then how can X be?); (4) draw out an implication (so what? what might be the wider significance of the argument I have made? what might it lead to if I’m right? or, what does my argument about a single aspect of this suggest about the whole thing? or about the way people live and think?), and (5) consider a possible explanation for the phenomenon that has been demonstrated (why might this be so? what might cause or have caused it?); (6) offer a qualification or limitation to the case you have made (what you’re not saying). The first of these reflections can come anywhere in an essay; the second usually comes early; the last four often come late (they’re common moves of conclusion).” — Gordon Harvey, “The Elements of the Academic Essay”
“Bits of information, explanation, and summary that orient the reader who isn’t expert in the subject, enabling such a reader to follow the argument. The orienting question is, what does my reader need here? The answer can take many forms: necessary information about the text, author, or event (e.g. given in your introduction); a summary of a text or passage about to be analyzed; pieces of information given along the way about passages, people, or events mentioned (including announcing or “set-up” phrases for quotations and sources). The trick is to orient briefly and gracefully.” — Gordon Harvey, “The Elements of the Academic Essay”
“The implied relationship of you, the writer, to your readers and subject: how and where you implicitly position yourself as an analyst. Stance is defined by such features as style and tone (e.g. familiar or formal); the presence or absence of specialized language and knowledge; the amount of time spent orienting a general, non-expert reader; the use of scholarly conventions of form and style. Your stance should be established within the first few paragraphs of your essay, and it should remain consistent.” — Gordon Harvey, “The Elements of the Academic Essay”
“The choices you make of words and sentence structure. Your style should be exact and clear (should bring out main idea and action of each sentence, not bury it) and plain without being flat (should be graceful and a little interesting, not stuffy).” — Gordon Harvey, “The Elements of the Academic Essay”
“It should both interest and inform. To inform—i.e. inform a general reader who might be browsing in an essay collection or bibliography—your title should give the subject and focus of the essay. To interest, your title might include a linguistic twist, paradox, sound pattern, or striking phrase taken from one of your sources (the aptness of which phrase the reader comes gradually to see). You can combine the interesting and informing functions in a single title or split them into title and subtitle. The interesting element shouldn’t be too cute; the informing element shouldn’t go so far as to state a thesis. Don’t underline your own title, except where it contains the title of another text.” — Gordon Harvey, “The Elements of the Academic Essay”
A student’s argument serves as the backbone to a piece of writing. Often expressed in the form of a one-sentence thesis statement, an argument forms the basis for a paper, defines the writer’s feelings toward a particular topic, and engages the reader in a discussion about a particular topic. Because an argument bears so much weight on the success of a paper, students may spend hours searching for that one, arguable claim that will carry them through to the assigned page limit. Formulating a decent argument about a text is tricky, especially when a professor does not distribute essay prompts—prompting students to come to the Writing Center asking that eternal question: “ What am I going to write about?!”
Formulating the Idea of an Argument (Pre-Writing Stage)
Before a student can begin drafting a paper, he or she must have a solid argument. Begin this process by looking at the writing assignment rubric and/or prompt assigned by the professor. If no particular prompt was assigned, ask the student what interests him or her in the class? Was there a reading assignment that was particularly compelling and/or interesting? Engage the student in a conversation about the class or the paper assignment with a pen and paper in their hand. When an interesting idea is conveyed, ask them to jot it down on a paper. Look for similarities or connections in their written list of ideas.
If a student is still lost, it’s helpful to remind them to remember to have a motive for writing. Besides working to pass a class or getting a good grade, what could inspire a student to write an eight page paper and enjoy the process? Relating the assigned class readings to incidents in a student’s own life often helps create a sense of urgency and need to write an argument. In an essay entitled “The Great Conversation (of the Dining Hall): One Student’s Experience of College-Level Writing,” student Kimberly Nelson remembers her passion for Tolkien fueled her to write a lengthy research paper and engage her friends in discussions concerning her topic (290).
Additional ideas for consultations during the pre-writing stage .
Formulating the Argument
The pre-writing stage is essential because arguments must “be limited enough in scope to be argued in a short composition” according to Harvey’s Elements of the Academic Essay . Narrow down the range of ideas so the student may write a more succinct paper with efficient language. When composing an argument (and later, a thesis), avoid definitive statements—arguments are arguable , and a great paper builds on a successive chain of ideas grounded in evidence to support an argument. It is of paramount importance to remind your student that the argument will govern the entire paper and not “disappear in places” (Harvey). When composing an actual paper, it’s helpful to Post-It note a summary of your argument on your computer screen to serve as a constant reminder of why you are writing.
Difficulties with Arguments and International Students
When international students arrive at Pomona College, they are often unsure of what the standard academic writing expectations are. If a student submits a draft to you devoid of any argument, it’s important to remember that the conventions of their home country may not match up to the standards we expect to see here. Some countries place more of an emphasis on a summary of ideas of others rather than generating entirely new arguments. If this is the case for your student, (gently) remind him or her that most Pomona College professors expect to see new arguments generated from the students and that “summary” papers are frowned upon. Don’t disparage their previous work—use the ideas present in their paragraphs as a launching point for crafting a new, creative argument.
“Students, like all writers, must fictionalize their audience.”
– Fred Pfister and Joanne Petrik, “A Heuristic Model for Creating a Writer’s Audience” (1980)
The main purpose of imagining or fictionalizing an audience is to allow the student to position his/her paper within the discourse and in conversation with other academics. By helping the student acknowledge the fact that both the writer (the student) and the reader (the audience) play a role in the writing process, the student will be better able to clarify and strengthen his/her argument.
Moreover, the practice of fictionalizing the audience should eventually help the student learn how to become his/her own reader. By adopting the role of both the writer and the reader, the student will be able to further develop his ability to locate his/her text in a discourse community.
During a consultation, you may notice that a student’s argument does not actually engage in a conversation with the members of its respective discourse community. If his/her paper does not refer to other texts or ask questions that are relevant to this particular discourse, you may need to ask the student to imagine who his/her audience is as well as what the audience’s reaction to the paper may look like.
Although the student’s immediate answer will most likely be his/her professor, you should advise the student to attempt imagining an audience beyond his/her class—an audience composed of people who are invested in this discourse or this specific topic.
If your student cannot imagine or fictionalize such an audience, it may be because the student may not believe that he/she know enough about the topic to address such a knowledgeable audience. In this case, you should advise the student to pretend that he/she is an expert on the topic or that the student’s paper will be published and read by other members of the discourse community.
The student, however, should not pander to the audience and “undervalue the responsibility that [he/she] has to [the] subject” (Ede and Lunsford, 1984). Advise him/her to avoid re-shaping the paper so that it merely caters to or appeases the audience.
- Good and bad News of The Elements of Style
Mailing Address
Pomona College 333 N. College Way Claremont , CA 91711
Get in touch
Give back to pomona.
Part of The Claremont Colleges
How to Write a Persuasive Essay (This Convinced My Professor!)
.png)
Table of contents

Meredith Sell
You can make your essay more persuasive by getting straight to the point.
In fact, that's exactly what we did here, and that's just the first tip of this guide. Throughout this guide, we share the steps needed to prove an argument and create a persuasive essay.
This AI tool helps you improve your essay > This AI tool helps you improve your essay >

Key takeaways: - Proven process to make any argument persuasive - 5-step process to structure arguments - How to use AI to formulate and optimize your essay
Why is being persuasive so difficult?
"Write an essay that persuades the reader of your opinion on a topic of your choice."
You might be staring at an assignment description just like this 👆from your professor. Your computer is open to a blank document, the cursor blinking impatiently. Do I even have opinions?
The persuasive essay can be one of the most intimidating academic papers to write: not only do you need to identify a narrow topic and research it, but you also have to come up with a position on that topic that you can back up with research while simultaneously addressing different viewpoints.
That’s a big ask. And let’s be real: most opinion pieces in major news publications don’t fulfill these requirements.
The upside? By researching and writing your own opinion, you can learn how to better formulate not only an argument but the actual positions you decide to hold.
Here, we break down exactly how to write a persuasive essay. We’ll start by taking a step that’s key for every piece of writing—defining the terms.

What Is a Persuasive Essay?
A persuasive essay is exactly what it sounds like: an essay that persuades . Over the course of several paragraphs or pages, you’ll use researched facts and logic to convince the reader of your opinion on a particular topic and discredit opposing opinions.
While you’ll spend some time explaining the topic or issue in question, most of your essay will flesh out your viewpoint and the evidence that supports it.
The 5 Must-Have Steps of a Persuasive Essay
If you’re intimidated by the idea of writing an argument, use this list to break your process into manageable chunks. Tackle researching and writing one element at a time, and then revise your essay so that it flows smoothly and coherently with every component in the optimal place.
1. A topic or issue to argue
This is probably the hardest step. You need to identify a topic or issue that is narrow enough to cover in the length of your piece—and is also arguable from more than one position. Your topic must call for an opinion , and not be a simple fact .
It might be helpful to walk through this process:
- Identify a random topic
- Ask a question about the topic that involves a value claim or analysis to answer
- Answer the question
That answer is your opinion.
Let’s consider some examples, from silly to serious:
Topic: Dolphins and mermaids
Question: In a mythical match, who would win: a dolphin or a mermaid?
Answer/Opinion: The mermaid would win in a match against a dolphin.
Topic: Autumn
Question: Which has a better fall: New England or Colorado?
Answer/Opinion: Fall is better in New England than Colorado.
Topic: Electric transportation options
Question: Would it be better for an urban dweller to buy an electric bike or an electric car?
Answer/Opinion: An electric bike is a better investment than an electric car.
Your turn: Walk through the three-step process described above to identify your topic and your tentative opinion. You may want to start by brainstorming a list of topics you find interesting and then going use the three-step process to find the opinion that would make the best essay topic.
2. An unequivocal thesis statement
If you walked through our three-step process above, you already have some semblance of a thesis—but don’t get attached too soon!
A solid essay thesis is best developed through the research process. You shouldn’t land on an opinion before you know the facts. So press pause. Take a step back. And dive into your research.
You’ll want to learn:
- The basic facts of your topic. How long does fall last in New England vs. Colorado? What trees do they have? What colors do those trees turn?
- The facts specifically relevant to your question. Is there any science on how the varying colors of fall influence human brains and moods?
- What experts or other noteworthy and valid sources say about the question you’re considering. Has a well-known arborist waxed eloquent on the beauty of New England falls?
As you learn the different viewpoints people have on your topic, pay attention to the strengths and weaknesses of existing arguments. Is anyone arguing the perspective you’re leaning toward? Do you find their arguments convincing? What do you find unsatisfying about the various arguments?
Allow the research process to change your mind and/or refine your thinking on the topic. Your opinion may change entirely or become more specific based on what you learn.
Once you’ve done enough research to feel confident in your understanding of the topic and your opinion on it, craft your thesis.
Your thesis statement should be clear and concise. It should directly state your viewpoint on the topic, as well as the basic case for your thesis.
Thesis 1: In a mythical match, the mermaid would overcome the dolphin due to one distinct advantage: her ability to breathe underwater.
Thesis 2: The full spectrum of color displayed on New England hillsides is just one reason why fall in the northeast is better than in Colorado.
Thesis 3: In addition to not adding to vehicle traffic, electric bikes are a better investment than electric cars because they’re cheaper and require less energy to accomplish the same function of getting the rider from point A to point B.
Your turn: Dive into the research process with a radar up for the arguments your sources are making about your topic. What are the most convincing cases? Should you stick with your initial opinion or change it up? Write your fleshed-out thesis statement.
3. Evidence to back up your thesis
This is a typical place for everyone from undergrads to politicians to get stuck, but the good news is, if you developed your thesis from research, you already have a good bit of evidence to make your case.
Go back through your research notes and compile a list of every …
… or other piece of information that supports your thesis.
This info can come from research studies you found in scholarly journals, government publications, news sources, encyclopedias, or other credible sources (as long as they fit your professor’s standards).
As you put this list together, watch for any gaps or weak points. Are you missing information on how electric cars versus electric bicycles charge or how long their batteries last? Did you verify that dolphins are, in fact, mammals and can’t breathe underwater like totally-real-and-not-at-all-fake 😉mermaids can? Track down that information.
Next, organize your list. Group the entries so that similar or closely related information is together, and as you do that, start thinking through how to articulate the individual arguments to support your case.
Depending on the length of your essay, each argument may get only a paragraph or two of space. As you think through those specific arguments, consider what order to put them in. You’ll probably want to start with the simplest argument and work up to more complicated ones so that the arguments can build on each other.
Your turn: Organize your evidence and write a rough draft of your arguments. Play around with the order to find the most compelling way to argue your case.
4. Rebuttals to disprove opposing theses
You can’t just present the evidence to support your case and totally ignore other viewpoints. To persuade your readers, you’ll need to address any opposing ideas they may hold about your topic.
You probably found some holes in the opposing views during your research process. Now’s your chance to expose those holes.
Take some time (and space) to: describe the opposing views and show why those views don’t hold up. You can accomplish this using both logic and facts.
Is a perspective based on a faulty assumption or misconception of the truth? Shoot it down by providing the facts that disprove the opinion.
Is another opinion drawn from bad or unsound reasoning? Show how that argument falls apart.
Some cases may truly be only a matter of opinion, but you still need to articulate why you don’t find the opposing perspective convincing.
Yes, a dolphin might be stronger than a mermaid, but as a mammal, the dolphin must continually return to the surface for air. A mermaid can breathe both underwater and above water, which gives her a distinct advantage in this mythical battle.
While the Rocky Mountain views are stunning, their limited colors—yellow from aspen trees and green from various evergreens—leaves the autumn-lover less than thrilled. The rich reds and oranges and yellows of the New England fall are more satisfying and awe-inspiring.
But what about longer trips that go beyond the city center into the suburbs and beyond? An electric bike wouldn’t be great for those excursions. Wouldn’t an electric car be the better choice then?
Certainly, an electric car would be better in these cases than a gas-powered car, but if most of a person’s trips are in their hyper-local area, the electric bicycle is a more environmentally friendly option for those day-to-day outings. That person could then participate in a carshare or use public transit, a ride-sharing app, or even a gas-powered car for longer trips—and still use less energy overall than if they drove an electric car for hyper-local and longer area trips.
Your turn: Organize your rebuttal research and write a draft of each one.
5. A convincing conclusion
You have your arguments and rebuttals. You’ve proven your thesis is rock-solid. Now all you have to do is sum up your overall case and give your final word on the subject.
Don’t repeat everything you’ve already said. Instead, your conclusion should logically draw from the arguments you’ve made to show how they coherently prove your thesis. You’re pulling everything together and zooming back out with a better understanding of the what and why of your thesis.
A dolphin may never encounter a mermaid in the wild, but if it were to happen, we know how we’d place our bets. Long hair and fish tail, for the win.
For those of us who relish 50-degree days, sharp air, and the vibrant colors of fall, New England offers a season that’s cozier, longer-lasting, and more aesthetically pleasing than “colorful” Colorado. A leaf-peeper’s paradise.
When most of your trips from day to day are within five miles, the more energy-efficient—and yes, cost-efficient—choice is undoubtedly the electric bike. So strap on your helmet, fire up your pedals, and two-wheel away to your next destination with full confidence that you made the right decision for your wallet and the environment.
3 Quick Tips for Writing a Strong Argument
Once you have a draft to work with, use these tips to refine your argument and make sure you’re not losing readers for avoidable reasons.
1. Choose your words thoughtfully.
If you want to win people over to your side, don’t write in a way that shuts your opponents down. Avoid making abrasive or offensive statements. Instead, use a measured, reasonable tone. Appeal to shared values, and let your facts and logic do the hard work of changing people’s minds.
Choose words with AI

You can use AI to turn your general point into a readable argument. Then, you can paraphrase each sentence and choose between competing arguments generated by the AI, until your argument is well-articulated and concise.
2. Prioritize accuracy (and avoid fallacies).
Make sure the facts you use are actually factual. You don’t want to build your argument on false or disproven information. Use the most recent, respected research. Make sure you don’t misconstrue study findings. And when you’re building your case, avoid logical fallacies that undercut your argument.
A few common fallacies to watch out for:
- Strawman: Misrepresenting or oversimplifying an opposing argument to make it easier to refute.
- Appeal to ignorance: Arguing that a certain claim must be true because it hasn’t been proven false.
- Bandwagon: Assumes that if a group of people, experts, etc., agree with a claim, it must be true.
- Hasty generalization: Using a few examples, rather than substantial evidence, to make a sweeping claim.
- Appeal to authority: Overly relying on opinions of people who have authority of some kind.
The strongest arguments rely on trustworthy information and sound logic.
Research and add citations with AI

We recently wrote a three part piece on researching using AI, so be sure to check it out . Going through an organized process of researching and noting your sources correctly will make sure your written text is more accurate.
3. Persuasive essay structure

If you’re building a house, you start with the foundation and go from there. It’s the same with an argument. You want to build from the ground up: provide necessary background information, then your thesis. Then, start with the simplest part of your argument and build up in terms of complexity and the aspect of your thesis that the argument is tackling.
A consistent, internal logic will make it easier for the reader to follow your argument. Plus, you’ll avoid confusing your reader and you won’t be unnecessarily redundant.
The essay structure usually includes the following parts:
- Intro - Hook, Background information, Thesis statement
- Topic sentence #1 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence
- Topic sentence #2 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence Topic sentence #3 , with supporting facts or stats
- Conclusion - Thesis and main points restated, call to action, thought provoking ending
Are You Ready to Write?
Persuasive essays are a great way to hone your research, writing, and critical thinking skills. Approach this assignment well, and you’ll learn how to form opinions based on information (not just ideas) and make arguments that—if they don’t change minds—at least win readers’ respect.
Share This Article:

How to Properly Conduct Research with AI: Tools, Process, and Approach

What’s a Double Negative? + How To Fix It

The Official Wordtune Guide
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Elements of a Research Essay
Stephanie Ojeda Ponce
This section is an overview of the elements or parts of a research essay. Scholarly essays are long. There are several different styles of research essays and each have their own structure. For the argument-driven research essay, these are the main elements:
- Purpose or research question
- Your claim or thesis.
- One or more reasons for your thesis.
- Evidence for each reason.
- Others’ objections, counterarguments, or alternative solutions.
- Your acknowledgment of others’ objections, counterarguments, or alternative solutions.
- Your response to others’ objections, counterarguments, or alternative solutions.
The Purpose or Goal
Sometimes your professor will give you the research question, but probably more often you will need to develop your own research topic. Even though you are likely writing an essay for an assignment or as part of a class, you are also developing your own purpose for the research and writing. This part of the essay may not be written down, but it can be helpful to keep in mind a purpose or overall question. That question might even be something you answer through your research, but don’t have
Examples: Purpose and Goal for Research Essays
- How do at least some animals’ bones help control their weight?
- Did the death of his beloved daughter have any effect on the writings of Mark Twain?
Your Claim or Thesis
You write the claim or thesis–it doesn’t come directly from a source. Instead, it is the conclusion you come to in answer to your question after you’ve read/listened to/viewed some sources. So it is a statement, not a question or a hypothesis that you plan to prove or disprove with your research.
After you’ve read/listened to/viewed more sources, you may need to change your thesis. That happens all the time–not because you did anything wrong but because you learned more.
Examples: Claims (or Theses) for Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers
- Bone cells monitor whether more or less weight is pressing down on the skeleton and send biochemical signals to appetite centers in their brains to turn appetite down or up, accordingly.
- Mark Twain wrote more urgently and with less humor during the four years immediately after the death of his daughter.
One or More Reasons
You write what you believe makes your claim or thesis (the answer to your research question) true. That’s your reason or reasons. Each reason is a summary statement of evidence you found in your research. The kinds of evidence considered convincing varies by discipline, so you will be looking at different sources, depending on your discipline. How many reasons you need depends on how complex your thesis and subject matter are, what you found in your sources, and how long your essay or research paper must be. It’s always a good idea to write your reasons in a way that is easy for your audience to understand and be persuaded by.
Examples: Reasons in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers
- Animals (including humans) have a biological tendency to regain any weight that they lose and lose any weight that they gain, seemingly in an effort to maintain whatever weight they have sustained for some time. Skeletons are logical places where any gains or losses could be noted, and recent studies seem to show that osteocytes (a kind of bone cell) are involved in whether appetites go up or down after weight gain or loss.
- My content analysis and a comparison of publication rates four years before and after Mark Twain’s daughter died indicate that his writing was more urgent and less humorous for four years after. It is reasonable to conclude that her death caused that change.
Evidence for Each Reason
You write this also. This is the evidence you summarized earlier as each reason your thesis is true. You will be directly quoting, paraphrasing, and summarizing your sources to make the case that your answer to your research question is correct, or at least reasonable.
Examples: Evidence for Reasons in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers
- Report the results of studies about osteocyctes’ possible effect on weight grain or loss.
- Report the results of your comparison of writing content and publication rate before and after Twain’s daughter’s death.
Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions
Do any of your sources not agree with your thesis? You’ll have to bring those up in your research paper. In addition, put yourself in your readers’ shoes. What might they not find logical in your argument? In other words, which reason(s) and corresponding evidence might they find lacking? Did you find clues to what these could be in your sources? Or maybe you can imagine them thinking some aspect of what you think is evidence doesn’t make sense.
Examples: Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers
- Imagine that some readers might think: The hormone leptin is released by fat cells when they are added to animals’ bodies so it is leptin that tells appetite centers to turn down when weight is gained.
- Imagine that some readers might think: Computerized content analysis tools are sort of blunt instruments and shouldn’t be used to do precise work like this.
Your Acknowledgement of Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions
So what will you write to bring up each of those objections, counterarguments, and alternative solutions? Some examples:
- I can imagine skeptics wanting to point out…
- Perhaps some readers would say…
- I think those who come from XYZ would differ with me…
It all depends on what objections, counterarguments, and alternative solutions your audience or your imagination come up with.
Examples: Acknowledgement of Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers:
- Some readers may point out that the hormone leptin, which is released by fat cells, signals appetite centers to lower the appetite when weight is gained.
- Readers may think that a computerized content analysis tool cannot do justice to the subtleties of text.
Response to Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions
You must write your response to each objection, counterargument, or alternative solution brought up or that you’ve thought of. (You’re likely to have found clues for what to say in your sources.) The reason you have to include this is that you can’t very easily convince your audience until you show them how your claim stacks up against the opinions and reasoning of other people who don’t at the moment agree with you.
Examples: Response to Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers:
- But leptin must not be the entire system, since many animals do keep on the new weight.
- Unlike other content tools, the XYZ Content Analysis Measure is able to take into account an author’s tone.
Adaptations
This page has been adapted from Where you Get the Components from Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research Copyright © 2015 by Teaching & Learning, Ohio State University Libraries. CC BY 4.0 DEED .
Reading and Writing Research for Undergraduates Copyright © 2023 by Stephanie Ojeda Ponce is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- I nfographics
- Show AWL words
- Subscribe to newsletter
- What is academic writing?
- Academic Style
- What is the writing process?
- Understanding the title
- Brainstorming
- Researching
- First draft
- Proofreading
- Report writing
- Compare & contrast
- Cause & effect
- Problem-solution
- Classification
- Essay structure
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Book review
- Research proposal
- Thesis/dissertation
- What is cohesion?
- Cohesion vs coherence
- Transition signals
- What are references?
- In-text citations
- Reference sections
- Reporting verbs
- Band descriptors
Show AWL words on this page.
Levels 1-5: grey Levels 6-10: orange
Show sorted lists of these words.
Any words you don't know? Look them up in the website's built-in dictionary .
Choose a dictionary . Wordnet OPTED both
Introduction How to get an essay started
Getting started can often be difficult. Even professional writers say that the hardest part of writing is the beginning. Writing an introduction to an essay can therefore seem a daunting task, though it need not be so difficult, as long as you understand the purpose and the structure of the introduction. An example essay has been given to help you understand both of these, and there is a checklist at the end which you can use for editing your introduction.
Purpose of the introduction
When writing an introduction to an academic essay, it is useful to remember the main purpose of the introduction. In general, the introduction will introduce the topic to the reader by stating what the topic is and giving some general background information. This will help the reader to understand what you are writing about, and show why the topic is important. The introduction should also give the overall plan of the essay.
In short, the main purpose of the introduction is to:
- introduce the topic of the essay;
- give a general background of the topic;
- indicate the overall plan of the essay.
This last purpose is perhaps the most important, and is the reason why many writers choose to write the introduction last , after they have written the main body , because they need to know what the essay will contain before they can give a clear plan.
Structure of the introduction
Although essays vary in length and content, most essays will have the same overall structure, including the introduction. The structure is related to the purpose mentioned above. The introduction to an essay should have the following two parts:
- general statements (to introduce the topic and give the background);
- a thesis statement (to show the structure).
General statements
The general statements will introduce the topic of the essay and give background information. The background information for a short essay will generally just be one or two sentences. The general statements should become more and more specific thesis statement , which is the most specific sentence of the introduction--> as the introduction progresses, leading the reader into the essay (some writers talk about "attracting the readers' attention", though for an academic essay, this is less important). For longer essays, the general statements could include one or more definitions , or could classify the topic, and may cover more than one paragraph.
The following is an example of background statements for a short essay ( given below ):
Although they were invented almost a hundred years ago, for decades cars were only owned by the rich. Since the 60s and 70s they have become increasingly affordable, and now most families in developed nations, and a growing number in developing countries, own a car.
These sentences introduce the topic of the essay (cars) and give some background to this topic (situation in the past, the situation now). These sentences lead nicely into the thesis statement (see below).
Thesis statement
The thesis statement is the most important part of the introduction. It gives the reader clear information about the content of the essay, which will help them to understand the essay more easily. The thesis states the specific topic, and often lists the main (controlling) ideas that will be discussed in the main body. It may also indicate how the essay will be organised, e.g. in chronological order, order of importance, advantages/disadvantages, cause/effect. It is usually at the end of the introduction, and is usually (but not always) one sentence long.
In short, the thesis statement:
- states the specific topic of the essay;
- often lists the main (controlling) ideas of the essay;
- may indicate the method of organisation of the essay;
- is usually at the end of the introduction;
- is usually one sentence.
Here is an example of a thesis statement with no subtopics mentioned:
While cars have undoubted advantages, they also have significant drawbacks.
This thesis statement tells us the specific topic of the essay (advantages and disadvantages of cars) and the method of organisation (advantages should come first, disadvantages second). It is, however, quite general, and may have been written before the writer had completed the essay.
In the following thesis statement, the subtopics are named:
While cars have undoubted advantages, of which their convenience is the most apparent, they have significant drawbacks, most notably pollution and traffic problems.
This thesis gives us more detail, telling us not just the topic (advantages and disadvantages of cars) and the method of organisation (advantages first, disadvantages second), but also tells us the main ideas in the essay (convenience, pollution, traffic problems). This essay will probably have three paragraphs in the main body.
Example essay
Below is a discussion essay which looks at the advantages and disadvantages of car ownership. This essay is used throughout the essay writing section to help you understand different aspects of essay writing. Here it focuses on the thesis statement and general statements of the introduction (mentioned on this page), topic sentences , controlling ideas, and the summary and final comment of the conclusion. Click on the different areas (in the shaded boxes to the right) to highlight the different structural aspects in this essay.
Although they were invented almost a hundred years ago, for decades cars were only owned by the rich. Since the 60s and 70s they have become increasingly affordable, and now most families in developed nations, and a growing number in developing countries, own a car. While cars have undoubted advantages, of which their convenience is the most apparent, they have significant drawbacks, most notably pollution and traffic problems . The most striking advantage of the car is its convenience. When travelling long distance, there may be only one choice of bus or train per day, which may be at an unsuitable time. The car, however, allows people to travel at any time they wish, and to almost any destination they choose. Despite this advantage, cars have many significant disadvantages, the most important of which is the pollution they cause. Almost all cars run either on petrol or diesel fuel, both of which are fossil fuels. Burning these fuels causes the car to emit serious pollutants, such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and nitrous oxide. Not only are these gases harmful for health, causing respiratory disease and other illnesses, they also contribute to global warming, an increasing problem in the modern world. According to the Union of Concerned Scientists (2013), transportation in the US accounts for 30% of all carbon dioxide production in that country, with 60% of these emissions coming from cars and small trucks. In short, pollution is a major drawback of cars. A further disadvantage is the traffic problems that they cause in many cities and towns of the world. While car ownership is increasing in almost all countries of the world, especially in developing countries, the amount of available roadway in cities is not increasing at an equal pace. This can lead to traffic congestion, in particular during the morning and evening rush hour. In some cities, this congestion can be severe, and delays of several hours can be a common occurrence. Such congestion can also affect those people who travel out of cities at the weekend. Spending hours sitting in an idle car means that this form of transport can in fact be less convenient than trains or aeroplanes or other forms of public transport. In conclusion, while the car is advantageous for its convenience , it has some important disadvantages, in particular the pollution it causes and the rise of traffic jams . If countries can invest in the development of technology for green fuels, and if car owners can think of alternatives such as car sharing, then some of these problems can be lessened.
Union of Concerned Scientists (2013). Car Emissions and Global Warming. www.ucsusa.org/clean vehicles/why-clean-cars/global-warming/ (Access date: 8 August, 2013)

GET FREE EBOOK
Like the website? Try the books. Enter your email to receive a free sample from Academic Writing Genres .
Below is a checklist for an essay introduction. Use it to check your own writing, or get a peer (another student) to help you.
Next section
Find out how to structure the main body of an essay in the next section.
Previous section
Go back to the previous section about essay structure .

Author: Sheldon Smith ‖ Last modified: 26 January 2022.
Sheldon Smith is the founder and editor of EAPFoundation.com. He has been teaching English for Academic Purposes since 2004. Find out more about him in the about section and connect with him on Twitter , Facebook and LinkedIn .
Compare & contrast essays examine the similarities of two or more objects, and the differences.
Cause & effect essays consider the reasons (or causes) for something, then discuss the results (or effects).
Discussion essays require you to examine both sides of a situation and to conclude by saying which side you favour.
Problem-solution essays are a sub-type of SPSE essays (Situation, Problem, Solution, Evaluation).
Transition signals are useful in achieving good cohesion and coherence in your writing.
Reporting verbs are used to link your in-text citations to the information cited.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
- Academic Paragraph Structure | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Academic Paragraph Structure | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on October 25, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on March 27, 2023.
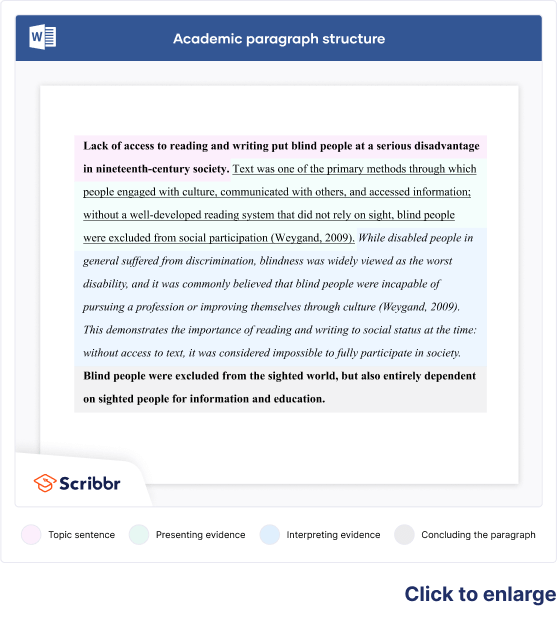
Every piece of academic writing is structured by paragraphs and headings . The number, length and order of your paragraphs will depend on what you’re writing—but each paragraph must be:
- Unified : all the sentences relate to one central point or idea.
- Coherent : the sentences are logically organized and clearly connected.
- Relevant : the paragraph supports the overall theme and purpose of the paper.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: identify the paragraph’s purpose, step 2: show why the paragraph is relevant, step 3: give evidence, step 4: explain or interpret the evidence, step 5: conclude the paragraph, step 6: read through the whole paragraph, when to start a new paragraph.
First, you need to know the central idea that will organize this paragraph. If you have already made a plan or outline of your paper’s overall structure , you should already have a good idea of what each paragraph will aim to do.
You can start by drafting a sentence that sums up your main point and introduces the paragraph’s focus. This is often called a topic sentence . It should be specific enough to cover in a single paragraph, but general enough that you can develop it over several more sentences.
Although the Braille system gained immediate popularity with the blind students at the Institute in Paris, it had to gain acceptance among the sighted before its adoption throughout France.
This topic sentence:
- Transitions from the previous paragraph (which discussed the invention of Braille).
- Clearly identifies this paragraph’s focus (the acceptance of Braille by sighted people).
- Relates to the paper’s overall thesis.
- Leaves space for evidence and analysis.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The topic sentence tells the reader what the paragraph is about—but why does this point matter for your overall argument? If this isn’t already clear from your first sentence, you can explain and expand on its meaning.
This support was necessary because sighted teachers and leaders had ultimate control over the propagation of Braille resources.
- This sentence expands on the topic and shows how it fits into the broader argument about the social acceptance of Braille.
Now you can support your point with evidence and examples. “Evidence” here doesn’t just mean empirical facts—the form it takes will depend on your discipline, topic and approach. Common types of evidence used in academic writing include:
- Quotations from literary texts , interviews , and other primary sources .
- Summaries , paraphrases , or quotations of secondary sources that provide information or interpretation in support of your point.
- Qualitative or quantitative data that you have gathered or found in existing research.
- Descriptive examples of artistic or musical works, events, or first-hand experiences.
Make sure to properly cite your sources .
Many of the teachers at the Royal Institute for Blind Youth resisted Braille’s system because they found the tactile method of reading difficult to learn (Bullock & Galst, 2009).
- This sentence cites specific evidence from a secondary source , demonstrating sighted people’s reluctance to accept Braille.
Now you have to show the reader how this evidence adds to your point. How you do so will depend on what type of evidence you have used.
- If you quoted a passage, give your interpretation of the quotation.
- If you cited a statistic, tell the reader what it implies for your argument.
- If you referred to information from a secondary source, show how it develops the idea of the paragraph.
This resistance was symptomatic of the prevalent attitude that the blind population had to adapt to the sighted world rather than develop their own tools and methods.
- This sentence adds detail and interpretation to the evidence, arguing that this specific fact reveals something more general about social attitudes at the time.
Steps 3 and 4 can be repeated several times until your point is fully developed. Use transition words and phrases to show the connections between different sentences in the paragraph.
Over time, however, with the increasing impetus to make social contribution possible for all, teachers began to appreciate the usefulness of Braille’s system (Bullock & Galst, 2009). Access to reading could help improve the productivity and integration of people with vision loss.
- The evidence tells us about the changing attitude to Braille among the sighted.
- The interpretation argues for why this change occurred as part of broader social shifts.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Finally, wrap up the paragraph by returning to your main point and showing the overall consequences of the evidence you have explored.
This particular paragraph takes the form of a historical story—giving evidence and analysis of each step towards Braille’s widespread acceptance.
It took approximately 30 years, but the French government eventually approved the Braille system, and it was established throughout the country (Bullock & Galst, 2009).
- The final sentence ends the story with the consequences of these events.
When you think you’ve fully developed your point, read through the final result to make sure each sentence follows smoothly and logically from the last and adds up to a coherent whole.
Although the Braille system gained immediate popularity with the blind students at the Institute in Paris, it had to gain acceptance among the sighted before its adoption throughout France. This support was necessary because sighted teachers and leaders had ultimate control over the propagation of Braille resources. Many of the teachers at the Royal Institute for Blind Youth resisted learning Braille’s system because they found the tactile method of reading difficult to learn (Bullock & Galst, 2009). This resistance was symptomatic of the prevalent attitude that the blind population had to adapt to the sighted world rather than develop their own tools and methods. Over time, however, with the increasing impetus to make social contribution possible for all, teachers began to appreciate the usefulness of Braille’s system (Bullock & Galst, 2009). Access to reading could help improve the productivity and integration of people with vision loss. It took approximately 30 years, but the French government eventually approved the Braille system, and it was established throughout the country (Bullock & Galst, 2009).
Not all paragraphs will look exactly like this. Depending on what your paper aims to do, you might:
- Bring together examples that seem very different from each other, but have one key point in common.
- Include just one key piece of evidence (such as a quotation or statistic) and analyze it in depth over several sentences.
- Break down a concept or category into various parts to help the reader understand it.
The introduction and conclusion paragraphs will also look different. The only universal rule is that your paragraphs must be unified , coherent and relevant . If you struggle with structuring your paragraphs, you could consider using a paper editing service for personal, in-depth feedback.
As soon as you address a new idea, argument or issue, you should start a new paragraph. To determine if your paragraph is complete, ask yourself:
- Do all your sentences relate to the topic sentence?
- Does each sentence make logical sense in relation to the one before it?
- Have you included enough evidence or examples to demonstrate your point?
- Is it clear what each piece of evidence means and why you have included it?
- Does all the evidence fit together and tell a coherent story?
Don’t think of paragraphs as isolated units—they are part of a larger argument that should flow organically from one point to the next. Before you start a new paragraph, consider how you will transition between ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, March 27). Academic Paragraph Structure | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/paragraph-structure/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, example of a great essay | explanations, tips & tricks, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, transition words & phrases | list & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
thus, Macbeth is ambitious") or list of elements found in the text. And the order should be supple enough to allow the writer to explore the topic, not just ham-mer home a thesis. (If the essay is complex or long, its structure may be briefly announced or hinted at after the thesis, in a road-map or plan sentence—or even in
In essays, arguments are almost always presented in a hierarchical relationship.3 The thesis statement is the highest level argument. Evidence, which may fall into categories that warrant their own paragraphs, is the next level. Details within each piece of evidence are the next level. You can display—and discover—relationships among your ...
Definition of Elements of an Essay. An essay is a piece of composition that discusses a thing, a person, a problem, or an issue in a way that the writer demonstrates his knowledge by offering a new perspective, a new opinion, a solution, or new suggestions or recommendations.An essay is not just a haphazard piece of writing. It is a well-organized composition comprising several elements that ...
What are the 5 parts of an essay? Explore how the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion parts of an essay work together. Dictionary Thesaurus Sentences ... three body paragraphs, and a conclusion paragraph, and they will always have that structure. With such a stable form, a writer truly only needs to worry about the contents of the ...
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement, a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas. The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ...
Revised on July 23, 2023. An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph, giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold. You'll sometimes be asked to submit an essay outline as a separate ...
High-flow topic sentences should look to include three key elements: An explicit reference to the topic of the essay. A reference to the main aspect of the previous paragraph; An introduction to the topic of the new paragraph; Consider the following examples of topic sentences in response to an essay question about Virtue Ethics.
Most essays follow a similar structure, including an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, as shown in the diagram below. Click on the plus icons for more information. Note. There is no set requirement for the number of paragraphs in an essay. The important point is that the argument is logically developed through a series of well ...
Your stance should be established within the first few paragraphs of your essay, and it should remain consistent. Style: the choices you make of words and sentence structure. Your style should be exact and clear (should bring out main idea and action of each sentence, not bury it) and plain without being flat (should be graceful and a little ...
Whether you are writing a narrative essay or trying your hand at an argumentative one, it is necessary to set up a structure where relevant things are aligned perfectly with their intended purpose. Three major elements constitute the whole essay: Introduction/ Opening. Main Body. Closing/ Conclusion.
Here are some general thoughts before you get started. A good essay is well-organized and structured. Good essays have a clear introduction, thesis, and conclusion. Body paragraphs in the essay connect back to the thesis. Essays should be cohesive and have a good flow. We can create this flow by using transition words and phrases to connect one ...
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement, a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas. The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ...
The "Elements of the Academic Essay" is a taxonomy of academic writing by Gordon Harvey. It identifies the key components of academic writing across the disciplines and has been widely influential. ... One of the most common issues we address in the writing center is the issue of structure. Many students never consciously address structure ...
The 5 Must-Have Steps of a Persuasive Essay. If you're intimidated by the idea of writing an argument, use this list to break your process into manageable chunks. Tackle researching and writing one element at a time, and then revise your essay so that it flows smoothly and coherently with every component in the optimal place. 1.
There are several different styles of research essays and each have their own structure. For the argument-driven research essay, these are the main elements: Purpose or research question. Your claim or thesis. One or more reasons for your thesis. Evidence for each reason. Others' objections, counterarguments, or alternative solutions.
The structure of an essay depends on the type, but it usually is written in first or third person, and, according to Toulmin, it can be broken down into these parts: Warrants: The general ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Getting started can often be difficult. Even professional writers say that the hardest part of writing is the beginning. Writing an introduction to an essay can therefore seem a daunting task, though it need not be so difficult, as long as you understand the purpose and the structure of the introduction. An example essay has been given to help you understand both of these, and there is a ...
Understanding these elements will enable you to structure your essay well, so you can write the most significant details from start to finish. Key Takeaways. A comprehensive argumentative essay must feature the following elements: Thesis statement: A thesis statement gives a summary of the main claim of the subject. Instead of being a fact or ...
Step 1: Identify the paragraph's purpose. First, you need to know the central idea that will organize this paragraph. If you have already made a plan or outline of your paper's overall structure, you should already have a good idea of what each paragraph will aim to do.. You can start by drafting a sentence that sums up your main point and introduces the paragraph's focus.