- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000

e-Governance – applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential
Last updated on March 8, 2024 by ClearIAS Team

What is e-governance? Why is it needed? What are the challenges? Is there any government initiatives? To answer these questions, read further.
e-Governance is the use of information and communication technology (ICT) to provide government services, exchange information, conduct transactions, and integrate previously existing services and information portals.
The “e” in “e-Governance” refers for “electronic.”
The Government of India’s Mission e-Governance, in combination with Digital India, has undergone a paradigm shift.
There is new thinking about how it engages with its citizens, as well as inter-state and inter-governmental functions.
India has put healthcare, e-education, agricultural assistance, financial services, and other economic and social obligations on the mission.
e-governance includes the Digital India initiative, the National Portal of India, the Prime Minister of India’s portal, Aadhaar, online tax filing and payment, digital land management systems, the Common Entrance Test, and so on.
India has undertaken numerous initiatives over the years to promote e-Governance holistically and improve the distribution of public services to its citizens. Its main pillars have been people, processes, technology, and resources.
Table of Contents
Need for e-governance
E-government is the use of information and communication technology (ICT) in government services to increase the effectiveness of communication and transactions between citizens, businessman, and the government.
For government
It saves the cost of physical monitoring and administration and thus leads to cost saving for the government. Now there will be efficient usage of public funds as they will be less prone to neglect and waste expenses.
Join Now: CSAT Course
It will remove the barriers and make the government better at administration and thus result in better governance.
It will increase the data collection and thus will help the administration in better evaluation, implementation, and better scheme outcomes.
Public policies result in better outcomes and hence public trust in administration will also increase with the reduced gap because of minimum government and maximum governance.
Increased accountability, coordination, and communication will arise from efficient file transfers and work delegation.
It will lead to better accessibility as the online resources are easier to find and thus the issues of loss and duplication will be reduced.

Additionally, it will lower the time and resource costs associated with transactions between the government and its citizens.
For Citizens
It will empower the citizens to hold the government accountable for their work and policies, and thus increased transparency will lead to an empowered citizenry, as the digital services due to their inclusivity goes beyond the geographical barriers and thus increases the scope of governance.
e-Governance leads to speedy justice delivery and resolves grievances faster and thus increasing the public trust and faith in the governance system.
e-Governance reduces the gap between the citizens and the government to a large extent, especially those who are vulnerable and historically lacked access like women, Dalits, and tribals.
Women-centric schemes are better implemented and the data collection, on the implementation of schemes, crimes prevailing, trends followed, etc are better gathered through e governance, same is true for other sections of society.
For Business
It helps in ease of doing business by making the compliance and performance better. With digital resources the businesses can now expand their market and client base beyond the geographical barriers and thus leading to the country’s growth and development and balance of trade.
With a paperless economy and fewer physical requirements the process of setting, maintaining, and coordinating businesses have become better and faster and thus results in reduced delays.
It helps in the implementation and formation of government policies and their objectives by promoting productivity gains inherent in the ICT thus resulting in the development of all.
Challenges of e-Governance
There will always be the risk of cybercrime and the private data of individuals and the state to be stolen. Along with this, there is a high cost of setting up the machines. The maintenance of such machines is also too high, making regular maintenance costs high. And many times the computers and the internet also break down resulting in delays in work.
Rural and remote areas of India still lack digital infrastructure and there persists the problem of the digital divide. Very less number of women have access to the internet, especially elderly women who don’t have proper access and understanding of the digital world.
It results in the loss of interpersonal relations, communications and the personal touch is missing which many people still consider very vital. Because of this and the change in the old system shows signs of many people being reluctant to its application.
There is a lack of uniformity as the different states follow different methods, lack of authority in dealing with the e-governance system, and not all state governments are following the same policy on digitalization.
Mostly all the e-governance applications and websites are available in English which is not understood by all and thus results in a language barrier issue.
India has a low literacy rate and even among that literate people very few are still not comfortable and have knowledge of information technology.
Government Initiatives
Health: Sugamya Bharat app, aarogya setu app, vaccine tracker, electronic health record, mera aspataal, swasth Bharat app, etc.
Women: NARI portal, SHe Box, HIMMAT app, Mahila e Haat etc.
Education: Swayam Prabha, DIKSHA portal, National digital library of India, SWAYAM, etc
Agriculture: Kisan call centers, Agriculture mission mode project, AGMARKNET, etc.
Government service and monitoring: Digital India , Aadhar, Digi Locker, UMANG, PRAGATI, e KRANTI, Lokvani, etc.
Way Forward
There is an urgent need for investment both from outside and internally from the government.
There is a need for active participation in civil society and for private sector involvement in innovation and management, especially those involved in the technology and the tech giants.
Make in India should be promoted as we should not rely on imports solely. Cloud computing is a way forward and Meghraj GI Cloud is a step in the right direction.
2nd ARC has also recommended that the state should create suitable opportunities for e-governance initiatives, public-private partnerships, re-engineering of the governance mechanisms, and skill development for both creating, maintaining, and monitoring to ensure the best outcomes.
Former Indian President Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam defined e-Governance in the Indian context as “a transparent smart Governance with seamless access, secure and authentic flow of information crossing the interdepartmental barrier and providing a fair and unbiased service to the citizen.”
Article written by Chetna Yadav.

Take a Test: Analyse Your Progress
Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?
About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
E-Governance
Introduction:
E-Governance, according to the 2nd Administrative Reform Commission (ARC) Report, is primarily related to carrying out governance tasks and achieving governance outcomes through the use of what is today known as ICT (information and communication technology).
Need for e-Governance
- Effective adoption of E-Governance initiatives may result in less corruption , improved accountability , greater convenience , revenue gains , and/or cost savings.
- The goal of implementing e-governance is to improve performance and assure proper service delivery.
- This will be accomplished through the use of five "SMART" e-governance characteristics.

- Rising numbers of mobile phone users and data consumption: According to a Nokia report, average data consumption per user in India reached 19.5GB per user a month in 2022.
- Due to the rising availability and falling cost of high-speed broadband and smartphones, India likely to have 900 million active internet users by 2025.
- Success of Digital India mission and eKranti : To help millions connect online, the Digital India programme is providing broadband internet to 250,000 gram panchayats.
- Rising eCommerce and digital economy : India is poised for the next phase of growth, creating tremendous economic value and empowering citizens as new digital applications permeate sector after sector.
- India's digital economy might generate $1 trillion in 2025.
- JAM trinity : 1.21 billion Indians enlisted in the government's biometric digital identity initiative.
- Jan Dhan Yojana and other government initiatives have enabled banking, pension (PMSBY and PMJJBY), and insurance (Atal Pension Yojana) services for average folks, digitally empowering them.

- Improved service delivery: The new India has pioneered e-government, using ICT for elections, census, computerising government offices , digi lockers, e-transportation, e-health, e-education, and e-taxation.
- Through MC21 data, corporates and other stakeholders will have convenient and secure online access to all registry-related services provided by the Union Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- Improve industry-business interaction : E-governance accelerates industrial growth processes.
- De-bureaucratization : E-governance narrows the distance between the people and the government in all services and reduces the people's dependence on the bureaucracy.
- Reducing corruption : E-governance tracked government activity online, eliminating corruption.
- Linking AADHAR with MGNREGA daily wage payments helped to eliminate bogus beneficiaries and reducing corruption.
- Hierarchy Elimination : ICT involved all levels in decision-making.
- Plug leakages : The e-governance ecosystem has helped the union government to plug about $27 billion in leakage by digitally transferring money via DBT.
- Automation in Administrative Processes: To eliminate the Great Indian Red Tape, Saharsa became Bihar's first paperless (e-office) district.
Challenges with e-Governance:
- Trust deficit : Any entity may commit financial, value, or personal information fraud. Departmental data is sometimes overlooked in government offices.
- Digital divide : According to the India Inequality Report 2022: Digital Divide by Oxfam, the richest 60 per cent Indians are four times more likely to use digital payment facilities than the poorest 40 per cent.
- Adoption Cost : India spends 3% of GDP on the implementation of e-governance initiatives. The government should encourage officials, administrators, and citizens to use e-governance services by using public funds wisely.
- Privacy and Security and infrastructure related issues.
- Hackers released all CoWIN data on Telegram.
- Screenshots of the data contained names, mobile numbers, Aadhaar card details, PAN card credentials, date of birth, and vaccination centre information. Some passport details were leaked.

- Accessibility : According to the India Inequality Report 2022: Digital Divide by Oxfam, access to the internet through any kind of device was found to be far better in urban India at 44 percent than in rural areas at 17 percent.
- Usability : Only 38 percent of households in the country are digitally literate.
- Use of local languages : Between mother tongue, second and third language, the 2011 census records that over 10% of Indians reported being able to speak some English.
- To improve e-services, the government should translate this language into regional languages.
- E-governance awareness: Due to illiteracy, rural internet access, lack of intent to use internet services, etc., many people in the country are unaware of it.
- Thus, informed citizens, concerned institutions, and departments should help rural populations use e-services.
- For this government came with the national e-governance policy (NeGP).
- E-governance operations and service upkeep cost the government a lot.
- Government models must be reusable. E-governance is a nationwide plan with software and modules for other administrations.
- Maintainability : Because the IT ministry develops new software to meet citizen wants. Thus, government introduced new schemes like digital India.
- Portability : For administration reuse, portable applications must be independent of hardware and software platforms.
- E-governance interoperability: Ministry-department cooperation hampers data processing and exchange.
- E-governance challenges include web-based data collection and format .
- Security : E-governance services like insurance, banking, and utility bill payments have security concerns.
- Cases related to online frauds have come down by about 17.5 per cent in 2022 to ?128 crore. But the number is still very high.
- Privacy : Government should protect citizen data.

- Greater Digital Infrastructure and Connectivity.
- Improve government-citizen dialogue.
- Services on Demand : With a bottom-up approach to planning using separate urban-rural socio-economic databases, government ministries must identify, evaluate, formulate, implement, and correct data-driven policies to meet population needs as soon as possible.
- Focus on Local E-governance: local governments are closest to residents and serve as many people's main point of contact with government.
- Deployment of Intermediaries: E-Governance is designed to maximise citizen happiness by increasing public service delivery and citizen participation in governance procedures.
- India's multilingual population benefits from e-government in regional languages.
- Understanding E-readiness: India's states are at varying levels of e-readiness, therefore e-Governance reforms must take this into account.

- Broadcasting Model : The model is based on dissemination; broadcasting of useful Governance information and it will also provide people with correct information.
- Critical Flow Model: The model is based on disseminating, channeling information of critical value to the targeted audience or into the wider public domain.
- Comparative Analysis Model: The model continuously assimilates best practices in the area of governance and use them as bench mark to evaluates other governance practices.
- The e-advocacy Model : This model helps the global civil society to impact on global decision-making process.
- The Interactive Service Model: the various services offered by the government and it became directly available to its citizen in an interactive manner.
- Example: CoWin app, Digilocker and UPI.
Important e-governance models given by the 2nd ARC:
Recent Government Initiatives to Promote E-Governance in India:
- MyGov Initiative: It has been established as Government of India’s Citizen Engagement Platform which collaborates with multiple Government bodies/Ministries to engage with citizens for policy formulation and seeks the opinion of people on issues of public interest and welfare.
- National e-Governance Plan: It is an initiative of the Government of India to make all government services available to the citizens of India via electronic media.
- National Center of Geo-informatics: It is a Geographic Information System (GIS) based decision support system platform, under National e-Governance Division (NeGD) of Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Darpan Portal: It is an initiative started by the National Informatics Centre and NITI Aayog. It facilitates an interchange of information between NGOs, Voluntary Organisations (VOs) and government departments, ministries and bodies.
E-Governance has improved citizen access to information and services, government efficiency, accountability, and reach. The research recognises that e-Governance projects must be built for specific settings and environments due to India's diverse conditions and vast range of e-Governance initiatives with various degrees of success.
Answer our survey to get FREE CONTENT

Feel free to get in touch! We will get back to you shortly
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Quality Enrichment Program (QEP)
- Total Enrichment Program (TEP)
- Ethics Marks Maximization Prog. 2024
- Interview Mentorship Program (IMP)
- Prelims Crash Course for UPSC 2024
- Science of Answer Writing (SAW)
- Intensive News Analysis (INA)
- Topper's UPSC PYQ Answer
- Essay Marks Maximization Program
- PSIR Optional
- NEEV GS + CSAT Foundation
- News-CRUX-10
- Daily Headlines
- Geo. Optional Monthly Editorials
- Past Papers
- © Copyright 2024 - theIAShub
Talk To Our Counsellor
National e-Governance Plan
National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) was formulated in 2006 by the Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG), Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (ME&IT), and Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions.
It is an important topic for IAS preparation. The e-Governance is functional to make all government services easily accessible to the common man while also ensuring efficiency, reliability, and transparency. All these are made available at a cost affordable for the common man to meet their basic needs. NeGP helped in the Digital India initiative. UMANG ‘s project (Unified Mobile Application for New-age Governance) made the NeGP possible.
Aspirants can visit the linked article and get details about the upcoming government exams that comprise current affairs and general awareness as an important topic in the syllabus.
What is e-Governance?
Electronic Governance or e-Governance is now a popular concept worldwide. In a demanding economy like India, which is also growing fast, e-governance is essential. It is defined as the government’s use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) so that various services are provided to businesses and citizens, and information is exchanged, etc. Communication and bringing together various individual service systems are also within the functionalities of e-governance.
What are the objectives of the National e-Governance Plan?
- Improvement in service delivery to citizens
- Ease in providing information
- Increase efficiency in working between states or between centre and state
- Improve interaction with businesses and different industries
- Bringing transparency and accountability in government matters
How can e-Governance transform India?
E-Governance has the biggest advantage of emphasising inclusiveness. This facilitates the social transformation of the country. National e-Governance Plan UPSC questions commonly ask about the following:
- MyGov – aims at establishing a link between Government and Citizens. Introducing UMANG mobile application
- DigiLocker – a platform where citizens can securely exchange documents with service providers and store them
- e-Hospital Online Registration Framework (ORF) – initiative for patients to avail online OPD appointments with government hospitals
- Reviving agricultural sector- digitisation of land records
- Digital payment- implementing digital payment tools like BHIM-UPI , Bharat QR Code, National Electronic Toll Collections
- Aadhar Enabled Payment System (AEPS)- for banking services and digital payment
- DARPAN– online tool to keep an eye on critical and high profile projects implemented state wise
- PRAGATI (Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation) – a system that aims at establishing e-accountability and implementing e-transparency
- Mobile Seva – services to people on their mobile phones and tablets
- National Scholarships Portal (NSP)– a centralised platform to apply and receive scholarships for students
- National Centre of Geo-informatics (NCoG)– a platform that uses Geographic Information System(GIS) platform
- National e-Governance Plan (NeGP)- integrate e-Governance across the country.
- Common Services Centres 2.0 (CSC 2.0)– information technology so that citizens receive social, government, and private services at the doorstep.
Aspirants can check the relevant links to prepare for the upcoming UPSC Civil Services exam –
How does e-Kranti promote the National e Government Plan?
e-Kranti framework means electronic service delivery through a Mission Mode Projects(MMP) portfolio that covers some departments under the government. It works to accelerate the spread and efficiency of e-Governance across India. Major focuses of e-Kranti in the Digital India initiative are:
- e-Education or use of Technology for Education mainly involves connecting schools to broadband providing free WiFi. Introducing a programme on Digital Literacy on the national level.
- e-Healthcare or Technology for Health covers the online supply of medicine, online medical records, online consultancy, etc.
- Technology for Farmers enables farmers to order necessary items online, avail relief payments through mobile banking services, enjoy an online loan facility and get real-time price information.
- Technology for Security – This provides disaster-related services to citizens to minimise the loss of lives and properties.
- Technology for Financial Inclusion includes mobile banking, post offices, micro-ATM services, etc.
- Technology for Justice includes applications like e- Jails, e-Courts, e-prosecution, and e-Police.
- Technology for Planning refers to the National GIS Mission Mode Project for better project designing, planning, and development.
- Technology for Cyber Security- This is about setting up the National Cyber Security Coordination Centre for safe and secure cyberspace.
What are the challenges e-Governance faces?
- Lack of Infrastructure facilities as basic as electricity, internet, etc.
- E-governance is a costly measure and would require huge amounts of public money.
- Security standards and safeguarding data is a major concern.
- The huge disparity between users and non-users of government services
- Unequal distribution and use of services due to diverse population
To score high in the current affairs quiz , the aspirants should note little details and the latest updates on this topic.
For the best preparation strategy for competitive exams candidates can visit the linked article and get detailed study material and preparation tips to excel in the examination.
Furthermore, check out the latest exam updates, study material and preparation tips for the upcoming civil services exam at BYJU’S.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

civilspedia.com
All you need to crack Civil Services
e-Governance (UPSC Notes)
Last Updated: June 2023 (e-Governance (UPSC Notes))
Table of Contents
This article deals with the ‘ e-Governance (UPSC Notes). ’ This is part of our series on ‘Governance’ series, which is an important pillar of the GS-2 syllabus respectively. For more articles, you can click here .
Introduction

It is of the following forms
Note : e-Governance is not just using Apps or Websites for the purpose of Governance (as people assume it commonly). In fact, it covers the use of a whole range of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) tools.
Models of e-Governance
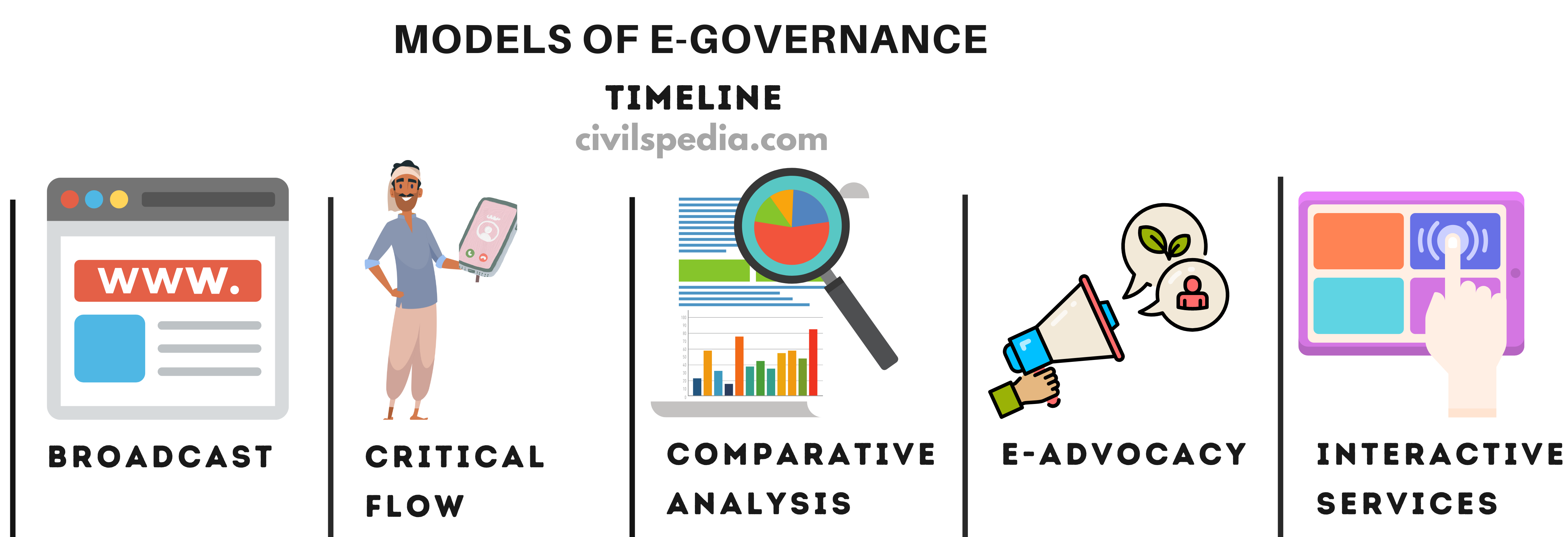
US Prof Arie Halachmi gave 5 models of e-Governance
1. Broadcasting
- Use of Information and Communication Technology & Media to disseminate/broadcast governance info that is already present in paper form.
- For example, Broadcasting Laws, Rules, Judgements, result-mark sheets on the internet.
2. Critical Flow
- Only critical information is released using ICT to the targeted audience (like weather forecasts or crop prices to farmers)
3. Comparative Analysis
- Benchmark parameters are created (like IMR, MMR, Life expectancy etc.) & then Regional parameters at District, State & National levels are measured and compared with the benchmark parameters
4. e-Advocacy Model
- Place the opinion of eminent persons or the opinion of the public collected through surveys on an online forum & try to change public opinion on certain laws or policy stances.
5. Interactive Services
- It is a 2-way channel that is used to provide public services online.
- For example E-Payment of Taxes, Electricity Bills etc.
Benefits/Potential of e-Governance
- Accessibility and Convenience: e-Governance makes government services accessible to citizens and saves them from visiting government offices physically. For instance, citizens can digitally apply for driving licenses and vehicle registrations using the “Parivahan” portal (by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways).
- Transparency and Accountability: e-Governance promotes transparency and accountability by making the information accessible to the public. E.g., the Right to Information (RTI) Act has a provision for digitizing documents, thus promoting transparency and increasing accountability.
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: e-Governance helps streamline administrative processes, leading to faster service delivery. E.g. Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) of subsidies into the bank accounts of beneficiaries. It decreases the leakages and also reduces the cost of transfers.
- Increased Citizen Engagement: e-Governance promotes citizen engagement in governance through processes such as citizen feedback and surveys. E.g., MyGov enables citizens to provide feedback and suggestion on various government initiatives.
- Financial inclusion: e-Governance initiatives such as Direct Benefit Transfers and UPI have helped in increasing financial inclusion in India.
- Data-driven Decision Making : e-Governance initiatives generate enormous data which can be utilized for data-driven, evidence-based decision making. E.g., National Health Stack (NHS) will integrate health data from different sources to create a comprehensive health information system enabling the government to make data-driven decisions to promote health services in India.
National e-Governance Plan (NeGP)
- NeGP is the joint initiative of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MEITY) and the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
- It was started in 2006.
- The NeGP comprises 31 Mission Mode Projects (MMPs) and 10 components.
- It aims at improving the delivery of government services to citizens and businesses with the vision of making Govt. services accessible to the common person through common service delivery outlets and ensuring transparency, reliability and efficiency of services at affordable costs.
- e-District: Aimed to digitize the delivery of services at the district level, like issuance of certificates, licenses, and permits.
- National Land Records Modernization Program (NLRMP): To computerize land records
- National Citizen Database: Create a comprehensive database of citizens, including demographic and biometric information
- e-Procurement: Digitize government procurement processes
- Common Service Centers (CSCs): Physical centres at the village level equipped with computers and internet connectivity to provide access to several government services to citizens.
- State Wide Area Networks (SWANs) : To establish robust and secure communication networks across states to connect government departments, enabling them to share data and information seamlessly with each other.
- State Data Centers (SDCs): Centralized repositories for storing and managing government data.
ICT Initiatives in Governance
G2G or Government to Government Initiatives
1. national e-vidhan application.
It is a mission-mode project to make the functioning of State Legislatures paperless .
It is a Software suite of
- Public website
- Secure website (for members)
- Mobile apps
that fully automate the functioning of the legislative assembly
What will be done?
- No papers in the House: All replies to questions, copies of bills and reports will be provided online
- MLAs will use touch-screen devices.
- Government departments will communicate with Vidhan Sabha online to send replies to approved questions .
- The government will cut down expenditures incurred on the use of paper and other overheads.
- Common people will also get access to important documents and videos. They can also ask questions from the MLAs and MPs.
2. PRAGATI (Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation)
- Aim : Timely implementation of government programs (especially in infrastructure, worth trillions of rupees.)
- The PMO, Union Government Secretaries, and State Chief Secretaries constitute the PRAGATI application, and hence it is a three-tier system.
- PM holds monthly meetings with Secretaries of the Union government and Chief Secretaries of all state governments to scan the progress of projects under implementation. Meetings are held through video conference.
3. e-Samiksha
- e-Samiksha is an online monitoring and compliance mechanism developed by the Cabinet Secretariat.
- It is used for tracking the progress of projects & policy initiatives by the cabinet secretary and PM on a real-time basis.
4. UPaAI System
- UPaAI (Unified Planning and Analysis Interface), or ‘solution’ in English, provides an integrated platform for data on infrastructure and social indices for each constituency to the MP and helps them take better decisions related to MPLAD funds and other Central Schemes.
- It is monitored by PMO too.
- In the next phase, it will be extended to include state schemes and bring district magistrates and members of legislative assemblies on the same platform.
5. e-Office
- NIC has developed an e-Office application to transform the traditional functioning of government departments .
- Unified Internal Messaging
- E-Files: To make digital files and share them with others
- E-Financial Management
- Knowledge Management System providing essential documents and files accessible at any place
G2C or Government to Citizen Initiaves
1. e-district.
- e-District digitize the delivery of services at the district level, like issuance of certificates, licenses, and permits through Common Service Centers (CSCs)
2. Digilocker
- It is a cloud-based application that allows people to store and access their documents digitally.
- Citizens can store their documents digitally and also shares them with government agencies and other organizations.
3. Pravahan
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways
- Pravahan allows citizens to digitally apply for and renew their driving licenses and vehicle registrations
- UMANG is a mobile app that provides access to various government services like passport services, income tax filing, and utility bill payments through a single platform.
5. e-Ticketing
An initiative of Indian Railways which allows passengers to book tickets, check seat availability, and make payments electronically.
- MyGov is an online citizen engagement platform that allows citizens to participate in policy-making and Governance through their suggestions and feedback on various government initiatives and programs.
G2B or Government to Business Initiatives
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs 21, or MCA21, allows electronic filing as well as retrieval of documents such as company registration and compliance certifications.
2. e-Biz Portal
- It is a unified platform for various regulatory clearances and permits.
- It has simplified the process of starting and operating businesses.
3. Government e-Marketplace (GeM)
- GeM helps to ensure that public procurement of goods and services is carried out through the online platform.
- It promotes transparency & eliminates corruption.
- Helpful in easy auditing because it will leave an audit trail.
4. Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN)
- GSTN is the technology platform that is the backbone of the GST regime.
- It handles the registration under GST, filing and payment of GST, handling complex system of GST credits etc.

6. Indiastack
- IndiaStack is a collection of open APIs and digital public goods.
- API or Application Programming Interface allows two applications to interact with each other.
- IndiaStack includes APIs of Aadhaar, Unified Payment Interface (UPI), DigiLocker, Aarogya Setu, eSanjeevani, UMANG, DIKSHA, etc.
- Software makers can use these APIs in their software to utilize their functionality. E.g., UPI API is used by Banking Applications of various banks.
- e-Governance is seen more as computerization & office automation rather than as a means to transform citizens from passive to active participants in Governance.
- Digital Divide: According to INDIA INEQUALITY REPORT 2022 by Oxfam, there is a huge digital divide in India. For instance, 61% of men-owned mobiles in contrast to 31% of women
- Funding for these programs is short in comparison to the huge ambitions we have placed on these schemes.
- Privacy & No Data Protection Law (Legal Vacuum) : Aadhar information & other records are to be used, but there is no law to ensure privacy.
- The quality of local content is not good . Most portals aren’t user-friendly.
- No special programs to make the public aware of these programs.
- A status-quo attitude of the government departments: Despite a push for e-governance initiatives, many government departments continue insisting upon physical forms and signatures.
According to Kentaro Toyama , formerly Microsoft India’s CEO, IT intervention has a limited impact on developmental outcomes when political will is absent. It is because technology can only be the ‘force multiplier’; it is not the force itself. The positive intent must originate in politics and motivate the bureaucracy to deliver on its mandate.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- भाषा : हिंदी
- Classroom Courses
- Our Selections
- Student Login
- About NEXT IAS
- Director’s Desk
- Advisory Panel
- Faculty Panel
- General Studies Courses
- Optional Courses
- Interview Guidance Program
- Postal Courses
- Test Series
- Current Affairs
- Student Portal

- Addressing the 24th National Conference on e- Governance in Hyderabad, Union Minister of Science and Technology emphasized that the e-governance initiatives should be citizen centric and increase transparency and accountability.
About e-Governance
- E-government is the use of technological communications devices, such as computers and the Internet, to provide public services to citizens and other persons in a country or region.
- E-government offers new opportunities for more direct and convenient citizen access to government and for government provision of services directly to citizens.
- Citizen and their government (C2G),
- Between governments and other government agencies (G2G),
- Between government and citizens (G2C),
- Between government and employees (G2E), and
- Between government and businesses/commerce’s (G2B).
Significance of e-Governance
- It has provided flexible timings and helped people especially employees during COVID pandemic.
- Ease of life: The purpose of e- governance is to bring ease of life for common citizens.
- One nation-one portal : Over grievances and redressal, the linking of the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System with that of the states is almost done realizing Prime Minister’s vision for one nation-one portal.
- Simplification : To support and simplify governance for government, citizens, and businesses.
- Transparent and accountable : To make government administration more transparent and accountable while addressing the society’s needs and expectations through efficient public services and effective interaction between the people, businesses, and government.
- Corruption : To reduce corruption in the government.
- Speedy delivery : To ensure speedy administration of services and information.
- To reduce difficulties : for business, provide immediate information and enable digital communication by e-business.
Issues/ Challenges of e-Governance
- Lack of computer literacy : India is still a developing country and a vast majority of the citizens lack computer literacy which hinders the effectiveness of e-governance.
- Lack of accessibility: to the internet or even computers in some parts of the country is a disadvantage to e-governance.
- E-Governance results in a loss of human interaction : As the system becomes more mechanized, lesser interaction takes place among people.
- Risk : It gives rise to the risk of personal data theft and leakage.
- E-Governance leads to a lax administration : The service provider can easily provide excuses for not providing the service on technical grounds such as “server is down” or “internet is not working”, etc.
Various initiatives by the Government towards E-governance
- Aadhaar is a unique identification number issued by UIDAI that serves as proof of identity and address on the basis of biometric data. It is being used to provide many benefits to the members of the society. One can e-sign documents using Aadhar.
- myGov.in is a national citizen engagement platform where people can share ideas and be involved with matters of policy and governance.
- UMANG i s a Unified Mobile Application which provides access to central and state government services including Aadhar, Digital Locker, PAN, Employee Provident Fund services, etc.
- Digital Locker helps citizens digitally store important documents like mark sheets, PAN, Aadhar, and degree certificates. This reduces the need for physical documents and facilitates easy sharing of documents.
- PayGov facilitates online payments to all public and private banks.
- Mobile Seva aims at providing government services through mobile phones and tablets. The m-App store has over 200 live applications which can be used to access various government services.
- Computerisation of Land Records ensures that landowners get digital and updated copies of documents relating to their property.
- DigiSevak platform connects interested citizens with the government to volunteer for various Digital India activities by Ministries and agencies of government.
- Online Registration System (ORS) is an online portal where citizens having Aadhaar can enroll for appointments in hospitals across various States and Union Territories of India.
- IndiaStack is a set of APIs that allows governments, businesses, startups and developers to utilize a unique digital Infrastructure to solve India’s hard problems towards presence-less, paperless, and cashless service delivery.
- PRAGATI (Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation) is aimed at starting a culture of Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation. It is also a robust system for bringing e-transparency and e-accountability with real-time presence and exchange among the key stakeholders.
Some State level e-governance initiatives
- E-Seva (Andhra Pradesh) facilitates payment of utility bills, issuance of certificates, licenses and permits.
- Khajane Project (Karnataka) digitalized the treasury system of the state.
- FRIENDS (Kerala) is a single-window facility to pay taxes and other financial dues to the State government.
- Lokvani Project (Uttar Pradesh) is a single-window solution relating to the handling of grievances; land record maintenance and providing a mixture of essential services.
Source: AIR
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Daily current affairs 15-04-2024, daily current affairs 13-04-2024, daily current affairs 12-04-2024, holistic approach to ‘one health’ .

NEXT IAS (Delhi)
Next ias (jaipur), next ias (bhopal), next ias (prayagraj).
A Brand of CLT Technologies & Edu-Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
Forgot password
If you haven’t created your account yet, please SIGN UP HERE
Quick Links Testimonials FAQ
Hybrid Classes
We provide offline, online and recorded lectures in the same amount.
Personalised Mentoring
Every aspirant is unique and the mentoring is customised according to the strengths and weaknesses of the aspirant
Topicwise Mindmaps
In every Lecture. Director Sir will provide conceptual understanding with around 800 Mindmaps.
Quality Content
We provide you the best and Comprehensive content which comes directly or indirectly in UPSC Exam.
If you haven’t created your account yet, please SIGNUP HERE
UPSC Courses
IAS Foundation 2024
- C2U-NCERT 2024
- Newspaper Analysis Program
- Basic Daily Answer Writing
Optional Classes
- Geography Crash Course
Current Affairs
- Daily Newspaper Analysis - DNA
- UPSC Facts & Data
- GS Prelims PT Pointers
- Press Information Bureau - PIB
- Good Morning Times - Subject Wise
- EASY TO PICK MONTHLY CURRENT
- GS Paper Wise Current Affairs
- Daily Question Practice (PT-Mains)
Test Series
- RAW Live MCQ
- Oral Test Session By Director Sir
Others Links
- Testimonials
UPSC Prelims Classes 2024
Crash Course
- Sanjeevani @ 60Days
- Morden History
- Science & Technology
Regular Modules 2024
- Mapping & Geography
- Environment
- Economics Basic To Advance
- Polity & History
- News Paper Analysis Programme
- Prelims Test Series
- About Civil Services
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus & Strategy
- UPSC Previous Years Paper
- Prelims Modular Batches
- UPSC Prelims - PT Pointers
- Exclusive Test Series - Mock
- CSAT Classes
- Prelims Sanjeevani 2024 Crash Course
Mains Classes 2024
- RAW GS Crash Course
- Target 50 Program
- Ethics & Case Studies
- Editorial & Current Affairs – QIP
- Writing Skill Development Program
Mains & Interview
- Mains Syllabus & Strategy
- Daily UPSC Answer Writing
- Target 50 For Mains Batch
- Personality Test
- Mains Crash Course
- MAINS Previous Papers
- Optionals Previous Papers
Mains Material
- Mains Kunji
- Prelims (Live-MCQ)
- Prelims PT Tricks-2024
- Daily Answer Writing
Free Study Material
- Important Video Lectures
- Previous Years Papers
- Newspaper Analysis & ENY Notes
- UPSC GS Mains Notes
- 2 nd ARC Report Summary
- Aspire IAS Notes
- Free Download - UPSC Content
- Paid Material(SLP)
- UPSC Optional Notes
Major Topics
- International Relation
- International Organization
- Government Policies And Interventions
2nd ARC on e-Governance

- 09 Jul,2023
Recommendations of 2nd ARC on E-Governance
Building a Congenial Environment
- Creating and displaying a will to change within the government
- Providing political support at the highest level
- Incentivizing E-Governance and overcoming the resistance to change within government
- Creating awareness in the public with a view to generating a demand for change.
Identification of E-Governance Projects and Prioritisation
- Information: Putting information on web-sites
- Interaction: Allowing citizens to enquire about services, procedures etc. and filling up forms and submitting them online
- Transaction: Allowing payments online
- Transformation: A mix of all the above and allowing the citizen to participate in governance through ICT.
Business Process Re-engineering (BPR)
- For every function a government organisation performs and every service or information it is required to provide, there should be a step-by-step analysis of each process to ensure its rationality and simplicity.
- Such analysis should incorporate the viewpoints of all stakeholders, while maintaining the citizen-centricity of the exercise.
Capacity Building and Creating Awareness
- Capacity building efforts must attend to both the organizational capacity building as also the professional and skills upgradation of individuals associated with the implementation of E-Governance projects.
- Each government organization must conduct a capacity assessment which should form the basis for training their personnel.
- A network of training institutions needs to be created in the States with the Administrative Training Institutes at the apex.
Implementation
- Breaking up entire E-Governance projects into components/ activities
- Planning each activity in detail
- Allocating resources, both human and financial
- Commencement of activities as per the plan and continuous tracking
- Need-based mid-course correction
Monitoring and Evaluation
- Monitoring of E-Governance projects should be done by the implementing organization during implementation in the manner in which project monitoring is done for large infrastructure projects.
- Evaluation of success or failure of e-Governance projects may be done by independent agencies on the basis of parameters fixed beforehand.
Protecting Critical Information Infrastructure Assets
- There is need to develop a critical information infrastructure assets protection strategy.
- This should be supplemented with improved analysis and warning capabilities as well as improved information sharing on threats and vulnerabilities.
Newsletter Subscription
Important links.
- Economic Issues
- International Relations
- Miscellaneous
- Human Geography
- Modern History
- Indian Society
- Art and Culture
- Government policies and interventions
- Biodiversity & Environment
- Bilateral Relations
- Important Bills
- Internal security
- Important reports
- Social issues
- Various acts
- International organisation
- International treaties and conventions
- Disaster and Disaster management
- Indian Polity
- World History
- Indian Geography
- Physical Geography
- Developmental Issues
- Indian Economy
- Government Policies & Reports
- Tolerance and Intolerance

Challenge UPSC 2024 - PT Tricks
Update Info
- Prelims Sanjeevani 2021 Crash Course
Mains & Interview
- Mains Sanjeevani 7Days Batch (coming soon)
- MAINS Test Series By Toppers
- RAW Prelims Live MCQ 2021
UPSC Resource
- General Studies Notes
- SLP - Paid Notes
- Skip to main content
India’s Largest Career Transformation Portal
E-governance in India : Concept, Advantages and Challenges Explained
September 26, 2019 by Sandeep
Technology has become a part of our daily life. For most of us, mobile is the first thing they need as soon as they get up. Technology has its presence in all aspects of our life. We can say that we are living in a technology era and it has made everything easy for us.
In today’s internet’s time, we can talk to someone who in another corner for the world and we can send an e-mail in just a few seconds. Technology and the internet have made the money transitions secure, fast and free from much human interference.
The process of globalisation is a gift of technology and due to the technology and its benefits, the concept of E-governance is introduced in India.
The ‘E’ in E-governance signifies electronic and E-governance means the governance with Information technology. The increasing demand for transparency in administration, faster information transfer and other demands that can be fulfilled by the E-governance only pushed the government and public sector to chose E-governance.
Many of us think that E-governance came to India’s governance system comparatively late but the fact is that E-governance started to work in India in 1987. In 1987 NICNET (national satellite-based computer network) was launched. It was the dawn of E-governance in India.
After NICNET, District Information System of the National Informatics Centre (DISNIC) was launched to computerise all district offices in the country. Later on, in 1990 both NICNET and DISNIC got connected and NICNET extended via the State capitals to all district headquarters.
Since then technology has improved a lot and so does the networking and the work at the district level. So the required improvements have been implemented to have a secure and hassle-free E-governance in India.
In today’s scenario, E-governance is essential for the state and central government. Further, in this essay, we will cover the topics like advantages and dis-advantages of E-governance and challenges in E-governance.
E-governance in India
The model of E-governance is highly successful in developed countries like the United Nations and others but in a counter like India, there were some doubts about its success. India is a country with much diversity. It has a different language, culture, and states with different geographical structure.
So it was not easy for all to understand the policies of the central government and roaming around the state and central government’s offices to get some of their work done. The idea of E-governance introduced efficiency, Promptness, transparency and better citizen friendly interface.
A few departments have implemented E-Governance with perfection and they are offering the best services to the citizen of the country. The railway is one of those departments who has applied E-Governance to offer better citizen friendly interface.
Now it has become easy for the countrymen to book the tickets for their train journey without visiting the railway station in their city or village.
In case of an emergency, the passengers can get help from the government with a tweet only. Another benefit of E-Governance is very much visible on E-Tender. Earlier it was said that there is always some scam or bribe was associated with the government tender systems but now with E-Tenders, it has almost vanished.
Almost all the ministries and the department of state and central government have their websites. From these websites, you can get the desired information. Both states and the central government are working to implement technology in government work.
The pace of some states is good and some are working steadily and slowly. India has a good position in Asia for the implementation of ICT (Information Communication Technology).
Advantages of E-governance
We all will be agreeing to this point that technology has made our life easy. If we talk about the advantages of E-Governance then we will have to agree that E-Governance has helped many Indians in many ways. Let’s have a look at the advantages of E-Governance.
1. Transparency
Bribe and corruption are the main concern in India and they are considered as the biggest hurdle for the development of society. E-Governance has brought transparency in the government system and it created an unfavorable situation for corruption.
ICT enables the citizen to see any information wherever they want. Now the common man can raise a finger on the government policies as now he can lodge the complaints on e-portals of government.
E-Governance provides the required information to the common or special person in no time.
3. Cost Reduction
The paper-based communication is much costlier than ICT. E-governance saves the cost of sending and receiving letters in order to get some information.
4. Expand Reach of Governance
E-governance has brought the government policies at the doorstep of common men. Now any Indian citizen can get access on the government policies and schemes. They can read them and ask queries online through their smartphones.
Disadvantages of E-governance
We have discussed the needs and advantages of E-Governance now let’s look at the other side of a coin. Here are the disadvantages of E-Governance.
1. Dependency
Our dependency on technology is fine until the technology is supporting us but once it stops working all the work stops. This dependency eats lots of time. For example in banks a very common phrase we listen to is. The server is not working so most of the work stops.
2. Literacy
To reach to the every Indian is the vision of government behind E-governance but in India, the literacy rate is not so high. The implementation of e-government will be more effective with a high literacy rate.
3. Availability of Computers
A computer is a common device but its not available at every home in India. In the absence of a computer, the facilities of E-Government can be enjoyed by accessing through Smartphone but it is also not available to every Indian.
4. Security
Security is a major concern for the government. The government has many E-governance projects and its government’s duty to maintain its security. Recently there was much chaos on the security of Aadhaar Card .
Challenges in E-governance
Lack of literacy, non-availability of computer and other devices is the biggest challenge in the implementation of E-governance. Marinating the cyber security is another challenge for E-governance. Insufficiency of funds, infrastructural problems, maintenance, and legal framework readiness are among the other challenges in E-Governance.
The technology is getting advanced with every passing day so to maintain the level of technology the government needs to spend some funds after a particular duration. The arrangement of funds is another challenge in E-governance as the cost of high-end technology servers is usually high.
E-governance has made many processes easy for us. Now we can check the live status of our speed posts through computerisation and networking of all post offices. Banks, UID, and many other processes helped the common man and they all come under the category of E-governance.
To conclude the complete easy on E-governance, we can say that it is the need of the hour. The government of India has launched many programmes to empower E-government.
E-Governance Explained
Relevance: Mains: GS II –
- Important Aspects Of Governance

- According to the World Bank, e-governance refers to the use by government agencies of information technologies (such as Wide Area Networks, the Internet, and mobile computing) that can transform relations with citizens, businesses, and other arms of government.
- e-Governance is a move towards SMART governance.
There are four types of interactions in e-Governance viz., government to citizens (G2C), government to business (G2B), government to government, that is, inter-agency relationships (G2G), and government to employees (G2E).
The Second Administrative Reforms Commission has explained the above four types of interactions in its report on in e-Governance in the following manner:
- G2C (Government to Citizens): In this case, an interface is created between the government and citizens which enables citizens to benefit from efficient delivery of a large range of public services. It gives citizens the choice of when to interact with the government (being available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week), from where to interact with the government (e.g., service centre, unattended kiosk, or from one’s home/workplace) and how to interact with the government (e.g., through the internet, fax, telephone, email, face-to-face, etc). The primary purpose is to make the government, citizen-friendly.
- G2B (Government to Business): Here, e-Governance tools are used to aid the business community to seamlessly interact with the government. The objective is to cut red tape, save time, reduce operational costs, and to create a more transparent business environment when dealing with the government. These measures help to provide a congenial environment to businesses to enable them to perform more efficiently.
- G2G (Government to Government): In this case, Information and Communications Technology is used not only to restructure the government processes involved in the functioning of government entities but also to increase the flow of information and services within and between different entities. This kind of interaction is, between different government agencies as well as between national, provincial, and local governments. The primary objective is to increase efficiency, performance, and output.
- G2E (Government to Employees): The government is by far the biggest employer and like any organisation, it has to interact with its employees regularly. This interaction is a two-way process between the organisation and the employee. The use of ICT tools helps in making these interactions fast and efficient on the one hand and increases satisfaction levels of employees on the other

- Recognizing the increasing importance of electronics, the Government of India established the Department of Electronics in 1970. The subsequent establishment of the National Informatics Centre (NIC) in 1977 was the first major step towards e-Governance.
- With the economic reforms in 1991 , the model of e-governance in India gained a fillip due to convergence in the availability of progressive technologies and opportunities in this field.
- A National Task Force on Information Technology and Software Development was set-up in 1998.
- The Ministry of Information Technology was created at the Centre in 1999.
- In the year 2000, a 12-point minimum agenda for e-Governance was identified for implementation in all the central ministries and departments. T he Information Technology Act (2000) was enacted.
- The National Policy on Information Technology (NPIT) was approved in 2012. It focuses on the deployment of ICT (Information and Communication Technology) in all sectors of the economy and providing IT-based solutions to address citizen-centric issues.
- And here we are now, at with ambitious project of Digital India , which will enable us to achieve the motive of “ minimum government, maximum governance”
- Governance is a challenge in a country as vast, diverse, and rapidly developing as India. That’s where new technologies intervene and enable large-scale transformation and help in the implementation of ambitious government plans.
- India is among the fastest developing economies in the world, we ranked 58th in 2019's Global Competitiveness Index. With this pace of growth, it needs to be equitable and inclusive.
- As a result, India is gearing up for an era of increased digitisation, after the advent of Industry 4.0, powered by new-age technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence, and Robotics.
ICT applications impact the structures of public administration systems.
Technological advancements facilitate administrative systems by enabling:
- Administrative Development; and
- Effective Service Delivery
1. ADMINISTRATIVE DEVELOPMENT:
Administrative reforms, often, have focused on procedural details and restructuring of systems and processes of government organisations. The basic objective of these reforms is to enhance the capacities of the systems. ICTs can be used and are being used now to give further impetus to the process. They help in the following manners:
- Automation of Administrative Processes- A truly e-governed system would require minimal human intervention and would rather be system driven. Now administrative departments are computerised and connected through a network. The departments have launched individual websites carrying information of their respective departments. This has enabled the online carrying of operations and file movements. Budgeting, accounting, data flow, etc. have become easy. This has increased the efficiency of office operations and processes and has reduced unnecessary delays.
- Paper Work Reduction
- Quality of Services- ICT helps governments to deliver services to the citizens with greater accountability, responsiveness, and sensitivity . Quality of services improves, as now the people can get services efficiently and instantaneously. By ensuring online redressal of grievances the accountability of officials is ensured
- Elimination of Hierarchy – Technology has reduced procedural delays caused by hierarchical processes in the organisation. Computerisation and communication patterns have increased efficiency and have led to the involvement of all levels in decision-making.
- Change in Administrative Culture- Bureaucratic structures have been plagued by characteristics aptly described by Victor Thompson as ‘bureau-pathology’. Efforts have been made to find ways to deal with the pathological or dysfunctional aspects of bureaucratic behaviour and to make the delivery of public services effective and efficient. With e-governance, public actions coming under public glare would certainly induce norms and values of accountability, openness, integrity, fairness, equity, responsibility, and justice in the administrative culture. Rather, the administration would become efficient and responsive
2. EFFECTIVE SERVICE DELIVERY
- Transparency- by dissemination and publication of information on the web. This provides easy access to information and subsequently makes the system publicly accountable. Also as web enables the free flow of information, it can be easily accessed by all without any discrimination.
- Economic Development- The deployment of ICTs reduces transaction costs, which makes services cheaper. For example, rural areas suffer on account of lack of information regarding markets, products, agriculture, health, education, weather, etc. and if all this could be accessed online would lead to better and more opportunities and thereby prosperity in these areas.
- Social Development- The access to information empowers the citizens. The Informed citizenry can participate and voice their concerns, which can be accommodated in the programme/ project formulation, implementation, monitoring and service delivery. Web-enabled participation will counter the discriminatory factors affecting our societal behaviour.

In 2006, the National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) was formulated by the Department of Electronics and Information Technology and Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances that aims at making all government services accessible to the common man, ensure efficiency, transparency, and reliability of such services at affordable costs to realise the basic needs of the common man.
The NeGP has enabled many e-governance initiatives like:
- Developing a secure and stable digital infrastructure
- Delivering government services digitally
- Achieving universal digital literacy
- Aadhar is a unique identification number issued by UIDAI that serves as proof of identity and address based on biometric data. It is being used to provide many benefits to the members of society. One can e-sign documents using Aadhar.
- myGov.in is a national citizen engagement platform where people can share ideas and be involved with matters of policy and governance.
- UMANG is a Unified Mobile Application that provides access to central and state government services including Aadhar, Digital Locker, PAN, Employee Provident Fund services, etc.
- Digital Locker helps citizens digitally store important documents like mark sheets, PAN, Aadhar, and degree certificates. This reduces the need for physical documents and facilitates easy sharing of documents.
- PayGov facilitates online payments to all public and private banks.
- Mobile Seva aims at providing government services through mobile phones and tablets. The m-App store has over 200 live applications that can be used to access various government services.
- Computerization of Land Records ensures that landowner gets digital and updated copies of documents relating to their property.
In addition to the above, State level e-governance initiatives include:
- E-Seva (Andhra Pradesh) facilitates payment of utility bills, issuance of certificates, licenses, and permits.
- Khajane Project (Karnataka) digitalized the treasury system of the state.
- FRIENDS (Kerala) is a single-window facility to pay taxes and other financial dues to the State government.
- Lokvani Project (Uttar Pradesh) is a single-window solution relating to the handling of grievances, land record maintenance, and providing a mixture of essential services.
Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam , former President of India and a visionary in the field of e-Governance has aptly summarized the basic challenge lying before the country in this regard:
“e-Governance has to be citizen-friendly. The delivery of services to citizens is considered a primary function of the government. In a democratic nation of over one billion people like India, e-Governance should enable seamless access to information and seamless flow of information across the state and central government in the federal set up. No country has so far implemented an e-Governance system for one billion people . It is a big challenge for us.
- Work Plan: The ‘Working Group on E-Government in the Developing World’ considers infrastructure, economic health, education, information policies, etc. as crucial factors for the success of e-governance projects. If these factors are well in place then they can lay down the roadmap for effective e-governance implementation. Countries like India, face problems of low connectivity, technical professionals, finances, and other resources coupled with inappropriate planning. Hence, it becomes difficult to develop specific applications and services.
- Different languages: India is a country where people with different cultures and different religions live. Governance applications are written in English which may not be understood by most people. Therefore, it becomes a challenge for the government to write e-Governance applications in regional languages, to reach the people.
- Low Digital literacy: only 10% of the population is digitally literate. There are efforts like 'PM Digital Saksharta Abhiyaan' going on, but we need to speed up them.
- Accessibility: Even though the Internet users are growing there is a major part of the Indian population that does not have access to e-Governance services for a variety of reasons, e.g. some people may not own mobile phones, internet connection, electricity issues, etc. The Digital divide among rural-urban areas, gender-wise is a major challenge.
- Limited financial resources: Its implementation in India is a humungous task due to the vast area and population. A huge cost is involved in the implementation, operational and evolutionary maintenance tasks of these activities. Added to it are the differential capacities of states and local governments.
- Resistance to change: this issue persists among citizens as well as the people within the administration. Citizens are adapted to paperwork and are apprehensive of online transactions. We need to establish their trust first.
- Privacy and Security: there is no data protection law in place, hence privacy is even more of a concern. The Adhaar Bill met with a lot of resistance due to this. Also, the government's critical infrastructure, websites are under threat of c yber attacks.
- Interoperability among various levels of government- centre, state, local; as well as among ministries is another issue.
The 11th report of 2nd ARC gives detailed recommendations in this case-
1. Building a congenial environment is a sine qua non for the successful implementation of e-Governance initiatives. This should be achieved by:
- Creating and displaying a will to change within the government
- Providing political support at the highest level
- Incentivising e-Governance and overcoming the resistance to change within government
- Creating awareness in the public to generate demand for change.
2. Identification of e-Governance Projects and Prioritisation:
Government organizations/departments at Union and State government levels need to identify e-Governance initiatives that could be implemented after prioritizing them based on ease of implementation, keeping the needs of the citizens in mind. Such initiatives may be categorized as follows:
- Initiatives that would provide timely and useful information to the citizens.
- Initiatives that allow for making elementary online transactions including the payment for services.
- Initiatives that require verification of information/data submitted online.
- Initiatives that require the creation and integration of complex databases.
3. Business Process Re-engineering (BPR):
The processes and structures in government organizations generally owe their existence to colonial times. We need to re-engineer them to suit them to today's times which have evolved enormously. We can do it by:
- Analyzing every function of institutions and government functioning to ensure its simplicity and rationality.
- After identifying steps that are redundant or which require simplification, and which are adaptable to e-Governance, the provisions of the law, rules, regulations, instructions, codes, manuals, etc. which form their basis should also be identified.
- Following this exercise, governmental forms, processes, and structures should be re-designed to make them adaptable to e-Governance, backed by procedural, institutional, and legal changes.
4. Capacity Building and Creating Awareness:
- Such efforts must attend to both the organizational capacity building as also the professional and skills up-gradation of individuals associated with the implementation of e-Governance projects.,
- A network of training institutions needs to be created in the States with the Administrative Training Institutes at the apex
- Lessons learned from previous successful e-Governance initiatives should be incorporated in training programmes.
- The recommendations made by the 2nd ARC in the report entitled ‘Unlocking Human Capital’ should be adopted for creating awareness among people concerning e-Governance initiatives.
6. Implementation:
- Should involve periodic independent evaluation of the information available on their websites from the citizens perspective and then re-design their websites based on the feedback obtained
- Planning each activity in detail
- Allocating resources, both human and financial
- Need-based mid-course correction
7. Monitoring and Evaluation:
- Even though e-Governance projects are generally rolled out after testing them at the pilot stage, such projects need continuous monitoring.
8. Protecting Critical Information Infrastructure Assets:
- There is a need to develop critical information infrastructure assets protection strategy.
- This should be supplemented with improved analysis and warning capabilities as well as improved information sharing on threats and vulnerabilities.
- It should involve finding out the implementation status at any given point of time, tracking the inputs against projected estimates, and identifying the corrective measures in case of any variations.
The COVID-19 pandemic came like a bolt from the blue and knocked our civilisation’s complacency for a loop.
Such incidents force us to reflect upon our position and velocity as an intelligent species and make us introspect on some flawed designs. In this case, e-governance which needs to be looked at with a different perspective. Digitisation can help bypass the vulnerabilities India faces in crises like the present pandemic.
- Human Resource: We track the human resource through census, surveys, etc. But the Aadhaar card is a living ID whose details can be updated instantly, whereas the Census wakes up only once in ten years. To fix this mismatch, Census will have to be both Aadhar-linked and fully digital. This will convert the Census from an exercise to a ‘super-card’ for every Indian which can subsume all individual IDs and become a field of data updatable in real-time, and serving as an engine for e-delivery of public services.
- Money: The complete money supply in India is already under the scanner of RBI which releases figures fortnightly on its website. However, with the advent of cryptocurrencies in the future, RBI’s radar may require a wider bandwidth.
- Land: Natural resources (including land) are perhaps the most imperfectly measured class of resources. The current pandemic must serve to fillip the government to expedite its Digital India Land Records Programme and make an extra effort to build it on a blockchain interface so that adequate land allocation can be done for residential, commercial and agricultural purposes. Similarly, man-made infrastructure like road, rail, electricity, etc. which are allocatable across different sectors requires mapping and recording digitally.
- There is a flow of goods and services among the sectors like household, administration, business, etc. For example, public services flow from the government to the household sector. Taxation is a flow in the opposite direction.
- These processes require coordination. The government acts as the heart of the entire coordination tree, and directly or indirectly (through its protocols) acts as the middleman in this flow between any two sectors.
- Realising this, the India Enterprise Architecture(IndEA) is being implemented by the National eGovernance Division of the government to streamline the complete government work-model based on a ‘one-government’ backbone.
- Thus so far it is evident how digitisation can streamline the recording, allocation, and coordination of resources across sectors.
- Aarogya Setu app and other allied initiatives like the National e-Health Authority and new telemedicine guidelines are coalescing towards a National Health Stack which is aimed to be completed by 2022. From filling healthcare needs in remote areas to building data-driven public policy on health, the use of technology fulfills many roles, and most importantly in some of the most remote areas of the country.
- Indian states used the COVID-19 opportunity to further spread the use of technology – whether it is the use of Collaborative Robots (Co-Bot) by the government of Jharkhand or the municipal corporation of Bengaluru, using drones to spray disinfectants , survey areas, monitor containment zones and make public announcements.
The importance of e-governance has never been felt more strongly than in this COVID-19 situation.
- After examining the various aspects of e-Governance reforms in India, it can be concluded that in any eGovernance initiative, the emphasis has to be first on governance reforms and ICT tools can be utilized to bring about those fundamental changes.
- The complex nature of governance in India demands a holistic approach. Shedding silos and embracing the principle of ‘Collaborative Creation’ should be the focus. If we achieve this, we pave the way towards building an inclusive society with the potential to tackle any crisis, including the current pandemic.
Recent Articles
An exchange – analyzing the vaibhav fellowship program | 26 january 2024 | upsc daily editorial analysis, india’s problem — different drugs, identical brand names – drug name confusion threatens patient safety in india | 25 january 2024 | upsc daily editorial analysis, the truth about india’s booming toy exports – protectionism or productivity | 24 january 2024 | upsc daily editorial analysis, tax contribution by states needs to be revisited – time to recognize state efficiency through tax contribution | 23 january 2024 | upsc daily editorial analysis, a revival of the imec idea amid choppy geopolitics – could india-middle east-europe economic corridor (imec) become the new silk road | 22 january 2024 | upsc daily editorial analysis.
- Gearing up for change – Monsoon Trends in India: Analyzing the Impact on Agriculture and Climate Resilience | 20 January 2024 | UPSC Daily Editorial Analysis
- Crafting a new phase in India-U.K. defence ties – Strengthening India-U.K. Defense Cooperation | 19 January 2024 | UPSC Daily Editorial Analysis
- Turning around Indian Ports – Enhancing India’s Global Competitiveness through Port Efficiency | 18 January 2024 | UPSC Daily Editorial Analysis
- A dated urban vision – Mumbai Trans Harbour Link: A Dated Mode of City-Making from Times Past | 17 January 2024 | UPSC Daily Editorial Analysis
- Tensions in Red Sea – Red Sea Threats Disrupt India’s Trade Flows | 16 January 2024 | UPSC Daily Editorial Analysis
Popular Articles
- UPSC CSE 2022 Mains GS 1 Paper Model Answers
- Model Answers for UPSC CSE 2021 GS 2 Paper
- SPR 2023 | SPECIES IN NEWS
- UPSC CSE 2023 Mains GS 2 Paper Model Answers
- Model Answers for UPSC CSE 2020 GS 2 Paper
- UPSC CSE 2023 Mains GS 1 Paper Model Answers
- PDS: objectives, functioning, limitations, revamping
- Land Revenue System during British rule in India
- Govt policies & interventions for development in various sectors, and issues arising out of their design and implementation
- UPSC CSE 2022 Mains GS 2 Paper Model Answers
Popular Topics
You might also be interested in:, download the samajho app.

SUBSCRIBE to Get FREE PDF Notes , Current Affairs, and Updates related to the UPSC Civil Services Exam.

Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

[Mission 2024] Current Affairs Quiz , 15 April 2024

Quiz-summary
0 of 10 questions completed
Information
The Current Affairs Quiz is a daily quiz based on the DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS AND PIB SUMMARY from the previous day, as posted on our website. It covers all relevant news sources and is designed to test your knowledge of current events. Solving these questions will help you retain both concepts and facts relevant to the UPSC IAS civil services exam.
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
0 of 10 questions answered correctly
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, ( 0 )
- Not categorized 0%
1 . Question
In India, which one of the following is mandated with facilitating monetization of non-core assets of government CPSEs under strategic disinvestment or closure and enemy property?
- (a) NITI Aayog
- (b) Reserve Bank of India
- (c) Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade
- (d) Department of Investment and Public Asset Management
Explanation:
- In India, the disinvestment process is overseen by the Department of Investment and Public Asset Management (DIPAM), operating under the Ministry of Finance. DIPAM’s main goal is to manage the government’s investments in public sector enterprises and supervise the disinvestment of government equity in these enterprises. Additionally, in 2005, the government established the National Investment Fund (NIF) to serve as a channel for the proceeds generated from the disinvestment of Central Public Sector Enterprises. The creation of NIF aimed to ensure transparent and efficient utilization of these funds for various developmental purposes.
Refer: https://www.insightsonindia.com/2024/04/13/disinvestment-in-india-a-key-agenda-for-the-next-government/
2 . Question
Which of the following statements about an Initial Public Offering (IPO) is correct?
- (a) An IPO is a process where an established public company buys shares of a startup.
- (b) An IPO is a type of loan that a company takes from the public.
- (c) An IPO is the process of a company buying back its shares from the public.
- (d) An IPO occurs when a private company offers its shares to the public for the first time.
- An Initial Public Offering (IPO) refers to the process by which a private company becomes a public company by offering its shares to the general public for the first time. This allows the company to raise capital from public investors. Option D correctly describes this process, making it the correct answer. The other options do not accurately describe what an IPO entails.
3 . Question
Which organization releases the Global Financial Stability Report?
- (a) International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- (b) World Bank
- (c) Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
- (d) Bank for International Settlements (BIS)
- Key findings: The IMF warns of rising cyber threats endangering macro-financial stability, with extreme losses reaching $2.5 billion. Cyberattacks have nearly doubled since the pandemic, with financial firms, especially banks, facing the brunt.
- India ranks 10th in cybercrime, with advance fee payment frauds being the most common, according to the World Cybercrime Index developed by the University of Oxford and UNSW Canberra
Refer: https://www.insightsonindia.com/2024/04/13/reports-in-news-4/
4 . Question
Plastic Overshoot Day 2024 Report was released by which organization?
- (a) World Health Organization (WHO)
- (b) United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- (c) Plastic Pollution Coalition
- (d) Earth Action
- Released by Earth Action
- Key Findings: In 2024, it’s projected for September 5th globally and April 23rd in India. There has been over 7% rise in global plastic waste since 2021, with 12 countries responsible for 60% of mismanaged plastic waste, including China, India, and Russia.
- India is categorized as a Low-Waste-Producing Polluter with a high Mismanaged Waste Index (MWI)
- Plastic Overshoot Day (similar to Earth Overshoot Day) marks when global plastic waste surpasses the world’s capacity to manage it, leading to pollution.
5 . Question
Which one of the following statements is not correct?
- (a) Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV.
- (b) Hepatitis B, unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine.
- (c) Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses are several times more than those infected with HIV.
- (d) Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years.
- Released by WHO
- India accounted for over 11% of the global burden of hepatitis B & C cases, ranking second after China.
- Hepatitis is liver inflammation caused by various factors, such as drugs, alcohol, and autoimmune disorders. Symptoms can range from jaundice and fever to chronic illness. The five main strains are A, B, C, D, and E, with B and C leading to chronic disease, liver cirrhosis, cancer, and death. While a vaccine exists for type B, none is available for type C
6 . Question
Consider the following statements:
- DTAA is an agreement between two countries to avoid double taxation of income earned in both countries by a resident of either country.
- DTAA only applies to individuals and not to companies.
- DTAA provides for exemption, credit, or deduction in the country of residence for taxes paid in the source country.
How many of the above statements about Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) is/are correct?
- (a) Only one
- (b) Only two
- (c) All three
- However, the amended protocol has not been ratified or notified by the Income Tax Department.
- There were concerns that investments through Mauritius might face increased scrutiny by tax authorities, potentially affecting past investments as well.
- To address this issue and encourage international economic activities, countries sign Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs).
- These agreements establish agreed-upon tax rates and jurisdictions for specific types of income received by tax residents of one country from another country.
- DTAA aims to prevent international double taxation and promote capital investment, trade, and economic activities between the signatory nations.
- The agreements may cover various categories of income, depending on the types of businesses and holdings citizens have in each other’s countries.
- S1 is Correct: DTAA is an agreement between two countries to avoid double taxation of income earned in both countries by a resident of either country.
- S3 is Correct: DTAA provides for exemption, credit, or deduction in the country of residence for taxes paid in the source country.
Refer: https://www.insightsonindia.com/2024/04/13/india-mauritius-tax-treaty/
7 . Question
- It is a government body set up under the Department of Financial Services (DFS), Ministry of Finance.
- It recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- It helps the Public Sector Banks in developing strategies and capital raising plans.
How many of the above statements about the Financial Services Institution Bureau (FSIB) is/are correct?
- Statements 1 and 2 are correct.
- Constituted in 2022 under the Department of Financial Services (Ministry of Finance), by the Central Government replacing the Bank Board Bureau.
- The Financial Services Institutions Bureau (FSIB) is an organization responsible for selecting directors for state-owned banks and financial institutions in India.
- It acts as a head-hunter, identifying and recommending suitable candidates for leadership positions within the financial sector.
Refer: https://www.insightsonindia.com/2024/04/13/financial-services-institutions-bureau-fsib-2/
8 . Question
Which of the following best describes Web3?
- (a) A new version of the World Wide Web that focuses on user-generated content and social media platforms.
- (b) An upgrade to Web2 that aims to improve website loading speeds and user experience.
- (c) A decentralized internet where users have more control over their data and interactions using blockchain technology.
- (d) A design framework for creating visually appealing and interactive websites.
- Context: India’s share of Web3 developers globally has surged from 3% in 2018 to 12% in 2023, leading among emerging markets, states a report by Hashed Emergent.
- The ecosystem is young, with over 50% of developers joining in the past two years, and female participation has risen from 3% to 14% in five years. The country has a thriving Web3 sector with 1,000 startups and received $250 million in investment in 2023, mainly in finance, entertainment, and infrastructure subsectors.

Refer: https://www.insightsonindia.com/2024/04/13/web3/
9 . Question
What is the primary source of energy that powers the explosion of a Type II supernova?
- (a) Gravitational collapse
- (b) Dark energy
- (c) Nuclear fusion
- (d) Magnetic fields
- Context: A significant astronomical discovery regarding the brightest burst of light ever recorded, occurred in 2022.
- Researchers found that the burst originated from an exploding star, known as a supernova, located in a distant galaxy. However, the intensity of the burst surpassed expectations, leading to questions about its cause and implications. The burst’s extraordinary brightness, labelled as the “Brightest Of All Time” (B.O.A.T.), puzzled astronomers.
- They are massive stellar explosions that occur at the end of a star’s life cycle. They produce and eject vast amounts of energy and material into space. These explosions are responsible for creating and dispersing heavy elements such as gold, platinum, lead, and uranium into the universe.
- A Type II supernova results from the rapid collapse and violent explosion of a massive star. A star must have at least eight times, but no more than 40 to 50 times, the mass of the Sun to undergo this type of explosion.
- Type II supernovae are distinguished from other types of supernovae by the presence of hydrogen in their spectra.
- The primary source of energy that powers the explosion of a Type II supernova is nuclear fusion. As the star runs out of nuclear fuel, it can no longer maintain its core against gravitational collapse, leading to a rapid fusion reaction and subsequent explosion.
Refer: https://www.insightsonindia.com/2024/04/13/brightest-ever-cosmic-explosion/
10 . Question
Which of the following statements about baobab trees is true?
- (a) Baobab trees are native to South America.
- (b) Baobab trees can store up to thousands of liters of water in their trunks.
- (c) Baobab trees are evergreen and lose their leaves during the dry season.
- (d) Baobab trees have a lifespan of only 20-30 years.
- Context: The Global Society for the Preservation of Baobabs and Mangroves (GSPBM) has launched a pioneering initiative to revive Madagascar’s iconic baobab trees.

Refer: https://www.insightsonindia.com/2024/04/13/baobab-trees-2/
Join our Official Telegram Channel HERE for Motivation and Fast Updates
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel HERE to watch Motivational and New
Join our Twitter Channel HERE
Follow our Instagram Channel HERE
Follow us on LinkedIn : HERE

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
e-Governance. e-Governance can be defined as the application of information and communication technology (ICT) for providing government services, exchange of information, transactions, integration of previously existing services and information portals. The "e" in e-Governance stands for 'electronic'.
The objectives of e governance are as follows-One of the basic objectives of e-governance is to make every information of the government available to all in the public interest. One of its goals is to create a cooperative structure between the government and the people and to seek help and advice from the people, to make the government aware of the problems of the people.
The topic of e governance and its significance comes under the subject of Indian Polity and governance in General Studies paper 2 of the UPSC Syllabus. It is an important concept frequently in news because of the government's push towards Digital India, and e governance is an integral part of this. The PIB Summary and Analysis initiative will ...
Introduction. The "e" in e-Governance stands for 'electronic'. Thus, e-Governance is basically associated with carrying out the functions and achieving the results of governance through the utilization of I C T (Information and Communications Technology).. While Governance relates to safeguarding the legal rights of all citizens, an equally important aspect is concerned with ensuring ...
e-Governance is the use of information and communication technology (ICT) to provide government services, exchange information, conduct transactions, and integrate previously existing services and information portals. The "e" in "e-Governance" refers for "electronic.". The Government of India's Mission e-Governance, in combination ...
Improved interactions with business and industry. Citizen empowerment through access to information or. More efficient government management. The broad goals of the e-Governance are: Better service delivery to the citizens. Ushering in transparency and accountability. Empowering people through information.
Recent Government Initiatives to Promote E-Governance in India: MyGov Initiative: It has been established as Government of India's Citizen Engagement Platform which collaborates with multiple Government bodies/Ministries to engage with citizens for policy formulation and seeks the opinion of people on issues of public interest and welfare. National e-Governance Plan: It is an initiative of ...
E-Governance or 'electronic governance' is basically the application of Information and Communications Technology to the processes of Government functioning in order to bring about 'Simple, Moral, Accountable, Responsive and Transparent' (SMART) governance. Simple: This principle promotes the simplification of government rules and ...
Evolution of E-Governance in India. Department of Electronics: The establishment of the Department of Electronics in 1970 was the first major step towards e-governance in India as it brought 'information' and its communication to focus. National Informatics Centre (NIC): established in 1977, launched the District Information System program ...
Some of these are noted below: 1- Reduces Red Tapism: E-governance helps in reducing excessive red tapism, further reducing the delay in the delivery of services. 2- Reduces the cost of government: With provision of goods and services possible through one touch, the cost of government has been fairly reduced.
National e-Governance Plan (NeGP)- integrate e-Governance across the country. Common Services Centres 2.0 (CSC 2.0)- information technology so that citizens receive social, government, and private services at the doorstep. Aspirants can check the relevant links to prepare for the upcoming UPSC Civil Services exam -.
Models of e-Governance. US Prof Arie Halachmi gave 5 models of e-Governance. 1. Broadcasting. Use of Information and Communication Technology & Media to disseminate/broadcast governance info that is already present in paper form. For example, Broadcasting Laws, Rules, Judgements, result-mark sheets on the internet. 2.
E-Governance. Electronic governance, often known as e-Governance, is the use of information and communication technology (ICT) to provide government services, exchange statics, conduct communication procedures, and integrate numerous independent systems and services. E-governance is the most effective use of information and communication technologies to transform and improve the coherence ...
E-Governance - Advantages, Challenges, Types, E-Governance UPSC PDF. E-governance is the usage of ICT (Information and Communication Technology) measures in the governance mechanism to ensure better efficiency, transparency, accountability, and effectiveness of public services. The "e" in e-governance stands for 'electronic'.
The National e-Governance Plan takes a holistic view of e-Governance initiatives across the country, integrating them into a collective vision, a shared cause. Around this idea, a massive countrywide infrastructure reaching down to the remotest of villages is evolving, and large-scale digitization of records is taking place to enable easy ...
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has defined four stages of e-government Projects, each one more demanding than the next. These are: Information: Putting information on web-sites. Interaction: Allowing citizens to enquire about services, procedures etc. and filling up forms and submitting them online.
E-Governance is an implementation of delivering government services, exchanging information, communicating transactions, integrating various stand-alone systems between government to citizen (G2C), government-to-business (G2B), government-to-government (G2G), Government-to-employees (G2E) as well as back-office processes and interconnection ...
The objectives of e governance are as follows-One of the basic objectives of e-governance is to make every information of the government available to all in the public interest. One of its goals is to create a cooperative structure between the government and the people and to seek help and advice from the people, to make the government aware of the problems of the people.
Let's have a look at the advantages of E-Governance. 1. Transparency. Bribe and corruption are the main concern in India and they are considered as the biggest hurdle for the development of society. E-Governance has brought transparency in the government system and it created an unfavorable situation for corruption.
According to the World Bank, e-governance refers to the use by government agencies of information technologies (such as Wide Area Networks, the Internet, and mobile computing) that can transform relations with citizens, businesses, and other arms of government. e-Governance is a move towards SMART governance. Types of interactions in e ...
E-governance involves the use of ICTs by government organizations for Exchange of information with citizens, businesses, or other government departments. It also ensures that the benefit reaches to the lowest section of society. It needs the participation of each section of society in the socio-political decision.
Insights IAS: Simplifying UPSC IAS Exam Preparation. InsightsIAS has redefined, revolutionized and simplified the way aspirants prepare for UPSC IAS Civil Services Exam. Today, it's India's top website and institution when it comes to imparting quality content, guidance and teaching for the IAS Exam.