
Home » Uncategorized » Five Reasons Why We Should Legalize Cannabis
The Yale Ledger is a student-led magazine showcasing content from around the Yale community.
If you are affiliated with the Yale student community and have an article you want to share, please email Layla Winston .
If you notice any spam or inappropriate content, please contact us so we can remove it.
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021


Five Reasons Why We Should Legalize Cannabis
Cannabis use in the United States has had a long and complicated history. For decades, people who used cannabis were subject to social ostracization and criminal prosecution. However, attitudes toward cannabis have been evolving in recent years. An increasing number of states have started to legalize cannabis for medical or recreational use. This shift in policy has been driven by a variety of factors including changing public attitudes and the potential economic benefits of legalization. In this article, we will explore the potential benefits of legalizing cannabis in our country.
1. Legalization for the Environment
Legalizing cannabis can have significant benefits for the environment. When cannabis is grown illegally, it is often done in environmentally damaging ways, such as using chemical pesticides or clearing primary forests to make room for crops. Legalization could allow customers to support more environmental growers. This will incentivize more responsible growing practices, such as the use of organic farming methods or the use of renewable energy sources to power indoor grow operations. In addition, the culture of growing cannabis can help to discover and preserve precious marijuana seeds , increasing biodiversity and facilitating a deeper understanding of cannabis plants and their cultivation.
2. Legalization for Justice
Where cannabis is illegal, people are being arrested and charged for possession or sale, which leads to costly court cases and a burden on the criminal justice system. Legalization would free up law enforcement resources to focus on more serious crimes and simultaneously reduce the number of people incarcerated for non-violent drug offenses. This could help to reduce the overall prison population and save taxpayers money.
In addition, legalization can have significant benefits for justice and equity, particularly for marginalized communities that have been disproportionately affected by the criminalization of cannabis. Communities of color have been particularly affected by the war on drugs, with Black Americans being nearly four times more likely to be arrested for cannabis possession than white Americans, despite similar rates of use.
By regulating cannabis cultivation and sales, legalization can help to eliminate the black market and reduce the involvement of criminal organizations in the cannabis industry. This can lead to safer communities and reduced drug-related violence in communities that have been most affected by the criminalization of cannabis.
3. Legalization for Public Health
Cannabis has been shown to have many beneficial and therapeutic effects on both physical and mental health. However, people may be hesitant to seek medical marijuana treatment due to fear of legal repercussions if cannabis is illegal. Legalization can allow more people to enjoy better health outcomes. It can also promote the safer use of cannabis by educating the public on appropriate cannabis use and providing quality control measures for cannabis products. Legalization can also lead to increased research into potential medical applications of cannabis and could lead to the development of innovative treatments.
Another potential perk of cannabis legalization is that it could reduce the use of more harmful drugs. In the absence of cannabis, people may turn to more dangerous drugs like heroin or fentanyl to manage chronic pain or other conditions. By legalizing cannabis, we can provide a safer alternative for these individuals and could reduce the overall demand for these more dangerous drugs. States that have legalized cannabis found a decrease in opioid overdose deaths and hospitalizations, suggesting that cannabis are an effective alternative to prescription painkillers.
4. Legalization for the Economy
The legalization of cannabis can generate significant tax revenue for governments and create new economic opportunities. When cannabis is illegal, it is sold on the black market, and no taxes are collected on these sales. However, when it is legal, sales can be regulated, and taxes can be imposed on those sales. In states that have legalized cannabis, tax revenue from cannabis sales has been in the millions of dollars , with California registering a whopping $1.2 billion in cannabis tax revenue in 2021. This impressive income can be used to reduce budget deficits, fund various public services such as education and healthcare, and create new opportunities for investment in projects that revitalize the economy.
Aside from tax revenue, legalizing cannabis can create new jobs. The cannabis industry is a rapidly growing industry, and legalization could lead to the creation of new jobs in areas such as cultivation, processing, and retail sales. This can help to reduce unemployment and create new gainful opportunities for people who may have struggled to find employment in other industries. Legalization can also lead to increased investment in related industries, such as the development of new products or technologies to improve cannabis cultivation or the creation of new retail businesses. There are now several venture capital funds and investment groups that focus solely on cannabis-related enterprises.
5. Legalization for Acceptance
Finally, legalization could help reduce the stigma surrounding cannabis use. Before cannabis legalization, people who use the plant were often viewed as criminals or deviants. Legalization can help change this perception and lead to more open and honest conversations about cannabis use. Ultimately, legalization could lead to a more accepting and inclusive society where individuals are not judged or discriminated against for their personal and healthcare choices. By legalizing cannabis, we can harness the power of a therapeutic plant. Legalization can heal not just physical and mental ailments of individuals but also the social wounds that have resulted from its criminalization.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Powered by WordPress / Academica WordPress Theme by WPZOOM
- Program Finder
- Admissions Services
- Course Directory
- Academic Calendar
- Hybrid Campus
- Lecture Series
- Convocation
- Strategy and Development
- Implementation and Impact
- Integrity and Oversight
- In the School
- In the Field
- In Baltimore
- Resources for Practitioners
- Articles & News Releases
- In The News
- Statements & Announcements
- At a Glance
- Student Life
- Strategic Priorities
- Inclusion, Diversity, Anti-Racism, and Equity (IDARE)
- What is Public Health?
The Evidence—and Lack Thereof—About Cannabis
Research is still needed on cannabis’s risks and benefits.
Lindsay Smith Rogers
Although the use and possession of cannabis is illegal under federal law, medicinal and recreational cannabis use has become increasingly widespread.
Thirty-eight states and Washington, D.C., have legalized medical cannabis, while 23 states and D.C. have legalized recreational use. Cannabis legalization has benefits, such as removing the product from the illegal market so it can be taxed and regulated, but science is still trying to catch up as social norms evolve and different products become available.
In this Q&A, adapted from the August 25 episode of Public Health On Call , Lindsay Smith Rogers talks with Johannes Thrul, PhD, MS , associate professor of Mental Health , about cannabis as medicine, potential risks involved with its use, and what research is showing about its safety and efficacy.
Do you think medicinal cannabis paved the way for legalization of recreational use?
The momentum has been clear for a few years now. California was the first to legalize it for medical reasons [in 1996]. Washington and Colorado were the first states to legalize recreational use back in 2012. You see one state after another changing their laws, and over time, you see a change in social norms. It's clear from the national surveys that people are becoming more and more in favor of cannabis legalization. That started with medical use, and has now continued into recreational use.
But there is a murky differentiation between medical and recreational cannabis. I think a lot of people are using cannabis to self-medicate. It's not like a medication you get prescribed for a very narrow symptom or a specific disease. Anyone with a medical cannabis prescription, or who meets the age limit for recreational cannabis, can purchase it. Then what they use it for is really all over the place—maybe because it makes them feel good, or because it helps them deal with certain symptoms, diseases, and disorders.
Does cannabis have viable medicinal uses?
The evidence is mixed at this point. There hasn’t been a lot of funding going into testing cannabis in a rigorous way. There is more evidence for certain indications than for others, like CBD for seizures—one of the first indications that cannabis was approved for. And THC has been used effectively for things like nausea and appetite for people with cancer.
There are other indications where the evidence is a lot more mixed. For example, pain—one of the main reasons that people report for using cannabis. When we talk to patients, they say cannabis improved their quality of life. In the big studies that have been done so far, there are some indications from animal models that cannabis might help [with pain]. When we look at human studies, it's very much a mixed bag.
And, when we say cannabis, in a way it's a misnomer because cannabis is so many things. We have different cannabinoids and different concentrations of different cannabinoids. The main cannabinoids that are being studied are THC and CBD, but there are dozens of other minor cannabinoids and terpenes in cannabis products, all of varying concentrations. And then you also have a lot of different routes of administration available. You can smoke, vape, take edibles, use tinctures and topicals. When you think about the explosion of all of the different combinations of different products and different routes of administration, it tells you how complicated it gets to study this in a rigorous way. You almost need a randomized trial for every single one of those and then for every single indication.
What do we know about the risks of marijuana use?
Cannabis use disorder is a legitimate disorder in the DSM. There are, unfortunately, a lot of people who develop a problematic use of cannabis. We know there are risks for mental health consequences. The evidence is probably the strongest that if you have a family history of psychosis or schizophrenia, using cannabis early in adolescence is not the best idea. We know cannabis can trigger psychotic symptoms and potentially longer lasting problems with psychosis and schizophrenia.
It is hard to study, because you also don't know if people are medicating early negative symptoms of schizophrenia. They wouldn't necessarily have a diagnosis yet, but maybe cannabis helps them to deal with negative symptoms, and then they develop psychosis. There is also some evidence that there could be something going on with the impact of cannabis on the developing brain that could prime you to be at greater risk of using other substances later down the road, or finding the use of other substances more reinforcing.
What benefits do you see to legalization?
When we look at the public health landscape and the effect of legislation, in this case legalization, one of the big benefits is taking cannabis out of the underground illegal market. Taking cannabis out of that particular space is a great idea. You're taking it out of the illegal market and giving it to legitimate businesses where there is going to be oversight and testing of products, so you know what you're getting. And these products undergo quality control and are labeled. Those labels so far are a bit variable, but at least we're getting there. If you're picking up cannabis at the street corner, you have no idea what's in it.
And we know that drug laws in general have been used to criminalize communities of color and minorities. Legalizing cannabis [can help] reduce the overpolicing of these populations.
What big questions about cannabis would you most like to see answered?
We know there are certain, most-often-mentioned conditions that people are already using medical cannabis for: pain, insomnia, anxiety, and PTSD. We really need to improve the evidence base for those. I think clinical trials for different cannabis products for those conditions are warranted.
Another question is, now that the states are getting more tax revenue from cannabis sales, what are they doing with that money? If you look at tobacco legislation, for example, certain states have required that those funds get used for research on those particular issues. To me, that would be a very good use of the tax revenue that is now coming in. We know, for example, that there’s a lot more tax revenue now that Maryland has legalized recreational use. Maryland could really step up here and help provide some of that evidence.
Are there studies looking into the risks you mentioned?
Large national studies are done every year or every other year to collect data, so we already have a pretty good sense of the prevalence of cannabis use disorder. Obviously, we'll keep tracking that to see if those numbers increase, for example, in states that are legalizing. But, you wouldn't necessarily expect to see an uptick in cannabis use disorder a month after legalization. The evidence from states that have legalized it has not demonstrated that we might all of a sudden see an increase in psychosis or in cannabis use disorder. This happens slowly over time with a change in social norms and availability, and potentially also with a change in marketing. And, with increasing use of an addictive substance, you will see over time a potential increase in problematic use and then also an increase in use disorder.
If you're interested in seeing if cannabis is right for you, is this something you can talk to your doctor about?
I think your mileage may vary there with how much your doctor is comfortable and knows about it. It's still relatively fringe. That will very much depend on who you talk to. But I think as providers and professionals, everybody needs to learn more about this, because patients are going to ask no matter what.
Lindsay Smith Rogers, MA, is the producer of the Public Health On Call podcast , an editor for Expert Insights , and the director of content strategy for the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Could Medical Marijuana Help Address the Opioid Epidemic?
Policy Is Public Health
Medical Marijuana Laws Linked to Health and Labor Supply Benefits in Older Adults
Related Content

How Dangerous is Dengue?

Research Identifies Characteristics of Cities That Would Support Young People’s Mental Health

Alumni Spotlight: Junrui Di, PhD '19

Child Diarrhea Has a Cheap and Easy Fix—Why Isn’t It Reaching Patients?
How Abortion Trigger Laws Impact Mental Health
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Occupational Therapy
- Healthy Aging
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
Pros and Cons of Legalizing Marijuana
The pros of legalizing marijuana, the cons of legalizing marijuana.
- Scientific Evidence
The pros and cons of legalizing marijuana are still being debated. Today, 37 U.S. states allow for the medical use of marijuana. A growing number allow recreational use.
However, as a Schedule I controlled substance, marijuana is illegal under federal law. This Drug Enforcement Administration designation means that marijuana is considered to have "no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse." It also limits medical studies into the potential benefits of cannabis .
This article explains the pros and cons of legalizing marijuana, as some have argued them.
Americans overwhelmingly support the legalization of marijuana. In fact, according to the Pew Research Center, 88% of Americans support legalizing marijuana. Of those, 59% say it should be legal for medical and recreational use and 30% say it should be legal for medical reasons only.
Several possible health benefits of medical marijuana have been proposed:
- Nausea : Marijuana is effective in relieving nausea and vomiting. Studies have shown that cannabis can decrease nausea caused by chemotherapy and almost eliminate vomiting.
- Spasticity : Marijuana can relieve pain and spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis.
- Appetite : Marijuana can help treat appetite loss associated with conditions like HIV/AIDS and certain types of cancers.
- Chronic pain : Marijuana can relieve certain types of chronic pain, including neuropathic pain, which is caused by nerve damage.
And arguments in favor of using medical marijuana include:
- It's safer : Marijuana is safer than some other medications prescribed to treat pain. For example, some people may use it instead of opioids for pain management. Opioids are highly addictive and are typically not recommended for long-term use in treating chronic pain.
- You can use it in many ways : You do not need to smoke cannabis for its benefits. Products such as cannabidiol oil (CBD), topical pain relief treatments, edibles, and other non-smoking applications are now available.
- You don't need to get high : As studies continue, researchers are finding benefits in the individual compounds in cannabis. When these chemicals are isolated—such as CBD has been—they can offer treatment options without the "high" produced by the compound commonly known as THC.
- It's natural : People have used marijuana for centuries as a natural medicinal agent with good results.
Recreational Marijuana
Marijuana is legal for recreational use in 20 states and the District of Columbia. In 20 other states, marijuana has been decriminalized. This means there are no criminal penalties in these states for minor marijuana-related offenses like possession of small amounts or cultivation for personal use.
Those who oppose the legalization of marijuana point to the health risks of the drug, including:
- Memory issues : Frequent marijuana use may seriously affect your short-term memory.
- Cognition problems : Frequent use can impair your cognitive (thinking) abilities.
- Lung damage : Smoking anything, whether it's tobacco or marijuana, can damage your lung tissue. In addition, smoking marijuana could increase the risk of lung cancer .
- Abuse : Marijuana carries a risk of abuse and addiction.
- Accidents : Marijuana use impairs driving skills and increases the risk for car collisions.
The fact that the federal government groups it in the same category as drugs like heroin, LSD, and ecstasy is reason enough to keep it illegal, some say. As Schedule I drugs are defined by having no accepted value, legalization could give users the wrong impression about where research on the drug stands.
Scientific Evidence Remains Limited
In the past, clinical trials to to determine if marijuana is effective in treating certain conditions have been restrictive and limited. However, as medical marijuana becomes more common throughout the world, researchers are doing more studies.
Expert reviews of current research continue to say more studies are needed. In addition, many hurdles involve controlling the quality and dosing of cannabis with what is legally available to researchers.
One review of research noted that the long-term effects of cannabis are still unknown. Without more research into dosage and adverse effects, scientific evidence of risks and therapeutic effects remains soft.
Researchers need to evaluate marijuana using the same standards as other medications to understand whether it is valuable for managing any conditions.
Until the federal government downgrades marijuana from a Schedule I drug, widespread clinical trials are unlikely to happen in the United States.
Medical marijuana is increasingly available in the U.S. It is often used to treat chronic pain, muscle spasms, and nausea and vomiting, and to increase appetite. However, it can affect thinking and memory, increase the risk of accidents, and smoking it may harm the lungs and lead to cancer.
More studies are needed to understand the benefits of medical marijuana. However, unless the federal government removes it as a Schedule I controlled substance, research, access, and legality will remain complicated.
A Word From Verywell
There are both benefits and risks to medical marijuana. If you're considering using marijuana medicinally, don't be afraid to talk to your doctor about it. They can help you determine whether marijuana may be the proper treatment for you.
Medical marijuana remains controversial, but it is gaining traction as a legitimate recommendation for various symptoms. Even though many states have legalized cannabis for medicinal purposes and recreational use, more research is needed.
National Conference of State Legislatures. State medical marijuana laws .
United States Drug Enforcement Administration. Drug scheduling .
Pew Research Center. Americans overwhelmingly say marijuana should be legal for recreational or medical use .
Badowski ME. A review of oral cannabinoids and medical marijuana for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: a focus on pharmacokinetic variability and pharmacodynamics . Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017;80(3):441-449. doi:10.1007/s00280-017-3387-5
Corey-Bloom J, Wolfson T, Gamst A, et al. Smoked cannabis for spasticity in multiple sclerosis: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial . CMAJ . 2012;184(10):1143-1150. doi:10.1503/cmaj.110837
American Cancer Society. Marijuana and Cancer .
Hill KP. Medical marijuana for treatment of chronic pain and other medical and psychiatric problems: A clinical review . JAMA. 2015;313(24):2474-83. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.6199
Choo EK, Feldstein Ewing SW, Lovejoy TI. Opioids out, cannabis in: Negotiating the unknowns in patient care for chronic pain . JAMA . 2016;316(17):1763-1764. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.13677
Corroon J, Sexton M, Bradley R. Indications and administration practices amongst medical cannabis healthcare providers: a cross-sectional survey . BMC Fam Pract. 2019;20(1):174. doi:10.1186/s12875-019-1059-8
Morales P, Reggio PH, Jagerovic N. An overview on medicinal chemistry of synthetic and natural derivatives of cannabidiol . Front Pharmacol . 2017;8:422. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00422
The Council of State Governments. State approaches to marijuana policy .
Harvard Health Publishing, Harvard Medical School. The Effects of Marijuana on your Memory .
Ghasemiesfe M, Barrow B, Leonard S, Keyhani S, Korenstein D. Association between marijuana use and risk of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis . JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(11):e1916318. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.16318
Preuss U, Huestis M, Schneider M et al. Cannabis use and car crashes: A review . Front Psychiatry . 2021;12. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.643315
Deshpande A, Mailis-Gagnon A, Zoheiry N, Lakha SF. Efficacy and adverse effects of medical marijuana for chronic noncancer pain: Systematic review of randomized controlled trials . Can Fam Physician. 2015;61(8):e372-81.
Hill KP, Palastro MD, Johnson B, Ditre JW. Cannabis and pain: a clinical review . Cannabis Cannabinoid Res . 2017;2(1):96-104. doi:10.1089/can.2017.0017
Maida V, Daeninck PJ. A user's guide to cannabinoid therapies in oncology . Curr Oncol. 2016;23(6):398-406. doi:10.3747/co.23.3487
Meier MH, Caspi A, Cerdá M, et al. Associations between cannabis use and physical health problems in early midlife: A longitudinal comparison of persistent cannabis vs tobacco users. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016;73(7):731-40. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.0637
By Angela Morrow, RN Angela Morrow, RN, BSN, CHPN, is a certified hospice and palliative care nurse.
Why We Must Legalize Marijuana
The federal prohibition of marijuana has been unnecessarily cruel—wasting billions of dollars, unjustly harming millions of lives, and furthering racist policies.
by Robert Reich
May 28, 2019
AP Photo/Richard Vogel
The federal prohibition on marijuana has been a disaster. For decades, millions of Americans have been locked up and billions of dollars have been wasted. It's also deepened racial and economic inequality.
We must end this nonsensical prohibition.
The facts are staggering. In 2017, more Americans were arrested for marijuana possession than for murder, rape, aggravated assault and robbery combined. That’s one marijuana arrest every minute.
The costs associated with enforcing this ban—including arrests, court costs, and incarceration— reach nearly $14 billion a year .
Prohibition also hurts the economy in terms of lost wages. And Americans with criminal records have a harder time finding a job and getting the education they need.
On the other hand, legalizing, taxing, and regulating is good for the economy and creates jobs.
By simply levying a tax on marijuana like we do cigarettes and alcohol, state and local governments could raise more than $6 billion a year . This doesn’t even include additional revenue from taxes on the marijuana industry.
States like Colorado and Washington that tax and regulate marijuana have already generated millions of dollars for health care, education, and other public investments.
But this is more than an economic issue. It's also a matter of racial justice and equality.
The federal prohibition on marijuana dates back to anti-Mexican sentiment in the 1930s. In large part, it was nothing more than another way to criminalize communities of color.
Today, black and brown Americans are still much more likely to be arrested for marijuana than white Americans , despite using marijuana at similar rates.
Given the racist legacy of these laws, it's particularly important that the economic gains of legalization extend to communities that have been most harmed by the war on drugs.
Support for marijuana legalization has surged in recent years, with two-thirds of Americans now in favor of it. Even a majority of Republicans are in support , and more states are taking action to reform their laws and move toward legalization.
Yet Donald Trump and his administration are trying to turn back the clock. They've even formed a task force to weaken public support for legalization and help spread misinformation about so-called “marijuana threats.”
Just as with the prohibition on alcohol in the 1920s, the federal prohibition of marijuana has been unnecessarily cruel—wasting billions of dollars, unjustly harming millions of lives, and furthering racist policies.
It's time to legalize marijuana.
You can count on the Prospect , can we count on you?
There's no paywall here. Your donations power our newsroom as we report on ideas, politics and power — and what’s really at stake as we navigate another presidential election year. Please, become a member , or make a one-time donation , today. Thank you!

About the Prospect / Contact Info
Browse Archive / Back Issues
Subscription Services
Privacy Policy
DONATE TO THE PROSPECT

Copyright 2023 | The American Prospect, Inc. | All Rights Reserved
2018 Theses Doctoral
Essays on Cannabis Legalization
Thomas, Danna Kang
Though the drug remains illegal at the federal level, in recent years states and localities have increasingly liberalized their marijuana laws in order to generate tax revenue and save resources on marijuana law enforcement. Many states have adopted some form of medical marijuana and/or marijuana decriminalization laws, and as of 2017, Washington, Colorado, Maine, California, Oregon, Massachusetts, Nevada, Alaska, and the District of Columbia have all legalized marijuana for recreational use. In 2016 recreational marijuana generated over $1.8 billion in sales. Hence, studying marijuana reforms and the policies and outcomes of early recreational marijuana adopters is an important area of research. However, perhaps due to the fact that legalized recreational cannabis is a recent phenomenon, a scarcity of research exists on the impacts of recreational cannabis legalization and the efficacy and efficiency of cannabis regulation. This dissertation aims to fill this gap, using the Washington recreational marijuana market as the primary setting to study cannabis legalization in the United States. Of first order importance in the regulation of sin goods such as cannabis is quantifying the value of the marginal damages of negative externalities. Hence, Chapter 1 (co-authored with Lin Tian) explores the impact of marijuana dispensary location on neighborhood property values, exploiting plausibly exogenous variation in marijuana retailer location. Policymakers and advocates have long expressed concerns that the positive effects of the legalization--e.g., increases in tax revenue--are well spread spatially, but the negative effects are highly localized through channels such as crime. Hence, we use changes in property values to measure individuals' willingness to pay to avoid localized externalities caused by the arrival of marijuana dispensaries. Our key identification strategy is to compare changes in housing sales around winners and losers in a lottery for recreational marijuana retail licenses. (Due to location restrictions, license applicants were required to provide an address of where they would like to locate.) Hence, we have the locations of both actual entrants and potential entrants, which provides a natural difference-in-differences set-up. Using data from King County, Washington, we find an almost 2.4% decrease in the value of properties within a 0.5 mile radius of an entrant, a $9,400 decline in median property values. The aforementioned retail license lottery was used to distribute licenses due to a license quota. Retail license quotas are often used by states to regulate entry into sin goods markets as quotas can restrict consumption by decreasing access and by reducing competition (and, therefore, increasing markups). However, license quotas also create allocative inefficiency. For example, license quotas are often based on the population of a city or county. Hence, licenses are not necessarily allocated to the areas where they offer the highest marginal benefit. Moreover, as seen in the case of the Washington recreational marijuana market, licenses are often distributed via lottery, meaning that in the absence of an efficiency secondary market for licenses, the license recipients are not necessarily the most efficient potential entrants. This allocative inefficiency is generated by heterogeneity in firms and consumers. Therefore, in Chapter 2, I develop a model of demand and firm pricing in order to investigate firm-level heterogeneity and inefficiency. Demand is differentiated by geography and incorporates consumer demographics. I estimate this demand model using data on firm sales from Washington. Utilizing the estimates and firm pricing model, I back out a non-parametric distribution of firm variable costs. These variable costs differ by product and firm and provide a measure of firm inefficiency. I find that variable costs have lower inventory turnover; hence, randomly choosing entrants in a lottery could be a large contributor to allocative inefficiency. Chapter 3 explores the sources of allocative inefficiency in license distribution in the Washington recreational marijuana market. A difficulty in studying the welfare effects of license quotas is finding credible counterfactuals of unrestricted entry. Therefore, I take a structural approach: I first develop a three stage model that endogenizes firm entry and incorporates the spatial demand and pricing model discussed in Chapter 2. Using the estimates of the demand and pricing model, I estimate firms' fixed costs and use data on locations of those potential entrants that did not win Washington's retail license lottery to simulate counterfactual entry patterns. I find that allowing firms to enter freely at Washington's current marijuana tax rate increases total surplus by 21.5% relative to a baseline simulation of Washington's license quota regime. Geographic misallocation and random allocation of licenses account for 6.6\% and 65.9\% of this difference, respectively. Moreover, as the primary objective of these quotas is to mitigate the negative externalities of marijuana consumption, I study alternative state tax policies that directly control for the marginal damages of marijuana consumption. Free entry with tax rates that keep the quantity of marijuana or THC consumed equal to baseline consumption increases welfare by 6.9% and 11.7%, respectively. I also explore the possibility of heterogeneous marginal damages of consumption across geography, backing out the non-uniform sales tax across geography that is consistent with Washington's license quota policy. Free entry with a non-uniform sales tax increases efficiency by over 7% relative to the baseline simulation of license quotas due to improvements in license allocation.
- Cannabis--Law and legislation
- Marijuana industry
- Drug legalization
- Drugs--Economic aspects

More About This Work
- DOI Copy DOI to clipboard
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Impact on Tax Revenue
Income and jobs, investment opportunities, saved money, the bottom line.
- Government & Policy
The Economic Benefits of Legalizing Marijuana
Mrinalini Krishna is the Senior Editor of investing news at Investopedia. She's been a journalist for more than 10 years covering business, personal finance, and investing news.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Mrinalini-Krishna-BW-WebReady-f6660a6f2b694fbaa3112fe3d02580d5.jpg)
Over the past several years, states have been voting to decriminalize marijuana, making it legal for both medicinal and recreational purposes—and also making it a big business. Taking a leaf out of Colorado or Washington's book, four states—New Jersey, South Dakota, Montana, and Arizona—passed measures in 2022 to make marijuana consumption for recreational purposes legal. Mississippi also voted to allow medical marijuana.
Still, state legislation remains heavily divided on the topic. Since the 2020 election, South Dakota Circuit Judge Christina Klinger ruled that the measure was unconstitutional. In November 2021, the South Dakota Supreme Court agreed and ruled against pot legalization. On the other hand, Arizona has collected more than $284 million of tax revenue since the legalization of marijuana in the state.
Key Takeaways
- There has been a growing popular movement in the United States to legalize marijuana for medicinal and recreational uses, with several states adopting such measures already.
- One motivation for legalization is the economic benefits that can come from the regulated commercial availability of marijuana.
- Increased tax revenues, job growth, and investment opportunities all are powerful incentives to push for legalization.
- As of November 2022, 21 states allow for personal consumption of marijuana, while 37 states allow medical usage.
- Although the collection of tax revenue has yet to start in many of these states, a total of $3.7 billion of proceeds were collected in 2021, more than double tax revenue generated in 2019.
All told, more and more states are moving to legalize marijuana (whether for medicinal or recreational use, or both). The legal changes have spawned a burgeoning industry of legal cannabis companies , including those that aim to research and develop cannabis-based medical products, those that are working to distribute and grow marijuana, and many others. But there are still some holdouts. In the 2022 midterm elections, for instance, two states voted to legalize marijuana (Maryland and Missouri), while three states voted down ballot measures to do so (North Dakota, South Dakota, and Arkansas).
Following the 2022 midterms in November, 37 states allow the use of medical cannabis products, with 21 states and the District of Columbia allowing the use of non-medical cannabis products for personal or recreational consumption. More states are continuing to propose new legislation to encourage legal activity. For instance, Delaware is circulating HB 305, a bill that would make marijuana legal for adults.
At the federal level, things are also looking more progressive. In October 2022, President Biden pardoned all prior federal offenses of simple possession of marijuana and asked the Justice Department to review the current classification of marijuana as a Schedule I controlled substance. These efforts could pave the way to nationwide decriminalization in the near future.
The economic benefits of legalizing weed have already been apparent as the first states have moved to change their legal positions. Overall, legal marijuana could mean a big push for state economies and big bucks for both the state and the federal governments. Though state law and federal law remain divided on the issue. let's explore some of the key economic benefits of legal marijuana.
Better-than-expected sales of marijuana in Colorado and Washington over the past several years have resulted in buoyant tax revenues. In 2021, Washington collected $559.5 million of legal marijuana revenue, over $85 million more revenue than 2020. Meanwhile, Colorado collected $423 million of marijuana tax revenue in 2021, up almost 10% from the year prior.
In 2019, total tax revenue collected by all states topped $1.7 billion. Two years later, the total dollar revenue had more than doubled. Aggregate revenue for all states hit $3.7 billion for legal, adult-use cannabis sales, and this does not include revenue generated for statewide budgets, cities, and towns. In addition, six states that have approved marijuana use had not started collecting marijuana tax revenue in 2021.
Should marijuana become legal on a federal level, the benefits to the economy could be exceptional: A report from cannabis analytics company New Frontier suggests that federally legal pot could generate an additional $105.6 billion in aggregate federal tax revenue by 2025.
Colorado began collecting marijuana tax revenue in 2014. In 2021, its total-to-date collections have surpassed $2 billion.
Setting up marijuana nurseries and dispensaries would be the first step for the states that voted in favor of medical marijuana. These would not only create jobs but also set the ball rolling for economic activity in the pot industry in these areas. In the case of states like California and Nevada where such infrastructure already exists, the economic impact has become more quantifiable as the sector has matured.
An RCG Economics and Marijuana Policy Group study on Nevada says that legalizing recreational marijuana in the state could support over 41,000 jobs till 2024 and generate over $1.7 billion in labor income. The ICF study estimates at least 81,000 additional direct, indirect, and induced jobs in California as a result of legalized marijuana sales. It also projects an increase in total labor income by at least $3.5 billion.
New Frontier's report predicting the impact of federally legal marijuana suggests that nationwide legalization could generate 1 million jobs by 2025. These jobs would likely come from the quickly growing industry that would spring up across the nation. Workers would be needed to farm, process, distribute, and sell marijuana-based products.
Further, there would be ample opportunities for secondary industries that are related to legal cannabis although not directly involved in its production and distribution. These might include software developers, financing services, construction companies, and many others.
Legal marijuana presents the possibility of tremendous benefits to economies on a local and a national scale. It also could help to secure the investment portfolios of investors across the country and further afield as well. While marijuana remains illegal on the federal level, it is difficult for investors to capitalize on the growth of the industry.
The number of marijuana-related companies trading on public stock exchanges is minuscule, and while investors do have the option of working with over-the-counter exchanges, many of the most successful businesses in the early legal cannabis space have been based in Canada or other countries.
Should marijuana become legal on the national level, marijuana companies would be free to list their stocks on all U.S. exchanges, thereby enhancing liquidity and opening up access to many more investors. Should the growth rates for the cannabis space continue as they have in recent years, it's likely that investors would express a keen interest in the industry.
As of 2022, the largest marijuana exchange-traded fund (ETF) was AdvisorShares Pure US Cannabis ETF ( MSOS ) with over $1 billion of assets under management .
When considering the economic benefits of legal marijuana, it's important to think of the money that might be saved as well as revenue that could be generated through such a process. Currently, federal marijuana enforcement costs several billion dollars per year. A 2013 report by the American Civil Liberties Union found that the costs at that time were approximately $3.6 billion per year.
The more states that legalize cannabis, the lower the cost of enforcement would likely be; if marijuana were to be legalized on a national level, these costs would likely drop considerably. If marijuana were removed from the list of controlled substances, far fewer court cases involving the substance would go to trial, resulting in fewer incarcerations and, in turn, more money saved.
Legalized marijuana also stands to benefit medical consumers of cannabis-based products. As marijuana becomes legal in more and more parts of the country, it's likely that the price will drop overall as a result of commoditization .
This may not immediately seem like good news for overall tax revenue or for marijuana companies looking to maximize profits. However, individuals utilizing marijuana-based products for medical treatment would stand to benefit considerably from lower prices for these items.
How Many States Have Legalized Marijuana?
As of 2022, 37 states have legalized the medical use of marijuana, with 21 of those allowing recreational use as well. The District of Columbia, Guam, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands also allow medical use by qualified individuals.
How Much Money Are States Collecting in Marijuana Tax Revenue?
In 2021, the states that legalized marijuana for personal consumption generated $3.7 billion in annual tax revenue. This revenue does not include city revenue or proceeds distributed to smaller municipalities.
What Is the Economic Impact of Legalizing Marijuana?
States that legalize marijuana have recognized various economic benefits. There are direct tax proceeds generated for the state. States employ thousands of employees of oversee the production, distribution, and management of the sector. There are also potential savings to the legal enforcement of the substance if certain criteria are no longer considered illegal.
There is ample pushback against the idea of legalizing marijuana across the country. Critics cite the potential for confusion among law enforcement officers aiming to keep up with shifting regulations, a concern about increased homelessness or youth use of the substance, the potential for decreased property values, and much more. Some are opposed to changing the regulatory status of marijuana simply because it means a change to the status quo.
All of these reasons combine to decrease the likelihood that marijuana will become legal at a national level any time soon. However, as more and more states move to individually decriminalize cannabis use in various ways, and as the economic benefits of a legal marijuana industry take effect, there are also many compelling reasons to consider nationwide legalization.
Ballotpedia. " Marijuana on the Ballot ."
PBS. " South Dakota Supreme Court Rules Against Pot Legalization ."
Arizona Department of Revenue. " Marijuana Tax Collection ."
National Conference of State Legislatures. " State Medical Cannabis Laws ."
Delaware General Assembly. " House Amendment 1 to House Bill 305 ."
The White House. " Statement from President Biden on Marijuana Reform ."
National Conference of State Legislatures. " Regulating Marijuana: Taxes, Banking and Federal Laws ."
Washington State Treasurer. " Washington Marijuana Revenue ."
Colorado Department of Revenue. " Marijuana Tax Reports ."
Marijuana Policy Project. " Cannabis Tax Revenue in States that Regulate Cannabis for Adult Use ."
New Frontier Data. " Cannabis Taxes Could Generate $106 Billion, Create 1 Million Jobs by 2025 ."
RCG Economics. " Economic Benefits of Legalized Adult-Use Marijuana in Nevada ."
ICF. " The Economic Impacts of Marijuana Sales in the State of California ."
AdvisorShares. " AdvisorShares Pure US Cannabis ETF ."
American Civil Liberties Union. " Report: The War on Marijuana Is Black and White ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/marijuana-plants-56a8d1265f9b58b7d0f5680d.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Home — Essay Samples — Law, Crime & Punishment — Marijuana Legalization — Why Marijuana Should Be Legalized and Its Benefits
Why Marijuana Should Be Legalized and Its Benefits
- Categories: Marijuana Legalization
About this sample

Words: 1013 |
Published: Jan 30, 2024
Words: 1013 | Pages: 2 | 6 min read
Introduction
- American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU). (n.d.). The War on Marijuana in Black and White. Retrieved from https://www.aclu.org/report/report-war-marijuana-black-and-white
- Drug Policy Alliance. (n.d.). Marijuana Arrests by the Numbers. Retrieved from https://www.drugpolicy.org/resource/marijuana-arrests-numbers
- Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA). (2014). Medical Cannabis Laws and Opioid Analgesic Overdose Mortality in the United States, 1999-2010. Retrieved from https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/1897424
- Leafly. (2020). Cannabis Jobs Report 2020. Retrieved from https://d3atagt0rnqk7k.cloudfront.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/07123735/Leafly-Jobs-Report-2020.pdf
- National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). (2021). Marijuana Research Report. Retrieved from https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/marijuana
- Tax Foundation. (2016). The Budgetary Effects of Ending Drug Prohibition. Retrieved from https://taxfoundation.org/budgetary-effects-ending-drug-prohibition

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Law, Crime & Punishment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 977 words
2 pages / 925 words
3 pages / 1303 words
3 pages / 1255 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Marijuana Legalization
The debate over the legalization of weed is a contentious and multifaceted issue, with implications for medicine, economics, ethics, and society. In this essay on whether weed should be legalized, we will explore the potential [...]
The debate surrounding the legalization of medical marijuana has been a contentious and evolving issue in many countries around the world. While it remains illegal in some places, an increasing number of regions are recognizing [...]
Legalizing marijuana has been a topic of debate for many years, with strong arguments on both sides of the issue. However, as scientific research and public opinion continue to evolve, it is becoming increasingly clear that the [...]
Marijuana, also known as cannabis, has been used for various medical purposes for centuries. However, its legality and acceptance as a medical treatment have been a subject of debate for many years. This essay will argue that [...]
Cannabis is a medication that is continually being discussed everywhere throughout the media. There is steady discussion on whether it ought to be legitimized or not. Likewise, banter on if it somehow happened to be authorized, [...]
“There are two sides to every story, and the truth usually lies somewhere in the middle.” – Jean Gati There is the “War on Drugs” on one side and Marijuana Legalization as a response to the failures of this war. The binge of [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Analysis of Arguments: Should Marijuana Be Legalized? Annotated Bibliography
Title of Article #1: Green, T. V. (2021). Americans overwhelmingly say marijuana should be legal for recreational or medical use. Pew Research Center. Web.
Pro Arguments (Support for your position):
- The majority of Americans agree on the necessity to legalize marijuana.
- Its medical and recreational use is a sufficient basis for this change.
Con Arguments (Opposing Views):
- The resistance of older populations to this idea is highly possible.
- This initiative is accompanied by concerns regarding the actual use of marijuana.
Definition(s)
History/background information.
Over the past years, the number of people in the United States supporting the legalization of marijuana doubled, which means the need for action.
Facts/Statistics/Expert Testimony
Numerous surveys conducted over the past decades confirm the support of marijuana legalization by 91% of Americans, whereas the opposition does not provide substantial objections.
Title of Article #2: Lopez, G. (2019). 9 questions about marijuana legalization you were too embarrassed to ask. The Vox. Web.
- Marijuana has already been legalized in eleven states, and their experience can be adopted.
- The need in unity in legislature is required for avoiding conflicts.
- With the development of marijuana market, manufacturers might avoid responsibility.
- The possibility of addiction does not allow introducing this change all over the country.
Over time, there has been no clear opinion of legislators regarding the legalization of marijuana, and the differences are attributed to the policies of Democratic and Republican activists.
Surveys among American indicate their support of the legalization of marijuana, but marijuana laws are varied across the country.
Title of Article #3: McCarthy, N. (2019). The arguments for and against marijuana legalization in the U.S. [Infographic]. Forbes. Web.
- New population groups, including adults aged 55 and older, begin to support this idea.
- The possibility of focusing on other crimes rather than the use of marijuana seems beneficial for their investigation.
- Driver safety after using marijuana does not make this idea an optimal initiative.
- The legalization of marijuana might encourage more people to use it.
In the past, the growing popularity of marijuana resulted in the formation of supporters and opponents of its legalization.
The conducted polls showed that both supporters and opponents of the legalization of marijuana provide substantial evidence for underpinning their particular views.
Green, T. V. (2021). Americans overwhelmingly say marijuana should be legal for recreational or medical use. Pew Research Center. Web.
Lopez, G. (2019). 9 questions about marijuana legalization you were too embarrassed to ask. The Vox. Web.
McCarthy, N. (2019). The arguments for and against marijuana legalization in the U.S. [Infographic]. Forbes. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, August 1). Analysis of Arguments: Should Marijuana Be Legalized? https://ivypanda.com/essays/analysis-of-arguments-should-marijuana-be-legalized/
"Analysis of Arguments: Should Marijuana Be Legalized?" IvyPanda , 1 Aug. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/analysis-of-arguments-should-marijuana-be-legalized/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Analysis of Arguments: Should Marijuana Be Legalized'. 1 August.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Analysis of Arguments: Should Marijuana Be Legalized?" August 1, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/analysis-of-arguments-should-marijuana-be-legalized/.
1. IvyPanda . "Analysis of Arguments: Should Marijuana Be Legalized?" August 1, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/analysis-of-arguments-should-marijuana-be-legalized/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Analysis of Arguments: Should Marijuana Be Legalized?" August 1, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/analysis-of-arguments-should-marijuana-be-legalized/.
- Why Is Marijuana Legalized In Some States And Not Others?
- Why Marijuana Should Be Legalized?
- Policy Brief: Why Marijuana Use Should Be Legalized in the Us
- How New York Would Benefit From Legalized Medical Marijuana
- Legalizing Marijuana: Pros and Cons
- Legalized Marijuana: Negative and Positive Sides
- Public Safety and Marijuana Legalization
- Minor and Major Arguments on Legalization of Marijuana
- Should Marijuana Be Legal?
- Marijuana Must Not Be Legalized
- Policy Development Draft Assignment: Social Networks
- The Concept of Defamation in the UAE as an Example
- Social Security Benefits: A Policy Proposal
- The Acme Fireworks Firm's Growth and Expansion
- Response to Marina Angel’s Article
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024

Regions & Countries
9 facts about americans and marijuana.

The use and possession of marijuana is illegal under U.S. federal law, but about three-quarters of states have legalized the drug for medical or recreational purposes. The changing legal landscape has coincided with a decades-long rise in public support for legalization, which a majority of Americans now favor.
Here are nine facts about Americans’ views of and experiences with marijuana, based on Pew Research Center surveys and other sources.
As more states legalize marijuana, Pew Research Center looked at Americans’ opinions on legalization and how these views have changed over time.
Data comes from surveys by the Center, Gallup , and the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health from the U.S. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Information about the jurisdictions where marijuana is legal at the state level comes from the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws .
More information about the Center surveys cited in the analysis, including the questions asked and their methodologies, can be found at the links in the text.
Around nine-in-ten Americans say marijuana should be legal for medical or recreational use, according to a January 2024 Pew Research Center survey . An overwhelming majority of U.S. adults (88%) say either that marijuana should be legal for medical use only (32%) or that it should be legal for medical and recreational use (57%). Just 11% say the drug should not be legal in any form. These views have held relatively steady over the past five years.
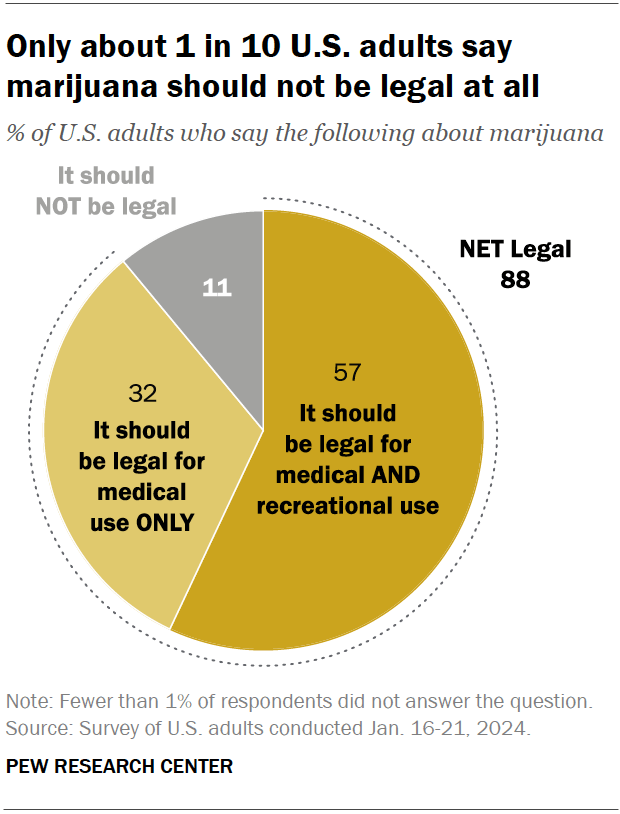
Views on marijuana legalization differ widely by age, political party, and race and ethnicity, the January survey shows.

While small shares across demographic groups say marijuana should not be legal at all, those least likely to favor it for both medical and recreational use include:
- Older adults: 31% of adults ages 75 and older support marijuana legalization for medical and recreational purposes, compared with half of those ages 65 to 74, the next youngest age category. By contrast, 71% of adults under 30 support legalization for both uses.
- Republicans and GOP-leaning independents: 42% of Republicans favor legalizing marijuana for both uses, compared with 72% of Democrats and Democratic leaners. Ideological differences exist as well: Within both parties, those who are more conservative are less likely to support legalization.
- Hispanic and Asian Americans: 45% in each group support legalizing the drug for medical and recreational use. Larger shares of Black (65%) and White (59%) adults hold this view.
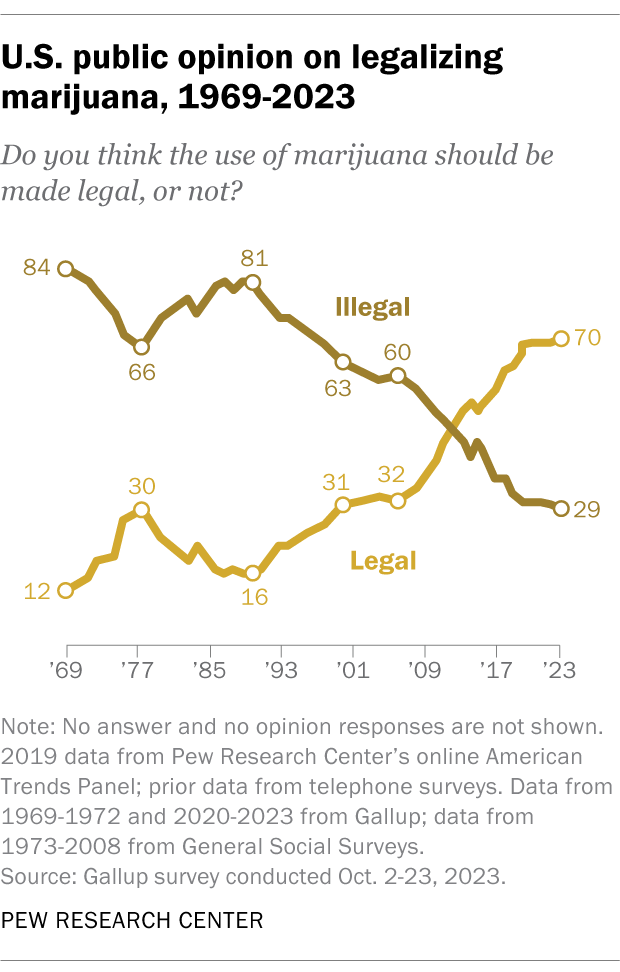
Support for marijuana legalization has increased dramatically over the last two decades. In addition to asking specifically about medical and recreational use of the drug, both the Center and Gallup have asked Americans about legalizing marijuana use in a general way. Gallup asked this question most recently, in 2023. That year, 70% of adults expressed support for legalization, more than double the share who said they favored it in 2000.
Half of U.S. adults (50.3%) say they have ever used marijuana, according to the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health . That is a smaller share than the 84.1% who say they have ever consumed alcohol and the 64.8% who have ever used tobacco products or vaped nicotine.
While many Americans say they have used marijuana in their lifetime, far fewer are current users, according to the same survey. In 2022, 23.0% of adults said they had used the drug in the past year, while 15.9% said they had used it in the past month.
While many Americans say legalizing recreational marijuana has economic and criminal justice benefits, views on these and other impacts vary, the Center’s January survey shows.
- Economic benefits: About half of adults (52%) say that legalizing recreational marijuana is good for local economies, while 17% say it is bad. Another 29% say it has no impact.
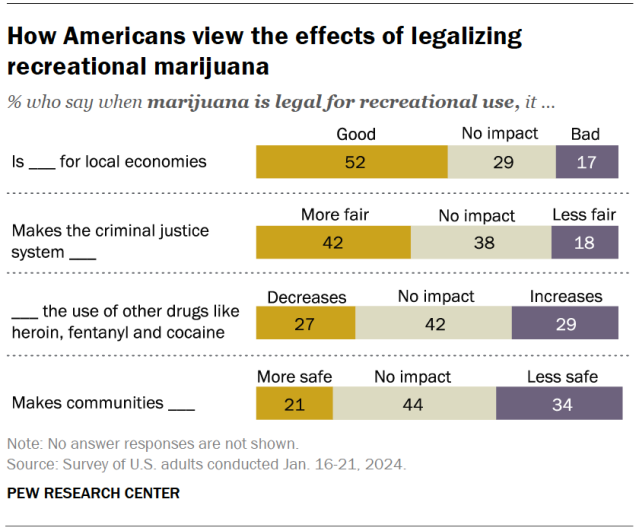
- Criminal justice system fairness: 42% of Americans say legalizing marijuana for recreational use makes the criminal justice system fairer, compared with 18% who say it makes the system less fair. About four-in-ten (38%) say it has no impact.
- Use of other drugs: 27% say this policy decreases the use of other drugs like heroin, fentanyl and cocaine, and 29% say it increases it. But the largest share (42%) say it has no effect on other drug use.
- Community safety: 21% say recreational legalization makes communities safer and 34% say it makes them less safe. Another 44% say it doesn’t impact safety.
Democrats and adults under 50 are more likely than Republicans and those in older age groups to say legalizing marijuana has positive impacts in each of these areas.
Most Americans support easing penalties for people with marijuana convictions, an October 2021 Center survey found . Two-thirds of adults say they favor releasing people from prison who are being held for marijuana-related offenses only, including 41% who strongly favor this. And 61% support removing or expunging marijuana-related offenses from people’s criminal records.
Younger adults, Democrats and Black Americans are especially likely to support these changes. For instance, 74% of Black adults favor releasing people from prison who are being held only for marijuana-related offenses, and just as many favor removing or expunging marijuana-related offenses from criminal records.
Twenty-four states and the District of Columbia have legalized small amounts of marijuana for both medical and recreational use as of March 2024, according to the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws (NORML), an advocacy group that tracks state-level legislation on the issue. Another 14 states have legalized the drug for medical use only.
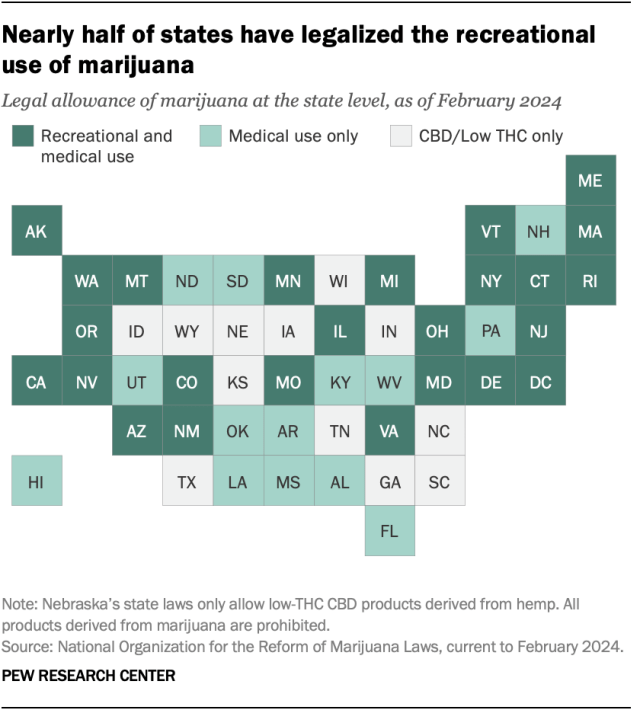
Of the remaining 12 states, all allow limited access to products such as CBD oil that contain little to no THC – the main psychoactive substance in cannabis. And 26 states overall have at least partially decriminalized recreational marijuana use , as has the District of Columbia.
In addition to 24 states and D.C., the U.S. Virgin Islands , Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands have legalized marijuana for medical and recreational use.
More than half of Americans (54%) live in a state where both recreational and medical marijuana are legal, and 74% live in a state where it’s legal either for both purposes or medical use only, according to a February Center analysis of data from the Census Bureau and other outside sources. This analysis looked at state-level legislation in all 50 states and the District of Columbia.
In 2012, Colorado and Washington became the first states to pass legislation legalizing recreational marijuana.
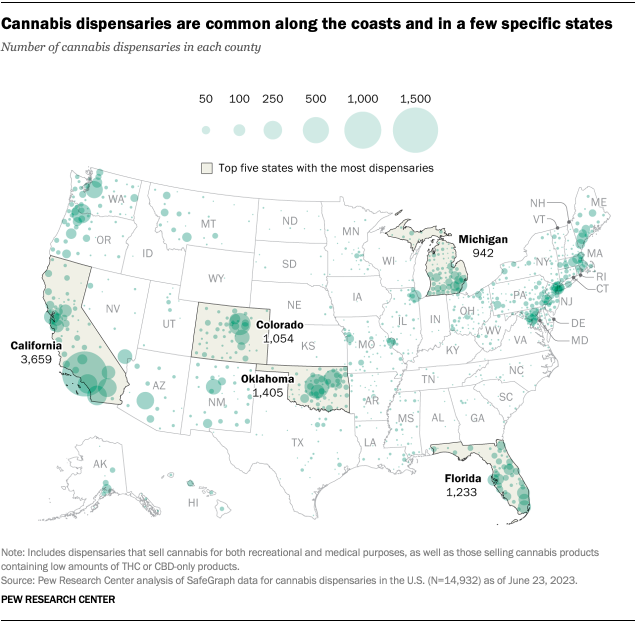
About eight-in-ten Americans (79%) live in a county with at least one cannabis dispensary, according to the February analysis. There are nearly 15,000 marijuana dispensaries nationwide, and 76% are in states (including D.C.) where recreational use is legal. Another 23% are in medical marijuana-only states, and 1% are in states that have made legal allowances for low-percentage THC or CBD-only products.
The states with the largest number of dispensaries include California, Oklahoma, Florida, Colorado and Michigan.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published April 26, 2021, and updated April 13, 2023.

Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
Americans overwhelmingly say marijuana should be legal for medical or recreational use
Religious americans are less likely to endorse legal marijuana for recreational use, four-in-ten u.s. drug arrests in 2018 were for marijuana offenses – mostly possession, two-thirds of americans support marijuana legalization, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.110(6); Nov-Dec 2013

More Reasons States Should Not Legalize Marijuana: Medical and Recreational Marijuana: Commentary and Review of the Literature
Recent years have seen substantial shifts in cultural attitudes towards marijuana for medical and recreational use. Potential problems with the approval, production, dispensation, route of administration, and negative health effects of medical and recreational marijuana are reviewed. Medical marijuana should be subject to the same rigorous approval process as other medications prescribed by physicians. Legalizing recreational marijuana may have negative public health effects.
Introduction
Recent years have seen a cultural shift in attitudes towards marijuana. At the time of this writing, medical marijuana is legal in 20 states and the District of Columbia; recreational marijuana is now legal in Washington and Colorado. A substantial and growing literature documents legalized marijuana may have adverse effects on individual and public health.
Medical Use of Marijuana
The term ‘medical marijuana’ implies that marijuana is like any other medication prescribed by a physician. Yet the ways in which medical marijuana has been approved, prescribed, and made available to the public are very different from other commercially available prescription drugs. These differences pose problems unrecognized by the public and by many physicians.
Lack of Evidence for Therapeutic Benefit
In the United States, commercially available drugs are subject to rigorous clinical trials to evaluate safety and efficacy. Data appraising the effectiveness of marijuana in conditions such as HIV/AIDS, epilepsy, and chemotherapy-associated vomiting is limited and often only anecdotal. 1 , 2 To date, there has been only one randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of smoked marijuana for any of its potential indications, which showed that marijuana was superior to placebo but inferior to Ondansetron in treating nausea. 3 Recent reviews by the Cochrane Collaboration find insufficient evidence to support the use of smoked marijuana for a number of potential indications, including pain related to rheumatoid arthritis, 4 dementia, 5 ataxia or tremor in multiple sclerosis, 6 and cachexia and other symptoms in HIV/AIDS. 2 This does not mean, of course, that components of marijuana do not have potential therapeutic effects to alleviate onerous symptoms of these diseases; but, given the unfavorable side effect profile of marijuana, the evidence to justify use in these conditions is still lacking.
Contamination, Concentration & Route of Administration
Unlike any other prescription drug used for medical purposes, marijuana is not subject to central regulatory oversight. It is grown in dispensaries, which, depending on the state, have regulatory standards ranging from strict to almost non-existent. The crude marijuana plant and its products may be contaminated with fungus or mold. 7 This is especially problematic for immunocompromised patients, 8 including those with HIV/AIDS or cancer. 9 Furthermore, crude marijuana contains over 60 active cannabinoids, 10 few of which are well studied. Marijuana growers often breed their plants to alter the concentrations of different chemicals compounds. For instance, the concentration of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the principal psychoactive ingredient, is more than 20-fold more than in marijuana products used several decades ago. Without rigorous clinical trials, we have no way of knowing which combinations of cannabinoids may be therapeutic and which may be deleterious. As marijuana dispensaries experiment by breeding out different cannabinoids in order to increase the potency of THC, there may be unanticipated negative and lasting effects for individuals who smoke these strains.
Marijuana is the only ‘medication’ that is smoked, and, while still incompletely understood, there are legitimate concerns about long-term effects of marijuana smoke on the lungs. 11 , 12 Compared with cigarette smoke, marijuana smoke can result in three times the amount of inhaled tar and four times the amount of inhaled carbon-monoxide. 13 Further, smoking marijuana has been shown to be a risk factor for lung cancer in many 14 , 15 but not all 16 studies.
High Potential for Diversion
In some states, patients are permitted to grow their own marijuana. In addition to contributing to problems such as contamination and concentration as discussed above, this practice also invites drug diversion. Patients seeking to benefit financially may bypass local regulations of production and sell home-grown marijuana at prices lower than dispensaries. We do not allow patient to grow their own opium for treatment of chronic pain; the derivatives of opium, like marijuana, are highly addictive and thus stringently regulated.
Widespread “Off-label” Use
FDA-approved forms of THC (Dronabinol) and a THC-analog (Nabilone), both available orally, already exist. Indications for these drugs are HIV/AIDS cachexia and chemotherapy-associated nausea and vomiting. Unlike smoked, crude marijuana, these medications have been subject to randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trials. Yet despite these limited indications where marijuana compounds have a proven but modest effect in high-quality clinical trials, medical marijuana is used overwhelmingly for non-specific pain or muscle spasms. Recent data from Colorado show that 94% of patients with medical marijuana cards received them for treatment of “severe pain.” 17 Similar trends are evident in California. 18 Evidence for the benefit of marijuana in neuropathic pain is seen in many 19 - 21 but not all 22 clinical trials. There is no high-quality evidence, however, that the drug reduces non-neuropathic pain; this remains an indication for which data sufficient to justify the risks of medical marijuana is lacking. 4 , 23 – 25
If marijuana is to be ‘prescribed’ by physicians and used as a medication, it should be subject to the same rigorous approval process that other commercially available drugs undergo. Potentially therapeutic components of marijuana should be investigated, but they should only be made available to the public after adequately powered, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials have demonstrated efficacy and acceptable safety profiles. Furthermore, these compounds should be administered in a way that poses less risk than smoking and dispensed via standardized and FDA-regulated pharmacies to ensure purity and concentration. Bypassing the FDA and approving ‘medicine’ at the ballot box sets a dangerous precedent. Physicians should be discouraged from recommending medical marijuana. Alternatively, consideration can be given to prescribing FDA-approved medicines (Dronabinol or Cesamet) as the purity and concentration of these drugs are assured and their efficacy and side effect profiles have been well documented in rigorous clinical trials.
Recreational Marijuana
The question of recreational marijuana is a broader social policy consideration involving implications of the effects of legalization on international drug cartels, domestic criminal justice policy, and federal and state tax revenue in addition to public health. Yet physicians, with a responsibility for public health, are experts with a vested interest in this issue. Recent legislation, reflecting changes in the public’s attitudes towards marijuana, has permitted the recreational use of marijuana in Colorado and Washington. Unfortunately, the negative health consequences of the drug are not prominent in the debate over legalizing marijuana for recreational use. In many cases, these negative effects are more pronounced in adolescents. A compelling argument, based on these negative health effects in both adolescents and adults, can be made to abort the direction society is moving with regards to the legalization of recreational marijuana.
Myth: Marijuana is Not Addictive
A growing myth among the public is that marijuana is not an addictive substance. Data clearly show that about 10% of those who use cannabis become addicted; this number is higher among adolescents. 26 Users who seek treatment for marijuana addiction average 10 years of daily use. 27 A withdrawal syndrome has been described, consisting of anxiety, restlessness, insomnia, depression, and changes in appetite 28 and affects as many as 44% of frequent users, 29 contributing to the addictive potential of the drug. This addictive potential may be less than that of opiates; but the belief, especially among adolescents, that the drug is not addictive is misguided.
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders
Marijuana has been consistently shown to be a risk factor for schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. 30 – 32 The association between marijuana and schizophrenia fulfills many, but not all, of the standard criteria for the epidemiological establishment of causation, including experimental evidence, 33 , 34 temporal relationship, 35 – 38 biological gradient, 30 , 31 , 39 and biological plausibility. 40 Genetic variation may explain why marijuana use does not strongly fulfill remaining criteria, such as strength of association and specificity. 41 , 42 As these genetic variants are explored and further characterized, marijuana use may be shown to cause or precipitate schizophrenia in a genetically vulnerable population. The risk of psychotic disorder is more pronounced when marijuana is used at an earlier age. 32 , 43

There is some evidence that compounds naturally found in marijuana have therapeutic benefit for symptoms of diseases such as HIV/AIDS, multiple sclerosis, and cancer. If these compounds are to be used under the auspices of ‘medical marijuana,’ they should undergo the same rigorous approval process that other medications prescribed by physicians, including randomized, placebo- and active-controlled trials to evaluate safety and efficacy, not by popular vote or state legislature.
Effects on Cognition
Early studies suggested cognitive declines associated with marijuana (especially early and heavy use); these declines persisted long after the period of acute cannabis intoxication. 44 – 46 Recently, Meier and colleagues analyzed data from a prospective study which followed subjects from birth to age 38; their findings yielded supportive evidence that cannabis use, when begun during adolescence, was associated with cognitive impairment in multiple areas, including executive functioning, processing speed, memory, perceptual reasoning, and verbal comprehension. 47 Rogeberg 48 criticized the study’s methodology, claiming that the results were confounded by differences in socioeconomic status; this claim, however, was based on sub-analyses that used very small numbers. Additional sub-analyses 49 of the original study cohort showed that marijuana was just as prevalent in populations of higher socioeconomic status, suggesting that socioeconomic status was not a confounding variable. Any epidemiological study is subject to confounding biases and future research will be needed to clarify and quantify the relationship between cognitive decline and adolescent marijuana use. However, the findings of the original study by Meier et al show there is indeed an independent relationship between loss of intelligence and adolescent marijuana use. This finding, moreover, is consistent with prior studies. 44
Other Negative Health Effects
Substantial evidence exists suggesting that marijuana is harmful to the respiratory system. It is associated with symptoms of obstructive and inflammatory lung disease, 11 , 50 an increased risk of lung cancer, 14 , 15 and it is suspected to be associated with reduced pulmonary function in heavy users. 51 Further, its use has been associated with harmful effects to other organ systems, including the reproductive, 52 gastrointestinal, 53 and immunologic 10 , 54 systems.
Social Safety Implications: Effects on Driving
Marijuana impairs the ability to judge time, distance, and speed; it slows reaction time and reduces ability to track moving objects. 55 , 56 In many studies of drug-related motor vehicle fatalities, marijuana is the most common drug detected except for alcohol. 57 , 58 Based on post-mortem studies, Couch et al determined that marijuana was likely an impairing factor in as many fatal accidents as alcohol. 59 One study showed that in motor vehicle accidents where the driver was killed, recent marijuana use was detected in 12% of cases. 57 Other research confirms a significantly increased risk of motor vehicle fatalities in association with acute cannabis intoxication. 60
Risk Perception and Use in Adolescents
Marijuana use among adolescents has been increasing. Data that has tracked risk perception and use of marijuana among adolescents over decades clearly shows an inverse relationship; as adolescent risk perception wanes, marijuana use increases. 61 As more states legalize medical and recreational marijuana, risk perception is expected to decrease, causing the prevalence of use among adolescent to continue to rise. This is among the most concerning of issues about the drug’s legalization because so many of the negative effects of marijuana—including cognitive impairment and risk for short- and long-term psychosis— are heightened when used during adolescence.

There is some evidence that compounds naturally found in marijuana have therapeutic benefit for symptoms of diseases such as HIV/AIDS, multiple sclerosis, and cancer. If these compounds are to be used under the auspices of ‘medical marijuana,’ they should undergo the same rigorous approval process that other medications prescribed by physicians, including randomized, placebo- and active-controlled trials to evaluate safety and efficacy, not by popular vote or state legislature. Furthermore, these therapeutic compounds should be administered via a route that minimizes long-term health risk (i.e., via oral pill) and should be dispensed by centrally regulated pharmacies to ensure the purity and concentration of the drug and allow for the recall of contaminated batches.
Marijuana for recreational use will have many adverse health effects. The drug is addictive, with mounting evidence for the existence of a withdrawal syndrome. Furthermore, it has been shown to have adverse effects on mental health, intelligence (including irreversible declines in cognition), and the respiratory system. Driving while acutely intoxicated with marijuana greatly increases the risk of fatal motor vehicle collision. Legalization for recreational use may have theoretical (but still unproven) beneficial social effects regarding issues such as domestic criminal justice policy, but these effects will not come without substantial public health and social costs. Currently there is a lack of resources devoted to educating physicians about this most commonly used illicit substance. The potential benefits and significant risks associated with marijuana use should be taught in medical schools and residency programs throughout the country.
Samuel T. Wilkinson, MD, is in the Department of Psychiatry at the Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Ct.
Contact: [email protected]

None reported.

THREE ESSAYS ON THE EFFECT OF LEGALIZING MARIJUANA ON HEALTH, EDUCATION, AND SOCIAL SECURITY
The legalization of marijuana has emerged as a critical public policy issue, with far-reaching implications for health, education, and government programs at both the state and federal levels. The three essays of this dissertation show that medical marijuana legalization (MML) has a negative effect in each of these areas. The first essay shows, that the enactment of MMLs can exacerbate the crisis of overdose deaths in the United States. The study analyzes three key areas: the rate of overdose deaths caused by both legal and illegal drugs, the impact of MML on social norms regarding the perceived harm of marijuana, and an investigation into the gateway theory by examining the use of other addictive drugs. I find that MMLs increase deaths attributed to overdose by 21.5% population. MMLs s also indicate increase the number of deaths due to prescribed opioids by 44.6%, and deaths from all opioids (heroin and cocaine in addition to prescribed opioids) by 37.2 % Results suggest an overall increase in the use of marijuana, primarily due to lower perceived risk among adolescents. Additionally, results show an increase in hospital admissions due to substance abuse. The analysis suggests that legalizing medical marijuana may exaggerate the current problem of drug overdose in the United States. The second essay examines the impact of improved access to medical marijuana, measured by the proximity of schools to the nearest dispensary, on the academic performance of high school students in California. Students in schools farther from a marijuana dispensary have higher academic performance as measured through AP, ACT, SAT scores, and average GPA, and lower number of suspensions due to violence and illicit drug use. To show this, I construct the first geocoded dataset on marijuana dispensary and high school locations, use newly developed difference-in-differences estimators that rule out any bias due to heterogeneous treatment effects over time, and explore dynamic responses. This essay reveals the importance of ensuring a largest possible distance between schools and dispensaries to protect adolescents from the potential harm caused by medical marijuana. Finally, the third essay shows that in the long term, MMLs increase the number of disabled workers who receive Social Security Disability Income (SSDI) because of mental health issues. SSDI is a major social insurance program that provides benefits to workers who become disabled, and understanding how policy changes in other areas may impact this program is important. In this study, there were important differences between the results of a two-way fixed effects model and a new model by Callaway and Santa’Anna. MMLs, in theory, could either increase or decrease the number of SSDI recipients, and traditional fixed effects models suggest both could be at play; however, only the negative effect is robust to correction for heterogeneous effects. This highlights the need for future research to understand the true impact of medical marijuana legalization
Contributors
Degree grantor, degree level, submission id, usage metrics.

- Health economics
- Welfare economics
- Epidemiology
- Health policy
- Public policy
- Medical and health law
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Ross Douthat
Legalizing Marijuana Is a Big Mistake

By Ross Douthat
Opinion Columnist
Of all the ways to win a culture war, the smoothest is to just make the other side seem hopelessly uncool. So it’s been with the march of marijuana legalization: There have been moral arguments about the excesses of the drug war and medical arguments about the potential benefits of pot, but the vibe of the whole debate has pitted the chill against the uptight, the cool against the square, the relaxed future against the Principal Skinners of the past.
As support for legalization has climbed, commanding a two-thirds majority in recent polling , any contrary argument has come to feel a bit futile, and even modest cavils are couched in an apologetic and defensive style. Of course I don’t question the right to get high, but perhaps the pervasive smell of weed in our cities is a bit unfortunate …? I’m not a narc or anything, but maybe New York City doesn’t need quite so many unlicensed pot dealers …?
All of this means that it will take a long time for conventional wisdom to acknowledge the truth that seems readily apparent to squares like me: Marijuana legalization as we’ve done it so far has been a policy failure, a potential social disaster, a clear and evident mistake.
The best version of the square’s case is an essay by Charles Fain Lehman of the Manhattan Institute explaining his evolution from youthful libertarian to grown-up prohibitionist. It will not convince readers who come in with stringently libertarian presuppositions — who believe on high principle that consenting adults should be able to purchase, sell and enjoy almost any substance short of fentanyl and that no second-order social consequence can justify infringing on this right.
But Lehman explains in detail why the second-order effects of marijuana legalization have mostly vindicated the pessimists and skeptics. First, on the criminal justice front, the expectation that legalizing pot would help reduce America’s prison population by clearing out nonviolent offenders was always overdrawn, since marijuana convictions made up a small share of the incarceration rate even at its height. But Lehman argues that there is also no good evidence so far that legalization reduces racially discriminatory patterns of policing and arrests. In his view, cops often use marijuana as a pretext to search someone they suspect of a more serious crime, and they simply substitute some other pretext when the law changes, leaving arrest rates basically unchanged.
So legalization isn’t necessarily striking a great blow against mass incarceration or for racial justice. Nor is it doing great things for public health. There was hope, and some early evidence, that legal pot might substitute for opioid use, but some of the more recent data cuts the other way: A new paper published in The Journal of Health Economics found that “legal medical marijuana, particularly when available through retail dispensaries, is associated with higher opioid mortality.” There are therapeutic benefits to cannabis that justify its availability for prescription, but the evidence of its risks keeps increasing: This month brought a new paper strengthening the link between heavy pot use and the onset of schizophrenia in young men.
And the broad downside risks of marijuana, beyond extreme dangers like schizophrenia, remain as evident as ever: a form of personal degradation, of lost attention and performance and motivation, that isn’t mortally dangerous in the way of heroin but that can damage or derail an awful lot of human lives. Most casual pot smokers won’t have this experience, but the legalization era has seen a sharp increase in the number of noncasual users. Occasional use has risen substantially since 2008, but daily or near-daily use is up much more, with around 16 million Americans , out of more than 50 million users, now suffering from what is termed marijuana use disorder.
In theory, there are technocratic responses to these unfortunate trends. In its ideal form, legalization would be accompanied by effective regulation and taxation, and as Lehman notes, on paper it should be possible to discourage addiction by raising taxes in the legal market, effectively nudging users toward more casual consumption.
In practice, it hasn’t worked that way. Because of all the years of prohibition, a mature and supple illegal marketplace already exists, ready to undercut whatever prices the legal market charges. So to make the legal marketplace successful and amenable to regulation, you would probably need much more enforcement against the illegal marketplace — which is difficult and expensive and, again, obviously uncool, in conflict with the good-vibrations spirit of the legalizers.
Then you have the extreme case of New York, where legal permitting has lagged while untold numbers of illegal shops are doing business unmolested by the police. But even in less-incompetent-seeming states and localities, a similar pattern persists. Lehman cites (and has reviewed ) the recent book “Can Legal Weed Win? The Blunt Realities of Cannabis Economics,” by Robin Goldstein and Daniel Sumner, which shows that unlicensed weed can cost as much as 50 percent less than the licensed variety. So the more you tax and regulate legal pot sales, the more you run the risk of having users just switch to the black market — and if you want the licensed market to crowd out the black market instead, you probably need to make legal pot as cheap as possible, which in turn undermines any effort to discourage chronic, life-altering abuse.
Thus policymakers who don’t want so much chronic use and personal degradation have two options. They can set out to design a much more effective (but necessarily expensive, complex and sometimes punitive) system of regulation and enforcement than what exists so far. Or they can reach for the blunt instrument of recriminalization, which Lehman prefers for its simplicity — with medical exceptions still carved out and with the possibility that possession could remain legal and that only production and distribution be prohibited.
I expect legalization to advance much further before either of these alternatives builds significant support. But eventually the culture will recognize that under the banner of personal choice, we’re running a general experiment in exploitation — addicting our more vulnerable neighbors to myriad pleasant-seeming vices, handing our children over to the social media dopamine machine and spreading degradation wherever casinos spring up and weed shops flourish.
With that realization, and only with that realization, will the squares get the hearing they deserve.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow The New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Twitter (@NYTOpinion) and Instagram .
Ross Douthat has been an Opinion columnist for The Times since 2009. He is the author of several books, most recently, “The Deep Places: A Memoir of Illness and Discovery.” @ DouthatNYT • Facebook
Argumentative Essay On Marijuana Legalization
Published by gudwriter on May 27, 2018 May 27, 2018
Most students have serious problems writing a quality essay as they lack the necessary experience. If you need help writing an essay on legalization of marijuana, the perfect solution is to buy thesis proposal from experts online.
Elevate Your Writing with Our Free Writing Tools!
Did you know that we provide a free essay and speech generator, plagiarism checker, summarizer, paraphraser, and other writing tools for free?
Why Marijuana Should be Legalized Argumentative Essay Outline
Introduction.
Thesis: Marijuana should be legalized as it is more beneficial that it may be detrimental to society.
Paragraph 1:
Marijuana has not caused turmoil in some of the countries where it has been legalized.
- Marijuana does not increase violent, and property crimes as many suggest.
- Studies reveal that in Colorado, violent crimes have declined following the legalization of marijuana.
Paragraph 2:
Prohibiting use of marijuana does not limit its consumption.
- In spite of the many laws prohibiting the use of marijuana, it is one of the most highly abused drugs.
- 58% of young people from all over the world use marijuana.
- It has not been attributed to any health complications.
Paragraph 3:
Legalization of marijuana would help state governments save taxpayers money.
- Governments spend lots of funds on law enforcement agencies that uphold laws restricting the use of marijuana.
- They also spend vast sums of money on sustaining arrested dealers and consumers in prison.
- Legalizing marijuana would result in saving vast sums of money.
Paragraph 4:
Marijuana is less noxious than other legal substances.
- Marijuana has less health side effects than other legal substances such as alcohol and tobacco.
- Alcohol is 114 times more destructive than marijuana.
Paragraph 5:
Marijuana has been proven to have medical benefits.
- Marijuana helps stop seizures in epileptic patients.
- It helps stop nausea in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy .
Paragraph 6:
Marijuana has been proven to be a stress reliever.
- Marijuana relieves stress and depression in their users by causing excitement.
- Its use reduces violence and deaths related to stress and depression.
Conclusion.
There are many misconceptions about marijuana existent in the modern world. People have continued to ignore health benefits linked to this substance citing their unproven beliefs. Owing to its ability to stop seizures, nausea, and stress in individuals governments should highly consider marijuana legalization. Its legalization will also help state governments reduce expenses that result from maintaining suspects convicted of marijuana possession and consumption.
Why Marijuana Should be Legalized Argumentative Essay
The argument that marijuana use should be made legal has gained momentum both in the U.S. and elsewhere in the world in recent years. This has seen the drug being legalized in some states in the U.S. such that by 2013, twenty states had legalized medical marijuana. As of the same year, Colorado and Washington had legalized recreational marijuana. The arguments behind the push for legalization majorly revolve around the idea that the drug has medicinal effects. However, there are also arguments that there are serious health effects associated with the drug and this has only further fueled the already raging debate. This paper argues that marijuana should be legalized as it is more beneficial that it may be detrimental to society.
Marijuana has not caused any notable negative effects in countries where it has been legalized. There is a general belief that marijuana consumers are violent. However, no authentic research can prove these assertions. As already seen, some states in the United States have legalized both medicinal and recreational marijuana. In spite of this, no cases of marijuana-related violence have been recorded so far in such states (Markol, 2018). Reports reveal that the rate of violence and property crimes have decreased in Colorado following the legalization of the drug. If marijuana does not increase violent crimes, there is no reason as to why it should not be legalized.
It is also noteworthy that prohibiting marijuana use does not limit its consumption. Less than 10% of countries in the world prevent the use of marijuana, but according to research, 58% of young people in most of these countries are marijuana users (Head, 2016). General reports reveal that marijuana is one of most commonly abused drug in the world. It is also readily available in most states as it is a naturally growing plant (Head, 2016). In spite of its continued use, there are few cases, if any, of marijuana-related health complications that have been reported in any of these countries (Head, 2016). Therefore, if the illegality of marijuana does not limit its consumption, then state governments should consider its legalization.
Legalization of marijuana would further help state governments save taxpayers’ money. It is widely known that in countries where marijuana is illegal, authorities are stringent and will arrest any individual found in possession of the drug (Sanger, 2017). However, as earlier mentioned, laws prohibiting the use of the drug do not prevent its consumption, and this means that many people are arrested and prosecuted for possessing it (Sanger, 2017). State governments therefore use a lot of funds to support law enforcement agencies that seek to uphold laws prohibiting the use of marijuana (Sanger, 2017). Many people have been arrested and incarcerated for either possessing or consuming the drug, and the government has to use taxpayers’ money to sustain such people in prison. Since these actions do not limit consumption of marijuana, state governments should legalize the drug so as to save taxpayers money.
Another advantage of marijuana is that it is less noxious than other legal substances. According to research, marijuana is the least harmful drug among the many legal drugs existent in the world today (Owen, 2014). There are millions of campaigns every year cautioning people against smoking cigarettes, but there has been none seeking to warn people about marijuana consumption (Owen, 2014). Lobby groups have even been making efforts to push for legalization of marijuana. If marijuana had severe health effects as many purport, state governments would be investing heavily in campaigns aimed at discouraging its consumption (Owen, 2014). According to studies, alcohol, which is legal in many countries, is 114 times more harmful than marijuana (Owen, 2014). Therefore, if such harmful substances can be legalized, then there are no justifications as to why marijuana should not be legalized.
Further, marijuana has been proven to have medicinal benefits. Several countries, particularly in Europe, and the United States have legalized both medicinal and recreational marijuana. Their move to legalize marijuana was based on medical reports that showed a variety of health benefits linked to the drug (Noonan, 2017). Research shows that marijuana can reduce seizures in epileptic persons. Several studies have also proven that the drug indeed has a variety of health benefits. For instance, Charlotte Figi, who is now aged 10, used to have more than 100 seizures every month at age three, but since Colorado legalized medicinal and recreational marijuana, her parents started treating her with the substance, and today her seizures have significantly reduced (Noonan, 2017). Marijuana has as well been proven to reduce nausea in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. Owing to this medicinal value, state governments should consider legalizing the drug.
Additionally, marijuana has been proven to be a stress reliever. Consumption of the drug causes excitement among its users enabling them to forget about troubling situations. Unlike alcohol which is likely to aggravate stress and depression, marijuana works wonders in alleviating anxiety and depression (Sanger, 2017). There are many health and social effects associated with stress, including mental disorders and violence against others (Sanger, 2017). To avoid cases of stress-related violence and mental disorders, state governments should make marijuana consumption legal.
There are many misconceptions about marijuana in the world today. People have continued to ignore the health benefits linked with this substance and have instead focused on citing yet-to-be proven misconceptions. Owing to the ability of the drug to stop seizures, nausea, and stress in individuals, governments should seriously consider its legalization. The legalization will also help state governments reduce expenses that result from sustaining suspects convicted of marijuana possession and consumption. So far, there is more than enough evidence proving that marijuana has lots of benefits to individuals, the society, and the government, and therefore should be legalized.
Head, T. (2016). “8 reasons why marijuana should be legalized”. ThoughtCo . Retrieved June 27, 2020 from https://www.thoughtco.com/reasons-why-marijuana-should-be-legalized-721154
Markol, T. (2018). “5 reasons why marijuana should be legalized”. Marijuana Reform . Retrieved June 27, 2020 from http://marijuanareform.org/5-reasons-marijuana-legalized/
Noonan, D. (2017). “Marijuana treatment reduces severe epileptic seizures”. Scientific American . Retrieved June 27, 2020 from https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/marijuana-treatment-reduces-severe-epileptic-seizures/
Owen, P. (2014). “6 powerful reasons to legalize marijuana”. New York Times . Retrieved June 27, 2020 from https://www.alternet.org/drugs/6-powerful-reasons-new-york-times-says-end-marijuana-prohibition
Sanger, B. (2017). “10 legit reasons why weed should be legalized right now”. Herb . Retrieved June 27, 2020 from https://herb.co/marijuana/news/reasons-weed-legalized
Why Marijuana Should be Legal Essay Outline
Thesis: Marijuana has health benefits and should thus be legal.
Benefits of Marijuana
Marijuana slows and stops the spread of cancer cells.
- Cannabidiol can turn off a gene called Id-1 and can therefore stop cancer.
- In an experiment, researchers were able to treat breast cancer cells with Cannabidiol.
Marijuana helps with pain and nausea reduction for people going through chemotherapy.
- Cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy suffer from severe pains and nausea.
- This can further complicate their health.
- Marijuana can stir up their appetite, decrease nausea, and reduce pain.
Paragraph 3:
Marijuana can control epileptic seizure.
- Marijuana extract stopped seizures in epileptic rats in ten hours.
- The seizures were controlled by the THC.
Disadvantages of Marijuana
Marijuana is addictive.
- One in ten marijuana users become addicted over time.
- If one stops using the drug abruptly, they may suffer from such withdrawal symptoms.
Marijuana use decreases mental health.
- Users suffer from memory loss and restricted blood flow to the brain.
- Users have higher chances of developing depression and schizophrenia.
Marijuana use damages the lungs more than cigarette smoking .
- Marijuana smokers inhale the smoke more deeply into their lungs and let it stay there for longer.
- The likelihood of lung cancer can be increased by this deeper, longer exposure to carcinogens.
Why Marijuana Should Be Legal
Paragraph 7:
Improved quality and safety control.
- Legalization would lead to the creation of a set of standards for safety and quality control.
- Users would know what they exactly get in exchange for the money they offer.
- There would be no risks of users taking in unknown substances mixed in marijuana.
Paragraph 8:
Marijuana has a medicinal value.
- Medical marijuana treats a wide assortment of “untreatable” diseases and conditions.
- Public health would be improved and the healthcare system would experience less of a drain.
Paragraph 9:
Among the major arguments against marijuana legalization is often that legalization would yield an increase in drug-impaired driving.
- This argument holds that even now when the drug is yet to be fully legalized in the country, it is a major causal factor in highway deaths, injuries, and crushes.
- It however beats logic why marijuana is illegalized on the ground that it would increase drug-impaired driving while alcohol is legal but also significantly contributes to the same problem.
Legalization of marijuana would have many benefits. The drug is associated with the treatment of many serious illnesses including the dreaded cancer. Legalization would also save users from consuming unsafe marijuana sold by unscrupulous people.
Why Marijuana Should Be Legal Essay
There is an ongoing tension between the belief that marijuana effectively treats a wide range of ailments and the argument that it has far-reaching negative health effects. There has nevertheless been a drive towards legalization of the drug in the United States with twenty nine states and the District of Columbia having legalized it for medical and recreational purposes. It was also found by a study that there is a sharp increase in the use of marijuana across the country (Kerr, Lui & Ye, 2017). Major public health concerns are being prompted by this rise. This should however not be the case because marijuana has health benefits and should thus be legal.
Marijuana slows and stops the spread of cancer cells. A study found that Cannabidiol can turn off a gene called Id-1 and can therefore stop cancer. A 2007 report by researchers at California Pacific Medical Center in San Francisco also indicated that the spread of cancer may be prevented by Cannabidiol. In their lab experiment, the researchers were able to treat breast cancer cells with this component (Nawaz, 2017). The positive outcome of the experiment showed that Id-1 expression had been significantly decreased.
Marijuana also helps with pain and nausea reduction for people going through chemotherapy. Cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy suffer from severe pains, appetite loss, vomiting, and painful nausea. This can further complicate their already deteriorating health. Marijuana can be of help here by stirring up the appetite, decreasing nausea, and reducing pain (Nawaz, 2017). There are also other cannabinoid drugs used for the same purposes as approved by the FDA.
It was additionally shown by a 2003 study that the use of marijuana can control epileptic seizure. Synthetic marijuana and marijuana extracts were given to epileptic rats by Virginia Commonwealth University’s Robert J. DeLorenzo. In about ten hours, the seizures had been stopped by the drugs (Nawaz, 2017). It was found that the seizures were controlled by the THC which bound the brain cells responsible for regulating relaxation and controlling excitability.
Some scientists claim that marijuana is addictive. According to them, one in ten marijuana users become addicted over time. They argue that if one stops using the drug abruptly, they may suffer from such withdrawal symptoms as anxiety and irritability (Barcott, 2015). However, the same argument could be applied to cigarette smoking, which is notably legal. There is need for more studies to be conducted into this claim being spread by opponents of marijuana legalization.
It is also argued that marijuana use decreases mental health. Those opposed to the legalization of recreational marijuana like to cite studies that show that users of the drug suffer from memory loss and restricted blood flow to the brain. They also argue that users have higher chances of developing depression and schizophrenia. However, these assertions have not yet been completely ascertained by science (Barcott, 2015). The claim about depression and schizophrenia is particularly not clear because researchers are not sure whether the drug triggers the conditions or it is used by smokers to alleviate the symptoms.
It is further claimed that marijuana use damages the lungs more than cigarette smoking. It is presumed that marijuana smokers inhale the smoke more deeply into their lungs and let it stay there for longer. The likelihood of lung cancer, according to this argument, can be increased by this deeper, longer exposure to carcinogens. However, the argument touches not on the frequency of use between marijuana and cigarette smokers (Barcott, 2015). It neither takes into account such alternative administration methods as edibles, tinctures, and vaporizing.
Legalization of marijuana would lead to improved quality and safety control. Purchasing the drug off the street provides end users with no means of knowing what they are exactly getting. On the other hand, legalizing it would immediately lead to the creation of a set of standards for safety and quality control (Caulkins, Kilmer & Kleiman, 2016). This would certainly work in the marijuana industry just as it is working in the tobacco and alcohol industries. Users would be able to know what they exactly get in exchange for the money they offer. Additionally, there would be no risks of users taking in unknown substances mixed in marijuana sold on the streets.
Marijuana should also be legal because it has a medicinal value. It has been proven that medical marijuana treats a wide assortment of “untreatable” diseases and conditions. These include problems due to chemotherapy, cancer, post-traumatic stress disorder, migraines, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, and Crohn’s disease (Caulkins, Kilmer & Kleiman, 2016). Public health would be improved and the healthcare system would experience less of a drain if medical cannabis products were made available to those suffering from the mentioned conditions. Consequently, more public funds would be available for such other public service initiatives as schools and roads.
Among the major arguments against marijuana legalization is often that legalization would yield an increase in drug-impaired driving. This argument holds that even now when the drug is yet to be fully legalized in the country, it has already been cited to be a major causal factor in highway deaths, injuries, and crushes. Among the surveys those arguing along this line might cite is one that was conducted back in 2010, revealing that of the participating weekend night-time drivers, “8.6 percent tested positive for marijuana or its metabolites” (“Why We Should Not Legalize Marijuana,” 2010). It was found in yet another study that 26.9% of drivers who were being attended to at a trauma center after sustaining serious injuries tested positive for the drug (“Why We Should Not Legalize Marijuana,” 2010). It however beats logic why marijuana is illegalized on the ground that it would increase drug-impaired driving while alcohol is legal but also significantly contributes to the same problem.
As the discussion reveals, legalization of marijuana would have many benefits. The drug is associated with the treatment of many serious illnesses including the dreaded cancer. Legalization would also save users from consuming unsafe marijuana sold by unscrupulous people. There are also other health conditions that can be controlled through the drug. Arguments against its legalization based on its effects on human health also lack sufficient scientific support. It is thus only safe that the drug is legalized in all states.
Barcott, B. (2015). Weed the people: the future of legal marijuana in America . New York, NY: Time Home Entertainment.
Caulkins, J. P., Kilmer, B., & Kleiman, M. (2016). Marijuana legalization: what everyone needs to know . New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Kerr, W., Lui, C., & Ye, Y. (2017). Trends and age, period and cohort effects for marijuana use prevalence in the 1984-2015 US National Alcohol Surveys. Addiction , 113 (3), 473-481.
Nawaz, H. (2017). The debate between legalizing marijuana and its benefits for medical purposes: a pros and cons analysis . Munich, Germany: GRIN Verlag.
Why We Should Not Legalize Marijuana. (2010). In CNBC . Retrieved June 25, 2020 from https://www.cnbc.com/id/36267223 .
More examples of Argumentative Essays written by our team of quality writers
- Same Sex Marriage Argumentative Essay, with Outline
- American Patriotism Argumentative Essay
- Euthanasia Argumentative Essay Sample
- Artificial Intelligence Argumentative Essay
- Argumentative Essay on Abortion – Sample Essay
- Gun Control Argumentative Essay – Sample Essay
- Can Money Buy Happiness Argumentative Essay
- Illegal Immigration Argumentative Essay
There are typical mistakes most students make when writing their argumentative papers . When writing your argumentative essay you ought to understand that it calls for the ability to present facts, provide supportive evidence, and use logical reasoning to illustrate points. This will help you write a quality paper.
You can relieve yourself all the tussle by buying an argumentative essay from a trustworthy argumentative essay help service. Hire Gudwriter now and you will never regret it.

Special offer! Get 20% discount on your first order. Promo code: SAVE20
Related Posts
Free essays and research papers, artificial intelligence argumentative essay – with outline.
Artificial Intelligence Argumentative Essay Outline In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become one of the rapidly developing fields and as its capabilities continue to expand, its potential impact on society has become a topic Read more…
Synthesis Essay Example – With Outline
The goal of a synthesis paper is to show that you can handle in-depth research, dissect complex ideas, and present the arguments. Most college or university students have a hard time writing a synthesis essay, Read more…

Examples of Spatial Order – With Outline
A spatial order is an organizational style that helps in the presentation of ideas or things as is in their locations. Most students struggle to understand the meaning of spatial order in writing and have Read more…
- Subscribe Now
Law students debate on legalizing medical marijuana in PH
Already have Rappler+? Sign in to listen to groundbreaking journalism.
This is AI generated summarization, which may have errors. For context, always refer to the full article.

MANILA, Philippines – Is it time to legalize the medical use of marijuana in the Philippines?
Debaters from the Ateneo de Manila University Law School and the University of Sto Tomas (UST) Law School discussed the issue at “The Law and Policy Debate: An Inter-university Dialogue” held at the House of Representatives on Tuesday, June 9.
It has been more than a year since Isabela 1st District Representative Rodolfo Albano III filed House Bill 4477 or the Compassionate Use of Medical Cannabis Bill, and it already has 69 co-authors to date.
The two debate teams argued on the necessity to passs HB 4477 , with Ateneo on the affirmative side, and UST on the negative side. (READ: PH doctors say no to medical marijuana bill )
While no team was declared a winner, Ateneo’s second affirmative speaker Pearl Simbulan was chosen as both Best Speaker and Best Interpellator.
Simbulan argued that legalizing medical marijuana will provide more options to patients who need it. It will also allow research and development on the “better uses” of marijuana to continue.
The adjudicators were former Philippine Permanent Representative to the World Trade Organization Manuel Teehankee, Likhaan director and co-founder Junice Melgar, and Malou Tiquia, host of CNN Philippines’ current affairs program Agenda.
Debate arguments
Below are the arguments of each speaker:
ATENEO LAW SCHOOL

1st affirmative speaker: John Michael Villanueva
- There is a necessity to pass this bill in order to comply with the constitutional mandates and international obligations of promoting the right to health.
- There is a need to distinguish between the ill and the criminals, which can only be done by this bill.
2nd affirmative speaker: Pearl Simbulan
- Legalizing medical marijuana is the only and the best comprehensive approach to health. What we think in legalizing medical marijuana is that we provide the optimal care: [providing] a range of options that a physician who is in the best position to make these decisions can do for the patient.
- Because we illegalized blanketly marijuana, research on these kinds of things stopped, and it has become harder for us to discover even better uses of marijuana.
3rd affirmative speaker: Patrick Vincent Cocabo
“The q uestion should not be whether marijuana is good or bad, but rather, how can we control it? What is the best strategy to save lives?”
- Government regulation is important.
- The bill provides an important mechanism of checks and balances of citizen accountability.
UST LAW SCHOOL

1st negative speaker: Marie Sybil Tropicales
- Medical marijuana should not be legalized because at present, its detriments outweigh its benefits. Medical marijuana is not necessary for legislation because essentially, it is not a cure in itself.
2nd negative speaker: John Paul Fabella
“The contentious documented benefits of medical marijuana cannot outweigh its adverse effects to the government and society.”
- On a socio-political level: Legalization sends a wrong message to public, especially to the youth, that marijuana is medically benevolent and not a harmful drug. The state cannot afford to risk our society to the dangers of increased marijuana use by implying a stance that it is not harmful.
- Legalizing medical marijuana is not advantageous to the government.
- Documented benefits are highly contentious at the moment and inconclusive.
- It undermines law enforcement by forcing officers to distinguish medical users and recreational users.
3rd negative speaker: Jackielyn Bana
- Is government ready for this? There are too much gray areas in the policy implementation at present, that no matter how noble the objective of the law is, that no matter how flawless its features are, it all go to waste because of the corrupt implementation of the laws.
- Example: Regulating tobacco, alocohol, sleeping pills, and prescription drugs
- This country has a problem with strict and faithful implementation of government policies and regulations.
- What guarantee do we have that a seriously addictive drug could be regulated when simple regulations on tobacco and alcohol products prove to be impossible to impose?
- Once marijuana is legalized, there is no possibility of regulating it.
Adjudicators comment
The adjudicators welcomed the law students’ interest in discussing the advantages and disadvantages of legalizing medical marijuana in the Philippines. (READ: Solon: Let’s start talking about medical marijuana )
“I’m happy that the youth are taking positions especially on an issue which is very, very real in your sector,” Tiquia said after all interpellations were done. She lauded the bill for being “very rigid,” and disagreed with UST’s Fabella that regulating marijuana means legitimizing it.
Melgar noted how “selective” the bill is on legalizing marijuana only for medical use. (READ: When medicines fail, marijuana is moms’ last hope )
“All the public knows about marijuana is the stereotype, that it’s all for getting high, and nobody shines a light on the few instances where it is the most compassionate for children who have epilepsy, for patients who have cancer,” Melgar added.
HB 4477 is still pending with the House committee on health. Albano said it is possible to enact the bill during the 16th Congress, but admitted the probability is “iffy” and will depend “on how fast they will settle the issue on the BBL (Bangsamoro Basic Law).”
Albano said Congress is “focused” on the Bangsamoro Basic Law, which reached the House plenary on June 1.
Tuesday’s debate was organized by the Teehankee Center for the Rule of Law and Ateneo’s St Thomas More Debate and Advocacy Society, in partnership with the Office of Representative Albano and the Office of Ang Nars party-list Representative Leah Paquiz. – Rappler.com
Medical marijuana image from Shutterstock
Add a comment
Please abide by Rappler's commenting guidelines .
There are no comments yet. Add your comment to start the conversation.
How does this make you feel?
Related Topics

Jee Y. Geronimo
Recommended stories, {{ item.sitename }}, {{ item.title }}.
Checking your Rappler+ subscription...
Upgrade to Rappler+ for exclusive content and unlimited access.
Why is it important to subscribe? Learn more
You are subscribed to Rappler+

IMAGES
COMMENTS
5. Legalization for Acceptance. Finally, legalization could help reduce the stigma surrounding cannabis use. Before cannabis legalization, people who use the plant were often viewed as criminals or deviants. Legalization can help change this perception and lead to more open and honest conversations about cannabis use.
Marijuana is less harmful compared to alcohol and tobacco, thus should be legalized. American history has for long held to the prohibition of cannabis while ignoring apparent and increasing harm substances such as alcohol and tobacco cause. According to Alternet organization, marijuana presents less addictive tendencies as compared to alcohol ...
Thirty-eight states and Washington, D.C., have legalized medical cannabis, while 23 states and D.C. have legalized recreational use. Cannabis legalization has benefits, such as removing the product from the illegal market so it can be taxed and regulated, but science is still trying to catch up as social norms evolve and different products ...
The Cons of Legalizing Marijuana. Those who oppose the legalization of marijuana point to the health risks of the drug, including: Memory issues: Frequent marijuana use may seriously affect your short-term memory. Cognition problems: Frequent use can impair your cognitive (thinking) abilities.
The federal prohibition of marijuana has been a disaster, wasting billions of dollars, unjustly harming millions of lives, and furthering racist policies. Legalizing, taxing, and regulating marijuana is good for the economy, the health, and the racial justice of the country.
Nearly two-thirds of conservative and moderate Democrats (63%) say marijuana should be legal for medical and recreational use. An overwhelming majority of liberal Democrats (84%) say the same. There also are racial and ethnic differences in views of legalizing marijuana. Roughly two-thirds of Black adults (68%) and six-in-ten White adults say ...
Essays on Cannabis Legalization. Thomas, Danna Kang. Though the drug remains illegal at the federal level, in recent years states and localities have increasingly liberalized their marijuana laws in order to generate tax revenue and save resources on marijuana law enforcement. Many states have adopted some form of medical marijuana and/or ...
This "Why Marijuanas Should Be Legal" essay will set out to argue that marijuana should be legal since the harmful effects of this substance are not as dire, and legalization would result in many benefits for society. The argumentative paper will rely on research to reinforce this claim.
opinion polls, two out of three Americans favor the legalization of marijuana (Gurley 2019; Lopez 2019). 2 Given this level of support, it seems likely that more states will legalize marijuana in upcoming years. Several U.S. senators have recently said that they will push to pass a marijuana reform bill in 2021to end the federal prohibition.
Cannabis is the most widely used illicit drug globally, particularly in North America and high-income countries in Europe and Oceania. Although the use of medicinal cannabis is legal in many countries, for example to treat chronic pain, poor appetite, or nausea due to chemotherapy, legalisation of non-medicinal or recreational cannabis is a topic of growing public discussion and debate globally.
In 2021, Washington collected $559.5 million of legal marijuana revenue, over $85 million more revenue than 2020. Meanwhile, Colorado collected $423 million of marijuana tax revenue in 2021, up ...
Why Marijuana should be legalized in America. There are several reasons to support the legalization of marijuana in America, some of which include the following: In each country, the citizens of the country have the right to freedom. This is to mean that they should be left to choose on whether to use or not use marijuana, but not to be forced ...
Request PDF | Why Marijuana Should be Legalized, an argumentative essay | Much debate has been conducted regarding the legalization of marijuana, with an unusual amount of contradicting research ...
This essay will argue that marijuana should be legalized for several reasons, including its potential medical benefits, the reduction of criminal activity, and the economic advantages it offers. In the realm of medical marijuana, there is a wealth of evidence supporting its potential therapeutic properties.
Marijuana is made up of the leaves and flowers of the Cannabis plant. THC, or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary active ingredient in marijuana. It enters the bloodstream and travels to the brain. This substance induces a state of relaxation in the body. There have been several debates on whether or not marijuana should be legalized.
Pro Arguments (Support for your position): The majority of Americans agree on the necessity to legalize marijuana. Its medical and recreational use is a sufficient basis for this change. Con Arguments (Opposing Views): The resistance of older populations to this idea is highly possible. This initiative is accompanied by concerns regarding the ...
A new survey finds that 53% favor the legal use of marijuana, while 44% are opposed. As recently as 2006, just 32% supported marijuana legalization, while nearly twice as many (60%) were opposed. Millennials (currently 18-34) have been in the forefront of this change: 68% favor legalizing marijuana use, by far the highest percentage of any age ...
Around nine-in-ten Americans say marijuana should be legal for medical or recreational use, according to a January 2024 Pew Research Center survey.An overwhelming majority of U.S. adults (88%) say either that marijuana should be legal for medical use only (32%) or that it should be legal for medical and recreational use (57%).Just 11% say the drug should not be legal in any form.
Data that has tracked risk perception and use of marijuana among adolescents over decades clearly shows an inverse relationship; as adolescent risk perception wanes, marijuana use increases. 61 As more states legalize medical and recreational marijuana, risk perception is expected to decrease, causing the prevalence of use among adolescent to ...
The legalization of marijuana has emerged as a critical public policy issue, with far-reaching implications for health, education, and government programs at both the state and federal levels. The three essays of this dissertation show that medical marijuana legalization (MML) has a negative effect in each of these areas. The first essay shows, that the enactment of MMLs can exacerbate the ...
Legalizing Marijuana Is a Big Mistake. May 17, 2023. Evelyn Freja for The New York Times. Share full article. 2652. By Ross Douthat. Opinion Columnist. Of all the ways to win a culture war, the ...
The web page provides an argumentative essay outline and a sample argumentative essay on why marijuana should be legalized. It claims that marijuana is less noxious, less harmful, and more beneficial than other legal substances, and that it has medical and social benefits. It also argues that legalizing marijuana would save taxpayers' money and reduce crime.
UST LAW SCHOOL. 1st negative speaker: Marie Sybil Tropicales. Medical marijuana should not be legalized because at present, its detriments outweigh its benefits. Medical marijuana is not necessary ...