- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In

Definition of homework
Examples of homework in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'homework.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
1662, in the meaning defined at sense 1
Dictionary Entries Near homework
Cite this entry.
“Homework.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/homework. Accessed 3 Apr. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of homework, more from merriam-webster on homework.
Thesaurus: All synonyms and antonyms for homework
Nglish: Translation of homework for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of homework for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about homework
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
The tangled history of 'it's' and 'its', more commonly misspelled words, why does english have so many silent letters, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - mar. 29, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 8 uncommon words related to love, 9 superb owl words, games & quizzes.


Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to do homework: 15 expert tips and tricks.
Coursework/GPA

Everyone struggles with homework sometimes, but if getting your homework done has become a chronic issue for you, then you may need a little extra help. That’s why we’ve written this article all about how to do homework. Once you’re finished reading it, you’ll know how to do homework (and have tons of new ways to motivate yourself to do homework)!
We’ve broken this article down into a few major sections. You’ll find:
- A diagnostic test to help you figure out why you’re struggling with homework
- A discussion of the four major homework problems students face, along with expert tips for addressing them
- A bonus section with tips for how to do homework fast
By the end of this article, you’ll be prepared to tackle whatever homework assignments your teachers throw at you .
So let’s get started!

How to Do Homework: Figure Out Your Struggles
Sometimes it feels like everything is standing between you and getting your homework done. But the truth is, most people only have one or two major roadblocks that are keeping them from getting their homework done well and on time.
The best way to figure out how to get motivated to do homework starts with pinpointing the issues that are affecting your ability to get your assignments done. That’s why we’ve developed a short quiz to help you identify the areas where you’re struggling.
Take the quiz below and record your answers on your phone or on a scrap piece of paper. Keep in mind there are no wrong answers!
1. You’ve just been assigned an essay in your English class that’s due at the end of the week. What’s the first thing you do?
A. Keep it in mind, even though you won’t start it until the day before it’s due B. Open up your planner. You’ve got to figure out when you’ll write your paper since you have band practice, a speech tournament, and your little sister’s dance recital this week, too. C. Groan out loud. Another essay? You could barely get yourself to write the last one! D. Start thinking about your essay topic, which makes you think about your art project that’s due the same day, which reminds you that your favorite artist might have just posted to Instagram...so you better check your feed right now.
2. Your mom asked you to pick up your room before she gets home from work. You’ve just gotten home from school. You decide you’ll tackle your chores:
A. Five minutes before your mom walks through the front door. As long as it gets done, who cares when you start? B. As soon as you get home from your shift at the local grocery store. C. After you give yourself a 15-minute pep talk about how you need to get to work. D. You won’t get it done. Between texts from your friends, trying to watch your favorite Netflix show, and playing with your dog, you just lost track of time!
3. You’ve signed up to wash dogs at the Humane Society to help earn money for your senior class trip. You:
A. Show up ten minutes late. You put off leaving your house until the last minute, then got stuck in unexpected traffic on the way to the shelter. B. Have to call and cancel at the last minute. You forgot you’d already agreed to babysit your cousin and bake cupcakes for tomorrow’s bake sale. C. Actually arrive fifteen minutes early with extra brushes and bandanas you picked up at the store. You’re passionate about animals, so you’re excited to help out! D. Show up on time, but only get three dogs washed. You couldn’t help it: you just kept getting distracted by how cute they were!
4. You have an hour of downtime, so you decide you’re going to watch an episode of The Great British Baking Show. You:
A. Scroll through your social media feeds for twenty minutes before hitting play, which means you’re not able to finish the whole episode. Ugh! You really wanted to see who was sent home! B. Watch fifteen minutes until you remember you’re supposed to pick up your sister from band practice before heading to your part-time job. No GBBO for you! C. You finish one episode, then decide to watch another even though you’ve got SAT studying to do. It’s just more fun to watch people make scones. D. Start the episode, but only catch bits and pieces of it because you’re reading Twitter, cleaning out your backpack, and eating a snack at the same time.
5. Your teacher asks you to stay after class because you’ve missed turning in two homework assignments in a row. When she asks you what’s wrong, you say:
A. You planned to do your assignments during lunch, but you ran out of time. You decided it would be better to turn in nothing at all than submit unfinished work. B. You really wanted to get the assignments done, but between your extracurriculars, family commitments, and your part-time job, your homework fell through the cracks. C. You have a hard time psyching yourself to tackle the assignments. You just can’t seem to find the motivation to work on them once you get home. D. You tried to do them, but you had a hard time focusing. By the time you realized you hadn’t gotten anything done, it was already time to turn them in.
Like we said earlier, there are no right or wrong answers to this quiz (though your results will be better if you answered as honestly as possible). Here’s how your answers break down:
- If your answers were mostly As, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is procrastination.
- If your answers were mostly Bs, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is time management.
- If your answers were mostly Cs, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is motivation.
- If your answers were mostly Ds, then your biggest struggle with doing homework is getting distracted.
Now that you’ve identified why you’re having a hard time getting your homework done, we can help you figure out how to fix it! Scroll down to find your core problem area to learn more about how you can start to address it.
And one more thing: you’re really struggling with homework, it’s a good idea to read through every section below. You may find some additional tips that will help make homework less intimidating.

How to Do Homework When You’re a Procrastinator
Merriam Webster defines “procrastinate” as “to put off intentionally and habitually.” In other words, procrastination is when you choose to do something at the last minute on a regular basis. If you’ve ever found yourself pulling an all-nighter, trying to finish an assignment between periods, or sprinting to turn in a paper minutes before a deadline, you’ve experienced the effects of procrastination.
If you’re a chronic procrastinator, you’re in good company. In fact, one study found that 70% to 95% of undergraduate students procrastinate when it comes to doing their homework. Unfortunately, procrastination can negatively impact your grades. Researchers have found that procrastination can lower your grade on an assignment by as much as five points ...which might not sound serious until you realize that can mean the difference between a B- and a C+.
Procrastination can also negatively affect your health by increasing your stress levels , which can lead to other health conditions like insomnia, a weakened immune system, and even heart conditions. Getting a handle on procrastination can not only improve your grades, it can make you feel better, too!
The big thing to understand about procrastination is that it’s not the result of laziness. Laziness is defined as being “disinclined to activity or exertion.” In other words, being lazy is all about doing nothing. But a s this Psychology Today article explains , procrastinators don’t put things off because they don’t want to work. Instead, procrastinators tend to postpone tasks they don’t want to do in favor of tasks that they perceive as either more important or more fun. Put another way, procrastinators want to do things...as long as it’s not their homework!
3 Tips f or Conquering Procrastination
Because putting off doing homework is a common problem, there are lots of good tactics for addressing procrastination. Keep reading for our three expert tips that will get your homework habits back on track in no time.
#1: Create a Reward System
Like we mentioned earlier, procrastination happens when you prioritize other activities over getting your homework done. Many times, this happens because homework...well, just isn’t enjoyable. But you can add some fun back into the process by rewarding yourself for getting your work done.
Here’s what we mean: let’s say you decide that every time you get your homework done before the day it’s due, you’ll give yourself a point. For every five points you earn, you’ll treat yourself to your favorite dessert: a chocolate cupcake! Now you have an extra (delicious!) incentive to motivate you to leave procrastination in the dust.
If you’re not into cupcakes, don’t worry. Your reward can be anything that motivates you . Maybe it’s hanging out with your best friend or an extra ten minutes of video game time. As long as you’re choosing something that makes homework worth doing, you’ll be successful.
#2: Have a Homework Accountability Partner
If you’re having trouble getting yourself to start your homework ahead of time, it may be a good idea to call in reinforcements . Find a friend or classmate you can trust and explain to them that you’re trying to change your homework habits. Ask them if they’d be willing to text you to make sure you’re doing your homework and check in with you once a week to see if you’re meeting your anti-procrastination goals.
Sharing your goals can make them feel more real, and an accountability partner can help hold you responsible for your decisions. For example, let’s say you’re tempted to put off your science lab write-up until the morning before it’s due. But you know that your accountability partner is going to text you about it tomorrow...and you don’t want to fess up that you haven’t started your assignment. A homework accountability partner can give you the extra support and incentive you need to keep your homework habits on track.
#3: Create Your Own Due Dates
If you’re a life-long procrastinator, you might find that changing the habit is harder than you expected. In that case, you might try using procrastination to your advantage! If you just can’t seem to stop doing your work at the last minute, try setting your own due dates for assignments that range from a day to a week before the assignment is actually due.
Here’s what we mean. Let’s say you have a math worksheet that’s been assigned on Tuesday and is due on Friday. In your planner, you can write down the due date as Thursday instead. You may still put off your homework assignment until the last minute...but in this case, the “last minute” is a day before the assignment’s real due date . This little hack can trick your procrastination-addicted brain into planning ahead!

If you feel like Kevin Hart in this meme, then our tips for doing homework when you're busy are for you.
How to Do Homework When You’re too Busy
If you’re aiming to go to a top-tier college , you’re going to have a full plate. Because college admissions is getting more competitive, it’s important that you’re maintaining your grades , studying hard for your standardized tests , and participating in extracurriculars so your application stands out. A packed schedule can get even more hectic once you add family obligations or a part-time job to the mix.
If you feel like you’re being pulled in a million directions at once, you’re not alone. Recent research has found that stress—and more severe stress-related conditions like anxiety and depression— are a major problem for high school students . In fact, one study from the American Psychological Association found that during the school year, students’ stress levels are higher than those of the adults around them.
For students, homework is a major contributor to their overall stress levels . Many high schoolers have multiple hours of homework every night , and figuring out how to fit it into an already-packed schedule can seem impossible.
3 Tips for Fitting Homework Into Your Busy Schedule
While it might feel like you have literally no time left in your schedule, there are still ways to make sure you’re able to get your homework done and meet your other commitments. Here are our expert homework tips for even the busiest of students.
#1: Make a Prioritized To-Do List
You probably already have a to-do list to keep yourself on track. The next step is to prioritize the items on your to-do list so you can see what items need your attention right away.
Here’s how it works: at the beginning of each day, sit down and make a list of all the items you need to get done before you go to bed. This includes your homework, but it should also take into account any practices, chores, events, or job shifts you may have. Once you get everything listed out, it’s time to prioritize them using the labels A, B, and C. Here’s what those labels mean:
- A Tasks : tasks that have to get done—like showing up at work or turning in an assignment—get an A.
- B Tasks : these are tasks that you would like to get done by the end of the day but aren’t as time sensitive. For example, studying for a test you have next week could be a B-level task. It’s still important, but it doesn’t have to be done right away.
- C Tasks: these are tasks that aren’t very important and/or have no real consequences if you don’t get them done immediately. For instance, if you’re hoping to clean out your closet but it’s not an assigned chore from your parents, you could label that to-do item with a C.
Prioritizing your to-do list helps you visualize which items need your immediate attention, and which items you can leave for later. A prioritized to-do list ensures that you’re spending your time efficiently and effectively, which helps you make room in your schedule for homework. So even though you might really want to start making decorations for Homecoming (a B task), you’ll know that finishing your reading log (an A task) is more important.
#2: Use a Planner With Time Labels
Your planner is probably packed with notes, events, and assignments already. (And if you’re not using a planner, it’s time to start!) But planners can do more for you than just remind you when an assignment is due. If you’re using a planner with time labels, it can help you visualize how you need to spend your day.
A planner with time labels breaks your day down into chunks, and you assign tasks to each chunk of time. For example, you can make a note of your class schedule with assignments, block out time to study, and make sure you know when you need to be at practice. Once you know which tasks take priority, you can add them to any empty spaces in your day.
Planning out how you spend your time not only helps you use it wisely, it can help you feel less overwhelmed, too . We’re big fans of planners that include a task list ( like this one ) or have room for notes ( like this one ).
#3: Set Reminders on Your Phone
If you need a little extra nudge to make sure you’re getting your homework done on time, it’s a good idea to set some reminders on your phone. You don’t need a fancy app, either. You can use your alarm app to have it go off at specific times throughout the day to remind you to do your homework. This works especially well if you have a set homework time scheduled. So if you’ve decided you’re doing homework at 6:00 pm, you can set an alarm to remind you to bust out your books and get to work.
If you use your phone as your planner, you may have the option to add alerts, emails, or notifications to scheduled events . Many calendar apps, including the one that comes with your phone, have built-in reminders that you can customize to meet your needs. So if you block off time to do your homework from 4:30 to 6:00 pm, you can set a reminder that will pop up on your phone when it’s time to get started.

This dog isn't judging your lack of motivation...but your teacher might. Keep reading for tips to help you motivate yourself to do your homework.
How to Do Homework When You’re Unmotivated
At first glance, it may seem like procrastination and being unmotivated are the same thing. After all, both of these issues usually result in you putting off your homework until the very last minute.
But there’s one key difference: many procrastinators are working, they’re just prioritizing work differently. They know they’re going to start their homework...they’re just going to do it later.
Conversely, people who are unmotivated to do homework just can’t find the willpower to tackle their assignments. Procrastinators know they’ll at least attempt the homework at the last minute, whereas people who are unmotivated struggle with convincing themselves to do it at a ll. For procrastinators, the stress comes from the inevitable time crunch. For unmotivated people, the stress comes from trying to convince themselves to do something they don’t want to do in the first place.
Here are some common reasons students are unmotivated in doing homework :
- Assignments are too easy, too hard, or seemingly pointless
- Students aren’t interested in (or passionate about) the subject matter
- Students are intimidated by the work and/or feels like they don’t understand the assignment
- Homework isn’t fun, and students would rather spend their time on things that they enjoy
To sum it up: people who lack motivation to do their homework are more likely to not do it at all, or to spend more time worrying about doing their homework than...well, actually doing it.
3 Tips for How to Get Motivated to Do Homework
The key to getting homework done when you’re unmotivated is to figure out what does motivate you, then apply those things to homework. It sounds tricky...but it’s pretty simple once you get the hang of it! Here are our three expert tips for motivating yourself to do your homework.
#1: Use Incremental Incentives
When you’re not motivated, it’s important to give yourself small rewards to stay focused on finishing the task at hand. The trick is to keep the incentives small and to reward yourself often. For example, maybe you’re reading a good book in your free time. For every ten minutes you spend on your homework, you get to read five pages of your book. Like we mentioned earlier, make sure you’re choosing a reward that works for you!
So why does this technique work? Using small rewards more often allows you to experience small wins for getting your work done. Every time you make it to one of your tiny reward points, you get to celebrate your success, which gives your brain a boost of dopamine . Dopamine helps you stay motivated and also creates a feeling of satisfaction when you complete your homework !
#2: Form a Homework Group
If you’re having trouble motivating yourself, it’s okay to turn to others for support. Creating a homework group can help with this. Bring together a group of your friends or classmates, and pick one time a week where you meet and work on homework together. You don’t have to be in the same class, or even taking the same subjects— the goal is to encourage one another to start (and finish!) your assignments.
Another added benefit of a homework group is that you can help one another if you’re struggling to understand the material covered in your classes. This is especially helpful if your lack of motivation comes from being intimidated by your assignments. Asking your friends for help may feel less scary than talking to your teacher...and once you get a handle on the material, your homework may become less frightening, too.
#3: Change Up Your Environment
If you find that you’re totally unmotivated, it may help if you find a new place to do your homework. For example, if you’ve been struggling to get your homework done at home, try spending an extra hour in the library after school instead. The change of scenery can limit your distractions and give you the energy you need to get your work done.
If you’re stuck doing homework at home, you can still use this tip. For instance, maybe you’ve always done your homework sitting on your bed. Try relocating somewhere else, like your kitchen table, for a few weeks. You may find that setting up a new “homework spot” in your house gives you a motivational lift and helps you get your work done.

Social media can be a huge problem when it comes to doing homework. We have advice for helping you unplug and regain focus.
How to Do Homework When You’re Easily Distracted
We live in an always-on world, and there are tons of things clamoring for our attention. From friends and family to pop culture and social media, it seems like there’s always something (or someone!) distracting us from the things we need to do.
The 24/7 world we live in has affected our ability to focus on tasks for prolonged periods of time. Research has shown that over the past decade, an average person’s attention span has gone from 12 seconds to eight seconds . And when we do lose focus, i t takes people a long time to get back on task . One study found that it can take as long as 23 minutes to get back to work once we’ve been distracte d. No wonder it can take hours to get your homework done!
3 Tips to Improve Your Focus
If you have a hard time focusing when you’re doing your homework, it’s a good idea to try and eliminate as many distractions as possible. Here are three expert tips for blocking out the noise so you can focus on getting your homework done.
#1: Create a Distraction-Free Environment
Pick a place where you’ll do your homework every day, and make it as distraction-free as possible. Try to find a location where there won’t be tons of noise, and limit your access to screens while you’re doing your homework. Put together a focus-oriented playlist (or choose one on your favorite streaming service), and put your headphones on while you work.
You may find that other people, like your friends and family, are your biggest distraction. If that’s the case, try setting up some homework boundaries. Let them know when you’ll be working on homework every day, and ask them if they’ll help you keep a quiet environment. They’ll be happy to lend a hand!
#2: Limit Your Access to Technology
We know, we know...this tip isn’t fun, but it does work. For homework that doesn’t require a computer, like handouts or worksheets, it’s best to put all your technology away . Turn off your television, put your phone and laptop in your backpack, and silence notifications on any wearable tech you may be sporting. If you listen to music while you work, that’s fine...but make sure you have a playlist set up so you’re not shuffling through songs once you get started on your homework.
If your homework requires your laptop or tablet, it can be harder to limit your access to distractions. But it’s not impossible! T here are apps you can download that will block certain websites while you’re working so that you’re not tempted to scroll through Twitter or check your Facebook feed. Silence notifications and text messages on your computer, and don’t open your email account unless you absolutely have to. And if you don’t need access to the internet to complete your assignments, turn off your WiFi. Cutting out the online chatter is a great way to make sure you’re getting your homework done.
#3: Set a Timer (the Pomodoro Technique)
Have you ever heard of the Pomodoro technique ? It’s a productivity hack that uses a timer to help you focus!
Here’s how it works: first, set a timer for 25 minutes. This is going to be your work time. During this 25 minutes, all you can do is work on whatever homework assignment you have in front of you. No email, no text messaging, no phone calls—just homework. When that timer goes off, you get to take a 5 minute break. Every time you go through one of these cycles, it’s called a “pomodoro.” For every four pomodoros you complete, you can take a longer break of 15 to 30 minutes.
The pomodoro technique works through a combination of boundary setting and rewards. First, it gives you a finite amount of time to focus, so you know that you only have to work really hard for 25 minutes. Once you’ve done that, you’re rewarded with a short break where you can do whatever you want. Additionally, tracking how many pomodoros you complete can help you see how long you’re really working on your homework. (Once you start using our focus tips, you may find it doesn’t take as long as you thought!)

Two Bonus Tips for How to Do Homework Fast
Even if you’re doing everything right, there will be times when you just need to get your homework done as fast as possible. (Why do teachers always have projects due in the same week? The world may never know.)
The problem with speeding through homework is that it’s easy to make mistakes. While turning in an assignment is always better than not submitting anything at all, you want to make sure that you’re not compromising quality for speed. Simply put, the goal is to get your homework done quickly and still make a good grade on the assignment!
Here are our two bonus tips for getting a decent grade on your homework assignments , even when you’re in a time crunch.
#1: Do the Easy Parts First
This is especially true if you’re working on a handout with multiple questions. Before you start working on the assignment, read through all the questions and problems. As you do, make a mark beside the questions you think are “easy” to answer .
Once you’ve finished going through the whole assignment, you can answer these questions first. Getting the easy questions out of the way as quickly as possible lets you spend more time on the trickier portions of your homework, which will maximize your assignment grade.
(Quick note: this is also a good strategy to use on timed assignments and tests, like the SAT and the ACT !)
#2: Pay Attention in Class
Homework gets a lot easier when you’re actively learning the material. Teachers aren’t giving you homework because they’re mean or trying to ruin your weekend... it’s because they want you to really understand the course material. Homework is designed to reinforce what you’re already learning in class so you’ll be ready to tackle harder concepts later.
When you pay attention in class, ask questions, and take good notes, you’re absorbing the information you’ll need to succeed on your homework assignments. (You’re stuck in class anyway, so you might as well make the most of it!) Not only will paying attention in class make your homework less confusing, it will also help it go much faster, too.

What’s Next?
If you’re looking to improve your productivity beyond homework, a good place to begin is with time management. After all, we only have so much time in a day...so it’s important to get the most out of it! To get you started, check out this list of the 12 best time management techniques that you can start using today.
You may have read this article because homework struggles have been affecting your GPA. Now that you’re on the path to homework success, it’s time to start being proactive about raising your grades. This article teaches you everything you need to know about raising your GPA so you can
Now you know how to get motivated to do homework...but what about your study habits? Studying is just as critical to getting good grades, and ultimately getting into a good college . We can teach you how to study bette r in high school. (We’ve also got tons of resources to help you study for your ACT and SAT exams , too!)
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of homework noun from the Oxford Advanced American Dictionary
- acquire/get/lack experience/training/(an) education
- receive/provide somebody with training
- develop/design/plan a curriculum/course/program/syllabus
- give/go to/attend a class/lesson/lecture/seminar
- hold/run/conduct a class/seminar/workshop
- moderate/lead/facilitate a discussion
- sign up for/take a course/classes/lessons
- go to/start preschool/kindergarten/nursery school
- be in the first, second, etc. grade (at school)
- study/take/drop history/chemistry/German, etc.
- finish/drop out of/quit school
- graduate from high school/college
- be the victim/target of bullying/teasing
- skip/cut/ ( informal ) ditch class/school
- cheat on an exam/a test
- get/be given a detention (for doing something)
- be expelled from/be suspended from school
- do your homework/a project on something
- work on/write/do/submit an essay/a dissertation/a thesis/an assignment/a paper
- finish/complete your dissertation/thesis/studies
- hand in/turn in your homework/essay/assignment/paper
- study/prepare/review/ ( informal ) cram for a test/an exam
- take/ ( formal ) sit for a test/an exam
- grade homework/a test
- do well on/ ( informal ) ace a test/an exam
- pass/fail/ ( informal ) flunk a test/an exam/a class/a course/a subject
- apply to/get into/go to/start college
- leave/graduate from college (with a degree in computer science)/law school
- study for/work towards a law degree/a degree in physics
- major/minor in biology/philosophy
- earn/receive/be awarded/get/have/hold a master's degree/a bachelor's degree/a Ph.D. in economics
Join our community to access the latest language learning and assessment tips from Oxford University Press!
- 2 ( informal ) work that someone does to prepare for something You could tell that he had really done his homework (= found out all he needed to know) .
Nearby words

What’s the Purpose of Homework?
Finding the right balance between school and home..
Posted November 4, 2014 | Reviewed by Jessica Schrader

Remember the days of sitting in class waiting eagerly for the bell to ring before the teacher said that dreaded word, “homework”? Sighs, rolling eyes, and grunts quickly filled the quiet classroom at the mention of that word. Well, not much has changed today except for the fact that many teachers post assignments electronically. I have yet to see a student jump for joy when the word homework is mentioned, nor have I seen students eager to get home to do their homework (maybe finish it, but not to do it). This brings up the question, “What’s the purpose of homework?”
Research shows mixed results when it comes to homework. Some research has shown that students aren’t doing any more homework than their parents did at their age. In a study, school-aged children and parents completed surveys about how much homework youth have. The results showed that the typical elementary student has 30-45 minutes of homework each night. The average high-school student has about 60 minutes per night. Interestingly, these numbers have remained consistent since 1984!
As an educator, I would like to see a replication of this study. Today's teens are taking college-level courses as early as the ninth and tenth grade. With the push of programs such as Advanced Placement, International Baccalaureate, and Dual Enrollment, it is amazing that teens are not completely burnt out. No wonder 8% of teen's age 13-18 years meet the criteria for an anxiety disorder. Too many teens are spending a lot of time on schoolwork outside of the classroom. Ask today's teen what has him/her so stressed and you'll find that about 80% of them will say school.

There are those who argue that homework does serve a purpose . For example, it helps to prepare students for national and statewide exams and tests. It helps to reinforce what’s being taught in the classroom. It enables parents to actively engage in their child’s education . Plus, it helps teach fundamental skills such as time management , organization, task completion, as well as responsibility. What’s more important is students get to demonstrate mastery of material without the assistance of a teacher.
How much homework should your child do each night? Organizations such as the National Parent Teacher Association support giving students about 10 minutes of homework each night, per grade level, starting in first grade. So a middle school student would have a full day in school and then an additional 60 minutes of homework after school. Is that too much? Are these guidelines being followed? I would recommend speaking with high-achieving teens and let them share how much of their time is consumed with homework. Many will tell you that they spend hours upon hours each night studying for tests, and preparing for papers and projects, etc.
According to Stanford University , more than a couple of hours of homework a night may be counterproductive. Researchers looked at students in high achieving communities, defined as a median household income exceeding $90,000, and 93% of the students attended post-secondary institutions. Students in these areas spent an average of three-plus hours on homework every night. So imagine a teen spending an entire day at school, going to work or extracurricular activities, then going home to do three or more hours of homework each night; only to get up the next day to do it all again.
Researchers have found that students who spend too much time on homework experience more levels of stress and physical health problems. Too much homework has also been shown to have a negative impact on students’ social lives. This is no surprise to the parents who rarely see their child because he/she is too busy working on homework, or to the parent who gets up at 12:30 A.M. to check to see if their child has made it to bed yet. Overall, high school students shouldn’t be spending over two hours on homework each night.

According to the Stanford study , too much homework leads to:
•Stress: 56% of the students surveyed considered homework a primary source of stress. Less than 1% of the students said homework was not a stressor.
•Poor health: Many students reported sleep deprivation, headaches, stomach problems, weight loss, and exhaustion.
•Less time for a social life : Students reported that spending too much time on homework led to pulling out of enjoyable activities, quitting extracurricular activities, and not spending much time with family and friends.
OK, I know not all students spend a lot of time doing homework. According to a survey by the U.S. Dept. of Education’s National Center for Education Statistics , the majority of youth spend an average of seven hours of homework outside of school each week. So while that doesn't seem like an unreasonable amount, what about the student who spends three-plus hours per night? Where is the happy medium?

There are definitely pros and cons to doing homework. I think the bigger question that educators need to address is “what’s the purpose of the assignment?” Is it merely a way to show parents and administration what's going on in the class? Is it a means to help keep the grades up? Is the homework being graded for accuracy or completion? If so, then what if the assignment is wrong? Have the necessary skills been taught so the student can master the material on his or her own? I read an article once that stated teachers underestimate the amount of homework they assign by 50%. If that's accurate then there is definitely cause for concern.
In summary, there seems to be no clear answer on the homework debate. I started the blog with a question “What’s the purpose of homework?” I’ll end with the same question. If a teacher who is assigning the homework can’t provide a clear rationale behind this question, then maybe the homework shouldn’t be assigned.
I welcome you to weigh in with your thoughts. Do you think students have too much homework? If you are a teen reading this, how much homework do you have on an average night?

Raychelle Cassada Lohman n , M.S., LPC, is the author of The Anger Workbook for Teens .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Grammar Coach ™
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
schoolwork assigned to be done outside the classroom ( distinguished from classwork ).
a single assignment of such schoolwork: Homeworks are due at the beginning of class.
paid work done at home , as piecework.
thorough preparatory study of a subject: to do one's homework for the next committee meeting.
Origin of homework
Words nearby homework.
- homewrecker
- homichlophobia
Dictionary.com Unabridged Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, © Random House, Inc. 2024
How to use homework in a sentence
Now, they log on to Zoom from their bedrooms, surrounded by unfinished homework assignments and tattered stuffed animals, waiting to be assigned calls, texts and emails by the trained therapists who oversee the program.
Yow started her homework and saw Frese had gone 35-22 with two winning seasons at Ball State, which hadn’t had a winning record in its previous nine seasons.
Do some homework before investing in a diamond, and that lifelong commitment.
Another poster included an image of their losses over what appeared to be online math homework .
As we countdown to Inauguration Day, I've been doing my homework —and looking to the past for inspiration.
“I can help my children with their homework and sometimes we text in English at my job,” Santos says.
Scheunemann, meanwhile, had no idea who Spencer was, and did some homework .
She jumped at the chance to watch RT, or jumped at the chance to skip calculus homework .
And we encourage parent-student “contracts,” for class attendance, homework submission and even extra-curriculum activities.
Adicéam did his homework , spending 50 days collecting pieces, many with unexpected stories behind them.
Much of this homework is done by a very bad light and the boy's eyes suffer much.
For homework we have prepared alphabets where the letters are printed in type-writing order.
His parents were always getting angry with him for losing his clothes, or his toys, or his homework .
Only at the time when he was going to Beauregard School, with his homework .
And once a week or twice a week she was sending her homework or something to him.
British Dictionary definitions for homework
/ ( ˈhəʊmˌwɜːk ) /
school work done out of lessons, esp at home
any preparatory study
work done at home for pay
Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1979, 1986 © HarperCollins Publishers 1998, 2000, 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2012
Other Idioms and Phrases with homework
see do one's homework.
The American Heritage® Idioms Dictionary Copyright © 2002, 2001, 1995 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company.

What’s the point of homework?
Deputy Dean, School of Education, Western Sydney University
Disclosure statement
Katina Zammit does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Western Sydney University provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
Homework hasn’t changed much in the past few decades. Most children are still sent home with about an hour’s worth of homework each day, mostly practising what they were taught in class.
If we look internationally, homework is assigned in every country that participated in the OECD’s Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) in 2012.
Across the participating countries, 15-year-old students reported spending almost five hours per week doing homework in 2012. Australian students spent six hours per week on average on homework. Students in Singapore spent seven hours on homework, and in Shanghai, China they did homework for about 14 hours per week on average.
Read more: Aussie students are a year behind students 10 years ago in science, maths and reading
Shanghai and Singapore routinely score higher than Australia in the PISA maths, science and reading tests. But homework could just be one of the factors leading to higher results. In Finland, which also scores higher than Australia, students spent less than three hours on homework per week.
So, what’s the purpose of homework and what does the evidence say about whether it fulfils its purpose?
Why do teachers set homework?
Each school in Australia has its own homework policy developed in consultation with teachers and parents or caregivers, under the guiding principles of state or regional education departments.
For instance, according to the New South Wales homework policy “… tasks should be assigned by teachers with a specific, explicit learning purpose”.
Homework in NSW should also be “purposeful and designed to meet specific learning goals”, and “built on knowledge, skills and understanding developed in class”. But there is limited, if any, guidance on how often homework should be set.
Research based on teacher interviews shows they set homework for a range of reasons. These include to:
establish and improve communication between parents and children about learning
help children be more responsible, confident and disciplined
practise or review material from class
determine children’s understanding of the lesson and/or skills
introduce new material to be presented in class
provide students with opportunities to apply and integrate skills to new situations or interest areas
get students to use their own skills to create work.
So, does homework achieve what teachers intend it to?
Do we know if it ‘works’?
Studies on homework are frequently quite general, and don’t consider specific types of homework tasks. So it isn’t easy to measure how effective homework could be, or to compare studies.
But there are several things we can say.
First, it’s better if every student gets the kind of homework task that benefits them personally, such as one that helps them answer questions they had, or understand a problem they couldn’t quite grasp in class. This promotes students’ confidence and control of their own learning.
Read more: Learning from home is testing students' online search skills. Here are 3 ways to improve them
Giving students repetitive tasks may not have much value . For instance, calculating the answer to 120 similar algorithms, such as adding two different numbers 120 times may make the student think maths is irrelevant and boring. In this case, children are not being encouraged to find solutions but simply applying a formula they learnt in school.
In primary schools, homework that aims to improve children’s confidence and learning discipline can be beneficial. For example, children can be asked to practise giving a presentation on a topic of their interest. This could help build their competence in speaking in front of a class.

Homework can also highlight equity issues. It can be particularly burdensome for socioeconomically disadvantaged students who may not have a space, the resources or as much time due to family and work commitments. Their parents may also not feel capable of supporting them or have their own work commitments.
According to the PISA studies mentioned earlier, socioeconomically disadvantaged 15 year olds spend nearly three hours less on homework each week than their advantaged peers.
Read more: 'I was astonished at how quickly they made gains': online tutoring helps struggling students catch up
What kind of homework is best?
Homework can be engaging and contribute to learning if it is more than just a sheet of maths or list of spelling words not linked to class learning. From summarising various studies’ findings, “good” homework should be:
personalised to each child rather than the same for all students in the class. This is more likely to make a difference to a child’s learning and performance
achievable, so the child can complete it independently, building skills in managing their time and behaviour
aligned to the learning in the classroom.
If you aren’t happy with the homework your child is given then approach the school. If your child is having difficulty with doing the homework, the teacher needs to know. It shouldn’t be burdensome for you or your children.
- Disadvantaged students

Events Officer

Lecturer (Hindi-Urdu)

Director, Defence and Security

Opportunities with the new CIEHF

School of Social Sciences – Public Policy and International Relations opportunities

What Is Homework?
Homework is work that teachers give students to complete outside of the school day. Homework is meant to provide students with practice for what was learned in school or an extension of what was done in class. Students are expected to complete the homework and return to school with the completed homework assignment.
Why Do Teachers Give Homework?
Most teachers give students homework so that they can practice something that was taught to them during class.
For example, if a teacher is teaching students how to add decimal numbers then the homework assignment would be for students to try adding decimals at home independently.
In my science class I never give my students homework that isn’t meaningful or practice towards a learning standard.
Gone are the days of giving homework that is “busy work”.
Also, when students return the following day their homework assignment is incorporated into the lesson so they quickly figure out that completing homework is necessary.
Some teachers, myself included, will use homework as a formative assessment.
If you are unsure what formative assessments are then you need to check out this article I wrote recently.

What Does Homework Look Like?
Homework can be almost anything.
Some examples of homework may include a simple worksheet to complete, a long term project, research, reading, a journal entry, completing something online, a drawing, or the continuation of something started in school, and just about anything else.
Homework isn’t limited to one specific thing.
With my eight grade students I have assigned videos for them to watch, creating a slideshow, completing a CER (more about the CER here) , conduct a survey for data collection, and more.
I have even had them collect leaves to identify the following day in our science class!
If you are a teacher reading this make sure to make your homework assignments interesting and worthwhile, don’t just assign homework as busy work.
Do Teachers Have To Give Homework?
No, teachers don’t have to give homework.
Usually teachers have discretion whether or not they are going to assign homework.
Personally, the principal or school district I work for has no idea how often I assign homework or what I assign for homework.
This decision to give or not give homework solely comes down to the classroom teacher.
The Importance Of Homework
The importance of homework is a heavily debated topic these days.
On one hand you have teachers that will say it is necessary that students continue learning outside the classroom in order to be more successful inside the classroom.
On the other hand some teachers will say that homework isn’t necessary as long as students are working hard during the school day.
Another reason homework is seen as not necessary is because students these days are so busy out of school that they don’t have time to complete homework.
Who is right?
I’d say it’s probably somewhere in the middle.
There is nothing wrong with a little homework for students but it shouldn’t be assigned every night.
Share this:
I (Allen) am currently teaching at a public school in a western suburb of Chicago. My teaching career started in 2004. Some of my interests outside of teaching is being with my family, biking, playing video games, travelling, and making the Teacher Adviser website.
Recent Posts
What Are Formative Assessments?
Formative assessments are assessments (feedback) used by the teacher to determine student learning during a unit. The teacher uses formative assessments to determine how they are going to teach or...
What Are Summative Assessments?
Summative assessments are the assessments/tests that are used to determine student understanding of a specific learning standard after the learning or practice has taken place. Summative assessments...
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Grammar: When to Use Do, Does, and Did

3-minute read
- 12th August 2022
Verbs are essential to creating complete sentences, as they help us express physical actions ( She jumped in the puddle) , mental actions ( He thought about puppies) , and states of being ( I am hungry) .
There are several types of verbs that can each be written in different tenses, so they can be tricky to work with, especially if English isn’t your first language . We’ve put together a guide to help you use one of the most common verbs, do , in your writing . Read on below to learn more!
Action Verbs
As the name suggests, action verbs are used to express actions completed by the subject of a sentence. The base verb do is conjugated according to the tense:
1. Present Tense
In the present tense, do takes the form do or does, depending on the subject:
Consider the following examples:
We do our homework every night.
She does her homework every night.
2. Past Tense
In the simple past tense , the base verb do takes the form did with all subjects:
We did our homework last night.
She did her homework last night.

Auxiliary Verbs
Auxiliary , or helping verbs, are used with another base verb to create negative sentences, questions, or add emphasis. Here’s how do should be used as an auxiliary verb:
1. Negative Sentences
Following the same subject–verb pairings introduced above, we combine the auxiliaries do , does , and did with the adverb not to create negative sentences:
We do not do our homework every night.
She did not do her homework last night.
Note that we can combine the auxiliary and the adverb to create the contractions don’t , doesn’t , and didn’t . You simply remove the space between the two words and replace the letter o in not with an apostrophe (’).
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Contractions are more common in conversations and informal writing and typically shouldn’t be used in formal writing (e.g., academic or business).
2. Questions
To create questions, the auxiliary is combined with the infinitive of another verb in this way: auxiliary verb + subject + infinitive verb .
● Simple present questions:
Do they sell children’s books?
Does he speak English?
Note that the third person verb speaks isn’t spelled with the s when paired with the auxiliary to form a question.
● Simple past questions:
Did you buy anything at the bookstore?
Did he learn how to speak English?
Note that did indicates the past tense, so the main verbs don’t also take the past tense (i.e., bought and learned ).
3. Emphasis
In positive sentences, we can also combine the auxiliaries do , does , and did with the main verb to emphasize that something is true:
We do sell children’s books.
He did learn to speak English.
Try saying these sentences aloud and adding emphasis to the auxiliary terms with your tone. It adds a dramatic effect!
Proofreading and Editing Services
Hopefully, this guide will help you feel more confident when using different forms of the verb do in your writing. If you’re still learning or want to be sure your work is error-free, our editors are ready to help. You can upload a free trial document today to learn more!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Our Mission

What’s the Right Amount of Homework?
Decades of research show that homework has some benefits, especially for students in middle and high school—but there are risks to assigning too much.
Many teachers and parents believe that homework helps students build study skills and review concepts learned in class. Others see homework as disruptive and unnecessary, leading to burnout and turning kids off to school. Decades of research show that the issue is more nuanced and complex than most people think: Homework is beneficial, but only to a degree. Students in high school gain the most, while younger kids benefit much less.
The National PTA and the National Education Association support the “ 10-minute homework guideline ”—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students’ needs, not the amount of time spent on it.
The guideline doesn’t account for students who may need to spend more—or less—time on assignments. In class, teachers can make adjustments to support struggling students, but at home, an assignment that takes one student 30 minutes to complete may take another twice as much time—often for reasons beyond their control. And homework can widen the achievement gap, putting students from low-income households and students with learning disabilities at a disadvantage.
However, the 10-minute guideline is useful in setting a limit: When kids spend too much time on homework, there are real consequences to consider.
Small Benefits for Elementary Students
As young children begin school, the focus should be on cultivating a love of learning, and assigning too much homework can undermine that goal. And young students often don’t have the study skills to benefit fully from homework, so it may be a poor use of time (Cooper, 1989 ; Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). A more effective activity may be nightly reading, especially if parents are involved. The benefits of reading are clear: If students aren’t proficient readers by the end of third grade, they’re less likely to succeed academically and graduate from high school (Fiester, 2013 ).
For second-grade teacher Jacqueline Fiorentino, the minor benefits of homework did not outweigh the potential drawback of turning young children against school at an early age, so she experimented with dropping mandatory homework. “Something surprising happened: They started doing more work at home,” Fiorentino writes . “This inspiring group of 8-year-olds used their newfound free time to explore subjects and topics of interest to them.” She encouraged her students to read at home and offered optional homework to extend classroom lessons and help them review material.
Moderate Benefits for Middle School Students
As students mature and develop the study skills necessary to delve deeply into a topic—and to retain what they learn—they also benefit more from homework. Nightly assignments can help prepare them for scholarly work, and research shows that homework can have moderate benefits for middle school students (Cooper et al., 2006 ). Recent research also shows that online math homework, which can be designed to adapt to students’ levels of understanding, can significantly boost test scores (Roschelle et al., 2016 ).
There are risks to assigning too much, however: A 2015 study found that when middle school students were assigned more than 90 to 100 minutes of daily homework, their math and science test scores began to decline (Fernández-Alonso, Suárez-Álvarez, & Muñiz, 2015 ). Crossing that upper limit can drain student motivation and focus. The researchers recommend that “homework should present a certain level of challenge or difficulty, without being so challenging that it discourages effort.” Teachers should avoid low-effort, repetitive assignments, and assign homework “with the aim of instilling work habits and promoting autonomous, self-directed learning.”
In other words, it’s the quality of homework that matters, not the quantity. Brian Sztabnik, a veteran middle and high school English teacher, suggests that teachers take a step back and ask themselves these five questions :
- How long will it take to complete?
- Have all learners been considered?
- Will an assignment encourage future success?
- Will an assignment place material in a context the classroom cannot?
- Does an assignment offer support when a teacher is not there?
More Benefits for High School Students, but Risks as Well
By the time they reach high school, students should be well on their way to becoming independent learners, so homework does provide a boost to learning at this age, as long as it isn’t overwhelming (Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). When students spend too much time on homework—more than two hours each night—it takes up valuable time to rest and spend time with family and friends. A 2013 study found that high school students can experience serious mental and physical health problems, from higher stress levels to sleep deprivation, when assigned too much homework (Galloway, Conner, & Pope, 2013 ).
Homework in high school should always relate to the lesson and be doable without any assistance, and feedback should be clear and explicit.
Teachers should also keep in mind that not all students have equal opportunities to finish their homework at home, so incomplete homework may not be a true reflection of their learning—it may be more a result of issues they face outside of school. They may be hindered by issues such as lack of a quiet space at home, resources such as a computer or broadband connectivity, or parental support (OECD, 2014 ). In such cases, giving low homework scores may be unfair.
Since the quantities of time discussed here are totals, teachers in middle and high school should be aware of how much homework other teachers are assigning. It may seem reasonable to assign 30 minutes of daily homework, but across six subjects, that’s three hours—far above a reasonable amount even for a high school senior. Psychologist Maurice Elias sees this as a common mistake: Individual teachers create homework policies that in aggregate can overwhelm students. He suggests that teachers work together to develop a school-wide homework policy and make it a key topic of back-to-school night and the first parent-teacher conferences of the school year.
Parents Play a Key Role
Homework can be a powerful tool to help parents become more involved in their child’s learning (Walker et al., 2004 ). It can provide insights into a child’s strengths and interests, and can also encourage conversations about a child’s life at school. If a parent has positive attitudes toward homework, their children are more likely to share those same values, promoting academic success.
But it’s also possible for parents to be overbearing, putting too much emphasis on test scores or grades, which can be disruptive for children (Madjar, Shklar, & Moshe, 2015 ). Parents should avoid being overly intrusive or controlling—students report feeling less motivated to learn when they don’t have enough space and autonomy to do their homework (Orkin, May, & Wolf, 2017 ; Patall, Cooper, & Robinson, 2008 ; Silinskas & Kikas, 2017 ). So while homework can encourage parents to be more involved with their kids, it’s important to not make it a source of conflict.

What’s the Purpose of Homework?

- Homework teaches students responsibility.
- Homework gives students an opportunity to practice and refine their skills.
- We give homework because our parents demand it.
- Our community equates homework with rigor.
- Homework is a rite of passage.
- design quality homework tasks;
- differentiate homework tasks;
- move from grading to checking;
- decriminalize the grading of homework;
- use completion strategies; and
- establish homework support programs.
- Always ask, “What learning will result from this homework assignment?” The goal of your instruction should be to design homework that results in meaningful learning.
- Assign homework to help students deepen their understanding of content, practice skills in order to become faster or more proficient, or learn new content on a surface level.
- Check that students are able to perform required skills and tasks independently before asking them to complete homework assignments.
- When students return home, is there a safe and quite place for them to do their homework? I have talked to teachers who tell me they know for certain the home environments of their students are chaotic at best. Is it likely a student will be able to complete homework in such an environment? Is it possible for students to go to an after school program, possibly at the YMCA or a Boys and Girls Club. Assigning homework to students when you know the likelihood of them being able to complete the assignment through little fault of their own doesn’t seem fair to the learner.
- Consider parents and guardians to be your allies when it comes to homework. Understand their constraints, and, when home circumstances present challenges, consider alternative approaches to support students as they complete homework assignments (e.g., before-or after-school programs, additional parent outreach).

Howard Pitler is a dynamic facilitator, speaker, and instructional coach with a proven record of success spanning four decades. With an extensive background in professional development, he works with schools and districts internationally and is a regular speaker at national, state, and district conferences and workshops.
Pitler is currently Associate Professor at Emporia State University in Kansas. Prior to that, he served for 19 years as an elementary and middle school principal in an urban setting. During his tenure, his elementary school was selected as an Apple Distinguished Program and named "One of the Top 100 Schools in America" by Redbook Magazine. His middle school was selected as "One of the Top 100 Wired Schools in America" by PC Magazine. He also served for 12 years as a senior director and chief program officer for McREL International, and he is currently serving on the Board of Colorado ASCD. He is an Apple Distinguished Educator, Apple Teacher, National Distinguished Principal, and Smithsonian Laureate.
He is a published book author and has written numerous magazine articles for Educational Leadership ® magazine, EdCircuit , and Connected Educator , among others.
ASCD is dedicated to professional growth and well-being.
Let's put your vision into action., related blogs.

Want Students to Love Science? Let Them Compete!

Rethinking Our Definition of STEM

How to Grow Strong and Passionate Writers

A Common Math Curriculum Adds Up to Better Learning

“Diverse” Curriculum Still Isn’t Getting It Right, Study Finds
To process a transaction with a purchase order please send to [email protected].
Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research Says
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.
The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early.
But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know:
For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline.
But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.”
A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders.
New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids.
The research
The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance.
Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework.
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework.
Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment.
Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school.
“Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?”
Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids.
“I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school.
The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework.
“The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.”
Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned.
“A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
More Must-Reads From TIME
- Jane Fonda Champions Climate Action for Every Generation
- Passengers Are Flying up to 30 Hours to See Four Minutes of the Eclipse
- Biden’s Campaign Is In Trouble. Will the Turnaround Plan Work?
- Essay: The Complicated Dread of Early Spring
- Why Walking Isn’t Enough When It Comes to Exercise
- The Financial Influencers Women Actually Want to Listen To
- The Best TV Shows to Watch on Peacock
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]
You May Also Like
- FanNation FanNation FanNation
- SI.COM SI.COM SI.COM
- SI Swimsuit SI Swimsuit SI Swimsuit
- SI Sportsbook SI Sportsbook SI Sportsbook
- SI Tickets SI Tickets SI Tickets
- SI Showcase SI Showcase SI Showcase
- SI Resorts SI Resorts SI Resorts
- Depth Chart

© Sam Navarro-USA TODAY Sports
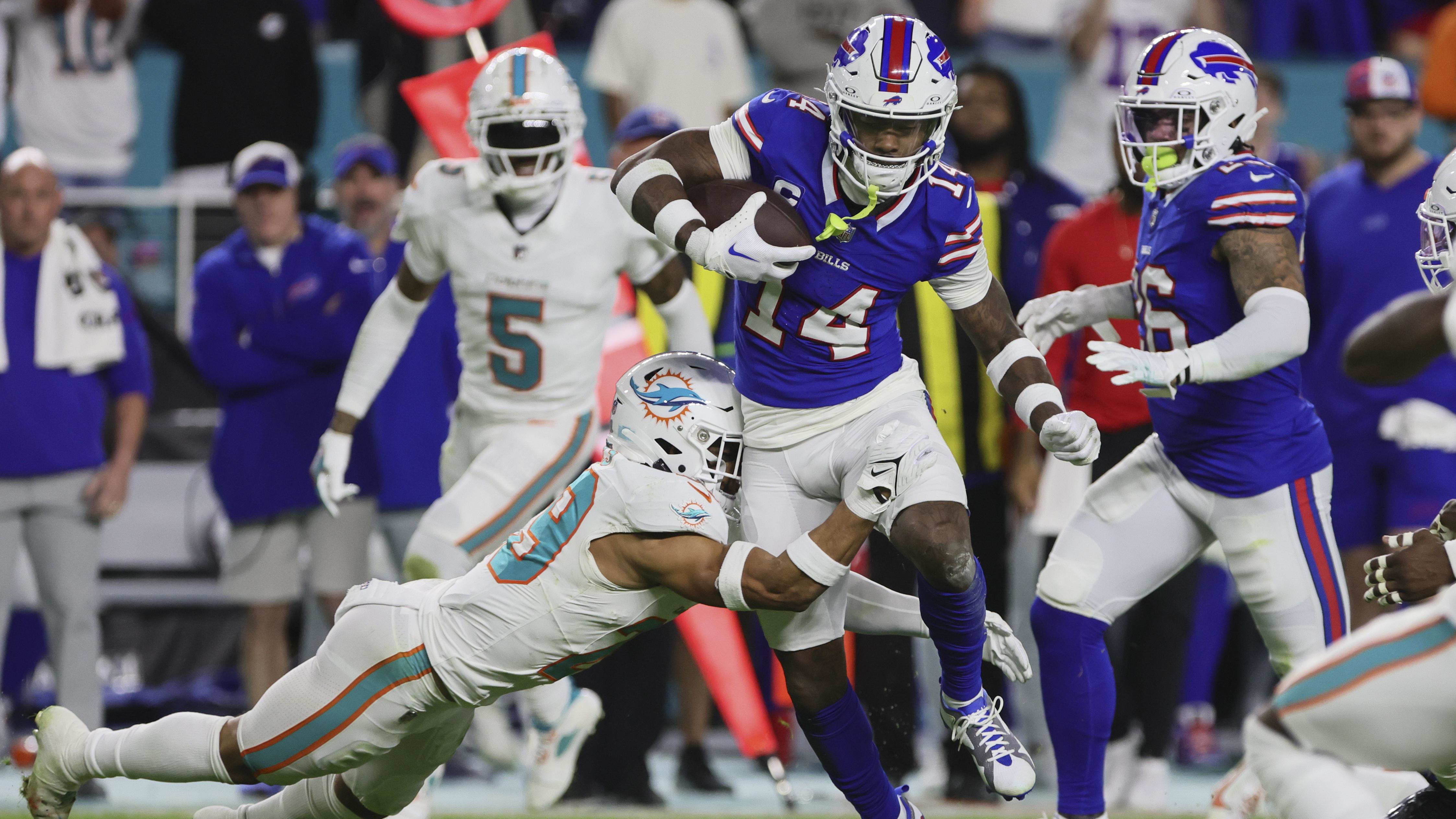
Kelly: Does Diggs' Departure Mean Buffalo's Dominance of AFC East Is Over?
Trading Stefon Diggs to Houston was the latest in a series of moves that likely will weaken the Buffalo Bills and open up the AFC East division
- Author: Omar Kelly
In this story:
Ding dong, the AFC East powerhouse is dead.
Well, maybe the Buffalo Bills still have a pulse, seemingly on life support considering we don’t know what’s next for that franchise.
At the very least, Buffalo’s run as the four-time division champions should be coming to a close based on the roster purge that franchise has undergone this offseason.
The move that should substantially close the gap between the Miami Dolphins and the Bills was Wednesday's trade that sent four-time Pro Bowl wide receiver Stefon Diggs, and a 2024 sixth-round pick and a 2025 fifth-round pick to the Houston Texans for a 2025 second-round pick.
HOW MUCH DOES DIGGS' DEPARTURE WEAKEN BILLS?
Considering Diggs wasn’t shy about letting the world know he was unhappy in Buffalo, for whatever reason, the fact that the diva receiver was moved this offseason wasn’t completely shocking.
But this trade seems more like a salary, and possibly a personality, dump than it was a franchise strategically positioning itself to improve for the upcoming season.
The Diggs trade was another cascading domino of a team acknowledging that its championship window was closing, and beginning the process of retooling its roster to make a resurgent push a season or two from now.
As good as quarterback Josh Allen is, and he’s clearly one of the top 10 players in the NFL, and a Dolphins assassin, the Bills have now had a mad exodus of starting talent.
Not only has Buffalo lost Diggs, and fellow starting receiver Gabe Davis this offseason, the Bills also released center Mitch Morse, cornerback Tre’Davious White and safety Jordan Poyer, who signed with the Dolphins. Linebackers Leonard Floyd and Tyrel Dodson have also taken their talents elsewhere, moving on from Buffalo via free agency.
COST OF DOING BUSINESS
When teams take an all-in approach to win a Lombardi Trophy, which is what Buffalo did when it acquired Diggs four seasons ago and then signed Von Miller to a lucrative, but irresponsible six-year, $120 million deal in 2022, eventually the bill comes due.
The unloading of Diggs and his $19 million salary is basically Buffalo’s attempt at paying down exorbitant credit card debt, and possibly give Allen a fresh start with emotionally stable receivers like Curtis Samuel and Mack Hollins, who both were added in free agency this offseason.
But the bottom line is a receiver unit that features Samuel, Hollins, Khalil Shakir, Andy Isabella and Tyrell Shavers isn’t keeping Kader Kohou up at night like the thought of facing Diggs would.
So unless there’s a second act to this latest NFL soap opera, and the Bills have another game-changing receiver in their scope, it's safe to conclude that Buffalo is coming back to the pack a little and that a Dolphins team that continues to retool its roster has closed some ground on the division’s biggest bully.
While the Dolphins have some voids to fill of their own because of the free agent exodus of 2024, which led to the departures of Christian Wilkins, Robert Hunt, Andrew Van Ginkel, Brandon Jones and DeShon Elliott, none of those players had the impact that Diggs had on the Bills during their tenure.
And now that Diggs is gone, Miami’s chances of dethroning Buffalo are better because Allen needs to find a new favorite target.
Latest Dolphins News

Odell Beckham to Visit Dolphins As Free Agency Interest Ramps Up

Top-Paid Players at Every Position After NFL Free Agency
Receiver Room Developments: River Back, Beckham Visit

Dolphins Take Look at Longhorns

Former Dolphins cornerback Xavien Howard continues to shoot his shot at Texans
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
What Do Diddy's Sex Trafficking Accusations Mean? A Legal Expert Explains
Diddy has not been charged with a crime, but his homes were raided by federal authorities
Daniel Zuchnik/WireImage
The rapper and music executive Sean “Diddy” Combs is facing a slew of sexual abuse allegations in several lawsuits , including some complaints that allege he trafficked victims.
Diddy’s legal troubles mounted last week when federal agents raided his homes in Miami and Los Angeles, though no charges have yet been filed. Homeland Security Investigations New York, which executed the search warrants, did not reveal many details about the searches, just that they were "part of an ongoing investigation," a spokesperson previously told PEOPLE.
In December, Diddy released a statement obtained by PEOPLE vehemently denying the lawsuits that had been filed up until that point. (The first lawsuit against Diddy was filed in November.)
“ENOUGH IS ENOUGH. For the last couple of weeks, I have sat silently and watched people try to assassinate my character, destroy my reputation and my legacy,” Diddy wrote. “Sickening allegations have been made against me by individuals looking for a quick payday.”
But what is sex trafficking, exactly? The Victims of Trafficking and Violence Protection Act of 2000 defines sex trafficking in a federal statute: “The recruitment, harboring, transportation, provision, obtaining, patronizing, or soliciting of a person for the purpose of a commercial sex act, in which the commercial sex act is induced by force, fraud, or coercion, or in which the person induced to perform such act has not attained 18 years of age.”
Neama Rahmani , a California-based attorney and former federal prosecutor, says the sex trafficking allegations are potentially the most serious ones Diddy faces, especially if he is ultimately charged with a sex trafficking crime.
“Under federal law, sex trafficking carries very significant penalties,” Rahmani says, noting that the maximum sentence is life in prison.
The lawsuit that first accused Diddy of sex trafficking was filed by his ex, the singer Casandra Ventura, better known as Cassie . She claimed Diddy subjected her to sex trafficking by forcing her to engage in sexual acts with sex workers and filmed the encounters, which he allegedly called “freak-offs.”
Dia Dipasupil/Getty
A settlement agreement between the two was reached the next day. After the settlement, Diddy’s attorney Ben Brafman told PEOPLE in a statement at the time that the agreement was “in no way an admission of wrongdoing.”
Cassie’s complaint alleged that Diddy would beat her during “freak-offs” and that “between the physical beating and recognizing his incredible power and incredible temper,” she felt that she was unable to say no to him. Further, she claimed Diddy would give her gifts before or during the encounters, which the complaint alleges reflected a gesture to compensate her for “work.”
Rahmani, who has prosecuted human trafficking cases in the past, says the threat of violence to compel a person to engage in a sexual act could constitute sex trafficking, as laid out in the statute.
“If you’re looking at [Cassie’s] allegations that she was raped, that she was forced to take drugs, that she was forced to have sex with male prostitutes while [Diddy] recorded, that’s how you sort of get to the force angle,” Rahmani says. “If there is force, it’s sex trafficking.”
A lawsuit filed on Dec. 6 by a woman identified as Jane Doe alleges that when she was 17, Diddy, former Bad Boy Entertainment President Harve Pierre and a third unnamed defendant trafficked her by flying her from Michigan to Diddy’s studio in New York City, where she claims she was “viciously gang raped.”
An attorney for Pierre did not immediately respond to a request for comment from PEOPLE.
Rahmani says that if true, Doe's allegations might fall under the Victims of Trafficking and Violence Protection Act, which specifies that trafficking applies to alleged victims under the age of 18.
Paras Griffin/Getty
In February, Diddy and several other associates were named as defendants in a lawsuit that accused the Bad Boy founder of sex trafficking as well as several other serious allegations including sexual assault, by producer Rodney “Lil’ Rod” Jones.
Diddy’s attorney Shawn Holley released a strong denial, obtained by PEOPLE.
“Lil Rod is nothing more than a liar who filed a $30 million lawsuit shamelessly looking for an undeserved payday. His reckless name-dropping about events that are pure fiction and simply did not happen is nothing more than a transparent attempt to garner headlines," Holley said, claiming he had “indisputable proof” the claims were false.
David M. Benett/Dave Benett/Getty
While no indictments have been filed, Rahmani says he would not be surprised if criminal charges were filed soon based on the timing of the raids.
“They’re not going to go get search warrants for Diddy’s home in L.A. and Miami unless they’re very close to arresting him,” Rahmani believes.
If you or someone you know has been sexually assaulted, please contact the National Sexual Assault Hotline at 1-800-656-HOPE (4673) or go to rainn.org .
Related Articles
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Definition of homework – Learner’s Dictionary
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- Go upstairs and do your homework.
- For your homework, please do exercise 3 on page 24.
- When I finish my homework, can I watch TV?
- Get on with your homework.
- She was trying to duck out of doing her homework.
(Definition of homework from the Cambridge Learner's Dictionary © Cambridge University Press)
Translations of homework
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
cloak-and-dagger
used to describe an exciting story involving secrets and mystery, often about spies, or something that makes you think of this

Shoots, blooms and blossom: talking about plants

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- do your homework
- Translations
- All translations
Add homework to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Watch CBS News
How did April Fools' Day start and what are some famous pranks?
By Aliza Chasan
April 1, 2024 / 6:00 AM EDT / CBS News
Historians aren't pulling your leg when they say no one is quite sure about the origins of April Fools' Day.
April 1, the annual day of shenanigans, pranks, tricks and hoaxes, falls on Monday this year. While historians are unsure of the exact source of the tradition, they do know the custom goes back centuries, at least back to Renaissance Europe and possibly back to Roman times. Here's a look at what the experts say.
Theories, both real and false, tie April Fools' Day to Roman times
Some believe April Fools' Day dates back to Hilaria festivals celebrated during classical Roman times. The festival was held on March 25 which, in Roman terms, was called the "eighth of the Calends of April," according to the Library of Congress.
One theory tying the source of April Fools' Day to Roman times is a hoax. In 1983, an Associated Press reporter reached out to Joseph Boskin, a historian at Boston University, to discuss the origins of April Fools' Day. Boskin spun a tall tale to the reporter, assuming it would be fact-checked and revealed as fake.
It wasn't.
According to the story Boskin made up, a group of jesters convinced Emperor Constantine to make one of them king for a day. The appointed jester, named Kugel, declared it would be a day of levity.
"I got an immediate phone call from an editor there, who was furious, saying that I had ruined the career of a young reporter," Boskin said in a Boston University post. "He said I told a lie. 'A lie?' I asked, 'I was telling an April Fools' Day story.'"
Middle Ages
Some historians believe France is responsible for the humorous tradition, tying it to a calendar change in 1582, according to the History Channel . That year, France implemented the Gregorian calendar, shifting the start of the New Year from the spring equinox, which usually falls around April 1, to January 1.
After the change, people who wrongly celebrated the new year in late March and early April were called "April fools."
The first clear reference to April Fools' Day is a 1561 Flemish poem by Eduard De Dene, which tells the story of a servant being sent on "fool's errands" because it's April 1, according to the Library of Congress.
What are some famous April Fools' Day pranks?
In 1957, the BBC ran a broadcast on the Italian spaghetti harvest that pretended the pasta was being harvested from trees.
The BBC also ran an April Fools' report on flying penguins in 2008.
In Los Angeles, airline passengers were greeted with a banner saying "Welcome to Chicago" after landing on April 1, 1992, CBS Sunday Morning previously reported.
Taco Bell in 1996 advertised that it had bought the Liberty Bell and renamed it the "Taco Liberty Bell," according to the company.
As part of a 1997 April Fools' Day joke, Alex Trebek, host of "Jeopardy," swapped places with "Wheel of Fortune" host Pat Sajak, according to jeopardy.com .
On April 1, 2015, streaming giant Netflix shared faux public service announcements to remind viewers to "Binge Responsibly."
- April Fools' Day
Aliza Chasan is a digital producer at 60 Minutes and CBSNews.com. She has previously written for outlets including PIX11 News, The New York Daily News, Inside Edition and DNAinfo. Aliza covers trending news, often focusing on crime and politics.
More from CBS News

How Americans in the solar eclipse's path of totality plan to celebrate the celestial event on April 8, 2024

Climber falls 1,200 feet to his death in Mount St. Helens crater

Botswana threatens to send 20,000 elephants to "roam free" in Germany

Forbes has released its list of the world's billionaires
What is Holy Saturday? What the day before Easter means for Christians around the world
Easter Sunday is this upcoming weekend, which means the preceding Saturday is known as Holy Saturday.
According to Britannica, Holy Saturday is a Christian religious observance that ends the Lenten season. The observance "commemorates the final day of Christ's death," according to Britannica, which many Christians traditionally associate with his "triumphant descent into hell or 'to the dead.'" The day comes between Good Friday and Easter Sunday.
Easter is an important holiday for the millions of people around the world who follow the Christian faith as the day celebrates the resurrection of Jesus Christ. The holiday occurs after a 40-day period known as Lent.
Church services, reflection and prayer are some ways that people observe the holiday. Others enjoy a more secular celebration of Easter filled with bunnies, baskets and colorful eggs.
Good Friday: Are banks, post offices, UPS and FedEx open? Here's what to know
When is Holy Saturday? When is Easter?
This year, Holy Saturday is on Saturday, March 30, 2024. Easter Sunday is on Sunday, March 31, 2024.
Why is Easter so early in 2024?
Easter's date changes depending on the year. The holiday is one of several "moveable feasts" in the liturgical year, the History Channel reports. Others include Ash Wednesday and Palm Sunday .
Easter is observed on the first Sunday following the Paschal full moon , which is the first full moon on or after the spring equinox . Since Western Christianity uses the Gregorian calendar, Easter typically falls on a Sunday between March 22 and April 25, according to the History Channel.
In Eastern Orthodox Christianity, the date of Easter also varies. The branch follows the Julian calendar, meaning orthodox Easter falls between April 4 and May 8, the History Channel reports. This year, it will take place on Sunday, May 5, 2024.
Contributing: Olivia Munson, USA TODAY
Gabe Hauari is a national trending news reporter at USA TODAY. You can follow him on X @GabeHauari or email him at [email protected].
Tasmania has elected a hung parliament. So what does that mean, and how do minority governments work?
As the numbers for the Tasmanian election rolled in on Saturday night, it quickly became clear neither Labor nor the Liberals would be able to form majority government.
But the Liberal party is projected to win more seats , with Jeremy Rockliff declaring victory on election night .
On Sunday, Labor leader Rebecca White conceded it was now up to Mr Rockliff to form government .
So now Mr Rockliff is tasked with gaining the support of the majority of parliament, from a minority position.
But what does this actually mean?
And how can the Liberals get there?
What is a hung parliament?
At Saturday's election, Tasmanians elected a hung parliament, which is when no party wins the majority of seats in the house of assembly, also known as the lower house.
This means no party has the mandate to form government in its own right.
The magic number of seats to form majority for this election was 18, as that would be more than half of the total 35 seats.
Currently, the Liberals sit on 13 and Labor are on 10.
In that instance, independents and minor parties — known as the crossbench — are called on to help one of the two major parties form government.
What is a minority government and why don't parties like them?
When there's a hung parliament, the incumbent government is given the first opportunity to approach independents and/or minor parties to try strike a deal.
If that party fails to get the majority of the house of assembly on side, the opposition may get the chance to give it a go.
In striking an agreement, crossbenchers may make policy requests in exchange for their support.
And there are different types of agreements, such as a coalition, where crossbenchers may be given ministerial portfolios in cabinet.
Another is a supply and confidence deal.
Guaranteeing supply means agreeing to pass the key bills authorising the government to spend money, while confidence refers to protecting the government against motions of no-confidence on the floor of parliament.
Governments generally prefer to be elected with a majority because it tends to make it easier to pass legislation, and means they don't have to enter deals with independents who may have different values and agendas from them.
Power-sharing arrangements tend to be a hot topic in Tasmanian election campaigns.
This time around, the Liberals repeatedly stated a vote for Labor was a vote for a "coalition of chaos" with the Greens, while Labor assured voters it would not enter deals.
But minority governments don't necessarily mean a parliament cannot function effectively.
In fact, they have been hailed as an example of "true democracy" because there are more checks and balances on the government.
How have minority governments worked in the past?
At the federal level, Labor Prime Minister Julia Gillard led a minority government from 2010 to 2013 with the Greens and independents, in a written agreement with the crossbench promising supply and confidence.
Tasmania is no stranger to minority government — about a third of its governments over the past 150 years have not held a majority.
At the 2010 Tasmanian election, the Labor and Liberal parties won 10 seats each, while the Greens won five. This led to a Labor-Green coalition, with the Greens getting two spots in cabinet.
Tasmania's last government ended up in minority when Lara Alexander and John Tucker left the Liberal party to sit as independents.
While Mr Rockliff had an agreement with the pair to continue governing, he didn't believe the arrangement was working well, so he sent the state to an early election to try win back majority .
That obviously didn't happen, and he will now need to secure support from the crossbench.
We know Mr Rockliff has already reached out to the Jacqui Lambie Network and independents (he's previously ruled out doing a deal with the Greens).
Whether they take up his offer, and what they might ask for in return, isn't yet clear.
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
A private investigator, a former british mayor – meet tasmania's possible new crossbench.
When Tasmania expanded the lower house to 35 seats, the Liberals didn't predict the independent vote would double
Rockliff claims victory in Tasmanian election, despite falling short of majority
'Trumpian' move to oust Liberal Party defectors from Tasmanian parliament blasted as 'undemocratic'
Record number of early votes cast as Tasmania waits for election results to roll in
- Liberal Party of Australia
- State and Territory Elections
- State and Territory Government
Advertisement
Supported by
What the Bridge Meant to Baltimore
The victims, the history, the void. Residents reflect on their collective pain, and the city’s strength.
- Share full article

By Anna Betts and JoAnna Daemmrich
Anna Betts reported from New York, and JoAnna Daemmrich reported from Baltimore.
Blue-collar workers crossed it. Families went crabbing around it. Teenagers celebrated new driver’s licenses by traversing it. And couples were known to get engaged near it.
Completed in 1977, the Francis Scott Key Bridge was a practical, final link to the beltway of roads that circled Baltimore Harbor, a much-needed solution to reduce Harbor Tunnel congestion. But for so many, it was more than that.
For some, it symbolized the working-class communities around it — for others, the city itself. The bridge also served as a reminder of a storied chapter in history: Near Fort McHenry, the bridge is believed by historians to be within 100 yards from where Key was held by the British during the War of 1812, when he witnessed the siege of the fort in September 1814 and wrote the poem that became the national anthem. (A star-spangled buoy commemorates the supposed spot.)
And the Key Bridge was simply a presence in people’s everyday lives. Since the collapse last week, residents have been processing the loss on many levels, from profound grief for the six workers who died, to concern for the immigrant communities affected by the port’s shutdown, to a sense of emptiness that has cast a pall over their memories.
Here are a few reflections from Baltimoreans, condensed and edited for clarity.
Dr. Panagis Galiatsatos, physician who grew up on the east side of Baltimore
“There’s not a lot of things that tend to unite this city, unfortunately, but this is one of them. Every single Baltimorean felt that bridge fall down. That’s our London Bridge. That’s our Golden Gate Bridge. It was like a friend constantly saying hello to me in the morning.
The bridge was one of the first jobs really available to a lot of the immigrant populations in Baltimore city. My dad, who worked as a painter on the bridge, said if you were an able-bodied person that knew how to do any level of construction or painting and you’re an immigrant, chances are you worked on that bridge.
Up until the bridge was built, you hear these stories from the locals, it would take hours sometimes to get to any place that was reasonable to work at, because of the back roads they had to take. The bridge was a lifeline to schools and work. That’s where my heart is at: These everyday people that live out there just lost a lifeline connection to these big resources such as supermarkets, schools, work.
Not to sound cheesy, but it was a bridge to the American dream. And the first and last hands touching that bridge were immigrants that came here to pursue that.”
Terry Turbin, pastor of Sonshine Fellowship Church in Dundalk and a onetime carpenter who worked on the bridge foundation
“I’m proud to be able to say I had a part in building it. When they get ready to rebuild it, I would like to work on it, even just one day. I went out on the barge in February 1975. After I got married, and found the bridge was being constructed, I wanted to get on the job and make better money. The bridgework was $8.10 an hour. My first day out, I actually asked myself, ‘Oh God, what did I get myself into?’ It was dangerous work. We were driving the pilings, and at that time of year, the wind was pretty stiff. You had to be very careful. The other part was always looking up to make sure nothing was falling on you. It was really stressful. When you got on dry land, you said a prayer of thanks. I have driven over the bridge a thousand times or more, and I would always tell my family, ‘This is where I was working, I was right under there.’ It was an emotional connection for me.”
Gustavo Torres, executive director of CASA, a nonprofit that provides services to immigrants in Baltimore
“For me, the Key Bridge was just another crossing. Its magnificence seemed, well, average. In its death, it has become so much more, its secret life revealed as the place where workers came together. Laborers born in places ranging from south Baltimore to central Honduras sharing companionship as they worked long after I had gone to sleep to make sure that my passage was uneventful. A place of heroism where workers toiled in the cold and throughout the pandemic so that my life was easier. Workers who are fathers, brothers, sisters and mothers. Workers who are neighbors, co-workers, friends from church. Workers, who in their commitment to all of us, are the best of America.”
Comfort, and anxiety
Congressman Kweisi Mfume, who represents Baltimore as part of Maryland’s 7th District
“I was a freshman in college when they started building [the bridge]. I was anxious for the bridge to go up because it was a quicker way to get to the other side of the harbor, but it also ended up being a kind of cathedral of architecture in that community because it was a beautiful bridge. You felt very comfortable seeing it, because its sturdiness suggested all is well elsewhere.
On the economic side, there’s a real sense of urgency because that bridge affects so many supply line issues all over the country. It’s a cascading kind of ripple effect that will add to an economy right now in the wrong way. There are a number of small businesses that are impacted, particularly those who deal in import-export.”
John Olszewski, known as Johnny O, Baltimore County executive
"I feel it in the very personal way, and in the very painful way, that the people who live here do. We’re still very much in shock and reeling from the loss, not just from our neighbors, people who are experiencing unspeakable tragedy right now, who were working on the bridge, but also our neighbors who have this incredible uncertainty about what their future means, who are port workers.
It’s the little memories: as a high schooler, driving around the beltway and crossing the bridge because it was the thing to do when you got your license, to spending evenings fishing in the channel. I’d do a little crabbing, recreationally, on the side of the bridge there. I have all these incredible memories, and then to have everything you’ve ever known come to a screeching halt … ” [His voice trailed off and he shook his head.]
A sense of home
Michelle Dobbs, veterinary pharmaceutical sales representative, resident of the Sparrows Point neighborhood who crossed the bridge twice a day
“Coming over the Key Bridge, I’d feel an instant lowering of blood pressure, a feeling that my day is done. It was a symbol of coming home. You’d have a beautiful view of the Baltimore skyline from the top of the bridge. I’d see the sailboats and cruise ships coming in and out; one time, I was lucky enough to see the Pride of Baltimore [a tall ship] come through. It never got old. It was just a part of my daily life. I don’t know when it’s not going to be so jarring. It’s unbelievable to have such an emotional attachment to a bridge.”
Joey Harkum, musician from Pasadena, a suburban area south of the bridge on the Patapsco River
“It’s absolutely important to northern Anne Arundel County — that’s how we get to Dundalk, that’s how we get to Fells Point. It’s so close to our house, there’s debris washing up on our beach now. We grew up right there on the river. We would take out a little boat and sneak out to Fort Carroll and just explore. Whenever people from out of town came, I’d drive them to the bridge and show them all the forts. I named my first band Pasadena. Our first album had a drawing of the Key Bridge, the smokestacks and the bridge, showing that’s where we were from. It was just part of our identity for people who lived south of the city."
Coming together
Shannon McLucas, ranger at Fort McHenry, a national monument about four miles across from the bridge
“Throughout the morning, we had a lot of regulars, locals walking along the seawall. Joggers, dog walkers, parents with babies, some come every morning to walk. They had the same emotional reaction I did at seeing this dramatically changed landscape. It was very busy but very eerily quiet. To me, that’s remarkable. There are moments when we have this shared humanity — from the park, you see the wreckage, but you also see the Coast Guard at work. We talk about the Battle of Baltimore, in 1814. People came from all over, from different walks of life, to defend the city, they came together. Now, 210 years later, this was an accident, but it’s one of those moments where you realize we do have a shared community.”
Laura Lippman, author
“All I can tell you is that I’m sad and I know others are sad, too. I love my hometown so much. My family moved here in ’65. I remember the riots after the assassination of M.L.K., I remember when homicides spiked in the ’80s, I remember Freddie Gray. It’s a city that’s forever getting knocked down — and getting back up again.
I went to Opening Day of the Orioles, arriving in time for the acknowledgment of those who died on the bridge. It was sincerely moving. As you may know, Baltimoreans shout the ‘O!’ at the end of the national anthem — for the Orioles, but also, I think, for the city. I have never shouted ‘O!’ as loudly as I did on Thursday.”
Miriam Jordan contributed reporting.
Anna Betts reports on national events, including politics, education, and natural or man-made disasters, among other things. More about Anna Betts

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
DO YOUR HOMEWORK meaning: 1. to study a subject or situation carefully so that you know a lot about it and can deal with it…. Learn more.
The meaning of HOMEWORK is piecework done at home for pay. How to use homework in a sentence. piecework done at home for pay; an assignment given to a student to be completed outside the regular class period…
You finish one episode, then decide to watch another even though you've got SAT studying to do. It's just more fun to watch people make scones. D. Start the episode, but only catch bits and pieces of it because you're reading Twitter, cleaning out your backpack, and eating a snack at the same time. 5.
We always use "do" with activities and "make" with objects that are being made. Just like we "do work", not "make work", we also "do homework", meaning the activity. The confusion arises from the fact that the most direct translation of "homework" into other languages often refers to the sheets of paper on which the ...
The homework assignments are worth 10% of the final grade. I have some homework to do on the Civil War. I want you to hand in this homework on Friday. The science teacher always gives a lot of homework. They get a lot of homework in English. They get masses of homework at secondary school. We had to write out one of the exercises for homework.
Meaning, pronunciation, picture, example sentences, grammar, usage notes, synonyms and more. Toggle navigation ... 1 work that is given by teachers for students to do at home I still haven't done my geography homework. How much homework do you get? I have to write up the notes for homework. compare classwork Topic Collocations Education ...
A person doing geometry homework Children preparing homework on the street, Tel Aviv, 1954. Homework is a set of tasks assigned to students by their teachers to be completed at home.Common homework assignments may include required reading, a writing or typing project, mathematical exercises to be completed, information to be reviewed before a test, or other skills to be practiced.
There are those who argue that homework does serve a purpose. For example, it helps to prepare students for national and statewide exams and tests. It helps to reinforce what's being taught in ...
Homework definition: . See examples of HOMEWORK used in a sentence.
These include to: establish and improve communication between parents and children about learning. help children be more responsible, confident and disciplined. practise or review material from ...
Homework is work that teachers give students to complete outside of the school day. Homework is meant to provide students with practice for what was learned in school or an extension of what was done in class. Students are expected to complete the homework and return to school with the completed homework assignment.
do (one's) homework. 1. Literally, to complete the school work that has been assigned by a teacher to be done at home. You can't watch any more television until you do your homework! 2. To be thoroughly prepared and informed about something or something, especially in advance of some process, action, or decision.
Homework has been in the headlines again recently and continues to be a topic of controversy, with claims that students and families are suffering under the burden of huge amounts of homework. School board members, educators, and parents may wish to turn to the research for answers to their questions about the benefits and drawbacks of homework.
Consider the following examples: We did our homework last night. She did her homework last night.. Auxiliary Verbs. Auxiliary, or helping verbs, are used with another base verb to create negative sentences, questions, or add emphasis.Here's how do should be used as an auxiliary verb:. 1. Negative Sentences. Following the same subject-verb pairings introduced above, we combine the ...
The National PTA and the National Education Association support the " 10-minute homework guideline "—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students' needs, not the amount of time spent on it.
Homework teaches students responsibility. Homework gives students an opportunity to practice and refine their skills. We give homework because our parents demand it. Our community equates homework with rigor. Homework is a rite of passage. But ask them what research says about homework, and you'll get less definitive answers.
For decades, the homework standard has been a "10-minute rule," which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 ...
Definition: the noun form of the word 'homework' refers to tasks or assignments given to students by their teachers to be completed at home. These assignments are typically meant to supplement classroom learning with additional practice or memorization and are an integral part of any schooling system.
1. To Assigning Homework, you have two options: a. To assign homework for a set that you do not own: go to the set preview page and select "Assign HW". b. To assign homework for a set that is yours: go to your "My Sets" page and select "Assign" on the set you wish to use. 2. Select a solo game mode. 3.
The unloading of Diggs and his $19 million salary is basically Buffalo's attempt at paying down exorbitant credit card debt, and possibly give Allen a fresh start with emotionally stable ...
Daniel Zuchnik/WireImage. The rapper and music executive Sean "Diddy" Combs is facing a slew of sexual abuse allegations in several lawsuits, including some complaints that allege he ...
With the finish line in sight, the Federal Court has provided another twist in Bruce Lehrmann's defamation case against Network Ten after the broadcaster yesterday won its bid to reopen the case ...
HOMEWORK definition: 1. work that teachers give their students to do at home: 2. work that teachers give their students…. Learn more.
HOMEWORK meaning: 1. work that teachers give students to do at home: 2. to prepare carefully for a situation: . Learn more.
After the change, people who wrongly celebrated the new year in late March and early April were called "April fools." The first clear reference to April Fools' Day is a 1561 Flemish poem by Eduard ...
According to Britannica, Holy Saturday is a Christian religious observance that ends the Lenten season. The observance "commemorates the final day of Christ's death," according to Britannica ...
What is a hung parliament? At Saturday's election, Tasmanians elected a hung parliament, which is when no party wins the majority of seats in the house of assembly, also known as the lower house.
The victims, the history, the void. Residents reflect on their collective pain, and the city's strength. By Anna Betts and JoAnna Daemmrich Anna Betts reported from New York, and JoAnna ...