

The Importance of Critical Thinking Skills in Research
Why is Critical Thinking Important: A Disruptive Force
Research anxiety seems to be taking an increasingly dominant role in the world of academic research. The pressure to publish or perish can warp your focus into thinking that the only good research is publishable research!
Today, your role as the researcher appears to take a back seat to the perceived value of the topic and the extent to which the results of the study will be cited around the world. Due to financial pressures and a growing tendency of risk aversion, studies are increasingly going down the path of applied research rather than basic or pure research . The potential for breakthroughs is being deliberately limited to incremental contributions from researchers who are forced to worry more about job security and pleasing their paymasters than about making a significant contribution to their field.
A Slow Decline
So what lead the researchers to their love of science and scientific research in the first place? The answer is critical thinking skills. The more that academic research becomes governed by policies outside of the research process, the less opportunity there will be for researchers to exercise such skills.
True research demands new ideas , perspectives, and arguments based on willingness and confidence to revisit and directly challenge existing schools of thought and established positions on theories and accepted codes of practice. Success comes from a recursive approach to the research question with an iterative refinement based on constant reflection and revision.
The importance of critical thinking skills in research is therefore huge, without which researchers may even lack the confidence to challenge their own assumptions.
A Misunderstood Skill
Critical thinking is widely recognized as a core competency and as a precursor to research. Employers value it as a requirement for every position they post, and every survey of potential employers for graduates in local markets rate the skill as their number one concern.
Related: Do you have questions on research idea or manuscript drafting? Get personalized answers on the FREE Q&A Forum!
When asked to clarify what critical thinking means to them, employers will use such phrases as “the ability to think independently,” or “the ability to think on their feet,” or “to show some initiative and resolve a problem without direct supervision.” These are all valuable skills, but how do you teach them?
For higher education institutions in particular, when you are being assessed against dropout, graduation, and job placement rates, where does a course in critical thinking skills fit into the mix? Student Success courses as a precursor to your first undergraduate course will help students to navigate the campus and whatever online resources are available to them (including the tutoring center), but that doesn’t equate to raising critical thinking competencies.
The Dependent Generation
As education becomes increasingly commoditized and broken-down into components that can be delivered online for maximum productivity and profitability, we run the risk of devaluing academic discourse and independent thought. Larger class sizes preclude substantive debate, and the more that content is broken into sound bites that can be tested in multiple-choice questions, the less requirement there will be for original thought.
Academic journals value citation above all else, and so content is steered towards the type of articles that will achieve high citation volume. As such, students and researchers will perpetuate such misuse by ensuring that their papers include only highly cited works. And the objective of high citation volume is achieved.
We expand the body of knowledge in any field by challenging the status quo. Denying the veracity of commonly accepted “facts” or playing devil’s advocate with established rules supports a necessary insurgency that drives future research. If we do not continue to emphasize the need for critical thinking skills to preserve such rebellion, academic research may begin to slowly fade away.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Intersectionality in Academia: Dealing with diverse perspectives
Meritocracy and Diversity in Science: Increasing inclusivity in STEM education
Avoiding the AI Trap: Pitfalls of relying on ChatGPT for PhD applications

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Critical thinking refers to deliberately scrutinizing and evaluating theories, concepts, or ideas using reasoned reflection and analysis. The act of thinking critically involves moving beyond simply understanding information, but going further by questioning its source, its production, and its presentation in order to expose potential bias or researcher subjectivity [i.e., evidence of being influenced by personal opinions and feelings rather than by external determinants ] . Applying critical thinking to investigating a research problem involves actively challenging basic assumptions and questioning the choices and potential motives underpinning how a study was designed and executed and how the author arrived at particular conclusions or recommended courses of action. Applying critical thinking to writing involves effectively synthesizing information and generating compelling arguments.
Hanscomb, Stuart. Critical Thinking: The Basics . 2nd edition. London: Routledge, 2023; Mintz, Steven. "How the Word "Critical" Came to Signify the Leading Edge of Cultural Analysis." Higher Ed Gamma Blog , Inside Higher Ed, February 13, 2024; Van Merriënboer, Jeroen JG and Paul A. Kirschner. Ten Steps to Complex Learning: A Systematic Approach to Four-component Instructional Design . New York: Routledge, 2017.
Thinking Critically
Applying Critical Thinking to Research and Writing
Professors like to use the term critical thinking; in fact, the idea of being a critical thinker permeates much of higher education writ large. In the classroom, the idea of thinking critically is often mentioned by professors when students ask how they should approach writing a research paper [other approaches your professor might mention include interdisciplinarity, compare and contrast, gendered perspective, global, etc.]. However, critical thinking is more than just an approach to research and writing. It is an acquired skill associated with becoming a complex learner capable of discerning important relationships among the elements of, as well as integrating multiple ways of understanding applied to, the research problem. Critical thinking is a lens through which you holistically interrogate a topic.
Given this, critical thinking encompasses a variety of inter-related connotations applied to writing a college-level research paper:
- Integrated and Multi-Dimensional . Critical thinking is not focused on any one element of research, but instead, is applied holistically throughout the process of identifying the research problem, reviewing the literature, applying methods of analysis, describing the results, discussing their implications, and, if appropriate, offering recommendations for further research. It permeates the entire research endeavor from contemplating what to write about to proofreading the final product.
- Humanizes the Research . Thinking critically can help humanize what is being studied by extending the scope of your analysis beyond the traditional boundaries of prior research. The scope of prior research, for example, could have involved only sampling homogeneous populations, only considered certain factors related to the investigation of a phenomenon, or was limited by the way the study was framed or contextualized. Critical thinking supports opportunities to think about incorporating the experiences of traditionally marginalized groups into the research, leading to a more inclusive and representative examination of the topic.
- Non-Linear . This refers to analyzing a research problem in ways that do not rely on sequential decision-making or rational forms of reasoning. Creative thinking relies on intuitive judgement, flexibility, and unconventional approaches to investigating complex phenomena in order to discover new insights, connections, and potential solutions . Thinking critically involves going back and modifying your thinking as new evidence emerges , perhaps multiple times throughout the research process, and then drawing conclusions from multiple perspectives as a result of questioning initial impressions about the topic.
- Normative . This refers to the idea that critical thinking can be used to challenge prior assumptions in ways that advocate for social justice, equity, and resilience, leading to research having a more transformative and expansive impact. In this respect, critical thinking can be viewed as a method for breaking away from dominant culture norms so as to produce research outcomes that illuminate previously hidden aspects of exploitation and injustice.
- Power Dynamics . Research in the social sciences often includes examining aspects of power and influence, focusing on how it operates, how it can be acquired, and how it can be maintained, thereby shaping social relations, organizations, institutions, and the production and maintenance of knowledge. Thinking critically can reveal how societal structures and forces perpetuate power in ways that marginalizes and oppresses specific groups or communities within the contexts of history , politics, economics, culture, and other factors.
- Reflection . A key component of critical thinking is practicing reflexivity; the act of turning ideas and concepts back onto yourself in order to reveal and clarify your own beliefs, assumptions, and perspectives. Being critically reflexive is important because it can reveal hidden biases you may have that could unintentionally influence how you interpret and validate information. The more reflexive you are, the better able and more comfortable you are in opening yourself up to new modes of understanding.
- Rigorous Questioning . Thinking critically is guided by asking questions that lead to addressing complex principles, theories, concepts, or problems more effectively, and in so doing, help distinguish what is known from from what is not known [or that may be hidden]. Critical thinking involves deliberately framing inquiries not only as hypotheses or axioms, but as a way to apply systematic, disciplined, in-depth forms of questioning about the research problem and in relation to your positionality as a researcher.
- Social Change . An overarching goal of critical thinking applied to research and writing is to seek to identify and challenge forces of inequality, exploitation, oppression, and marinalization that contribute to maintaining the status quo within institutions of society. This can include, for example, schools, court system, businesses, government agencies, or religious organizations that have been created and maintained through certain ways of thinking within the dominant culture. Thinking critically fosters a sense of awareness and empathy about where social change is needed within the overall research process.
Critical thinking permeates the entire research and writing process. However, it applies in particular to the literature review and discussion sections of your paper. These two sections of a research paper most clearly reflect the external/internal duality of thinking critically.
In reviewing the literature, it is important to reflect upon specific aspects of a study, such as, 1) determining if the research design effectively establishes cause and effect relationships or provides insight into explaining why certain phenomena do or do not occur; 2) assessing whether the method of gathering data or information supports the objectives of your study; and, 3) evaluating if the assumptions used t o arrive at a specific conclusion are evidence-based and relevant to addressing the topic. Critically thinking applies to these elements of reviewing prior research by assessing how each source might perpetuate inequalities or hide the voices of others, thereby, limiting its applicability for understanding the scope of the problem and its impact throughout society.
Critical thinking applies to the discussion section of your paper because this is where you contemplate the results of your study and explain its significance in relation to addressing the research problem. Discussion involves more than just summarizing findings and describing outcomes. It includes deliberately considering the importance of the findings and providing reasoned explanations why your paper helps to fill a gap in the literature or expand knowledge and understanding in ways that inform practice. Critical thinking uses reflection to examine your own beliefs concerning the significance of the results in ways that avoid using biased judgment and decision making.
Using Questions to Enable Critical Thinking
At its most fundamental level, critical thinking is thinking about thinking in ways that improve the effectiveness of your ability to reason, analyze, synthesize, evaluate, and report information and, as a result, it advances deeper explorations of the topic*. From a practical standpoint, critical thinking is an act of introspective self-examination that involves formulating open-ended questions that inspire higher levels of reasoning about a research problem. The purpose of asking questions during the research process is to apply a framework of inquiry that challenges conventional assumptions, scrutinizes the evidence presented, determines how effectively arguments have been supported by that evidence, discerns patterns or trends in the findings, and helps imagine alternative outcomes if new or different factors were introduced.
Below are examples of questions that can stimulate critical thinking:
- Why is this a problem?
- Why does this research problem matter?
- Does the problem matter to everyone or just certain groups?
- How might your perspective change if you were on the other side of the argument?
- What patterns or connections can you see in the results?
- What key factors could have altered the outcomes described in the results?
- What evidence would be needed to support any alternative outcomes?
- Should there be any additional or alternative interpretations of the research outcomes?
- What is the explanation for the cause of an event or phenomenon?
- Why has a particular situation or condition arisen?
- Who will be impacted by the recommendations posed by the author?
- Who might be excluded from the author’s recommendations?
- When and how will you know that the recommendations have worked?
- In what ways can you apply knowledge from this study to new situations?
- What is another way to look at how the study was designed?
- How does the study contradict or confirm your understanding of the research problem?
- Do the outcomes of the study inform your own lived experiences?
- What do you think is the significance of this study and why?
- What are the overall strengths and weakness of this study?
NOTE: Being a critical thinker doesn't just happen. Casting a critical eye on how effectively others have studied a research problem requires developing self-confidence in your own abilities to actively engage with information, to consistently ask how and why questions about the research, and to deliberately analyze arguments and recommendations set forth by the author. Examining critically your own beliefs and feeling about your writing involves a willingness to be comfortable questioning yourself in a way that promotes a strong sense of self-awareness and introspection. Together, these outward and inward looking habits can help improve your critical thinking skills and inform how to effectively research and write a college-level research paper.
* Kharbach, Med. “Examples of Critical Thinking Questions for Students.” Educational Technology and Mobile Learning blog , Last Update: November 10, 2023.
Behar-Horenstein, Linda S., and Lian Niu. “Teaching Critical Thinking Skills in Higher Education: A Review of the Literature.” Journal of College Teaching and Learning 8 (February 2011): 25-41; Bayou, Yemeserach and Tamene Kitila. "Exploring Instructors’ Beliefs about and Practices in Promoting Students’ Critical Thinking Skills in Writing Classes." GIST–Education and Learning Research Journal 26 (2023): 123-154; “Bloom's Taxonomy.” Centre for Teaching Excellence. University of Waterloo; “Higher Order Thinking: Bloom’s Taxonomy.” The Learning Center. University of North Carolina; Butcher, Charity. "Using In-class Writing to Promote Critical Thinking and Application of Course Concepts." Journal of Political Science Education 18 (2022): 3-21; Krathwohl, David R. “A Revision of Bloom's Taxonomy: An Overview.” Theory into Practice 41 (Autumn 2002): 212-218; Loseke, Donileen R. Methodological Thinking: Basic Principles of Social Research Design. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2012; Mintz, Steven. "How the Word "Critical" Came to Signify the Leading Edge of Cultural Analysis." Higher Ed Gamma Blog , Inside Higher Ed, February 13, 2024; Hart, Claire et al. “Exploring Higher Education Students’ Critical Thinking Skills through Content Analysis.” Thinking Skills and Creativity 41 (September 2021): 100877; Lewis, Arthur and David Smith. "Defining Higher Order Thinking." Theory into Practice 32 (Summer 1993): 131-137; Sabrina, R., Emilda Sulasmi, and Mandra Saragih. "Student Critical Thinking Skills and Student Writing Ability: The Role of Teachers' Intellectual Skills and Student Learning." Cypriot Journal of Educational Sciences 17 (2022): 2493-2510. Suter, W. Newton. Introduction to Educational Research: A Critical Thinking Approach. 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2012; Van Merriënboer, Jeroen JG and Paul A. Kirschner. Ten Steps to Complex Learning: A Systematic Approach to Four-component Instructional Design. New York: Routledge, 2017; Vance, Charles M., et al. "Understanding and Measuring Linear–Nonlinear Thinking Style for Enhanced Management Education and Professional Practice." Academy of Management Learning and Education 6 (2007): 167-185; Yeh, Hui-Chin, Shih-hsien Yang, Jo Shan Fu, and Yen-Chen Shih. "Developing College Students’ Critical Thinking through Reflective Writing." Higher Education Research & Development 42 (2023): 244-259.
- << Previous: Academic Writing Style
- Next: Choosing a Title >>
- Last Updated: May 25, 2024 4:09 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Archives & Special Collections home
- Art Library home
- Ekstrom Library home
- Kornhauser Health Sciences Library home
- Law Library home
- Music Library home
- University of Louisville Hospital home
- Interlibrary Loan
- Off-Campus Login
- Renew Books
- Cardinal Card
- My Print Center
- Business Ops
- Cards Career Connection
Search Site
Search catalog, critical thinking and academic research: intro.
- Information
- Point of View
- Assumptions
- Implications
Critical Thinking and Academic Research
Academic research focuses on the creation of new ideas, perspectives, and arguments. The researcher seeks relevant information in articles, books, and other sources, then develops an informed point of view within this ongoing "conversation" among researchers.
The research process is not simply collecting data, evidence, or "facts," then piecing together this preexisting information into a paper. Instead, the research process is about inquiry—asking questions and developing answers through serious critical thinking and thoughtful reflection.
As a result, the research process is recursive, meaning that the researcher regularly revisits ideas, seeks new information when necessary, and reconsiders and refines the research question, topic, or approach. In other words, research almost always involves constant reflection and revision.
This guide is designed to help you think through various aspects of the research process. The steps are not sequential, nor are they prescriptive about what steps you should take at particular points in the research process. Instead, the guide should help you consider the larger, interrelated elements of thinking involved in research.
Research Anxiety?
Research is not often easy or straightforward, so it's completely normal to feel anxious, frustrated, or confused. In fact, if you feel anxious, it can be a good sign that you're engaging in the type of critical thinking necessary to research and write a high-quality paper.
Think of the research process not as one giant, impossibly complicated task, but as a series of smaller, interconnected steps. These steps can be messy, and there is not one correct sequence of steps that will work for every researcher. However, thinking about research in small steps can help you be more productive and alleviate anxiety.
Paul-Elder Framework
This guide is based on the "Elements of Reasoning" from the Paul-Elder framework for critical thinking. For more information about the Paul-Elder framework, click the link below.
Some of the content in this guide has been adapted from The Aspiring Thinker's Guide to Critical Thinking (2009) by Linda Elder and Richard Paul.
- Next: Purpose >>
- Last Updated: Jul 10, 2023 11:50 AM
- Librarian Login

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.5 Critical Thinking and Research Applications
Learning objectives.
- Analyze source materials to determine how they support or refute the working thesis.
- Identify connections between source materials and eliminate redundant or irrelevant source materials.
- Identify instances when it is appropriate to use human sources, such as interviews or eyewitness testimony.
- Select information from sources to begin answering the research questions.
- Determine an appropriate organizational structure for the research paper that uses critical analysis to connect the writer’s ideas and information taken from sources.
At this point in your project, you are preparing to move from the research phase to the writing phase. You have gathered much of the information you will use, and soon you will be ready to begin writing your draft. This section helps you transition smoothly from one phase to the next.
Beginning writers sometimes attempt to transform a pile of note cards into a formal research paper without any intermediary step. This approach presents problems. The writer’s original question and thesis may be buried in a flood of disconnected details taken from research sources. The first draft may present redundant or contradictory information. Worst of all, the writer’s ideas and voice may be lost.
An effective research paper focuses on the writer’s ideas—from the question that sparked the research process to how the writer answers that question based on the research findings. Before beginning a draft, or even an outline, good writers pause and reflect. They ask themselves questions such as the following:
- How has my thinking changed based on my research? What have I learned?
- Was my working thesis on target? Do I need to rework my thesis based on what I have learned?
- How does the information in my sources mesh with my research questions and help me answer those questions? Have any additional important questions or subtopics come up that I will need to address in my paper?
- How do my sources complement each other? What ideas or facts recur in multiple sources?
- Where do my sources disagree with each other, and why?
In this section, you will reflect on your research and review the information you have gathered. You will determine what you now think about your topic. You will synthesize , or put together, different pieces of information that help you answer your research questions. Finally, you will determine the organizational structure that works best for your paper and begin planning your outline.
Review the research questions and working thesis you developed in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , Section 11.2 “Steps in Developing a Research Proposal” . Set a timer for ten minutes and write about your topic, using your questions and thesis to guide your writing. Complete this exercise without looking over your notes or sources. Base your writing on the overall impressions and concepts you have absorbed while conducting research. If additional, related questions come to mind, jot them down.
Selecting Useful Information
At this point in the research process, you have gathered information from a wide variety of sources. Now it is time to think about how you will use this information as a writer.
When you conduct research, you keep an open mind and seek out many promising sources. You take notes on any information that looks like it might help you answer your research questions. Often, new ideas and terms come up in your reading, and these, too, find their way into your notes. You may record facts or quotations that catch your attention even if they did not seem immediately relevant to your research question. By now, you have probably amassed an impressively detailed collection of notes.
You will not use all of your notes in your paper.
Good researchers are thorough. They look at multiple perspectives, facts, and ideas related to their topic, and they gather a great deal of information. Effective writers, however, are selective. They determine which information is most relevant and appropriate for their purpose. They include details that develop or explain their ideas—and they leave out details that do not. The writer, not the pile of notes, is the controlling force. The writer shapes the content of the research paper.
While working through Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , Section 11.4 “Strategies for Gathering Reliable Information” , you used strategies to filter out unreliable or irrelevant sources and details. Now you will apply your critical-thinking skills to the information you recorded—analyzing how it is relevant, determining how it meshes with your ideas, and finding how it forms connections and patterns.
Writing at Work
When you create workplace documents based on research, selectivity remains important. A project team may spend months conducting market surveys to prepare for rolling out a new product, but few managers have time to read the research in its entirety. Most employees want the research distilled into a few well-supported points. Focused, concise writing is highly valued in the workplace.
Identify Information That Supports Your Thesis
In Note 11.81 “Exercise 1” , you revisited your research questions and working thesis. The process of writing informally helped you see how you might begin to pull together what you have learned from your research. Do not feel anxious, however, if you still have trouble seeing the big picture. Systematically looking through your notes will help you.
Begin by identifying the notes that clearly support your thesis. Mark or group these, either physically or using the cut-and-paste function in your word-processing program. As you identify the crucial details that support your thesis, make sure you analyze them critically. Ask the following questions to focus your thinking:
- Is this detail from a reliable, high-quality source? Is it appropriate for me to cite this source in an academic paper? The bulk of the support for your thesis should come from reliable, reputable sources. If most of the details that support your thesis are from less-reliable sources, you may need to do additional research or modify your thesis.
- Is the link between this information and my thesis obvious—or will I need to explain it to my readers? Remember, you have spent more time thinking and reading about this topic than your audience. Some connections might be obvious to both you and your readers. More often, however, you will need to provide the analysis or explanation that shows how the information supports your thesis. As you read through your notes, jot down ideas you have for making those connections clear.
- What personal biases or experiences might affect the way I interpret this information? No researcher is 100 percent objective. We all have personal opinions and experiences that influence our reactions to what we read and learn. Good researchers are aware of this human tendency. They keep an open mind when they read opinions or facts that contradict their beliefs.
It can be tempting to ignore information that does not support your thesis or that contradicts it outright. However, such information is important. At the very least, it gives you a sense of what has been written about the issue. More importantly, it can help you question and refine your own thinking so that writing your research paper is a true learning process.
Find Connections between Your Sources
As you find connections between your ideas and information in your sources, also look for information that connects your sources. Do most sources seem to agree on a particular idea? Are some facts mentioned repeatedly in many different sources? What key terms or major concepts come up in most of your sources regardless of whether the sources agree on the finer points? Identifying these connections will help you identify important ideas to discuss in your paper.
Look for subtler ways your sources complement one another, too. Does one author refer to another’s book or article? How do sources that are more recent build upon the ideas developed in earlier sources?
Be aware of any redundancies in your sources. If you have amassed solid support from a reputable source, such as a scholarly journal, there is no need to cite the same facts from an online encyclopedia article that is many steps removed from any primary research. If a given source adds nothing new to your discussion and you can cite a stronger source for the same information, use the stronger source.
Determine how you will address any contradictions found among different sources. For instance, if one source cites a startling fact that you cannot confirm anywhere else, it is safe to dismiss the information as unreliable. However, if you find significant disagreements among reliable sources, you will need to review them and evaluate each source. Which source presents a sounder argument or more solid evidence? It is up to you to determine which source is the most credible and why.
Finally, do not ignore any information simply because it does not support your thesis. Carefully consider how that information fits into the big picture of your research. You may decide that the source is unreliable or the information is not relevant, or you may decide that it is an important point you need to bring up. What matters is that you give it careful consideration.
As Jorge reviewed his research, he realized that some of the information was not especially useful for his purpose. His notes included several statements about the relationship between soft drinks that are high in sugar and childhood obesity—a subtopic that was too far outside of the main focus of the paper. Jorge decided to cut this material.
Reevaluate Your Working Thesis
A careful analysis of your notes will help you reevaluate your working thesis and determine whether you need to revise it. Remember that your working thesis was the starting point—not necessarily the end point—of your research. You should revise your working thesis if your ideas changed based on what you read. Even if your sources generally confirmed your preliminary thinking on the topic, it is still a good idea to tweak the wording of your thesis to incorporate the specific details you learned from research.
Jorge realized that his working thesis oversimplified the issues. He still believed that the media was exaggerating the benefits of low-carb diets. However, his research led him to conclude that these diets did have some advantages. Read Jorge’s revised thesis.
Although following a low-carbohydrate diet can benefit some people, these diets are not necessarily the best option for everyone who wants to lose weight or improve their health.
Synthesizing and Organizing Information
By now your thinking on your topic is taking shape. You have a sense of what major ideas to address in your paper, what points you can easily support, and what questions or subtopics might need a little more thought. In short, you have begun the process of synthesizing information—that is, of putting the pieces together into a coherent whole.
It is normal to find this part of the process a little difficult. Some questions or concepts may still be unclear to you. You may not yet know how you will tie all of your research together. Synthesizing information is a complex, demanding mental task, and even experienced researchers struggle with it at times. A little uncertainty is often a good sign! It means you are challenging yourself to work thoughtfully with your topic instead of simply restating the same information.
Use Your Research Questions to Synthesize Information
You have already considered how your notes fit with your working thesis. Now, take your synthesis a step further. Analyze how your notes relate to your major research question and the subquestions you identified in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , Section 11.2 “Steps in Developing a Research Proposal” . Organize your notes with headings that correspond to those questions. As you proceed, you might identify some important subtopics that were not part of your original plan, or you might decide that some questions are not relevant to your paper.
Categorize information carefully and continue to think critically about the material. Ask yourself whether the sources are reliable and whether the connections between ideas are clear.
Remember, your ideas and conclusions will shape the paper. They are the glue that holds the rest of the content together. As you work, begin jotting down the big ideas you will use to connect the dots for your reader. (If you are not sure where to begin, try answering your major research question and subquestions. Add and answer new questions as appropriate.) You might record these big ideas on sticky notes or type and highlight them within an electronic document.
Jorge looked back on the list of research questions that he had written down earlier. He changed a few to match his new thesis, and he began a rough outline for his paper.

Review your research questions and working thesis again. This time, keep them nearby as you review your research notes.
- Identify information that supports your working thesis.
- Identify details that call your thesis into question. Determine whether you need to modify your thesis.
- Use your research questions to identify key ideas in your paper. Begin categorizing your notes according to which topics are addressed. (You may find yourself adding important topics or deleting unimportant ones as you proceed.)
- Write out your revised thesis and at least two or three big ideas.
You may be wondering how your ideas are supposed to shape the paper, especially since you are writing a research paper based on your research. Integrating your ideas and your information from research is a complex process, and sometimes it can be difficult to separate the two.
Some paragraphs in your paper will consist mostly of details from your research. That is fine, as long as you explain what those details mean or how they are linked. You should also include sentences and transitions that show the relationship between different facts from your research by grouping related ideas or pointing out connections or contrasts. The result is that you are not simply presenting information; you are synthesizing, analyzing, and interpreting it.
Plan How to Organize Your Paper
The final step to complete before beginning your draft is to choose an organizational structure. For some assignments, this may be determined by the instructor’s requirements. For instance, if you are asked to explore the impact of a new communications device, a cause-and-effect structure is obviously appropriate. In other cases, you will need to determine the structure based on what suits your topic and purpose. For more information about the structures used in writing, see Chapter 10 “Rhetorical Modes” .
The purpose of Jorge’s paper was primarily to persuade. With that in mind, he planned the following outline.

Review the organizational structures discussed in this section and Chapter 10 “Rhetorical Modes” . Working with the notes you organized earlier, follow these steps to begin planning how to organize your paper.
- Create an outline that includes your thesis, major subtopics, and supporting points.
- The major headings in your outline will become sections or paragraphs in your paper. Remember that your ideas should form the backbone of the paper. For each major section of your outline, write out a topic sentence stating the main point you will make in that section.
- As you complete step 2, you may find that some points are too complex to explain in a sentence. Consider whether any major sections of your outline need to be broken up and jot down additional topic sentences as needed.
- Review your notes and determine how the different pieces of information fit into your outline as supporting points.
Collaboration
Please share the outline you created with a classmate. Examine your classmate’s outline and see if any questions come to mind or if you see any area that would benefit from an additional point or clarification. Return the outlines to each other and compare observations.
The structures described in this section and Chapter 10 “Rhetorical Modes” can also help you organize information in different types of workplace documents. For instance, medical incident reports and police reports follow a chronological structure. If the company must choose between two vendors to provide a service, you might write an e-mail to your supervisor comparing and contrasting the choices. Understanding when and how to use each organizational structure can help you write workplace documents efficiently and effectively.
Key Takeaways
- An effective research paper focuses on presenting the writer’s ideas using information from research as support.
- Effective writers spend time reviewing, synthesizing, and organizing their research notes before they begin drafting a research paper.
- It is important for writers to revisit their research questions and working thesis as they transition from the research phase to the writing phrase of a project. Usually, the working thesis will need at least minor adjustments.
- To organize a research paper, writers choose a structure that is appropriate for the topic and purpose. Longer papers may make use of more than one structure.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Critical Thinking in Academic Research - Second Edition
(4 reviews)
Cindy Gruwell, University of West Florida
Robin Ewing, St. Cloud State University
Copyright Year: 2022
Last Update: 2023
Publisher: Minnesota State Colleges and Universities
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Julie Jaszkowiak, Community Faculty, Metropolitan State University on 12/22/23
Organized in 11 parts, this his textbook includes introductory information about critical thinking and details about the academic research process. The basics of critical thinking related to doing academic research in Parts I and II. Parts III –... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
Organized in 11 parts, this his textbook includes introductory information about critical thinking and details about the academic research process. The basics of critical thinking related to doing academic research in Parts I and II. Parts III – XI provide specifics on various steps in doing academic research including details on finding and citing source material. There is a linked table of contents so the reader is able to jump to a specific section as needed. There is also a works cited page with information and links to works used for this textbook.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
The content of this textbook is accurate and error free. It contains examples that demonstrate concepts from a variety of disciplines such as “hard science” or “popular culture” that assist in eliminating bias. The authors are librarians so it is clear that their experience as such leads to clear and unbiased content.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
General concepts about critical thinking and academic research methodology is well defined and should not become obsolete. Specific content regarding use of citation tools and attribution structure may change but the links to various research sites allow for simple updates.
Clarity rating: 5
This textbook is written in a conversational manner that allows for a more personal interaction with the textbook. It is like the reader is having a conversation with a librarian. Each part has an introduction section that fully defines concepts and terms used for that part.
Consistency rating: 5
In addition to the written content, this textbook contains links to short quizzes at the end of each section. This is consistent throughout each part. Embedded links to additional information are included as necessary.
Modularity rating: 4
This textbook is arranged in 11 modular parts with each part having multiple sections. All of these are linked so a reader can go to a distinct part or section to find specific information. There are some links that refer back to previous sections in the document. It can be challenging to return to where you were once you have jumped to a different section.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
There is clear definition as to what information is contained within each of the parts and subsequent sections. The textbook follows the logical flow of the process of researching and writing a research paper.
Interface rating: 4
The pictures have alternative text that appears when you hover over the text. There is one picture on page 102 that is a link to where the downloaded picture is from. The pictures are clear and supportive of the text for a visual learner. All the links work and go to either the correct area of the textbook or to a valid website. If you are going to use the embedded links to go to other sections of the textbook you need to keep track of where you are as it can sometimes get confusing as to where you went based on clicking links.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
This is not really a grammatical error but I did notice on some of the quizzes if you misspelled a work for fill in the blank it was incorrect. It was also sometimes challenging to come up with the correct word for the fill in the blanks.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
There are no examples or text that are culturally insensitive or offensive. The examples are general and would be applicable to a variety of students study many different academic subjects. There are references and information to many research tools from traditional such as checking out books and articles from the library to more current such as blogs and other electronic sources. This information appeals to a wide expanse of student populations.
I really enjoyed the quizzes at the end of each section. It is very beneficial to test your knowledge and comprehension of what you just read. Often I had to return and reread the content more critically based on my quiz results! They are just the right length to not disrupt the overall reading of the textbook and cover the important content and learning objectives.
Reviewed by Sara Stigberg, Adjunct Reference Librarian, Truman College, City Colleges of Chicago on 3/15/23
Critical Thinking in Academic Research thoroughly covers the basics of academic research for undergraduates, including well-guided deeper dives into relevant areas. The authors root their introduction to academic research principles and practices... read more
Critical Thinking in Academic Research thoroughly covers the basics of academic research for undergraduates, including well-guided deeper dives into relevant areas. The authors root their introduction to academic research principles and practices in the Western philosophical tradition, focused on developing students' critical thinking skills and habits around inquiry, rationales, and frameworks for research.
This text conforms to the principles and frames of the Framework for Information Literacy for Higher Education, published by the Association of College and Research Libraries. It includes excellent, clear, step-by-step guides to help students understand rationales and techniques for academic research.
Essential for our current information climate, the authors present relevant information for students who may be new to academic research, in ways and with content that is not too broad or too narrow, or likely to change drastically in the near future.
The authors use clear and well-considered language and explanations of ideas and terms, contextualizing the scholarly research process and tools in a relatable manner. As mentioned earlier, this text includes excellent step-by-step guides, as well as illustrations, visualizations, and videos to instruct students in conducting academic research.
(4.75) The terminology and framework of this text are consistent. Early discussions of critical thinking skills are tied in to content in later chapters, with regard to selecting different types of sources and search tools, as well as rationales for choosing various formats of source references. Consciously making the theme of critical thinking as applied to the stages of academic research more explicit and frequent within the text would further strengthen it, however.
Modularity rating: 5
Chapters are divided in a logical, progressive manner throughout the text. The use of embedded links to further readings and some other relevant sections of the text are an excellent way of providing references and further online information, without overwhelming or side-tracking the reader.
Topics in the text are organized in logical, progressive order, transitioning cleanly from one focus to the next. Each chapter begins with a helpful outline of topics that will be covered within it.
There are no technical issues with the interface for this text. Interactive learning tools such as the many self-checks and short quizzes that are included throughout the text are a great bonus for reinforcing student learning, and the easily-accessible table of contents was very helpful. There are some slight inconsistencies across chapters, however, relative to formatting images and text and spacing, and an image was missing in the section on Narrowing a Topic. Justifying copy rather than aligning-left would prevent hyphenation, making the text more streamlined.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
(4.75) A few minor punctuation errors are present.
The authors of this text use culturally-relevant examples and inclusive language. The chapter on Barriers to Critical Thinking works directly to break down bias and preconceived notions.
Overall, Critical Thinking in Academic Research is an excellent general textbook for teaching the whys and hows of academic research to undergraduates. A discussion of annotated bibliographies would be a great addition for future editions of the text. ---- (As an aside for the authors, I am curious if the anonymous data from the self-checks and quizzes is being collected and analyzed for assessment purposes. I'm sure it would be interesting!)
Reviewed by Ann Bell-Pfeifer, Program Director/ Instructor, Minnesota State Community and Technical College on 2/15/23
The book has in depth coverage of academic research. A formal glossary and index were not included. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The book has in depth coverage of academic research. A formal glossary and index were not included.
The book appears error free and factual.
The content is current and would support students who are pursuing writing academic research papers.
Excellent explanations for specific terms were included throughout the text.
The text is easy to follow with a standardized format and structure.
The text contains headings and topics in each section.
It is easy to follow the format and review each section.
Interface rating: 5
The associated links were useful and not distracting.
No evidence of grammatical errors were found in the book.
The book is inclusive.
The book was informative, easy to follow, and sequential allowing the reader to digest each section before moving into another.
Reviewed by Jenny Inker, Assistant Professor, Virginia Commonwealth University on 8/23/22
This book provides a comprehensive yet easily comprehensible introduction to critical thinking in academic research. The author lays a foundation with an introduction to the concepts of critical thinking and analyzing and making arguments, and... read more
This book provides a comprehensive yet easily comprehensible introduction to critical thinking in academic research. The author lays a foundation with an introduction to the concepts of critical thinking and analyzing and making arguments, and then moves into the details of developing research questions and identifying and appropriately using research sources. There are many wonderful links to other open access publications for those who wish to read more or go deeper.
The content of the book appears to be accurate and free of bias.
The examples used throughout the book are relevant and up-to-date, making it easy to see how to apply the concepts in real life.
The text is very accessibly written and the content is presented in a simple, yet powerful way that helps the reader grasp the concepts easily. There are many short, interactive exercises scattered throughout each chapter of the book so that the reader can test their own knowledge as they go along. It would be even better if the author had provided some simple feedback explaining why quiz answers are correct or incorrect in order to bolster learning, but this is a very minor point and the interactive exercises still work well without this.
The book appears consistent throughout with regard to use of terminology and tone of writing. The basic concepts introduced in the early chapters are used consistently throughout the later chapters.
This book has been wonderfully designed into bite sized chunks that do not overwhelm the reader. This is perhaps its best feature, as this encourages the reader to take in a bit of information, digest it, check their understanding of it, and then move on to the next concept. I loved this!
The book is organized in a manner that introduces the basic architecture of critical thinking first, and then moves on to apply it to the subject of academic research. While the entire book would be helpful for college students (undergraduates particularly), the earlier chapters on critical thinking and argumentation also stand well on their own and would be of great utility to students in general.
This book was extremely easy to navigate with a clear, drop down list of chapters and subheadings on the left side of the screen. When the reader clicks on links to additional material, these open up in a new tab which keeps things clear and organized. Images and charts were clear and the overall organization is very easy to follow.
I came across no grammatical errors in the text.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
This is perhaps an area where the book could do a little more. I did not come across anything that seemed culturally insensitive or offensive but on the other hand, the book might have taken more opportunities to represent a greater diversity of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
This book seems tailor made for undergraduate college students and I would highly recommend it. I think it has some use for graduate students as well, although some of the examples are perhaps little basic for this purpose. As well as using this book to guide students on doing academic research, I think it could also be used as a very helpful introduction to the concept of critical thinking by focusing solely on chapters 1-4.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Part I. What is Critical Thinking?
- Part II. Barriers to Critical Thinking
- Part III. Analyzing Arguments
- Part IV. Making an Argument
- Part V. Research Questions
- Part VI. Sources and Information Needs
- Part VII. Types of Sources
- Part VIII. Precision Searching
- Part IX. Evaluating Sources
- Part X. Ethical Use and Citing Sources
- Part XI. Copyright Basics
- Works Cited
- About the Authors
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Critical Thinking in Academic Research - 2nd Edition provides examples and easy-to-understand explanations to equip students with the skills to develop research questions, evaluate and choose the right sources, search for information, and understand arguments. This 2nd Edition includes new content based on student feedback as well as additional interactive elements throughout the text.
About the Contributors
Cindy Gruwell is an Assistant Librarian/Coordinator of Scholarly Communication at the University of West Florida. She is the library liaison to the department of biology and the College of Health which has extensive nursing programs, public health, health administration, movement, and medical laboratory sciences. In addition to supporting health sciences faculty, she oversees the Argo IRCommons (Institutional Repository) and provides scholarly communication services to faculty across campus. Cindy graduated with her BA (history) and MLS from the University of California, Los Angeles and has a Masters in Education from Bemidji State University. Cindy’s research interests include academic research support, publishing, and teaching.
Robin Ewing is a Professor/Collections Librarian at St. Cloud State University. Robin is the liaison to the College of Education and Learning Design. She oversees content selection for the Library’s collections. Robin graduated with her BBA (Management) and MLIS from the University of Oklahoma. She also has a Masters of Arts in Teaching from Bemidji State University. Robin’s research interests include collection analysis, assessment, and online teaching.
Contribute to this Page

- Teaching Tips
On Critical Thinking
Several years ago some teaching colleagues were talking about the real value of teaching psychology students to think critically. After some heated discussion, the last word was had by a colleague from North Carolina. “The real value of being a good critical thinker in psychology is so you won’t be a jerk,” he said with a smile. That observation remains one of my favorites in justifying why teaching critical thinking skills should be an important goal in psychology. However, I believe it captures only a fraction of the real value of teaching students to think critically about behavior.
What I s Critical Thinking?
Although there is little agreement about what it means to think critically in psychology, I like the following broad definition: The propensity and skills to engage in activity with reflec tive skepticism focused on deciding what to believe or do
Students often arrive at their first introductory course with what they believe is a thorough grasp of how life works. After all, they have been alive for at least 18 years, have witnessed their fair shares of crisis, joy, and tragedy, and have successfully navigated their way in to your classroom.
These students have had a lot of time to develop their own personal theories about how the world works and most are quite satisfied with the results. They often pride themselves on how good they are with people as well as how astute they are in understanding and explaining the motives of others. And they think they know what psychology is. Many are surprised- and sometimes disappointed- to discover that psychology is a science, and the rigor of psychological research is a shock. The breadth and depth of psychology feel daunting. Regardless of their sophistication in the discipline, students often are armed with a single strategy to survive the experience: Memorize the book and hope it works out on the exam. In many cases, this strategy will serve them well. Unfortunately, student exposure to critical thinking skill development may be more accidental than planful on the part of most teachers. Collaboration in my department and with other colleagues over the years has persuaded me that we need to approach critical thinking skills in a purposeful, systematic, and developmental manner from the introductory course through the capstone experience, propose that we need to teach critical thinking skills in three domains of psychology: practical (the “jerk avoidance” function), theoretical (developing scientific explanations for behavior), and methodological (testing scientific ideas). I will explore each of these areas and then offer some general suggestions about how psychology teachers can improve their purposeful pursuit of critical thinking objectives.
Practical Domain
Practical critical thinking is often expressed as a long-term, implicit goal of teachers of psychology, even though they may not spend much academic time teaching how to transfer critical thinking skills to make students wise consumers, more careful judges of character, or more cautious interpreters of behavior. Accurate appraisal of behavior is essential, yet few teachers invest time in helping students understand how vulnerable their own interpretations are to error.
Encourage practice in accurate description and interpretation of behavior by presenting students with ambiguous behavior samples. Ask them to distinguish what they observe (What is the behavior?) from the inferences they draw from the behavior (What is the meaning of the behavior?). I have found that cartoons, such as Simon Bond’s Uns p eakable Acts, can be a good resource for refining observation skills. Students quickly recognize that crisp behavioral descriptions are typically consistent from observer to observer, but inferences vary wildly. They recognize that their interpretations are highly personal and sometimes biased by their own values and preferences. As a result of experiencing such strong individual differences in interpretation, students may learn to be appropriately less confident of their immediate conclusions, more tolerant of ambiguity, and more likely to propose alternative explanations. As they acquire a good understanding of scientific procedures, effective control techniques, and legitimate forms of evidence, they may be less likely to fall victim to the multitude of off-base claims about behavior that confront us all. (How many Elvis sightings can be valid in one year?)
Theoretical Domain
Theoretical critical thinking involves helping the student develop an appreciation for scientific explanations of behavior. This means learning not just the content of psychology but how and why psychology is organized into concepts, principles, laws, and theories. Developing theoretical skills begins in the introductory course where the primary critical thinking objective is understanding and applying concepts appropriately. For example, when you introduce students to the principles of reinforcement, you can ask them to find examples of the principles in the news or to make up stories that illustrate the principles.
Mid-level courses in the major require more sophistication, moving students beyond application of concepts and principles to learning and applying theories. For instance, you can provide a rich case study in abnormal psychology and ask students to make sense of the case from different perspectives, emphasizing theoretical flexibility or accurate use of existing and accepted frameworks in psychology to explain patterns of behavior. In advanced courses we can justifiably ask students to evaluate theory, selecting the most useful or rejecting the least helpful. For example, students can contrast different models to explain drug addiction in physiological psychology. By examining the strengths and weaknesses of existing frameworks, they can select which theories serve best as they learn to justify their criticisms based on evidence and reason.
Capstone, honors, and graduate courses go beyond theory evaluation to encourage students to create theory. Students select a complex question about behavior (for example, identifying mechanisms that underlie autism or language acquisition) and develop their own theory-based explanations for the behavior. This challenge requires them to synthesize and integrate existing theory as well as devise new insights into the behavior.
Methodological Domain
Most departments offer many opportunities for students to develop their methodological critical thinking abilities by applying different research methods in psychology. Beginning students must first learn what the scientific method entails. The next step is to apply their understanding of scientific method by identifying design elements in existing research. For example, any detailed description of an experimental design can help students practice distinguishing the independent from the dependent variable and identifying how researchers controlled for alternative explanations. The next methodological critical thinking goals include evaluating the quality of existing research design and challenging the conclusions of research findings. Students may need to feel empowered by the teacher to overcome the reverence they sometimes demonstrate for anything in print, including their textbooks. Asking students to do a critical analysis on a fairly sophisticated design may simply be too big a leap for them to make. They are likely to fare better if given examples of bad design so they can build their critical abilities and confidence in order to tackle more sophisticated designs. (Examples of bad design can be found in The Critical Thinking Companion for Introductory Psychology or they can be easily constructed with a little time and imagination). Students will develop and execute their own research designs in their capstone methodology courses. Asking students to conduct their own independent research, whether a comprehensive survey on parental attitudes, a naturalistic study of museum patrons’ behavior, or a well-designed experiment on paired associate learning, prompts students to integrate their critical thinking skills and gives them practice with conventional writing forms in psychology. In evaluating their work I have found it helpful to ask students to identify the strengths and weaknesses of their own work- as an additional opportunity to think critically-before giving them my feedback.
Additional Suggestions
Adopting explicit critical thinking objectives, regardless of the domain of critical thinking, may entail some strategy changes on the part of the teacher.
• Introduce psychology as an ope n-end ed, growing enterprise . Students often think that their entry into the discipline represents an end-point where everything good and true has already been discovered. That conclusion encourages passivity rather than criticality. Point out that research is psychology’ s way of growing and developing. Each new discovery in psychology represents a potentially elegant act of critical thinking. A lot of room for discovery remains. New ideas will be developed and old conceptions discarded.
• Require student performance that goes beyond memorization . Group work, essays, debates, themes, letters to famous psychologists, journals, current event examples- all of these and more can be used as a means of developing the higher skills involved in critical thinking in psychology. Find faulty cause-effect conclusions in the tabloids (e.g., “Eating broccoli increases your IQ!”) and have students design studies to confirm or discredit the headline’s claims. Ask students to identify what kinds of evidence would warrant belief in commercial claims. Although it is difficult, even well designed objective test items can capture critical thinking skills so that students are challenged beyond mere repetition and recall.
• Clarify your expectations about performance with explicit, public criteria. Devising clear performance criteria for psychology projects will enhance student success. Students often complain that they don’t understand “what you want” when you assign work. Performance criteria specify the standards that you will use to evaluate their work. For example, perfonnance criteria for the observation exercise described earlier might include the following: The student describes behavior accurately; offers i nference that is reasonable for the context; and identifies personal factors that might influence infer ence. Perfonnance criteria facilitate giving detailed feedback easily and can also promote student self-assessment.
• Label good examples of critical thinking when these occur spontaneously. Students may not recognize when they are thinking critically. When you identify examples of good thinking or exploit examples that could be improved, it enhances students’ ability to understand. One of my students made this vivid for me when she commented on the good connection she had made between a course concept and an insight from her literature class, “That is what you mean by critical thinking?” There after I have been careful to label a good critical thinking insight.
• Endorse a questioning attitude. Students often assume that if they have questions about their reading, then they are somehow being dishonorable, rude, or stupid. Having discussions early in the course about the role of good questions in enhancing the quality of the subject and expanding the sharpness of the mind may set a more critical stage on which students can play. Model critical thinking from some insights you have had about behavior or from some research you have conducted in the past. Congratulate students who offer good examples of the principles under study. Thank students who ask concept-related questions and describe why you think their questions are good. Leave time and space for more. Your own excitement about critical thinking can be a great incentive for students to seek that excitement.
• Brace yourself . When you include more opportunity for student critical thinking in class, there is much more opportunity for the class to go astray. Stepping away from the podium and engaging the students to perform what they know necessitates some loss of control, or at least some enhanced risk. However, the advantage is that no class will ever feel completely predictable, and this can be a source of stimulation for students and the professor as well.
As far back as I can remember over 50 yrs. ago. I have been talking psychology to friends, or helping them to solve problems. I never thought about psy. back then, but now I realize I really love helping people. How can I become a critical thinker without condemning people?
using a case study explain use of critical thinking in counseling process.
Do you have any current readings with Critical Thinking Skills in Psychology, besides John Russcio’s work?
APS regularly opens certain online articles for discussion on our website. Effective February 2021, you must be a logged-in APS member to post comments. By posting a comment, you agree to our Community Guidelines and the display of your profile information, including your name and affiliation. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations present in article comments are those of the writers and do not necessarily reflect the views of APS or the article’s author. For more information, please see our Community Guidelines .
Please login with your APS account to comment.
About the Author
Jane Halonen received her PhD from the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee in 1980. She is Professor of Psychology at Alverno College in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, where she has served as Chair of Psychology and Dean of the Behavior Sciences Department. Halonen is past president of the Council for Teachers of Undergraduate Psychology. A fellow of APA's Division 2 (Teaching), she has been active on the Committee of Undergraduate Education, helped design the 1991 APA Conference on Undergraduate Educational Quality, and currently serves as a committee member to develop standards for the teaching of high school psychology.

Student Notebook: Five Tips for Working with Teaching Assistants in Online Classes
Sarah C. Turner suggests it’s best to follow the golden rule: Treat your TA’s time as you would your own.
Teaching Current Directions in Psychological Science
Aimed at integrating cutting-edge psychological science into the classroom, Teaching Current Directions in Psychological Science offers advice and how-to guidance about teaching a particular area of research or topic in psychological science that has been
European Psychology Learning and Teaching Conference
The School of Education of the Paris Lodron University of Salzburg is hosting the next European Psychology Learning and Teaching (EUROPLAT) Conference on September 18–20, 2017 in Salzburg, Austria. The main theme of the conference
Privacy Overview

Critical & Creative Thinking in Research
by Janet Salmons, PhD Research Community Manager for Sage Research Methods Community
Critical thinking and creative thinking are distinctly different, but highly interconnected.
Nowhere is the symbiotic relationship of creative and critical thinking more apparent than in the practices inherent to research design, conduct, and dissemination. What do these terms mean, and how can we use them to better understand our roles as researchers? While a search yields lengthy philosophical ruminations, the Oxford Living Dictionary offers a simple and concise definition of critical thinking :
The objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement.
Oxford's definition of creative thinking is:
Relating to or involving the use of the imagination or original ideas to create something.
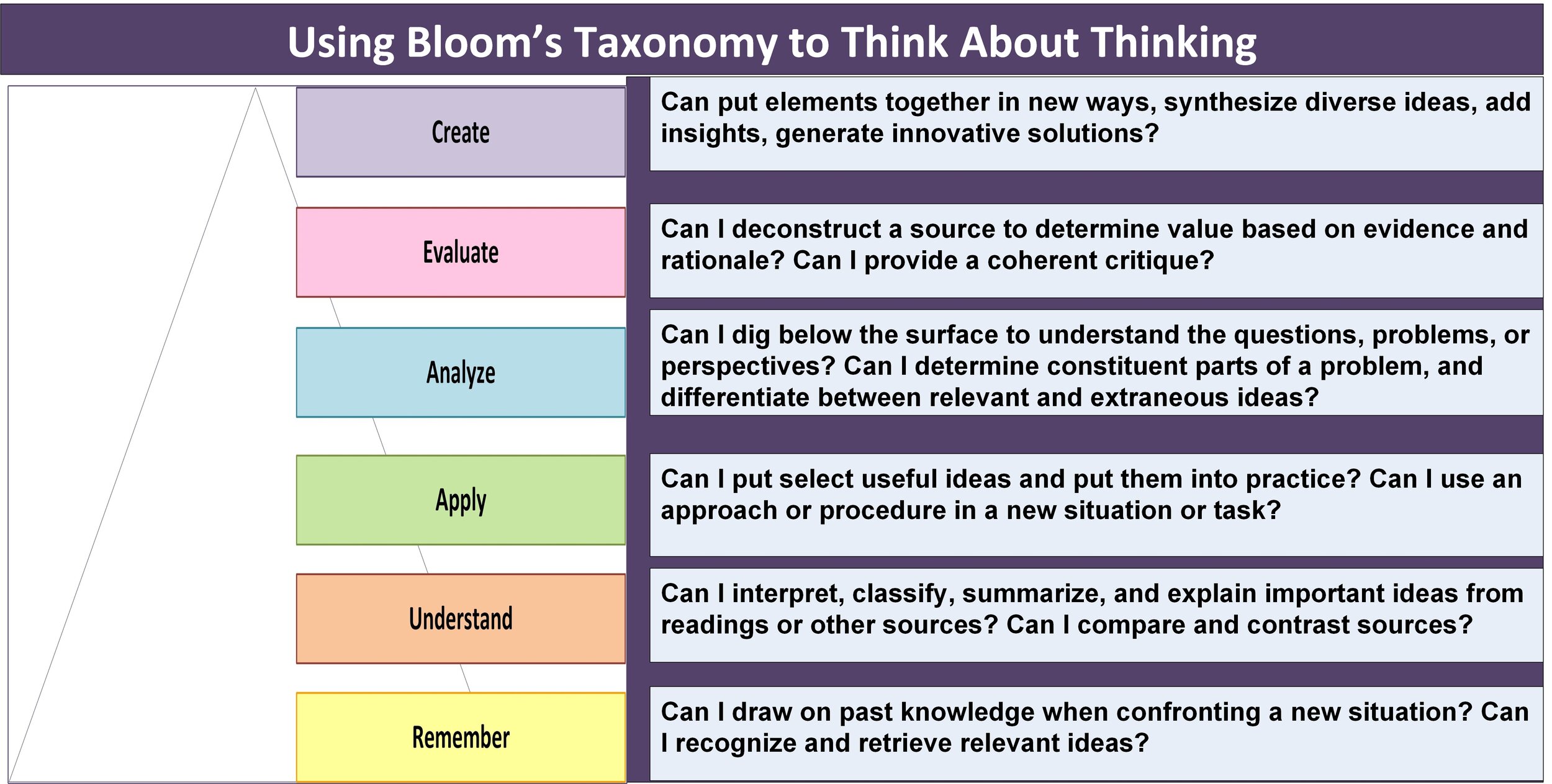
To connect these definitions and situate them in a research context, I'll draw on the (updated) Bloom's Taxonomy (2000). This taxonomy lays out dimensions of thinking involved with acquiring, using, and generating knowledge. We can see that thought processes associated with analysis and evaluation, central to the Oxford definition for critical thinking, build towards the ability to create new ideas or solutions. Critical and creative sides of the thinking process are essential if we are to accomplish the goal central to scholarly research: to make an original contribution.While presented in a linear manner in this figure, the categories interrelate in various ways, depending on the task at hand. There are times when, in the course of analyzing or evaluating a problem, we realize that we lack some important foundations so we need to read more literature and improve our understanding. We might also see an important path from the new solutions derived at the creative stage, to their application in practice. In short, as researchers we need the ability to move across these dimensions, using both critical and creative thinking at various stages.Here is one way to consider intersections between critical and creative thinking over the course of a study:
Use Critical and Creative Thinking at Each Research Stage
Planning the Study
Evaluate potential research problem(s) from multiple angles.
Look beyond the typical ways research problems are identified.
Analyze the scholarly literature.
Evaluate perspectives from other schools or thought or disciplines.
Draw ideas from related contemporary writings, media, social media to learn from viewpoints outside of academia.
Designing the Study
Articulate clear, concise research questions and/or hypotheses.
Evaluate and select theoretical and methodological options.
Invent theories or methodologies.
Adapt theories or methodologies from other cultures or disciplines.
Evaluate data needs and select population, collection options.
Develop/adapt interview questions, observation guides, instruments.
Consider visual or creative methods for collecting data.
Conducting the Study
Continue to analyze and evaluate study progress and adjust as necessary.
When collecting data from human participants, use ingenious ways to gain cooperation of gatekeepers, and to develop rapport conducive to questioning/surveying participants.
Making Sense of the Data
Critically analyze the data.
Interpret the themes and trends emerging from the analysis.
Visualizing the data.
Sharing Results
Analyze and describe results in ways that will help readers understand the significance of the study.
Discover imaginative ways to present findings and reach those who can use them. Use visuals, graphics, media, links to related resources.
Applying the Results for Impact
Understand needs in the field, evaluate ways findings match needs, take steps to apply
Imagine new ways to use what you learned from the study.
How would you map your own research? Do you feel your own strengths are on the critical or the creative side? What can you do to develop a more holistic set of research skills?
Anderson, L., Bloom, B. S., Krathwohl, D., & Airasian, P. (2000). Taxonomy for learning, teaching and assessing: A revision of Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives (2nd ed.). New York: Allyn & Bacon, Inc.
More Sage Research Methods Community Posts about Critical Thinking

At last! Agent computing for economics policy
Agent computing in economics: a rough path towards policy applications.

- Schools & departments

Critical thinking
Advice and resources to help you develop your critical voice.
Developing critical thinking skills is essential to your success at University and beyond. We all need to be critical thinkers to help us navigate our way through an information-rich world.
Whatever your discipline, you will engage with a wide variety of sources of information and evidence. You will develop the skills to make judgements about this evidence to form your own views and to present your views clearly.
One of the most common types of feedback received by students is that their work is ‘too descriptive’. This usually means that they have just stated what others have said and have not reflected critically on the material. They have not evaluated the evidence and constructed an argument.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the art of making clear, reasoned judgements based on interpreting, understanding, applying and synthesising evidence gathered from observation, reading and experimentation. Burns, T., & Sinfield, S. (2016) Essential Study Skills: The Complete Guide to Success at University (4th ed.) London: SAGE, p94.
Being critical does not just mean finding fault. It means assessing evidence from a variety of sources and making reasoned conclusions. As a result of your analysis you may decide that a particular piece of evidence is not robust, or that you disagree with the conclusion, but you should be able to state why you have come to this view and incorporate this into a bigger picture of the literature.
Being critical goes beyond describing what you have heard in lectures or what you have read. It involves synthesising, analysing and evaluating what you have learned to develop your own argument or position.
Critical thinking is important in all subjects and disciplines – in science and engineering, as well as the arts and humanities. The types of evidence used to develop arguments may be very different but the processes and techniques are similar. Critical thinking is required for both undergraduate and postgraduate levels of study.
What, where, when, who, why, how?
Purposeful reading can help with critical thinking because it encourages you to read actively rather than passively. When you read, ask yourself questions about what you are reading and make notes to record your views. Ask questions like:
- What is the main point of this paper/ article/ paragraph/ report/ blog?
- Who wrote it?
- Why was it written?
- When was it written?
- Has the context changed since it was written?
- Is the evidence presented robust?
- How did the authors come to their conclusions?
- Do you agree with the conclusions?
- What does this add to our knowledge?
- Why is it useful?
Our web page covering Reading at university includes a handout to help you develop your own critical reading form and a suggested reading notes record sheet. These resources will help you record your thoughts after you read, which will help you to construct your argument.
Reading at university
Developing an argument
Being a university student is about learning how to think, not what to think. Critical thinking shapes your own values and attitudes through a process of deliberating, debating and persuasion. Through developing your critical thinking you can move on from simply disagreeing to constructively assessing alternatives by building on doubts.
There are several key stages involved in developing your ideas and constructing an argument. You might like to use a form to help you think about the features of critical thinking and to break down the stages of developing your argument.
Features of critical thinking (pdf)
Features of critical thinking (Word rtf)
Our webpage on Academic writing includes a useful handout ‘Building an argument as you go’.
Academic writing
You should also consider the language you will use to introduce a range of viewpoints and to evaluate the various sources of evidence. This will help your reader to follow your argument. To get you started, the University of Manchester's Academic Phrasebank has a useful section on Being Critical.
Academic Phrasebank
Developing your critical thinking
Set yourself some tasks to help develop your critical thinking skills. Discuss material presented in lectures or from resource lists with your peers. Set up a critical reading group or use an online discussion forum. Think about a point you would like to make during discussions in tutorials and be prepared to back up your argument with evidence.
For more suggestions:
Developing your critical thinking - ideas (pdf)
Developing your critical thinking - ideas (Word rtf)
Published guides
For further advice and more detailed resources please see the Critical Thinking section of our list of published Study skills guides.
Study skills guides
This article was published on 2024-02-26
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
What Are Critical Thinking Skills and Why Are They Important?
Learn what critical thinking skills are, why they’re important, and how to develop and apply them in your workplace and everyday life.
![it important to use critical thinking in research [Featured Image]: Project Manager, approaching and analyzing the latest project with a team member,](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/1SOj8kON2XLXVb6u3bmDwN/62a5b68b69ec07b192de34b7ce8fa28a/GettyImages-598260236.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
We often use critical thinking skills without even realizing it. When you make a decision, such as which cereal to eat for breakfast, you're using critical thinking to determine the best option for you that day.
Critical thinking is like a muscle that can be exercised and built over time. It is a skill that can help propel your career to new heights. You'll be able to solve workplace issues, use trial and error to troubleshoot ideas, and more.
We'll take you through what it is and some examples so you can begin your journey in mastering this skill.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to interpret, evaluate, and analyze facts and information that are available, to form a judgment or decide if something is right or wrong.
More than just being curious about the world around you, critical thinkers make connections between logical ideas to see the bigger picture. Building your critical thinking skills means being able to advocate your ideas and opinions, present them in a logical fashion, and make decisions for improvement.
Build job-ready skills with a Coursera Plus subscription
- Get access to 7,000+ learning programs from world-class universities and companies, including Google, Yale, Salesforce, and more
- Try different courses and find your best fit at no additional cost
- Earn certificates for learning programs you complete
- A subscription price of $59/month, cancel anytime
Why is critical thinking important?
Critical thinking is useful in many areas of your life, including your career. It makes you a well-rounded individual, one who has looked at all of their options and possible solutions before making a choice.
According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [ 1 ]:
Crucial for the economy
Essential for improving language and presentation skills
Very helpful in promoting creativity
Important for self-reflection
The basis of science and democracy
Critical thinking skills are used every day in a myriad of ways and can be applied to situations such as a CEO approaching a group project or a nurse deciding in which order to treat their patients.
Examples of common critical thinking skills
Critical thinking skills differ from individual to individual and are utilized in various ways. Examples of common critical thinking skills include:
Identification of biases: Identifying biases means knowing there are certain people or things that may have an unfair prejudice or influence on the situation at hand. Pointing out these biases helps to remove them from contention when it comes to solving the problem and allows you to see things from a different perspective.
Research: Researching details and facts allows you to be prepared when presenting your information to people. You’ll know exactly what you’re talking about due to the time you’ve spent with the subject material, and you’ll be well-spoken and know what questions to ask to gain more knowledge. When researching, always use credible sources and factual information.
Open-mindedness: Being open-minded when having a conversation or participating in a group activity is crucial to success. Dismissing someone else’s ideas before you’ve heard them will inhibit you from progressing to a solution, and will often create animosity. If you truly want to solve a problem, you need to be willing to hear everyone’s opinions and ideas if you want them to hear yours.
Analysis: Analyzing your research will lead to you having a better understanding of the things you’ve heard and read. As a true critical thinker, you’ll want to seek out the truth and get to the source of issues. It’s important to avoid taking things at face value and always dig deeper.
Problem-solving: Problem-solving is perhaps the most important skill that critical thinkers can possess. The ability to solve issues and bounce back from conflict is what helps you succeed, be a leader, and effect change. One way to properly solve problems is to first recognize there’s a problem that needs solving. By determining the issue at hand, you can then analyze it and come up with several potential solutions.
How to develop critical thinking skills
You can develop critical thinking skills every day if you approach problems in a logical manner. Here are a few ways you can start your path to improvement:
1. Ask questions.
Be inquisitive about everything. Maintain a neutral perspective and develop a natural curiosity, so you can ask questions that develop your understanding of the situation or task at hand. The more details, facts, and information you have, the better informed you are to make decisions.
2. Practice active listening.
Utilize active listening techniques, which are founded in empathy, to really listen to what the other person is saying. Critical thinking, in part, is the cognitive process of reading the situation: the words coming out of their mouth, their body language, their reactions to your own words. Then, you might paraphrase to clarify what they're saying, so both of you agree you're on the same page.
3. Develop your logic and reasoning.
This is perhaps a more abstract task that requires practice and long-term development. However, think of a schoolteacher assessing the classroom to determine how to energize the lesson. There's options such as playing a game, watching a video, or challenging the students with a reward system. Using logic, you might decide that the reward system will take up too much time and is not an immediate fix. A video is not exactly relevant at this time. So, the teacher decides to play a simple word association game.
Scenarios like this happen every day, so next time, you can be more aware of what will work and what won't. Over time, developing your logic and reasoning will strengthen your critical thinking skills.
Learn tips and tricks on how to become a better critical thinker and problem solver through online courses from notable educational institutions on Coursera. Start with Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking from Duke University or Mindware: Critical Thinking for the Information Age from the University of Michigan.
Article sources
University of the People, “ Why is Critical Thinking Important?: A Survival Guide , https://www.uopeople.edu/blog/why-is-critical-thinking-important/.” Accessed May 18, 2023.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Adv Med Educ Prof
- v.2(3); 2014 Jul
The role of critical thinking skills and learning styles of university students in their academic performance
Zohre ghazivakili.
1 Emergency medical services department, Paramedical school, Alborz University of Medical Sciences, Karaj, Iran;
ROOHANGIZ NOROUZI NIA
2 Educational Development Center, Alborz University of Medical Sciences, Karaj, Iran;
FARIDE PANAHI
3 Nursing and midwifery school, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran;
MEHRDAD KARIMI
4 Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Public Health School, Tehran, Iran;
HAYEDE GHOLSORKHI
5 Medical school, Alborz University of Medical Sciences, Karaj, Iran;
ZARRIN AHMADI
6 Amirkabir University of Technology(Polytechnic), Tehran, Iran
Introduction: The Current world needs people who have a lot of different abilities such as cognition and application of different ways of thinking, research, problem solving, critical thinking skills and creativity. In addition to critical thinking, learning styles is another key factor which has an essential role in the process of problem solving. This study aimed to determine the relationship between learning styles and critical thinking of students and their academic performance in Alborz University of Medical Science.
Methods: This cross-correlation study was performed in 2012, on 216 students of Alborz University who were selected randomly by the stratified random sampling. The data was obtained via a three-part questionnaire included demographic data, Kolb standardized questionnaire of learning style and California critical thinking standardized questionnaire. The academic performance of the students was extracted by the school records. The validity of the instruments was determined in terms of content validity, and the reliability was gained through internal consistency methods. Cronbach's alpha coefficient was found to be 0.78 for the California critical thinking questionnaire. The Chi Square test, Independent t-test, one way ANOVA and Pearson correlation test were used to determine relationship between variables. The Package SPSS14 statistical software was used to analyze data with a significant level of p<0.05.
Results: Our findings indicated the significant difference of mean score in four learning style, suggesting university students with convergent learning style have better performance than other groups. Also learning style had a relationship with age, gender, field of study, semester and job. The results about the critical thinking of the students showed that the mean of deductive reasoning and evaluation skills were higher than that of other skills and analytical skills had the lowest mean and there was a positive significant relationship between the students’ performance with inferential skill and the total score of critical thinking skills (p<0.05). Furthermore, evaluation skills and deductive reasoning had significant relationship. On the other hand, the mean total score of critical thinking had significant difference between different learning styles.
Conclusion: The results of this study showed that the learning styles, critical thinking and academic performance are significantly associated with one another. Considering the growing importance of critical thinking in enhancing the professional competence of individuals, it's recommended to use teaching methods consistent with the learning style because it would be more effective in this context.
Introduction
The current world needs people with a lot of capabilities such as understanding and using different ways of thinking, research, problem solving, critical thinking and creativity. Critical thinking is one of the aspects of thinking that has been accepted as a way to overcome the difficulties and to facilitate the access to information in life ( 1 ).
To Watson and Glizer, critical thinking is a combination of knowledge, attitude, and performance of every individual. They also believe that there are some skills of critical thinking such as perception, assumption recognition deduction, interpretation and evaluation of logical reasoning. They argue that the ability of critical thinking, processing and evaluation of previous information with new information result from inductive and deductive reasoning of solving problems. Watson and Glizer definition of critical thinking has been the basis of critical thinking tests that are widely used to measure the critical thinking today ( 2 ).
World Federation for Medical Education has considered critical thinking one of the medical training standards so that in accredited colleges this subject is one of the key points. In fact, one of the criteria for the accreditation of a learning institute is the measurement of critical thinking in its students ( 3 ).
In addition to critical thinking, learning style, i.e. the information processing method, of the learners, is an important key factor that has a major role in problem solving. According to David Kolb’s theory, learning is a four-step process that includes concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization and active experimentation. This position represents two dimensions: concrete experience versus abstract thinking, and reflective observation to active experimentation. These dimensions include four learning styles: divergent, convergent, assimilate, and accommodate. According to Kolb and Ferry, the learner needs four different abilities to function efficiently: Learning styles involve several variables such as academic performance of learner, higher education improvement; critical thinking and problem solving ( 4 ).
Due to the importance of learning styles and critical thinking in students' academic performance, a large volume of educational research has been devoted to these issues in different countries. Demirhan, Besoluk and Onder (2011) in their study on critical thinking and students’ academic performance from the first semester to two years later have found that contrary to expectations the students’ critical thinking level reduced but the total mean of students’ scores increased. This is due to the fact that the students are likely to increase adaptive behavior with environment and university and reduce the stress during their education ( 1 ).
In another study over 330 students in Turkey, the students who had divergent learning style, had lower scores in critical thinking in contrast with students who have accommodator learning style ( 5 ).
Also Mahmoud examined the relationship between critical thinking and learning styles of the Bachelor students with their academic performance in 2012. In this study all the nursing students of the university in the semesters four, six and eight were studied. The results did not show any significant relationship between critical thinking and learning styles of nursing students with their academic performance ( 6 ).
Another research by Nasrabadi in 2012 showed a positive relationship between critical thinking attitudes and student's academic achievement. The results showed that there was a significant difference between the levels of critical thinking of assimilating and converge styles. Also converging, diverging, assimilating and accommodating styles had the highest level of critical thinking, respectively ( 4 ). Among other studies we can refer to Sharma’s study in 2011 whose results suggested a relationship between the academic performance and learning styles ( 7 ).
Today university students should not only think but also should think differently and should not only remember the knowledge in their mind but also should research the best learning style among different learning styles. Therefore, the study on the topic of how the students think and how they learn has received great emphasis in recent years. In this regard, with the importance of the subject, researchers attempted to doa research in this area to determine the relationship between critical thinking and learning styles with academic performance of the students at Alborz University of Medical Sciences.
This study is a descriptive-analytic, cross sectional study and investigates the relationship between critical thinking and learning styles with students’ academic performance of Alborz University of Medical Science in 2012. After approval and permission from university’s authorities and in coordination with official faculties, the critical thinking and learning styles questionnaire was given to the undergraduate students in associate degree, bachelor, medicine (second semester and after that). The total number of participants in the study was 216 students with different majors such as medical, nursing and midwifery, and health and medical emergency students. The tool to collect the data was a two-part questionnaire of Kolb's learning styles and California's critical thinking skills test (form B). The Kolb's questionnaire has two parts. The first part asks for demographic information and the second part includes 12 multiple choice questions. The participants respond to the questions with regard to how they learn, and the scores of respondents are ranked from 1 to 4 in which 4 is most consistent with the participants’ learning style 3 to some extent, 2 poorly consistent and 1 not consistent To find the participants’ learning styles, the first choice of all 12 questions were added together and this was repeated for other choices. Thus, four total scores for the four learning styles were obtained, the first for concrete experience learning style, the second for reflective observation of learning style, the third for abstract conceptualization learning style and the forth for active experimentation learning style. The highest score determined the learning style of the participant. The California critical thinking skills test (form B) includes 34 multiple choice questions with one correct answer in five different areas of critical thinking skills, including evaluation, inference, analysis, inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning. The answering time was 45 minutes and the final score is 34 and the achieved score in each section of the test varies from 0 to 16. In the evaluation section, the maximum point is 14, in analysis section 9, in inference section 11, in inductive reasoning 16 and in deductive reasoning the maximum point was 14. So there were 6 scores for each participant, which included a critical thinking total score and 5 score for critical thinking skills. Dehghani, Jafari Sani, Pakmehr and Malekzadeh found that the reliability of the questionnaire was 78% in a research. In the study of Khalili et al., the confidence coefficient was 62% and construct validity of all subscales with positive and high correlation were reported between 60%-65%. So this test was reliable for the research. Collecting the information was conducted in two stages. In the first stage, the questionnaires were given to the students and the objectives and importance of the research were mentioned. In the next stage, the students' academic performance was reviewed. After data collection, the data were coded and analyzed, using the SPSS 14 ( SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA) software. To describe the data, descriptive statistics were used such as mean and standard deviation for continues variables and frequency for qualitative variables. Chi Square test, Independent t-test, one way ANOVA and Pearson correlation test were used to determine the relationship between variables at a significant level of p<0.05.
Research hypothesis
- There is a relationship between Alborz University of Medical Sciences students’ learning styles and their demographic information.
- There is a relationship between Alborz University of Medical Sciences students’ critical thinking and their demographic information.
- There is a relationship between Alborz University of Medical Sciences students’ academic performance and their demographic information.
- There is a relationship between Alborz University of Medical Sciences students’ learning styles and their academic performance.
- There is a relationship between Alborz University of Medical Sciences students’ learning styles and their critical thinking.
225 questionnaires were distributed of which 216 were completely responded (96%). The age range of the participants was from 16 to 45 with the mean age of (22.44±3.7). 52.8% of participants (n=114) were female, 83.3% (n=180) were single, 30.1% of participants’ (n=65) major was pediatric anesthesiology of OR, 35.2% of participants (n=76) were in fourth semester, 74.5% (n=161) were unemployed and 48.6 % (n=105) had Persian ethnicity.
The range of participants’ average grade points, which were considered as their academic performance, were from 12.51 to 19.07 with a mean of (16.75±1.3). According to Kolbs' pattern, 42.7% (n=85) had the convergent learning style (the maximum percentage) followed by 33.2 % (n= 66) with the assimilating style and only 9.5%, (n= 19) with the accommodating style (the minimum percentage).
Among the 5 critical thinking skills, the maximum mean score belonged to deductive reasoning skill (3.38±1.58) and the minimum mean score belonged to analysis skill (1.67±1.08).
Table 1 shows the frequency distribution and demographic variables and the academic performance of the students. According to the Chi-square (Χ 2 ) p-value, there was a significant relationship between gender and learning style (p=0.032), so that nearly 50 percent of males had the assimilating learning style and nearly 52 percent of the females had the convergent learning style.
The relationship between demographic variable and student’s academic performance with learning styles
The relationship between employment, major and semester of studying with the learning style was significant at a p-value of 0.049, 0.006, 0.009 and 0.001, respectively. The mean and standard deviation of age and students' academic performance in the four learning styles are reported in Table 1 .
Using the one way analysis of variance (One way ANOVA) and comparing the mean age of four groups, we found a significant relation between age and academic performance with learning style (p=0.049).
The students with convergent learning style had a better academic performance than those with other learning styles and in the performance of those with the assimilating learning style the weakest.
Table 2 shows the relationship between the total score of critical thinking skills and each of the demographic variables and academic performance. The results of the t-test and one way ANOVA variance analysis are reported to investigate the relationship between each variable with skills below the mean standard deviation.
Relationships between CCT Skills and demographic variables Using t-test and ANOVA. Pearson Correlation coefficient between age and Student's performance with CCT Skills was reported
* Significant in surface 0.05
** Significant in surface 0.01
Based on the t-test and ANOVA, p-value of t and F, the mean of total score of critical thinking skills had only significant relationship with students’ major (p=0.020). Also a significant relationship was found between the major of students and gender with inference skill; semester of study with deductive reasoning skill, and ethnicity with 2 skills of inference and deductive reasoning (p<0.05).
Also regarding the relationship between age and the student academic performance with each of the critical thinking skills, the Pearson correlation coefficient results indicated a significant positive relationship but a negative relationship between age and analysis skill, i.e. with the increase of age, the score of analysis skill was reduced (p<0.05). Academic performance of the students had a direct significant relationship with critical thinking total score and inference skill; the more the score, the better the academic performance of students (p<0.05).
Table 3 shows the mean and standard deviation of learning styles score in the 4 groups of learning style. Using ANOVA one way ANOVA, the relationship between learning style and critical thinking skills and the comparison of the mean score for each skill in four styles are reported in the last column of the Table 3 .
The Relationship between critical thinking styles with learning styles
Based on the p-value of ANOVA, the mean of evaluation skill and inductive reasoning skill had a significant difference and the relationship between these two skills with learning style was significant (p<0.05). Also the mean of critical thinking’s total score was significantly different in the four groups and the relationship between total score with learning style was significant, too (p<0.05).

The mean and confidence interval of university students’ performance in four learning styles

The mean and confidene interval of critical thinking skills
The study findings showed that the popular learning style among the students was the convergent style followed by the assimilating style which is consistent with Kolb's theory stating that medical science students usually have this learning style ( 8 ). This result was consistent with the results of other studies ( 9 , 10 ). In Yenice's study in which the student of training teacher were the target of the project, the most frequent learning styles were divergent and assimilating styles and these differences originate from the different target group of study in 2012 ( 11 ).
This study showed a significant relationship between learning style and gender, age, semester and employment. Meyari et al. did not find any significant relationship between learning style, age and gender of the freshman but for the fifth semester students, a significant relationship with age and gender was found ( 10 ). Also in Yenice's study, no relationship with learning style, gender, semester and age was found.
Furthermore, in the first semester divergent style, in the second semester assimilating style and in the third and fourth semester divergent style were accounted for the highest percentage. Also in the group age of 17-20 years the assimilating style and the age of 21-24 years the divergent style were dominant styles ( 11 ).
In the present study, it was found a significant positive relationship between convergent learning style and academic performance. Also in the study of Pooladi et al. the majority of the students had convergent style and they also found a significant relationship between learning style, total mean score and the mean of practical courses ( 12 ). Nasrabadi et al. found that students with the highest achievement were those with convergent style with a significant difference with those with divergent style ( 4 ). But the results are inconsistent to Meyari et al.’s ( 10 ).
In this study, the obtained mean score from the critical thinking questionnaire was (7.15±2.41) that was compared with that in the study of Khalili and Hoseinzadeh which was to validate and make reliable the critical thinking skills questionnaire of California (form B) in the Iranian nursing students; the mean of total score was about the 11th percentile of this study ( 13 ).
In other words, the computed score for critical thinking of the students participating was lower than 11 score that is in the 50th percentile and of course is lower than normal range.
Hariri and Bagherinezhad had shown that the computed score for Bachelor and Master students of Health faculty was also lower than the norm in Iran ( 14 ). Also Mayer and Dayer came to a similar conclusion in critical thinking skill in the Agricultural university of Florida’s students in 2006 ( 15 ).
But in Gharib et al.’s study, the total score of critical thinking test among the freshman and senior of Health-care management was in normal range ( 16 ). Wangensteen et al., found that the critical thinking skills of the newest graduate nursing students were relatively high in Sweden in 2010 ( 17 ).
In this study, students of all levels (Associate, Bachelor and PhD) with various fields of study participated but other studies have been limited to certain graduate courses that may explain the differences in levels of special critical thinking skills score in this study. In this study we found a significant relationship between total score of critical thinking and major of the students. This result is consistent with Serin et al. ( 18 ).
It was found a significant relationship between major of participants, gender and inference skill, semester and deductive reasoning skill, ethnicity and both inference and deductive reasoning skills.
In the Yenice's study significant relationship between critical thinking, group of age, gender and semester was seen ( 11 ). In Wangensteen et al.’s ( 17 ) study in the older age group, the level of critical thinking score increased. In Serin et al.’s ( 18 ) study the level of communication skills in girls was better than that in boys. And also a significant relationship was found between critical thinking and academic semester, but in Mayer and Dayer’s study no significant relationship between critical thinking levels and gender was found ( 4 , 15 ).
The results also showed that the total score of critical thinking and analytical skills of students and their performance had a significant relationship. Nasrabady et al.’s study also showed that there was a positive relationship between critical thinking reflection attitude and academic achievement ( 4 ). This is contradictory with what Demirhan, Bosluk and Ander found ( 6 , 15 ).
The results of the relationship between learning style and critical thinking indicated that the relationship between evaluation and inductive reasoning was significant to learning style (p<0.05). The relationship of critical thinking total score with learning style was also significant (p<0.05). Thus the total score for those with the conforming style of critical skills was more than that with other styles. But in the subgroup of inference skills, those with the convergent style had a higher mean than those with other styles.
Yenice found a negative relationship between critical thinking score and divergent learning style and a positive relation between critical thinking score and accommodating style ( 11 ).
Siriopoulos and Pomonis in their study compared the learning style and critical thinking skills of students in two phases: at the beginning and end of education and came to this conclusion that the learning style of students changed in the second phase.
For example, the divergent, convergent and accommodating styles languished and the assimilating style (combination of abstract thinking and reflective observation) was noticeably strengthened. However, those with converging learning style had higher levels of critical thinking.
The level of students’ critical thinking was lower in all international standards styles. Perhaps it was because of widely used teacher-centered teaching methods (lectures) in that university ( 19 ).
The results in the study of Nasrabady et al. showed that there was a significant difference between the level of learners’ critical thinking and divergent and assimilating styles ( 4 ).
Those with converging, diverging, assimilating and accommodating styles had the highest level of critical thinking, respectively.
Also there was a positive significant relationship between the reflective observation method and critical thinking and also a negative significant relationship between the abstract conceptualization method and critical thinking ( 4 ). But in another study that Mahmud has done in 2012, he did not find any significant relationship between learning style, critical thinking and students’ performance ( 6 ).
The results of this study showed that the students’ critical thinking skills of this university aren't acceptable. Also learning styles, critical thinking and academic performance have significant relationship with each other. Due to the important role of critical thinking in enhancing professional competence, it is recommend using teaching methods which are consistent with the learning styles.
Acknowledgment
This study is based on a research project that was approved in Research Deputy of Alborz University of Medical sciences. We sincerely appreciate all in Research Deputy of Alborz University of Medical sciences who supported us financially and morally and all students and colleagues who participated in this study.
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
References:

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Critical Thinking and Decision-Making - What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking and decision-making -, what is critical thinking, critical thinking and decision-making what is critical thinking.

Critical Thinking and Decision-Making: What is Critical Thinking?
Lesson 1: what is critical thinking, what is critical thinking.
Critical thinking is a term that gets thrown around a lot. You've probably heard it used often throughout the years whether it was in school, at work, or in everyday conversation. But when you stop to think about it, what exactly is critical thinking and how do you do it ?
Watch the video below to learn more about critical thinking.
Simply put, critical thinking is the act of deliberately analyzing information so that you can make better judgements and decisions . It involves using things like logic, reasoning, and creativity, to draw conclusions and generally understand things better.
This may sound like a pretty broad definition, and that's because critical thinking is a broad skill that can be applied to so many different situations. You can use it to prepare for a job interview, manage your time better, make decisions about purchasing things, and so much more.
The process
As humans, we are constantly thinking . It's something we can't turn off. But not all of it is critical thinking. No one thinks critically 100% of the time... that would be pretty exhausting! Instead, it's an intentional process , something that we consciously use when we're presented with difficult problems or important decisions.
Improving your critical thinking

In order to become a better critical thinker, it's important to ask questions when you're presented with a problem or decision, before jumping to any conclusions. You can start with simple ones like What do I currently know? and How do I know this? These can help to give you a better idea of what you're working with and, in some cases, simplify more complex issues.

Real-world applications

Let's take a look at how we can use critical thinking to evaluate online information . Say a friend of yours posts a news article on social media and you're drawn to its headline. If you were to use your everyday automatic thinking, you might accept it as fact and move on. But if you were thinking critically, you would first analyze the available information and ask some questions :
- What's the source of this article?
- Is the headline potentially misleading?
- What are my friend's general beliefs?
- Do their beliefs inform why they might have shared this?

After analyzing all of this information, you can draw a conclusion about whether or not you think the article is trustworthy.
Critical thinking has a wide range of real-world applications . It can help you to make better decisions, become more hireable, and generally better understand the world around you.

/en/problem-solving-and-decision-making/why-is-it-so-hard-to-make-decisions/content/

Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students
Why Is Critical Thinking Important? A Survival Guide
Updated: December 7, 2023
Published: April 2, 2020

Why is critical thinking important? The decisions that you make affect your quality of life. And if you want to ensure that you live your best, most successful and happy life, you’re going to want to make conscious choices. That can be done with a simple thing known as critical thinking. Here’s how to improve your critical thinking skills and make decisions that you won’t regret.
What Is Critical Thinking?
You’ve surely heard of critical thinking, but you might not be entirely sure what it really means, and that’s because there are many definitions. For the most part, however, we think of critical thinking as the process of analyzing facts in order to form a judgment. Basically, it’s thinking about thinking.
How Has The Definition Evolved Over Time?
The first time critical thinking was documented is believed to be in the teachings of Socrates , recorded by Plato. But throughout history, the definition has changed.
Today it is best understood by philosophers and psychologists and it’s believed to be a highly complex concept. Some insightful modern-day critical thinking definitions include :
- “Reasonable, reflective thinking that is focused on deciding what to believe or do.”
- “Deciding what’s true and what you should do.”
The Importance Of Critical Thinking
Why is critical thinking important? Good question! Here are a few undeniable reasons why it’s crucial to have these skills.
1. Critical Thinking Is Universal
Critical thinking is a domain-general thinking skill. What does this mean? It means that no matter what path or profession you pursue, these skills will always be relevant and will always be beneficial to your success. They are not specific to any field.
2. Crucial For The Economy
Our future depends on technology, information, and innovation. Critical thinking is needed for our fast-growing economies, to solve problems as quickly and as effectively as possible.
3. Improves Language & Presentation Skills
In order to best express ourselves, we need to know how to think clearly and systematically — meaning practice critical thinking! Critical thinking also means knowing how to break down texts, and in turn, improve our ability to comprehend.
4. Promotes Creativity
By practicing critical thinking, we are allowing ourselves not only to solve problems but also to come up with new and creative ideas to do so. Critical thinking allows us to analyze these ideas and adjust them accordingly.
5. Important For Self-Reflection
Without critical thinking, how can we really live a meaningful life? We need this skill to self-reflect and justify our ways of life and opinions. Critical thinking provides us with the tools to evaluate ourselves in the way that we need to.

6. The Basis Of Science & Democracy
In order to have a democracy and to prove scientific facts, we need critical thinking in the world. Theories must be backed up with knowledge. In order for a society to effectively function, its citizens need to establish opinions about what’s right and wrong (by using critical thinking!).
Benefits Of Critical Thinking
We know that critical thinking is good for society as a whole, but what are some benefits of critical thinking on an individual level? Why is critical thinking important for us?
1. Key For Career Success
Critical thinking is crucial for many career paths. Not just for scientists, but lawyers , doctors, reporters, engineers , accountants, and analysts (among many others) all have to use critical thinking in their positions. In fact, according to the World Economic Forum, critical thinking is one of the most desirable skills to have in the workforce, as it helps analyze information, think outside the box, solve problems with innovative solutions, and plan systematically.
2. Better Decision Making
There’s no doubt about it — critical thinkers make the best choices. Critical thinking helps us deal with everyday problems as they come our way, and very often this thought process is even done subconsciously. It helps us think independently and trust our gut feeling.
3. Can Make You Happier!
While this often goes unnoticed, being in touch with yourself and having a deep understanding of why you think the way you think can really make you happier. Critical thinking can help you better understand yourself, and in turn, help you avoid any kind of negative or limiting beliefs, and focus more on your strengths. Being able to share your thoughts can increase your quality of life.
4. Form Well-Informed Opinions
There is no shortage of information coming at us from all angles. And that’s exactly why we need to use our critical thinking skills and decide for ourselves what to believe. Critical thinking allows us to ensure that our opinions are based on the facts, and help us sort through all that extra noise.
5. Better Citizens
One of the most inspiring critical thinking quotes is by former US president Thomas Jefferson: “An educated citizenry is a vital requisite for our survival as a free people.” What Jefferson is stressing to us here is that critical thinkers make better citizens, as they are able to see the entire picture without getting sucked into biases and propaganda.
6. Improves Relationships
While you may be convinced that being a critical thinker is bound to cause you problems in relationships, this really couldn’t be less true! Being a critical thinker can allow you to better understand the perspective of others, and can help you become more open-minded towards different views.
7. Promotes Curiosity
Critical thinkers are constantly curious about all kinds of things in life, and tend to have a wide range of interests. Critical thinking means constantly asking questions and wanting to know more, about why, what, who, where, when, and everything else that can help them make sense of a situation or concept, never taking anything at face value.
8. Allows For Creativity
Critical thinkers are also highly creative thinkers, and see themselves as limitless when it comes to possibilities. They are constantly looking to take things further, which is crucial in the workforce.
9. Enhances Problem Solving Skills
Those with critical thinking skills tend to solve problems as part of their natural instinct. Critical thinkers are patient and committed to solving the problem, similar to Albert Einstein, one of the best critical thinking examples, who said “It’s not that I’m so smart; it’s just that I stay with problems longer.” Critical thinkers’ enhanced problem-solving skills makes them better at their jobs and better at solving the world’s biggest problems. Like Einstein, they have the potential to literally change the world.
10. An Activity For The Mind
Just like our muscles, in order for them to be strong, our mind also needs to be exercised and challenged. It’s safe to say that critical thinking is almost like an activity for the mind — and it needs to be practiced. Critical thinking encourages the development of many crucial skills such as logical thinking, decision making, and open-mindness.
11. Creates Independence
When we think critically, we think on our own as we trust ourselves more. Critical thinking is key to creating independence, and encouraging students to make their own decisions and form their own opinions.
12. Crucial Life Skill
Critical thinking is crucial not just for learning, but for life overall! Education isn’t just a way to prepare ourselves for life, but it’s pretty much life itself. Learning is a lifelong process that we go through each and every day.
How to Think Critically
Now that you know the benefits of thinking critically, how do you actually do it?
How To Improve Your Critical Thinking
- Define Your Question: When it comes to critical thinking, it’s important to always keep your goal in mind. Know what you’re trying to achieve, and then figure out how to best get there.
- Gather Reliable Information: Make sure that you’re using sources you can trust — biases aside. That’s how a real critical thinker operates!
- Ask The Right Questions: We all know the importance of questions, but be sure that you’re asking the right questions that are going to get you to your answer.
- Look Short & Long Term: When coming up with solutions, think about both the short- and long-term consequences. Both of them are significant in the equation.
- Explore All Sides: There is never just one simple answer, and nothing is black or white. Explore all options and think outside of the box before you come to any conclusions.
How Is Critical Thinking Developed At School?
Critical thinking is developed in nearly everything we do. However, much of this important skill is encouraged to be practiced at school, and rightfully so! Critical thinking goes beyond just thinking clearly — it’s also about thinking for yourself.
When a teacher asks a question in class, students are given the chance to answer for themselves and think critically about what they learned and what they believe to be accurate. When students work in groups and are forced to engage in discussion, this is also a great chance to expand their thinking and use their critical thinking skills.
How Does Critical Thinking Apply To Your Career?
Once you’ve finished school and entered the workforce, your critical thinking journey only expands and grows from here!
Impress Your Employer
Employers value employees who are critical thinkers, ask questions, offer creative ideas, and are always ready to offer innovation against the competition. No matter what your position or role in a company may be, critical thinking will always give you the power to stand out and make a difference.
Careers That Require Critical Thinking
Some of many examples of careers that require critical thinking include:
- Human resources specialist
- Marketing associate
- Business analyst
Truth be told however, it’s probably harder to come up with a professional field that doesn’t require any critical thinking!
Photo by Oladimeji Ajegbile from Pexels
What is someone with critical thinking skills capable of doing.
Someone with critical thinking skills is able to think rationally and clearly about what they should or not believe. They are capable of engaging in their own thoughts, and doing some reflection in order to come to a well-informed conclusion.
A critical thinker understands the connections between ideas, and is able to construct arguments based on facts, as well as find mistakes in reasoning.
The Process Of Critical Thinking
The process of critical thinking is highly systematic.
What Are Your Goals?
Critical thinking starts by defining your goals, and knowing what you are ultimately trying to achieve.
Once you know what you are trying to conclude, you can foresee your solution to the problem and play it out in your head from all perspectives.
What Does The Future Of Critical Thinking Hold?
The future of critical thinking is the equivalent of the future of jobs. In 2020, critical thinking was ranked as the 2nd top skill (following complex problem solving) by the World Economic Forum .
We are dealing with constant unprecedented changes, and what success is today, might not be considered success tomorrow — making critical thinking a key skill for the future workforce.
Why Is Critical Thinking So Important?
Why is critical thinking important? Critical thinking is more than just important! It’s one of the most crucial cognitive skills one can develop.
By practicing well-thought-out thinking, both your thoughts and decisions can make a positive change in your life, on both a professional and personal level. You can hugely improve your life by working on your critical thinking skills as often as you can.
Related Articles
Translate this page from English...
*Machine translated pages not guaranteed for accuracy. Click Here for our professional translations.
Research in Critical Thinking
Each year it sponsors an annual International Conference on Critical Thinking and Educational Reform. It has worked with the College Board, the National Education Association, the U.S. Department of Education, as well as numerous colleges, universities, and school districts to facilitate the implementation of critical thinking instruction focused on intellectual standards.
The following three studies demonstrate:
- the fact that, as a rule, critical thinking is not presently being effectively taught at the high school, college and university level, and yet
- it is possible to do so.
To assess students' understanding of critical thinking, we recommend use of the International Critical Thinking Test as well as the Critical Thinking Interview Profile for College Students . To assess faculty understanding of critical thinking and its importance to instruction, we recommend the Critical Thinking Interview Profile For Teachers and Faculty . By registering as a member of the community, you will have access to streaming video, which includes a sample student interview with Dr. Richard Paul and Rush Cosgrove.
RESEARCH TITLES
View Abstract - View Full Dissertation (Adobe Acrobat PDF)
A Critical Analysis of Richard Paul's Substantive Trans-disciplinary Conception of Critical Thinking
by Enoch Hale, Ph.D.
Union Institute & University - Cincinnati, Ohio - October 2008
View Abstract Dissertation Table of Contents
Effect of a Model for Critical Thinking on Student Achievement in Primary Source Document Analysis and Interpretation, Argumentative Reasoning, Critical Thinking Dispositions and History Content in a Community College History Course Abstract of the Study, conducted by Jenny Reed, in partial fulfillment for her dissertation (October 26, 1998) View Abstract - View Full Dissertation (Adobe Acrobat PDF)
The Effect of Richard Paul's Universal Elements and Standards of Reasoning on Twelfth Grade Composition A Research Proposal Presented to the Faculty Of the School of Education Alliant International University In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Arts in Education: Teaching Study conducted by J. Stephen Scanlan, San Diego (2006) View Abstract - View Full Dissertation (Adobe Acrobat PDF)
Study of 38 Public Universities and 28 Private Universities To Determine Faculty Emphasis on Critical Thinking In Instruction
Principal Researchers: Dr. Richard Paul, Dr. Linda Elder, and Dr. Ted Bartell
View Abstract - View the full study
Substantive Critical Thinking as Developed by the Foundation for Critical Thinking Proves Effective in Raising SAT and ACT Test Scores at West Side High School: Staff Development Program Utilizes Critical Thinking Instruction to Improve Student Performance on ACT and SAT Tests, and in Critical Reading, Writing and Math Dr. John Crook, West Side High School Principal View the Report
Teaching Critical Thinking Skills to Fourth Grade Students Identified as Gifted and Talented by Debra Connerly Graceland University - Cedar Rapids, Iowa - December 2006 View the Report
The Loss of the Space Shuttle Columbia: Portaging Leadership Lessons with a Critical Thinking Model
by Rob Niewoehner, Ph.D. U.S. Navy Graceland University - Cedar Rapids, Iowa - December 2006 View the Report

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

13.6: Quotation, Paraphrase, and Summary
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 40526

- Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Using Information From Sources
There are several ways to effectively incorporate information from sources in essays. Which type of source integration you use will depend on the purpose of the material. Every literary essay should strike a balance between quoting, paraphrasing, and summarizing—and articulating your own perspective. Whether summarizing, paraphrasing, or quoting, you need to include both in-text and Works Cited citations for every source. It is also very important to not pass off quotation as paraphrase: this could be considered plagiarism.
Summarizing refers to the action of boiling down an author’s ideas into a shorter version in your own words. Summary demonstrates your understanding of a text, but it also can be useful in giving background information or making a complex idea more accessible. In a literature essay, you might briefly summarize the plot of a text through the perspective of your topic before diving deeply into the analysis portion of the essay.
When we paraphrase, we are processing information or ideas from another person’s text and putting it in our own words. The main difference between paraphrase and summary is scope: if summarizing means rewording and condensing, then paraphrasing means rewording without drastically altering length. However, paraphrasing is also generally more faithful to the spirit of the original; whereas a summary requires you to process and invites your own perspective, a paraphrase ought to mirror back the original idea using your own language. Paraphrasing is helpful for establishing background knowledge or general consensus, simplifying a complicated idea, or reminding your reader of a certain part of another text. It is also valuable when relaying statistics or historical information, both of which are usually more fluidly woven into your writing when spoken with your own voice.
A direct quote uses quotation marks (“ ”) to indicate where you’re borrowing an author’s words verbatim in your own writing. Use a direct quote if someone else wrote or said something in a distinctive or particular way and you want to capture their words exactly. Direct quotes are good for establishing ethos and providing evidence. In a research essay, you will be expected to use some direct quotes; however, too many direct quotes can overwhelm your thesis and actually undermine your sense of ethos.
For literature, quotation is most effective when attempting to analyze literary devices such as tone, character, metaphor, and so forth.
Below, you can see three examples of these tools. Consider how the direct quote, the paraphrase, and the summary each could be used to achieve different purposes.
Original Passage
It has been suggested (again rather anecdotally) that giraffes do communicate using infrasonic vocalizations (the signals are verbally described to be similar—in structure and function—to the low-frequency, infrasonic “rumbles” of elephants). It was further speculated that the extensive frontal sinus of giraffes acts as a resonance chamber for infrasound production. Moreover, particular neck movements (e.g. the neck stretch) are suggested to be associated with the production of infrasonic vocalizations.
Baotic et al. conducted a study on giraffe hums in response to speculation that these noises are used deliberately for communication.
Giraffes emit a low-pitch noise; some scientists believe that this hum can be used for communication with other members of the social group, but others are skeptical because of the dearth of research on giraffe noises. According to Baotic et al., the anatomy of the animal suggests that they may be making deliberate and specific noises (3).
Some zoological experts have pointed out that the evidence for giraffe hums has been “rather anecdotally” reported (Baotic et al. 3). However, some scientists have “speculated that the extensive frontal sinus of giraffes acts as a resonance chamber for infrasound production” (Ibid. 3).
Important Reminder!
Whether summary, paraphrase, or quotation, you need to use an in-text citation! For every in-text citation, ensure there is a matching entry on the Works Cited page! Also, remember to use information from sources only to support your own argument. For a research essay, a healthy ratio is generally no more than 10% to 20% material from sources to 80% your own original ideas, argument, interpretation, analysis, and explanation. This is not a rule as much as a reminder to think critically about how much your writing relies on the ideas of others: unless the assignment is a summary or literature review, the emphasis should be on your ideas!
Contributors and Attributions
- Adapted from "Research and Argumentation" EmpoWord: A Student-Centered Anthology & Handbook for College Writers b y Shane Abrams of the Portland State University, 2018 CC BY-NC 4.0
Enhancing students’ critical thinking and creative thinking: An integrated mind mapping and robot-based learning approach
- Published: 16 May 2024
Cite this article

- Min-Chi Chiu 1 , 2 &
- Gwo-Jen Hwang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5155-276X 3 , 4
174 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Fostering students’ critical thinking and creative thinking is an important aim in education. For example, art courses not only focus on artwork creation, but also on theoretical knowledge for identifying artworks. In the conventional lecture-based instruction mode for theoretical knowledge delivery, students’ learning outcomes could be affected owing to the lack of student-teacher interactions, and hence researchers have started to employ interactive learning technologies, such as robots, to cope with this problem. However, without proper guidance and support, students’ learning outcomes in such an interactive learning mode could be limited. To improve students’ learning effectiveness, this study proposed a mind mapping-assisted robot (MM-R) approach for an art course. A quasi-experimental design was adopted to explore the effects of the proposed learning approach on students’ performance in art appreciation, digital painting creation, creative thinking tendency, and critical thinking awareness. A total of 48 students from two classes in a university in central Taiwan were recruited to participate in this study. One class was the experimental group ( n = 25) adopting the MM-R approach, while the other class was the control group ( n = 23) adopting the conventional robot (C-R) approach. The results indicated that the integration of the MM-R approach improved students’ learning achievement, performance in digital painting creation, creative thinking tendency, and critical thinking awareness.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price excludes VAT (USA) Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
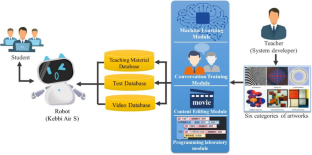
Similar content being viewed by others

Arts and crafts robots or LEGO® MINDSTORMS robots? A comparative study in educational robotics

A Learning Environment for Geography and History Using Mixed Reality, Tangible Interfaces and Educational Robotics

Learning Robotics in a Science Museum Theatre Play: Investigation of Learning Outcomes, Contexts and Experiences
Data availability.
The data and materials are available upon request to the corresponding author.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abd Karim, R., & Abu, A. G. (2018). Using mobile-assisted mind mapping technique (mammat) to improve writing skills of esl students. Journal of Social Science and Humanities, 1 (2), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.26666/rmp.jssh.2018.2.1
Article Google Scholar
Abd Karim, R., & Mustapha, R. (2022). TVET student’s perception on digital mind map to stimulate learning of technical skills in Malaysia. Journal of Technical Education and Training, 14 (1), 1–13.
Afari, E., & Khine, M. S. (2017). Robotics as an educational tool: Impact of Lego mindstorms. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 7 (6), 437–442. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijiet.2017.7.6.908
Alam, A. (2022). Employing adaptive learning and intelligent tutoring robots for virtual classrooms and smart campuses: Reforming education in the age of artificial intelligence. In Advanced Computing and Intelligent Technologies , 395–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2980-9_32
Alkhatib, O. J. (2019, March 1–8). A framework for implementing higher-order thinking skills (problem-solving, critical thinking, creative thinking, and decision-making) in engineering & humanities . In 2019 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET), IEEE.
An, J. S., & Huh, Y. J. (2019). Effect of creative thinking through art collaboration class. Journal of the Korea Convergence Society, 10 (7), 121–131. https://doi.org/10.15207/JKCS.2019.10.7.121
Andrews, R. (2015). Critical thinking and/or argumentation in higher education. The Palgrave handbook of critical thinking in higher education (pp. 49–62). Palgrave Macmillan US.
Chapter Google Scholar
Astrodjojo, D. R. (2018). The development of teaching materials using learning cycle 5E to increase critical thinking skills and students learning outcome of high school students on the subject of reaction rate. JPPS (Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan Sains), 8 (1). https://doi.org/10.26740/jpps.v8n1.p%25p
Aykac, V. (2015). An application regarding the availability of mind maps in visual art education based on active learning method. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 174 , 1859–1866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.848
Bezanilla, M. J., Domínguez, H. G., & Ruiz, M. P. (2021). Importance and possibilities of development of critical thinking in the university: The teacher’s perspective. REMIE: Multidisciplinary Journal of Educational Research, 11 (1), 20–48.
Bhuvaneswari, T., & Beh, S. L. (2013). Changes in teaching and learning through digital media for higher education institutions. International Journal of Mobile Learning and Organisation, 2 (3), 201–215. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMLO.2008.020315
Bonk, C. J., & Cunningham, D. J. (2012). Searching for learner-centered, constructivist, and sociocultural components of collaborative educational learning tools. Electronic collaborators (pp. 25–50). Routledge.
Bravo, F. A., Hurtado, J. A., & González, E. (2021). Using robots with storytelling and drama activities in science education. Education Sciences, 11 (7), 329.
Bravo Sánchez, F. Á, González Correal, A. M., & Guerrero, E. G. (2017). Interactive drama with robots for teaching non-technical subjects. Journal of Human-Robot Interaction, 6 (2), 48–69.
Brown, G. T., & Wang, Z. (2013). Illustrating assessment: How Hong Kong university students conceive of the purposes of assessment. Studies in Higher Education, 38 (7), 1037–1057. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2011.616955
Buzan, T., & Buzan, B. (2002). How to mind map . Thorsons.
Google Scholar
Buzan, T., & Buzan, B. (2006). The mind map book . Pearson Education.
Bybee, R. W., & Trowbridge, J. H. (1990). Applying standards-based constructivism: A two-step guide for motivating students . Cambridge University Press.
Carless, D., & Lam, R. (2014). The examined life: Perspectives of lower primary school students in Hong Kong. Education 3–13, 42 (3), 313–329. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004279.2012.689988
Chai, C. S., Deng, F., Tsai, P. S., Koh, J. H. L., & Tsai, C. C. (2015). Assessing multidimensional students’ perceptions of twenty-first-century learning practices. Asia Pacific Education Review, 16 (3), 389–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12564-015-9379-4
Chang, C. W., Lee, J. H., Wang, C. Y., & Chen, G. D. (2010). Improving the authentic learning experience by integrating robots into the mixed-reality environment. Computers & Education, 55 (4), 1572–1578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2010.06.023
Chang, C. Y., Panjaburee, P., Lin, H. C., Lai, C. L., & Hwang, G. H. (2022). Effects of online strategies on students’ learning performance, self-efficacy, self-regulation and critical thinking in university online courses. Educational Technology Research and Development, 70 (1), 185–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-021-10071-y
Chao, J. Y., Liu, C. H., & Kao, H. C. (2023). Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics Curriculum Design for Teaching Mathematical Concept of Perspective at Indigenous Elementary School using Robots. Sensors and Materials, 35 (5), 1547–1556.
Chassignol, M., Khoroshavin, A., Klimova, A., & Bilyatdinova, A. (2018). Artificial Intelligence trends in education: A narrative overview. Procedia Computer Science, 136 , 16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.08.233
Chen, C. H., & Chung, H. Y. (2023). Fostering computational thinking and problem-solving in programming: Integrating Concept maps into Robot Block-based programming. Journal of Educational Computing Research . https://doi.org/10.1177/07356331231205052
Chen, X., Cheng, G., Zou, D., Zhong, B., & Xie, H. (2023). Artificial Robots for Precision Education. Educational Technology & Society, 26 (1), 171–186.
Chen Hsieh, J. (2022). Multimodal Digital Storytelling Presentations among Middle-School learners of English as a Foreign Language: Emotions, grit and perceptions. RELC Journal . https://doi.org/10.1177/00336882221102233
Chin, K. Y., Hong, Z. W., & Chen, Y. L. (2014). Impact of using an educational robot-based learning system on students’ motivation in elementary education. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 7 (4), 333–345.
Chiu, M. C., Hwang, G. J., & Tu, Y. F. (2022). Roles, applications, and research designs of robots in science education: a systematic review and bibliometric analysis of journal publications from 1996 to 2020. Interactive Learning Environments, 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2022.2129392
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches (3rd ed.). SAGE Publications.
Cristea, A. D., Berdie, A. D., Osaci, M., & Chirtoc, D. (2011). The advantages of using mind map for learning web dynpro. Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 19 (1), 201–207.
Cruickshank, D. (1996). The ‘art’of reflection: Using drawing to uncover knowledge development in student nurses. Nurse Education Today, 16 (2), 127–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0260-6917(96)80069-4
Davies, M. (2011). Concept mapping, mind mapping and argument mapping: What are the differences and do they matter? Higher Education, 62 (3), 279–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-010-9387-6
Deaver, S. P. (2012). Art-based learning strategies in art therapy graduate education. Art Therapy, 29 (4), 158–165. https://doi.org/10.1080/07421656.2012.730029
Debbag, M., Cukurbasi, B., & Fidan, M. (2021). Use of digital mind maps in technology education: A pilot study with pre-service science teachers. Informatics in Education, 20 (1), 47–68.
Dewey, J. (1934). In J. Boydston (Ed.), Art as experience, reprinted in 1989, John dewey: The later works, 1925–1953. (Vol. 10). Southern Illinois University.
Dong, Y., Zhu, S., & Li, W. (2021). Promoting sustainable creativity: An empirical study on the application of mind mapping tools in graphic design education. Sustainability, 13 (10), 5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105373
Dorouka, P., Papadakis, S., & Kalogiannakis, M. (2020). Tablets and apps for promoting robotics, mathematics, STEM education and literacy in early childhood education. International Journal of Mobile Learning and Organisation, 14 (2), 255–274.
Dumitru, D. (2019). Creating meaning. The importance of arts, humanities and Culture for critical thinking development. Studies in Higher Education, 44 (5), 870–879. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2019.1586345
Edwards, S., & Cooper, N. (2010). Mind mapping as a teaching resource. The Clinical Teacher, 7 (4), 236–239. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-498X.2010.00395.x
Edwards, C., Edwards, A., Spence, P. R., & Lin, X. (2018). I, teacher: Using artificial intelligence (AI) and social robots in communication and instruction. Communication Education, 67 (4), 473–480. https://doi.org/10.1080/03634523.2018.1502459
Eppler, M. J. (2006). A comparison between concept maps, mind maps, conceptual diagrams, and visual metaphors as complementary tools for knowledge construction and sharing. Information Visualization, 5 (3), 202–210.
Evripidou, S., Amanatiadis, A., Christodoulou, K., & Chatzichristofis, S. A. (2021). Introducing algorithmic thinking and sequencing using tangible robots. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 14 (1), 93–105. https://doi.org/10.1109/TLT.2021.3058060
Fadillah, R. (2019). STUDENTS’perception on the use of mind mapping application software in learning writing. Celtic: A Journal of Culture English Language Teaching Literature and Linguistics, 6 (1), 58–64.
Fan, X., & Zhong, X. (2022). Artificial intelligence-based creative thinking skill analysis model using human–computer interaction in art design teaching. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 100 , 107957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.107957
Fish, B. J. (2019). Response art in art therapy: Historical and contemporary overview. Art Therapy, 36 (3), 122–132. https://doi.org/10.1080/07421656.2019.1648915
Freire, P. (1973). Education for critical consciousness (Vol. 1). Bloomsbury Publishing.
Fridin, M. (2014). Storytelling by a kindergarten social assistive robot: A tool for constructive learning in preschool education. Computers & Education, 70 , 53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.07.043
Fu, Q. K., Lin, C. J., Hwang, G. J., & Zhang, L. (2019). Impacts of a mind mapping-based contextual gaming approach on EFL students’ writing performance, learning perceptions and generative uses in an English course. Computers & Education, 137 , 59–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.04.005
Gerecke, U., & Wagner, B. (2007). The challenges and benefits of using robots in higher education. Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing, 13 (1), 29–43. https://doi.org/10.1080/10798587.2007.10642948
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research . Routledge.
Goldstain, O. H., Ben-Gal, I., & Bukchin, Y. (2011). Evaluation of telerobotic interface components for teaching robot operation. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 4 (4), 365–376. https://doi.org/10.1109/TLT.2011.19
Goldston, M. J., Day, J. B., Sundberg, C., & Dantzler, J. (2010). Psychometric analysis of a 5E learning cycle lesson plan assessment instrument. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 8 (4), 633–648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-009-9178-7
Hardiman, M. M., JohnBull, R. M., Carran, D. T., & Shelton, A. (2019). The effects of arts-integrated instruction on memory for science content. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 14 , 25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tine.2019.02.002
Hayadi, B. H., Bastian, A., Rukun, K., Jalius, N., Lizar, Y., & Guci, A. (2018). Expert system in the application of learning models with forward chaining method. International Journal of Engineering Technology, 7 (2.29), 845–848.
Heyvaert, M., Maes, B., & Onghena, P. (2013). Mixed methods research synthesis: Definition, framework, and potential. Quality & Quantity, 47 , 659–676.
Hidayati, N., Zubaidah, S., Suarsini, E., & Praherdhiono, H. (2019). Examining the relationship between creativity and critical thinking through integrated problem-based learning and digital mind maps. Universal Journal of Education Research , 7 (9A), 171–179. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujer.2019.071620
Ho, T. K. L., & Lin, H. S. (2015). A web-based painting tool for enhancing student attitudes toward learning art creation. Computers & Education, 89 , 32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.08.015
Howitt, C. (2009). 3-D mind maps: Placing young children in the centre of their own learning. Teaching Science: The Journal of the Australian Science Teachers Association , 55 (2).
Hölling, H. (2016). The aesthetics of change: on the relative durations of the impermanent and critical thinking in conservation. Authenticity in Transition: Changing Practices in Art Making and Conservation, 13–24.
Hsu, T. C., & Chen, M. S. (2022). The engagement of students when learning to use a personal audio classifier to control robot cars in a computational thinking board game. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 17 (1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41039-022-00202-1
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Huang, Z. M. (2021). Exploring imagination as a methodological source of knowledge: Painting students’ intercultural experience at a UK university. International Journal of Research & Method in Education, 44 (4), 366–378. https://doi.org/10.1080/1743727X.2020.1796958
Hutson, J., & Olsen, T. (2022). Virtual reality and art history: A case study of digital humanities and immersive learning environments. Journal of Higher Education Theory and Practice, 22 (2).
Hwang, G. J., Yang, T. C., Tsai, C. C., & Yang, S. J. H. (2009). A context-aware ubiquitous learning environment for conducting complex science experiments. Computers & Education, 53 (2), 402–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2009.02.016
Hwang, G. J., Lee, H. Y., & Chen, C. H. (2019). Lessons learned from integrating concept mapping and gaming approaches into learning scenarios using mobile devices: Analysis of an activity for a geology course. International Journal of Mobile Learning and Organisation, 13 (3), 286–308.
Ishiguro, C., & Okada, T. (2022). How can inspiration be encouraged in art learning? Arts-based methods in education around the world (pp. 205–230). River.
Jung, S. E., & Won, E. S. (2018). Systematic review of research trends in robotics education for young children. Sustainability, 10 (4), 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10040905
Kalaitzidou, M., & Pachidis, T. P. (2023). Recent robots in STEAM Education. Education Sciences, 13 (3), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13030272
Kokotovich, V. (2008). Problem analysis and thinking tools: an empirical study of non-hierarchical mind mapping. Design studies, 29 (1), 49–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.destud.2007.09.001
Kanda, T., Hirano, T., Eaton, D., & Ishiguro, H. (2004). Interactive robots as social partners and peer tutors for children: A field trial. Human–Computer Interaction, 19 (1–2), 61–84.
Köhler, C., Hartig, J., & Naumann, A. (2021). Detecting instruction effects-deciding between covariance analytical and change-score approach. Educational Psychology Review, 33 , 1191–1211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-020-09590-6
Kotcherlakota, S., Zimmerman, L., & Berger, A. M. (2013). Developing scholarly thinking using mind maps in graduate nursing education. Nurse educator , 27 (6), 252–255. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.NNE.0000435264.15495.51
Konijn , E. A., & Hoorn, J. F. (2020). Robot tutor and pupils’ educational ability: Teaching the times tables. Computers & Education , 157 , 103970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103970
Kuo, Y. T., Garcia Bravo, E., Whittinghill, D. M., & Kuo, Y. C. (2023). Walking into a modern painting: The impacts of using virtual reality on student learning performance and experiences in art appreciation. International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2023.2278929
Lai, C. L., & Hwang, G. J. (2014). Effects of mobile learning time on students’ conception of collaboration, communication, complex problem-solving, meta-cognitive awareness and creativity. International Journal of Mobile Learning and Organisation, 8 (3), 276–291. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMLO.2014.067029
Lai, C. L., & Hwang, G. J. (2015). An interactive peer-assessment criteria development approach to improving students’ art design performance using handheld devices. Computers & Education, 85 , 149–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.02.011
Lee, C. S., Wang, M. H., Kuan, W. K., Huang, S. H., Tsai, Y. L., Ciou, Z. H., Yang, C. K., & Kubota, N. (2021). BCI-based hit-loop agent for human and AI robot co-learning with AIoT application. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03487-0
Liang, J. C., & Hwang, G. J. (2023). A robot-based digital storytelling approach to enhancing EFL learners’ multimodal storytelling ability and narrative engagement. Computers & Education, 201 , 104827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2023.104827
Lin, C. J., Hwang, G. J., Fu, Q. K., & Chen, J. F. (2018). A flipped contextual game-based learning approach to enhancing EFL students’ English business writing performance and reflective behaviors. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 21 (3), 117–131.
Lin, H. C., Hwang, G. J., & Hsu, Y. D. (2019). Effects of ASQ-based flipped learning on nurse practitioner learners’ nursing skills, learning achievement and learning perceptions. Computers & Education, 139 , 207–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.05.014
Liu, H., Sheng, J., & Zhao, L. (2022). Innovation of teaching tools during robot programming learning to promote middle school students’ critical thinking. Sustainability, 14 (11), 6625. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116625
Malycha, C. P., & Maier, G. W. (2017). Enhancing creativity on different complexity levels by eliciting mental models. Psychology of Aesthetics Creativity and the Arts, 11 (2), 187. https://doi.org/10.1037/aca0000080
Mernick, A. (2021). Critical arts pedagogy: Nurturing critical consciousness and self-actualization through art education. Art Education, 74 (5), 19–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/00043125.2021.1928468
Meyer, T. (2017). Next art education: Eight theses future art educators should think about. International Journal of Education through Art, 13 (3), 369–384. https://doi.org/10.1386/eta.13.3.369_1
Mijwil, M. M., Aggarwal, K., Mutar, D. S., Mansour, N., & Singh, R. (2022). The position of artificial intelligence in the future of education: an overview. Journal of Applied Sciences, 10 (2).
Miles, M. B., Huberman, A. M., & Saldaña, J. (2013). Qualitative data analysis: A methods sourcebook (3rd ed.). SAGE Publications, Inc.
Moraiti, I., Fotoglou, A., & Drigas, A. (2022). Coding with block programming languages in educational robotics and mobiles, improve problem solving, creativity & critical thinking skills. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies , 16 (20). https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v16i20.34247
Mubin, O., Stevens, C. J., Shahid, S., Al Mahmud, A., & Dong, J. J. (2013). A review of the applicability of robots in education. Journal of Technology in Education and Learning , 1 (209 – 0015), 13. https://doi.org/10.2316/Journal.209.2013.1.209-0015
Nurkhin, A., & Pramusinto, H. (2020). Problem-based learning strategy: Its impact on students’ critical and creative thinking skills. European Journal of Educational Research, 9 (3), 1141–1150.
O’Connell, R. M. (2014). Mind mapping for critical thinking. In Cases on teaching critical thinking through visual representation strategies , 354–386. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-4666-5816-5.ch014
Oreck, B. (2004). The artistic and professional development of teachers: A study of teachers’ attitudes toward and use of the arts in teaching. Journal of Teacher Education, 55 (1), 55–69. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022487103260072
Otukile-Mongwaketse, M. (2018). Teacher centered approaches: Their implications for today’s inclusive classrooms. International Journal of Psychoogy and Counseling, 10 (2), 11–21. https://doi.org/10.5897/IJPC2016.0393
Park, Y. S. (2023). Creative and critical entanglements with AI in Art Education. Studies in Art Education, 64 (4), 406–425. https://doi.org/10.1080/00393541.2023.2255084
Patton, R. M., & Buffington, M. L. (2016). Keeping up with our students: The evolution of technology and standards in art education. Arts Education Policy Review, 117 (3), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/10632913.2014.944961
Ramdani, A., Jufri, A. W., Gunawan, G., Fahrurrozi, M., & Yustiqvar, M. (2021). Analysis of students’ critical thinking skills in terms of gender using Science Teaching materials based on the 5E learning cycle Integrated with local Wisdom. Jurnal Pendidikan IPA Indonesia, 10 (2), 187–199. https://doi.org/10.15294/jpii.v10i2.29956
Rim, H., Choi, I., & Noh, S. (2014). A study on the application of robotic programming to promote logical and critical thinking in mathematics education. The Mathematical Education, 53 (3), 413–434. https://doi.org/10.7468/mathedu.2014.53.3.413
Ryu, H. J., Kwak, S. S., & KIM, M. S. (2008). Design factors for external form of robots as elementary school teaching assistants. Bulletin of Japanese Society for the Science of Design, 54 (6), 39–48. https://doi.org/10.11247/jssdj.54.39_3
Sajnani, N., Mayor, C., & Tillberg-Webb, H. (2020). Aesthetic presence: The role of the arts in the education of creative arts therapists in the classroom and online. The Arts in Psychotherapy, 69 , 101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aip.2020.101668
Sari, R., Sumarmi, S., Astina, I., Utomo, D., & Ridhwan, R. (2021). Increasing students critical thinking skills and learning motivation using inquiry mind map. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 16 (3), 4–19. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v16i03.16515
Saunders, G., & Klemming, F. (2003). Integrating technology into a traditional learning environment: Reasons for and risks of success. Active Learning in Higher Education, 4 (1), 74–86. https://doi.org/10.1177/1469787403004001006
Setiawan, I. W. P., Suartama, I. K., & Putri, D. A. W. M. (2017). Pengaruh Model Pembelajaran Learning Cycle 5e Berbantuan Mind Mapping Terhadap Hasil Belajar Matematika. Mimbar PGSD Undiksha, 5 (2). https://doi.org/10.23887/jjpgsd.v5i2.10841
Štuikys, V., & Burbaitė, R. (2018). Smart devices and educational robotics as technology for STEM knowledge. Springer , 57–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78485-4_3
Sun, M., Wang, M., & Wegerif, R. (2019). Using computer-based cognitive mapping to improve students’ divergent thinking for creativity development. British Journal of Educational Technology, 50 (5), 2217–2233. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12825
Sun, Q., Lu, Z., & Ren, X. (2023). The influence of humanities on art and design learning performance: An empirical study. International Journal of Art & Design Education . https://doi.org/10.1111/jade.12474
Ulger, K. (2018). The effect of problem-based learning on the creative thinking and critical thinking disposition of students in visual arts education. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-Based Learning, 12 (1).
Usengül, L., & Bahçeci, F. (2020). The Effect of LEGO WeDo 2.0 education on academic achievement and attitudes and computational thinking skills of Learners toward Science. World Journal of Education, 10 (4), 83–93. https://doi.org/10.5430/wje.v10n4p83
Utami, D., & Subali, B. (2019, October). The effectiveness of 5E learning cycle accompanied by mind mapping on creative thinking. In Proceeding of the 2nd International Conference Education Culture and Technology, ICONECT 2019, 20–21 August 2019, Kudus, Indonesia .
Van den Berghe, R., Verhagen, J., Oudgenoeg-Paz, O., Van der Ven, S., & Leseman, P. (2019). Social robots for language learning: A review. Review of Educational Research, 89 (2), 259–295. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654318821286
Ververi, C., Koufou, T., Moutzouris, A., & Andreou, L. V. (2020, April 20–21). Introducing robotics to an English for academic purposes curriculum in higher education: The student experience . In 2020 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), Porto, Portugal.
Walia, D. N. (2012). Traditional teaching methods vs. CLT: A study. Frontiers of Language and Teaching, 3 (1), 125–131.
Westlund, J. K., & Breazeal, C. (2015, March 65–66). The interplay of robot language level with children’s language learning during storytelling. In Proceedings of the tenth annual ACM/IEEE international conference on human-robot interaction extended abstracts, New York, United States.
Woolf, B., Burleson, W., Arroyo, I., Dragon, T., Cooper, D., & Picard, R. (2009). Affect-aware tutors: Recognising and responding to student affect. International Journal of Learning Technology, 4 (3–4), 129–164. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJLT.2009.028804
Wu, H. Z., & Wu, Q. T. (2020). Impact of mind mapping on the critical thinking ability of clinical nursing students and teaching application. Journal of International Medical Research, 48 (3). https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060519893225
Wu, W. L., Hsu, Y., Yang, Q. F., Chen, J. J., & Jong, M. S. Y. (2021). Effects of the self-regulated strategy within the context of spherical video-based virtual reality on students’ learning performances in an art history class. Interactive Learning Environments, 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2021.1878231
Yang, J., & Zhang, B. (2019). Artificial intelligence in intelligent tutoring robots: A systematic review and design guidelines. Applied Sciences , 9 (10), 2078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9102078
Yang, Q. F., Lian, L. W., & Zhao, J. H. (2023). Developing a gamified artificial intelligence educational robot to promote learning effectiveness and behavior in laboratory safety courses for undergraduate students. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 20 (1), 18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-023-00391-9
Yu, F. Y., & Liu, Y. H. (2005). Potential values of incorporating a multiple-choice question construction in physics experimentation instruction. International Journal of Science Education, 27 (11), 1319–1335. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500690500102854
Yuliyanto, A., Basit, R. A., Muqodas, I., Wulandari, H., & Mifta, D. (2020). Alternative learning of the future based on Verbal-Linguistic, and visual-spatial intelligence through Youtube-based mind map when Pandemic Covid-19. Jurnal JPSD (Jurnal Pendidikan Sekolah Dasar), 7 (2), 132–141. https://doi.org/10.12928/jpsd.v7i2.16925
Zampetakis, L. A., Tsironis, L., & Moustakis, V. (2007). Creativity development in engineering education: The case of mind mapping. Journal of Management Development, 26 (4), 370–380. https://doi.org/10.1108/02621710710740110
Zhang, X., Chen, Y., Li, D., Hu, L., Hwang, G. J., & Tu, Y. F. (2023). Engaging young students in effective robotics education: an embodied learning-based computer programming approach. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 62 (2), 532–558. https://doi.org/10.1177/07356331231213548
Download references
This study is supported in part by the National Science and Technology Council of Taiwan under contract numbers NSTC 112-2410-H-011-012-MY3 and MOST 111-2410-H-011 -007 -MY3. The study is also supported by the “Empower Vocational Education Research Center” of National Taiwan University of Science and Technology (NTUST) from the Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education (MOE) in Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Information Management, Ling Tung University, Taichung, Taiwan
Min-Chi Chiu
Department of Multimedia Design, National Taichung University of Science and Technology, Taichung, Taiwan
Graduate Institute of Educational Information and Measurement, National Taichung University of Education, Taichung, Taiwan
Gwo-Jen Hwang
Graduate Institute of Digital Learning and Education, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taipei, Taiwan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Min-Chi Chiu. Project administration were performed by Gwo-Jen Hwang and Min-Chi Chiu. Methodology and supervision were performed Gwo-Jen Hwang and Min-Chi Chiu. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Min-Chi Chiu. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gwo-Jen Hwang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval.
The ethical requirements for research in this selected university were followed.
Consent to participate
The participants all agreed to take part in this study.
Consent for publication
The publication of this study has been approved by all authors.
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
There is no potential conflict of interest in this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Chiu, MC., Hwang, GJ. Enhancing students’ critical thinking and creative thinking: An integrated mind mapping and robot-based learning approach. Educ Inf Technol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12752-6
Download citation
Received : 14 August 2023
Accepted : 29 April 2024
Published : 16 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12752-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Mind mapping
- Intelligent robot
- 5E instructional model
- Artwork appreciation
- Creative thinking tendency
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Critical Thinking Skills.
Ai generator.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze information objectively and make a reasoned judgment. It involves evaluating sources, such as data, facts, observable phenomena, and research findings. Developing critical thinking skills is essential for academic success and everyday decision-making. Here are strategies and examples to help enhance critical thinking skills.
1. Ask Questions
Asking questions is fundamental to critical thinking. Encourage curiosity and in-depth understanding by asking questions like:
- What evidence supports this claim?
- Are there alternative perspectives?
- What are the implications of this decision?
2. Analyze Assumptions
Identifying and analyzing assumptions helps in understanding underlying biases and beliefs.
- Example : When reading a news article, identify the assumptions the author makes and consider how they influence the argument.
3. Evaluate Evidence
Evaluating evidence involves assessing the reliability and validity of information sources.
- Example : When researching a topic, compare information from multiple sources and evaluate their credibility.
4. Develop Hypotheses
Formulating and testing hypotheses can strengthen analytical skills.
- Example : In a science experiment, develop a hypothesis, conduct experiments to test it, and analyze the results.
5. Reflect on Your Thinking Process
Reflection helps in recognizing and improving your thought process.
- Example : After making a decision, reflect on the steps you took, what you learned, and how you could improve in the future.
6. Engage in Discussions
Participating in discussions encourages the exchange of ideas and perspectives.
- Example : Join a debate club or discussion group to practice presenting and defending your viewpoints.
7. Practice Problem-Solving
Solving problems systematically can enhance critical thinking.
- Example : Use problem-solving frameworks, like SWOT analysis, to evaluate a business case study.
8. Use Critical Thinking Exercises
Incorporate exercises and activities designed to boost critical thinking skills.
- Example : Engage in brainteasers, puzzles, and logic games that challenge your reasoning abilities.
Examples of Critical Thinking in Action
- Case Study: Socratic Method : Used in law schools, the Socratic method involves asking a series of questions to help students think deeply about the subject matter.
- Example: Reflective Journals : Students keep journals where they reflect on their learning experiences, analyze their thinking processes, and develop insights.
Developing critical thinking skills is crucial for academic success and informed decision-making. By asking questions, analyzing assumptions, evaluating evidence, developing hypotheses, reflecting on thinking processes, engaging in discussions, practicing problem-solving, and using critical thinking exercises, individuals can enhance their ability to think critically.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The answer is critical thinking skills. The more that academic research becomes governed by policies outside of the research process, the less opportunity there will be for researchers to exercise such skills. True research demands new ideas, perspectives, and arguments based on willingness and confidence to revisit and directly challenge ...
Critical thinking is important for making judgments about sources of information and forming your own arguments. It emphasizes a rational, objective, and self-aware approach that can help you to identify credible sources and strengthen your conclusions. Critical thinking is important in all disciplines and throughout all stages of the research ...
In recent decades, approaches to critical thinking have generally taken a practical turn, pivoting away from more abstract accounts - such as emphasizing the logical relations that hold between statements (Ennis, 1964) - and moving toward an emphasis on belief and action.According to the definition that Robert Ennis (2018) has been advocating for the last few decades, critical thinking is ...
4. Critical Thinking as an Applied Model for Intelligence. One definition of intelligence that directly addresses the question about intelligence and real-world problem solving comes from Nickerson (2020, p. 205): "the ability to learn, to reason well, to solve novel problems, and to deal effectively with novel problems—often unpredictable—that confront one in daily life."
Critical thinking refers to deliberately scrutinizing and evaluating theories, concepts, or ideas using reasoned reflection and analysis. The act of thinking critically involves moving beyond simply understanding information by questioning its source, its production, and its presentation in order to expose potential bias or researcher subjectivity [i.e., evidence of being influenced by ...
Critical thinking is inherent to the research process. Critical thinking starts with a curious and open mind, and a willingness to look deeper and wider than those who explored this topic before. We look deeply at sources, and the questions at the heart of those sources. We look widely to cross established boundaries of field, discipline, and ...
Critical Thinking and Academic Research. Academic research focuses on the creation of new ideas, perspectives, and arguments. The researcher seeks relevant information in articles, books, and other sources, then develops an informed point of view within this ongoing "conversation" among researchers. The research process is not simply collecting ...
The Critical Thinking Community (2016) defined it this way: Critical thinking is self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, and self-corrective thinking. It presupposes assent to rigorous standards of excellence and mindful command of their use. It entails effective communication and problem-solving abilities, as well as a commitment to ...
Select information from sources to begin answering the research questions. Determine an appropriate organizational structure for the research paper that uses critical analysis to connect the writer's ideas and information taken from sources. At this point in your project, you are preparing to move from the research phase to the writing phase.
About the Book. Critical Thinking in Academic Research - 2nd Edition provides examples and easy-to-understand explanations to equip students with the skills to develop research questions, evaluate and choose the right sources, search for information, and understand arguments. This 2nd Edition includes new content based on student feedback as ...
Arguably, an important component of critical thinking skills is the ability to critically examine and understand published research in one's professional area of interest . Requiring students to critique published research is one way of addressing the goal of teaching students to critically evaluate research while gaining experience doing it ...
Fig. 2 presents the numbers of publications from 2000 to 2021, which was used to uncover the diachronic development of critical thinking research in education. No results were returned in 2000 and 2001, and the number of publications from 2002 to 2021 steadily increased. Further observation found very low production, with less than 10 publications, for the period from 2002 to 2006.
Theoretical Domain. Theoretical critical thinking involves helping the student develop an appreciation for scientific explanations of behavior. This means learning not just the content of psychology but how and why psychology is organized into concepts, principles, laws, and theories. Developing theoretical skills begins in the introductory ...
Sep 5, 2018. by Janet Salmons, PhD Research Community Manager for Sage Research Methods Community. Critical thinking and creative thinking are distinctly different, but highly interconnected. Nowhere is the symbiotic relationship of creative and critical thinking more apparent than in the practices inherent to research design, conduct, and ...
Critical thinking is the art of making clear, reasoned judgements based on interpreting, understanding, applying and synthesising evidence gathered from observation, reading and experimentation. Essential Study Skills: The Complete Guide to Success at University (4th ed.) London: SAGE, p94. Being critical does not just mean finding fault.
According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [ 1 ]: Universal. Crucial for the economy. Essential for improving language and presentation skills. Very helpful in promoting creativity. Important for self-reflection.
The current world needs people with a lot of capabilities such as understanding and using different ways of thinking, research, problem solving, critical thinking and creativity. Critical thinking is one of the aspects of thinking that has been accepted as a way to overcome the difficulties and to facilitate the access to information in life ( 1 ).
Simply put, critical thinking is the act of deliberately analyzing information so that you can make better judgements and decisions. It involves using things like logic, reasoning, and creativity, to draw conclusions and generally understand things better. This may sound like a pretty broad definition, and that's because critical thinking is a ...
Critical thinking is a kind of thinking in which you question, analyse, interpret , evaluate and make a judgement about what you read, hear, say, or write. The term critical comes from the Greek word kritikos meaning "able to judge or discern". Good critical thinking is about making reliable judgements based on reliable information.
Browne and Keeley (2013) go on to say that the term "critical. thinking" refers to: 1) awareness of a set of interrelated critical questions; 2) ability to ask. and answer critical questions ...
Critical thinking can help you better understand yourself, and in turn, help you avoid any kind of negative or limiting beliefs, and focus more on your strengths. Being able to share your thoughts can increase your quality of life. 4. Form Well-Informed Opinions.
Here's how you can enhance your critical thinking abilities for the future in Research Skills. Powered by AI and the LinkedIn community. 1. Ask Questions. Be the first to add your personal ...
The Center conducts advanced research and disseminates information on critical thinking. Each year it sponsors an annual International Conference on Critical Thinking and Educational Reform. It has worked with the College Board, the National Education Association, the U.S. Department of Education, as well as numerous colleges, universities, and ...
255803. Literacy is the ability to read and write. Broadly, literacy may be viewed as "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. Critical thinking is the analysis of available facts, evidence, observations ...
ACTION RESEARCH: DEVELOP CRITICAL THINKING SKILLS 6 work through many factors in order to deduce a commonsensical conclusion. Slavin (2012) stated critical thinking skills are utilized for deductive reasoning and problem solving in order to uncover reasonable discrepancies and myths. Additionally, for critical thinking skills to develop
Literacy and Critical Thinking Writing and Critical Thinking Through Literature (Ringo and Kashyap) ... It also provides a free research course to aid students in using databases. However, watch out, because it is such a massive database it also contains a lot of book reviews (which are not literary criticism) and a lot of really, really old ...
For every in-text citation, ensure there is a matching entry on the Works Cited page! Also, remember to use information from sources only to support your own argument. For a research essay, a healthy ratio is generally no more than 10% to 20% material from sources to 80% your own original ideas, argument, interpretation, analysis, and explanation.
Overall, mind maps enhance learning efficiency, creativity, and critical thinking, and are an important resource in teaching and learning. ... The engagement of students when learning to use a personal audio classifier to control robot cars in a computational thinking board game. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 17(1), 1 ...
Critical thinking is a cognitive process that involves analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to form reasoned judgments or decisions. It goes beyond simply accepting information at face value and instead requires individuals to actively engage with and question the content, considering its reliability, relevance, and implications.
Example: Use problem-solving frameworks, like SWOT analysis, to evaluate a business case study. 8. Use Critical Thinking Exercises. Incorporate exercises and activities designed to boost critical thinking skills. Example: Engage in brainteasers, puzzles, and logic games that challenge your reasoning abilities.